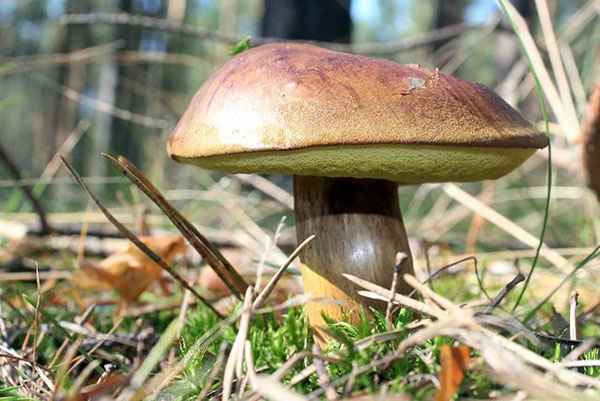
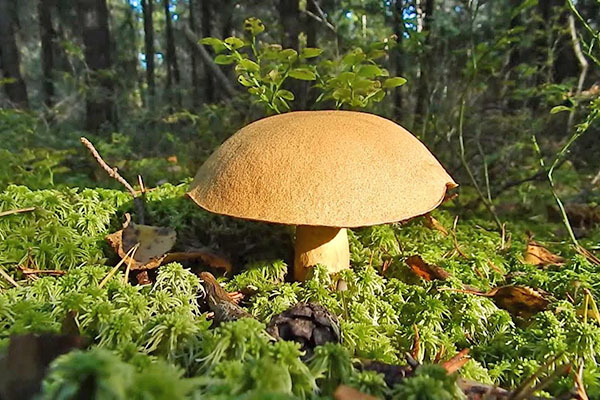
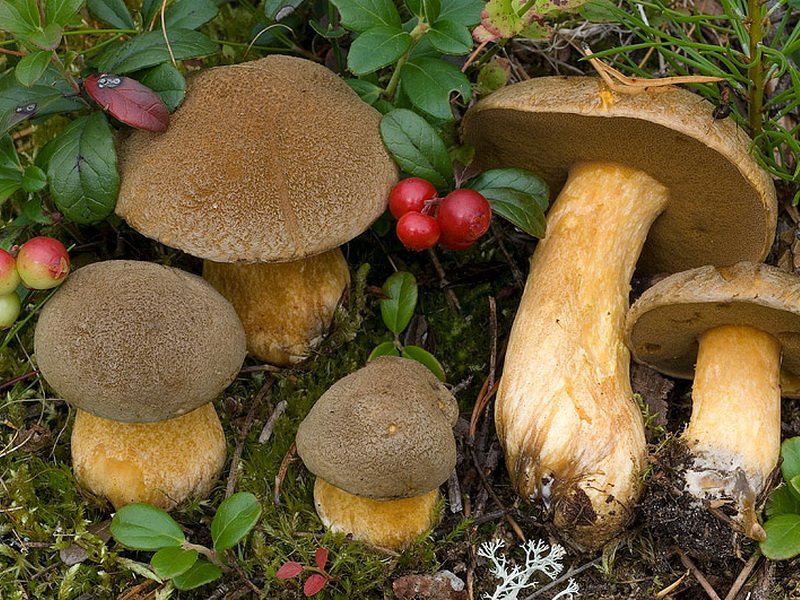
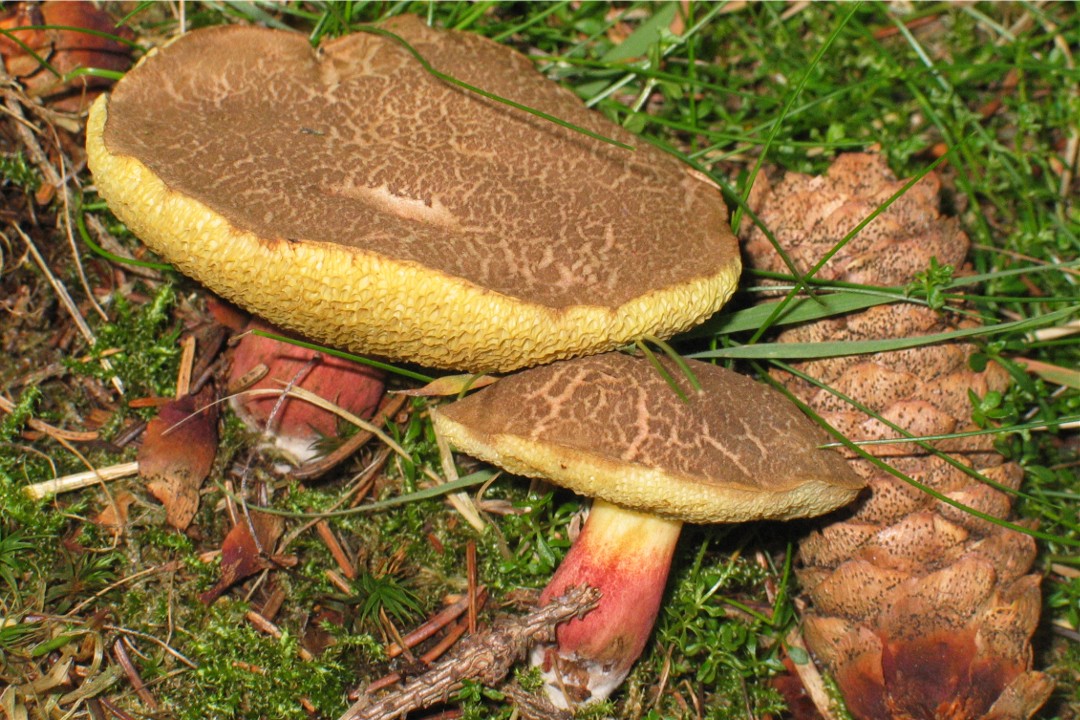
