Application
Representatives of this mushroom family are used not only for the preparation of all kinds of culinary dishes. They are widely used in cosmetology and folk medicine.
It is believed that mokruha has a beneficial effect on all organs of our body. The presence of antibacterial substances in this mushroom determines the effectiveness of its use as a therapeutic and prophylactic agent. Modern medicine confirms that mokruha is effective in treating viral diseases. In many countries, this mushroom is used to treat migraines, nervous system disorders, headaches and insomnia. It is assumed that such a product has a positive effect on the general condition of the body, helps to strengthen the immune system and is effective in combating chronic fatigue.
Cosmetics containing spruce moss mushroom (making such drugs at home will not be difficult) make the skin more elastic and silky. Lotions, infusions and decoctions relieve redness and inflammation. Along the way, they have a beneficial effect on skin color - it becomes even and matte. Moisture creams are recommended for those with oily skin prone to enlarged pores.
Decoctions and special masks from mokruha help strengthen and grow hair. After using these products, the hair becomes silky and shiny. Since ancient times, in folk medicine, this mushroom has been used to eliminate dandruff and split ends.
Description of appearance
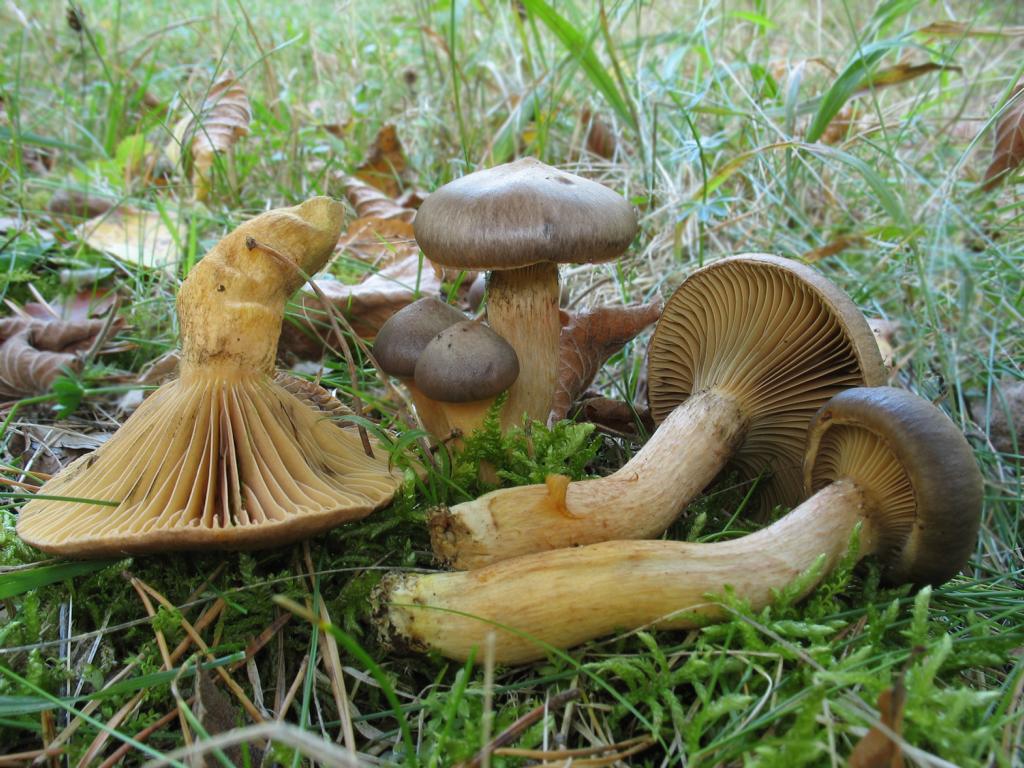
Among other representatives of the mushroom kingdom, it is distinguished by its large size, the cap can grow up to 15 centimeters. It is usually gray and may have dark or purple spots on it. The season for the appearance of mokruha in the forests is August - September. Loves coniferous and mixed forests. Creates mycorrhiza with pine or birch. On the territory of Russia, it can be found almost everywhere - in the Caucasian mountains, in the Siberian latitudes, the Far Eastern forests and other places. Usually grows one at a time, less often in small groups. They called it wet because a mucous membrane forms on it. If you are going to collect mixed mushrooms, then you need to take a separate container for mokruha. Otherwise, it will stain the rest of the mushrooms with mucus.
The calorie content of purple moss reaches 192 kilocalories.
The use of wet fur for food
It is an absolutely edible mushroom filled with forest scents. Its rich taste will not leave indifferent any mushroom lover. Makruhi got their name from the fact that when cooked, their color changes to purple. When cooking, you should first clean the mucous skin from the mushroom and rinse it well, and then cook as you like. Of all the mushrooms, mokruha tastes the most like boletus.
You can cook all the same dishes from them as from ordinary mushrooms. Perfect for preparing pickles, you can make a delicious mushroom sauce or just fry as a side dish for meat or fish. There are many recipes for salads with the addition of various mushrooms, including mokruh. Due to the fact that they turn purple during heat treatment, all ready-made dishes with them in the composition will look unusual and memorable. For example, adding them to a salad will give you vibrant blotches of color in your dish, making it more appetizing.
This is not only delicious, but also insanely healthy mushroom. Eating them strengthens the immune system, restores the nervous system, improves blood circulation and memory. The general condition becomes satisfactory, and fatigue disappears without a trace.The active substances that make up the purple moss have a positive effect on the hematopoietic organs, in this regard, they contribute to hematopoiesis and the renewal of all cells in the body.
In some peoples, this type of mushroom has been used since time immemorial, it has been used to relieve headaches, treat insomnia and alleviate the course of diseases of the nervous system.
Cosmetology is also a branch of medicine that successfully uses purple moss. Creams, masks, serums, tonics, shampoos, balms and so on are produced from them. The skin becomes elastic and taut, and the hair is strong and silky. When using cosmetics based on mokruh, you can achieve an evening of skin color and giving it a matte shade. Shampoos and balms promote hair renewal, strengthen the hair follicle and protect hair from cutting in the future.
Healing properties
The yellow-footed peat is the absolute champion in the amount of nutrients and amino acids. It contains:
- Vitamin C. Its deficiency is manifested in the loss of teeth, heart weakness, rapid fatigability. It strengthens the immune system, improves performance.
- Riboflavin. Its deficiency can cause eye diseases, hair loss. Vitamin B 2 plays an important role in oxygen enrichment of cells.
- Thiamin. This vitamin regulates metabolic processes, the work of the heart and blood vessels, and affects the activity of the nervous system.
- Vitamin E. Increases libido, promotes successful conception and bearing of a child.
Traditional healers use this mushroom to prepare ointments, which are used to treat neurogenic and common dermatitis. An alcohol-based product is made.
The principle of preparation of the medicine is the same as that of the red mushroom ointment:
- It is necessary to chop the caps of 10 mushrooms and put them in a 1 liter container.
- Then it should be tightly closed with a lid and left in a warm place for 3 days.
- After the passed interval, moonshine must be poured with moonshine or alcohol to the top so that a layer of liquid of 1 cm forms above them.
- The container must be sealed again and left for a month.
The resulting composition is lubricated with a cotton pad. This should be done at night. The ointment is stored for no more than 3 years in a dark place.
Growing an olive tree from cuttings
Olive trees are also grown from cuttings. For this, 2-3-year-old twigs with a diameter of 2-3 cm are cut from an adult plant. They are divided into segments of 20-25 cm. The lower cut is treated with a preparation that stimulates root formation, and the upper cut is smeared with garden pitch.
Then the cuttings are stuck into wet sand at a slope to a depth of 10-12 cm. The container with sand is covered with foil and placed in a warm (20-25 °) shaded place. Next, you need to raise the film for 1 hour every day for ventilation and, if necessary, spray the sand from a spray bottle. Rooted cuttings can be planted after 2-4 months.
Now you need to water the plant all the time and wait. The room temperature must be at least 20 ° С
Please note that cuttings do not like waterlogging very much, so water infrequently, and try to spray the plants daily. To ensure sufficient humidity, cover the sprout with a plastic bag and make a few holes in it for ventilation.
To check if roots have formed or not, lightly tug on the stem. If he resists, then the roots are gradually growing back. Do not pull forcibly, as this will simply rip up the plant. The rooting process can take more than 3 months. If three months have already passed, and there are no roots, do not be discouraged.
Pay attention to the stalk, if it is green and vigorous, then everything is in order, continue to water the European olive
Growing an olive tree from a seed in a pot: a step-by-step process
Olive is an evergreen tree belonging to the olive family. Its homeland is Africa, Australia, southern parts of Europe and Asia.In the world, the olive tree is known for making healthy oil, and the fruits - olives - are pickled. There are many legends about its origin. Despite the fact that the olive grows only in warm countries, it can also be grown at home.
