Contraindications to the use of champignons

With pancreatitis, gout and gastritis, you should refrain from eating chives. Mushrooms are not recommended for stomach ulcers. If these diseases are not in the stage of exacerbation, then the use of mushrooms in a small amount will not harm the body. It is worth giving preference to dishes that are cooked not in vegetable oil, but in water.
Any mushrooms are an allergen, therefore, they are recommended to be consumed in moderate doses. And allergy sufferers should first find out if they have a mushroom intolerance. Peppers are also contraindicated during lactation.
Their use is not contraindicated for diabetics.
It does not matter what type of diabetes we are talking about. Peaches are also used for cancer
If we talk about age restrictions, then mushrooms are not recommended for young children. It is better to introduce peppers into the diet of children at the age of 4-6 years. This is due to the fact that chitin in mushrooms is poorly absorbed by the child's body.
The benefits and harms of champignons
Since globular fungi are rich in folic acid, which is indispensable in the production of red blood cells, metabolism, the work of the cardiovascular, nervous and digestive systems, they have a positive effect on the human body. In addition, acid plays an important role in a woman's reproductive system, participating in the formation of the placenta and the healthy development of the fetus. The presence of amino acids, vitamins and minerals in the composition of the forest product also benefits pregnant women.
Mushrooms are low in calories, high in energy, contain a large amount of proteins and antioxidants, which makes them dietary and affordable for diabetics. For example, mushrooms contain more B vitamins than fresh vegetables. Due to the large amount of plant fibers and beneficial properties, dishes made from this product not only quickly satisfy hunger, but also help to improve metabolism. That is why nutritionists recommend using champignons for those who want to lose extra pounds, as well as for strengthening muscle mass in the gym. In addition, the dietary product improves memory and concentration.
To prepare primordially Russian food from champignons, you should use sunflower oil, which is used for frying and dressing all tubular mushrooms. The processing of mushrooms includes both preparation and preparation for use.
When collecting champignons, it is important not to confuse them with poisonous counterparts that will harm health. It is not recommended to pick mushrooms in unsafe areas (near industrial plants, highways, landfills), since fruiting bodies absorb harmful substances from the surrounding atmosphere
Health harm can be caused by a canned product made from raw materials that have been improperly stored or in violation of the cooking technology. It is advisable for pregnant women not to eat salted, pickled and dried mushrooms. If there is an allergy or problems with the digestive system, you also need to give up the herbal product.
We also recommend reading:
Why are milk mushrooms useful and dangerous for the human body? Time and rules for collecting mushrooms and other edible mushrooms Technology and secrets of growing champignons at home The most mushroom places in Volgograd and other regions of Russia
Edible champignons in nature
Pay attention to the list of edible specimens that can be found in the forest:
- Augustowski.
- Dark red.
- Coppice.
- Forest.
These types of wild forest mushrooms (they are also known as peppers) cannot be found in the spring: they begin to appear only in the summer - not earlier than July. Moreover, most often these varieties completely disappear in mid-October. It should also be noted that the forest mushroom prefers to grow under fir trees - that is, in coniferous stands. For the rest of the specimens, people hunt mainly in deciduous or mixed plantings.
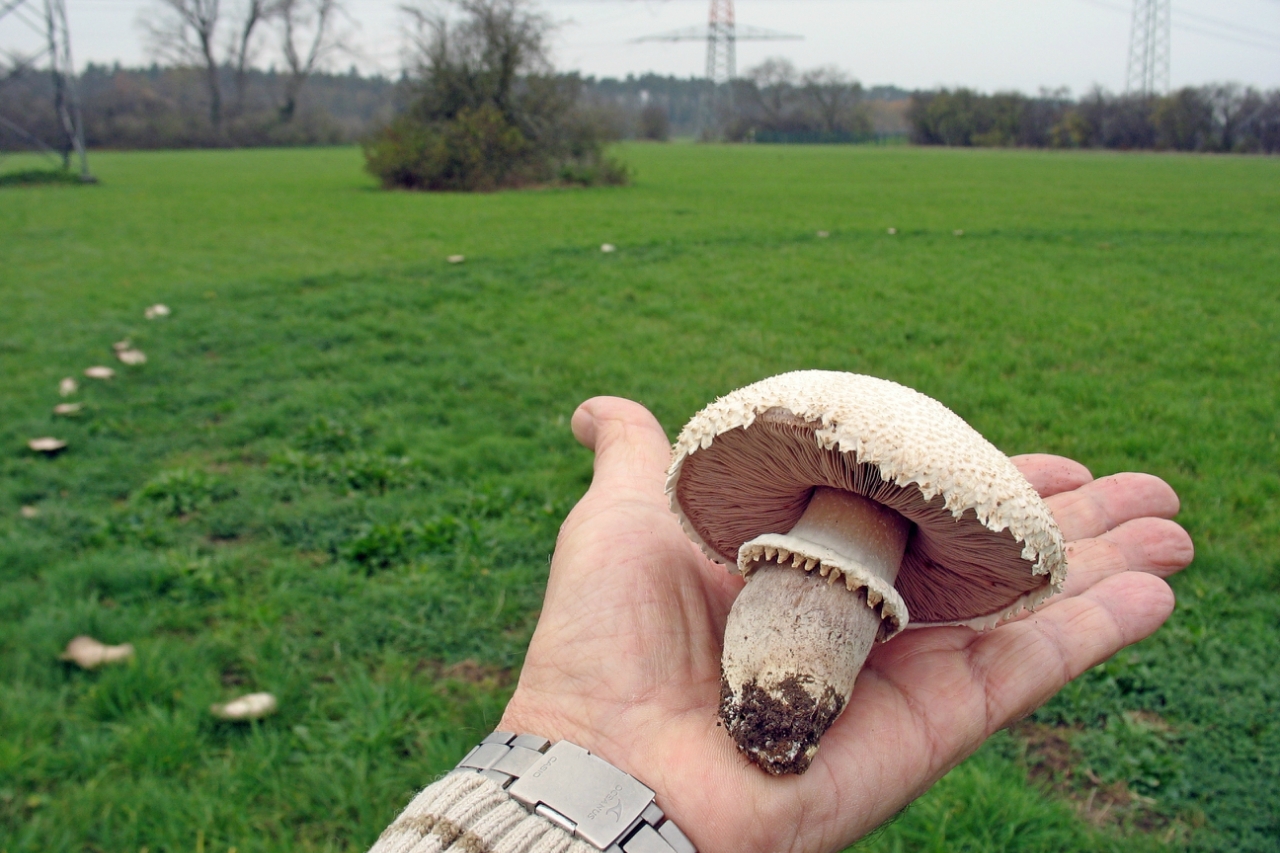
Look at the photo of a striking representative of forest mushrooms: the pictures show a blaghushka, the cap of which can reach 10 cm in diameter.Its characteristic feature is an egg-shaped brown-brown top, which eventually acquires a convex shape. In addition, the surface of the cap of this specimen is covered with peculiar scales. The leg of this variety is approximately 15 cm long and differs by a slight thickening at the base. In addition, you can find a similar delicacy near anthills in coniferous forests. Most often found by mushroom pickers from mid-summer to early October. This champignon's counterpart is the deadly toadstool.
Sheep, or field mushroom, is characterized by such a characteristic as a rather large top - 20 cm in diameter - which turns yellow from a sensitive touch. It can be distinguished from poisonous specimens only due to its natural aniseed smell and a nutty taste. Quite often it is seen in parks and pastures, but a sheep mushroom can also be found in the forest or gardens. This edible specimen is harvested by gourmets from May to about mid-October. You need to be extremely careful, since these field mushrooms are also similar to the aforementioned pale toadstool. You can not confuse them due to their specific color: plates of young specimens suitable for consumption have a white, pale pink, and then a dark chocolate shade, while in a poisonous brother they always remain snow-white.
The so-called caps are the most famous representatives of meadow mushrooms. According to some scientists, this mushroom can be considered unsuitable for use in cooking. However, most experts claim that young species are completely harmless. These meadow mushrooms can be seen in the fields of the countryside, and even in vegetable gardens. They appear from the beginning of June to the end of August, and their distinguishing feature is that they can only be seen growing one by one.