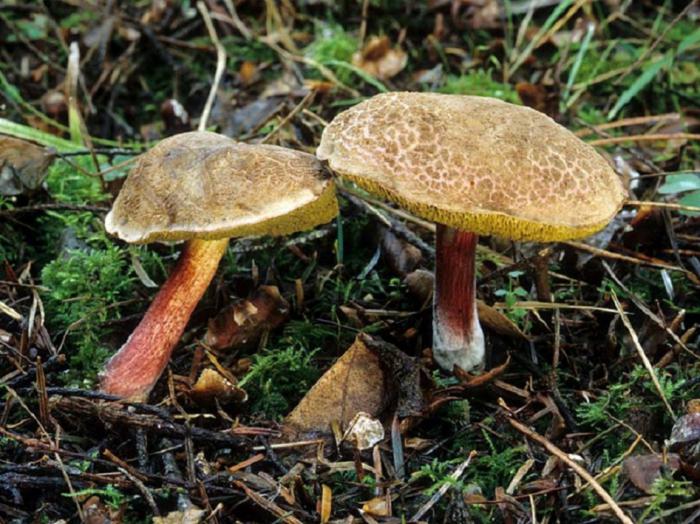
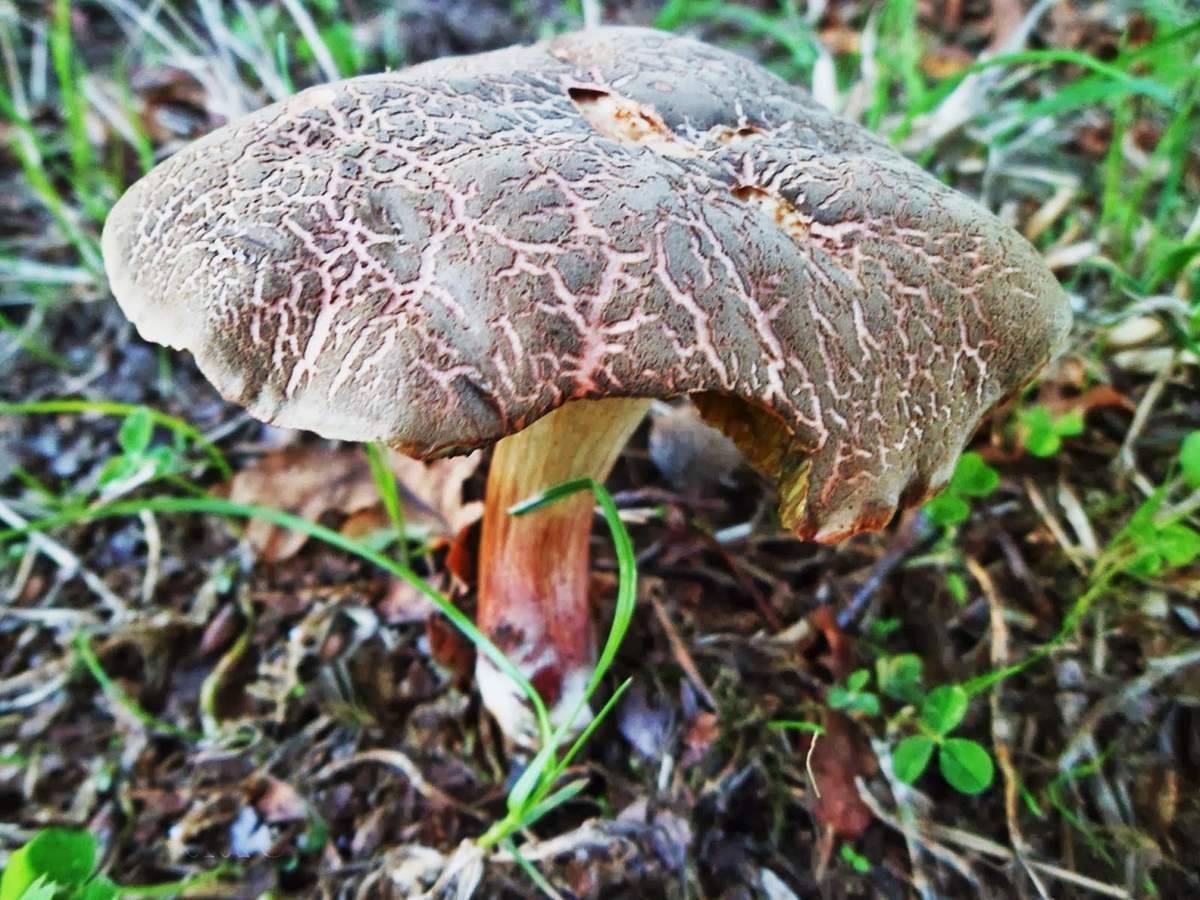
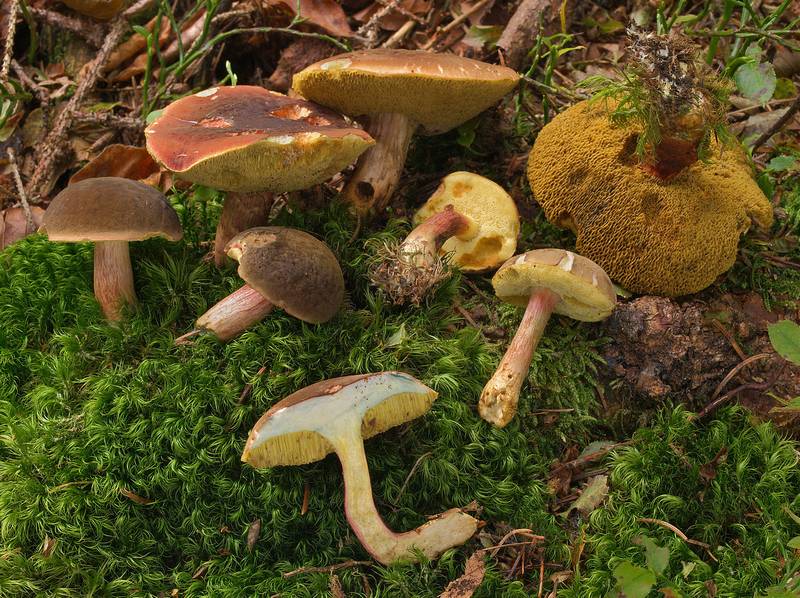
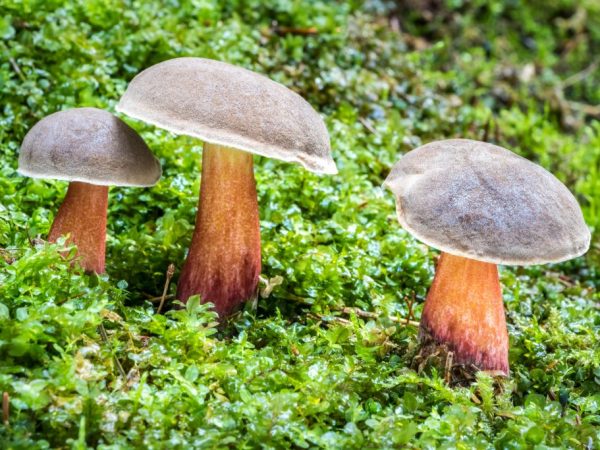