This can be done from a seed - a bone. However, eating delicious fruits from such a tree will not work - they will be tasteless and will appear only 10 years after planting. Plants in this way can only be grown for decorative purposes. Read about how to grow an olive tree at home in our article.
Is an evergreen tree related to
Its homeland is Africa, Australia, southern parts of Europe and Asia. In the world, the olive tree is known for making healthy oil, and the fruits - olives - are pickled. There are many legends about its origin. Despite the fact that the olive grows only in warm countries, it can also be grown at home.
If you were already going to place a bone from a canned olive just eaten into the ground, then we hasten to disappoint you - such planting material will not germinate. You only need fresh fruit seeds, which can be purchased at a specialized store.
To begin with, the bones should be placed in an alkaline solution (10%) for 18 hours. This is necessary in order to somewhat soften the shell, which in this state can already be pierced by the hatched sprouts. After processing, the seeds are washed and dried. They must be placed in the soil only completely dry. The sharp end is cut with a knife, secateurs or sawed before planting.
You can also place the seeds in a bowl of moist compost for several weeks for germination. The container will need to be kept at a warm temperature, constant humidity and sufficient sunlight. This procedure can help increase the germination rate.
The following composition of the substrate will be the best for planting an olive:
- river sand - two parts;
- turf land - one part;
- garden land - one piece.
In the soil for the olive tree, you will also need to add a little peat and dry hydrated lime powder (20-25 g per 1 kg).
If you will be using a commercially available substrate, then you need to mix the soil for growing cacti (three parts) and ordinary soil (one part), thinning the mixture slightly with sand.
Capacity
The capacity for planting olive trees should initially be large - at least 60 cm in depth and width. A prerequisite is the drainage holes, which will pass excess moisture well or take the required amount of liquid from the pan. The main enemy of the evergreen tree is the increased moisture of the soil, its stagnation is like death.
A layer of fine charcoal or brick chips should be laid at the bottom of the pot as drainage.
Spruce peel with cauliflower
Prepare a delicious and beautiful meal for dinner.
Ingredients:
- mushrooms - 300 g;
- cauliflower - 1 small head of cabbage;
- onions - 1 pc.;
- cheese - 70 g;
- vegetable oil - 60 g;
- butter - 60 g;
- bread crumbs - 30 g;
- salt to taste.
Cooking steps:
- Boil mokruh, cut them into small pieces.
- Chop the onion, fry it together with the moss until golden brown.
- Disassemble the cabbage into inflorescences, boil it in salted water for 5 minutes. Mix the blanks with breadcrumbs and fry them in butter.
- Stir the prepared foods, place them in a baking dish and sprinkle with grated cheese.
- Bake the dish in an oven preheated to 180 ° C for 15 minutes.
Serve hot.
Contraindications
Experts say that mokruha cannot be harmful, since it is very difficult to confuse it with other mushrooms. When cutting off the flesh, the cut always takes on a reddish tint.
But by following simple rules, you can avoid discomfort and health problems. First of all, harvesting near highways and large cities or enterprises is not recommended.Also, do not get carried away with mushroom dishes for people suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Their use is also undesirable for children, since the fiber and chitin that are part of the pulp are absorbed with difficulty by the child's body.
Individual intolerance to the product can provoke allergic manifestations and even Quincke's edema.
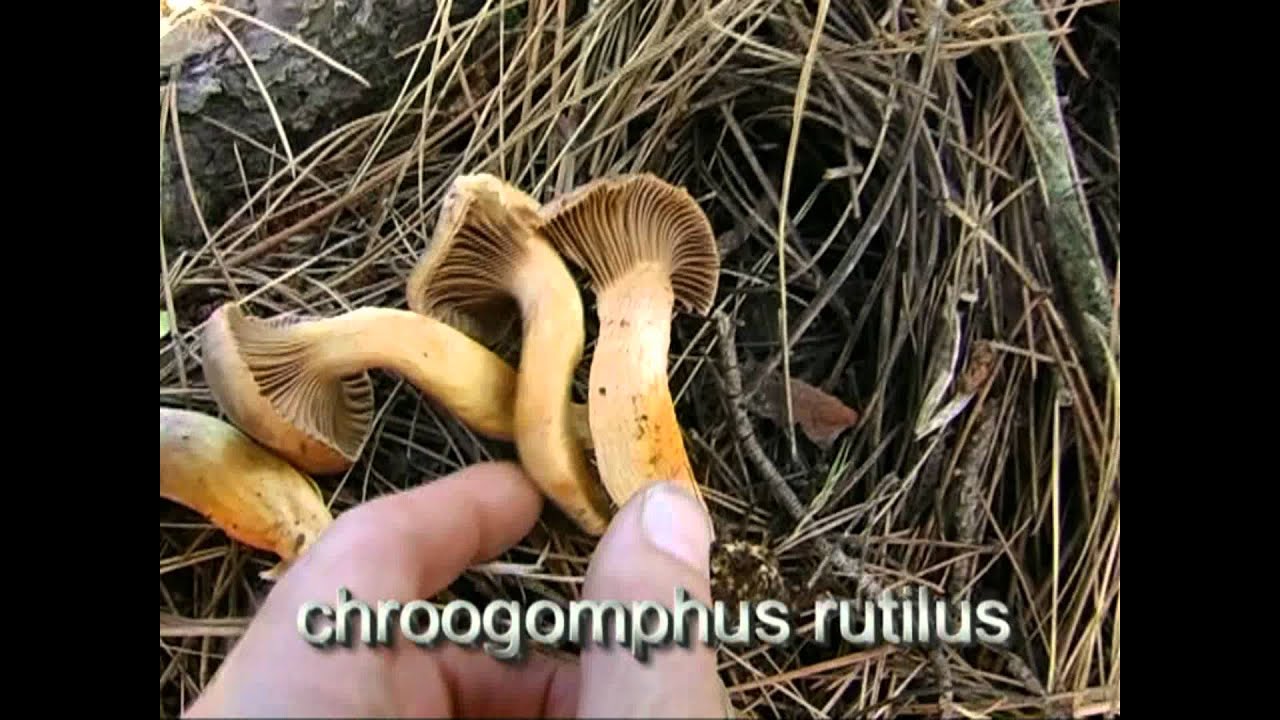
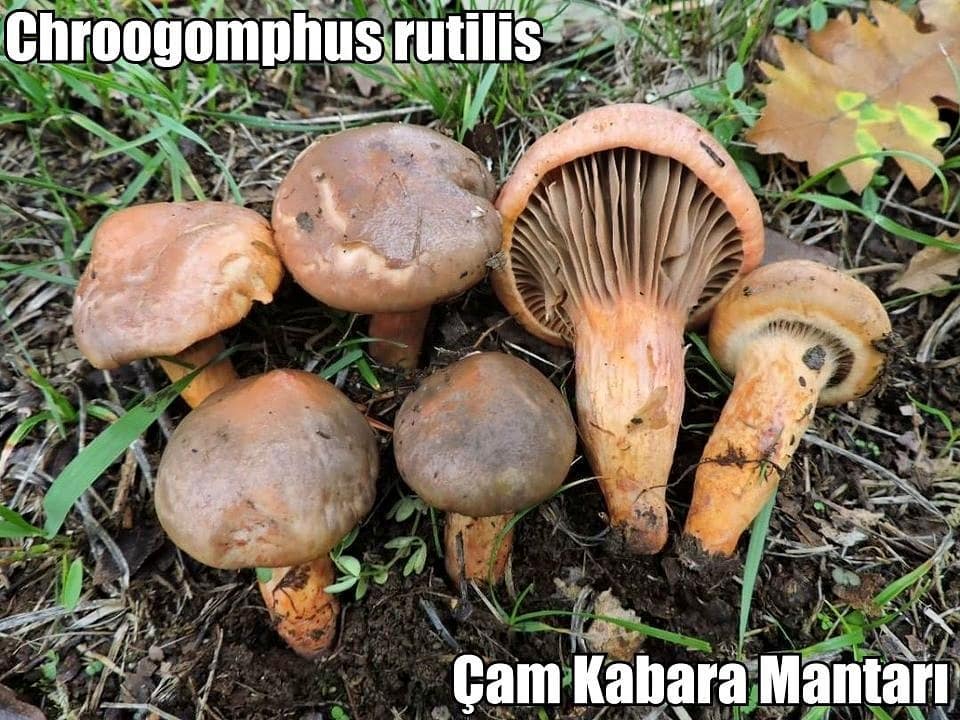
Video: purple moss (Chroogomphus rutilus)
Somehow a couple of years ago, while scouring the forest in search of mushrooms, I came across a rather cute, but unfamiliar species to me.
Even the little ones had a powerful red leg, the mushroom itself was reddish-brown, lamellar, and the larger specimens were brown, but with a brown or purple tint, some were slimy, resembling oil cans.
We typed at your own peril and risk. At home, having plunged into the Internet, I found that it was not in vain that I brought such a crop, the mushroom is called purple moss or yellow-footed moss
... Such mushrooms grow in pine forests, have a good taste and, most importantly, they do not have poisonous counterparts.
