What can be confused with the purple rowing
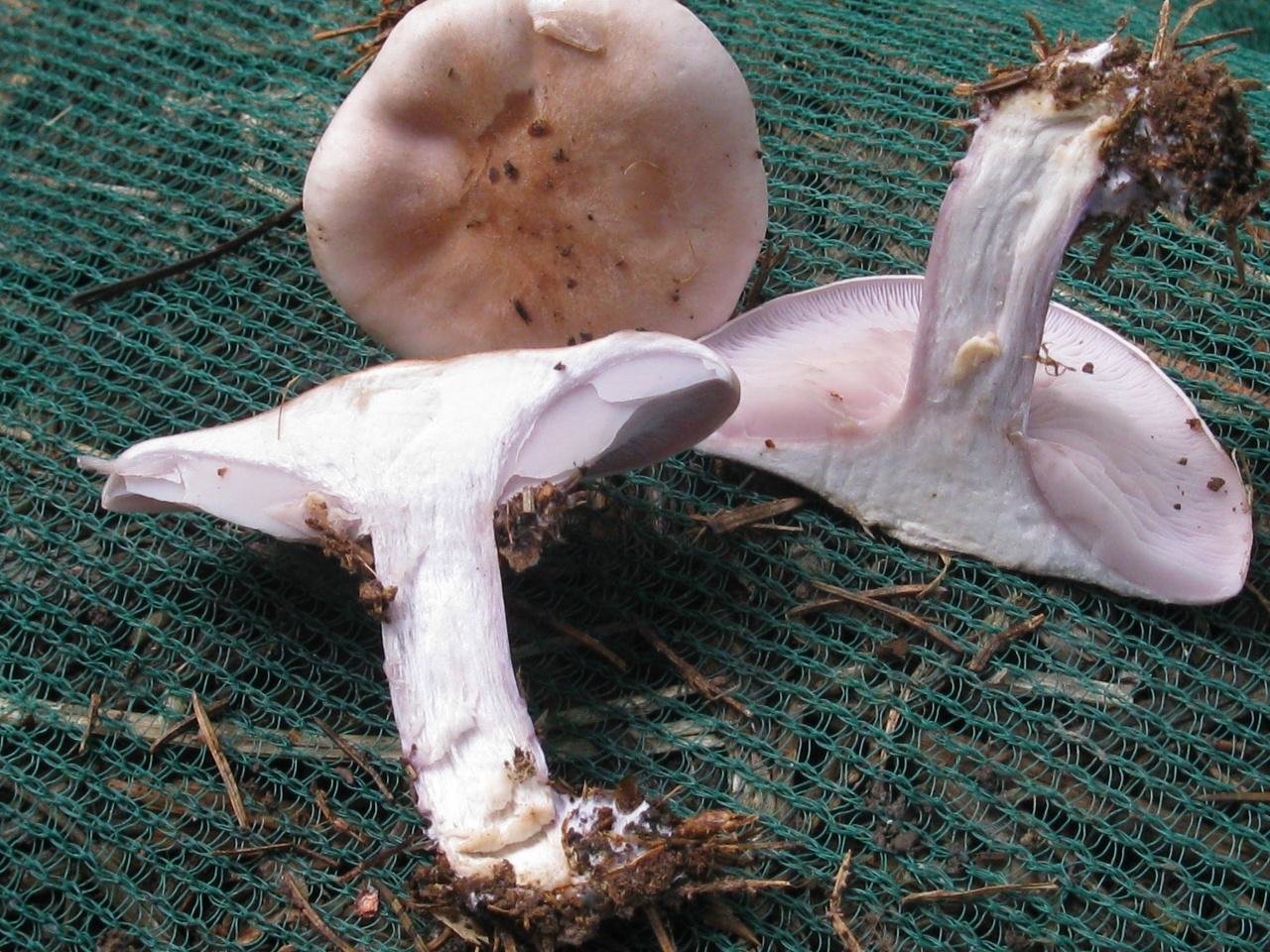
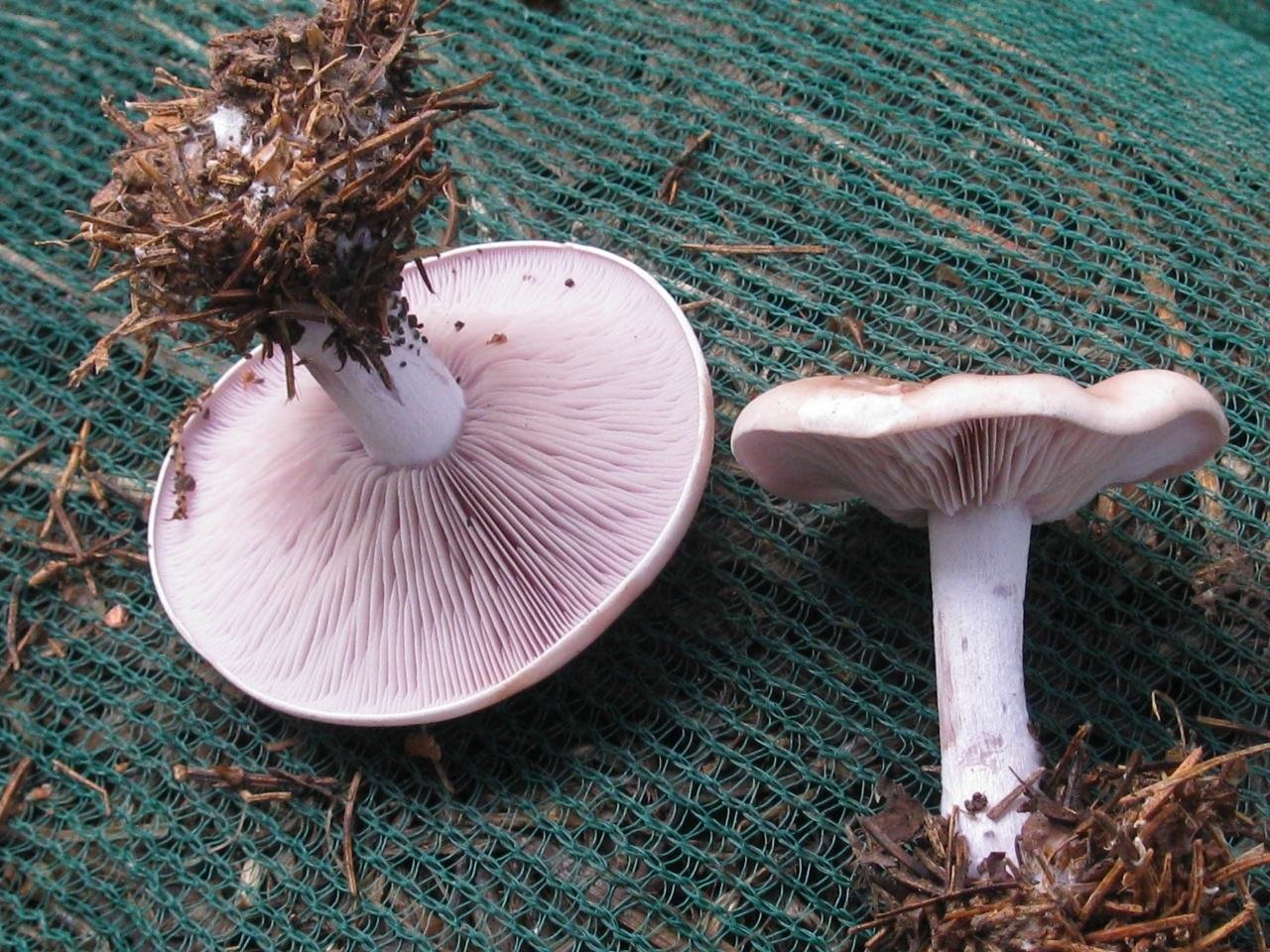
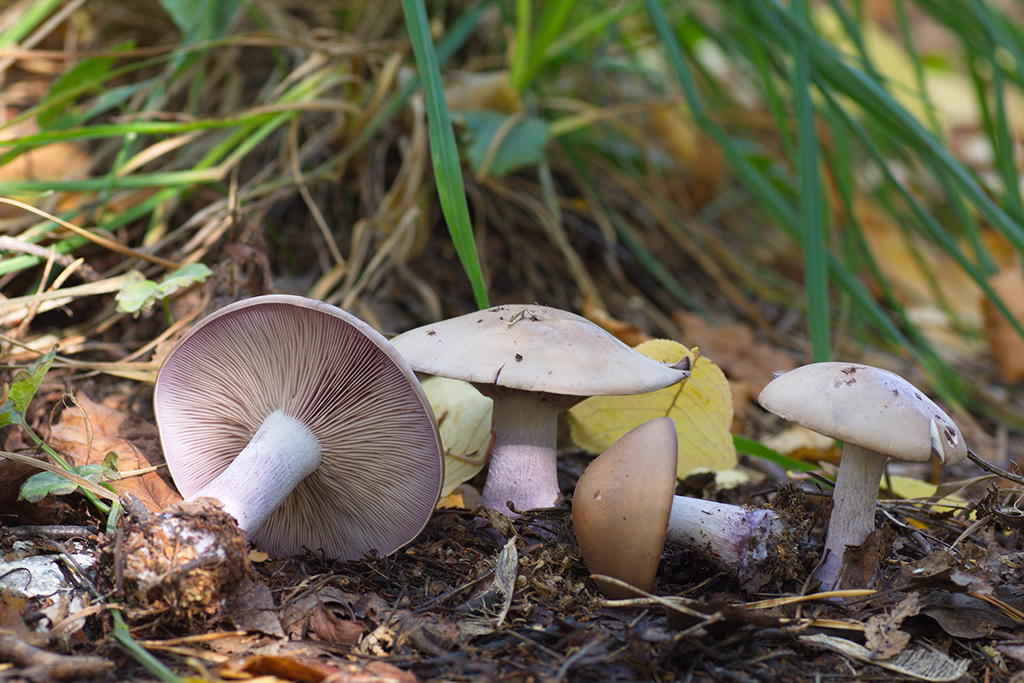
At first glance, it seems that the bright purple or lilac color of the mushroom makes it completely unique in appearance. But this is not so, there are many rows with a purple leg and false doubles, and the mushroom can easily be confused with both edible and toxic doubles.
