Mushroom growing
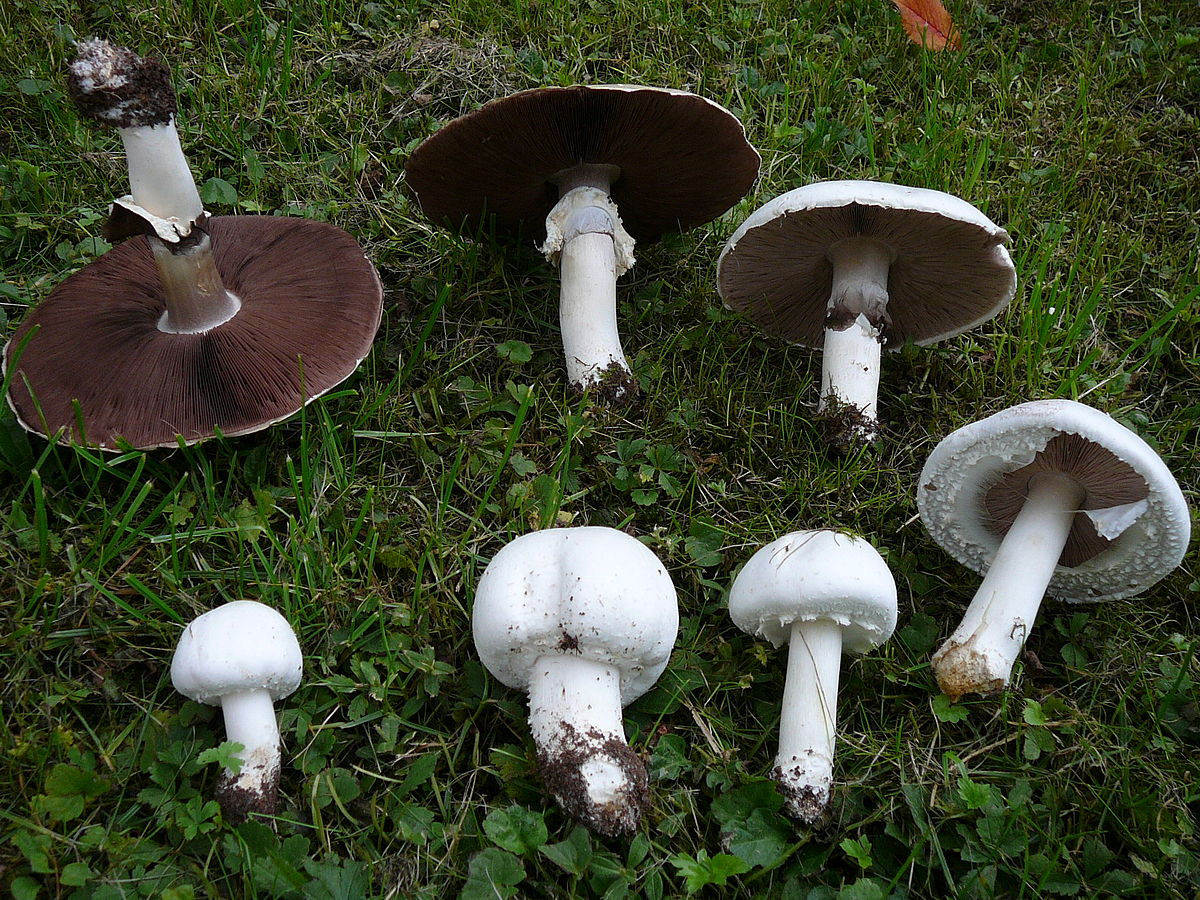
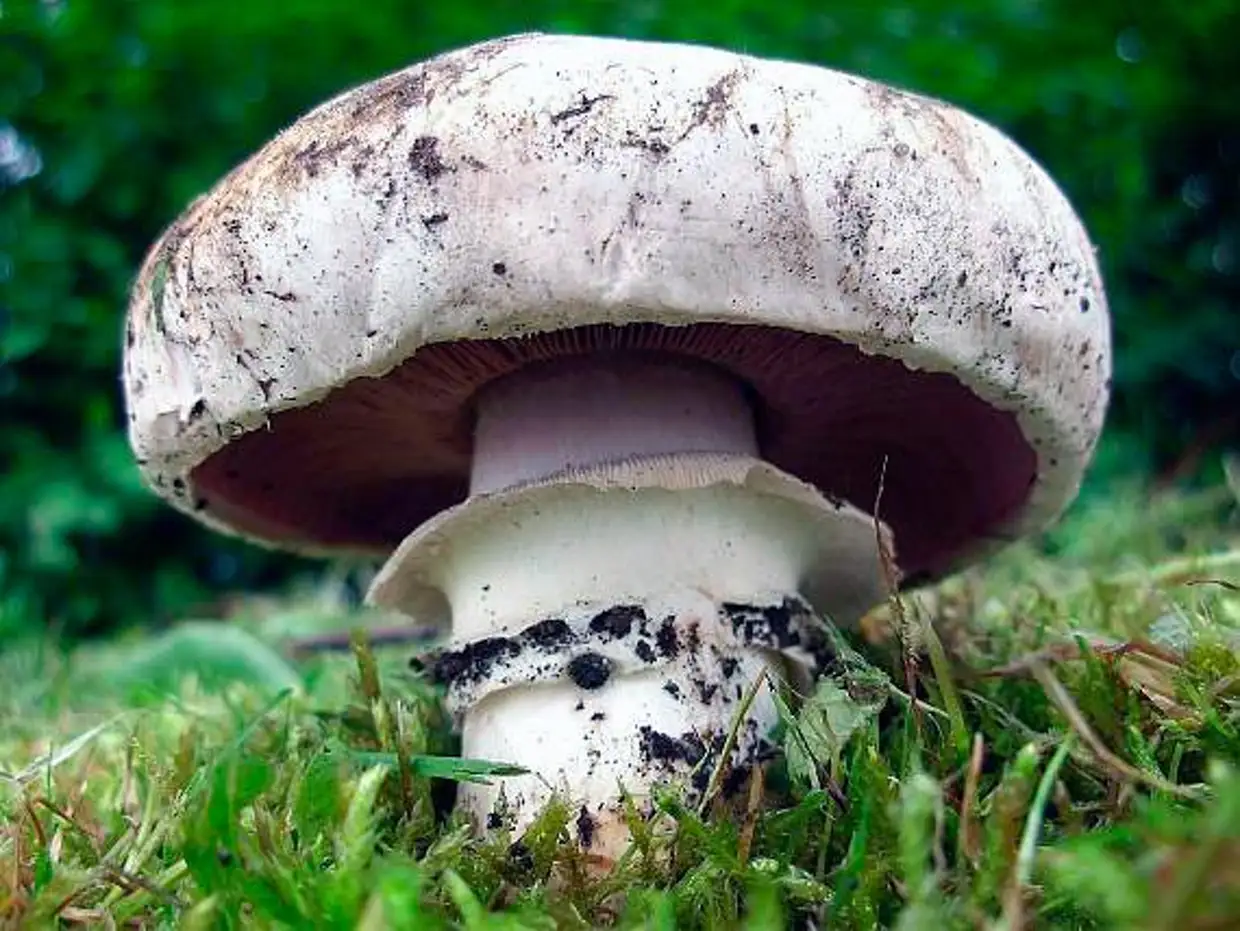
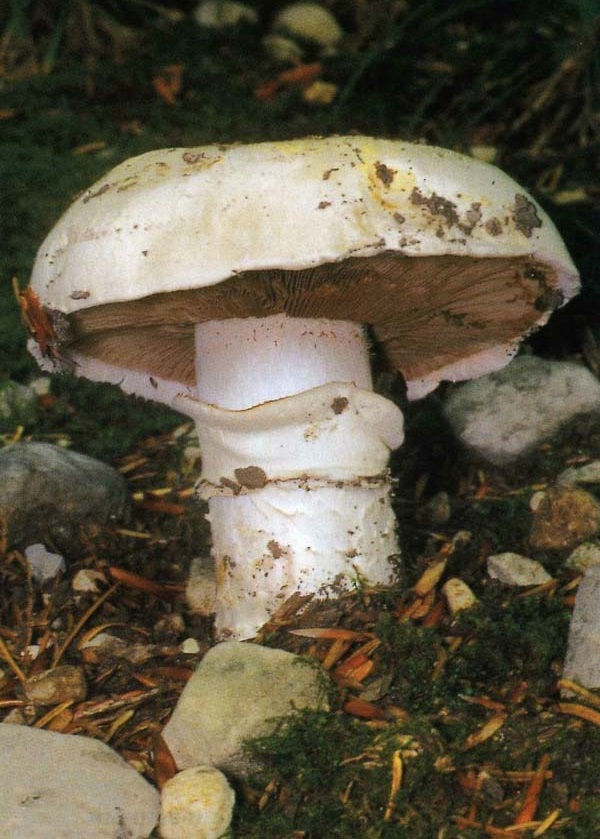
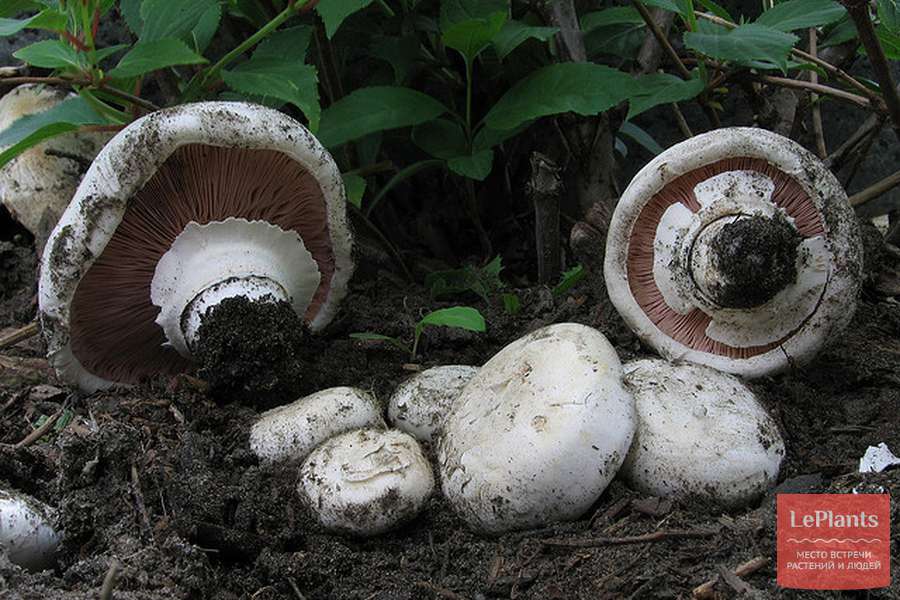
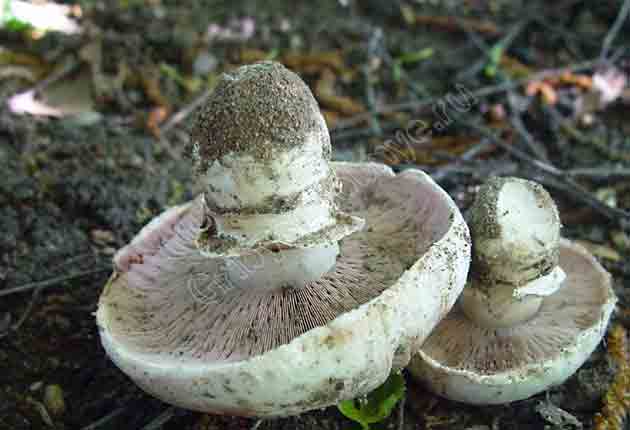
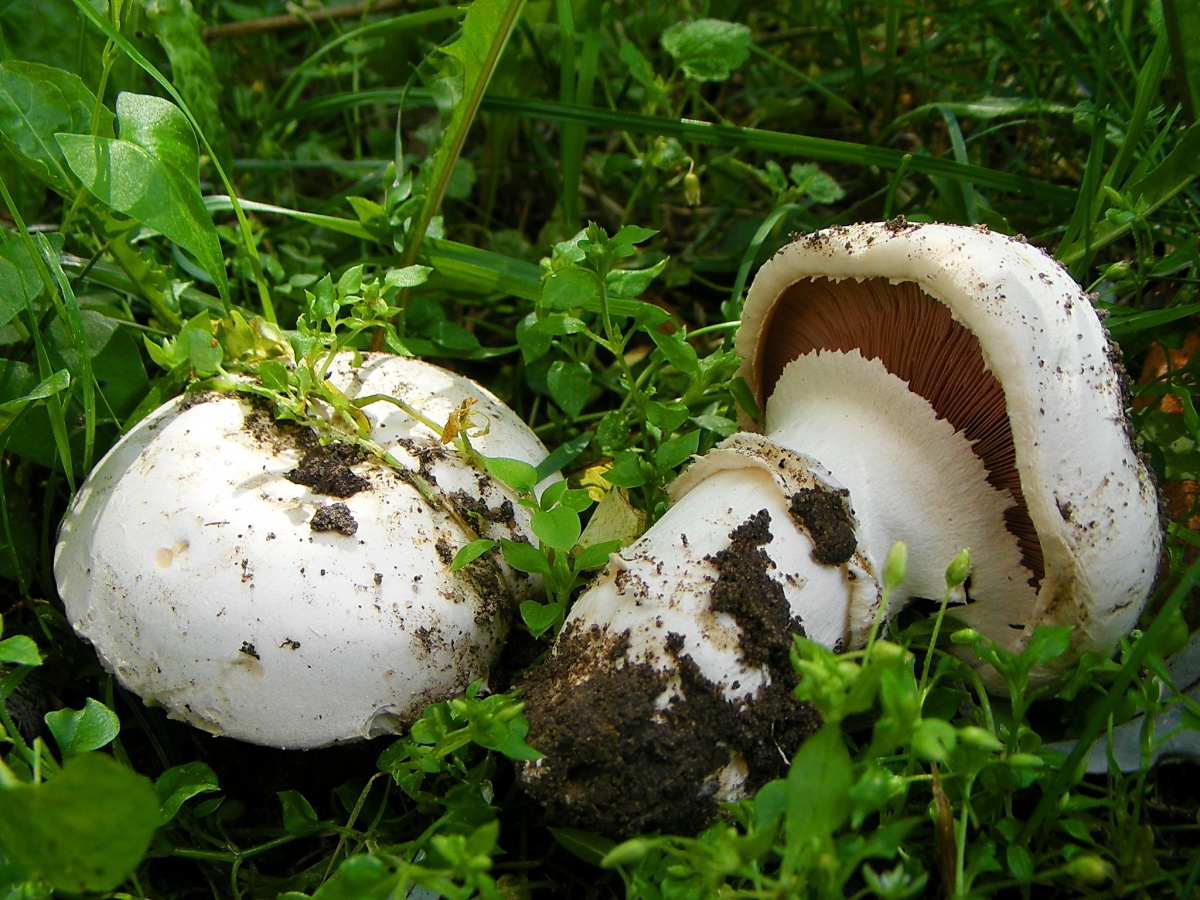
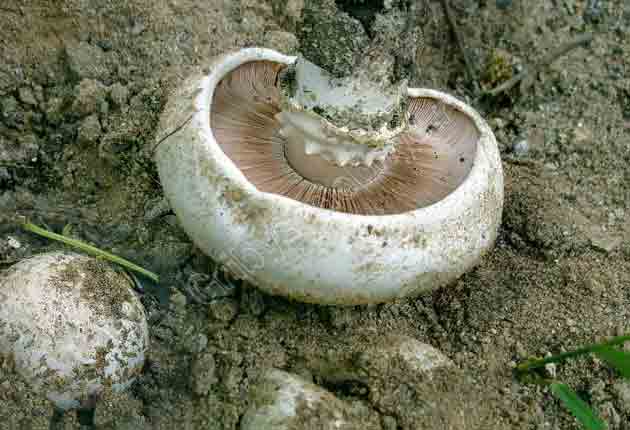
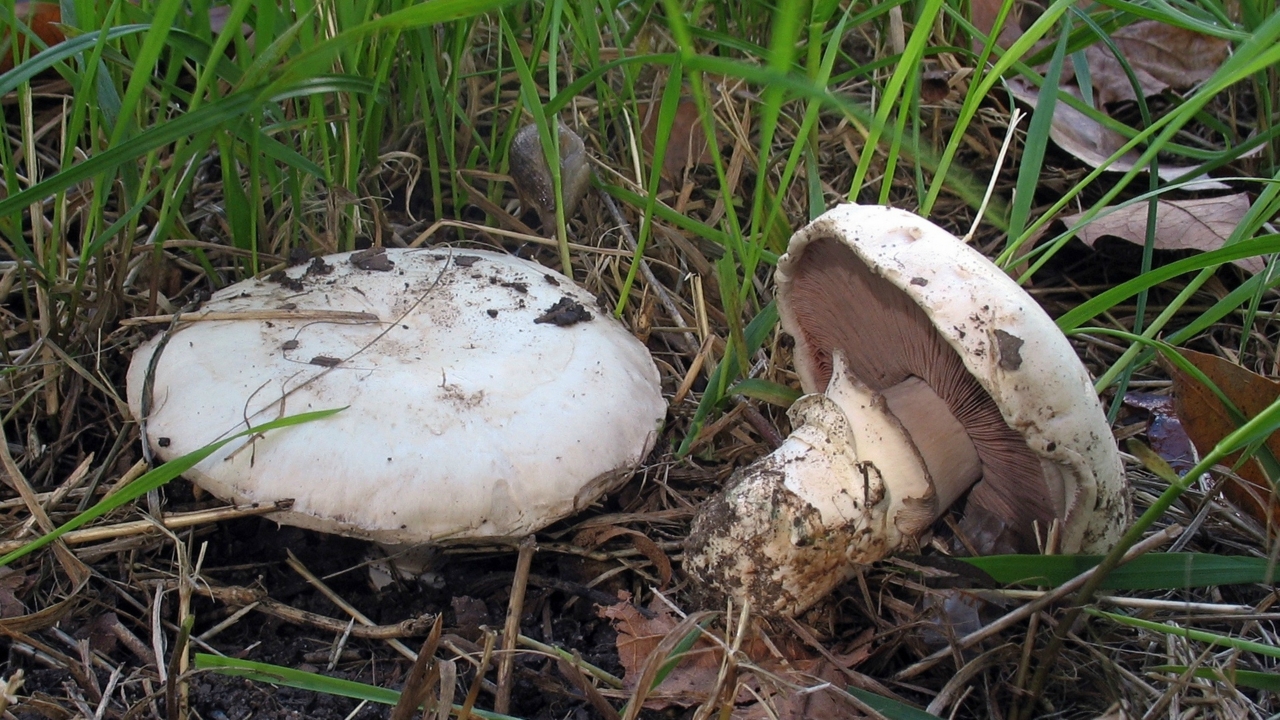
