Tiger row (Tricholoma pardinum)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Row poisonous
- Row leopard
Synonyms:
- Agaricus unguentatus
- Tricholoma unguentatum

First officially described by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon in 1801, Tricholoma pardinum has an intricate taxonomic history that spans over two centuries. In 1762, the German naturalist Jacob Christian Schäffer described the species Agaricus tigrinus with an illustration corresponding to what is believed to be T. pardinum, and hence the name Tricholoma tigrinum was mistakenly used in some European works.
As of now (Spring 2019): Some sources believe that the name Tricholoma tigrinum is synonymous with Tricholoma pardinum. However, authoritative databases (Species Fungorum, MycoBank) support Tricholoma tigrinum as a separate species, although at present this name can hardly be used in practice and there is no modern description for it.
Description
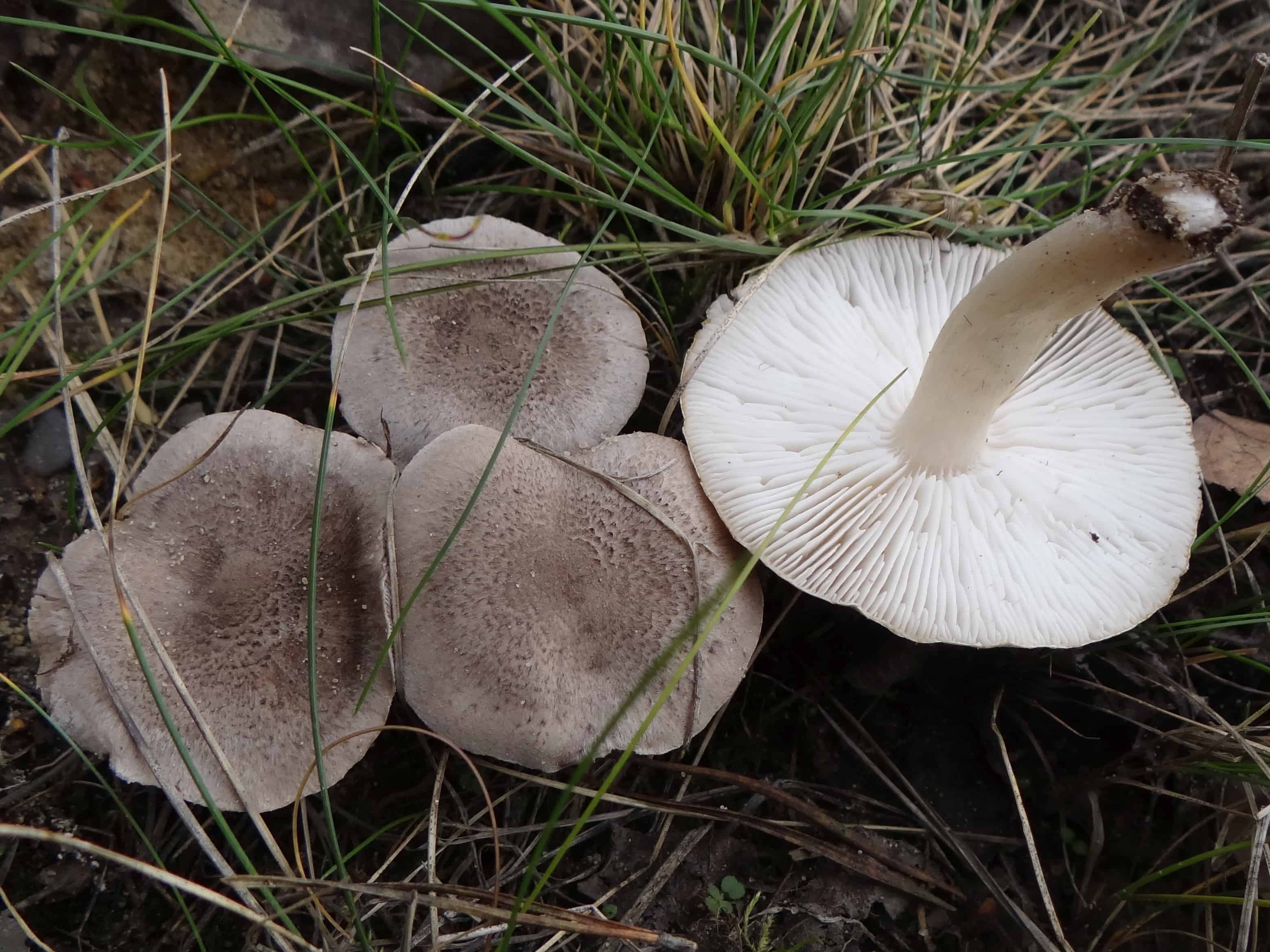
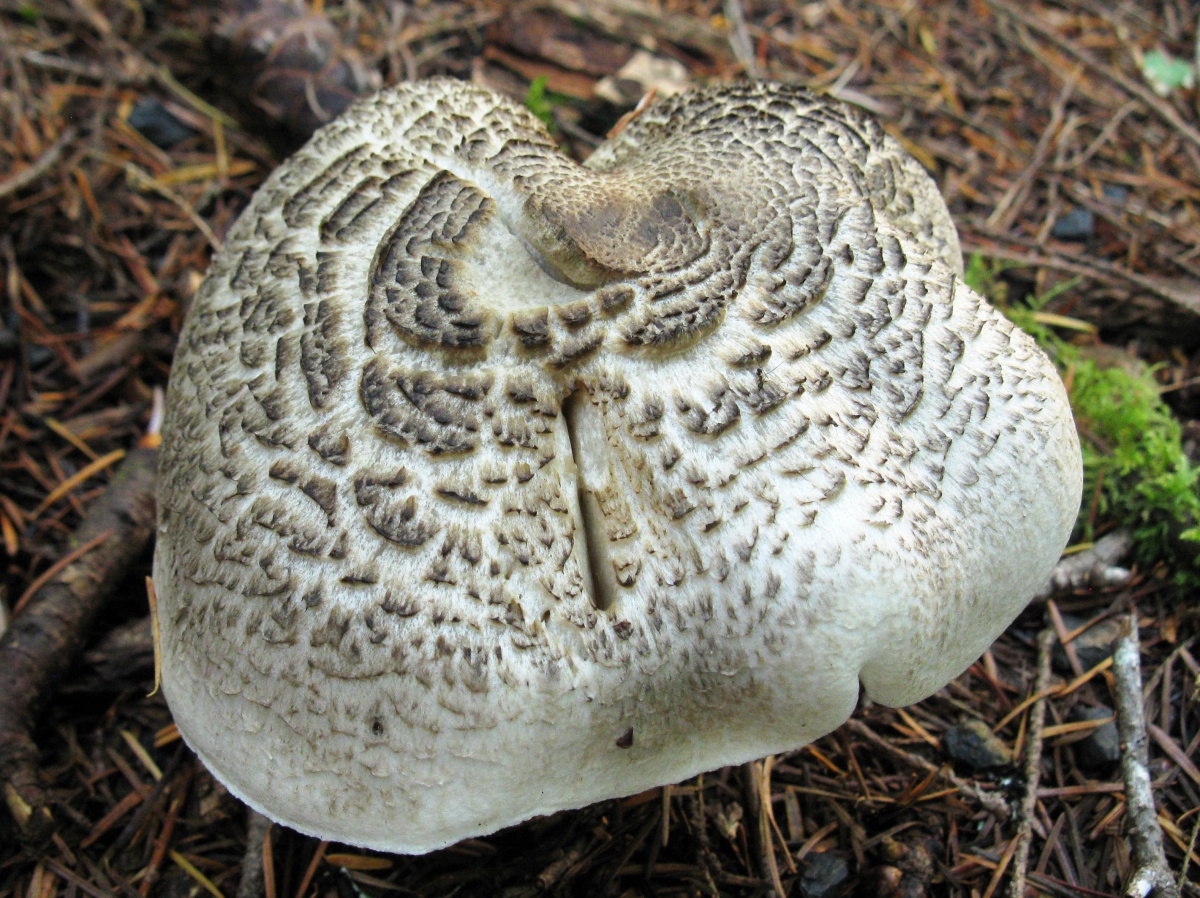
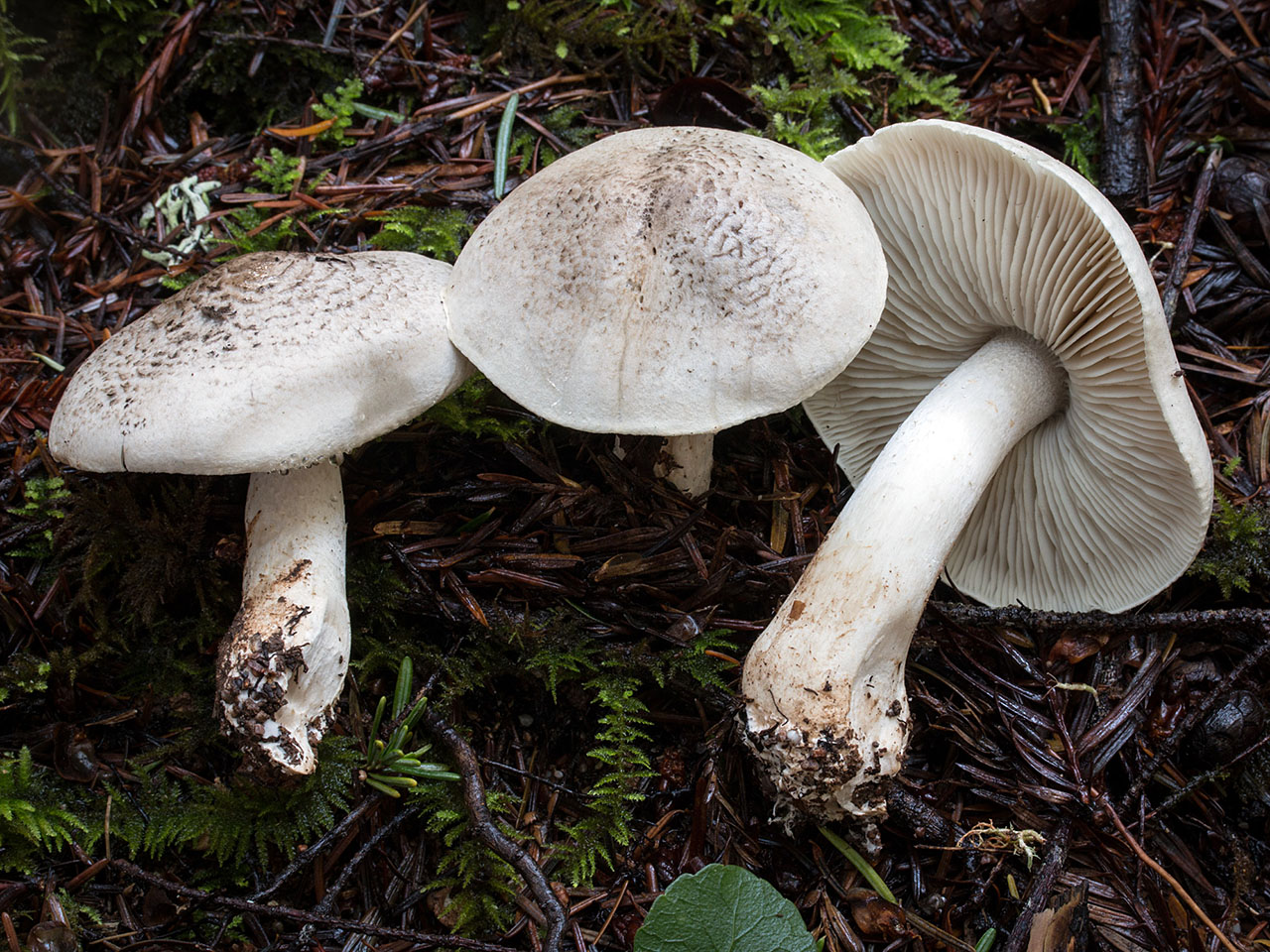
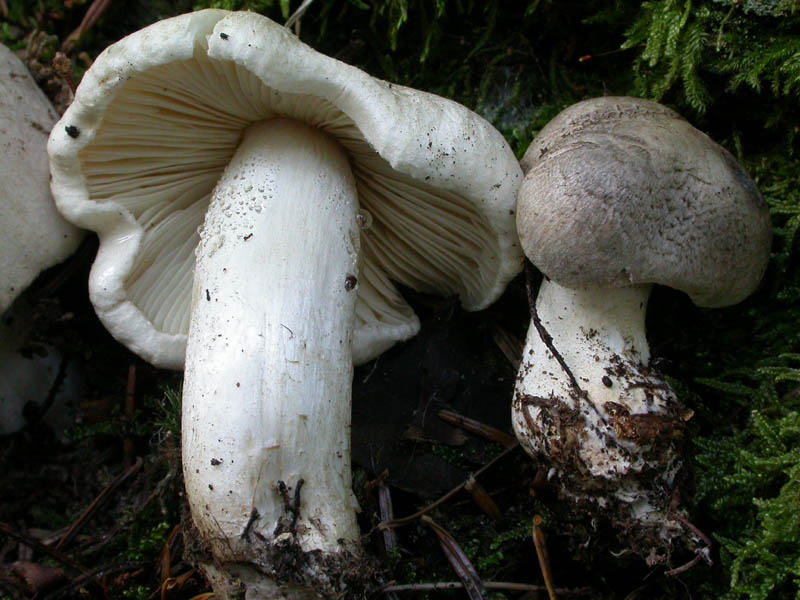
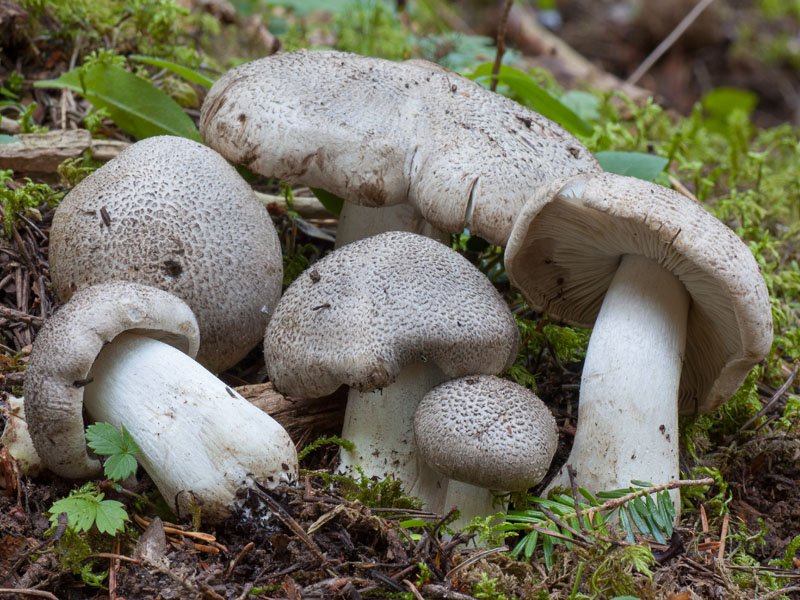
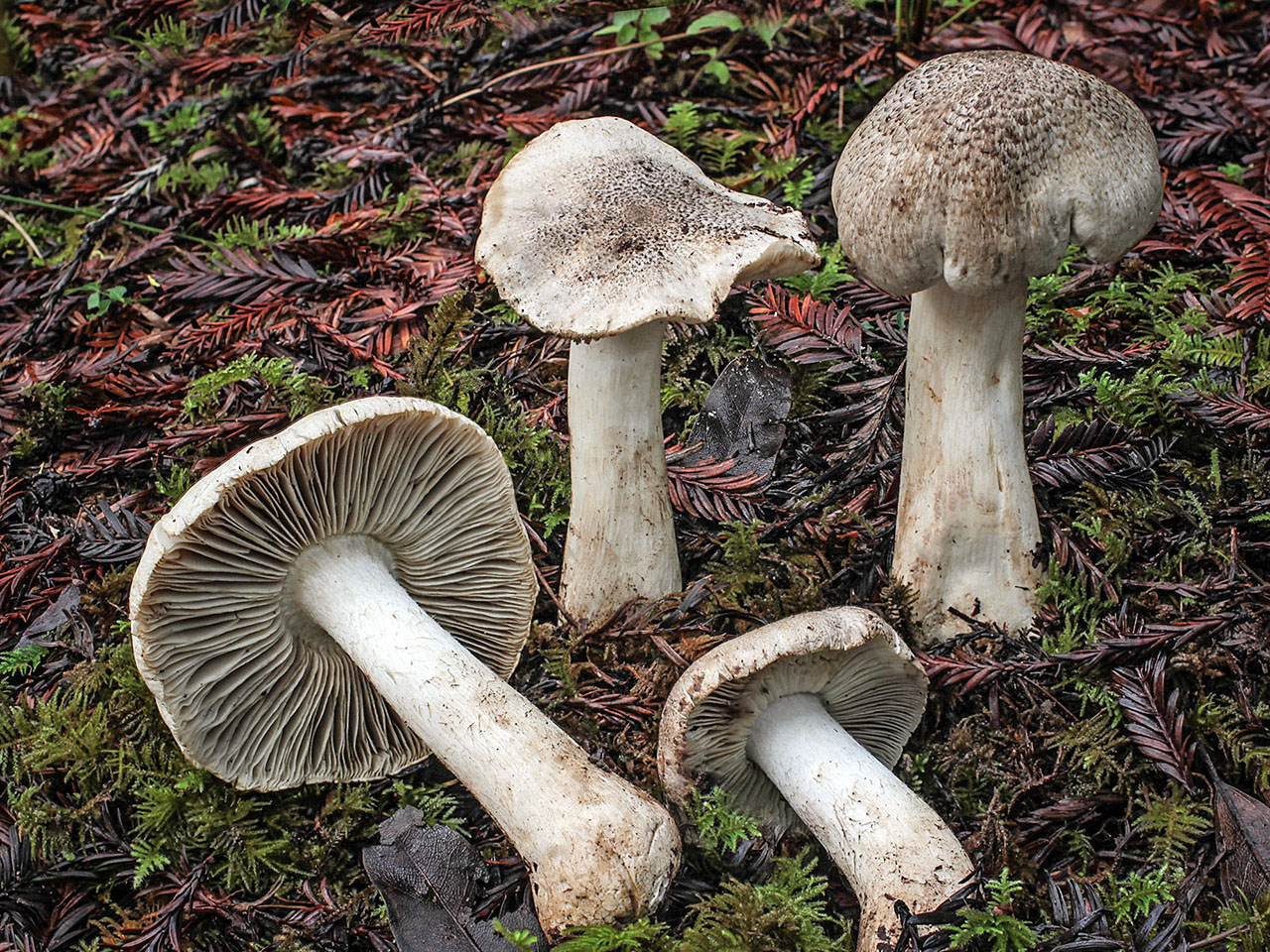
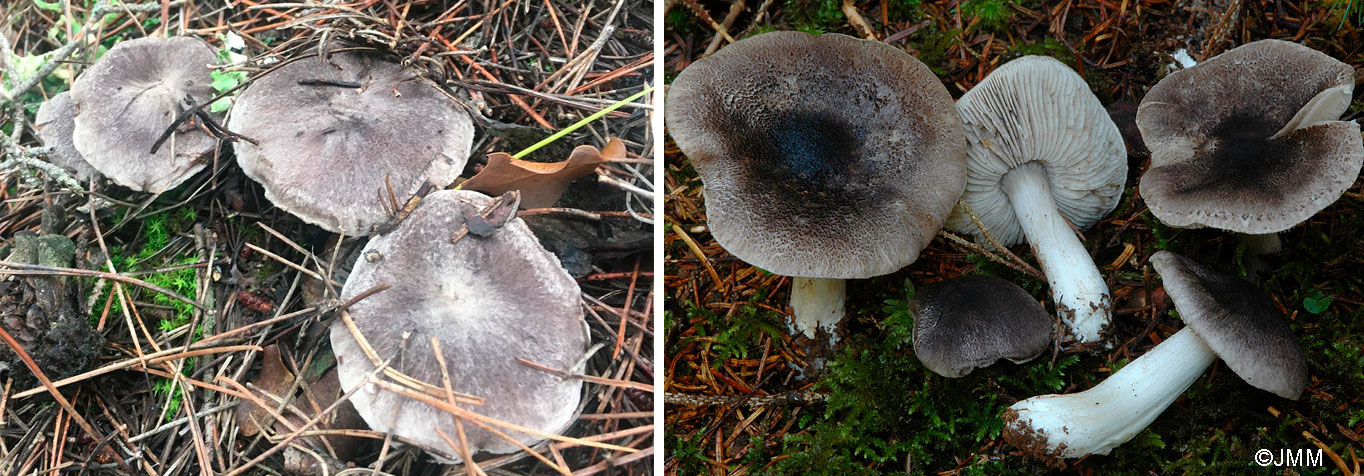
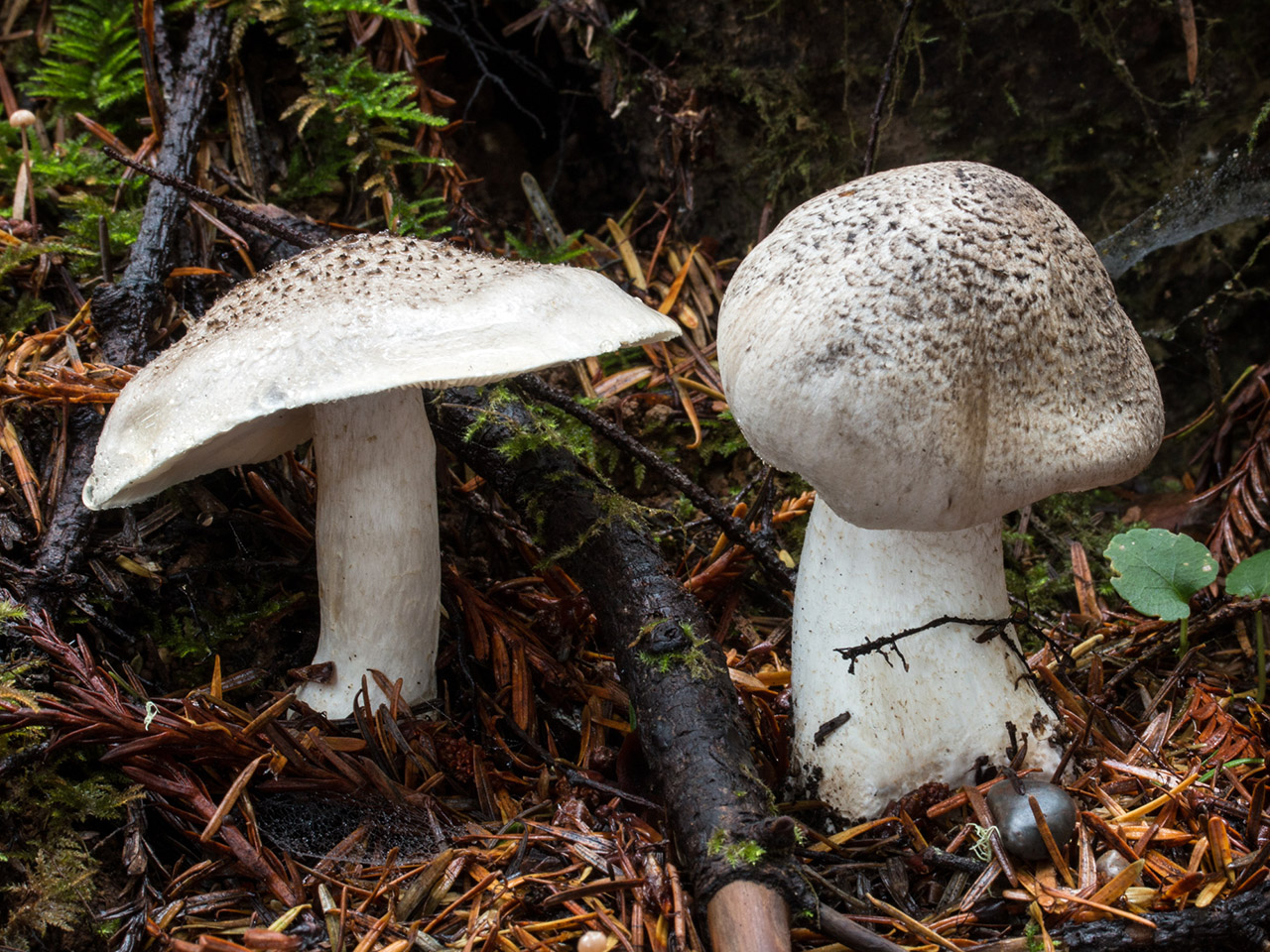
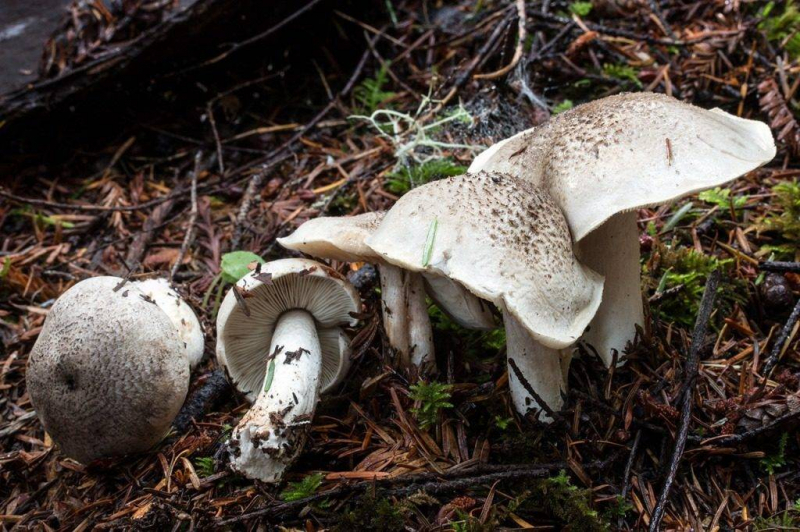