Blue-legged, or lepistal-legged
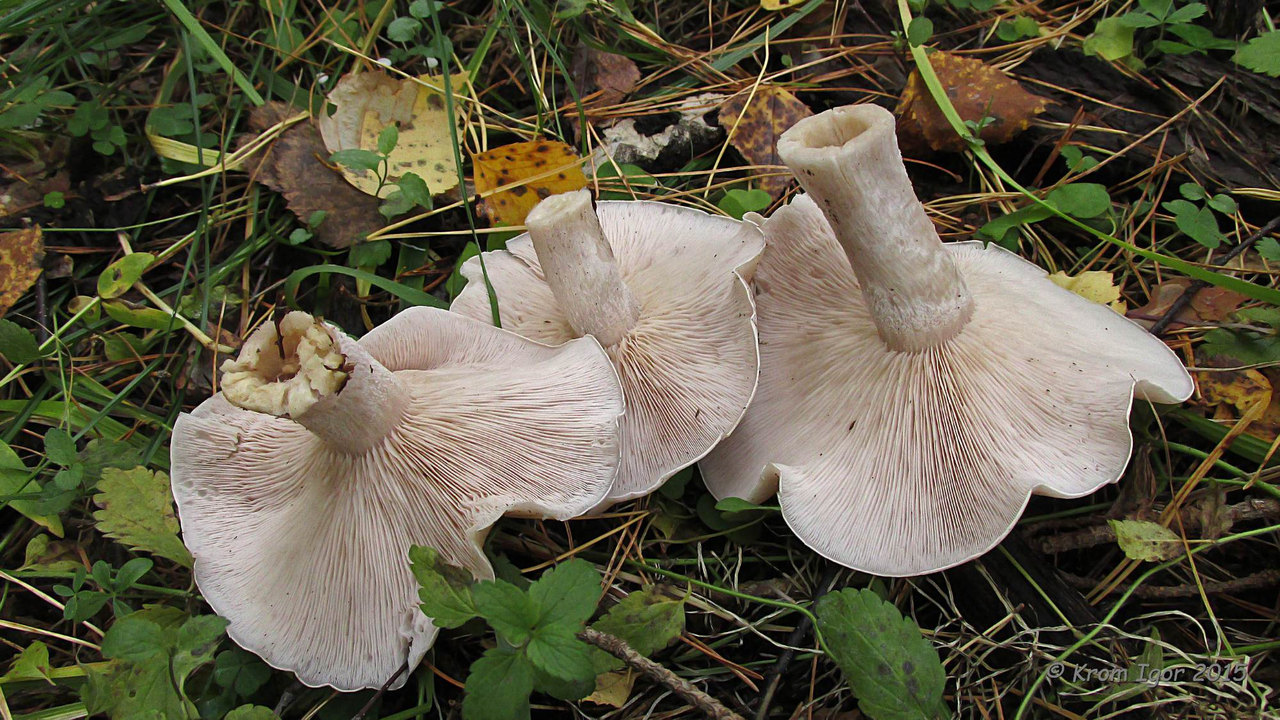
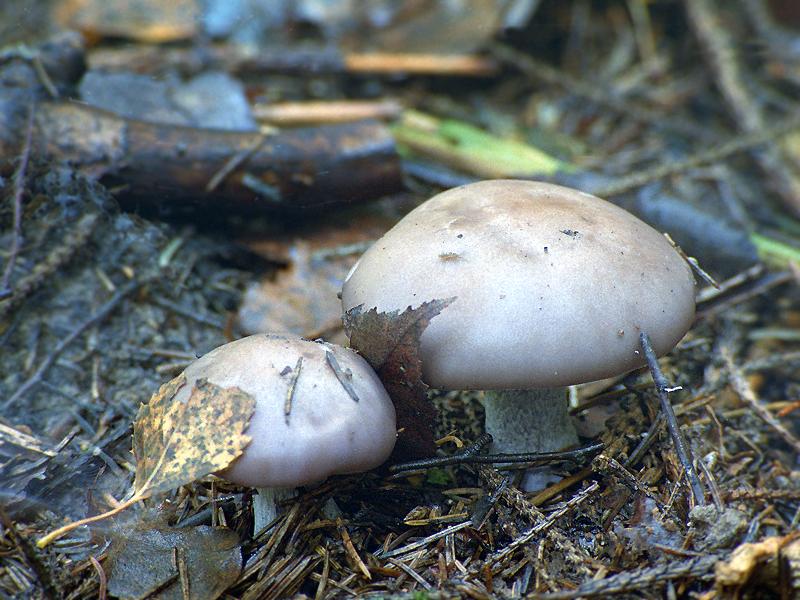
This conditionally edible mushroom is similar to cyanosis in its external structure; it has a fleshy, slightly convex cap with a lamellar lower surface and a purple leg. However, there are important differences - the mushroom cap is much lighter and closer to white. In addition, a false purple row, or bluefoot, grows in warm subtropical regions, mainly in fields and meadows, and it can be found already from mid-spring.
Violet Lepista
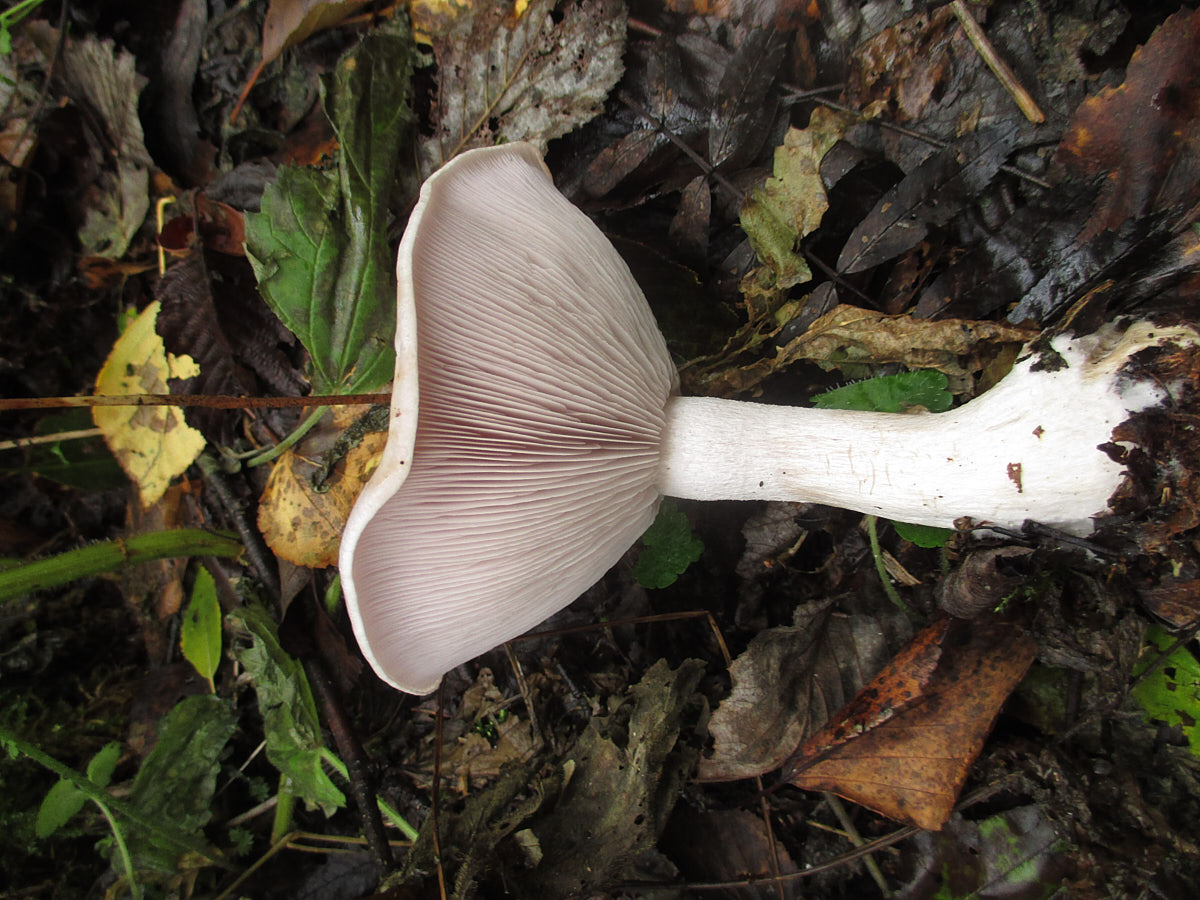
Another conditionally edible lamellar mushroom grows in temperate climates and is found mainly in forests. The cap of the violet lepista is convex, its edges are uneven. However, the color of the mushroom is not purple, but rather pinkish brown or whitish. In addition, the flesh of this species of Lepista gives off a distinct violet scent at the break.
Lilac varnish
The fungus is classified as conditionally edible and grows in temperate climates from early summer to mid-autumn. The lacquer is similar to a purple ryadovka in its shade, at a young age it is bright purple, as it grows it turns pale and fades. Also, the mushroom has a flattened fleshy cap with a slight bulge in the center, and the underside of the cap is covered with thin plates.
