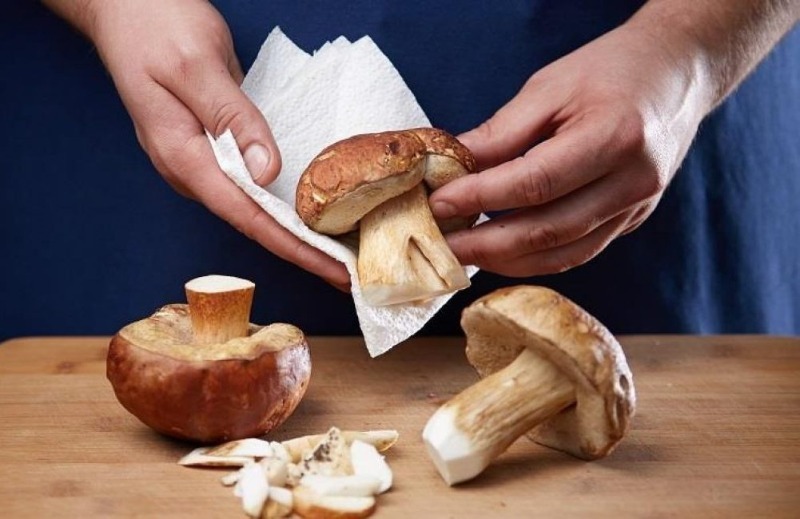
How to clean a porcini mushroom cap
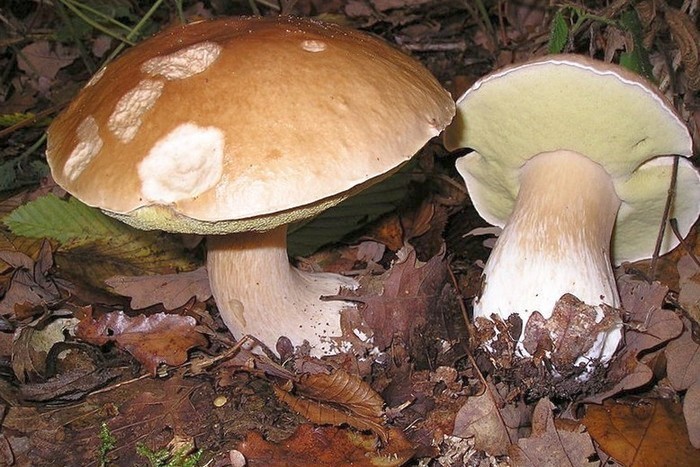
If the boletus are collected in dry weather, there will be no particular difficulties in processing. If, however, during the rain or immediately after, then the cap may contain a lot of sand or earth in the lower part, where they fall in large quantities. Therefore, in the first case, it is enough to wipe the upper part of the mushroom with a soft cloth. In the second, rinse thoroughly under running water and brush with an old toothbrush. Sometimes it is necessary to remove part of the cap due to rot or worm infestation.
An easily peeled skin indicates that the mushroom has begun to deteriorate. Therefore, special care must be taken to prevent potentially hazardous parts from entering food.
How to clean porcini mushrooms at home
Boletus are unique in their own way. They grow in any forests - deciduous, coniferous, mixed. These fruiting bodies are not capricious to the soil. Therefore, they can be found both on sand and on clayey lands, even in mosses among swamps. Whites love the sun and moisture, if both are enough - they can appear in May and October.
Boletus grows all over the globe with the exception of the poles. White ones are not called royal mushrooms for nothing. They are very tasty and aromatic, they do not lose their snow-white cut color and shape during any type of culinary processing. Strong, beautiful, these mushrooms can grow to gigantic proportions.
It should be stored after harvest no more than 3-4 hours, especially in hot weather. Can be kept in the refrigerator or cellar for 1-2 days, but only if absolutely necessary. To preserve the full flavor and maximum benefit, the mushrooms should be peeled immediately after harvest. Ideally, still in the forest. But it is much more convenient to do this at home, so most mushroom pickers prefer to clean boletus in their own kitchen.