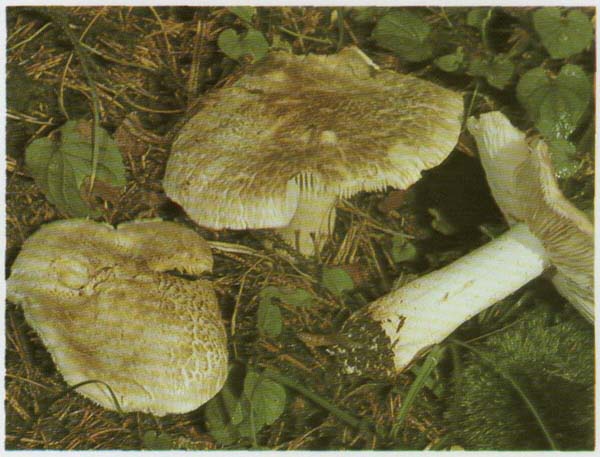
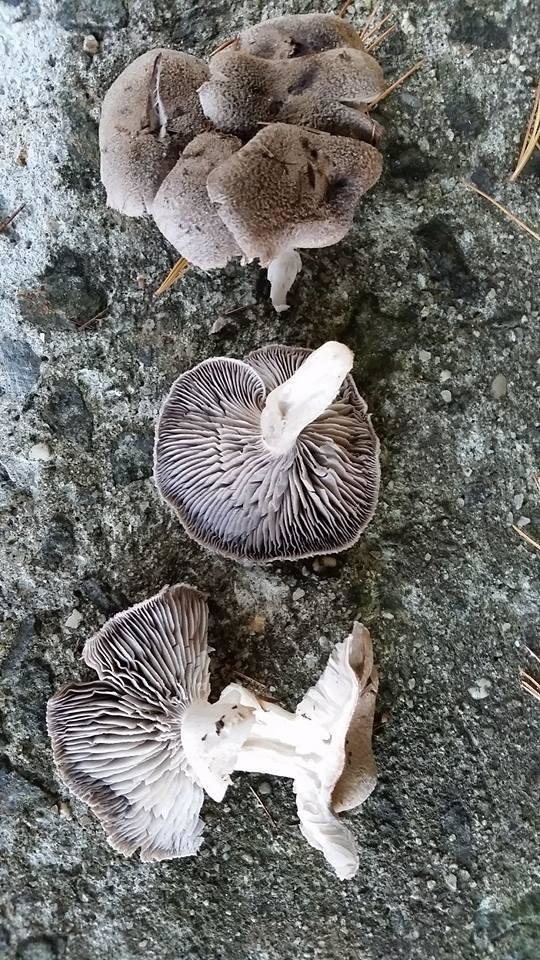
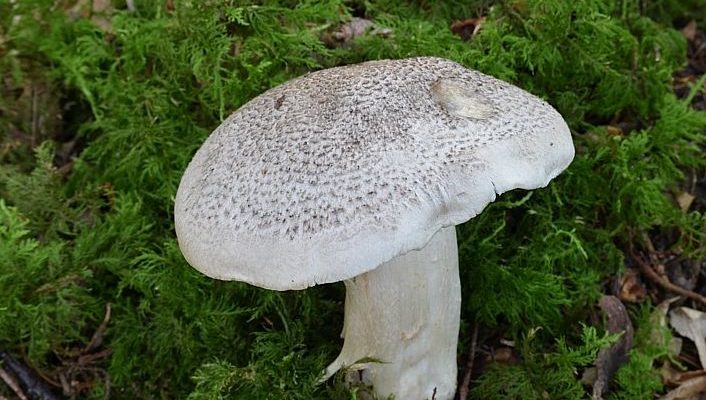
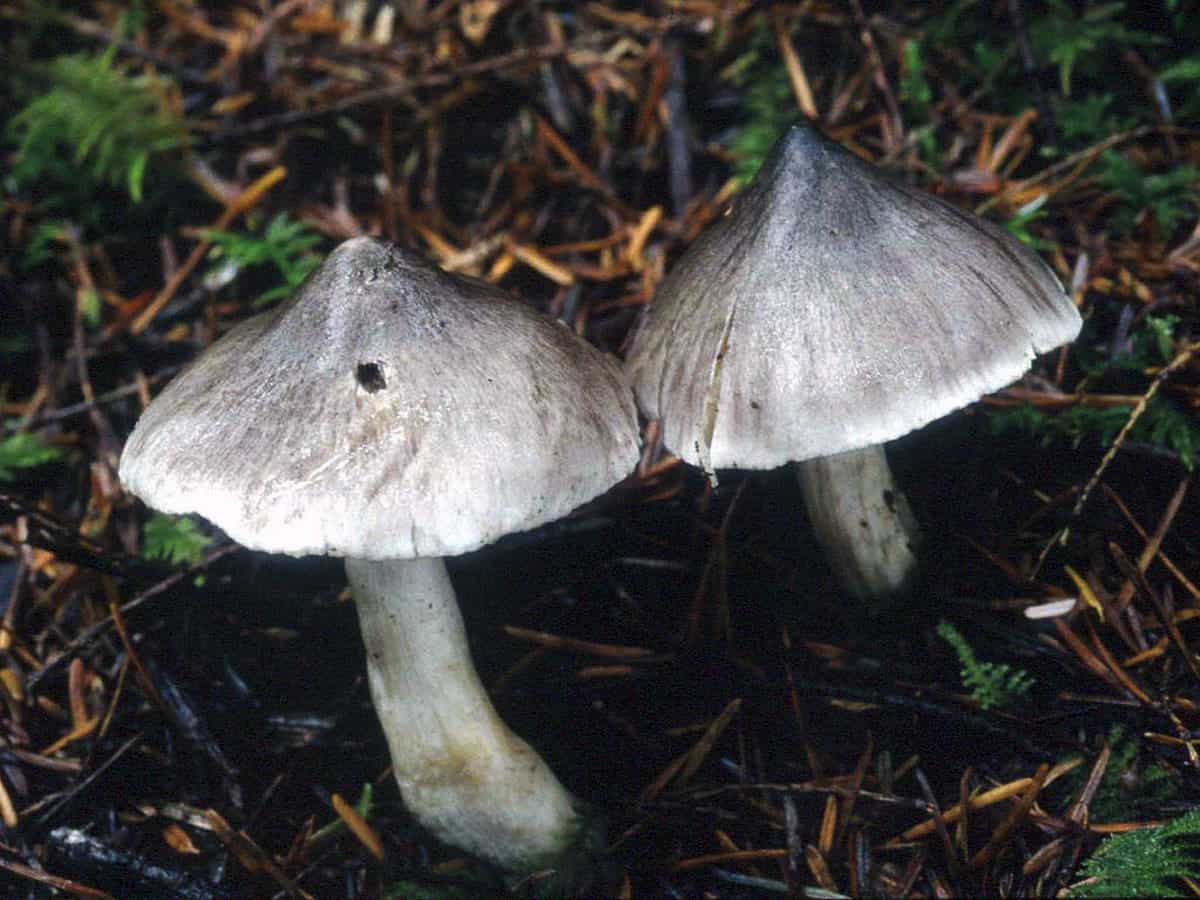
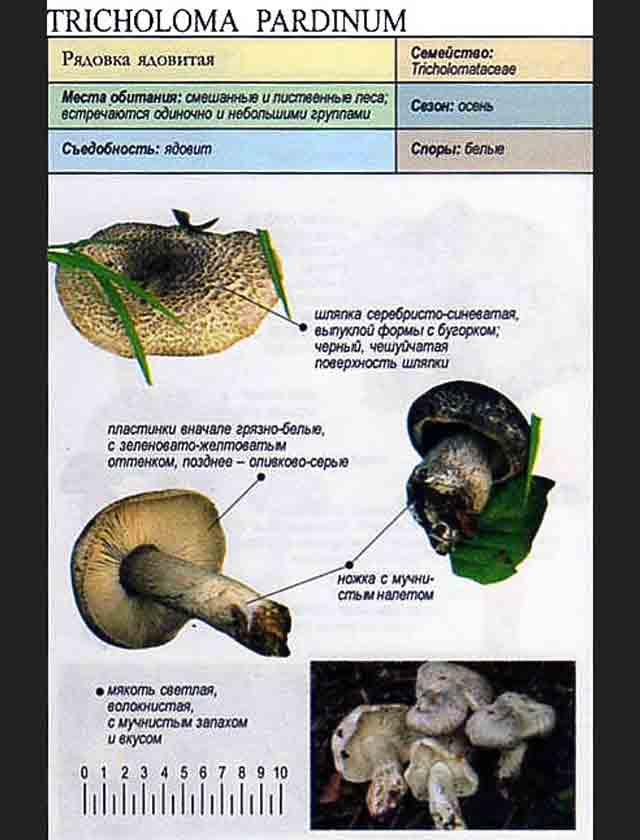
Hat: 4-12 cm, under favorable conditions up to 15 centimeters in diameter. In young mushrooms it is spherical, then bell-convex, in mature mushrooms it is flat-spread, with a thin, curled inward edge. It is often irregular in shape, with cracks, curves and bends. The skin of the cap is off-white, grayish white, light silvery gray or blackish gray, sometimes with a bluish tinge. Covered with darker, flaky scales, arranged concentrically, which give some "streak", hence the name - "tiger".
