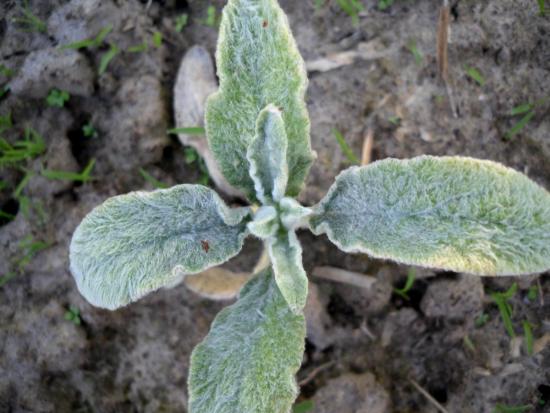
How to plant sheep ears
Seat selection
Best of all, the plant develops its foliage and shows its decorative effect in places open to the sun. The soil is needed loose, with good drainage and moderate fertility. The poorer the land, the finer and more silvery the foliage.
Preparing the soil for planting
The selected area is dug onto a shovel bayonet, and a bucket of sand per square meter is added to the heavy soil during digging. If the soil is acidic, you can add kg of chalk per square meter. meter. For sheep ears, neutral or slightly acidic soil is preferable. In very poor soil, you can add 5-6 kg of rotted humus or compost. The introduction of 40 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate per 1 sq. M. will also have a beneficial effect on the planted plant.
Planting methods: seeds in open ground and through seedlings
Sheep ears tolerate frost well. You can sow seeds in the fall. To do this, you need to make grooves in the prepared soil immediately after collecting the seeds. Sow seeds and cover them with soil. Shoots will appear in 8-10 days. Before winter, the plant will have time to grow a rosette of leaves. It hibernates, as a rule, without shelter.
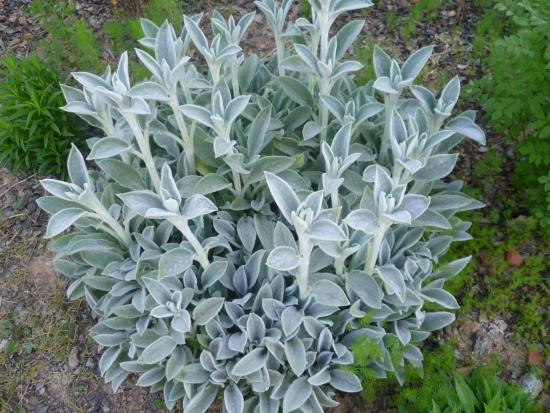

