Mushroom composition, benefits
The mushroom composition contains up to 90% water, and the dry part is predominantly protein. That is why the gifts of the forest are often called "forest meat" or "forest bread".
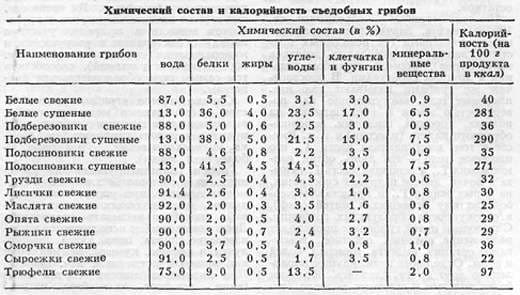
The nutritional value:
- The mushroom protein contains almost all amino acids, and even essential ones. Mushrooms are an important part of the diet, however, due to the fungin content, it is better to exclude them from the menu for people suffering from kidney, liver and gastrointestinal tract diseases.
- Carbohydrates in "forest meat" are much less than protein. A mushroom carbohydrate is different from a vegetable one and is better absorbed, much like a milk or bread carbohydrate.
- Fatty substances are absorbed like animal fats by 92-97%.
- The composition contains tartaric, fumaric, citric, malic and other acids.
- The composition contains a large amount of vitamins PP, B1, A. Some varieties contain B2, C, D.
- Mushrooms are rich in iron, phosphorus, calcium, sodium, potassium.
- The composition contains trace elements - zinc, fluorine, manganese, iodine, copper.
The edible gifts of the forest have many benefits, since ancient times they have been used to treat diseases. Now it is healthy and tasty food, and vegetarians replace meat with them.
Mushrooms are able to increase immunity, cleanse blood vessels and lower cholesterol levels, fight depression and obesity. They help maintain the beauty of hair, skin and nails. Read more about contraindications and beneficial properties of mushrooms on our website.
Why is it undesirable to eat "wormy" mushrooms?
First of all, of course, there is a question of quantity. If you see one wormhole somewhere out there, you can pretend not to notice. If there are a lot of them, if you can see not only holes eaten by worms and larvae, but also the worms themselves, you need to think carefully. And the jokes "mushrooms with meat" are not always to the point, there are so many worms that they are no longer mushrooms with meat, but meat with mushrooms.
Do not get fooled by the advice "hold the mushrooms in salty water, the worms will crawl out."
The worms themselves may crawl out, so the problem is not in them, the eastern cuisine considers all this crawling-wriggling a delicacy. The problem is that all these living creatures not only ate the mushroom, they also digested it, and dumped the digestive products there, in the mushroom. Do you want to eat mushrooms with poop of worms and larvae? It's like eating a chicken with dung or a cow with dung.
Examples, look, everything has already been eaten, we have nothing left! Worm dust and waste:



And, of course, a very important factor is that all these invaders greatly spoil the taste and smell of the mushroom.
Distinguishing a medicine from a poison
Edible mushrooms have been harvested in the forest for a long time, they are known for their beneficial properties, pleasant taste and the store of microelements that have a beneficial effect on human health. But recognizing edible mushrooms is actually not easy.
As such, there are no divisions into "edible" and "non-edible" in mushrooms, there are signs of quality, knowing which one can understand whether the crop is suitable for eating or not.
Those who at school were distinguished by attentiveness and disciplined behavior should know that mushrooms cannot be classified as plants and animals, because mushrooms are a separate group of living organisms. That is why it is more interesting to study them, and to eat more frightening.
On the Internet and on television channels, programs about mushrooms are often shown, where people are trying to find out what kind of creature it is, who appeared from nowhere on planet Earth. There are many guesses, both good and bad, but nothing stops people from getting pleasure from eating mushrooms, but this must be done wisely.

Edible mushrooms are distinguished by light flesh inside, the absence of rings on the leg and not very bright colors. They often lack a pronounced taste and aroma.But do not rely on these properties, because they, nevertheless, are conditional. You can try to compare an edible mushroom from a photo or video, but it is better not to eat those that are in doubt.
The territory also plays an important role. It is better to collect mushrooms in proven places, so there is less chance of throwing poison into the basket. Ask friends, acquaintances, relatives or colleagues at work if they know mushroom spots. This will give you the advantage and confidence in your harvest.