Plates: wide, 8-12 mm wide, fleshy, of medium frequency, adherent with a tooth, with plates. Whitish, often with a greenish or yellowish tinge, mature mushrooms emit small watery droplets.
Spore powder: white Spores: 8-10 x 6-7 microns, ovoid or ellipsoidal, smooth, colorless.
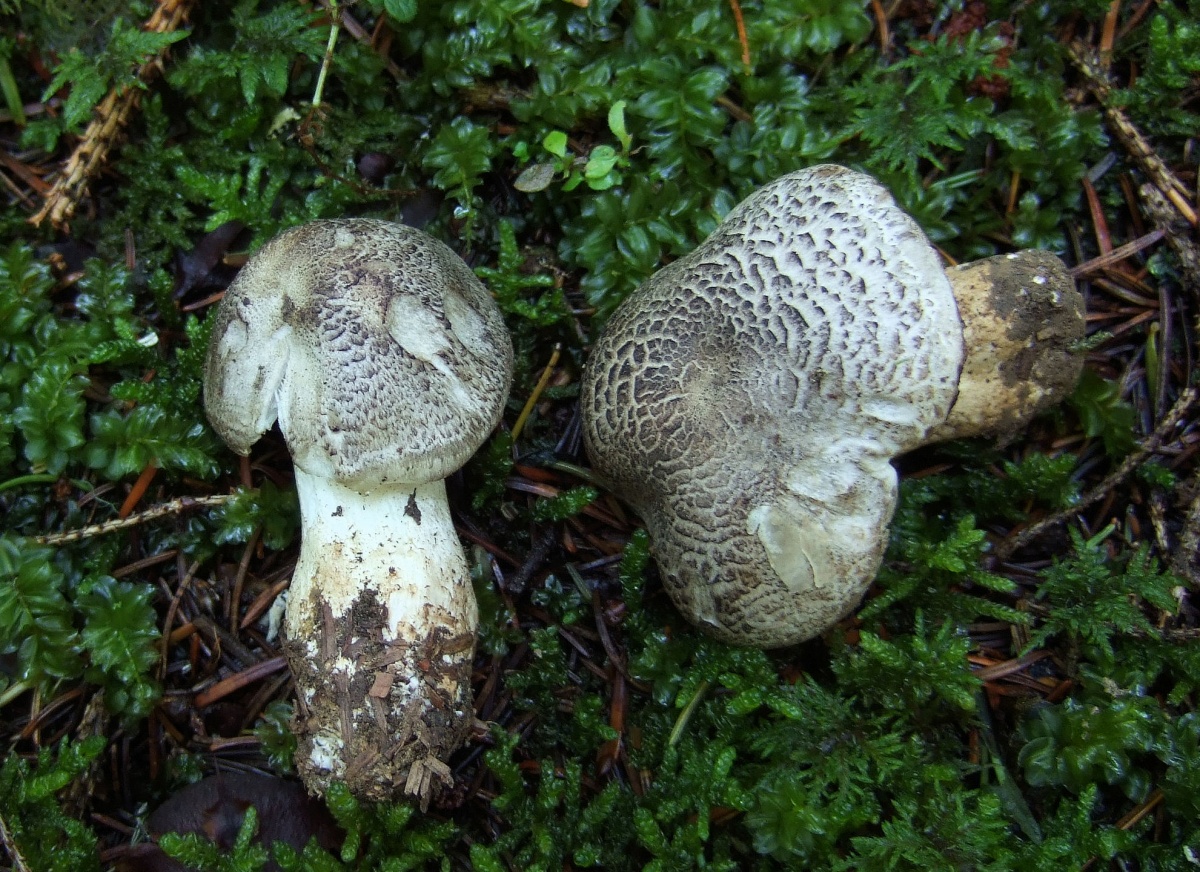
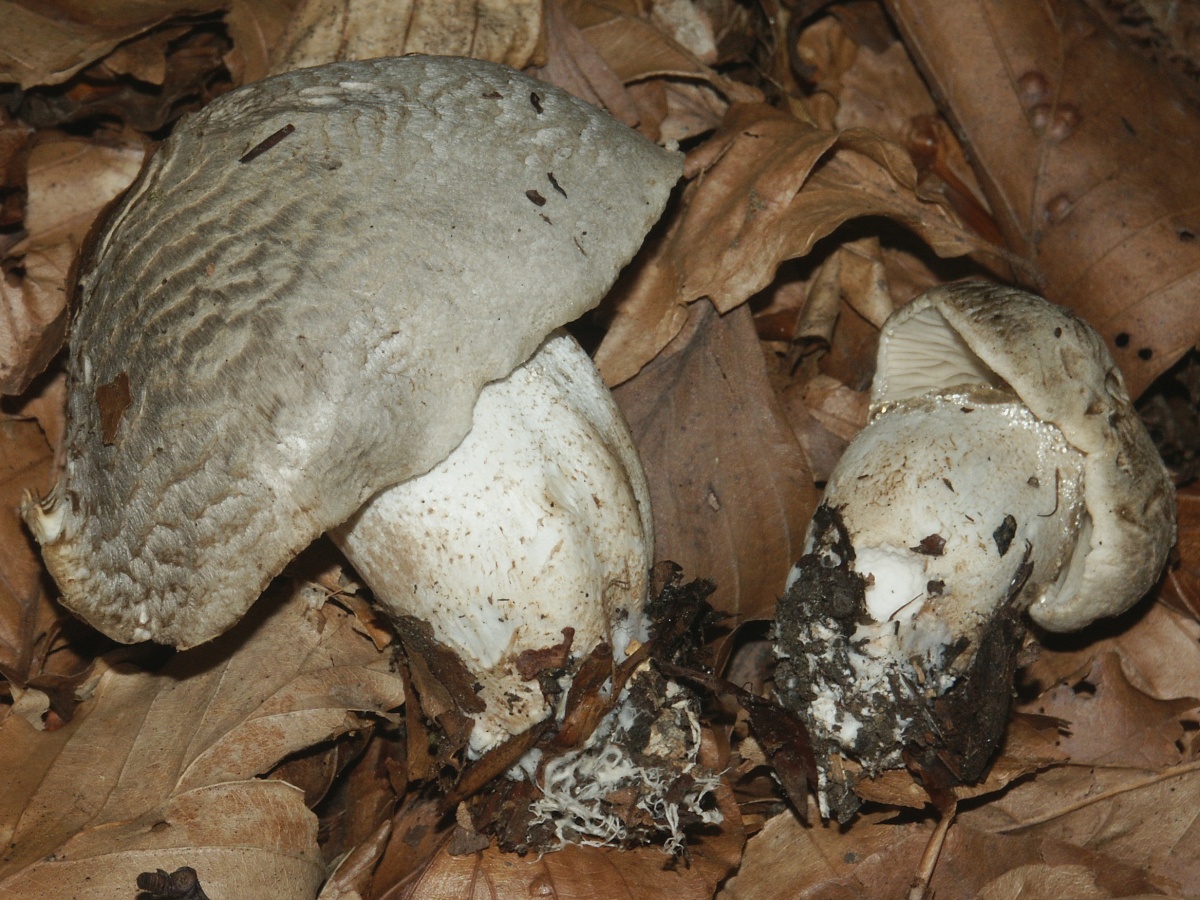
Stem: 4-15 cm in height and 2-3.5 cm in diameter, cylindrical, sometimes thickened at the base, solid, in young mushrooms with a slightly fibrous surface, later almost glabrous. White or with a slight ocher bloom, ocher-rusty at the base.