What is required
To clean the fruit bodies, you need to prepare three large, cleanly washed enamel basins. Fill one with warm water, mushrooms and a knife will be rinsed in it during processing. The second will be needed for waste. And the third will fit peeled whites.
The knife should be made of stainless steel, with a short blade and a comfortable, non-slippery handle. Vegetable is best. A small piece of clean, soft cloth or an old toothbrush will make cleaning the bonnets easier.
Step by step actions
Consider how to properly peel porcini mushrooms before cooking:
After soaking, rinse under running water, paying particular attention to the bottom surface of the caps most susceptible to contamination. This helps to get rid of sand and debris in the spongy layer of the fruiting body.
Leave in a colander or strainer for a few minutes to drain off excess moisture.
With a soft cloth, wipe the top of the caps from adhering leaves, needles or sand (after soaking, these contaminants are removed without effort).
Use a knife to update the cut on the legs.
If the skin on the caps comes off easily, you need to peel it off.
For most processing, the leg must be detached.
Properly inspect the boletus caps - there may be wormholes in them
Too badly damaged - throw away, where you can cut - do it as carefully as possible.
The legs are cleaned from top to bottom with a sharp knife. Particular attention should be paid to the thick part - it is here that the greatest pollution is found (with moss, needles, earth).
Throw away the wormy legs, the rest will go to work.
In a bowl of warm water, lightly rinse the peeled mushroom and put the cap down in a clean dish. If the legs are separated, they need to be folded into a separate container.
Cut large caps into several parts. Leave small ones intact.
Thick legs are cut across with 3-4 cm thick stumps. Thin legs are cut lengthwise into 2 or 4 parts. Slicing is done just before freezing, marinating, drying or boiling.
The boletus is now prepared for subsequent use according to the recipe.
After collecting in the forest
During the "quiet hunt", you can immediately prepare boletus mushrooms for further processing. To do this, you need to properly assemble them and cut off the excess in place. This way you will not bring home waste or infect healthy fungi with worms.
It is necessary to collect boletus, carefully twisting it out of the ground, in contrast to mushrooms, mushrooms or mushrooms, which must be cut off with a sharp knife. Thus, the mycelium will be preserved, and the fruiting body will not receive mechanical damage.
Before you put white in the basket, you need to carefully examine it. Remove all rotten, wormy parts, clean the leg, especially at the root. Wipe off the hat from the remnants of forest debris (leaves, needles, earth).
Put the porcini mushrooms in a bucket or basket with the caps down. So they better retain their shape, do not wrinkle and do not break during transportation. After cleaning the forest, the only thing left to do is to wash and cook the boletus.
Mechanical restoration
First, the harvested crop is carefully examined. If there are unfamiliar specimens that are in doubt, it is better to throw them away. Fruit bodies are not consumed if they:
- wormy;
- rotten;
- with mold;
- with mucus;
- damaged.
Sorting
Mechanical processing is carried out regardless of whether the mushrooms are to be used immediately, fresh or intended for canning. They are sorted by type and size because they are prepared in different ways and also differ in taste. Only medium-sized fruiting bodies are suitable for harvesting. Mushrooms are divided into those that are fried immediately, and those that require preliminary boiling.
Cleaning
It is worth getting rid of debris and small insects brought from the forest along with the harvest. To do this, use a soft brush or rag. You can handle fruiting bodies with a knife. If the product is to be dried, fried, baked, then it is not washed.
Areas of fruit bodies damaged by pests are carefully cut out with a knife. All darkening and damage is removed. In old tubular mushrooms, the inner (lower) part of the cap is removed - the tubular hymenophore.
