Contamination of fungi with radionuclides
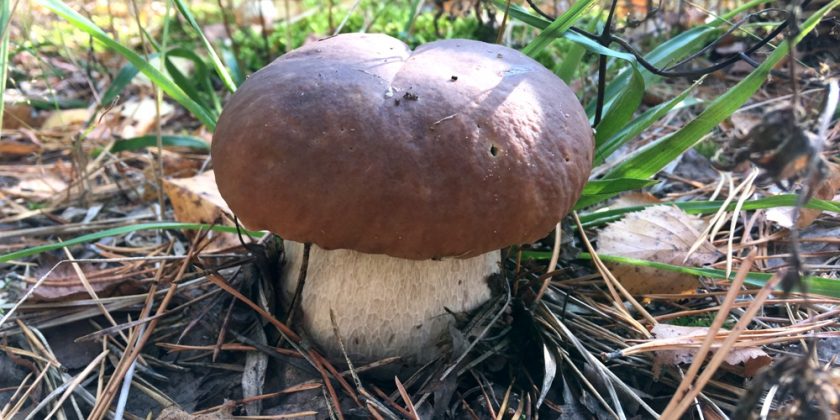
Edible mushrooms are harmful to human health if they are contaminated with radioactive substances. This problem became urgent after the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. The fruit body actively absorbs cesium-137 and strontium-90.
Scientists have proven that mushrooms contain more radionuclides than soil, water and the trees that surround them. The level of radioactive substances does not depend on its age, but there are more toxins in the cap than in the leg. It also matters:
- type of mushroom;
- the amount of radionuclides in soil, water, air;
- atmospheric conditions and more.
Different types of fungi accumulate cesium-137 and strontium-90 in different ways. There are species that accumulate radioactive substances well: butter dish, Polish mushroom, milk mushroom, mushroom, podgruzdok and others. Foresters do not recommend collecting them in contaminated areas and eating them.

Ryzhiks accumulate radioactive substances more than other mushrooms
Mushrooms with a medium and low level of absorption (russula, camelina, chanterelles, boletus, morels, honey mushrooms, common stitching, champignon and others) are advised by foresters to harvest.
Before the hike, you should first inquire about the level of radioactive contamination of the area. Information can be obtained from the forester or the sanitary station. Mushrooms are allowed to be harvested with a total pollution of up to 2 Curies per square kilometer. You cannot collect them near the industrial area, near the road, sewers, and so on.
Destructive impact
All pollutants can irreversibly affect plant organisms, causing both morphological and physiological and biochemical changes. These impacts are usually nonspecific. For example, heavy metals and radionuclides, entering plant cells, can interact with various proteins, which leads to changes in cellular metabolism - the processes of photosynthesis, respiration are disrupted, the functions of cell membranes change, etc.
At the morphological level, there can be changes in the size, shape, color of leaves and flowers, their wilting or abscission. Often the crown of trees dries up, the integrity of the bark is disrupted, the root system is deformed, and some organs grow together. In conifers, changes in the size of the needles are noted. With strong atmospheric pollution in various trees and shrubs, a violation of the intensity of branching is observed.
Atmospheric pollutants can also affect plant pollen, changing the surface and shape of pollen grains, disrupting the integrity of the shells and causing them to stick together.
In general, the nature of the impact of pollutants depends on their amount in the environment, on their chemical structure, as well as on the genetic and species characteristics of the plants themselves, which differ in their resistance to the toxic effects of increased concentrations of pollutants.
What products contain

Photo: Nadezhda Kay
Cadmium and mercury are often found in fish and seafood. So, the first is more common in mussels and oysters, and the second - in large predatory fish, which include shark, tuna, beluga, pike and swordfish. The fact is that these species live longer than others, and, accordingly, have time to accumulate more methylmercury. In addition, they feed on small fish, which also contain mercury. That is why doctors advise to give up such fish, and reduce the consumption of the rest to one or two meals a week.
