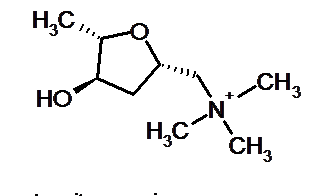How does muscarine poisoning manifest?
Signs of poisoning with pure muscarine and poisonous mushrooms containing this substance can be very different. This is due to the fact that toadstools also contain other toxins that can cause new symptoms, enhance or block the action of muscarin itself. Therefore, the use of fly agarics almost never gives a clinical picture of muscarine poisoning.
By the way, to get a lethal dose of muscarine from red fly agaric, you have to eat about 3-4 kg of freshly picked mushrooms without heat treatment, since the substance decomposes under the influence of high temperature. Few people are capable of such a "feat".
The rate of manifestation of muscarine poisoning depends on the dose received. Usually, the first signs appear about 0.5-2 hours after the toxin enters the body. The main symptoms include:
- Strong and rapid constriction of the pupils and the development of false (reversible) myopia, which leads to a spasm of accommodation;
- Uncontrolled salivation and lacrimation, severe sweating;
- Sharp twisting pain in the abdomen, accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea;
- Trembling in the body and convulsions (in case of poisoning with piece muscarine);
- Rapid decrease in blood pressure;
- Difficulty breathing.
Treating muscarine poisoning
The antidote to muscarine is atropine. Muscarine receptors are blocked under the influence of atropine. In turn, muscarine is an antidote (or antagonist) to atropine, so these alkaloids are so-called mutual antagonists.
Antidotes for this mushroom poison can also be:
-
aconitine alkaloid contained in aconite;
- veratrin;
- hyoscyamine;
- physostigmine;
- digitalin;
- camphor;
- chloral hydrate.
The antidote effect of atropine is due to paralysis of the parasympathetic nerves.
Atropine also stops the increased peristalsis of the stomach, the activity of the salivary glands. In order for the antidote effect to be activated, only 0.1 grams of atropine is needed.
In addition to using the antidote, treatment consists of the following procedures.
- To reduce the amount of muscarine in the blood, infusion therapy is used - the introduction of intravenous solutions of glucose, electrolytes, blood plasma substitutes.
- To remove muscarine from the intestines, castor oil, enemas, and heating pads are prescribed.
- With the help of abundant drinking, diuresis is caused.
- Camphor and caffeine are used to stimulate cardiac activity.
- Oxygen supply prevents the development of respiratory failure.
The prognosis for mushroom poisoning with muscarine is much more favorable than for pale toadstool. However, when the patient is in a prolonged unconscious state and a drop in cardiac activity, the prognosis worsens. In favorable cases, recovery occurs on the second or third day. In the worst cases of poisoning and with a progressive drop in cardiac activity, death can occur after a few hours or on the second day with symptoms of respiratory failure.
So, muscarine poisoning is a rather serious condition, which, however, is effectively treated in modern conditions. Timely seeking medical help is the key to successful treatment.
Characteristics of muscarine

