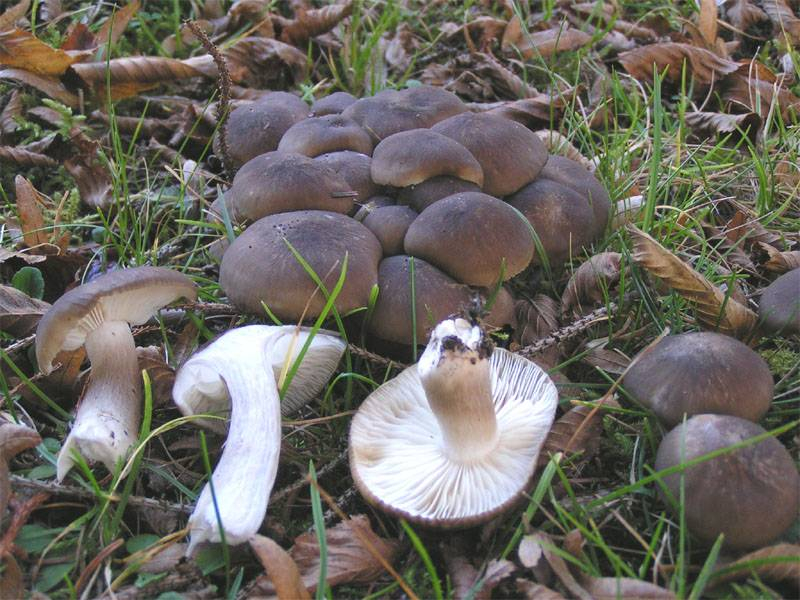
Pickled poplars
It is very easy to marinate podpolniki for the winter. The peeled fruit bodies should be boiled for about half an hour or blanched for no more than seven minutes, removing the foam. Arrange boiled or blanched mushrooms in sterilized jars, adding black peppercorns, cloves and bay leaves. To prepare the marinade, for each liter of water, add three tablespoons of vinegar, a tablespoon of salt and one and a half tablespoons of sugar. Pour the mushrooms laid out in the jars with hot marinade and roll up the jars. Such canned mushrooms are stored for at least a year.
It should be noted that in addition to very good taste characteristics, the substances included in the composition of the mushroom pulp help to improve appetite, accelerate metabolic processes and lower cholesterol levels. The pulp of ryadovka poplar is able to stimulate the work of the gastrointestinal tract, and also contains few calories, therefore it perfectly complements the menu of vegetarians or people adhering to a diet.
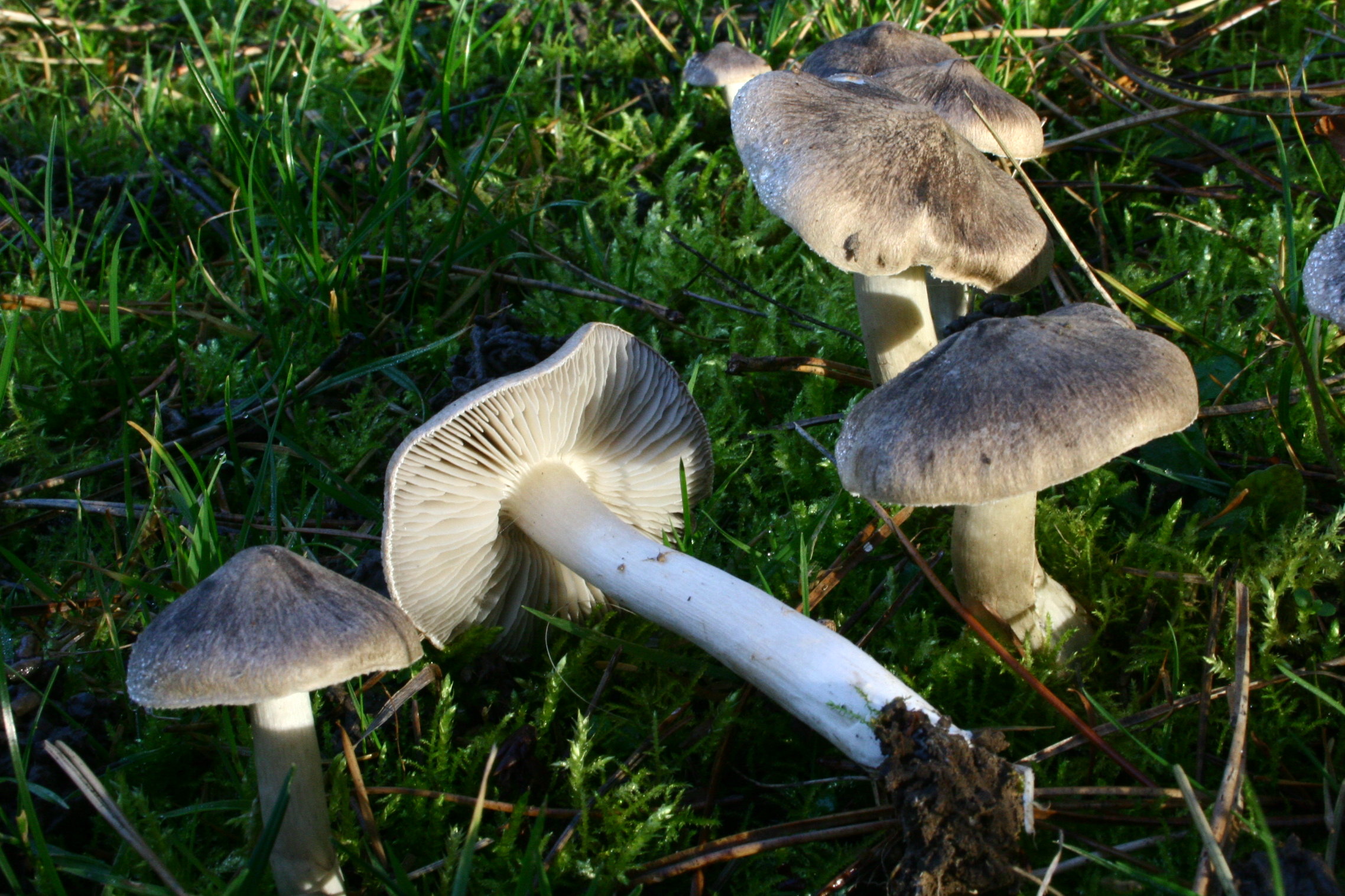
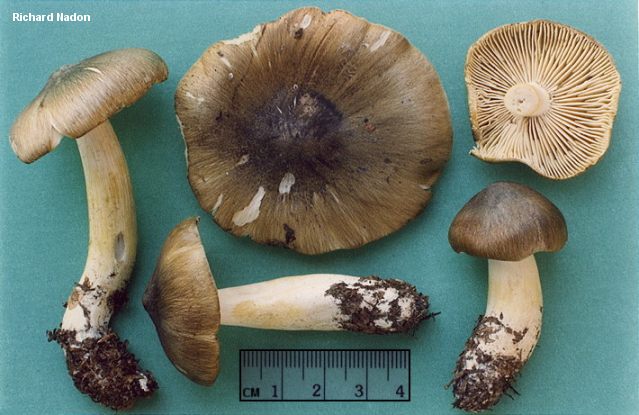
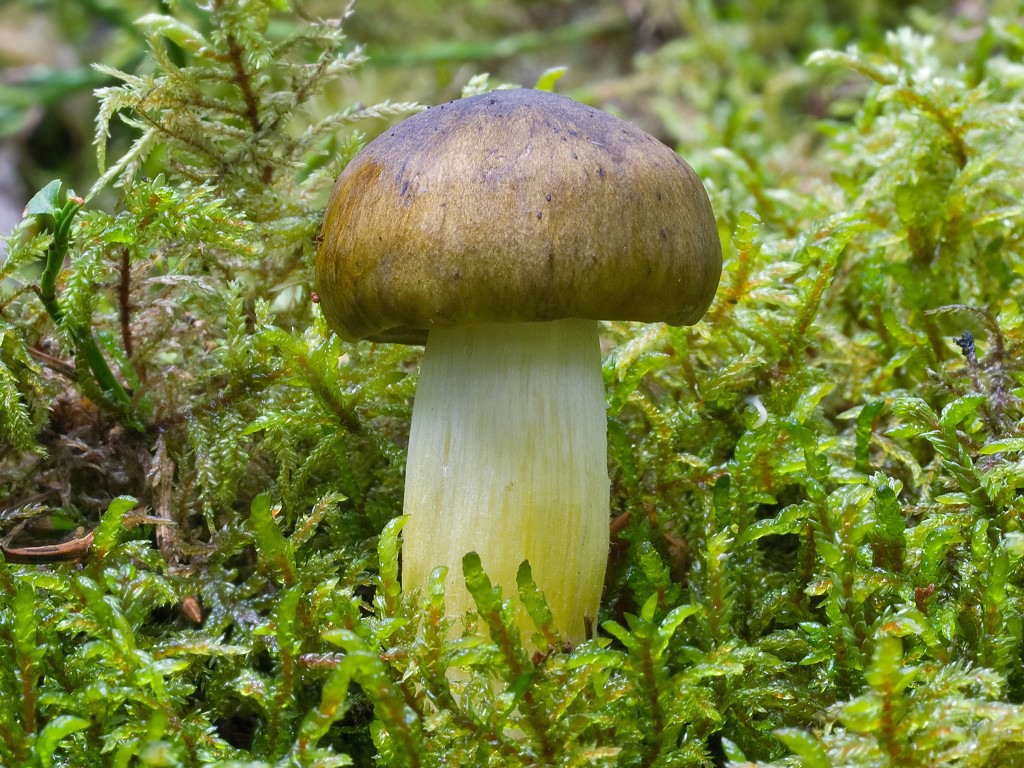
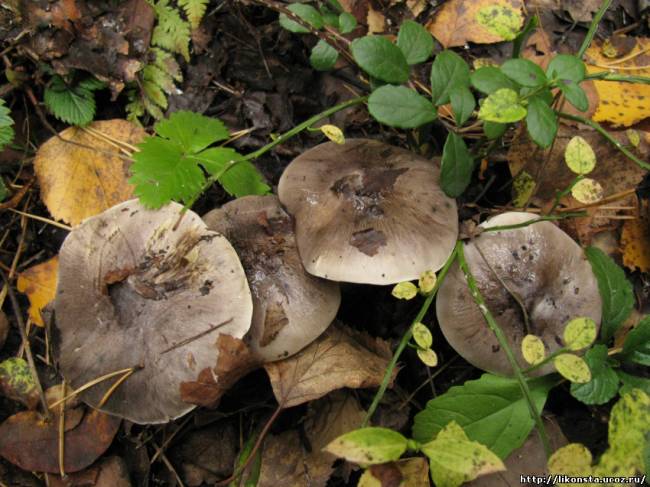
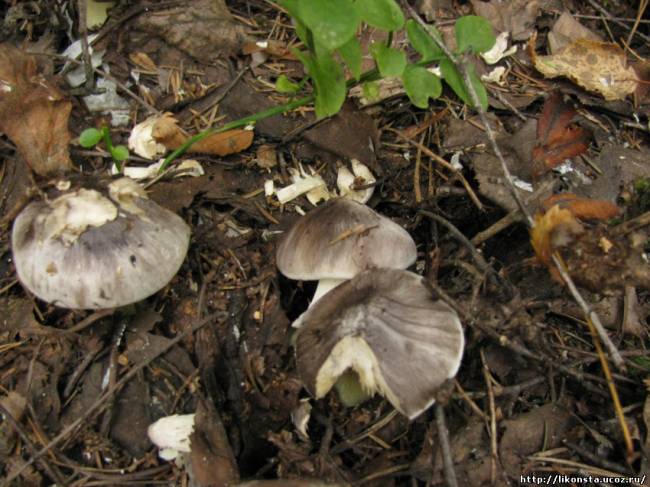
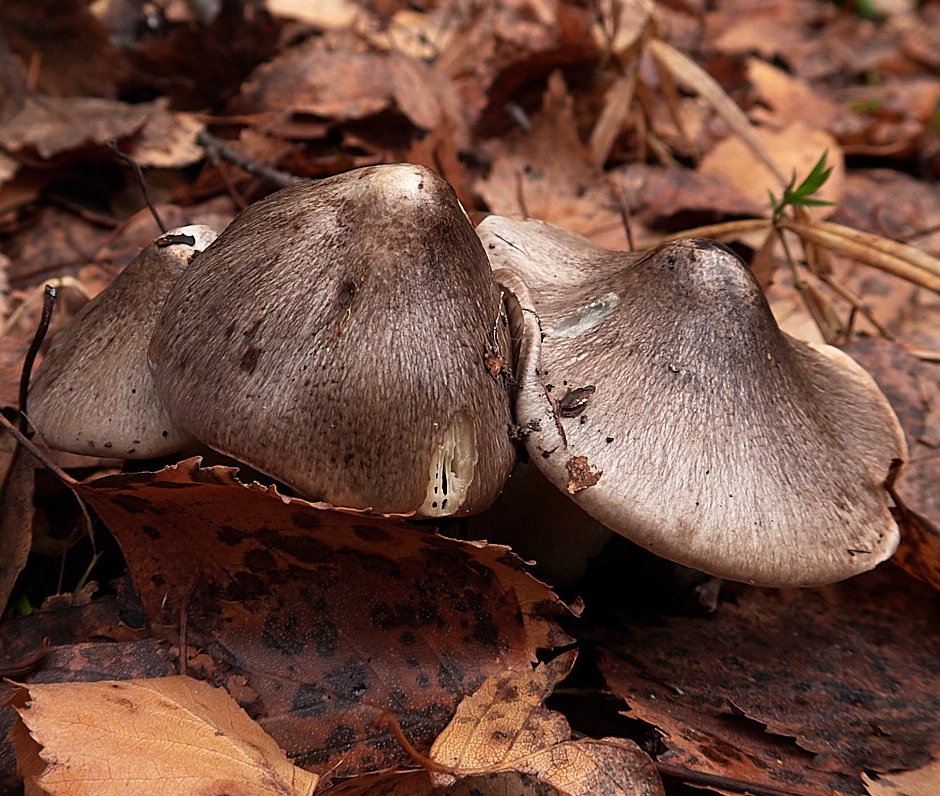
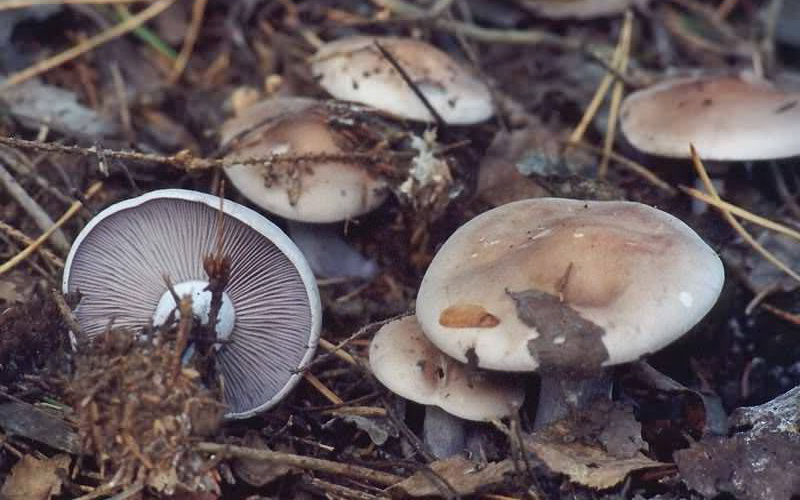
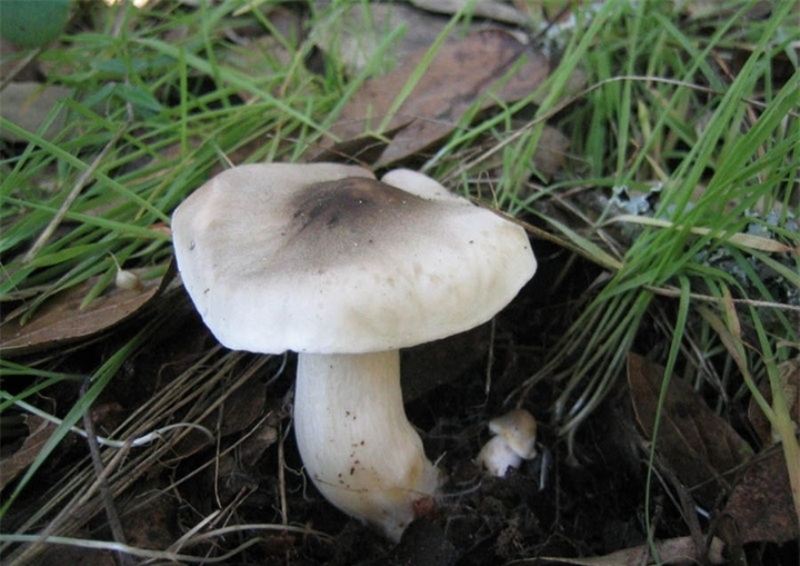
Gray row (Tricholoma portentosum)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Podsosnovik
- Serushka
- Podgreen
- Sandpiper gray
Synonyms:
- The row is strange
- Podsosnovik
- Podgreen
- Sandpiper gray
- Serushka
- Agaricus portentosus
- Gyrophila portentosa
- Gyrophila sejuncta var. portentosa
- Melanoleuca portentosa
Description
Cap: 4-12, up to 15 centimeters in diameter, broadly bell-shaped, convex-spread with age, then flat-spread; in adult specimens, the edge of the cap may be slightly wavy and fissured. A wide tubercle remains in the center. Light gray, darker with age, with a yellowish or greenish tint. The skin of the cap is smooth, dry, pleasant to the touch, in wet weather it is sticky, covered with pressed fibers of a darker, blackish color radiating radially from the center of the cap, therefore the center of the cap is always darker than the edges.
