Information about false poisonous and edible doubles
The mushroom bears similarities to the following counterparts:
| Species name | Description |
Dictyophora bell-shaped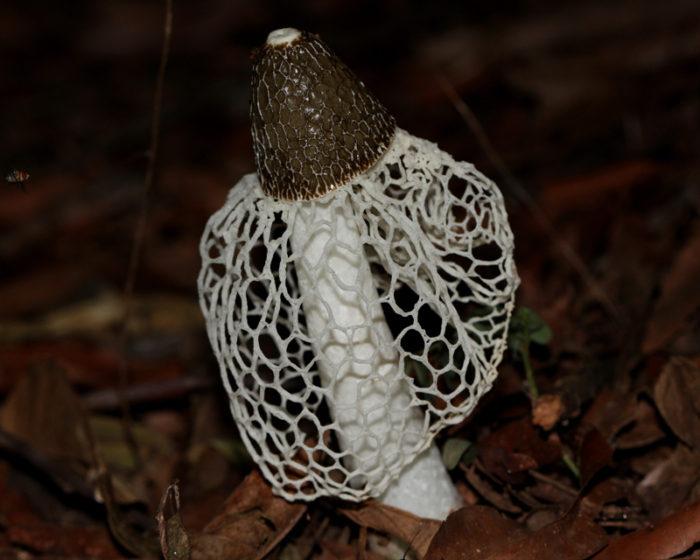 |
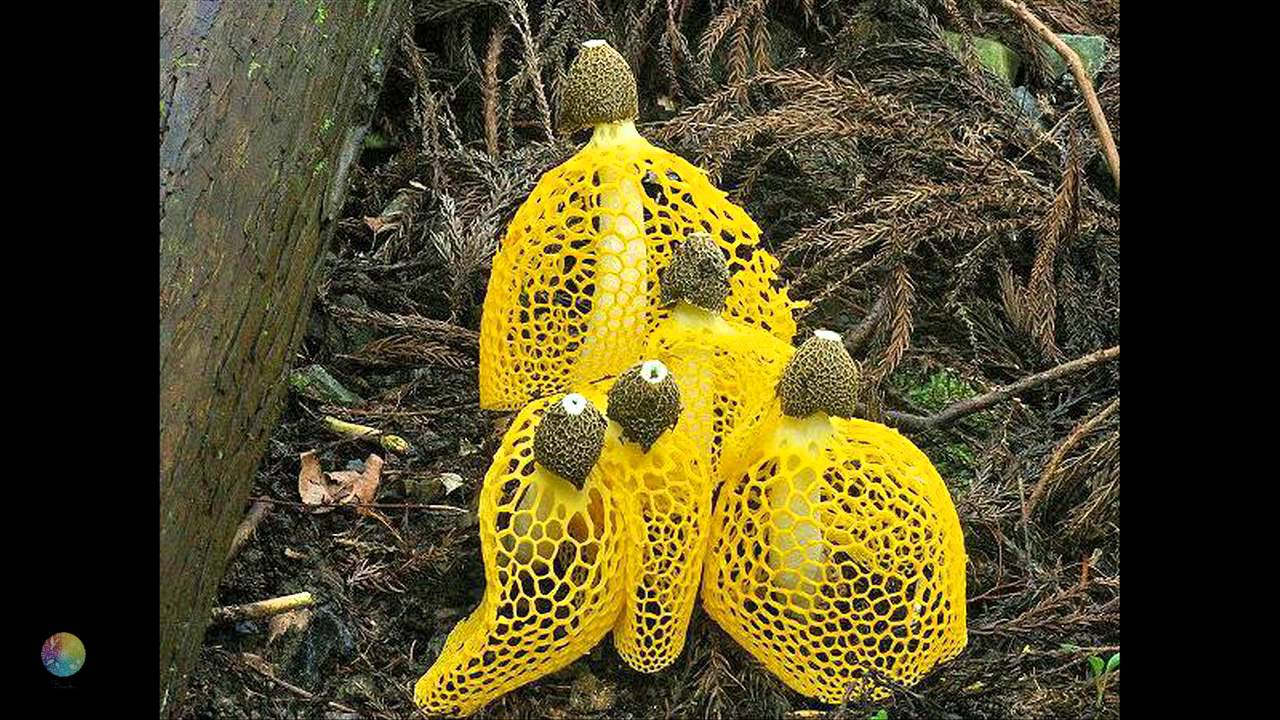
It is larger and grows only in South America. As well as a double net-nose, it has a "veil". The mushroom lives only a day. |
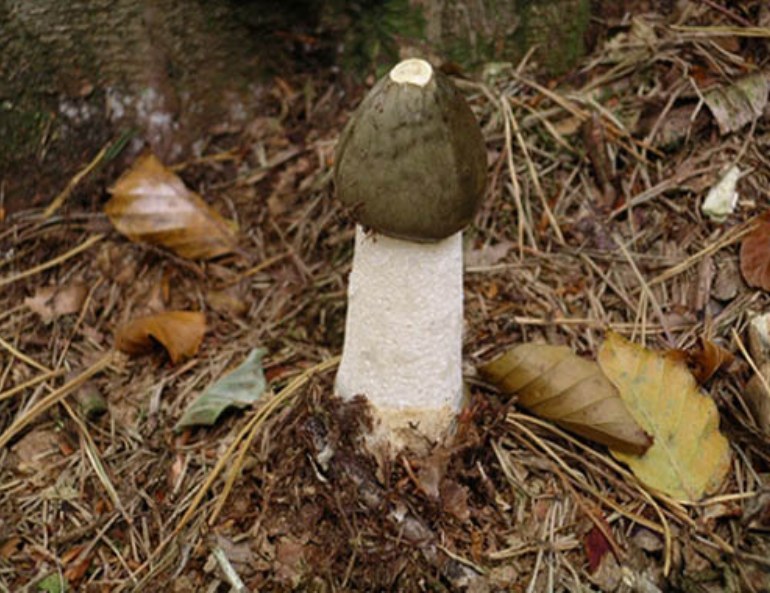
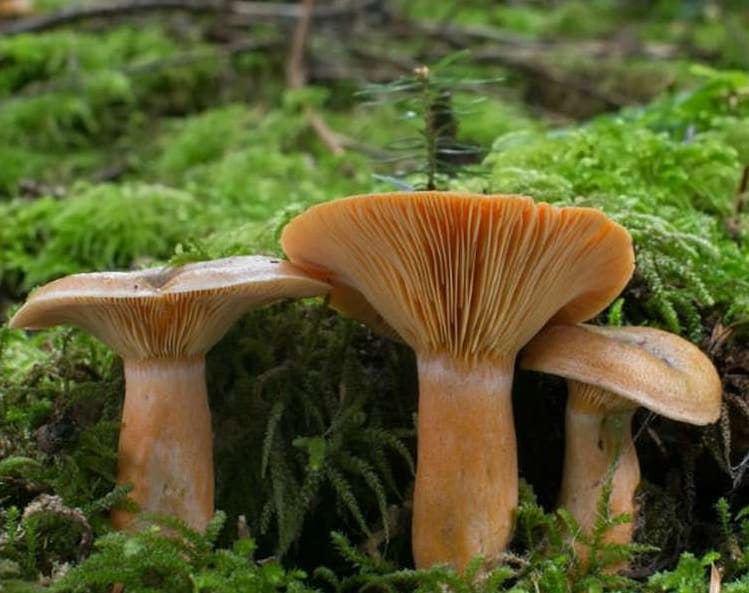
Veselka ordinary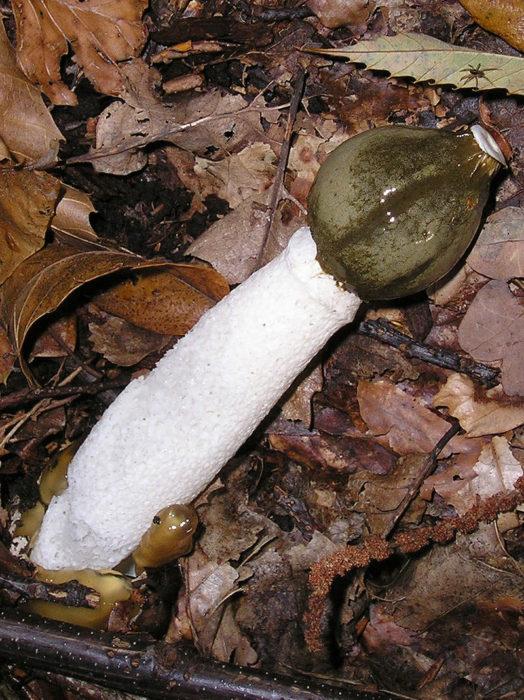 |
After ripening of the fruit egg of a dirty white hue, it grows up to 15 cm; has a greenish cap with a honeycomb structure. The mushroom smells like carrion. |
Veselka Hadrian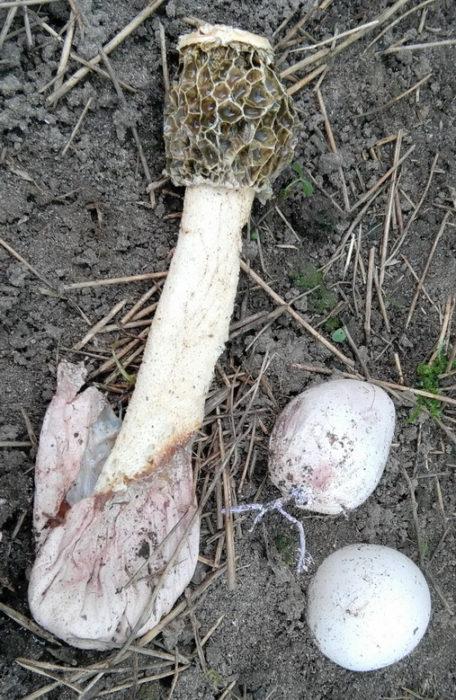 |
Before ripening, this species has an oblong shape with a diameter of 4–6 cm and is colored pink-purple. Sometimes it comes out of the ground by half. After the rupture of the membrane, a porous leg grows with a wrinkled, slimy dark cap that looks like a bell. The mushroom smell is disgusting and attracts many insects. |
Double mesh
Dictyophora duplicata (Bose) E. Fischer =
D. indusiata (Pers.) Fisch.) = D. sibirica Lavrov
Family Veselkovye - Phallaceae
Category and status.
Category 3 (R) Rare species. A relic of the nemoral flora.
A promising object for biotechnology.
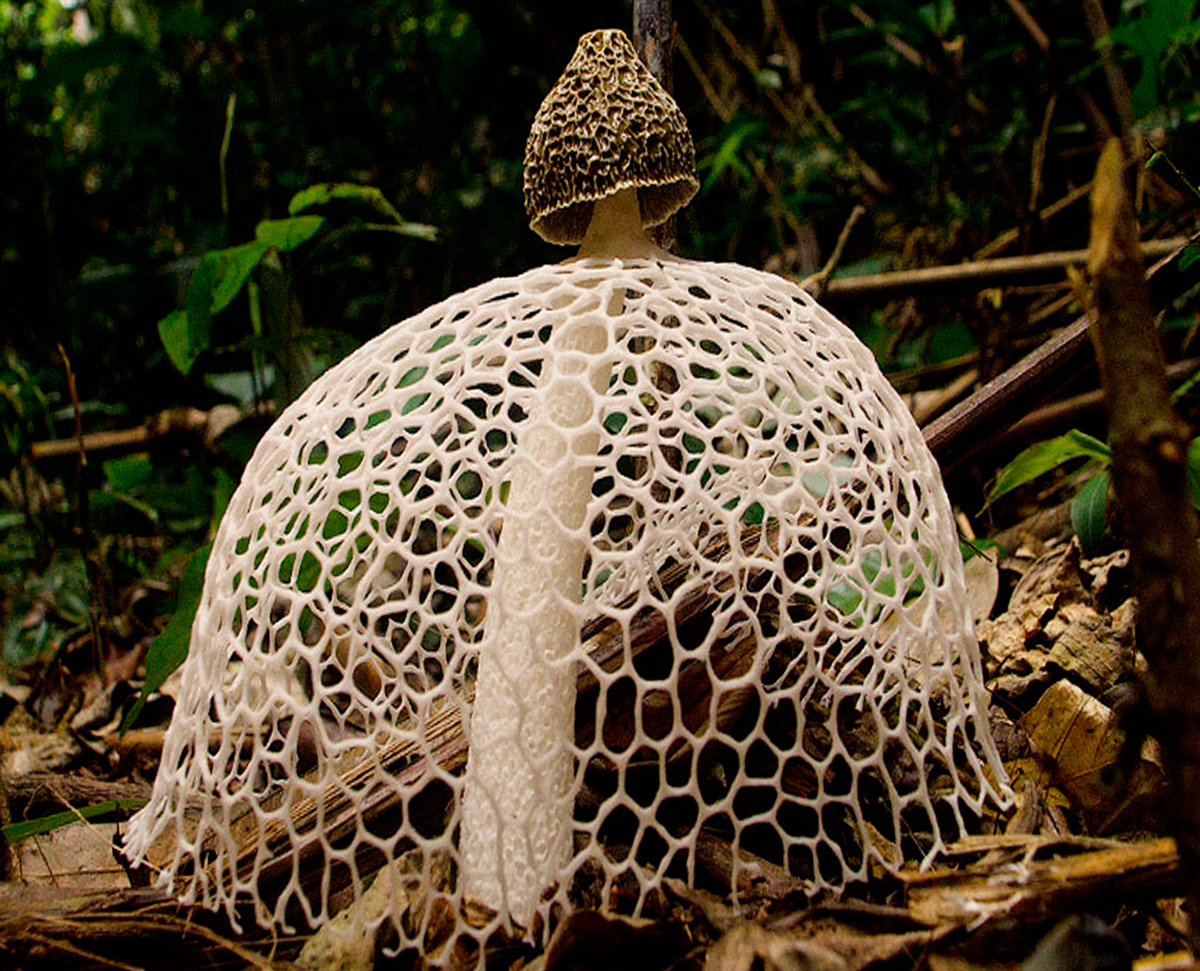
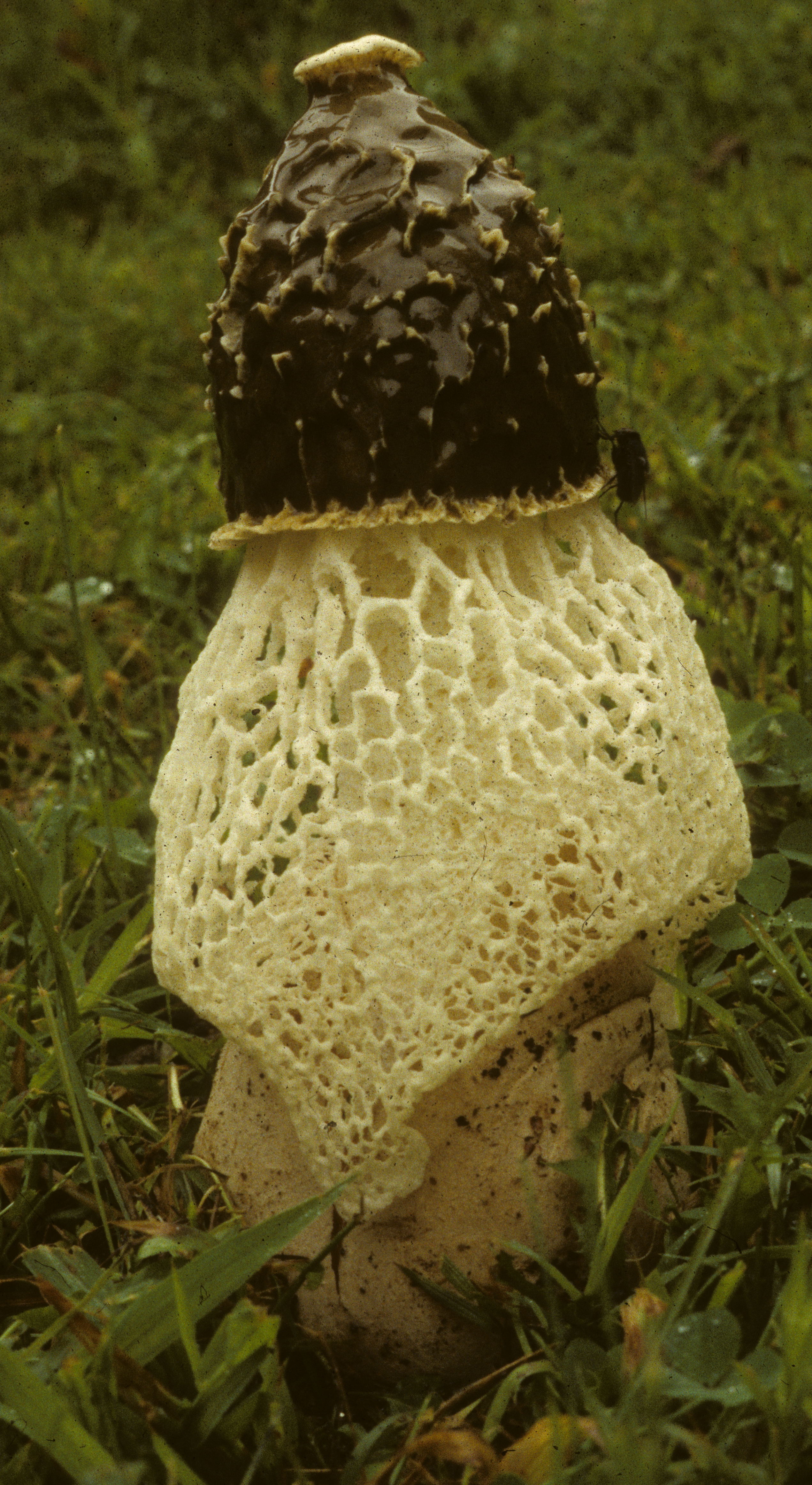
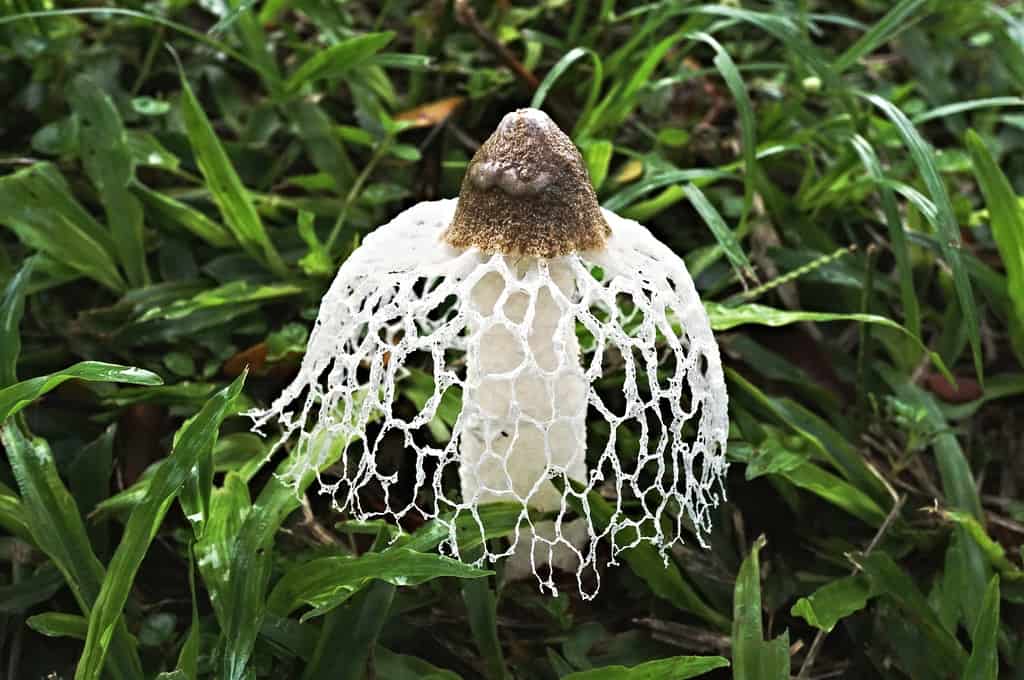
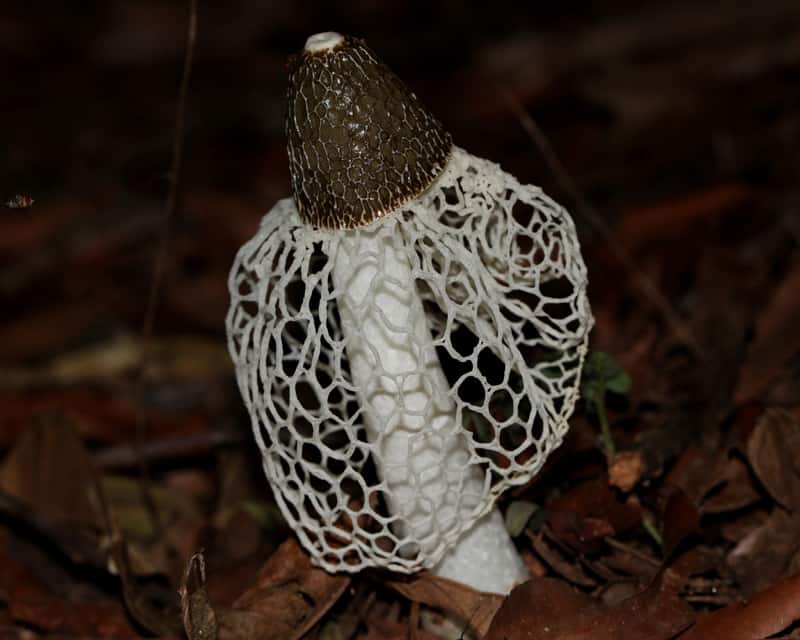
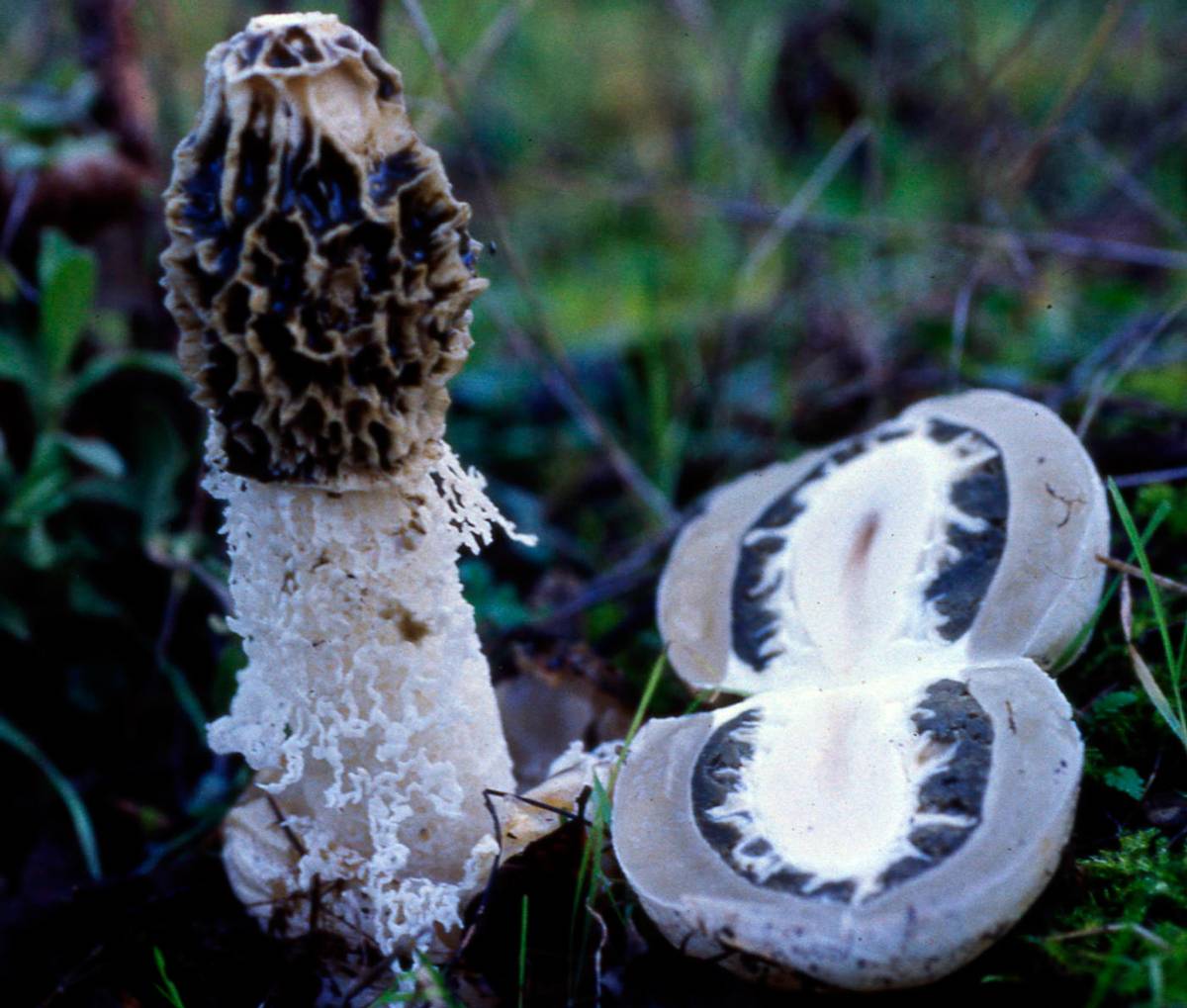
Short description. Young fruiting bodies develop inside a common veil, almost spherical, ovoid, up to 4-5 cm in diameter, smooth, white, yellowish-white, folded-wrinkled at the base, with white mycelial strands. After the rupture, the coverlet remains in the form of a multi-blade volva at the base of a cylindrical recipe recessed into it, up to 15-20 cm long and 2.5-4.5 cm in diameter, recipe-kula. The latter tapers at the top and bottom, hollow, elastic, hard, (cut with a knife with a crunch), looks like a fine-mesh foam. The thickness of the walls of the recipe is up to 0.5 cm. In the upper part, there is a cone-shaped honeycomb head, the top of which ends with a collar disc. The lateral surface of the cap on the outside with a reticular relief of accrete and branched ribs, bearing Gleb with a spore-bearing layer. Below the cap, an Hindu is attached to the recipe, which hangs down in a cone, like a lace skirt or bedspread, large-bladed along the lower edge. All this splendor is white, in places creamy yellow, elastic, cartilaginous. Mesh (Indus) at the beginning of the development of the fruiting body unites the cap and the volva. As the recipe grows, the mesh remains attached to it, and the cone-shaped cap that bears Gleb breaks through it along with the recipe. The surface of the receptacle at the point of contact with the mesh remains finely meshed. Gleb, which is located on the head of the receptacle, turns from brown as the spores mature, greenish-gray, jelly-mucous, with a strong unpleasant odor. Basidia 6-8 spore. Spores are ellipsoidal, smooth, 3.5-4.5 x 1.2-2 microns.
Ecology and biology. Humus saprotroph. Inhabits deciduous and mixed, mainly floodplain, fir-field forests or shrub thickets; but much more often near dwellings, in suburban forests and summer cottages, on soil rich in humus and organic residues. Solitary basi-diomes are extremely rare, in July - August.
Spreading. Representatives of this family live mainly in tropical forests, and only a few species are found in the temperate zone of the Holarctic - in Europe, Asia, North America, everywhere it is extremely rare. The twinned set is the only representative of the genus Dictyophora, which is recorded in Russia, mainly in the European part, in Central Asia, in the south of Siberia and the Far East. On the territory of the Irkutsk region, it was recorded in the Slyudyansky (Kultuk settlement) and Irkutsk (Irkutsk, Istok village, Bol. Koty settlement, Granovshchina village) regions. From the adjacent regions, finds of the netkonos are known for the Tomsk, Novosibirsk, Amur regions, as well as the Altai, Krasnoyarsk, Primorsky territories.
Limiting factors. Features of biology and low competitiveness in biocenosis
