Podgruzdok black white and blackening: description of the mushroom and what a dry milk mushroom looks like in the photo
Active growth requires a lot of light and little heat. This mushroom grows in huge quantities in deciduous and mixed forests of the middle zone of our country. Usually, its mycelium dislocations are located near aspens and birches. It is these trees that create the most favorable conditions for their existence.
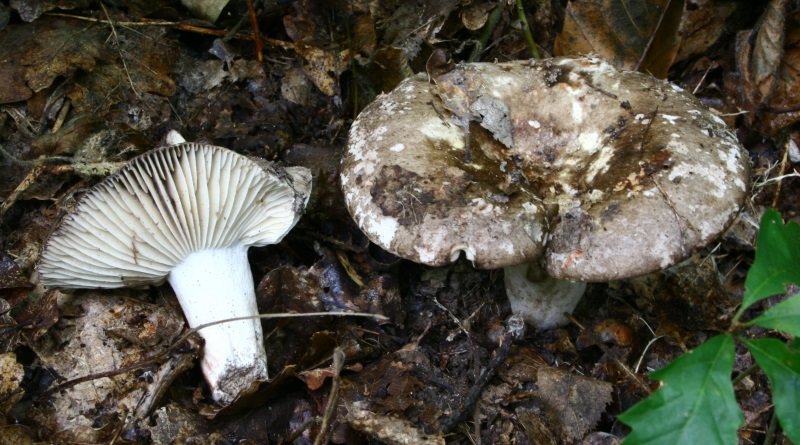
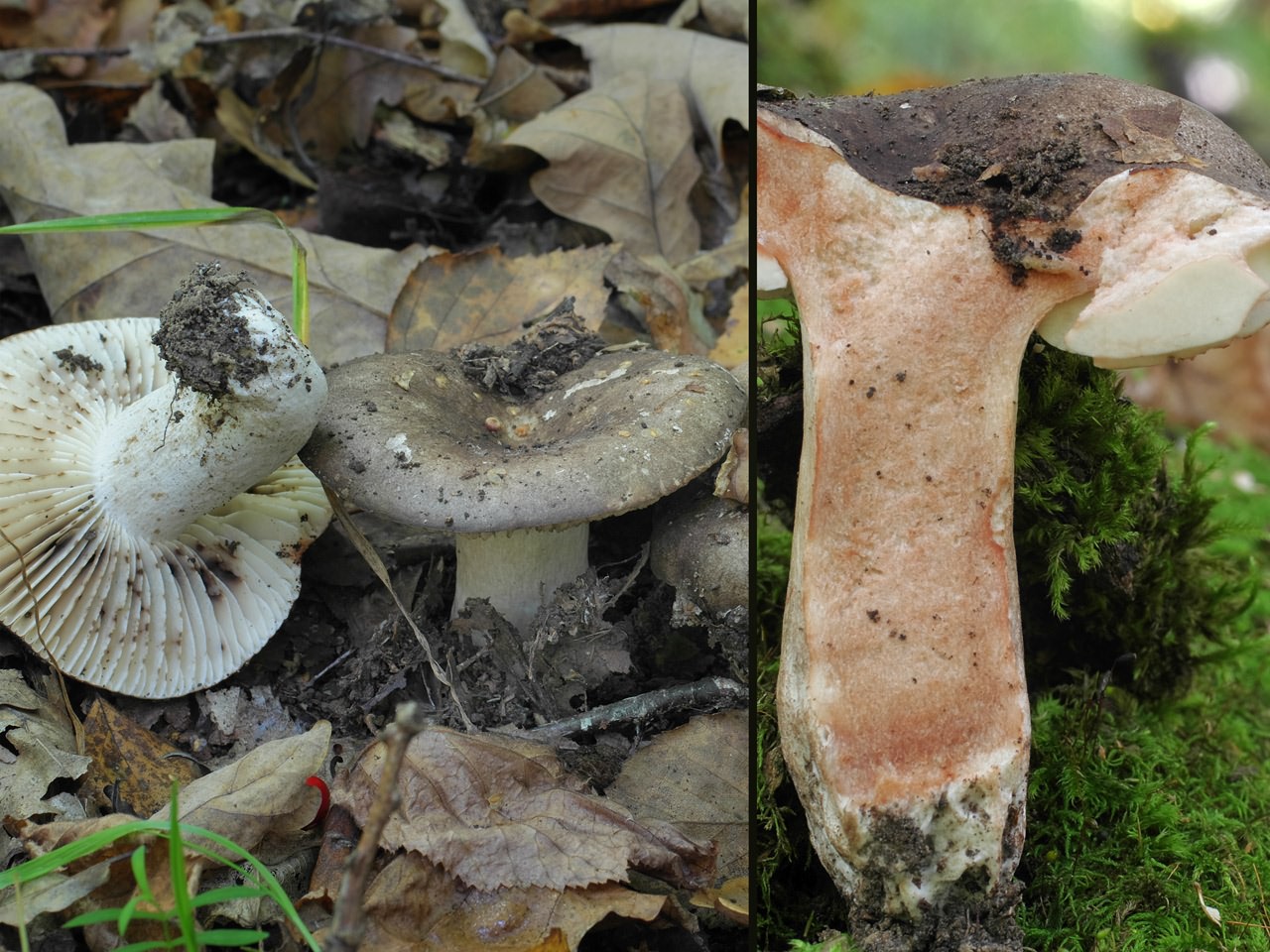
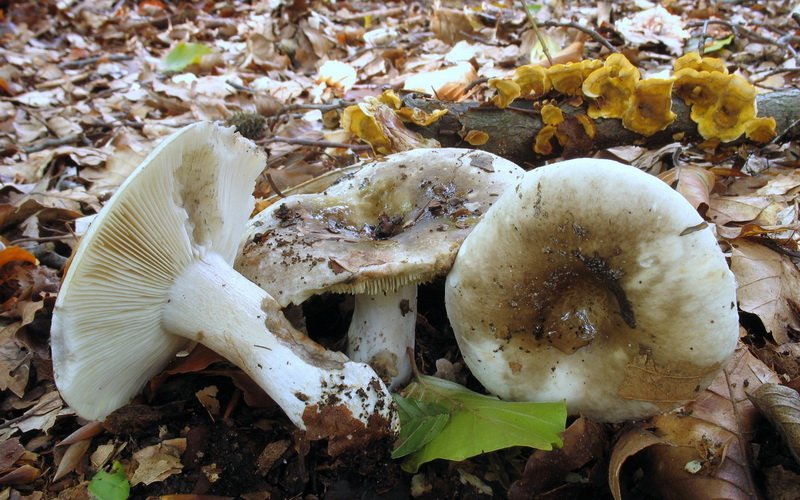
Podgruzdok popularly has a simpler name. This is a dry lump. It is not by chance that the mushroom is called that. In from common mushrooms, they are never covered with mucus and do not become wet. The surface of their caps is always dry and slightly rough to the touch.
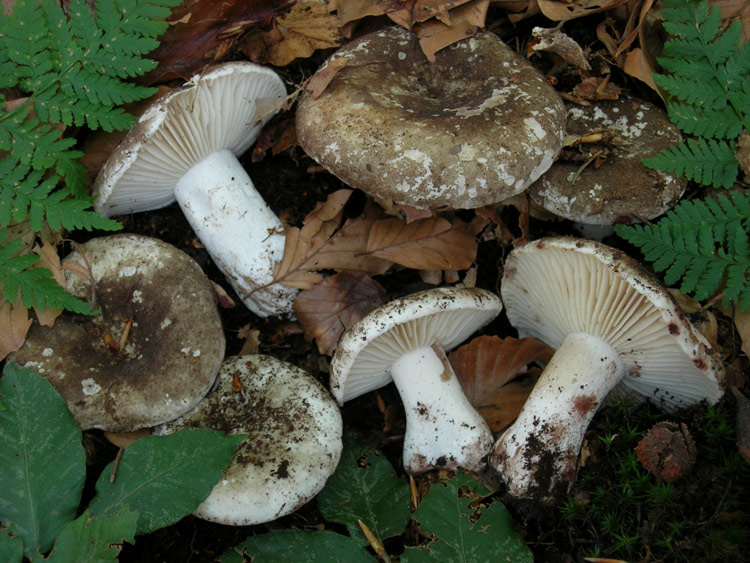
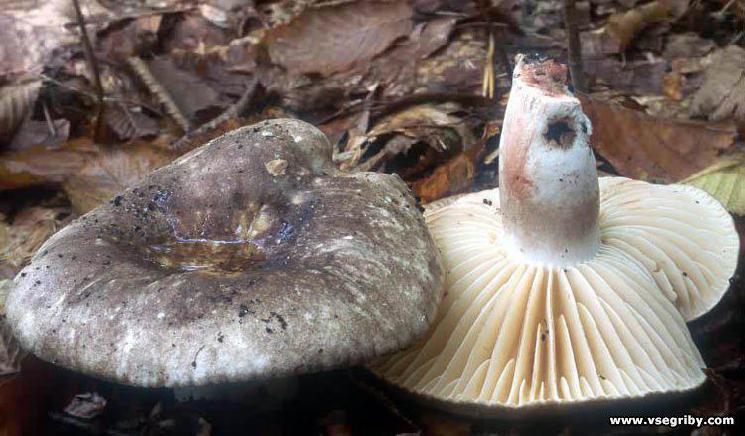
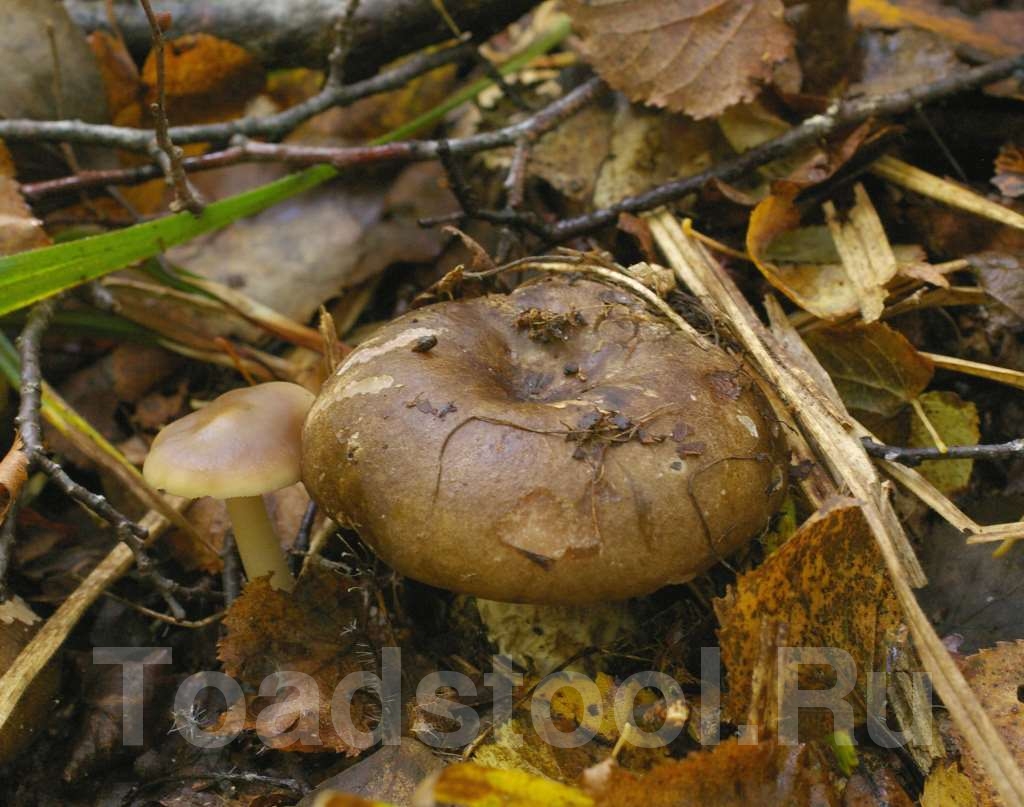
A regular load looks like this. This is a fairly strong cap with edges bent inward and up to 20 cm in diameter. The upper surface of the cap is matte white with yellowish blotches. During the growth process, the fungus is prone to cracking. A characteristic feature is the absence of milky juice on the cut of the stem and cap. Podgruzdok or dry lump belongs to the second category of edibility. It can be used for salting and pickling without first soaking in water
Podgruzdod black or black
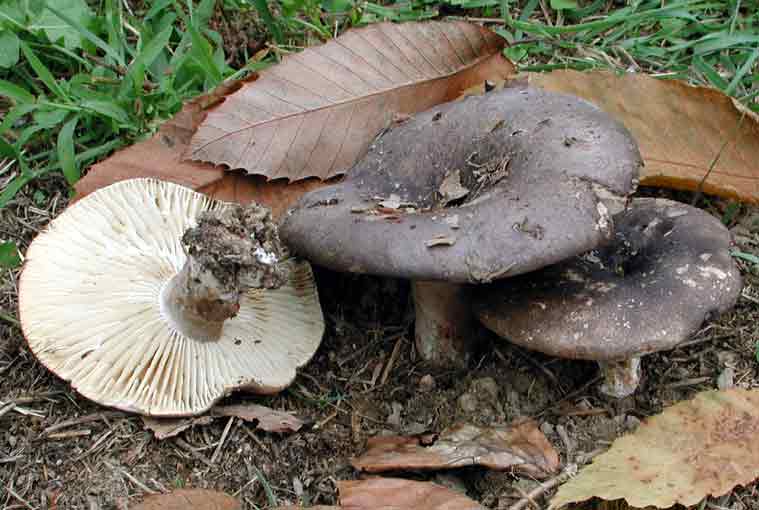
From the beginning of July to the very end of October, the coniferous and deciduous forests of our country can delight you with a rich harvest of another type of dry milk mushroom. This is a black load. It is also called black russula. And this is no coincidence. Outwardly, the black podgruzdok really resembles a russula. The hat is up to 15 cm in diameter and has a glossy dark blue, almost black surface. There is no milky juice.