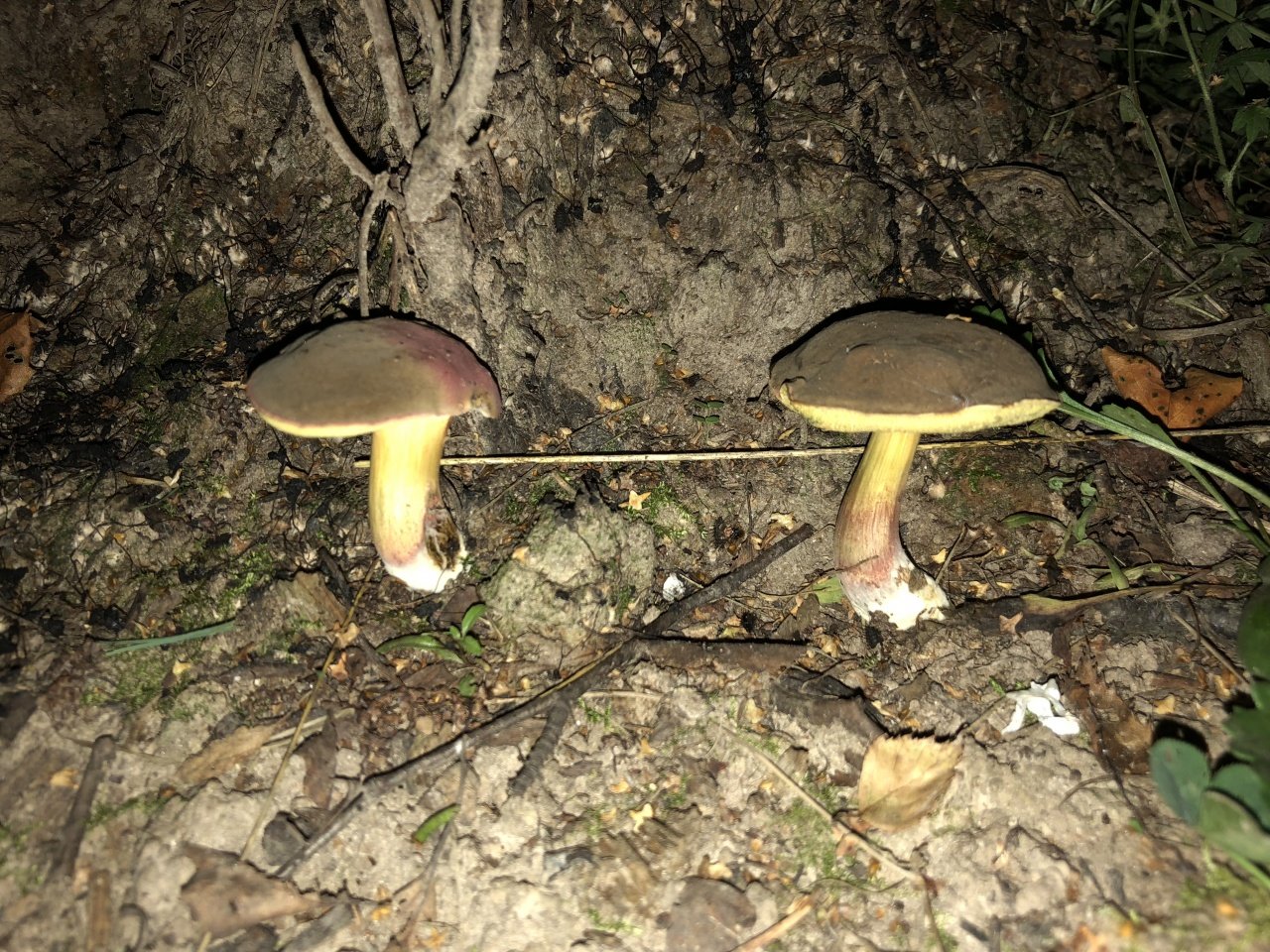
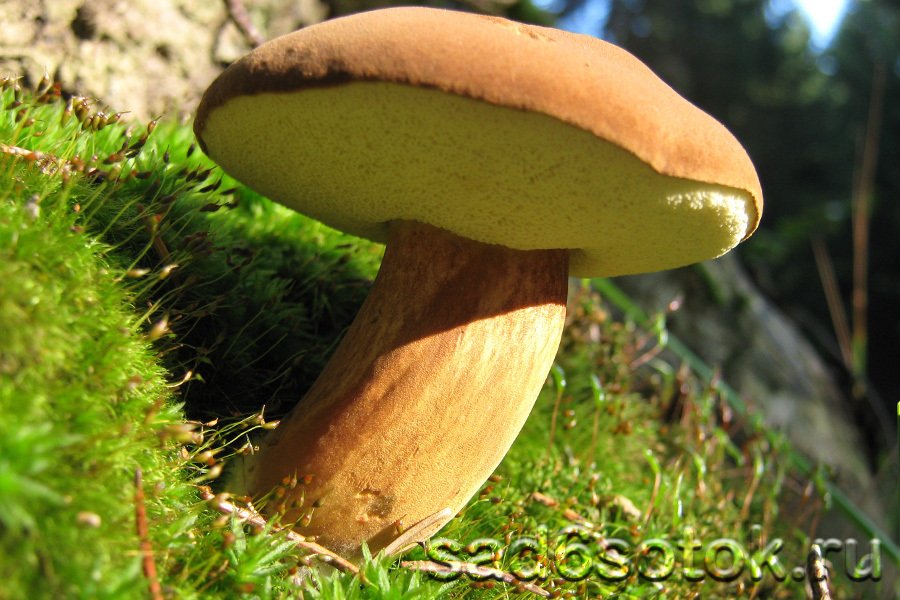
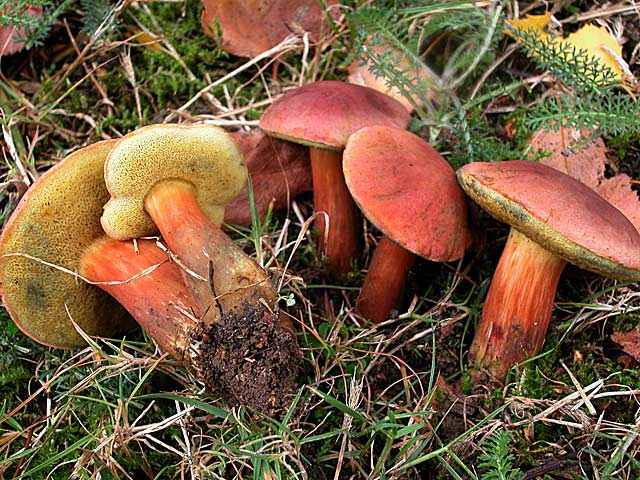
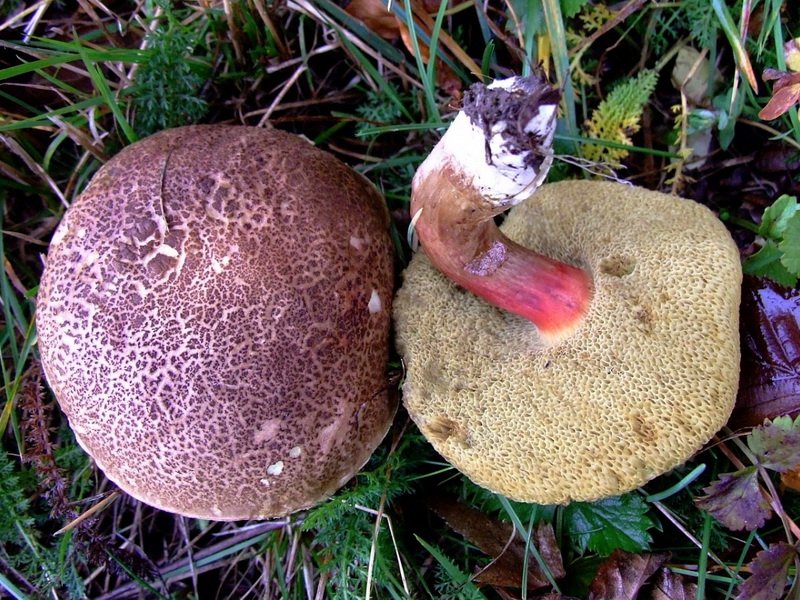
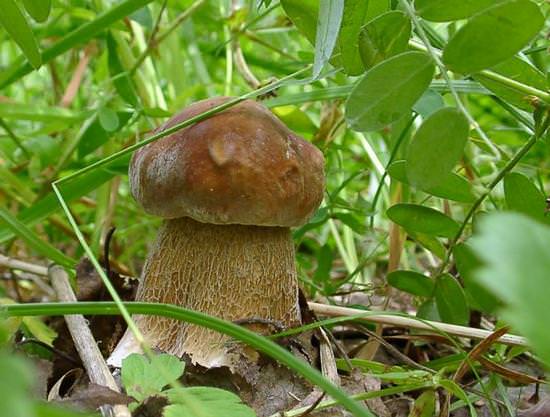