After lying in water, mokrukh acquire a reddish-cherry hue of wine, and after boiling them, they become inky-purple. Since then, we have been collecting them all the time. Fortunately, large specimens are large, very fleshy and even babies have a high leg, and therefore it is easy and pleasant to collect them. I cook soup from them, use them as a filling for pies, pancakes, prepare for the winter: marinade, and freeze the boiled ones.
They make various delicious dishes. Today I will cook a roast with mushrooms and potatoes. First we sort out the mushrooms, wash them well, cut them into pieces and boil for fifteen minutes, put them in a colander.
We clean the potatoes, cut them into thin circles. And peeled onions into half rings. Pour vegetable oil on a baking sheet or roasting pan, spread a layer of onions, a layer of potatoes, and mushrooms on top.
Of course, it is not at all necessary to take mokruha, any mushrooms will do, I have also come across boletus. Sprinkle with sunflower oil on top and put in a preheated oven, in the lowest position.
If the potatoes dry up during the baking process, you can pour the mushroom broth over it. When the roast is almost ready, turn on only the top fire and put the baking sheet on the very top so that the potatoes are browned.
We take it out of the oven and put it on a dish or directly on plates to hungry mushroom pickers. The potatoes are crispy and soaked in mushroom flavor. I do not add any seasonings or spices to this dish, so as not to kill the mushroom aroma.
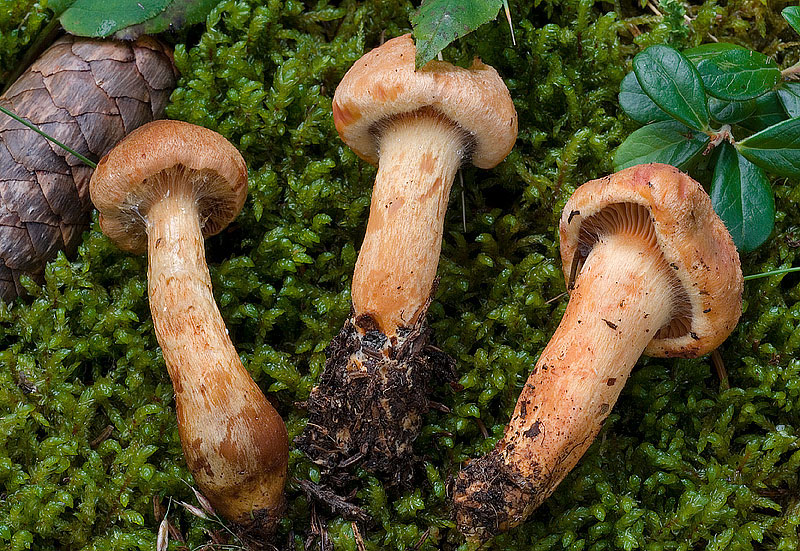
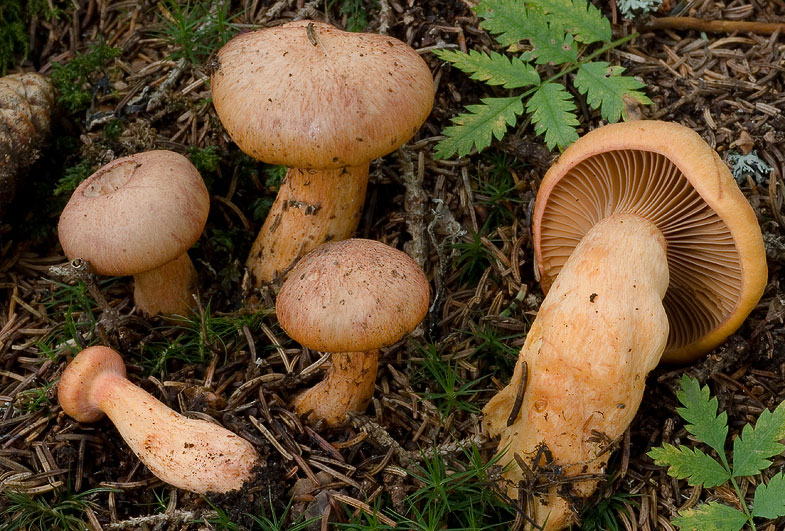
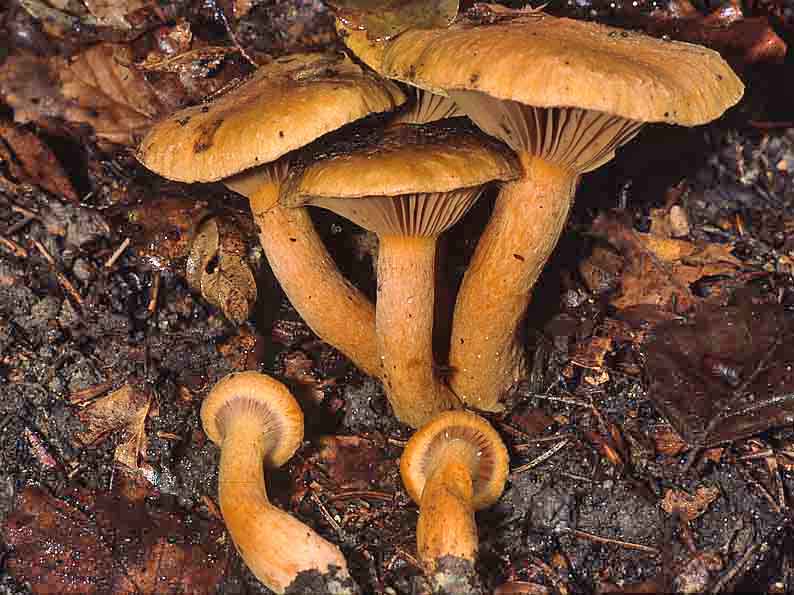
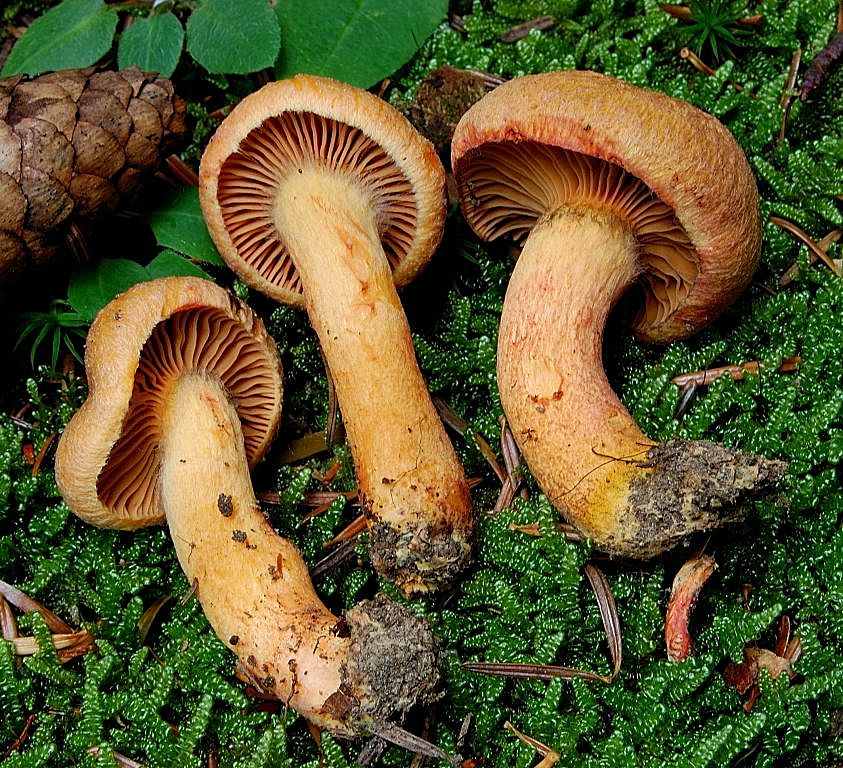
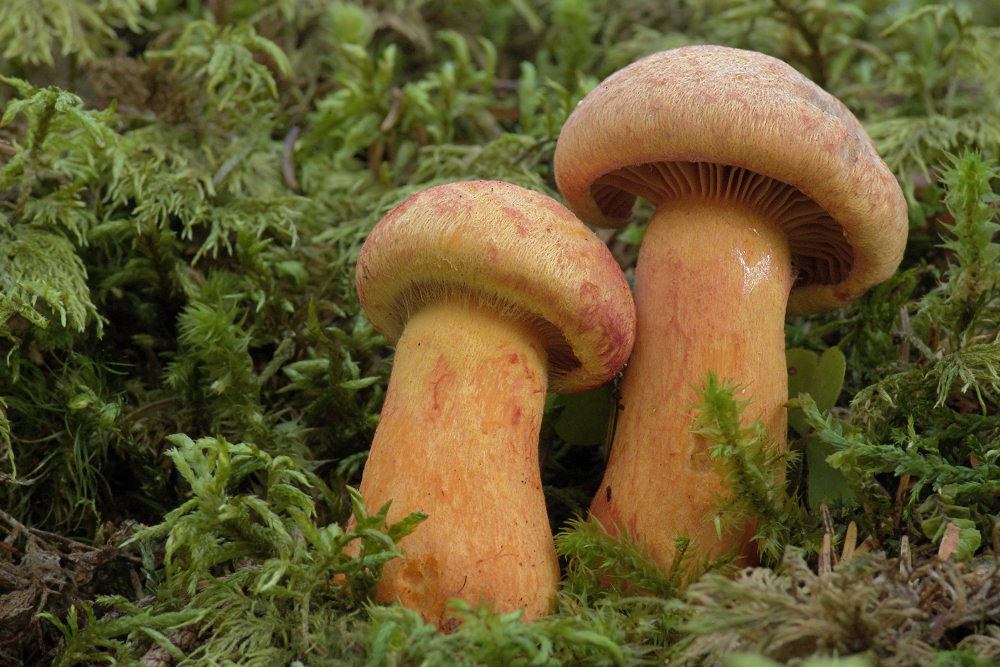
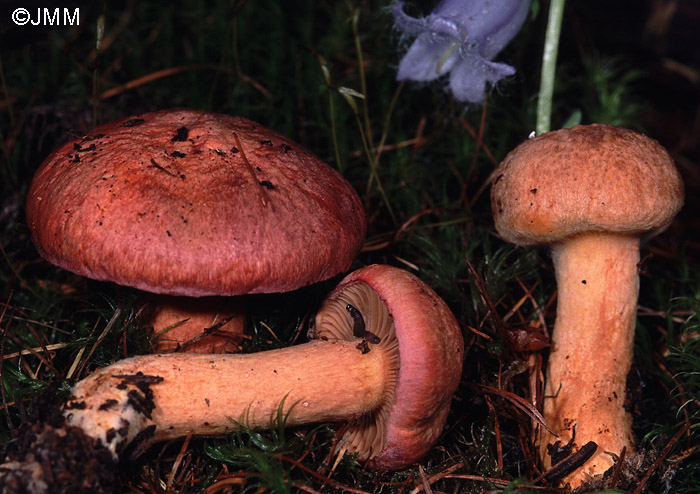
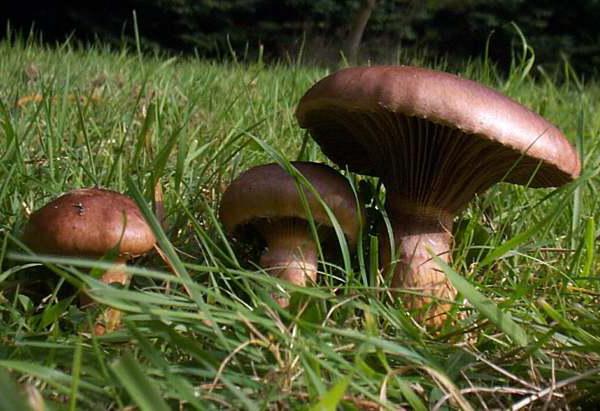
Mokruha purple
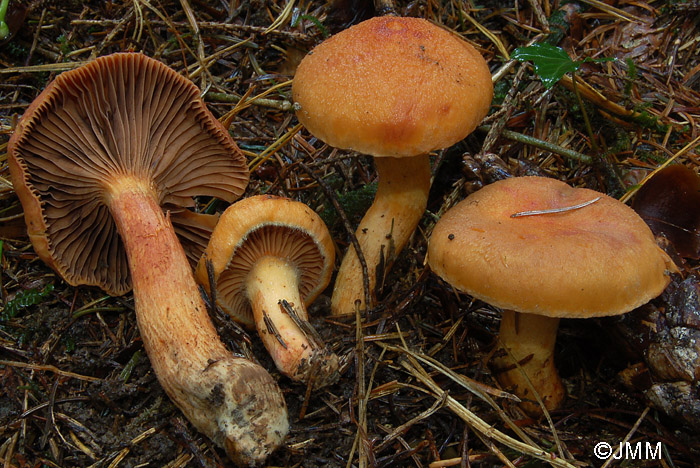
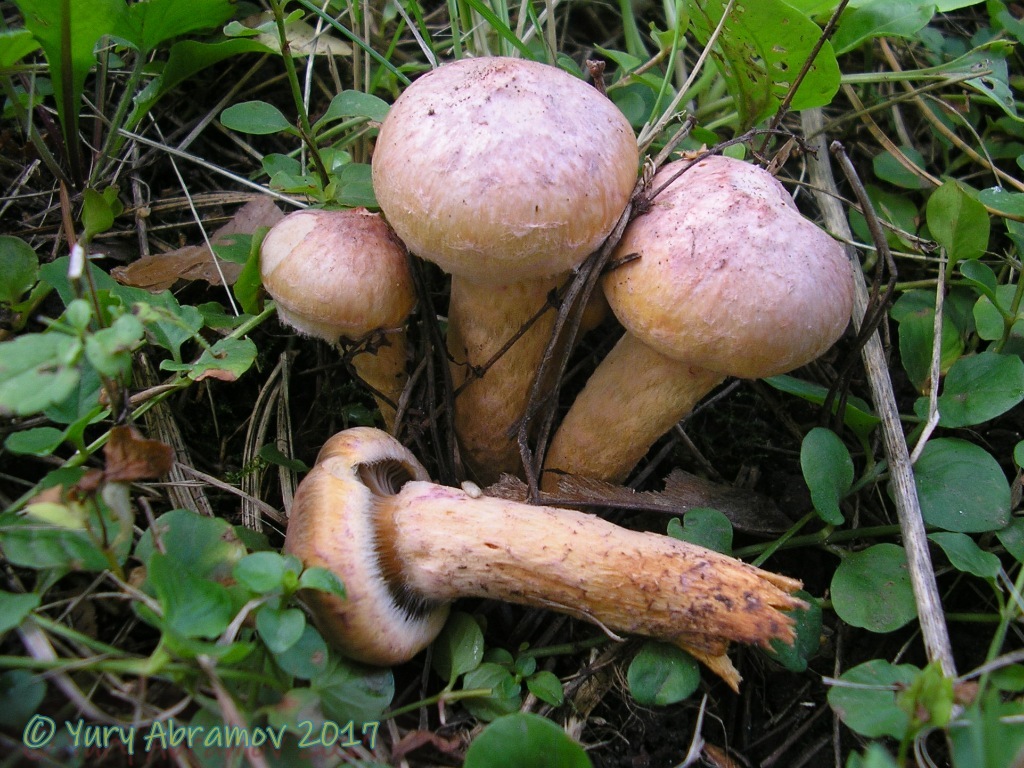
It got its name due to the fact that the mushroom pulp turns purple when boiled. The people have such names as mucous moss, shiny moss and yellow-legged copper-red. It forms a symbiosis with pine, therefore it is found in pine and forests mixed with pine. Prefers bright places, hills, calcareous soil. Grows in groups and singly from mid-August to early October.