Hunting and fishing in the Tver region
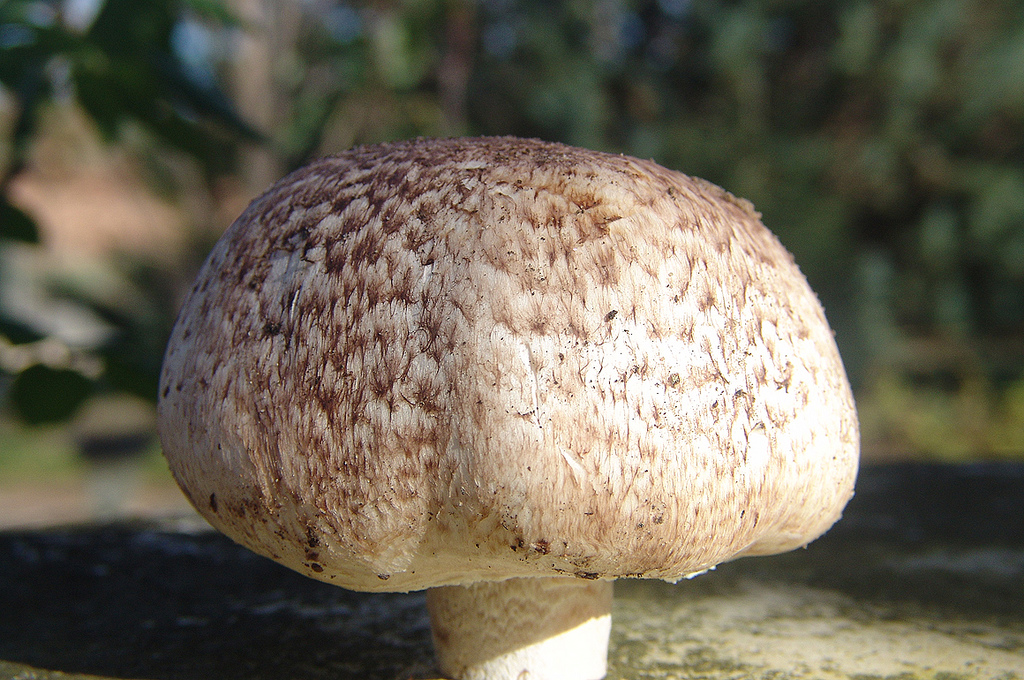
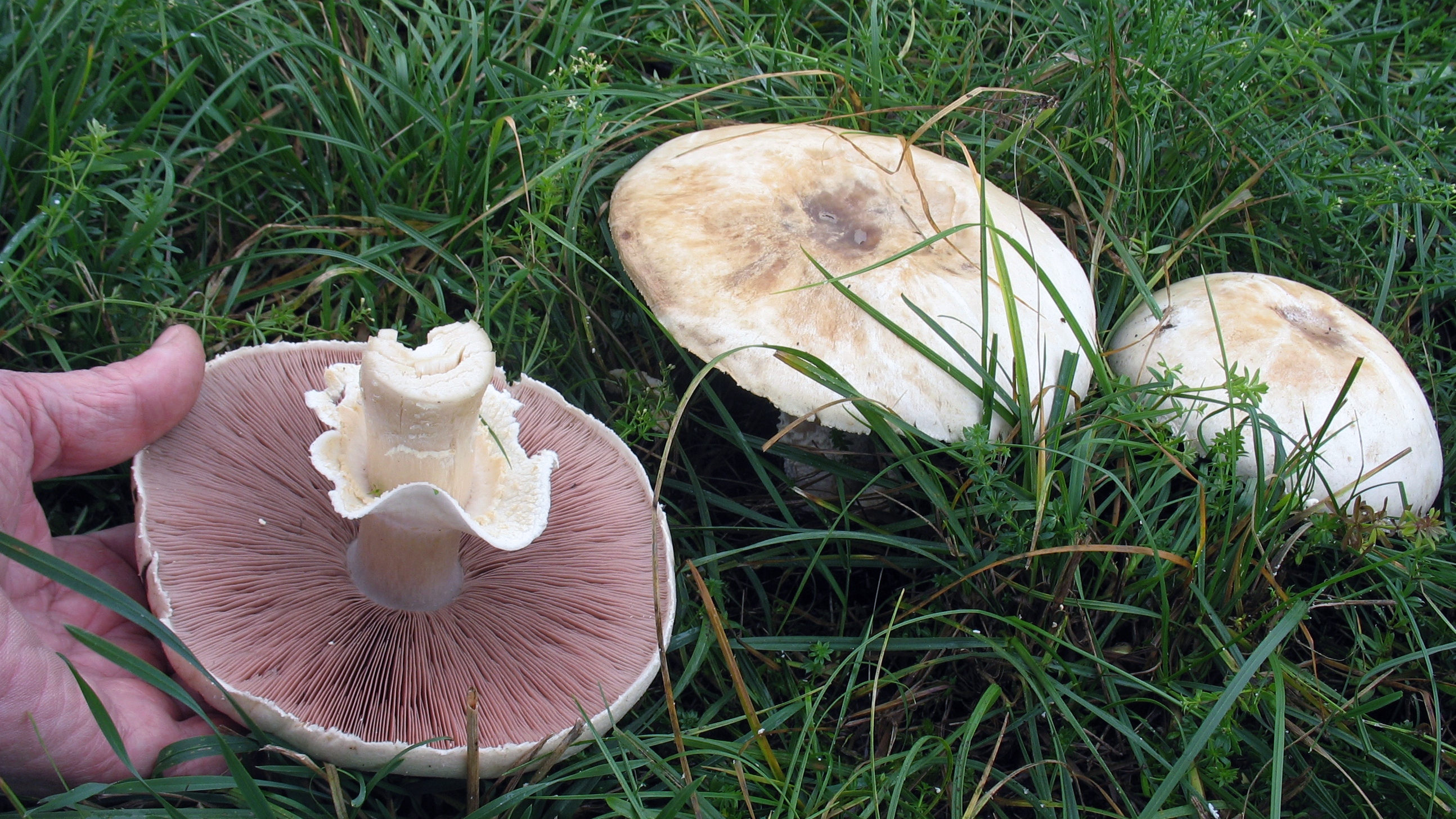
Hat: 5-12 cm in diameter, from hemispherical in young mushrooms to half-open, flattened at the top and with rolled edges, at maturity; develops mainly underground or under asphalt, appearing on the surface only in old age. For this reason, the flat caps of the two-ring mushroom are often covered with a camouflage mound of earth. The color of the caps is white or grayish, the flesh is thick, light, turns pink at the break, with a pleasant "champignon" smell and taste.
Plates: Loose, frequent, narrow, in young mushrooms, light cream, almost white, gradually acquire pink, red-brown, dark brown and almost black color with age. In the early stages of development, the mushroom plates are reliably protected by a thick double ring.
Spore powder: Dark brown.
Leg: Thick, short (3-5 cm in height, 2-4 cm in width), solid or slightly executed, the color of the cap. The remnants of a private bedspread are clearly visible - a double thick gray-white ring, in mature mushrooms it is dark in the upper part from raining spores.
Distribution: Agaricus bitorquis is a widespread mushroom, found in large, but usually loose, scattered groups from mid-May to late September in gardens, vegetable gardens, parks, preferring richly fertilized fertile soil. A common mushroom for cities in central Russia.The two-ring champignon develops mainly under the soil, which makes it inconspicuous, but once you have explored the place of growth, you can return to it several times per season and, picking out the characteristic tubercles, release round, dense, heavy champignons from the soil. Quite often the double-peeled champignon is not satisfied with its usual growing areas and breaks the asphalt, sprouting under the sidewalks and bike paths.
Similar species: There are quite a few similar light champignons. Agaricus bitorquis is easily distinguished from closely related species by its characteristic double ring, short thick stem and flat, stool-like cap.
Edible: Refers to first-class edible multi-purpose mushrooms; It should be noted that mushrooms should not be harvested in cities and on the roadsides even more than, say, mycorrhizal mushrooms.
Author's notes: For me, two-ring champignon is a mushroom from a happy childhood. I don't remember at all how it happened and why they completely trusted me at home in terms of mushrooms, but already from the second grade I did not return from school without prey. The whole September was devoted to mushrooms - leaving school, I purposefully walked around all the courtyards and squares, bringing a whole package of a variety of mushrooms, among which were white and gray dung beetles, and a variety of raincoats, and a few, from which even more valuable mushrooms and, of course , rare city mushrooms. Often my father joined my searches, but as a rule, my parents played only a culinary role in this matter. Again, I don't remember what the full confidence in my mushroom skills was based on, but everything I brought home went into food - I know for sure. I myself would probably not have been able to trust my child so much, but my parents somehow managed, and well - gambling, filled with some difficult to describe meaning, walks through the courtyards became for me one of the brightest impressions of this period of my life. It's a pity that September is such a short month, and then the mushrooms leave for a long time from where they appear in spring or autumn - into oblivion ...
Forest mushroom
Forest mushroom (lat.Agaricus silvaticus)
Forest mushroom (lat. Agaricus silvaticus)
Popularly referred to as a wolf mushroom. Also known as blagushka and cap.
It is less popular with mushroom pickers because of its reddening pulp. It can be eaten in all forms, even raw. It got its name because of its "residence". It has a pleasant smell and excellent taste. It grows mainly in spruce and coniferous forests. Less common in mixed forests. It prefers to grow near anthills and, in frequent cases, at their very top.
The leg is straight or curved. In young mushrooms, it is whole, becoming hollow over time. The thickening in the lower part of the leg becomes thin closer to the cap. Height 5-10 cm. The color of the leg is dirty gray. It has a thin ring at the top. During the ripening process, the ring disappears.
The cap of the young forest mushroom is ovate-bell-shaped, the color varies from light gray to brown-brown in maturity. At this age, the cap takes on a prostrate shape. The size of the cap is 5-10 cm, often up to 15. The cap is covered with large brown scales. The pulp, unlike most champignon mushrooms, is rather thin and light. When cut, it turns red.
Forest mushroom photo
Forest mushroom (lat.Agaricus silvaticus) Forest mushroom (lat.Agaricus silvaticus) Forest mushroom (lat.Agaricus silvaticus)
Varieties of champignons
There are several classifications:
- If we talk about the presence of rings, then the two-ring and single-ring mushrooms are distinguished;
- If we talk about the habitat, then they distinguish the garden, forest and meadow champignon (herbophiles). The latter group includes porcini mushrooms, coppice champignon that grows near beeches or spruces.
Each type of champignon has slight external differences and a special taste.There are also differences in the structure and color of the pulp.
All of the above varieties are edible. But inedible and poisonous mushrooms are found in nature, which the mushroom picker must be able to distinguish from edible ones. There are also double mushrooms or false champignons, which are similar in description to the common champignon. If you look closely, it's not hard to spot the differences.
Description
Forest champignon (Agaricus silvaticus), a mushroom of the champignon family, popularly also called: blagushka, cap. The structure of the fruiting body really resembles a rounded cap set on a long stem.