But even more often, an excess of cadmium is found in vegetables, melons, potatoes and greens. Most of it is found in beans, cilantro, dill, parsley and celery. In addition, cadmium and lead are most commonly found in apples. And sometimes cadmium is found in completely unexpected places - for example, in seasonings.
Drinking water often contains mercury - even bottled water that is supposedly suitable for baby food. So, in 2016, experts from Roskontrol discovered an excess of mercury content in the water of the FrutoNyanya, Vinni and Nutrilak brands. However, the latest research by Roskachestvo rehabilitated the first sample.
Treatment of intoxication with infected mushrooms
At the hospital, the toxicologist needs to be told that the state of health worsened after eating mushrooms. Information about this species is valuable, where they were collected, how they were prepared, how many people ate toxic food, and so on.

Treatment depends on the type of toxic substance
The doctor necessarily prescribes gastric and intestinal lavage, general clinical tests and sorbents. Further, treatment depends on the type of toxic substance, since poisoning with heavy metals and radionuclides is distinguished by additional symptoms. Heavy metal intoxication requires the introduction of antivenom.
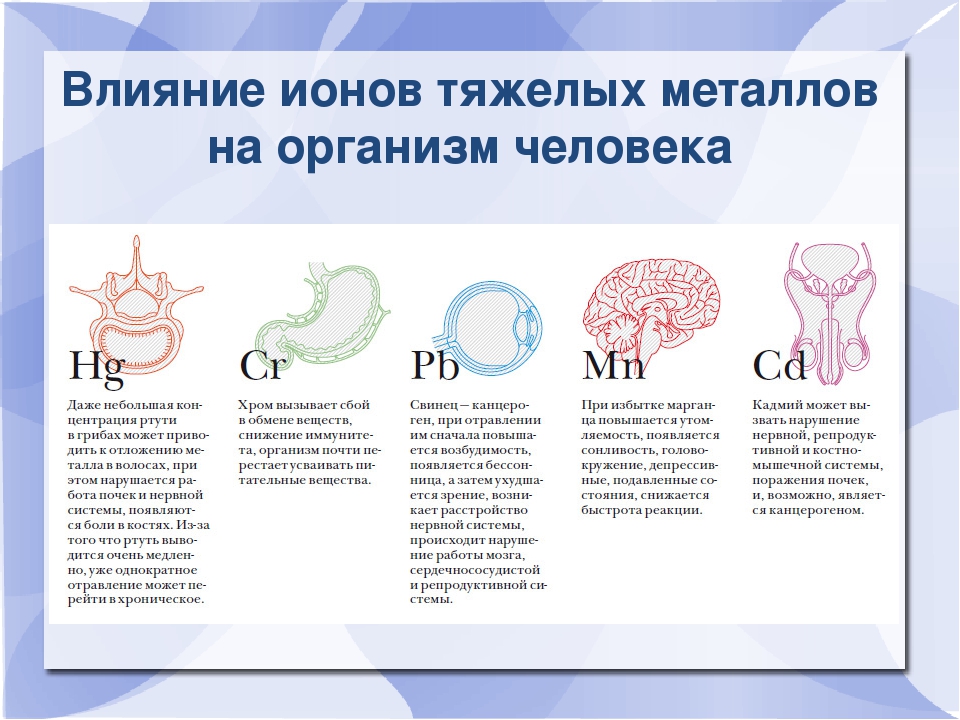
In case of mercury poisoning, the kidneys and hematopoietic functions of the human body are disrupted. Excessive amount of cadmium disrupts all types of metabolism. Lead is a powerful poison that attacks the intestines, liver, nervous system, blood vessels and protein fermentation. Copper has a pathological effect on the kidneys and liver. Thallium remains in the human body for 6 months and longer, causing damage to the visual and musculoskeletal system.
During the rehabilitation period, toxicologists recommend that the victim adhere to a special diet to restore the normal functioning of systems and organs.
Which mushrooms are more susceptible to radiation pollution?
