How to distinguish false counterparts of an inedible mushroom?
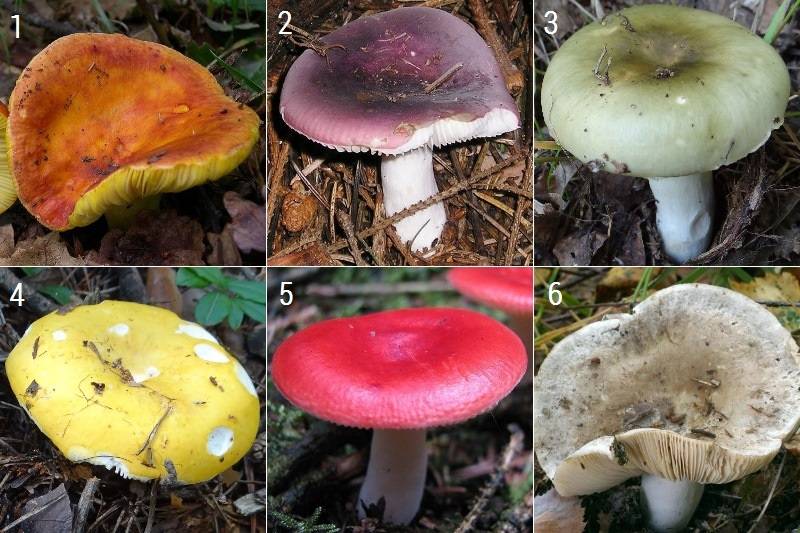
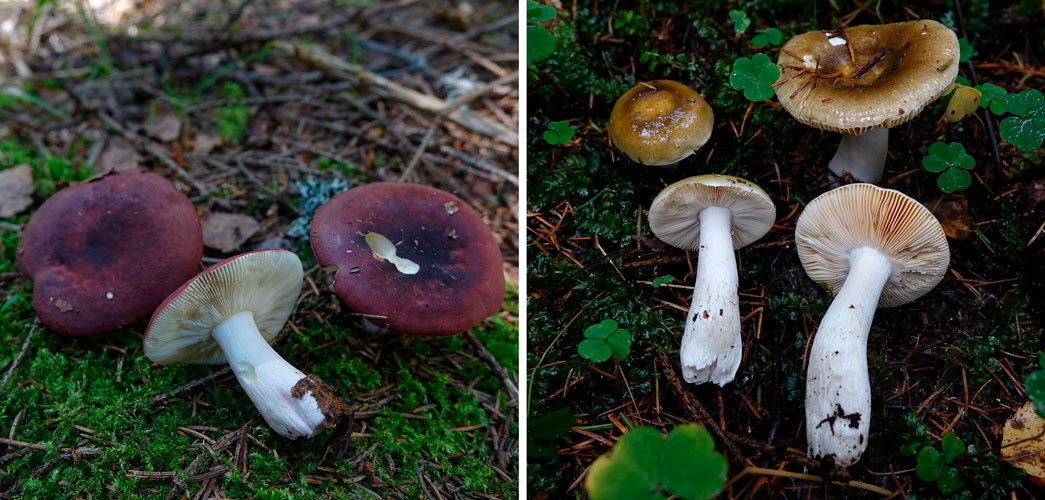
There are no twins of the burning russula. But it is easy to confuse it with russula brittle, ocher and marsh. However, there are a number of differences that make it possible to determine the type of fungus for sure. Table 1 presents the collected and presented distinctive features.
| Distinctive sign | Russula fragile |
Buffy russula
|
Marsh russula
|
| The size | Smaller in size | Same size | Same size |
| Hat | Explicit purple | Yellowish in color and at high humidity becomes immediately covered with mucus | The same shade, type of plates, but completely dry to the touch |
| Leg | Not white, but yellowish or creamy | Thin and long, with slight wrinkles | Shaped like a mace |
| Smell of pulp | Fruity smell is present | No fruity smell | Fruity smell is present |
Difference from ordinary edible russula
Among the edible species, the stinging beetle is similar to the beautiful and food one. Sometimes even experienced mushroom pickers find it difficult to distinguish false russules from edible ones, because they look almost the same. Their main difference is the absence of an unpleasant, pungent taste, so one of the simplest and most reliable ways to distinguish these mushrooms is to lightly lick the pulp at the break point.
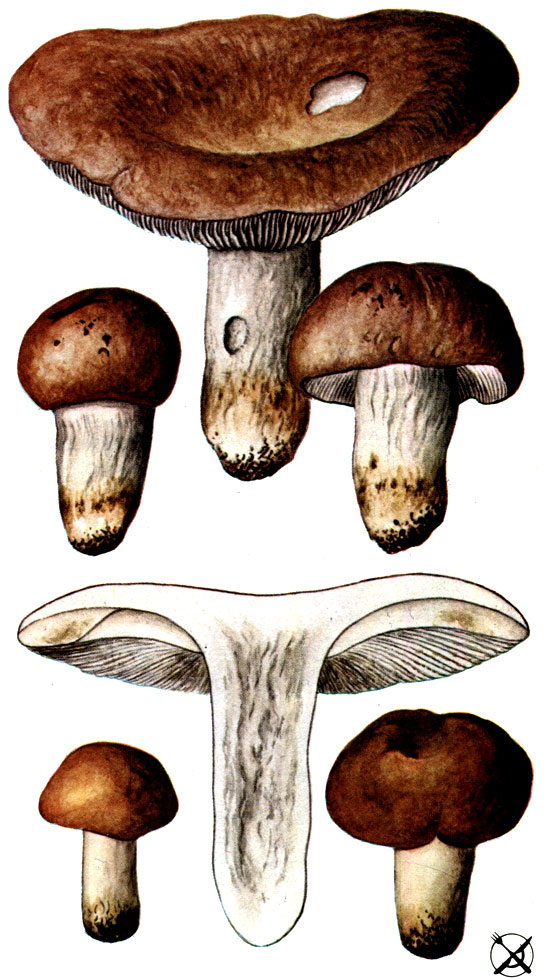
Russula: description and photos of mushrooms. What does a russula look like?