Washing
You need to process mushrooms with cold water. Immediately after this, they wait for the excess liquid to drain from the fruit bodies. Longer rinsing is required for species with an uneven surface. These include morels, stitches, etc. Sand adheres to the folded surface of the caps of these specimens, which needs to be washed. If the fruiting bodies are intended for drying or frying, such manipulations are not performed.
Soaking
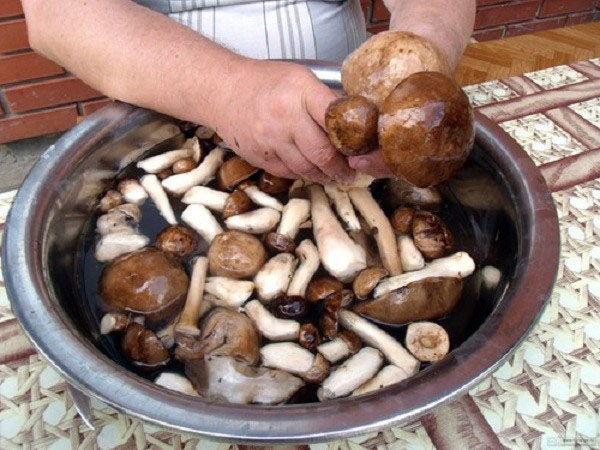
This is achieved by immersing mushrooms in salted water for several hours or a day. The liquid is periodically changed to fresh. For this, a low and wide vessel is selected; basins or bowls are best suited for these purposes. After that, the bitterness will go away. Dry fruit bodies are also soaked. This helps restore moisture. Experienced mushroom pickers recommend cutting the milk mushrooms into slices before soaking - this way it will be better to leave the bitterness from the fruit chalk. By the way. It is not recommended to use aluminum or stainless utensils to soak the mushrooms, in order to avoid chemical reactions between the surface of the container and the released juice (even if mixed with water).
Slicing
Large specimens are divided into parts. To make the dish taste good, the leg is cut into circles across the fibers. The hats are divided into equal parts. For canning, small fruiting bodies are used entirely.
We wash and soak the collected mushrooms
Washing and soaking mushrooms is often the first step in any mushroom culinary. If mushrooms are not intended for boiling, but for drying, in no case should they be washed and soaked! Such mushrooms only need to be cleaned of debris and wiped with a damp, clean cloth.If the mushrooms were cleaned and washed correctly and in time, then any dish with their participation, including fried mushrooms with potatoes, will acquire an amazing taste and aroma!
Several rules for the competent washing of mushrooms;
Do not wash mushrooms for too long under hot water, because if they absorb a lot of water, then during the cooking process you will encounter certain problems (long cooking); Mushrooms should be washed under running water for 1-2 minutes, and then left on a dry clean towel (drain); Before cooking, porcini mushrooms must be scalded with boiling water several times so that later they do not crumble during cutting and are more elastic and elastic.
Mushrooms contain proteins, fats, sugar, minerals, vitamins A, C, B, PP and group B. They are rich in extractive substances, therefore they have a good taste and aroma, they are widely used for making soups and sauces. Edible mushrooms in structure are: spongy - white, boletus, boletus, boletus; plac-tint - champignons, russula, chanterelles, honey agarics; marsupials - smor-chki, lines. Mushrooms are supplied to public catering enterprises fresh, salted, dried, pickled.
Fresh mushrooms.
Mushrooms are immediately processed, as they quickly deteriorate. Primary processing of mushrooms consists of the following operations: cleaning, washing, sorting and cutting.
Porcini mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, chanterelles, russula are treated in the same way: they are cleaned of leaves, needles and blades of grass, the lower part of the leg and damaged areas are cut off, the contaminated skin is scraped off and washed thoroughly 3-4 times. When processing syringes, the skin is removed from the cap. To do this, they are pre-steamed with boiling water. The legs of the oil are cleaned and the caps are cut off, the spoiled and wormy places are cut out, the mucous skin is removed from the cap and washed.