In more detail, it looks like this:
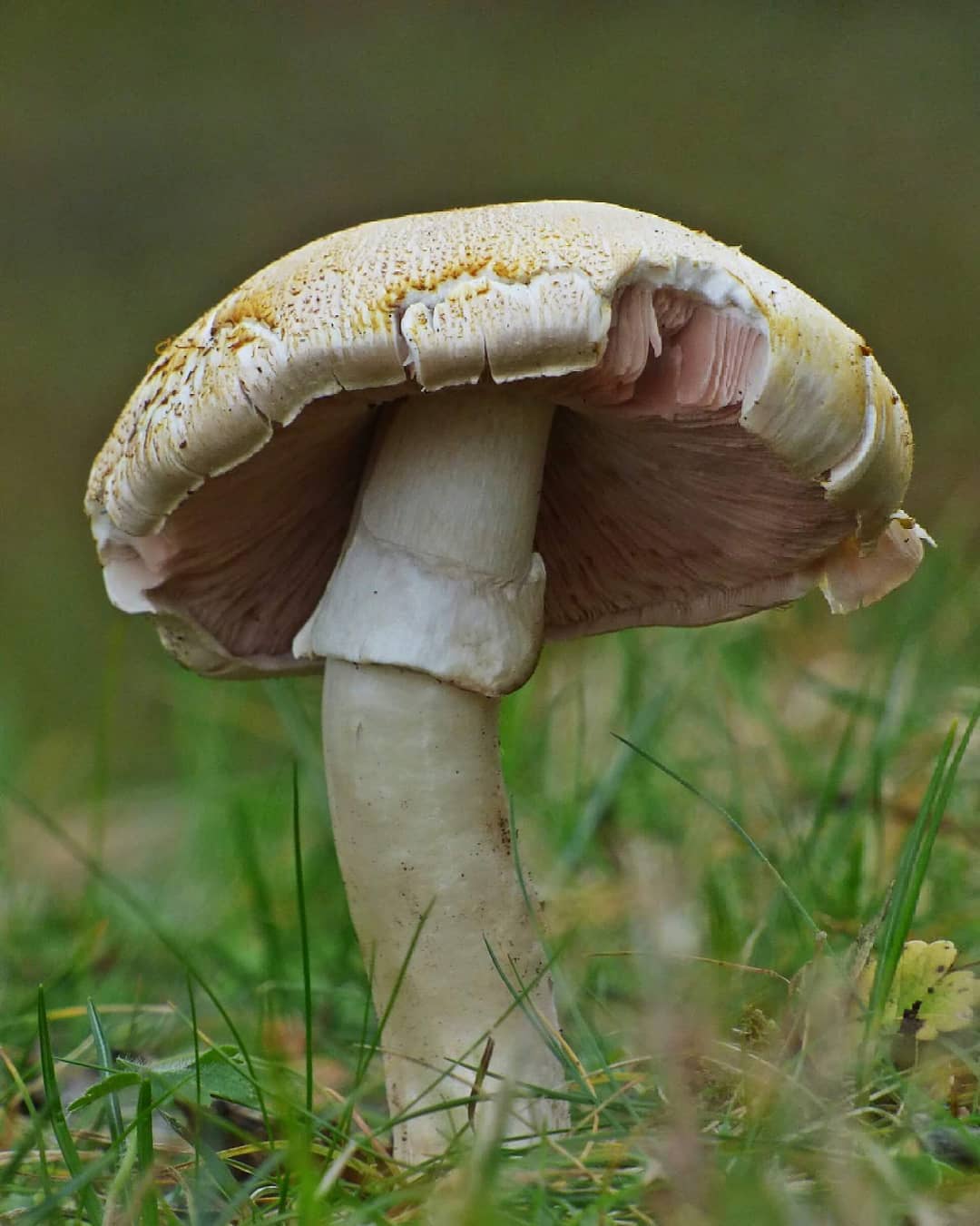
- the cap is initially campanulate-ovoid, subsequently straightens, becomes flat-convex, reaching about 15 cm in diameter, retains the central tubercle, is radially covered with small brownish-brown scales, the cuticle is most often painted pinkish-gray, there are variants of brownish or yellow-brown color ;
- finely fleshy white pulp, quickly reddening at the break, has a pleasant mushroom aroma;
- the plates are often spaced, loose, at first white or light gray, then turn chocolate brown;
- ellipsoidal spores, light brown;
- cylindrical leg 5 to 10 cm long, 0.5-1.5 cm thick, with a slight swelling at the base, becomes hollow with age, off-white in color at first, later - light brown, with a white filmy hanging ring, disappearing into the growth process. Fibrous scales may also be present on the peduncle.
Yellow-skinned champignon (Agaricus xanthodermus)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Red champignon
- Yellow-skinned peasant
Synonyms:
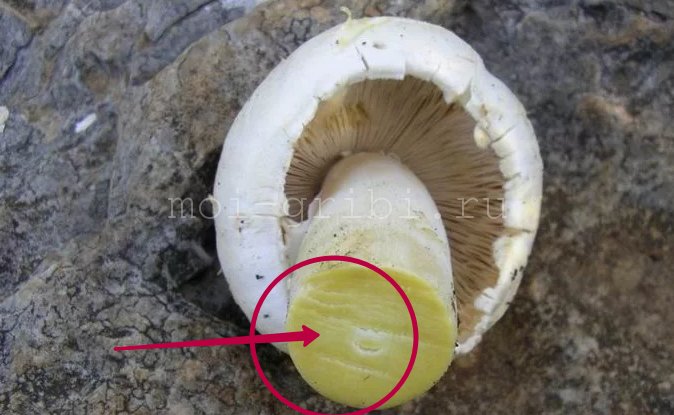
Description: Yellow-skinned champignon is also called yellow-skinned peppermint. The fungus is very poisonous, poisoning with it leads to vomiting and numerous disorders in the body. The danger of the peppers lies in the fact that in their appearance it is very similar to many edible mushrooms, which, for example, are edible champignons.
The yellow-skinned peasant is decorated with a yellow-skinned white cap with a brownish blotch in the center. When pressed, the cap becomes yellowish. Mature mushrooms have a bell-shaped cap, while young mushrooms have a rather large and rounded cap, reaching fifteen centimeters in diameter.
The plates are at first white or pinkish; with age, the fungus turns gray-brown.
The leg is 6-15 cm long and up to 1-2 cm in diameter, white, hollow, tuberous-thickened at the base with a wide white, thickened along the edge of the two-layer ring.
The brownish-colored flesh at the base of the leg turns yellow quite strongly. During heat treatment, the pulp emits an unpleasant, intensifying phenolic odor.
The emerging spore powder is dark brown in color.
Spreading:
Yellow-skinned champignon bears fruit actively in summer and autumn. It appears especially in abundant quantities after rains. It is found not only in mixed forests, but also in parks, in gardens, in all areas overgrown with grass. This type of mushroom is widespread throughout the world.
Habitat: from July to early October in deciduous forests, parks, gardens, meadows.
Grade:
The fungus is poisonous and causes stomach upset.
The chemical composition of this mushroom is currently not established, but, despite this, the mushroom is used in folk medicine.
Video about the yellow-skinned champignon mushroom:
Note: The distinguishing features of the yellow-skinned champignon from the edible mushroom are its yellowing places when touched and an unpleasant phenolic odor emitted.
Professional mushroom pickers easily distinguish yellow-skinned champignon from edible types of mushrooms, knowing its signs. But inexperienced amateurs mushroom pickers need to recognize and distinguish the distinguishing features of this poisonous mushroom. A mushroom mistakenly eaten will cause poisoning, albeit mild, but quite unpleasant for a person.
The name comes from "xanthos" (Greek) - yellow and "derma" (Greek) - leather.
Similar species
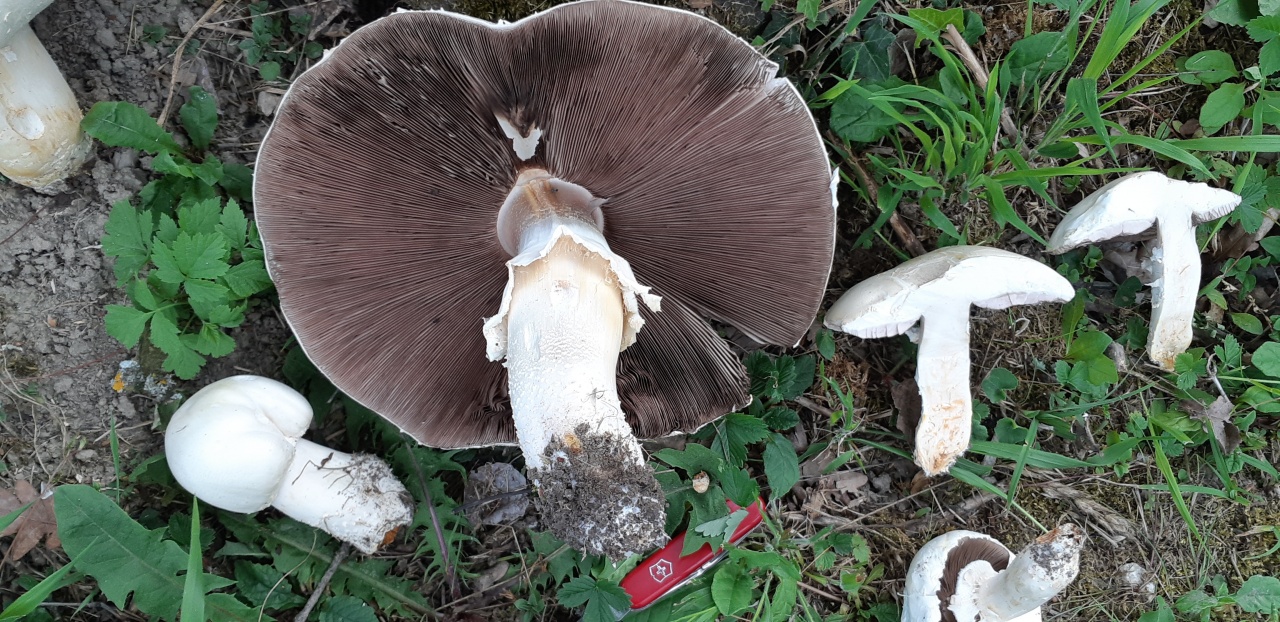