The structure of the toxin has not yet been established, so chemists use the empirical formula of natural muscarine. An alkaloid is a thick liquid of neutral odor and taste with basic PH values. If, after drying, a few drops of any inorganic acid are added to the dry mixture, a violent chemical reaction will occur. It will result in the formation of small, colorless muscarine crystals that are unstable in the open air.Just a few minutes is enough for the alkaloid to lose its solid form and take on a syrupy appearance.
Muscarine is capable of rapidly dissolving in aqueous and alcohol-containing liquids, but in ethers it is absolutely insoluble. The poisonous substance manifests itself in the process of chemical reactions as follows:
- At the boiling point of water, the alkaloid decomposes to form a faint tobacco smoke aroma.
- If liquid muscarine is treated with lead oxide or a strong base, a tertiary amine is formed, which is flammable and hygroscopic.
- Sulfuric and hydrochloric acids hydrolyze the alkaloid, turning it into colorless crystals.
Scientists tried to isolate natural muscarine at the beginning of the last century. Poisonous compounds were obtained from the urine of rabbits, cats, as well as the decaying corpse of navaga. But they are all just isomers of mushroom muscarine. This does not interfere with combining all alkaloids into one group and not abandoning attempts to synthesize an artificial toxin, which would be a complete analogue of the poison from fly agaric.
First aid to the victim
If someone close to you is poisoned by mushroom muscarine, the very first action is to call an ambulance. While the doctor is in a hurry to see the patient, it is necessary to urgently provide standard first aid for poisoning - to rinse the stomach. The procedure is as follows:
- We sit down the patient, give him 3-4 glasses of warm water to drink. Then we press on the base of the tongue with two fingers or tickle the back of the pharynx. This will provide a gag reflex, and the liquid will come out along with the poison.
You need to drink plenty of water
- We repeat several times until the water is clear. If you are not sure what kind of poison a person received with muscarine, it is better not to take risks with sorbents. And use clean water.
- Muscarine, like other toxins, is absorbed most rapidly in the intestines, so a laxative is needed. The best option is cheap and safe castor oil.
- When the stomach and intestines are completely cleansed, it is time for sorbents. Ordinary activated carbon has an effective effect. You need to crush it into powder (a tablet per 1 kg of weight) and drink.
First aid for poisoning

The lethal dose of muscarine is 0.5 g. If even minor symptoms of poisoning occur, an ambulance should be called immediately. Before the arrival of the doctor, it is necessary to alleviate the condition of the victim by taking the following measures of assistance:
- lay the person on his side, calm him down;
- induce vomiting with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate until clear water leaves the stomach;
- give the victim toxin-binding drugs: adsorbents or enterosorbents.
Strong sweet tea binds muscarine well, since it contains a lot of tannin. The doctor, if necessary, will hospitalize the patient, inject him with an antidote, put on a drip with salt and glucose solutions. You can not carry out self-treatment with the use of antispasmodics or diuretics. Ignorance of the mechanisms of poisoning will lead to serious complications, death of a person.
Symptoms and stages of poisoning
Consuming pure muscarine and mushrooms containing it leads to completely different consequences. So, in the same toadstools, in addition to this substance, there are others in the composition, which together causes a completely new symptom complex.
Due to the fact that muscarine does not penetrate the central nervous system, it does not cause hallucinations, delirium, increased agitation and other reactions that are characteristic of mushroom poisoning. As a rule, the first negative symptoms are noticeable 1-2 hours after the ingestion of the poison.
Negative symptoms that are caused by the ingress of toxin into the body:
- nausea, vomiting;
- a sharp narrowing of the pupils;
- excessive sweating, hypersalivation;
- false myopia;
- sharp abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- trembling in the body, turning into tetanic convulsions;
- labored breathing;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- in especially severe cases - collapse as a frequent manifestation of acute vascular insufficiency.

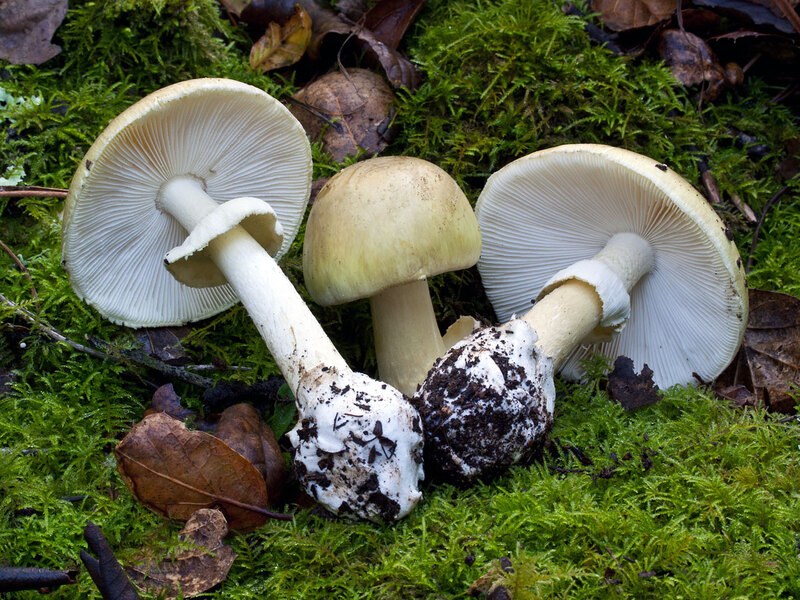
Where is muscarine
Mushroom lovers need to know which mushrooms contain muscarine so that they do not accidentally fall into the basket.
pigs
In addition to fly agaric, a dangerous substance is contained in whitish talker, fibrous, as well as in mushrooms of the spiderweb genus. Among them - gebeloma, fire.
The presence of muscarine in pigs has also been proven. This conditionally edible mushroom is very cunning. So, overgrown specimens are capable of accumulating muscarine. It has been proven that under favorable conditions for growth, muscarine can accumulate in a slender pig in a sufficiently large amount. So it is best to refuse to use pigs. You should not collect a fat pig either, as it accumulates a lot of toxic substances, and even has a very mediocre taste.
Muscarine Poisoning Symptoms