According to laboratory radiometric control, the degree of accumulation of radioactive substances, namely cesium in mushrooms, can be divided into four groups:
- Weakly accumulated - autumn mushrooms.
- Medium accumulated - porcini mushrooms, chanterelles, boletus.
- Strongly accumulating - russula.
- Radionuclide accumulators - Polish mushrooms and boletus.
Polish mushrooms are real champions in their ability to accumulate radionuclides and literally suck them out of the soil. These mushrooms got their name due to the fact that earlier they were brought to the market from Poland, where they are considered one of the best edible mushrooms. In the CIS, Polish mushrooms grow in Belarus, the Baltic States and Ukraine. As a result of repeated measurements of the radiation level of fresh mushrooms of this species, it could be noted that the cesium content in them was at the upper level of the norm, equal to 500 Bq / kg. Such mushrooms are subject to rejection and disposal. Recently, even porcini mushrooms have begun to accumulate radionuclides.
This is due to the penetration of radiation pollution into the deeper layers of the soil, where the mycelium of these fungi is contained. Nowadays, inedible bile mushrooms are referred to as bioindicators. It should be noted that in coniferous forests there is no significant migration of long-lived radioactive elements deep into the soil due to the excessive accumulation of coniferous trees.
The radioactivity of the soil is maintained at approximately the same level. If you buy mushrooms on the market, even such as champignons and oyster mushrooms, be sure to ask the sellers for a coupon for checking the level of radioactive contamination. It should indicate the dose of the radionuclide content. Such a coupon is valid for 1 day. Champignons grown on radioactive soil also have an increased content of radionuclides or residues of fertilizers, such as nitrates. For mushrooms that are grown on an industrial scale, a hygienic certificate must be issued, which must constantly accompany the goods.
The intensity of cesium absorption depends on the density of distribution of contamination along soil profiles, on species characteristics, primarily on the depth of the mycelium and growing conditions. Studies have shown that there is less cesium in wood-destroying mushrooms, such as honey agarics.The main long-lived radionuclides that are part of the most radioactive contamination of the environment of nuclear energy origin, regardless of the types of sources, are cesium, strontium, with an extremely small amount of plutonium. The decay rate of these radionuclides is much lower than the rate of their accumulation in the environment; in modern protection systems and standards for the release of radionuclides into the environment, it leads to the accumulation of emitters in ecosystems. It becomes obvious that in conditions of technogenic pollution, the most effective measure is simply not to use mushrooms collected in the forest for food and to grow them under artificial conditions. Champignons and porcini mushrooms absorb mercury well. The consumption of such mushrooms in food leads to severe poisoning. And in this case, no penetration will help. Heavy metals are firmly embedded in the protein structures of fungi. It should be remembered that edible mushrooms can also be poisoned if they have been kept warm for a long time, because the proteins in them quickly disintegrate, forming poison.
Mushrooms play an essential role in the human diet. The aromatic substances contained in them give this product a unique taste and smell. Therefore, most of the people, despite the warnings and prohibitions, will definitely collect them and eat them. But there is no doubt that they cannot be bought on spontaneous markets. And where the next batch of mushrooms was brought from is not recognized by any of the sellers. If readers are inclined to experiment with health and believe that an additional "dose" of radioactive cesium will not hurt them and their children, then they should remember that all wild mushrooms, without exception, must be prepared according to a special scheme before use. A decrease in the cesium content in mushrooms can be achieved by boiling them for 15-60 minutes in salted water, then every 15 minutes the broth is drained.
For those mushroom lovers who use the only culinary treatment - only toasting without prior cooking, we definitely recommend changing their habits. And remember that it is strictly forbidden to eat mushrooms for children under 12 years old.
Svetlana Poperechnaya, veterinary medicine doctor
The presence of heavy metals in mushrooms
Edible mushrooms are dangerous because they can absorb heavy metals. If the amount of toxins is outside the normal range, they cause serious food intoxication and allergic reactions in the human body.