Leg: 5-8 (and up to 10) centimeters long and up to 2.5 cm thick. Cylindrical, sometimes slightly thickened at the base, can be curved and go deep into the soil. White, grayish, grayish-yellowish, light lemon-yellowish, slightly fibrous in the upper part or may be covered with very small dark scales.
Plates: adherent with a tooth, medium frequency, wide, thick, thinning towards the edge. White in young mushrooms, with age - grayish, with yellowish spots or completely yellowish, lemon-yellow.
Bedspread, ring, volva: none.
Spore powder: white Spores: 5-6 x 3.5-5 microns, colorless, smooth, broadly ellipsoid or ovoid-ellipsoid.
Flesh: The gray ryadovka is rather fleshy in the cap, where the flesh is white, under the skin it is gray. The leg is dense with yellowish flesh, yellowness is more intensely manifested in mechanical damage. Odor: mild, pleasant, mushroom and a little floury, in old mushrooms sometimes unpleasant, floury. Taste: soft, sweetish.
Season and distribution
From autumn to winter frosts. With a little freezing, it completely restores taste. Earlier it was indicated that Ryadovka gray grows mainly in the southern regions (Crimea, Novorossiysk, Mariupol), but its region is much wider, it is found throughout the temperate zone. Recorded in Western Siberia. Fruiting unevenly, often in large groups.
Ecology
The fungus appears to form mycorrhiza with pine. It grows on sandy soil in pine and pine-mixed forests and old plantings. It often grows in the same places as Green Ryadovka (green tea,). According to some reports, it also occurs on rich soils in deciduous forests with the participation of beech and linden (information from the STP).
Edibility
A good edible mushroom, used after heat treatment (boiling). Suitable for preservation, pickling, pickling, can be eaten freshly prepared.It can also be harvested for future use by drying.
It is important that even very adults retain their taste (not bitter).
M. Vishnevsky notes the medicinal properties of this row, in particular, the antioxidant effect
Similar species
There are a great many rows with a predominance of the gray scale in the color, let's name only the main similar ones.
