Cooking a row of green
A green row or green tea can be prepared in any convenient way - stew, boil, bake, pickle and salt. Beforehand, it is imperative to peel the cap and rinse the mushrooms thoroughly. To simplify the process, they need to be soaked in cool water for 1 hour. During this time, greenfinches need to be gently mixed several times so that the sand is washed out of the opened plates. Then the green rows should be washed in running water and boiled for 20 minutes with the addition of salt.

Soups, thick sauces, mushroom caviar are prepared from green rows. These mushrooms have a bright aroma, so some cooks do not recommend mixing them with other species. Zelenukha goes well with potatoes, garlic, peppers, onions, mayonnaise, pasta, rice and buckwheat. It harmonizes with meat dishes, is used as a filling for rich, savory pastries.
How to distinguish mouse rows
The mouse ryadovka is especially dangerous because of its strong resemblance to the earthy-gray, which is classified as a conditionally edible group.

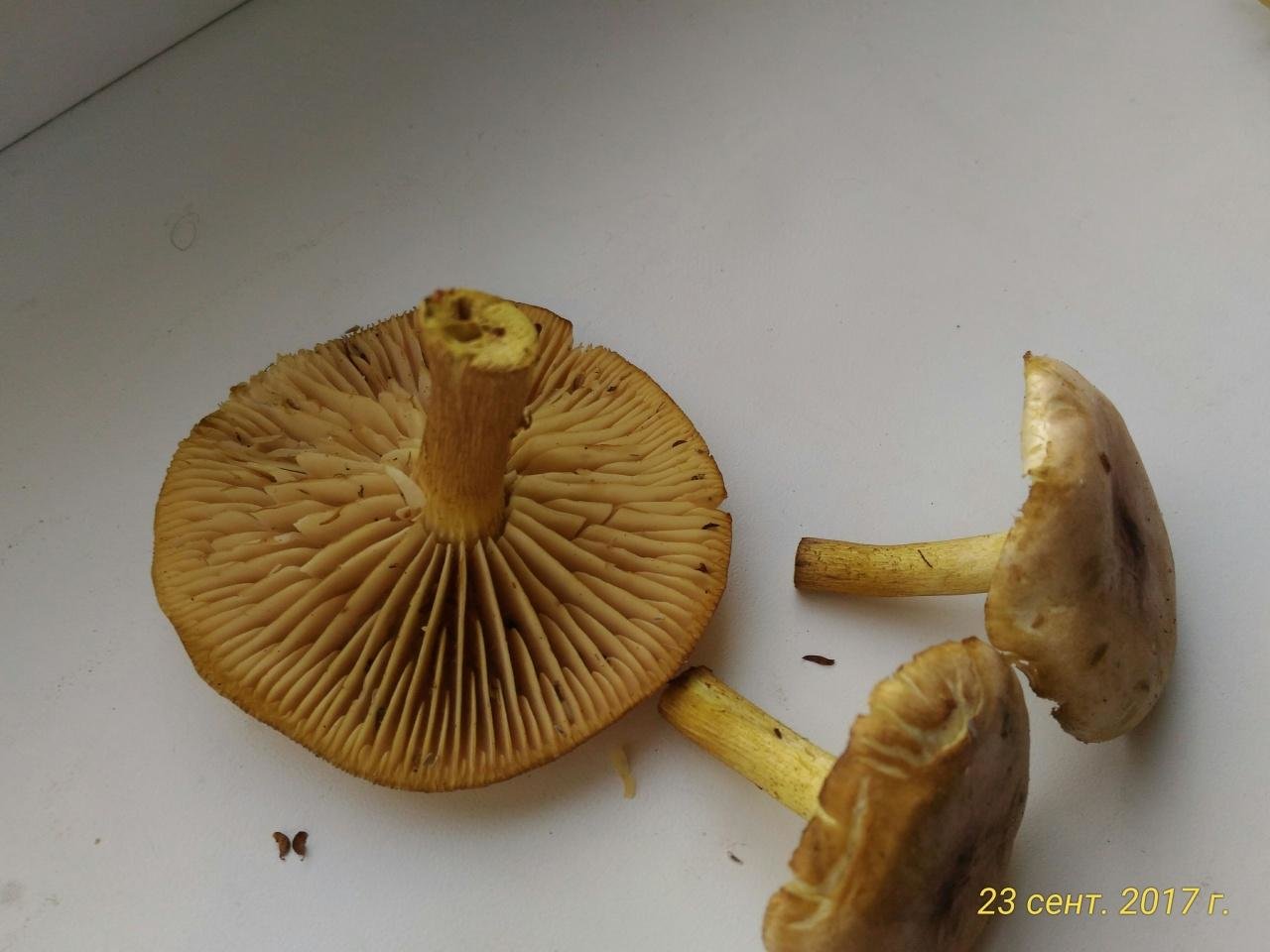
A double with a pleasant delicate mushroom smell, sweetish in taste. The surface of the cap is gray-brown, the edges are covered with the remnants of the veil; the mouse veil is absent. The edible mushroom is of a larger size, the main difference is that the protective layer of the cap surface is not smooth, but finely flaked. The leg is thicker and shorter.
Further, the gray ryadovka is a delicious edible mushroom suitable for all processing methods.