Flesh: dense, whitish, at the cap, under the skin - grayish, in the stem, closer to the base - yellowish on the cut, does not change color at the cut and break.
Chemical reactions: KOH is negative on the surface of the cap.
Taste: soft, not bitter, not associated with anything unpleasant, sometimes a little sweet. Smell: mild, flour.
Season and distribution
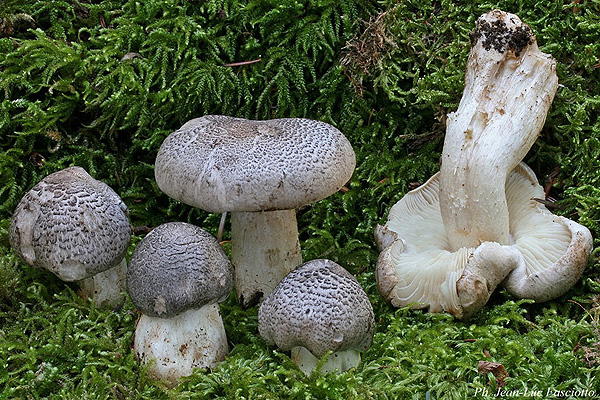
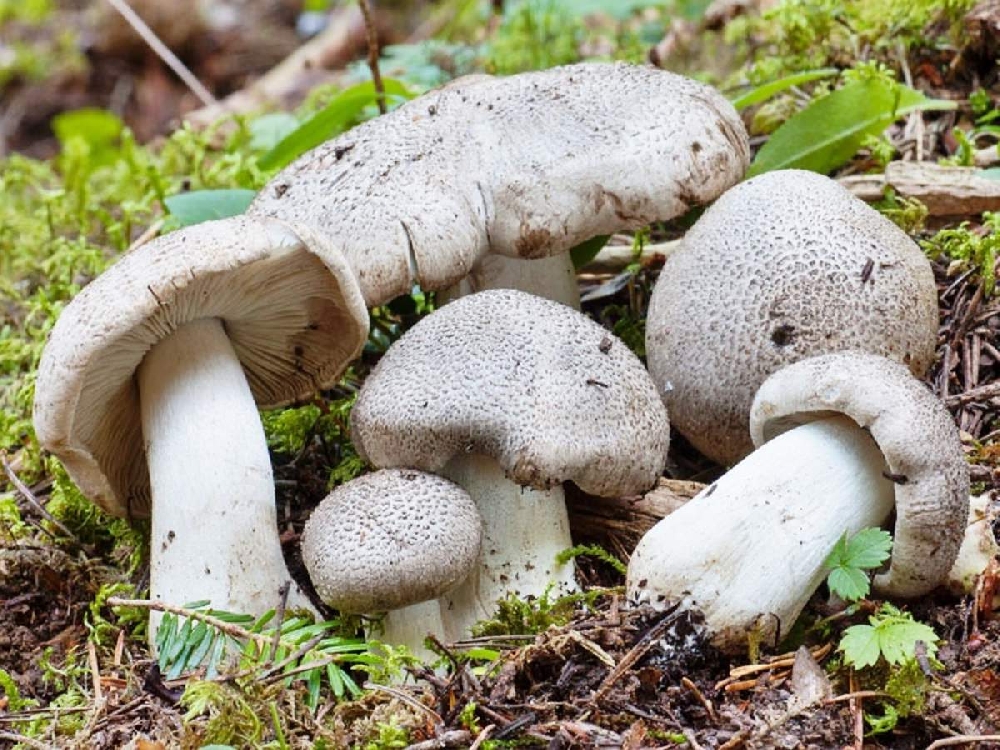
It grows on soil from August to October in coniferous and mixed with conifers, less often deciduous (with the presence of beech and oak) forests, on the edges. Prefers calcareous soils. Fruiting bodies appear both singly and in small groups, can form "witch circles", can grow in small "concretions". The fungus is common throughout the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, but rather rare.
Edibility
The fungus is poisonous, often indicated as deadly poisonous. According to toxicological studies, the toxic substance has not been precisely identified. After taking tiger ryadovka in food, extremely unpleasant gastrointestinal and general symptoms appear: nausea, increased sweating, dizziness, convulsions, vomiting and diarrhea. They occur within 15 minutes to 2 hours after consumption and often persist for several hours, with full recovery usually taking 4 to 6 days. Cases of liver damage have been reported. The toxin, the identity of which is unknown, appears to cause sudden inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the stomach and intestines. At the slightest suspicion of poisoning, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Similar species
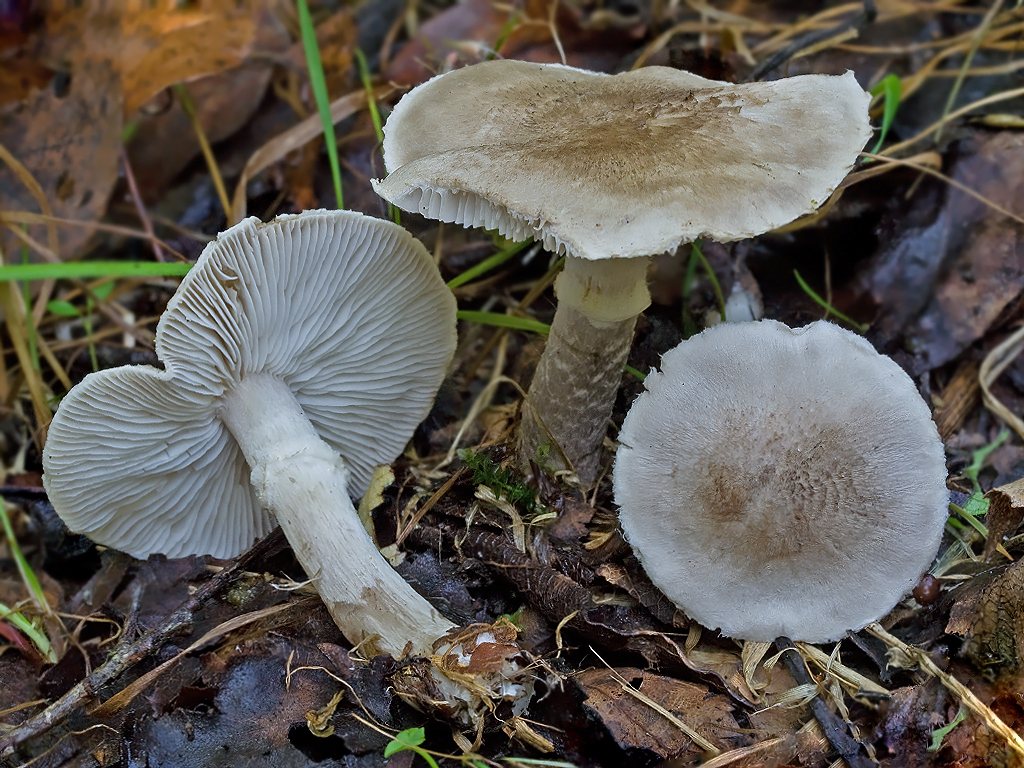
The row is earthy-gray (Tricholoma terreum) is much less "fleshy", pay attention to the location of the scales on the cap, in the Myshat the cap is radially striated, in the tiger scales they form stripes. Other rows with white and silver scaled caps
Primary processing and preparation
The earthy ryadovka is equally good for pickling, pickling, using in soups, salads. If necessary, when there are traces of worm infestation on the mushrooms, you can soak them for 2 hours in salted water.In general, all preliminary preparation is reduced to cleaning from soil residues and thorough washing from debris accumulated in the plates. Then the mushrooms are boiled, and after heat treatment, you can already make blanks for future use, freeze, cook your favorite dishes.
The earthy ryadovka is easy and pleasant to collect, the list of its culinary uses is wide enough, it has excellent taste - all these advantages are unlikely to leave indifferent both an experienced mushroom picker and a beginner on the "quiet hunt" trail.
Edible species and their description with photos
The most common edible track types are:
- Yellow-brown.
- Gray.
- Pigeon.
How to distinguish from false, inedible mushrooms?
Edible rows are confused with inedible and poisonous rows.
Most often, the following types are false mushrooms:
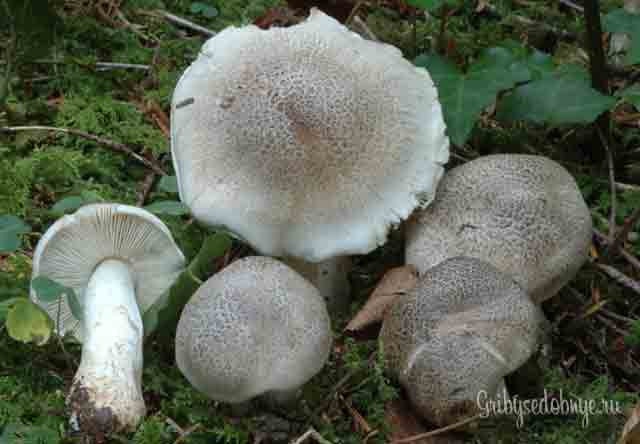
- Leopard - differs in the presence of plates and a leopard pattern on the surface of the cap.
 Tiger or leopard row
Tiger or leopard row
 Row pointed Soapy - can be recognized by the sugary smell, reminiscent of concentrated fruit soap, and by the pulp, which acquires a reddish tint on the cut.
Row pointed Soapy - can be recognized by the sugary smell, reminiscent of concentrated fruit soap, and by the pulp, which acquires a reddish tint on the cut.
 The row is soapy Brown - it has a brown flattened cap with a darkening spot in the center, as well as the flesh that turns red at the break.
The row is soapy Brown - it has a brown flattened cap with a darkening spot in the center, as well as the flesh that turns red at the break.
 Row brownWhite - has a completely white open hat and a special pulp, which turns pink at the break and emits a pungent smell, reminiscent of the smell of radish.
Row brownWhite - has a completely white open hat and a special pulp, which turns pink at the break and emits a pungent smell, reminiscent of the smell of radish.
 Row white
Row white
The main distinguishing feature of the edible species is their mealy odor. Sometimes even edible lane varieties can contain toxins. You can check the rows for toxicity in an elementary way: cut the pulp. If it is white, you can safely put the track in the basket. If the pulp has a yellowish or brownish tint, it is better to leave such a mushroom in the clearing.
How to distinguish poisonous mushrooms from podgreens?