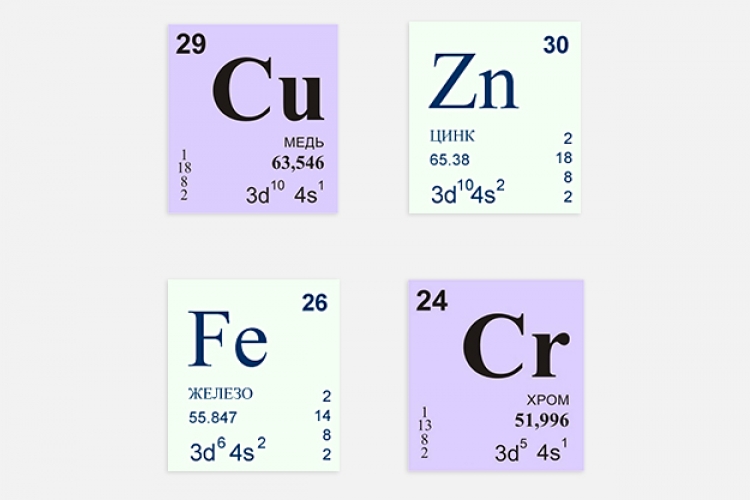
Scientists have determined that the main chemical elements that fungi are able to absorb are zinc, copper, lead, mercury, chromium, cadmium. The ability to accumulate heavy metals is determined by the type of mushroom: the umbrella mushroom absorbs cadmium, the champignon accumulates mercury, the raincoat and black milk mushrooms - copper.
The presence of toxins is determined by their chemical composition, the type of fungus and the characteristics of its mycelium, as well as the quality of soil, water and climatic conditions. The cap and the fruiting body accumulate the greatest amount of toxic substances.

The fruiting body of the fungus absorbs heavy metals mainly through the mycelium
Of particular danger are mushrooms that appeared after hot weather. They are definitely contaminated with heavy metals, since there are few of them. Rains help wash out toxic substances from the soil.
It is important to remember that the fruiting body absorbs heavy metals and other toxins mainly through the mycelium, which is in the substrate and lives longer. Therefore, several generations can be infected
Some types of these food products constantly contain heavy metals (there is arsenic in raincoats and ryadovki).
Environmentalists and mycologists recommend refraining from eating mushrooms due to the environmental situation in the world
If this cannot be avoided, then adhere to the precautions and recommendations of the forester, sanitary epidemiological station and experienced mushroom pickers
Than dangerous

Heavy metals include lead, cadmium, mercury and nickel, all of which are considered toxic.They enter the human body with food, water, polluted air, and even through nickel-plated dishes.
According to the Autonomous Non-Profit Organization Center for Biotic Medicine, most often Russians are exposed to lead, which can accumulate in the body. Basically, it gets there with air mixed with exhaust gases from cars, as well as with vapors from industrial and domestic waste. With an excess of lead, a person develops cardiovascular diseases, as well as diseases of the nervous system and kidneys.
As for cadmium, it enters the body through inhalation of tobacco smoke. In addition, in some regions of Russia there is industrial pollution with cadmium associated with the activities of metallurgical plants and the storage of household and industrial waste. If cadmium accumulates in the blood and internal organs, it can lead to liver damage, anemia, osteoporosis and hypertension.
Mercury enters the body through food, drinking water, and through dental fillings (some of them are 50% mercury!). When poisoned with this substance, a person develops mood and sleep disorders, asthenic syndrome and even tremors of the hands.
Nickel can seep into the bloodstream with food or through the skin and mucous membranes - for example, if you are in the habit of eating from nickel-plated dishes. Dental crowns also contain certain doses of nickel. By the way, according to the WHO, nickel is one of the most dangerous substances that pollute the environment. Nickel poses the greatest danger to children, especially when combined with excess cadmium. This "explosive mixture" provokes severe allergies and reduces immunity.
By the way, chronic intoxication caused by any of the above substances can cause more serious health problems, including cancer.