At first glance, outwardly, the species are similar; upon closer examination, the following differences from the mouse, edible twin, are noted:
- larger in size;
- there is no conical sharpening in the center of the cap, the surface is smooth, slippery in wet weather;
- the shape in adult mushrooms is strongly prostrate with uneven curved and concave edges;
- the leg is short, tapering towards the base.
The smell is pleasant, mushroom, the pulp is thick, sweetish. Grows in dense colonies, abundant fruiting from the end of summer.
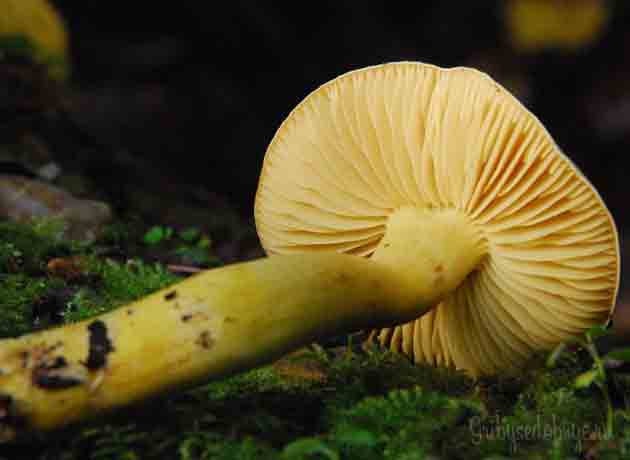
What a green mushroom looks like
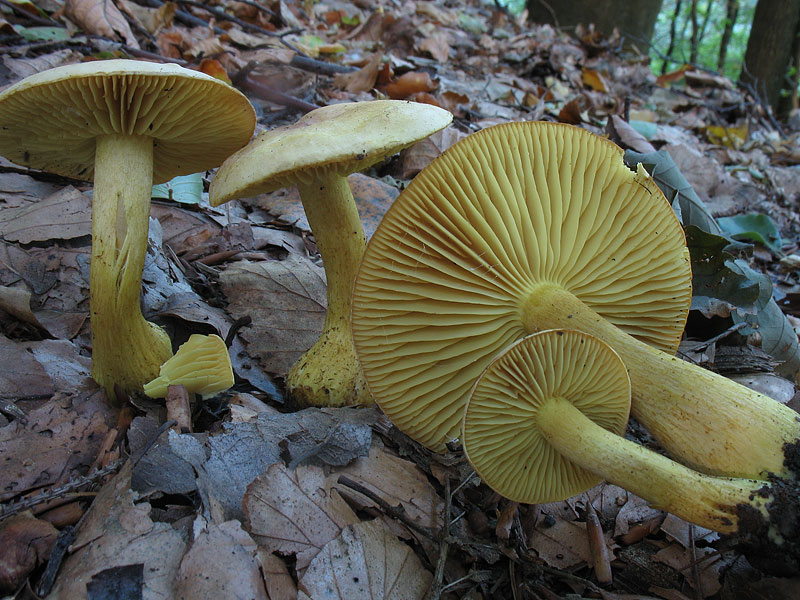
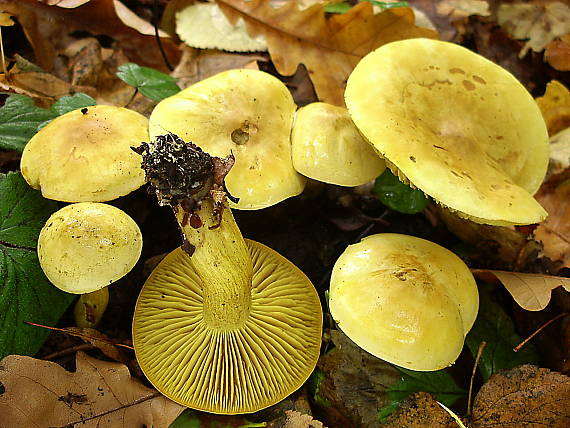
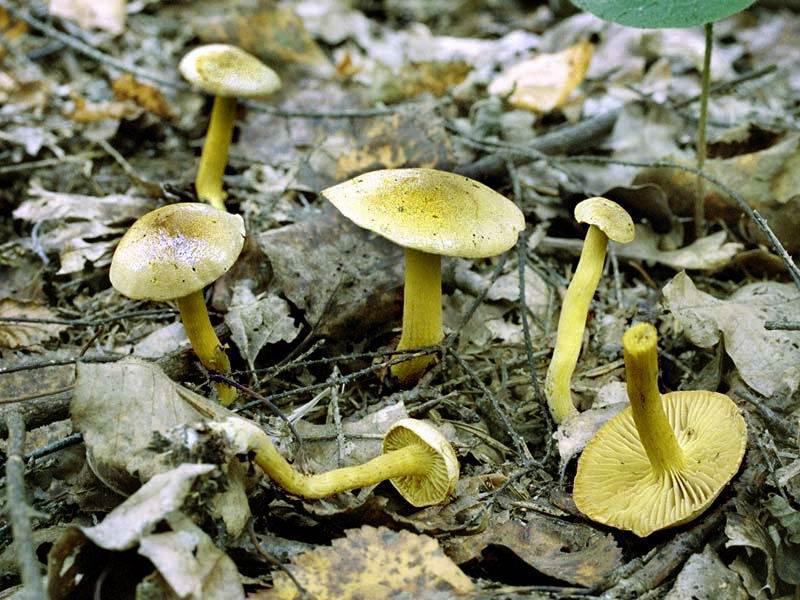
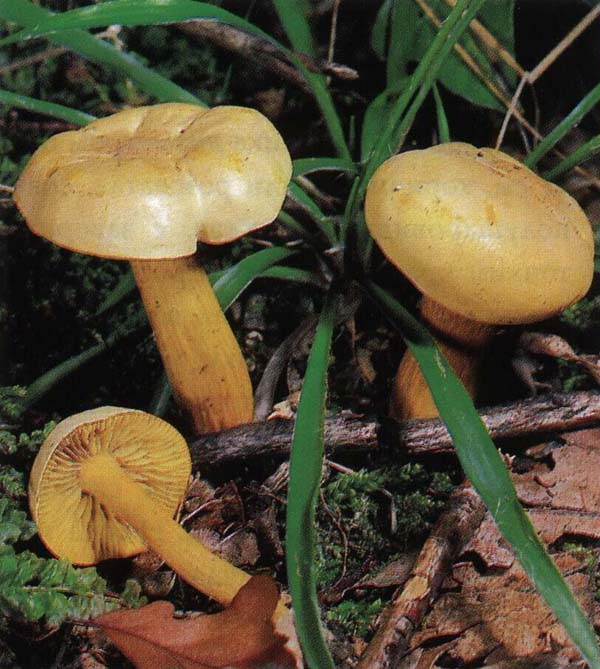
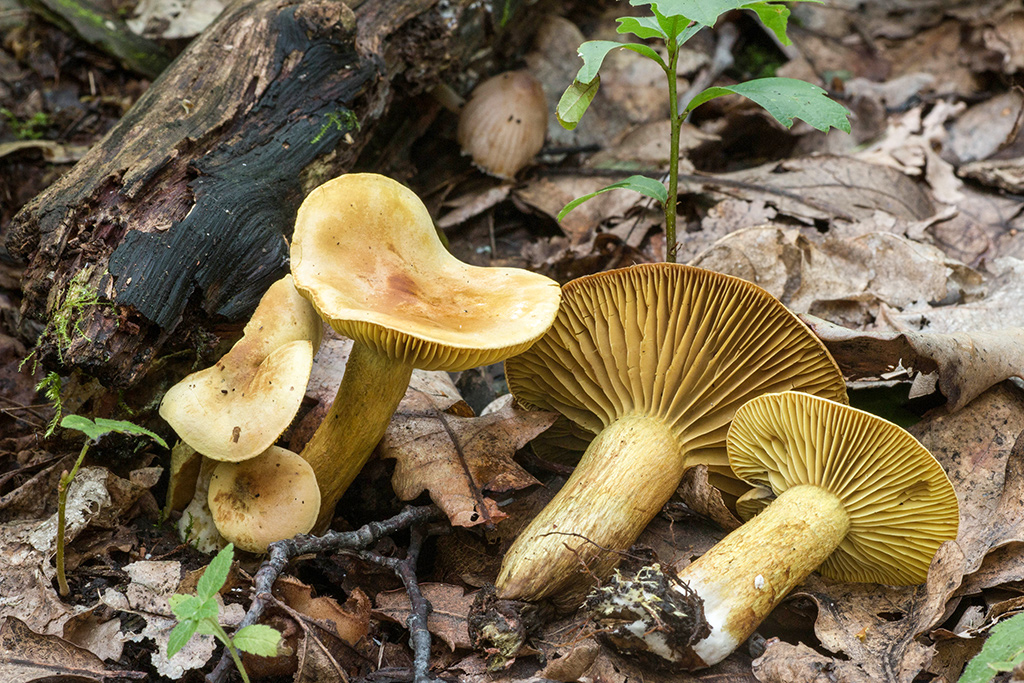