- Smell. Dangerous doubles smell unpleasant, smell of powdery or laundry soap.
- Brittleness. Podgreen is an extremely fragile mushroom, it must be collected and processed very carefully.
- The color of the plates should be white, with a slightly yellowish tint, without any inclusions.
- The hat of the ryadovka gray is smooth and has stripes from the center to the edges, in the counterparts on the head there are scales, a pointed center, and a darker color of the inner circle.
- The taste is also different, it is bitter. This will help to unmistakably recognize the poisonous species.
The mice have an inconspicuous appearance. But they are pleasant to the taste, fragrant
To distinguish useful individuals from poisonous ones, it is important to learn how to distinguish them by description. It should be remembered that if edible mushrooms come into contact with poisonous mushrooms during growth, they can receive a portion of the poison from a neighbor.
It is better to leave such representatives in the forest. It is necessary to sort the mushrooms before they get into the general basket. Take those mushrooms in which you are 100 percent sure - this simple method will save you from poisoning.
Poisonous mushrooms ryadovka: types, description, names, photos
As mentioned above, poisonous rows are much more toxic than fly agaric.
Therefore, it is important to distinguish between those mushrooms that cannot be eaten in order to avoid severe poisoning. Types, description, names and photos of poisonous mushrooms of the row:
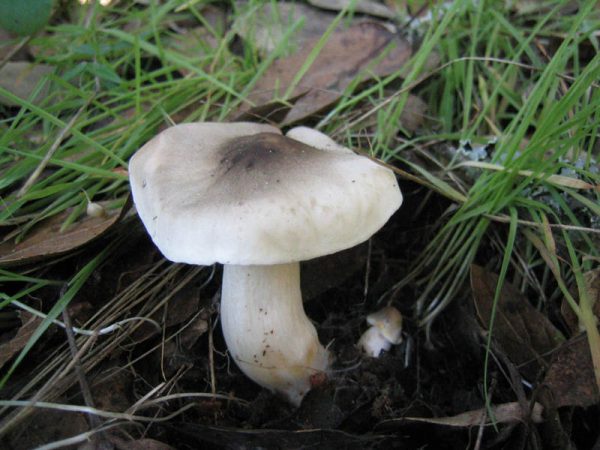
The row is white (from the Latin Tricholoma album). Outwardly it resembles a champignon. The leg is long - up to 10 cm, there is a slight thickening at the bottom. The color of the leg is the same as that of the cap. In mature individuals, the thickening below becomes brown. The cap is at first rounded, then it becomes wide and open - up to 10 cm. The flesh is white, when cut it becomes pink. The smell is specific - musty.

Poisonous mushrooms ryadovka: description, names, photo of ryadovka white
