Ruby Butter Edible Or Not
Rubinoboletus is an edible mushroom with good taste. In terms of nutritional value, it belongs to group 2, along with edible champignon, oak, boletus and other types of boletus. Its pulp does not have a pronounced smell and taste; some specimens have a barely noticeable bitterness. The chemical composition of ruby oiler includes:
- vitamin B2 (riboflavin);
- vitamin B6;
- carbohydrates;
- lecithin;
- amino acids;
- fatty acid;
- essential oils.
100 g of the product contains only 19.2 kcal, the use of oil helps to eliminate uric acid from the body and reduce cholesterol levels. However, biologists strongly recommend refraining from collecting these mushrooms, since the species is on the verge of extinction.
Edibility
With regard to the edibility of pepper oil, Russian and foreign scientists and practitioners show an amazing "unfriendliness".

There are three main opinions that their own group defends with equal zeal:
- The mushroom is classified as inedible. The official opinion of the Russian-speaking science. Biochemists stated that these boletus contain rare and highly toxic compounds that are not destroyed by heat treatment. They slowly but consistently destroy the liver, leading to cirrhosis and cancer.
- The butter dish is edible. The official opinion of English-speaking science. Some European mushroom pickers openly call its taste "amazing".
- The mushroom is conditionally edible. Opinion of Russian mushroom pickers practitioners. “Experientially,” they found out that when a pepper mushroom is boiled in two or three waters, its bitter taste is significantly weakened and gives the dish a pleasant piquancy. Some people believe that such a butter dish is good for food not only as a seasoning, but also in pickled, salted and even fresh form. But the rest of the mushroom pickers hold the opinion of the diametrically opposite and do not recognize the pepper oil can in any form.
One thing can be said for sure - this mushroom is not definitely poisonous, causing severe poisoning and quick death.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi.In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
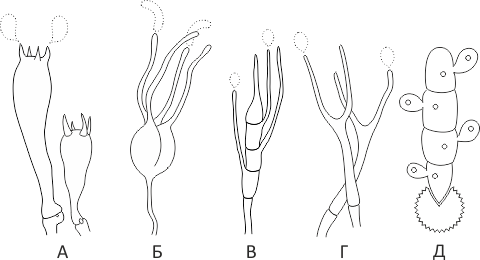
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
Difference from similar edible and inedible mushrooms
Pepper fungus has no poisonous counterparts, but it can be confused with some edible mushrooms.
First of all, he is similar to his fellow boletus, among which he belongs. In case of confusion, pepper flywheel can significantly spoil the taste of a canning or other dish due to its bitter taste. The main difference is the absence of a pedicle ring and the red color of the spores, while in other species the spores are yellow and there is a characteristic pedicle ring.

This species is often confused with another representative of the Boletov family - Kozlyak. The shape and color of the cap are of a similar color. Mushrooms can be distinguished from each other due to the color of the tubular layer and pulp. The goat always has a milky or dirty pink color of the spores, while in the pepper flywheel it is brown and brown. The color of the flesh of the goat is white, and that of the pepper flywheel is yellow.
Gorchak is another double that can be mistaken for a pepper oil can. It is similar to its counterpart in color of the cap and legs, but also has characteristic distinctive features: pink flesh, gray-yellow tint of the tubular layer and mild spicy taste. By these signs, it can be confidently recognized while in the forest.

Despite a certain similarity, all these types of mushrooms can be distinguished by careful examination of their structure and structure.
Is the mushroom edible or not?
Pepper mushroom is not used as a separate dish, but if dried and crushed, it makes a wonderful seasoning. Dried fruits can be used to make hot sauces. It is usually used in small quantities and is not very popular with mushroom pickers.
There are opinions that with prolonged cooking, you can completely get rid of the peppery taste, but is it worth the risk and waste time cooking mushrooms that will not bring gastronomic pleasure?
In what cases is mushroom poisoning possible?
Poisoning with a pepper flywheel is possible when it is improperly cooked. Fruiting bodies contain chitin, which is difficult for the body to digest and can provoke a severe disorder. Also, pepper mushroom is not recommended for children under 12 years old.
Pregnant and lactating women should refrain from eating any mushrooms. In addition, various diseases of the internal organs, especially the liver and gastrointestinal tract, are an undeniable reason for refusing to collect and use them for food.
Most often, this type of forest harvest is used by mushroom pickers in a mixture with others, and therefore it will not work to eat a large amount that caused a sharp poisoning.