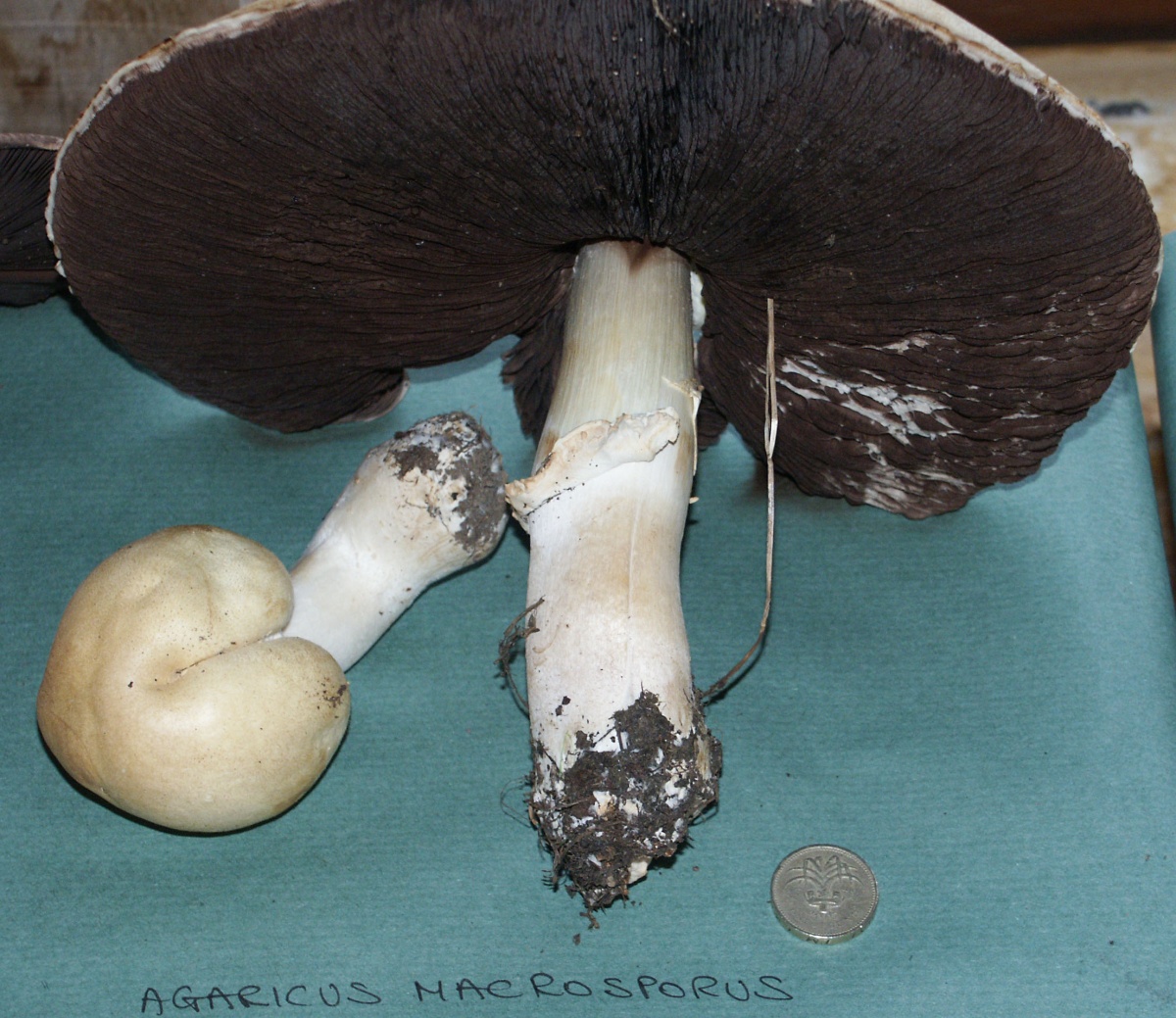
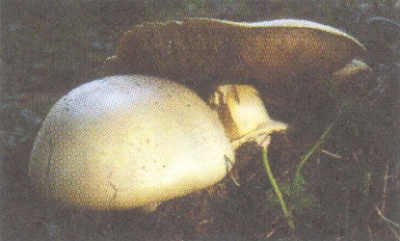
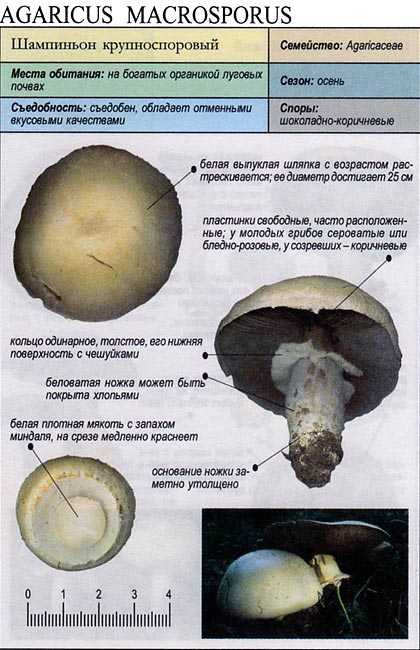
Due to its particularly large size, large-spore champignon is difficult to confuse with other species, but young specimens may look like some edible mushrooms:
The main difference is that this species is predominantly forest, and it grows mainly among the pines. It looks like it has a significant thickening of the base of the leg. By maturity, the hymenophore of fungi of this species acquires a black and red coloration, while in large spore it remains brown.
Most similar view. He is also large and prefers open spaces. Some sources even consider the large-spore champignon to be a species of field mushroom (Psalliota arvensis subsp. Macrospora), so there are no clear differences between them.
1-Champignon curve 2-Field champignon
Yellow-skinned champignon
In addition to harmless, edible species, there is also a poisonous double - this is Yellow-skinned or false champignon. It stands out with a distinct smell of gouache paint. Has a yellowish coloration of the base of the leg.
Also, young specimens may look like toadstools or fly agarics. Champignon can distinguish colored plates and slight reddening of the flesh when cut from the pale toadstool and the smelly fly agaric.
Thus, some doubles of the large-spore champignon can be very dangerous.
Therefore, you should pay attention to a number of their distinctive properties.
Useful properties of bakers
Pastries are rich in protein, so they can replace meat. In addition to protein, they contain amino acids necessary for the normal functioning of the body, minerals and carbohydrates. Peppers are also popular with nutritionists. Their indicators KBZHU (calorie content, the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates) are as follows: calorie content is only 270 kcal per kg of product, and the glycemic index is 15 units. With such a calorie content, bakers have a high energy value. Few foods on the calorie table are so low and do not have such energy value.
Fresh, boiled and baked product has a low calorie content. Dried peppers contain 2-2.5 times more calories.
Also, peppers hold the record for the content of B vitamins. Medicine knows about the presence of antioxidant properties in them and folic acid necessary for women's health. Also, peppers are rich in fiber and are useful for high cholesterol.
At the moment, there are discussions about the benefits of fresh baking. Of course, a fresh product contains much more nutrients than one that has undergone heat treatment. But the organism, during the cultivation of which insecticides were used, will easily be poisoned. It is better to heat the purchased products. Cooked bakers taste much better.
When heat-treated, the mushrooms should be cut rather than cooked whole, this will help determine if the organism is edible. And only then it can be cooked, fried or extinguished. Poached mushrooms are tasty, i.e. fried on minimum heat in butter for 5-7 minutes. Cooking and stewing does not exceed 15 minutes. Peppers are digested for a long time, which is why you should not use them at night.
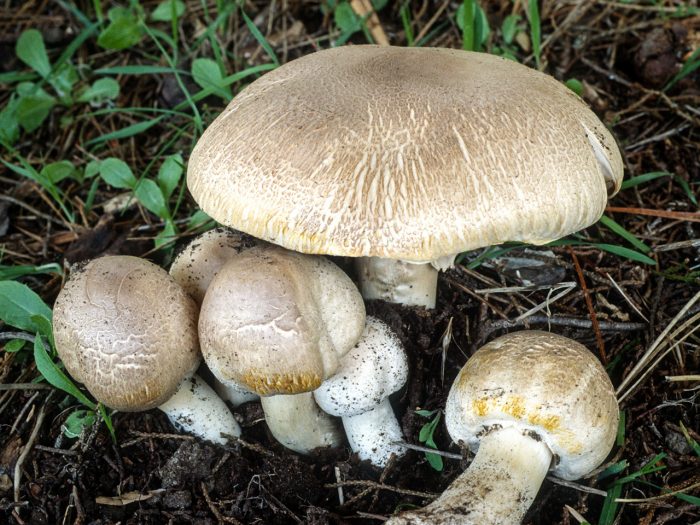
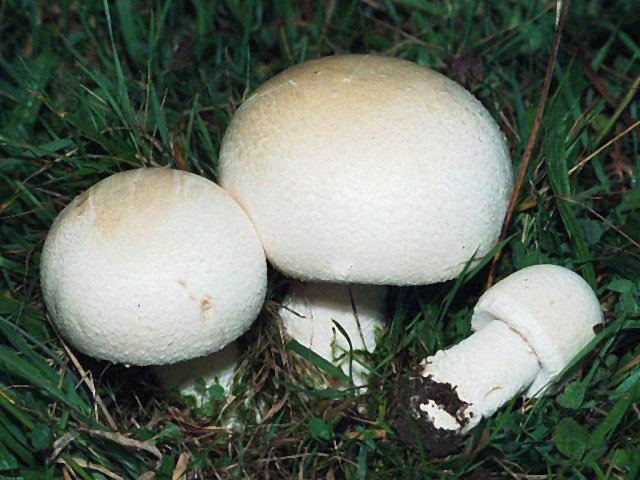
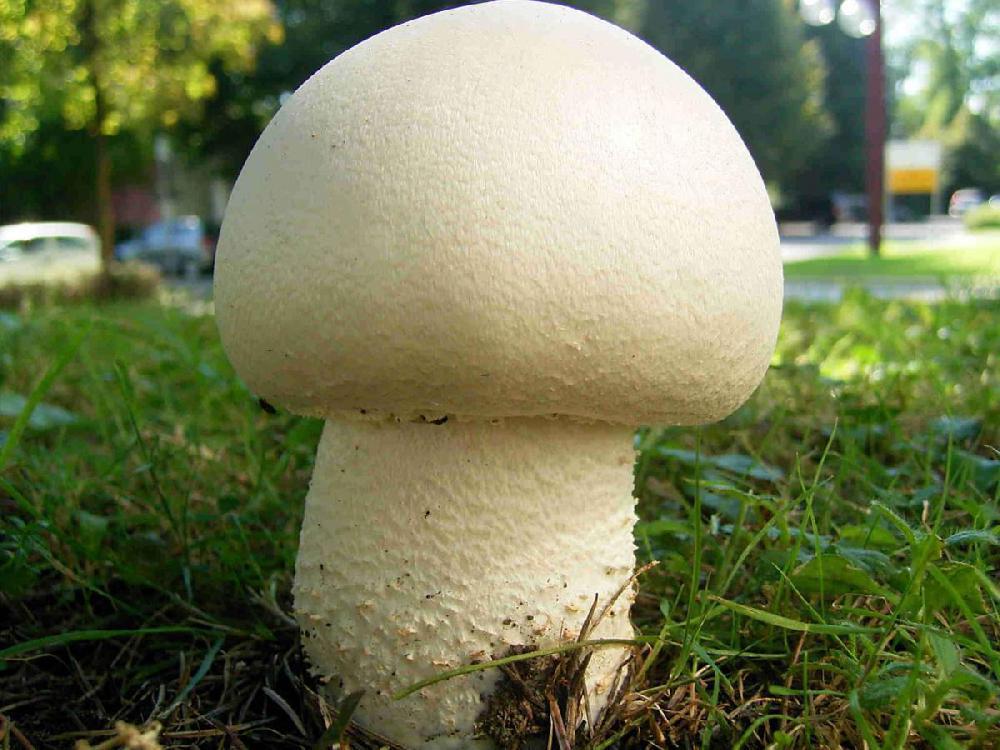
Garden champignon
Garden champignon (lat. Agaricus bisporus)
Common names for this species are cultivated champignon, double-peeled champignon, cultivated champignon.