Black podgruzdok can be eaten boiled, fried and salted. Does not require soaking before direct use.
Podgruzdok porcini and mushroom rusk
Podgruzdok porcini and mushroom rusk are the names of the same specimen. This is a type of mushrooms and lamellar mushrooms that grow in large numbers in bright places in deciduous forests. They can be eaten without boiling or steeping. They are distinguished by the absence of bitterness and unpleasant taste. belong to the category of little-known. But don't neglect them. They contain a fairly large amount of protein and various active substances that improve digestion. Dry milk mushrooms make an excellent powder for sauces and seasonings.
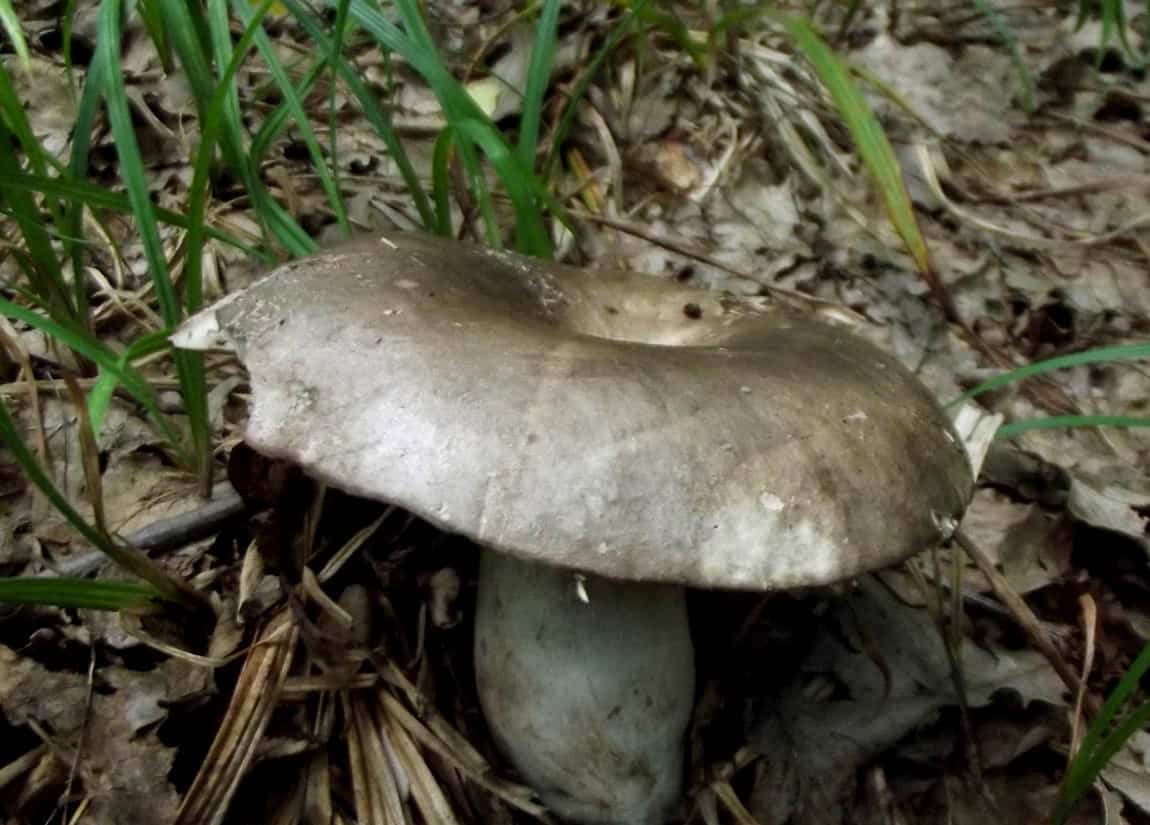
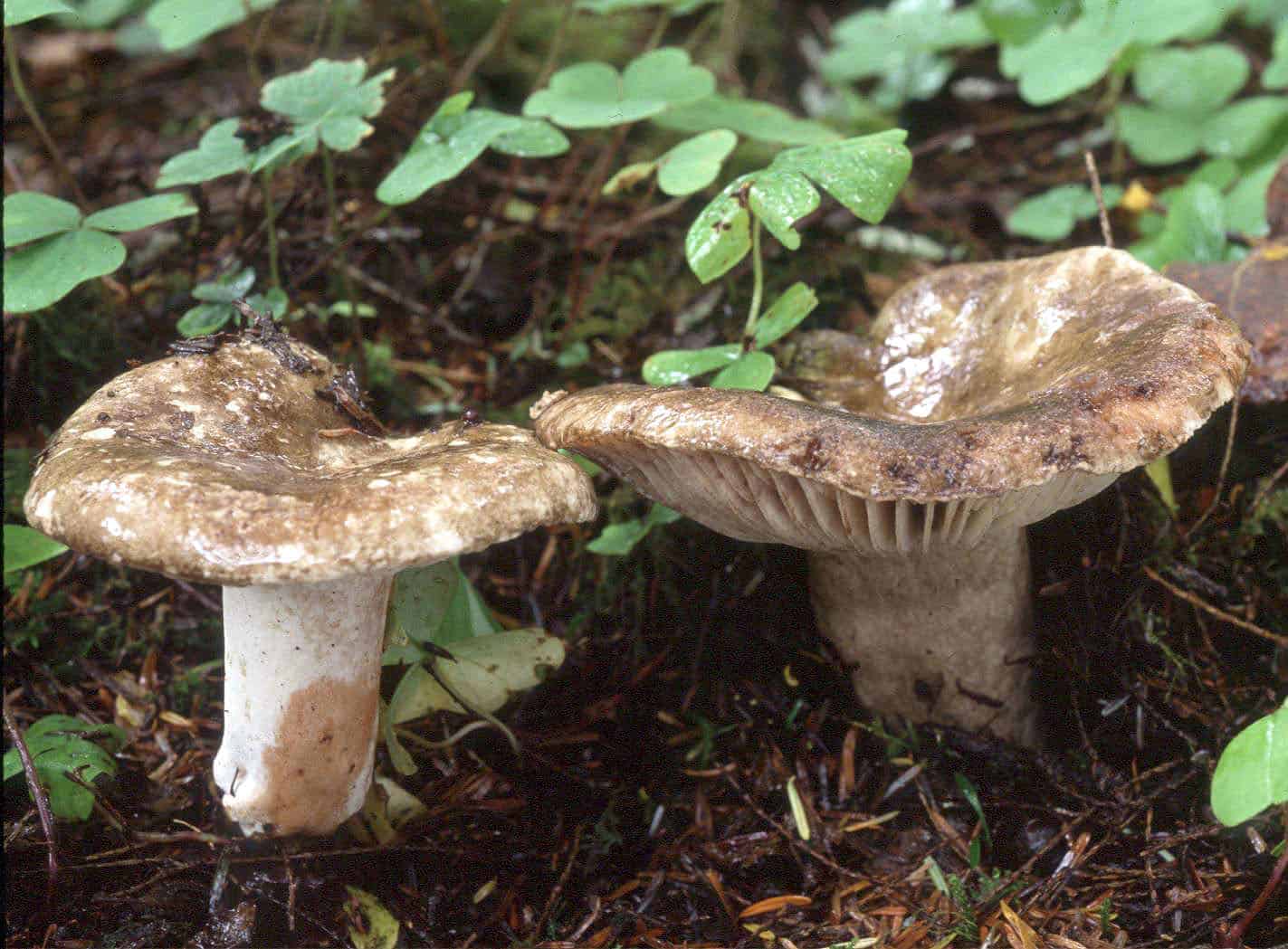
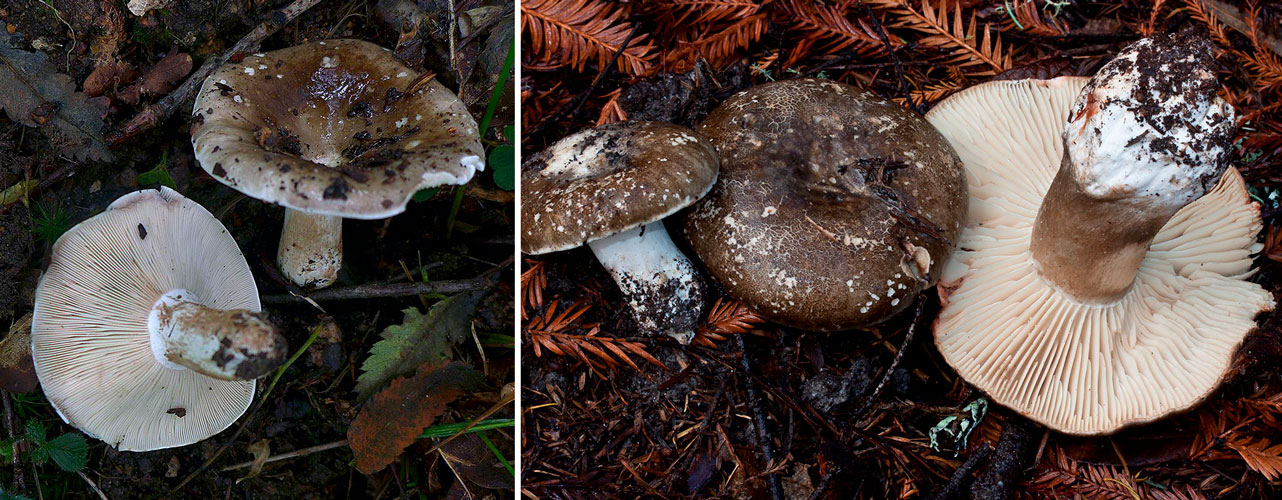
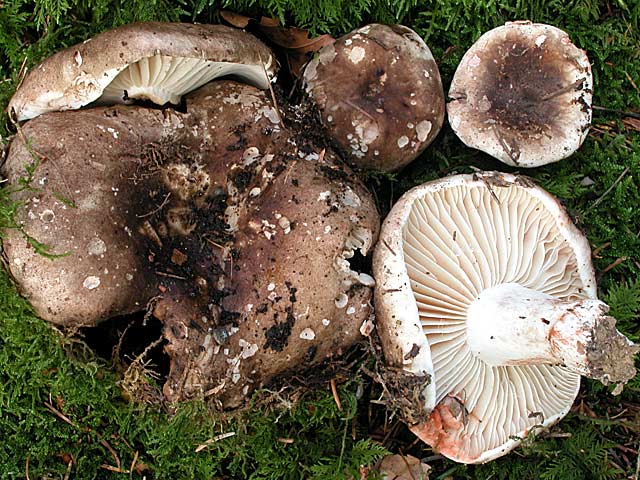
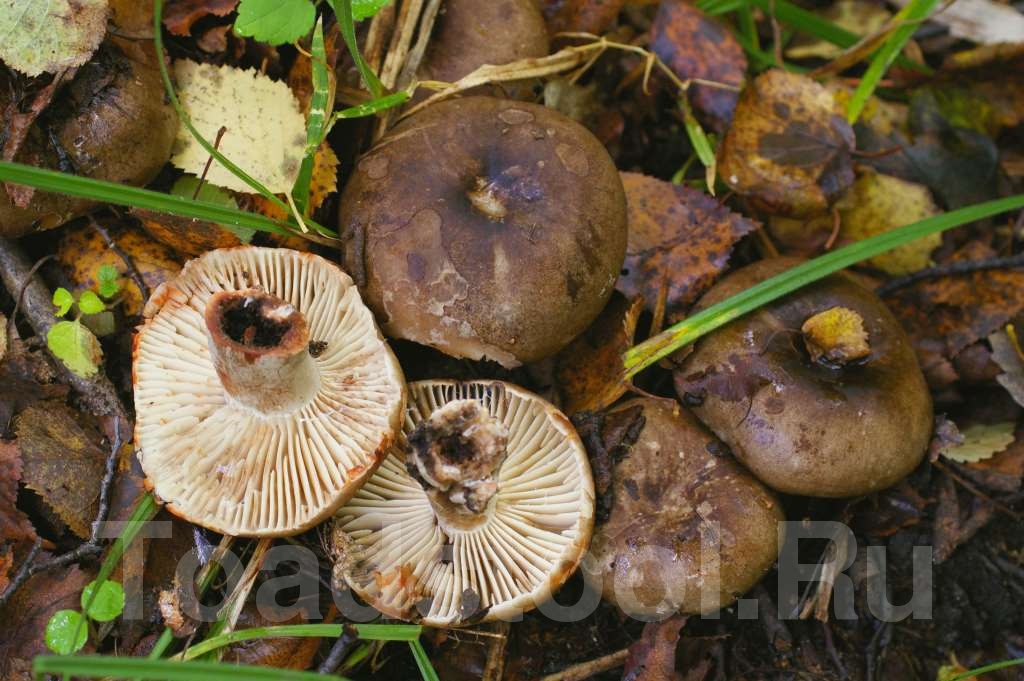
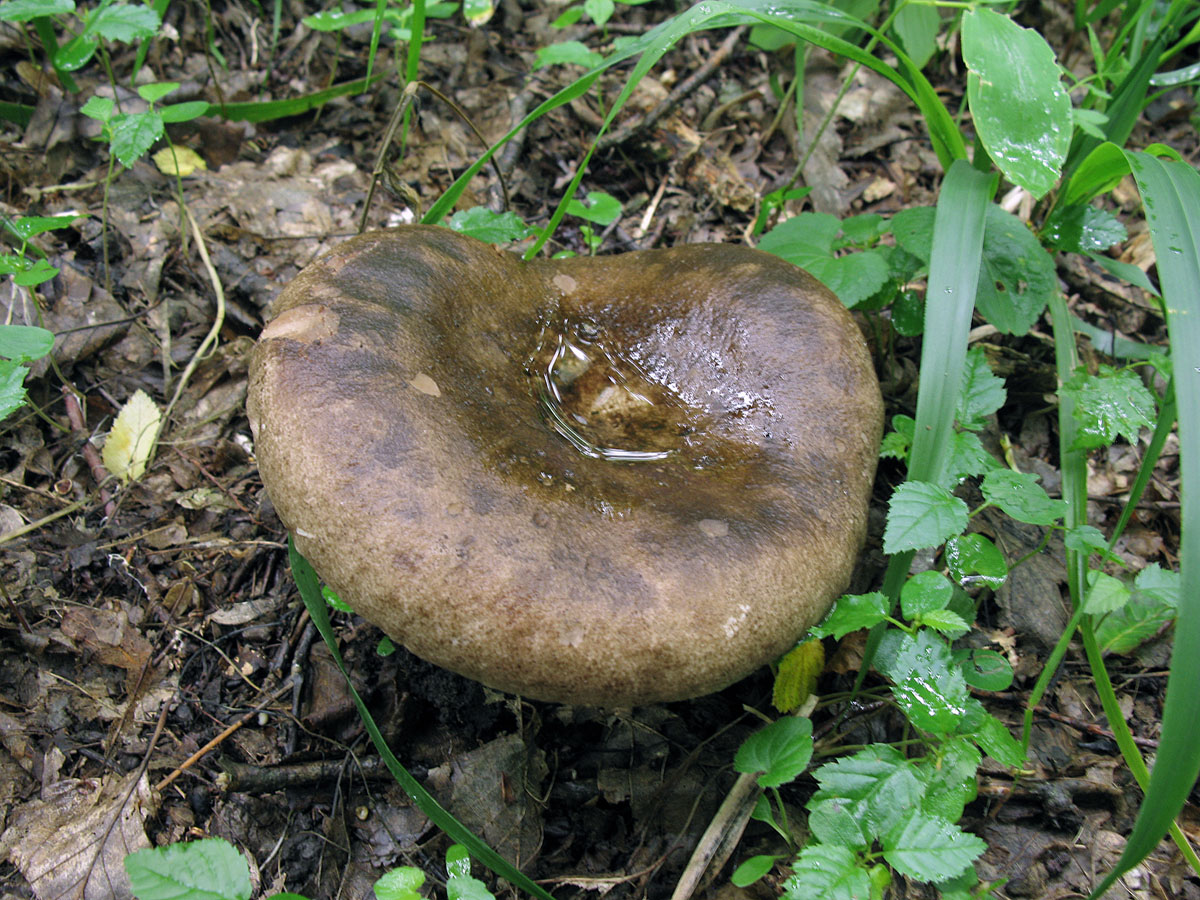
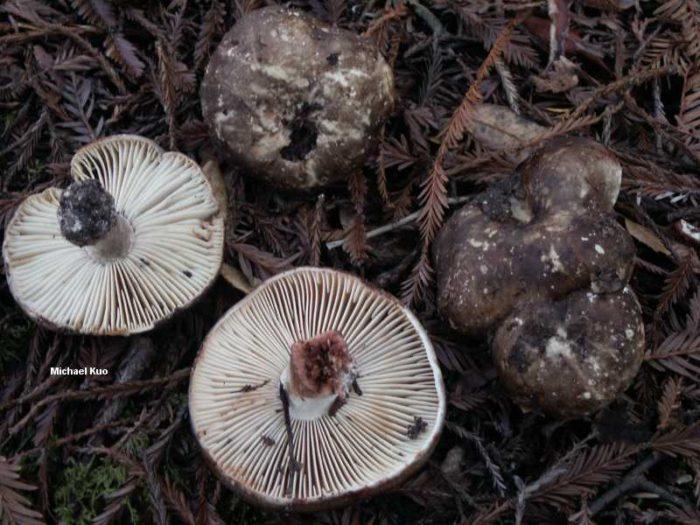
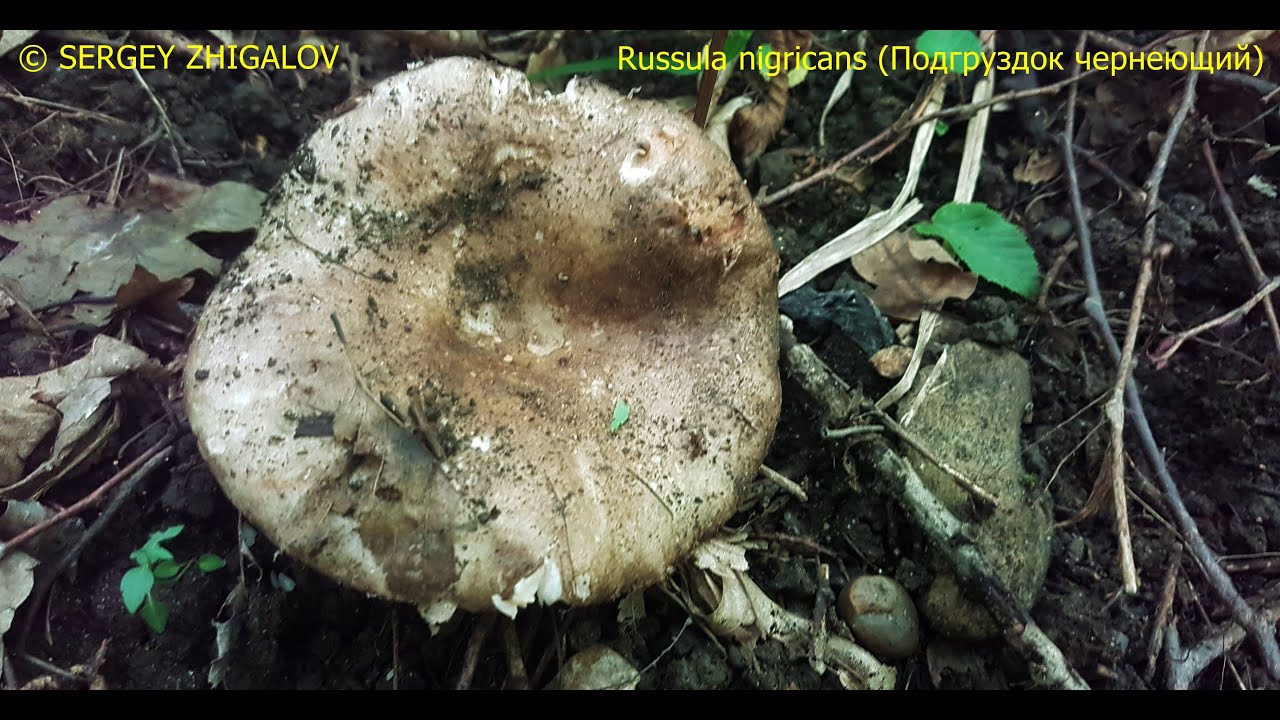
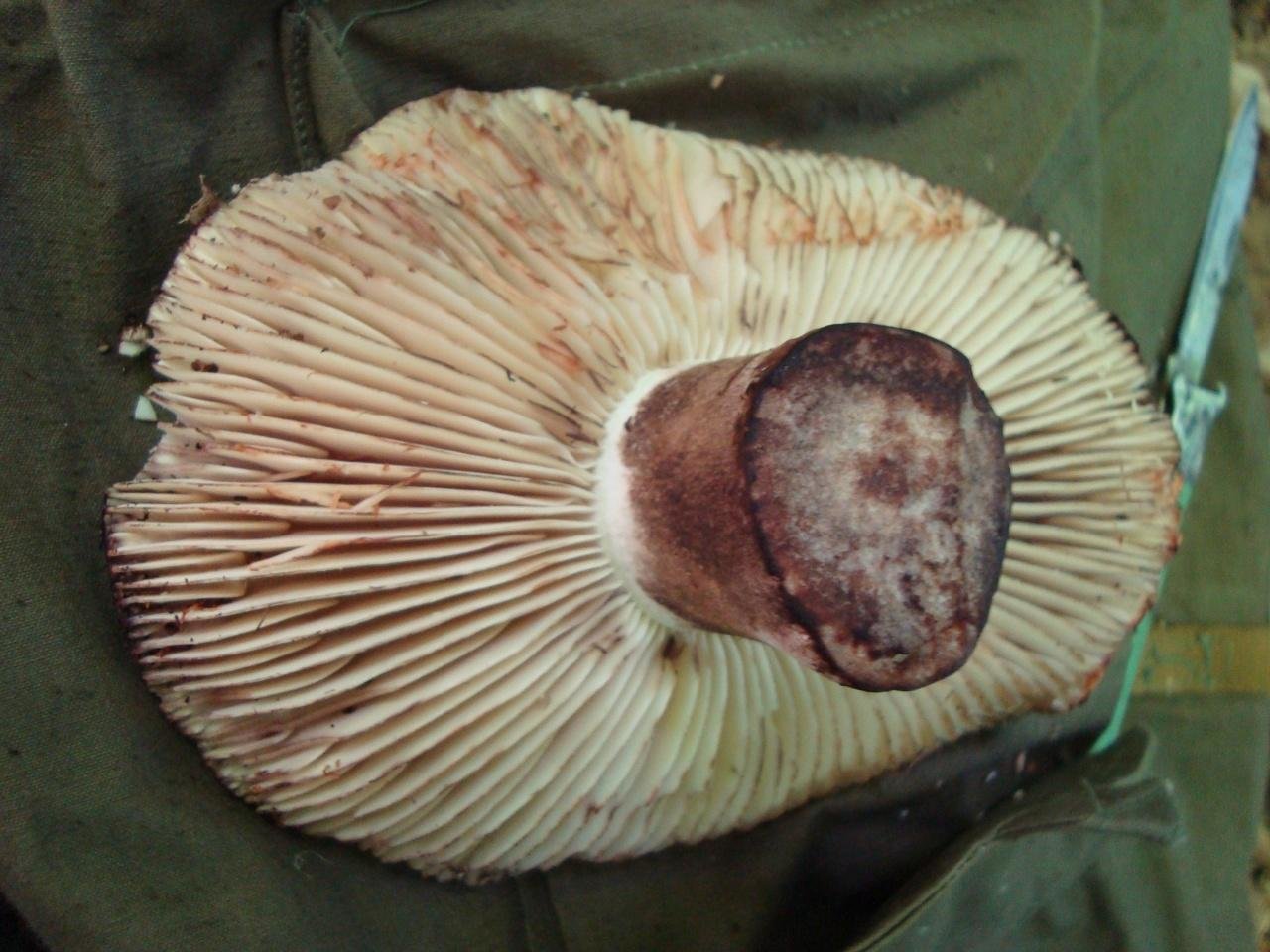
What does a blackening load look like
Blackening podgruzdok is another type of lamellar mushrooms that are found by mushroom pickers in mixed and deciduous forests and at the same time go unnoticed. Many confuse them with poisonous and inedible due to their unsightly appearance. But let's try to figure it out.
There is a certain opinion among mushroom pickers that the edible lamellar must necessarily produce milky juice. Dry milk has no milky juice. And this does not mean that it is poisonous. The blackening podgruzdok in appearance resembles a real lump. But unlike him, over time, his cap and leg begin to turn black. Older specimens are almost black in all parts.
Primary processing and preparation
The opinions of mycologists regarding the category to which black podgruzdok can be classified in terms of taste differ. Some publications say that this mushroom belongs to category 3, others - that to 4. However, in any case, only young black pods are collected - mature representatives of this species are tasteless and tough. In addition, worms are very fond of them - this is another argument in favor of collecting small fungi that have not yet been affected by larvae.