Seasoning preparation
Here is a recipe for making a pepper oil can as a seasoning:
- First of all, the mushrooms should be washed and dried.
- Then cut or break the caps and legs with your hands and boil. In order to remove the unpleasant taste, they should be cooked for at least 2 hours. It is often advisable to change the water while cooking.
- Then let the mushrooms drain and place on a baking sheet on top of baking paper or on foil.
- Dry for about 4 hours, while turning over from time to time. It will take a long time to prepare the seasoning, but the result will exceed all expectations.
When finished, the mushroom will crumble in your hands.For grinding, it is convenient to use a coffee grinder, and then dry it again in the oven for about half an hour. The seasoning should be stored in a hermetically sealed jar. It is used for soups, side dishes and meats. Further processing of the mushroom is not required. Do not leave the seasoning in the sun or in a warm place.
Seasoning preparation
Pepper mushrooms have a special property - they make a wonderful spicy seasoning, which perfectly replaces hot peppers in the right dish, at the same time giving the dish a mushroom aroma. It is very simple to prepare it:
- wash and break mushrooms well;
- boil;
- dry (if in the oven - dry for at least three hours: first, turning twice after an hour, then every half hour until final drying);
- grind;
- dry again;
- pour into a storage jar.
Professional chefs use this seasoning "in collaboration" with ordinary pepper, which delights gourmets. The best taste and aroma will be given by mushroom powder, sprinkled on an almost finished dish.
Despite all the special recommendations of lovers of culinary experiments, we do not recommend taking risks
Pepper mushroom is not the only mushroom richness of our forests, so it is better to pay attention to the taste characteristics of more useful specimens.
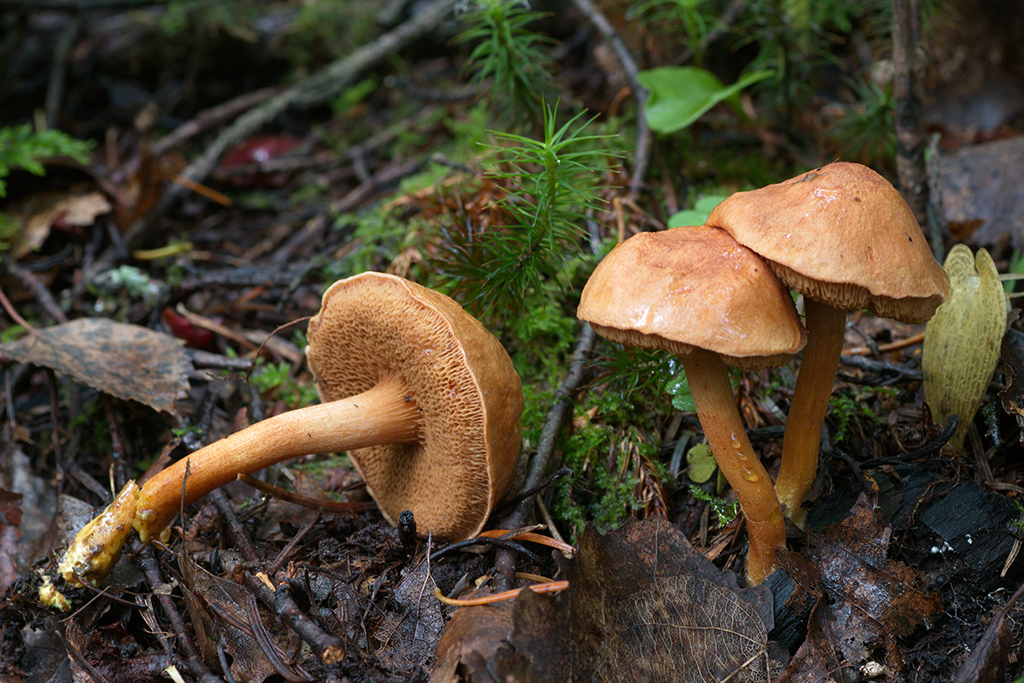
Pepper mushroom and goat. Pepper Mushroom, Chalciporus piperatus

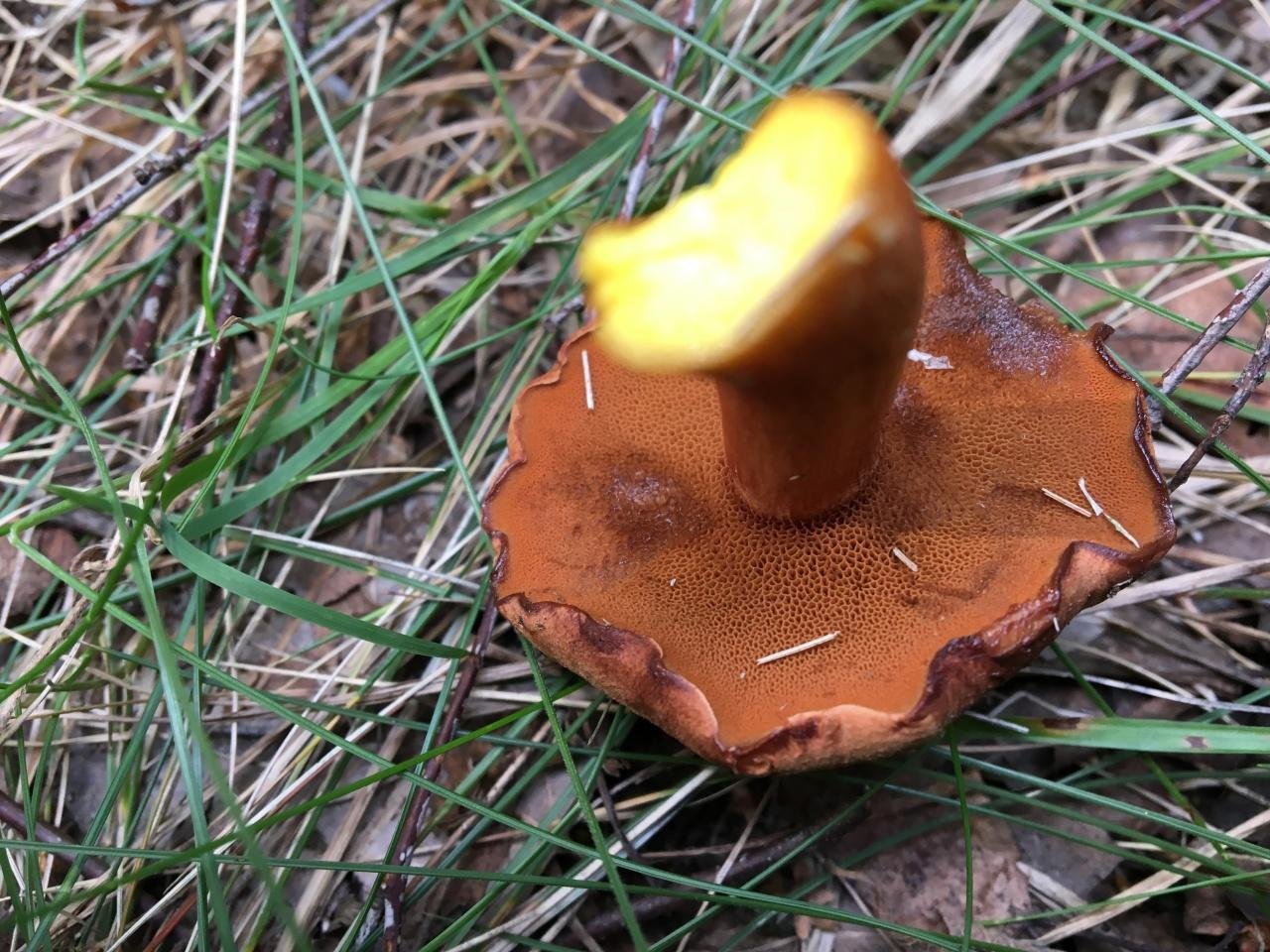
Current name (according to Index Fungorum): Chalciporus piperatus Hat: Copper-red to dark rusty color, rounded-convex, 2-6 cm in diameter. The surface is dry, slightly velvety. The pulp is sulfur-yellow, it turns red on the cut. The taste is quite spicy, peppery. The smell is weak.
Hymenophore: Tubules descending along the stem, cap color or darker, with uneven wide pores, quickly turn dirty brown when touched.
Spore powder: Yellow-brown.
Leg: Length 4-8 cm, thickness 1-1.5 cm, cylindrical, solid, often curved, sometimes narrowed to the bottom, the same color as the cap, yellowish at the bottom. There is no ring.