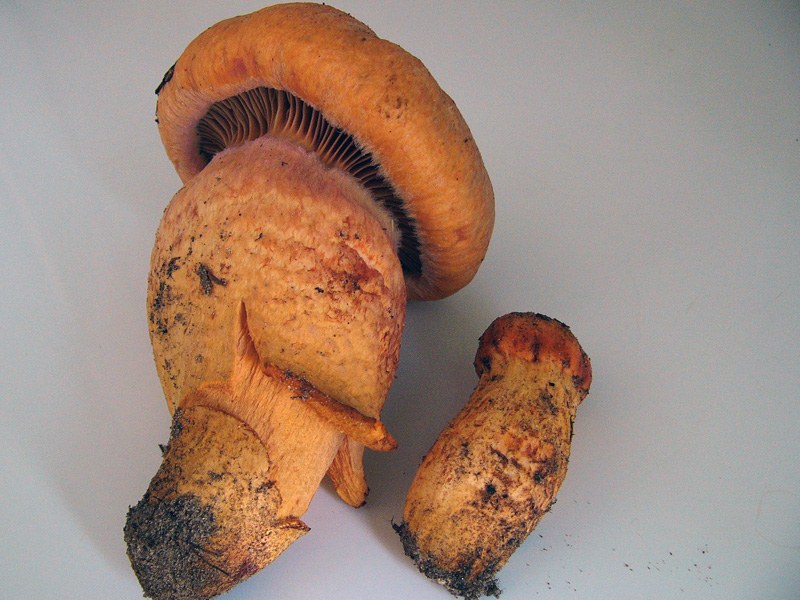
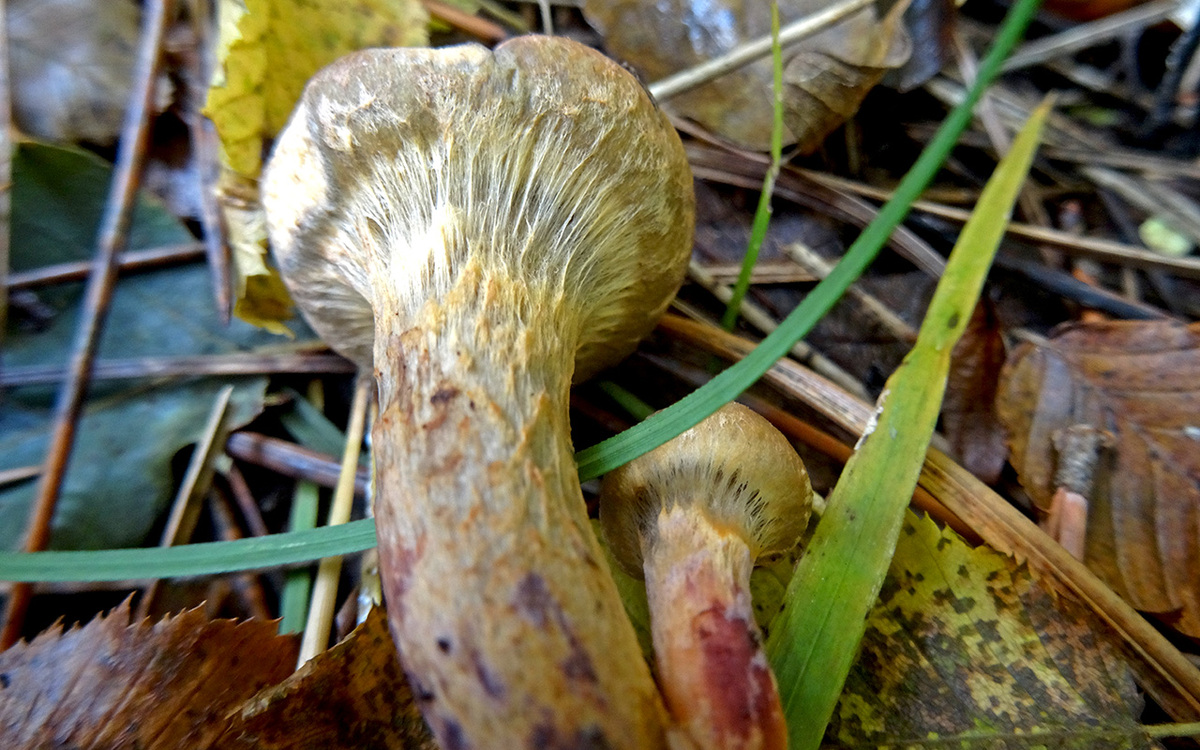
The hat at first has a conical-rounded shape with a cobweb blanket, later it transforms into a convex-tuberous one with curled edges. The surface of the cap is smooth, reddish-ocher-brown, fading. It becomes sticky in wet weather.
The plates are arcuate descending, of medium frequency are first ocher-pink, and later brownish-brown, then black-brown. Easily detached from the cap. In young mushrooms, the lamellar part is covered with a film.
The leg is up to 6 cm long and up to 2 in diameter has a cylindrical shape, in adults it is narrowed to the base, often curved. The surface is silky, it may be a little sticky. The structure is longitudinally fibrous. Has a dark disappearing ring. In color, the cap is several tones lighter, yellowish at the base, more reddish at the top.
The pulp is fleshy, soft, fibrous in the leg has a yellow-pink or orange-brownish color. At the base, the pulp is bright yellow-orange. It turns pink at the cut. Has no pronounced smell and taste.
The taste is similar to butter.Requires preliminary boiling for 15 minutes and removal of the mucous skin of the cap. Suitable for frying, salting and pickling.
How to cook mushrooms
Mokrukha, like any other types of mushrooms, is soaked for several minutes, the top sticky layer is removed from the entire surface and washed thoroughly. Since these mushrooms are conditionally edible, they must be boiled. Many housewives claim that after preliminary processing, these gifts of the forest must be placed in salted water, brought to a boil and cooked over low heat for 15-30 minutes. However, in fact, long-term cooking of wet moss is undesirable. From this, their flesh becomes tough and fibrous. During heat treatment, the color of the mushrooms can change significantly: from a light pulp it turns dark purple, almost black.
They are not very good as an independent dish, but as an addition to a side dish or as part of a sauce, they are simply excellent and give an original taste to the main dish. It is difficult to confuse mokruha with something in the composition of the dish.

Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