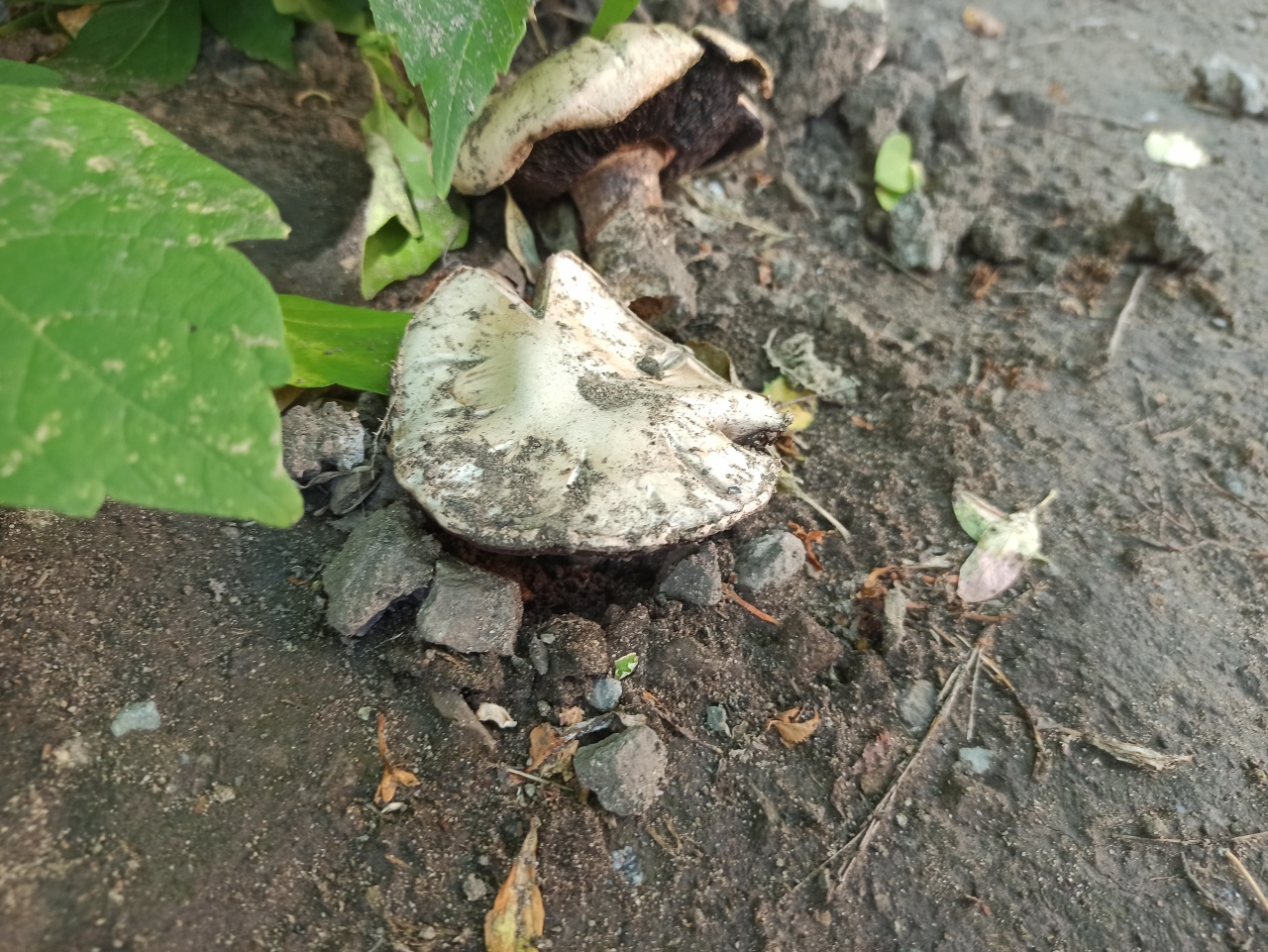
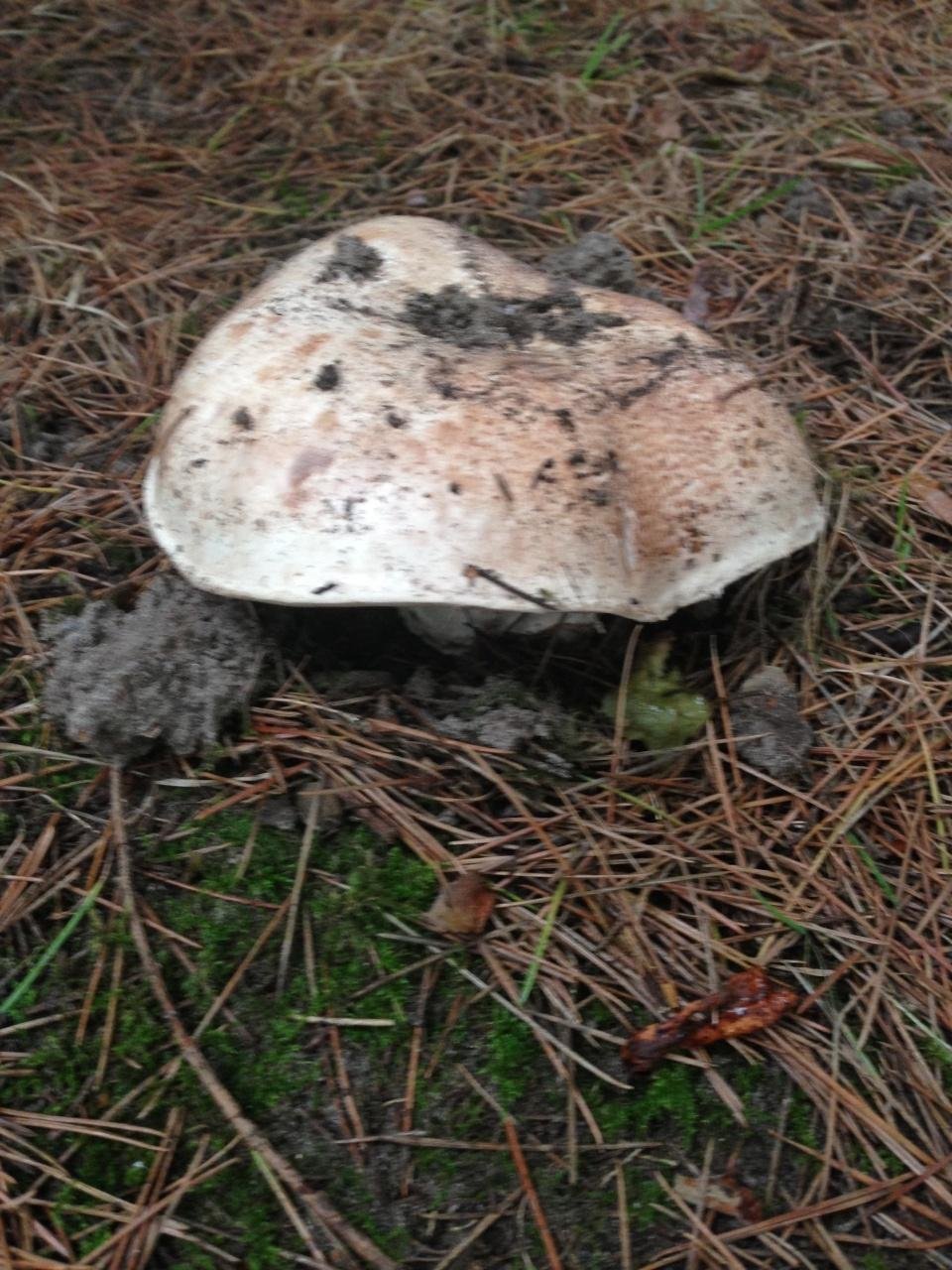
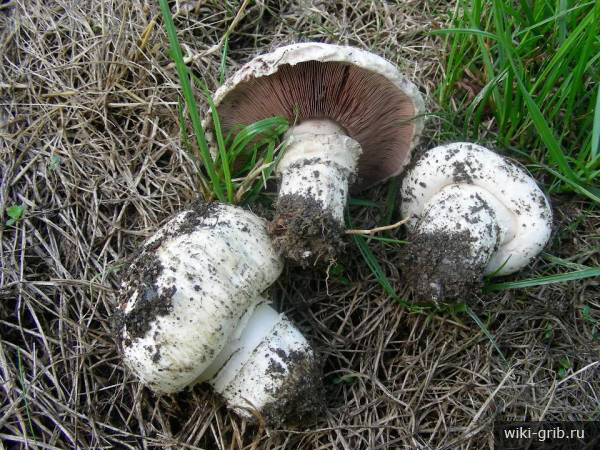
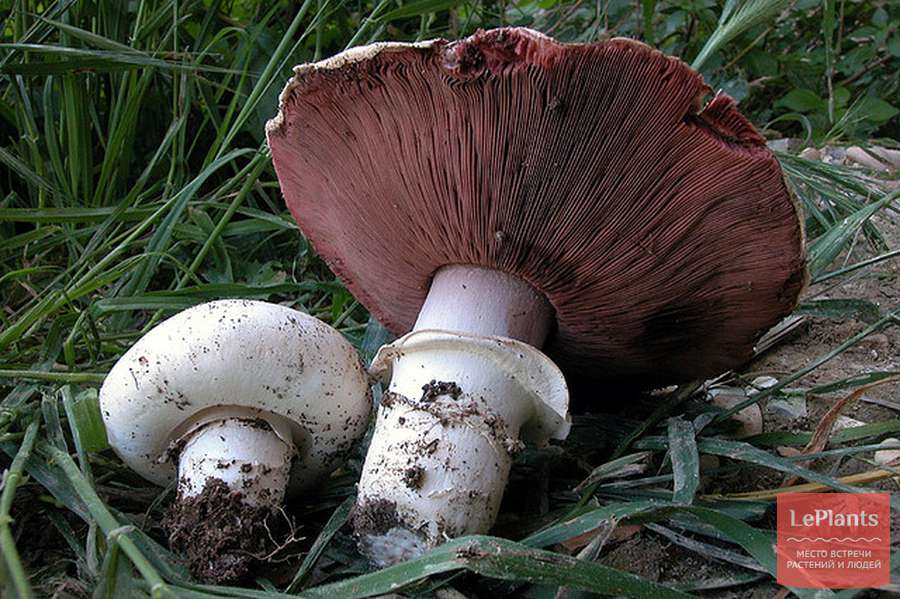
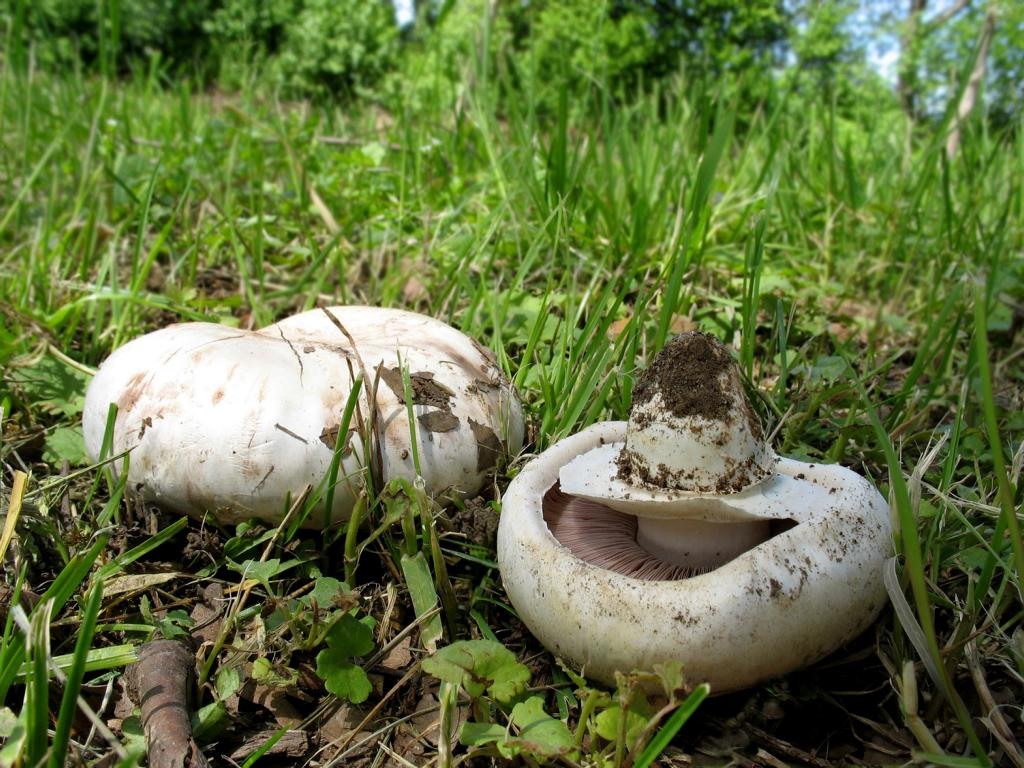
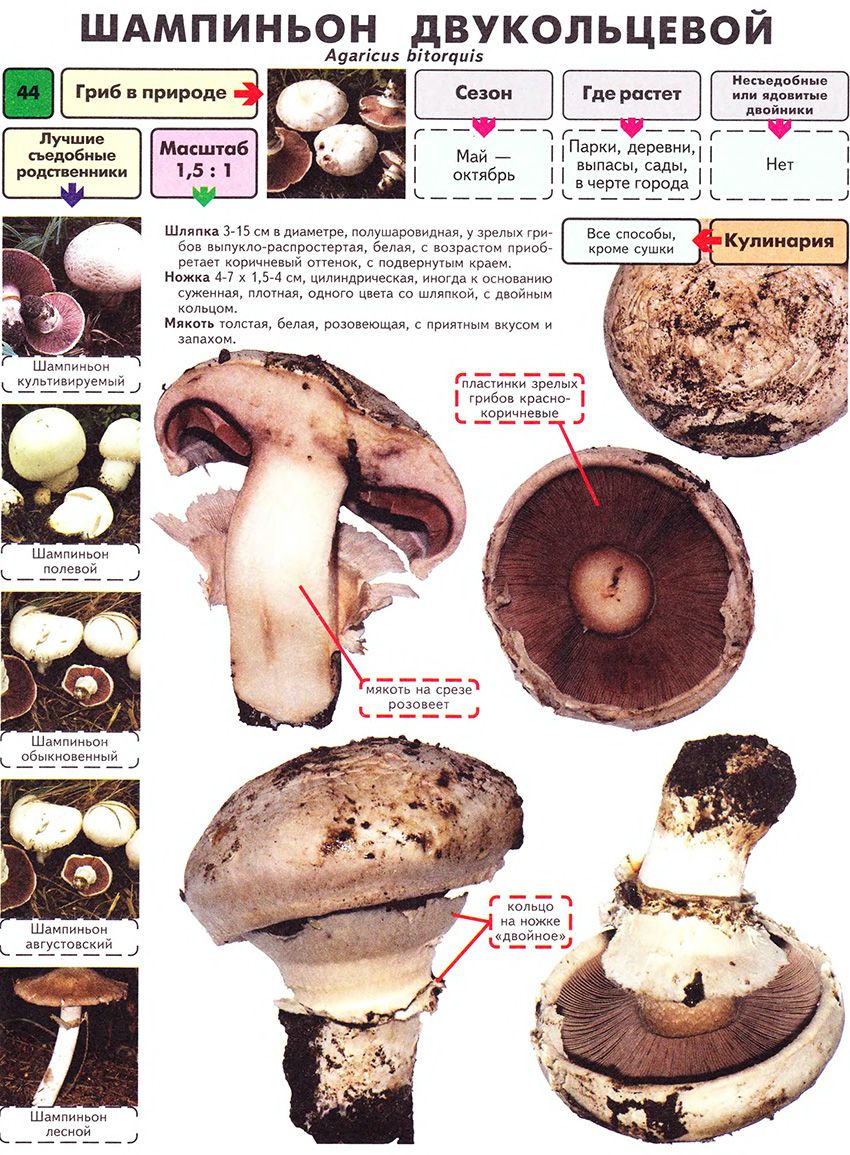
The cap of the two-ring champignon is 3-15 cm in diameter, thick-fleshed (the flesh is up to 2.5 cm thick), round, semicircular, later convex-prostrate, sometimes pressed in the center, white, dirty-whitish, ocher-brown, does not change when touched, occasionally painted in ocher color, matte, naked, smooth, sometimes in the center with inconspicuous appressed scales, fibrous to the edge, with a tucked thin slightly furrowed edge.