At the end of May, the plant can be planted in a permanent place. When grown through seedlings, seeds are sown in boxes at the end of March, planted in the ground at the end of May. Leave the distance between the bushes 15 - 20 cm. After planting, the plant needs to be watered.
Planting with nodules
Nodules can also be planted in fall and spring. The holes are made at a distance of 15 - 20 cm, the distance between the rows of holes is about 50 - 60 cm. The depth of the holes is 6-7 cm. The nodules germinate after about 10 - 14 days.
Planting by cuttings
For rooting, cuttings are cut with two to three leaves. Prepare a mixture of peat and sand, moisten it and deepen the cuttings by 1/3 of their length. After about 21 days, rooting will begin. Rooted cuttings are planted in a permanent place next spring.
Planting by dividing
Once every 3-4 years, the mother bushes need to be dug up. This can be done not only in spring, but also in summer and autumn. Divide the plant into 2-3 parts and plant in a new place. The survival rate of stachis is very high. After transplanting, new bushes require moderate watering.
Description
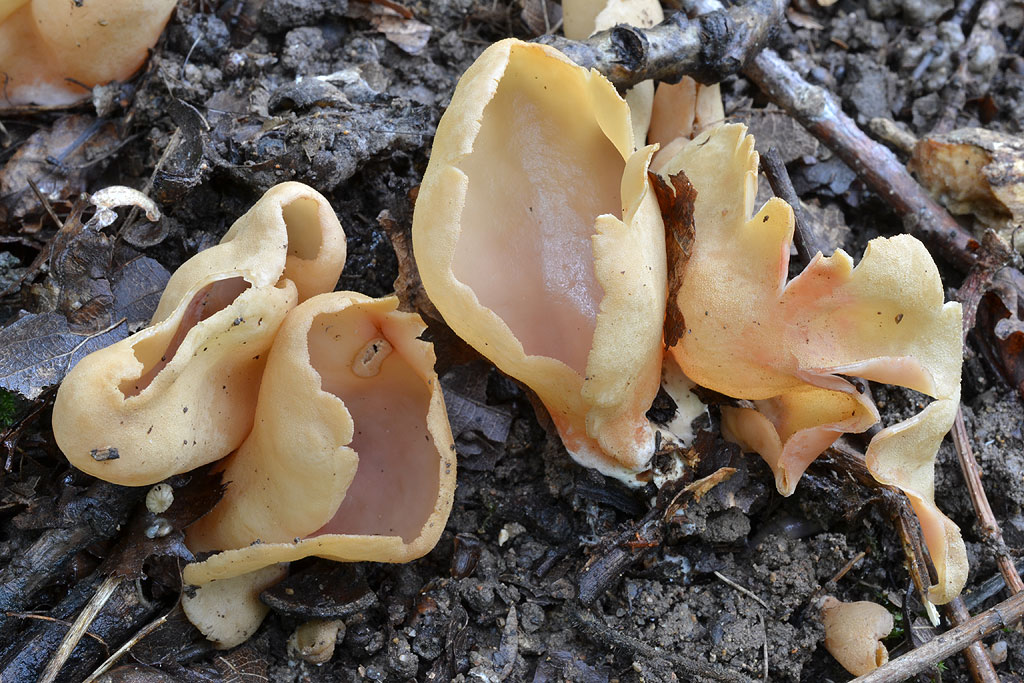
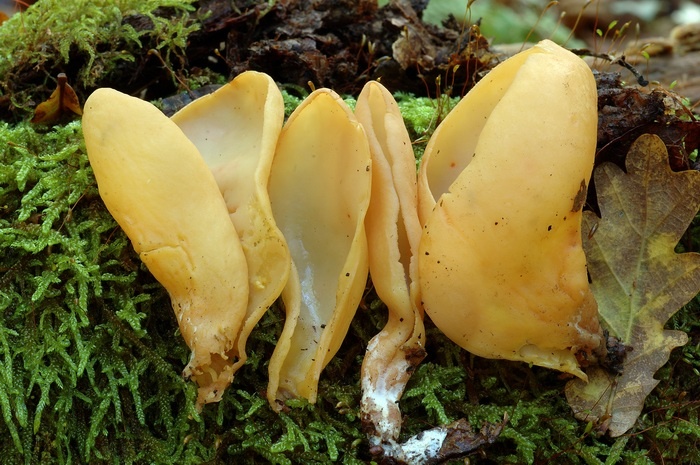
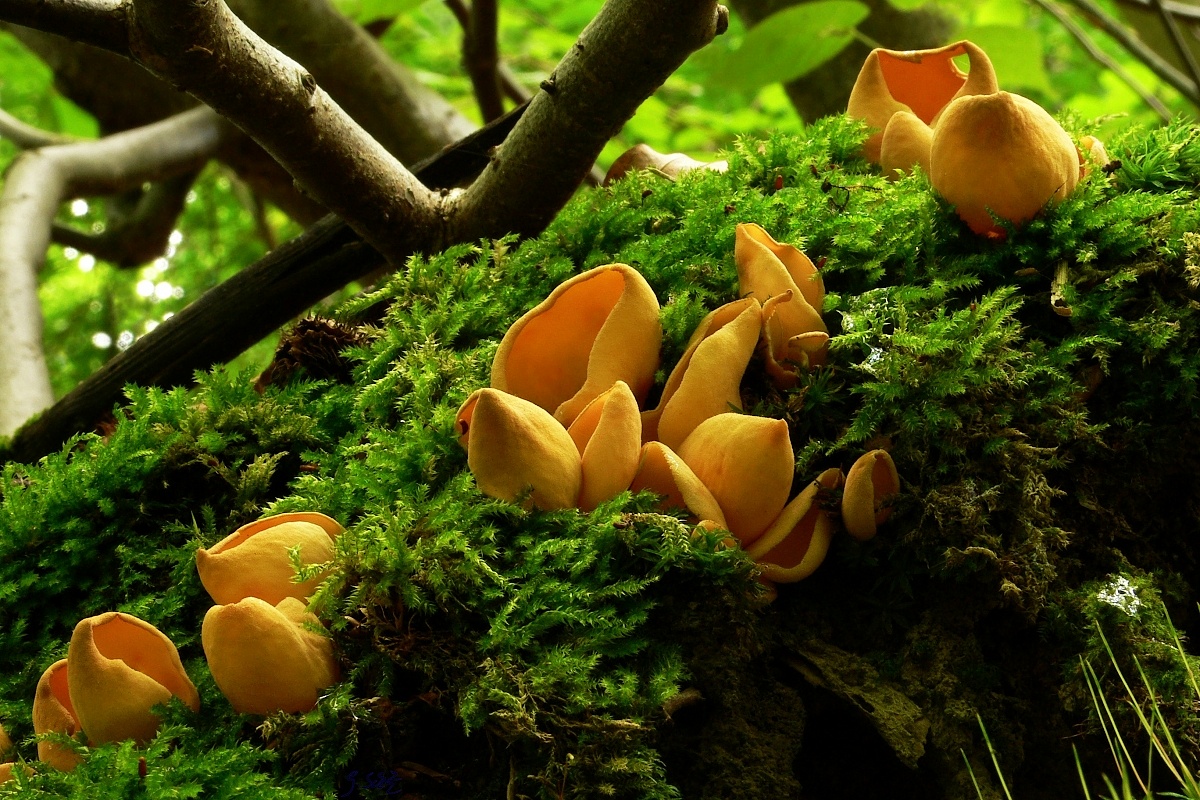
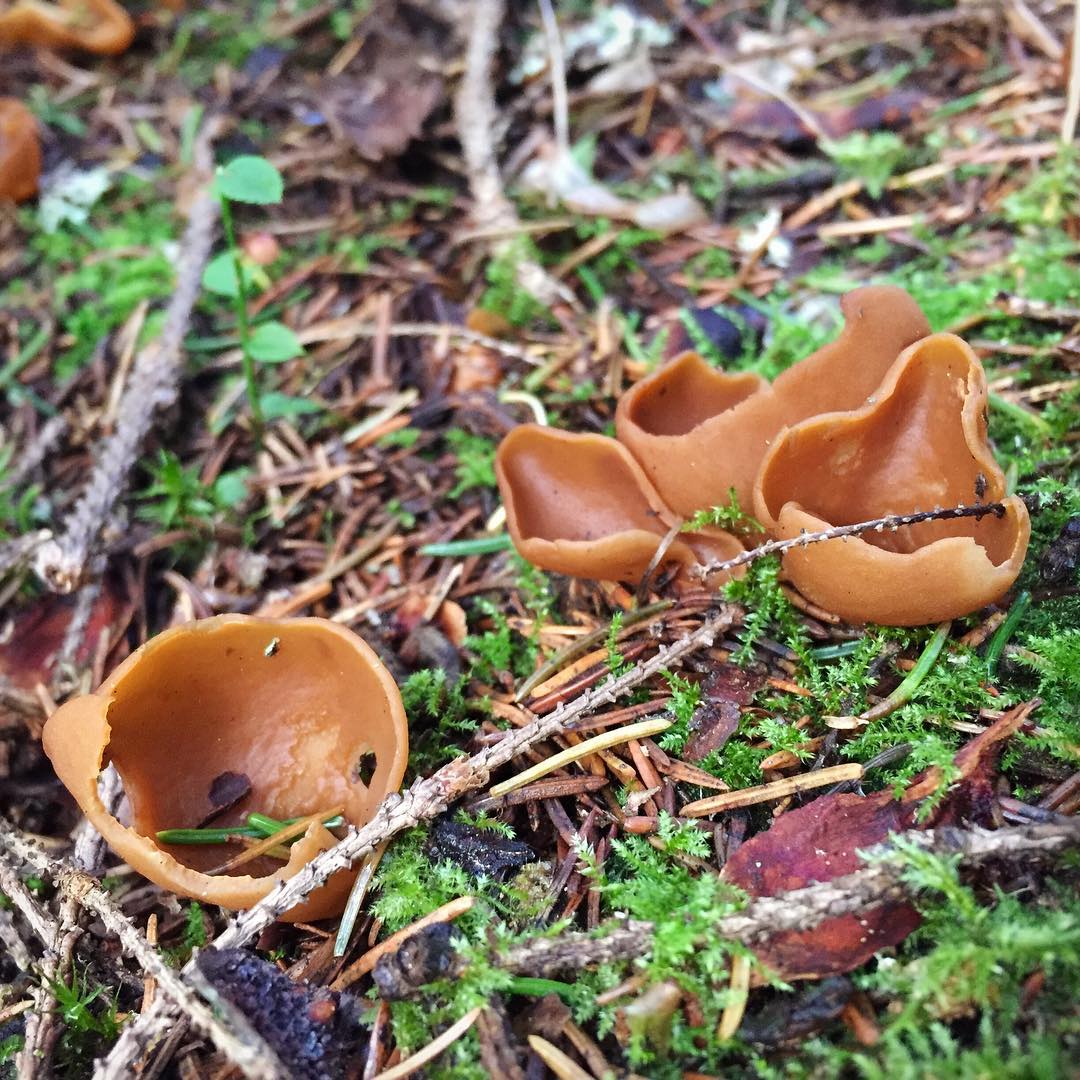
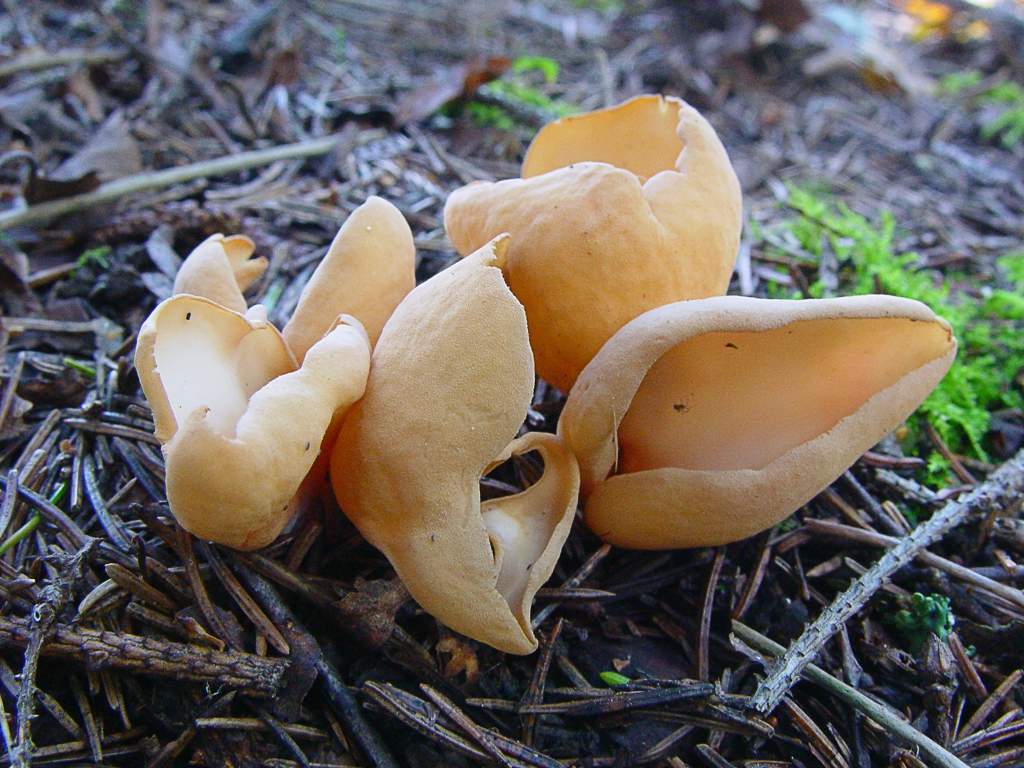
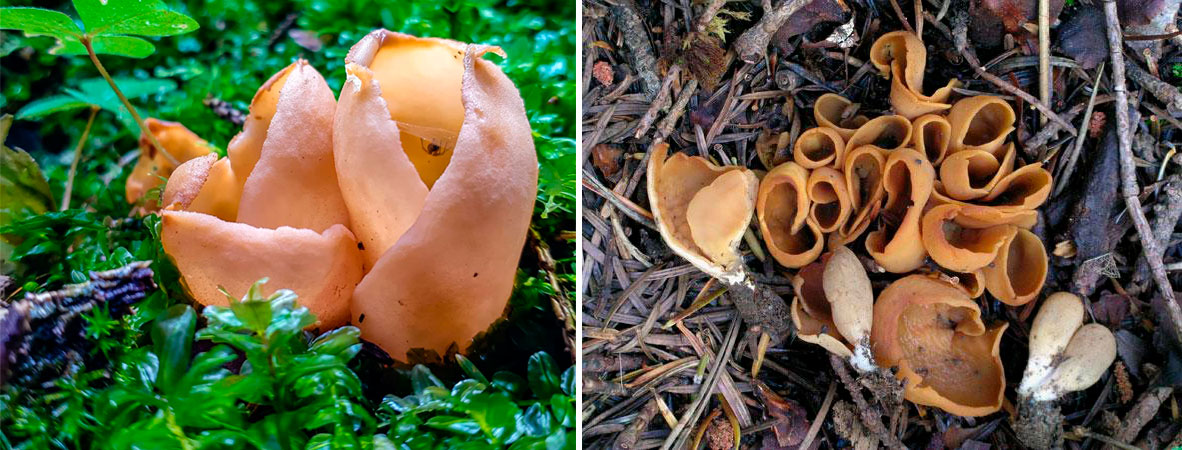
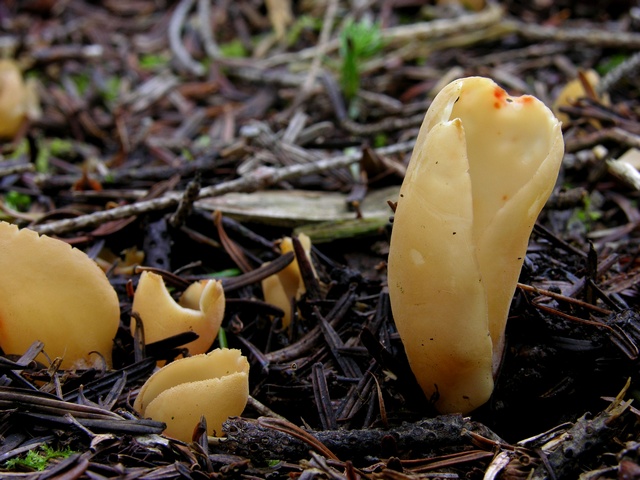
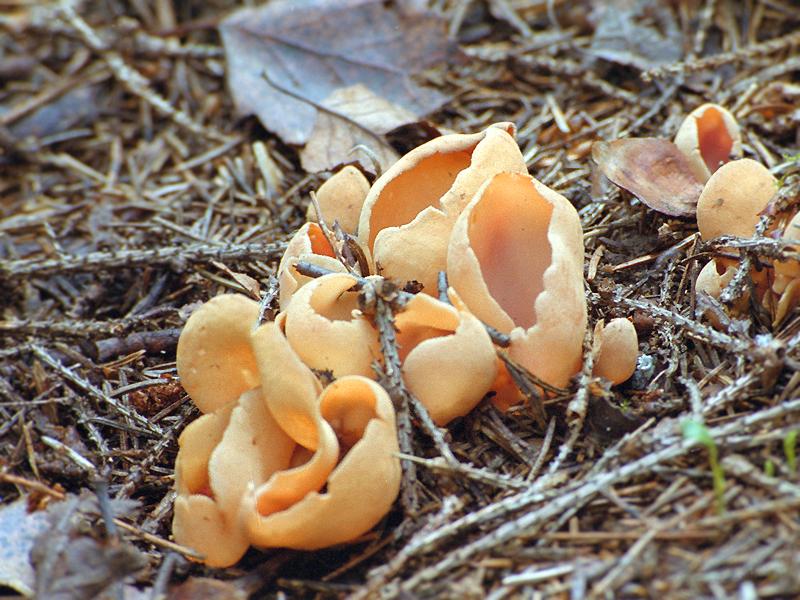
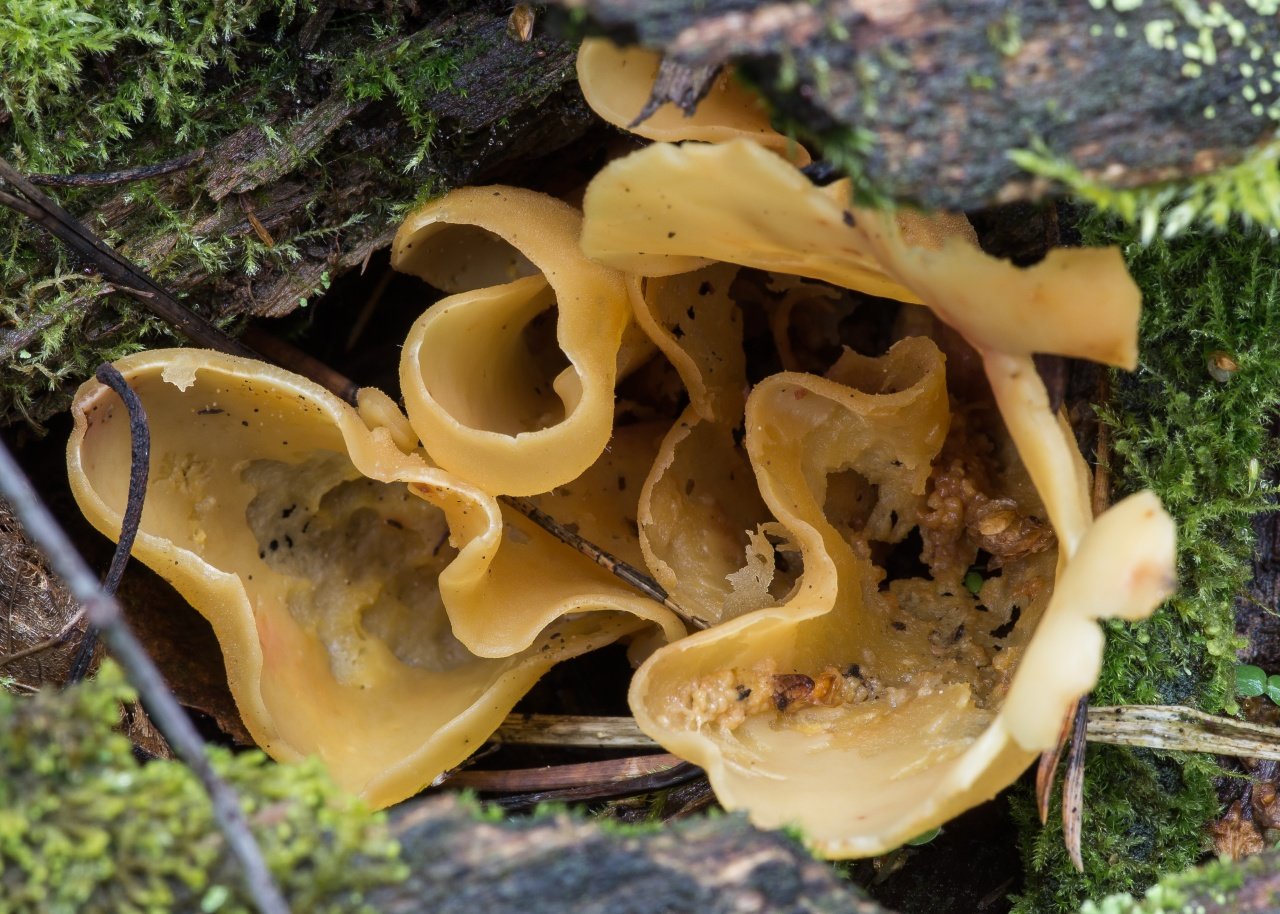