Breeding and Engineering
To obtain plants that are resistant to unfavorable anthropogenic influences, methods of modern cell selection, as well as genetic cell engineering, are actively used.
For example, specially bred hybrid poplars are capable of transforming and destroying various solvents, including organochlorine ones. They also have a deeply penetrating root system, a high growth rate, and are able to adapt well to various climatic conditions.
Special attention is also paid to the production of heavy metal hyperaccumulator plants. Species with high productivity are taken as a basis and a bacterial genome is introduced, which is responsible for the formation in plants of the ability to adsorb or transform pollutants in significant quantities
This method is especially effective for breeding resistant lawn grasses.
Accumulation of heavy metals by fungi
Fungi can accumulate heavy metals: cadmium, mercury, lead, copper, zinc and others. The concentration of these metals in mushrooms is higher than in the soil on which they grow. This concentration is often not enough to cause severe poisoning, but heavy metals can affect enzyme systems, complicating the processes of neutralizing toxins contained in mushrooms.
The concentration of heavy metals in mushroom caps is higher than in stems. Much depends on the type of mushroom. It was found that pigs, as well as black milk mushrooms, accumulate copper especially intensively, while champignons and porcini mushrooms accumulate mercury.
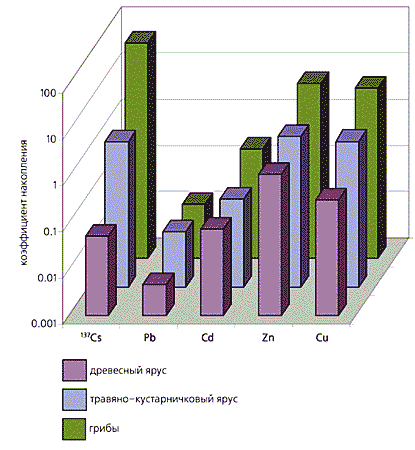
Mushrooms have a selective ability to accumulate elements, in particular those hazardous to human health. The tendency of edible mushrooms to accumulate heavy metals is especially dangerous. This ability is expressed in them much more sharply than in higher plants and other organisms. Thus, the content of copper in fungi can be 13 times higher, lead - 2 times, cadmium - 7, nickel - 2, chromium - 2.5 times.
The thing is that mushrooms are non-photosynthetic plants (actually, mushrooms are not plants or animals, they are a separate kingdom in the classification of living beings), which have a different feeding mechanism; they have a specific affinity for certain elements. The highest degree of accumulation by fungi (accumulation index) is characteristic of mercury, cadmium, copper, zinc and selenium. The boletus and the umbrella are distinguished by the biological accumulation of cadmium, and the mushroom and the raincoat of copper. Honey mushrooms stand out with a special ability to accumulate cobalt and zinc.
Many researchers note that mushrooms intensively accumulate heavy metals; moreover, they have a specific affinity for some of them. They can accumulate Cd, Cu, Zn, Hg and a number of other elements. So, mercury in them can be 550 times more than in the substrate on which they grow. Species of the genus Leccinum (obabok), Macrolepiota (umbrella mushroom) absorb Cd well; slender pig (Paxillus involutus), black milk mushroom (Lactarius necator) and giant slicker (Lycoperdon maximum) - Cu; species of the genus Agaricus (champignon) and porcini mushroom (Boletus edulis) - Hg. Heavy metals irreversibly affect the biochemical apparatus of fungi, and their use leads to severe poisoning.
In general, the accumulation of heavy metals, like radionuclides, is determined by the chemical nature of the element itself, the biological characteristics of fungal species, as well as the conditions of their growth.
According to literature data, for some mushrooms the content of individual elements is borderline or exceeding normal (Cd - in white and bile; Cu - in bitter; Zn - in white, bitter and russula). In this case, their concentration in mushrooms increases by 2-5 times. Among the pollutant elements, the minimum concentration fluctuations are typical for Pb, and the maximum for Cu. A higher content of heavy metals in fungi is observed in ecotopes of different storage capacity. As a rule, this is closely related to the presence of mobile forms of elements in soils and weakly to the total content.