However, a photo of a purple false row allows you to distinguish it from a real mushroom. The difference is primarily in size - varnish usually reaches no more than 5 cm in diameter and belongs to miniature mushrooms.
Purple spider web
This conditionally edible mushroom from the Webinnikov family of the same name grows in coniferous and deciduous forest plantations in a temperate climate. It looks like a young purple ryadovka in the shape of a hat, but usually has a darker color - deep purple or brownish, the same color and a plate on the underside of its cap.
The purple flesh of the cobweb gives off a nutty aroma, not a fruity one. The leg of the mushroom noticeably thickens in the lower part, and you can also notice traces of a coverlet on it, similar to a light cobweb.
Important! The purple spider web is a fungus listed in the Red Book, so you can rarely find it in the forests.
White and purple spider web
This mushroom from the Webinnikov family belongs to the category of inedible, it cannot be eaten. The convex or bell-shaped cap of the mushroom reaches 8 cm in diameter, and the webcap can rise 8 cm above the ground on the leg.
You can distinguish an inedible mushroom from a purple ryadovka not only by its shade, but also by its pulp - in the cobweb it is soft, quickly turning brown in the cut, and at the same time it emits a noticeable smell of mold.
Goat webcap
Another inedible mushroom is distinguished by a convex hemispherical cap up to 6-12 cm in diameter and a thick short leg with a thickening near the ground. The goat webcap has a bluish-purple tint of the leg and cap, its flesh is grayish-purple. The peak of fruiting occurs at the end of summer, and the mushroom can be found in conifers and mixed plantings of the middle lane until the beginning of October.
You can distinguish a poisonous purple ryadovka mushroom from a real edible one both in color and shape, and in smell. The inedible mushroom emits an unpleasant aroma of acetylene and does not at all make you want to taste the pulp.
Pure mycene
The hemispherical cap of a miniature inedible mushroom can reach 4 cm in diameter, and the mycene can rise 9 cm above the ground.It vaguely resembles a ryadovka, but much thinner and smaller in size, the color of the mycena is rather grayish than lilac, sometimes pale brown. Its pulp is also gray or pale gray, watery and with a distinct unpleasant odor. When the mycene breaks, it secretes a very large amount of milky juice.
Pure mycene differs from the purple ryadovka not only in external features. It is difficult to confuse the species due to the different growing dates - the rowing refers to autumn mushrooms, while the inedible mycene is found in temperate climates from early spring to the end of June.
Colossus row (Tricholoma colossus)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Row gigantic
- The row is huge
- The row is giant
- Row-giant
Other names:
- Row colossus;
- Row-giant;
- The row is huge;
- The row is gigantic.
The Colossus Ryadovka (Tricholoma colossus) (translated from the Latin “terra” means “earth”) is an edible mushroom from the Tricholomov family, belonging to the Ryadovok genus.
External description
The fruiting body of the described fungus is capped, has a fairly large size. Initially, the shape of the cap of the giant row is semicircular, has turned up edges, but gradually it becomes flat-convex and even outstretched. The edges of the cap in mature mushrooms become raised, wavy.
The diameter of the gigantic ryadovka cap varies from 8 to 20 cm, and thin fibers are visible on its surface. To the touch, the cap of the described mushroom is smooth, and in color, it is reddish-brown, reddish or brown. At the edges, the shades of the mushroom cap are slightly lighter than in the middle.
The leg of the giant ryadovka is very large, massive, dense, characterized by a cylindrical shape. Its length varies within 5-10 cm, and its thickness can be 2-6 cm. The shape of the leg is predominantly cylindrical. At the base, the leg thickens, becoming tuberous. The color of the leg at the bottom, just below the ring, is the same as that of the cap, or slightly lighter. The upper part of the leg, right under the cap, is often whitish, and in the center its color can be red-brown or yellowish.
The hymenophore of the described fungus is lamellar. The plates in it are very wide, often located, in young fruiting bodies - cream (sometimes pale pink). In ripe mushrooms, the hymenophore plates darken, becoming reddish-brown.
The mushroom pulp is characterized by its white color, compactness and high density. On the cut, the main color of the pulp can change to yellowish or reddish. The smell of the pulp is pleasant, and the taste is bitter, similar to the taste of an unripe walnut.
The surface of fungal spores is smooth, and they themselves are pear-shaped or oval in shape, without color. Their size is 8-10 * 5-6 microns. These particles are part of the white spore powder.
Season and habitat of the mushroom
The colossus ryadovka (Tricholoma colossus) belongs to the rare species of fungi, which nevertheless have a significant and wide habitat. Within its limits, a gigantic ryadovka is found in small populations. On the territory of Russia, the mushroom is widespread in the Leningrad and Kirov regions, as well as in the Krasnoyarsk Territory. You can find the described type of mushroom in some countries of the European continent, in Japan and North Africa.
The gigantic ryadovka forms mycorrhiza with pine, begins to bear fruit in August and yields a harvest until the end of September. The fungus prefers to live mainly in pine forests. You can meet the giant ryadovka in mixed forests, in the mountainous part of the Crimean peninsula.
Edibility
Colossus row (Tricholoma colossus) is an edible mushroom, however, due to the rarity of the species, it is not recommended to collect such rows. In addition, in some regions of Russia and Europe, this mushroom is considered rare, and is listed in the Red Book.
Other information about the mushroom
Row colossus is not cultivated by people, and in some regions of Russia (St. Petersburg, Kirov region, Leningrad region) the mushroom is listed in the Red Book of Nature.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
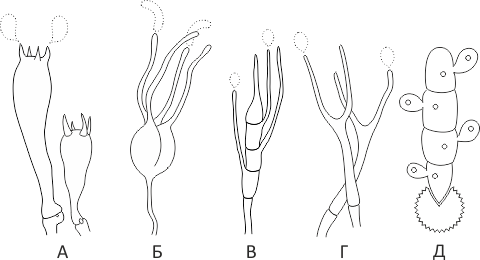
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
How curb roses reproduce
Miniature beauties reproduce in 3 ways:
- cuttings;
- dividing the bush (seedlings);
- seeds.
It is considered the easiest way. From May to July, semi-lignified shoots can be cut, divided into parts so that 2-3 buds remain on each of them. Everything the leaves on them are shortened by half.
Each shoot is planted only after 3-4 hours of keeping them in a root-forming solution. The distance between them when planting is 30-35 cm. Then each shoot is watered abundantly and covered with a container (glass jar, large plastic bottle). They stay in such a "greenhouse" for about a month and a half. All this time it is necessary to water them regularly. Once the shoots have developed roots, they can be dug up and transplanted to a new location in the garden.
Florists very rarely resort to the propagation of a border rose by seeds, since this is a long and troublesome process.
All harvested (purchased) seeds are germinated at a temperature of 20 ° C for 2 weeks before planting. They can be sown in a container with fertile light soil in late autumn. Seeds are embedded 0.5 cm deep
Throughout the winter, it is important to maintain a temperature of 3 to 5 ° C for them. In late spring or early summer, the seeds will begin to sprout
Shelf life. Expired seeds may not fully germinate or not germinate at all.
The color of the purchased variety. The selected miniature roses should be combined with plants already growing in the garden, and should match them in color.
Longitude of flowering.It is different for all varieties: some have early, others late flowering. It will be nice if the selected variety of roses complements the overall flowering of the plants.
Planting requirements and care. To get active growth and flowering, you need to know the basic rules for growing the purchased variety.
Boarding time
This is also important, since many species are grown indoors for some time before being planted outdoors.
No need to regret the time spent growing roses in the garden. Miniature plants, in response to the care and maintenance of them, will delight everyone with their long and lush flowering.