The row is sulphurous (from the Latin Tricholoma sulphureum). This mushroom is considered to be of low toxicity, but accordingly, it still cannot be used for food.It's just that the poisoning will not be as strong as when using, for example, a white row. The leg and cap are of an unpleasant gray-yellow color.
The old mushroom will turn brown over time, and the cap will become velvety and grow from 3 to 8 cm. There is a notch in the middle of the fossa. The leg is long - up to 11 cm. The bottom is covered with scales and thickened. It can also expand at the top. The plates are sparsely located, uneven. The pulp smells simultaneously of hydrogen sulfide, tar and acetylene.
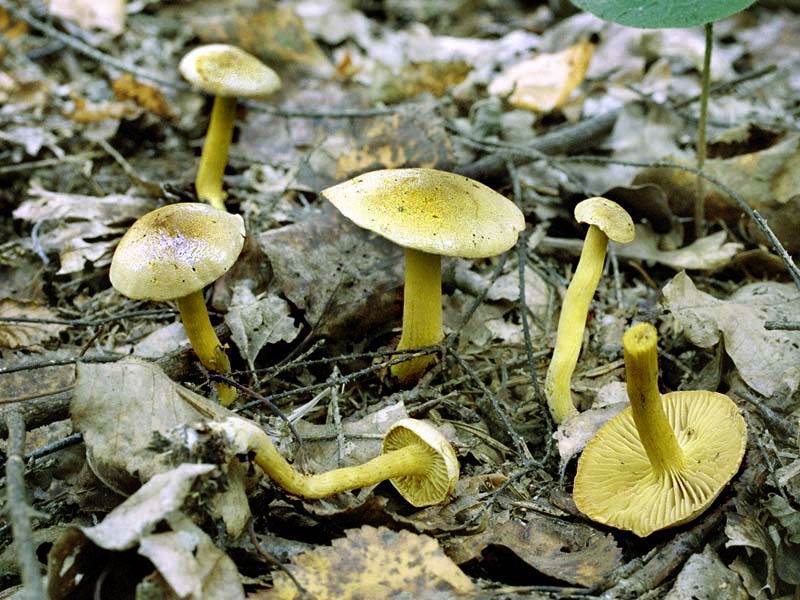

Poisonous mushrooms ryadovka: description, names, photo of ryadovka sulphurous
Row pointed mouse (from Latin Tricholoma virgatum). A highly poisonous mushroom. Small size hat with diameter up to 5 cm. It resembles a bell of a young mushroom. As it grows, it becomes prostrate, but the tubercle in the middle remains. Mouse-gray skin.
The leg is long - up to 15 cm, thin. The color of the leg is white; towards the bottom, the surface turns pink or yellow. The plates may be covered with yellow spots. The pulp is odorless, but has an unpleasant bitter and even pungent taste.
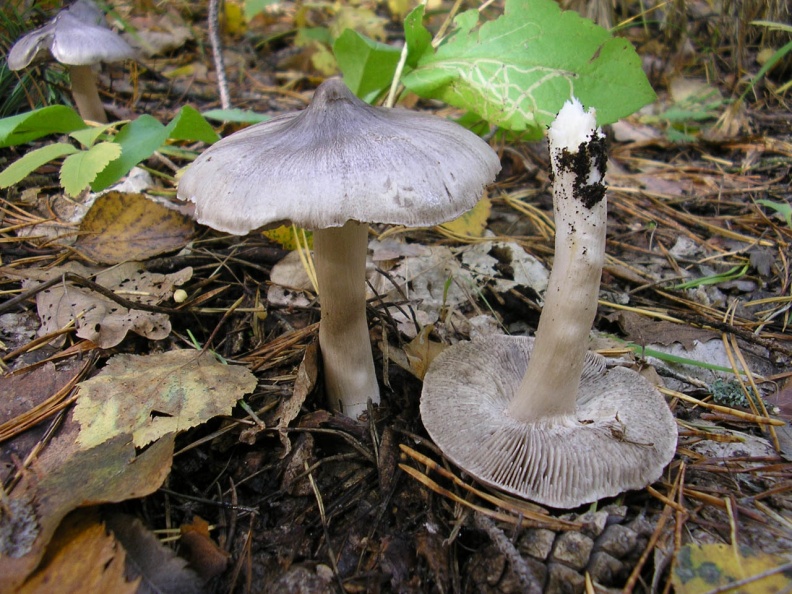

Poisonous mushrooms ryadovka: description, names, photo of ryadovka with a pointed mouse
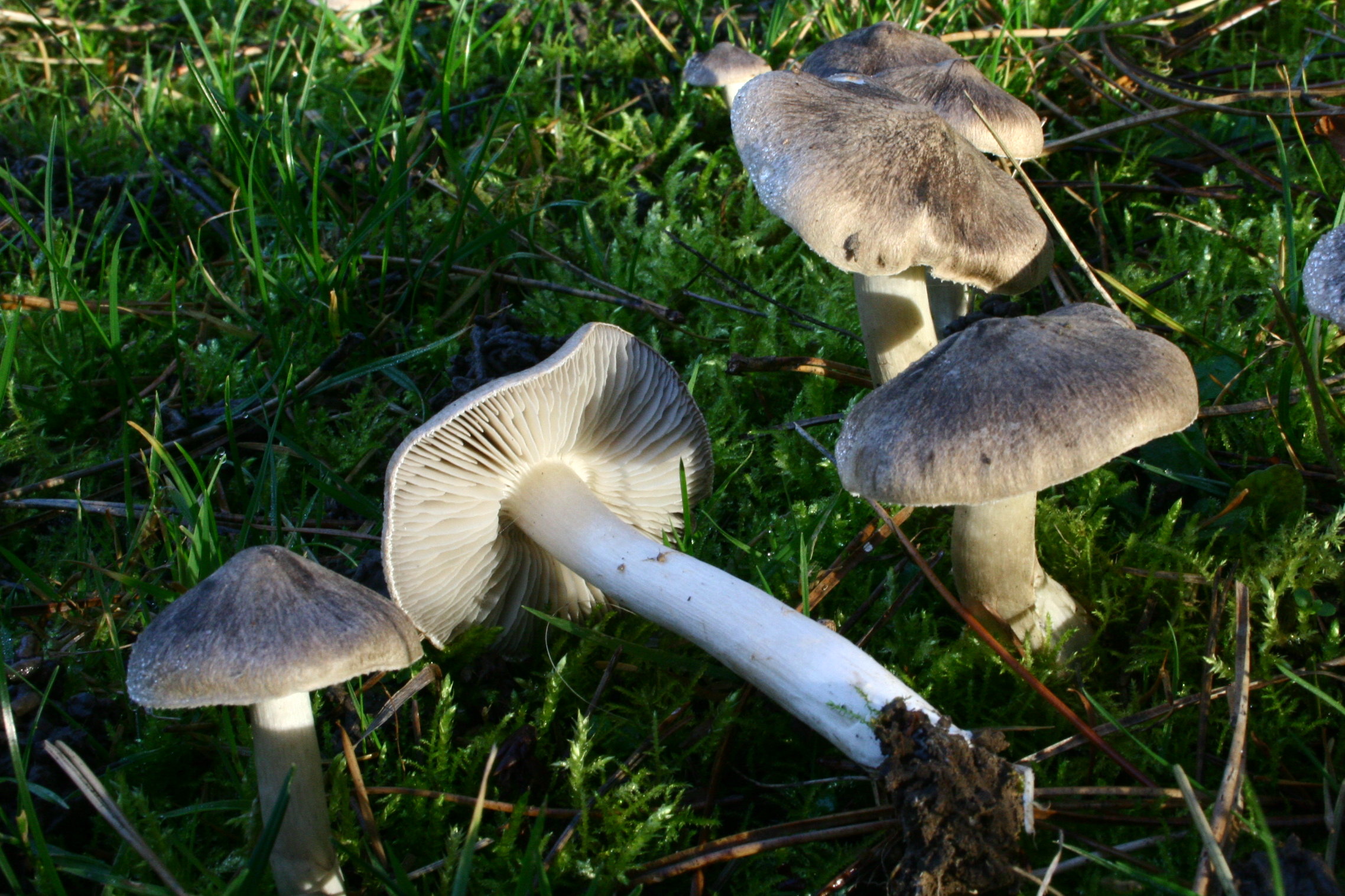
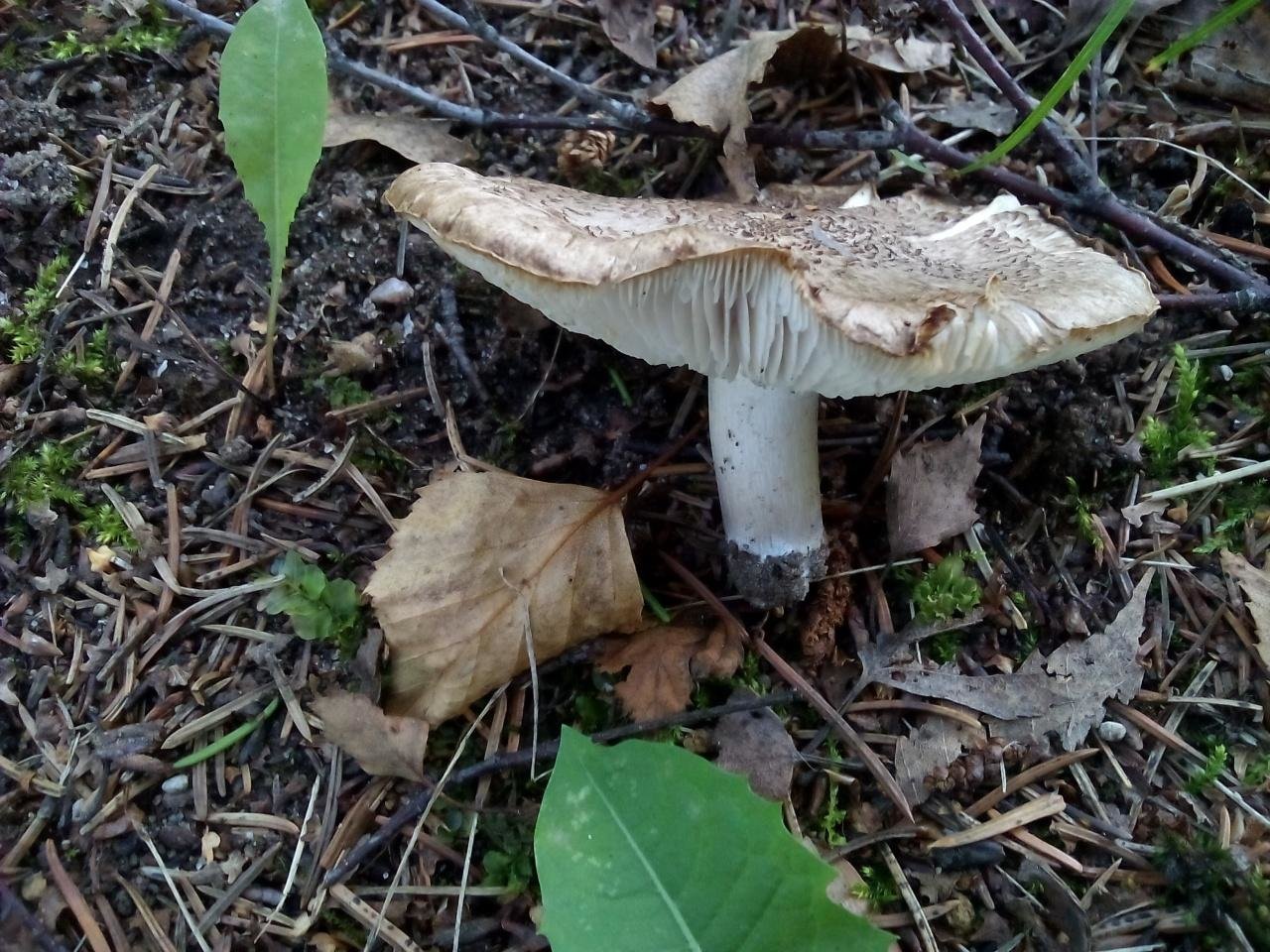
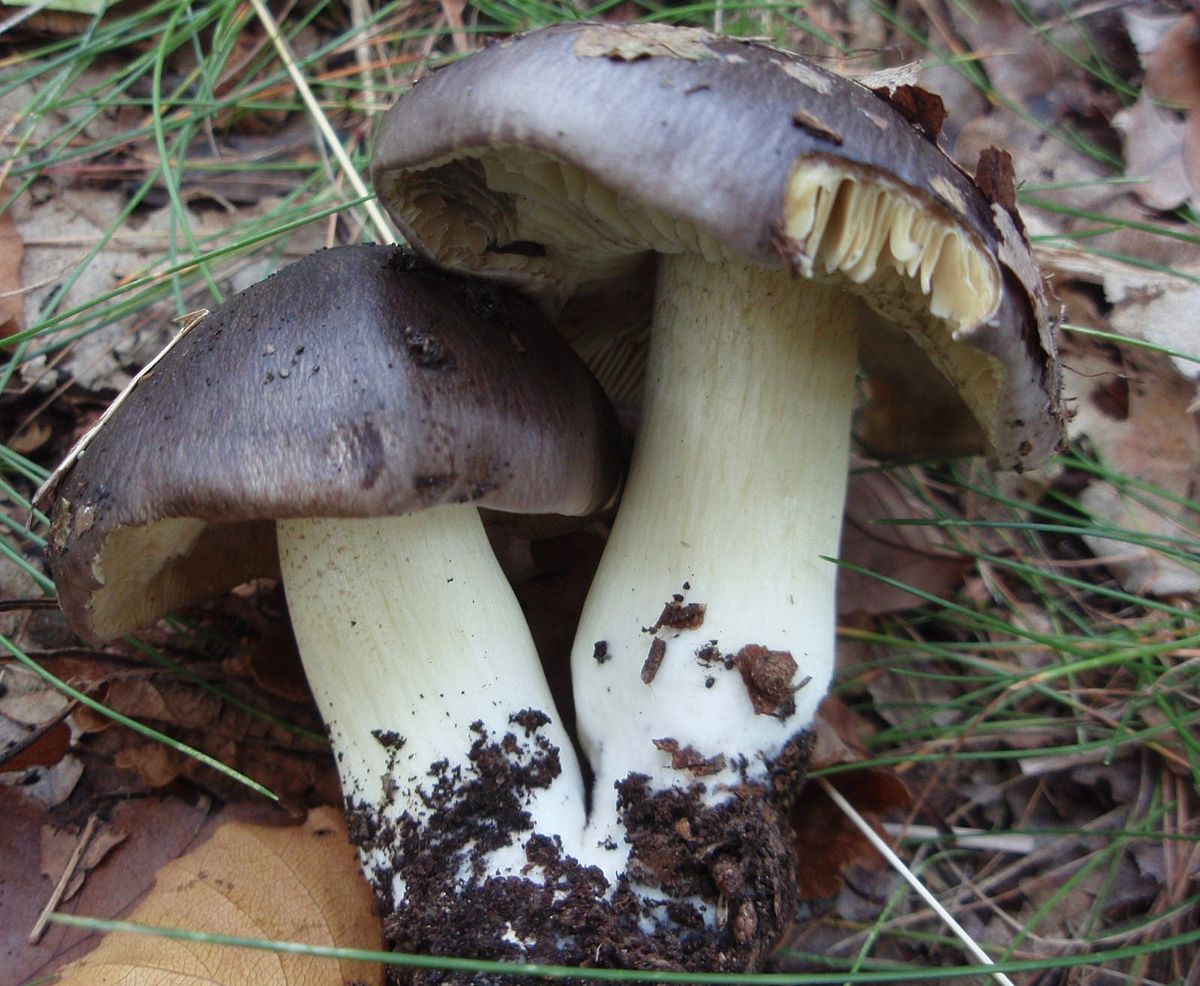
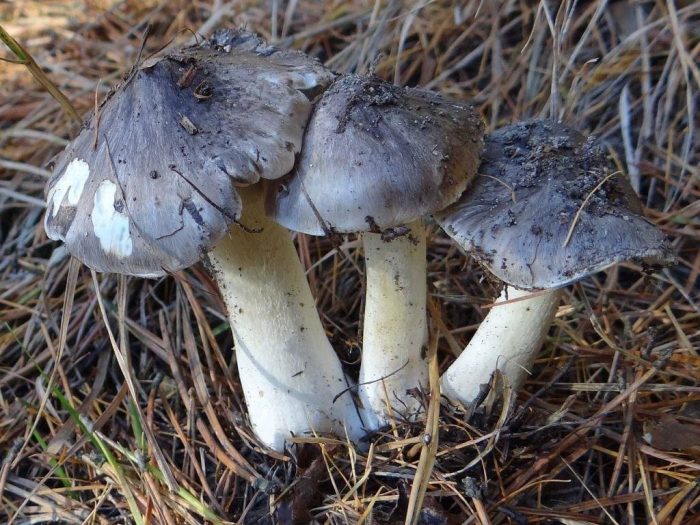
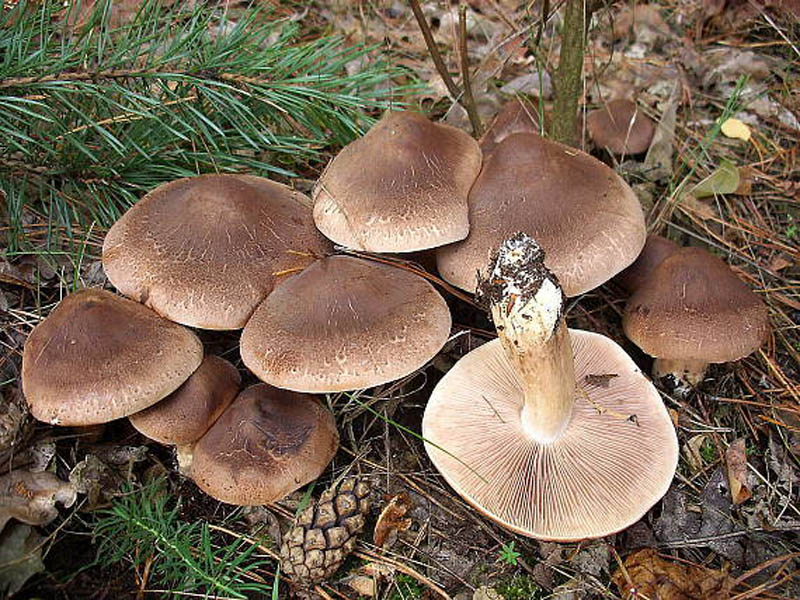
The row is tiger, poisonous leopard (from the Latin Tricholoma pardinum). This mushroom is rare and highly poisonous and can easily be confused with edible species. The cap is large with a diameter of up to 12 cm. In a young mushroom, it looks like a ball, then it lengthens and resembles the shape of a bell. The old mushroom takes on a flat, wide cap. The skin is of an ugly, dirty gray color, covered with dark scales in the form of flakes.