Mushrooms are sorted by size into small, medium and large. Small mushrooms and caps of medium mushrooms are used whole, large ones are chopped or chopped. Porcini mushrooms are poured with boiling water two to three times, the rest of the mushrooms are boiled for 4-5 minutes so that they are soft and do not crumble when cutting.
The mushrooms are supplied to enterprises from greenhouses. They should be not overgrown, the plates on the underside of the cap -
pale pink in color. When processing mushrooms, remove the film covering the plates, peel the root, remove the skin from the cap and rinse in water with the addition of citric acid or vinegar so that they do not darken.
Morels and lines are sorted out, the roots are cut off, placed in cold water for 30-40 minutes, in order to soak off the sand and motes, washed several times. Then the mushrooms are boiled for 10-15 minutes in a large amount of water to destroy and remove the poisonous substance - helvelic acid, which turns into a decoction during cooking. After boiling, the mushrooms are washed with hot water, and the broth must be poured out.
When processing fresh mushrooms, you must carefully select them, since some of them have similarities with inedible and poisonous mushrooms.
Dried mushrooms.
The best dried mushrooms are porcini, as they give a light, aromatic and tasty broth when cooked. Podberezov-vetch, boletus, boletus darken when dried, so they are of little use for broths.
Dried mushrooms are sorted out, washed several times, soaked in cold water for 3-4 hours, then the water is drained, filtered and used to boil mushrooms. After soaking, the mushrooms are washed.
How to handle and conditionally edible mushrooms after harvest
How to distinguish edible mushrooms
Is there a difference between poisonous and inedible mushrooms? Isn't it the same thing? No. The fact is that inedible mushrooms are not eaten in most cases, not because they are capable of causing great harm to the body, but because of:
- unpleasant taste or odor;
- small fruiting bodies;
- hardness of the pulp;
- growths on the fruiting body (scales, thorns, etc.);
- the specificity of the place of growth;
- rarities.
In addition to the listed parameters, the inedibility of mushrooms can also be expressed in the content of a certain amount of hazardous substances in them. The use of such mushrooms will not lead to death, but it can cause poisoning. In no case should you eat poisonous mushrooms, under any circumstances! Even during the cooking and drying process, hazardous substances do not evaporate from them, and poisoning with them can lead to death. The most poisonous mushroom currently is a pale toadstool.
This memo will help inexperienced or uncertain mushroom pickers in their knowledge to distinguish conditionally edible mushrooms from poisonous ones. Use it when picking mushrooms!
There are various ways to prepare mushrooms. They are boiled, fried, stewed, dried, baked, canned, and sauces are prepared from them. Whatever you are going to do with them, do not forget about the preliminary processing of mushrooms - sorting, cleaning from debris, washing, as we talked about above.
Rules for collecting conditionally edible mushrooms

- never pick old, wormy, diseased mushrooms;
- never take mushrooms grown on the edge or near a motorway, railway, factory, etc. The fact is that these gifts of nature, like sponges, absorb all harmful substances from the environment, therefore in some places even edible mushrooms, " »Toxins and other hazardous substances can become toxic;
- never pick suspicious mushrooms. If there is even the slightest doubt about the edibility of the mushroom, it is better to throw it away;
- do not store mushrooms for a long time! The sooner you use them for their intended purpose, the less likely they are to deteriorate and harm your body.
Features of processing conditionally edible mushrooms after harvest
You should not deny yourself the pleasure of eating mushrooms, which appeared in the column under the heading "Conditionally Edible". This name literally means "edible, but subject to certain conditions." Usually this is a special preparatory treatment, that is, before cooking a certain dish from the mushrooms, they should be boiled, soaked or dried. These methods are presented in a strict sequence: as the time for pre-processing of mushrooms increases.