Usually, the mushroom is salted after prolonged soaking or boiling, thus getting rid of its specific smell and bitterness. A salty load has a pleasant, slightly sweetish taste. When salted, it turns black.
Some mushroom pickers also roast or pickle this species.
Black podgruzdok bears fruit well and in a lean year may well replace real milk mushrooms. Moreover, this species has no counterparts among poisonous mushrooms, so you can safely collect and harvest it.
Collection rules
It is best to go for mushrooms in the early morning. It was at this time that the optimal lighting mode was. It is necessary to know the characteristics of the collected mushrooms. In a new forest, in a different climate, it is better for the country to collect under the supervision of a local mushroom picker. Familiar species may turn out to be poisonous counterparts. An error can lead to fatal consequences.
The terrain is of no small importance. It is not recommended to collect a load of blackening in forest belts next to highways, cemeteries, fertilized agricultural fields, chemical industry enterprises
When collecting mushrooms, it is important to pay attention to the shape, color of the cap, color and smell of the pulp, characteristic features, soil. This will help you recognize the venomous species.
Blackening podgruzdok is able to grow in the substrate. After a few days, it appears on the surface and breaks down the top layer. At this point, cracking of the soil is noted. Another feature of the type is slow decomposition in vivo. In the process, the fruiting body darkens. A dried specimen can survive until the next season.
After returning from the forest, the obligatory stage is the bulkhead of the crop. It is then that suspicious and dangerous species are cut off.