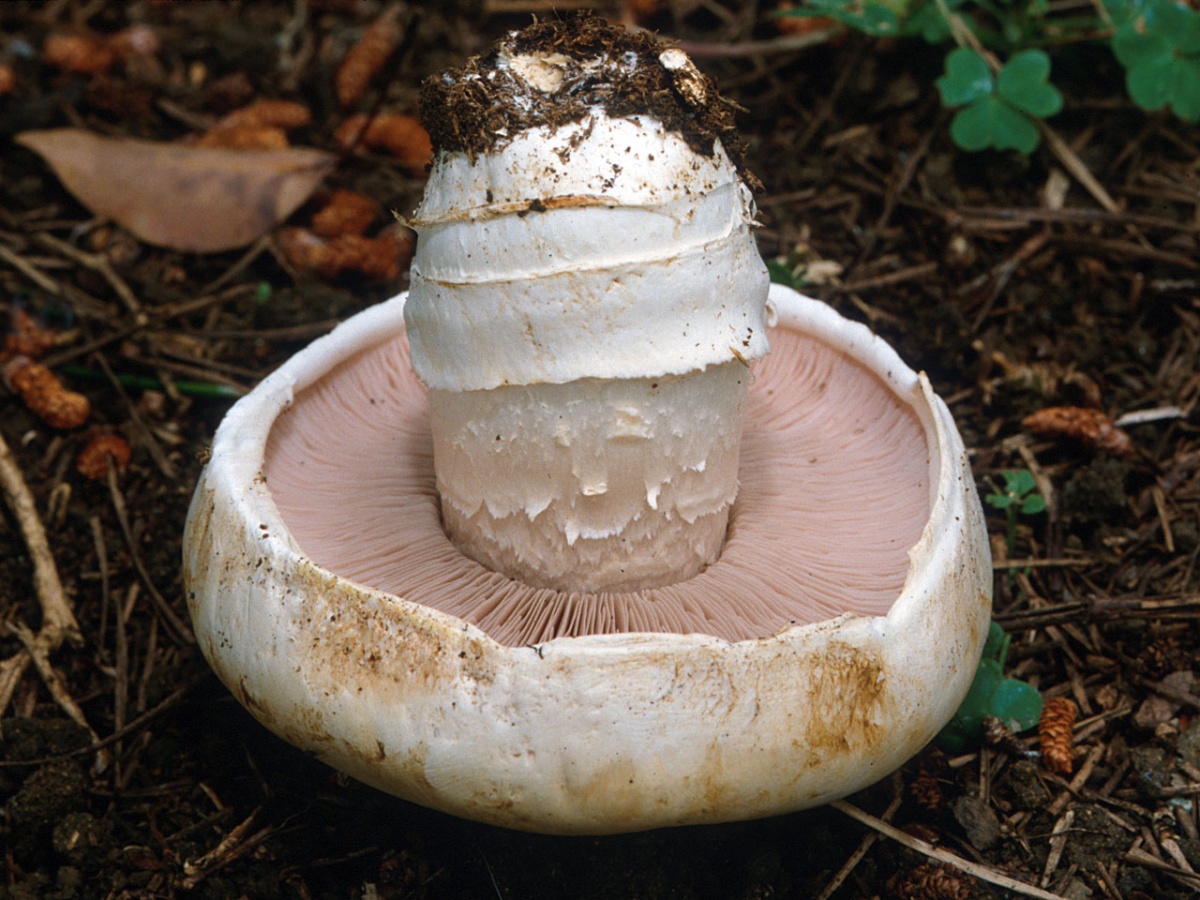
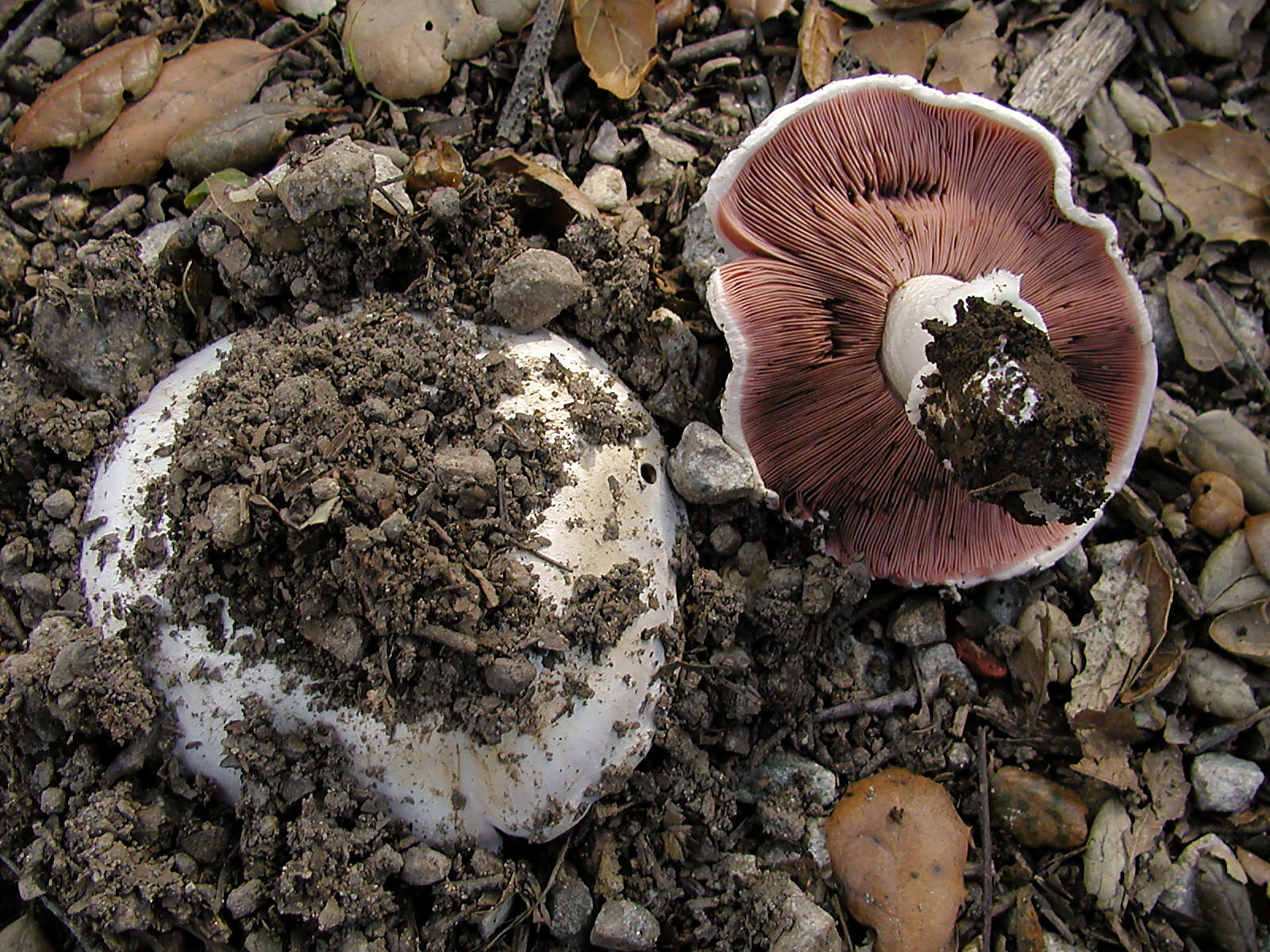
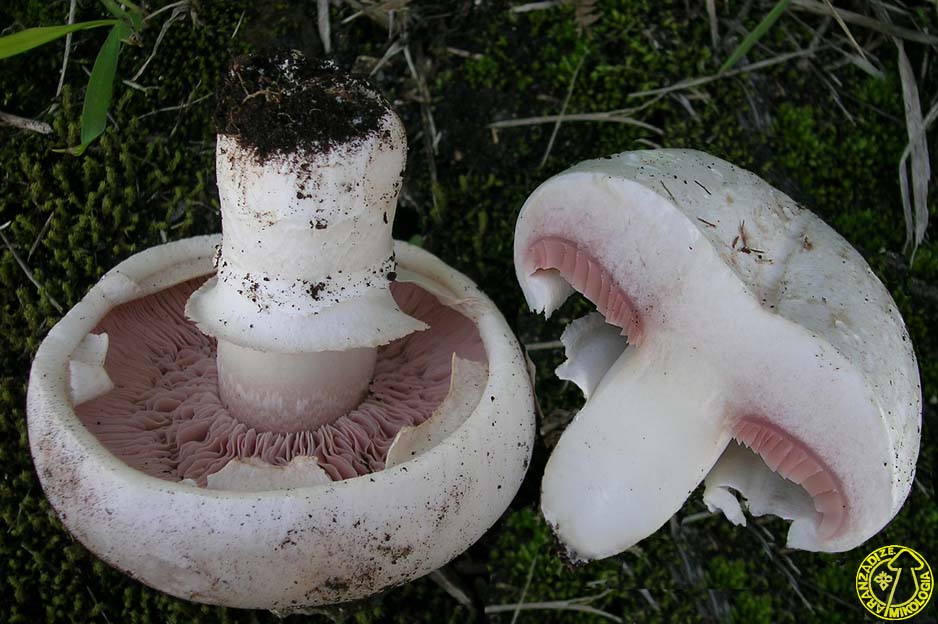
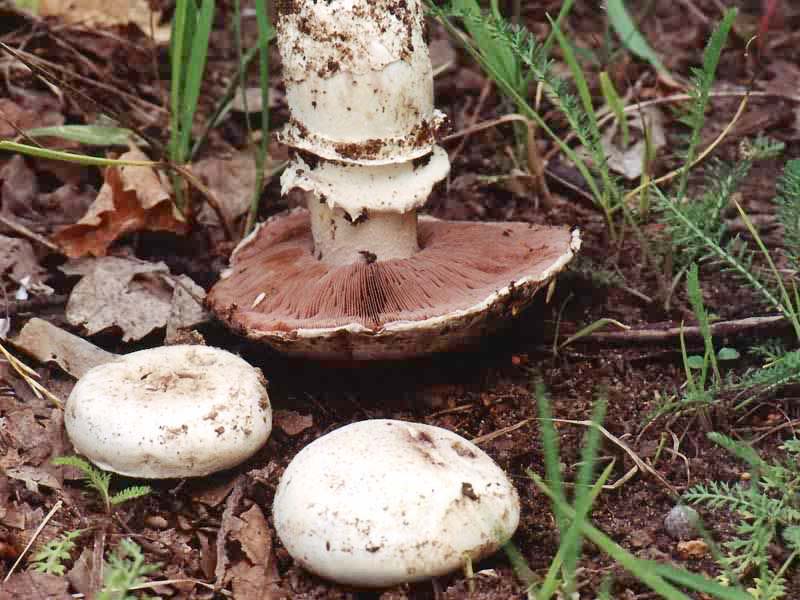
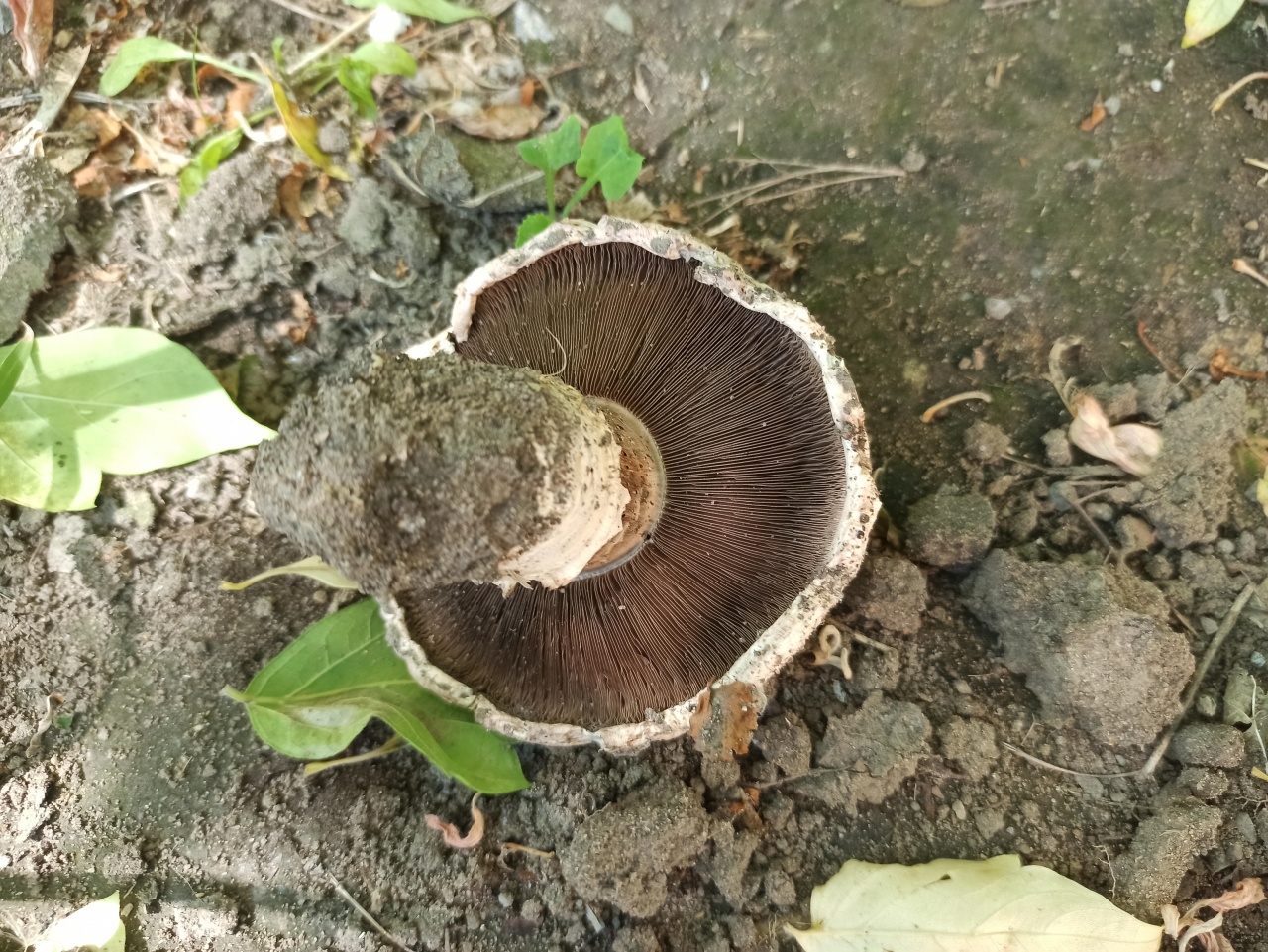
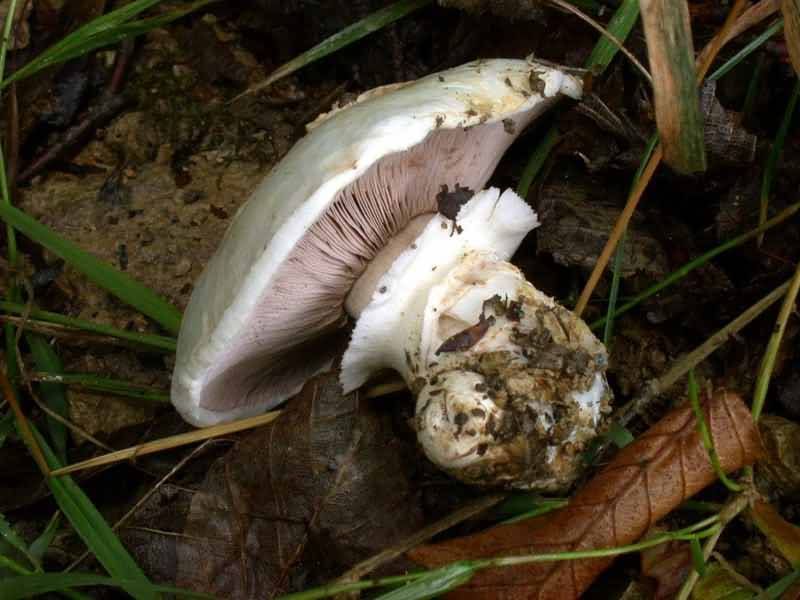
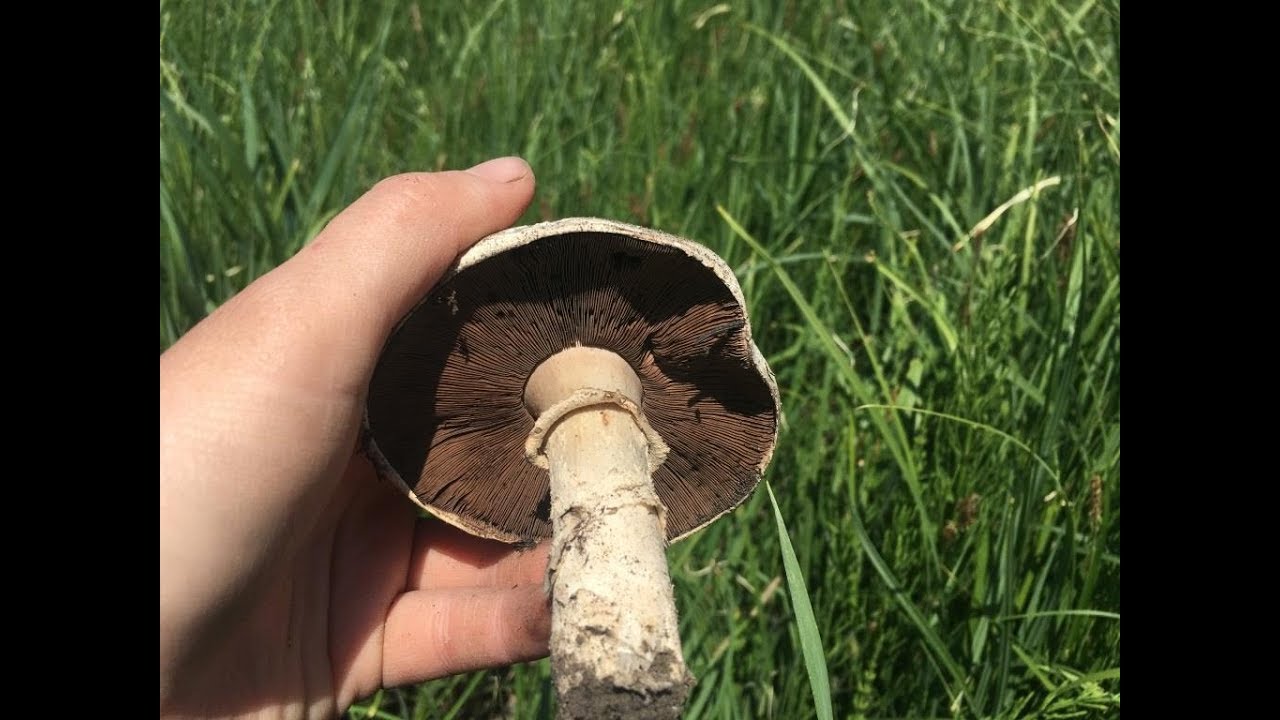
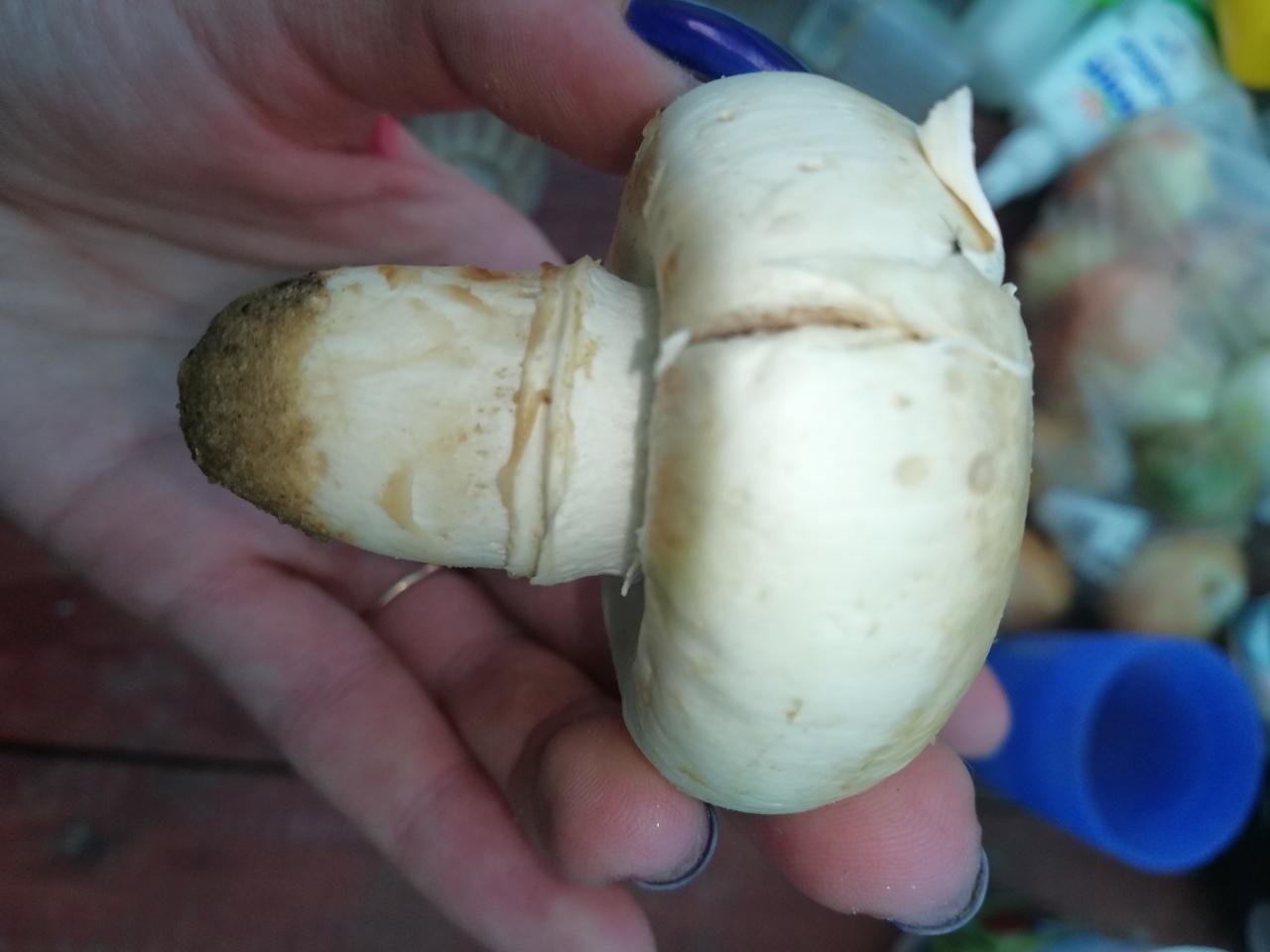
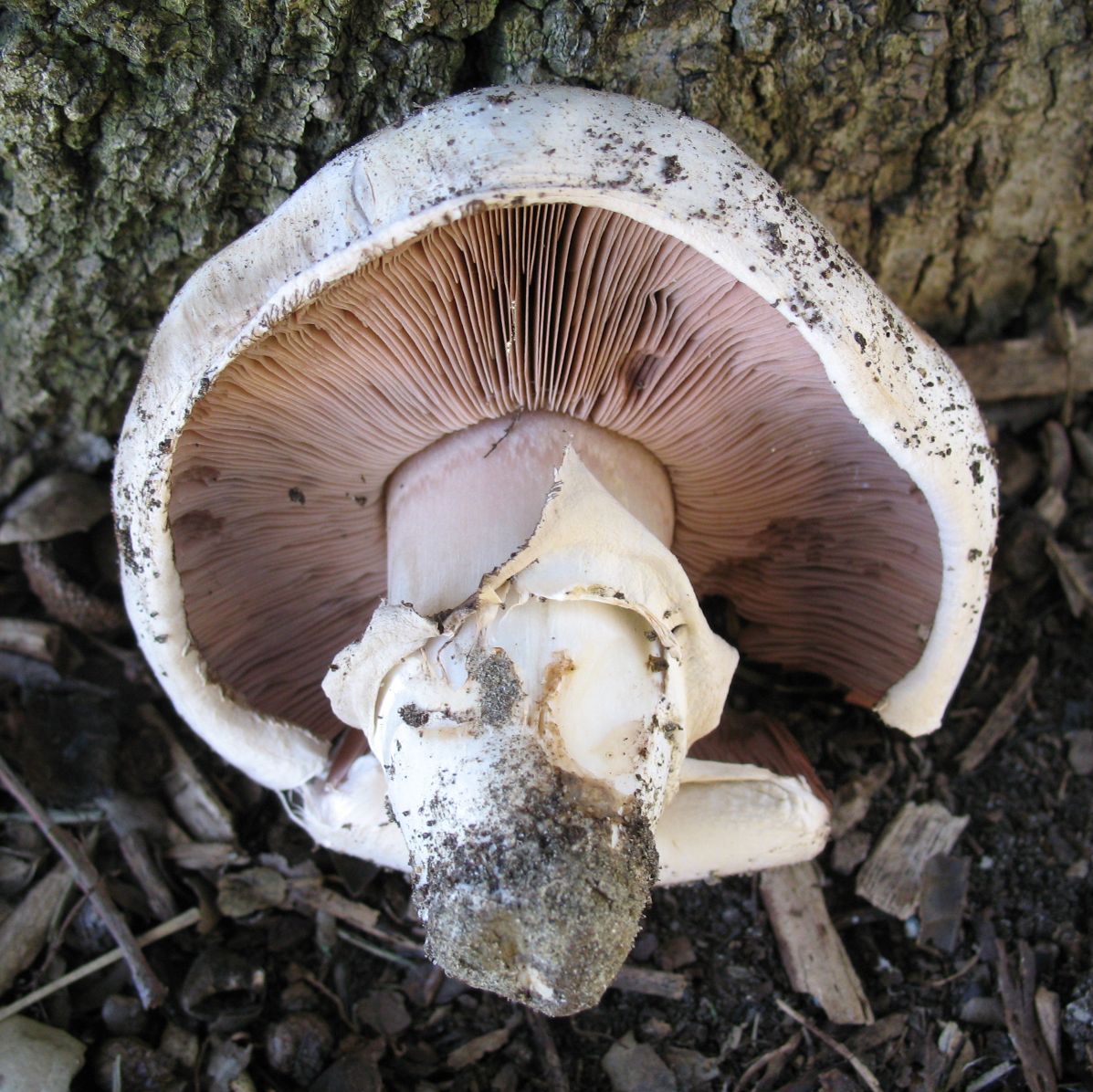
Blades of two-ring champignon are free, characteristic of edible and some conditionally edible mushrooms, thin, frequent, pink, dirty pink, later dark brown, with a lighter sterile edge. Tram of plates in young carpophores is correct, later incorrect. Leg 4-7 by 2-4.0 cm, central, even, cylindrical, often slightly swollen in the middle, tapering to the base, made, dense, one-color with a cap, smooth, fibrous, with two rings located in the middle of the leg: upper whitish the ring is formed by a private veil, the lower one is whitish-ocher - the remains of a common veil. The pulp is white, with autooxidation it gradually becomes pinkish with a reddish tinge (mainly in the stem), with a pleasant smell and taste. With Schaeffer's reagent, the reaction is negative. Basidia are four-spore, 25-40 by 6-10 microns, clavate. Sterigmata 2.5-3 microns long. Cheilocystids 10-40 by 5-15 microns, numerous, broad-headed, hyaline or slightly brownish. Pleurocystids are absent. The spore powder is dark brown. Spores 5-5.6 x 4-5 microns, light brown, large, broadly ovate, with a lateral apiculus, smooth, with one or two fluorescent drops.
Ecology. The two-ring champignon grows in parks, orchards, vegetable gardens, pastures, heaps of garbage, cemeteries, city streets in cracked asphalt (sometimes it is the cause of the asphalt turning out). Geographic distribution - Cosmopolitan. This champignon is found on all continents of the globe, except for Antarctica. Europe (everywhere); Asia: India, China, Mongolia, Turkey, Iran, Israel, Sri Lanka, Japan, Kazakhstan, Central Asia, Western and Eastern Siberia, Krasnoyarsk Territory; North. America: Canada, USA, Mexico; South. America: Chile; Africa: Algeria, Zaire, Morocco; Australia; islands Cuba, Madagascar, Trinidad and Tobago, Solomon.