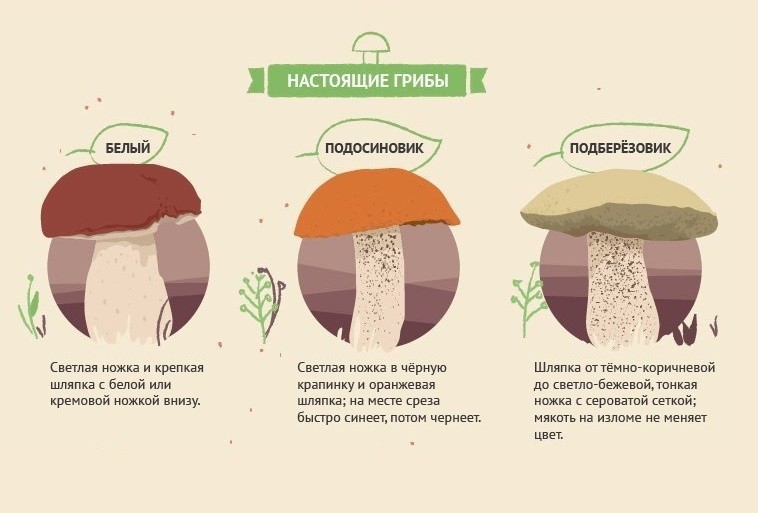
The most common mushrooms are edible and inedible
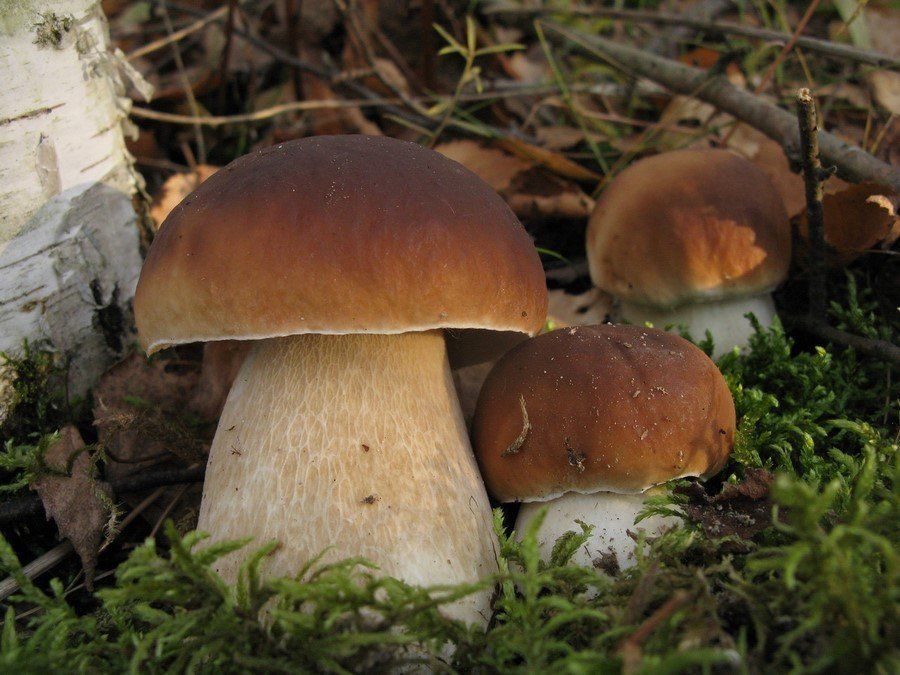
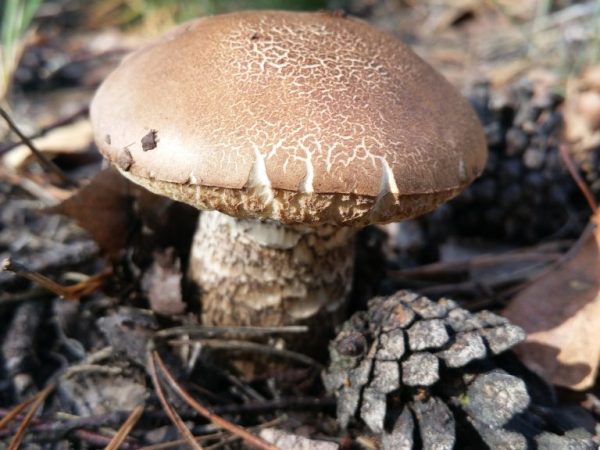
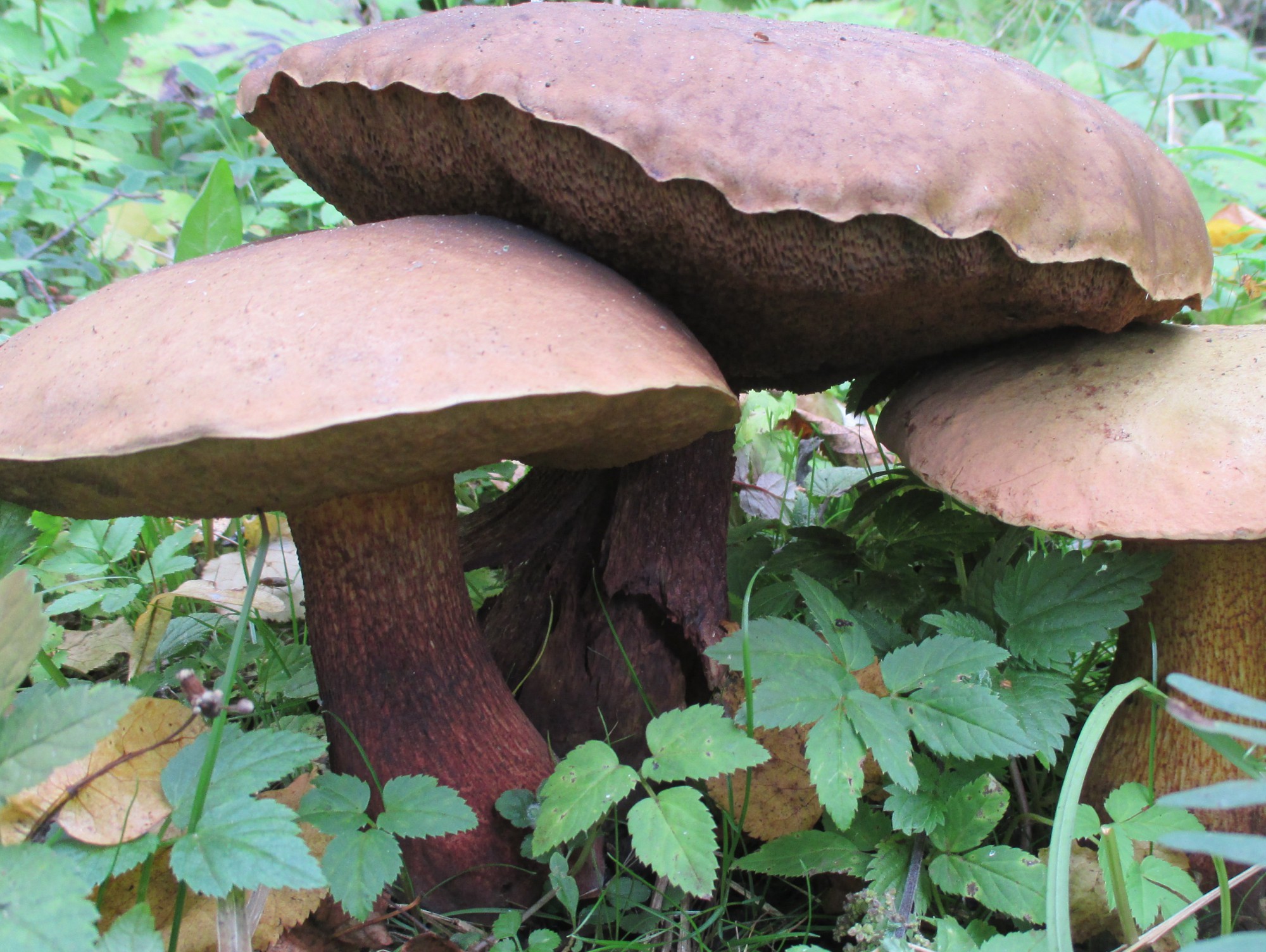
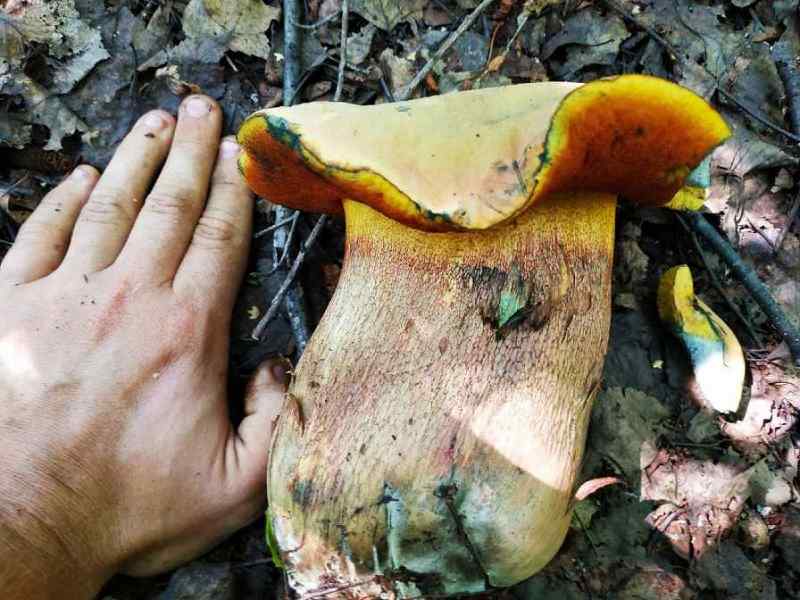
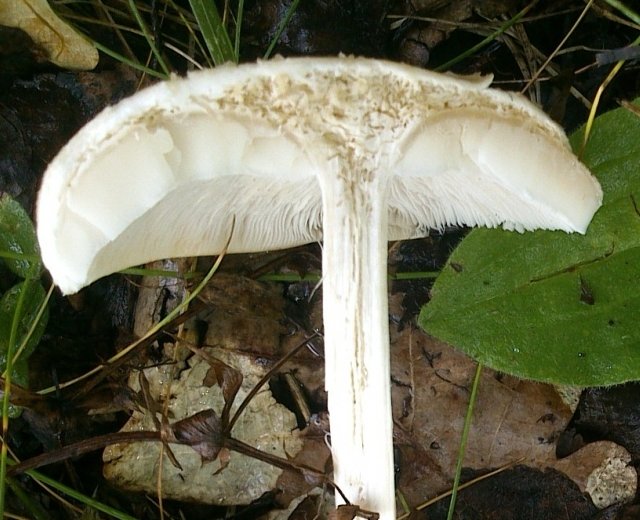
White mushroom, or boletus, is the best representative of the group of undoubtedly edible mushrooms of the first category of nutritional value. Although it has a rather distinctive appearance by which it is easily recognizable, the boletus has an inedible twin - the gall mushroom or bitterness. Edible porcini mushrooms can be identified by their thick, cylindrical stem and reddish brown cap. The flesh of the boletus always remains white, while the gall mushroom is distinguished by the fact that at the break, its flesh acquires a pink tint, and the mushroom itself is very bitter.