Pre-boiling mushrooms for processing. Cut the carefully selected, washed and peeled mushrooms into pieces and boil for 20 minutes, then drain the water, wash them thoroughly with cold water and cook again for 20 minutes. Be sure to drain the water again, wash the mushrooms with cold water, put them in a colander and you can safely use them for cooking any dishes.

Soaking mushrooms for processing. Pour plenty of cold water over the mushrooms and leave for two days. Then drain the water. This must be done without fail, because it takes in all the toxic and poisonous substances contained in conditionally edible mushrooms. Wash the mushrooms thoroughly with running water and use as directed.

Drying mushrooms for processing. Hazardous substances can not only be boiled and soaked, but also dried from mushrooms. For this, they should be dried in the fresh air under direct exposure to sunlight or in a well-ventilated area directly near a heat source. After reaching full readiness, the mushrooms need to be removed in a dark place for 2-3 months. You can cook food from them only after such a period.
If you correctly understood how to process mushrooms after harvesting and used our tips to distinguish conditionally edible mushrooms, you can not only prepare mushrooms for the winter, but also benefit from mushroom dishes.
Kira Stoletova
Porcini mushrooms are popular with mushroom pickers because of their taste and ease of preparation. Their disadvantage is the need for careful preparation before eating. The cleaning of porcini mushrooms is done to get rid of harmful particles that are on the surface when growing in the forest.

How to properly carry out the primary processing of mushrooms?
Adding an article to a new collection
Mushrooms are a valuable source of protein, a huge amount of trace elements, vitamins and amino acids
Mushrooms can be used to prepare a lot of mouth-watering dishes and seals for the winter, but at the same time it is important to initially process the collected mushrooms correctly.
Mushrooms can be classified as perishable, so they need to be processed on the day of harvest, no later than 4-5 hours later. If this is not possible, the mushrooms should be placed in a refrigerator, cellar, or spread out in a single layer on a bedding on a balcony, under trees in a garden, or in another cool place.
1. We sort and clean
Before culinary processing, the mushrooms are carefully sorted out, rejecting old and inedible ones, slightly cleaned of large debris, sorted by type, size. If possible, the garbage is scraped off the smooth caps with a knife, and the skin is also removed from the caps of butter, milk mushrooms and russula. Mushrooms with caustic milky juice (volnushki, milk mushrooms, valui) are soaked in cold water in a deep bowl.
Mushrooms need to be sorted
By the way, mushrooms should be kept in water as little as possible (except for soaking), where they quickly lose their aromatic and soluble solids. It is better to quickly wash the mushrooms under running water (mushrooms for salting are not washed at all, but cleaned with a damp cloth or sponge).
Mushrooms are cleaned of debris and cut into large pieces
Sorting out mushrooms, large caps are cut into pieces. The legs are cut across or in circles 2-3 cm thick, they are boiled separately, since this takes more time. Many mushrooms (boletus, mushrooms, champignons, mushrooms, aspen mushrooms) contain easily oxidizing substances, so they darken almost instantly on contact with air. To prevent this from happening, they are sorted out as quickly as possible and immediately immersed in water, having previously added a little salt or citric acid to it.
2. Soak
Sorted mushrooms are poured into a bucket or large basin, cold water is poured and a circle made of hardwood bars (you can do with a regular flat lid) is placed on top of the mushrooms with a small load so that they are all covered with water. In water, all dry leaves and grass will be soggy and will be easier to separate when cleaning. After a few minutes, the water is drained, and the mushrooms are cleared of debris. Then they are thoroughly rinsed under running water and placed in a saucepan in which they will cook.
Peeled mushrooms are soaked
3. Cook
Better yet, dip the peeled mushrooms in a pot of hot water. It is poured a little (4-5 cm) to cover the bottom layer of the product. As the mushrooms heat up, they secrete juice and after a while are completely covered with liquid. Salt and spices are added to the water. Boil mushrooms over low heat (caps - 8-10 minutes, legs - 15-20 minutes), periodically removing the resulting foam. During this time, they should be boiled and acquire a pleasant taste and aroma. Then they can be fried or pickled.