Distribution: Pepper fungus is common in dry coniferous forests, occurs quite often, but usually not too abundantly, from July to late autumn. It can also, according to old data, form mycorrhiza with deciduous species, for example, with young birches. However, the serious site "Mushrooms of the Novosibirsk Region" indicates that in fact Chalciporus piperatus parasitizes on. Looking at the speed with which the science of mycology is ahead of the human mind, it becomes somehow strange.
Similar species: Chalciporus piperatus can be confused with various representatives of the genus (in other words, with boletus). Pepper mushroom differs from butter, firstly, by its radical taste, secondly - by the red color of the spore-bearing layer (in buttermilk it is closer to yellow), thirdly - it never has a ring on the stem. a fungus named Chalciporus rubinus - it is associated with deciduous trees and has dark red pores. Obviously, it is found much less often - or simply so similar to a more common species that it does not attract much attention of amateurs. At the same time, the contradiction between the obvious edibility and the described bitterness of the mushroom leads to suspicions that we are not very good at distinguishing between pepper mushroom and Chalciporus rubinus, mainly dealing with the latter.
Edible: The mushroom is definitely not poisonous. Many sources report that C. piperatus is "inedible due to its pungent peppery taste." A rather controversial statement - unlike, say, a gall mushroom that tastes disgusting (), the taste of a pepper mushroom can be called spicy, but pleasant. In addition, after prolonged culinary processing, the pungency disappears altogether.
Author's Notes: For a long time I have been collecting and, accordingly, using for its intended purpose the pepper mushroom, not really thinking about its edibility.Having learned that, according to our literature, this mushroom is "inedible because of its spicy peppery taste," I decided, as they say, to put my fingers in my wounds - I scored this mushroom for a full-fledged roast, which was not so easy, since in my area it can be found even often, but always a little, - fried and ate for natural research purposes. It must be admitted that some grain of truth is present in the assessments of our myco-culinary specialists. Yes, the mushroom is quite spicy, not for everybody. (True, I am just an amateur.) But you can eat. And in the composition of the "mushroom platter" - and at all for a sweet soul. Thus, we have an exception (which, by the amazingness of its existence, emphasizes the rule): our sources consider the mushroom inedible, and most Western sources strictly contradict them. It is usually the other way around. "Rare case."

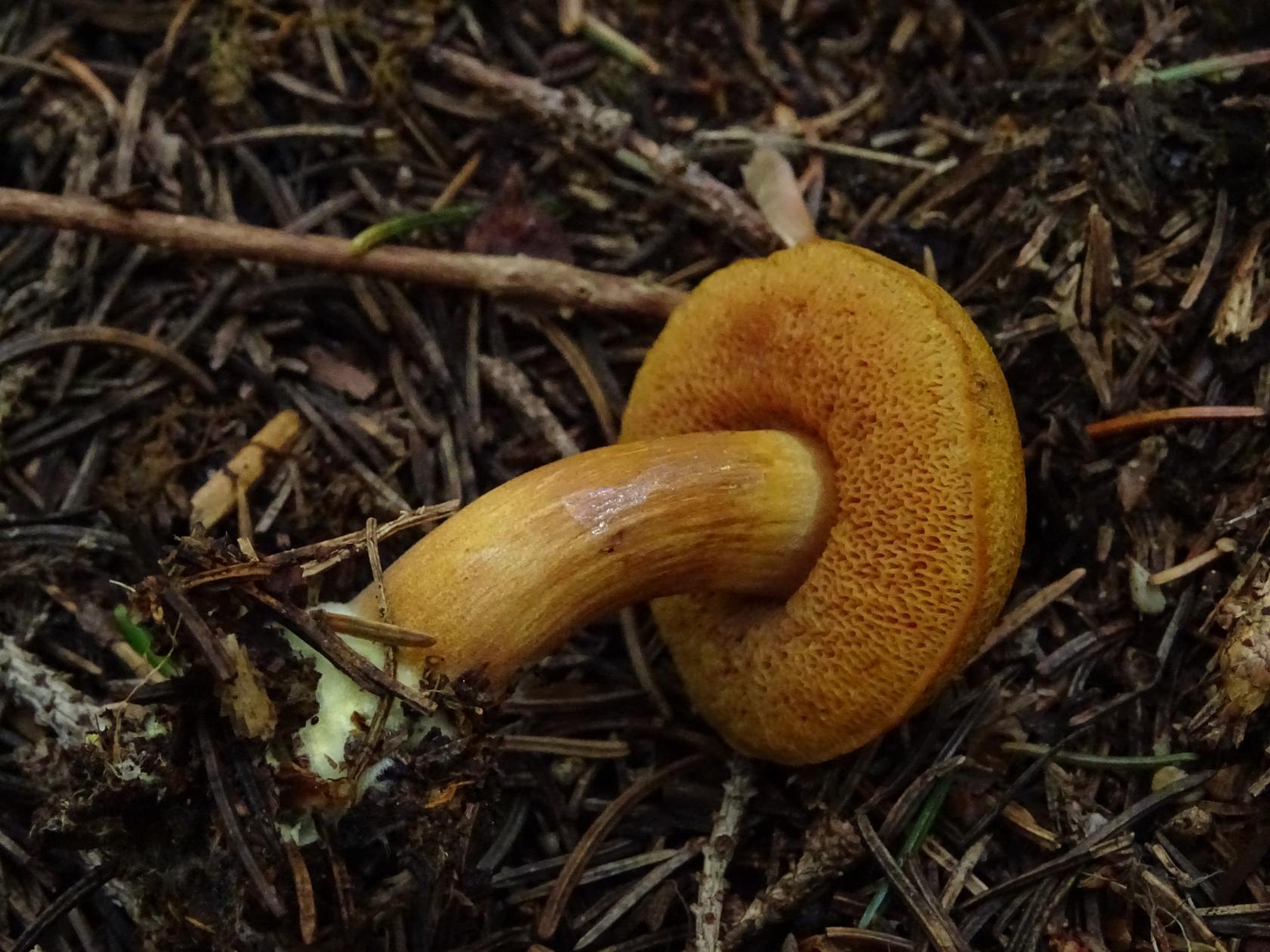
Peppery or not peppery? There is a great temptation to declare this mushroom as some kind of special, perhaps even rare, representative of its kind. However, large angular pores, a tubular layer sliding onto the stem, and the general carelessness of the outlines leave no doubt: this is still the same pepper mushroom, although, perhaps, at the limit of its variability.

