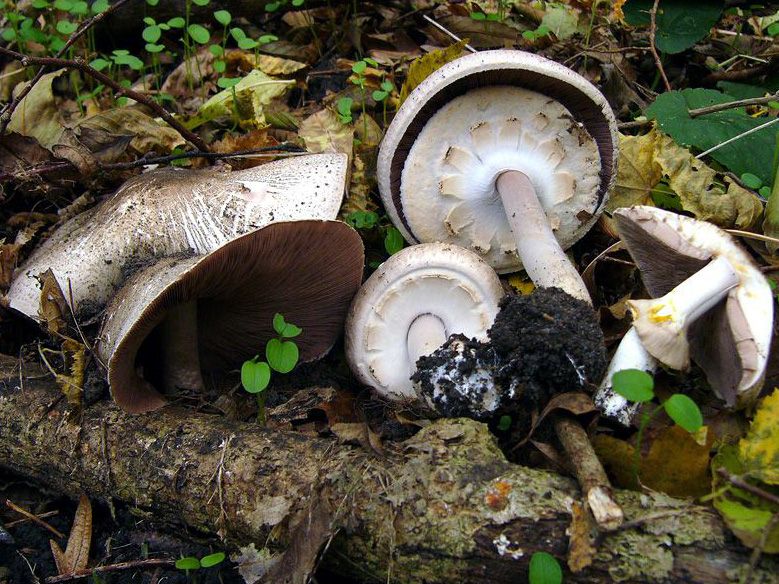
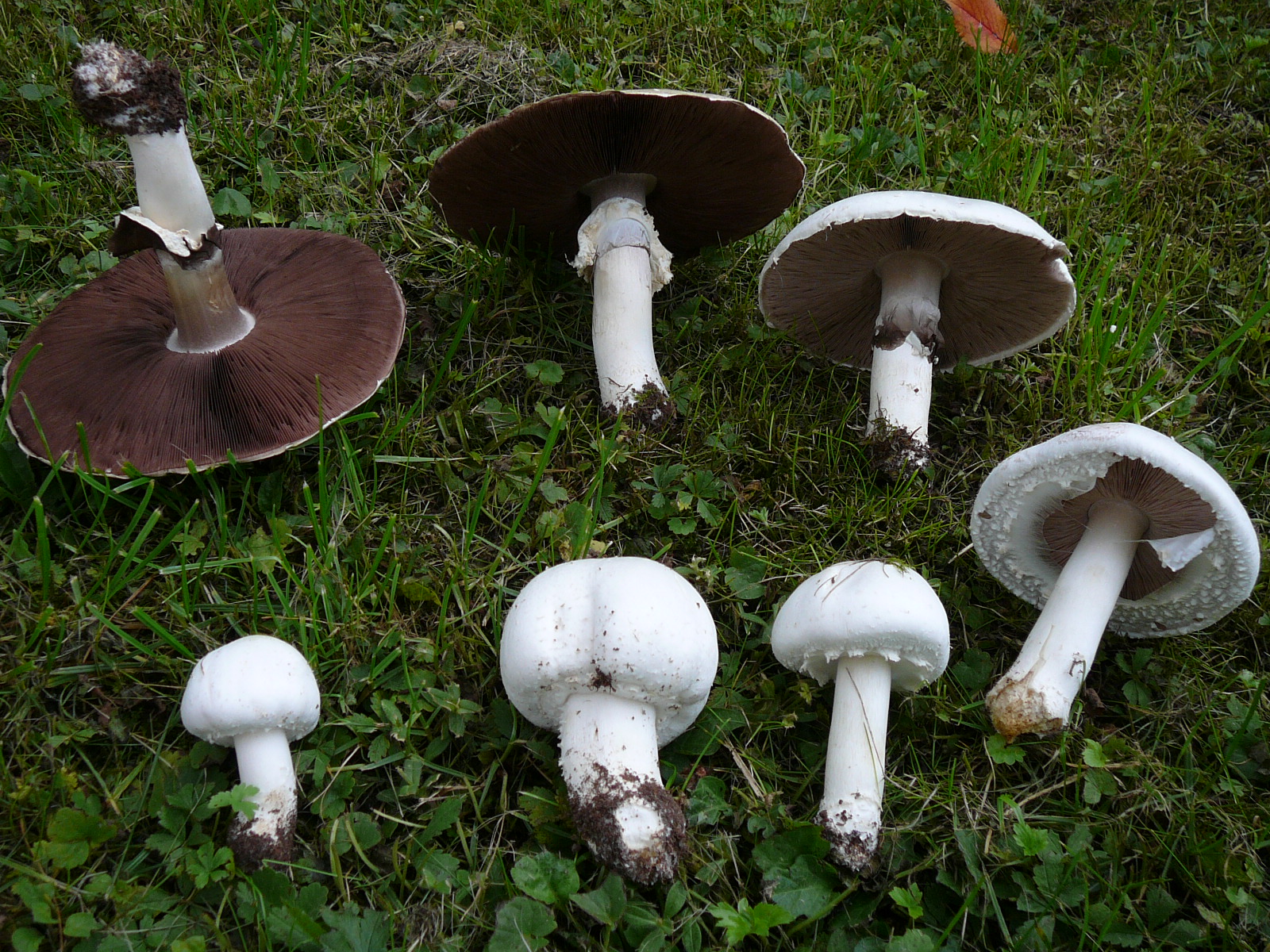
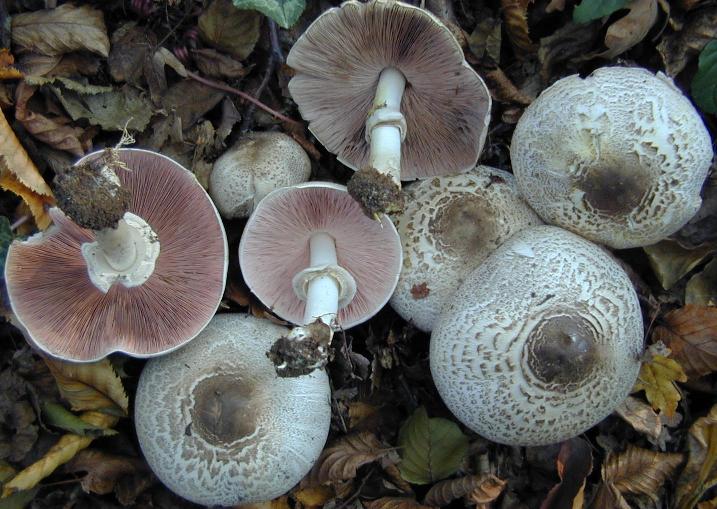
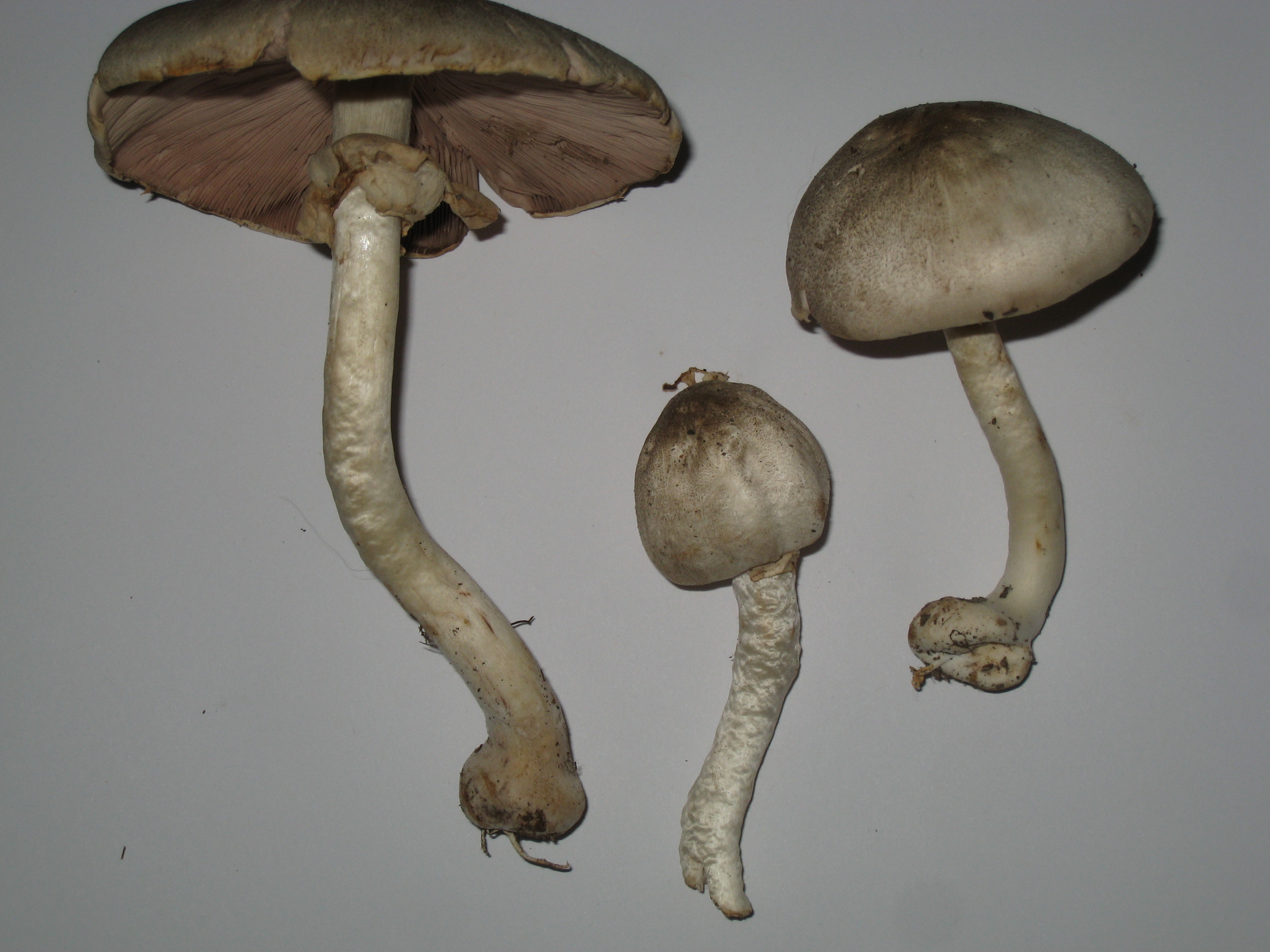
Description of tabular champignon
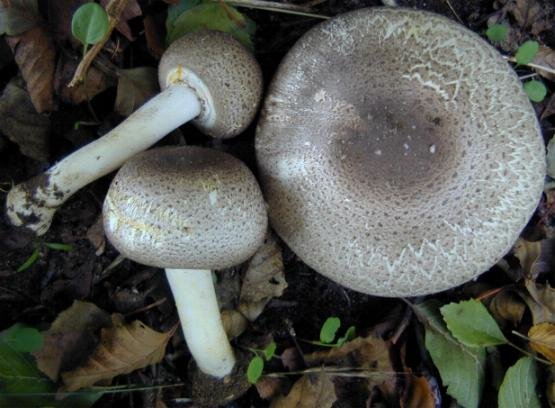
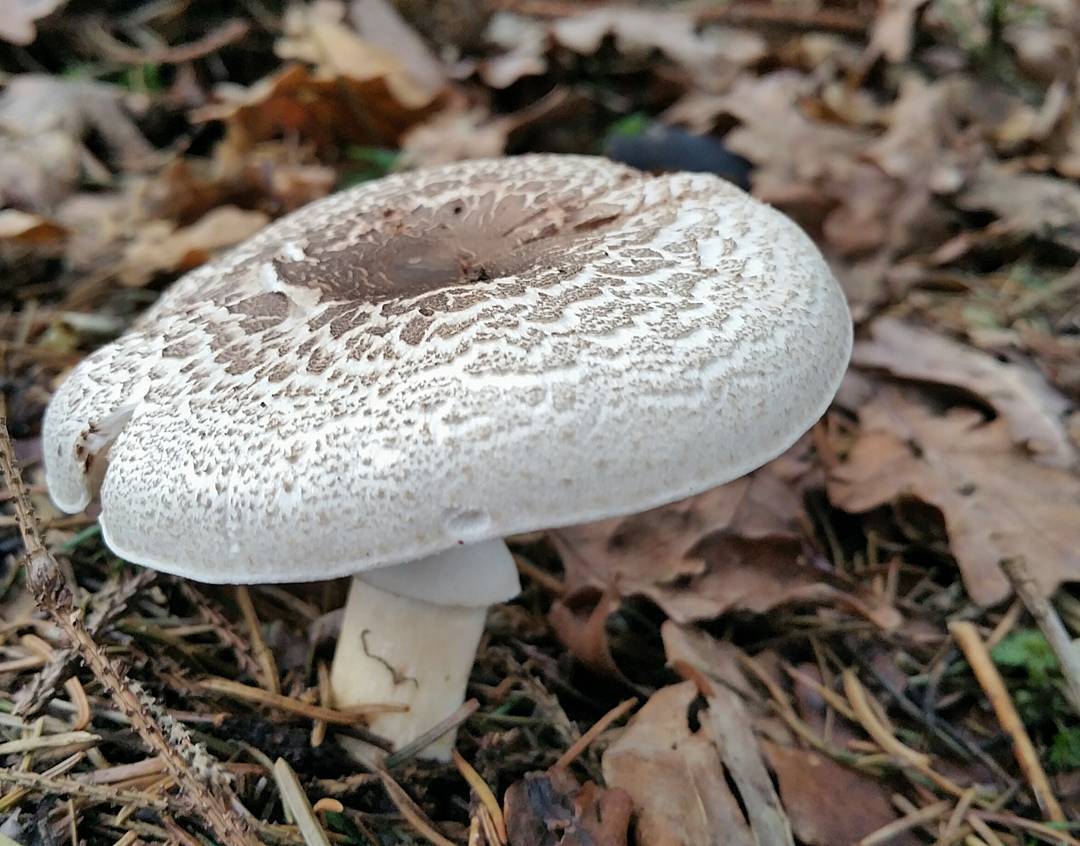
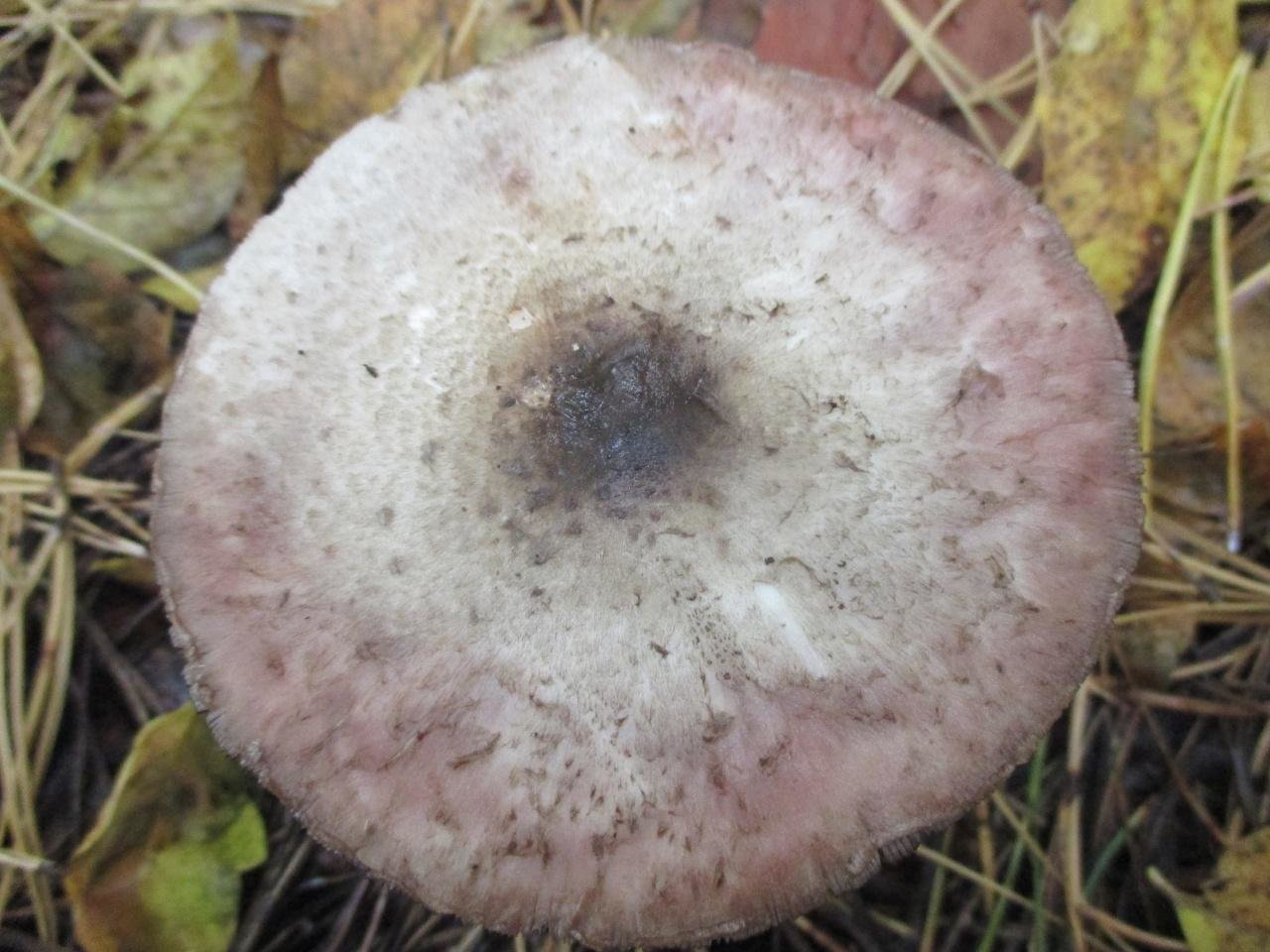
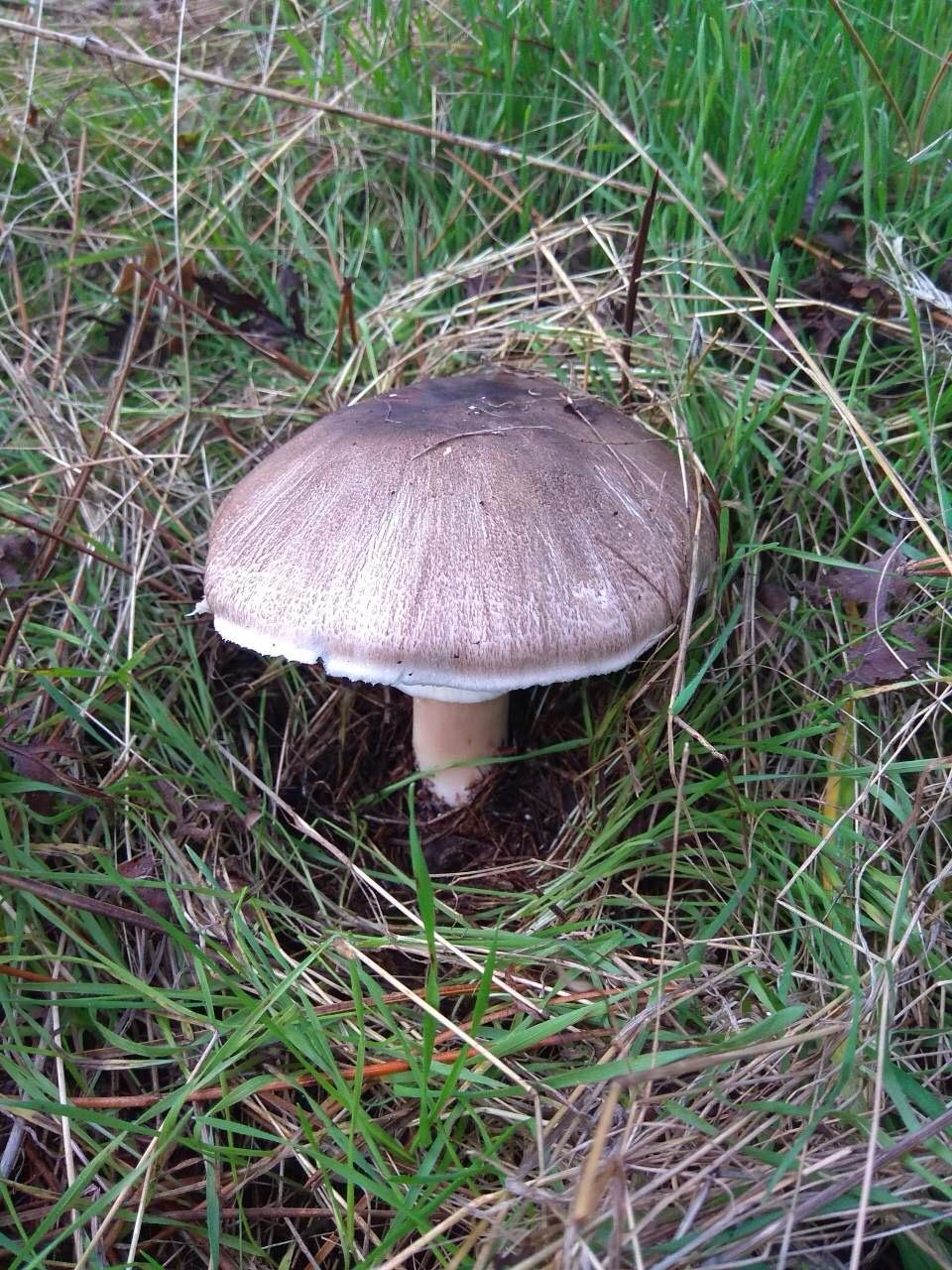
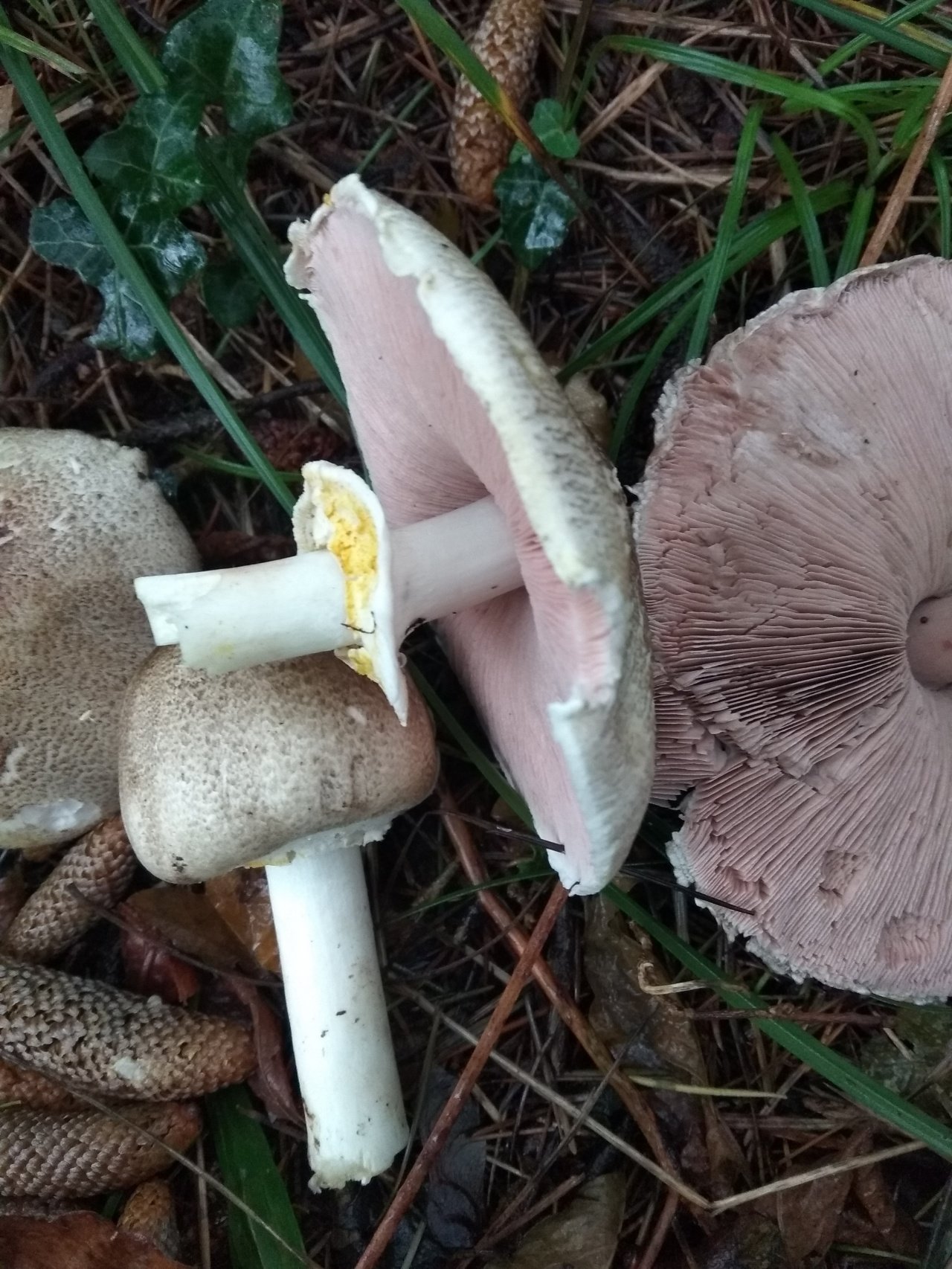
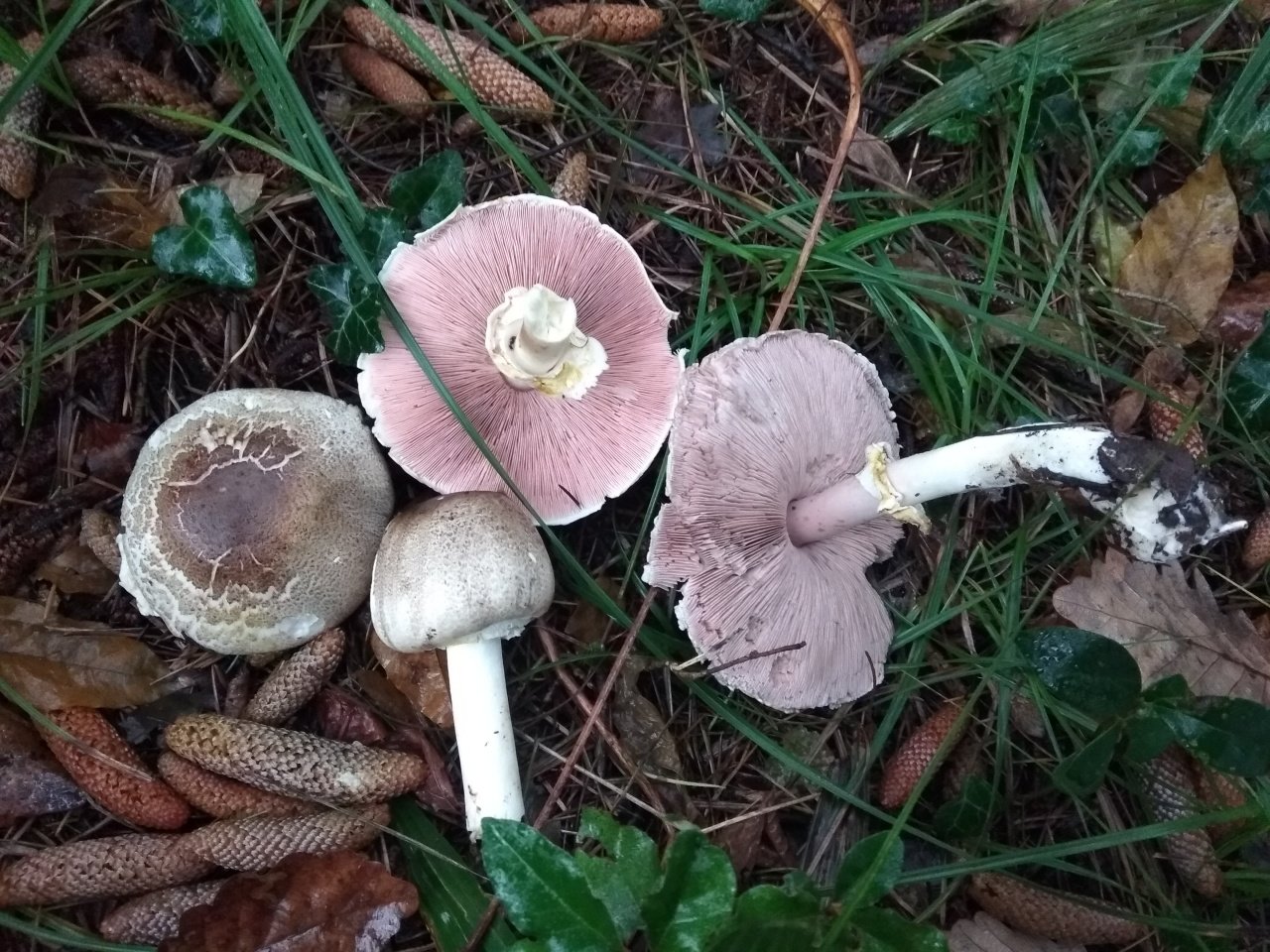
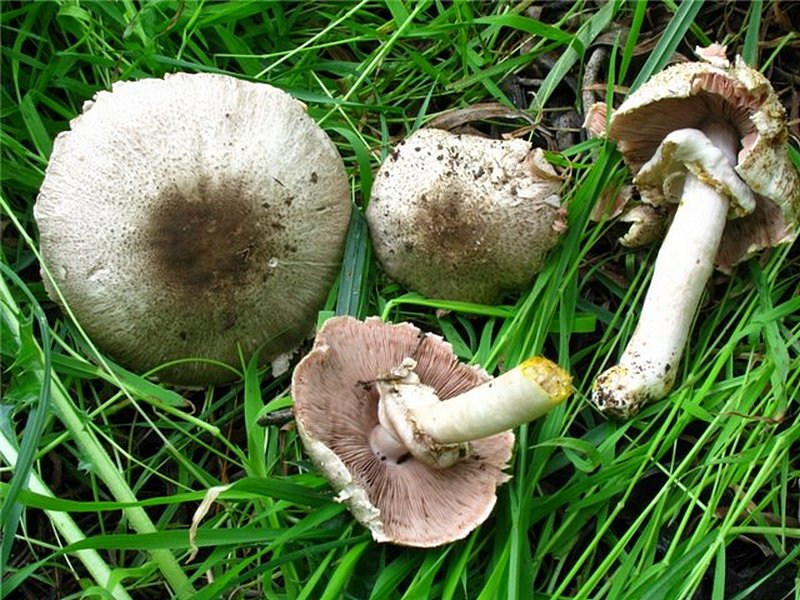