Signs of intoxication:
- Increased body temperature, fever, chills.
- The digestive system is disrupted. There is a feeling of nausea, vomiting, painful sensation in the stomach.
- With a slight use of the poison, sour belching, increased gas formation, a bitter taste in the mouth, diarrhea appear.
- Bright blush on the cheeks, heavy sweating, pale and dry skin, dilated pupils.
- Slow heart rate, slow and threadlike pulse, shallow, difficult breathing.
- Dysfunction of the organs of the excretory system appears. The color of urine is dark with a pungent, unpleasant odor.
- There is a decrease in blood pressure to a minimum. Increased risk of collapse due to low volume and rate of blood flow through the body.
A quarter of an hour after the development of intoxication, the patient develops a tremor of the extremities, which turns into intense convulsions. There is an unreasonable feeling of anxiety, increased drowsiness, dizziness. After 30 minutes, there is a violation of coordination of movement, a decrease in reflexes.
The main sign of an overdose is a spasm of the eye muscles, which causes a decrease in vision, the appearance of myopia. Respiratory dysfunction and cardiac arrest are the leading causes of death.
In acute poisoning, the patient's negative state continues for 2 days, and then death occurs.
Where is muscarine found
The main site of localization of muscarine and similar poisons are fly agarics. More than 150 years ago, it was found in these mushrooms and then synthesized artificially. Thus, it can be found not only in nature, but also as a pure toxin obtained in laboratories, where today it is produced in two varieties. The first is an exact copy of the mushroom poison, the second is created from choline (a vitamin-like substance from which acetylcholine is synthesized in the body). Poisoning by these two species manifests itself in almost the same way, but there are slight differences, which are due to the different chemical structure.
You can get muscarine from fresh fly agarics using alcohol. In its pure form, it is a colorless viscous liquid with an alkaline reaction, which has neither taste nor color. It is easy to transfer it to various other states. So, if it is placed over sulfuric acid and dried, it will become crystals, and if it is placed back in the air, it will again turn into a thick syrup. At a temperature of about 100 ° C, the poison is destroyed.
It should be noted that in nature this substance is present only in mushrooms, but in very small quantities. For example, the fly agaric contains only 0.0003-0.02 g of poison, which is not enough to obtain severe intoxication.