It is clearly seen here that the peeled mushroom is still not a goat, Suillus bovinus. Does a goat have such a developed hymenophore? The goat does not have such a developed hymenophore. And there is no pungent peppery taste. It's strange to be confused.

As a rule, a pepper mushroom is distinguished not by a heroic article, but by an intricate curvature. Although they do not often grow together with their heads, it affects that Chalciporus piperatus is a loner by nature.
The edibility of the mushroom
The edibility of the flywheel has been controversial for many years and mycologists have not come to a consensus on whether it is edible or not. There are three options regarding the properties of the mushroom and its assignment to one of the classes:
- Edible - can be eaten after heat treatment. For its unusual taste, it is especially respected by some people who add it to their dishes to enhance the piquancy.
Conditionally edible - the Russian interpretation of mushroom pickers-practitioners, during cooking the fruit body loses its bitterness. You can marinate, boil, fry, and make seasoning powder.
Inedible - the official domestic version due to the fact that even during processing the toxins from the oiler do not completely leave and can accumulate in the body. Not recommended for use in any form.
The decision as to whether to eat it or not is left to the individual discretion.
Similar species
Who else can you confuse the pepper oil can with?
Of course, with the usual oil can, which is found in spruce forests. The diameter of his cap reaches from 3 to 15 cm, while his cap is convex only at the very beginning of growth, but by the middle of the season it becomes flat. If you touch the cap of the oiler, then it is no longer dry and velvety, but smooth. If direct sunlight shines on it, then it has a glossy shine, if the area is wet, then a small mucus begins to cover the mushroom from above.
As for the red hat, it has a yellow-brown hue, much less often a red-brown color. If you touch the pulp, you will feel how dense it is, and at the same time, very textured.
As for the leg, here it overtook the pepper oil can. The length reaches 200 mm, the thickness is generally about 2 cm. The color of the leg is always lighter than the color of the upper part of the cap.
This oiler grows alone, so it can easily form mycorrhiza with trees.
Gorchak
It differs from a pepper mushroom in a light cap, as well as an orange stem. It has a more pleasant taste in the pulp, and when cut it is pale pink, while it does not change its color.
Goat
An edible twin. Differs in pink, not red flesh, as well as a bright yellow leg. It has a delicious, strong spicy aroma that literally drives you crazy.
How to prepare pepper oil

In European countries, not only a spicy seasoning is prepared from pepper pot, but it is also used as the main ingredient in various dishes.