This type of champignon is quite rare in nature. Grows in large groups in roadside ditches, compost heaps, orchards and fields. However, the garden mushroom is grown industrially in more than 70 countries. It is the most common cultivated mushroom.
Its resemblance to common champignon has given scientists the assumption that this species is a kind of common champignon.But in the process of a detailed study in 1906, scientists discovered significant differences between these species, which allowed them to draw conclusions, compare the differences, which ultimately led to the fact that the double-peeled champignon was taken out as an independent species.
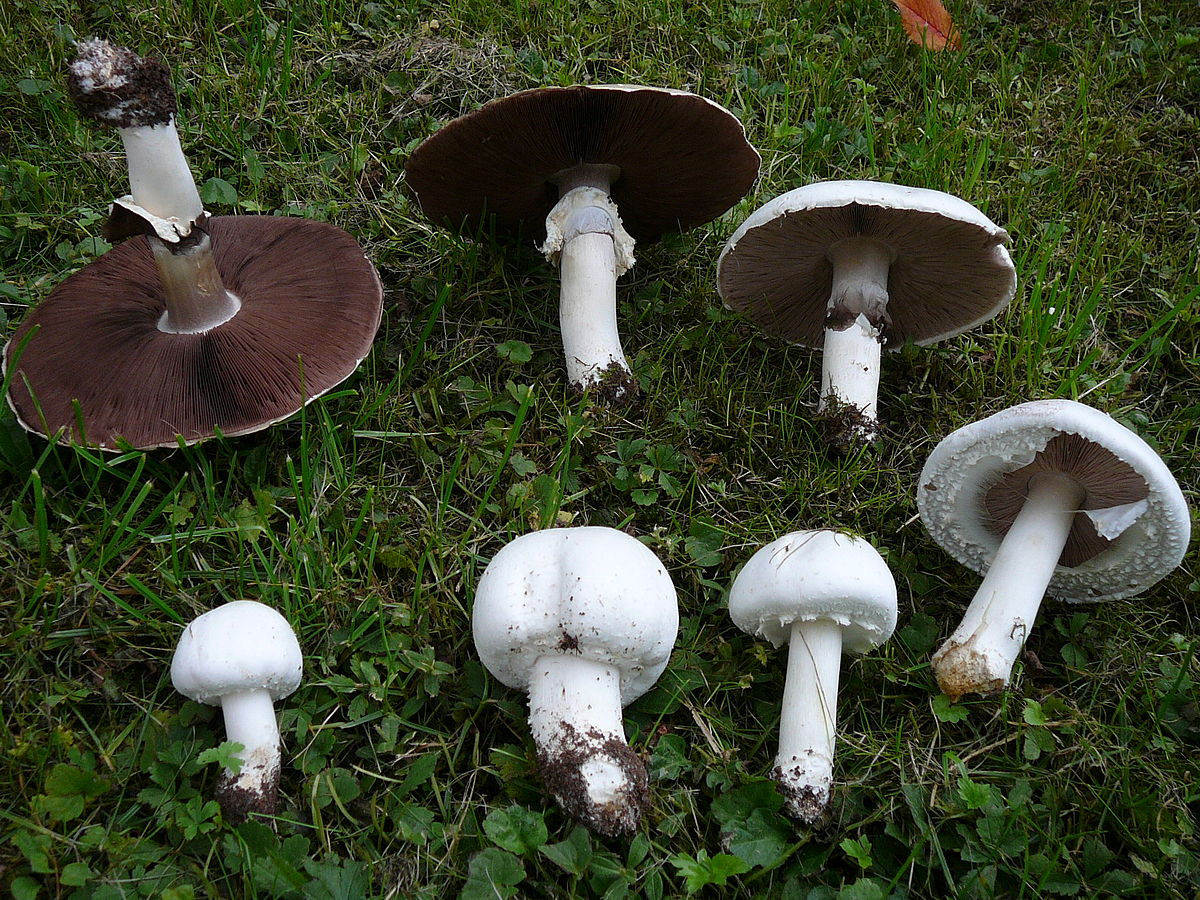
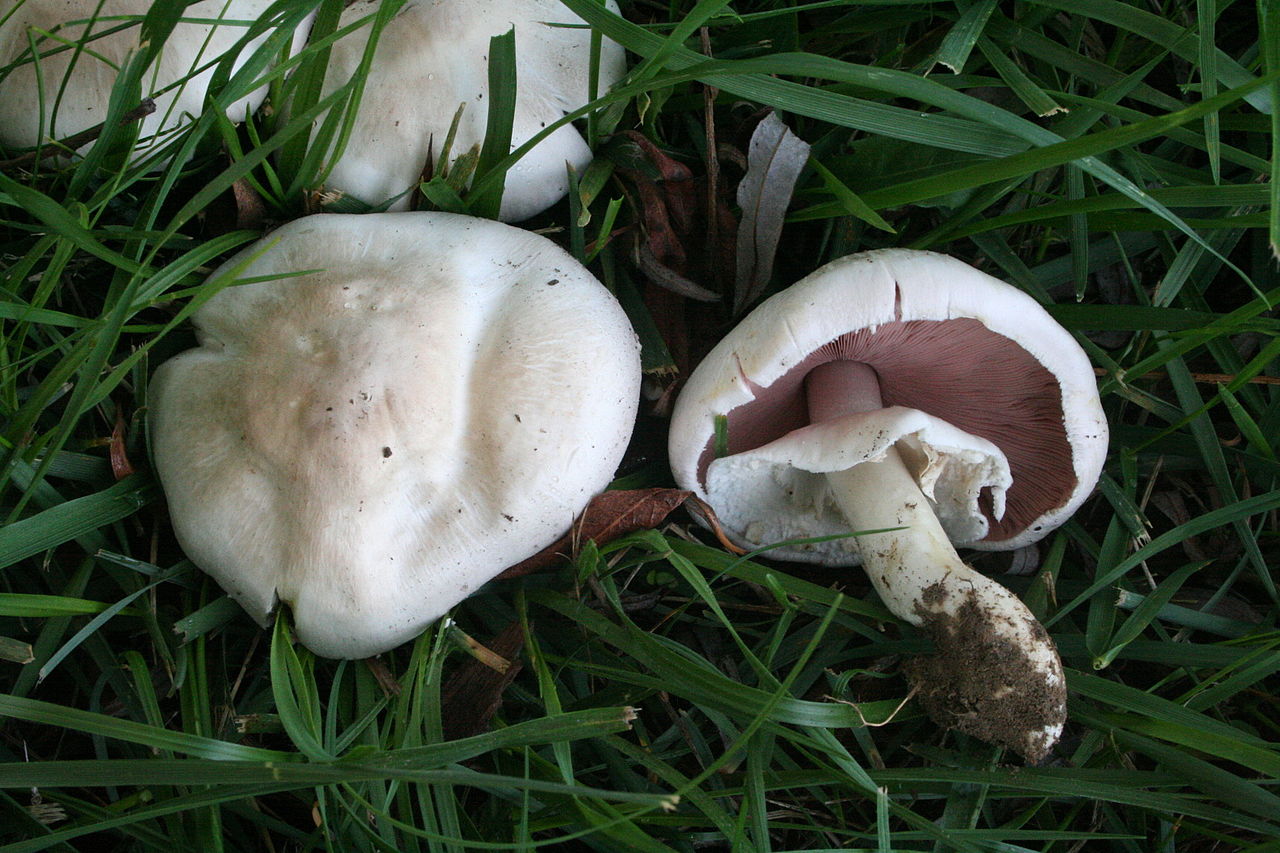
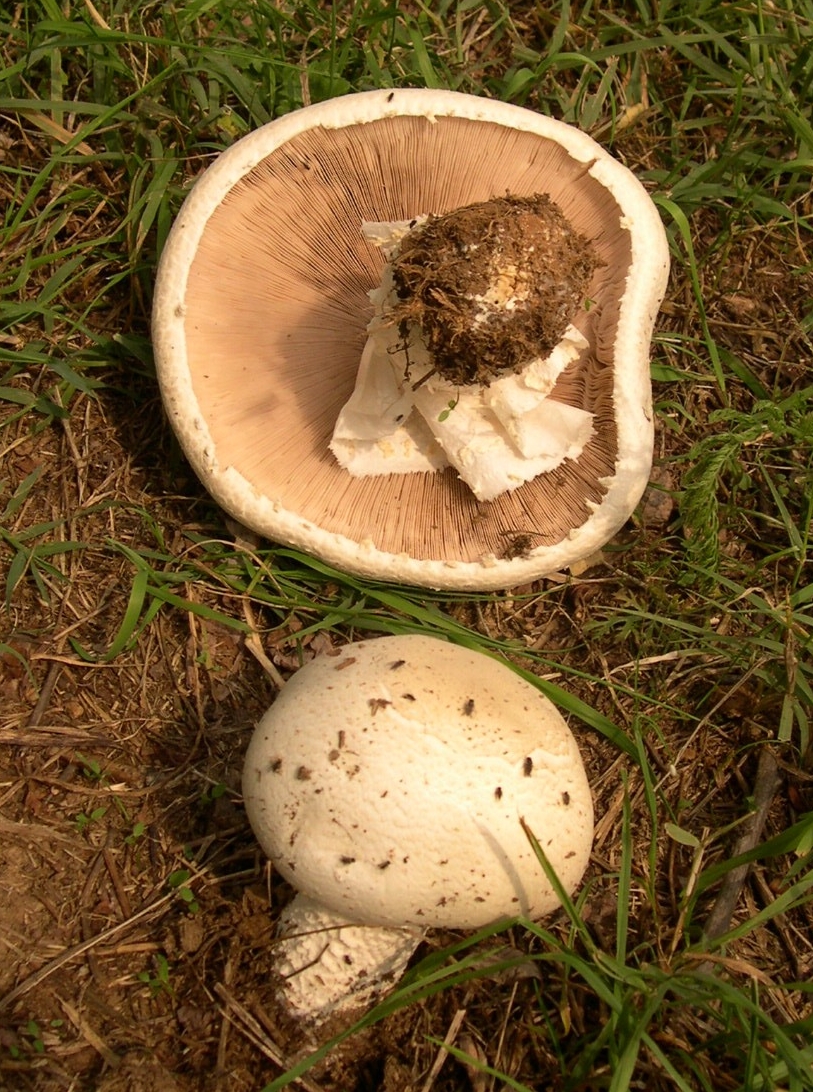
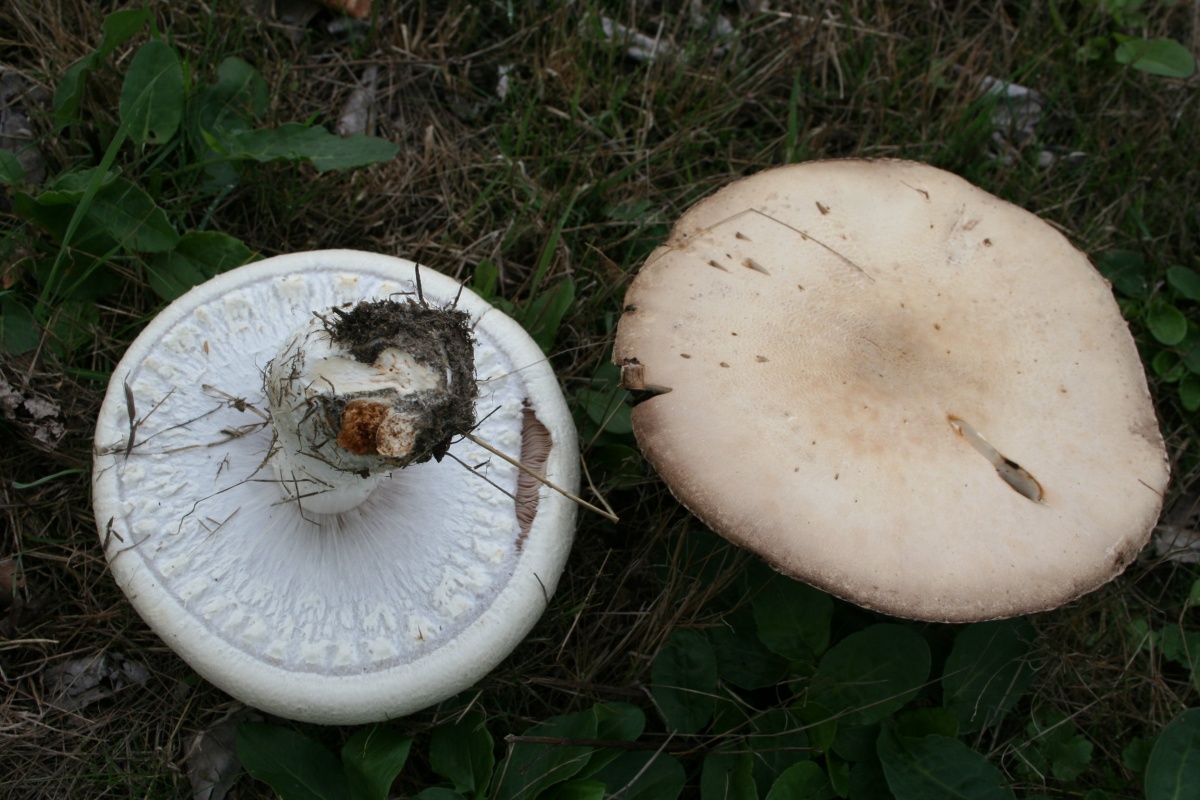
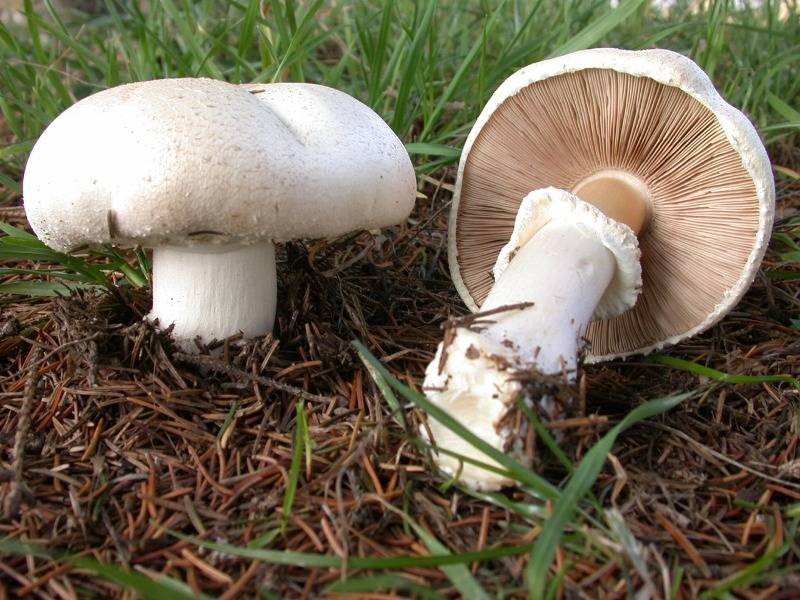
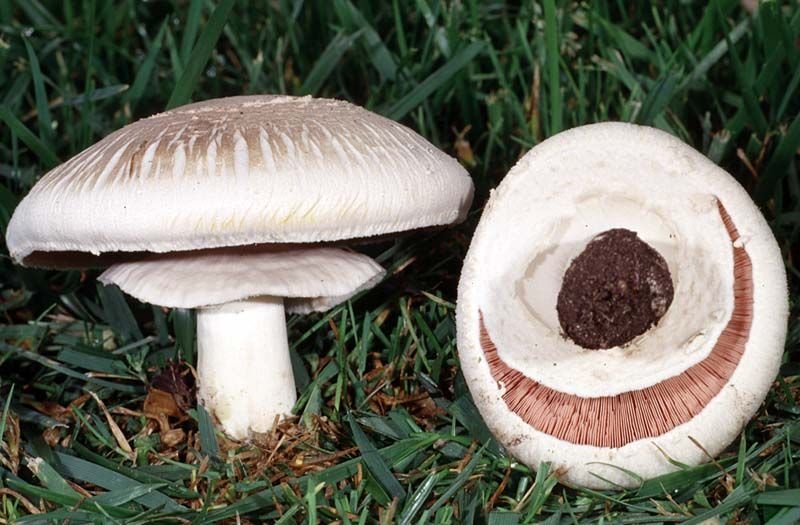
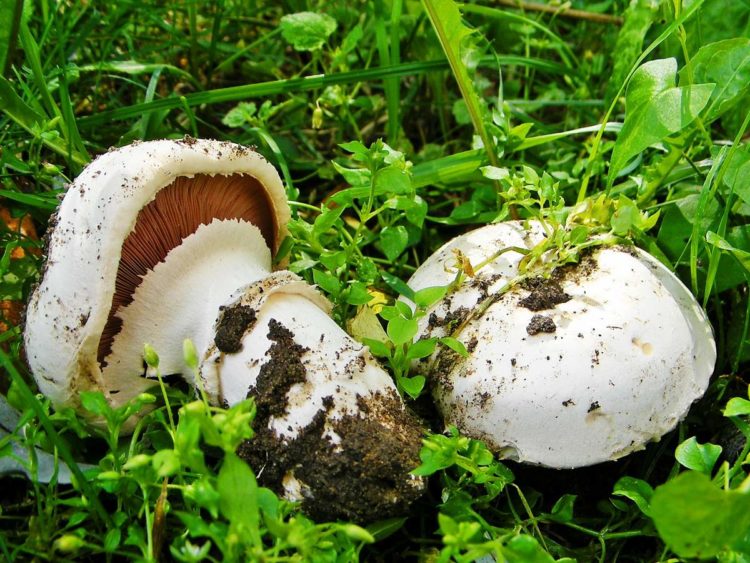
The cap of the garden champignon reaches 4-8 cm in diameter, is rounded, the edges are bent. At the end of the edges there are remnants of a torn cotton bedspread. The surface of the cap is smooth to gloss in the middle, smooth and smooth at the edges. Champignon has three varieties: white, cream and brown, of which white and brown are found in nature, and cream is only cultivated. The flesh of the cap is juicy and dense. When cut, turns pink or red.
The plates of the young champignon are pink. Over time, the color changes to dark brown.
The leg bears a well-defined ring. It reaches a height of 4-10 cm. It has a cylindrical shape. It happens, both filled and almost hollow. Mostly white, sometimes with brown spots. The ring is white. Has a characteristic mushroom smell and sour taste.
Due to its taste, it has gained great popularity. Therefore, it is cultivated in very large quantities in many countries of the world, as well as in individual households.
False mushroom food poisoning