The aimless destruction of attention-grabbing unusual and foul-smelling mushrooms.Much less often, the collection of basidiomas as a medicinal raw material - the so-called earth oil has long been used in oriental medicine, now it is often included in various pharmaceutical and cosmetic ointments
Adopted and necessary security measures. It is included in the Red Data Book of the RSFSR, respectively, and in many regional Red Data Books. It is necessary to monitor the state of known populations and regulate recreational loads, as well as competent environmental propaganda. It is desirable to introduce East Siberian strains into international collections of pure cultures.
Sources of information: 1 - Vasilkov, 1955; 2 - Garibova, Sidorova, 1997; 3 - Red Book of Krasnoyarsk. 2005; 4 - Red Data Book of Novosibirsk. 2008; 5 - Red Book of the RSFSR, 1988; b - Red Data Book of the Republic of Buryatia, 2002; 7 - Red Data Book of the Republic of Khakassia, 2002; 8 - Lavrov, 1937; 9 - Lavrov, 1938; 10 - Petrov, 1991; 11 - Petrov, 2008; 12-Unique. 1990; 13-Courtcuisse 1994; 14 - Julich, 1984; 15 - Imazeki, Hongo, 1998; 16 - data of the compilers.
Compiled by A.N. Petrov, E.A. Matosov.
Application
The netkonosku was often compared to a flowering fern, only they were looking for it for medicinal purposes. This species is widely known for its beneficial properties, which have been actively used in traditional medicine.
Medicinal properties and restrictions on use
The main indications for treatment are:
- gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- thrombophlebitis;
- impaired renal function;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
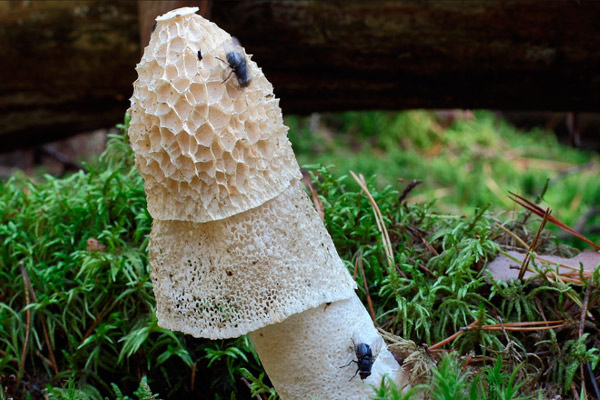 Double mesh
Double mesh
In folk medicine, decoctions and infusions were often used to treat benign and malignant tumors. Mesh socks are rich in polysaccharides, which affect the synthesis of perforin in the body. In turn, perforin damages the membranes of cancer cells, thus killing them.
Thanks to the beneficial properties in the body, the level of cholesterol and blood pressure is reduced, which contributes to the treatment of hypertension. Diktyophora has also received many good reviews for its effectiveness in the treatment of gout and rheumatism.
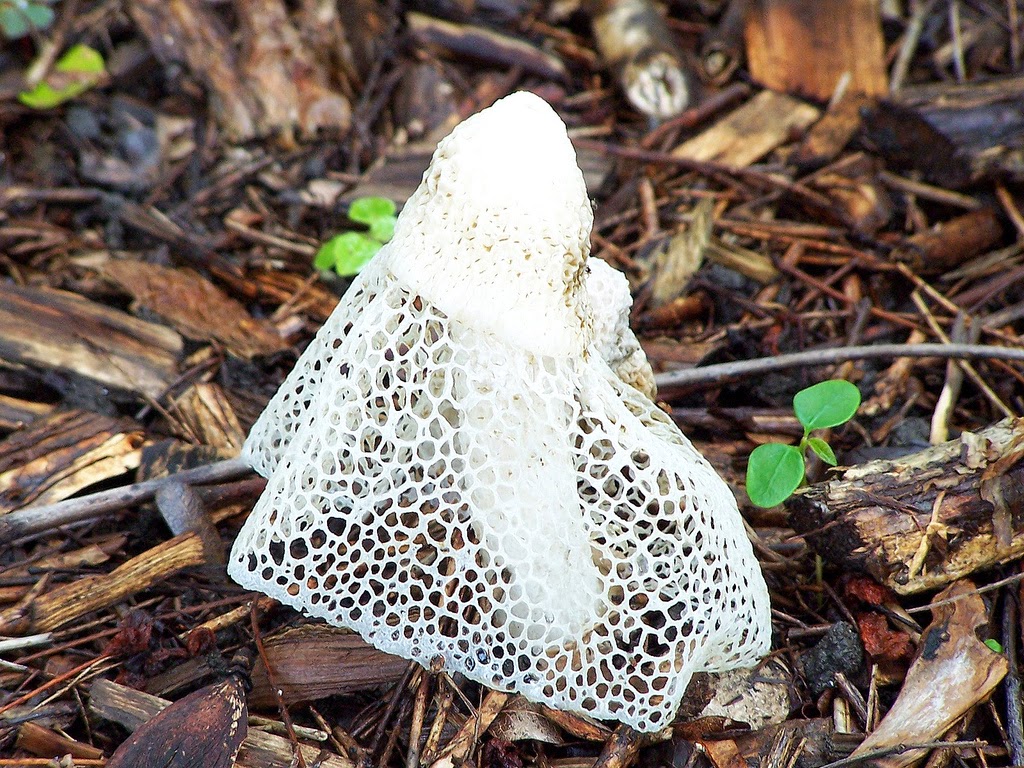
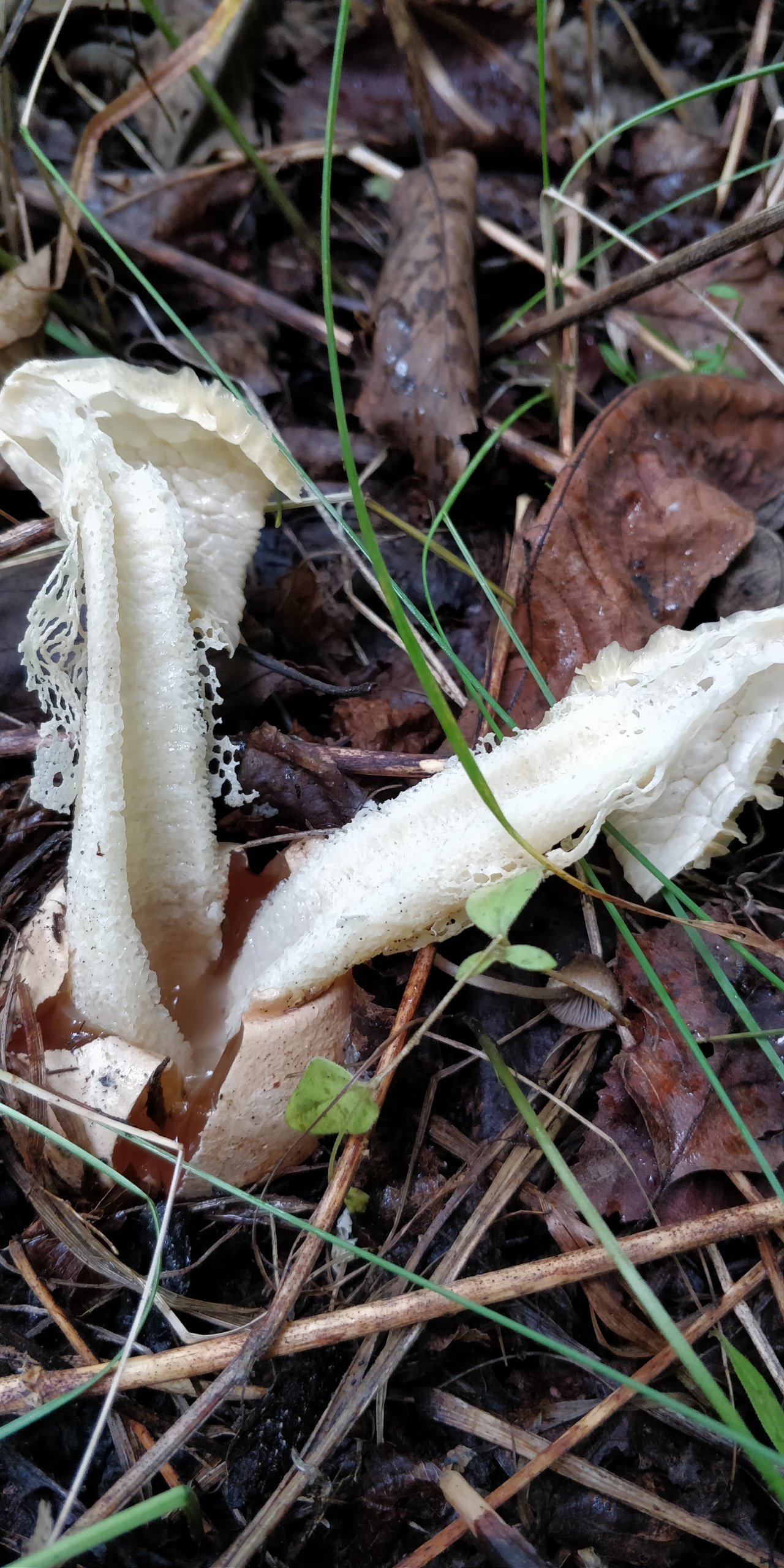
 Stage of rupture of exoperidium at Setkonoski
Stage of rupture of exoperidium at Setkonoski
It is often used for skin inflammations and diseases, for non-healing wounds, insect bites, ulcers, bedsores and tumor processes. The mushroom contains phytoncides, which have antibacterial and antiviral effects. Also, the fishnet was able to cope with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. For the treatment of diseases, a vodka-based tincture was prepared from the mesh.
Netnose is also considered a powerful aphrodisiac that energizes when the body reboots and during periods of extreme fatigue. It was not recommended to treat the fungus for pregnant and breastfeeding women, children under the age of 5 years, people with hypersensitivity and patients with diabetes mellitus.
Recipes and cooking features
You can use this type only at the stage of eggs in fried, boiled or dried form. Initially, after harvesting, the fruit part was fried and peeled from the outer skin. After that it was stewed with vegetables, sour cream and spices. For drying, the nets were thoroughly washed and cleaned, cut into two parts and strung on a thread. You need to dry it in a cold, dark place, then put it in a container and close it. Such blanks can be stored for no more than three years.
Characteristic features of the variety
Double dictyophora is very easy to distinguish from other representatives of the kingdom due to the peculiarities of its external signs and morphology. This species belongs to the genus Veselka and the Veselkov family.
A characteristic feature of dictyophora is its two-phase development, where each phase has its own characteristics. Since Phallus duplicatus belongs to the gasteromycete species, the fruit part remains completely closed until the spores mature. At the moment, there is a decrease in the number of the species.
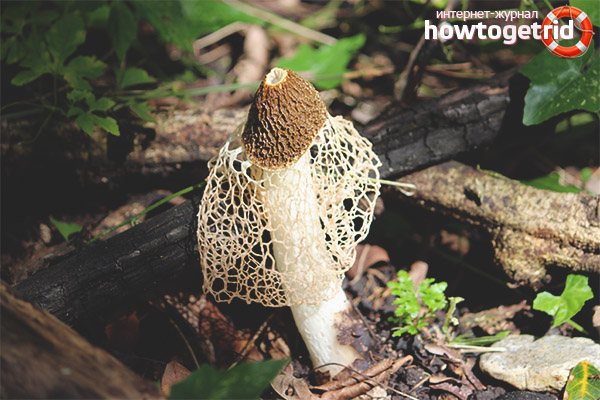
Description of double mesh and photo of the mushroom
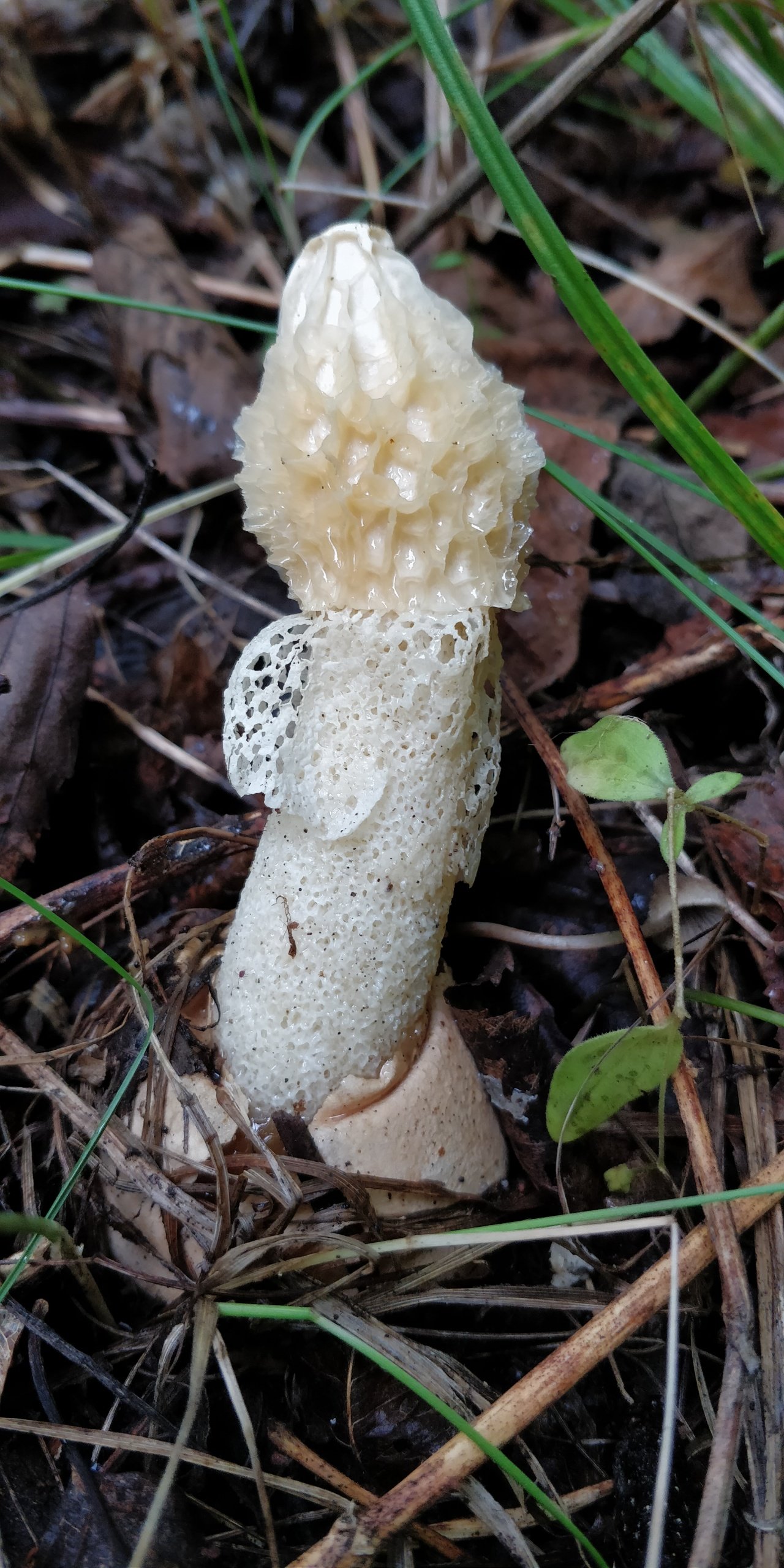
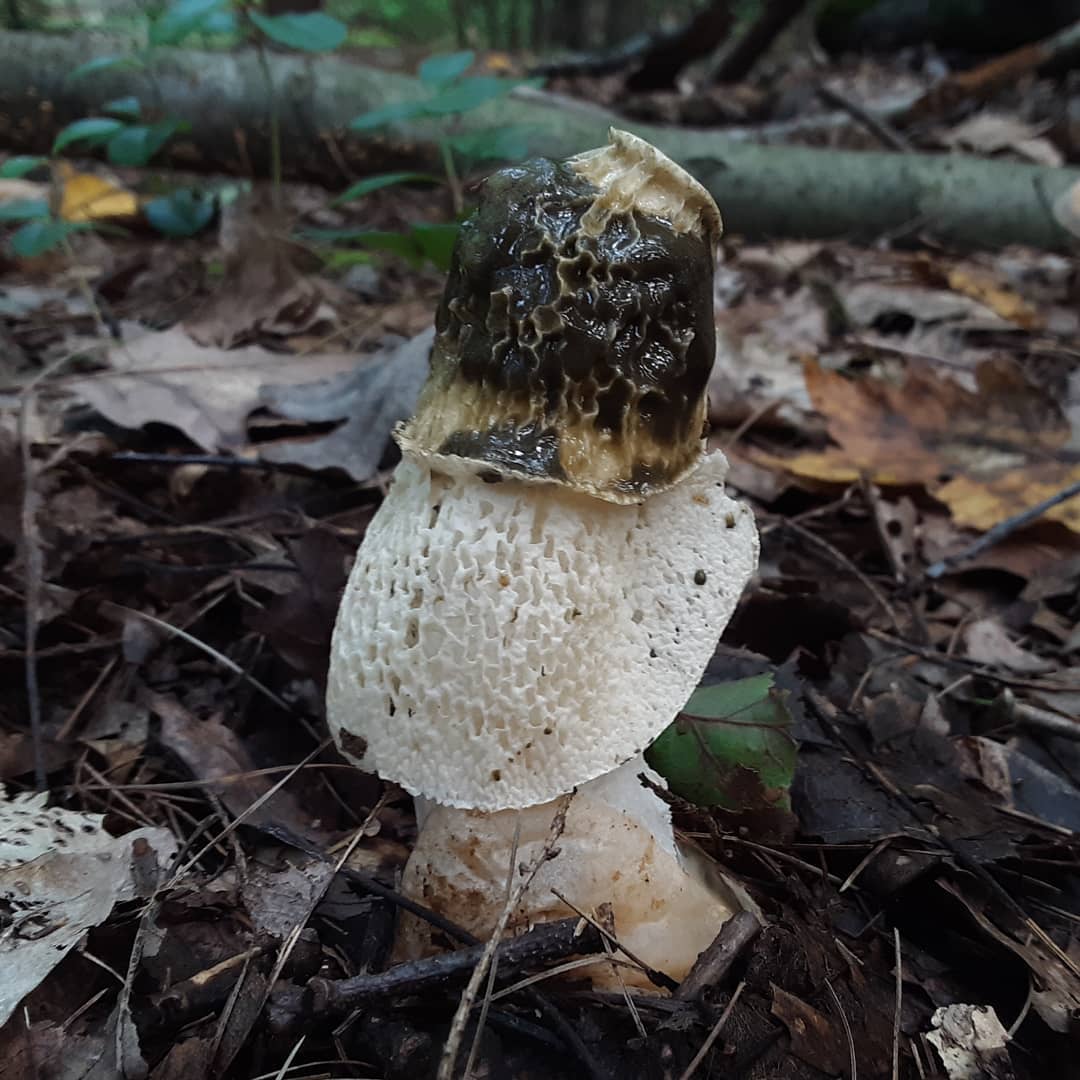