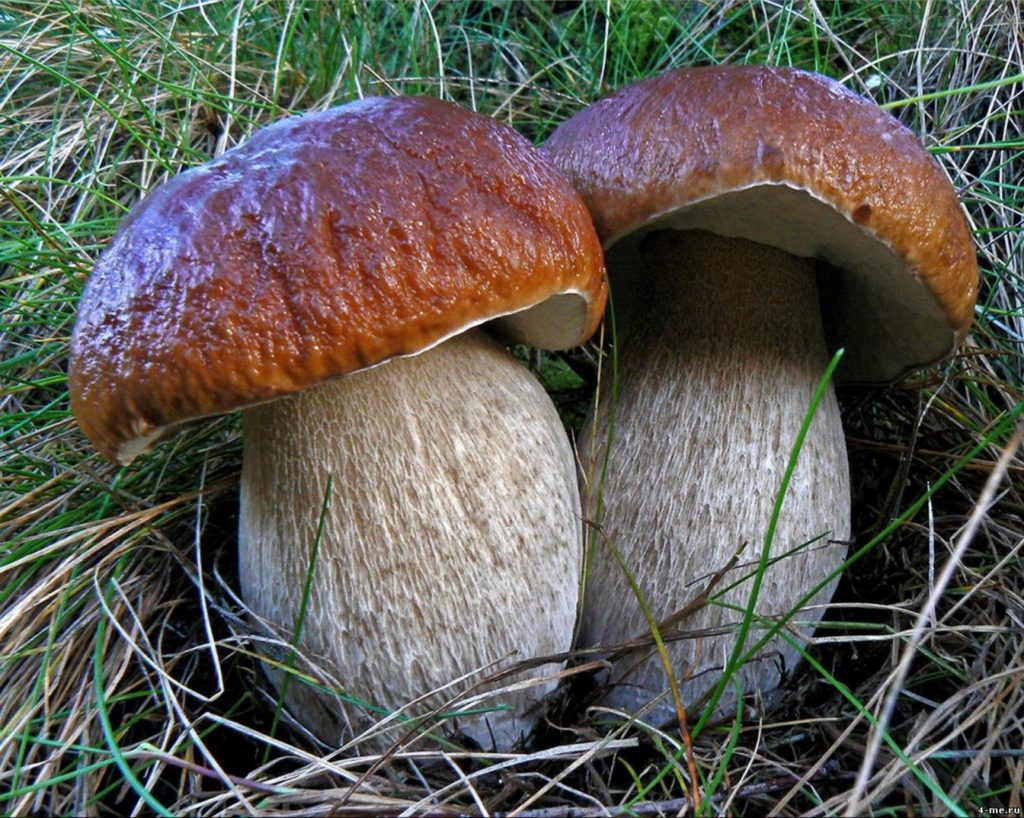
Red boletuses are also edible forest mushrooms that are very popular among Russians. They have a dense brown-red cap. They can be easily distinguished from other mushrooms by their pulp, which quickly turns blue at the cut. Despite the name, they can grow not only next to aspens, but also with other deciduous trees (never next to conifers). But for safety, it is better to collect such mushrooms only under aspen and poplar trees. However, the boletus is rather difficult to confuse with other mushrooms, since it has no false counterparts.

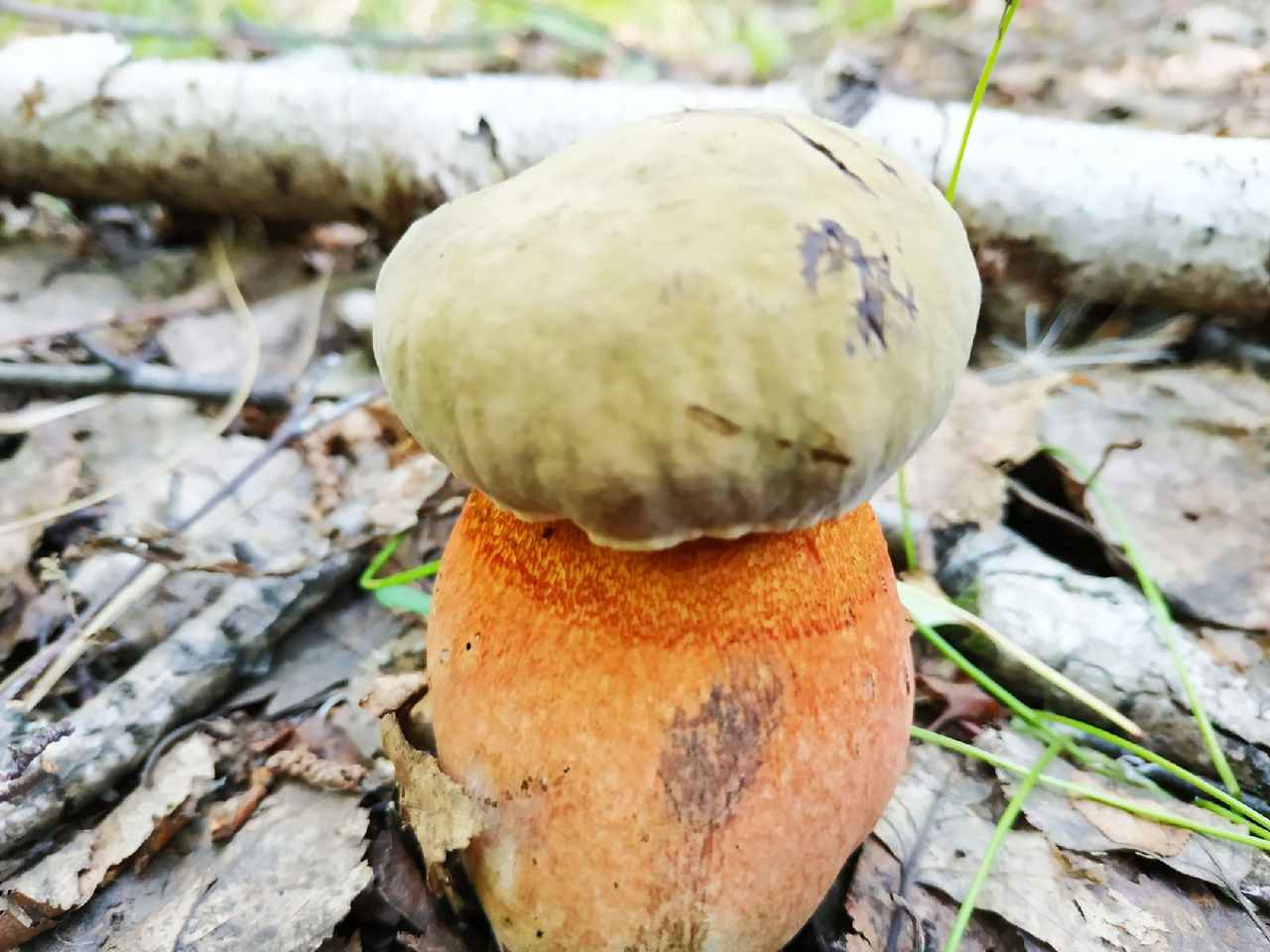
Butterlets are very popular and beloved in Russia. They can be recognized by the yellow color of the legs, and the cap is covered with a sticky brown skin that can be easily removed with a knife. There is a characteristic tubular structure under the head. As a rule, when they talk about edible tubular mushrooms, they mean oil. Adult mushrooms are almost always abundant in worms, which is also a good sign.