Taxonomy
Views
- Lepista caespitosa (Bres.) Singer, 1951 - Sod Lepista
- Lepista densifolia (J. Favre) Singer & Clémençon, 1972 - Lepista densifolia
- Lepista diemii Singer, 1954
- Lepista fibrosissima Singer, 1954
- Lepista flaccida (Sowerby) Pat., 1887 - Lepista reverse, or reddish-brown
- Lepista glaucocana (Bres.) Singer, 1951 - Lepista blue-gray, or lilac-gray
- Lepista irina (Fr.) H.E. Bigelow, 1959 - Violet Row, or Violet Lepista, or Perfume Row
- Lepista luscina (Fr.) Singer, 1951
- Lepista multiformis (Romell) Gulden, 1983
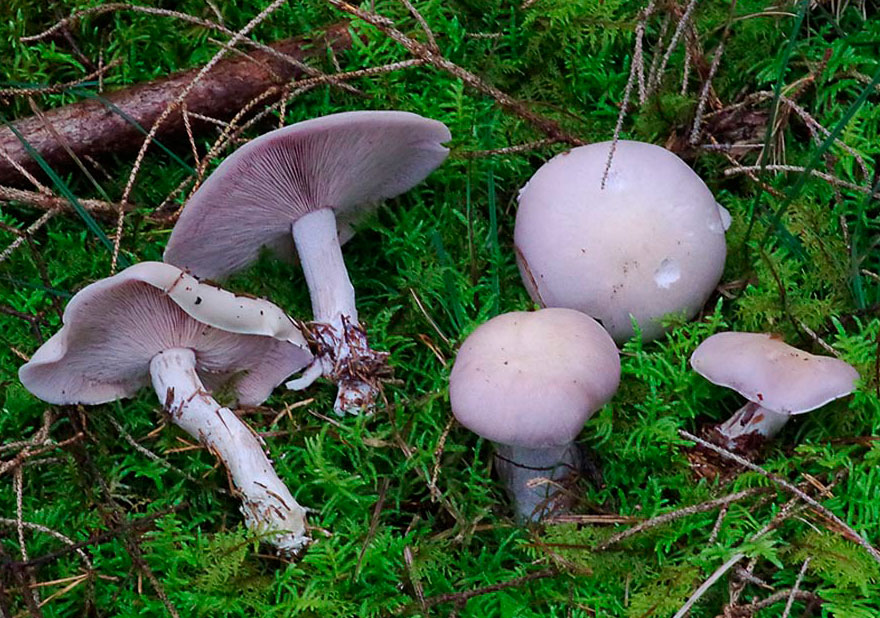
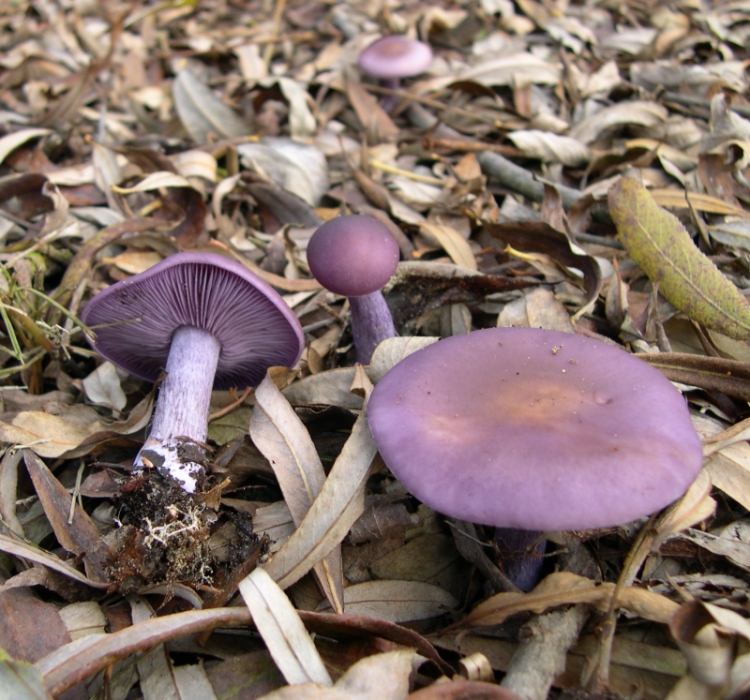
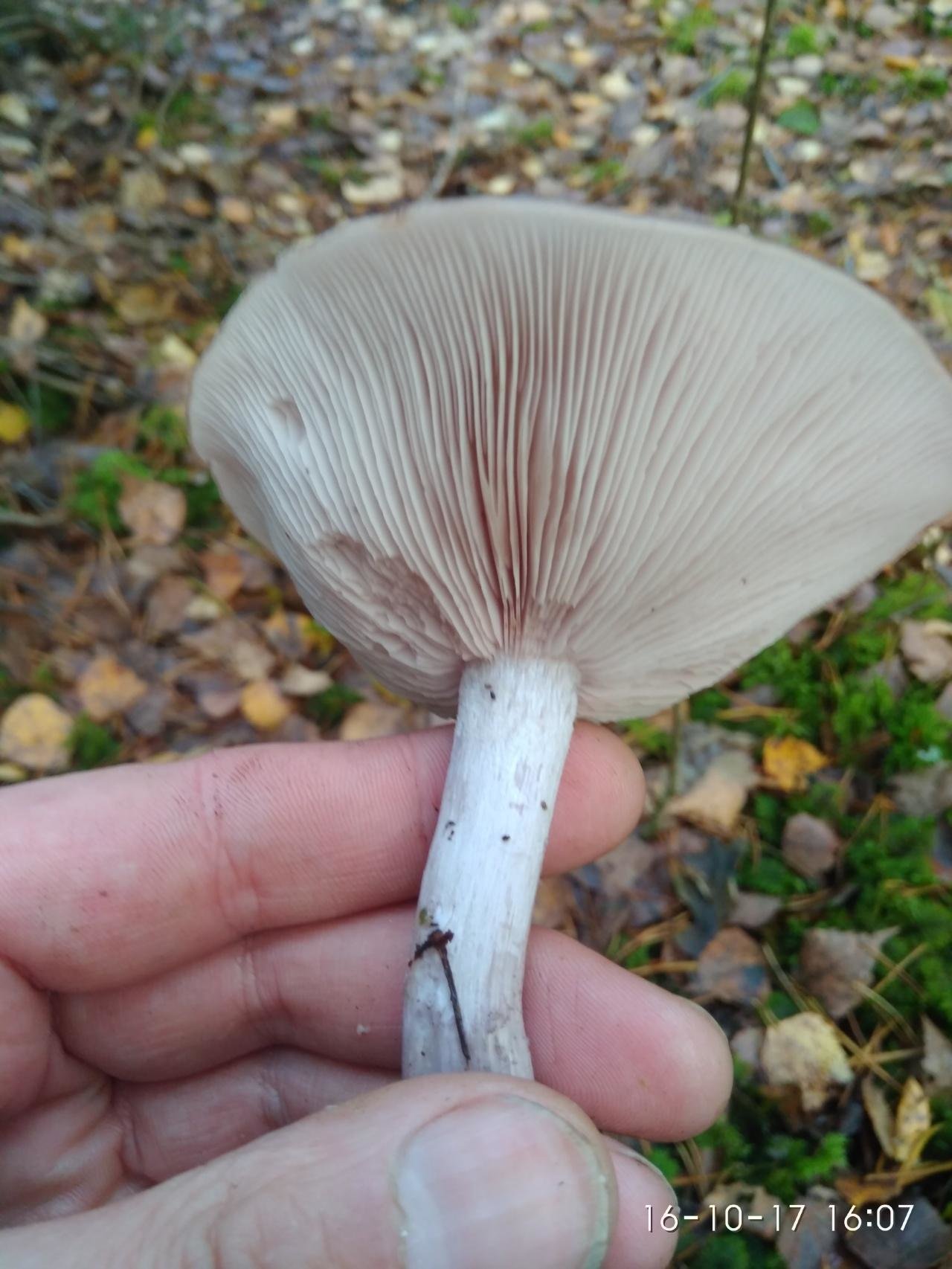
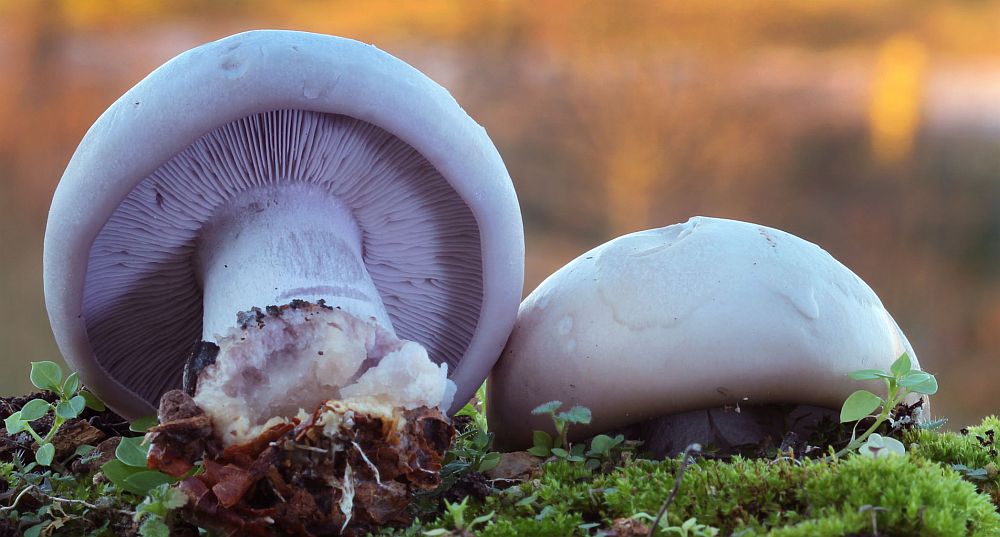
- Lepista nuda (Bull.) Cooke, 1871 - Row purple, or Lepista naked
- Lepista ovispora (J.E. Lange) Gulden, 1983
- Lepista panaeolus (Fr.) P. Karst., 1879