Two-ring champignon is successfully cultivated artificially, however, it requires more difficult microclimate conditions, since this mushroom is sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity. Therefore, cultivation rooms are better insulated using mineral insulation, which allows you to create an optimal temperature for the growth of mushrooms. For these purposes, you can use, for example, Ursa insulation made on the basis of fiberglass, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of which will create a favorable temperature regime in the mycelium.
Two-ring champignon
Two-ring champignon differs from double-peeled champignon in a number of properties that make its cultivation promising. The fruiting bodies of the two-ring champignon are white, with dense pulp - retain their original appearance after 2-3 days of storage, do not darken from pressure and mechanical damage. Losses in the mass of fruiting bodies in two-ring champignon after storage are 58–65% lower than in double-ring champignon. The temperature requirements for mycelium growth (30 ° C) and fruiting development (25 ° C) in this species are about 5 ° C higher than that of the double-horned champignon. In addition, it can grow at a higher concentration of CO 2 than double-pore champignon. Therefore, it is advisable to grow two-ring champignon in the southern regions of the country and in the Crimea.The disadvantages of two-ring champignon strains include the fact that the first wave of fruiting begins later than that of the double-peeled champignon, by 8-12 days, and the interval between waves is 3-5 days longer. In this regard, the fruiting period of the two-ring champignon lasts longer than that of the double-peeled champignon. Since the two-ring champignon has a very short stem, mechanical harvesting of the mushrooms is impossible. In addition, the fruiting bodies of the two-ring champignon must be harvested at the “buds” stage, since their plates quickly darken when exposed to air. At the same time, the period between the undisclosed and open stages in the two-ring champignon is much shorter than in the double-peeled champignon. When preserved, its fruiting bodies acquire a gray tint, so it is advisable to sell them fresh.
One of the most important characteristics of the two-ring champignon is its resistance to viral diseases. However, in comparison with champignon dvusporovym other diseases of cultivated mushrooms (false truffle, bacterial spotting) occur in two-ring champignon more intensively and quickly (probably due to the high temperature required for growing this mushroom).
For cultivation of two-ring champignon, you can use the same substrate as for double-ring champignon. The preparation of the seed mycelium is also the same. Sowing rate of grain mycelium is 2-3 kg per 1 ton of compost. Since the mycelium of the two-ring mushroom grows better with an increased concentration of carbon dioxide, the compost must be compacted immediately after sowing. To prevent drying, racks with compost inoculated with two-ring mushroom mycelium are covered with paper or plastic wrap. The average temperature in the compost during mycelium growth should be at least 30 ° C, ventilation should be minimal. As in the case of growing two-pore champignon, the mycelium of two-ring champignon dies at temperatures above 32–33 ° C. Since the mycelium of the two-ring champignon is thinner than that of the double-peeled champignon, the compost looks less "white" than when the mycelium of the double-peel champignon develops.
Casing soil can be poured onto the compost 12-14 days after sowing. The covering soil is prepared in the same way as for the double-peeled champignon. It is applied in a layer of 2 cm. After finishing, the temperature in the substrate is maintained at 30 ° C. Ventilation cannot be used at this time, since strong ventilation of the air shortly after finishing leads to the formation of fruiting bodies inside the earthen layer. Fresh air can be supplied to prevent a strong temperature rise in the substrate only 6–8 days after the application of the casing layer. During this period, it is also necessary to maintain high humidity. Sometimes brown mold develops in the casing layer, probably due to high humidity and temperature. In 12 days after finishing, the temperature in the compost can be lowered to 25 ° C, ventilation during this period is 2–4 m 3 / m 2 per hour. The amount of fresh air supplied must be maintained at the same level during the first wave of fruiting. Subsequently, the air supply should be reduced: the air circulation should also be reduced to a minimum.
When fruit bodies the size of a large pea appear (about 25 days after the application of the casing layer), watering can gradually begin. Since fruit bodies are sensitive to ventilation and air humidity, brown spots appear on them with excessive air supply and insufficient humidity (less than 70%). The interval between fruiting waves is 10–12 days. The first wave is the most productive. During fruiting, the temperature in the chamber must be kept at 25 ° C. The fruiting period lasts 8-9 weeks. The yield can be up to 25 kg / m 2.
This text is an introductory fragment.
Hunting and fishing in the Tver region

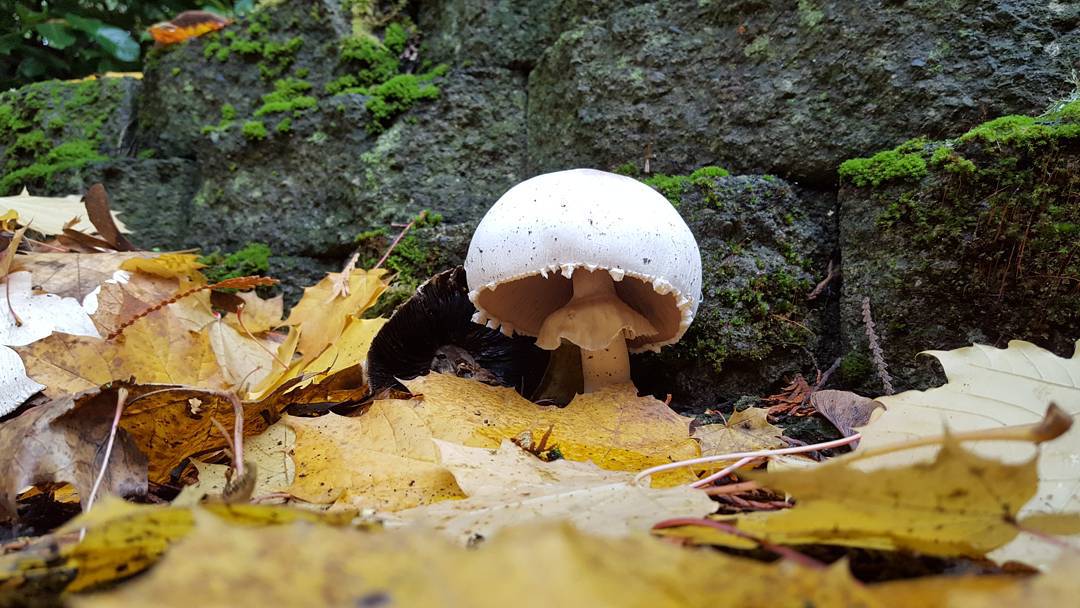
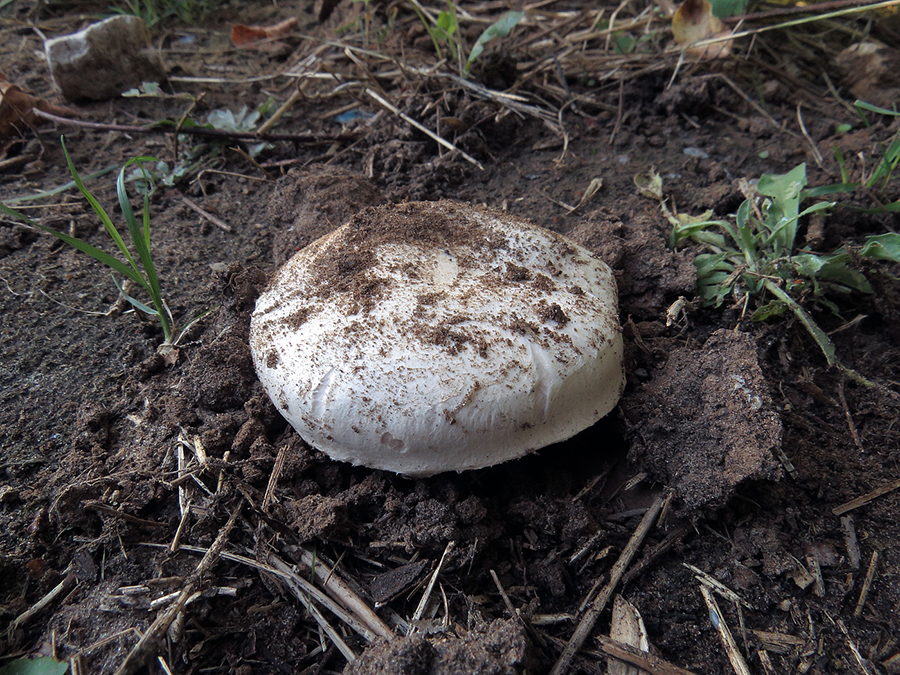
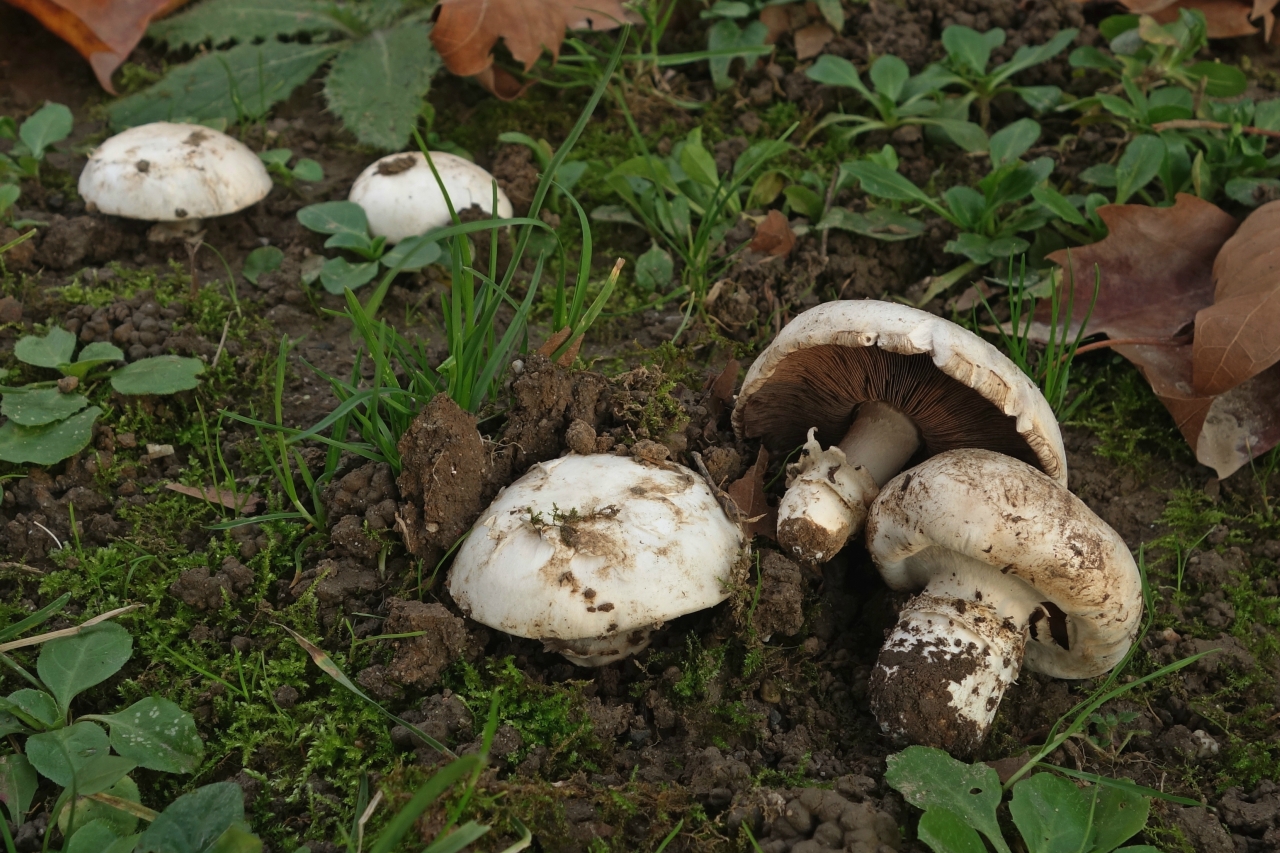
Hat: 5-12 cm in diameter, from hemispherical in young mushrooms to half-open, flattened at the top and with rolled edges, at maturity; develops mainly underground or under asphalt, appearing on the surface only in old age. For this reason, the flat caps of the two-ring mushroom are often covered with a camouflage mound of earth. The color of the caps is white or grayish, the flesh is thick, light, turns pink at the break, with a pleasant "champignon" smell and taste.
Plates: Loose, frequent, narrow, in young mushrooms, light cream, almost white, gradually acquire pink, red-brown, dark brown and almost black color with age. In the early stages of development, the mushroom plates are reliably protected by a thick double ring.
Spore powder: Dark brown.