Chanterelles have a rather unusual appearance by which they can be easily identified among the rest of the edible mushrooms in the forest. However, they have a very similar twin, which you identify by a more saturated orange hue (the edible mushroom is lighter), a hollow stem (in a real one, it is dense and whole) and white secretions on the break of the cap.

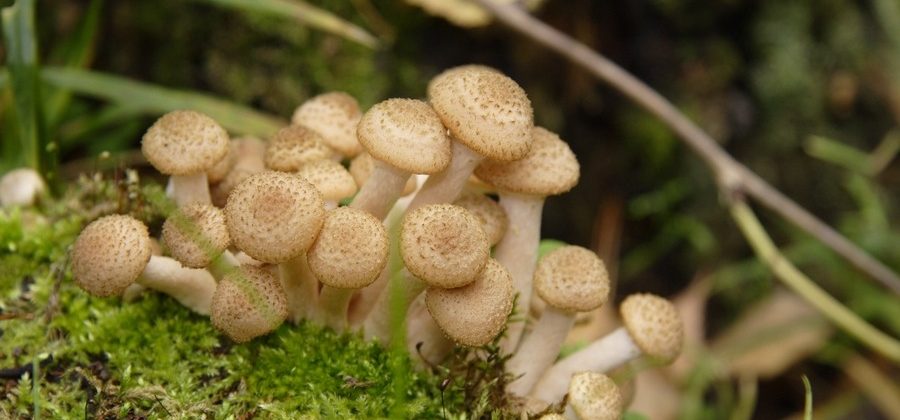
Honey mushrooms are edible mushrooms known for their characteristic rich taste. Since in fact several types of mushrooms are called mushrooms at once, it is sometimes difficult to give them a single description. For safety, it is recommended to collect only those mushrooms that grow exclusively in the roots, on stumps and on fallen trunks. They have ocher-colored caps with scales on it and a white ring on the leg. False mushrooms are also several types of mushrooms. Honey mushrooms should be avoided if they grow on the ground, their cap has a yellow or brownish-red tint and is devoid of scales. While the real honey agaric has a cap with whitish plates, in the false honey agaric they are olive, dark gray or brownish. Also, there is no ringlet on the leg of the pseudo-foam.
Russula are widespread edible mushrooms of the middle lane. This name is used for several species at once, the differences of which from inedible relatives are in the presence of an easily removable skin on the caps.
The most popular mushrooms: how not to make the wrong choice
The distinguishing features of true mushrooms and the species masquerading as them are not always obvious. We understand the features of the most popular mushrooms:
White mushroom (boletus)
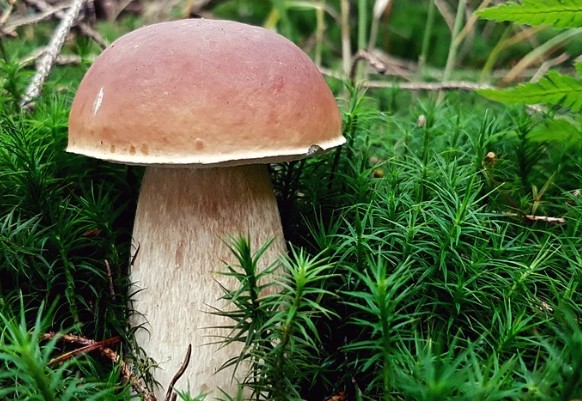

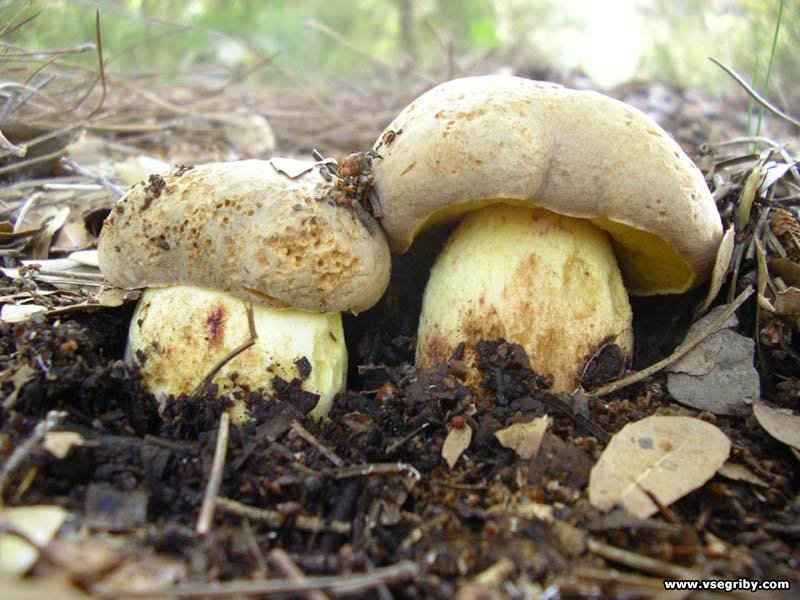
The porcini mushroom has two counterparts - bile and satanic.
Edible porcini mushroom:
The pulp has a pleasant mushroom smell or does not smell at all
Smooth color of the flesh when cut: white, cream
The color of the inner side of the cap is white, yellowish or olive.
All other shades indicate that the mushroom is poisonous.
In an inedible gall fungus:
If you cut the mushroom lengthwise, its flesh will turn pink.