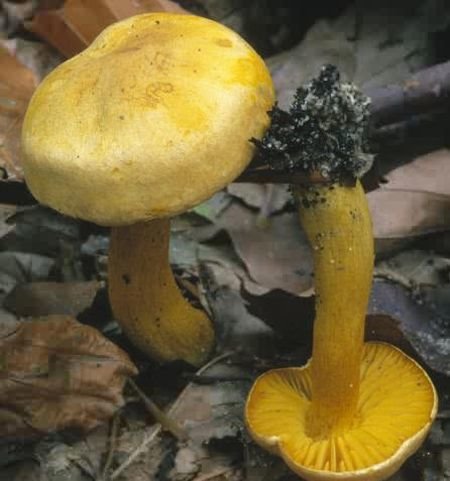
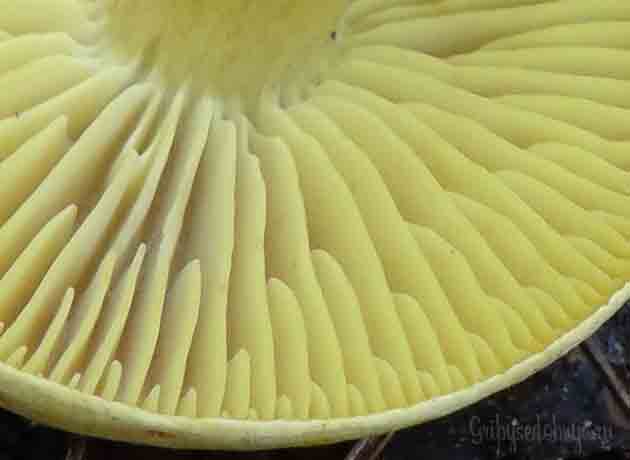
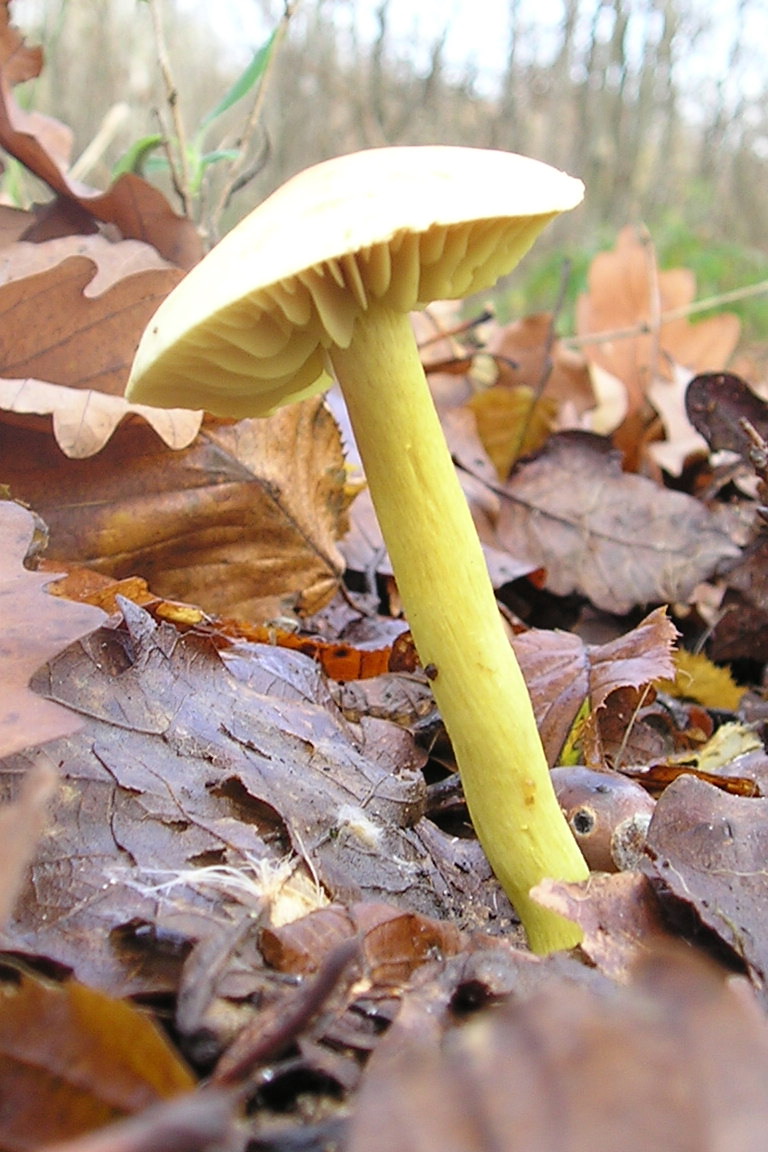
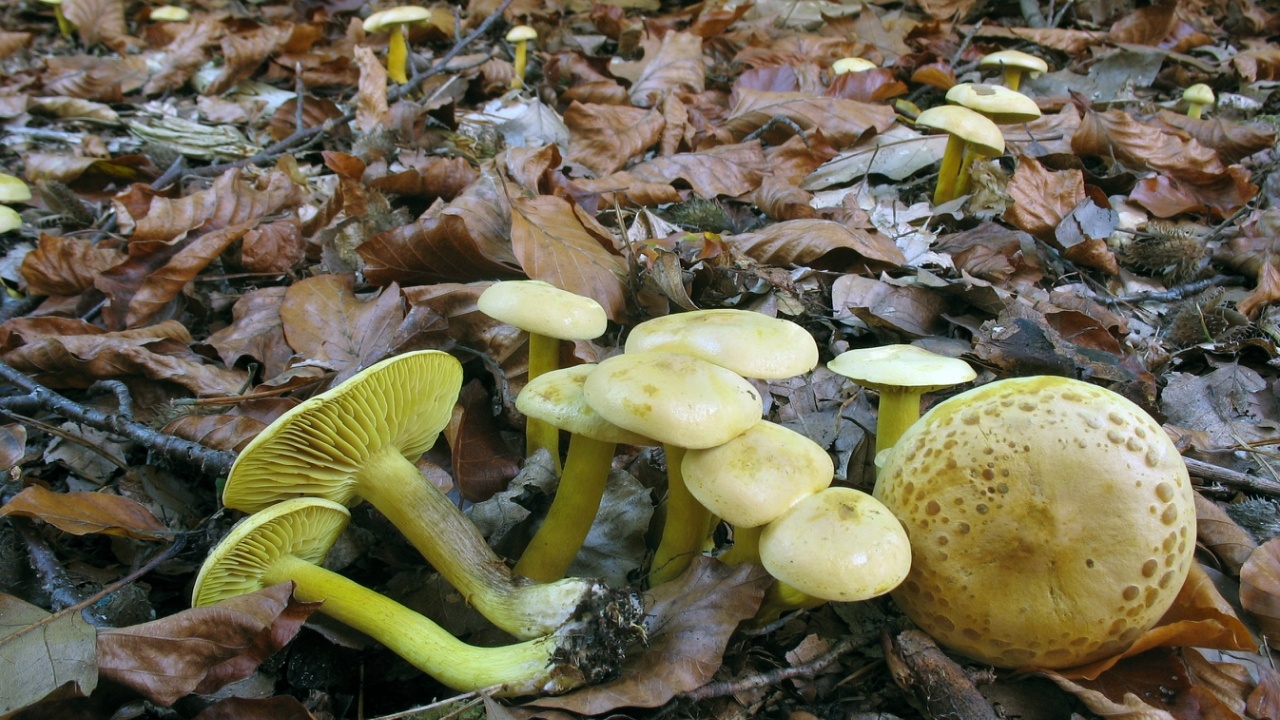
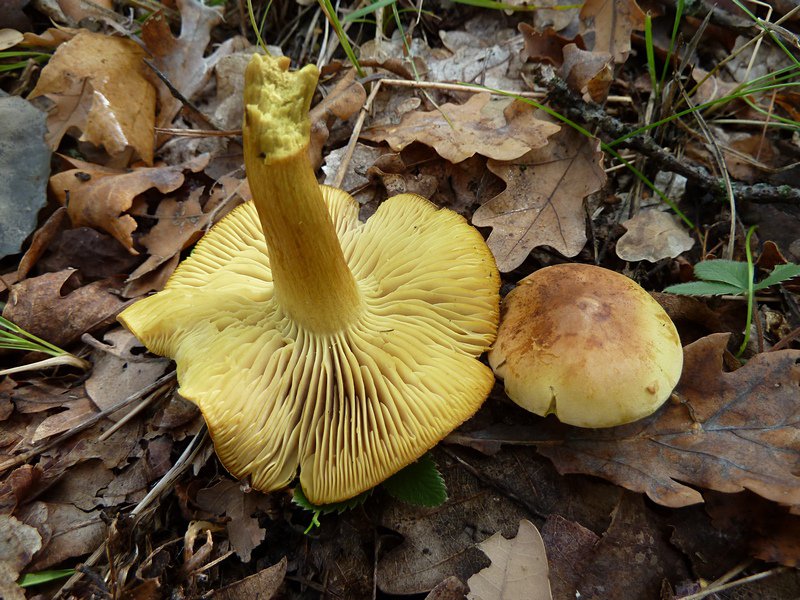
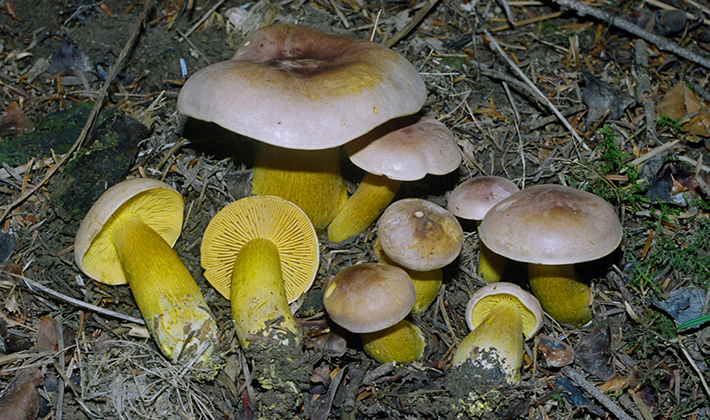
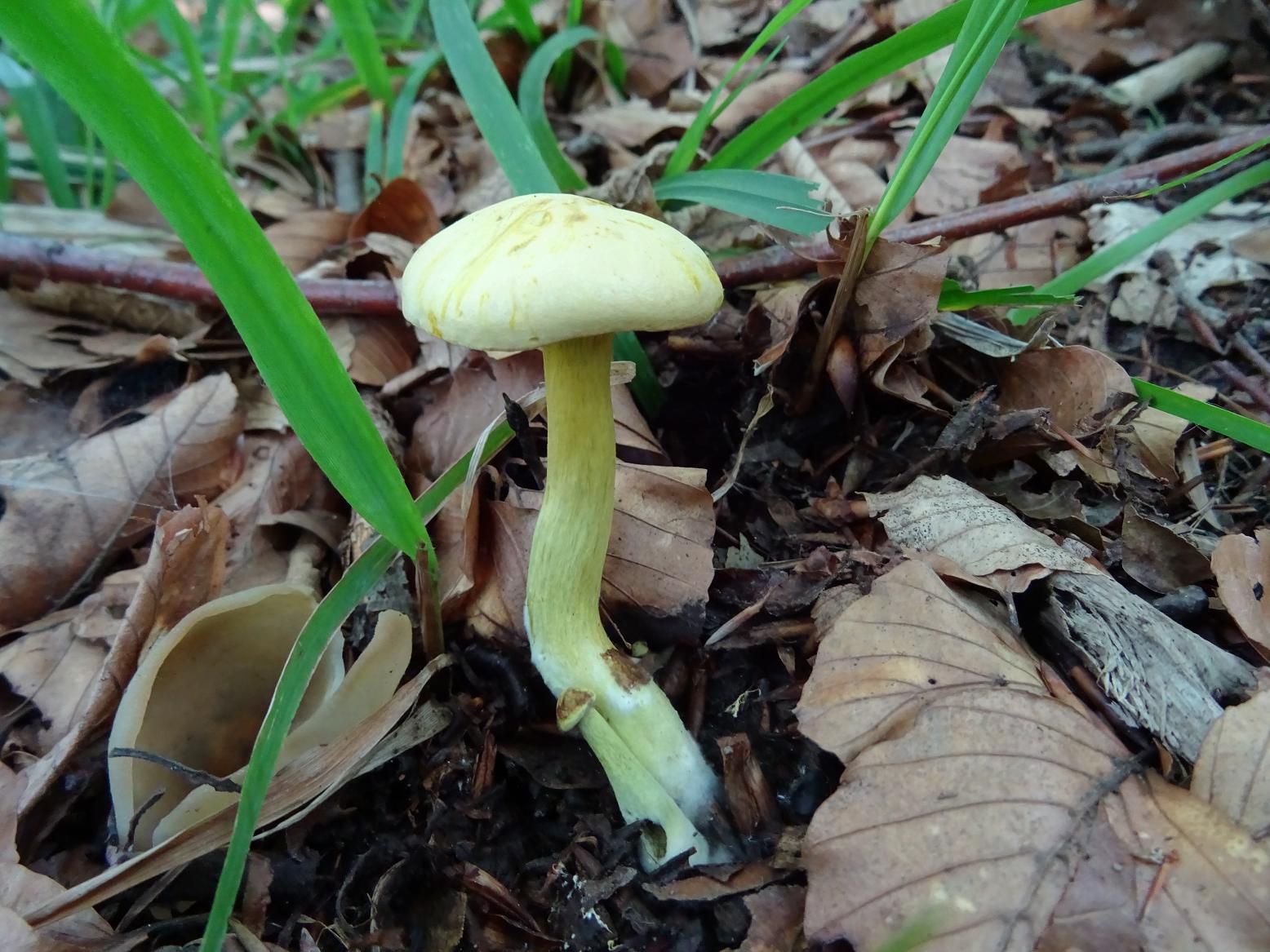
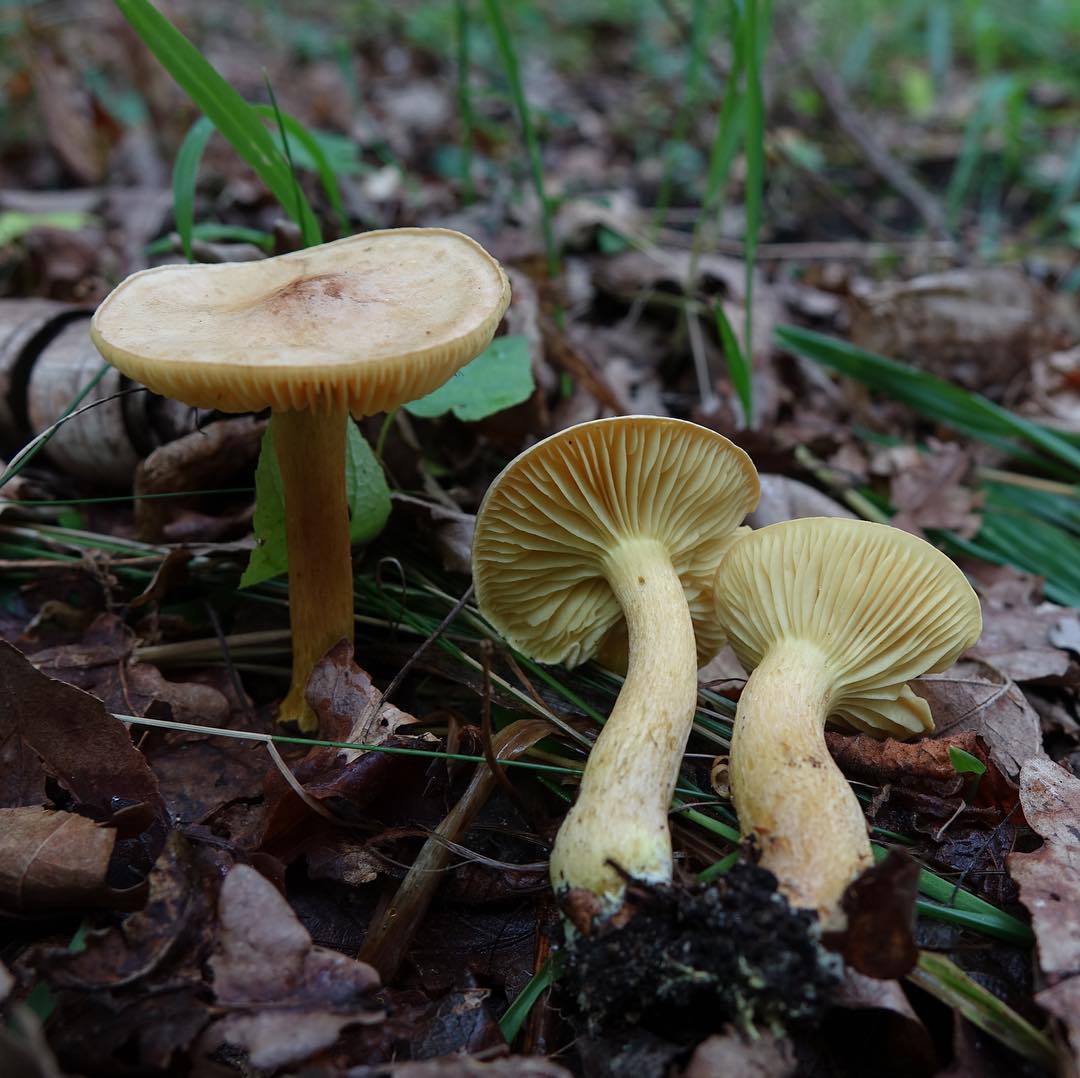
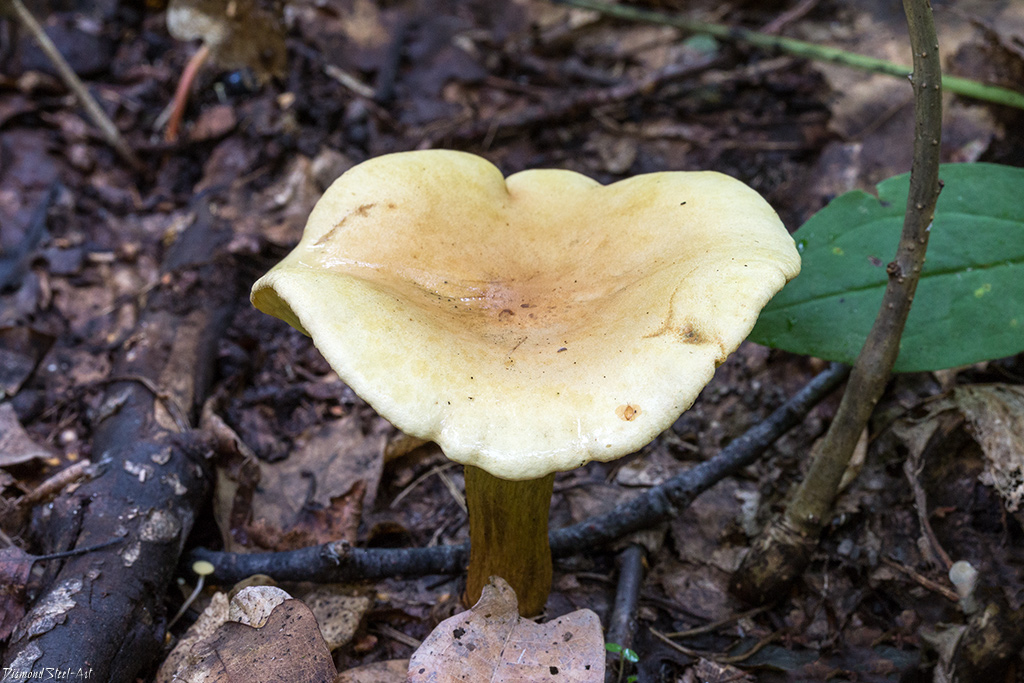
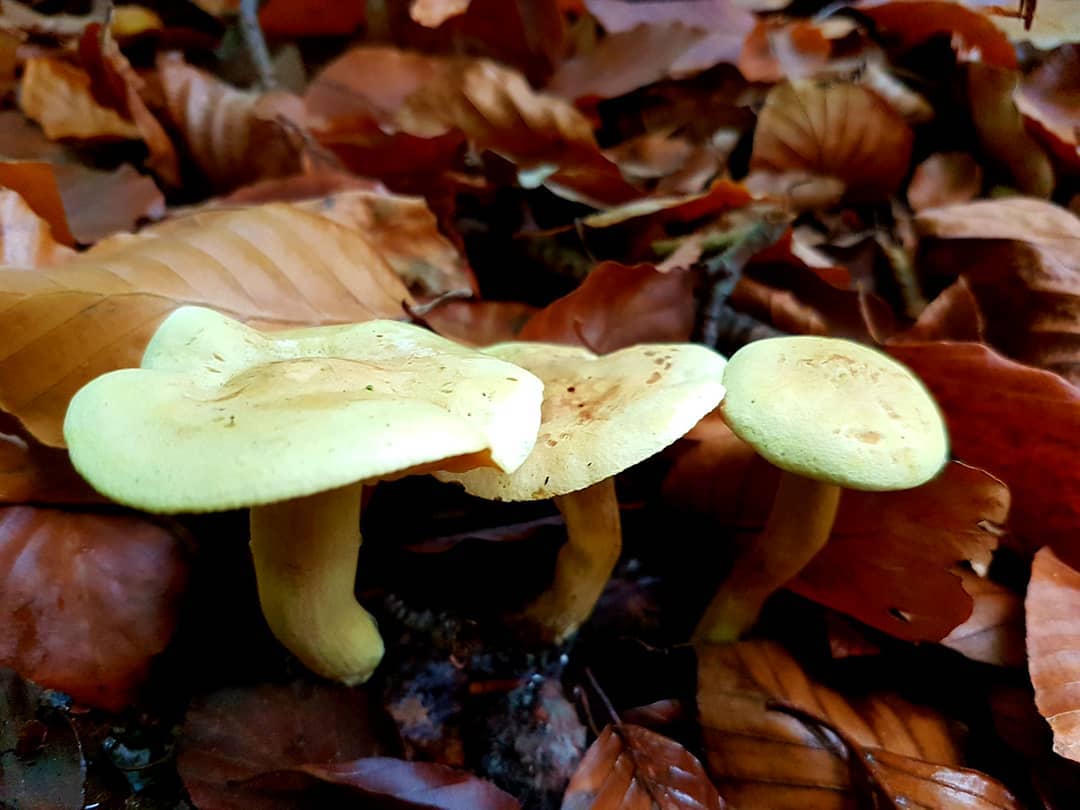
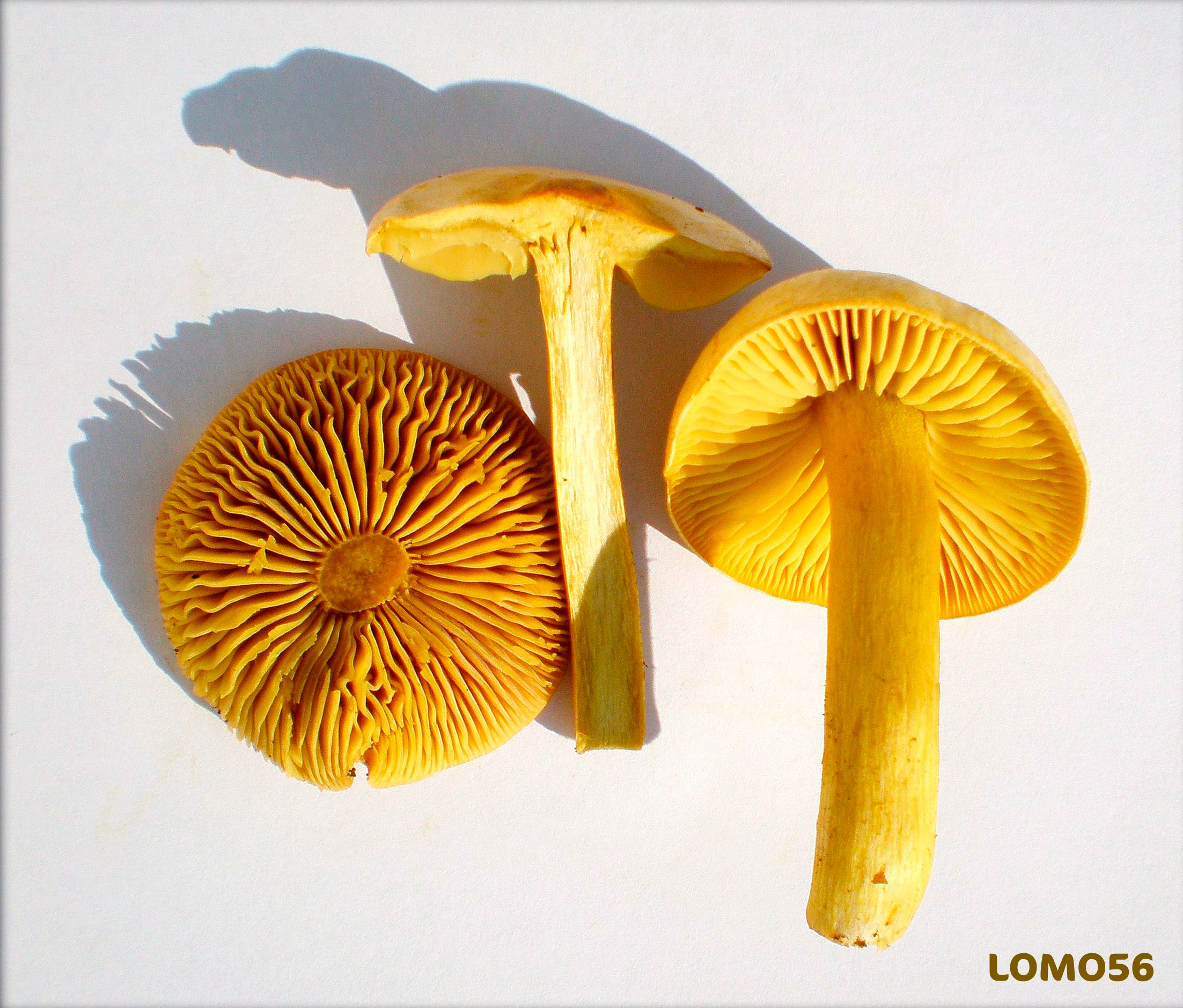
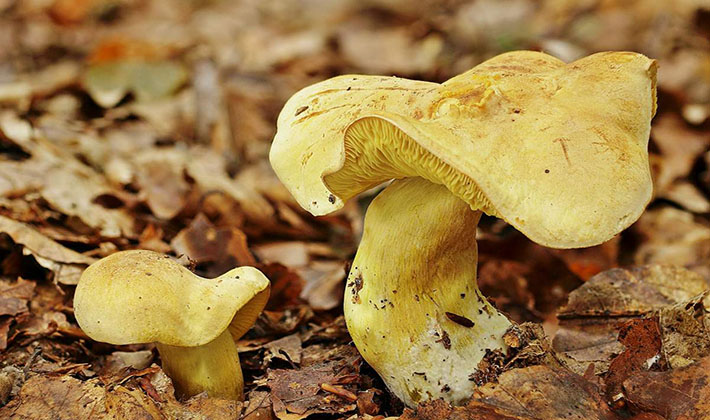
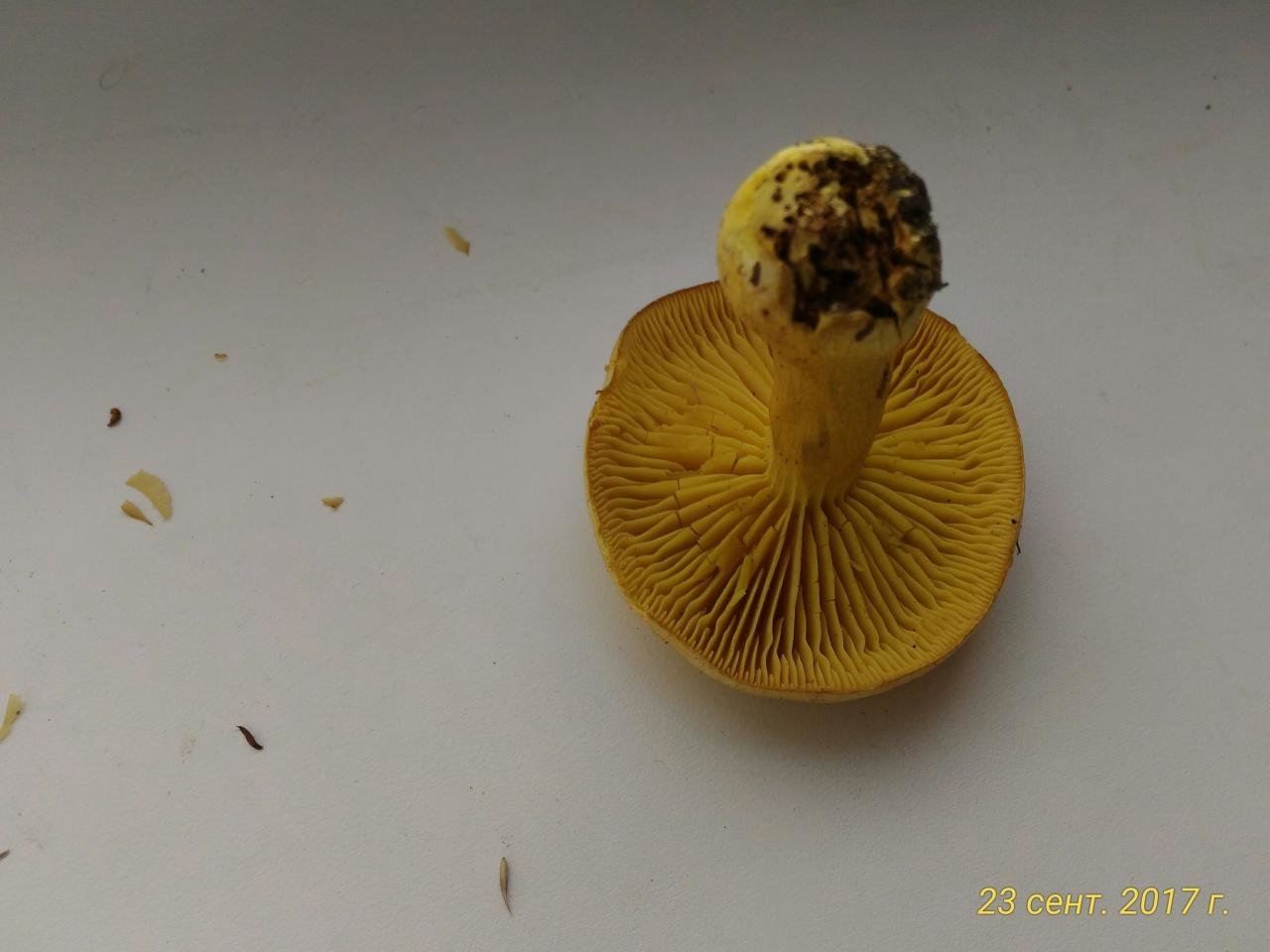
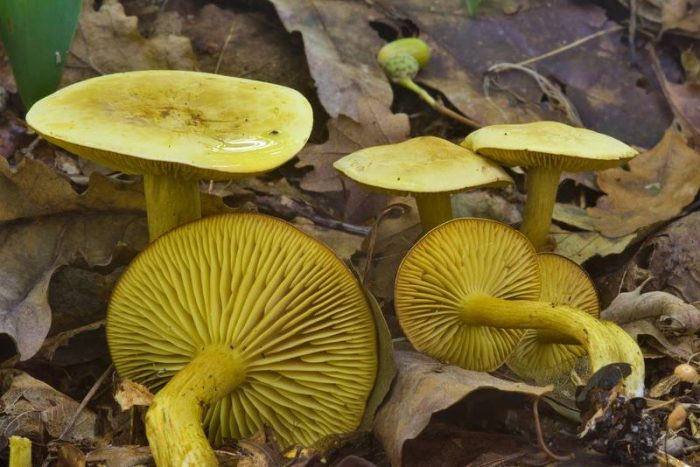
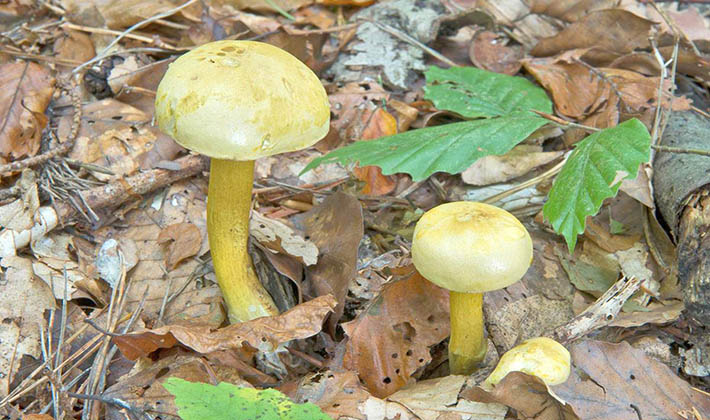
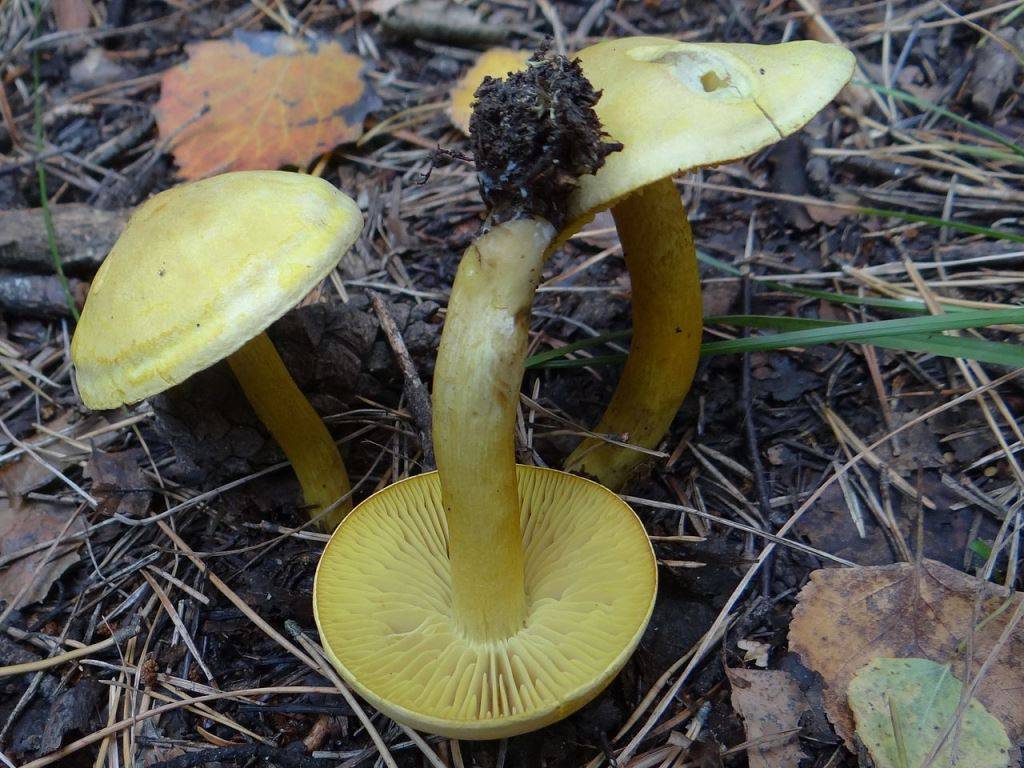
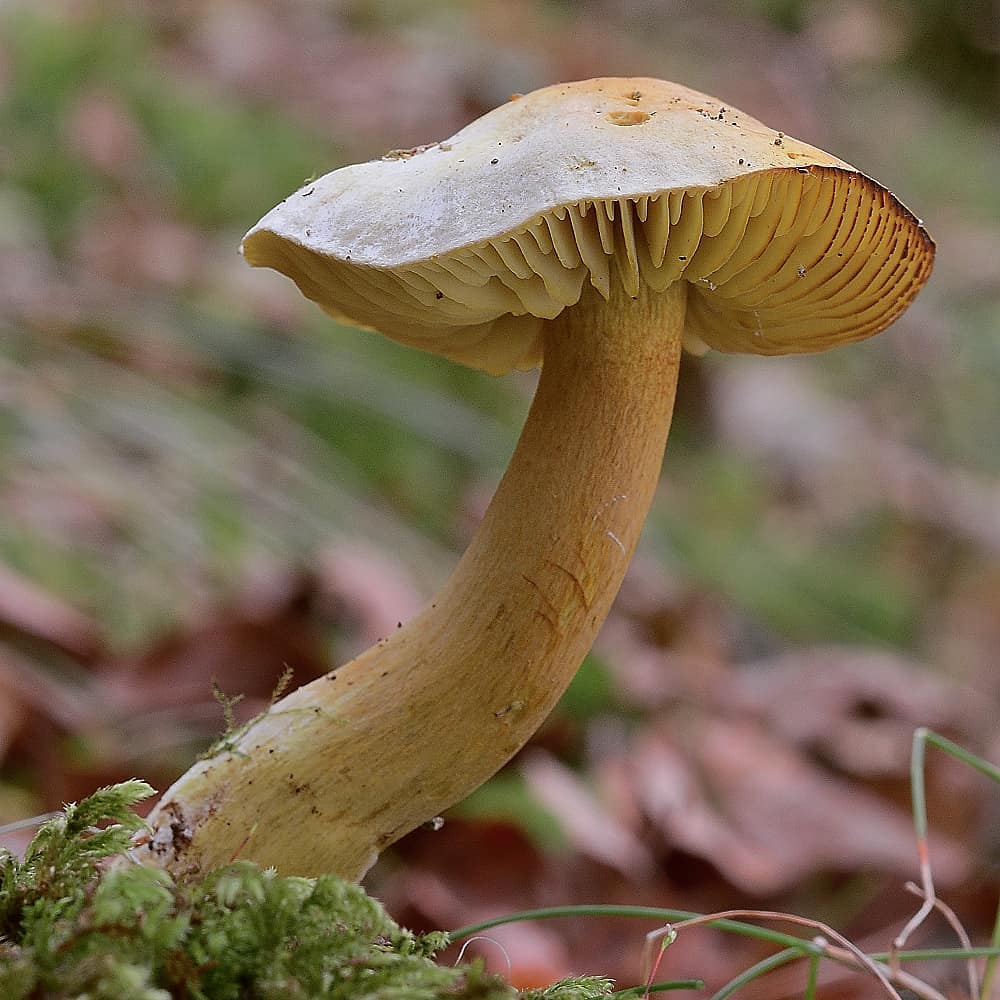
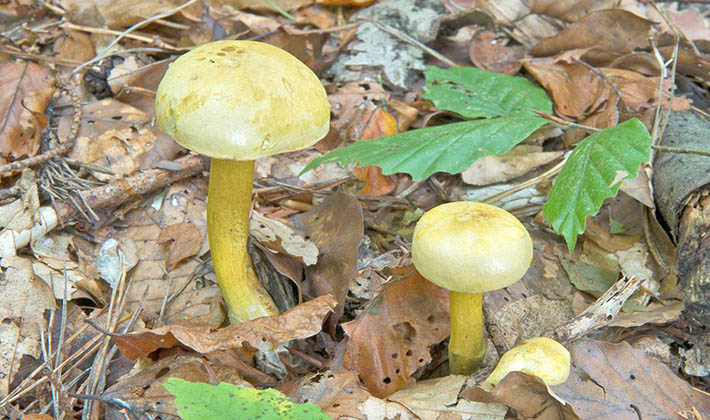