Mushrooms are stewed with onions and sour cream. After proper heat treatment, they lose some of their sharpness and become very pleasant to the taste, according to lovers of savory dishes.
For seasoning, the mushrooms need to be dried and chopped. But first, the pepper oil cans are boiled for about two hours, changing the water several times. Cooking sequence:
- Boiled mushrooms must be washed.
- Put on a baking sheet covered with parchment.
- Dry in the oven for 4 - 5 hours, stirring.
- Cool down.
- Then grind in a coffee grinder.
A properly dried pepper mushroom is easy to grind, even with your hands.
Seasoning is added instead of hot pepper to meat and vegetable dishes.
False mushrooms. How to distinguish doubles?
Edible mushrooms, which are hunted by mushroom pickers, have counterparts - inedible, conditionally edible or poisonous. Here are the most famous pretenders:
- Bile and satanic mushroom. These are doubles of boletus - the most valuable representative of the mushroom kingdom. But distinguishing doubles is as easy as shelling pears. The first has a dark mesh of veins on the leg, the second has a reddish one. You can also cut off a piece of the leg to see if its color changes. If after a minute the color of the cut does not change, the boletus can be put in the basket. In doubles, the color from white will change to pink - in the bile, and purple - in the satanic mushroom.
- False boletus. His hat is darker than the real one. The color of the cut of the leg does not change, but in a real redhead, on the contrary, it darkens.
- False boletus. It can be distinguished from an edible mushroom by a darker cap and a bluish cut. Another sure sign is the place of growth. False boletuses do not grow under birches.
- False chanterelles. To distinguish them from edibles, you need to be careful. Look at the color of the hats. In real chanterelles, they are light orange, almost yellow. False specimens are bright orange in color, and when broken, drops of white juice appear.
- False mushrooms. There are many poisonous and inedible mushrooms that look like honey mushrooms. Real mushrooms from false ones can be distinguished by a brownish or brownish-yellow scaly cap. Moreover, the caps are pale, in the false ones they are bright, for example, red-brown or rusty-red. Edible honey mushroom can also be identified by its smell - it has a pleasant and rich mushroom spirit. False gather give off the smell of mold and damp earth.
Honey mushrooms and false mushrooms
If royal mushrooms have a bright appearance and it is difficult to confuse them with something, then ordinary mushrooms are not so lucky. Two varieties of false agarics are trying to imitate them at once - with a yellow and orange-brick color of the cap.
But do not be intimidated and avoid honey agarics, since in this case everything is quite simple. Both of these varieties differ from the edible original by the absence of a "skirt" on the leg
Advice: pay attention to the leg and then you will never go wrong when collecting honey agarics
False honey fungus False honey mushrooms
Now you know how to avoid the presence of unwanted species in your mushroom basket. And remember that even long-term heat treatment is not able to get rid of toxins such as pale toadstool and sulfur-yellow false foams.
Going into the forest, do not forget that in nature you can come across not only poisonous mushrooms, but also dangerous snakes. About what poisonous snakes live in the vastness of our country, you can find out in one of our previous materials.
Can I eat
Unfortunately, there is no definite answer to this question. Various sources contain conflicting information on this subject, classifying the mushroom as conditionally edible, inedible and even poisonous.
Check out the list of common edible, conditionally edible, and poisonous mushrooms.
If you believe the numerous encyclopedias of the mushroom picker, then there is no poison in the pepper oil can. It is ranked as conditionally edible because of the bitterness in the taste.However, there are sources that claim that its taste is not pungent, but pleasant, and the bitterness goes away after heat treatment. Therefore, this oiler is advised to be used as a hot seasoning replacing pepper. To spice up the dish, pepper mushrooms are boiled and added in this form, or dried and ground into powder. According to the reviews of people who cooked the pepper mushroom, it is delicious both dried and fried. It is also pickled and salted.

In some Western and Russian sources on mushroom families, Chalcíporus piperátus is ranked among inedible and poisonous specimens. It is believed that its pulp contains toxic substances that are not removed by heat treatment and tend to accumulate in the human body. They provoke the destruction of the liver, and can lead to cirrhosis and cancer. Symptoms of poisoning, as a rule, do not appear immediately after eating the mushroom, but only after a few months. Therefore, it is difficult to prove exactly that it is the mushroom dish that is the cause of a person's poor health.
Note that most of the authors of the literature on the mushroom theme are still inclined to consider the pepper oil can conditionally edible. It does not lead to rapid poisoning or death.