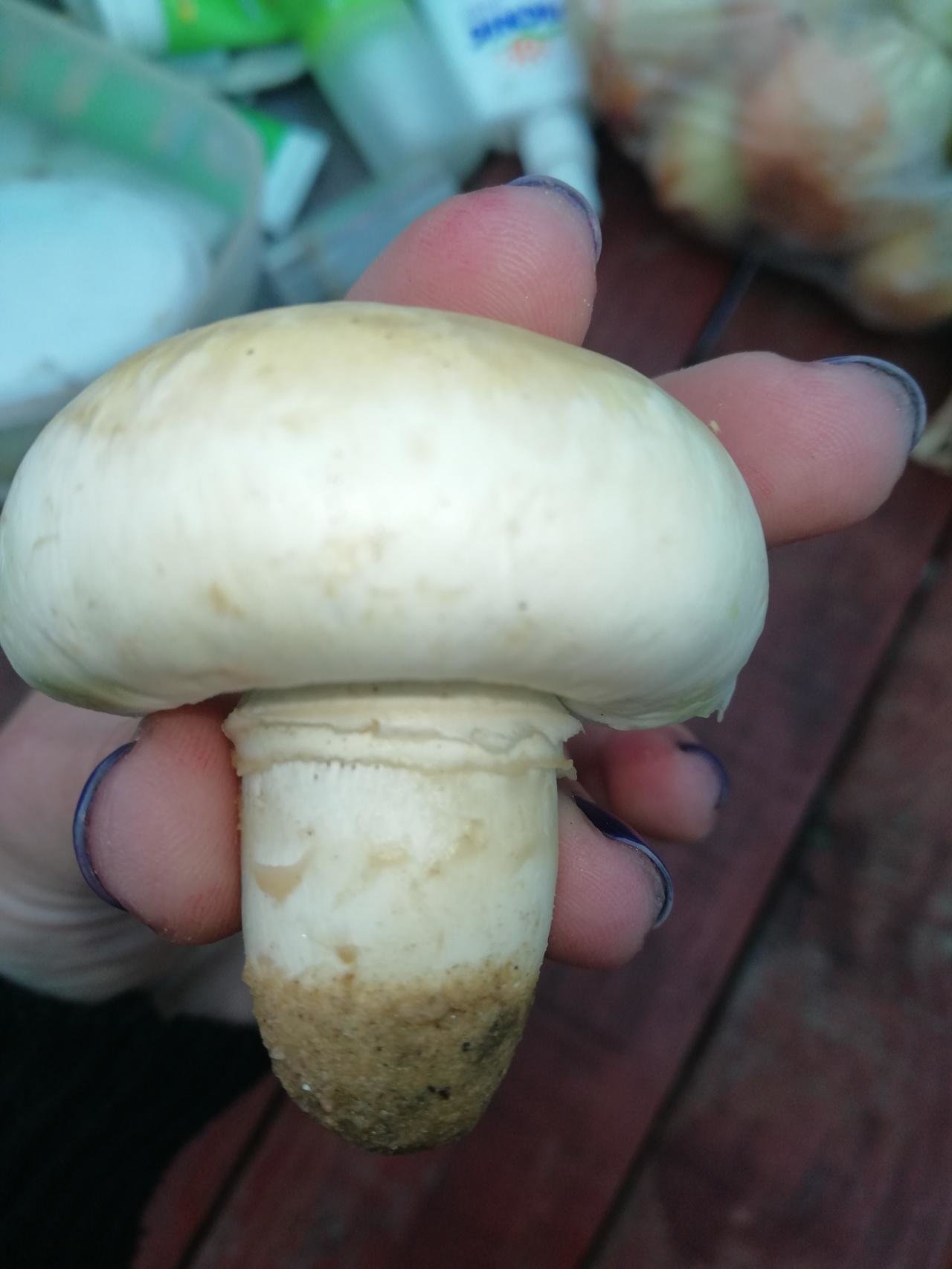
Leg: Thick, short (3-5 cm in height, 2-4 cm in width), solid or slightly executed, the color of the cap. The remnants of a private bedspread are clearly visible - a double thick gray-white ring, in mature mushrooms it is dark in the upper part from raining spores.
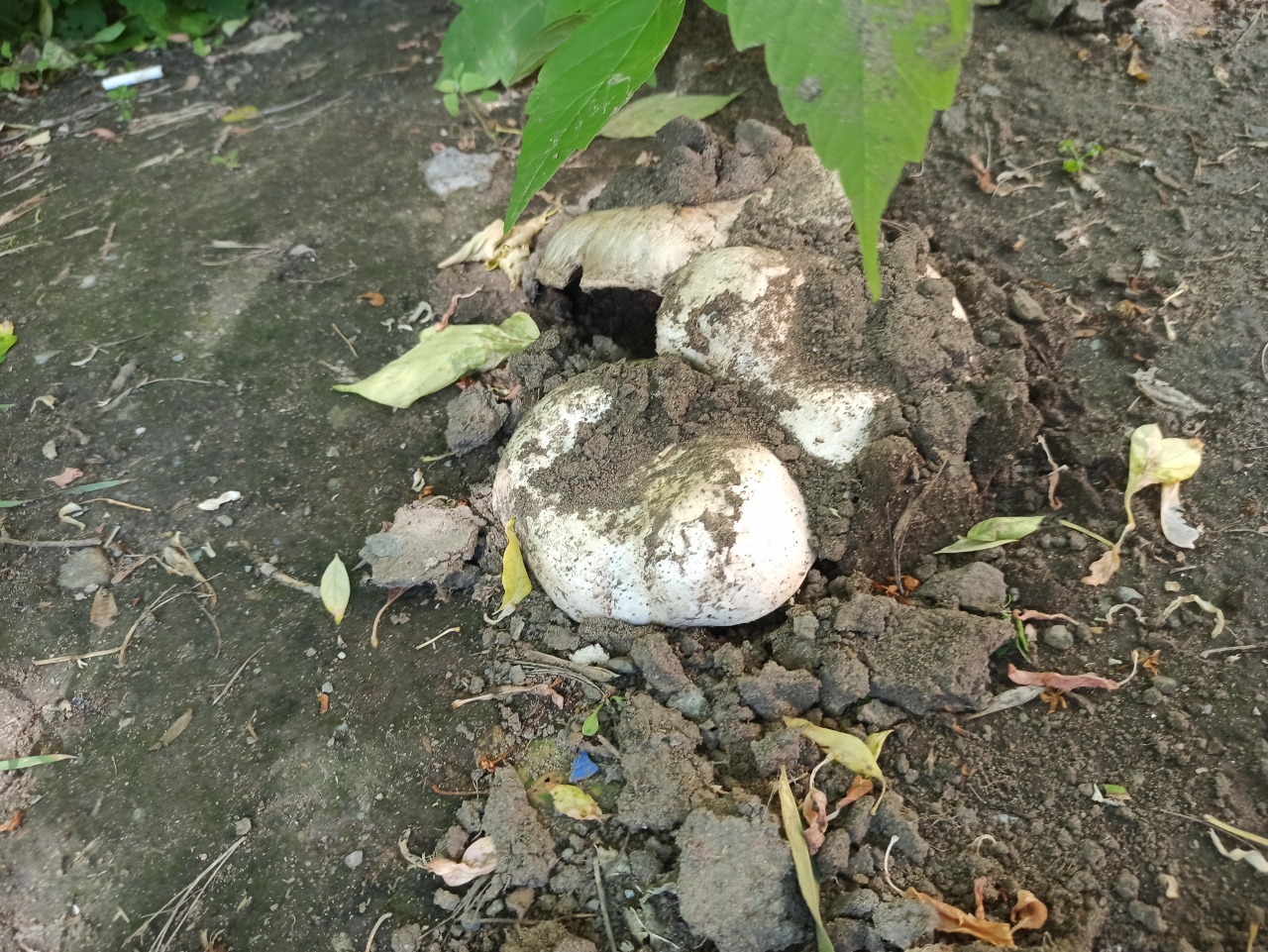
Distribution: Agaricus bitorquis is a widespread mushroom, found in large, but usually loose, scattered groups from mid-May to late September in gardens, vegetable gardens, parks, preferring richly fertilized fertile soil. A common mushroom for cities in central Russia. The two-ring champignon develops mainly under the soil, which makes it inconspicuous, but once you have explored the place of growth, you can return to it several times per season and, picking out the characteristic tubercles, release round, dense, heavy champignons from the soil. Quite often the double-peeled champignon is not satisfied with its usual growing areas and breaks the asphalt, sprouting under the sidewalks and bike paths.
Similar species: There are quite a few similar light champignons. Agaricus bitorquis is easily distinguished from closely related species by its characteristic double ring, short thick stem and flat, stool-like cap.
Edible: Refers to first-class edible multi-purpose mushrooms; It should be noted that mushrooms should not be harvested in cities and on the roadsides even more than, say, mycorrhizal mushrooms.
Author's notes: For me, two-ring champignon is a mushroom from a happy childhood. I don't remember at all how it happened and why they completely trusted me at home in terms of mushrooms, but already from the second grade I did not return from school without prey. The whole September was devoted to mushrooms - leaving school, I purposefully walked around all the courtyards and squares, bringing a whole package of a variety of mushrooms, among which were white and gray dung beetles, and a variety of raincoats, and a few, from which even more valuable mushrooms and, of course , rare city mushrooms. Often my father joined my searches, but as a rule, my parents played only a culinary role in this matter. Again, I don't remember what the full confidence in my mushroom skills was based on, but everything I brought home went into food - I know for sure. I myself would probably not have been able to trust my child so much, but my parents somehow managed, and well - gambling, filled with some difficult to describe meaning, walks through the courtyards became for me one of the brightest impressions of this period of my life. It's a pity that September is such a short month, and then the mushrooms leave for a long time from where they appear in spring or autumn - into oblivion ...
Champignon two-ring (four-spore) mycelium (UkrMycelium)
Important
The mycelium is sent from another warehouse and in a separate parcel.
There is no minimum order amount! But prepayments are required:
- for orders up to UAH 200;
- for goods made to order - 100% prepayment;
Discounts
When ordering for 3,000 UAH - 3% discount, 5,000 UAH - 5% discount, 10,000 - 10% discount
Discounts are not cumulative!
Receive gifts by ordering online
Each customer who makes an order online (by registering in the store and making purchases through the basket) receives a gift from the Seed Supermarket, a package of seeds and a calendar (inserted into the order from September to January).
Contacts for ordering in the ATO zone
We accept orders for vegetable seeds from the ATO zone
Telephone: 066 061 04 03
Two-ring champignon (Champignon chetyrehsporovy) - description:
A hat with a caliber of 3-15 cm, thick and fleshy, white or gray-white in color. The upper fabric is smooth, sometimes scales are visible in the middle. The plates are densely arranged, colored pink. The flesh is firm, turning pink in the cut.
The height of the leg is 3-10 cm, the volume is 2-4 cm, the surface is white, smooth. It has a double ring on it. The upper ring is formed from the remains of the upper layer, and the second from the remains of the lower one.
Two-ring champignon is a very tasty mushroom that is suitable for all types of consumption. Productivity - 12 kg of mushrooms per square meter per season.
Beneficial features:
This type of champignon is very useful. It contains fiber, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, iron b vitamins D, E, PP, B. It contains no sugars, sodium and fat. Therefore, this mushroom is ideal for the dietetic nutrition of diabetics and those on a diet.
Champignon growing technology:
1 package of mycelium is enough for sowing the mushroom on a plot of 2.5-3 sq.m. Champignon prefers to grow in shade or partial shade, it should not be exposed to the sun. Before sowing, the soil must be loosened, the roots of weeds and grasses do not need to be removed, the mushroom can grow well with them.
The mycelium is evenly scattered on the ground and covered with an even layer of 12-15 cm of compost. Fruiting will begin in 60-75 days and will last from spring to autumn. It is at this time that it can be planted.
But the best periods for sowing mycelium are September-December and February-May. In the cold season, the field does not need to be mulched. Spores cannot die from frost, they only stop growing. In the spring they will wake up and bring the next harvest.
Once a year, cover the area with a layer of humus, compost, or dry plant residues. Fertilizers are recommended to be applied in autumn, when the field is sprinkled. The mycelium lives from 4 to 6 years, expanding slightly every year.
Any utility room (barn, basement, garage, etc.) is suitable for cultivation all year round. If you plant a champignon indoors, it wakes up to harvest all year round. In this case, the mushrooms are sown in boxes or bags.
At the bottom of the container, soil is poured in a layer of 10-12 cm, then mycelium and compost. The first mushrooms will grow in 45 days. The mycelium will bear fruit 4-5 times a year, only each time the yield will be lower.
Crops need to be systematically moistened or placed in a container with water, which evaporates to moisten the mushrooms. The room temperature should be 14-26 degrees Celsius.
As the temperature drops, the mushrooms will grow more slowly. More detailed instructions are attached to the mycelium upon purchase.
Distribution, period and place of collection
The fruiting season is from May to October. Field champignon is widespread throughout Russia, especially in the north of the temperate climate.
Prefers open spaces, loves fields, meadows, overgrown with grass, found in open forest clearings, in gardens and parks, sometimes in pastures. It can grow not only on plains, but also in mountains. It grows both singly and in very large groups, forms "witch circles".