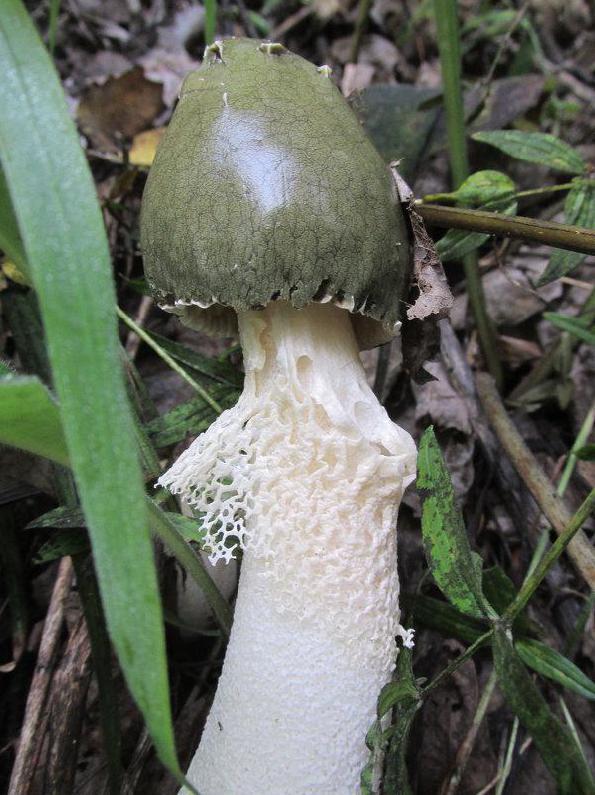
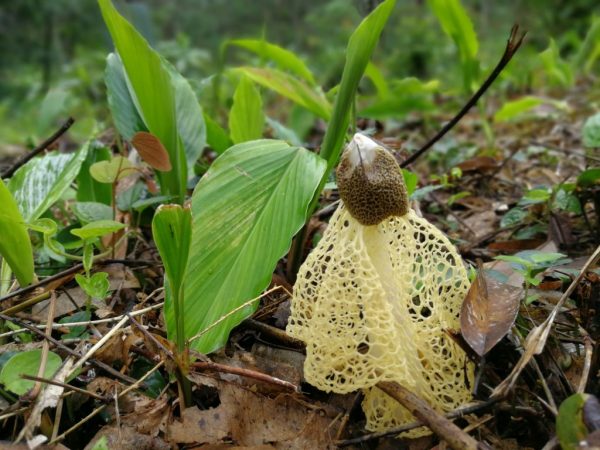
The mushroom is small in size. It has a cone-shaped olive-colored hat, the surface looks smooth and slippery. An openwork mesh grows from the edges of the cap, which can completely cover the leg. The mesh is white, in the dark it takes on a green tint.
The leg is barrel-shaped, high, up to 20 cm. Externally, the net-beetle resembles Hadrian's veil, the ordinary veselka and the bell-shaped dictyophora. Below are photos and a detailed description of the variety.
Morphology
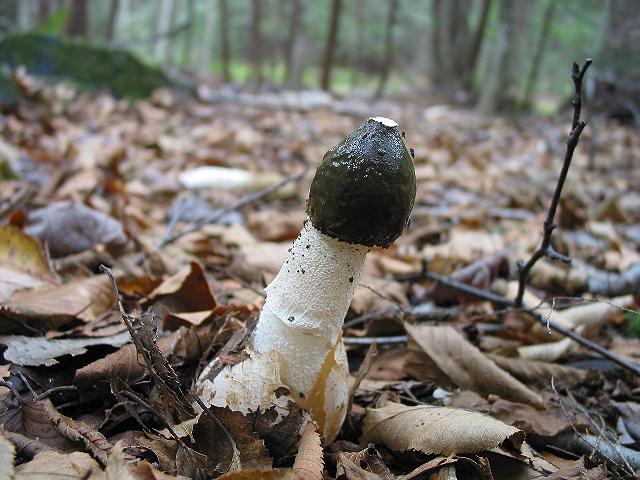
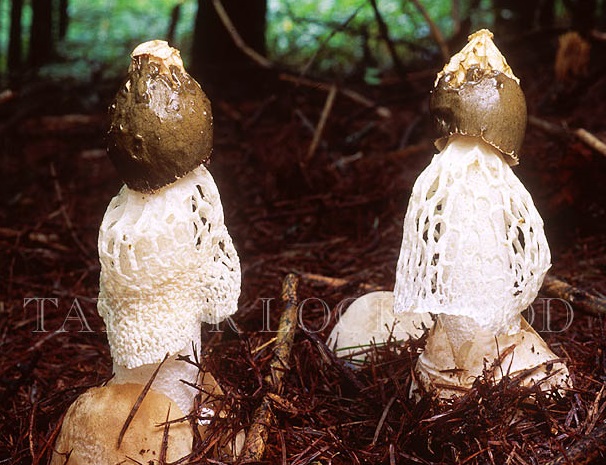
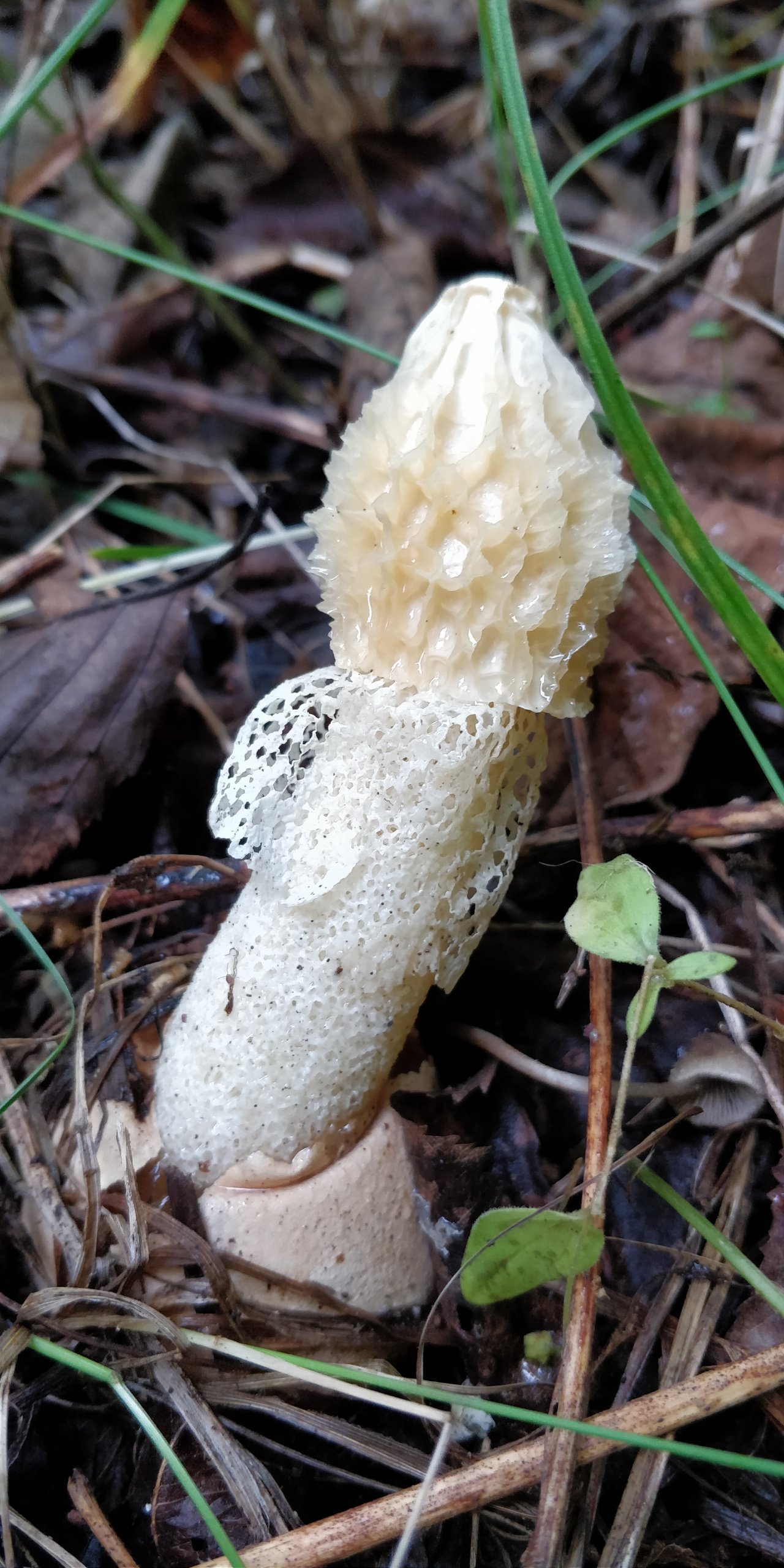
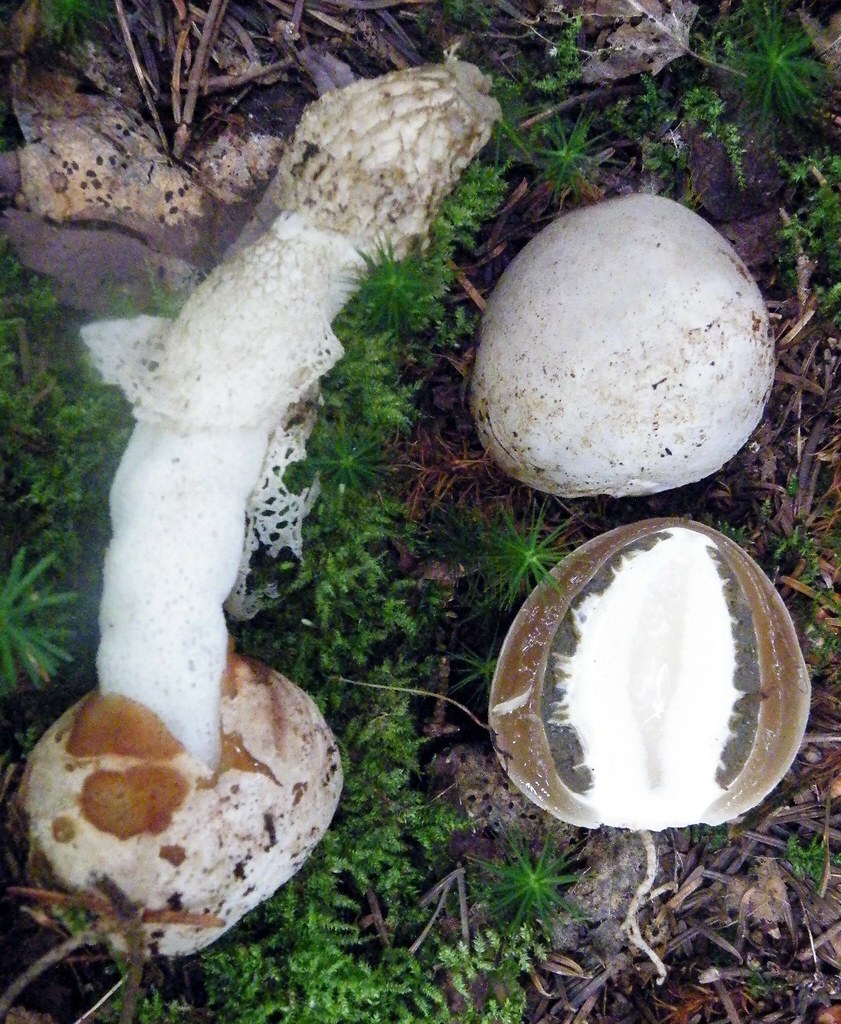
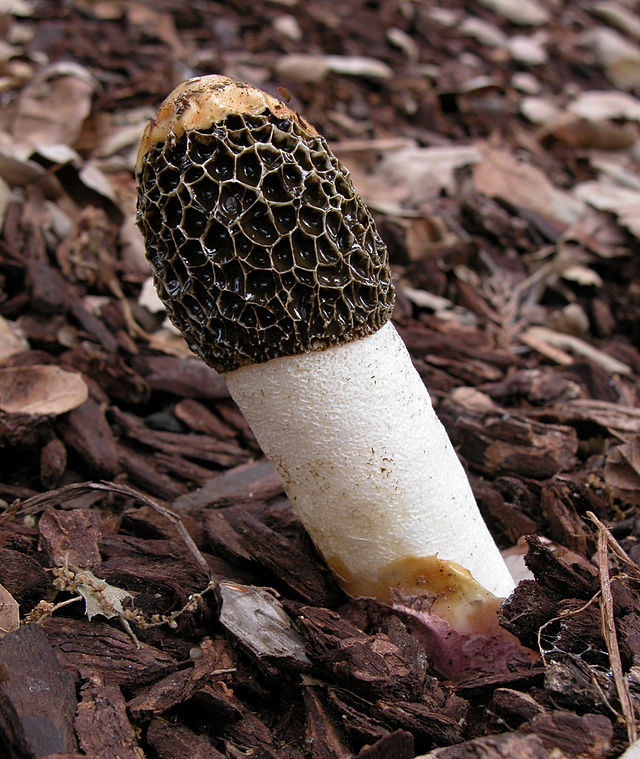
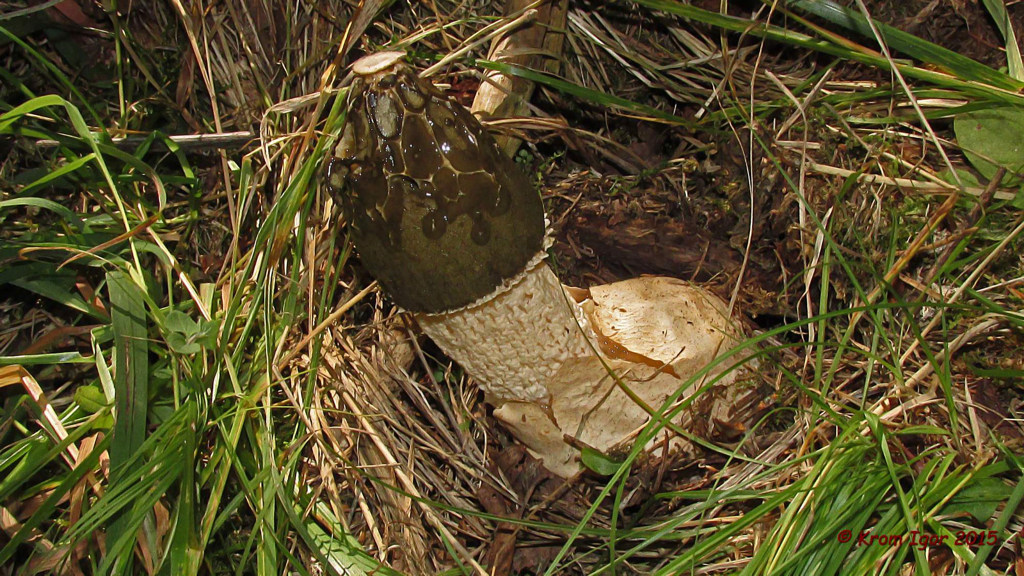
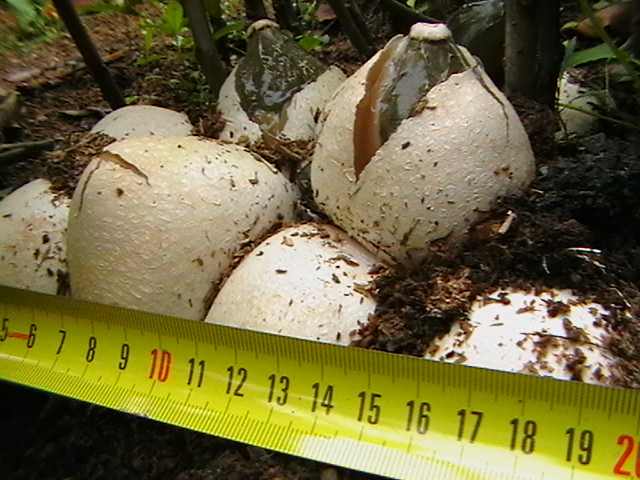
At the place of growth of the fruit part, a rounded base initially appears with a jelly-like mass inside. This mass contains the rudiments of the fruit part. Then the rounded base takes on the shape of a cylinder or a chicken egg (for which it was nicknamed the witches' egg) and reaches 7 cm in height. The formation is initially white, gradually turns yellow and becomes brownish. After that, the base is torn into two parts and a mature fruit body emerges from them.
The hat is cellular in structure, has the shape of a cone and is covered on top with a mucous slippery layer
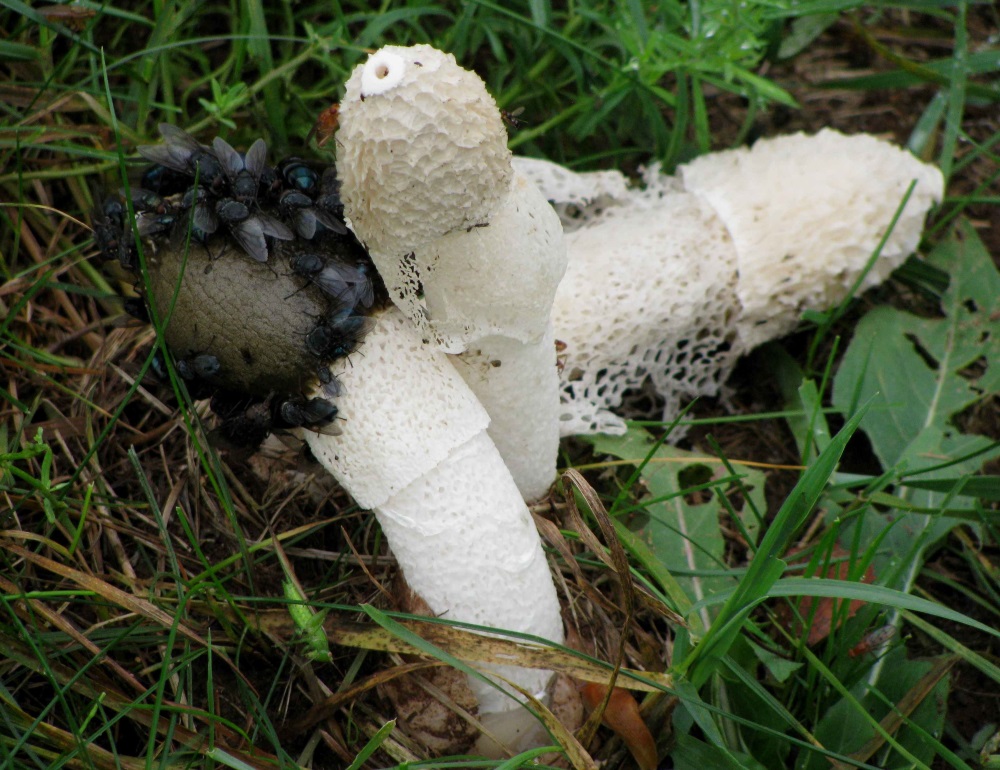
The fruit body, after it comes out, emits an unpleasant putrid odor, which repels mushroom pickers, but attracts the attention of insects. Due to this smell, flies often land on the surface, spreading spores, and the lace part increases the area for insects.
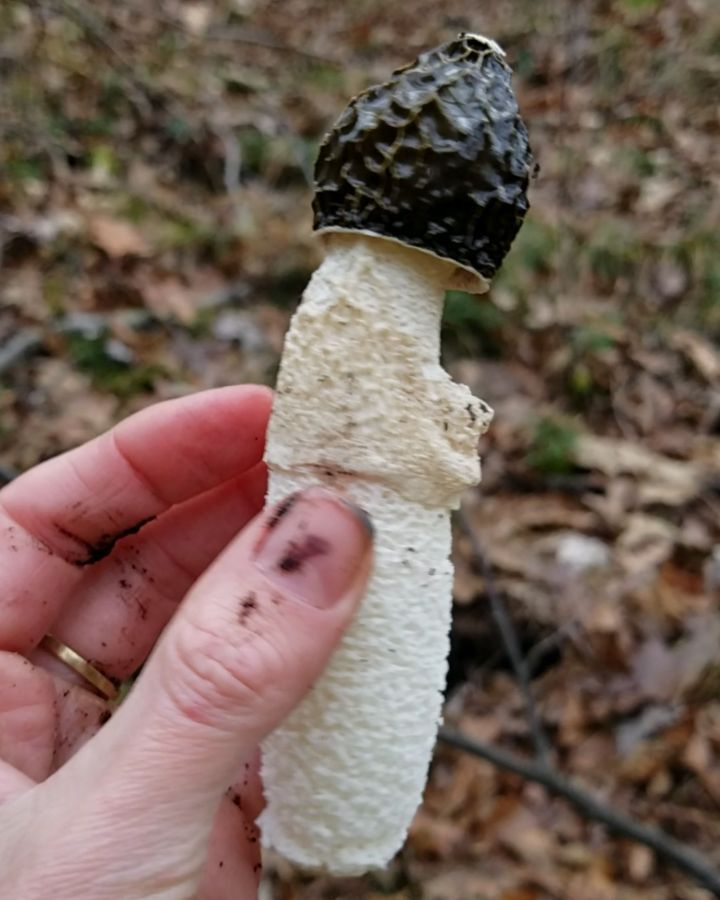
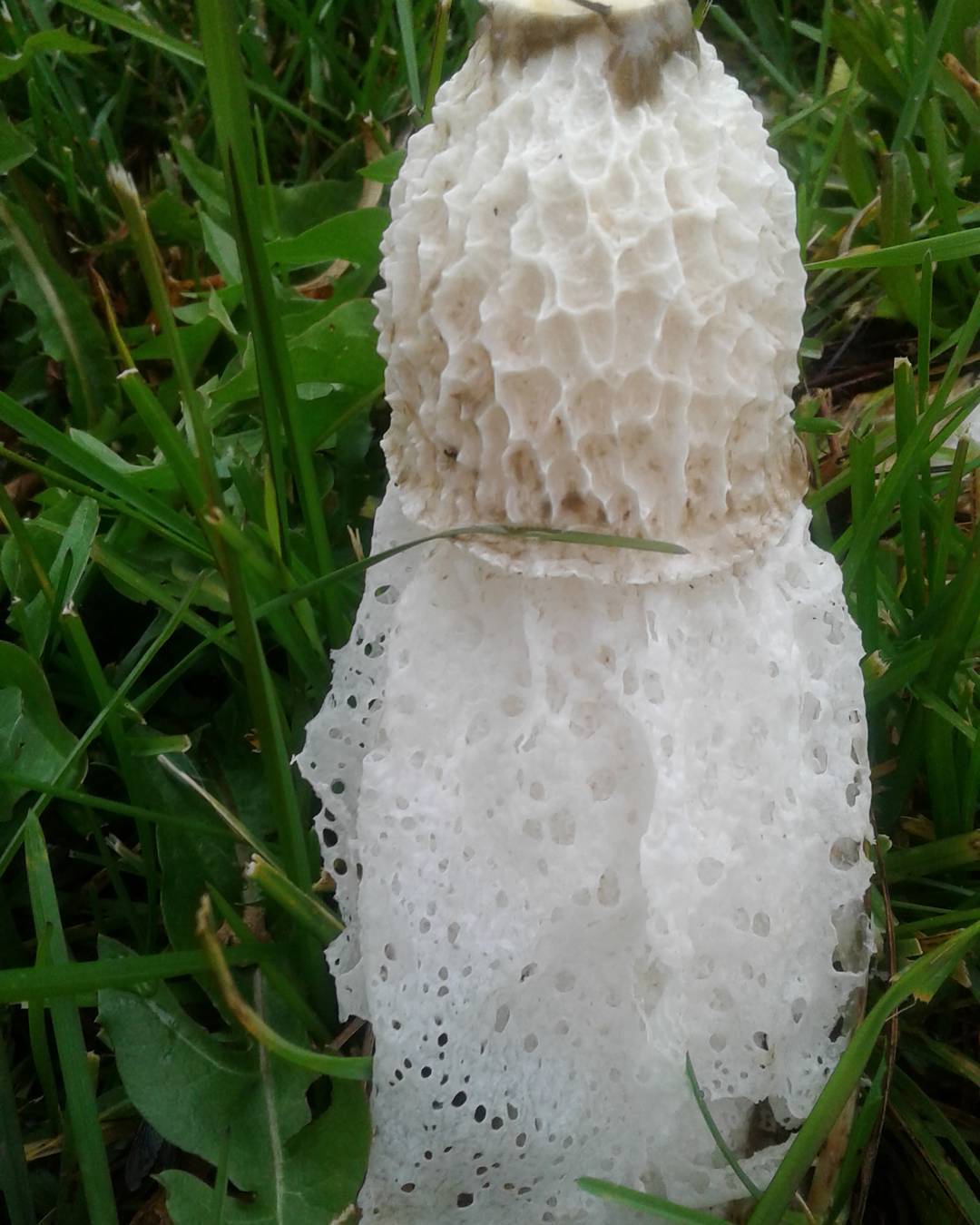
The cap reaches 5 cm in height. In the upper part there is a disc-shaped slit. The veil falls off the edges of the cap and can cover half or all of the mushroom. The veil has cells of the same rounded shape. The leg is high, porous in texture, resembles a sponge and has the shape of a cylinder. It expands towards the center and has a diameter of about 2-3 cm.
Place of distribution
Most often it grows in deciduous or mixed forests, preferring places near poplars, firs and shrubs. It can also be found in forest plantations near the city, near residential buildings and summer cottages. The fungus attracts a substrate rich in organic matter. This species grows singly and rarely bears fruit. Yields peak in mid to late summer. In Russia, it can be found throughout the territory, although it is extremely rare.
Edible or inedible
Setkonoska belongs to edible varieties when it is at the initial stage of development and does not exceed the size of a hen's egg. It was during this period that it is eaten.
Attention! Today, mushroom picking is prohibited, as the species is considered endangered.
In folk medicine, there were many recipes according to which the mushroom was used to treat gout. It was also consumed fried or boiled, with sour cream and spice dressing. Mature mushrooms were not eaten, which is associated with a specific smell that comes from the leg and the net.
When and how to collect correctly
Dictyophora double occurs from the beginning of summer, and its peak yield falls in the middle of summer. Due to the fact that the mushroom is a rare and endangered species, collecting it is strictly prohibited.
Such mushrooms are protected by the state, and their collection entails administrative responsibility and punishment in the form of a fine. Today, if you are lucky enough to see this specimen, you can only admire it and move on.
How to distinguish from similar mushrooms?
Diktyophora bears similarities with some representatives of the Veselka species, from which it differs in its color. Most often, netnosets are confused with Adrian's veselka, which has a pink-purple color of the egg from which it develops, and also mature mushrooms thin out a pleasant aroma reminiscent of yeast.
Interesting! Another difference is that Adriana's Veselka is edible not only at the egg stage, but also in the form of a ripe fruit.
Where does the double-netting mushroom grow: description, useful properties and application
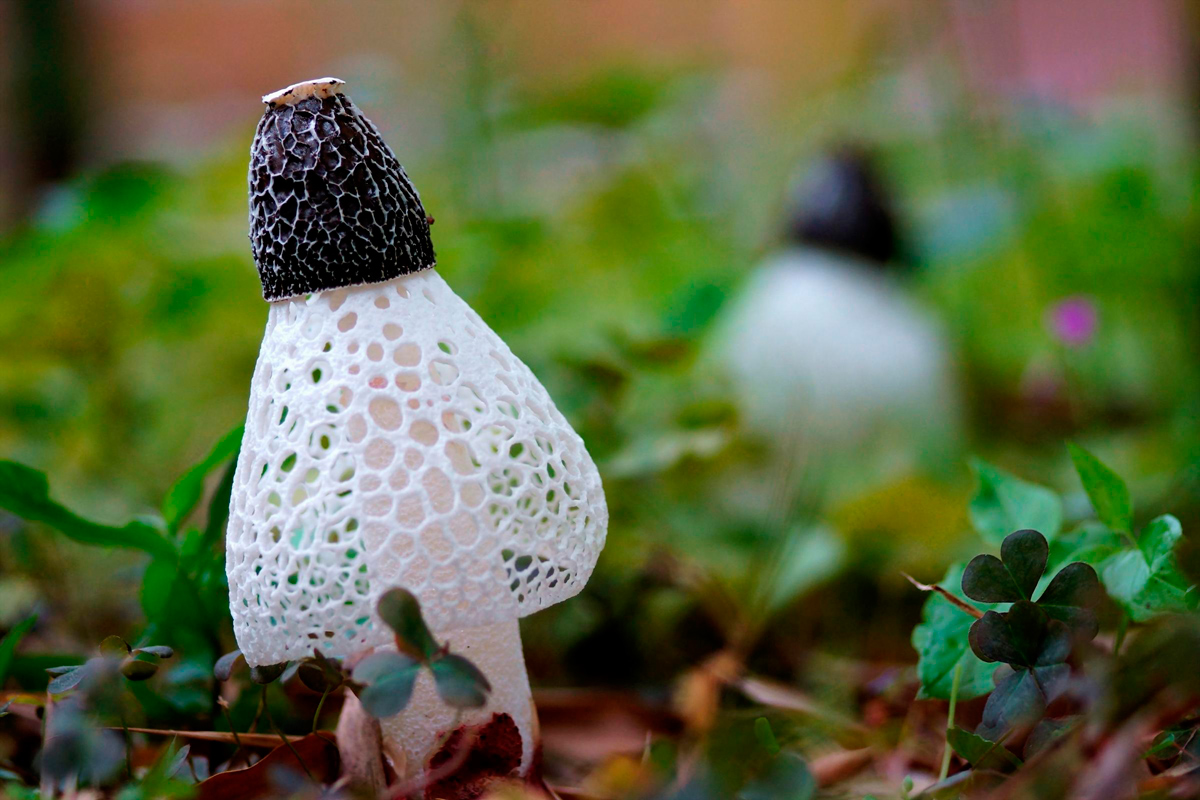