Apparently, mushrooms poorly or do not assimilate sparingly soluble forms at all. It is known that metabolic processes are most intense in the caps, therefore the concentration of macro- and microelements there is higher than in the legs. With the development of fruiting bodies, the intensity of the accumulation of elements also changes. As a rule, there are more of them in young fruit bodies than in old ones.
A lower concentration of all heavy metals is characteristic of saprotrophs, and a higher concentration is characteristic of symbiotrophs. But since the selectivity of individual fungi in relation to metals is not the same, it is rather difficult to isolate species-bioindicators for heavy metals.
Thus, Pb is maximally absorbed by the bile fungus; Zn - white, bitter and russula; Cu - russula and bitter; Cd is white. Nevertheless, as a first approximation, we can say that bitter (Lactarius rufus) and gall fungus (Tylopilus felleus) have the best bioindicator properties in relation to heavy metals.
Prevention of intoxication with infected mushrooms
Preventive measures are designed to protect people from the severe consequences of toxic mushroom poisoning. These simple guidelines will help preserve human health and life.
During assembly, foresters and experienced people advise paying attention to:
- the degree of pollution of the territory where mushrooms grow;
- avoid areas close to roads and railways;
- do not collect them in an industrial area, near mines, in city parks;
- availability of documents on environmental verification (upon purchase);
- not to buy canned mushrooms in spontaneous markets and more.
The collected mushrooms must be thoroughly washed and cleaned. Then they should be boiled in salted water with acetic or citric acid. They should simmer for about an hour. During this time, you need to change the water three times. This pre-preparation procedure will help reduce the amount of radioactive isotopes and heavy metals.
You need to dry only clean mushrooms, since the level of radionuclides in dry ones is the same as in fresh ones. Pediatricians do not recommend giving this product to children because their stomachs cannot digest such heavy food. Due to the risk of contamination of these products, they should be excluded from the diet of baby food.
Pollution of the forest ecosystem leads to the appearance of edible, but toxic, mushrooms. With them, heavy metals and radiation can enter the human body, since these representatives of the flora are able to absorb and retain toxins in themselves.
Therefore, these food products must be treated with caution.
Filter plants
Herbaceous plants are used for phytostabilization of pollution - reducing their mobility in the soil due to adsorption or precipitation on the roots in the form of insoluble compounds (phosphates, carbonates, hydroxides, etc.). In this case, they usually choose species that are resistant to pollution, capable of forming a dense herbaceous cover, bind pollutants in the process of intensive root exchange.
For example, when creating lawns on acidic soils with a high copper content, various types of bent grass and fescue are planted in zinc, some legumes are introduced on calcareous soils with a high lead content.
Leguminous plants, together with microorganisms-symbionts from the root zone, can also participate in biodegradation - the decomposition of various organic pollutants.
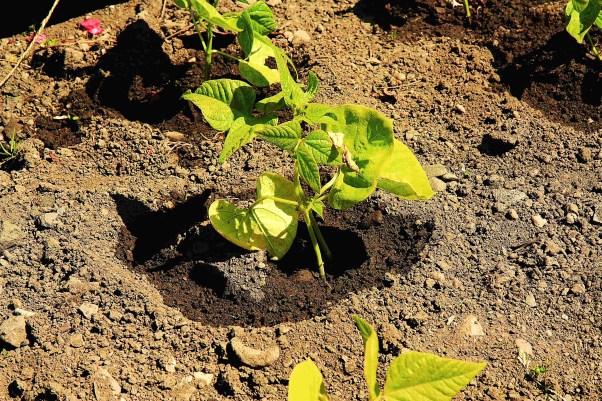

Legumes help improve lead-rich soils
Some plants - sedge, various types of beans, wheat, rice - are capable of phytotransformation of pesticides, solvents, fuel residues, transforming (metabolizing) them using their own intracellular enzyme systems.