It can be rarely found with trees, but it is supportive of spruce trees, for this very reason it is quite common in the Crimea, it is found both in the mountains and in the fields. However, he prefers nettles more.
It is ubiquitous in Europe and Asia. In Russia, it grows within the temperate zone of the middle zone, in the Urals and Siberia, as well as in the Far East, in the mountains and foothills of the Caucasus and Crimea.
Description of yellow-skinned champignon
A yellow-skinned peasant, a red or false champignon has a whitish-brown cap with edges slightly curved inward.The diameter of the cap is 5 to 15 centimeters. Young mushrooms have a rounded cap, in old ones they straighten and become convex-flat, slightly cracking at the edges.
The yellow-skinned peasant is a lamellar mushroom. The young ones have pink plates, tightly fitting to the leg and covered with a film, the old ones - the film turns into a “skirt” that hugs the leg in a ring, and the plates themselves change their color to gray-brown.
The leg, 1-2 cm thick, has a brownish thickening in the lower part, inside there is an empty cavity. On the cut of the cap or leg, the mushroom is yellow, but not immediately. Yellowing occurs gradually, so be careful when picking.
Mushroom spread
Distribution sites are mixed and deciduous forests, grassy areas, as well as gardens and parks almost all over the world. Spores of the red-headed champignon were brought even to Australia and took root well there.
The time when you can collect these mushrooms for medicinal purposes is from the second half of May to the end of September. Depending on the climatic conditions of the area, this period may vary, but the bulk still grows within summer and early autumn.
Especially abundant fruiting is observed in damp, warm weather, after heavy rains, during this period you can find "witch circles" created by the mycelium. This is due to the fact that poisonous mushrooms are of little concern and they grow from the center outward, gradually increasing the diameter of the "witch's circle".
The toxicity of yellow-skinned champignons
Poisonous substances contained in yellow-skinned peppers can provoke an upset stomach, expressed by diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. According to the degree of danger, it belongs to the medium poisonous. If you suspect poisoning, it is recommended to do:
- gastric lavage using a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate in a volume of at least 1.5 liters;
- take a sorbent at the rate of 0.5-1 g per kilogram of the victim's weight;
- provide a plentiful drink in the form of strong tea or water;
- apply a warm heating pad to the legs and abdomen to prevent circulatory disorders;
- contact a medical institution.
How to distinguish yellow-skinned champignon from edible mushrooms?
The distribution of champignons and a large number of their varieties, among which, in addition to ordinary, mainly edible, mushrooms, rare poisonous ones can also be caught, require attention during collection and processing. Without a careful examination, it is difficult to distinguish a poisonous mushroom from an edible one:
- the shape and color of young mushrooms are similar;
- an unpleasant smell can only be detected when breaking or boiling;
- growing conditions are similar, as are the places of distribution, so they can be nearby.
Gambling can lead to loss of self-control, especially if there are beginners and children among mushroom pickers. The "prey" collected by them should be sorted out especially carefully, trying to explain to the child how to correctly determine the edibility of mushrooms.
For safety, you need to know the main differences in the description of yellow-skinned and other types of champignons:
- The main sign, thanks to which the yellow-skinned peasant got its name, is a change in color when the cap or leg of the mushroom is damaged. When broken, pressed or damaged by pests, the pulp acquires a characteristic yellow color. Seeing a yellowing cut, you should get rid of unwanted treats.
- A pungent, phenolic, unpleasant odor, which intensifies during heat treatment, should serve as another signal that poisonous ones have been caught among the mushrooms. Edible champignons have a pleasant mushroom aroma.
Where is it applied?
The chemical composition of false champignon has not yet been fully studied, its use in food is strongly discouraged. It can be used as a medicinal plant in traditional medicine recipes thanks to its natural antibiotics. The substances isolated by scientists, agaricin and psalliotin, are able to resist salmonella and gram-positive bacteria. There is a possibility that substances derived from these fungi can resist the growth of cancer cells.
Champignons are famous mushrooms famous for their pleasant smell and taste. However, among them there are poisonous species. One of these is yellow-skinned champignon, skillfully disguising itself as its edible "relatives". Find out what its features are, and what you need to do in case of accidental poisoning with this mushroom.
Influence on the body
Agaricus has an effect on man similar to drug intoxication. The effect does not come immediately, but after 1-2 hours. Conventionally, the action of the mushroom is divided into 4 phases:
- Light excitement. The state is akin to a moderate degree of intoxication. A person becomes cheerful, energetic, talkative, sociable, loving.
- The excitement increases. Loquacity turns into incoherent speech. The patient is not oriented in space. Large objects seem small to him. He easily carries heavy things that in the usual state could not budge. The grass under the feet seem to be logs, the patient is trying to "climb" over them, lifting his legs high. Convulsive twitching of the limbs, face, eyes begins.
- Arousal is at its peak. The patient violently rushes at others, shouts, tries to injure himself. In this phase, the patient is dangerous both for society and for himself. He is not aware of what is happening. At the end of the phase, energy is replaced by a state of lethargy.
- Depression, apathy, confusion. The impression that the arousal persists, but the body and mind are unable to respond to it. This is evidenced by single screams, body twitching, lack of sleep.
The most famous champignon is ordinary
We are all accustomed to buying the considered mushroom fruits in supermarkets or in the markets - white balls with edges curved to the leg, resemble a perfect ball and are pleasant to the touch. The light skin of the young representative resembles velvet. With age, the delicacy begins to open up and increases several times in size, the color darkens. This species grows on a very fertile substrate, most often it is soil rich in humus, or meadows naturally fertilized with the manure of herbivorous livestock.
The ripening period of the "ordinary" species is from the end of May to the end of October (November - for warm regions). The crop can be harvested several dozen times over the entire season. The mushroom tastes good and is used to prepare various dishes, from salads to complex sauces or baked goods.


Here we will say a few words about the forest representative of the family. It resembles a bell on a high leg. The hat is covered with dark scales. Safe for humans.
Species table
| Name | From latin | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Elegant | Agaricus comtulus | good edible mushroom |
| Tabular | Agaricus tabularis | conditionally edible mushroom |
| Big forest | Agaricus mediofuscus | good edible mushroom |
| Carbolic | Agaricus placomyces Peck | inedible non-toxic mushroom |
| Crooked | Agaricus abruptibulbus | good edible mushroom |
| Field | Agaricus arvensis | good edible mushroom |
| Augustow | Agaricus augustus | good edible mushroom |
| Beneš | Agaricus benesii | good edible mushroom |
| Bernard | Agaricus bernardii | good edible mushroom |
| Cultivated | Agaricus bisporus | excellent edible mushroom |
| Two-ring | Agaricus bitorquis | good edible mushroom |
| Lugovoi | Agaricus campester | good edible mushroom |
| Dark red | Agaricus haemorrhoidarius | good edible mushroom |
| Large spore | Agaricus macrosporus | excellent edible mushroom |
| Motley | Agaricus meleagris | inedible non-toxic mushroom |
| Blushing | Agaricus semotus | conditionally edible mushroom |
| Forest | Agaricus silvaticus | good edible mushroom |
| Steam | Agaricus varoparius | good edible mushroom |
| Yellow-skinned | Agaricus xanthodermus | toxic mushroom |
| Redhead | Agaricus xanthodermus | toxic mushroom |
Field champignon: description of appearance and photo
Category: edible.
In 1762, the field champignon (Agaricus arvensis) was singled out into a separate group by the professor of the Wittenberg and Tübingen Universities, Jacob Scheffer, a botanist, ornithologist and entomologist.


In appearance, the field mushroom is slightly different from other species. Hat (diameter 7-22 cm): white, gray, cream or light ocher (in old mushrooms) with remnants of the coverlet.It has the shape of a small egg or bell, but over time becomes almost prostrate with a noticeable tubercle in the center. The edges of young mushrooms are wrapped inward, and later become wavy. In dry weather, they can severely crack, due to which they become uneven and torn. Smooth to the touch, in rare cases it may have small scales. Stem (height 5-12 cm): usually the same color as the cap, turns yellow when pressed, fibrous, cylindrical and has a large double-layer ring. Often tapers from bottom to top. In young mushrooms, it is solid, but becomes hollow over time. Easily detaches from the cap.
Plates: can be white-gray, brownish, with a mustard or purple tint, in old mushrooms they are dark brown or black.
Flesh: white or light yellow, very firm, turns yellow on the cut and on contact with air. Tastes sweet.


The description and photo of the field mushroom are similar to the description and photo of the pale toadstool (Amanita phalloides) and the yellow-skinned mushroom (Agaricus xanthodermus).
However, the toadstool has no aniseed scent and has a single-layer ring on the stem. And the yellow-skinned champignon has a strong medicinal smell of carbolic acid.


Field mushrooms grow from late May to early November in the northern regions of Russia.


Where it can be found: In open areas of forests, fields and pastures, it can be found in mountainous areas, nettle thickets or near fir trees. Large groups of field mushrooms sometimes form "witch's rings".
Eating: both fresh and after any kind of processing. A very tasty mushroom, in many countries it is considered a delicacy.
Application in traditional medicine (data have not been confirmed and have not undergone clinical trials!): In the form of an extract as an effective remedy in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Broths have been used since ancient times in the outback as an antidote for snake bites.
Important! Field mushrooms often accumulate heavy metals. Cadmium, copper and other elements in high doses can be hazardous to health
Try to pick mushrooms in an ecologically clean area.
The British call the field mushroom horse mushroom, because it often grows on horse dung.
Literature [| ]
- The world of plants: in 7 volumes / Ed. Academician A.L. Takhtadzhyan. T.2. Slime molds. Mushrooms - 2nd ed., Rev. - M .: Education, 1991 .-- 475 p. (P. 286).
- Aurel Dermek. Mushrooms. - Bratislava: Slovart, 1989. - pp. 112-113.
- Z.A. Klepina and E.V. Klepina. Handbook of the mushroom picker. - Moscow: AST-PRESS, 2006. - 256 p. (pp. 99-100)
- "Mushrooms. Directory — determinant. More than 120 species "/ Author - compiled by N.Ye. Makarova - Moscow: AST, Minsk: Harvest, 2005 - 320 p. (pp. 252-253)
- "Mushrooms". Directory. / per. with ital. F. Dvin - Moscow: AST. Astrel, 2004 .-- 303 p. (p. 181)
- Lesso, Thomas. Mushrooms. Determinant. / per. from English - Moscow: AST, 2007 .-- 304 p. (p. 157)
Extended
Great ovens can be developed practically in all regions of Russia, as well as in Europe and the Caucasus, among other climatic minds. Most mushrooms grow on fertilized organic soils, vibrate in the open fields without tall trees. Some stinks are created in girskii micevost, sprinkling buds, growing either in groups or in groups, setting arcs.
So, if you want to take a large number of peppers, then come to respect the little trees of the forest roads, small parks and forest majdans, as the trees are overflowing with trees. Bezposeredno at the trees you can see the peppers, ale tilki yaksho mova yde about the fishes.
Two-ring champignon
Two-ring champignon (lat.Agaricus bitorquis)
Two-ring champignon (Latin Agaricus bitorquis)
People also call it sidewalk mushroom, edible, urban. This is the most unpretentious mushroom in its family. It cannot be confused with other mushrooms due to its shape. its leg is twice ringed, hence the name of this mushroom).
This type of champignon belongs to the second category in terms of its nutritional value. The mushroom is edible. Grows in deciduous forests rich in humus soils.In addition to woodlands, two-ring champignon can be found everywhere in the urban area, on the roadside, flower beds, garbage heaps, in parks, orchards and vegetable gardens. Given the unpretentious growing conditions, the double-ring mushroom has gained popularity in industrial conditions and in personal plots and dachas.
"Loves" a warm climate. By its taste, the mushroom is delicious. You can use it by boiling, frying or drying.
The cap of the mushroom reaches 12-15 cm in diameter. At an early age, it is spherical, flattened, the edges are bent inward. With age, it becomes prostrate, with a depressed center. Thick and dense. Smooth. It has a variety of color shades from off-white to brownish and even brown.
Very thin, frequent and narrow plates. Loose or weakly adherent. In adolescence, they are dirty pink. Over time, they turn dark brown or brownish brown.
Spores are dark brown in color. On the cut, the pulp slowly turns pink.
The leg is fleshy, dense. The height of the leg is 3-7 cm. The thickness is 1.5-4 cm. The leg is cylindrical, even, sometimes slightly narrowed at the base. In large cases, the color is the same as that of the cap.
The two-ring champignon begins to bear fruit from the end of May and ends in November, with the appearance of the first frosts. Like all mushrooms, double-ring champignon tends to accumulate harmful substances in itself, therefore, when collecting it in cities and along roads, be careful when processing it and using it for food.
Two-ring champignon (lat.Agaricus bitorquis)