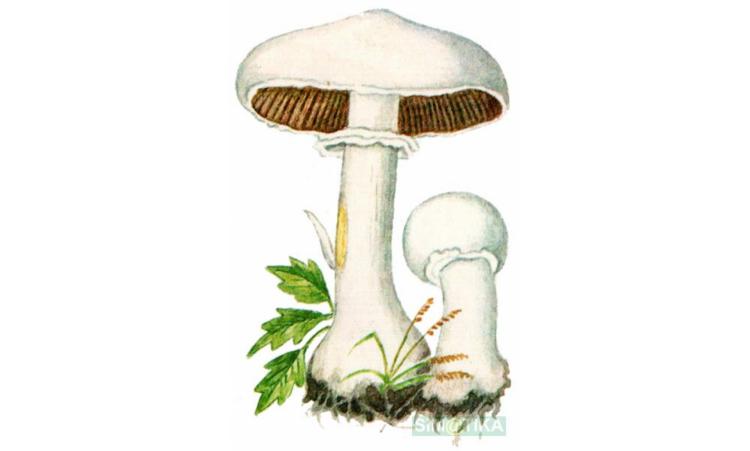
The diameter of its cap can be 5-20 centimeters. The cap is fleshy, very thick, at first semicircular in shape, and eventually convex-outstretched, while sometimes in the center it is flat. The color of the cap is whitish or whitish-gray, if touched, it will turn yellow.
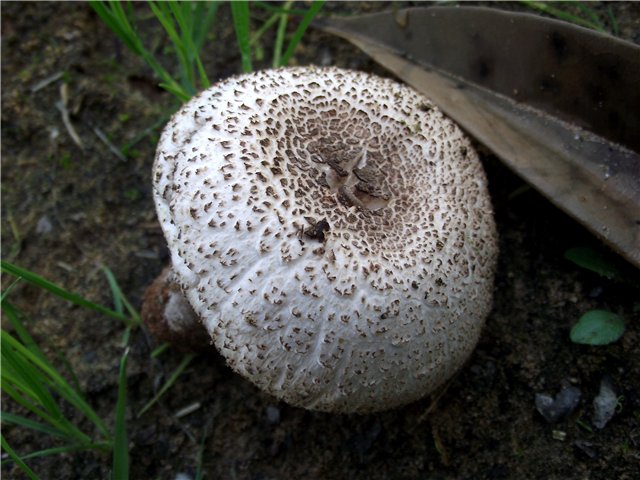
With age, the cap cracks into pyramidal cells arranged in horizontal parallel rows. The surface of the cap is tabular-fissured or