Cruciferous plants are used for phytoextraction - removing contaminants from the soil. They are accumulators of heavy metals and radionuclides that enter plants through the root system and are deposited in aboveground organs (stems and leaves). The plant biomass can then be collected and processed. The most widely used phytoextraction is to remove lead, zinc, cadmium, nickel from the soil.
Some fern species, which are typical representatives of forest ecosystems, are also quite active in accumulating heavy metals.
For example, the common ostrich is able to absorb cadmium ions from the soil and accumulate in the leaves, which does not have a significant inhibitory effect on the green (photosynthesizing) part of the plant itself.

The common ostrich is able to absorb cadmium ions from the soil
What's really wrong with mushrooms?
You can get poisoned. To the harm of fungi for the body and poisoning occurs due to incorrect identification of the fungus - poisonous is taken for edible. WHO recommends "avoiding the consumption of any wild mushrooms in the absence of full confidence in their harmlessness."
The safest way is to buy cultivated mushrooms in the store.
They accumulate heavy metals. Accumulated dangerous heavy metals in wild mushrooms - mercury, arsenic, cadmium and lead. Their content depends on various factors - primarily on the type of fungus and the place where it grows.
Mushrooms harvested in contaminated areas, such as near metallurgical plants, are best avoided. But, as shown in the review of works for 2000-2009, even in unpolluted areas, the content of mercury in porcini mushrooms sometimes exceeded the permissible values.
The permissible content of some metals can be exceeded if a certain type of mushroom is eaten regularly (for example, the cadmium content in the Finnish line of ordinary). Therefore, it is better not to lean on the same type of wild mushrooms for weeks.
Cooking reduces toxic metals. For the greatest effect, boil the mushrooms for at least 20 minutes. In addition, the concentration of metals is reduced by soaking, but not for too long: after 8 hours, the concentration may begin to rise again.
The content of heavy metals in cultivated mushrooms is insignificant.
May cause allergies. Allergy to the mushrooms themselves is rare - in 1 percent of people. More often, allergies are associated with mold allergies and occur as a result of a cross-reaction - when a protein in a food is similar to the protein that causes the allergy. But in general, the question "can there be an allergy to mushrooms" is not forbidden to answer in the affirmative.
What's good about mushrooms?
Cellulose. In a cup of fried mushrooms, 1.9 grams of fiber, that's 7.6% of the RDI. But here mushrooms lose out to vegetables: for comparison, a cup of broccoli contains 5.1 grams of fiber, which is more than 20% of the daily value.
Protein. In 100 g of mushrooms, 4 grams of protein at a daily rate of 50 grams. This is not much, but if there are other categories of products along with mushrooms, the norm will easily be typed. For comparison: in 100 g of chicken meat - 27 g, in 100 g of mozzarella cheese - 22 g, in 100 g of boiled white beans - 10 g.
Low in calories, fat and cholesterol. A portion of fried champignons contains 28 calories (in a small piece of meat it is almost ten times more), broccoli - 55. There is almost no fat, no cholesterol at all.
Low sodium. Excess sodium is associated with cardiovascular disease, and its main source is food salt. Mushrooms have a bright taste due to the high content of glutamate - umami. This allows you to use less salt in mushroom dishes without losing flavor.
Helps control weight. A diet that replaces red meat with mushrooms can help reduce weight. Therefore, for example, American researchers propose replacing some of the meat in burgers from the school cafeteria with mushrooms - most children do not notice the substitution. It can help fight obesity in children.
They can accumulate vitamin D. Vitamin D almost does not enter the body with food. Among the exceptions are mushrooms. When exposed to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet radiation, they accumulate vitamin D. Forest mushrooms, such as chanterelles, are a better source of vitamin D compared to cultivated mushrooms, which are usually grown in dark greenhouses. However, in a number of countries - the United States, Holland, Ireland and Australia - large farms are already exposing mushrooms to ultraviolet radiation, so that a portion of these mushrooms can cover the daily need for vitamin D.