As for the sharp putrid odor, it is no coincidence that the nets start to emit it - thus it attracts flies and other small insects. It is noteworthy that the cap of adult fruits is covered with mucus, although a similar gluten is observed in mushroom spores, which resemble externally small egg clutches.

The structure and features of the species
The structure of the fungus directly depends on its age. For example, a young fruiting body is a kind of ball with an average diameter of 5 centimeters. As they grow older, the formation of a fungus occurs, which gradually changes the color of its shell, starting from a yellowish-white and ending with a light brown tint.
A cavity is formed inside the leg, while the flesh of a young netnose is soft without a pronounced taste and smell. Over time, the structure of the fungus invariably changes, as a result of which it becomes denser and more porous. As for the sharp putrid odor, it is not by chance that the nets start to exude it, because in this way it attracts flies and other small insects.
Where it grows, in what forests and how to collect
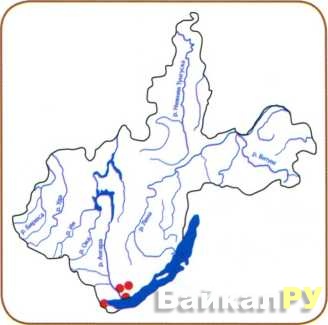
Unfortunately, the netkonoska is a rather rare forest inhabitant, which is why this species was included in the Red Book. It is most likely to be found in the mixed forests of Belarus, Kazakhstan, the Baltic states, Central Asia and Ukraine, as well as in such regions of the Russian Federation as Belgorod, Tomsk and Moscow. You can see representatives of this family in Transbaikalia, as well as in the Primorsky and Krasnoyarsk Territories.