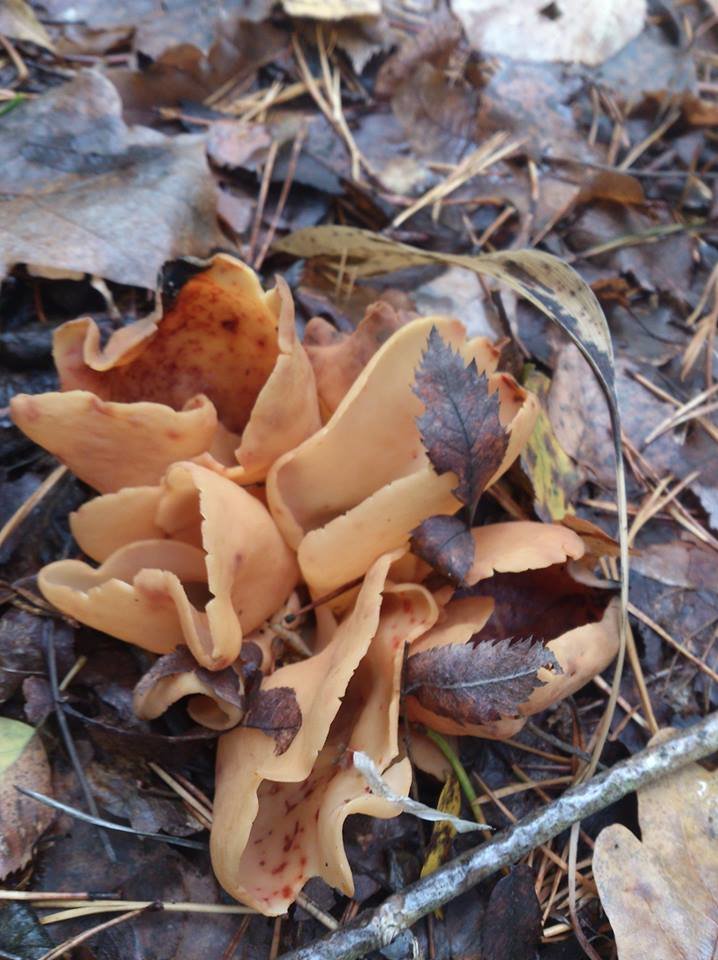
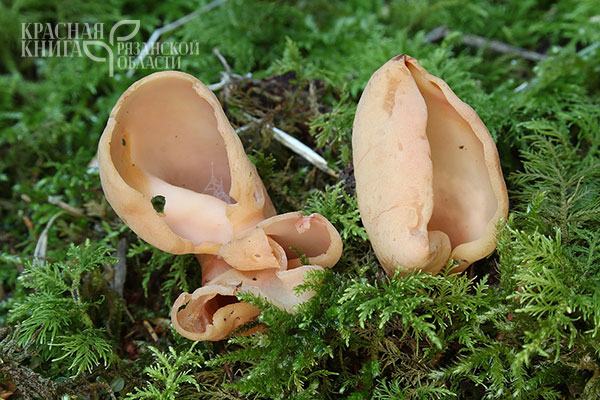
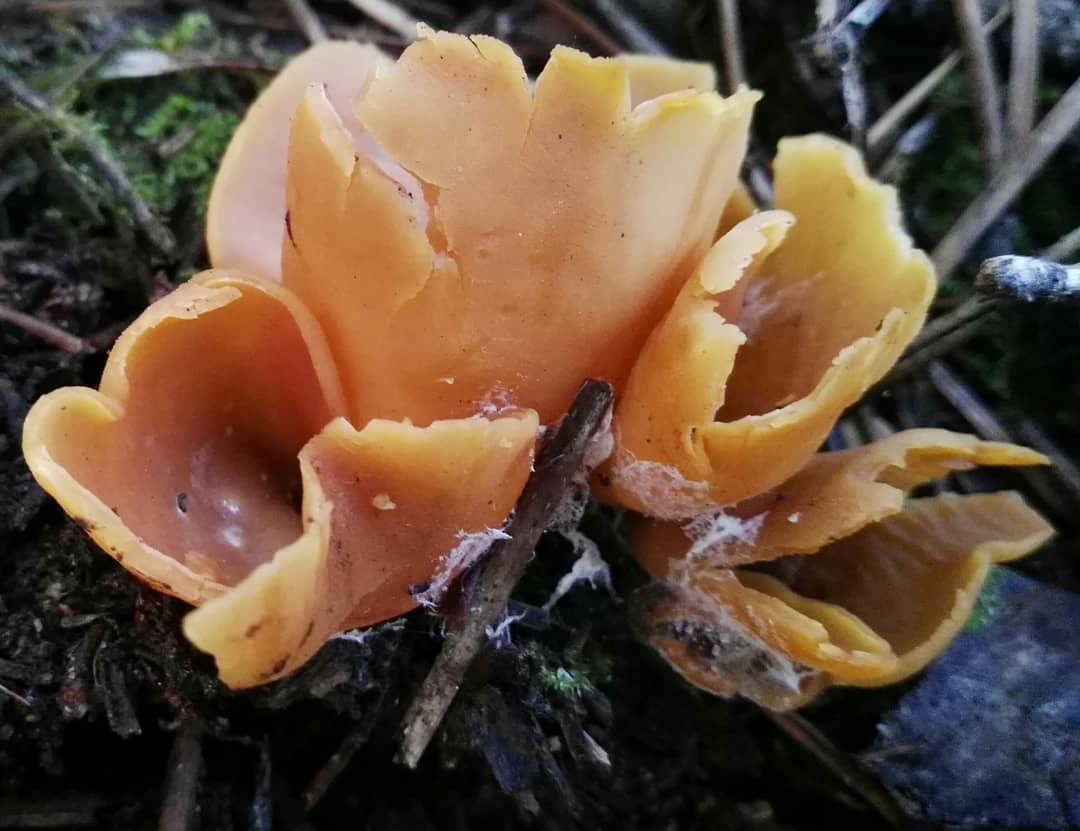
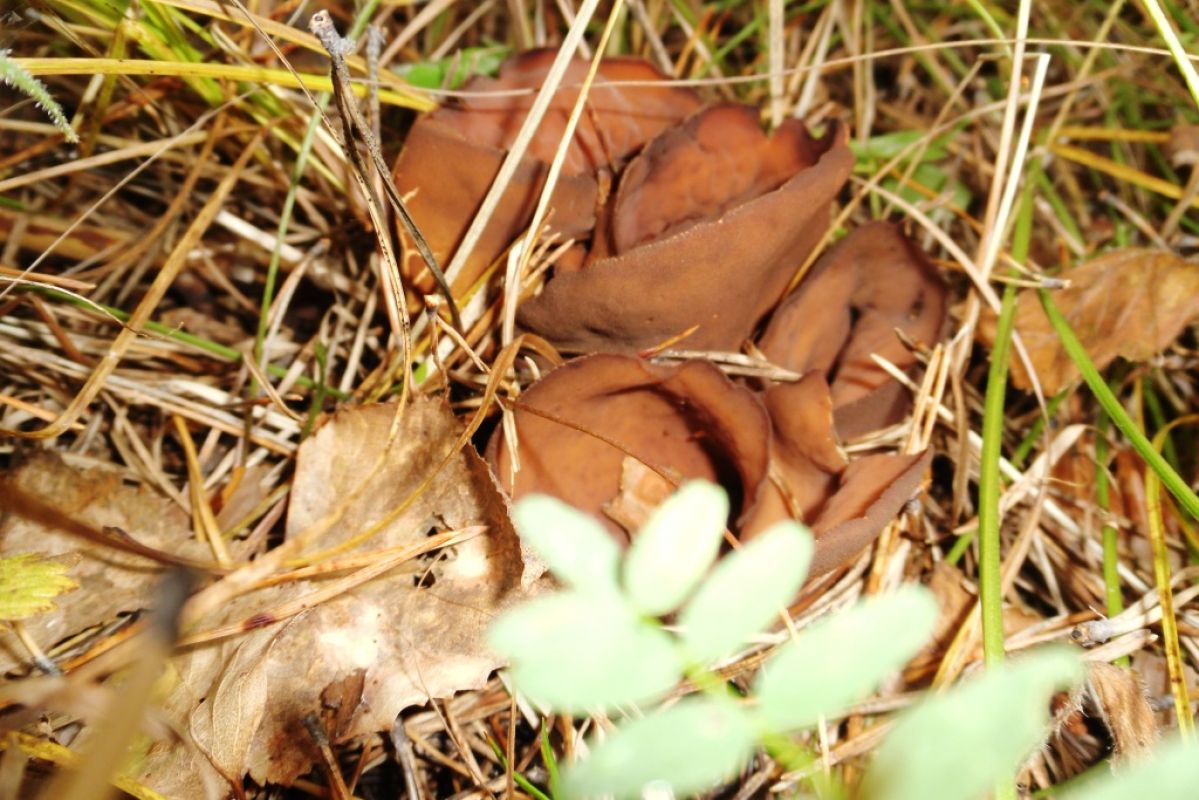
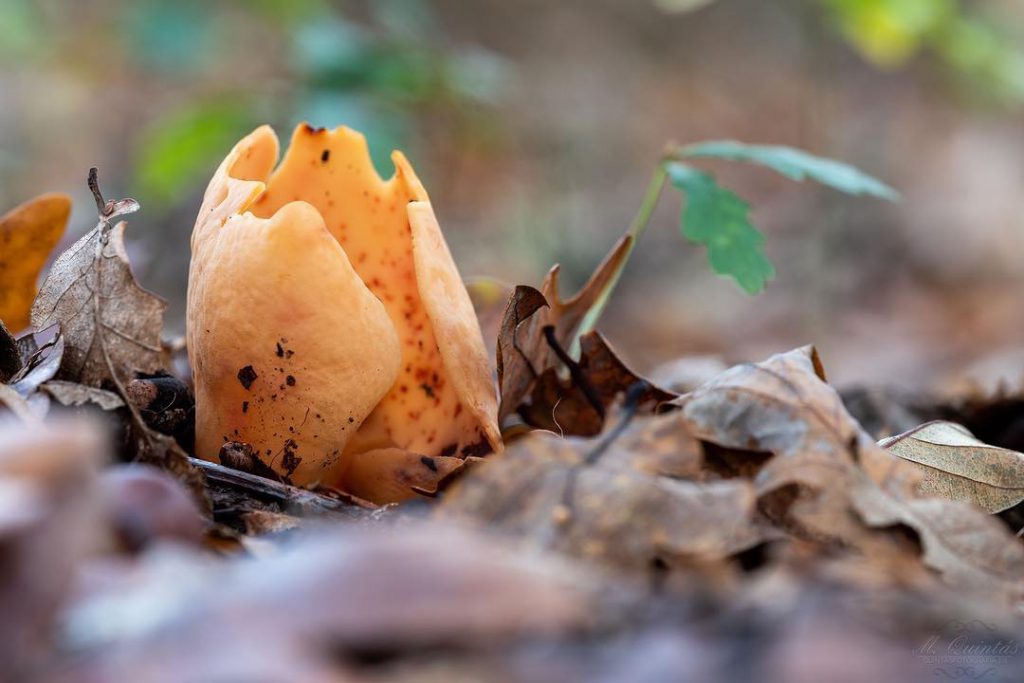
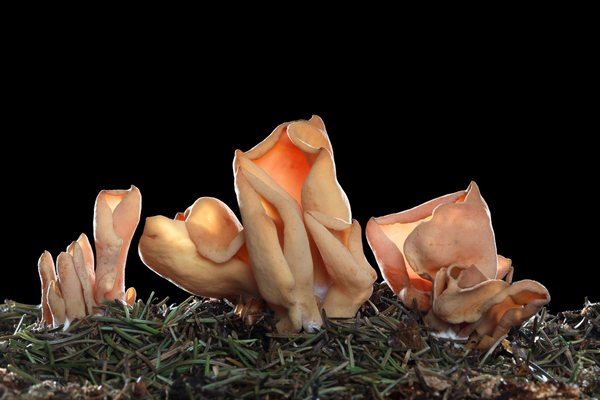
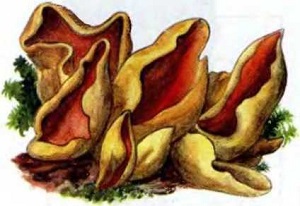
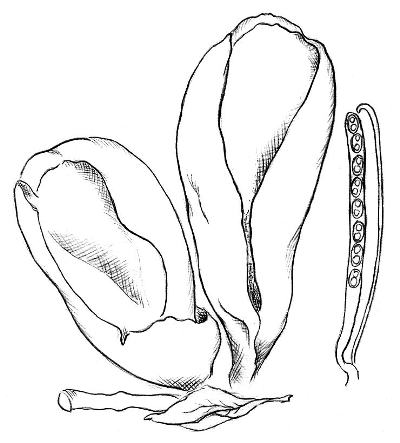
Lateral erect cup-shaped (ear-shaped) discomycete. The fruiting body is 2-6 cm in diameter, up to 10 cm in height, in the form of an ear-shaped bowl, adherent not to the center, but to the lateral part. The inner spore-bearing surface (hymenophore) is dark orange or ocher-yellow, often with a pinkish tinge, smooth. The outer sterile surface is devoid of a pinkish tint, but not lighter than the inner one. The false pedicle is poorly expressed, with ingrown pieces of substrate, paler than the "bowl" itself.
The pulp is strong, fragile, without any special taste or smell.
Spores are white in mass, 10-13 × 5-8 µm, elliptical, smooth, with two droplets. Asci up to 250 × 10 μm, non-amyloid, cylindrical, with amyloid ends. Paraphysis with curved ends.
Edible mushroom of poor quality, does not have a special taste and aroma, thin flesh.
Similar species
Otydea is one of the genera of fungi, the identification of the species of which is difficult without microscopy.