When is medical attention needed?
With mild muscarine poisoning, the symptoms are not too pronounced, they usually disappear within a day, and the condition of the victims improves.However, it is impossible to independently determine the severity of the poisoning, therefore, it is always necessary to seek medical help if you suspect muscarine poisoning.
It is especially important to do this quickly when the poisoning occurs with intense symptoms or happened in a pregnant woman, elderly person or child.
In the hospital, the victims are washed with a gastric tube.
The antidote to muscarine is atropine. The dose and frequency of administration is determined by the doctor, taking into account the degree of poisoning and the individual characteristics of the patient.
In addition to specific therapy for muscarine poisoning, drug correction of existing disorders is carried out.
Complications and prevention
Recovery reactions in the body are slow. In the blood, a persistent increase in the level of leukocytes is observed for a long time, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Also, the consequences include a slowed down process of blood coagulation.
Taking foods containing muscarine during pregnancy increases the risk of early labor or miscarriage due to severe intestinal spasm.
Muscarine poisoning requires immediate treatment, otherwise the patient becomes comatose. Death is diagnosed in 1.5-2 days due to cardiac arrest and severe edema of the respiratory system
At the first signs of intoxication, it is important to provide first aid and go to the hospital for further treatment, recovery of the body
What is Muscarine
Muscarine is an alkaloid that is extremely hazardous to health. It was discovered in the 19th century in the red fly agaric. The fungus is often found in the forests of the European continent and Siberia. It is noteworthy that fresh fly agaric is poisonous to flies, but in dried form it is absolutely harmless to them.
Until now, scientists do not fully know what muscarine is, since many peoples use it for food or for medicinal purposes. Thus, the indigenous peoples of Kamchatka make a drink with intoxicating properties from fly agarics. In addition, other alkaloids with toxic properties have been found in the fly agaric.

Muscarine - an alkaloid is a colorless liquid, very thick and gradually turning into crystals when dried in the presence of sulfuric acid. In air, the crystals become liquid again. It dissolves well in water and ethyl alcohol. Muscarine is destroyed by heating, contact with alkalis, lead oxide.
What is Muscarine?
The structure of the toxic compound has not been established. It is for this reason that chemists use the natural muscarine formula. The appearance of an alkaloid substance is a thick liquid with a neutral odor and taste. The state of the poison is variable.
Scientists have synthesized muscarine in the laboratory. The fact was noted that the artificially created toxic substance is significantly different from the natural one found in fresh poisonous mushrooms. Experiments on animals have shown that natural and artificial muscarine cannot be called identical in properties. The toxic substance is readily soluble in water, alcohols, and insoluble in ethers.
Useful information! The toxin acts on the cranial and spinal nerves. This fact helps scientists to invent and find new methods of treating the studied diseases, but it is not used in pharmacology.
The toxin is contained in the fly agaric, but not in sufficient quantities to get severe intoxication. Muscarine poisoning is obtained when pigs are introduced into food. They contain the greatest amount of toxin that can develop intoxication. Also, poison is contained in whitish govorushka, lamellar toadstools, fiber.
Literature
| Tropane | Atropine • Hyoscyamine • Scopolamine • Cocaine • Ecgonine |
| Piperidine | Koniin • Lobelin • Piperine |
| Quinolizidine | Cytisine • Pachikarpin |
| Pyridine | Nicotine • Anabazine |
| Isoquinoline | Morphine • Codeine • Tebaine • Papaverine • Licorin |
| Quinoline | Quinine • Quinidine • Echinopsin |
| Indole | Serotonin • Psilocin • Psilocybin • DMT • 4-HO-MET • 5-MeO-DMT • Bufotenin • Garmin • Harmaline • Physostigmine • Ergotamine • Ergometrine • Yohimbine • Reserpine • Mitraginine • Ibogaine • Strychnine • Brucine |
| Pudding | Xanthines (Caffeine • Theobromine • Theophylline) • Saxitoxin |
| Phenylethylamine | Catecholamines (Norepinephrine • Adrenaline • Dopamine) • Ephedrine • Pseudoephedrine • Norephedrine • Cathine • Cathinone • Mescaline |
| Terpenes | Aconitine • Delfinin • Elatin |
| Other | Pilocarpine • Muscarine • Muscaridin • Colchicine • Galantamine • Capsaicin • Solanine |
| This is a draft article on toxicology. You can help the project by supplementing it. |
| This is an article on organic matter. You can help the project by supplementing it. |
Poisoning symptoms
It is impossible to poison yourself with pure muscarine, since this poison is not used in medicine. Therefore, the only source from which the alkaloid enters the human body and causes poisoning is the eaten mushroom. The picture of poisoning may be similar to that described above or differ from it, since the mushroom mushroom also contains other poisonous substances. They sometimes stop the action of muscarine. Symptoms of poisoning appear 0.5 to 2 hours after the poison has entered the body.
Therefore, a person who has been exposed to poisons, or suffers from pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. But sometimes the mushroom acts in a different way: it becomes very intoxicated. Then the following symptoms make themselves felt:
- excitement accompanied by delirium;
- dizziness;
- sweat, saliva, tears flow;
- a person has a desire to destroy everything;
- he wants to move a lot, break everything, destroy everything;
- then a tremor passes through his body, convulsions, pupils dilate, breathing is disturbed, body temperature drops and a person develops a collapse.
The lethal amount of an alkaloid for humans is 0.5 - 0.7 g, which is usually contained in 3-4 kg of fresh red fly agaric. There are cases when these mushrooms caused hallucinations. But they have nothing to do with the action of muscarine, because this poison does not act on the central nervous system, they are caused by other poisons. And the effect of psilocybin mushrooms is precisely to induce visions.