How to properly process a poplar row
For many mushroom pickers, poplar rows are considered popular. This is a conditionally edible mushroom, popularly called poplar. These fruiting bodies grow in large rows near or directly below poplars. These mushrooms are usually very contaminated, so let's take a look at the information on how to properly process a poplar row.
- The first step, which will tell you how to process the rows, is soaking in cold water for 3 days. In this case, you need to change the water 2 or 3 times daily. Thanks to this approach, all the bitterness leaves the mushrooms and soaks the dirt. Note that if the temperature of the water for soaking the mushrooms is higher than + 16 ° C, this is bad, since the fruit bodies can ferment. Therefore, change the water more often to protect the mushroom crop from spoilage.
- Rows are boiled in water with the addition of salt for 30 minutes.
- The mushroom broth is poured, washed in running water and allowed to drain.
How to handle and conditionally edible mushrooms after harvest
In order for the collected mushrooms to be not only a valuable trophy, but also to turn into delicious dishes, you need to know the rules and sequence of mushroom processing.
First, you need to learn to distinguish edible mushrooms from inedible ones, and especially from poisonous ones.
Secondly, it is important to have a clear idea of how to prepare this or that "trophy", because, for example, mushrooms belonging to the so-called conditionally edible species can be eaten only after special and very careful processing.
Thirdly, in order to successfully complete the business you have begun and please your family with a delicious dinner, you need to be able to cook mushrooms correctly, for which you should first study which type of mushrooms is better to fry, and from which to cook soup, etc. Sorting mushrooms after collecting
Do not mix different types of mushrooms together. It is advisable to sort them and use them separately.
Sorting mushrooms after harvest. Do not mix different types of mushrooms together. It is advisable to sort them out and use them separately.
Cleaning mushrooms from debris. Rubbish, pine needles, leaves from mushrooms can be carefully removed with a soft brush, brush, sponge or cloth.
Washing mushrooms. Wash the mushrooms with cold running water.
How to distinguish edible mushrooms
Is there a difference between poisonous and inedible mushrooms? Isn't it the same thing? No. The fact is that inedible mushrooms are not eaten in most cases, not because they are capable of causing great harm to the body, but because of:
- unpleasant taste or odor;
- small fruiting bodies;
- hardness of the pulp;
- growths on the fruiting body (scales, thorns, etc.);
- the specificity of the place of growth;
- rarities.
This memo will help inexperienced or uncertain mushroom pickers in their knowledge to distinguish conditionally edible mushrooms from poisonous ones. Use it when picking mushrooms!
There are various ways to prepare mushrooms. They are boiled, fried, stewed, dried, baked, canned, and sauces are prepared from them. Whatever you are going to do with them, do not forget about the preliminary processing of mushrooms - sorting, cleaning from debris, washing, as we described above.
Rules for collecting conditionally edible mushrooms
- never pick old, wormy, diseased mushrooms;
- never take mushrooms grown on the edge or near a motorway, railway, factory, etc. The fact is that these gifts of nature, like sponges, absorb all harmful substances from the environment, therefore in some places even edible mushrooms, " »Toxins and other hazardous substances can become toxic;
- never pick suspicious mushrooms. If there is even the slightest doubt about the edibility of the mushroom, it is better to throw it away;
- do not store mushrooms for a long time! The sooner you use them for their intended purpose, the less likely they are to deteriorate and harm your body.

Features of processing conditionally edible mushrooms after harvest
You should not deny yourself the pleasure of eating mushrooms, which appeared in the column under the heading "Conditionally Edible". This name literally means "edible, but subject to certain conditions." Usually this is a special preparatory treatment, that is, before cooking a certain dish from the mushrooms, they should be boiled, soaked or dried. These methods are presented in a strict sequence: as the time for pre-processing of mushrooms increases.