- Otidea leporina (Batsch) Fuckel, 1870 - Otidea hare grows mainly in coniferous forests, is painted in pale yellow-brown tones, does not have a pinkish tint. Spores 12-15 × 6-8 microns, elliptical, smooth, with two droplets-guttula, paraphysis with strongly curved ends.
- Otidea unicisa (Peck) Harmaja, 1986 is often mistaken for a donkey or hare. The shape of the fruit bodies of this species is rather not ear-shaped, but as if "cut off", not pointed upwards. This is the only species of the genus with ornamented spores, their size is 14-17 × 6-7 µm.
- Otidea tuomikoskii Harmaja, 1976 grows mainly under fir. Fruit bodies are ear-shaped, with a noticeably prickly sterile surface.Spores 8.5-11 × 5-6 microns.
Places of growth of hare ears.
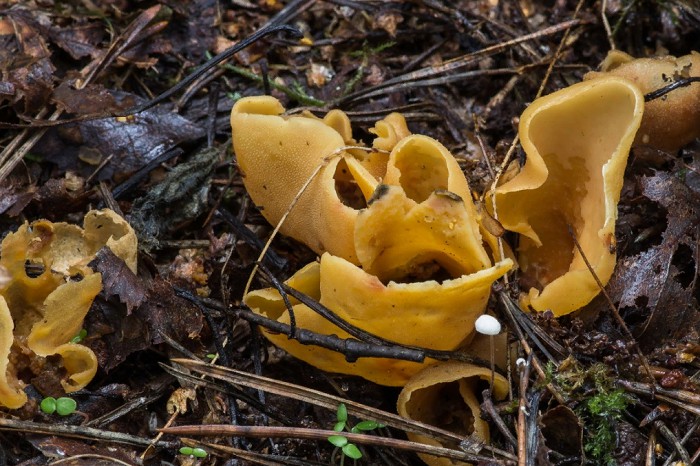
These are saprotroph mushrooms. They settle on the ground, litter, often among heather or moss. Hare ears grow in coniferous and mixed with spruce and pine forests. According to some reports, they come across in deciduous forests.

Fruit bodies these mushrooms grow groups, sometimes groups can be large. Rabbit ears do not bear fruit often, not annually. These mushrooms are found from August to October. The fruiting layer is most often only one and at the same time short.
Hare ears are common in the temperate and northern zones. They grow in Western Europe, Belarus, central Russia, the Caucasus, Kazakhstan, the Far East, the Urals and North America.