There is a mesh pattern on the mushroom stalk
The inside of the cap is a dirty pink color
In the inedible satanic mushroom:
The hat is velvety and large
The leg is wide, fleshy, red-yellow
Has an unpleasant odor
On the cut it turns red, and then turns blue
Boletus

This mushroom, like the cep, can be confused with the gall fungus.
This boletus boletus has the following distinctive features:
Bright orange and red hat
Pleasant aroma
Black scales on the leg
Turns blue on the cut
Chanterelles
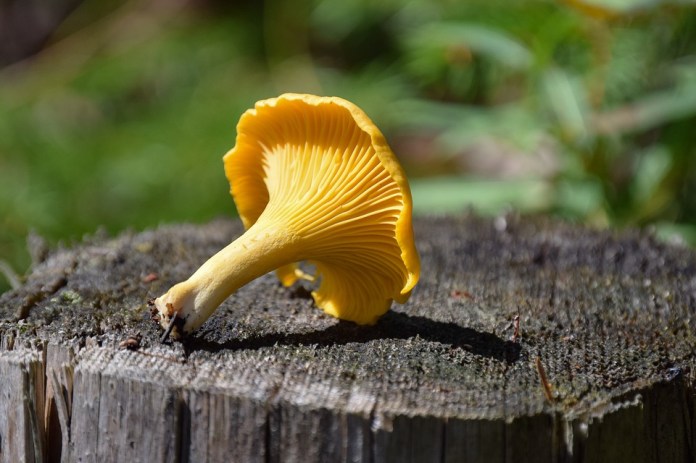

Chanterelles are known for their beneficial properties. Disguised as mushrooms are not poisonous, but the so-called conditionally edible - most often orange talkers. Such mushrooms can cause an eating disorder if they are not cooked properly. Better to refuse them.
Real chanterelles:
They grow in large colonies in meadows Red hat with wavy edges The leg is strong, thick, the same color as the hat The hat and leg merge Pleasant fruity smell In the section you can see the white center and yellow edges No traces of parasite infestation due to chitin mannosis, a toxin harmful to humans
"False chanterelles" or orange talkers:
They grow as single specimens on fallen trees, stumps Hat orange or golden yellow with a funnel shape Hat and leg do not merge, have clear outlines Loose, porous flesh Pungent odor In the context of color does not change There are traces of parasite infestation
Poisonous species
Poisonous mushrooms should not be picked
Avid mushroom pickers are familiar with poisonous species and will not put them in a basket. They know the blacklisted species. But sometimes even the most professional assemblers make mistakes. Before going into the forest, it is better to remember what poisonous and inedible mushrooms are found in the Urals. The most famous and frequently encountered are the following:
- false mushroom;
- Satanic;
- bilious;
- death cap;
- fly agaric;
- yellow-skinned champignon;
- the chanterelle is false.
Death cap
This fungus, not very large and simple in appearance, is dangerous. Its toxins are so strong that they can even penetrate the skin. Therefore, mushroom pickers do not touch the toadstool, they leave it to grow in its place. One touch of her on completely edible mushrooms will make them poisonous.
According to the description, it looks like a russula or mushroom, but there is no "skirt" on the leg. Her hat is whitish or brown-olive. There is almost no smell, completely tasteless. Grows in birch groves from June to the very frost.
Fly agaric
Of the poisonous, fly agaric is especially dangerous. In these forests, rare giant individuals are found, especially after good rains. It is after the rains that it is easy to confuse fly agarics with russula, because the white spots on their caps are washed out by water, they become almost invisible.
- the leg is high and slender;
- the color of the leg is white (or yellowish);
- grow in height up to 23-30 cm;
- the cap is flat, lamellar;
- the surface of the cap is reddish;
- there is a characteristic thin "skirt" under the hat;
- cap size - up to 30 cm.
Sometimes the cap is orange or pink, which makes it look like russula. The pulp is odorless and yellow in color.
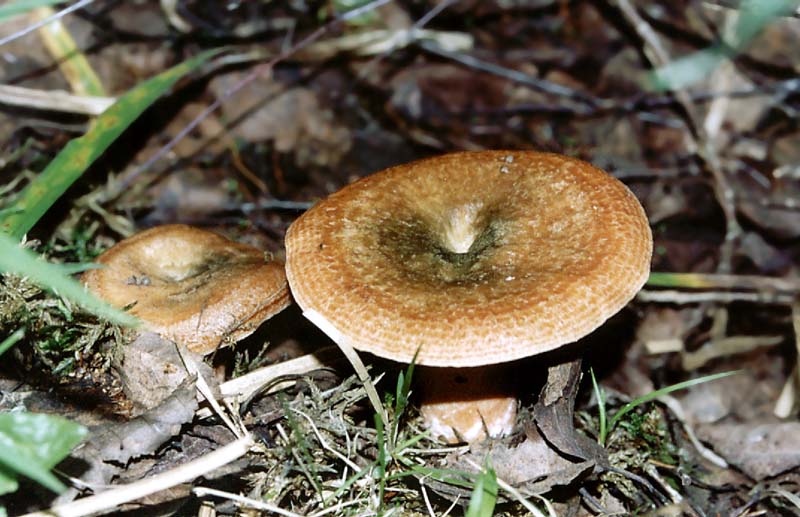
False chanterelle
This representative of poisonous mushrooms grows in conifers. The hat looks like an orange-red funnel. The leg is hollow, cylindrical. These are autumn mushrooms. The mushroom places are the same as in the edible species, the common chanterelle, or cockerel.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
The fact that you cannot eat false chanterelles was an axiom for all mushroom pickers until recently. Recently, evidence has appeared that the false chanterelle (orange talker) has already been classified as conditionally edible mushrooms. But with the following caveats:
- before eating, this mushroom needs a particularly careful pre-treatment;
- people with a weak digestive system are strictly prohibited from eating them.