tabular-cellular, while the cells are often covered with pressed small scales. The edges of the cap are first tucked up, later they become open, often the remnants of the bedspread are visible on them.

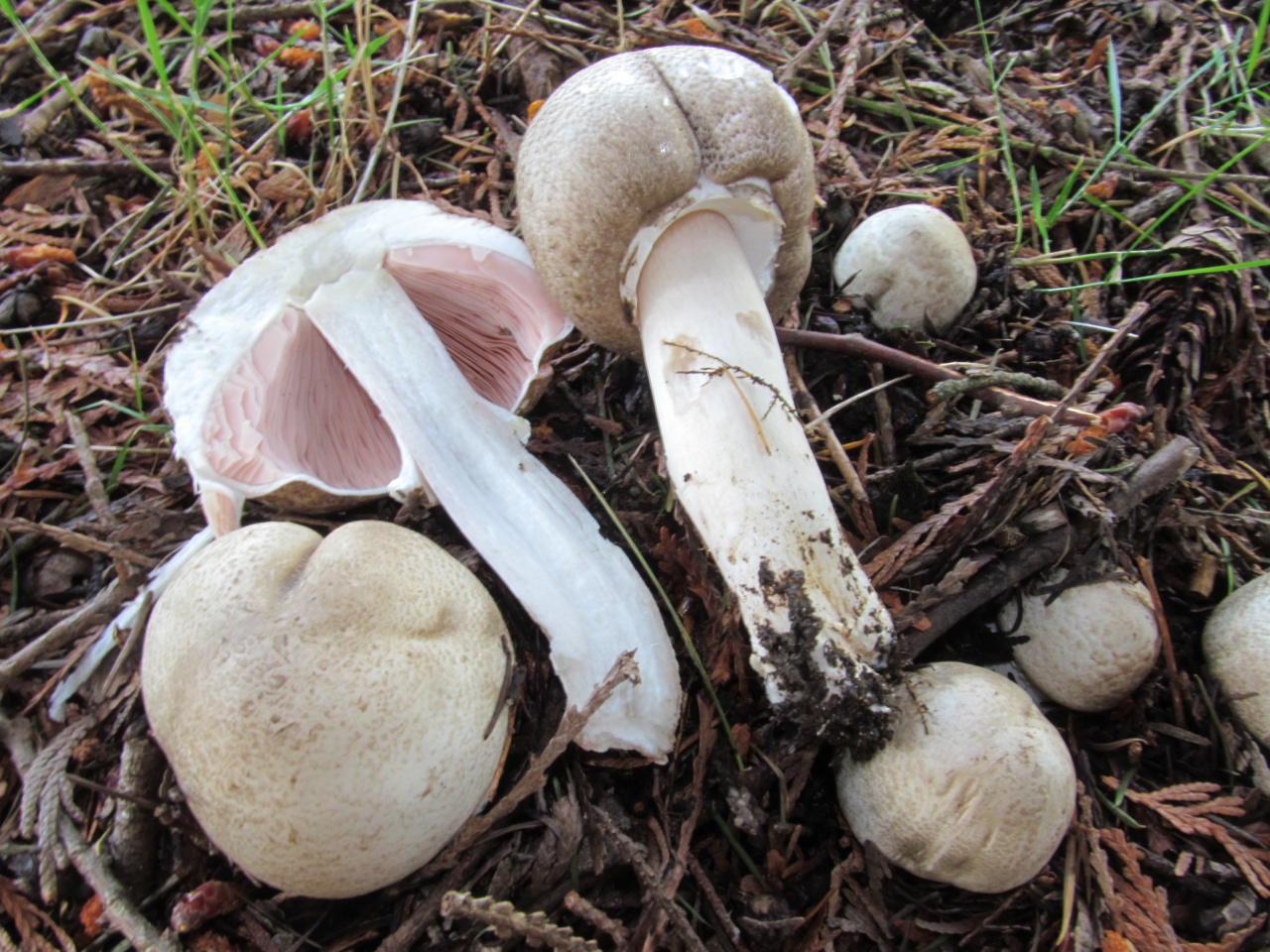
The pulp of this mushroom is white. At the base of the stem and above the plates, the flesh can turn pink with age. When touched, the pulp turns yellow. Dark brown spore powder. The plates are loose, narrow, becoming black-brown in maturity.