Even proven mushrooms can cause poisoning if they are harvested in the wrong place. These are the sides of large roads, areas near industrial facilities, landfills. Mushrooms, like a sponge, absorb toxic substances, including carcinogens.
Having studied the description of the places where the false forest mushroom grows, look at the photo of this specimen in natural conditions.
It is almost impossible to determine the presence of toxins in it at home.
Another nuance to remember: these mushrooms are dangerous to pickle and roll up for the winter. If they are undercooked, undersalted, or rolled up in a leaky can, botulinus bacteria will begin to develop inside the product. They cause severe food poisoning that can lead to further health problems. In the factory, mushrooms undergo heat treatment, which destroys pathogenic bacteria.
It is not worth mentioning that one toxic champignon can turn all preservation into a poisonous product.
In order to find a dangerous "neighbor" in time, having studied the descriptions given earlier, take another look at the photos of false mushrooms that resemble champignons.
Most of them surpass in severity the usual toxicoinfections. Children and people with weakened health are especially acutely tolerated by the ingress of toxic substances into the blood.
The degree of poisoning with cooked false champignon depends on which mushrooms have skillfully "disguised" themselves as it. If it is yellow-skinned, variegated, Californian species or white fly agaric, symptoms may appear within a couple of hours. Nausea and stomach pains are the reason for immediate medical attention.
It is much more difficult to define pale toadstool poisoning. The malaise does not appear earlier than after 8 hours, and sometimes - in 1-2 days after eating it.
Edibility of large-spore mushrooms
Large-spore champignon is an edible mushroom. These mushrooms have excellent taste.
Necessary measures to protect the number of large-spore mushrooms
The state of the population of these fungi requires control and the search for new locations. Artificial cultivation of champignons in protected areas would be a good option.