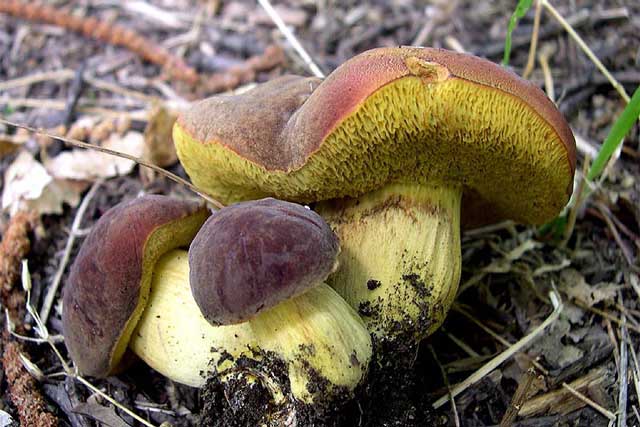
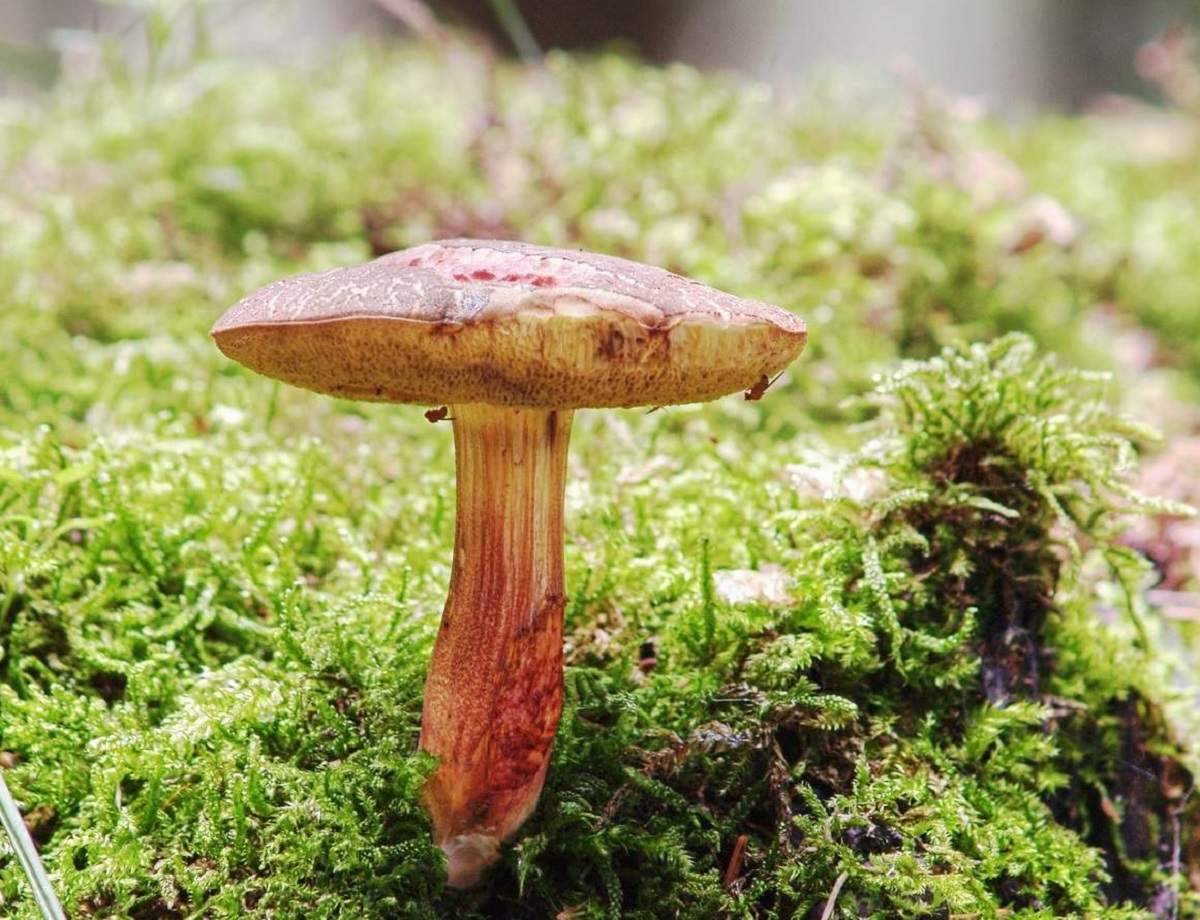
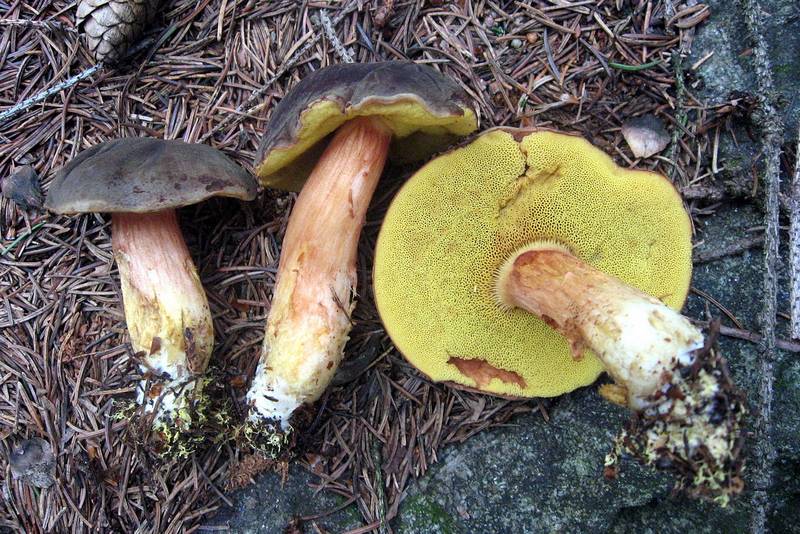
Description of the motley flywheel