Hat
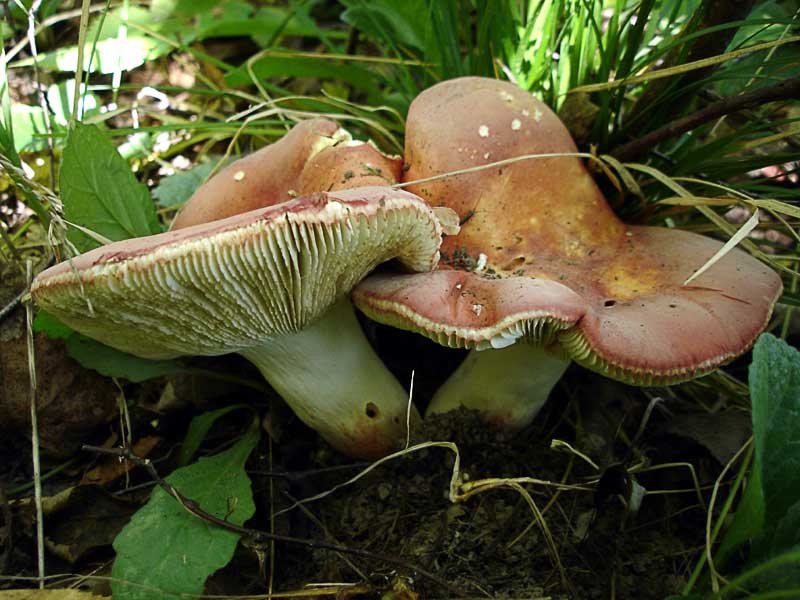
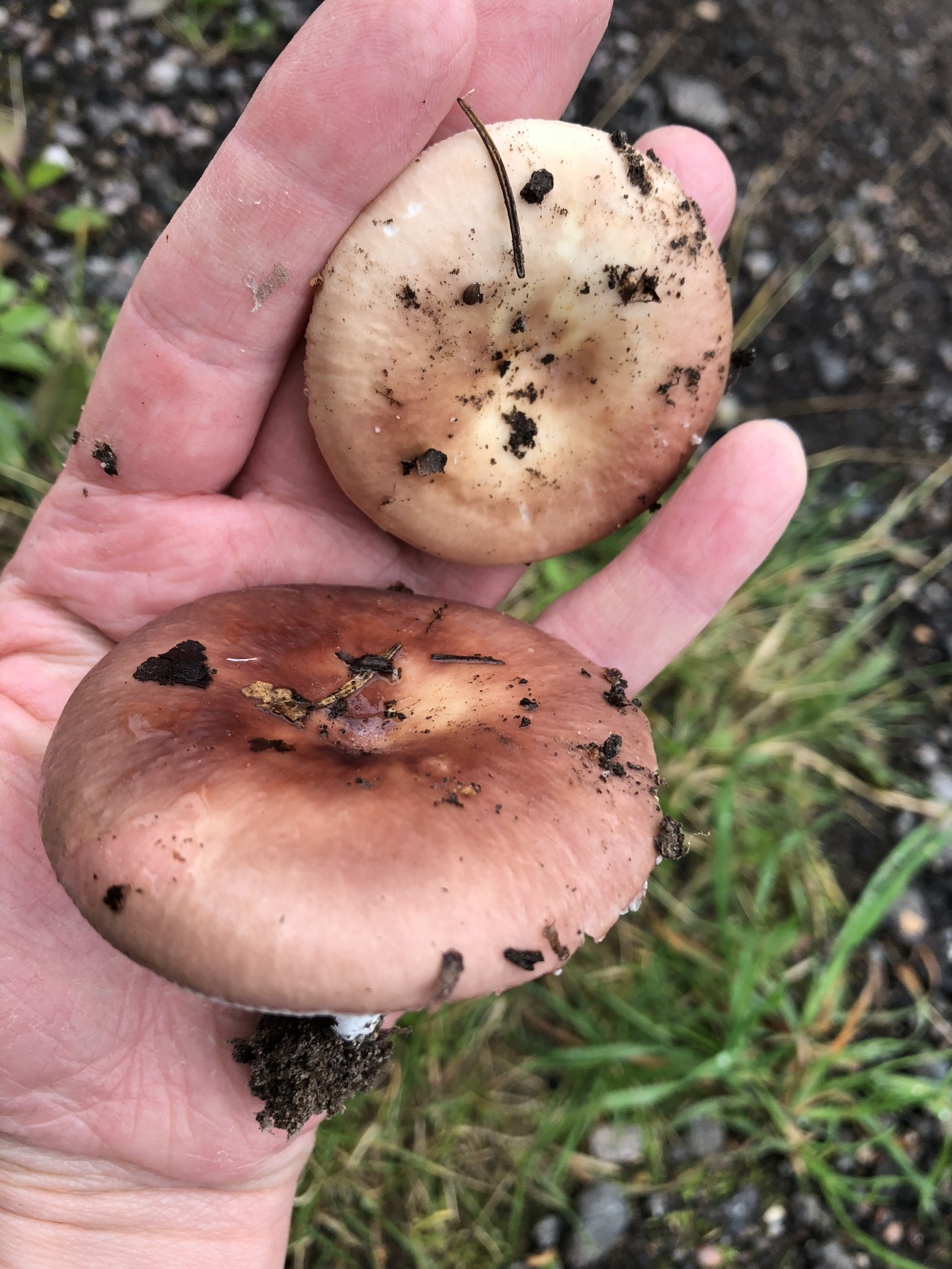
The fruit body of russula consists of a cap and a leg. The shape of the cap changes as it grows and develops. In young russula, it is semicircular, almost spherical, hemispherical; then it becomes convex or convex-outstretched, and in old mushrooms - flat with a concave center or funnel-shaped.
The edges of the cap in different species of russula can be ribbed, wavy-curved, tuberous or smooth, changing with age. In some species, the edges are straight, in others they are lowered or raised. The sizes of the caps vary from 2 to 15 cm.
The skin covering the cap, even in mushrooms of the same species, can have:
- either smooth, damp and sticky;
- or dry, matte, soft velvety.
The adhesive surface can dry out over time, and sometimes it is dry initially.
The peel from the pulp of the cap lags behind in different ways:
- easy (in birch russula (lat.Russula betularum);
- up to half (in the solar russula (lat.Russula solaris);
- only along the edge (at the golden russula (lat.Russula aurea).
The color of the russula cap includes almost all shades of the solar spectrum: red, yellow, green, purple, bluish, brown. The color is not always monochromatic: sometimes it has uneven spots and various color transitions, as if fading in the sun.
Hymenophore
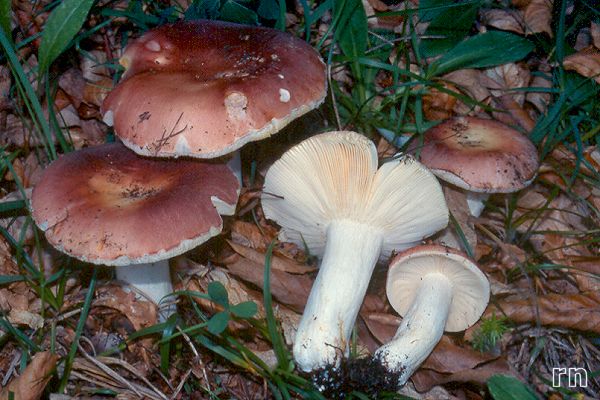
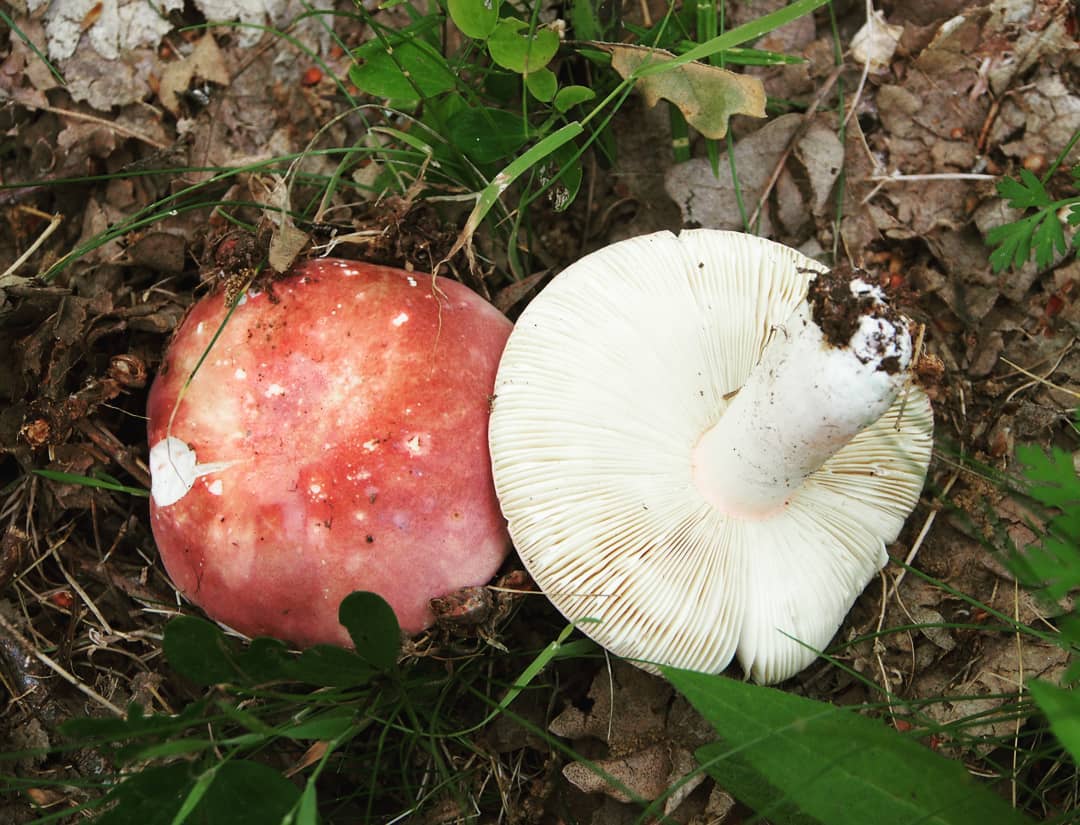
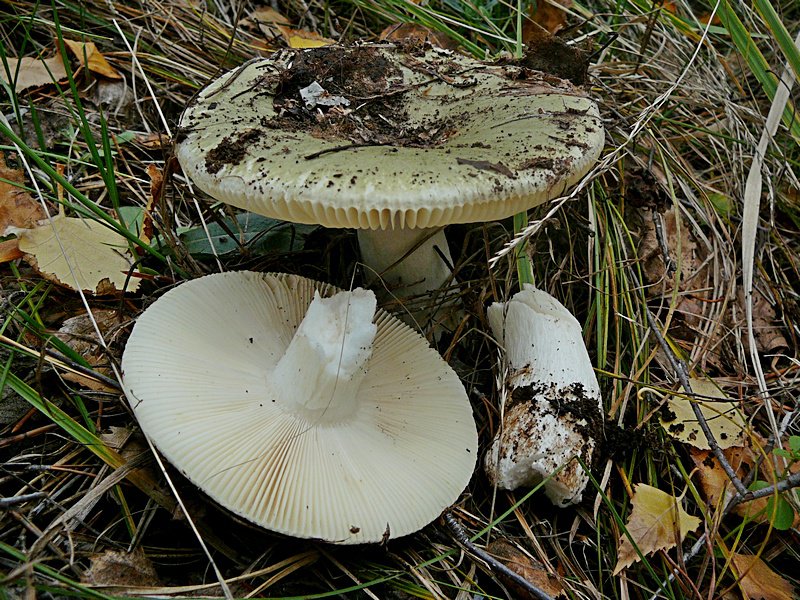
The russula hymenophore, or the lower surface of the cap, consists of widely or narrowly adhered plates of various lengths, thicknesses, frequencies and colors. Russula plates can be white, light yellow, light cream, slightly pinkish, ocher, lemon yellow.