An inexperienced mushroom picker may confuse Ryadovka gray with the poisonous Ryadovka pointed (Tricholoma virgatum), which has a bitter taste and a more pronounced, pungent tubercle.
The earthy-gray (earthy) row (Tricholoma terreum) does not turn yellow with age and on damage, in addition, very young specimens of Tricholoma terreum have a private veil that collapses very quickly.
Row Gulden (Tricholoma guldeniae) is more tied to spruce than pine, and prefers to grow on loamy or calcareous soils, while Ryadovka gray prefers sandy soils.
Photo: Sergey.
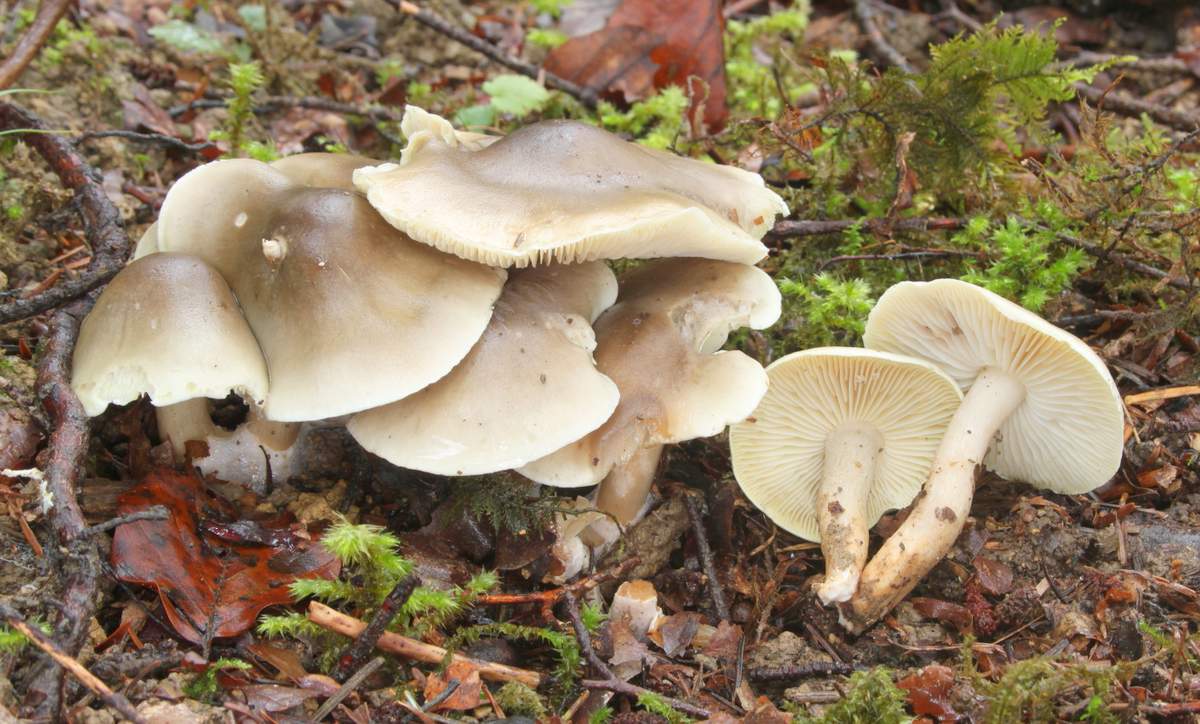
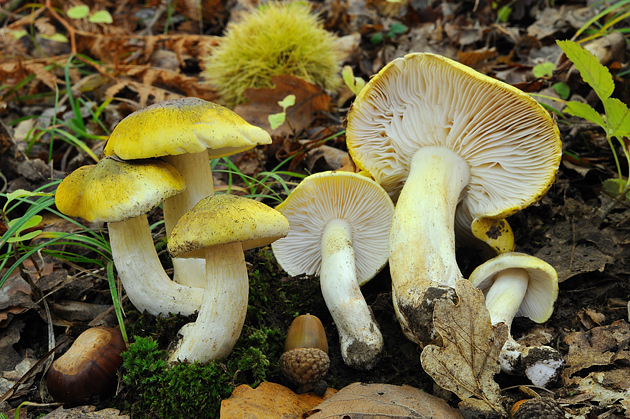
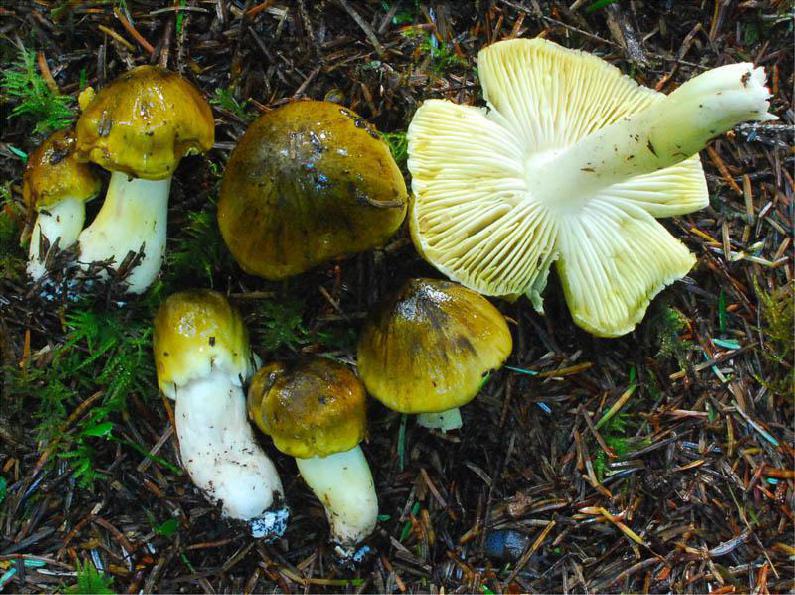
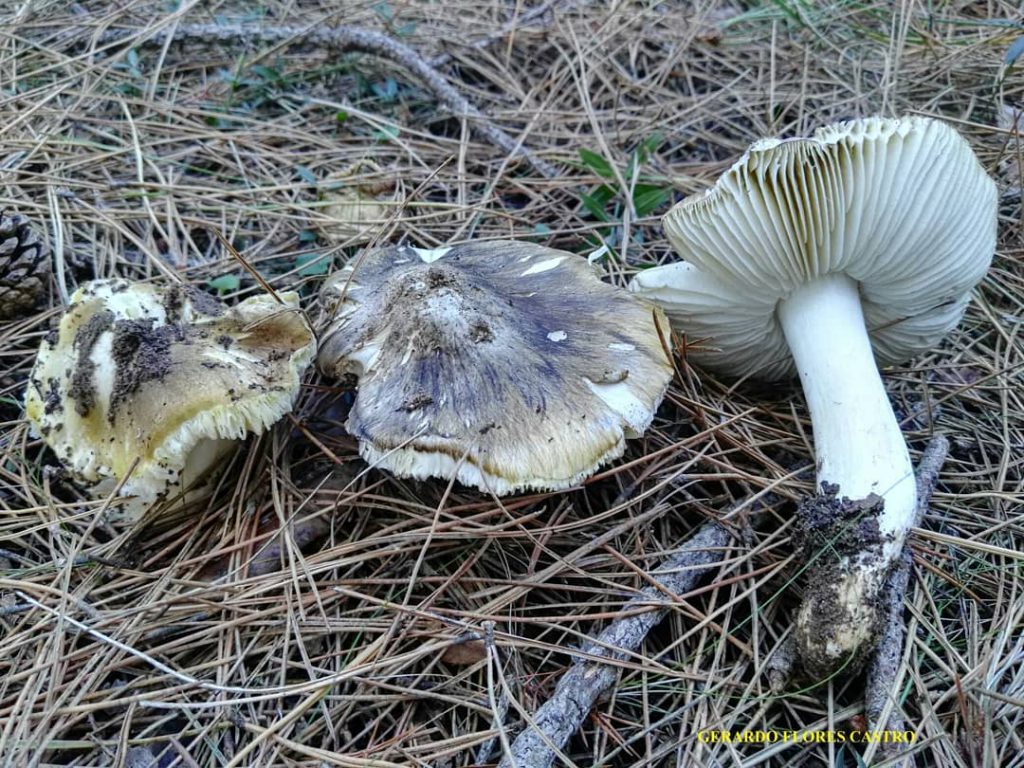
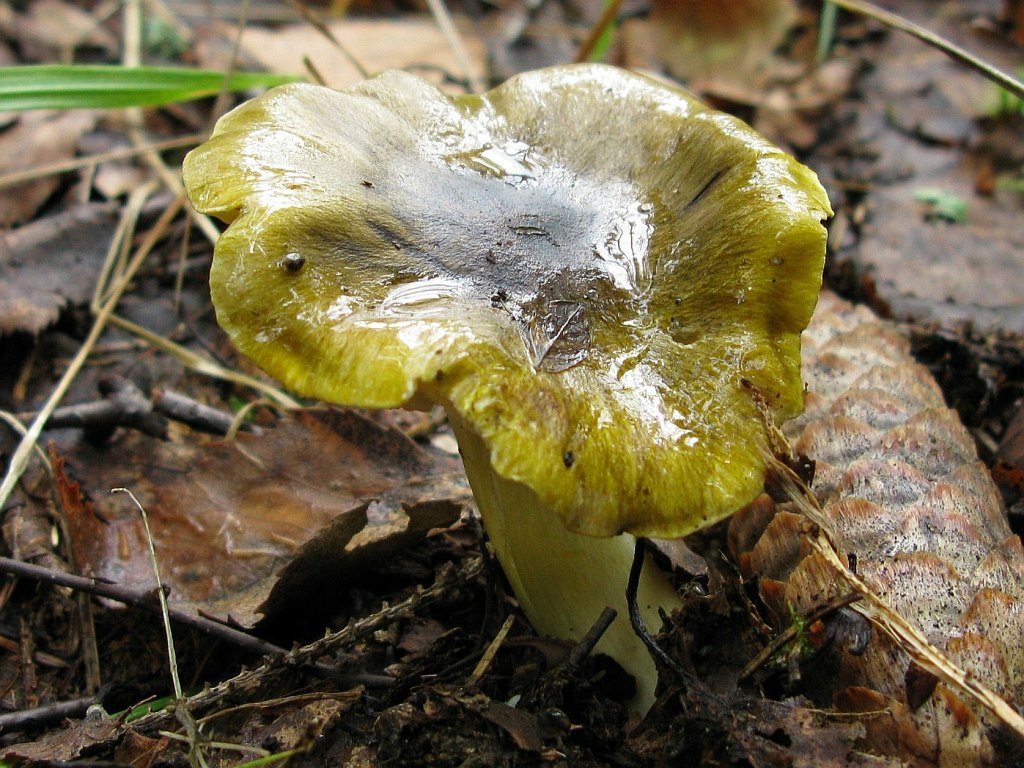
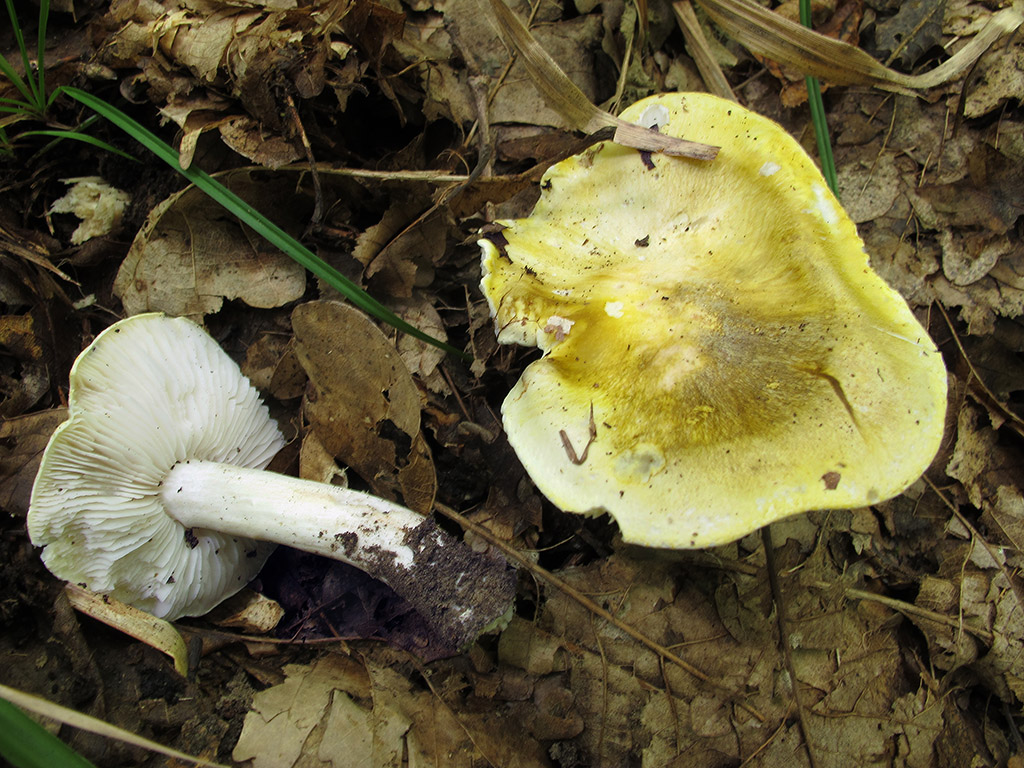
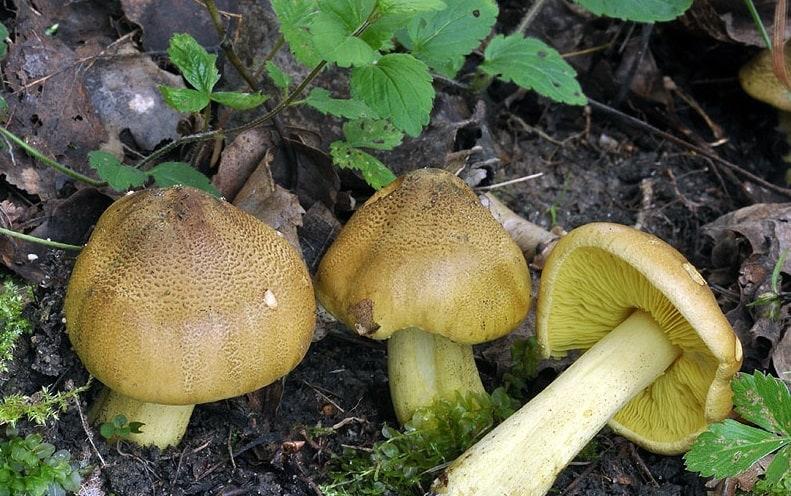
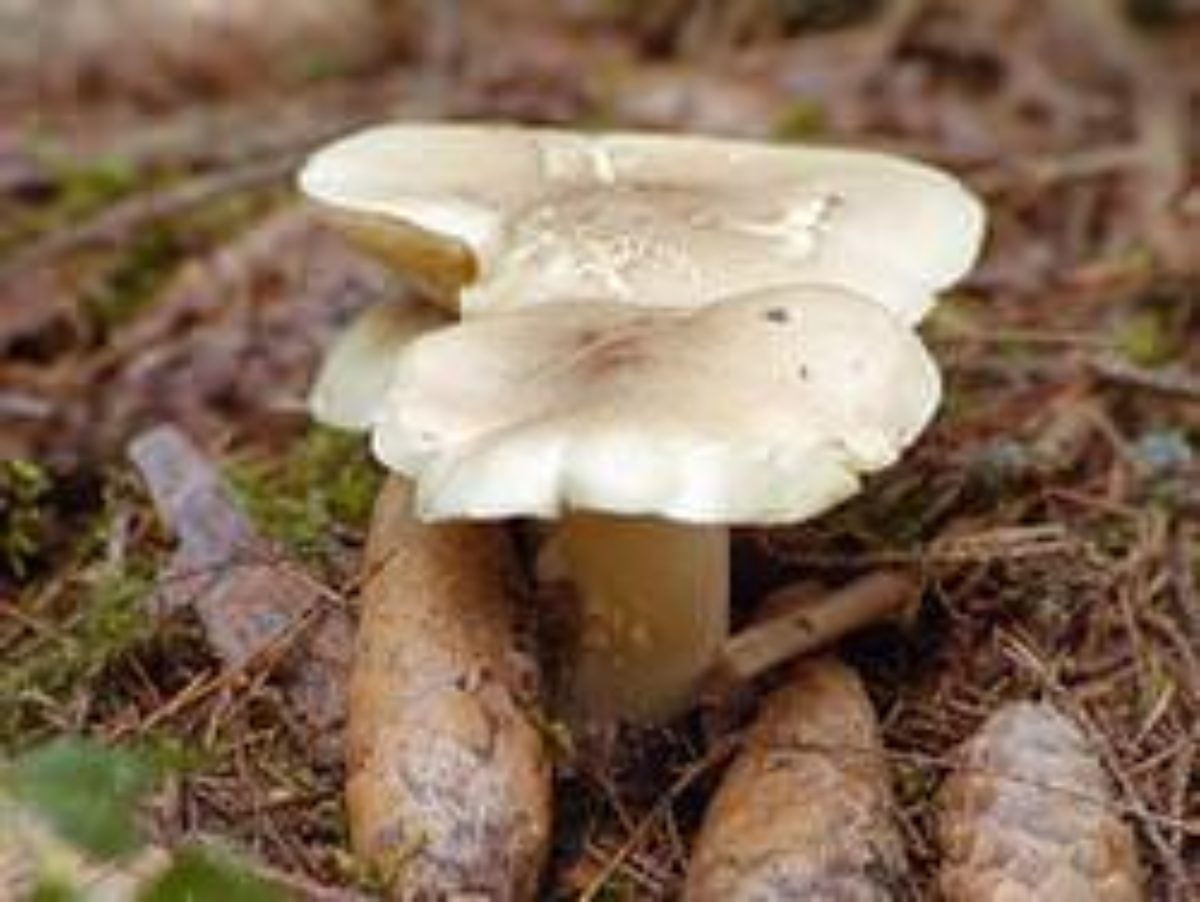
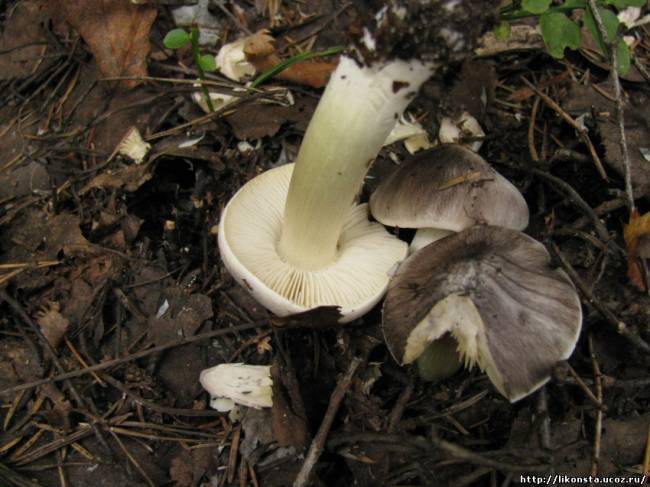
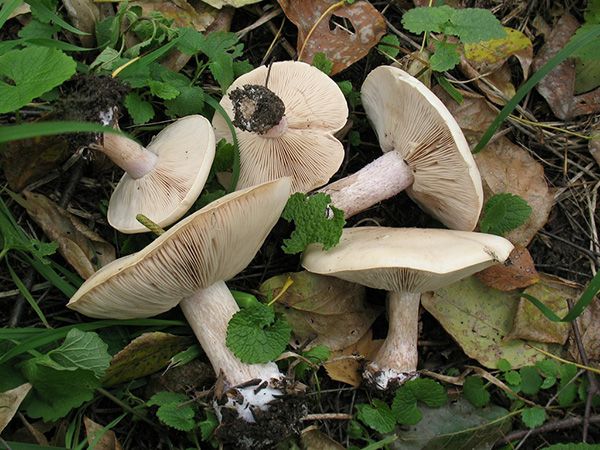
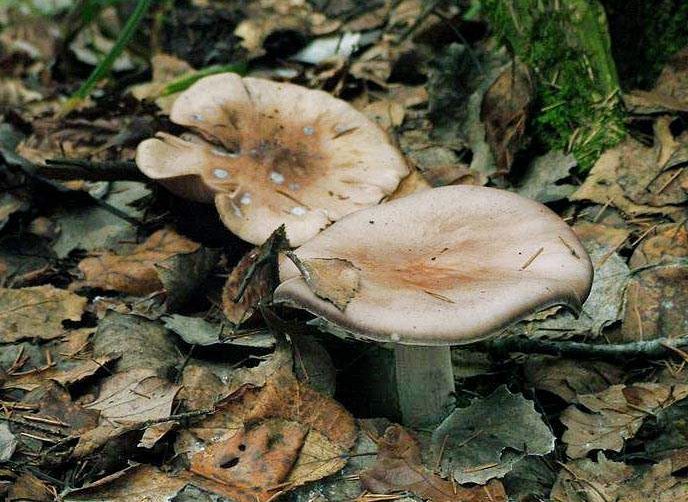
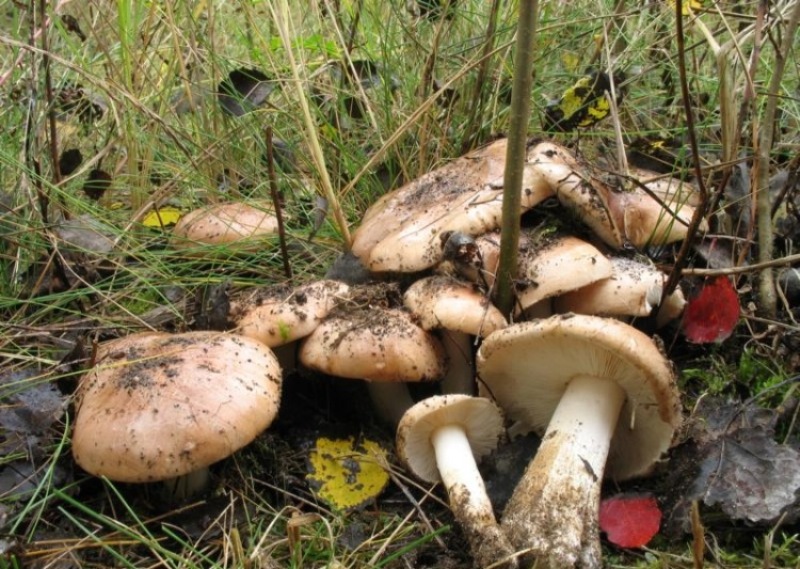
Poplar row (Tricholoma populinum)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Poplar
- Sandpiper
- Sandstone
- Poplar row
- Subtopolevik
- Podtopolnik
Shinoim:
- Poplar row
- Subtopolevik
- Podtopolnik
The Ryadovka poplar mushroom belongs to the lamellar mushrooms, which means that it reproduces by the spores in its plates.
Description
At a young age, his plates are white or cream-colored, frequent and thin. And, as the fungus grows, they change their color to pinkish-brownish.
His hat at the beginning has a semi-spherical and slightly convex shape, with thin edges tucked inward, then it straightens and slightly bends, becomes fleshy, in the rain it is slightly slippery, pinkish-brownish in color. The diameter of the cap varies from 6 to 12 cm. The flesh is slightly reddish under the skin of the cap.
The stem of a row of poplar is of medium size, rather fleshy, cylindrical in shape and solid inside, with a flaky-scaly bloom, fibrous and smooth, pinkish-white or pinkish-brown in color, when pressed, it becomes covered with brown spots.
The flesh of the mushroom is fleshy, soft, white, brownish under the skin, with a flour aftertaste.
Spreading