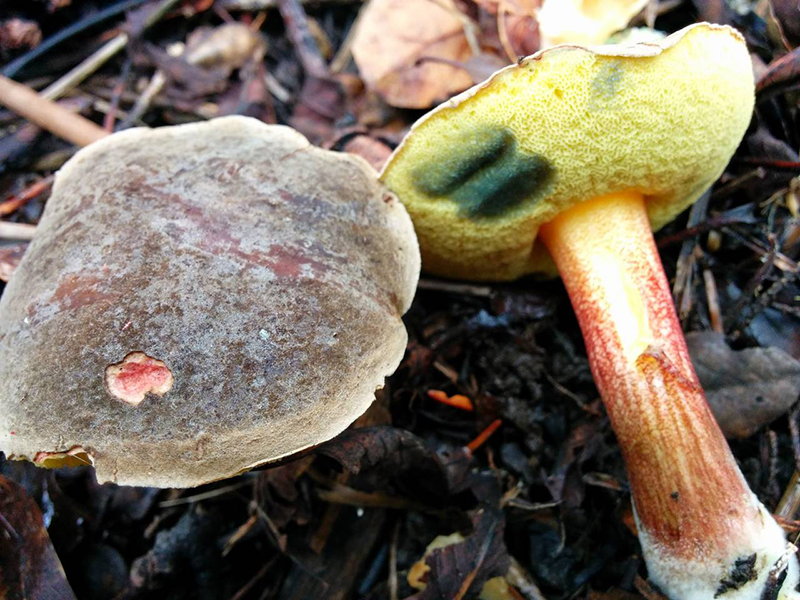
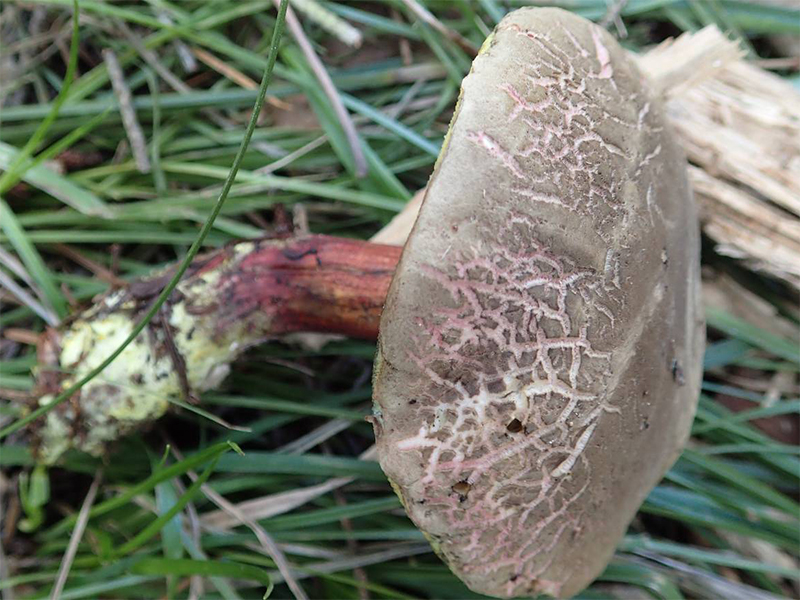
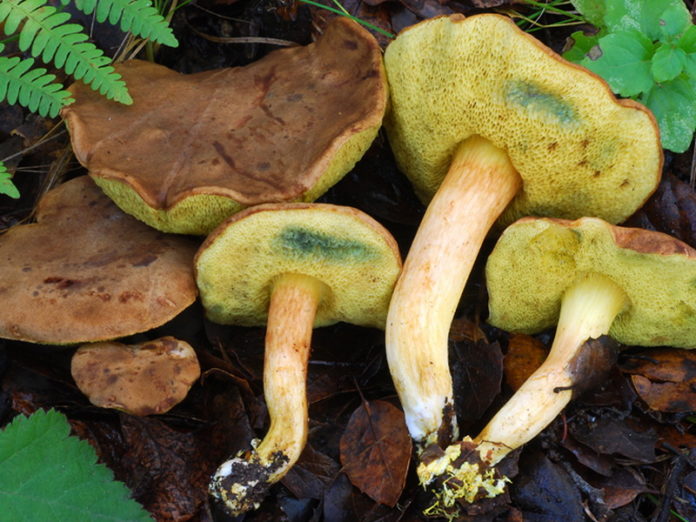
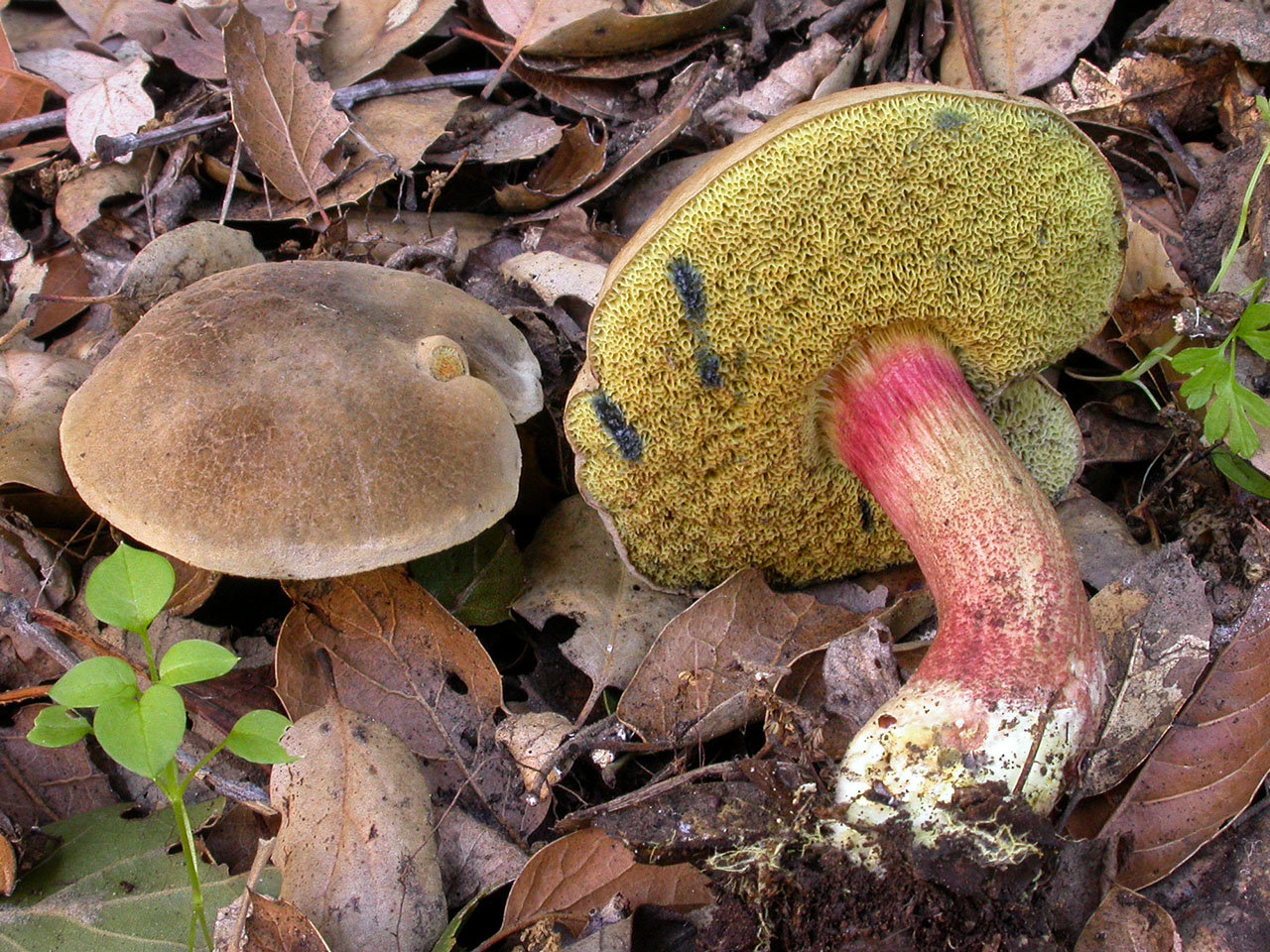