Popular varieties of mushroom
Today, scientists distinguish several varieties of netnose, first discovering this species back in 1562 in the Netherlands forests. Despite this, the first scientific description of the fungus dates back only to 1972, when the Italian biologist Micheli described the genus, calling it Phallus, and divided it into two separate subspecies. A little later, this list was expanded, although the most popular are the common and Adrian's.
Veselka ordinary
Like other representatives of the genus, the most common variety, Veselka vulgaris, is a conditionally edible mushroom that has been widely used in medicine. A peculiarity of its structure is very interesting: at the initial stage of development, one can observe a spherical body cracking over time and releasing a long porous barrel with a double cone-shaped cap.

Edibility, useful properties and restrictions on use
The stench of the mushroom does not allow it to rise above the 4th category in consumer and taste qualities, although at a young age it is quite edible. As for the cooking options, usually young fruits are cleaned of debris, mucus and a thin upper shell, eaten raw with sour cream, or added to salads and soups. You do not need to remove thin flakes for frying.
Application in medicine
The main value of the mushroom lies in its medicinal properties, so it is not surprising that it is actively used in traditional medicine. So, the use of a double mesh is indicated for such common ailments as rheumatism, gout and impotence, although in combination with other healing cultures, it helps to treat other pathologies.
Moshe Safdie's "brutal" house
A reinforced concrete structure reminiscent of an Asian slum is nothing more than a luxury home located in Montreal. Initially, the architect who worked on the project planned to prove that it is not necessary to build up the city with the same type of high-rise buildings.
After his project was made a reality, the cost per square meter in it exceeded all expectations. Thus, the house, located almost in the center of the city and consisting of 150 individual apartments, turned out to be one of the most expensive in the area.
Today the residential complex "Habitat 67" is a favorite place for parkour enthusiasts trying to climb to its top at any time of the day.
Spreading