Poplar rowing grows from August to October in large groups (whole ridges) under poplars, deciduous forests with a predominance of aspen, can be found in plantings along roads, in parks. Distributed in the European part of Russia, Siberia. The mushroom has a pleasant aroma of fresh flour.
The Ryadovka poplar mushroom got its name for its adaptability to grow under poplars and in the immediate vicinity of them, during the autumn leaf fall. The poplar ryadovka, at a young age, is a bit like a ryadovka crowded in color and shape, but, unlike it, it is much larger in size and has a slightly bitter taste due to the fact that it grows in such conditions that the cut mushroom is almost completely covered with sand or fine debris. It can also be confused with the poisonous tiger row. But they are distinguished by two main features. Firstly, the poplar row always grows in large groups and, secondly, it always grows close to poplars.
Edibility
According to its taste and consumer qualities, poplar ryadovka is related to edible mushrooms of the fourth category.
Poplar ryadovka is a completely edible mushroom, but only after it has been washed, soaked and boiled to eliminate bitterness. The poplar row grows in deciduous plantings under poplars, well covered with fallen leaves, always in large colonies. Poplar rows are common wherever poplars grow - these are the territories of North America and Canada, Western and Eastern Europe, Central Asia, as well as central and southern Russia, the Urals, Siberia and the Far East. The main period of her growth begins in the season of autumn leaf fall, somewhere from the end of August, and it ends at the end of October.
The poplar row is eaten exclusively in salted or pickled form after thorough washing, soaking and boiling.
Video about the mushroom Ryadovka poplar:
Preparation
Mushrooms lend themselves well to various processing methods and are used in almost any form: they are boiled, fried, stewed, pickled and salted.
Primary processing and how to soak mushrooms?