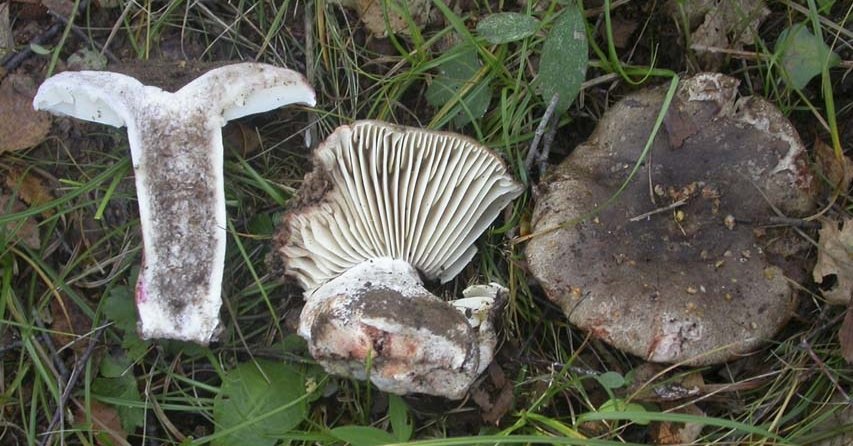
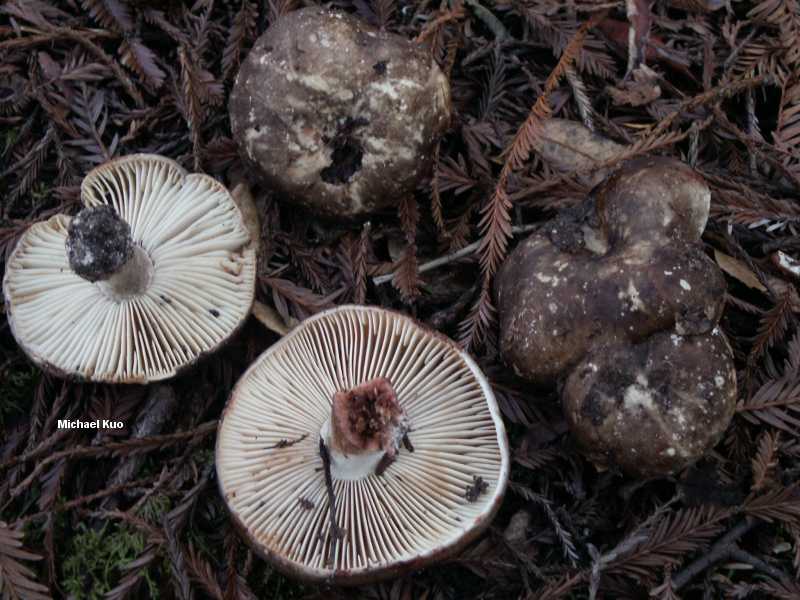
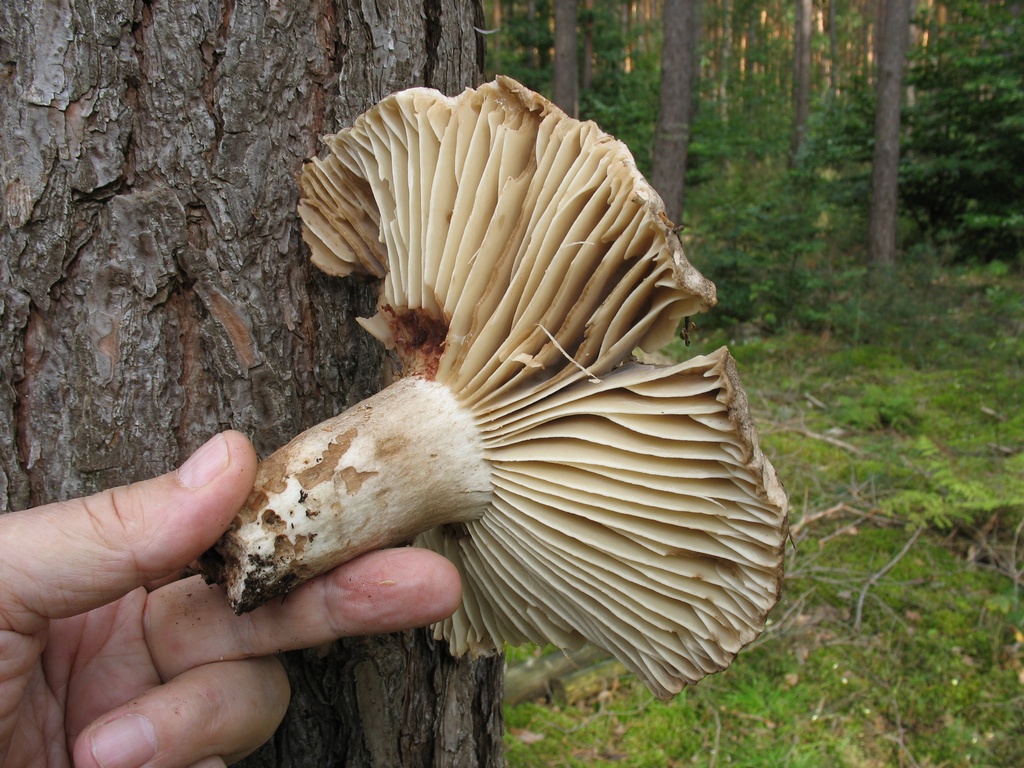
Frequent lamellar loading

In the photo Frequent plate podgruzdok
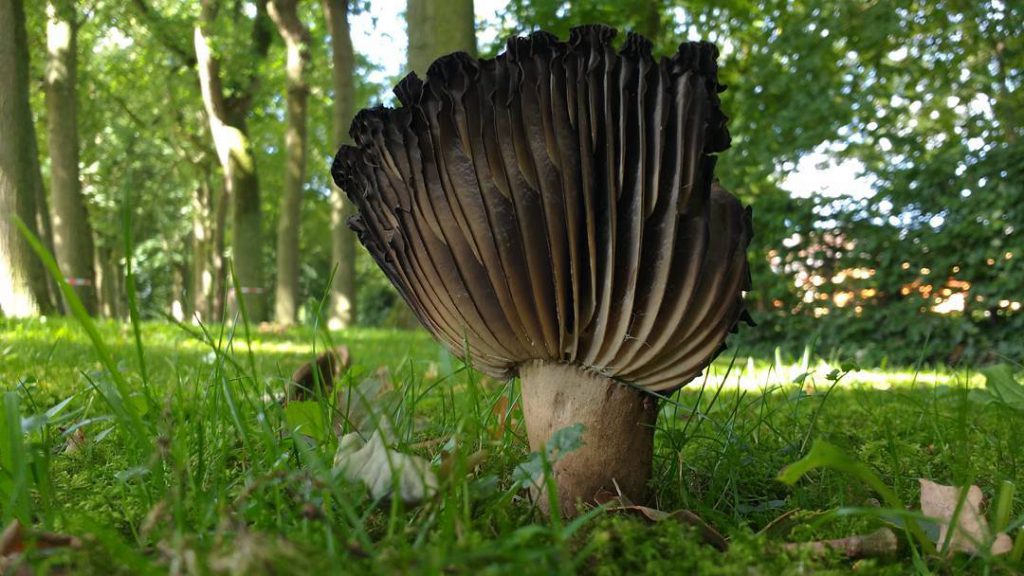
Another name for this species is lamellar black. It is found more often in the south of Russia, in coniferous, mixed or deciduous forests.
The hat is distinguished by a more grayish, sometimes brownish tint, which, with the growth of the mushroom, becomes olive, and sometimes brown. Its diameter is rarely more than 12 cm. In young mushrooms, the cap is sticky, with age it becomes dry. The leg is the same shade as the cap.
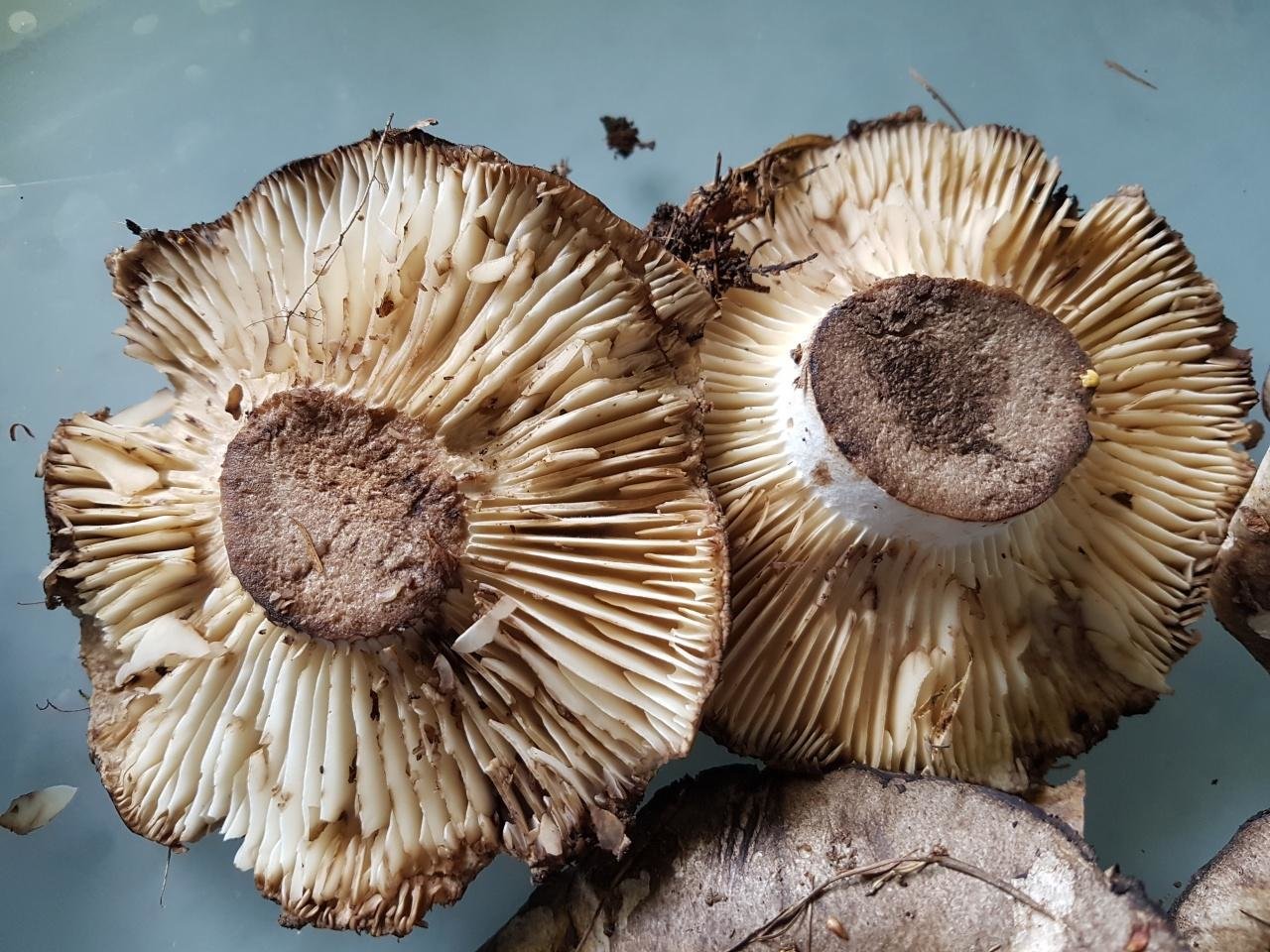
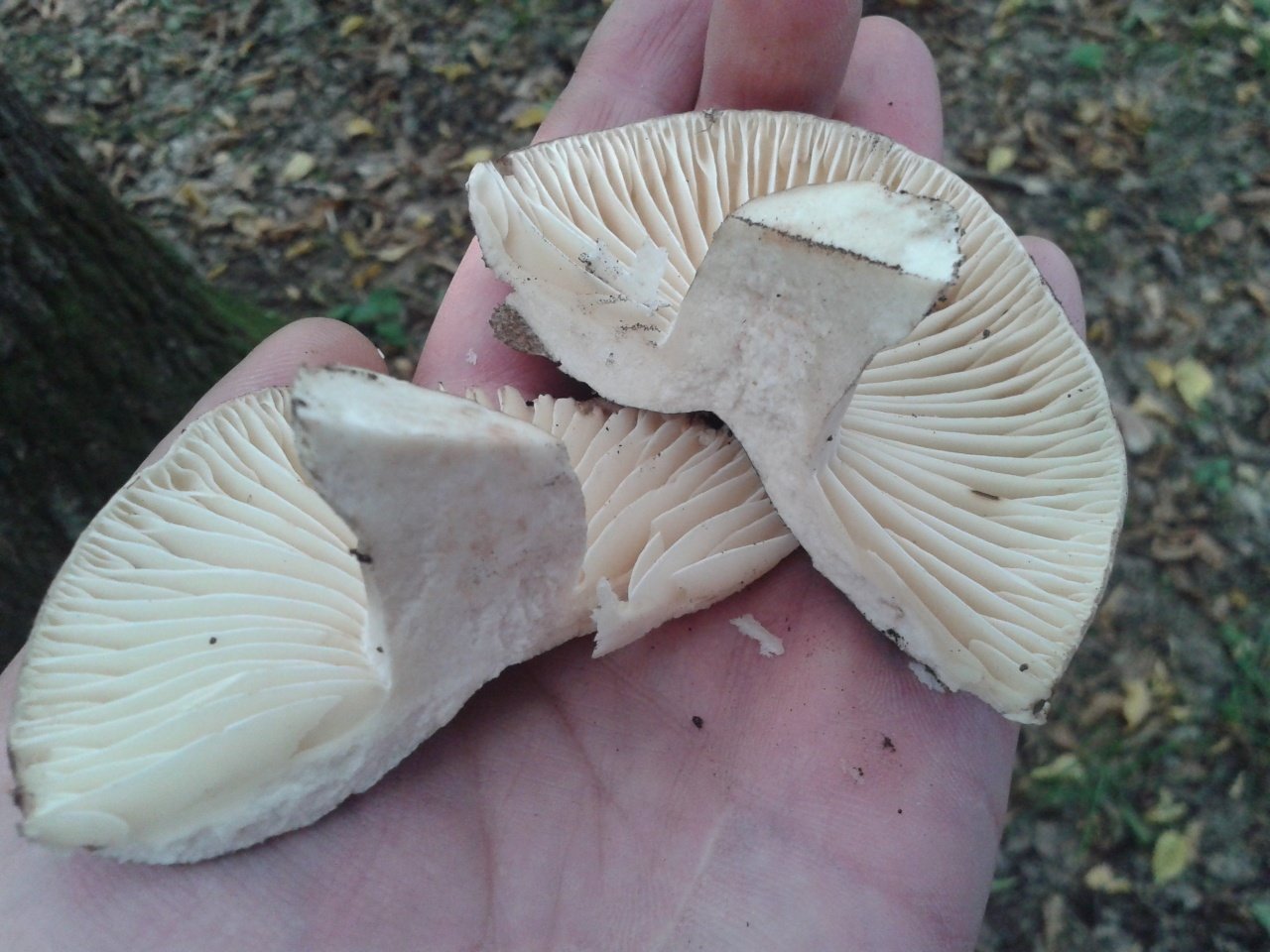
The pulp on the break turns red, then brown, and then turns black. This lump has light plates that do not reach its legs.