Did you know? Mushrooms contain more minerals such as iron, phosphorus and calcium than any meat. They also contain 5-10 times more niacin (vitamin B3) than greens and vegetables.
Growing geography and harvest time
It grows everywhere in the northern regions with moderate climatic conditions, including the European part, the North Caucasian, Ural, Siberian and Far Eastern forests.
Outside of Russia, it is found in most European countries, it was found on the Australian island of Tasmania.

The mushroom can be harvested before the onset of cold weather
Prefers coniferous forests, but sometimes occurs in mixed and deciduous forest belts. It grows more often in places where pines grow, with which it enters into a symbiotic association (forms mycorrhiza or fungal root), much less often in the vicinity of spruces.
Fruiting covers the period from July to October, until the first autumn frosts. Grows singly, much less often - in small groups, up to 3 specimens.
Application
In traditional medicine
Surprisingly, this mushroom is used not only in folk but also in traditional medicine. The healing properties of this mushroom are very much appreciated, as well as its special composition, which contains substances useful for the human body.
Various preparations are made on the basis of the pepper oil can. Basically, they are aimed at the following effect on the body.
- It has a positive effect on the immune system.
- May work to reduce plaque cholesterol.
- Helps to start brain activity.
- It has a positive effect on blood pressure.
- Helps cleanse the liver.
- May significantly strengthen the nervous system.
- Metabolism increases several times.
As a result of the fact that the mushroom contains a record amount of vitamins, it was found that it is very beneficial for metabolism. Also, the use of such a mushroom is recommended for those who dream of losing weight.

In addition, pepper mushroom is a natural antibiotic due to the fact that it contains a huge amount of phytoncides.
Pepper oiler is not used in its pure form, but as a carefully processed component that is able to fight various kinds of infections, both viral and bacterial.
By the way, it is worth noting that you should not engage in self-medication if you develop one of the listed diseases and there are a large number of such mushrooms. Unfortunately, apart from poisoning or an upset stomach, you will not earn anything for yourself.
In folk medicine
Surprisingly, the pepper mushroom is also widely used in folk medicine. True, not in its pure form. An extract is made from it, which is then subsequently processed into an ointment.It can be used against various skin imperfections, including papillomas and warts.
You can make a tincture from the mushroom. It helps to properly influence the economy of conjunctivitis.
If you have any eye conditions that imply swelling, then you need pepper powder, which is soaked in an herbal solution. Thanks to its use, rapid tissue scarring can be expected.
Also, this mushroom is effective for the treatment of pyelonephritis and urolithiasis, promotes the rapid removal of stones from the body.
Useful properties, use in medicine and restrictions on use
According to a number of studies, the fungus contains a toxic substance that is not neutralized during heat treatment and is not excreted from the body. It can trigger cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Nevertheless, this type is used in traditional medicine. The mushroom contains substances such as leucine and alanine, which help to lower blood sugar levels and normalize weight. It is also rich in phytoncide, which is a natural antibiotic. Fruits contain protein, phosphorus, magnesium, selenium, folic acid.

Pepper mushroom
Due to its chemical composition, pepper flywheel is used in medicine for the manufacture of drugs that help to cope with the following conditions:
pressure stabilization;
improving the functioning of the immune system;
destruction of cholesterol;
strengthening the nervous system;
activation of brain activity.
Cooking complete meals from a pepper oil can is not practiced, but it is often used as an additive to other types or as a spicy touch in the preparation of other foods. Restrictions on the use of such food apply to children, pregnant women and people with chronic diseases.
White mushroom and its counterparts
Porcini mushrooms, by their taste and nutritional properties, are at the top of the pyramid of edible mushroom variety. Perhaps Europeans who prefer truffles will disagree with this, but for a mushroom picker in central Russia there is no more valuable find than a glade with porcini mushrooms. However, this species has two counterparts - dangerous relatives belonging to the same family of boletes. It is a satanic disease, better known as a satanic mushroom, and a gall mushroom.
White mushroom
Even after lying for several hours after cutting, the porcini mushroom retains the white color of the leg, and this circumstance will help preserve your health, since its counterparts do not have such a wonderful feature. Their legs turn pink and blue, betraying the poisonous essence of their owners.
In addition, pay attention to the outer part of the leg: in the edible mushroom, it is grayish or brown with light veins, and not yellow or red.





















