The green ryadovka cap is very fleshy, at first bell-shaped, later prostrate-curved. In its middle there is a small tubercle, the edges are raised, often wavy or cracked, the size ranges from 4-15 cm. To the touch, the greenfinch cap is dense, smooth, sticky, especially in wet weather. The skin is yellow-olive or yellow-green at the edges and brownish in the center, smooth or scaly. Young mushrooms are colored in light colors, they darken with age. The plates are loose, frequent, thin, lemon-yellow or greenish-yellow. The leg is straight, rigid, thickened downwards. It is the same color as the hat or slightly lighter. It has a dense fibrous structure, at the base it is covered with small brownish scales. The flesh of a young ryadovka is green, white, dense, yellowish under the skin, with a faint flour smell. As the fungus grows, it darkens a little. Does not change color on cut.
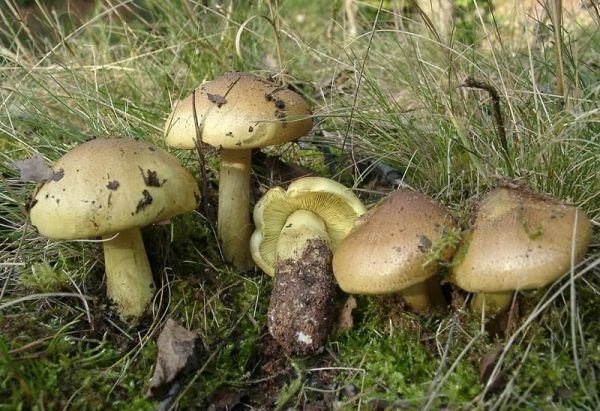