7 species of the genus Otidea grow on the territory of the countries of the former USSR.
Doubles of the mushroom hare ears.
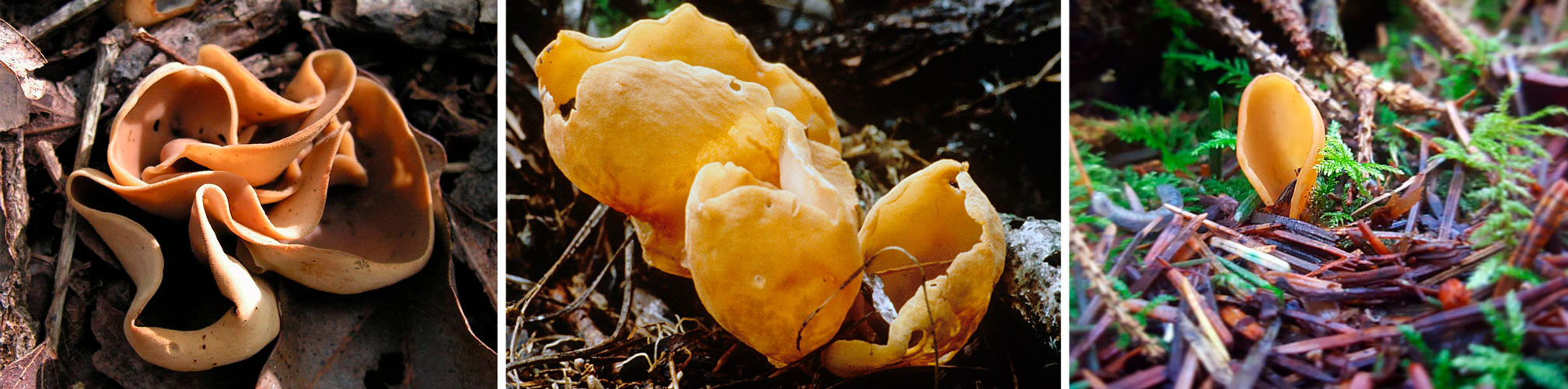
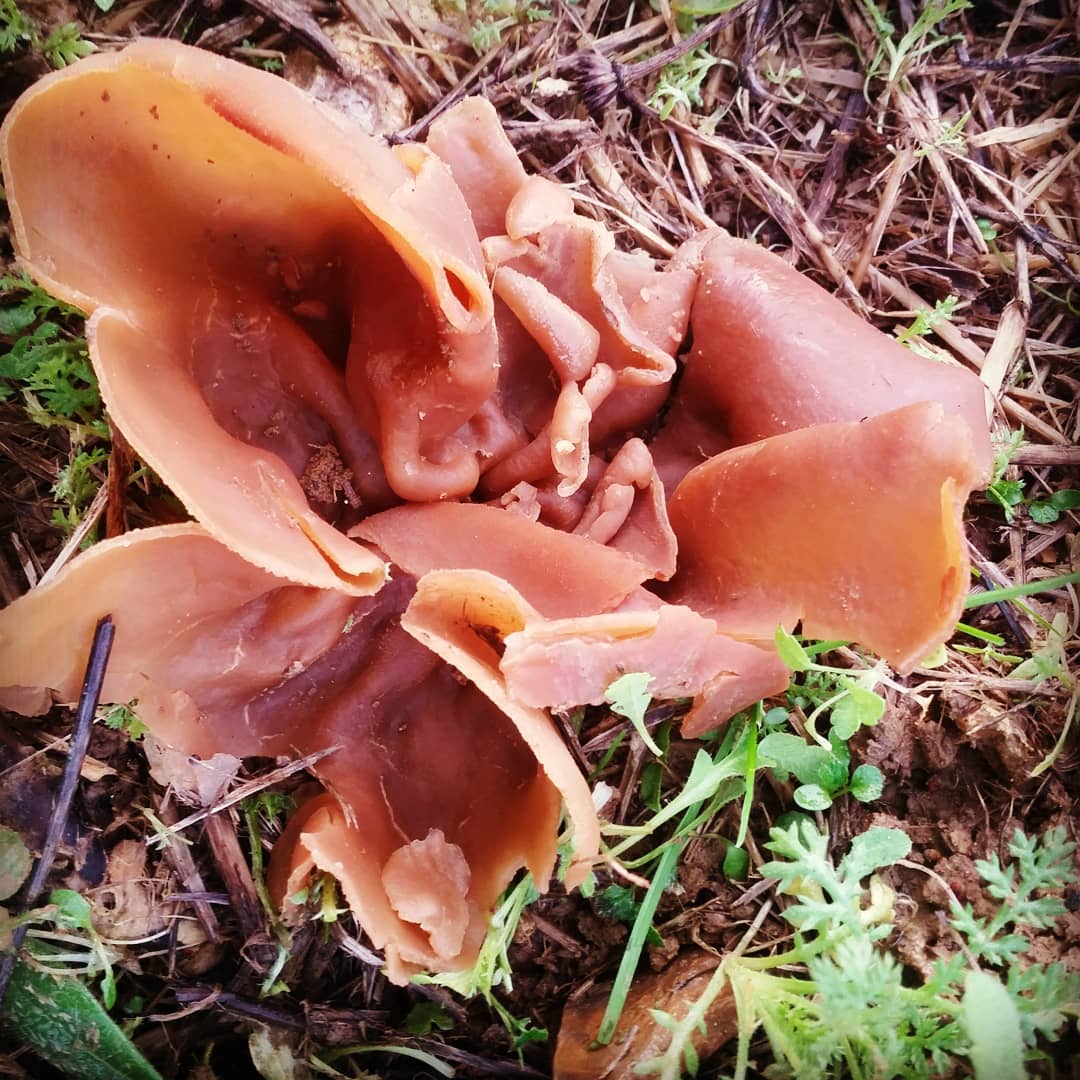
Hare ears are similar to the closest relative - from the idea of a donkey or a donkey's ear. But the donkey's ear is larger and has a brighter color. The inside of the mushroom is yellow-orange or ocher-orange, and the outside is ocher.
There is also a resemblance to the amazing idea, but it is much darker. The color of this mushroom is dark brown inside and light brown outside.

Another similar close relative is the graceful otidea, it has a more open fruit body of a small size, lemon-yellow in color.
Otydea spiral or conch-shaped differs from hare ears by a twisted fruiting body, inside is red or chestnut in color, and outside it is gray-brown in color with a powdery coating. The smell of this mushroom is specific. These mushrooms grow on soil or on wood buried in the soil.

Evaluation of the edibility of the rabbit ears mushroom.
This is a little known mushroom. It is considered conditionally edible. Rabbit ears have low nutritional quality - 4th category. These mushrooms are fried after a preliminary ten-minute boiling. Rabbit ears, like other otide, are not very tasty.
How the sheep ears plant reproduces
Woolly stachis can be propagated in several ways:
- seminal
- dividing the bush
- cuttings
- nodules
When growing stachis, most often the peduncles are cut off immediately after flowering ends, without waiting for the seeds to ripen. This is done to avoid self-seeding. To collect seeds, you need to leave several peduncles, wait for the bolls to ripen in early September and cut them off. Dry in an open age and get seeds for planting. If stachis is not yet on the site or you need another variety of it, then the seeds can be found in seed stores.
The bushes are divided throughout the season, but the best time for this process is spring. Sheep ears can also be propagated by cuttings, which take root quite well. Nodules are formed on the roots of the plant, which can also become planting material; nodules can be prepared in the fall. Store them underground in sand boxes. In spring, you need to select the strongest tubers for planting.
Ringed cap

It is urgent now to raise a voice in defense of one of the most massive autumn mushrooms, which are so shamelessly trampled and crumbled underfoot by ignorant mushroom pickers, to whom only young boletus should be served ... We are talking about a ringed cap (Rozites caperatus). This pinkish-red mushroom is fondly called chicken by Belarusians. And also in different regions - swamps, mistakenly - mushrooms.
To be honest, I was somehow broke before collecting them, because I can find other good too - there would only be time. Yes, a couple of years ago, Elena Laptenok boasted that she had collected chickens, they say, so delicious. In short, intrigued.
Let me remind you that they grow everywhere from late July to October in large families.
Pay attention and do not trample them. Chickens deserve a better life!