The leg is wide, thick and dense. Its length is 4-7 centimeters and its width ranges from 1 to 3 centimeters. Its shape is cylindrical, the leg is located in the center of the cap, towards the base it becomes narrower. The color of the leg is whitish.
The surface of the leg is silky fibrous. There is a ring on the leg, it is smooth on top and fibrous below. The color of the ring is white. The ring lags behind the leg, it hangs down with age.
Places of growth of tabular mushrooms
These rare mushrooms are found in semi-deserts and deserts of Central Asia and Kazakhstan. They also grow in the steppes of Ukraine, this is the first finding of these mushrooms in the European continent.

Inedible cousins
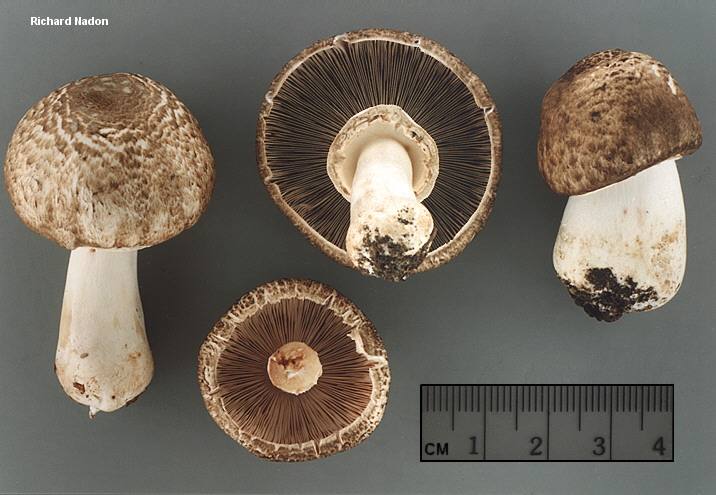
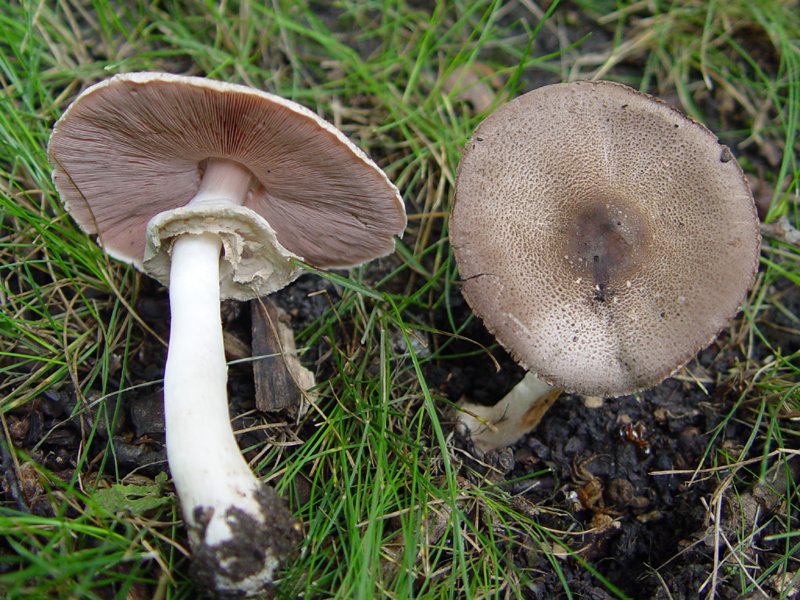
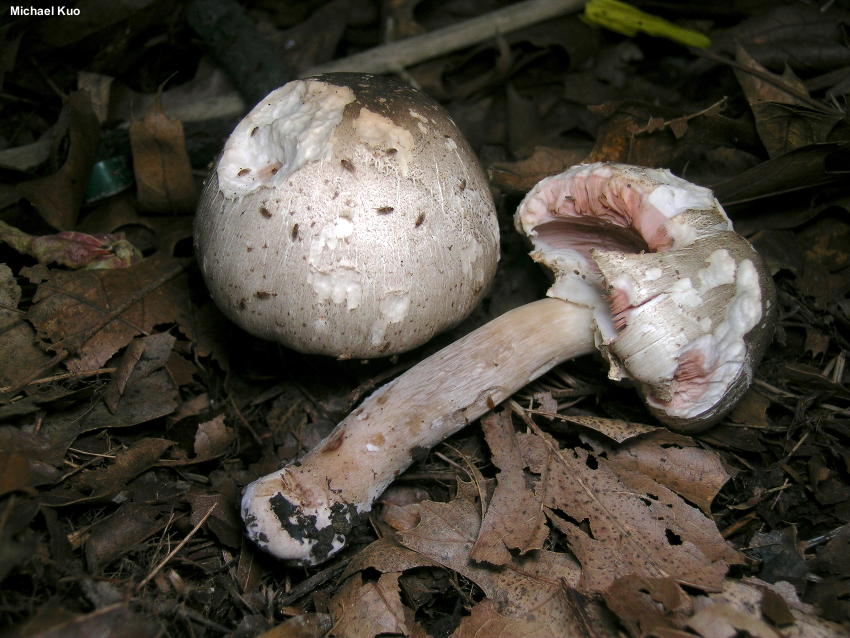
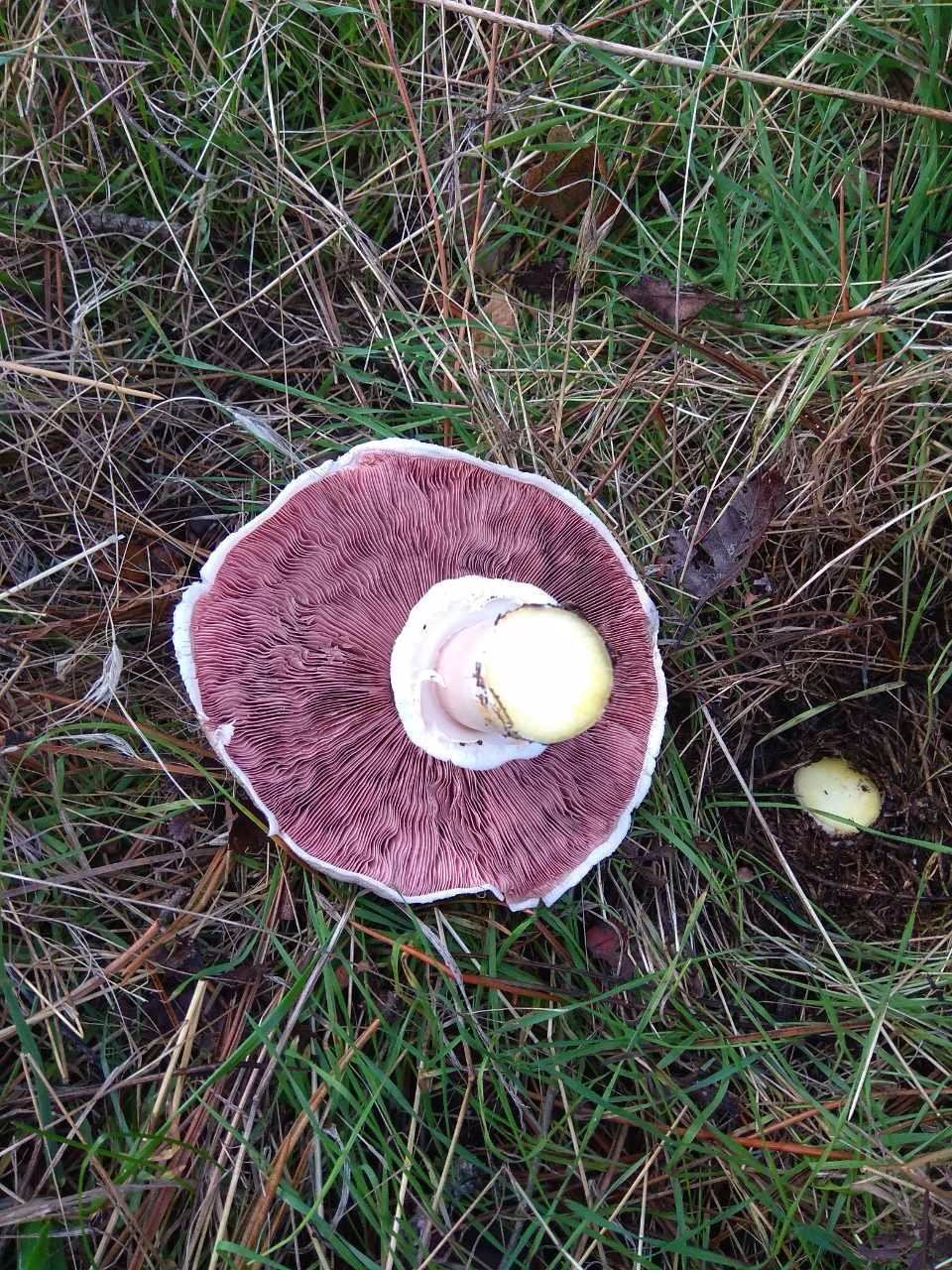
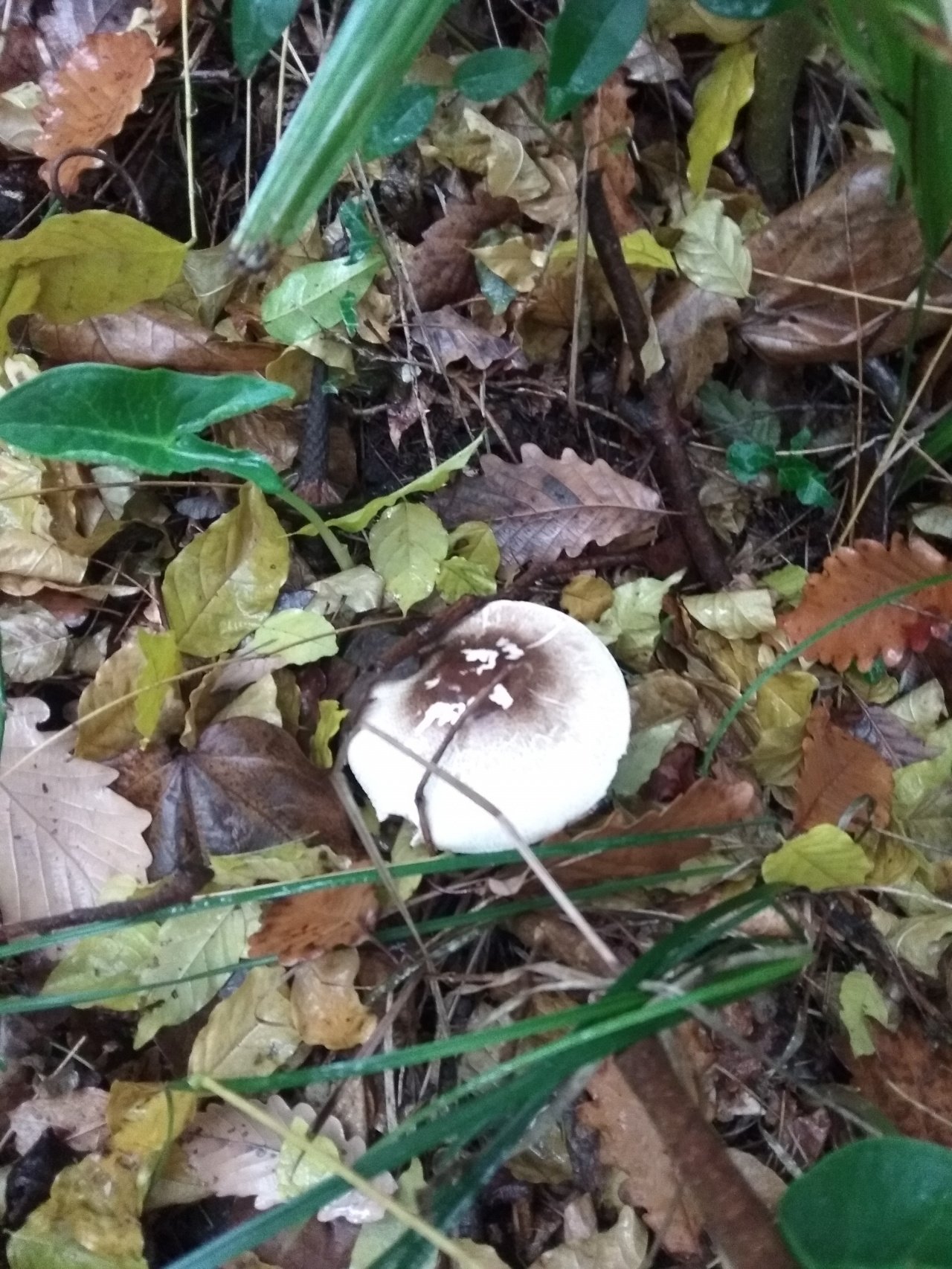
Champignon yellow-skinned or reddish - a poisonous mushroom. Outwardly, this inedible mushroom is similar to many other mushrooms, which is its danger. His hat is white, with a brownish blotch in the center. If you press on the cap, it turns yellow. In mature specimens, the caps are bell-shaped, and at a young age they are rounded.