Hay dung
If a person has tried poisonous psilocybin mushrooms, that is, bluish konosib, hay dung, visible flakes, etc., popular hallucinogens, then the symptoms of poisoning will be different. They peak after 4 hours. A person has hallucinations, visual illusions, anxiety, agitation, etc. All these symptoms disappear in 6-12 hours.
Method of administration and dosage
In ophthalmic practice - 1 or 2% solution 2–4 times a day, less often 5 and 6% solutions are prescribed. Before going to bed, you can put 1 or 2% ointment behind the eyelids. Systems with prolonged release of pilocarpine (eye films) 20 or 40 mcg are prescribed in cases when 3-4 times instillation per day is not enough to normalize intraocular pressure; the film is placed with eye tweezers behind the lower eyelid 1-2 times a day (immediately after that, the eye should be kept motionless for 30-60 s, until the film is wetted and transitions to a soft state).
Muscarine Poisoning Symptoms
Muscarine poisoning has the following symptoms:
 profuse sweat
profuse sweat
- copious secretion of saliva;
- profuse sweat;
- severe redness of the face;
- nausea and vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea;
- heart rhythm disorders;
- lowering blood pressure up to a collaptoid state (a life-threatening condition with a deterioration in the blood supply to all organs);
- contraction of the bronchi and significant secretion of the bronchial glands lead to the fact that there is difficulty in breathing, blue discoloration of the skin, convulsions.
Such symptoms appear within 15-30 minutes after taking muscarine inside.In pregnant women, the alkaloid leads to lactation, that is, to the separation of milk
Attention is drawn to a visual disorder caused by a spasm of accommodation - false myopia. In this case, the victim sees all objects indistinctly, his field of vision is blurred
During the day, the condition of the poisoned improves. However, in some cases, the poisoning progresses and death occurs. The cause of death is respiratory distress. The prognosis for mild muscarine poisoning is significantly improved.
Hospital treatment
A specific antidote is Atropine, which blocks muscarinic receptors. The drug is administered subcutaneously in an amount of 1 ml with an interval of 10 minutes (according to indications). Under the influence of Atropine, gastrointestinal spasms are relieved, the pupil dilates, sweating and salivation stops, and the bladder normalizes.
Other muscarine antagonists: Camphor, Adrenaline, Chloral hydrate, Veratrine.
If poisoning with muscarine occurs, treatment is carried out by intravenous infusion of glucose solutions and plasma substitutes in order to purify the blood. To remove fluid from the body, they resort to the appointment of diuretics. In order to maintain cardiac activity, Camphor and Cordiamin are used. In the event of a malfunction of the respiratory system, the patient is provided with oxygen.
The value of muscarine for medicine and toxicology