- Lepista personata (Fr.) Cooke, 1871 - Row two-color, or Lepista two-color, or Lepista purple-legged
- Lepista pseudoectypa (M. Lange) Gulden, 1983
- Lepista rickenii Singer, 1948
- Lepista sordida (Schumach.) Singer, 1951 - The row is dirty, or Lepista is dirty
- Lepista subaequalis (Britzelm.) Singer, 1951
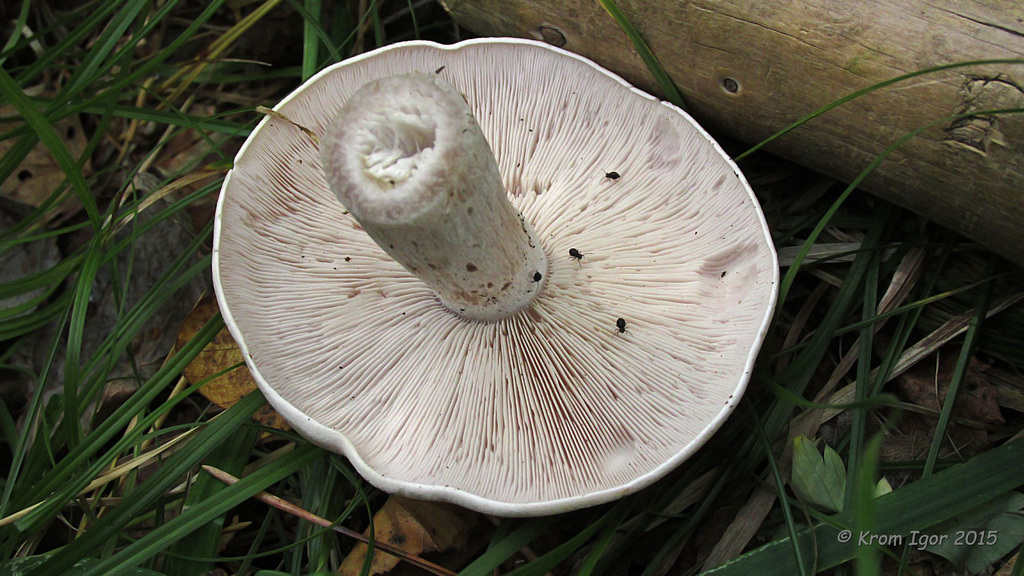
Weed row (Lepista sordida)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- The row is dirty
- Titmouse
- Lepista dirty
- Lepist weed
Other names:
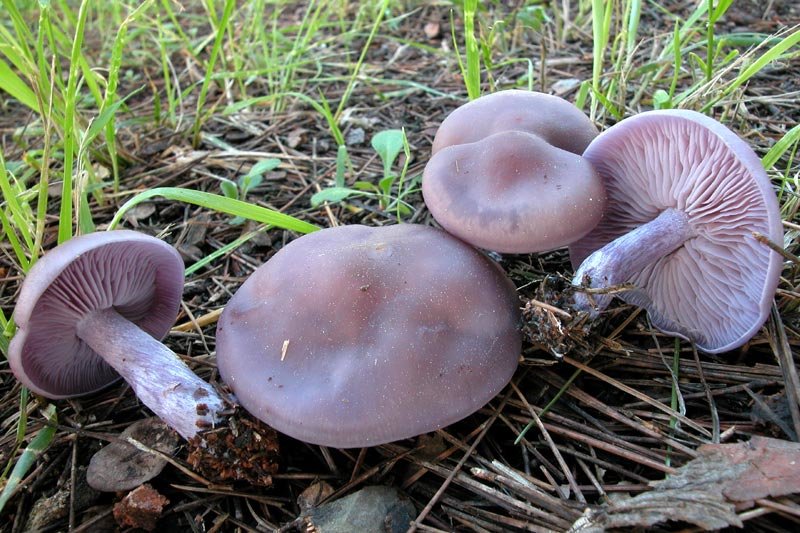

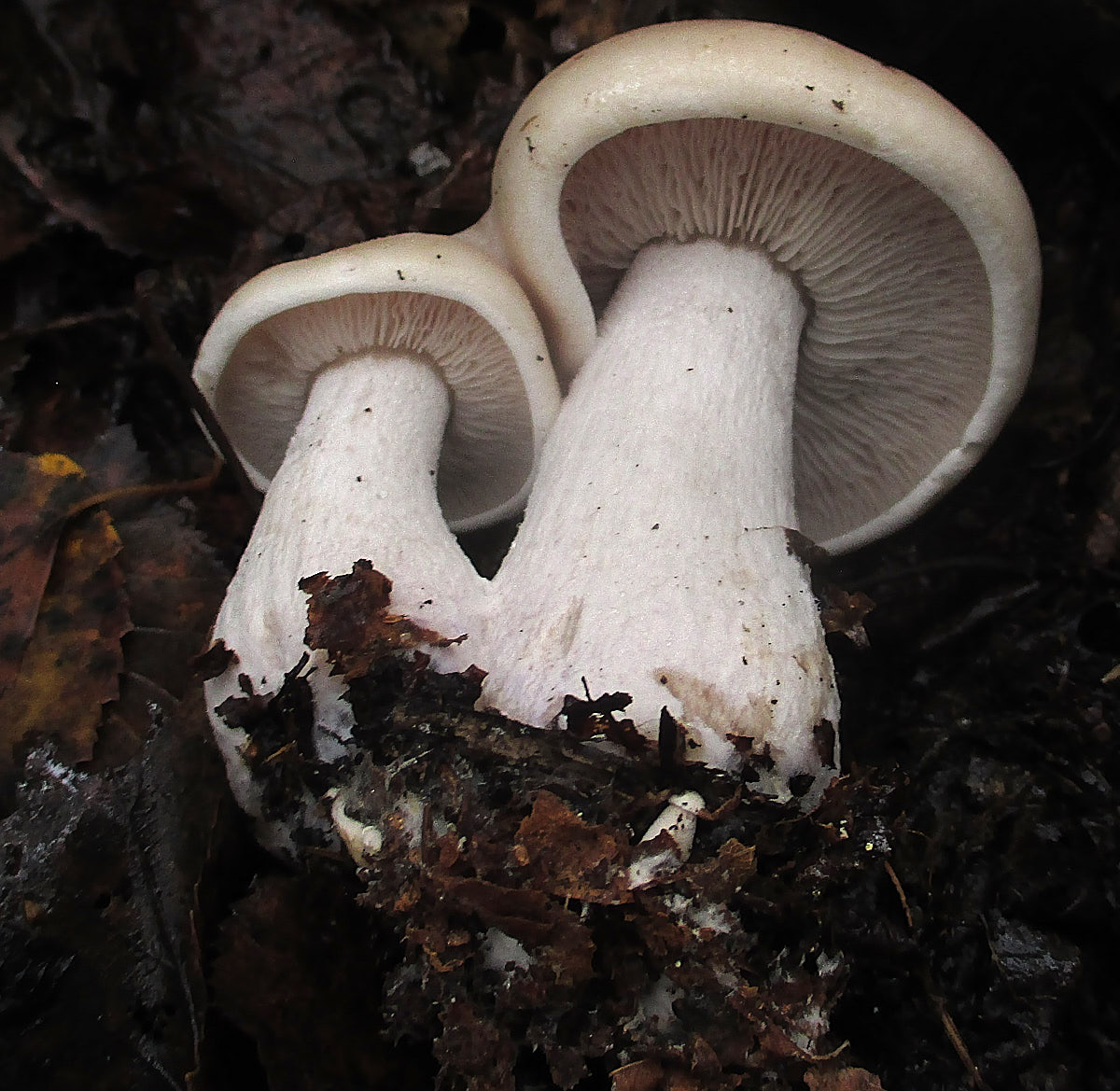
Weed ryadovka (Lepista sordida) is a little-studied mushroom belonging to the Tricholomov family (Ryadovkov) and the Ryadovok genus.
External description
Weed row (Lepista sordida) is a mushroom that grows singly or in small groups. In colonies, the fruiting bodies of this species grow together with the base of the legs.
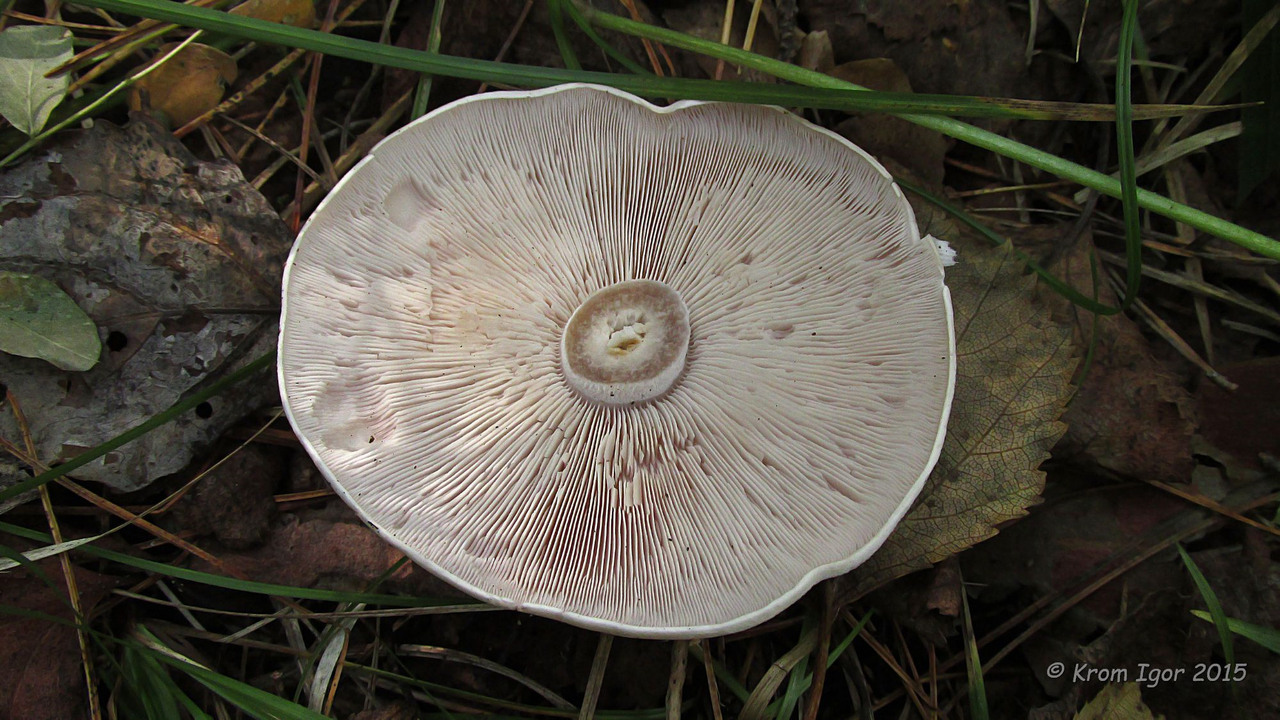