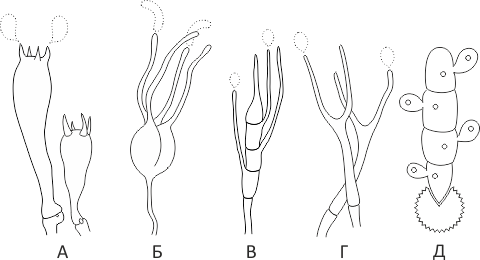
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Pileipellis (Pileipellis)
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Amyloid (Amyloid structure)
-
The structure is called amyloid if from Melzer's reagent (solution of 0.5 g of crystalline iodine + 1.5 g of potassium iodide + 20 ml of chloral hydrate + 20 ml of distilled water) turns blue, violet, sometimes almost black.
See Dextrinoid structure.
Edible and conditionally edible types of moss
Among all the representatives of this family, there are no really poisonous mushrooms - when they are used, the maximum that can happen is diarrhea or nausea. All types are divided into edible and conditionally edible mushrooms, belonging to the fourth category.
The most popular and widespread are pink, spruce, spotted, felt, purple moss.
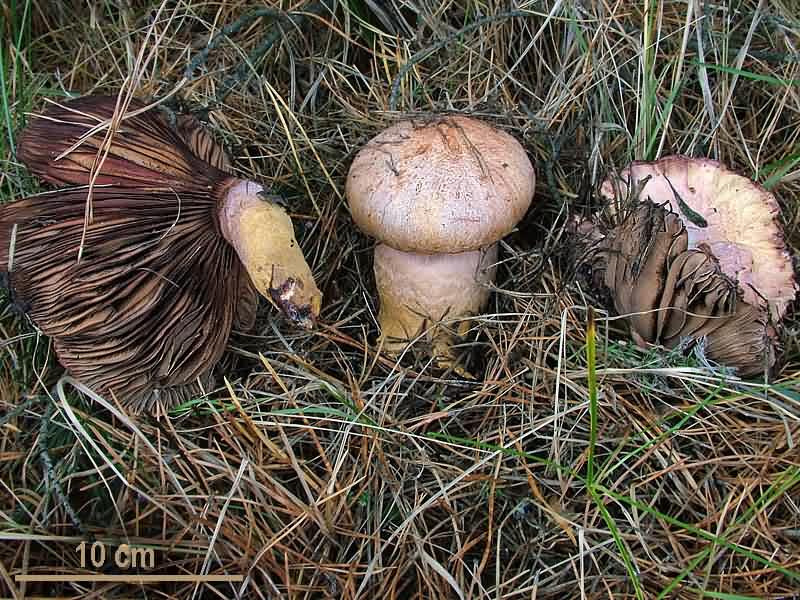
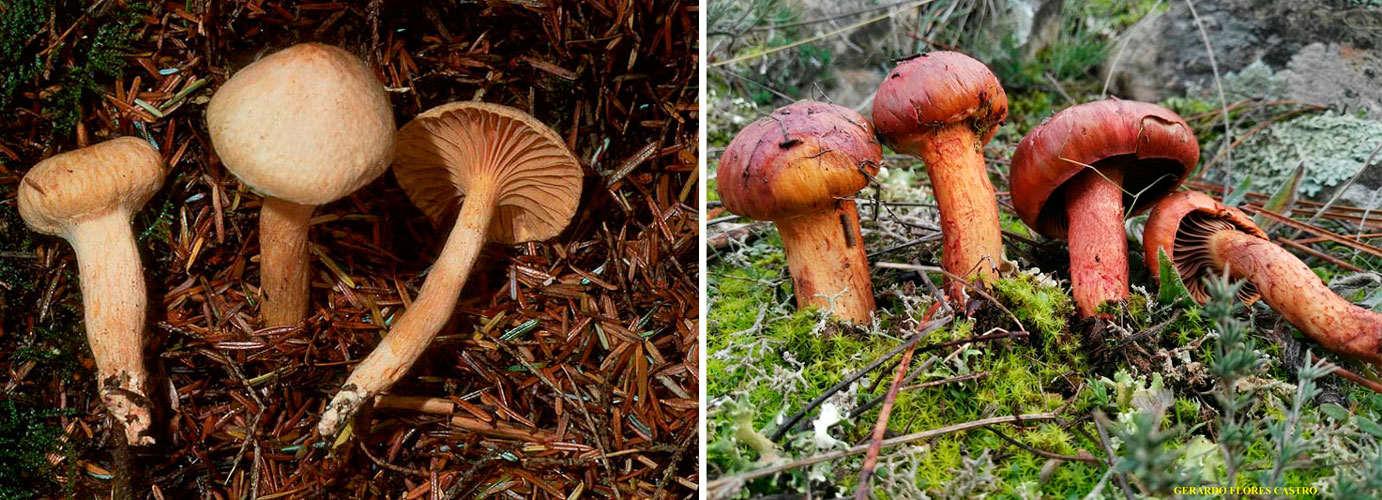
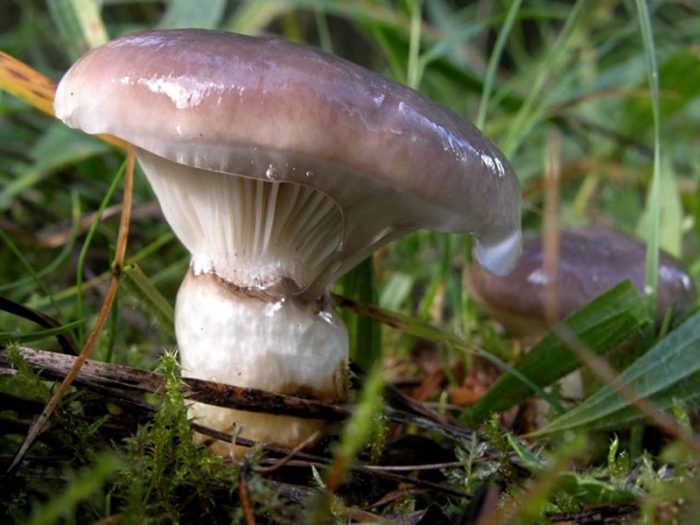
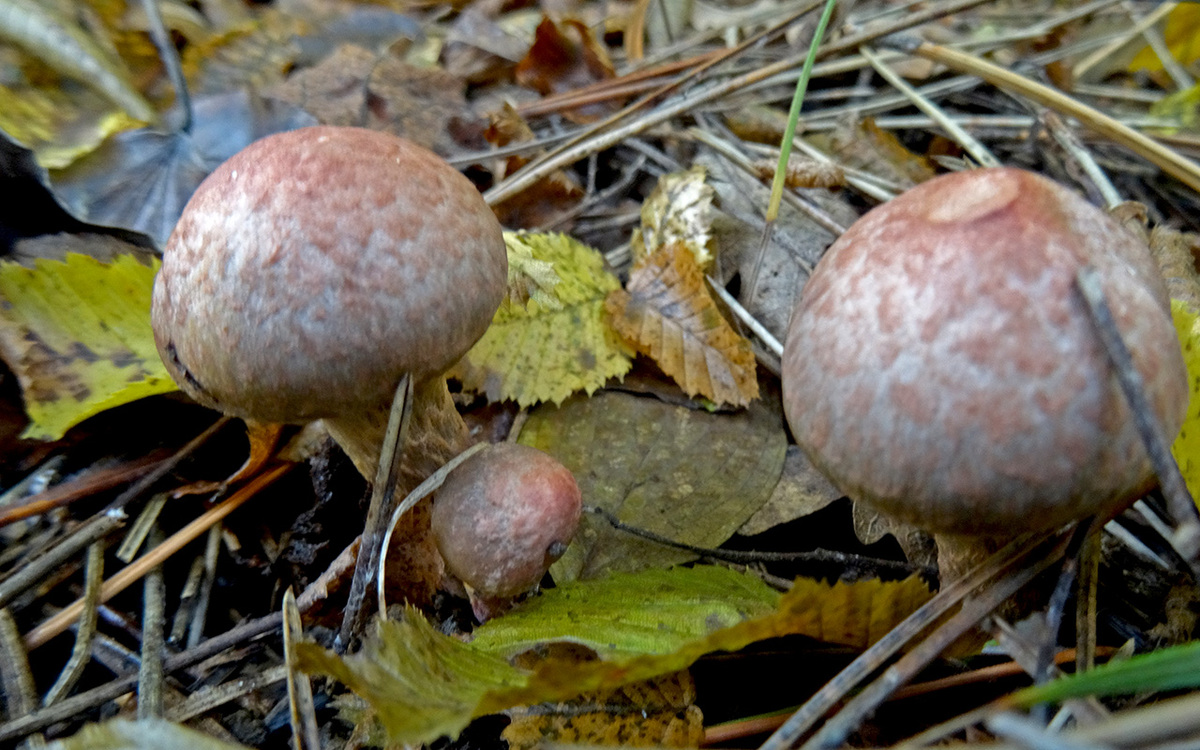
Mokruha pink
This type of mushroom is edible. The hat of pink moss can reach about 6 centimeters in diameter - these are small fruits relative to other species. The hat has a pink tint that fades in the center. The edges are wavy and do not deform over time. The surface is completely covered with a layer of mucus, which is typical for wet moss. The leg is up to five centimeters long and has a regular cylindrical shape. There is a slimy ring on it, which can completely disappear in mature fruits.
The mushroom has no twins
... You can find it on moist coniferous soil.
Used in pickled and salted form.
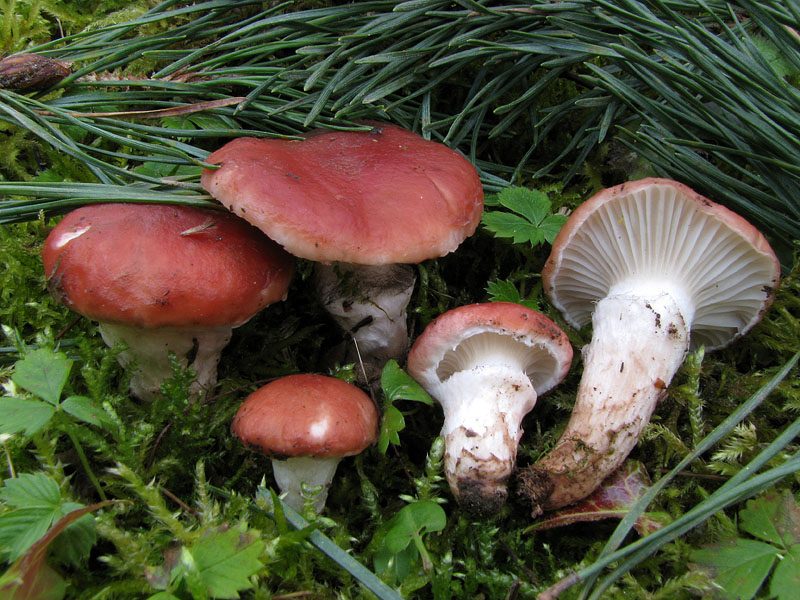

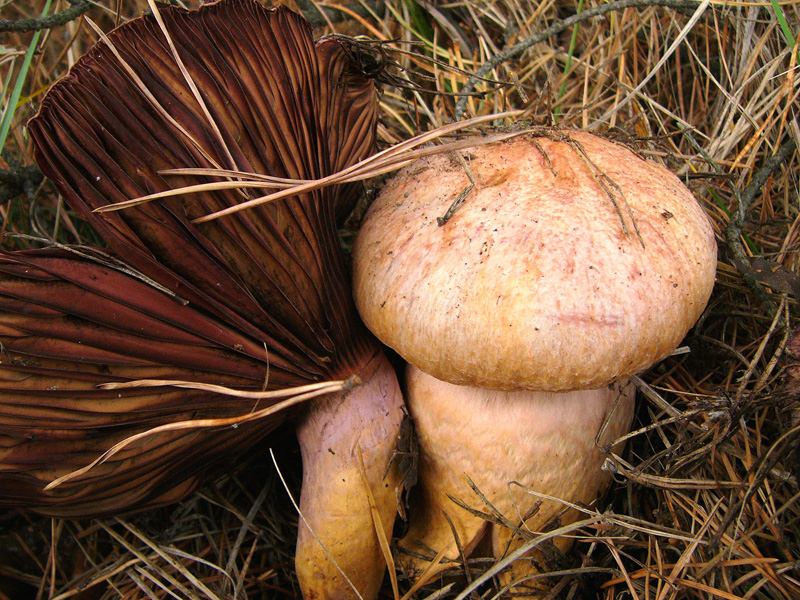
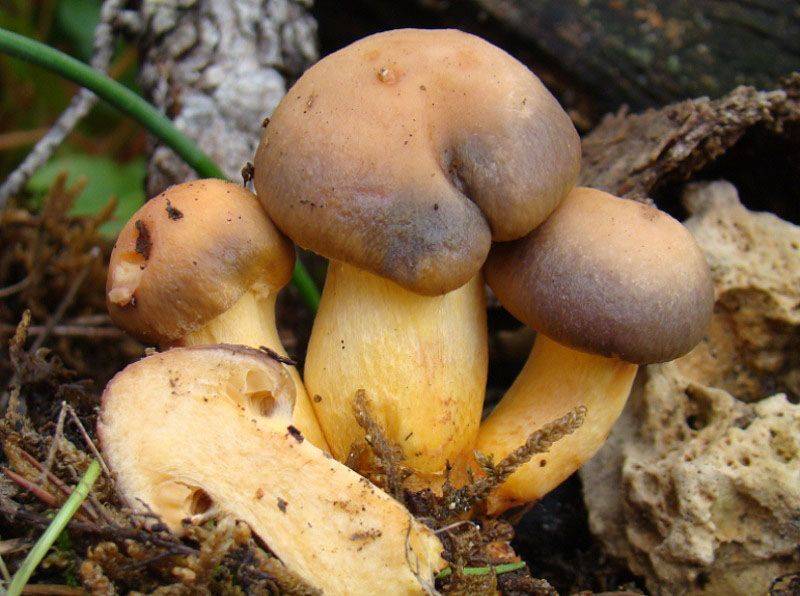
Purple mokruha is an edible fruit, the name of which is translated from Latin as "golden red". The color of the cap may not always be red or pink - the color depends on the region of growth, the impact of weather conditions. The hat reaches a diameter of 14 centimeters, has a brown or red color, as well as a conical shape with a small protrusion in the center. The leg is 10 centimeters long and is also covered with mucus. The pulp is juicy, slightly fibrous, yellow in color.