The nutritional value
Zelenushka is not very high in calories, having only 19 kilocalories for every one hundred grams. It consists of 46% protein, rich in valuable amino acids.

Another part of its composition, 49%, is occupied by carbohydrates, represented mainly by glycogen. And the fats in the composition (5%) are mainly expressed in the form of phosphatides, lecithin and cholesterol.
We recommend reading: Technical characteristics and descriptions of MAZ-5440 trucks: 5440A5, 5440A8, 5440A9, 5440V5, 5440V3, 5440S9, 5440M9, 5440E9, 544008, 544018, 544019, 544028, 544029, 544069. Design features of modifications of the popular model of Min truck tractors automobile plant
The protein of the rowing green has a whole range of amino acids useful for humans:
- tryptophan;
- arginine;
- lysine;
- serine;
- valine;
- glycine;
- histidine;
- threonine;
- isoleucine;
- aspartic acid;
- leucine;
- glutamic acid;
- methionine;
- phenylalanine.
- cystine;
- proline;
- tyrosine;
- alanine.

The greenhouse is very saturated with micro- and macroelements, among which there is the most phosphorus, and also presented:
- iron;
- potassium;
- calcium;
- magnesium;
- zinc;
- selenium;
- sodium;
- manganese;
- copper.
Vitamins are well represented in this mushroom in the form of:
- vitamin C;
- vitamin B6;
- vitamin B12;
- vitamin E;
- riboflavin;
- thiamine;
- vitamin D;
- vitamin D2;
- nicotinic acid;
- vitamin K1;
- pantothenic acid;
- folic acid;
- choline.
Read also: Mushroom on a tree (50 photos): edible, what parasites, what is the name, do it yourself, you can eat it, orange, nutty

Collection rules
Greenfinches are harvested in late autumn, when other mushrooms are already finishing fruiting. The main part of the fruiting body of the fungus, as a rule, is hidden in a thick layer of soil, fallen leaves or needles. In an adult specimen, only the cap is visible above the surface of the earth, while the young one gives itself out as a small bump or crack in the soil.
Zelenushka is carefully cut with a sharp knife at the root, then the base of the leg with adhered earth is also cut off. The soil and forest debris firmly adhere to the sticky skin, from which the green rowing must be cleaned when collecting. Dirt is removed with a special brush or scraped off with a knife. When collecting green rows, preference should be given to young specimens that do not have signs of spoilage. It is characteristic that this variety of tricholas is practically not damaged by insects.
Attention! When collecting mushrooms, you cannot leave part of the leg in the ground, it will rot, which can cause the death of the entire mycelium
Pointed row (Tricholoma virgatum)
The row is burning-sharp
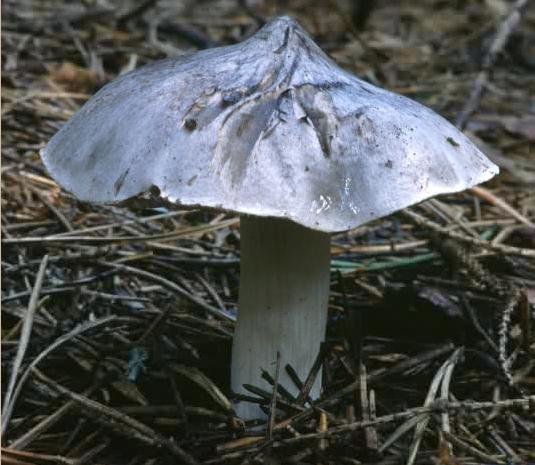