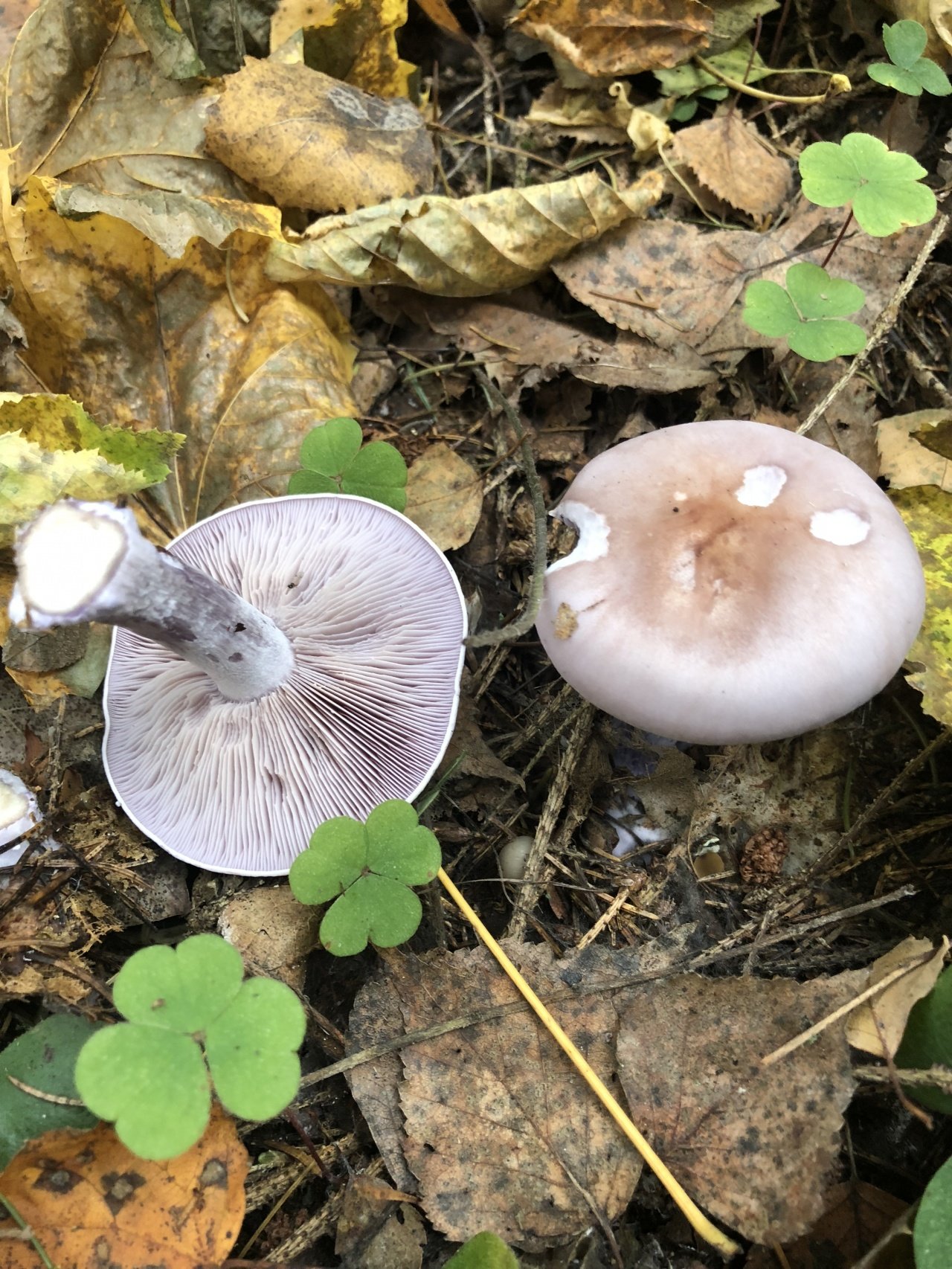
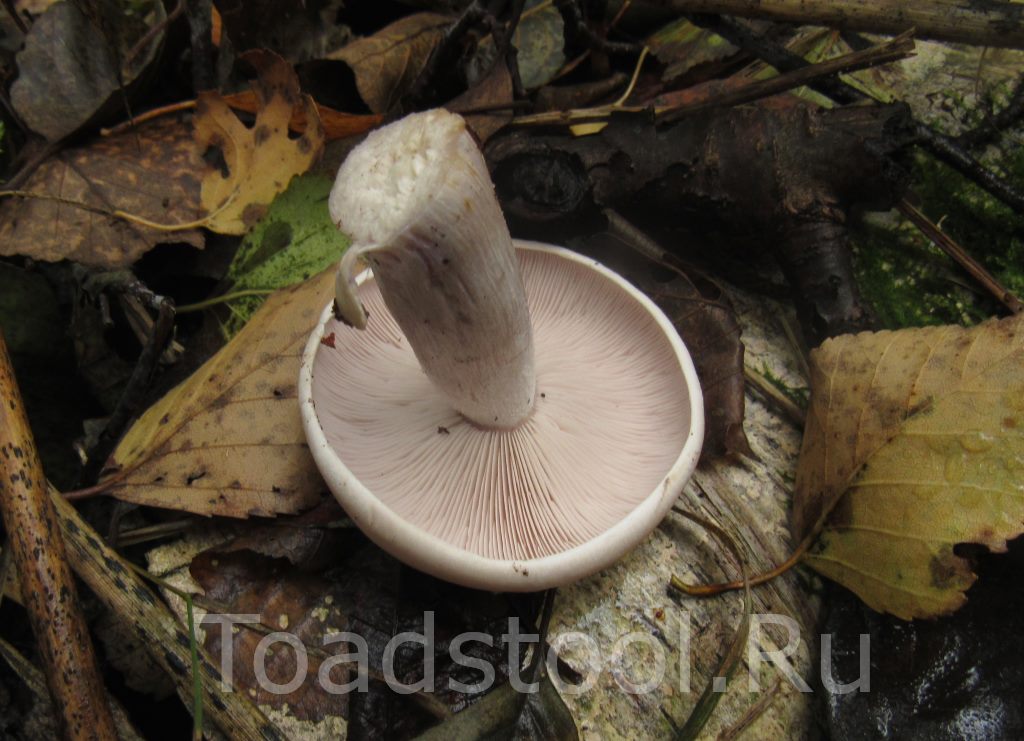
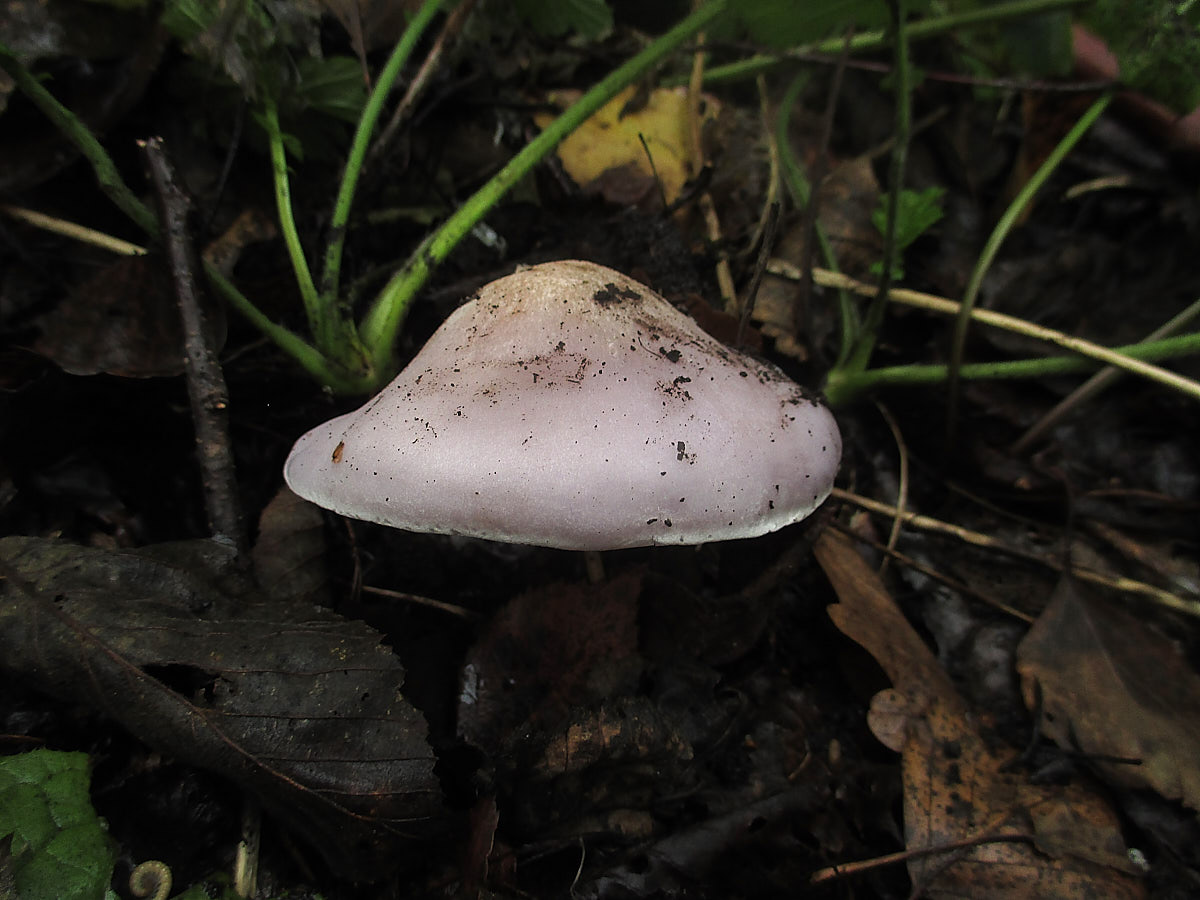
The cap of this mushroom can be 3-8 cm in diameter. Its shape in young mushrooms is more often spherical, and in mature fruiting bodies it becomes widespread, characterized by a lilac or brown-purple hue, and eventually loses the brightness of colors. It can also be brownish or red-brown in color, slightly ribbed, has barely noticeable stripes on the surface. In its central part, a tubercle is visible in mature mushrooms. At the edges, the head of a dirty row can be wavy. In immature mushrooms, the edges of the cap are often turned up, gradually straighten, becoming wavy, and even when ripe can even be bent upward. The mushroom pulp near the dirty ryadovka is very thin, oversaturated with moisture, has a pleasant aroma and taste, and is characterized by a gray-violet color.