However, there are no confirmatory factors for the edibility of the orange talker, but there are reports of poisoning with this mushroom.
Weakly poisonous false chanterelles contain toxic compounds that are destroyed under the influence of high temperatures, or, in other words, thermolabile. However, at home, it is impossible to determine whether they all collapsed during cooking and the mushroom became harmless to health. Therefore, it will be safer to treat them as inedible mushrooms.
In the forests of the middle zone, in the mountains of Kamchatka and on the Kola Peninsula, in the forest belts of the North Caucasus and the famous steppes of Kazakhstan, in the regions of Central Asia, more than 300 species of edible mushrooms grow, which lovers of "quiet hunting" like to collect so much.
Indeed, the activity is very exciting and interesting, which, moreover, allows you to feast on the harvested crop. However, you need to know the mushrooms so that poisonous ones do not get into the basket along with the edible ones, using which you can get severe food poisoning. Edible mushrooms with photos, names and descriptions are offered for familiarization to everyone interested in picking mushrooms.
Interesting Facts
- Bluefoot in some countries is considered a delicacy: it is grown and exported.
- Mushroom powder is used in cosmetology to prepare a lotion that can reduce the production of sebum;
- The bluefoot can be cultivated in the home or garden.
- The bluefoot mushroom has a powerful antiviral effect.
Bluefoot is a common mushroom with an unusual color, it has good taste. Great for boiled, fried and pickled. It is noteworthy that mushrooms grow in large groups. More than 10 kg can be collected in one hunt
Before collecting, it is important to familiarize yourself with the double rowing, since most of them are poisonous
Due to the abundance of topics about mushrooms, I decided to write this post.
Characters: neighbors, 4 adults and 4 children (Lesha 11 years old, Zhenya 8 years old, Tanya- (This is me) 4 years old and Lena 4 years old)
It was back in 90, when I was 4 years old, so I am telling you from words, because I myself remember vaguely. For fun, and not for profit, two families went to the forest (Krasnodar Territory), and along the way to pick up mushrooms. It was in early October, they were collecting honey agarics. Having walked pretty well in the forest, we stopped by a familiar mushroom scientist to check the catch for edibility. He weeded out the dubious, and gave the go-ahead for the rest.
As usual in our area, after such events, a feast follows. Everyone went about their business and after a while everyone was already sitting at the table on which there was a huge frying pan of fried potatoes with freshly picked mushrooms, and of course a bottle of forty degrees.
The gatherings lasted for a long time, the children played in the next room, sometimes running for some delicious potatoes, and the adults were already using it only as a snack.
Closer to the next day, everyone went to bed, the party was a success !!! In the morning, after drinking, my parents were not very good, they did not get out of bed, although I really asked to play with me. Well, okay I thought, I can handle it myself
In the evening, a neighbor who did not participate in yesterday's gatherings came to visit us, seeing that the parents felt bad, said that the same picture was with the neighbors opposite. Then, even without even having a home phone, the parents could not associate this condition with mushrooms, but attributed it to badun.
A neighbor ran to the nearest phone and called an ambulance.
The ambulance took everyone to the hospital, after an examination, they let me go home, my mother says that “yesterday” I asked to choose only potatoes, and even the mushrooms that came across, carefully left on the edge of the plate. The rest with severe poisoning were placed in wards, the degree of poisoning depended on the amount of alcohol drunk, the principle worked here more drank - less poisoning, respectively, the children were in a more serious condition.
Parents were constantly interested in the condition of their children, offered to buy medicines that were not enough, asked if there was enough, in general they did not sit still. But they were told that everything was under control ………
On the 3rd day of his stay in the hospital, Zhenya died, I will not say how shocked everyone was, then I did not understand this, but now I can only imagine. Only after that, Lesha and Lena were urgently transferred to intensive care. They were in serious condition for a long time, but gradually they got out.
Doctors said that there had never been such a general poisoning, that Krasnodar hospitals were overcrowded that year.
Many years later, our families communicate in the next generation, but this topic is closed for discussion ………
As for me, I still don’t understand why I didn’t eat mushrooms, it seems I have a guardian angel !!!! Since then, I have not eaten mushrooms, only this year my husband forced me to overcome my fear. We went, collected the whites.
My friend Zhenya will forever remain in my memory, for me he was then an adult mentor. We spent a lot of time together. He taught me to collect flowers, catch butterflies, cut rain out of paper !!!!! Mom says we were inseparable.
They ask me "after all, you were little, how do you remember him?" Zhenya's funeral, he would be 33 now! Rest in peace Zhenechka !!!
Only please, do not have a shit about the mountain parents, they already know this, they curse that day, those mushrooms, those potatoes to this day. I just shared a story from my life.
Mushrooms
Mushroom places of the Rostov region
Throughout the Rostov region, mushrooms are found quite often - there is a suitable soil for them and a favorable climate. But in some places, mushroom hunting can be especially successful. First of all, these include:
- Millerovo region, especially the vicinity of the village of Dyogtevo, pine plantations of the town of Millerovo;
- environs of the city of Kamensk-Shakhtinsky;
- Chertkovsky district;
- there are a lot of different mushrooms in the pine plantations of the Nizhnekundryuchenskaya stanitsa;
- Tarasovsky district;
- Semikarakorsk region;
- the coastal area of the Don;
- Schepkinsky forest in Rostov-on-Don.

Did you know? Mushrooms
—some of the most ancient creatures on Earth, because their age exceeds 400 million years. They existed along with ferns back in the days of the dinosaurs, but, unlike ferns, they not only did not die out, but did not even shrink. It is believed that all the species that existed in prehistoric times have survived to this day.