The fruiting season of the mushroom begins at the end of August and lasts a month and a half. Wormwood is widespread in Siberia, as well as in the North Caucasus.

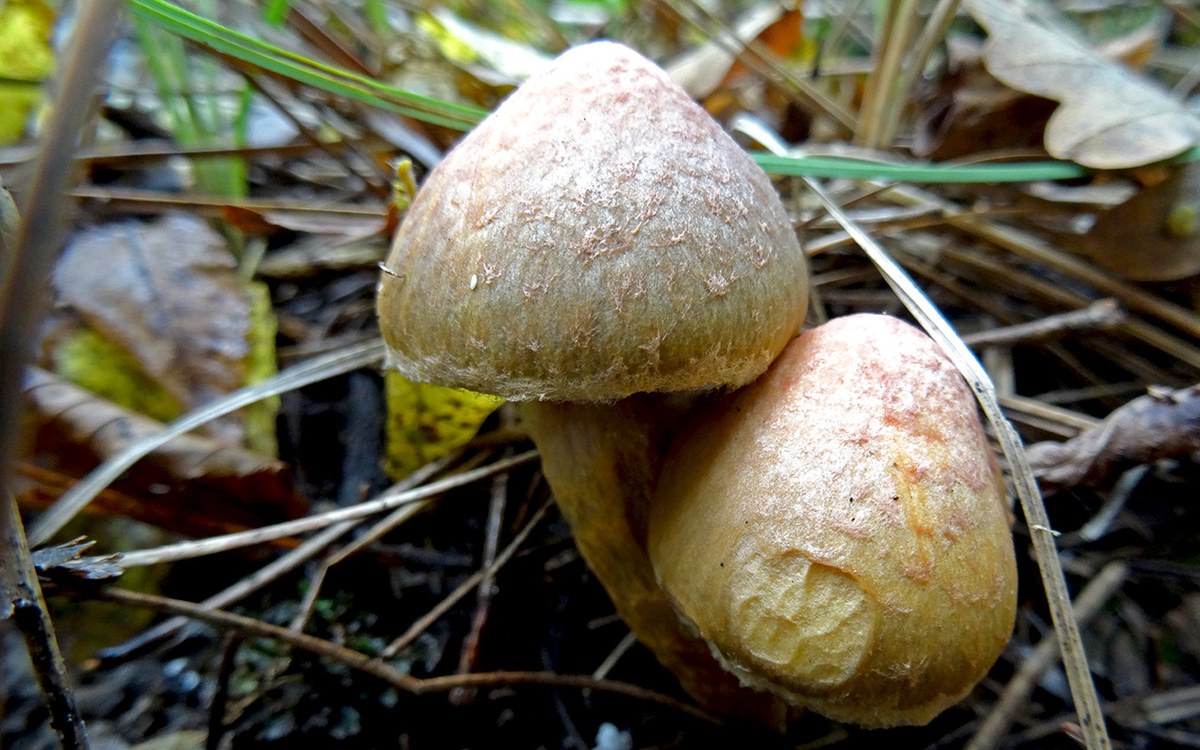
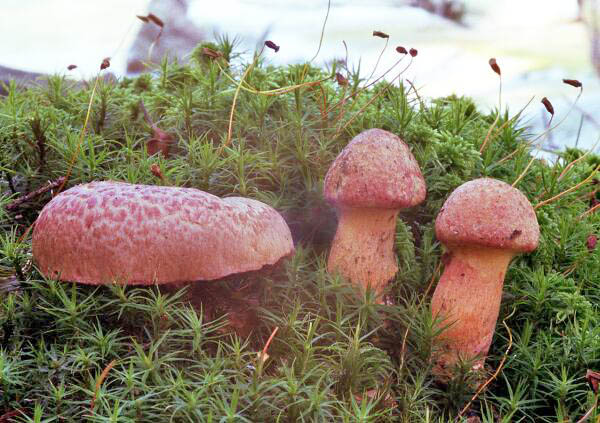
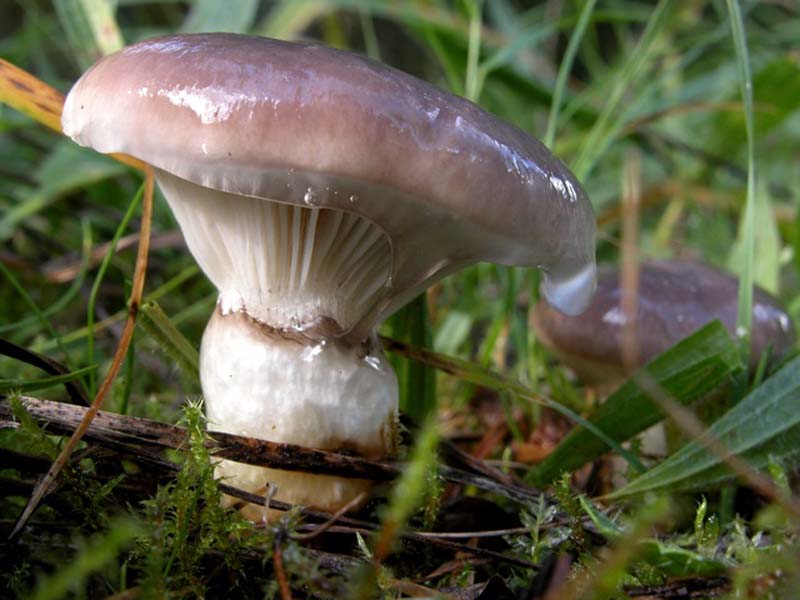
Mokruha sticky (spruce)
The hat of spruce moss has a gray tint, and the shape itself is represented by a cone. Depending on the weather, it can be with dark spots, have a purple tint. The pulp of the mushroom is yellow or lemon bright in color, and darkens when pressed. The whole is covered with small scales, which greatly complicates the process of cleaning the mushroom. The leg is cylindrical and regular in shape, as sticky as the cap. Has a mucous ring, which is sometimes deformed in ripe fruits.
The mushroom grows in the north of the Eurasian continent and bears fruit from August to October. Wherein it has no counterparts and is difficult to confuse with other fruits.

Mokruha felt
Felt moss has caps that reach a diameter of about ten centimeters. It is convex in shape, which deforms over time and becomes flatter. Its surface does not have mucus in dry weather, and at high humidity it becomes a little sticky. The leg reaches 5-19 centimeters in length, has a regular cylindrical shape. The pulp is yellow or orange in color, and if damaged, it acquires a wine tint.
Grows in coniferous forests, near black fir
... Distributed in the Far East.