The taste is inexpressive, the smell is weak.
In medicine, an extract from a lamellar load is used. It has antimicrobial activity. To relax muscles in medicine, it is the properties of this type of mushroom that are used.
In the kitchen, the podgruzdok is often fried, broths are made, marinated and salted. The mushroom does not need to be pre-cooked.
Description of the russula blackening.
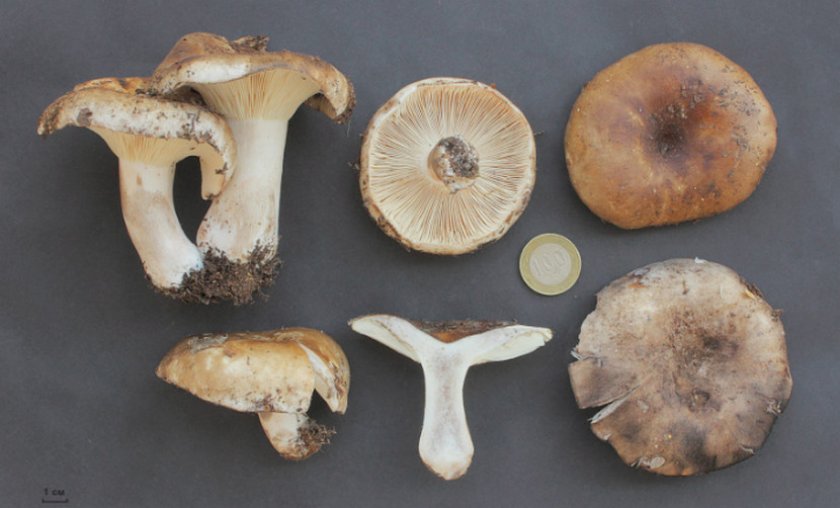
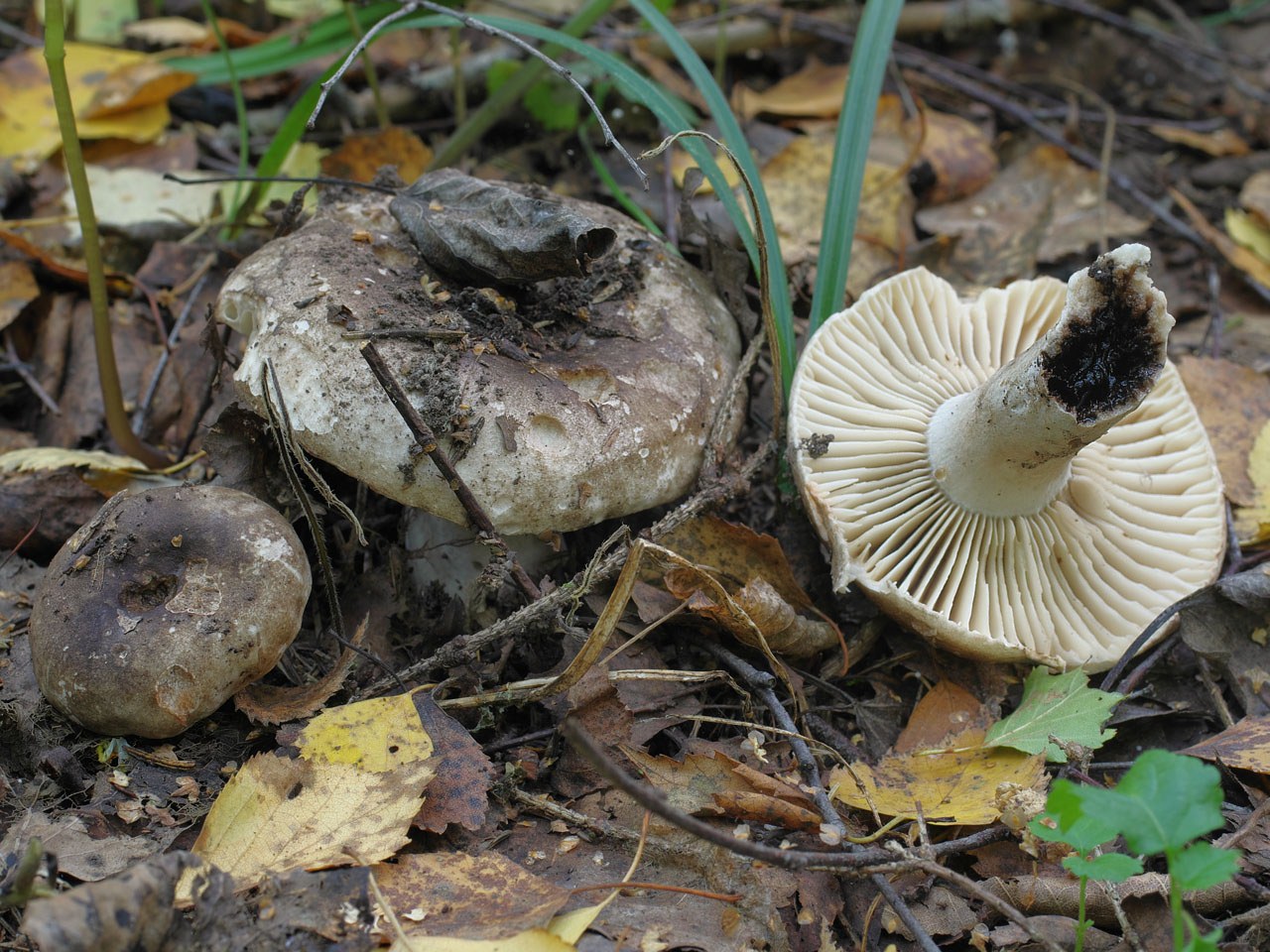
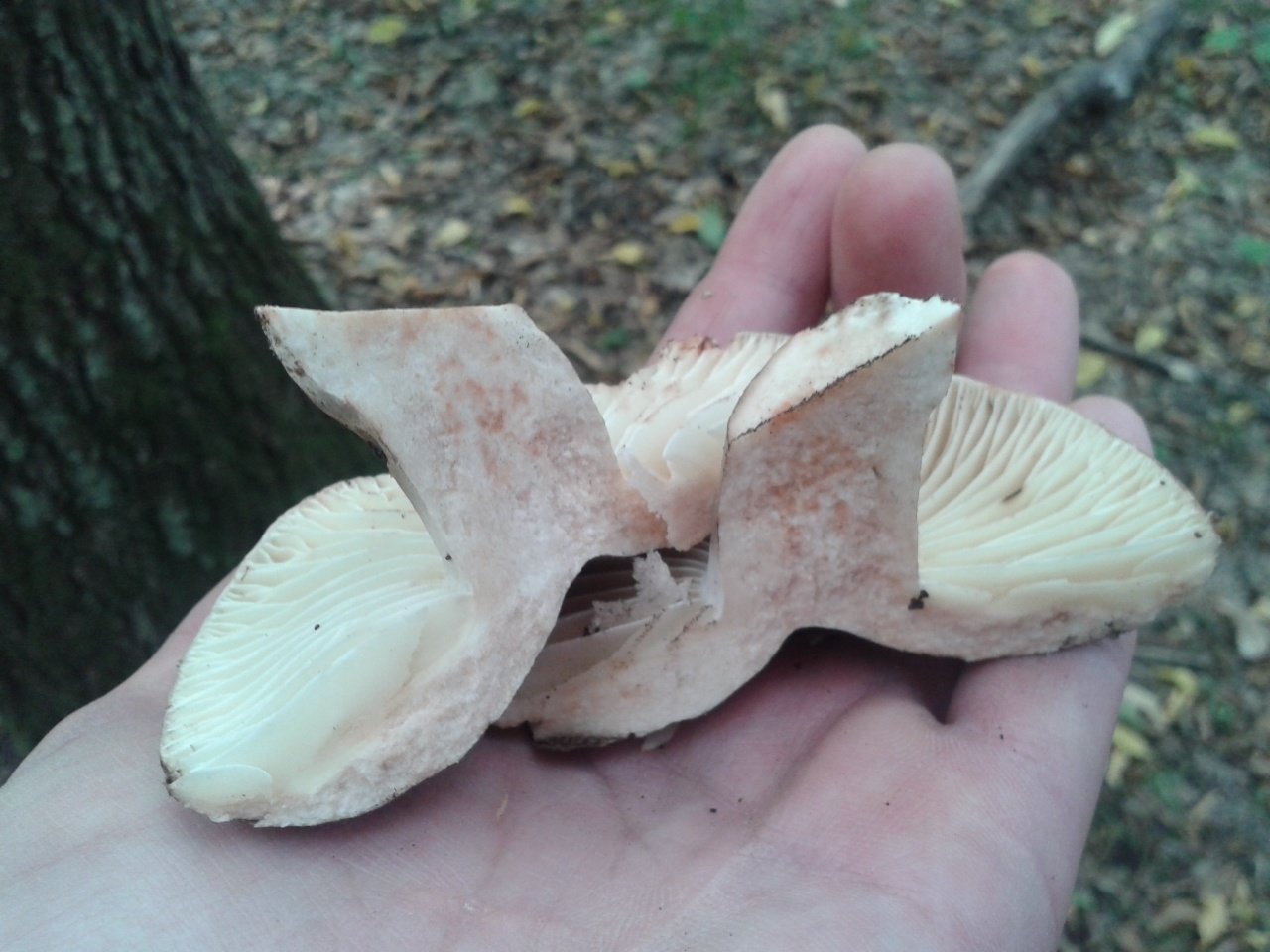
The shape of the cap is usually convex at a young age, but later it becomes flat, with a smooth central part. Its diameter is generally 5-15 centimeters, but sometimes there are large fruiting bodies with caps up to 25 centimeters in diameter. The color of the cap is whitish at a young age, but later turns dirty gray or brown. You can also find brown specimens with an olive tint. The central part of these mushrooms is darker, and the edges are lighter.

The surface of the cap of the blackener is smooth, dry, in wet weather there may be a slight admixture of mucus. On the surface there may be particles of earth, dirt and various forest debris. Cracks may form on the cap with age, through which the white flesh is visible.
Under the head of a blackening russula is a lamellar hymenophore. The plates are large, thick, they are rarely located. The color of the plates is at first white, and with age they turn gray or brown with a pinkish tinge. There are also atypical specimens with black plates.

The length of the leg of a blackening load reaches 10 centimeters. Its shape is cylindrical. The leg is strong in structure.The color of the leg is light, whitish, but becomes dirty brown with age.
The flesh of the blackening russula is thick, but brittle. Its color is most often white; if damaged, it slowly turns red. The taste of the pulp is pleasant, slightly bitter, the aroma is weak, delicate. Upon contact with ferrous sulfate, the pulp turns pink and then turns green.
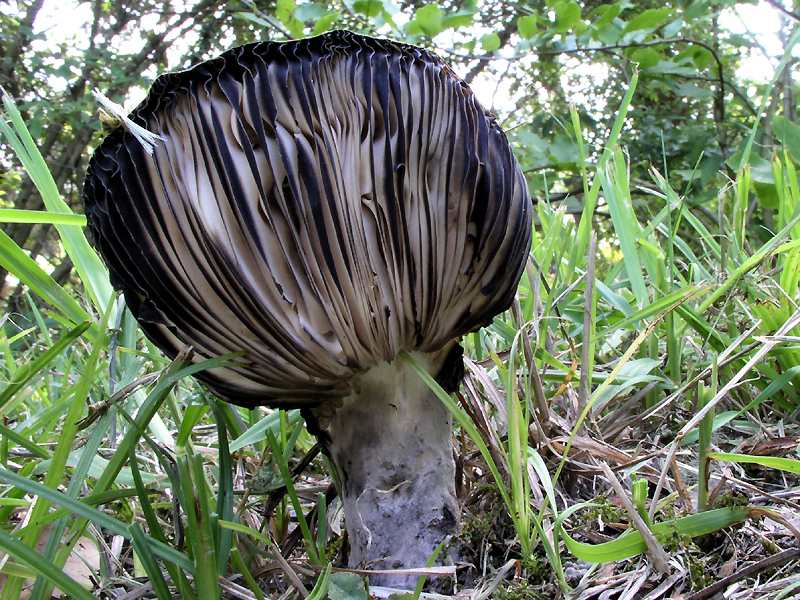
Russula blackening
The cap is 8-10 (20) cm in diameter, densely fleshy, convex, then flat-spread, slightly depressed, with a sharp, smooth edge. The peel is adherent, at first sticky, then dry, naked, smooth, in a dry state matte, grayish-brown, almost black. The plates are attached, rare, thick, wide, forked, with plates and anastomoses, white, cream, blackening with age. The leg is 2-6 x 1-3 cm, cylindrical, at first hard, then brittle, made or with cavities, naked, smooth or finely felt, colored to a tone lighter than the cap. The pulp is fragile, loose, white, reddening in the air and then blackening, the taste is fresh, soft, without a special smell. When exposed to FeSO4, it turns dark green. Spore powder is white.