Unusual mushrooms of the world: names
Despite the fact that Russia is a truly mushroom country, very unusual specimens can be found not only here, but all over the world.
We offer you several options for unusual edible and poisonous varieties with photos and names (Figure 8):
- Blue is a bright azure color. Found in India and New Zealand. Despite the fact that its toxicity is poorly understood, it is not recommended to eat it.
- A bleeding tooth is a very bitter variety that is theoretically edible, but its unattractive appearance and bad taste make it unsuitable for food. Found in North America, Iran, Korea and some European countries.
- The bird's nest is an unusual New Zealand variety that really resembles a bird's nest in shape. Inside the fruiting body there are spores that spread around under the influence of rainwater.
- Blackberry is also found in Russia. Its taste is similar to shrimp meat, but outwardly resembles a shaggy heap. Unfortunately, it is rare and listed in the "Red Book", so it is grown mainly artificially.
- The giant golovach is a distant relative of the champignon. It is also edible, but only young specimens with white flesh. It is found everywhere in deciduous forests, fields and meadows.
- The devil's cigar is not only a very beautiful, but also a rare variety that is found only in Texas and several regions of Japan.

Figure 8.The most unusual mushrooms in the world: 1 - blue, 2 - bleeding tooth, 3 - bird's nest, 4 - blackberry comb, 5 - giant bighead, 6 - devil's cigar Another unusual representative is the brain tremor, which is found mainly in temperate climates. You cannot eat it, as it is deadly poisonous. We have given a far from complete list of unusual varieties, since specimens of strange shapes and colors are found all over the world. Unfortunately, most of them are inedible.
An overview of the world's most unusual mushrooms is shown in the video.
When and where mushrooms grow
In Russia and the CIS countries, mushroom areas are found almost throughout the territory, from the tundra to the steppe zones. Mushrooms grow best in humus-rich soil that warms up well. The gifts of the forest do not like strong waterlogging and excessive dryness. The best places for them are in the clearing, where there is shade, on the edges, forest roads, in plantings and copses.

If the summer is rainy, mushroom places should be looked for on a hill, and if it is dry, near trees in the lowlands, where there is more moisture. Typically, specific species grow near specific trees. For example, camelina grows near pines and spruce; white - near birch, pine, oak; aspen boletus.
Mushrooms in different climatic zones appear at different times, one after the other. Let's analyze the middle lane:
- The first spring forest harvest - stitches and morels (April, May).
- In early June, boletus, boletus, boletus, russula appear. The duration of the wave is about 2 weeks.
- From mid-July, the second wave begins, which lasts 2-3 weeks. In rainy years, there is no break between the June and July waves. The mass appearance of the mushroom harvest begins in July.
- August is marked by a massive growth of mushrooms, especially white ones.
- From mid-August to early autumn, huge families of chanterelles, mushrooms, milk mushrooms grow in favorable weather.
In deciduous forests, the main season lasts from June to October, and from November to March, winter mushrooms can be found in the forests. In the steppes, field mushrooms are more common: umbrellas, champignons, a raincoat, meadow mushrooms. The season is from June to November.
Evaluation of taste, medicinal properties, benefits and possible harm
Blue feet have excellent taste. Their flesh resembles chicken meat and is similar to young mushrooms. It has antibacterial, antioxidant, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
Rowing advantages:

- has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system;
- relieves chronic fatigue, headache;
- normalizes blood sugar levels;
- increases physical and mental activity;
- normalizes the work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- removes toxins and toxins;
- strengthens the immune system.
In folk medicine, the bruise is used to make antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. An extract is created from the mycelium, which reduces the activity of cancer cells. Infusion and lilac-footed rowers are used to prepare various ointments for the treatment of skin diseases. Doctors recommend eating mushrooms for nervous disorders and diabetes. Rowing is useful for people suffering from diseases of the liver and genitourinary system.
Eating raw blue feet can cause serious disorders. Overgrown mushrooms absorb various harmful substances: copper, mercury, cadmium, pesticides. Eating such mushrooms leads to flatulence, pain and heaviness in the stomach. It is not recommended to eat many catnip with low acidity. Serious contraindications are: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, chronic gastrointestinal diseases and gallbladder dysfunction.
Composition and calorie content
This type of mushroom has a varied composition:
- minerals - calcium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, sodium, zinc, manganese, iron, copper;
- vitamins - a group of vitamins B, betaine, choline, ascorbic acid, vitamins A and D;
- amino acids - there are 18 amino acids in the rows (the highest concentration of lysine, threonine, alanine, phenylalanine, glutamic, aspartic and stearic acids);
- natural antibiotics - clitocin and fomecin;
- polysaccharides;
- phenol is an antiseptic substance.
How to distinguish forest mushroom from pale toadstool
This mushroom can be confused with the very poisonous pale toadstool. The real champignon has a dry, smooth or slightly scaly rounded cap, white or grayish in color. The plates under the cap darken when touched. In the case of the pale toadstool, the plates do not change color. In addition, the toadstool has absolutely no bag-like film at the base of the leg, which is characteristic of an edible champignon. And one more clear sign of the difference - real champignons grow in open, well-lit places, on the edges or along forest roads, in swampy areas and even in a vegetable garden. And pale toadstools love deciduous forests.
To paraphrase a well-known expression, we can say that mushroom picking is a delicate matter. Each season of the collection of this delicacy, a huge number of mushroom pickers end up in a hospital bed. And all because they could not distinguish edible mushrooms from poisonous or inedible ones. Experienced lovers of quiet hunting can also make a mistake. But an experienced mushroom picker will never take a mushroom if there is even the slightest doubt about its quality.