Other mushrooms of this genus
The flat mushroom champignon is an inedible member of the family. The diameter of the cap is 5-9 centimeters. At first, its shape is ovoid, but becomes flat with age. The peel of the champignon is grayish with a lot of gray-brown scales. The stem has a tuberous thickening, fibrous with a rather large ring.

Mushroom mushrooms grow in mixed and deciduous forests, sometimes they come across near dwellings. They often grow in witch circles.In some sources, these mushrooms are called inedible, and in others poisonous. After eating them, gastrointestinal upset may occur.
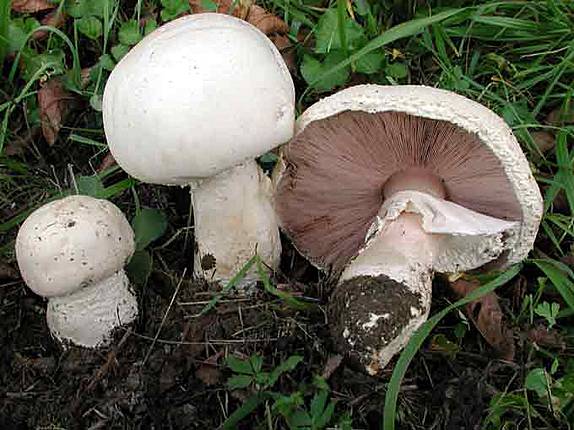
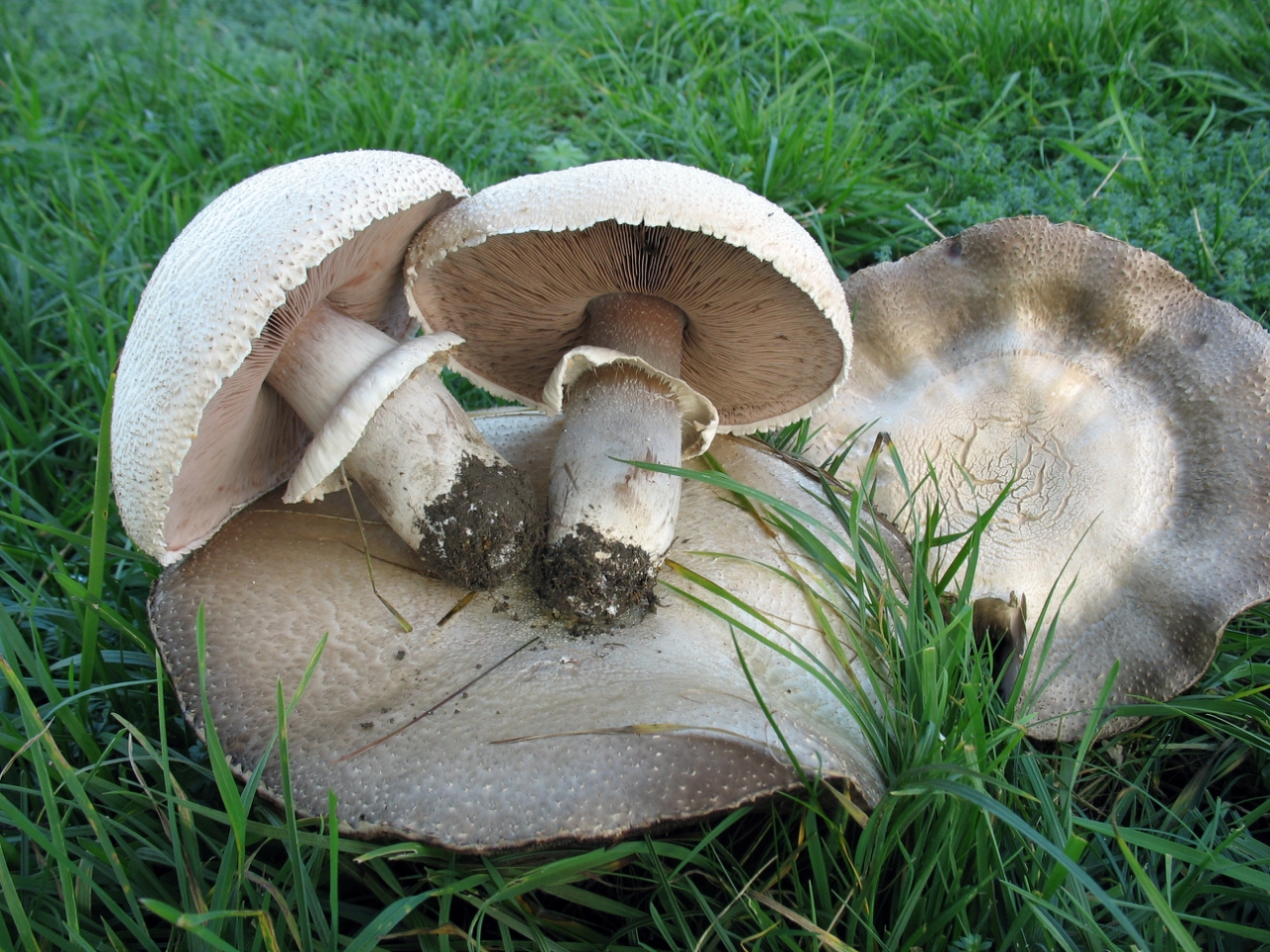
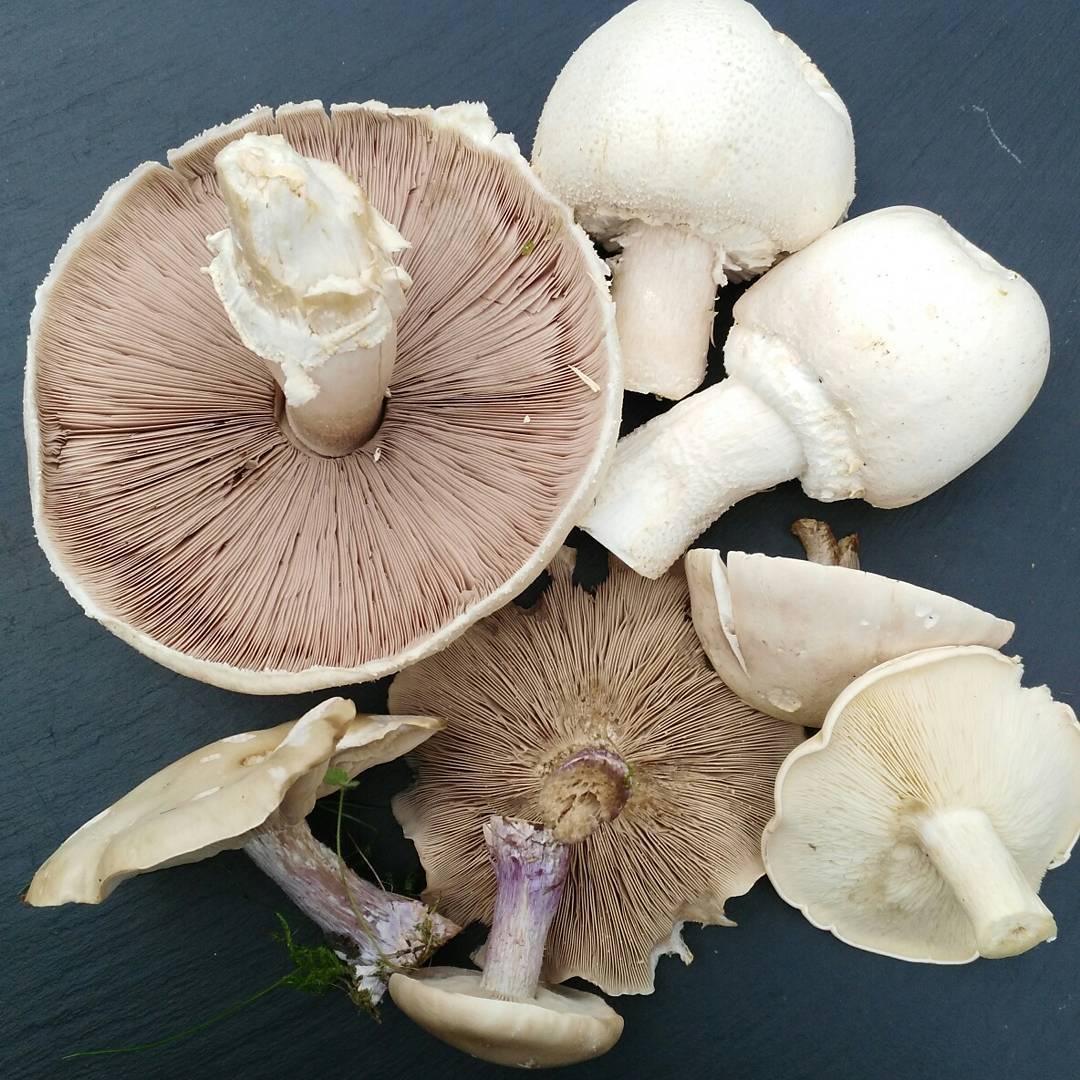
Champignon meadow or common champignon - edible mushroom. The diameter of its spherical cap reaches 15 centimeters, over time it becomes convexly outstretched. In the center, the cap is covered with small brown scales, and along the edge it is white. The leg is straight, cylindrical, narrowed towards the base. It is light in color with a rusty or brown base. There is a thin white ring on the leg, which disappears with age.
Meadow mushrooms bear fruit from May to September. They grow in open spaces, on fertilized soils. They can be found in vegetable gardens, orchards, and meadows. Meadow mushrooms are healthy and tasty mushrooms, according to their taste they belong to the 2nd category.

Champignons - type, description of mushrooms, where they grow in nature
Main types and characteristics
Champignons are the most popular mushrooms in our time. They are very tasty, healthy and even medicinal, as they contain proteins, carbohydrates and mineral salts. In terms of nutritional value and nutritional value, mushrooms are equated to meat.