Habitat - deciduous, coniferous and mixed forests. It occurs from July to October. Grows in groups.
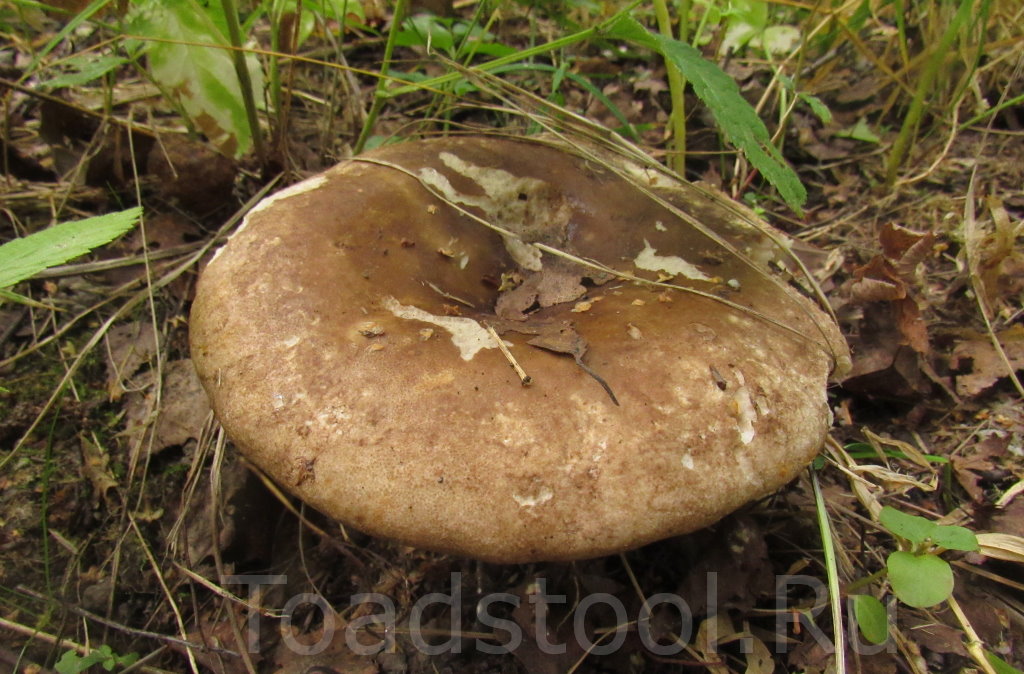
The cap is up to 15 cm in diameter, at first convex, in a mature mushroom it is depressed, with curved edges, dirty gray, then brown or black, sticky. The pulp is white, brittle, without milky juice, turns red at a break or cut, then turns brown and finally turns black. The taste is sweetish.
The plates are adherent to the pedicle or descending, white, darken from pressure. Spore powder is white.
The leg is up to 5 cm long, 2.5-3 cm thick, even, dense, of the same color as the cap.
Little known edible of the third category. It is consumed boiled and salted. When salted, it turns black. It is very badly damaged by insects.
And blackening: description of the mushroom and what the milk mushroom looks like in the photo
Active growth requires a lot of light and little heat. This mushroom grows in huge quantities in deciduous and mixed forests of the middle zone of our country. Usually, its mycelium dislocations are located near aspens and birches. It is these trees that create the most favorable conditions for their existence.
Podgruzdok popularly has a simpler name. This is a dry lump. It is not by chance that the mushroom is called that. Unlike ordinary ones, they are never covered with mucus and do not get wet. The surface of their caps is always dry and slightly rough to the touch.
A regular load looks like this. This is a fairly strong cap with edges bent inward and up to 20 cm in diameter. The upper surface of the cap is matte white with yellowish blotches. During the growth process, the fungus is prone to cracking. A characteristic feature is the absence of milky juice on the cut of the stem and cap. Podgruzdok or dry lump belongs to the second category of edibility. It can be used for salting without pre-soaking in water
Podgruzdod black or black
From the beginning of July to the very end of October, the coniferous and deciduous forests of our country can delight you with a rich harvest of another type of dry milk mushroom. This is a black load. It is also called black russula. And this is no coincidence. Outwardly, the black podgruzdok really resembles a russula. The hat is up to 15 cm in diameter and has a glossy dark blue, almost black surface. There is no milky juice.
Black podgruzdok can be eaten boiled, fried and salted. Does not require soaking by direct use.
Podgruzdok porcini and mushroom rusk
Podgruzdok porcini and mushroom rusk are the names of the same specimen. This is a variety of mushrooms and lamellar mushrooms, which are abundant in bright places in deciduous forests. They can be eaten without boiling or steeping. They are distinguished by the absence of bitterness and unpleasant taste. belong to the category of little-known.But don't neglect them. They contain a fairly large amount of protein and various active substances that improve digestion. Dry mushrooms make an excellent mushroom powder for sauces and seasonings.
What does a blackening load look like
Blackening podgruzdok is another type of lamellar mushrooms that are found by mushroom pickers in mixed and deciduous forests and at the same time go unnoticed. Many confuse them with poisonous and inedible due to their unsightly appearance. But let's try to figure it out.
There is a certain opinion among mushroom pickers that the lamellar must necessarily produce milky juice. Dry milk has no milky juice. And this does not mean that it is poisonous. The blackening podgruzdok in appearance resembles a real lump. But unlike him, over the course of his hat, and the leg begin to turn black. Older specimens are almost black in all parts.
Benefit and harm
The pulp contains a blackening load:
- vitamins E, PP, F, B1, B2;
- mono- and disaccharides, dietary fiber;
- saturated, unsaturated acids;
- trace elements: sodium, phosphorus, iron, calcium, potassium, magnesium.
Mushrooms are nutritious and dietary food. They have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Promote the improvement of metabolic processes in the body.
It should be remembered that mushrooms with illiterate preparation can provoke severity, pain, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. They are not advised to use them for people with stomach problems. Heavy food can be dangerous for people of age who still have diseases of the liver, kidneys, gall bladder, and immunity.
Even edible varieties can be troublesome with individual sensitivities. A person can react sharply to a particular type of mushroom. It is not recommended to eat blackening food for children under 12 years old, pregnant and lactating mothers.
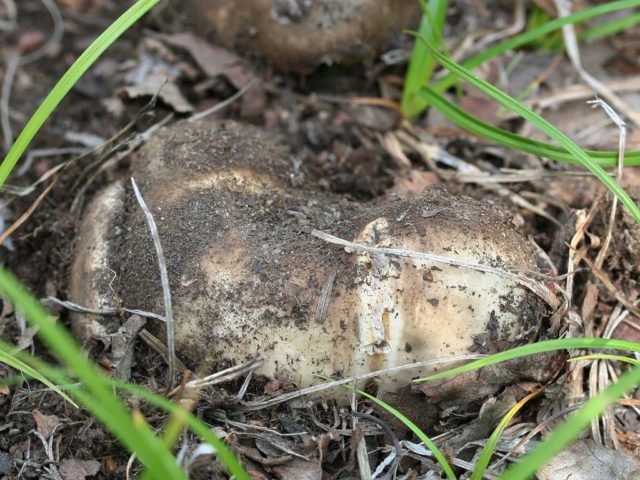

Load and value
The well-known Valui mushroom and the lesser-known black and white podgruzdok belong to the russula genus. They are characterized by a fragile leg. They are usually collected a little, since more valuable mushrooms are always found in the forest. The same mushrooms are conditionally edible. They are salted, less often pickled, but must be pre-soaked in cold water to destroy bitterness or boiled.
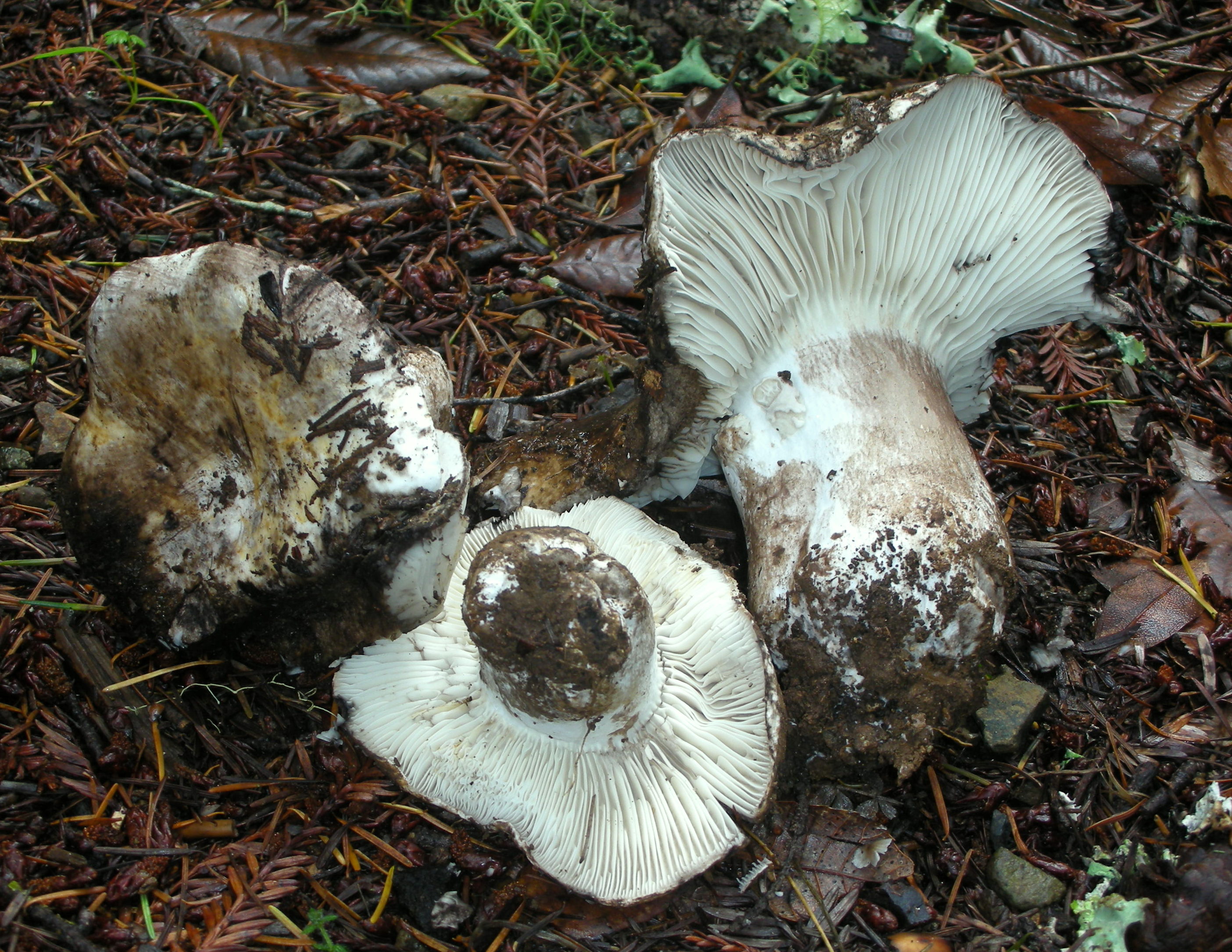
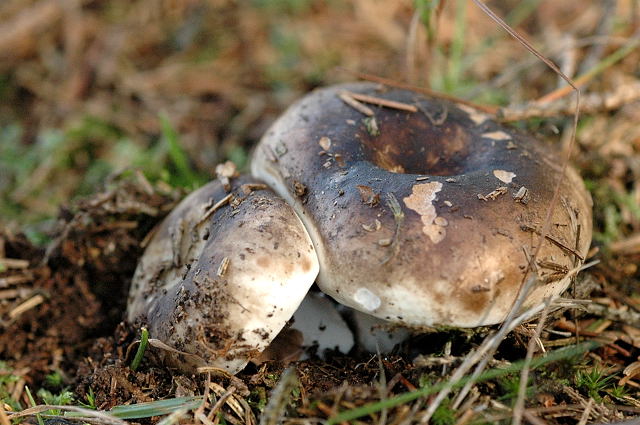
Podgruzdok black
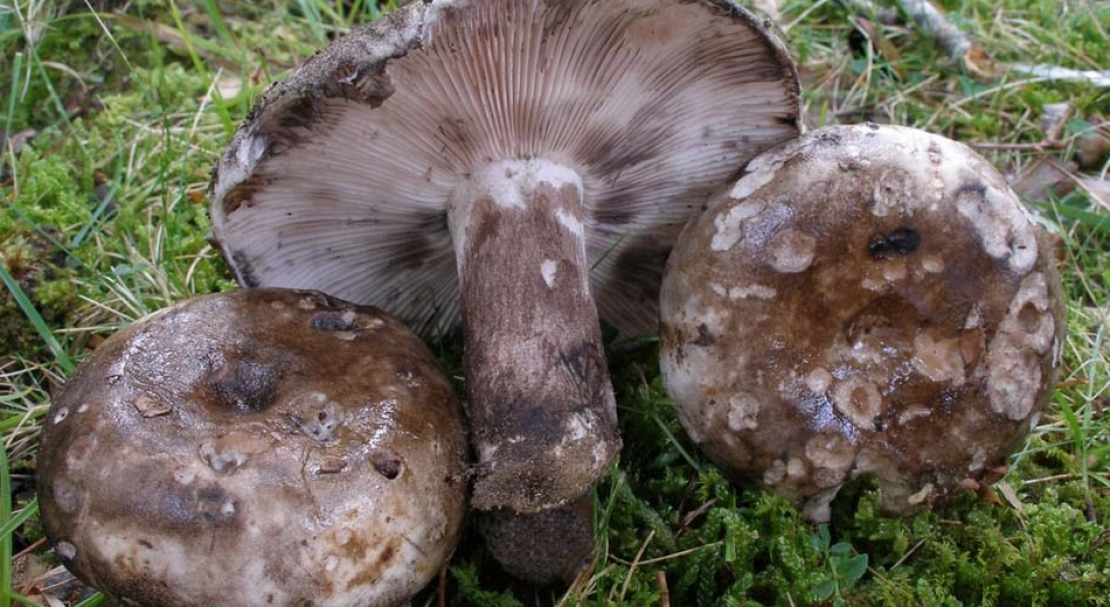
This mushroom is also called black russula. It is found in all forests, especially in deciduous ones, it grows all summer from June to October in groups.