- The discussed fruiting bodies in most cases predominantly live in mixed and deciduous strips. Such mushrooms give preference to poplars, firs and dense shrubs. Often, specimens are found in the forests that are in the suburbs.
- Mushrooms can be found near residential buildings and even in summer cottages. The fruiting bodies in question prefer soil that is rich in organic debris. Moreover, such mushrooms rarely bear fruit and grow mainly alone.
- The specimens are widespread on the southern coast of Lake Baikal, southern Siberia, Buryatia, the European part of Russia, Central Asia, Primorsky Krai, Lithuania, North Africa and America. Fruiting occurs from mid to late summer. In addition, it is extremely difficult to find a mushroom on the territory of Russia, it is rare.
- The double netting grows in the same way in the soil, as does an ordinary egg-shaped jellyfish. By many external factors, it is somewhat similar to a raincoat mushroom. In the common people, the specimens in question are called "witch's egg".
Application in medicine
The main value of the mushroom lies in its medicinal properties, so it is not surprising that it is actively used in traditional medicine. So, the use of a double mesh is indicated for such common ailments as rheumatism, gout and impotence, although in combination with other healing cultures, it helps to treat other pathologies.
Dictyophora double is used in the treatment of gout and rheumatism
Do not forget that we are talking not about the main, but about auxiliary therapy, which gives an effect exclusively in combination with medications.
It is worth noting that all the recommendations given are useful, but practically inapplicable, because the entry of the mushroom into the Red Book does not allow collecting it, even if by some lucky chance it will be possible to find it. This moment must be taken into account when going to the forest, because you cannot encroach on the uniqueness of nature, which is already seriously suffering from human activities.
Description of double mesh
The young fruiting body is ovoid, spherical or cylindrical in shape. Its diameter is 4-5 centimeters. The color of the fruiting body is first white, and then yellow-white and light brown. Over time, the shell covering the fruiting body breaks into blades and remains at the base.