The diameter of the cap reaches 15 centimeters. The leg length ranges from 6 to 15 centimeters, and the thickness is 1-2 centimeters. At the base, it is tuberous-thickened. The color of the leg is white. It has a thick two-layer ring.
Yellow-skinned champignon is very poisonous, when poisoning occurs vomiting and various disorders in the body. These mushrooms bear fruit actively from summer to autumn. They appear abundantly after rains. Yellow-skinned champignons grow in mixed forests, gardens and parks. They are distributed all over the world.
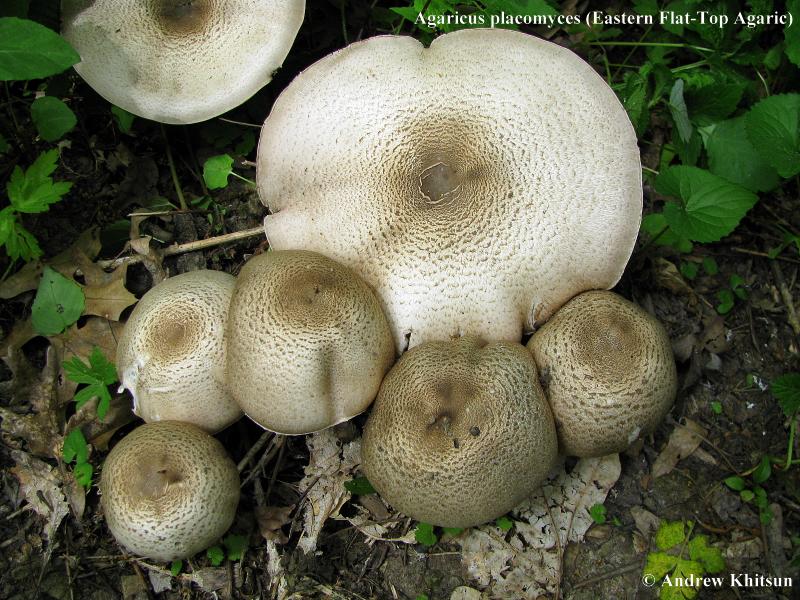
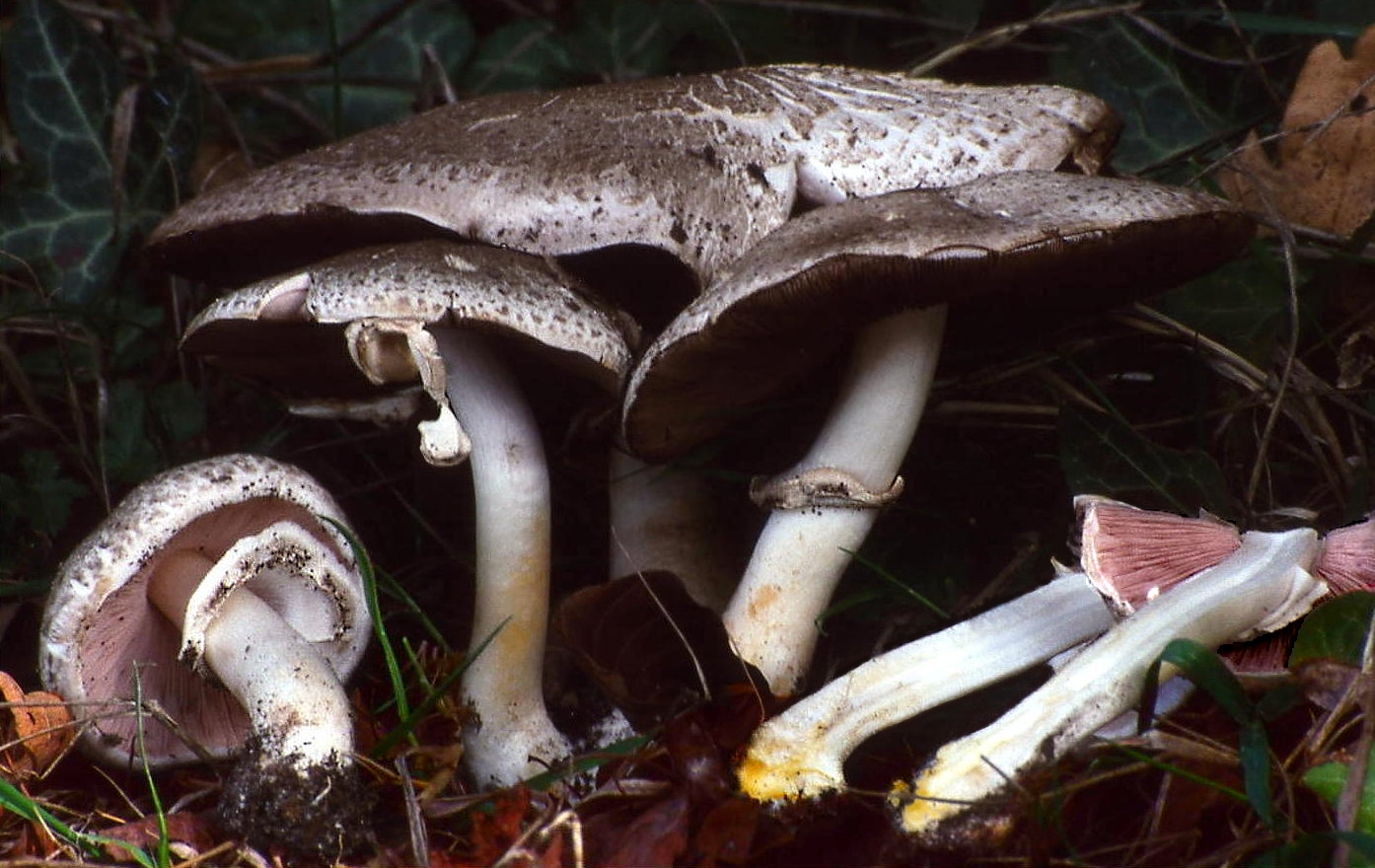
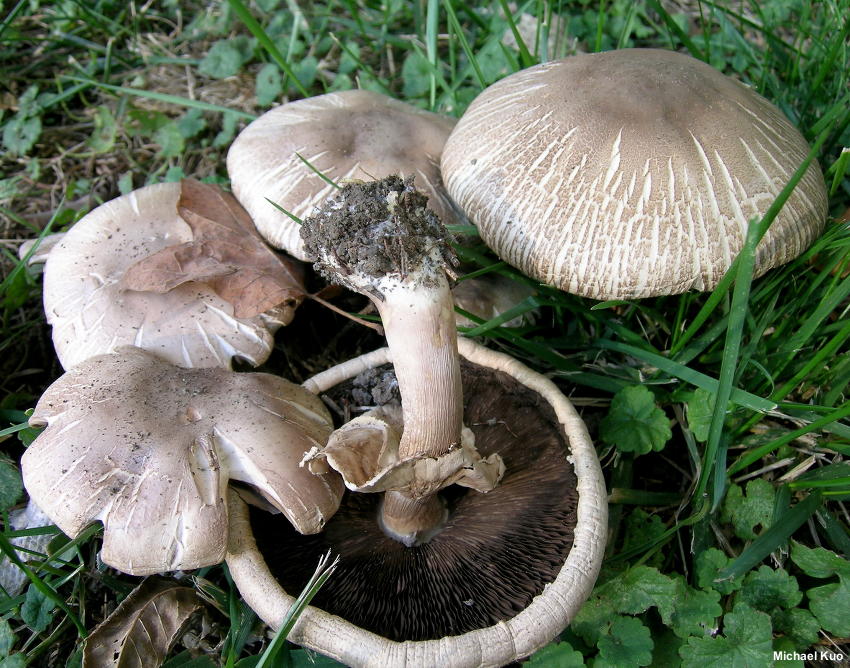
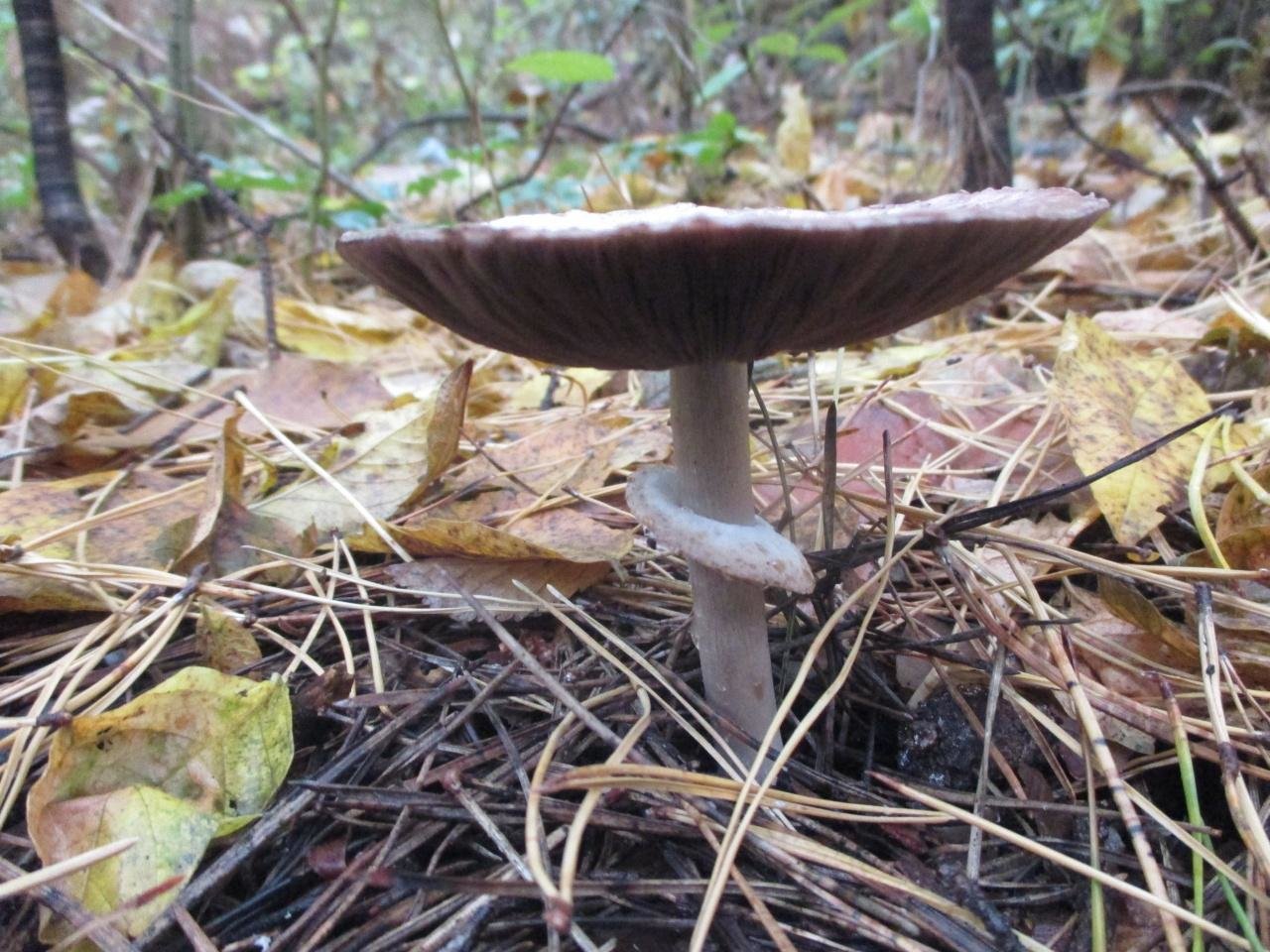
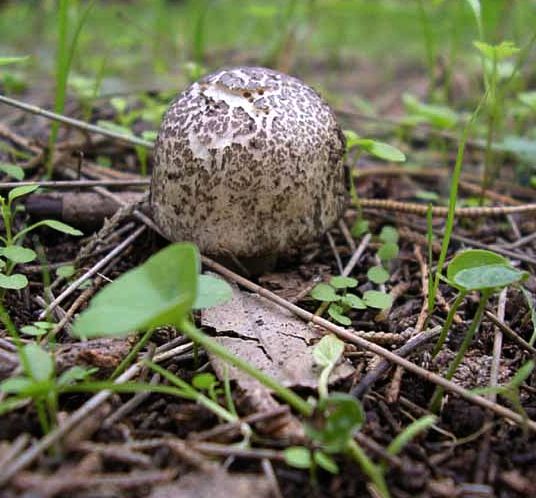
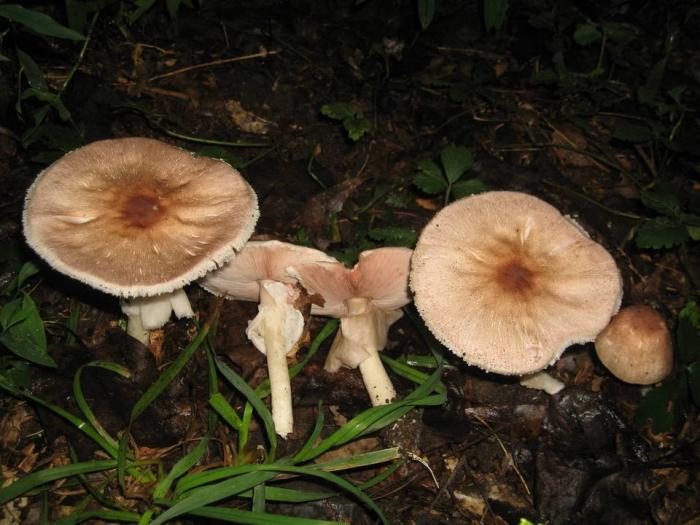
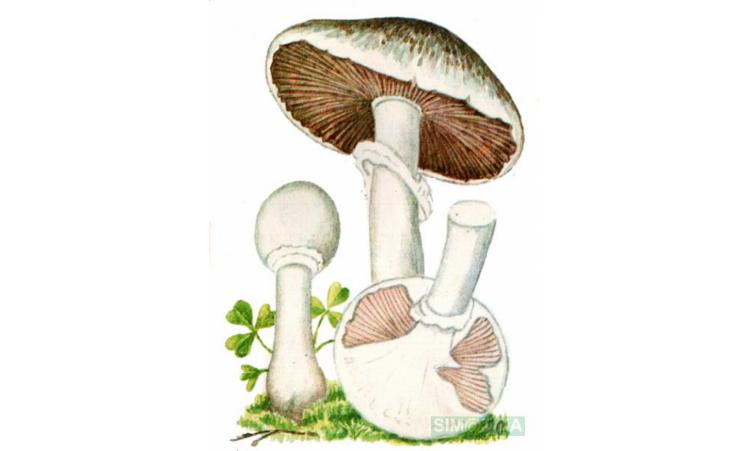
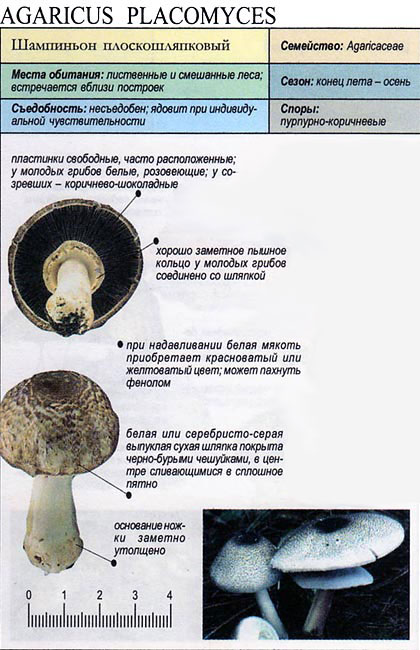
The flat mushroom champignon is an inedible mushroom. The diameter of its cap reaches 9 centimeters. The shape of the cap at a young age is ovoid, after which it straightens and reaches