Leg
More often there are russules with cylindrical, regular-shaped legs, less often - with fusiform (olive russula (lat.R. olivacea), clavate (golden russula (lat.R. aurea), cylindrical, but narrowed towards the base (food russula, or edible (lat. R. vesca). The leg is attached to the middle of the cap. Its flesh changes with age, in young mushrooms it can be full, that is, loose, cotton-like or dense. With aging, cavities appear in it, it becomes spongy and The color of the leg can be light: white, yellowish, cream, pinkish, or dark: gray or brown. Rusty spots may be present at its base, such as, for example, in the green russula (Latin R. aeruginea). The surface of the leg is smooth , naked, silky or velvety, may become slightly wrinkled with age.
Pulp
The flesh of the cap is mostly white or very light in color; thick or thin; odorless or with a faint aroma and a different taste. When the fruiting body of the russula breaks, the milky juice is not released.
The plates, pulp and legs of russula are very fragile. Fragility and fragility of these mushrooms is given by spherocysts - special groups of vesicular cells that are found in the fruiting body.
Spore powder
The russula spore powder also has a different color: whitish, cream, light cream, yellow, light ocher.
The benefits and harms of russules. Is it possible to get poisoned with russules?
The fruit bodies of russules include:
- vitamins B1, B2, C, E, PP,
- minerals: potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorus and iron.
Russula mushrooms are suitable for the nutrition of athletes and people who monitor their weight, as they are a low-calorie product and a source of easily digestible protein. In terms of the amount of vitamins and minerals, russula surpasses, for example, cranberries, which are known for their beneficial properties. Some types of russula are capable of antibacterial action for abscesses. They can be used as a blood thinner and prevent blood clots.