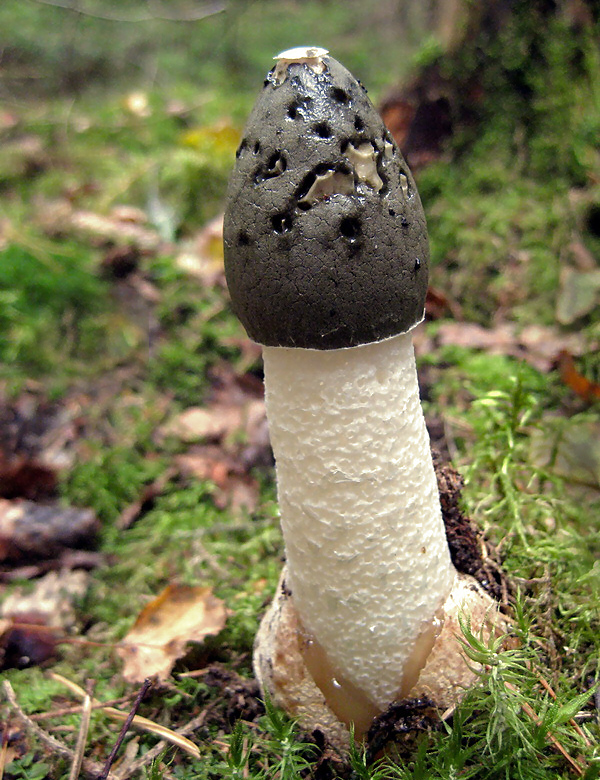
The leg is cylindrical, hollow inside, spongy. The stem color is white, and its upper part ends with a conical ribbed-mesh cap. With age, the cap becomes olive green, slimy. From the place where the cap is attached to the leg, a kind of mesh departs, this formation hangs down to half or to the end of the leg.

Double mesh spread
These mushrooms were found in the Iskitimsky district - in the village of Klyuchi, in a mixed forest. In addition, they grow in the Bolotninsky district, in the village of Novobibeyevo. Also twinned nettails are known in Central Asia, Ukraine, Lithuania and Kazakhstan.
These mushrooms grow in deciduous forests. They settle on humus-rich soil or on decayed woody debris. There are very rare twinned netnopos. They grow in groups or singly. Fruiting from July to September.

Edible double mesh
Young specimens are edible. In addition, double mesh nets are used in folk medicine, with their help they treat rheumatism and gout.
The number of the netnopsock is double
These mushrooms are on the pages of the Red Book of Russia, the Moscow region and Ukraine. The number of this species is decreasing, but factors that contribute to this trend have not been identified. It is believed that the disappearance of twinned nets is associated with climate change.

Other mushrooms of this genus
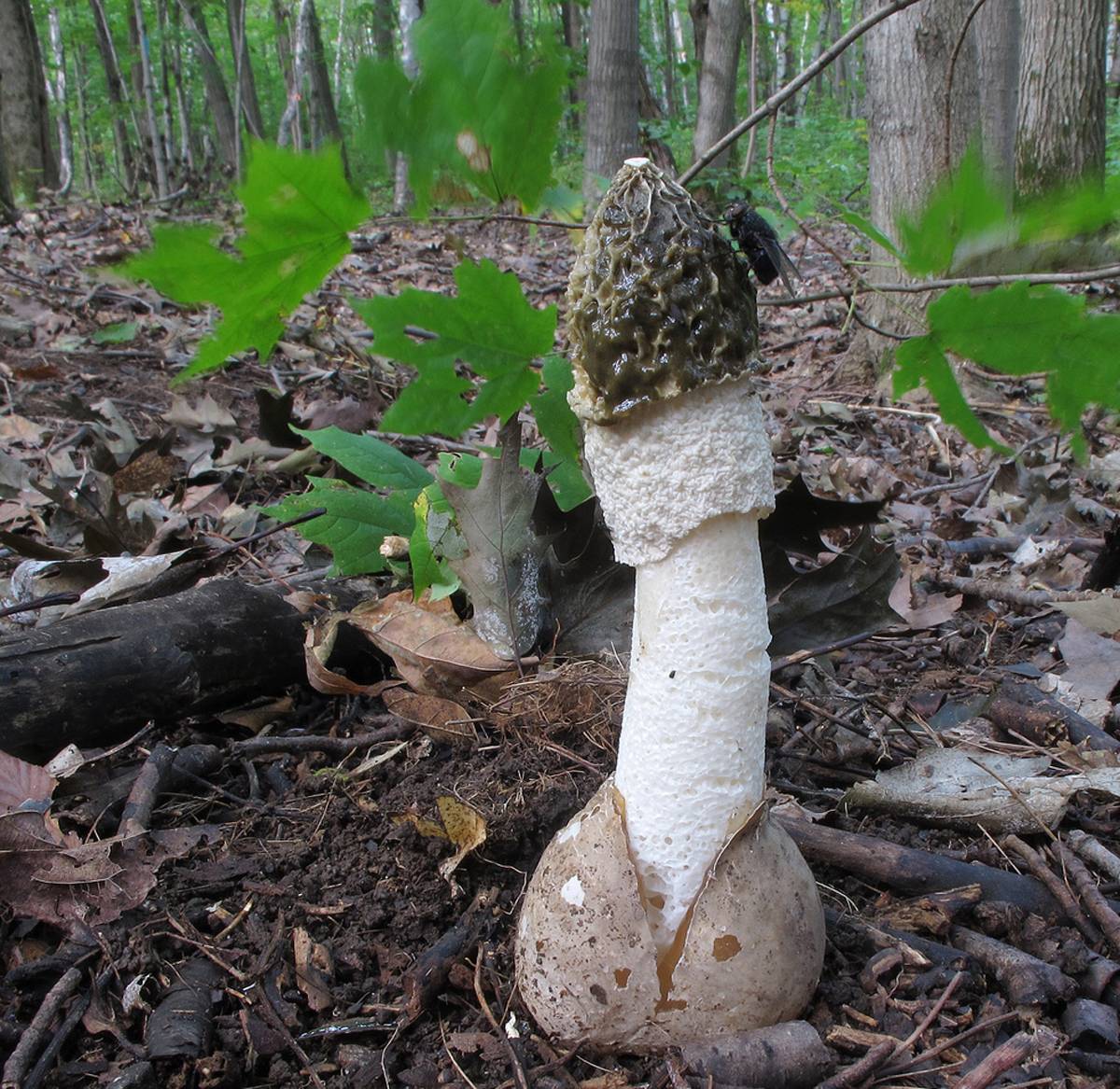
Veselka vulgaris is a conditionally edible mushroom used in medicine. At the first stage of development, the fungus has an ovoid fruiting body, off-white or yellow in color, 4-6 centimeters high and 3-5 centimeters wide. The fun is in this stage for a long time. Then the egg cracks, and a mushroom begins to grow out of it, the height of which reaches 10-15 centimeters. The growth rate is 5 millimeters per minute. The stem of the fruiting body is hollow; on it there is an adjoining cap with brown-olive-colored mucus. This mushroom exudes a pungent smell of carrion, which attracts insects.
Egg-shaped jellyfish can be seen in mid-July, and hat-shaped fruiting bodies develop a little later. These mushrooms grow in grass and deciduous woodlands, on rich soils. At the egg stage, these mushrooms are considered edible. Veselka ordinary is actively used in folk medicine, mainly as a means to increase potency.

Veselka Hadriana is a conditionally edible medicinal mushroom. The shape of the fruiting body is initially oblong, ovoid. The diameter of the fruiting body is 4-6 centimeters. The fungus sometimes comes out of the ground only half. The mushroom is covered with a pink or purple shell. When the shell breaks, a porous white stem with a wrinkled dark cap begins to grow. The length of the mushroom can be up to 20 centimeters. The cap looks like a bell, its surface is slimy. At the base of the mushroom, a pink volva remains. This mushroom has a disgusting odor that attracts flies.
Hadrian's jolly is quite rare. These mushrooms grow in gardens and deciduous forests. They settle most often on sandy soil. Rarely grow in groups. Fruiting from July to October. Mushrooms with light flesh can be eaten, but they have an unpleasant taste. This mushroom has the same medicinal properties as the common jellyfish.
Cooking features
During the period of human history, when dictyophora was a fairly common species in nature, it was used for food until it released its veil.
The egg-like fruit shape was carefully harvested, fried and peeled from the outer skin. Then they were fried with vegetables or stewed in sour cream sauce.
We stored the blanks in a dried form, cutting the fruit bodies in half and stringing them onto a string. The shelf life of the stock was 3 years, after which the useful properties were lost.
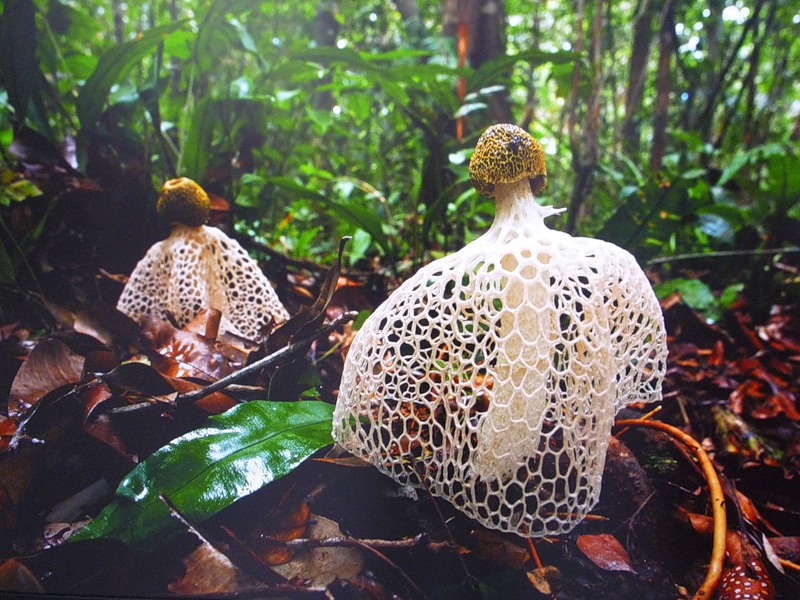
Mushrooms Mushrooms Setkonoska double, she is a lady with a veil
medicinal mushroom - double mesh
The netweed mushroom releases its veil.
An unusual, bright and spectacular mushroom is still very rare, protected by law, so its use for medicinal and culinary purposes is almost impossible.
If you are lucky enough to observe the appearance of the "lady with a veil" while walking through the woods, then you should admire her from afar and mentally wish you good luck in the difficult matter of survival.
Use
Young ovoid fruiting bodies are usually eaten raw, peeled off and seasoned with salt and spices. You can use the product with sour cream. Dictyophora double is not salted or pickled.
Fruiting bodies of the nets can be fried without removing the shell. But it is believed that after heat treatment, their beneficial properties disappear.
Some gardeners are trying to grow the netnose moth in their backyards as an exotic thing. To do this, it is recommended to do this:
- To get spores, the cap is removed from the double mesh and wrapped in mulch from the forest floor.
- In the conditions of a personal plot, a hat with a layer of forest substrate is placed under the garden organic soil and periodically watered.
- The place where the cap is located must not be dug up and loosened.
Attention! Under favorable conditions, after 2 - 3 years, mycelium will sprout from the spores, and then the first fruiting bodies of the nets
Unusual "House-basket"
Not only is this house completely transparent, it does not have a strict architectural stance.Instead of the rooms familiar to everyone, there is only a platform located at different levels. They are interconnected by small transitions from several steps.