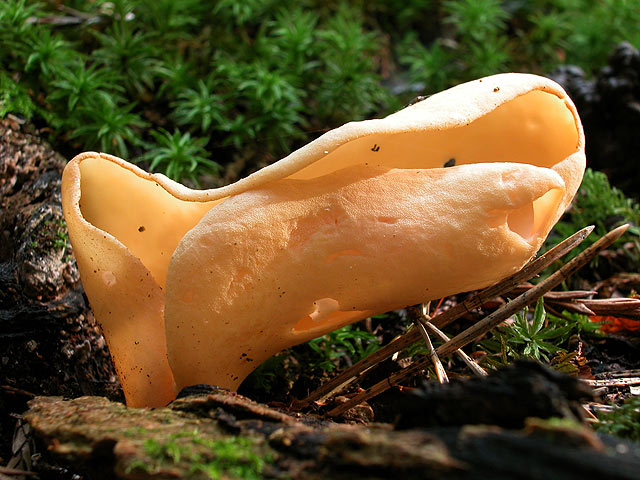
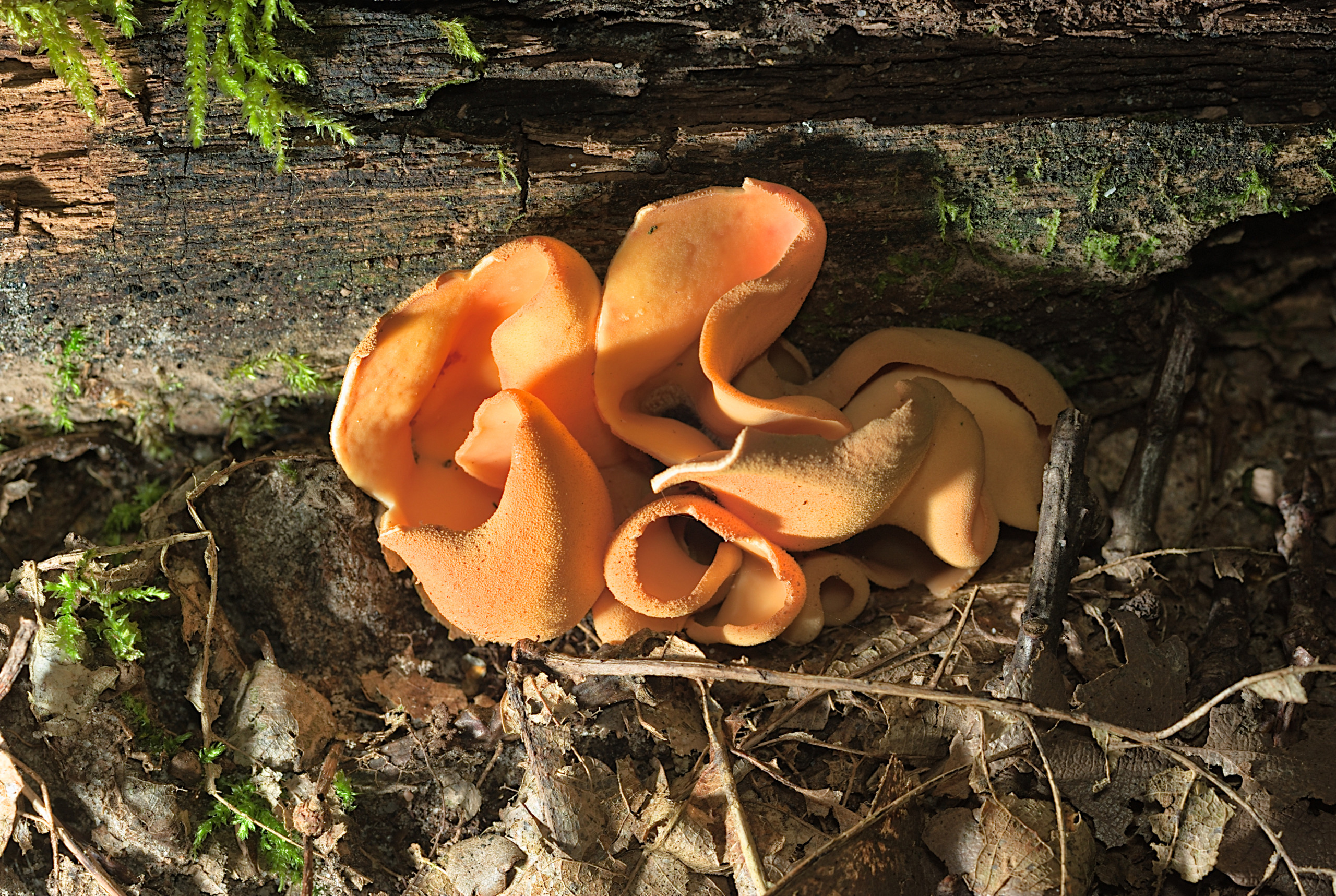
Description of the donkey otidia
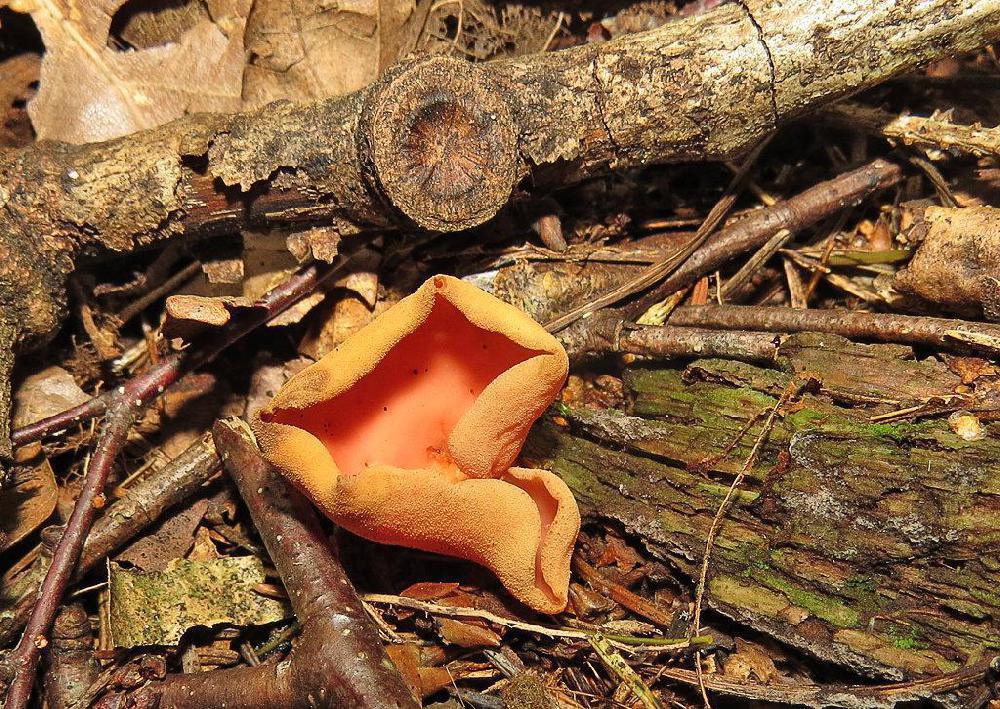
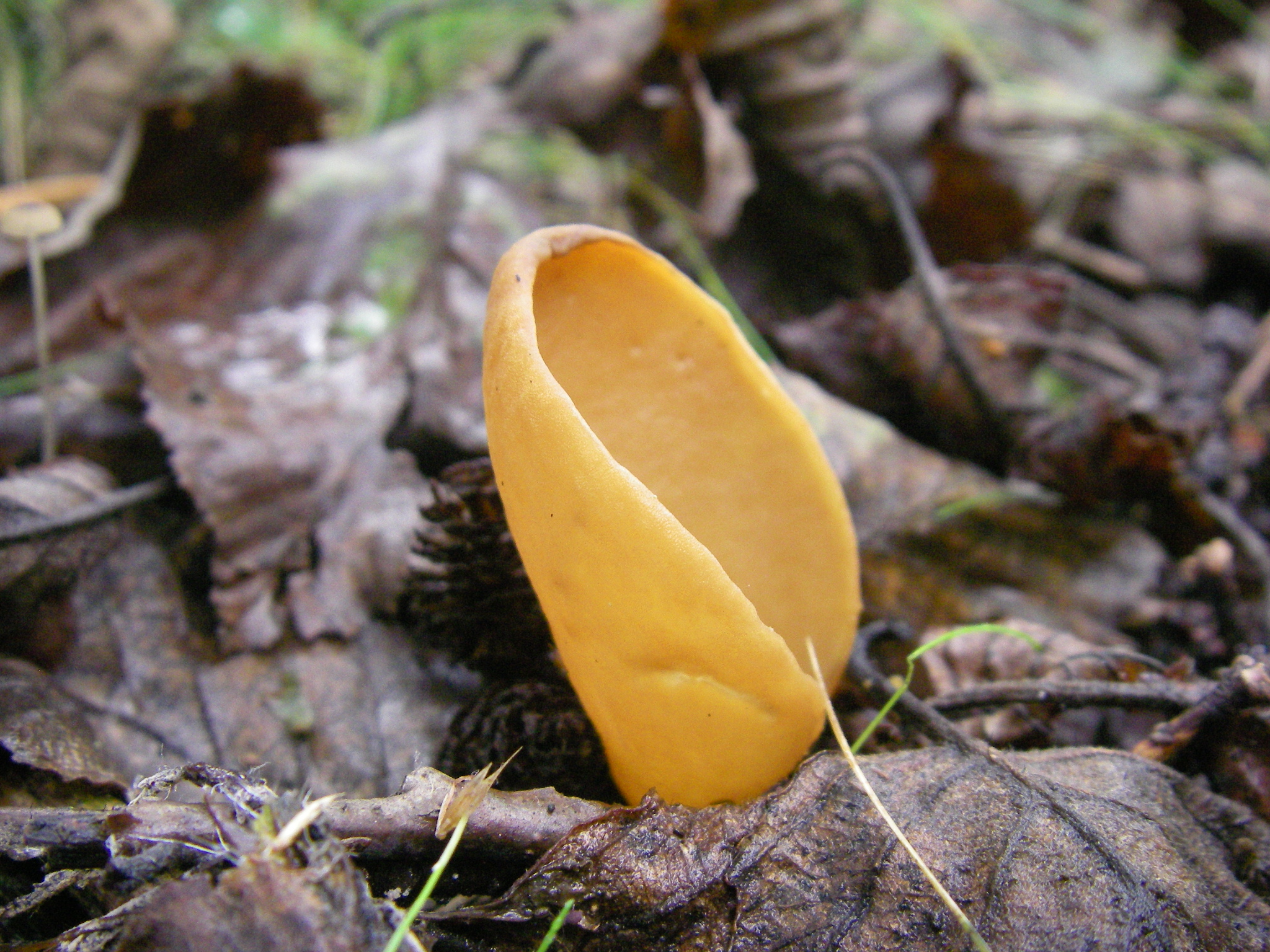
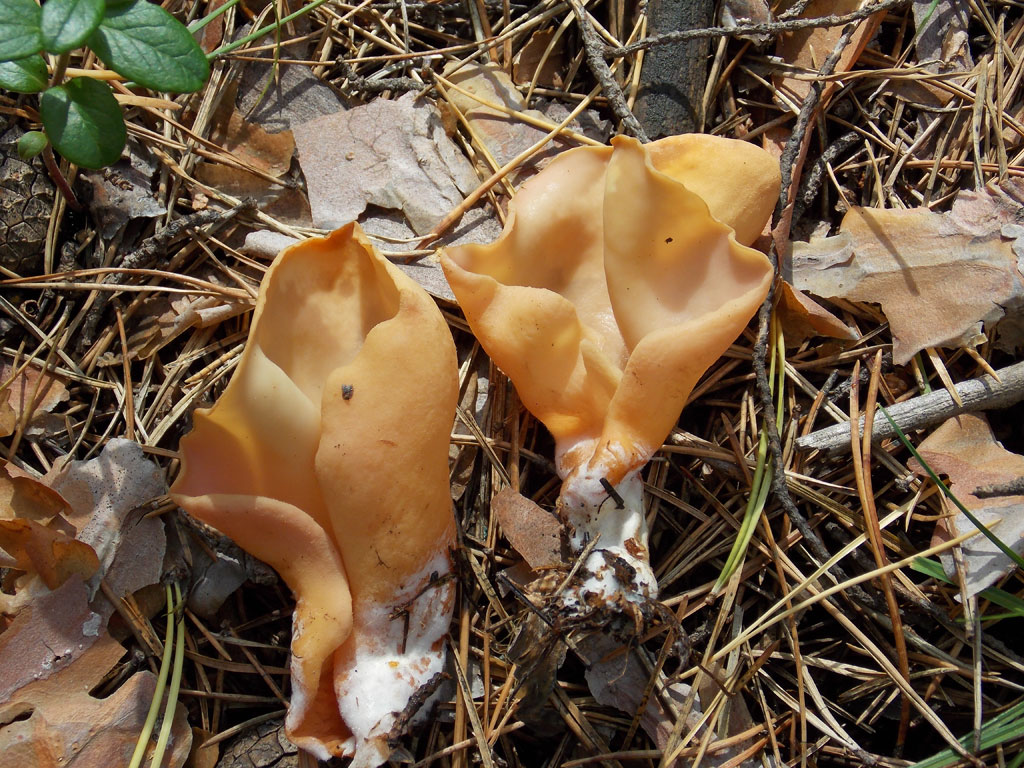
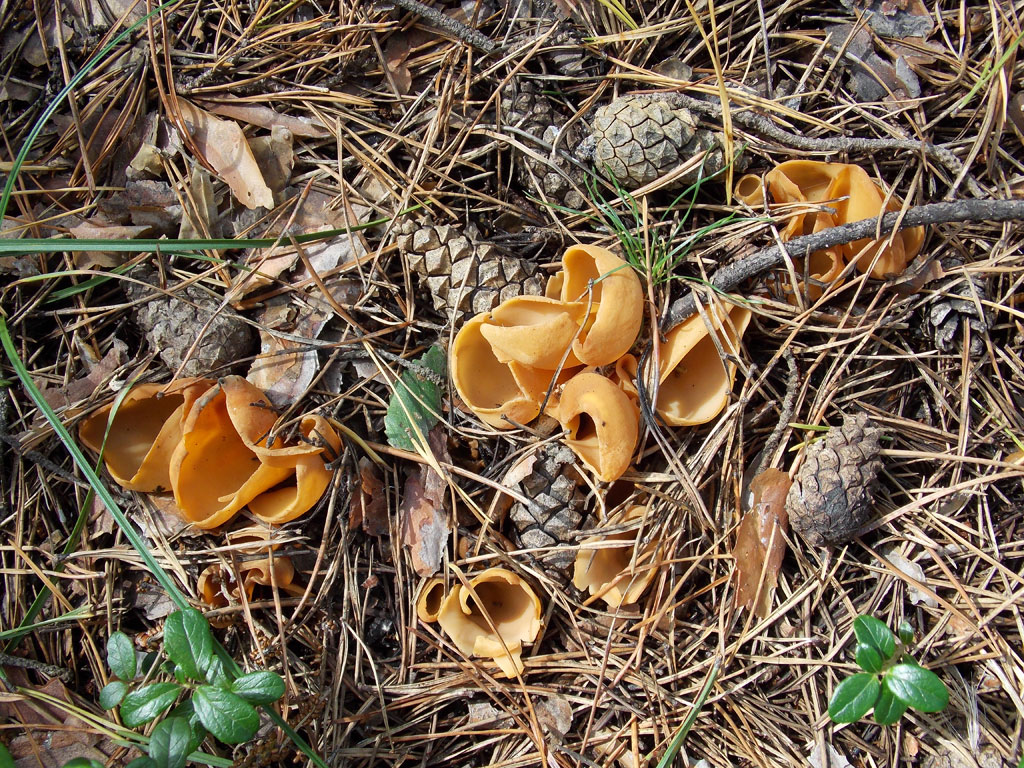
The shape of the fruiting body is elongated, outwardly it is similar to the ear of a donkey. The resemblance to a donkey's ear is also due to the fact that the inner surface of the mushroom is smooth, and the outer surface is fleecy. The height of the fruiting body is 3-8 centimeters, and the diameter is 1-3 centimeters. At the bottom, the fruiting body transforms into a small stalk.
The edges of the cap are folded inward.The diameter of the donkey's cap is from 6 to 10 centimeters. The hat has a one-sided appearance: its inner surface is yellow with an ocher tint, and the outer surface is either darker or lighter. The leg will repeat the shape of the cap, they also match in color.

The pulp is dense, but thin, and resembles rubber in consistency. The pulp has no smell and taste. Spore white powder.
Spreading from the idea of a donkey
These mushrooms prefer cool climates. Donkey ear can most often be found on fertilized, fertile and humus soils in various types of forests. They are mainly found in groups, and rarely grow singly. Otydea donkey grow in clearings and fires. The fruiting time of these mushrooms falls on October-November.

Donkey Ear Assessment
Donkey ear has no nutritional value due to its tough pulp and small size. But in principle, these mushrooms can be eaten, they are not dangerous for health. Mushroom pickers appreciate them only for their rarity and original appearance.
Similarity with other species
Outwardly, the donkey ear is most similar to the mushroom spatula - Spathularia flavida. This is also a poorly studied and rare species of mushrooms. The shape of the fruiting body is similar to the shoulder blade. The color of the fruiting body is yellow. The length of the scapula rarely exceeds 5 centimeters. Mushroom pickers do not consider this mushroom valuable.