But it should be borne in mind that mushrooms are heavy food for the liver and stomach, therefore, people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver, the elderly, pregnant women and children should use them with caution. It is quite difficult to distinguish russula
Care should be taken not to ingest inedible species, as they can cause poisoning and malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. If symptoms of poisoning appear, the following measures must be taken:
It is quite difficult to distinguish russula. Care should be taken not to ingest inedible species, as they can cause poisoning and malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. If symptoms of poisoning appear, the following measures must be taken:
- call a doctor;
- flush the stomach, causing vomiting;
- take a sorbent, for example, activated carbon, smecta, polysorb or enterosgel;
- provide an abundant drink;
- put the victim to bed with a warm heating pad to his feet.
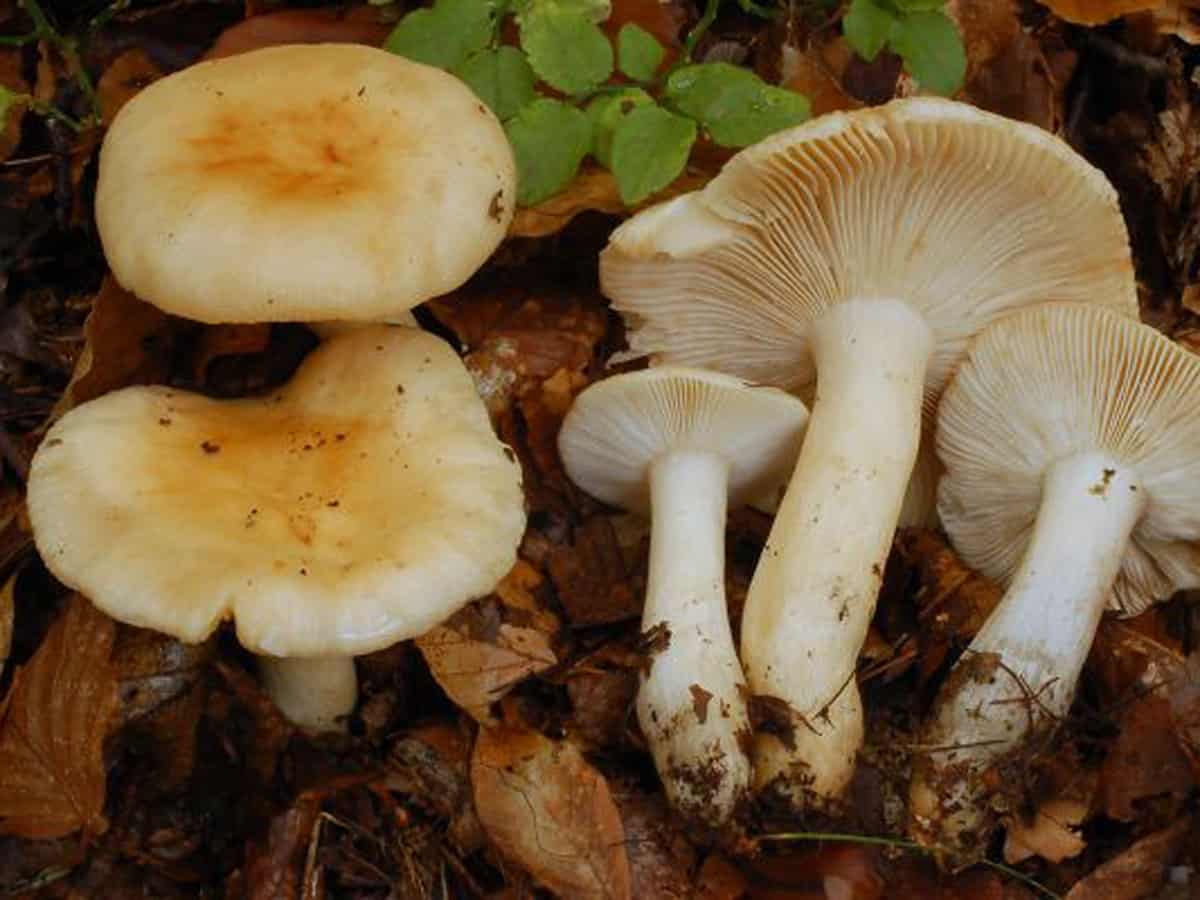
Food russula - description, where it grows, the toxicity of the mushroom

The appearance of the mushroom
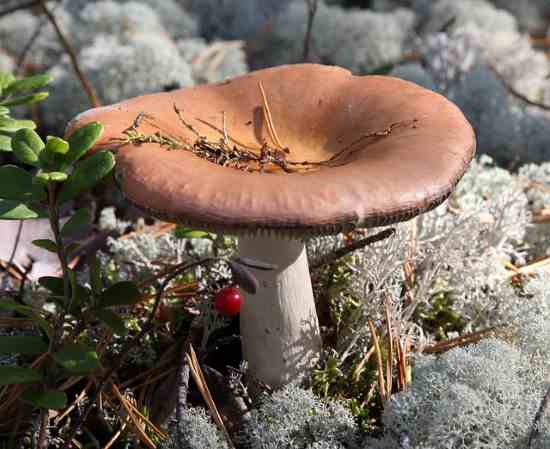
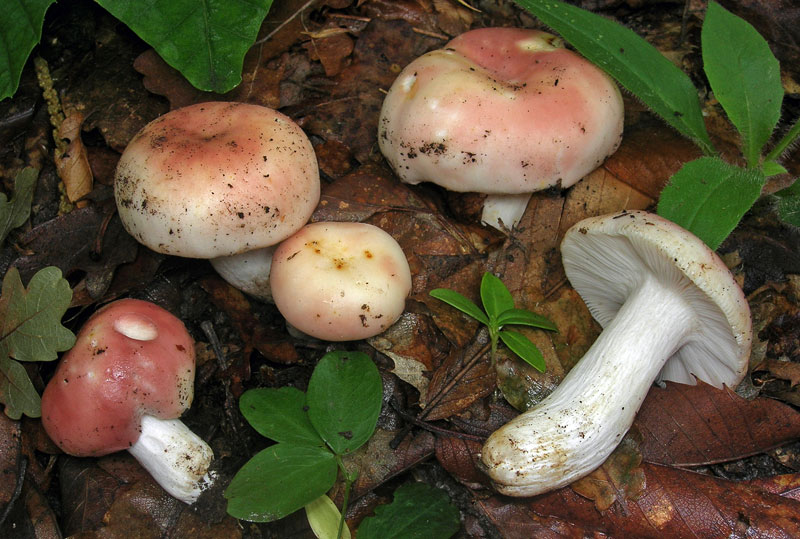
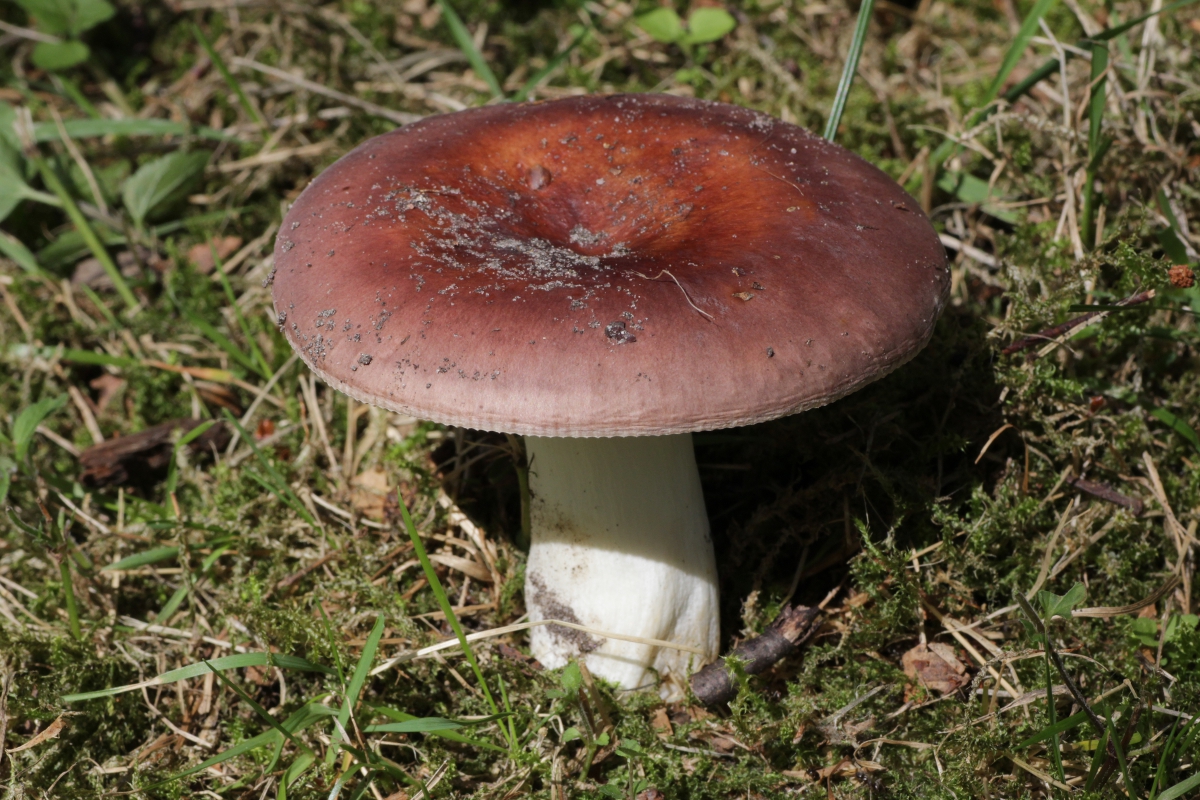
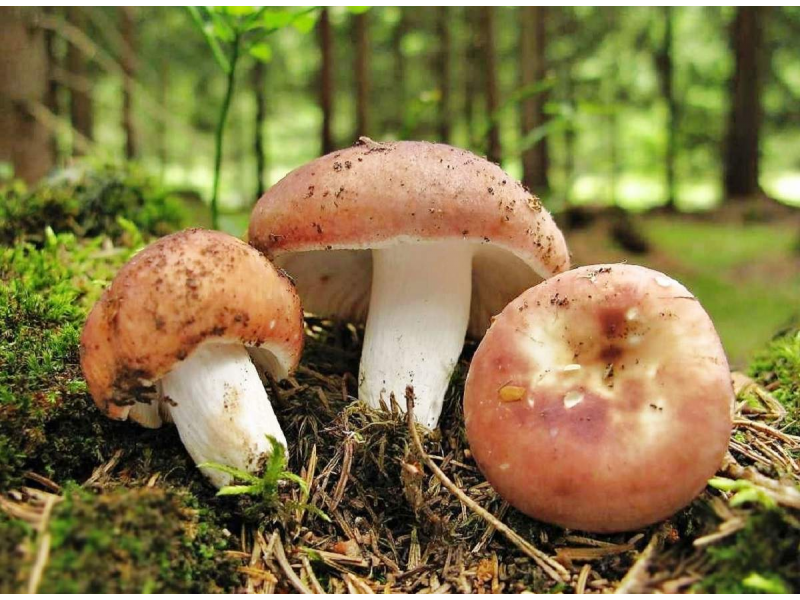
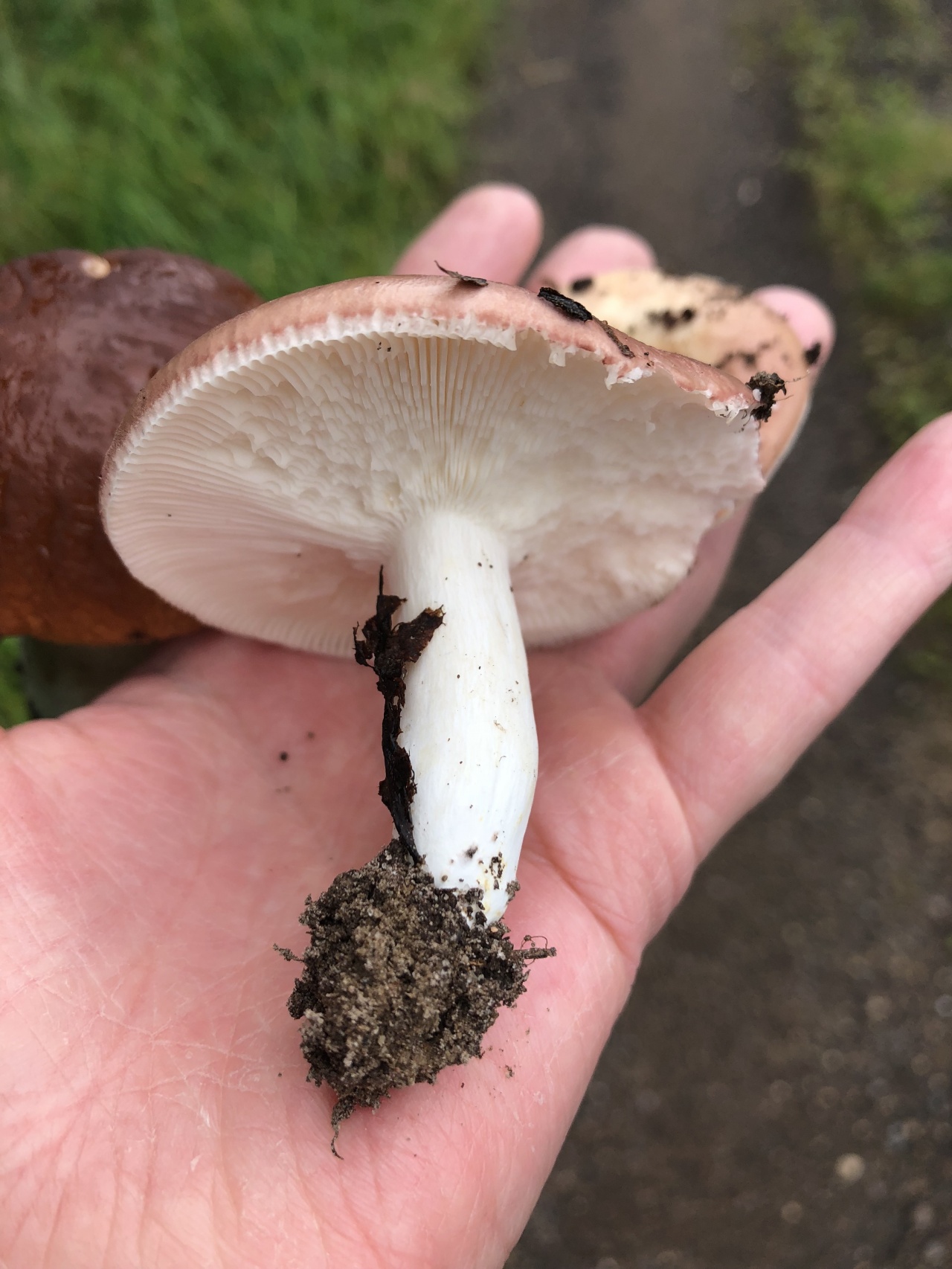
The representative of this species has a white and pink hat. There is also a dark pink appearance. The hat is about 10 centimeters in diameter. Sympathy has a rather dense structure. Does not fall through when pressed. The mushroom leg is also dense. An edible russula can be easily identified by its skin on its cap. It recedes slightly over the edges of the surface. There is a small valley in the middle part of the cap. You can also see white streaks on the hat that cover it here and there.