The fungal hymenophore is lamellar, and its constituent elements (plates) grow together with the surface of the fruiting body with a tooth, have a dirty purple hue, and are often located. The spore powder in this type of mushroom is characterized by a pinkish color.
The leg of a dirty row reaches 4-6 cm in length, and can be from 0.7 to 1 cm in thickness. It is characterized by strong fiber and the same color as the cap, has a cylindrical shape, located in the center. Near the base, the leg may expand slightly. In young fruiting bodies of a row of dirty, the leg is dense, complete, and in ripe mushrooms, it becomes empty inside.
Season and habitat of the mushroom
Grows in gardens, orchards, parks, squares, on the edges of forests or not deep in light forests. Can be found in meadows. It grows in a group / bunch of several fruiting bodies, rarely occurs singly.
The most active fruiting of this type of rowing begins in July and continues until the end of September.

Edibility
Despite the low popularity among fans of mushroom picking, the Ryadovka weedy mushroom belongs to the edible category. It is advisable to boil it before eating, but the broth from it is not suitable for consumption and therefore it is better to pour it out. Also, dirty rows are delicious when pickled.
Similar types and differences from them
In appearance, the dirty rowing (Lepista sordida) looks like a purple rowing. Its main difference from the named mushroom is thinner, not fleshy pulp and fragility.In addition, in dirty rows, the caps fade, and the pulp of the purple row has a characteristic smell of fruit. The dimensions of the fruit bodies in dirty rows are smaller than in purple ones. The purple row forms "witch circles" and rows, and the Dirty one - in small heaps.
Evaluation of taste
The mushroom is considered edible, has a high taste, it is equated with a purple ryadovka. Lepista can cause minor, non-life-threatening stomach upset and should therefore be eaten unless contraindicated.
Primary processing and cooking recipes
Mushrooms need to be processed as soon as possible after harvest. Rows should not be kept in water for a long time, they will become tasteless. It is better to rinse them under running water. It is necessary to clear the fruits of forest debris, sort out, remove the rotten and wormy ones. Then pre-boiling is required. The water with the addition of salt is brought to a boil to taste, the lepists are dipped into it and boiled for 30 minutes.
The mushrooms are now ready for further processing. Violet rows can be frozen, fried, salted and pickled. They are wonderful in a mushroom mixture, stewed with sour cream. In order to salt, for 2 kg of fruit you will need:
- salt - 4 tbsp. l .;
- laurel - 6 pcs.;
- allspice peas - 6 pcs.;
- dill umbrellas - 3 pcs.;
- garlic - 6 cloves.
Salting process:
- Pre-boiled mushrooms are laid out in layers in a prepared container, alternating with salt.
- As the layers form, place the spices evenly over the entire area; they can be laid out on each row or through one.
- Sprinkle everything on top with salt, cover with gauze and press down with a load, set the container in a dark, cool place.
- After 3 weeks, the mushrooms can be tasted, and you can also put them in jars and refrigerate on the lower shelf.
It is necessary to pay attention to the formation of brine, which should appear no later than three days after salting, to increase the load as necessary. If you need to freeze the mushrooms for the winter, then after boiling they should be cooled and laid out in portioned containers, which are removed to the freezer.
You can take it out as needed, defrosting before cooking is not required
If you need to freeze the mushrooms for the winter, then after boiling, they should be cooled and laid out in portioned containers, which are removed to the freezer. You can take it out as needed; defrosting is not required before cooking.
For pickling a row of violet, for 2 kg of mushrooms you will need:
- salt - 2 tbsp. l .;
- water - 2 l;
- sugar - 1 tbsp. l .;
- peppercorns - 5 pcs.;
- laurel - 3 pcs.;
- cloves - 3 pcs.;
- garlic - 3 cloves;
- horseradish and currant leaves, 2 pcs.;
- vinegar - 4 tbsp. l.
Cooking process:
- Bring water with salt and sugar to a boil.
- Place pepper, laurel, cloves, crushed garlic, horseradish leaves and currants there. Boil for a minute.
- Add vinegar, then fruiting bodies.
- Cook for 10-15 minutes.
- Put the rows in jars, pour marinade over them so that the fruits are completely covered with liquid. Put in the refrigerator.
The blank can be eaten immediately and served.
How should you care for a flower garden?
Caring for a curb rose will not cause difficulties even for those who are engaged in its cultivation for the first time. If the basic requirements for pruning, watering, feeding are met, the plant will thank you with good growth and lush flowering.
Miniature roses need regular, but not abundant irrigation. Drying and waterlogging of the earth must not be allowed. Watering is best done in the evening using sun-warmed and settled water.
Top dressing
Spring and autumn composting works well on miniature roses. It is laid out under the bushes at the rate of 5-6 kg per m2.
When the first buds form, the plant can be fed with calcium nitrate (1 tablespoon per bucket of water). This fertilizer has its own peculiarities of use:
- before feeding, the roses should be well watered so as not to burn them;
- after feeding - water again;
- the time of the procedure is in the morning or in the evening (when the heat subsides).
Additionally, every 15-20 days, you can feed it with mullein, mineral fertilizers or herbal infusions. Liming is necessary in September.
Leaving on hot days
Miniature roses do not tolerate rainy and very hot weather. It causes stress in them. During this period, reanimation agents will help to "cheer up" the plants: "Zircon", "Epin", "Ecosil", potassium humate.
It is important to protect the culture from overheating. A temperature rise above 25 ºC leads to overheating of the roots and deterioration of the condition of the roses.
Peat and hay laid under the bushes will help to cool them a little.
Pruning
Leaving includes another important point - competent pruning. It consists in removing damaged and dry shoots, in the formation of a beautiful and correct aerial part.
If the shoot is damaged, it is cut from above between 2-3 leaves
It is important to cut wild growth from grafted roses. Elimination of the "wild" above ground level will not give a result - it will grow again
Correct pruning is the removal of wild shoots from the very base (from the root collar).
In order for the bushes to grow proportionally, in the 1st year of their life it is necessary to pinch all the shoots that appear after 4 and 5 leaves, remove the buds. In "old" bushes, the central shoots growing vertically are not trimmed, only the lateral ones are trimmed a little.
Preparing for winter

Despite the fact that many varieties of border roses can withstand frost, they must be insulated for the winter. But first, all shoots and fallen leaves are removed. The first night frosts are a signal for the start of insulation. The sequence is as follows:
- to spud the plant, and the height of the embankment should not be less than 20 cm;
- put spruce or pine branches around;
- on them, gently pressing to the soil, lay the shoots;
- cover on top with dry leaves or spruce branches.
Many gardeners make a frame for insulating roses and cover it with a moisture-repellent material (roofing felt, insulating paper) folded in several layers. A plastic wrap is additionally laid on top. As soon as the thaw begins in spring, flowers can be opened slightly.
Caring for border roses is quite simple compared to other varieties of an exquisite flower, and includes only a number of standard activities.
The bushes should be watered systematically, but in small portions, so that the soil does not have time to dry out, but also is not waterlogged. Moisturizing roses is carried out at the root, which helps to avoid droplets of water on the shoots.
- At the beginning of spring, it is worth adding compost for digging at the rate of 6 kg per m2.
- Before the beginning of the formation of buds and during the flowering period, fertilizing is carried out with the help of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- In the fall, the choice should be on organic.
To preserve the cleanliness of the beds and the loose structure of the soil, the trunks should be systematically loosened, while removing the weeds. A layer of mulch under the bushes will also be useful.
During the season, sanitary pruning is carried out, in which sick, injured shoots and faded inflorescences are removed. In grafted roses, shoots are necessarily destroyed directly from the root collar.
How to plant?

Landing should take place in an area protected from gusts of wind. In this case, there should be enough sunlight. A strong wind will take moisture from the crop, and its lack will affect growth and flowering.
This condition is also important for roses growing in pots. The effect of the wind is enhanced, since the roots have a limited area of soil from which they could make up for the lack of moisture
You can not plant it on a site where other representatives of the Rosaceae family grew for a long time. The effect of "soil fatigue from roses" arises when it is severely depleted by these plants and spores of fungal diseases, viruses and pests can be found in it.
Miniature beauties are undemanding to the composition of the soil. They grow on any soil, as long as it is not too dry, dense and waterlogged.Before planting, it is recommended to improve the soil by mixing it with drainage or organic fertilizers.
Planting is done in a hole, the size of which should slightly exceed the diameter of the planted root system. When planting, the roots are gently straightened, their neck is buried into the soil by only 3-5 cm.
The optimum distance between seedlings is 25-30 cm. After planting, the soil around the bush is carefully compacted and watered abundantly.
Customization
Sensitivity is indicated by the letters "SENS" on the housing. This setting is the most difficult. You should adjust the parameter so that the sensor does not react to small pets, but at the same time it works if a person enters the room. Set the SENS control to maximum, wait until the light turns off, and check how the sensor works. Decrease the sensitivity until you reach the optimum value.