flat, while there is a small tubercle in the center. The skin on the cap is grayish or whitish with many greyish-brown plates. The leg at the bottom has a tuberous thickening, its length reaches 9 centimeters, and its diameter does not exceed 1.2 centimeters. There is a rather large ring on the leg.

Flathead mushrooms grow in deciduous and mixed forests. Sometimes they can come across near housing. They bear fruit in the fall. Witch circles are often formed. In some sources, these mushrooms are classified as inedible species, and in others - as weakly poisonous. They can cause gastrointestinal upset.
Description of flat mushroom mushroom
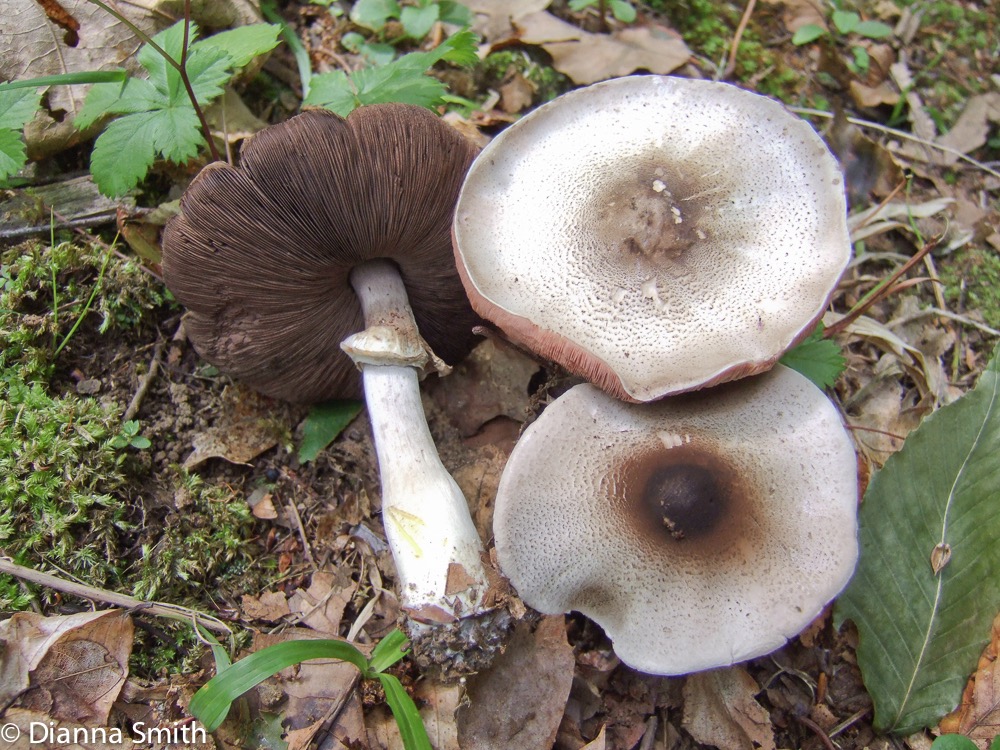
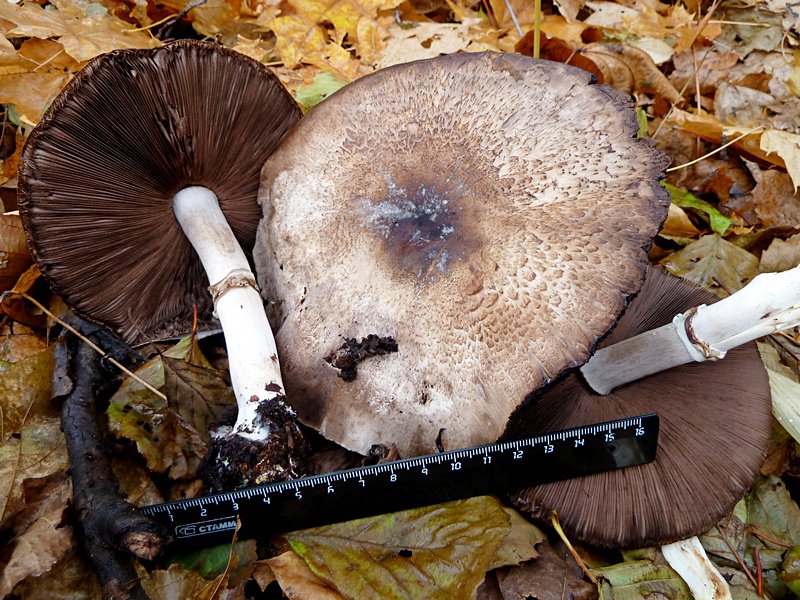
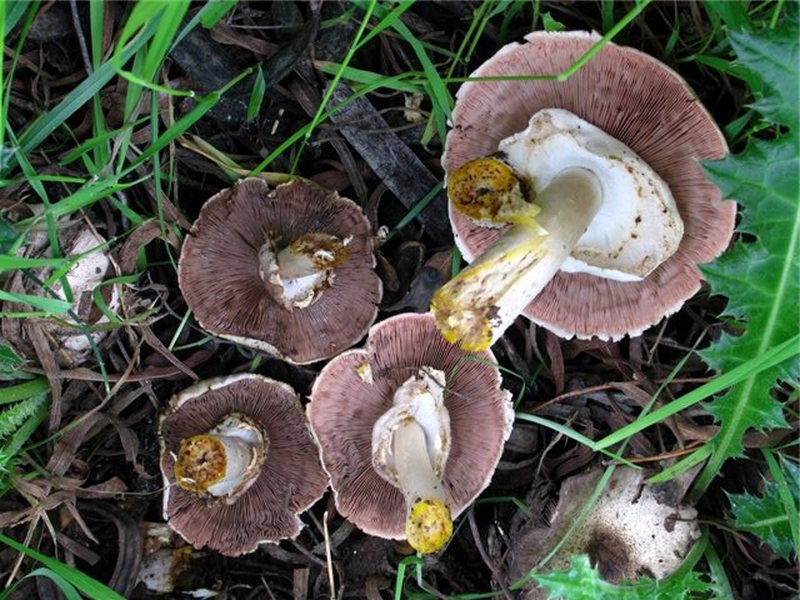
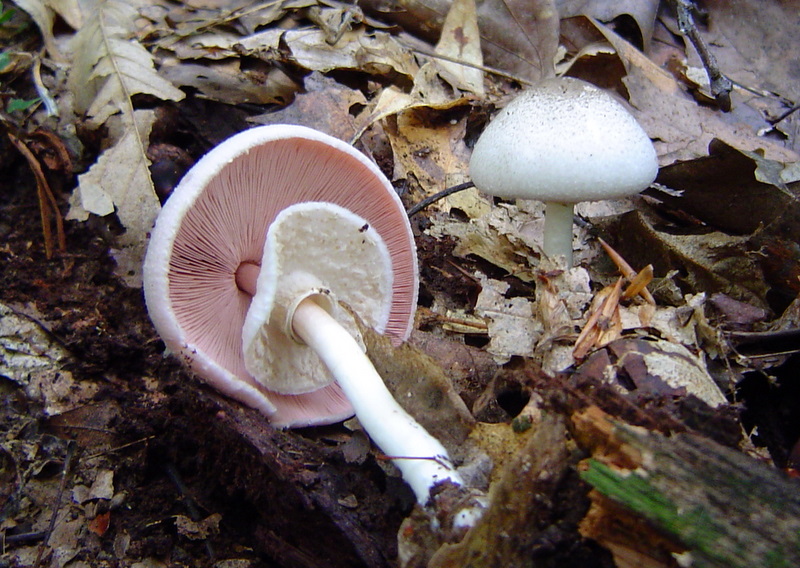
The diameter of the cap of this mushroom is 5-9 centimeters. In young specimens, the caps are ovoid, but, as the name implies, they become flat as they grow, with a small tubercle visible in the center. The cap is covered with dry grayish or white skin.