The plates on the inside of the cap turn yellow over time. In (then the mushroom is young, they remain white. As they grow, they have a golden hue. It is very easy to determine the age of the mushroom by them. So even quite old russula retain the density of the leg, which is why they are especially appreciated by mushroom pickers.
Growing places
Most often, this kind of fungus is found in dry places on sandy soils with a small amount of grass. It can be found in European forests and in central Russia. Yes, it does not grow in mountainous areas. Mainly only in deciduous forests. The main fraction of these mushrooms grows in the summer-autumn period. From June to September.
The edibility of the mushroom
The name of the mushroom is sometimes misleading. It is better not to taste it raw. He will be forced to undergo minimal heat treatment.
This mushroom is very healthy. It contains a lot of substances necessary for the body, among which you can carve out:
- Magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, which strengthens the mortal remains.
- Sodium and potassium, which normalizes the water-salt balance.
- Iron needed to benefit anyone from hemoglobin.
The calorie content of this mushroom is about 19 kcal.This is a rather nutritious mushroom, it contains dietary fiber, useful elixir of life and active biological substances. Due to its low calorie content, it is used to treat and cleanse the gastrointestinal tract. With regular use, the thing of the heart is restored and blood pressure normalizes.
But most mushroom pickers are in a hurry to take this mushroom into their baskets. All because of the brittle pulp. Therefore, it is difficult to convey them in the future to the house as a whole.
Also another property of russula is its vocation to curdle milk. Therefore, it is sometimes used in cheese making. So far, one component of russula is very useful for the body. It contains lecithin, one or the other prevents the formation of cholesterol.
How to cook russula
Some people in this family have a slightly bitter taste. This does not apply only to those that have a pink, egg or greenish tint. But it is better to soak the food russula in water in advance, then, without fear of it, you can eat it well. It can also be dried. It is a non-poisonous mushroom, but it should learn minimal processing.

It got its name due to the fact that it takes a little time in all respects to prepare it. Just 5-7 minutes is enough so that it only remains to be eaten. It can be consumed fried, boiled and salted. Yes, it is also used as a blank for the winter.
Correct waste
You can store russula in the refrigerator for 5 days. But to be this you need to know that they have unimportant (= unimportant) contact with each other, otherwise they will quickly begin to deteriorate. You can save by wrapping each mushroom in a damp cloth. To preserve the mushrooms, keep them for a longer period, they will have to be dried or tightened. Dried mushrooms are stored in a tightly closed dark container in a cool dry place. Frozen goblin meat can be stored for 8-10 months, but the temperature should not be higher than -18 degrees.
On the right not to be mistaken with a choice
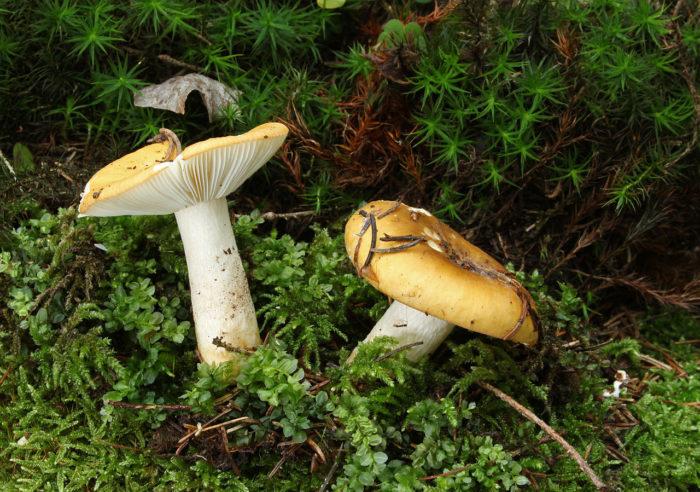
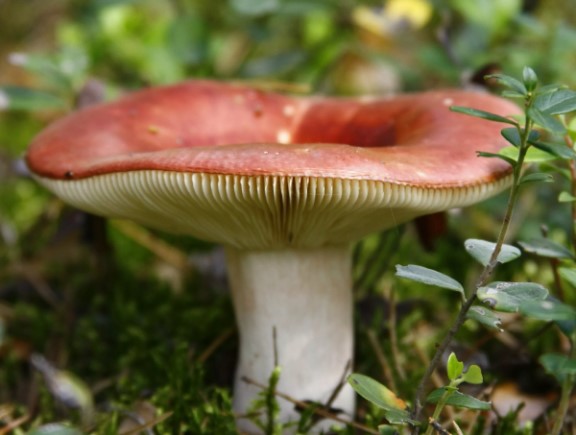
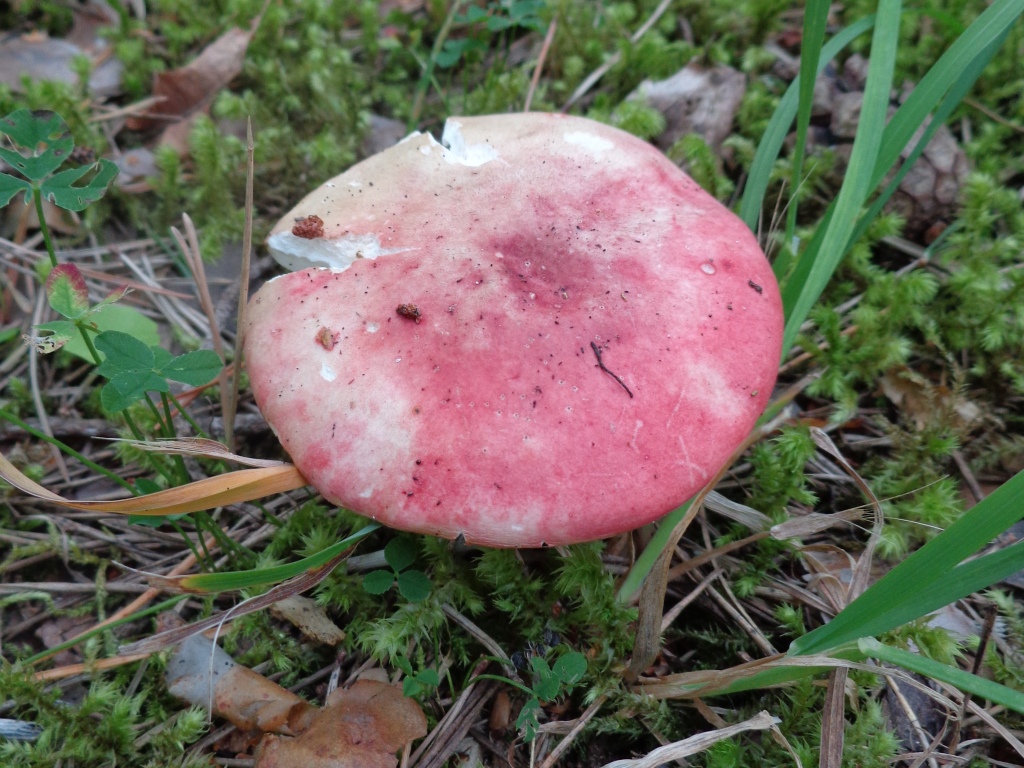
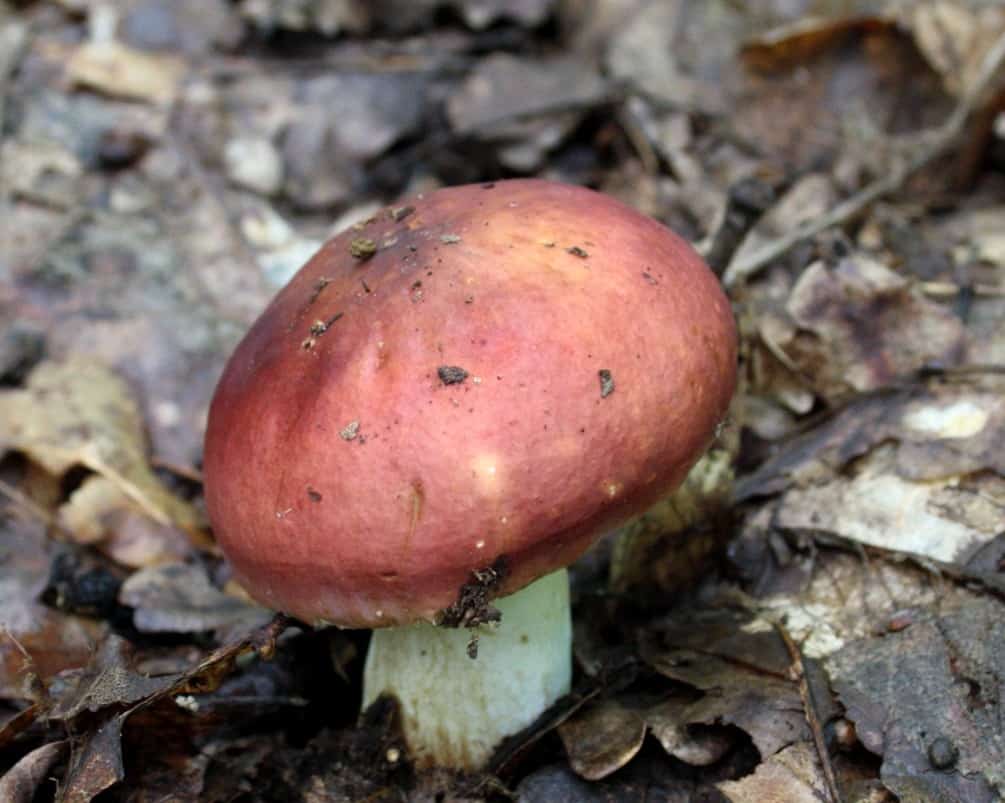
The russula is dangerous because, exactly without knowing whether the mushroom is edible or not, it fell into a rake, mushroom pickers begin to eat them. But this should not be done. Because this can lead to unpleasant consequences. For example, this type of goblin meat is known as russula vomit. He fully lives up to his nasty nomination. This mushroom has a brighter reddish cap. After the use of such a mushroom, vomiting may begin, the mucous membranes will be irritated.
Safe russules are pinkish or slightly yellowish in color. They have a slightly sweet taste. Such unprofitable russula will harm the body even in its raw form, but it is easier not to risk it. False russula are distinguished by their smell. They exude an antipathy, even pungent odor. The russula has a weak mushroom food, glimpses of a nutty aroma.
Russula is a nutritious and very tasty goblin meat, but it is necessary to correctly distinguish it among inedible species, after which the body will receive only benefits.
How to distinguish russula from doubles
The russula are very diverse and are a very difficult genus in terms of identifying and limiting species. The differences between species are sometimes very small, making it difficult to identify these fungi. Accurate determination can be made using microscopic features as well as chemical reactions. When determining, it is necessary to have specimens of the same species at different stages of development.