Donkey's ear has no resemblance to poisonous mushrooms growing in our country.

Other mushrooms of the genus
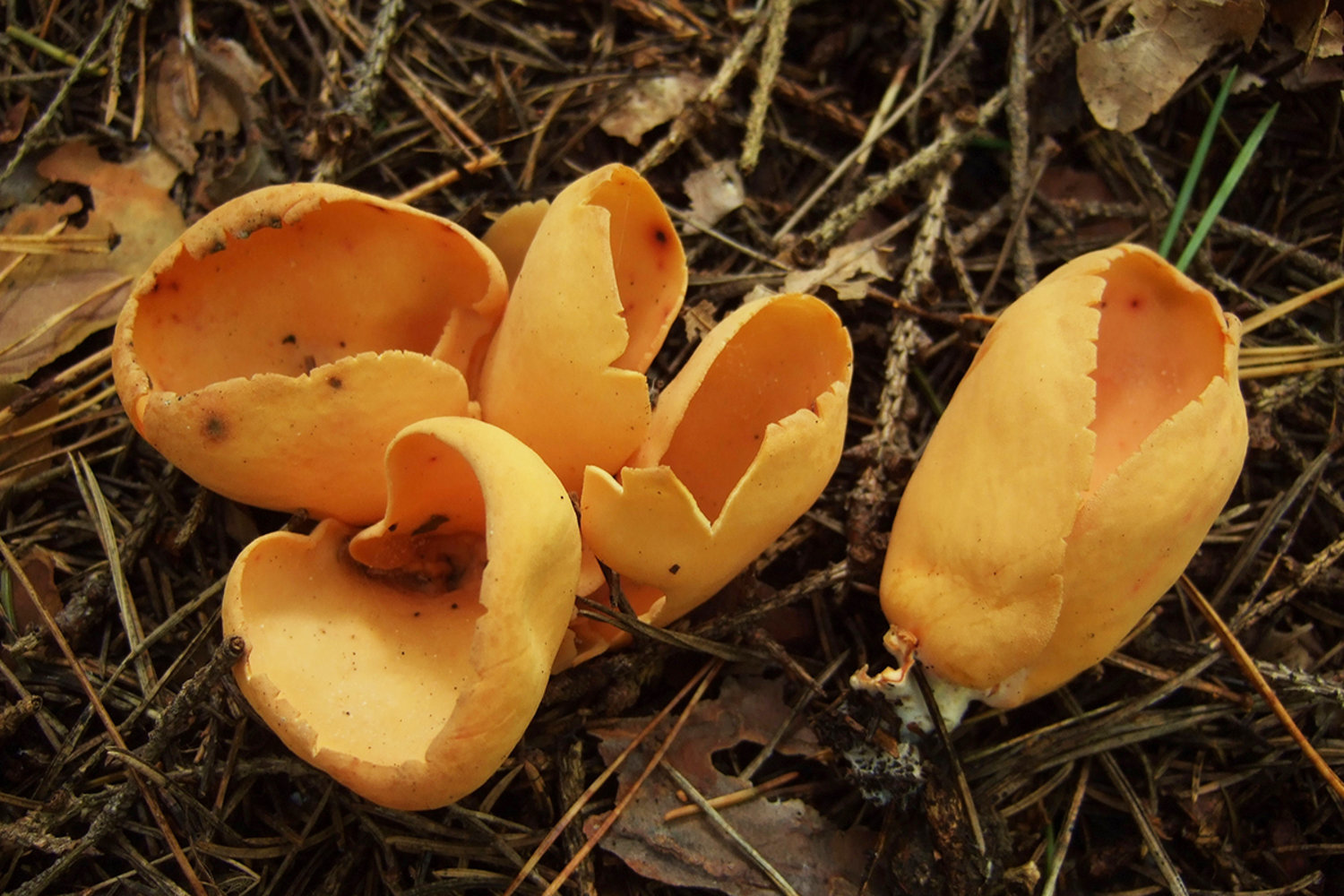
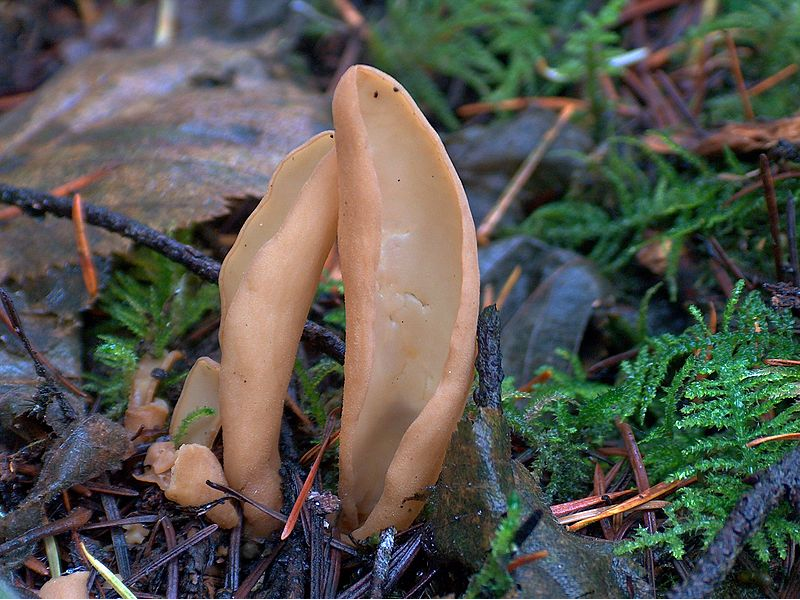
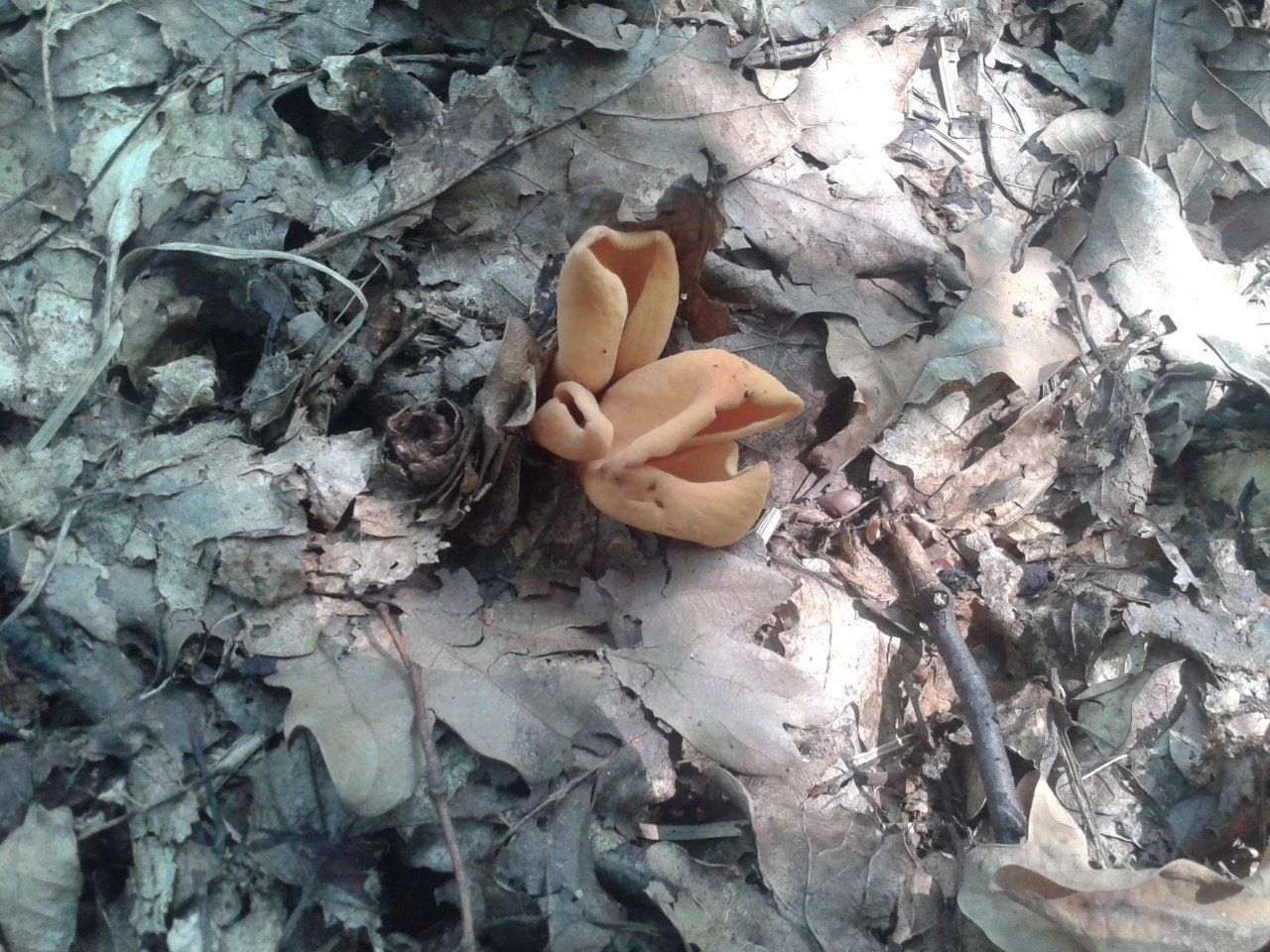
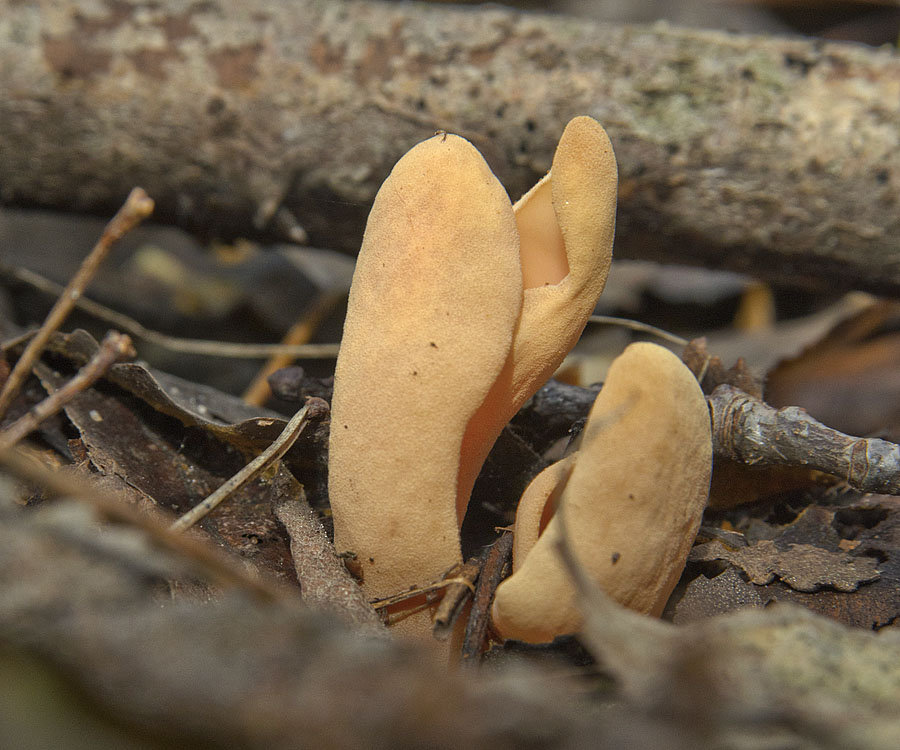
A close relative of the donkey is the hare, this mushroom is also called hare ears or hare skodelina. Outwardly, the fruiting body resembles an ear beveled to the side. The edge of the fetal body is beveled, and the leg is short. The height of the mushroom does not exceed 5 centimeters, while the diameter reaches 3 centimeters. The surface of the side of the hare is smooth and dry, with a thin nap. The color of the fruit body is dark yellow. The pulp is elastic, thin, rubbery, odorless and tasteless.
Otidea hare grow in large groups. Fruiting from July to early October. These mushrooms live in mixed and coniferous trees. In this case, the soil is chosen, overgrown with a thick layer of moss. These mushrooms can be eaten, but they need preliminary soaking. Most often, first courses are prepared from them.

Motley Hericium

Acquaintance with this mysterious mushroom happened relatively recently, in 2004, in the Gomel region. We went with a friend to pick mushrooms, right under the very Ukrainian border, where he has a dacha. And there I "raised" several pieces of an unknown mushroom. A lot of time passed until it was possible to identify it: a hedgehog mushroom, or, correctly, a motley hedgehog, a motley sarkadon, a hawk. Regional Belarusian names: Volovin's language (Belostochina), elk (Vileyshchina, Gomelshchyna), elk mushroom (Myadelshchina), bear (Lidchina), goat, sarny (Brest region), teetka (Svetlogorsk-Parichi-Ozarichi) ...
And I tried it later - I was a little afraid of such exoticism. Why am I writing about him now? Because they climb out late, from the second half of August until November.