The surface of the cap is scaly. The scales are grayish brown, in the center they merge and form a dark spot.
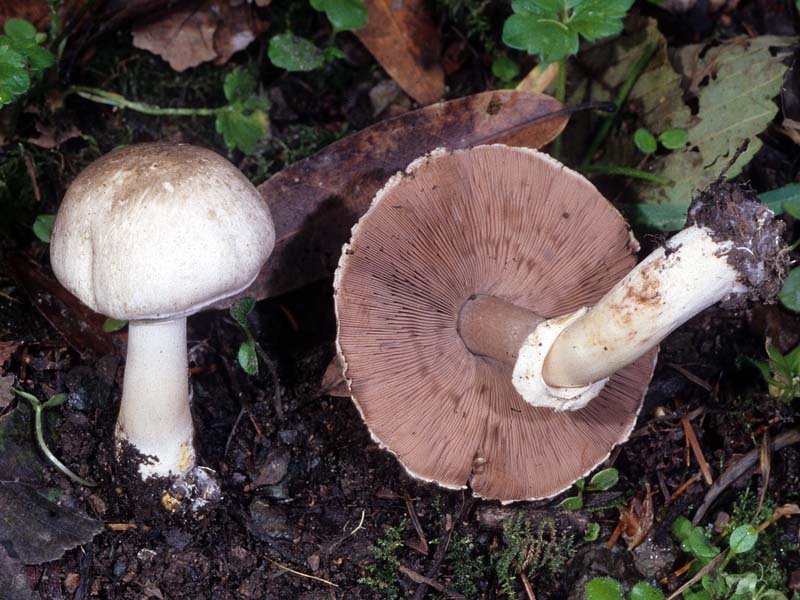
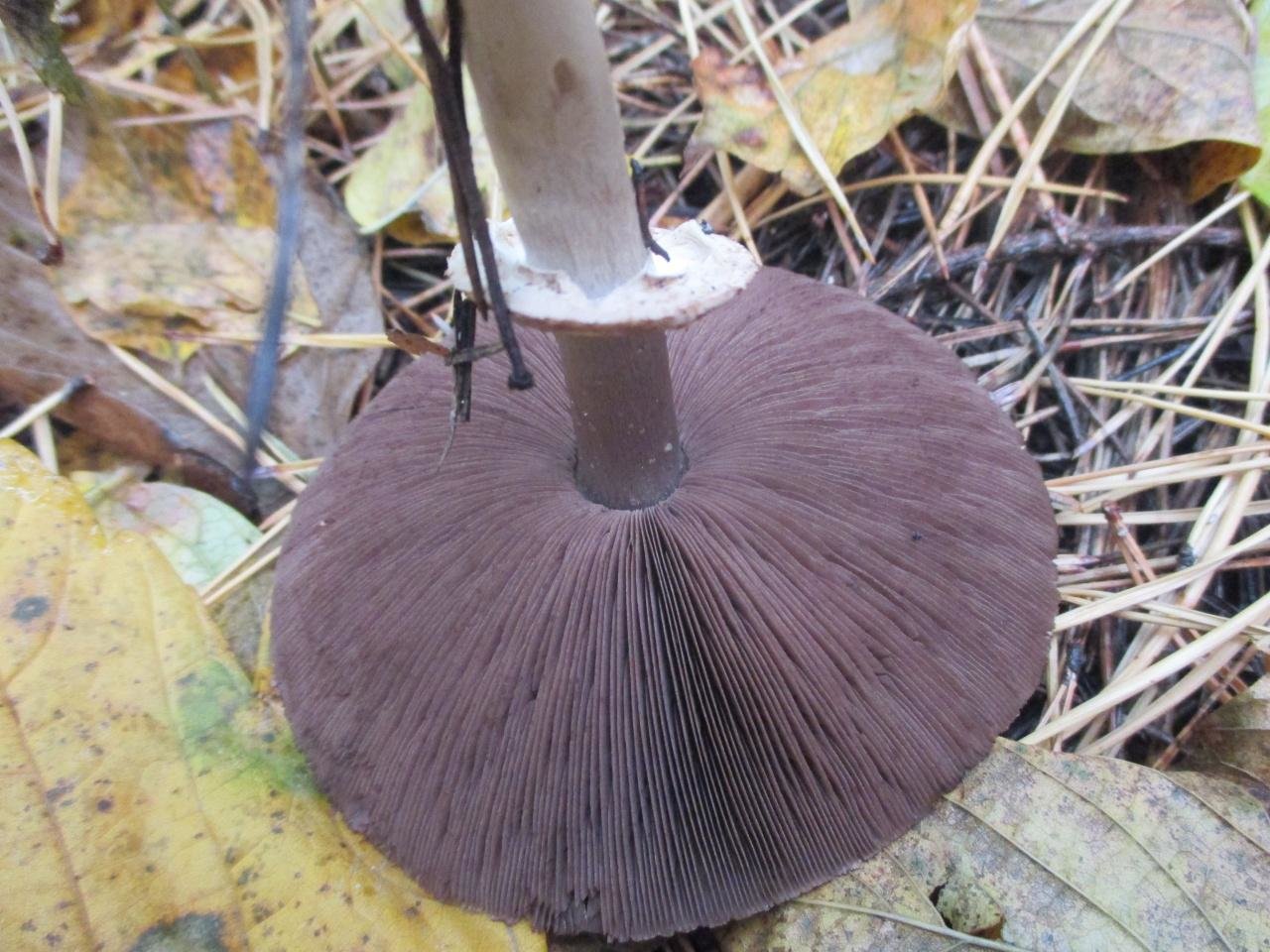
The plates are free, often located, at a young age they are slightly pink, but over time they darken, and their color becomes black-brown. Spore powder of brown-purple color. Elliptical spores.
The length of the stem of the flat-cap champignon is 6-9 centimeters, and the thickness is 1-1.2 centimeters. In the lower part there is a tuberous thickening. The stem is fibrous, with a rather large ring. In young mushrooms, the leg is connected to the cap.
The pulp is quite thin, whitish in color, if damaged, it turns yellow. In older specimens, the flesh turns brown. The smell of the pulp is of varying strength, often strongly unpleasant, reminiscent of "chemical" or "pharmacy".

Distribution of flat mushroom mushrooms
These mushrooms are found most often in the fall. Distribution sites are mixed and deciduous forests. Sometimes they come across near dwellings. Often they form "witch rings".
Similar species
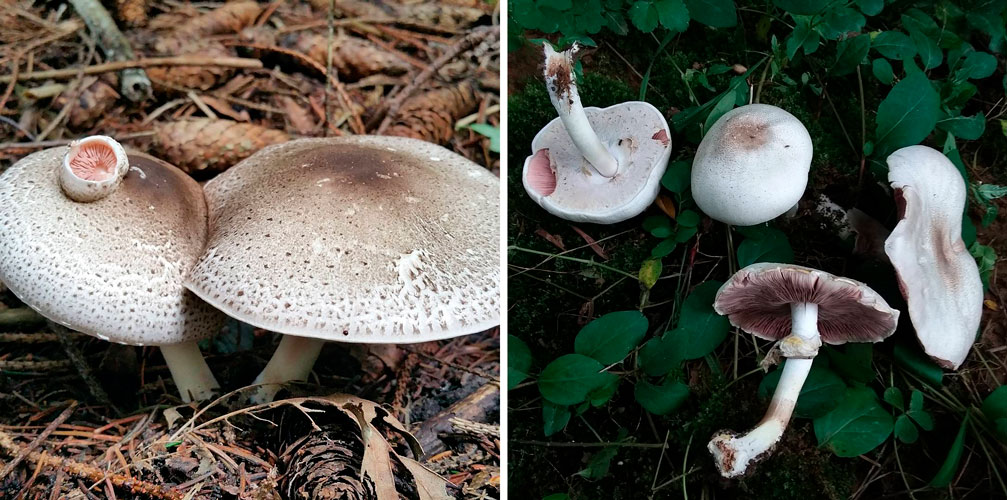
Due to its particularly large size, large-spore champignon is difficult to confuse with other species, but young specimens may look like some edible mushrooms:
The main difference is that this species is predominantly forest, and it grows mainly among the pines. It looks like it has a significant thickening of the base of the leg. By maturity, the hymenophore of fungi of this species acquires a black and red coloration, while in large spore it remains brown.
Most similar view. He is also large and prefers open spaces. Some sources even consider the large-spore champignon to be a species of field mushroom (Psalliota arvensis subsp. Macrospora), so there are no clear differences between them.
1-Champignon curve 2-Field champignon
Yellow-skinned champignon
In addition to harmless, edible species, there is also a poisonous double - this is Yellow-skinned or false champignon. It stands out with a distinct smell of gouache paint. Has a yellowish coloration of the base of the leg.
Also, young specimens may look like toadstools or fly agarics. Champignon can distinguish colored plates and slight reddening of the flesh when cut from the pale toadstool and the smelly fly agaric.
Thus, some doubles of the large-spore champignon can be very dangerous.
Therefore, you should pay attention to a number of their distinctive properties.