Soaking mushrooms for processing. Pour plenty of cold water over the mushrooms and leave for two days. Then drain the water. This must be done without fail, because it takes in all the toxic and poisonous substances contained in conditionally edible mushrooms. Wash the mushrooms thoroughly with running water and use as directed.
Drying mushrooms for processing. Hazardous substances can not only be boiled and soaked, but also dried from mushrooms.For this, they should be dried in the fresh air under direct exposure to sunlight or in a well-ventilated area directly near a heat source. After reaching full readiness, the mushrooms need to be removed in a dark place for 2-3 months. You can cook food from them only after such a period.
If you correctly understood how to process mushrooms after harvesting and used our tips to distinguish conditionally edible mushrooms, you can not only prepare mushrooms for the winter, but also benefit from mushroom dishes.
Primary processing of mushrooms
Primary processing of mushrooms is the first and main requirement in processing - a thorough examination of the mushrooms. Often slugs sit on mushrooms, and various flies and bugs sit in the pits of morels. Mushrooms should be processed only young, completely healthy, not broken, not wormy, with trimmed roots, without any debris: needles, leaves, earth, and only freshly cut.
Sorting and cleaning
For pickling in a hermetically sealed container, take only a boletus cap, a mushroom sock and a curl from the rest. Porcini and camelina, intended for canning in a hermetically sealed glass container, are also sorted by color or place of growth: spruce, pine, oak, birch boletus; pine and spruce mushrooms. In accordance with the distribution of grades, the leg is also cut off. The peel from the remaining stump at the cap is scraped off with a knife. In addition, mushrooms are thoroughly cleaned of adhering debris, needles, twigs and particles of earth, and all wormy specimens are discarded. Wormholes are cut out of less wormy ones. Peel off the oil. Mushrooms intended for drying and salting mushrooms are finally cleaned with a wet cloth, and the rest are washed.
Treatment
Mushroom washing is an important step in the processing of fresh mushrooms. It should be borne in mind that with prolonged washing, there is a loss of aromatic and soluble dry substances. Therefore, the washing time must be limited. It is possible to wash the mushrooms well without loss within 10 minutes with running and continuously replaceable water.
To prevent mushrooms from darkening in the air, after cleaning and cutting, they should be stored in a 1 - 2% solution of salt or citric acid. Mushrooms that produce a pungently bitter juice can only be eaten after soaking.
The mushrooms are soaked in cold water, changing the water 2-3 times during the day. Milk mushrooms, podgruzki, volnushki soak for 2-3 days, bitters - up to 8 days in a cool room at a temperature of 14 - 15 ° C to avoid acidification. Morels are soaked, dried or boiled for at least 10 minutes - until the bitterness disappears completely, the lines must be dried for a long time before eating.
Water after soaking is not used for food and is not given to animals. You can not soak the mushrooms in cold water, but blanch at 100 ° C for 7-10 minutes. If the mushrooms are not fresh enough, then before processing fresh or canning, they must be blanched at 100 ° C in saline or a weak solution of acetic acid. Then rinse thoroughly in cold water until the taste of salt or the smell of vinegar completely disappears.