It is not very famous, even rare, but if you come across it, you can immediately cut a whole heap. Has a specific aroma with bitterness. But after 5 minutes of cooking, the bitterness goes away, and then the hedgehog can be boiled, fried, salted, pickled, dried. You should know that it is better to eat young mushrooms. And overripe, they say, are too bitter and tough.
Hedgehogs grow mainly in sandy pine forests, under pine trees, where there are a lot of needles.
The literature also mentions the yellow hedgehog, but I have not yet had any culinary contacts with him.
In a word, if the summer is wasted, then in October you can still run into "hedgehogs" and satisfy your mushroom itch.
Care of woolly stachis
Despite its tolerance to dry periods, the plant needs to be watered regularly, but moderately, in the absence of precipitation. Otherwise, the leaves will lose their elegant look, changing their color. With a systematic lack of moisture, the plant can generally throw off the leaves, as a result of which, instead of a fluffy carpet, thin bare stems will remain in the flower bed.
The loss of silver content can also occur with an excess of nitrogen and humus in the soil. In this case, the leaves acquire an ordinary green color. If, during the growth of the bush, a bald patch forms in the center, then it must be carefully dug up and planted in the middle of a young seedling. This technique will allow you to keep a solid carpet of leaves.
This is very important when stachis is grown as a groundcover.
After the winter period, old stems should be cut from the bushes, and during the flowering period, the peduncles must be systematically removed along with the buds. In the summer, you need to cut out overgrowing rhizomes. The plant almost does not suffer from diseases and pests, it tolerates severe frosts well. However, it may suffer from damping off in late winter - early spring in conditions of high snow cover and waterlogging of the soil as a result of its melting.