Natural mushroom alkaloids, like synthetic ones, are not used for the treatment of diseases. In pharmacology, medicine, toxicology, studies of muscarine are being carried out for possible use as a medicine. Several decades ago, doctors tried to use a toxic compound to relieve symptoms of epilepsy, benign and malignant neoplasms.
An alkaloid belongs to a type of parasympathicotropic toxins. This group of poisons stimulates the peripheral nervous system, showing a selective effect. This rare ability opens up great prospects for further study of the physicochemical properties of muscarin, its possible use in the treatment of various pathologies.
The toxic compound is used in experimental studies to study the functional activity of cholinergic processes, the structure of cholinergic receptors. After the introduction of small doses of alkaloid, amphibians were diagnosed with a violation of the heart rhythm. If the amount of poison used was above average, then the systolic contractions at first slowed down and became weaker. And the diastolic phase was characterized by complete cardiac arrest. Muscarine, isolated from mushrooms, has the following properties:
- increases the secretion of bile, increases the secretion of pancreatic juice;
- activates the glands located in the gastrointestinal tract;
- increases the activity of the salivary, sweat and lacrimal glands.
Muscarine irritates the nerve endings, provoking an increased work of any gland. The study of the alkaloid allowed scientists to synthesize an effective antidote. With the introduction of the antidote at various stages of poisoning, complete recovery of the victims was noted.
What is Muscarine

Muscarine formula
This toxic substance became the first mushroom toxin obtained by chemical means - back in the 70s of the XIX century. The first drug came out with many impurities of other alkaloids, but the scientists did not calm down. And after several decades, they still received a pure toxin and thoroughly found out its properties.
The source of muscarine is the most common red fly agaric with white spots, the most beautiful and deadly mushroom that grows in almost all forests of our country. Today, in chemical laboratories, 2 muscarinic varieties are used: a natural preparation (natural, or mushroom) and an artificial one. The latter is obtained from vitamin-like choline. The action of the two subtypes of mushroom poison is slightly different.
Natural muscarine
Natural muscarinic poison is removed from fresh fly agarics using regular alcohol. It looks like a viscous colorless liquid, alkaline, practically odorless and tasteless. A substance easily passes from one state to another. If you dry it over sulfuric acid, it will turn into crystals, return it to the air - it will again become a thick syrup. And if you heat the mushroom toxin to 100 ° C, it will collapse.
Where is muscarine found
It is often said that muscarine contains the mushroom fly agaric. However, this is an erroneous conclusion. There is indeed muscarine in fly agarics, but there is very little of it. Therefore, not only muscarine is responsible for the symptoms of poisoning that appear in those who ate this mushroom, but also other toxins that it contains (mucitol, ibotenic acid, etc.). So, a raw mushroom contains 0.0003-0.0016% muscarine, and to obtain this alkaloid in an amount of 0.25 g, you need 125 kg of fly agaric. To kill a person, you need 0.5 g of muscarine.
Also, this alkaloid is contained in such poisonous mushrooms as a talker, a whitewashed talker, a luminous talker, a torn fiber, an earthen fiber. In special conditions, the poison contains a mushroom such as pig. Not every mushroom is poisonous, usually it is a thin old pig. But scientists could not establish the exact amount of poison.

Muscarine is contained in torn fiber
The value of poison for medicine and pharmaceuticals
Having isolated pure muscarine from fly agarics, scientists at first tried to use it to treat various diseases - epilepsy, oncological formations, ulcers, eye diseases. But all attempts were unsuccessful, since it is a very toxic substance. Therefore, now it is not used in this direction.
Currently, pure toxin is used exclusively in theoretical studies. With its help, they act on the peripheral parasympathicotropic nerves. This allows the development of new drugs and the search for new treatments for existing diseases.
Features of the effects of an alkaloid on the body
Muscarine is a poison with a rather specific action. Unlike many other toxic substances that affect entire organs and systems, it binds pointwise to individual cholinergic receptors of the parasympathetic system (muscarinic receptors).
As a result, the nerves of the respiratory tract are paralyzed, and the muscles of the smooth muscles of the stomach and intestines contract more intensively, which can be seen even from the outside through the abdominal wall. This often leads to vomiting. At the next stage, similar excitement passes to other smooth muscle organs - the bladder, uterus, spleen, etc.
The alkaloid has no effect on the central nervous system. This is due to the fact that he cannot overcome the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from the penetration of infection and foreign toxins. However, it is capable of affecting peripheral innervation, which leads to severe sweating, salivation (excess salivation), watery eyes and other symptoms. From the gastrointestinal tract, gastric juice and bile begin to vigorously secreted.
Muscarine, synthesized artificially, affects the motor nerves, thereby causing paralysis. At the same time, a similar effect was not observed in a natural natural alkaloid.