To begin with, they are sorted out, clearing them of leaves, dirt and grass. After that, it should be thoroughly washed or soaked for several hours. Pour clean water into a container, add vinegar there and put on fire. After boiling, washed mushrooms are placed in the liquid and boiled for ten minutes. Then the broth is removed, and the rows are again poured with fresh water and vinegar and boiled for another twenty minutes. In order to remove the mealy smell, a peeled onion is added to the container and the cooking time is extended by another ten minutes. Then the fruits are discarded in a colander.
Cooking
For cooking you will need:
- Take a kilogram of processed mushrooms.
- Pour a liter of water into a saucepan, add 30 g of salt and a pinch of citric acid. Bring the liquid to a boil.
- Pour the rows into a bowl and cook for 20 minutes. under a closed lid.
- After 10 minutes. cooking, throw a couple of clove buds, lavrushka and six black peppercorns into the pan. After 20 minutes. Put boiled mushrooms in a colander.
Pickling method
To marinate rows we need:
- 1 kilogram of mushrooms;
- vinegar 6% (three tablespoons);
- sugar (one and a half tablespoons)
- black peppercorns (five pcs.);
- salt (tbsp. spoon);
- lavrushka leaf (two);
- carnation (four inflorescences).
How to pickle:
- Select dense rows.
- Cut large mushrooms (leave small ones as they are).
- Pour into a saucepan and cook, descaling.
- Add vinegar.
- Put the mushrooms (without cooling) into sterilized jars and cork.
- Cool preservation and store in a cool place.
Frying
Peel half a kilo of fresh mushrooms, rinse and put in a deep container. Add 2 liters of water and 30 grams of salt, boil the mass and boil for 20 minutes. Throw the boiled rows in a colander and let them drain. Then put on a preheated frying pan greased with vegetable oil and fry for 10 minutes, stirring regularly.
Salting method
Ingredients:
- 1 kilogram of rows;
- 3 cloves of garlic;
- 3 horseradish leaves;
- a few sprigs of dill;
- 10 peppercorns;
- 50 grams of salt.
Preparation:
- Boil the rows, rinse and discard in a colander, letting them drain and cool.
- Place horseradish leaves in banks.
- Spread the mushrooms in layers, sprinkling each with salt and garlic.
- Seal banks.
- The mushrooms will be ready in six weeks. Salted rows are stored in a cool place for up to a year.
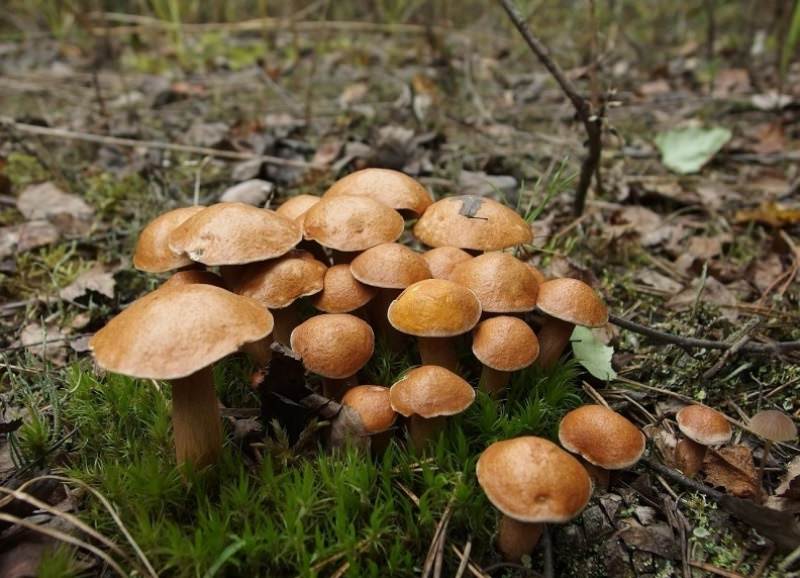
Characteristic features of the variety
All mushrooms have their own unique characteristics. The paths are characterized by a mealy smell and grow in large groups strictly in a row.