The cap is up to 15 cm in diameter, in a young mushroom it is convex, in a mature one it is depressed, with curved edges, dirty gray, later brown or black, sticky. The pulp is white, brittle, without milky juice, turns red at the break, then turns brown and finally turns black. The mushroom is very similar to the milk mushroom, although it belongs to the genus russula.
Black differs from all podgruzdok podgruzdok in that it does not have milky juice. The plates are adherent to the pedicle or descending, white, darken from pressure. The leg is up to 5 cm long, 2.5–3 cm thick, smooth, dense, of the same color as the cap. These fungi are severely damaged by insects.
Mushroom little-known, edible, 3rd category, eaten boiled and salted, turns black when salted.
Valuy
It grows in deciduous and mixed forests from July to October, occurs frequently and abundantly, and is one of the most common mushrooms in our forest zone.
The cap of a young mushroom is spherical, tightly attached to the stem, later straightens and becomes flatter, up to 8–15 cm in diameter, with a ribbed-striped edge, buffy-yellow or yellow-brown, very slippery in wet weather, and shiny in dry weather. The skin peels off easily. The pulp is dense, white, yellowish in old mushrooms, very bitter, with an unpleasant odor. The plates are adherent, in young mushrooms are white, in mature ones they are yellow or rusty-yellow with brownish spots and with droplets of transparent liquid. The leg is up to 10 cm long, up to 3 cm thick, sometimes thickened in the middle, white, loose, hollow.
Mushroom conditionally edible, 3rd category. After boiling, it is suitable for pickling.It is recommended to collect young mushrooms with an unopened cap.
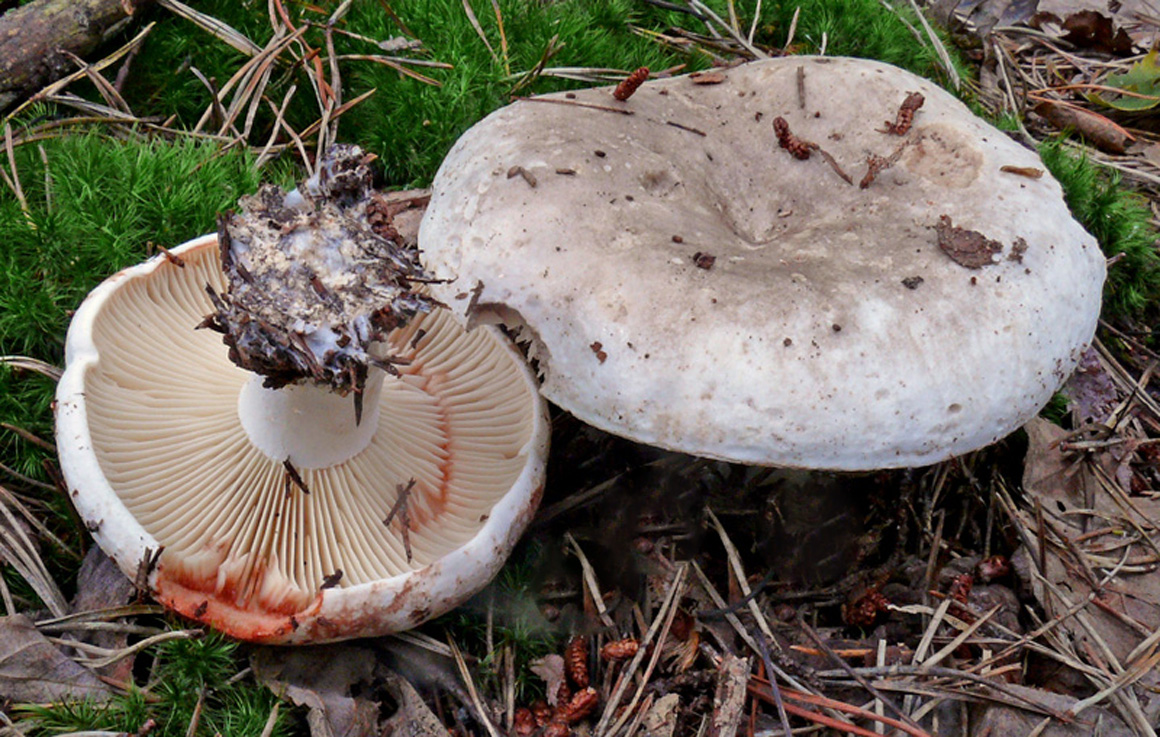
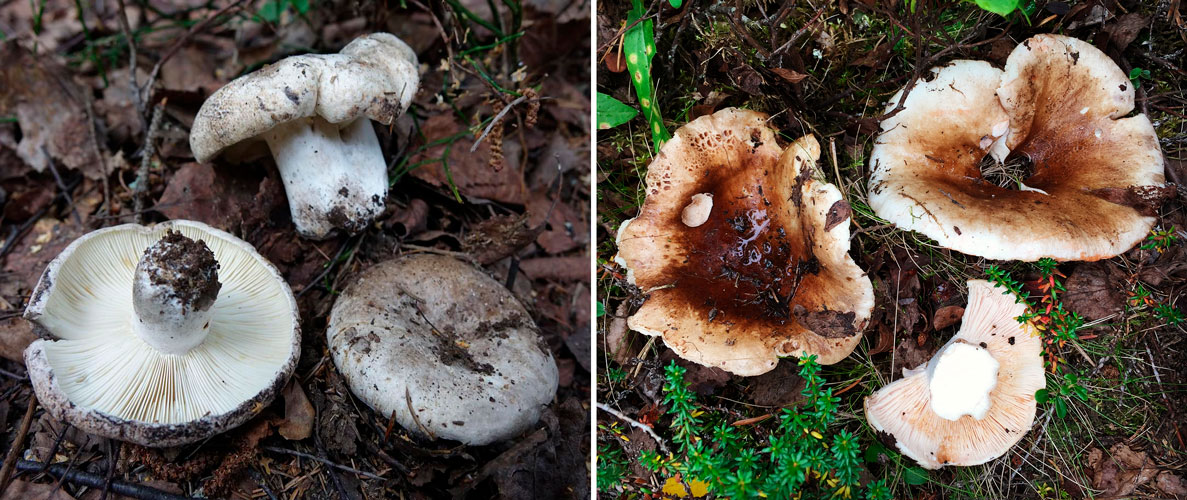
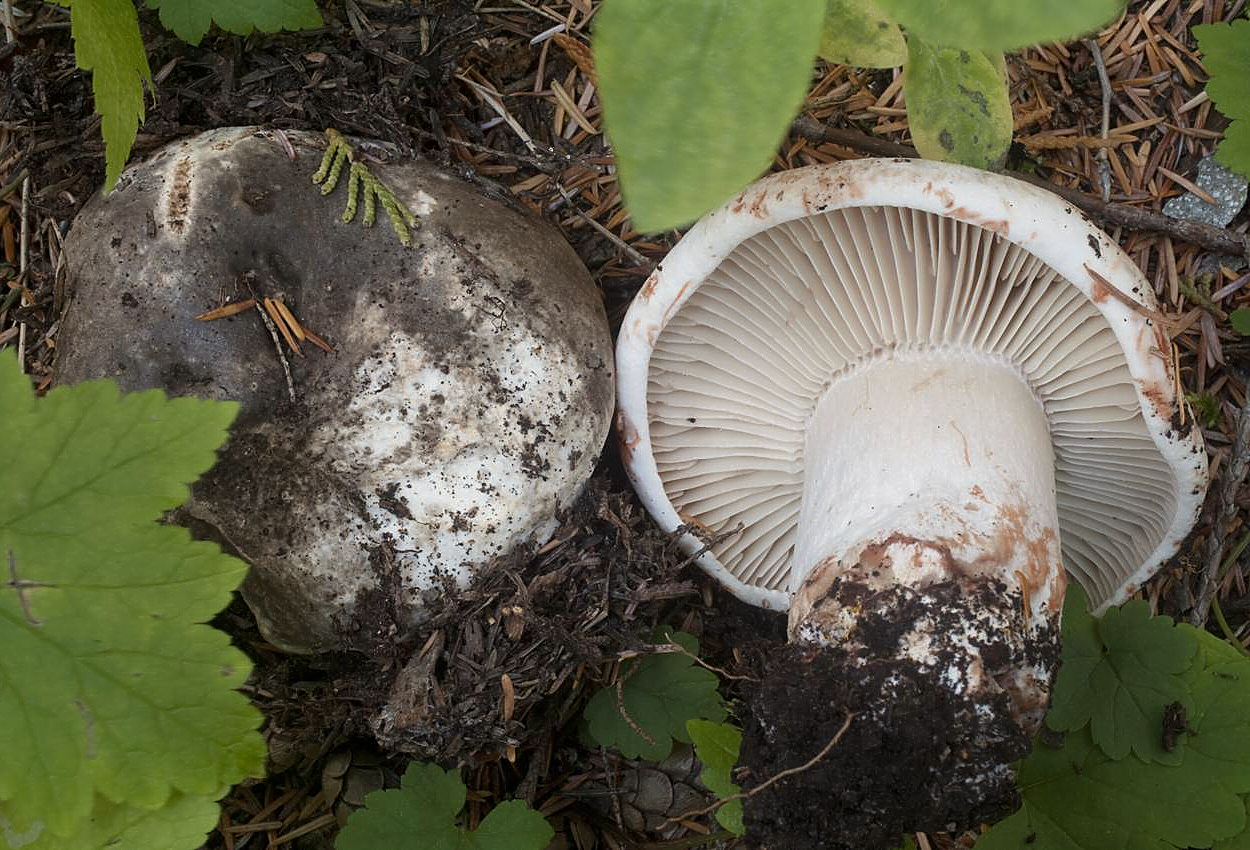
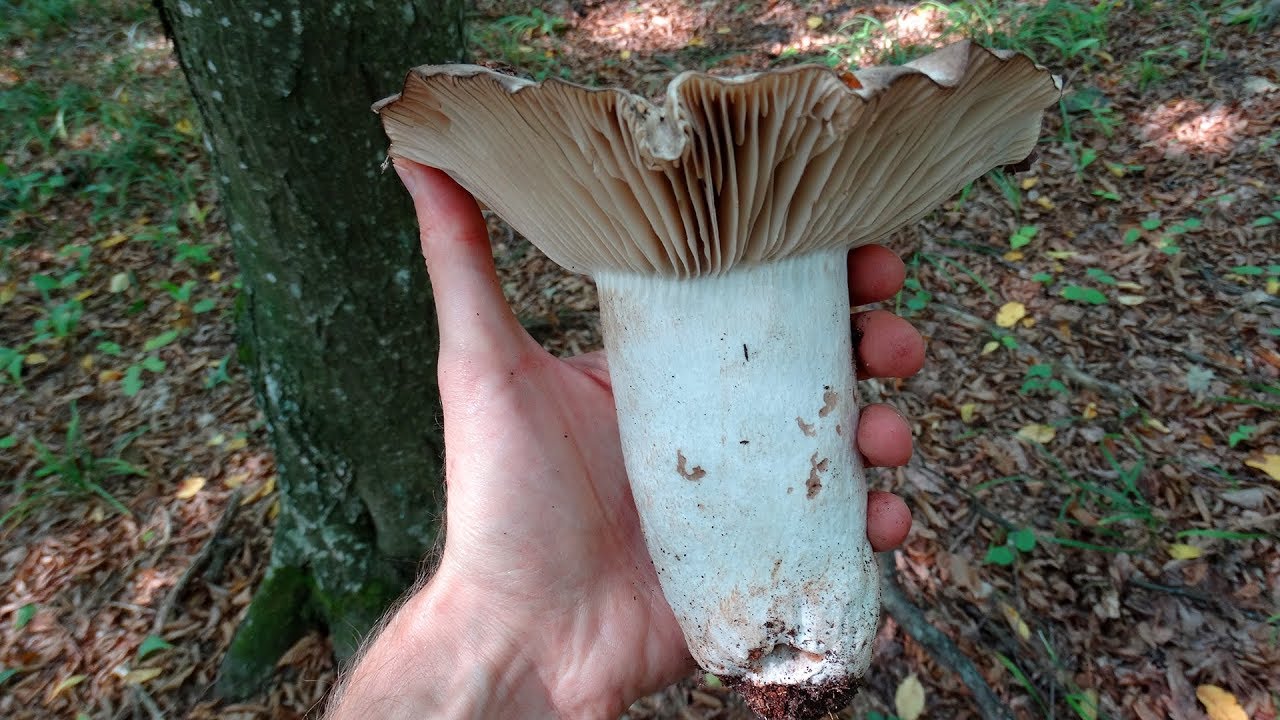
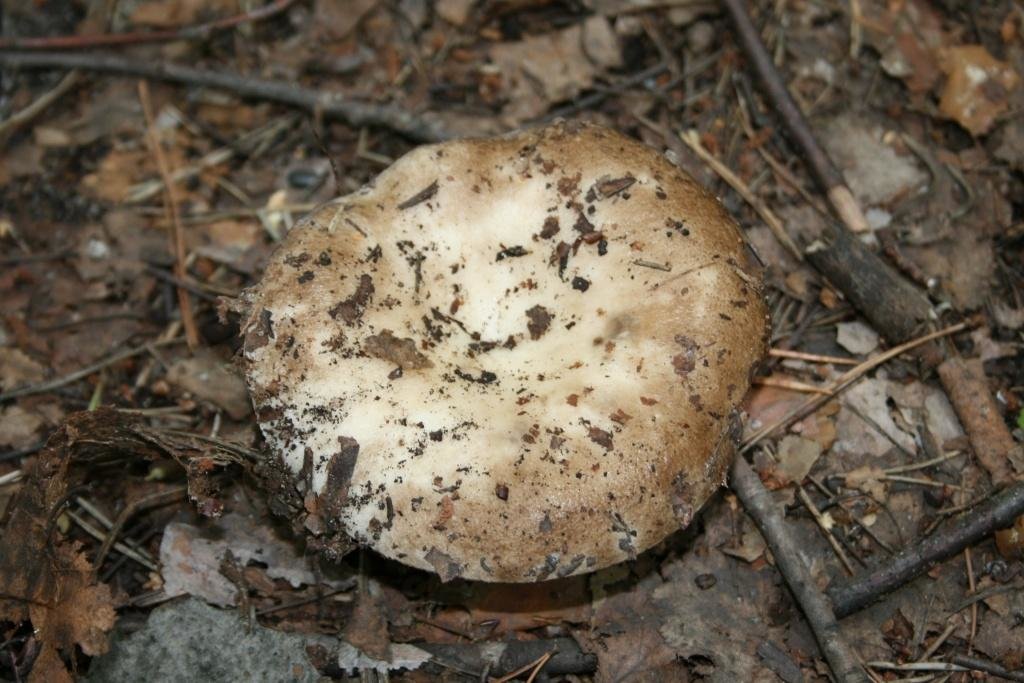
Podgruzdok white
Often and quite abundantly found in coniferous and deciduous forests, it grows mainly under birch and aspen trees from July to October, it differs from all mushrooms in that it does not have milky sap. The hat is the same as that of a real breast, only its edges are not fringed, and on top it is always dry and often with adhered earth, up to 20 cm in diameter, matte, white, sometimes with yellow-brown spots. The pulp is white, dense, does not change color at the break. Descending plates, frequent, thin, bluish-white. The leg is white, in a young mushroom it is even, solid, later it becomes hollow.