Treating muscarine poisoning
If you can remove the main signs of intoxication yourself, then further treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. So, in most cases, the antidote is introduced - atropine. This is another alkaloid found in nightshades. Camphor, aconitine, veratrin, chloral hydrate, etc. can also be used.
Treatment activities:
- Gastric lavage using laxatives to remove toxin from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Subcutaneous administration of atropine.
- Infusion detoxification therapy, the purpose of which is to remove toxins from the blood. Usually glucose solution, electrolytes, etc. are injected.
- With the development of respiratory failure, it is possible to use an oxygen mask and artificial ventilation.
Despite the rather pronounced effect of muscarine on the body, the prognosis for poisoning is maximally positive.
It is important to call doctors on time and start treatment. As a result of complex therapy, recovery will begin after 2-3 days.
And only in the most severe cases is it possible to develop extremely unfavorable consequences, up to and including death.

About muscarine
This poisonous alkaloid was discovered by Schmiederberg. Muscarine obtained from mushrooms is called natural. This alkaloid is odorless, tasteless, and similar to syrup. If this poison is heated to a temperature of 100 degrees, it is destroyed. At this moment, a tangible smell of tobacco is felt. Schmiederberg proved that if this alkaloid is obtained artificially, then it does not resemble natural in its properties.
The sensitivity of different animals to muscarine is different. If a cat is injected subcutaneously with this poison at a dose of 4 mg, then it will die in a few hours. And a dose of 12 mg will kill her in 10-15 minutes. Dogs have a higher tolerance to the poison. Also, scientists have found that the human body tolerates this poison well. Koppé and Schmiederberg injected themselves with this poison at a dose of 3 mg. They found that even in such quantities, it causes poisoning. How it manifests itself:
- saliva flows strongly;
- blood rushes to the head;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- be sick;
- I have a stomachache;
- the skin turns red;
- visual disturbances;
- sweat runs out, especially on the face.

Isomuscarin affects the heart rate, slows it down
In medicine, this alkaloid has not found application. They wanted to use this alkaloid contained in poisonous mushrooms to cure cancer and epilepsy, ulcers, but they thought it was too dangerous. Anhydromuscarin does not affect the heart or eyes, but it does cause sweat and drool. A person dies due to respiratory paralysis. Isomuscarin affects the heart rate, slows it down, but does not stop the heart, does not affect the mammalian eyes and intestines.
Pharmacology
Pharmacological action - antiglaucoma.
Stimulates muscarinic smooth muscle receptors, incl. the iris of the eye and the glands of the digestive, bronchial, external secretions (salivary, sweat, etc.). It causes contraction of the circular (miosis) and ciliary (accommodation spasm) muscles.
Ingestion is rapidly absorbed, time to reach Cmax is about 60 minutes. Metabolized at synapses and plasma. T1/2 is 0.76 hours and increases in proportion to the dose. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys, in the urine it is found unchanged and in the form of metabolites. In the conjunctival sac, it is practically not absorbed and has no general effect. Systems with prolonged release of the active component (eye film), wetted by the lacrimal fluid, swell and are retained in the lower conjunctival fornix. The release of pilocarpine begins immediately after contact of the film with the conjunctiva.
In angle-closure glaucoma, it constricts the pupil, causes a displacement of the iris from the angle of the anterior chamber, and facilitates the opening of the Schlemm's canal and fountain spaces. In patients with open-angle glaucoma, it also opens the Schlemm canal and trabecular fissures and increases the tone of the ciliary muscle. In primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, a single instillation of a 1% solution causes a decrease in intraocular pressure by 25–26%. The action begins in 30-40 minutes, reaches a maximum in 1.5-2 hours and lasts 4-8 hours. Systems with prolonged release of pilocarpine provide control of intraocular pressure for 1 day, while the induced myopia developing during the first hours decreases rapidly and usually does not exceed 0.5 diopters.