The pointed row (Latin Tricholoma virgatum) is a type of mushroom included in the genus Ryadovka (Tricholoma) of the family Ryadovkovy (Tricholomataceae).
Grows in moist deciduous and coniferous forests. It is often found in September - October.
The cap is 4-8 cm in ∅, first bell-conical, then hump-shaped, ash-gray, dark in the center, with a striped edge.
The pulp is soft, at first grayish-whitish, then white, with a bitter taste and a flour smell.
The plates are frequent, wide, adherent with a tooth to the pedicle or almost free, deeply indentable, white or grayish, then gray. Spore powder is white. Disputes are oblong, wide.
Leg 6-8 cm long, 1.5-2 cm ∅, cylindrical, slightly thickened at the base, dense, whitish or grayish, longitudinally striped.
The mushroom is poisonous. It can be confused with an edible mushroom in an earthy-gray row row.
Mushroom photo Row pointed
from questions in recognition:
| Group: | Lamellar |
| Plates: | White |
| Colour: | Ash gray |
| Info: | Bump in the center of the cap |
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Agaricomycetidae |
| Order: | Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar) |
| Family: | Tricholomataceae (Tricholomaceae or Ordinary) |
| Genus: | Tricholoma (Tricholoma or Ryadovka) |
| View: | Tricholoma virgatum (Pointed row) |
The pointed row belongs to inedible mushrooms because of the burning-bitter taste. Some sources call this type of rowing poisonous.
First aid for poisoning
At the first suspicion of poisoning, you must seek qualified help. Before the ambulance arrives, a number of measures are taken to alleviate the symptoms and prevent the toxin from spreading throughout the body.
Important! Mouse poisoning can lead to kidney or liver failure. Without treatment, the pathology quickly turns into a chronic form, it can be fatal
First aid for poisoning:
- The main task is to get rid of the remains of the fungi in the stomach. Use warm boiled water with the addition of manganese, the solution should turn out pale pink.
- It is drunk in one gulp in small portions, about 300 g. Immediately induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue. After five minutes, the procedure is repeated. The drunk norm of the solution is at least 1.5 liters.
- If there is no diarrhea in the symptoms, it is caused by any laxatives, it is necessary to cleanse not only the stomach, but also the intestines.
- If the funds do not give a positive result, make an enema with warm water or the same solution of potassium permanganate.
- After the enema, give any absorbent.
The patient must be laid down, covered with a warm blanket, and constant drinking must be provided until the doctor arrives.
Beneficial features
There is hardly another natural product with such a unique composition as mushrooms:
- more minerals than fruits;
- carbohydrates - as in vegetables;
- more proteins than meat.
And edible rows are no exception. They are wholesome food.
The low calorie content of the rowers (20 kcal per 100g of fresh mushrooms) makes them indispensable in weight loss programs.
These mushrooms are natural antibiotics. The antioxidant and immunostimulating properties of drugs obtained from certain types of rows have been proven:
- on the basis of violet, a drug has been developed to control hypoglycemia;
- giant - contains the antibiotic clitocin, which kills cancer cells;
- drugs are made from the broken ones that infect the tubercle bacillus;
- powder from fruit bodies of a row of crowded reduces the level of cholesterol in the blood.
Contraindications and harm
And yet, the rows are not recommended for everyone. In case of problems with the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, it is better to exclude them from the diet. Abundant and regular use can lead to gastritis: the rowers contain chitin protein, which is not digested by our body, and its excess leads to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Poisonous species and differences from edible
Eating poisonous ryadovki is very dangerous for human health. These include the following types:
- spruce;
- white;
- toad;
- smelly;
- conical (pointed);
- brindle (leopard);
- spotted;
- scorched (tanned).
Edible ”species can only be confused with white, spotted and leopard rows. You can distinguish them like this:
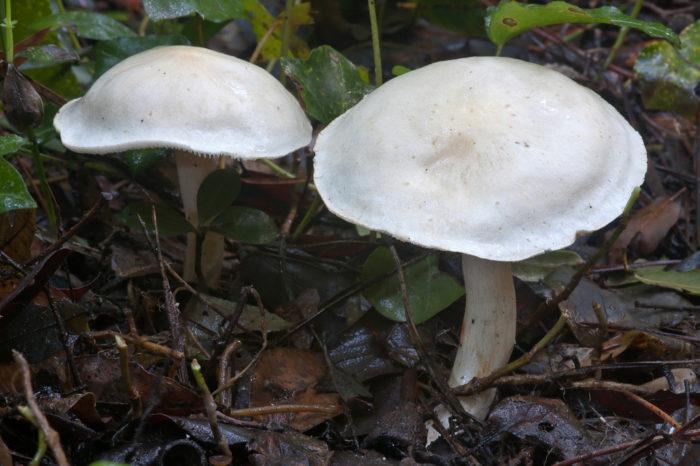
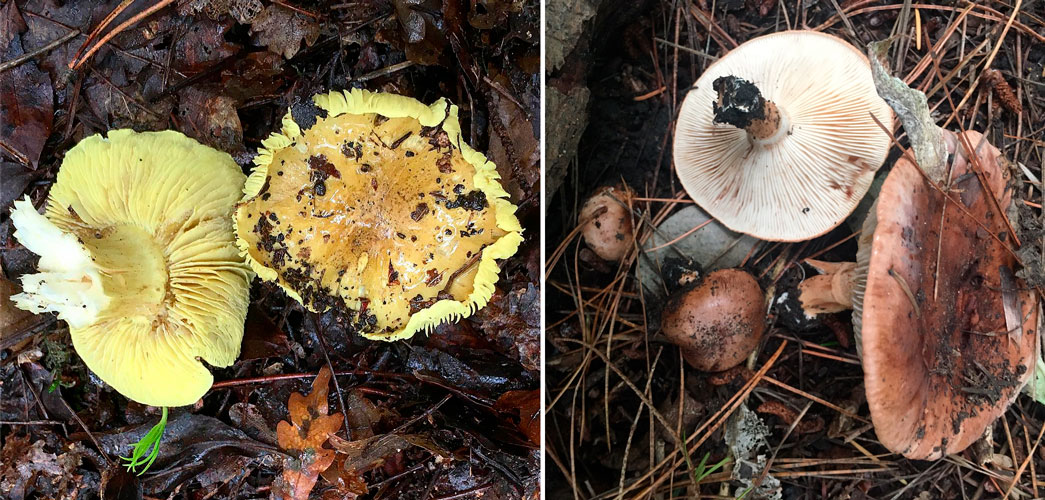
- The white ryadovka is distinguished by a snow-white, sometimes yellowish color. The hat is open and velvety. The leg is cylindrical, slightly curved. Its surface repeats the color of the cap. You can recognize the mushroom by its pulp. It tends to change its color upon contact with air, therefore, at a break, it instantly turns pink. A sharp unpleasant smell of radish emanates from the pulp.
White row
The cap of the spotted row is spread out and slippery, with a small depression in the middle. It is colored light brown. Dark brown longitudinal stripes and spots of the same shade are clearly visualized over the entire surface. The edges of the cap are slightly lighter. The leg is widened at the base. From below it repeats the color of the cap, and from above it is white.
 Row leopard
Row leopard
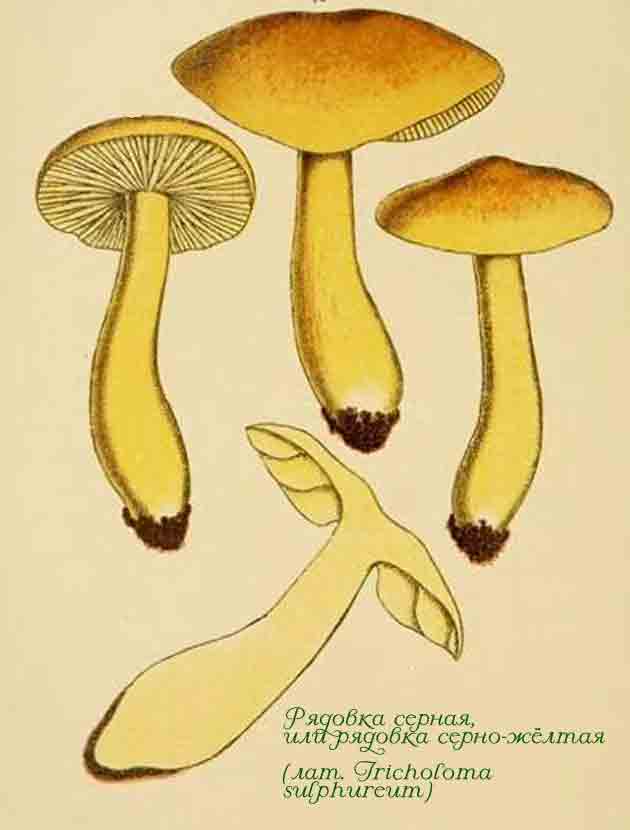
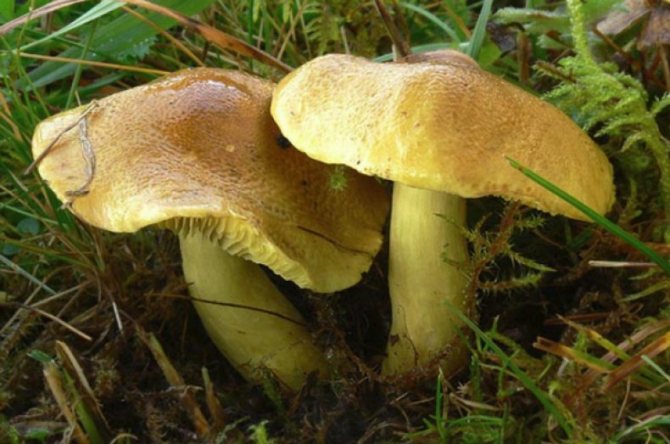
Biological description of ryadovka sulfuric.
Her cap is initially convex or spherical in shape, and in adulthood the shape becomes flattened, while there may be a small depression in the center. The color of the cap is gray-yellow. The cap has rusty-brown fibers, which are especially pronounced in the center. Its surface may be dry or damp, but most often it is velvety.

In sulfuric rows, the hymenophore is lamellar. The plates are relatively sparse, notched, thick, wide, adherent to the peduncle, with uneven edges. The color of the plates is also sulfur-yellow. Spores are almond-shaped or ellipsoidal. Spore white powder.
The leg is both thickened and, on the contrary, narrowed downward. Its height is 3-11 centimeters, and the girth reaches 1.8 centimeters. The upper part of the leg is bright yellow, and at the bottom it becomes sulfur-yellow with pronounced longitudinal fibers, which can be of the same color with the general background or darker. In old rows, the lower part of the leg may be covered with brownish scales.