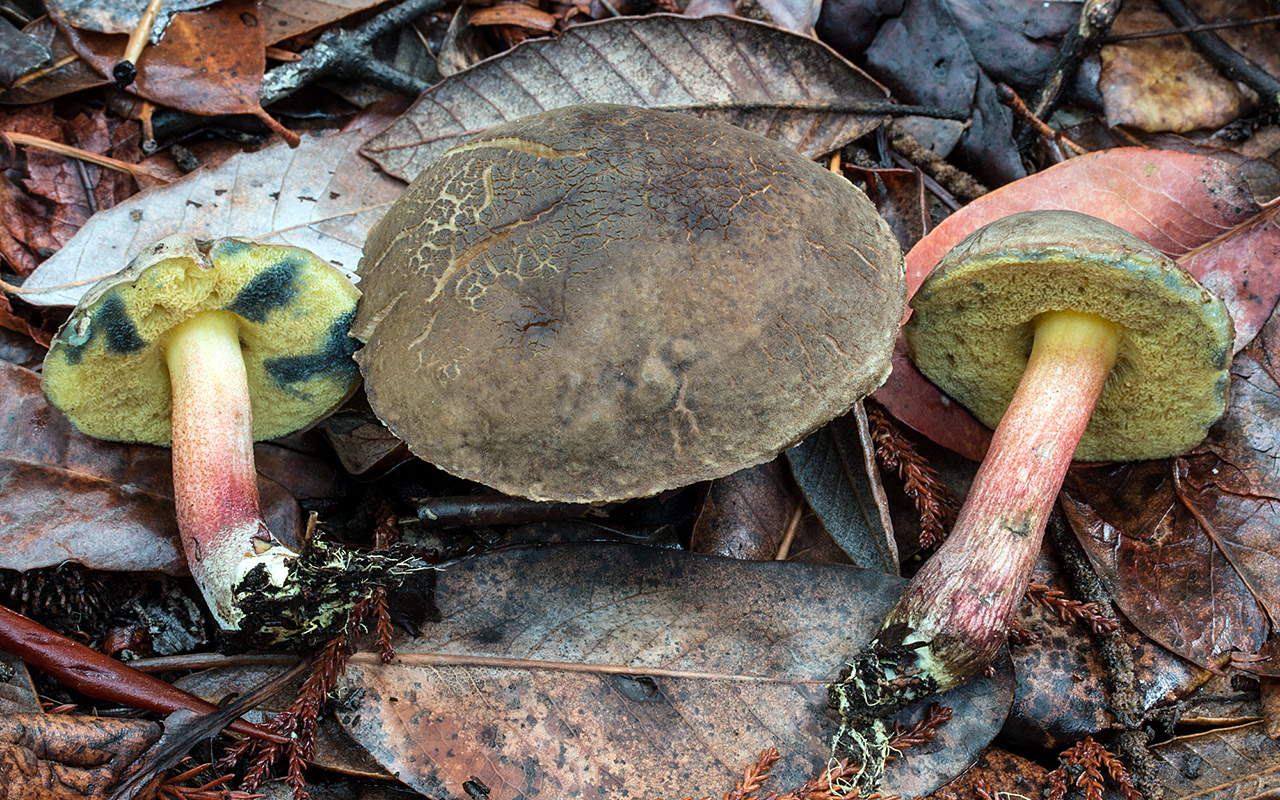
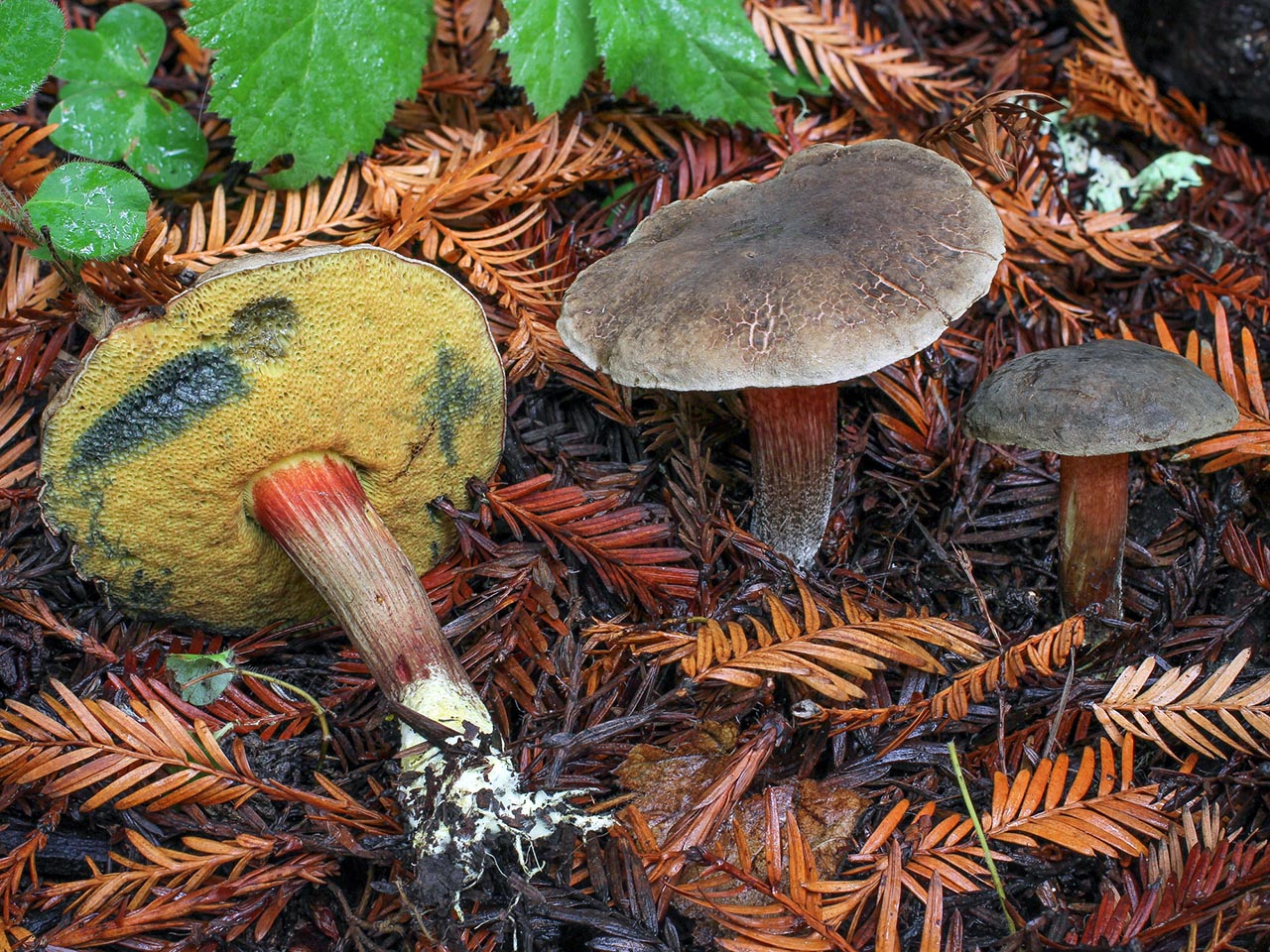
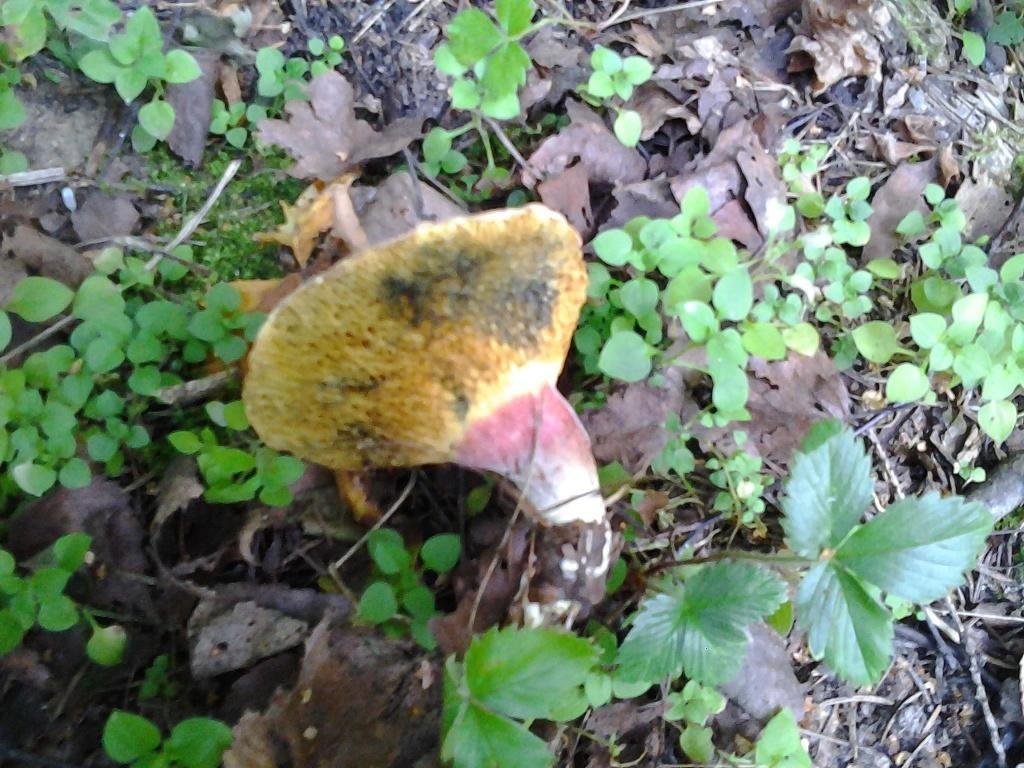
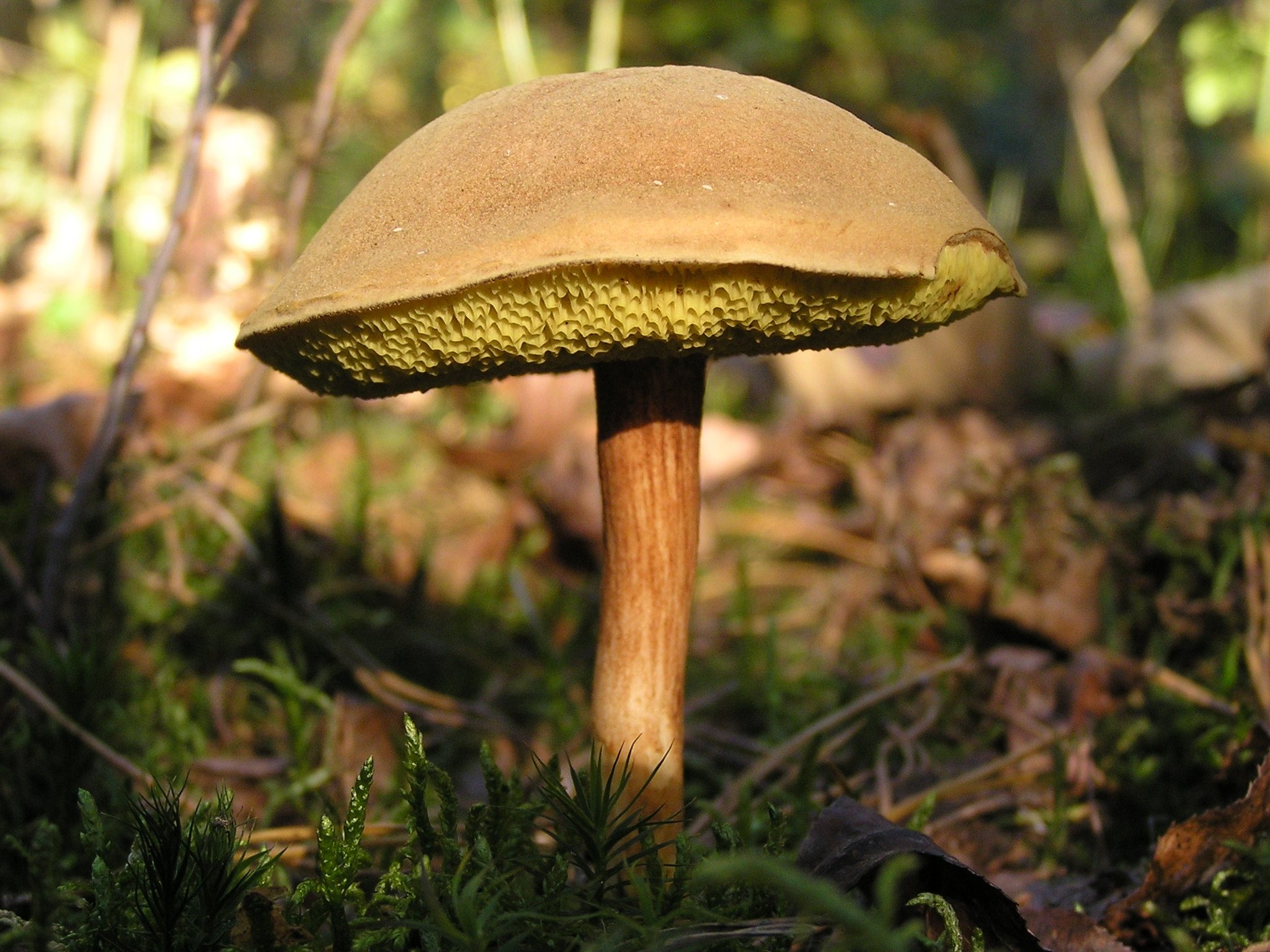