Most russula are edible mushrooms, mainly of the 3rd and 4th categories. The economic value of russula is reduced due to the fragility of the fruit chalk. Few of them are poisonous, inedible, or of no practical value.
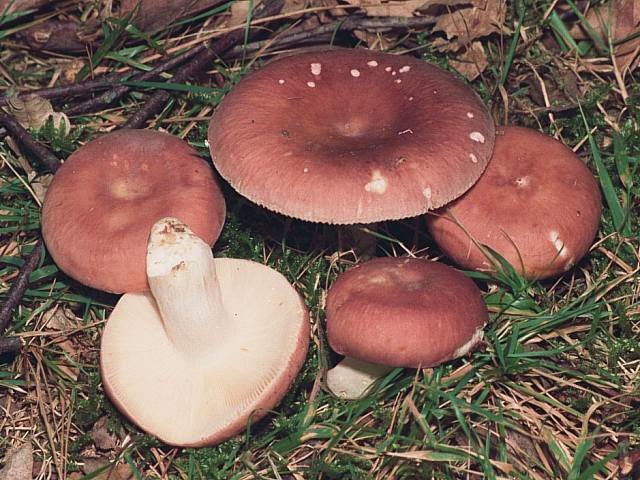
Both in appearance and in their structure, all types of russules are in general very similar: the caps of young mushrooms are completely spherical, becoming a little funnel-shaped by old age.Almost all russula have white, even legs, white dense flesh in young mushrooms, becomes fragile, brittle, crumbly with age. Even if you carefully put the russula in the basket, you still risk bringing home only mushroom crumbs, and only the young, with the hat still unopened, remain intact. For this brittle pulp, russula, in general, cannot be confused with any other mushrooms.
Russula in foliage.
The russula is burning.
Valuiform russules.
From the name of these mushrooms, it might seem like they can be eaten raw. In fact, everything is quite the opposite, raw these mushrooms are a terrible pungent bitterness, and the name "russula" can be translated as "raw pungency", so as not to try and try them. But in salting and during heat treatment, the acridity of russula completely disappears.
Most mushroom pickers do not distinguish russula by name at all. For them russula is russula: red, yellow, lilac, pink, green. So do not worry if you suddenly failed to determine the type of this or that russula: they are all edible. There are no poisonous russules among the russules, there are only inedible ones because of their bitter or unpleasant taste. The main thing is to be able to distinguish between such inedible species - but most of them are marked with a red leg or an unpleasant odor.
A stinging inedible russula.
There are also mushrooms in the russula family, which some mistakenly classify as mushrooms, calling them dry mushrooms. These are loads. Indeed, they have a weight-like appearance, not a russula: large, dense, with a short stem, with curled edges of funnel-shaped caps, with plates descending to the stem. But one cannot fail to notice their main difference from milk mushrooms - this is the complete absence of milky juice. Therefore, these mushrooms are popularly called dry mushrooms, that is, not weeping.
The flesh of the cap is mostly white or very light in color; thick or thin; odorless or with a faint aroma and a different taste. When the fruiting body of the russula breaks, the milky juice is not released. The plates, pulp and legs of russula are very fragile. Fragility and fragility of these mushrooms is given by spherocysts - special groups of vesicular cells that are found in the fruiting body.
Several types of russula are called podgruzki, but most often two: white podgruzdok (Russula delica) and black podgruzdok (Russula adusta). The fruiting body of these mushrooms is formed underground, and when the fungus appears on the surface of the soil, there is always a lot of adhering debris on its cap. Loads, even very young ones, are often wormy. They grow in large groups, they love humus-rich soil.
Spore coloration is an important sign of russula. When determining russula, it is necessary to determine the color of the spore powder macroscopically in the mass. The color of the powder in different species ranges between pure white and intense yellow, with various transitions and shades.
Features of russula varieties
Russula is the most common mushroom belonging to the russula family. At the moment, more than 270 species of russula are known, about 10 species grow on our territory. Almost all members of this family are either suitable for human consumption or of little use, being conditionally edible or toxic mushrooms.
The cap of russules can be spherical, bell-shaped. In mature mushrooms, it is spread or flat. Sometimes funnel-shaped with a curled or straight edge (in some representatives, the edge is ribbed). Skin color from greenish-brown to red shades (in poisonous russula), dry to the touch, shiny or matte. Easily separates from the pulp (grown in some mushrooms). The plates are descending (free), adherent, of various lengths, frequent (rare in some representatives), brittle. Their color ranges from white to yellowish shades.
The russula mushroom has a dense pulp, fragile in the leg. The color is white, changing when notched and as it ripens. The leg of russula is cylindrical in shape, even, sometimes thickened at the base.The color is white (or to match the cap). The leg is hollow inside.