A huge office building that looks like a basket is the headquarters of a company that specializes in wickerwork. It is located near the city of Columbus.
The main challenge for the architects was to design the structure so that it expands at the top. The result was 2,200 m2 on the base and 2,750 on the top floor. The construction cost Longaberger $ 29.7 million.
Where it grows and when can it be harvested
Diktyophora doubled is the most northern species of all representatives of the genus. It was found even in England and Denmark, in addition to some regions of Russia (Primorsky Krai, southern Siberia) and the CIS countries (Kazakhstan, Lithuania, Ukraine).
By the way of feeding the dictyophore, the doubled one is a saprophyte, i.e. an organism that uses the dead remains of animals and plants for its nutrition and living. More precisely, experts call it, like a number of other representatives of the order Phallus - forest soil gasteromycetes-saprophytes. It is a hygrophilous species.
To see the emergence of this amazing mushroom, you will have to go to deciduous or mixed forests.
Most often, you can find a netkonosk near shrubs, firs and poplars. She prefers substrates saturated with organic matter, therefore she often appears near summer cottages and residential areas.
Like other mushrooms, it quickly accumulates harmful substances from industrial waste, exhaust gases and becomes poisonous.
It is very difficult to find a double dictiophora, it grows one by one, most often it is noticed already at the stage of unfolding the veil.
The season starts in the middle of summer and practically ends in the first days of September. The collection of these mushrooms is prohibited by law, and violators face a large fine.
Description of the doubled nets (double dictyophores), the spread of the fungus
It is extremely rare in Russian forests to find an unusual mushroom in an openwork "skirt". This is a double net nest - a species listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation.
Description
The conditionally edible twinned netnose or twin dictyophora (Phallus duplicatus or Dictyophora duplicata), which is also called the “lady with the veil”, belongs to the genus of the jolly family of the phallus or merry ones.

This fungus is characterized by the development of the fruiting body in two stages with characteristic species characteristics:
- growth begins with an underground spherical formation containing a dense gelatinous mass with the rudiments of the stem and cap of the fungus. It acquires an ovoid, less often cylindrical shape and emerges on the soil surface, reaching 6-8 cm in diameter. The white powdery outer shell becomes yellowish, brownish and breaks into several lobes, which remain at the bottom of the leg;
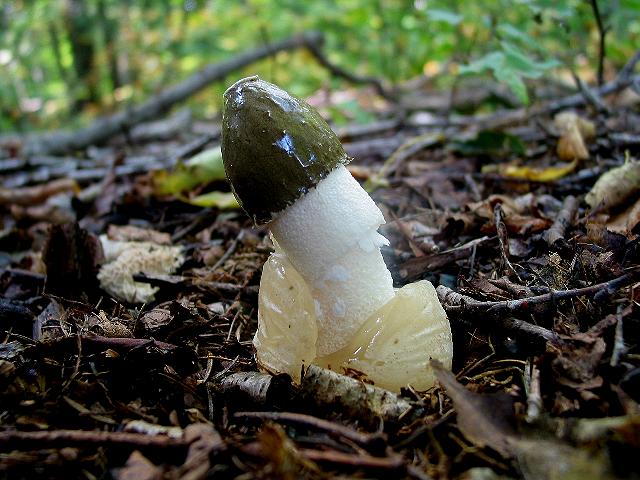
- a cap with a ribbed-cellular surface has a conical shape, covered with a mucous olive-green spore mass. After the release of the fruiting body from the spherical formation, the fungus acquires a strong smell of carrion, disgusting for humans, but attractive for insects that carry fungal spores. The height and diameter of the cap is from 3 to 5 cm. There is a small disc-shaped opening at the apex.
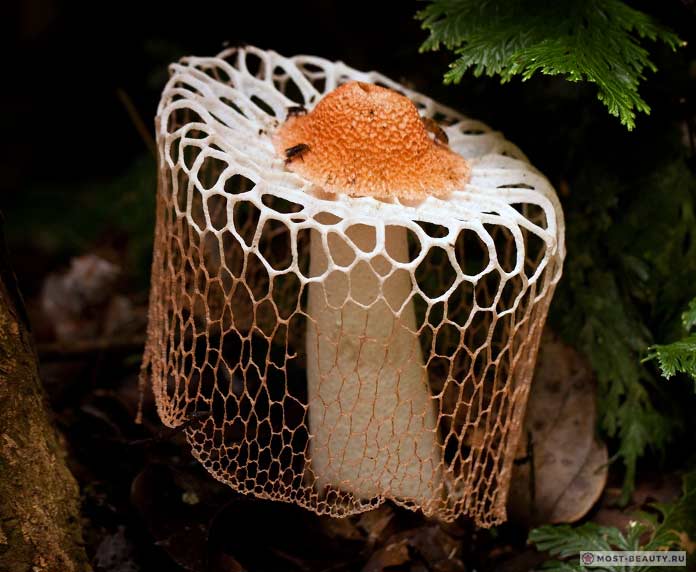
- From under the cap to the middle, sometimes to the base of the leg, a conical openwork mesh formation with rounded cells falls like a veil, the white color of which later becomes light brown with a pink or green tint. At night, the "veil" emits a greenish light;
- the white cylindrical leg is hollow, spongy. In the upper and lower parts it tapers slightly, grows in length up to 15-25 cm, in thickness - up to 2-3 cm.
Places of distribution and period of fruiting

Diktyophora double settles on fertile soil saturated with humus and rotted wood, it can grow in shrubs, mixed forests, in the suburbs and even in the country.Across the entire territory of Russia, the double netting is extremely rare; it is found singly or in groups of no more than 6 specimens. Fruiting from July to September.
Similar types and differences from them
The reticule, which is double in shape and stages of development, is similar to other conditionally edible representatives of the genus Veselykovy - the common fune (Phallus impudicus) with a brown-green honeycomb cap and the rarer Hadrian's fune (Phallus Hadriani) in a pink-purple cocoon. The mature fruiting bodies of both jellyfish do not have a net covering. A much larger twin with a "veil", the bell-shaped dictyophora, grows only in inaccessible regions of South America.
Edibility
In the early period of growth, at the “egg” stage, the double netted snout belongs to the conditionally edible species of the 4th category. In principle, if you forget about the Red Book and keep in mind the ability of this variety to help in the treatment of rheumatism and gout, the mushroom "egg" can be fried or, freed from the outer shell, eaten raw, seasoned with salt and sour cream. At the stage of caps, stalks and covers, the fruiting bodies become inedible due to a strong unpleasant odor.
Such a find, as a relict double netskock, is a rare piece of luck. Despite the fundamental edibility, it is better to leave the mushroom intact - after all, the collection of fruit bodies of this species is prohibited throughout the territory of the Russian Federation. The place of discovery of the "Red Book" should be reported to the environmental services, which take into account and control such populations.
Phytoncides, polysaccharides and perforins
Phytoncides are biologically active substances secreted by plants that kill or suppress the growth and development of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms.
Now about the perforins. According to the Japanese professor Toki Mori, in any organism, cells can be reborn into cancerous due to various factors, in fact, we can say that any person has cancer cells.
But our body produces special enzymes - cytotoxic proteins perforins, which track and destroy tumor and virus-infected cells, destroying their nucleus. At a young age, perforin is produced well, but with age, the strength of perforin production weakens, and when it practically ceases to be produced, malignant cells begin to rapidly divide, and a person develops a malignant tumor.
Scientists conducted a number of experiments and proved that polysaccharides of the veselka mushroom increase the production of perforin in the body several times! Accordingly, as you already guessed, if you make a tincture (or infusion) from the veselka and take at least 1 course per year for prevention, then you will significantly strengthen your immunity, health and reduce the likelihood of illness, including cancer!
What fun treats
Thanks to the unique combination of components gathered in this miracle of nature, the Veselka mushroom treats the following diseases:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), liver and kidneys;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems;
- atherosclerosis and hypertension;
- relieves inflammation and joint pain;
- rheumatism and gout;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- diseases of the blood and lymph;
- diabetes;
- varicose veins and thrombophlebitis;
- male impotence and female pathologies: inflammation, fibroids, mastopathy, infertility.
Veselka also treats viral hepatitis, herpes, influenza, allergies and its symptoms, hypertension - due to the ability of the active substances Veselka to reduce the level of bad cholesterol, lower blood pressure. , non-healing wounds), resolves benign and even malignant tumors, treats AIDS.
Contraindications
Veselka is not recommended for children under the age of ten, as well as for women during pregnancy and lactation.
Take with caution to persons with chronic pathologies of the heart, liver, kidneys, pancreas; persons with autoimmune diseases, since biologically active substances (BAS) of the Veselka mushroom quite sharply raise immunity, which can provoke an exacerbation of diseases of this kind
Veselka for treatment
For the treatment and prevention of diseases, vodka tincture of the Veselka mushroom is usually used (tincture on vodka, alcohol diluted to 38-40 degrees, good moonshine of the same strength). Inside, it is used to treat all of the above diseases, in addition, it is used in the form of compresses for the treatment of skin diseases, psoriasis, trophic ulcers, bedsores.
Other forms of mushroom preparation are dried halves (quarters) of the mushroom, as an option - dried veselka in the form of a powder (grind on a coffee grinder). It is also used for the preparation of tinctures, as well as infusions (not decoctions, without boiling)!
In this form, the veselka retains its medicinal properties for several years, but in no case should it be frozen - the frozen veselka loses its medicinal properties.
There are also some rather rare options for the preparation of Veselka mushroom, used for the treatment and prevention of diseases, such as lotion, balm, all kinds of ointments, candles for external use.
Fermented (sour) juice is also made (it is used to treat the liver, purify the blood in diabetes mellitus) and oil tincture. The tincture is used externally for the treatment of burns, bedsores, fistulas, trophic ulcers; inside - for the treatment of diseases of the stomach, intestines, kidneys, but in case of problems with the liver, it is undesirable to use oil.
To prepare the oil tincture, pour a teaspoon of mushroom powder with 500 ml of warm olive or linseed oil. Stir and leave for a day at room temperature, then another week in the refrigerator, do not filter. Shake well before each use.
This seems to be all, now you know what diseases the common mushroom can cure, and next time I will tell you how to properly prepare the vodka infusion of the veselka.
Popular varieties of mushroom
Today, scientists distinguish several varieties of netnose, first discovering this species back in 1562 in the Netherlands forests. Despite this, the first scientific description of the fungus dates back only to 1972, when the Italian biologist Micheli described the genus, calling it Phallus, and divided it into two separate subspecies. A little later, this list was expanded, although the most popular are the common and Adrian's.
Veselka ordinary
Like other representatives of the genus, the most common variety, Veselka vulgaris, is a conditionally edible mushroom that has been widely used in medicine. A peculiarity of its structure is very interesting: at the initial stage of development, one can observe a spherical body cracking over time and releasing a long porous barrel with a double cone-shaped cap.

Veselka ordinary
It is worth noting that this base remains with the fungus until the very end of its life cycle, making its shape even more bizarre. The growth rate of the mushroom is also surprising, and every minute it adds 5 mm.
The fruit reaches its maximum of 10-15 cm, usually in a matter of days. But it is this miracle of nature that has the ability to exude a sickening smell, attracting flies and scaring away animals and people.
Merry Adriana
Veselka Adriana or Hadriana is also conditionally edible, it has a shape and diameter of the fruit body similar to that of the Setkonos. As for the differences, one of them is the shell of the fungus, which can have a pinkish or purple hue. In addition, the stem of the fungus can only partially come out to the surface, leaving its base in the Volvo.

Merry Adriana
Almost the entire surface of Adrian's vest is covered with a thin layer of mucus, and its pulp also has an unpleasant odor and taste, although it is good for consumption. This variety is even less common, and it is almost impossible to see a whole group of veselka fruits. In addition to deciduous and mixed forests, the fungus grows in gardens and other areas with sandy soil.



















