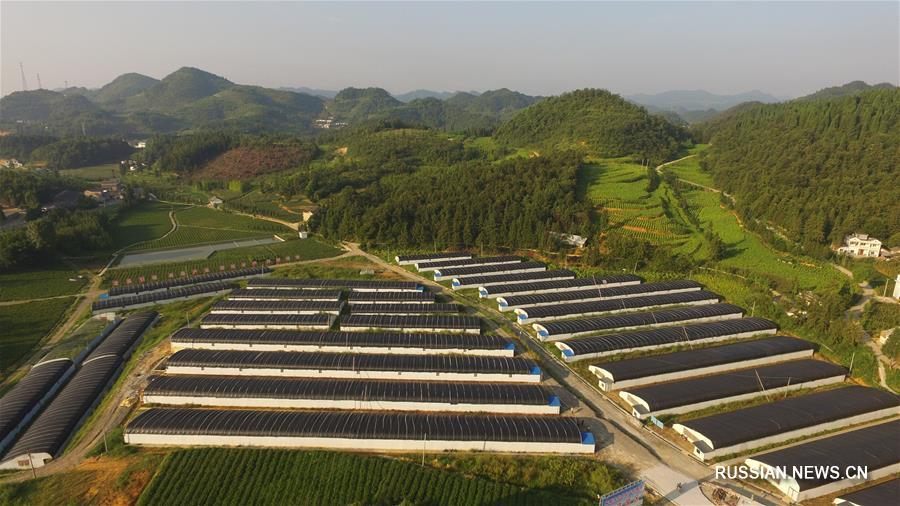
Growing porcini mushrooms indoors
Growing porcini mushrooms indoors, be it a greenhouse, basement or loggia, is much more difficult.
Here you will have to artificially create suitable conditions, so it is important that the room allows you to do this. For planting, it is more convenient to use purchased mycelium, although the method of breeding with spores is also allowed
The Dutch boletus variety, resistant to the artificial environment, is popular among mushroom growers. The whole process of growing mushrooms at home can be conditionally divided into stages.
Room preparation
The first condition for growing mushrooms is a clean room. This can be achieved by regularly treating all surfaces with a 1% chlorine solution to prevent pests and mold.Sanitization must be carried out every day due to the very high humidity - from 90%. All work must be carried out with gloves.
Humidity and temperature control is possible using climatic equipment. But if it is not, it is recommended to install several open containers with water and boxes with sawdust around the perimeter. The sawdust is regularly moistened: they perfectly retain moisture and, thus, maintain the humidity in the room.

Also in the greenhouse, shelves for substrate bags will be useful. Next to each of them, it is necessary to make ventilation holes to ensure air circulation in the phase of active growth of fungi. The hole, if necessary, should be easily and tightly closed. If we talk about the lighting of the landings, then it should be muted. Low wattage fluorescent lamps can be used.
Substrate preparation
The next important stage is the preparation of the substrate in which the boletus will grow. For him, they take waste of wood and plant origin: husk of seeds and buckwheat, straw of cereals, corn stalks and cobs, sawdust and shavings of oak, pine or birch. Additionally put oak leaves, pine needles and bark. The whole mass is thoroughly mixed and crushed.
Further, the substrate is sterilized, but not by boiling, which will destroy most of the nutrients. The mass is steamed for three hours with hot water at a temperature of 70-80 ° C. After the completion of the treatment, all excess water is drained and the mass is left to cool down to a room temperature of 22-25 ° C.
The cooled substrate is checked for readiness - they take a handful of it and squeeze it. A properly prepared substrate should spring back when compressed without emitting water. If excess moisture is present, allow it to drain, even if it takes several days. Waterlogging is unacceptable!
The finished substrate is taken to a sterile room, where it is carefully mixed with the mycelium. Work must be carried out with sterile gloves, ventilation must be turned off and doors must be closed
Then the planting material is placed in sterilized polypropylene bags or specially prepared boxes.
The weight of the bags can be about 8-12 kg. Small cuts 0.5-1.5 cm are made in them on the sides with a sterile knife or blade, you can cross on the cross. Then the bags are placed on shelves at a distance of more than 5 cm from each other so that access to the perforation remains open.
Growing mushrooms
When the bags are stacked on the shelves, the mushroom growing process begins. The incubation period will be from 
As soon as the first caps of the mushrooms hatch, the temperature is lowered to 10 ° C and the ventilation is turned on, which is required for the growth of boletus. The duration of daylight hours is no more than 5-6 hours. Mushrooms are sprayed from a spray bottle twice a day. The first crop is harvested approximately 3-4 weeks after planting.