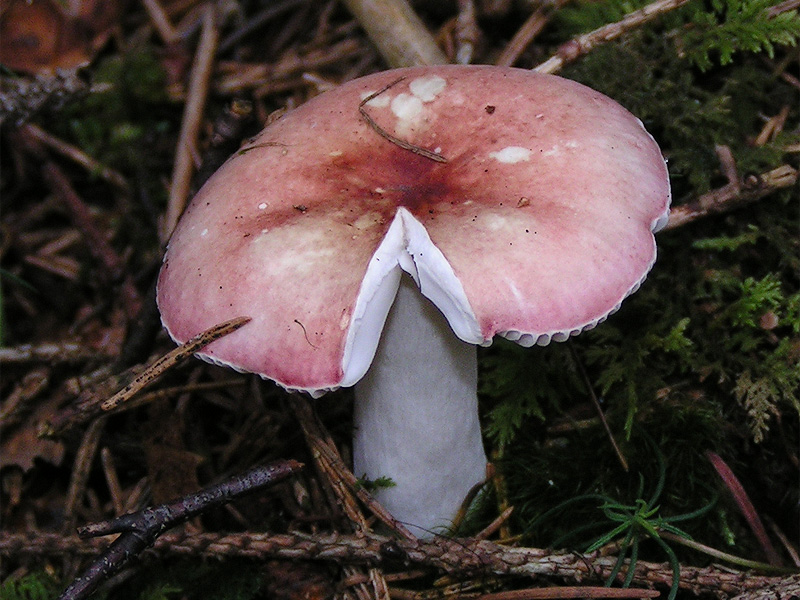
Undulating russula is an edible representative of russula that grows in deciduous forests. It features a purple hat with a depressed center. Sometimes there are yellow spots on the cap. The leg of the wavy russula is short, clavate, of white (cream) shades. The pulp is white, with a pungent taste. Pale green russula is an edible mushroom belonging to the 4th category.
Its main difference is the color of the cap. It ranges from olive green to off-white with a faded center. At first, the cap has a hemispherical shape; in mature mushrooms, it straightens. Slightly sticky to the touch, with a thin ribbed edge. The skin on the cap is easily separated from the pulp. The leg reaches 5 cm in length, 2 cm in diameter. Inhabits deciduous, less often coniferous forests. Young mushrooms look like a poisonous relative - the pale toadstool. You can distinguish it by the absence of a Volvo, a bedspread.
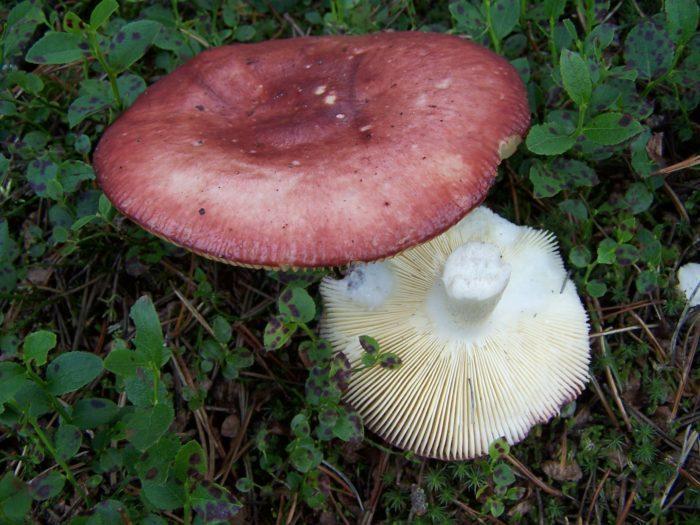
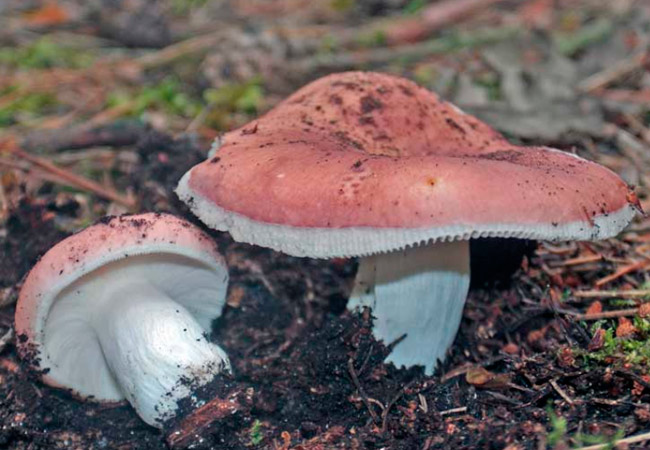
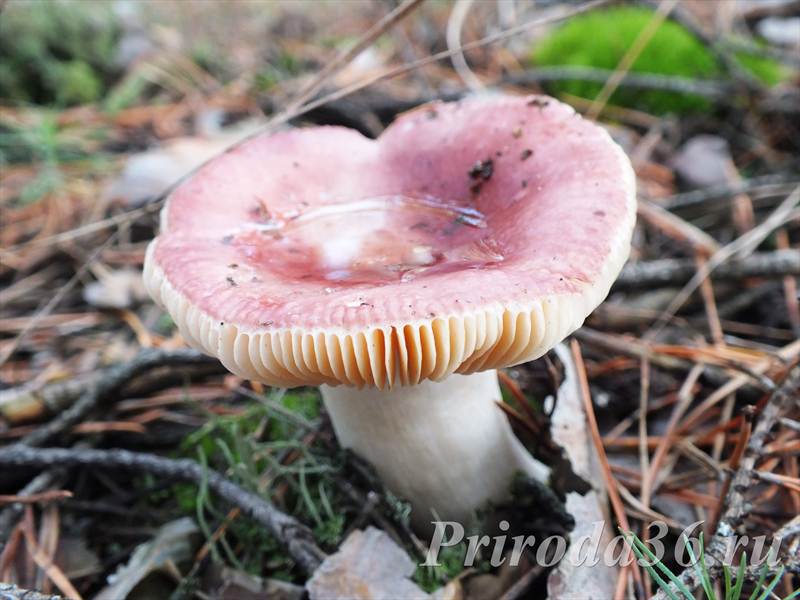
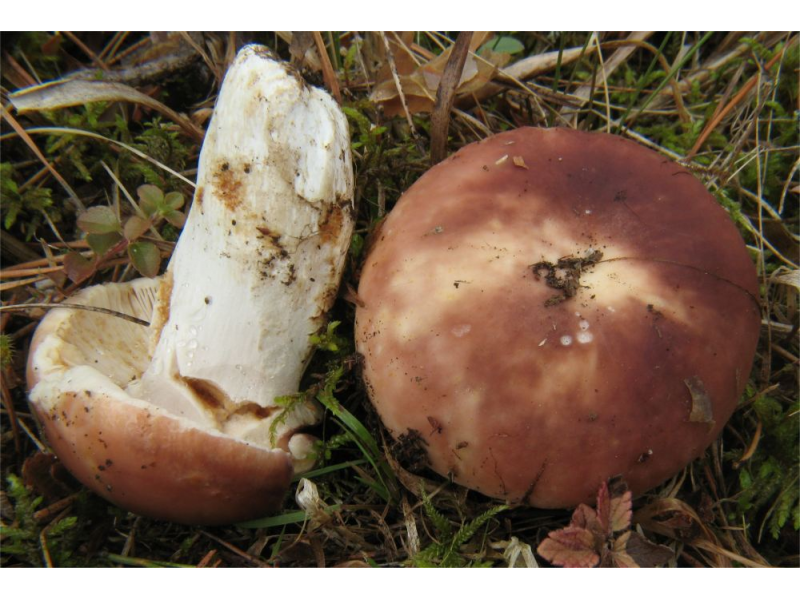
Edible russula is a mushroom belonging to category 3, considered one of the most delicious in russula. Differs in the shape and color of the cap. Most often it has a hemispherical shape, sometimes wavy-curved. Sticky in wet weather, matte in dry weather. The color is pinkish, brick reddish, brownish red. Often colored unevenly, with light spots. The skin is easily separated from the white flesh. The leg is short, up to 3-5 cm. Likes to grow in deciduous forests in well-lit places.
Muscarine in russula
The russula caustic (vomit) is a poisonous mushroom that causes food poisoning. It tastes very bitter, contains the toxic alkaloid muscarine, which causes collapse and respiratory failure. The russula vomit bears fruit at the same time as the edible russula, it is distinguished by a bright red, light red color of the cap. The edge of the cap is down, blunt. The pulp is pinkish, with a bitter taste and fruity aroma. Grows near deciduous (sometimes coniferous) trees.
In large quantities, this mushroom is deadly. In terms of chemical structure, muscarine is trimethylammonium chloride salt of 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-5-aminomethyltetrahydrofuran. Only 50 mg of the substance can cause severe poisoning in an adult. Symptoms may take several hours to appear. Poisonings of this nature are the most dangerous, since the poison can no longer be removed completely from the body. Even after recovery, liver failure and high blood pressure are observed for a long time. Fortunately, inedible russules contain small amounts of muscarine, which makes them less dangerous. But even small doses of a toxic substance in the composition provoke severe digestive upset.