Description of mushroom paths
The appearance of the track depends on its grade. Mushrooms can reach 3 to 8 cm in height, have thin (1.5-2 cm) or massive (up to 4 cm) legs. The color of the track can have the following shades:
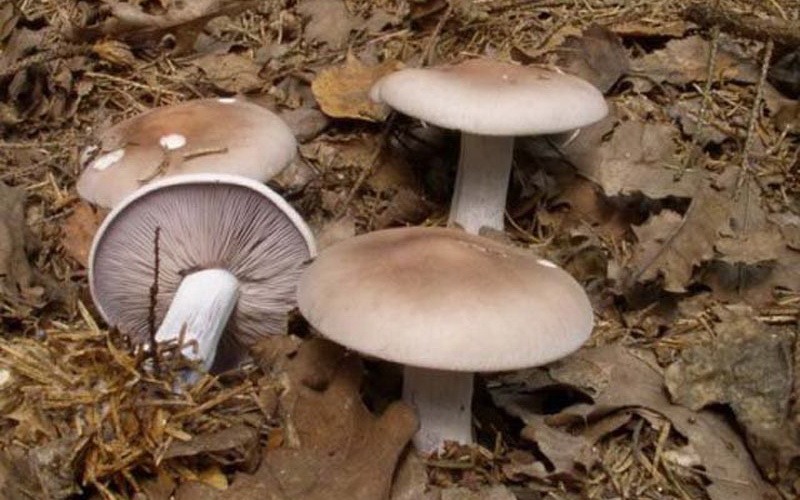
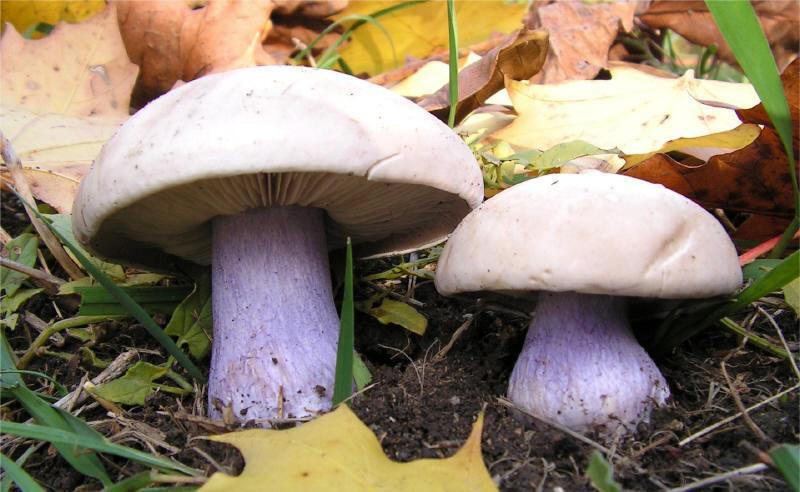
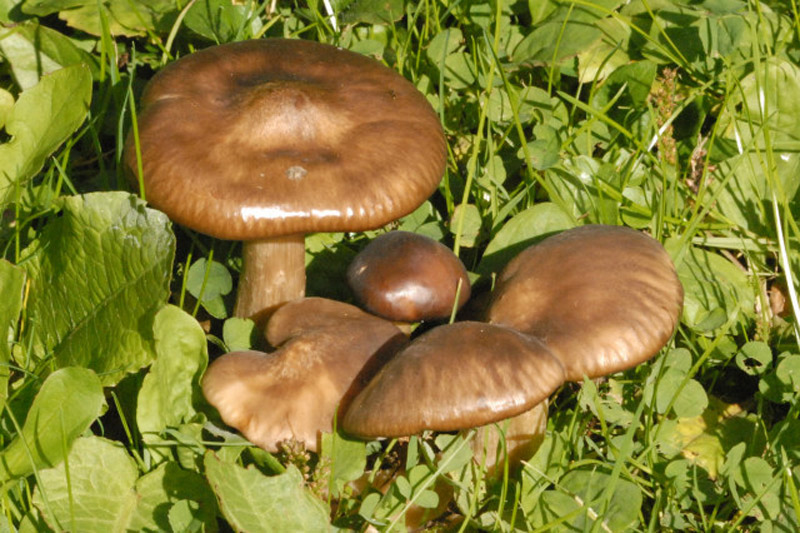





Usually the flesh of the mushroom is white. As it grows older, it acquires a yellowish tint. In some species, the flesh turns pink at the cut. Details of the appearance of the mushroom tracks can be seen in the photo.
Morphology (species differences)
The fleshy cap initially has a hemispherical shape, but straightens out as it matures. The edge of the cap is thin, rolled up, cracked. The surface is most often wet, slippery, but there are types with dry, velvety. The stem is usually cylindrical, but some varieties are tuberous.






In some species, it changes color as it ages. All tracks have records. In some species, they are thin and frequent, while in others, they are dense and sparse. The pulp is firm. In many varieties, at the break, it emits a pleasant aroma that can be compared with the smell of freshly ground flour or with a cucumber smell.
Place of distribution
The paths are very popular mushrooms. They are common in Europe, Asia, America, Kazakhstan. In Russia, they are especially common in the region of Saratov, Volgograd, Omsk, and are also common in the Altai Territory.These regions cannot boast of mushroom abundance, so ryadovki are consumed here much more than in other places in Russia.
Edible or inedible
Edible paths include the following types:
- black-scaled;
- giant;
- pigeon;
- yellow-brown;
- massive;
- blushing;
- poplar;
- Gray;
- carved;
- earthy.
Mongolian and matsutake varieties are considered the most delicious edible mushrooms. The rest of the rowing types belong to the following categories:
| Conditionally edible species | Inedible species | Poisonous species |
|---|---|---|
| Silver | White-brown | Sunburnt |
| Golden | Broken | Spotted |
| Shod | Open-shaped | Tiger |
| Greenfinch | Rough | Pointed |
| Scaly | Soapy | Smelly |
| Yellow-red | Dark | Toad |
| Bearded | Detached | White |
| Sulfur | Spruce | |
| Pointed |
Some conditionally edible varieties are used for food after careful processing.
When and how to collect correctly?
Rows can be found not only on the edges of coniferous and deciduous forests, but also in parks, roadside plantings. They skillfully burrow into the soil or hide under leaves, needles. Experienced mushroom pickers recommend collecting young growth, because old mushrooms can be toxic. Rows tend to absorb harmful substances from the external environment.