Conditionally edible mushroom, 2nd category, it is salted and pickled, but pre-soaked.
Vyacheslav stepanov: mushrooms of the kaluga region - black podgruzdok (russula adusta)
Common names
Common names
Cap Hat: 5-10 (15) cm in diameter, first convex, then convex-outstretched with a bent, later raised edge, slightly depressed, sometimes funnel-shaped, often strongly wavy-bent, sticky, at first pale yellow, pale brownish, grayish-brownish , then dirty brownish, brown, brownish brown, darker in the middle, with a light, almost white edge, with numerous adhering particles of earth and debris.
Gills: Medium frequency, slightly descending, whitish at first, then dirty gray, with dark brown and black spots, pungent taste, darkens when pressed. Controversy
Spores Spore powder white.
Stem Leg: short, 3-5 cm long and 2-3 cm in diameter, cylindrical, dense, solid, then finished, whitish, then grayish, darkens when pressed. Pulp
Flesh Pulp: dense, then loose in the stem, brittle, white, then grayish, on the cut it turns gray and darkens almost to black, in old mushrooms it is almost black with a weak unpleasant sour smell, very often becomes wormy, starting from the stem. Fruiting calendar
Calendar
Accepted designations / Legend
- the appearance of single mushrooms / seldom
- layers of poor fruiting / not much
- periods of stable, massive fruiting / a lot
The divisions on the time scale correspond to five days of the month
Ticks on the time axis correspond to the five-day weeks of the month Habitat
Habitat Habitat: from early July to October in deciduous (with birch), coniferous and mixed (with pine) forests, in bright places, glades, along paths, in groups, not infrequently, annually. More common in more northern forested regions Edible
Edibility
Edible or conditionally edible mushroom (4 categories), used salted, sometimes (after thorough washing!) Pickled (after boiling for about 15-20 minutes). Before boiling, some mushroom pickers soak to soften the acridity of the plates. In the workpieces it turns black.
Mushroom Pictures On The Internet
Other photographs of this mushroom in the WEB
Remarks
Addition: young mushrooms follow, and not because they smell nicer, but because it is almost impossible to find a large and non-wormy mushroom. Old mushrooms are finally black and thoroughly eaten, rot for a week or two, standing out on the grass in a black handful. There are three more types of half-load with blackening pulp: blackening podgruzdok (see below), Black-and-white podgruzdok (Russula albonigra) with a whitish, dirty-grayish cap and rapidly blackening pulp, rarely found in autumn in birch and spruce forests; Russula densifolia with a brownish-brown cap and very frequent lamellae (characteristic) with reddening and then blackening flesh and a pungent taste, rarely found in autumn in coniferous and deciduous forests, all of which are used in salty form Mentioned in reports
Sergei Appolonov dated July 26, 2004
Kirill Bykov from 11.09.2004
Yuri Semenov dated July 28, 2002
Yuri Semenov dated 08.25.2002
Yuri Semenov dated July 14, 2003
Yuri Semenov from 08/11/2003
Report by Stanislav Sviridov dated 06.10.2002
Load and value
Widely known Valui mushroom
and less podgruzdok black and podgruzdok white belong to the genus russula. They are characterized by a fragile leg. They are usually collected a little, since more valuable mushrooms are always found in the forest. The same mushrooms are conditionally edible. They are salted, less often pickled, but must be pre-soaked in cold water to destroy bitterness or boiled.
This mushroom is also called russula black
... It is found in all forests, especially in deciduous ones, it grows all summer from June to October in groups.
The cap is up to 15 cm in diameter, in a young mushroom it is convex, in a mature one it is depressed, with curved edges, dirty gray, later brown or black, sticky. The pulp is white, brittle, without milky juice, turns red at the break, then turns brown and finally turns black. The mushroom is very similar to the milk mushroom, although it belongs to the genus russula.
From all the lumps load black
differs in that it has no milky juice. The plates are adherent to the pedicle or descending, white, darken from pressure. The leg is up to 5 cm long, 2.5-3 cm thick, even, dense, of the same color as the cap. These fungi are severely damaged by insects.
Mushroom little-known, edible, 3rd category, eaten boiled and salted, turns black when salted.
Valuy
It grows in deciduous and mixed forests from July to October, occurs frequently and abundantly, and is one of the most common mushrooms in our forest zone.
The cap of a young mushroom is spherical, tightly attached to the stem, later straightens and becomes flatter, up to 8-15 cm in diameter, with a ribbed-striped edge, buffy-yellow or yellow-brown, very slippery in wet weather, and shiny in dry weather. The skin peels off easily. The pulp is dense, white, yellowish in old mushrooms, very bitter, with an unpleasant odor. The plates are adherent, in young mushrooms are white, in mature ones they are yellow or rusty-yellow with brownish spots and with droplets of transparent liquid. The leg is up to 10 cm long, up to 3 cm thick, sometimes thickened in the middle, white, loose, hollow.
Mushroom conditionally edible, 3rd category. After boiling, it is suitable for pickling. It is recommended to collect young mushrooms with an unopened cap.
Podgruzdok white
Often and quite abundantly found in coniferous and deciduous forests, it grows mainly under birch and aspen trees from July to October, it differs from all mushrooms in that it does not have milky sap. The hat is the same as that of a real breast, only its edges are not fringed, and on top it is always dry and often with adhered earth, up to 20 cm in diameter, matte, white, sometimes with yellow-brown spots. The pulp is white, dense, does not change color at the break. Descending plates, frequent, thin, bluish-white. The leg is white, in a young mushroom it is even, solid, later it becomes hollow.
Conditionally edible mushroom, 2nd category, it is salted and pickled, but pre-soaked.
False doubles
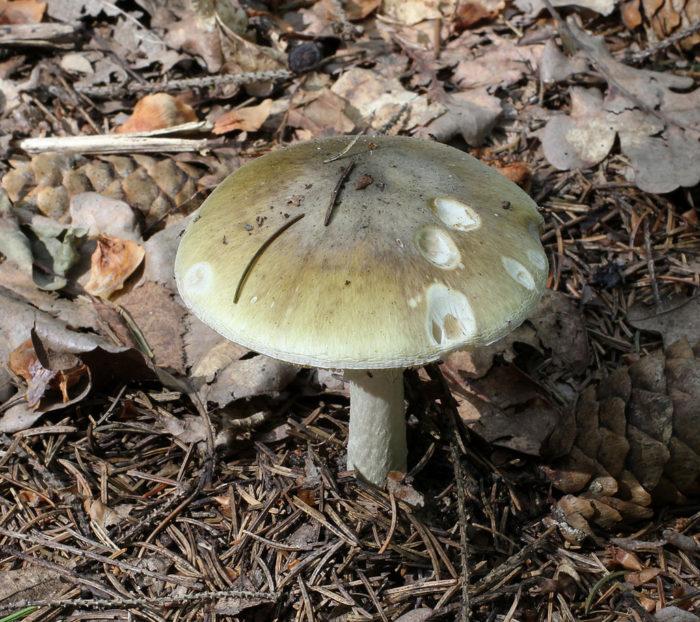
Podgruzdok blackening, like some other types of russula, an inexperienced mushroom picker can confuse with a pale toadstool. Such a mistake is unlikely, but almost always costs life. Compare these two views:
| Podgruzdok blackening
|
Death cap
|
|
| Hat | The shape changes with age from convex to funnel-shaped, the color - from off-white to brown and black. | Spherical or flat, grayish, olive or greenish in color |
| LPs | Yellowish or off-yellow, no ring | White, young specimens have a ring that disappears with age |
| Leg | White, turns brown over time, turns black | Whitish, with a "pouch" at the base, covered with a mesh pattern |
| Pulp | White, turns red and black on the cut | White, does not change color when cut |
There is a load of blackening and completely harmless doubles that will keep him company in the basket. It looks like this type of podgruzdok black, but it has a sticky cap, grayish, straw or brown in color, and the plates are gray.
The black-and-white podgruzda has a dark hat and white plates.The podgruzdok is often lamellar a little lighter, the plates are located more often. The flesh of these mushrooms also turns red and black when damaged. And the white cap is lighter, the flesh does not change color.
Podgruzdok white-black (Russula albonigra)
or
Russula white-black
Podgruzdok white-black (Russula albonigra) - belongs to the genus russula, is included in the russula family. There are also such names of the mushroom: Podgruzdok black and white, Russula white and black, Chernushka white and black. The mushroom has an interesting minty pulp flavor.
The white and black podgruzdok has a hat with a diameter of seven to twelve centimeters. At first, the pulp is convex, but then it has a tucked edge. As the fungus develops, the cap flattens and becomes concave. The color of the cap also changes - from white with a dirty tint to brown, almost black. Has a matte surface, smooth. Usually it is dry, only in wet weather - sometimes sticky. Often, various forest debris can adhere to such a hat. The skin is easily removed from the cap.
The plates of such a mushroom are narrow and frequent. As a rule, they are of different lengths, often transitioning to a short stem. The color of the plates is first white or slightly creamy, and then they gradually turn black. Spore powder - white or light cream shade.
The white-black podgruzdok has a small leg - from three to seven centimeters. Its thickness is up to two and a half centimeters. It is smooth, dense, cylindrical in shape. As the mushroom matures, it gradually turns black.
This mushroom has a dense, hard stem. If the mushroom is young, then it is white, but then it becomes darker. The smell of the mushroom is weak, vague. But the taste is mild, has a slight mint note. Occasionally, specimens with a more pungent taste may come across.
White-black podgruzdok grows in many forests - coniferous, broad-leaved. Growing time - from July to early October. But it is quite rare in the forests of Europe, Asia and North America.
It belongs to edible mushrooms, but its taste is rather mediocre. According to some Western researchers, it is still inedible or even poisonous. The fungus can cause gastrointestinal upset.
Similar species
- Blackening podgruzdok - Compared to white-black, this is a larger mushroom. He does not have such frequent plates, and the pulp turns red, and then turns black on the cut.
- Frequent podgruzdok (russula) - Quite often found in our forests. He has the same frequent plates, and the flesh on the cut also changes its color from light to dark and black. But the pulp of this mushroom has an unpleasant burning taste.
- Black russula - The pulp of this mushroom tastes good, and it also turns black when cut. The plates of this mushroom are frequent, dark in color.
Such mushrooms, together with a white-black load, are included in a special group of blackening mushrooms. This is due to the characteristic behavior of the flesh when cut, because it changes its color to black without going through the so-called brown stage. And if you act on the pulp of the mushroom with iron sulfate, then the color changes are completely different: at first it becomes pink, and then it acquires a green tint.
Edibility
Blackening podgruzdok is quite an edible mushroom, however, as a rule, only young specimens are harvested for cooking due to the soft and tasty pulp. In adult mushrooms, the pulp is very tough with a pronounced bitter taste. Another indisputable fact in favor of collecting nigella for subsequent preparation is that this species is a real delicacy for many forest insects and worms.
The most popular are salted nigella, which are thoroughly soaked and boiled before that. Such processing allows you to get rid of the specific bitterness and aroma. Salted podgruzdki have a pleasant taste and aroma, the fruit body darkens when salted.
Also, often the preparation of young podgruzdkov implies such heat treatment as stewing, frying and marinating. A prerequisite in this case is the initial treatment (soaking and subsequent boiling for 20-30 minutes). Blackening podgruzdok, like many types of mushrooms, can be dried, in this form it can be stored for one year.
Important! For cooking, it is better to use young black mushrooms. Old specimens are not used for culinary purposes due to the fact that their pulp is too tough
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that blackening podgruzdok is a well-fruiting type of mushroom, and in lean seasons it can become a full-fledged replacement for real milk mushrooms