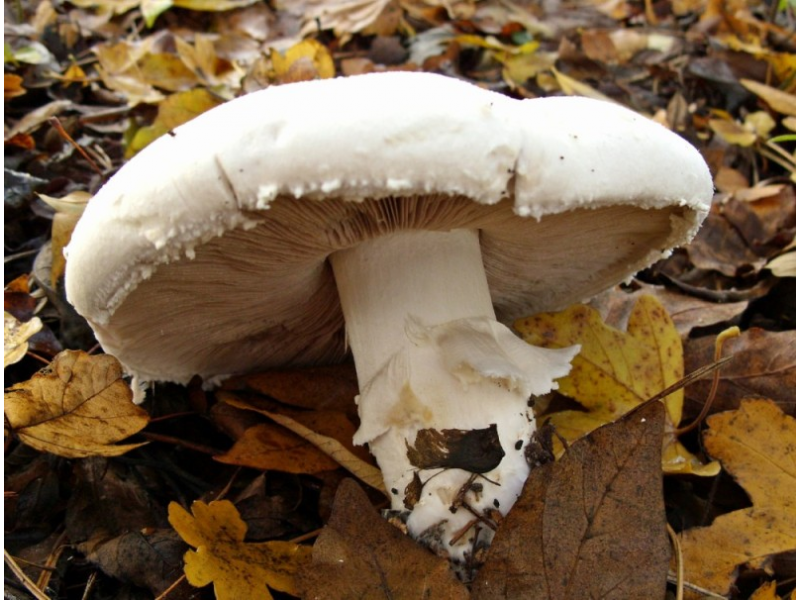
These mushrooms can be easily recognized by their appearance. Usually white and less often brown fleshy caps. The pulp is white, but when interacting with oxygen it changes color to red or yellow. The plates in young specimens are pinkish. Over time, they acquire a brown color. The leg is dense, white, up to 10 cm high.
Here are the most popular of them, which won the love of mushroom pickers and ordinary people:
- Garden (double-sided). It grows on cultivated and fertilized soils - in a greenhouse, in a vegetable garden and pasture. In the wild, it is found in temperate countries of Europe, where the soil is completely free of grass cover. Juicy light flesh, which turns pink when broken. White leg, almost hollow, cylindrical in shape.
- Steppe (Bernard). The main place of its growth is desert or semi-desert. This type of champignon loves saline soils. Grows in groups. Can be confused with common champignon. The color of the cap is varied: from white to brown. Plates are located below the cap. The leg is of the same color as the head.
- Two-ring. The people also have the name sidewalk or city mushroom. This is an unpretentious and sharply different champignon from other mushrooms in its family. A rather large hat sits on a fleshy low leg. Loves a warm climate. Fruiting from late May until November.
- Dark scaly. Occurs in deciduous or mixed forests from July to September. The hat is convex. The plates are wide and sparsely located. Hollow white leg. The pulp of the mushroom is also white when pressed, first turns yellow, then turns brown.
- Small-scaled (Benesha champignon). It grows in both coniferous and deciduous forests. His flesh is white, but when pressed, it quickly turns red. In cooking, they are often consumed raw. This species can be called stocky, since a fleshy cap sits on a low, but very dense leg. The plates are located close to each other, pinkish hue.
- Steam. Found throughout Europe in mixed forests. It can also grow in meadows and pastures. Does not like direct sunlight. It is usually harvested in the autumn. The hat has a rounded shape that is covered with scales. There are many thin plates under it. The stem itself is of medium length, but goes deep into the soil and has a thickening at the base. The pulp is white and fleshy, with an interesting chicory scent.
- Augustowski. A rare type of champignon found in Europe. They grow in groups from August to October in the park area, near anthills. The cap, like that of other representatives of champignons, changes shape over time, and is covered with orange-brown scales. The pulp has a pleasant almond scent. The mushroom is quite tall.
- Large spore. It grows in Eurasia.Loves meadow soils rich in organic matter. This species is quite large. The cap is smooth and convex, on which large scales appear over time, and the edges become velvety. Such a cap can only be held by a dense high leg, which thickens at the base. A ripe large-spore mushroom has a peculiarity - a smell that flows from a pleasant almond to a pungent smell of ammonia.
What do false champignons look like?
Mushroom pickers can also face more serious dangers, because young mushrooms are very similar to pale toadstool and light amanita, which are very poisonous. These twins are light in color and outwardly differ little from edible mushrooms. But in real representatives, the plates darken with age, but in the fly agaric and pale toadstool they always remain white. In addition, if you press the flesh of these mushrooms, it will not change its color, and their legs are always in root "pots" - volvas. You need to be very careful to see them, because they are almost invisible. Poisonous twins are found, as a rule, in coniferous and mixed forests, therefore they are most often confused with coppice mushroom.
If, when collecting mushrooms, you are not sure of their edibility, then it is better not to take risks and not take such specimens. The ability to recognize a false champignon among real ones requires a lot of attention and experience, so you should think about whether you need to risk your health when you can buy completely normal mushrooms in the store without worrying about your safety.

Common champignon has many types, and most of them are eaten. It is very difficult to remember the features of each, therefore, lovers of "quiet hunting" are often guided by common signs. This can provoke poisoning: among the Agaricaceae (Champignon) family there are species that are harmful to human health.
Industrial cultivation allows you to enjoy the taste of the product without harm to health, but the number of poisoning with false mushrooms, which are "disguised" as edible specimens, is not decreasing. People are attracted by the "quiet hunt" and the opportunity to save money on the purchase of mushrooms. In addition, each individual species has its own flavor: it cannot be found in a standard product from store shelves.
Precautionary measures
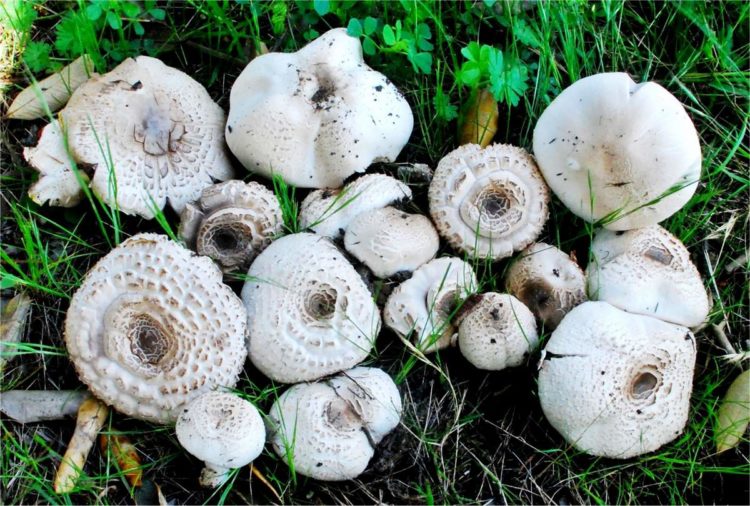

As a rule, champignon is easily recognizable among other varieties, because its dangerous counterparts are very rare, practically not found in our latitudes. But, nevertheless, you need to know absolutely everything about them in order to avoid trouble.
A dangerous double is a false champignon, it looks very much like an edible mushroom, but you can notice a sharp yellowing of the flesh at the cut site. Another feature of the false mushroom is that it is found only in the forest, in open meadows it is impossible to find it.
We must not forget about the basic safety rules that apply to absolutely all mushroom pickers. Firstly, you cannot take those mushrooms in your basket that you are not absolutely sure of, and secondly, you should never go hunting for mushrooms in polluted areas, near cemeteries, industrial enterprises, and highways.
What false champignons look like: photo and description of the appearance of mushrooms
Most often, such representatives of the Agaric family are taken for edible specimens:
- Agaricus xanthodermus.
- Agaricus meleagris.
- Agaricus californicus.
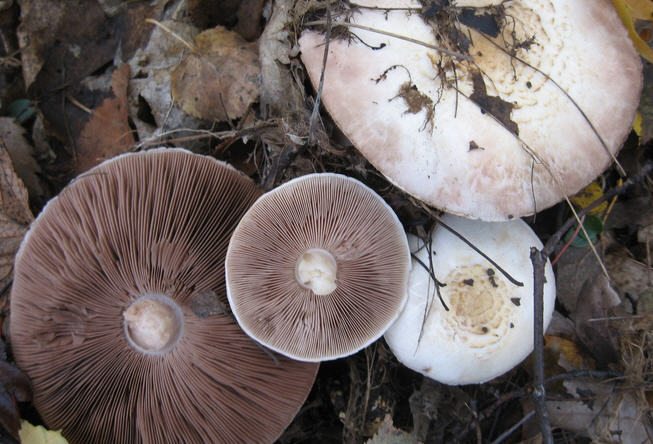
Typical examples of false champignons are shown in the photo.
A number of features will help to distinguish such specimens from edible ones. On the cap, the poisonous twin has a speck of brown color, which is located in the center. If you press on it, light yellow spots will appear. But this method is not guaranteed, so it is better to use it in tandem with other traits.
When broken, the pulp of false forest and field mushrooms begins to turn yellow and smells unpleasant with carbolic acid, and during cooking, the water and the mushrooms themselves turn bright yellow for a short time, but this color quickly disappears.Long-term heat treatment will not be able to rid the product of toxins.
Take a look at the photo and study the description of the appearance of false forest mushrooms.
The color of the cap and its shape can change under the influence of the environment, therefore, special attention is paid to the pulp, its smell, shade and changes during cooking. Another mushroom that disguises itself as an edible is a pale toadstool.
Outwardly, it resembles a champignon, while it does not have a smell by which it could be recognized. There are volves (root sacs) at the base of the toadstool, but people don't always notice them. If you have the slightest doubt about the suitability of the mushroom, you should break the pulp and see if it turns yellow, and then check the color change of the water during cooking. This is one of the most accurate and proven ways to distinguish real edible champignons from false ones.
Another mushroom that disguises itself as an edible is a pale toadstool. Outwardly, it resembles a champignon, while it does not have a smell by which it could be recognized. There are volves (root sacs) at the base of the toadstool, but people don't always notice them. If you have the slightest doubt about the suitability of the mushroom, you should break the pulp and see if it turns yellow, and then check the color change of the water during cooking. This is one of the most accurate and proven ways to distinguish real edible mushrooms from false ones.
You can only confuse the "young" pale toadstool: over time, bulges will appear on its hat, it will become smooth, and the fringe will become saggy. Toadstool appears from the first half of June, its growth peak falls in August. The height of the toadstool can reach 20-25 cm, and the diameter of the cap does not exceed 15 cm.
Inexperienced mushroom pickers can mistake one of the light amanitas for good mushrooms. In this case, the unpleasant smell that the pulp has will save from poisoning.
If you don't know what poisonous false mushrooms look like, take a look at the photo: these are common mushrooms that are often mistaken for edible ones.