At the first signs of muscarine poisoning (stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, sometimes convulsions, dizziness, loss of orientation in space, vision and hallucinations appear), you should immediately seek medical help.
Description of russula food
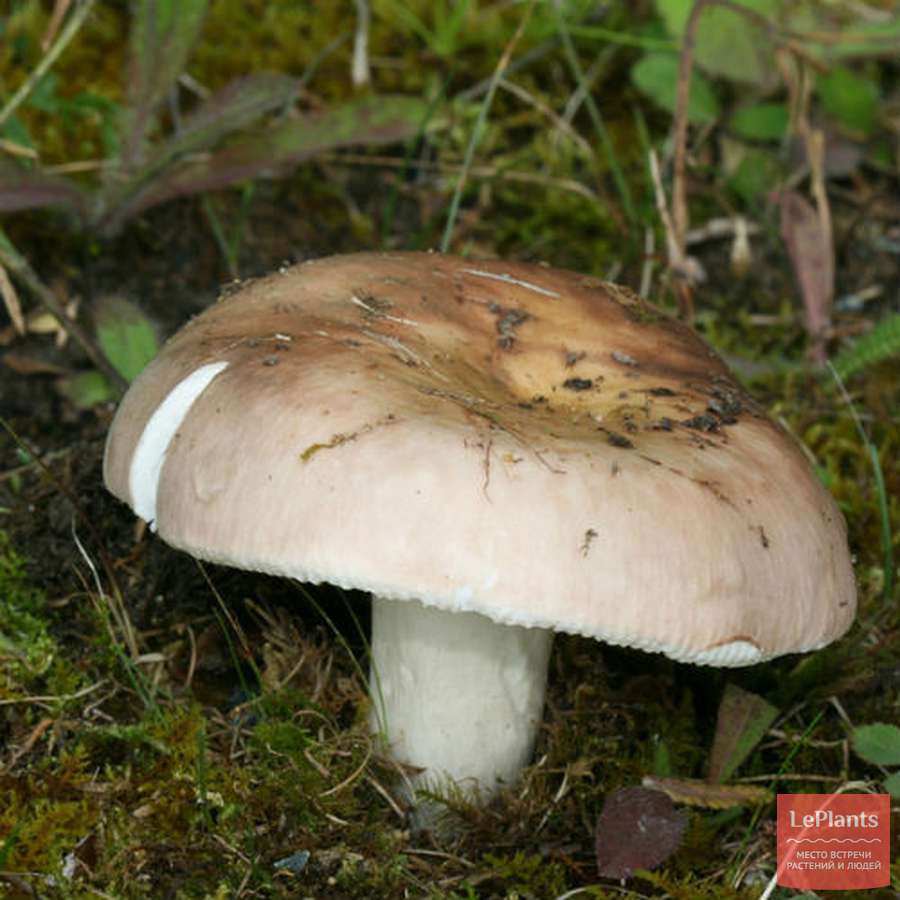
The diameter of the food russula cap ranges from 5 to 9 cm. Most often, the color of the cap is pink or brownish-pink. The cap is a little sticky to the touch, but becomes dull as it dries. The structure of the cap is fleshy. In young specimens, the shape of the cap resembles a hemisphere, but with age it opens and becomes flat-convex. The skin of the cap does not reach a little from the edges to the middle and can be easily removed.

The plates of the russula are white in color, they are located quite often, sometimes rusty spots are noticeable on them. The pulp is dense with a pleasant mushroom aroma and a light nutty flavor. Spore powder is white. Ovoid spores are finely warty. The leg is white, but over time, spots form on it, like on plates.
Growing places of edible russula
Edible russula live in coniferous and deciduous forests. They bear fruit mainly in the summer-autumn period. Edible russula are widespread in Eurasia. They can be found near beech, oak and other broadleaf trees. These mushrooms do not grow in mountain forests.
Evaluation of the taste of edible russula
Mostly there are red russula, with excellent taste, which can be tasted by biting off a plate. These mushrooms are widely used in food, as they have a great taste and pleasant smell.

The main disadvantage of edible russula is its fragility.
If you touch it inadvertently or put it on the bottom of the basket, it will crumble into several parts.
Interesting facts about russula
- The most delicious are gray and green types of russula. Red species tend to have a bitter taste. However, the pink and red russules that appear in May are not bitter.
- To check if russula are bitter or not, you can try a small amount of their pulp. There will be no harm from this, because in order to get poisoned with russules, you need to eat a large amount of these mushrooms.
- From similar mushrooms, pale toadstool and fly agaric, russules are distinguished by the absence of a ring on the leg, a volva at the base of the leg and the fragility of their pulp.
- The enzyme russulin is found in the mycelium of some fresh red russula. Only 500 mg of this substance curdles 200 liters of milk in 30 minutes. It is used in the production of cottage cheese and rennet cheeses. This enzyme has partially replaced the more expensive rennin previously obtained from the stomachs of lambs and calves. A similar substance is also produced by some types of bacteria.
- In France and Germany, russula are not harvested, as they are considered inedible mushrooms.
- Reindeer, moose and wild boars love and enjoy eating russula.
- In terms of taste and economic value, white podgruzdok belongs to the second category of mushrooms. This is the most delicious russula. Other mushrooms of this genus are classified in lower categories.
Description

Food russula (Russula vesca) or, as it is also called, edible russula, has the following specific characteristics:
- the color of the cap is reddish-brown with yellowish-gray areas; intensity and tone can vary from light wine red to brown with a purple tint. Convex hemispherical at the beginning, with age acquires a flat shape, depressed towards the center. The edges are wavy, sometimes serrated. A somewhat sticky skin becomes dull when dry, it is easily removed only at the edge; sometimes it wrinkles and does not reach the edge of the cap by 1-2 mm. The diameter is 5 to 11 cm;
- white, then creamy plates are relatively frequent, adherent, branching near the stem, visible along the edge of the cap through the skin;
- white spores;
- the cylindrical stalk narrows slightly at the base, dense, white, yellowish or rusty ocher at the base in mature fruiting bodies. In length from 3 to 10 cm, diameter - 1.5 - 2.5 cm;
- dense white flesh under the skin has a shade of a hat, a light mushroom aroma and a taste of hazelnut are felt.
Belongs to the category of edible mushrooms.
How to collect and prepare russula?
Collecting russula should be carried out only in baskets or enameled buckets. The plates of mushrooms are brittle, crumble quickly, so you cannot carry them in bags, backpacks, plastic bags and on the bottom of dishes under other mushrooms, where they break easily.
It doesn't matter if you cut the mushroom with a knife, twist it or just pull it: there will be no harm from this branched underground mycelium. The harvested "crop" cannot be stored for a long time, it must be processed as soon as possible
You can clean brittle russula after scalding or keeping in boiling water for 20 minutes, or by soaking the mushrooms in cold water for a while. During cleaning, you need to remove various twigs, needles, leaves and other forest debris, cut out darkened, as well as places eaten by worms and insects. From the caps of red russula, it is imperative to remove the skin, which is bitter. After cleaning, the mushrooms must be washed. The mushrooms are usually not washed before drying.
Like other mushrooms, russula can be:
- fry,
- cook,
- salt,
- marinate,
- ferment,
- freeze for the winter.
Drying them is undesirable, due to the fact that many species have a bitter taste.
Pickled russula is a fairly tasty dish.To remove the bitterness before frying or boiling, it is advisable to soak the mushrooms for 10-12 hours, changing cold water 2-3 times. After that, they are rinsed and boiled for 5 minutes in lightly salted water. Then the mushrooms are placed in an enamel or glass container and poured with a solution prepared from water, salt and sugar, currant leaves are placed on top and, covering everything so that the brine comes out from above, left to ferment at a temperature of 20 ° C. In a month, fermented russula will be ready.
For the subsequent preparation of dishes, you need to cook russula for at least 30 minutes, salt, add spices and periodically remove the resulting foam. Then they need to be thrown into a colander. If the conditionally edible russula is bitter, during cooking, the bitterness will go into the water, which you simply drain. You can fry boiled, soaked and not even soaked russula: the main thing is that they do not have a burning or bitter taste. While frying, you can add onions, spices, lemon juice, garlic, and other ingredients.
Russula are salted and pickled in the same way as other mushrooms. Moreover, unlike other mushrooms, russula can be salted in a day and even faster. After cleaning and a short soaking, the mushrooms are transferred to an enamel bowl, salt, garlic and spices are added to your taste, covered with a lid and left for at least 12 hours. After this time, russula can be eaten.