A similar edible row has the same hat, but sticky and smooth. The leg is long - up to 15 cm, thin. Expands towards the bottom. Has a velvety ocher coating. The plates are sparse, but dense and fleshy. In adults, droplets of moisture can be seen between the plates. The flesh is gray, yellow at the leg. It does not taste bitter, and has a mealy smell.

Poisonous mushrooms ryadovka: description, names, photo of ryadovka leopard
In this article, we talked about the most popular edible types of ryadovok mushrooms, conditionally edible, which can be eaten, but they have a minimum nutritional value. Remember the description and save a photo of poisonous and toxic row mushrooms. If you find a mushroom and doubt its quality, it is better not to take it, because health is more important than the amount of the harvested crop!
Growing places
Poisonous ryadovka tiger grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, but is more common in conifers. If it grows on a deciduous tree, then it must be beech. The fungus prefers calcareous soil and sandy terrain. Most often it grows in groups, which seasoned mushroom pickers often call the "witch's circle".
The growing season for the tiger row is from August to October. Growth peaks in September.
Tiger rowing among the people, as well as in some reference books and encyclopedias, is called poisonous ryadovka, tiger ryadovka, leopard ryadovka. You can meet it from the second decade of August to the first decade of October in mixed (the presence of oak or beech is required) or coniferous (pine) forests. Grows singly or in small groups. In the northern and European parts it comes across quite rarely, in the southern regions it is more common.
The hat is from 4 to 12 cm in diameter, at first it has a bell-shaped shape, then it is convex-outstretched with a lobed cracked edge. The surface is gray, gray-brownish with a bluish tint with a darker center. Black-brown scales are concentrically located on the surface. Thanks to its scales at a distance, the mushroom looks like a spotted one.
The plates are frequent and adherent, at first, a dirty whitish color with a barely noticeable greenish tinge, later darker, up to yellow-olive. In mature mushrooms, small watery droplets may form on the plates.
The stem is cylindrical or clavate, rather short, up to 5 cm long, and 1-3 cm in diameter. The structure is dense, solid. Above, light, whitish, brownish downward with scales.
The pulp is loose, light, slightly pink at the cut of the leg, has a pleasant flour smell and taste.
Tiger ryadovka is a highly poisonous mushroom. Poisoning occurs 1-3 hours after consumption. There is severe gastrointestinal upset, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Eating a large amount of these fungi and not providing first aid can be fatal.
It can be confused with other types of rowing (edible), for example, rowing with gray. The main difference is the presence of scales on the gray cap. Also, a poisonous ryadovka should be protected by mushroom pickers, who are accustomed to determining the edibility of a mushroom by taste and smell, which it has very pleasant.
Similar species and how to distinguish from them
The poisonous tiger rower can be confused with useful representatives of the row family. To prevent this from happening - you need to look at the mushroom carefully. The main feature of the poisonous species is a silvery-gray cap with a bluish tint, abundantly covered with dark-colored scales, with a mealy bloom on the stem.
It is possible to distinguish useful mushrooms of the family from poisonous ryadovki by several signs.
- Earthy (Tricholoma terreum) - smaller, the back layer of the cap does not have yellow and green tints, in the pulp - the smell and taste of flour. Dark mouse gray without a blue tint.
- Gray (Tricholoma portentosum) - no scales on the cap.
- On the entire surface of the black-scaly (Tricholoma atrosquamosum) there are dark scales, the edge of the cap is not wrapped. The leg is light, blackening to the base.
Evaluation of taste and recipes
Pigeon ryadovka is an edible mushroom that is suitable for preparing a wide variety of dishes. It is good in sauces and soups, it is dried, boiled, grilled, served on a festive table. And what an extraordinary aroma of doves gives to meat! All types of edible rows can be pickled and salted for the winter. Cooking them is not at all difficult.
Primary processing
Soak the mushrooms in cold water before cooking. Further, if desired, you need to remove the skin. Then the heat treatment is carried out for fifteen minutes.
Cooking
Add 1 tbsp to a liter of water. l. salt and half a teaspoon of citric acid.
- Bring to a boil in a container.
- Pour the mushrooms into boiling water, cook for 20 minutes under the lid.
- After 10 minutes, add a bay leaf, a few clove buds and a couple of black peppercorns.
- Leave to infuse for a while, then drain the water. You can enjoy the great taste of the dove.
Pickling
Ingredients:
- half a liter of wine vinegar (it will give a special aroma and smell);
- one and a half kg of rows;
- one onion;
- one carrot;
- a few peppercorns;
- laurel leaves;
- a pair of carnation buds;
- 2 tsp Sahara;
- 2 tsp salt.
Marinating rows:
- Mushrooms are washed, sorted, large ones are cut.
- Place in a suitable dish and soak in water.
- Then cook for about twenty minutes.
- Finely chop the onions and carrots.
- Vegetables along with spices are immersed in a container of vinegar.
- The marinade is boiled for about a quarter of an hour.
- Next, the mushrooms are mixed with the marinade and kept on fire for another five minutes.
- In the meantime, you should prepare containers for canning. They are washed with baking soda and sterilized.
- All vegetables and mushrooms are put in jars.
- The marinade is cooked for ten minutes and is also placed in jars.
- After all the above manipulations, the rows are immediately rolled up.
How to pickle a dove
Ingredients:
- 400 grams of salt;
- 10 kg rows;
- dill, pepper, garlic;
- laurel, black currant leaves and horseradish.
Preparation:
- Pre-washed and prepared mushrooms must be placed in a sterile container. Rows should be laid out with their legs up. Sprinkle each layer with spices and salt. Place a few horseradish leaves and dill on the bottom.
- Next, the cans are rolled up and moved to a cool place.
- After 40-50 days, pickles can be served.
Description of appearance
The poisonous ryadovka has a fleshy structure and an elastic dense consistency. Its spore powder is white and spreads over long distances without problems.
The cap of young mushrooms reaches 12 cm in diameter and has a spherical shape. At a more mature age, the ryadovka cap becomes flat, with thin curled edges and a slight bulge in the center. The skin of the cap is covered with peculiar scales, which are darker in color than the rest of the body of the mushroom. Most often, there are specimens with an off-white, gray, white or gray-white, blackish-gray or light blue shade of the cap.
The width of the plate also reaches 12 cm. They are serrated in structure, rather rare and fleshy. Young plates are whitish, often with yellow or green blotches. Watery drops appear in places on mature mushrooms.
Tiger row grows on high (up to 15 cm) legs of medium width (2-3.5 cm). The shape of the leg is solid, perfectly straight, less often - extended towards the base. In a young fungus, the surface of the leg is slightly fibrous and almost glabrous. The color scheme of this part of the row varies from white with an ocher bloom to an ocher-rusty hue.
The pulp is very dense, gray or yellowish in color; when cut, it does not tend to change color. The taste is mushroom without bitterness, the smell of flour.
Back to content
Similar types and differences from them
Most often, the earthy ryadovka is confused with the poisonous ryadovka (tiger) (Tricholoma pardinum) and the pointed ryadovka (Tricholoma virgatum). With a similarity in the outlines of the fruit body, these both species differ in the larger sizes of the caps.
Detailed differences are shown in the table.
| Variety name | Hat | LPs | Leg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poisonous | Silver-gray or bluish-brown tones, up to 12 cm in diameter, with curled edges, no tubercle | Serrated indentations fused with the stem, off-white with an olive-yellow or gray-green tint | Dense, 4-8 cm in height, 1-3 cm thick, light or brownish, with a mealy bloom |
| Pointed | Ash gray with stripes at the edges, about 8 cm in diameter | Deeply recessed, almost free | Whitish or light gray tone, with longitudinal stripes, 6-8 cm high and 1.5-2 cm thick, swollen near the soil |
In coniferous and deciduous forests, you can fearlessly collect a similar edible variety, carved row (Tricholoma scalpturatum). Its differences from the earthy row:
- more miniature sizes - the diameter of the cap is 3-5 cm, the thickness of the leg is 0.5-0.7 cm;
- the presence of a slight swelling near the base of the leg;
- tender, delicate, with a mealy tinge, taste and smell of pulp.
Description and characteristics of the mouse mushroom
The mouse belongs to the lamellar mushrooms. This species is also called undergrowth, shaded ryadovka, gray ryadovka, gray sandpiper, podosnovik, cockerels.
The cap of the mushroom is small, 10–12 cm in diameter, of various colors - from white to dark gray. The hat is fleecy, sometimes smooth. After rain, it becomes sticky mucous. In young fungi, it is twisted to the stem, in more mature ones it turns outward and may crack at the edges. Dark stripes extend from the center to the edges.
Under the cap there are sparse, wide, winding plates of white (sometimes yellow) color. The leg is dense, up to 10 cm high, often curls at the cut. The mushroom has a rather pleasant, definite smell.
Mushroom umbrella description
The edible umbrella mushrooms live up to their name. In the process of growth, forest gifts open their hats, previously adjacent to the legs, like an umbrella. However, many mushroom pickers do not know special signs confirming the edibility of the mushroom and distinguishing it from the toadstool counterparts and undeservedly bypass the delicious mushrooms.
- Edible umbrellas smell nice where the cap is broken, resembling a nut. The cut point does not change color upon contact with air.
- The leg of the non-poisonous mushroom has a three-layer ring framing it in the form of a skirt. Such an accessory can be easily moved up and down, while in inedible representatives it is firmly attached or completely absent.
- An important criterion by which you can immediately recognize a good umbrella mushroom is size.Edible individuals, when opened, reach 30 cm in height with a cap diameter of 40 cm, while externally identical toadstools have legs no more than 13 cm high and caps no wider than 14 cm in diameter.
- In the process of growing, the caps of umbrella mushrooms are covered with scales, which are often concentrated at the edges. Above, the cap is darker in color and smoother.
- The most common types of umbrella mushrooms are white, variegated and reddening.
Umbrellas can grow very large after heavy rains. The head of such a mushroom reaches a diameter of 35 to 45 cm, and the height of the leg grows to 30-40 cm.
On average, the mushroom has a stem length of about 8-10 cm and a diameter of the cap within 10-15 cm. The surface of the cap is dry and finely scaly; at the edges, the skin may crack and hang in the form of a fringe. The pulp and juice are of a light shade with a pleasant mushroom smell and delicate taste. The leg is thickened at the base, it has a characteristic mobile membranous ring.