The pulp has a very strong odor, reminiscent of tar, hydrogen sulphide, acetyl or luminescent gas. A flour smell may sometimes be present. The taste of the pulp is unpleasant, sometimes bitter. The color of the pulp is greenish or sulfur-yellow.
False doubles
It is sometimes easy to confuse soapy row with other types. Photos of mushrooms and their description will help you understand them correctly.
-
Brown row.Conditionally edible, with a brown cap and edges tucked inward. The skin color is usually reddish or yellow-orange. In the center, the cap is always darker than at the edges. One of the main distinguishing marks is a high leg.
- Gray. An edible mushroom with a whitish, firm flesh. The smell is pleasant - like fresh flour. The taste is poorly expressed. The leg is rooted and buried in moss or fallen leaves.
-
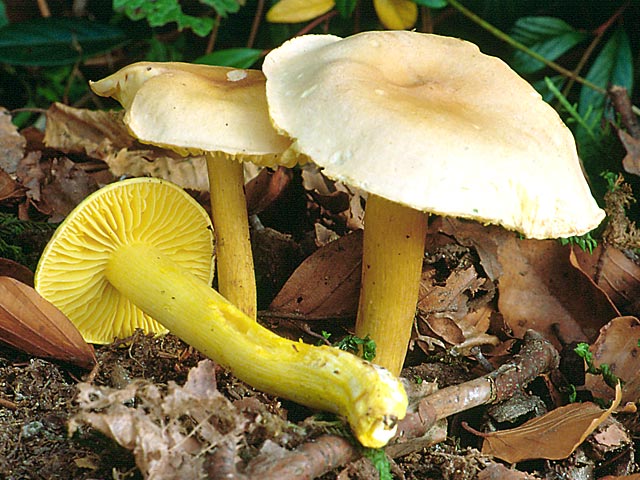
Green. It is also called green tea. It has a short stem that is practically hidden in the ground. The flesh is firm and white. The fungus rarely grows stale. The color of the cap is greenish-yellow, with a pleasant scent of cucumber.
- Golden. Low quality edible mushroom. Its peculiarity is the release of juice droplets. The stalk is always visible with a pronounced area of red scales. The flour aroma is weak. The flesh of the mushroom is white and firm.
Dangerous doubles
| Name | Description |
| Tiger row
|
Black and brown hat with spots and green tint. The smell of the mushroom is pungent, but pleasant. Young specimens have a fibrous surface. The length of the leg is different: from 3 to 12 cm. The pulp of the mushroom is white with a gray bloom under the skin. The main difference from other species: the presence of scales on the hat. |
| Pointed row
(other names: mouse ryadovka and burning-sharp ryadovka). |
It has a gray or black bell-shaped hat with striped edges; plates are grayish or whitish. The bitter taste of the pulp; in color, it is first gray-white, and then brightens. The stem of the mushroom is cylindrical and dense; about 8 cm high. |
| The row is white or smelly
|
The mushroom has a rather dense cap with closed edges; a small tubercle may form in its center. Skin color is white or grayish. The elastic and dense leg is a cylinder. The color of the pulp is white. A distinctive feature is the smell: if the fruit body is damaged, it is very unpleasant. |
Symptoms of poisoning with poisonous species can be detected approximately 3 hours after eating. They are manifested by weakness, vomiting, sharp pain in the stomach. Confusion of consciousness is not observed. But in any case, in case of poisoning, you must consult a doctor.
Taxonomy
Synonyms
- Agaricus coronarius Pers., 1801
- Agaricus sulphureus Bull. 1784basionym
- Gymnopus sulphureus (Bull.) Gray, 1821
- Gyrophila sulphurea (Bull.) Quél., 1886
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. coronarium (Pers.) Nüesch, 1923
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. verrucosum Naveau, 1923
Varieties
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. hemisulphureum Kühner, 1989 differs from the typical variety in pinkish or gray-lilac edges of the plates.
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. pallidum Bon, 1974 is distinguished by a lighter color and a sweetish, spicy smell.
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. rhodophyllum Métrod, 1939 grows in the alpine zone, is painted in very light colors.
Poisoning symptoms
When poisoning with a mouse ryadovka, the symptoms depend on the amount of fruit chalk used. The manifestation of intoxication can be mild or severe. The first signs appear after 2-4 hours. The mild form proceeds with the following symptoms:
- cramping pain in the stomach and intestines;
- nausea;
- headache;
- diarrhea;
- vomit.
The severe form, in addition to the listed symptoms, is accompanied by:
- constriction of the pupils;
- a slowdown in the heartbeat;
- severe dizziness;
- sweating;
- difficulty breathing;
- possible salivation and lacrimation.
Without the provision of timely assistance, convulsions and an extreme irreversible process are observed - coma.
Cooking recipes
Only young specimens are used for cooking. Old mushrooms are tough and bitter, which, of course, has a bad effect on the taste of the dish.
IMPORTANT. Mushrooms are not recommended for people with digestive problems, as they are a product that is difficult to digest and assimilate.
Primary processing
Mushrooms are a perishable product, which means they need to be processed no later than 4–5 hours after harvesting. First, they must be sorted out and damaged and old fruit bodies removed.Dry, chop and start cooking directly.
Cooking
It is imperative to boil mushrooms. In this case, the first broth should be drained after boiling. Then you need to rinse the mushrooms with cold water and cook again for 30-40 minutes.
Pickling
The pickled row can be stored in the basement or refrigerator for up to six months. To prepare it, take 1 kg of boiled mushrooms, put it in jars and pour it with marinade:
- 3 tbsp. l. 9% vinegar;
- 1 tbsp. l. salt;
- 1.5 tbsp. l. Sahara;
- 250 ml of water;
- spices to taste (allspice, garlic, bay leaf).
Frying
The process takes a minimum of time, and the dish turns out to be tasty and aromatic. For 1 kg of a row, 250-300 g of onions and 300 g of fatty sour cream will be required. Mushrooms are pre-boiled, draining the water once. Vegetable oil is poured into a frying pan, onions are fried on it, then mushrooms are added and after 5 minutes sour cream. Spices can be anything you like. Best served hot.
Salting
It is believed that yellow-brown row suitable for salting. This is the best way to cook it.
To prepare a delicious snack you will need:
- 6 kg of mushrooms;
- 8 tbsp. l. coarse salt;
- Bay leaf;
- 20 cloves of garlic;
- peas of black allspice;
- several dill umbrellas.
- The lower part of the leg is removed from the mushroom and filled with cold water for three days. In this case, the water should be drained every 5 hours.
- Spices are placed on the bottom of the jar in a small layer, then a layer of mushrooms 5–6 cm. After that, spices again.
- The last layer should be salt. The jar is closed with clean gauze and a tight lid. After 30 days, a delicious snack is ready.
Similar types and differences from them
This mushroom is quite easy to confuse with representatives of the Champignon genus, but if you look closely or sniff, you can find obvious differences: the plates near the row do not darken, and the pulp emits a noticeable pungent smell. Champignons, on the other hand, have a pleasant mushroom aroma. It also differs from other types of edible rows by the presence of an unpleasant odor. By the way, another difference between the white ryadovka and the champignon is the absence of a ring on the leg or a blanket under the hat.
It is easy to confuse it with yet another species - a stinking row. It is also an inedible mushroom, and it smells like lamp gas. Smelly ryadovka is an organism whose fruiting body contains hallucinogens that can cause the development of both auditory and visual hallucinations.
In order to get your bearings and not be mistaken while picking mushrooms, before going into the forest, pay attention to the photo of the white row presented in this article - having seen how it looks, you certainly will not be mistaken and will not confuse it with other species.
Accidentally eating a white line can cause stomach upset. Yes, and her smell is so persistent that it is not removed even during prolonged heat treatment. It is better not to risk it and simply throw the suspicious mushroom out of your basket.
The classic recipe for salting for the winter in jars
To salt brilliant green in the classic way, you need the following ingredients:
- freshly harvested brilliant green - 1 kg;
- water - 2 liters;
- salt - 40 g;
- sugar - 25 g;
- a few sprigs of dried dill;
- raspberry leaves - 8 pcs.;
- cherry leaves - 8 pcs.;
- black pepper - 10 pcs.;
- bay leaf - 3 pcs.;
- vinegar - 50 ml.
How to pickle greenfinches mushrooms for the winter:
- First, you should properly prepare the rows for conservation: rinse thoroughly and clean the green leaves.
- To prepare mushrooms for the winter, you need to make a brine. Add the required amount of spices and salt to the water and put the pan on a medium heat.
- Bring to a boil and turn off heat.
- Let the brine cool for 15 minutes.
- Next, transfer the prepared peeled green stuff into jars, tamping them tightly. Mushrooms should take up more than half of the container.
- Pour in some brine and add more rows on top.
- Top up the remaining marinade up to the rim of the jar. Pickled brilliant green mushrooms are immediately covered with lids and removed to a warm place for several weeks.
Mushroom ryadovka sulfur-yellow: photo and description
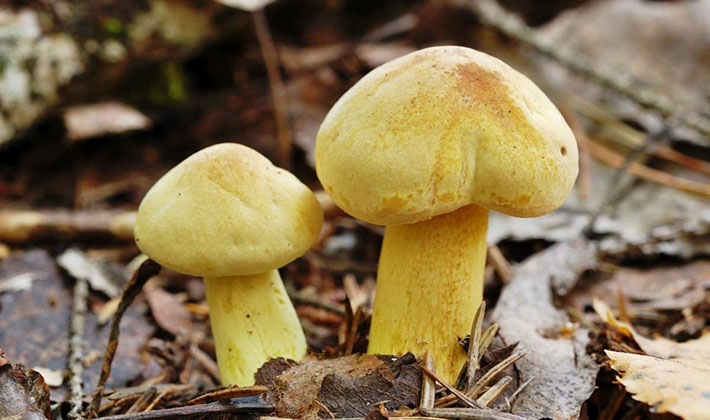 For acquaintance, we suggest looking at a detailed description of the sulfur-yellow row and a photo.
For acquaintance, we suggest looking at a detailed description of the sulfur-yellow row and a photo.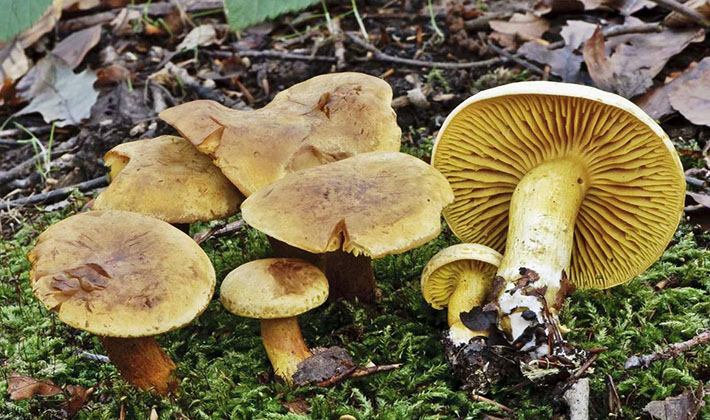


 Latin name: Tricholoma sulphureum.
Latin name: Tricholoma sulphureum.
Family: Ordinary.
Synonyms: ryadovka sulfur, false sulfur ryadovka.
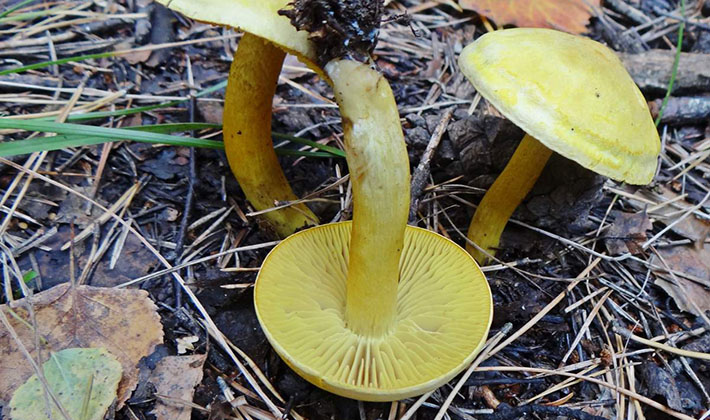
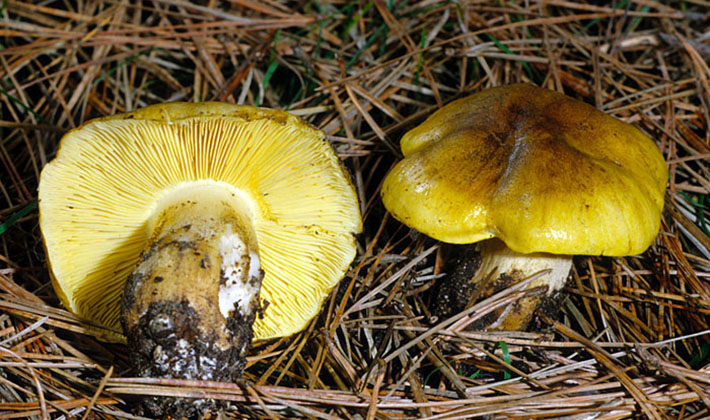
 Hat: the diameter varies from 3 to 8 cm, some specimens reach 10 cm. At first, this part of the fruiting body has a convex or hemispherical shape. With age, the cap becomes flat-convex with a depression in the central part. The surface of the cap has a sulfur-yellow color, which over time acquires a brown tint with mild fibers. It is velvety to the touch and slippery in wet weather. This feature is clearly shown in the photo of the sulfur-yellow row, taken after the rain:
Hat: the diameter varies from 3 to 8 cm, some specimens reach 10 cm. At first, this part of the fruiting body has a convex or hemispherical shape. With age, the cap becomes flat-convex with a depression in the central part. The surface of the cap has a sulfur-yellow color, which over time acquires a brown tint with mild fibers. It is velvety to the touch and slippery in wet weather. This feature is clearly shown in the photo of the sulfur-yellow row, taken after the rain:
Leg: the height varies from 3 to 12 cm, and the thickness is from 0.5 to 2 cm. Sometimes it has a thickening in the upper part, or vice versa - thinning. The color of the leg under the caps is bright yellow, downward it becomes sulfur-yellow. At a more mature age, longitudinal monochromatic or dark fibers are visible on the surface. The legs of older specimens are curved and sometimes densely covered with brown scales.
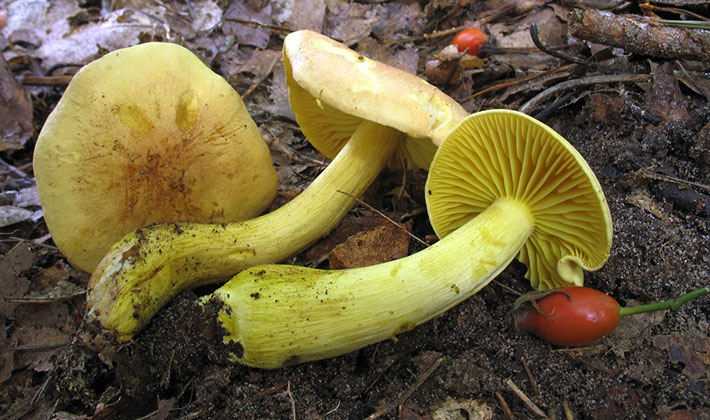
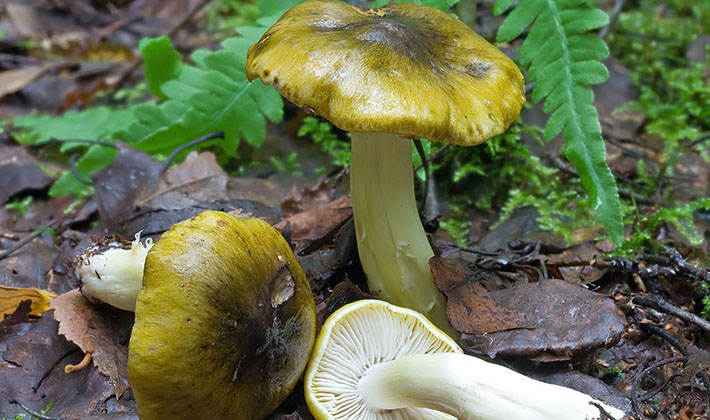
 Flesh: the color can be sulfur-yellow or with a greenish tinge. The last color feature leads to the fact that the false sulfur ryadovka is confused with green tea - an edible mushroom. The smell of the pulp is very unpleasant, reminiscent of the smell of acetylene or tar, sometimes hydrogen sulfide or lamp gas. The pulp of ryadovka sulfur-yellow tastes bitter.
Flesh: the color can be sulfur-yellow or with a greenish tinge. The last color feature leads to the fact that the false sulfur ryadovka is confused with green tea - an edible mushroom. The smell of the pulp is very unpleasant, reminiscent of the smell of acetylene or tar, sometimes hydrogen sulfide or lamp gas. The pulp of ryadovka sulfur-yellow tastes bitter.
Plates: adherent to the peduncle and notched, with an uneven edge. According to the description of the ryadovka, its sulfur-yellow plates are rather rare, thick and wide. They have a gray-yellow color, with the same colored edge.
Spores: white, almond-shaped, often irregular.
Application: not used in cooking, as it is considered an inedible mushroom.
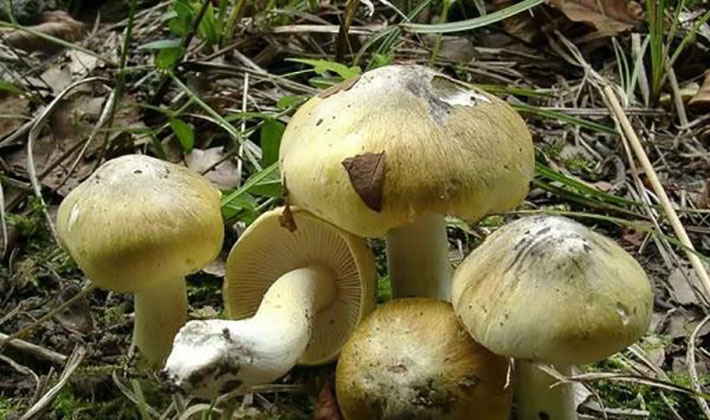
 Edible: an inedible or poisonous mushroom of low toxicity, capable of causing mild stomach poisoning. As already noted, this type of ryadovka has a pungent smell, reminiscent of the smell of hydrogen sulfide, as well as an unpleasant bitter taste.
Edible: an inedible or poisonous mushroom of low toxicity, capable of causing mild stomach poisoning. As already noted, this type of ryadovka has a pungent smell, reminiscent of the smell of hydrogen sulfide, as well as an unpleasant bitter taste.
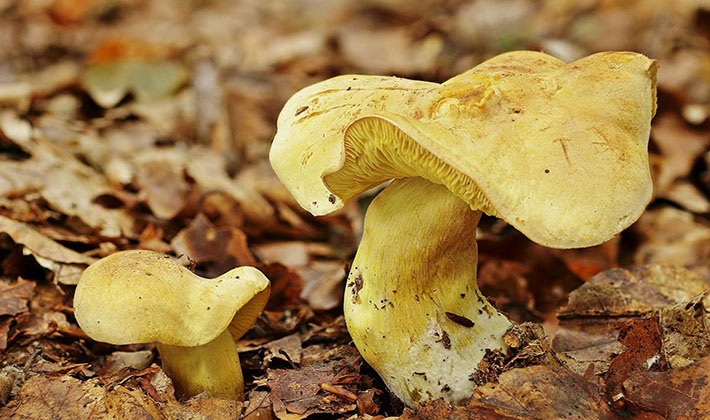
Similarities and differences: often this type of fruit body is confused with edible rows - isolated, earthy gray, gray and yellow-red
Pay attention to the photo of the sulfur false row to make it easier to distinguish from other species. Sometimes the row can be confused with green tea, but it is much larger in size, with frequent blades and white or yellowish pulp
 Distribution: usually prefers deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests. Grows in groups or rows, resembling "witch circles", on rich limestone and sandy soils. Often forms mycorrhiza with beech, oak, a little less often with fir and pine. The sulfur-yellow row can often be found on the roadsides, in park areas and even in summer cottages.
Distribution: usually prefers deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests. Grows in groups or rows, resembling "witch circles", on rich limestone and sandy soils. Often forms mycorrhiza with beech, oak, a little less often with fir and pine. The sulfur-yellow row can often be found on the roadsides, in park areas and even in summer cottages.
Fruiting: the sulfur-yellow ryadovka mushroom begins fruiting in August and ends in October.
Is it possible to eat a green row
The green ryadovka belongs to conditionally edible mushrooms. It has been proven that the skin and pulp contain toxins that have a negative effect on the human body. Even prolonged soaking and heat treatment does not lead to their complete destruction. Excessive consumption of greenfinches can cause food poisoning, disturbances in the work of the cardiovascular system and kidneys. It is believed that the largest amount of toxins is in the skin, and if it is removed, then the problem will be solved. But this is not the case. Toxins are present throughout the fruiting body and this must be taken into account. The green row can be eaten only cooked and in small quantities.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Trichoderma (Trichoderma)
-
The type of cap skin, usually consists of straight, septate elements located more or less perpendicular to the surface and laid both at the same and at different levels; the ends of the hyphae can be morphologically modified and represent dermatocystids. The surface of the cap is velvety to almost felt.
Lat. Trichoderm.
Trichoderma, in turn, is subdivided into intertwined trichoderma and irregular trichoderma.
Intertwined trichoderm (Intricate trichoderm) - trichoderm, consisting of intertwined hyphae, located not parallel to each other and forming a tomentose pubescence.
Irregular trichoderm - Trichoderma, consisting of irregularly branching hyphae.
See Dermatotsistida, Hypha, Septa.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
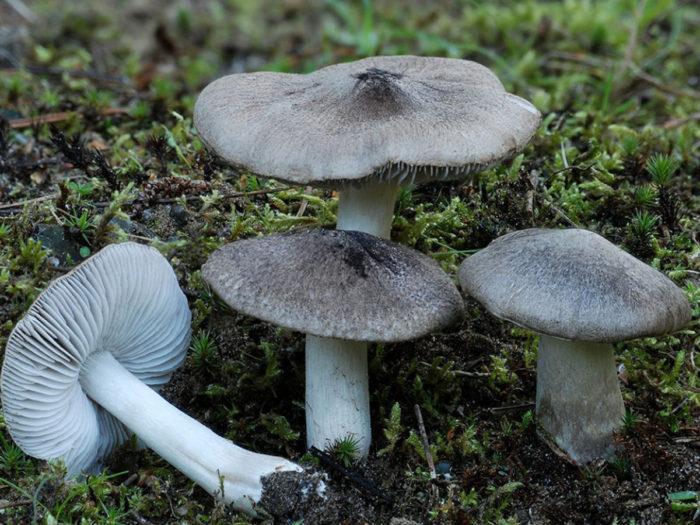
What mouse rows look like
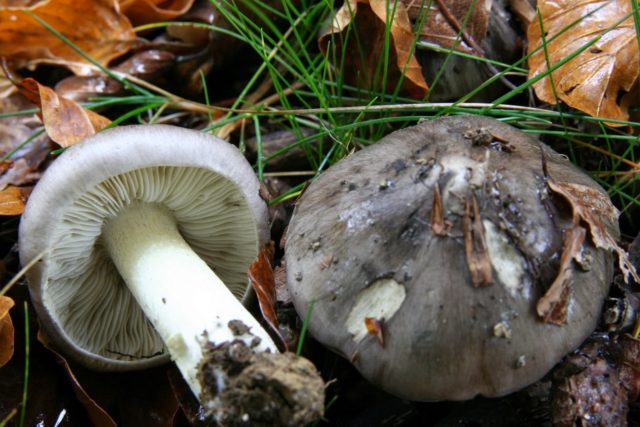
The Ryadovkovy family includes edible species that outwardly resemble a mouse row. In order not to confuse mushrooms and not to collect poisonous fruits, below are photos and a description of the appearance of the mouse row.