The first mushrooms appear at the end of summer. The main collection lasts until October. But some species survive until the first frost. You can only collect tracks in ecologically clean areas. Rows must be cut with a knife so as not to damage the mycelium.
Due to their habit of hiding, it can be very difficult to find the rows. But if at least one specimen was found, the basket is guaranteed to fill up soon. Rows tend to grow in large families. The myceliums are arranged in rows.
Eating poplar mushrooms
Conditionally edible poplar rows cannot be used to prepare meals immediately after harvest. They are pre-soaked for at least a day in cold water. This helps to remove soil particles from young mushrooms and remove bitterness.
The water should be no higher than 16 ° C so that the harvested crop does not ferment. For better removal of bitterness and good washing, poplar rows are periodically stirred and water is often changed. Another way to reduce the bitter taste is to remove the skins from the caps.
After soaking for 1-3 days, boil the poplar rows and drain the water. After all the excess water has drained from the boiled mushrooms, the semi-finished product is ready for use.
The poplar row is universal. You can:
- fry;
- cook;
- marinate;
- salt.
Pickled and salted are used for making salads and as an appetizer. Can be used in any mushroom recipe.
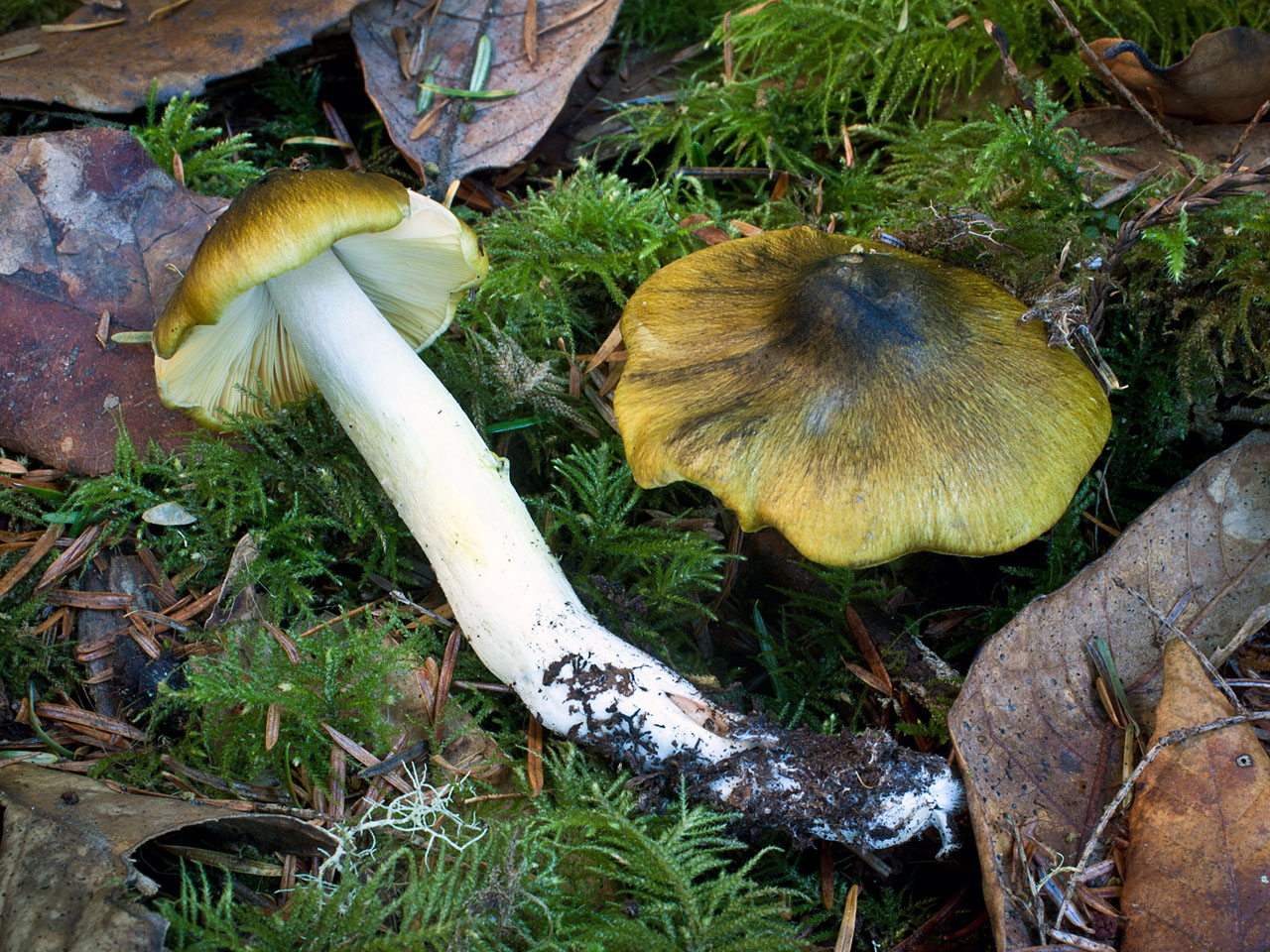
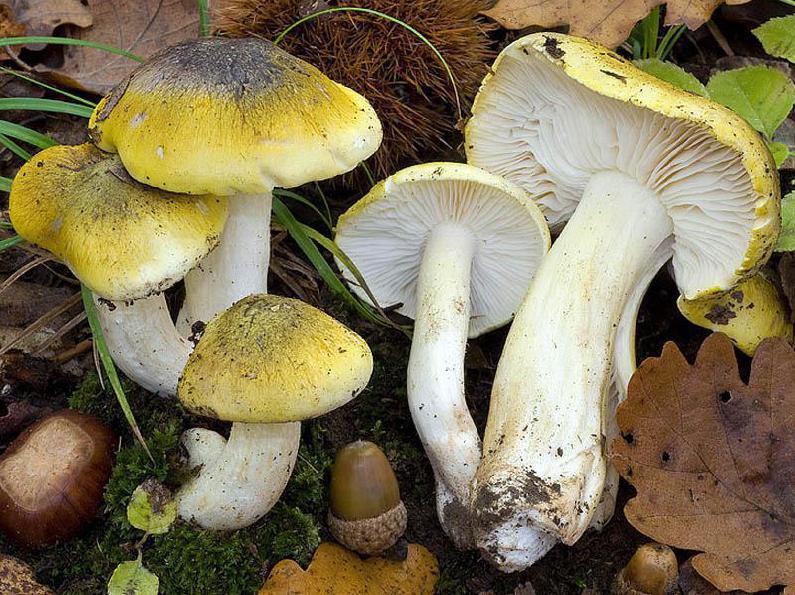
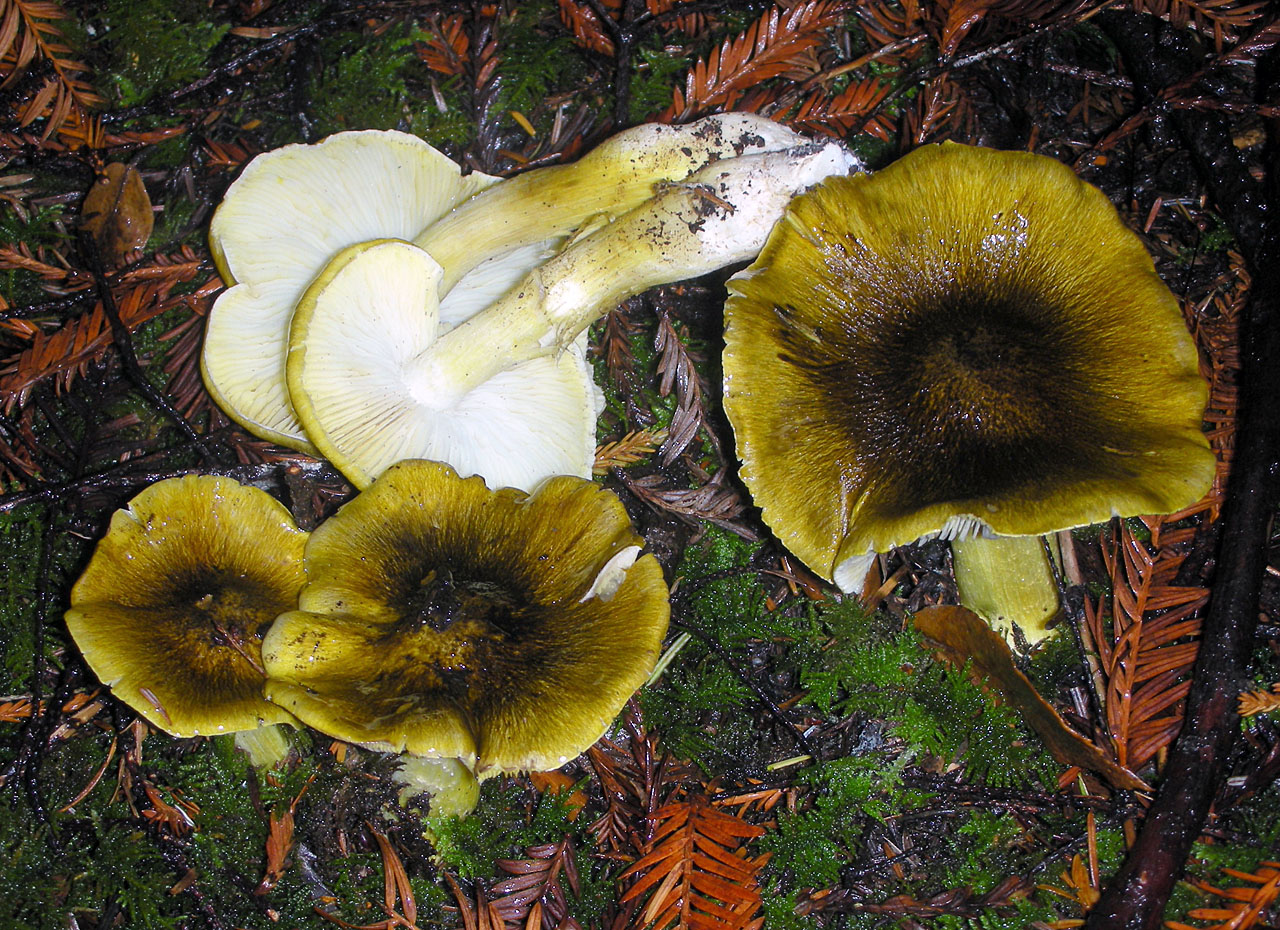
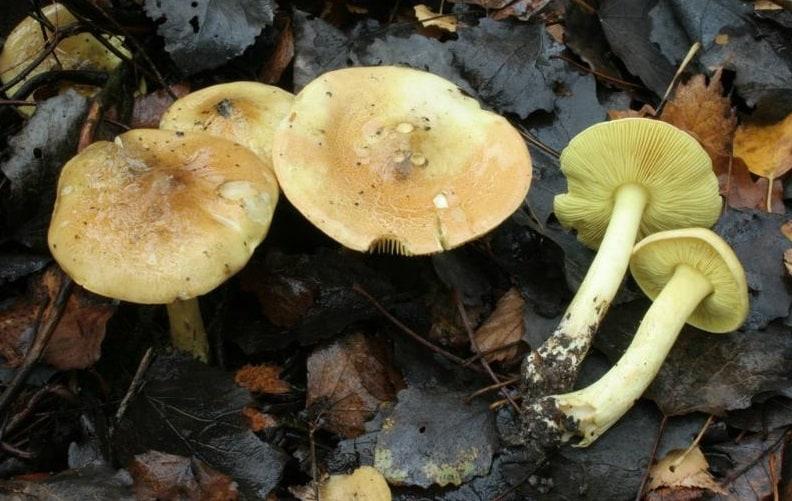
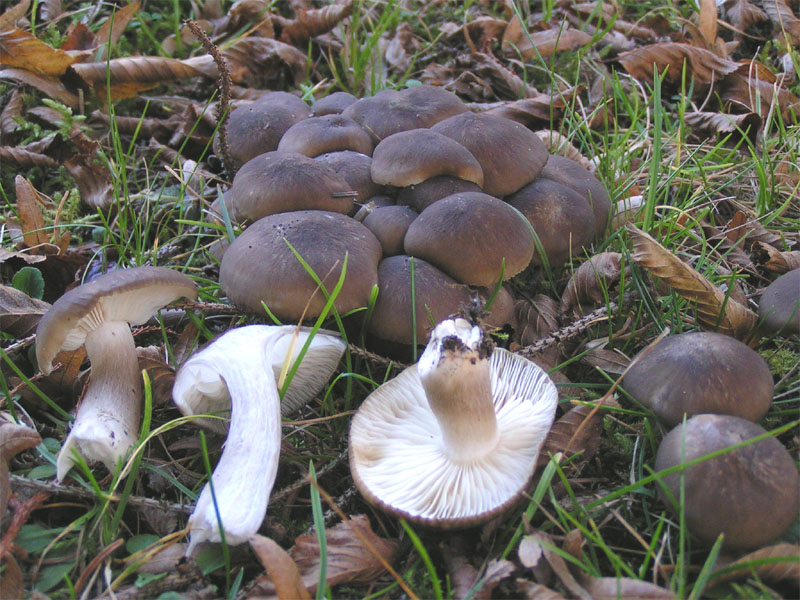
Mushroom ryadovka openkovidny or bandaged (tricholoma focale): photo and description, distribution and application
A row of honeydew-shaped or tied - a very rare lamellar representative of the mushroom "kingdom", which forms mycorrhiza with pine. It is classified as conditionally edible, which means that this fruit body can be eaten after thorough heat treatment.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the appearance of the honeycomb ryadka thanks to the photo and description.
Description of the row of crimson (bandaged)
Latin name: Tricholoma Focale.
Family: Ordinary.
Synonyms: bandaged ryadovka, skull. Latin synonyms: Armillaria zelleri, Tricholoma zelleri.
Hat: 5 to 10 cm in diameter, sometimes up to 12 cm.
Young specimens have a convex cap, but as they mature, it straightens out and becomes convex-outstretched, and then almost flat. Sometimes fibrous-scaly, the edges are often cracking, sometimes you can observe the remnants of a flocculent blanket on their surface.