Description
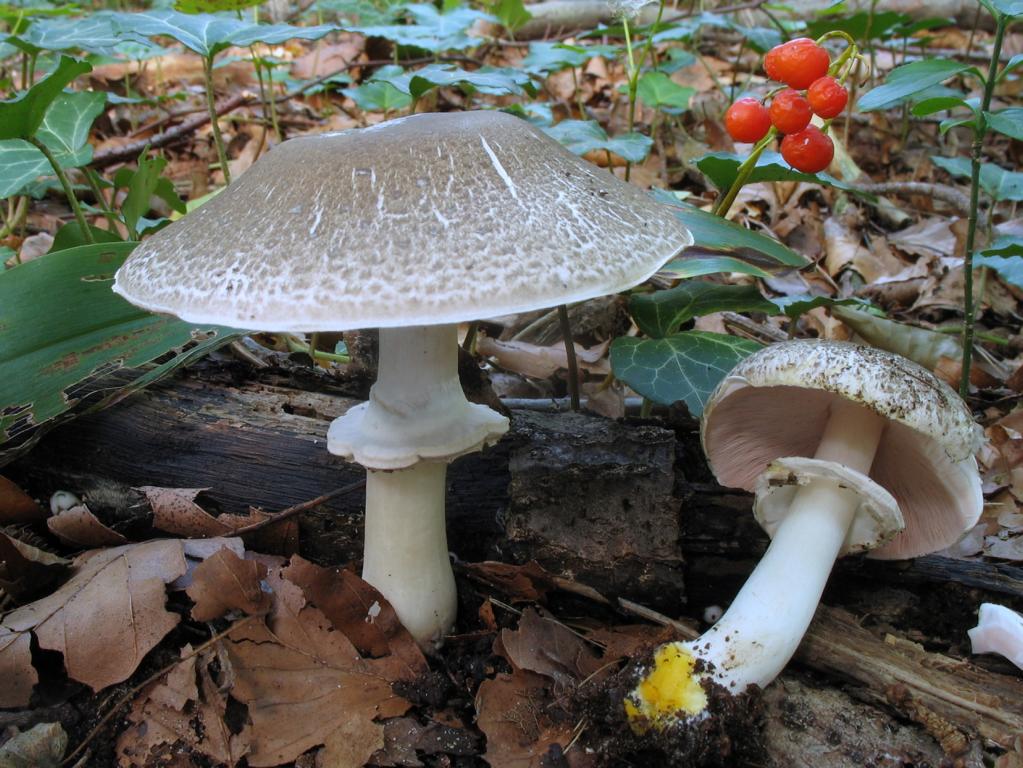
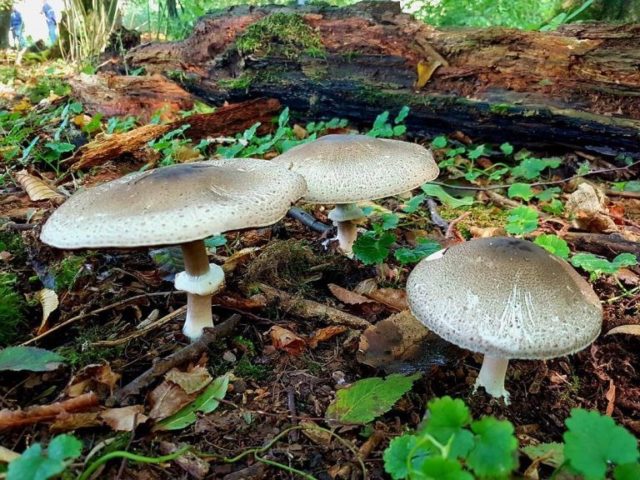
Steam champignon (greenhouse) probably got this name, as it prefers organic-rich soil, which is found in vegetable gardens and, in particular, in greenhouses.
 Hat
Hat
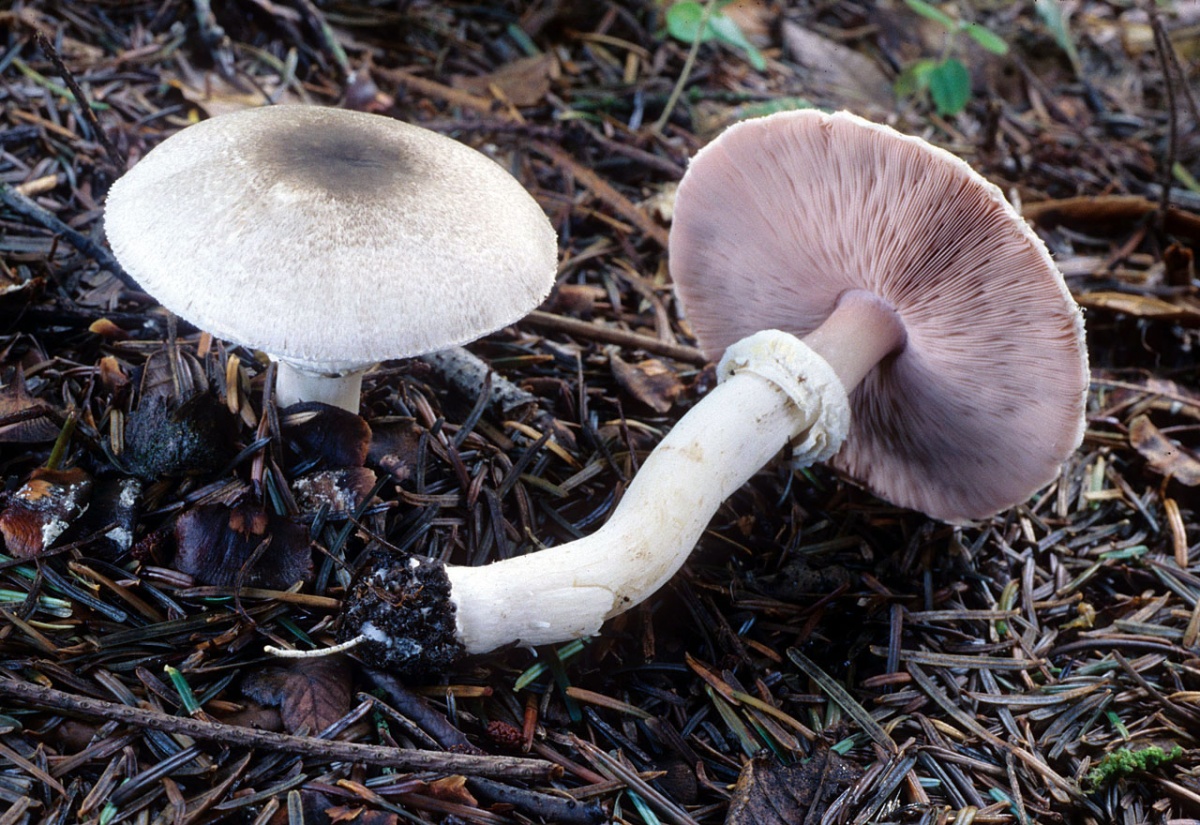
Reaches 8 or 10 cm in diameter. It is painted in brownish-red tones, with rare and large scaly formations on the surface. Its shape in the process of maturation and growth changes from bell-shaped to almost flat. The surface is usually dry, but can become tacky in particularly humid weather.
 Leg
Leg
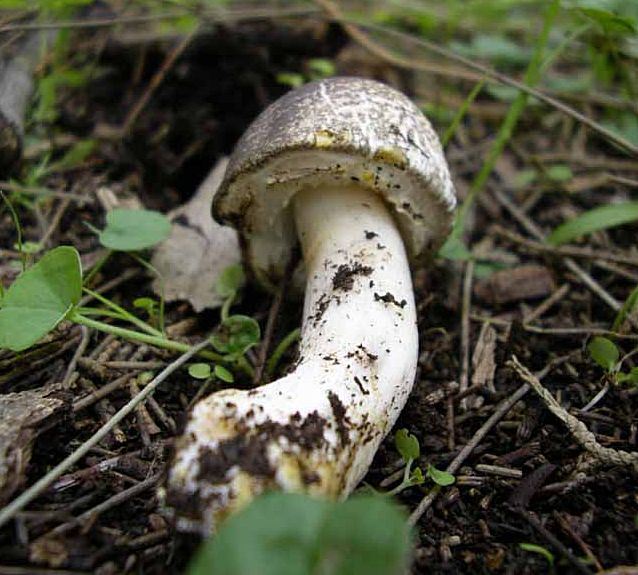
It is characterized by a white color. In young mushrooms, it is dense, and becomes hollow when ripe. Also, in young specimens, it is fibrous, and then it becomes completely smooth. The length of the leg reaches 10 cm. There is a single ring on it, the edges of which sag significantly downward. The leg, as a rule, has a thickening from top to bottom.
 Spore-bearing layer
Spore-bearing layer
Presented by plates. They are narrow and frequent, do not have a rigid fixation to the stem. Their color in youth is reddish, then acquires a chocolate brown tint.
Pulp
 The mushroom has a persistent cyclonic pulp smell at any age. The color turns reddish when cut from white. The consistency is quite firm and firm.
The mushroom has a persistent cyclonic pulp smell at any age. The color turns reddish when cut from white. The consistency is quite firm and firm.
Two-ring champignon
| Group: | Lamellar |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Pink, light brown |
| Colour: | White to light brown |
| Info: | The pulp turns pink at the cut |
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Agaricomycetidae |
| Order: | Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar) |
| Family: | Agaricaceae (Champignon) |
| Genus: | Agaricus (Champignon) |
| View: | Agaricus bitorquis (Two-ring champignon) |
The edible mushroom belongs to the second food category. Another representative of the champignon family.
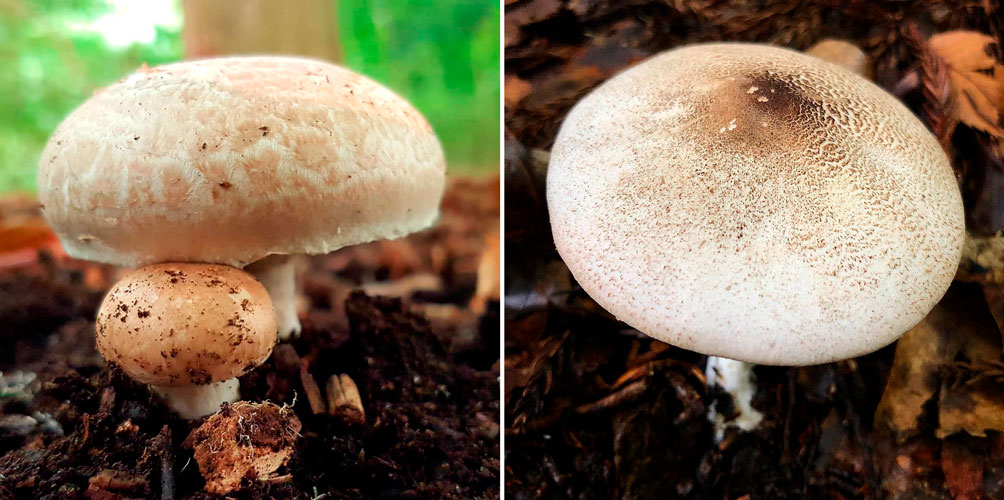
If many other species are quite similar to each other and can be easily confused, then two-ring champignon can be recognized almost instantly, as soon as you pick it up. The word "chunky" suits this champignon perfectly. Fat meat, on an uncharacteristically short leg and already with two rings on it.
This variety has one more advantage. This champignon can be found much more often practically in urban areas than in the forest. But it is worth remembering that champignons are a real sponge for heavy metals and other harmful derivatives of human life. Therefore, you need to be extremely careful when picking mushrooms in urban areas.
Hat
The skin is dry, slightly rough to the touch, with sparse few scales near the center of the cap. The structure is dense, the old mushroom is loose, fleshy. The cap is colored from white to light brown. The edges of the cap are folded inward. In size it reaches from 6 to 12 cm. The skin is separated from the pulp with difficulty.
Spore-bearing layer
The plates are often located, not adherent. By old age, the color changes to a deep brown. The spore powder is brown.
Leg
Reaches 10 cm in height and up to 4 cm in diameter. Dense, powerful, with firm flesh. There are two leathery rings on the leg. The leg is painted white, sometimes with a cream shade, color.
Pulp
With a weak mushroom aroma and a slightly pronounced pleasant sourish taste. At the site of a break or cut, it slowly changes color from white to pink.
Distribution and collection
The two-ring champignon is one of those mushrooms that prefer to settle near human habitation and are quite rare at any distance from it. This mushroom can easily be found along the edges of paths, in parks, gardens, pastures and pastures. It is found, as a rule, in groups of 3-7 specimens.
Similar species
From the dangerous double of all champignons, the two-ring champignon is distinguished by the absence of an egg-shaped depression at the base, a darker hymenophore, a powerful constitution and a double ring on the stem.
Almost all champignons that can be found in our latitudes are in one way or another similar to the two-ring champignon. It is quite easy to distinguish it from its fellows:
- First, the ratio of the length of the stem to the general constitution of the fungus is striking; it is disproportionately short.
- Secondly, no other mushroom species has a double ring anymore.
Use
The double-ring champignon does not require any pretreatment. It can be used both raw in a salad and fried, boiled, stewed. Champignons can also be harvested in salted or pickled form, but they are much tastier when fresh.
Interesting Facts
Two-ring champignon is an extremely strong mushroom. If the fruit body grows under the asphalt or even the pavement, it is capable of lifting and breaking through even such a powerful obstacle.
Due to the short legs, this type of champignon is not cultivated on an industrial scale, since this feature excludes the machine method of picking mushrooms.