The color of the fruiting body is light or dark gray. The color of the cap is uneven, the central part is darker. In young specimens, the surface is even, the protective film is solid. As the cap unfolds, the top layer breaks, forming white longitudinal lines of various shapes and sizes along the edge.
The description of the mushroom is as follows:
- The shape of the upper part at the beginning of growth is rounded, conical, then convex with a pronounced sharpening in the center.
- The edges are concave, even or wavy.
- The protective film is glossy, fibrous, cracks in dry weather and peels off the surface.
- The diameter in an adult specimen is up to 5 cm.
- The pulp is thin, dense, white with a mouse tint. When broken, the color does not change. There is no smell, the taste is slightly bitter or pungent.
- The hymenophore consists of thin loose plates with wavy edges. They are densely located with a clear border near the stem. The color of young specimens is light gray. Over time, yellow spots appear.
- The stem is central, cylindrical, of the same thickness from base to top, growing up to 15 cm. The structure is fibrous, hollow. The color is the same with the bottom of the cap, near the mycelium it can be pinkish or yellow.
Surface with longitudinal lines, smooth.
Varieties of sulfur rows.
There are several varieties of these mushrooms:
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. Hemisulphureum differs from the type species by the edges of the plates, which have a gray-lilac or pinkish color;
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. Rhodophyllum is very light in color. This variety grows only in the alpine zone;
- Tricholoma sulphureum var. Pallidum has a pleasant odor and a lighter color.
Places of growth of a row of sulfuric.
Rows grow sulfur-yellow most often in groups. You can find them in mixed and deciduous forests. Sometimes they can settle on the roadsides. This type of mushroom prefers to grow in lime-rich soils.

Sulfur rows enter into mutually beneficial alliances (mycorrhiza) with beeches and oaks, and in more rare cases - with firs and pines. This species is widespread in Europe - its range extends from the Mediterranean to the cold arctic zones.
Evaluation of the edibility of a row of sulfur.
Sulfuric row is classified as a weakly poisonous species. These mushrooms sometimes cause mild stomach upset. Their smell is strong, unpleasant, so they do not seem appetizing.

Related species.
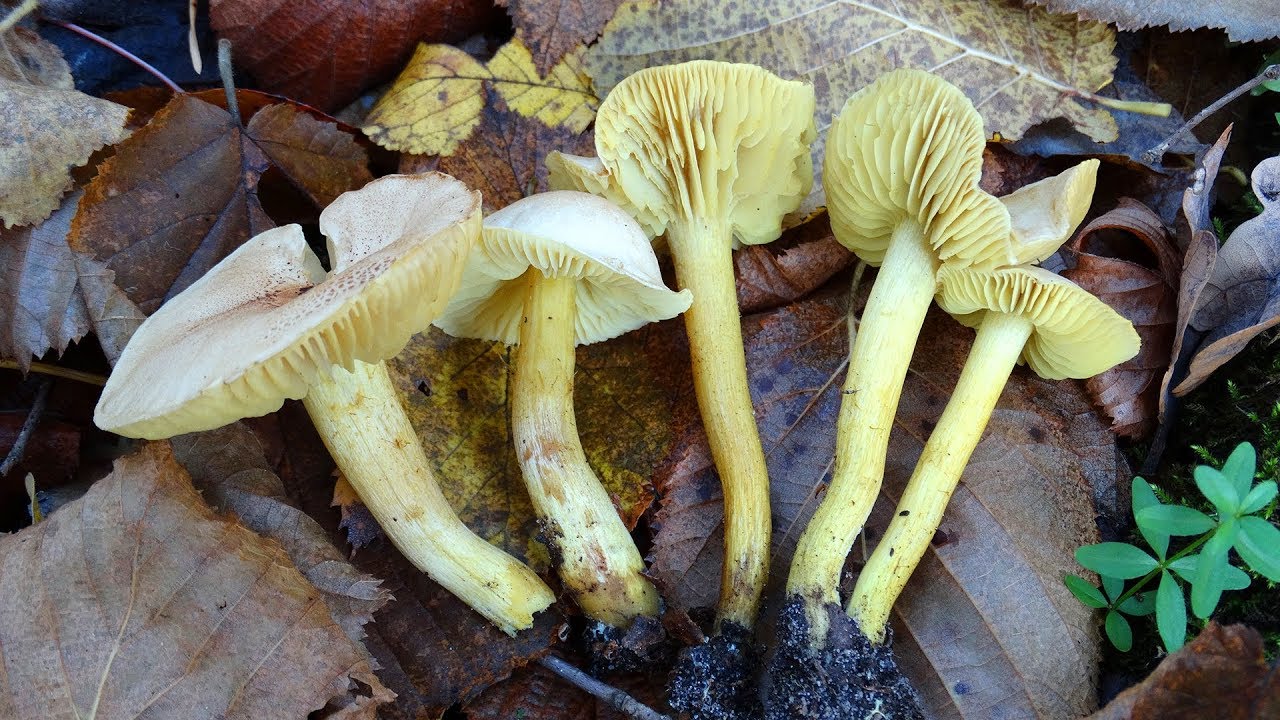
The green ryadovka or greenfinch has an external resemblance to the sulfur ryadovka. It is a conditionally edible species. Her hat is fleshy and dense. Its color is greenish-yellow, over time it darkens. The skin is thick, smooth, sticky. The leg is short, most often submerged in the ground, cylindrical in shape. The color of the leg is greenish or yellow, the base with brown scales. The pulp is dense, white. Worms in it are extremely rare. The smell of flour pulp, but the taste is not pronounced.

Green rows are found in dry pine forests, sometimes in mixed forests. Sandy and sandy soil is suitable for them. Greenfinches bear fruit in groups, from September to the very frost.
The decorated row is a conditionally edible relative of the chamois row. The hat at the decorated ryadovka is convex or flattened, yellowish, with brownish-brown scales. The leg is hollow inside, sulfur-yellow in color. The pulp is fibrous, yellowish in color, with a bitter taste and woody odor.

Decorated rows grow in coniferous and mixed forests. They prefer to settle on rotten needles and stumps. This species is rare. These mushrooms grow in small groups. Fruiting occurs from August to October.