The photo shows that the bandaged row has a reddish-brown, orange-red or brick-brown hat, the edges of which are lowered down.
Leg: long (from 4 to 10 cm) and thick (up to 3 cm in diameter), cylindrical, fusiform, sometimes narrowed at the base.At a young age, the structure is hard and dense, and at an old age it becomes hollow, longitudinally fibrous.
The leg of the row of the honeycomb is shown in the photo below:
Pulp: white, dense, firm, has a weak smell of fresh flour and slightly bitter taste, sometimes completely tasteless. As for the leg mushroom ryadovka honeydew, then here the pulp is fibrous. Under the skin, the pulp has a slight reddish tint.
Blades: notched, frequent, partially adhered to the peduncle, white or slightly yellowish. In young specimens, the plates are completely hidden under a fibrous cover of a reddish-brown hue. With age, this veil breaks, leaving traces.
Spores: ovate or globular, white.
Edible: conditionally edible mushroom, but abroad it is classified as poisonous. Can be eaten only after preliminary heat treatment. After boiling for 30 minutes, the broth must be drained, without the possibility of further use.
Similarities and differences: it is almost impossible to confuse with any poisonous representative. The only species that looks like a bandaged row is the white-brown row (Tricholoma albobrunneum). The latter also grows in groups, preferring pines.
However, these species have noticeable differences: the white-brown row has a very strong bitterness and an unusual two-zone, even leg. Although there is information that this mushroom is boiled and then eaten.
A photo and description of the mushroom ryadovka honeydew will help to correctly distinguish it from inedible similar species.
Application and distribution of a row
Application: applied fresh (after boiling), fried, salted and pickled. In addition, the tied row produces delicious mushroom caviar, as well as first courses.
Distribution: grows in pine forests, preferring green mosses and sandy soils. Grows in small groups or singly from mid-August to mid-October.
Some specimens can grow even after the first snows, but the weather does not allow them to ripen to the end for spores to appear. The fungus is widespread in the forests of Europe and North America.
Those mushroom pickers who are familiar with the appearance and taste of the tied row (Tricholoma Focale) note that this is a very beautiful, strong fruit body. In addition, this representative has a juicy, dense pulp that does not wrinkle or crumble.
Many people are impressed by the honeycomb ryadovka, because its structure perfectly tolerates both heat treatment and freezing. Thanks to this feature, the mushroom has a great advantage - unique crunchiness. Experienced lovers of "quiet hunting" note that it is better to use young and closed fruiting bodies.
Sometimes the smell of ryadovka is not pleasant to all "fans" of mushroom dishes, but this is fixable - you can get rid of the specific aroma with the help of spices and herbs.
Loading…
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
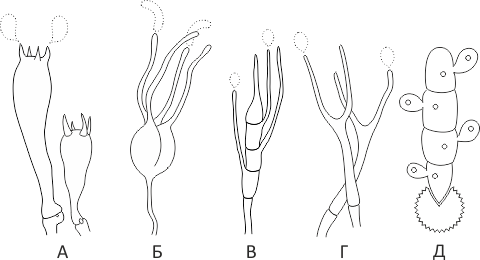
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Trichoderma (Trichoderma)
-
The type of cap skin, usually consists of straight, septate elements located more or less perpendicular to the surface and laid both at the same and at different levels; the ends of the hyphae can be morphologically modified and represent dermatocystids. The surface of the cap is velvety to almost felt.
Lat. Trichoderm.
Trichoderma, in turn, is subdivided into intertwined trichoderma and irregular trichoderma.
Intertwined trichoderm (Intricate trichoderm) - trichoderm, consisting of intertwined hyphae, located not parallel to each other and forming a tomentose pubescence.
Irregular trichoderm - Trichoderma, consisting of irregularly branching hyphae.
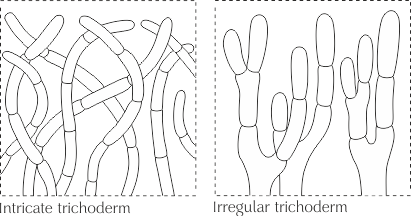
See Dermatotsistida, Hypha, Septa.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
Poisoning signs and first aid
If you accidentally eat a pointed row, the first symptoms of poisoning will appear in 40 minutes, some people do not feel any discomfort for up to 5 hours. The result will be intoxication, the poison of this row affects not only the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but also the kidneys, liver, etc.
You will need to take urgent measures and call an ambulance if the person who has eaten the mushrooms has the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- Severe, persistent abdominal cramps
- diarrhea;
- loss of orientation;
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- pain in the region of the heart.
While the ambulance is on its way, it is necessary to carry out priority measures that will help improve health and facilitate further treatment. Gastric lavage is carried out in simple ways:
- Dissolve 0.5 tsp. salt in a glass of water and drink in small sips.
- Dissolve potassium permanganate in water, you should get a light pink shade, take a glass of solution at short intervals.
- Drink plenty of clean water, preferably slightly warm and boiled.
After that, you will need:
- Induce vomiting (if not already present).
- Grind 10 tablets of activated carbon into powder, add to water and drink, shaking constantly.
- Lay the patient in a horizontal position, warm his arms and legs (you can use a heating pad).
- In the absence of diarrhea, give a laxative, from the simplest remedy - 1 tbsp. l. petroleum jelly.
- If the head is very dizzy, there is a strong weakness, give strong black tea to drink.
If symptoms of poisoning occur, in no case should you eat, drink alcohol, take drugs that will reduce diarrhea or stop vomiting, antipyretic drugs and pain relievers are prohibited.
Important! Regardless of edibility, mushrooms are forbidden to be eaten by children under 7 years old, pregnant and lactating women.Collect in the forest only those fruits in which you are sure
Do not eat large amounts of forest products, even if they are edible. All species, without exception, are extremely difficult to digest. Even the best and tastiest specimens can cause flatulence, malfunction of the gallbladder, an acute reaction of the pancreas, let alone poisonous ones that can harm all body systems
Collect in the forest only those fruits in which you are sure. Do not eat large amounts of forest products, even if they are edible. All species, without exception, are extremely difficult to digest. Even the best and tastiest specimens can cause flatulence, malfunction of the gallbladder, an acute reaction of the pancreas, let alone poisonous ones that can harm all body systems.
Cooking recipes
Rows are used boiled, fried, pickled, added to soups, sauces and casseroles are prepared. Caviar made from them is especially tasty.
Primary processing
After harvesting, the fruits are examined, wormy specimens and forest debris are removed, washed under running water. In case of heavy contamination and to remove possible bitterness, they are soaked for 2-3 hours.
Cooking
This is the main type of processing. It is carried out in 2 stages with the subsequent draining of the broth.
Ingredients:
- mushrooms - 1 kg;
- water - 1 l;
- vinegar - 1 tbsp. l.
The process is step by step:
- Heat water, add vinegar.
- Dip the mushrooms in a boiling mixture, boil for 10 minutes.
- Drain the liquid.
- Place the mushrooms in a colander and cool.
- Boil in a new portion of water with vinegar for 10-15 minutes.
- Rinse.
After that, the rows are prepared in various other ways.
Pickling
For 1 kg of boiled fruits you will need:
- water - 1 l;
- salt, sugar - 2 tbsp each l .;
- bay leaf - 3-4 pcs.;
- peppercorns - 4 pcs.;
- garlic - 1 clove;
- table vinegar 9% - 1 tbsp. l.
How to prepare:
- Cook the marinade from the above ingredients for 15 minutes, at the end add another 1 tbsp. l. vinegar.
- Arrange the mushrooms in sterilized jars, pour the hot mixture.
- Cool at room temperature, then put in a cool place.
The product will be ready in a month.
Frying
In this form, ryadovki are used as an independent dish and in combination with other relatives and potatoes:
- boiled skulls –250–300 gr;
- vegetable oil - 3-4 tbsp. l .;
- onions - 2-3 pcs.;
- salt, spices - to taste.
Preparation:
- Peel the onion, chop, fry until transparent.
- Add mushrooms, fry for 12-15 minutes until golden brown.
- Salt, season.
Salting (classic method)
- rows - 1 kg;
- salt - 40–45 gr;
- black peppercorns - 6-7 pcs.;
- currant leaves, horseradish - 3-5 pcs.;
- bay leaf - 3-4 pcs.;
- dill umbrellas - 2 pcs.;
- garlic - 3-4 cloves.
Preparation:
- Rinse the fruit bodies, soak in cold water for 10-15 minutes.
- Divide the horseradish leaves and dill umbrellas into portions, cut the garlic into thin slices.
- Put 1/4 of the spices in the prepared container, add a layer of mushrooms on top, salt.
- Alternate layers: spices and seasonings – ryadovki – salt. The last layer is spices.
- Put under oppression.
- Store in a cool place.
The product is ready in 1.5-2 months.
Row caviar
- mushrooms - 200-300 gr;
- onions - 1 large or 2 medium-sized heads;
- vegetable oil - 3-4 tablespoons;
- salt, spices - to taste.
Preparation:
- Peel the fruits, rinse, boil.
- Cool, drain off excess liquid.
- Grind or grind in a food processor.
- Fry the onions in vegetable oil until light golden brown.
- Combine with chopped mushrooms, mix well, add salt and spices.
Ecology and distribution:
The period of growth of floodplains is from mid-August to early October. The main difference between the mushroom and others is its aroma. The underfloor units have a pleasant aroma of fresh flour. Thanks to this wonderful smell, underfloors are especially tasty when pickled or salted. It is better to pick mushrooms when young, when the mushroom cap has not yet opened. During this period, the pulp of the mushroom is hard, and practically not subject to worminess.
Poplar rows are common wherever poplars grow - these are the territories of North America and Canada, Western and Eastern Europe, Central Asia, as well as central and southern Russia, the Urals, Siberia and the Far East. The main period of her growth begins in the season of autumn leaf fall, somewhere from the end of August, and it ends at the end of October.























