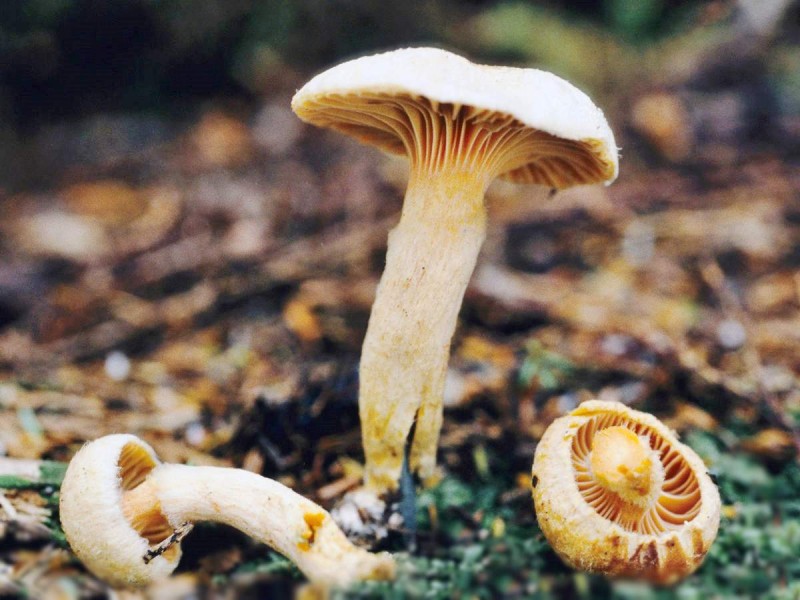

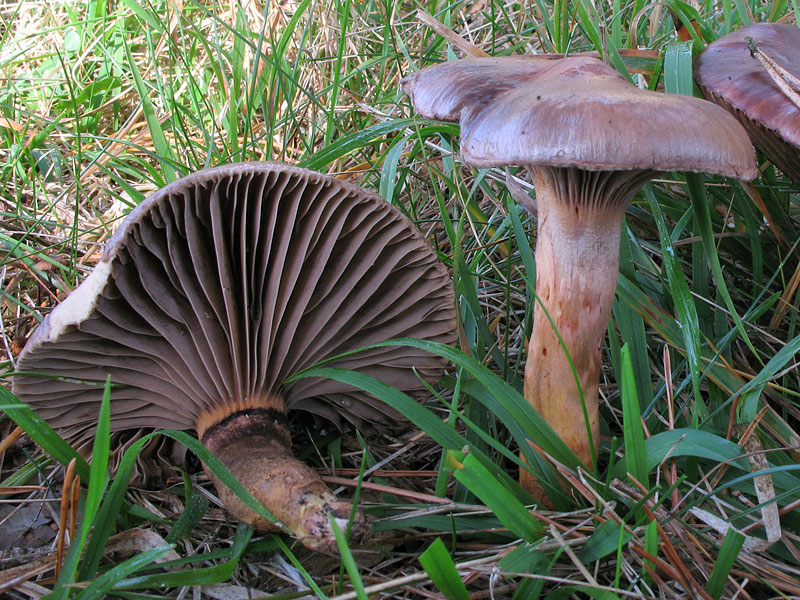
Mokruha spotted
Spotted moss is an edible mushroom with a pleasant taste. For normal growth, it needs the formation of mycorrhiza with conifers such as larch and spruce. The hat is 7 centimeters in diameter and has a convex shape. The plates are located under the cap rather rarely, they can branch. In young fruits, they are white, and then turn brown. The leg is long (about 11 centimeters), yellow in color. When damaged, the pulp turns red.
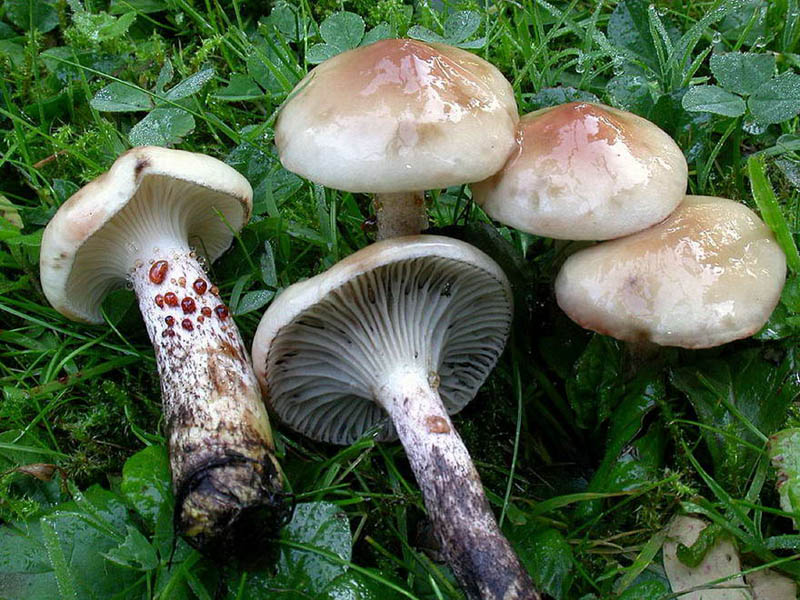

Other members of the family
Pink mokruha stands out noticeably from the family of these mushrooms. Her bright pink hat, slightly burnt in the center, attracts and at the same time frightens off many mushroom pickers. Young pink mushrooms have a noticeably convex cap, but over time it becomes almost flat, while its edges begin to curl upward.The surface is slimy, sticky in wet weather. Wide plates smoothly descend to a short cylindrical leg, on which there is a mucous ring. The flesh of this mushroom is very light, fleshy and soft. When cooked, it turns black. There is almost no smell.
Mokruha slender got its name because of its size and shape. It looks very much like purple moss, but differs in a higher strong leg and a small cap with dark spots. It has rare plates descending to the stem. However, this is a completely different species, so they should not be confused.
Felt mushroom is another representative of the mokruh family. Its other names are felt yellowfoot and swiss moss. The small cap is usually orange-brown in color and has a felt or scaly structure. In dry weather, it is mostly dry, but after rain it becomes slimy. It has dense pale pink plates that fall down to a thin, often curved stem. With age, these plates can turn black. The stem of the mushroom is not high, it can reach 8 cm in height, at the base it most often narrows slightly. Usually the color of the leg is identical to the color of the cap. The fields of the cap of young mushrooms can be connected to the stem with a light, dry, fibrous tissue. This species is widespread in upland coniferous forests and cedars.

Mokruh recipes
Different types of mushrooms are suitable for different purposes. Most often, roast is prepared from mokruha, as well as first courses and filling for baking. The fruits are suitable for freezing.
Sandwiches
Spruce wet sandwiches can be served as a snack or appetizer with a main course. They are aromatic, tasty and moderately juicy. Cheese and herbs give the sandwiches a creamy flavor.
For cooking you will need:
- 2 slices of toasted wheat bread
- 12 pieces of mushrooms;
- 2 tablespoons of butter;
- 50 grams of hard Russian cheese;
- 2 tablespoons of herbs.
Peel the mucous from the slimy skin, rinse under water and cut into slices. Fry the fruits in a dry skillet - five minutes after the start of frying, they will begin to release liquid. You need to fry the mushrooms until it evaporates completely.
Leave the bread in the toaster for a few minutes. Spread it with butter, sprinkle with cheese, add mushrooms and fry on both sides until golden brown. Serve with herbs.

Spruce wet sandwiches can be served as a snack or appetizer with a main course
Mushroom platter
For its preparation, it is recommended to take many different types of mushrooms. The more varieties are involved in cooking, the better and more varied the taste will be. For the recipe, other components are also needed, the amount of which is selected to taste:
- Dill;
- laurel leaves;
- black currant leaves;
- black peppercorns;
- garlic;
- cinnamon;
- Carnation.
All types of fruits must be boiled in salted water. For this, an enameled large container is suitable - a saucepan or bucket. Add salt and other spices to boiled mushrooms. Cinnamon will add sweetness to the dish, cloves - freshness, and dill and currants will make the mushrooms crispy and moderately sour. Stir the mushrooms with seasonings, and then add a decoction of noble and not bitter mushrooms. Leave to infuse, and then roll up in sterilized jars. Store in a cool place.
The benefits of mokruha
The beneficial effect on the entire body of this product is enormous. The mushroom improves memory, eliminates chronic fatigue and strengthens the body's defenses. Experts say that the fungus is able to fight viral diseases, improves the processes of hematopoiesis and allows you to actively renew blood cells.
It is worth noting that most countries use this product in traditional medicine to combat migraines, headaches, insomnia and nervous system disorders.
Also, this mushroom has found application in cosmetology. Cosmetics, which contain it, allow the skin to remain elastic, silky and elastic longer.Fungus-based creams and lotions are recommended for oily skin, as the special ingredients in their composition narrow the pores and the skin becomes matte.
An equally positive effect occurs on the condition of the hair. Among folk recipes, masks based on mushrooms are used, the problem of split ends, dandruff and hair loss is eliminated. As a result, the hair becomes shiny, elastic and healthy.
Similar species
All types of moss (childbirth Gomphidius
andChroogomphus ) have a certain similarity.
- Mokruha spruce is distinguished by a grayish, bluish color of the cap; is a symbiont of spruce.
- Mokrukha pink is easily distinguishable by its bright pink cap and light plates.
- Mokrukha spotted is distinguished by a gray-brown color of the cap; it is found under larch trees.
- Mokruha Swiss (Chroogomphus helveticus ) has a hat with a “felt” surface, painted in ocher tones.
- Felt wet (Chroogomphus tomentosus ) the cap is covered with a whitish tomentose pubescence.
Purple moss has no resemblance to poisonous and inedible mushrooms.
























