The LUX parameter is used to set the detector to turn on the lighting only when it gets dark. At the first adjustment, it is necessary to set the maximum, and in the evening adjust the optimal time period at which the sensor will be triggered.
Time - delay time. Detectors are sold in which, with each subsequent turn on, the delay time increases. First, set the regulator to minimum to quickly perform a parameter check.
Tips & Tricks
Experts recommend building a floor plan before installing and marking the installation locations of devices. Diagrams are drawn showing the directions of action of the detectors, and the places of their installation are changed so that the devices are triggered when a person enters the room and moves through it, and at the same time the lamps continue to work.
Motion sensors in everyday life are actively used in security and alarm systems, for an economical mode of power consumption in lighting systems and other needs. If their operating mode is violated, do not rush to call a specialist or send the device to a service center for repair. In most cases, a malfunction occurs due to changes in the environment or in the power supply circuits, the consequences of this can be easily eliminated on their own.
Diseases and pests

Any plants, including the curb rose, can be attacked by insects and get sick.
Neighborhood with many species of plants can prevent the appearance of insect pests. If roses are planted next to marigolds, sage or onions, they will never have caterpillars, aphids, sawflies, spider mites.
In order to prevent and with a single lesion, rose bushes can be sprayed with infusions of onions, yarrow, garlic, calendula, and sprinkle the ground around them with ash. If pests nevertheless appeared en masse, you should not immediately run for chemicals. Try natural, less harsh remedies first.
Dissolve laundry soap in 10 liters of hot water and add a few branches of wormwood, mix, boil for 15 minutes. After the solution has cooled, mix everything again, strain and spray the bushes.
If after treatment the pests have not died, re-spraying can be repeated after 5-7 days.
Miniature roses are highly susceptible to diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- black spot;
- rust;
- alteriosis.
It is easy to prevent their appearance. It is enough to spray the culture with solutions of copper sulfate (3%), DNOC (1-3%) or nitrophenol (2%) before sheltering the culture for the winter and after opening.
If an infection has occurred, then the following means are used in the treatment.
- Water-soluble sulfur (1%), Bordeaux mixture (1%) are effective against powdery mildew.
- Copper oxychloride (0.2%), Bordeaux (1%) mixture will help get rid of black spot.
- Rust can be cured with water-soluble sulfur (1%) and copper oxychloride (0.2%).
- Spraying with foundation (0.2%) or copper oxychloride (0.4%) will help to cure an infectious leaf burn.
Some fungal diseases (for example, powdery mildew) appear if the care and planting conditions have been violated: bushes are planted close to each other, abundant watering.

False doubles
Similar species are ryadovka naked (purple) and gray-blue, which are very similar to each other.
The row is naked or purple
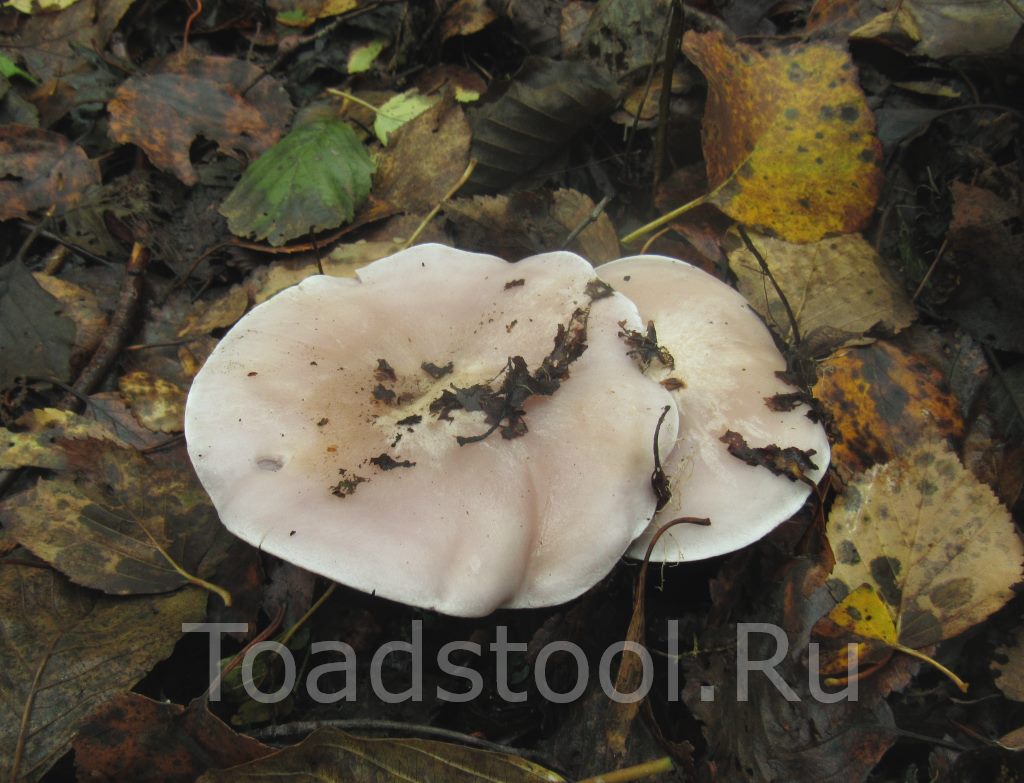
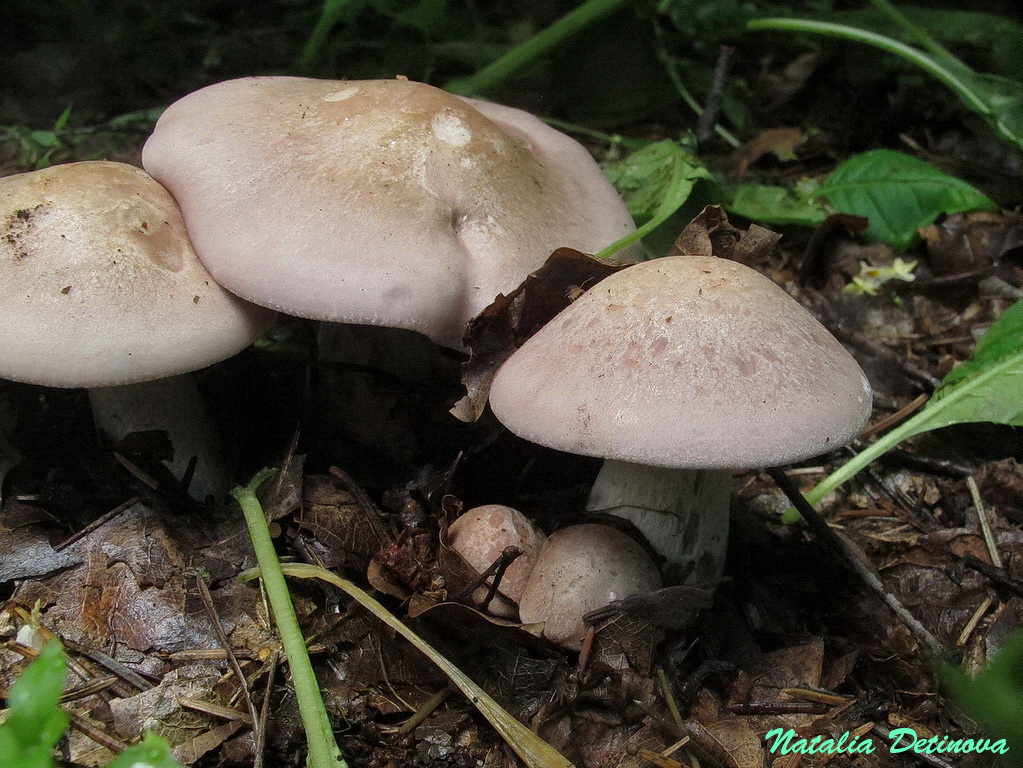
It has a convex fleshy large cap, first brownish, and later purple.
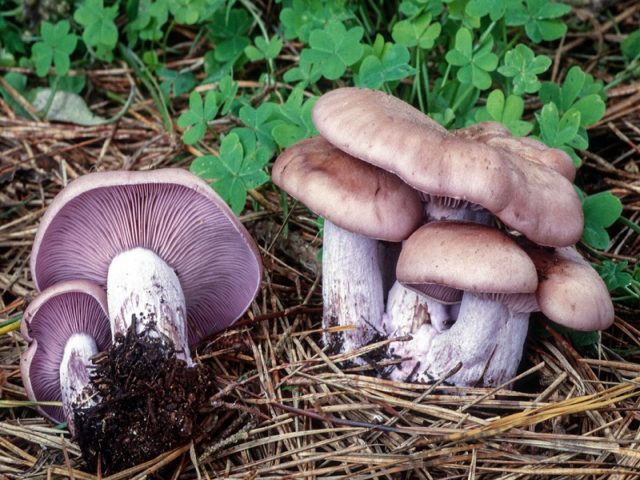

The leg, in contrast to the weed row, is smooth, its size is larger. Produces a pleasant fruity scent. The mushroom is classified as conditionally edible, with the obligatory heat treatment. Grows in coniferous forests under litter.
You can see what this double looks like in the video:
Row gray-blue
The cap of this representative is large, up to 16 cm in diameter, changes with age from conical to spherical. The skin is smooth. Color - lilac, lilac with a cream shade. The smell is light, fruity or almost absent. The leg is covered with small scales. The species grows in forest humus, along roads and paths in large groups. It belongs to conditionally edible, requires heat treatment.
























