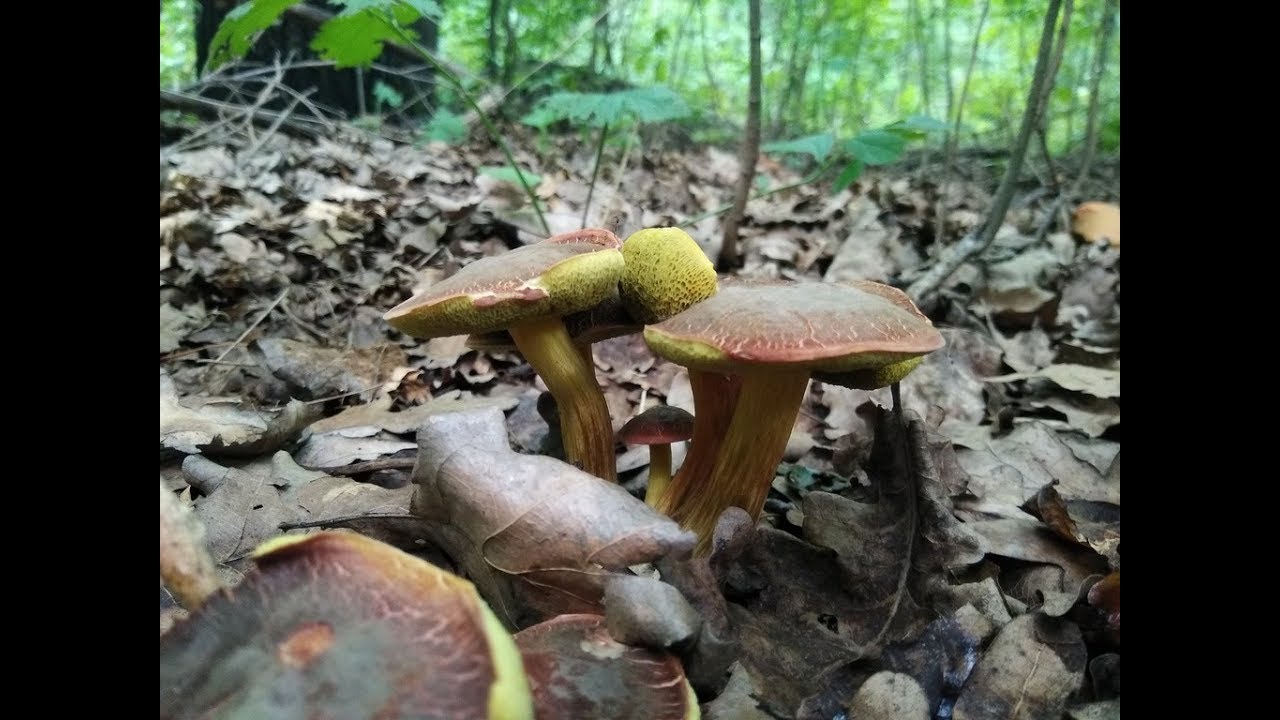
The diameter of the cap of the variegated flywheel reaches 10 centimeters. The hat is fleshy, convex, felt outside, dry. The color of the cap varies from dark brown to light brown. In places of damage and in cracks, the flesh is reddish. The edge of the cap is sometimes decorated with a red-purple edging.
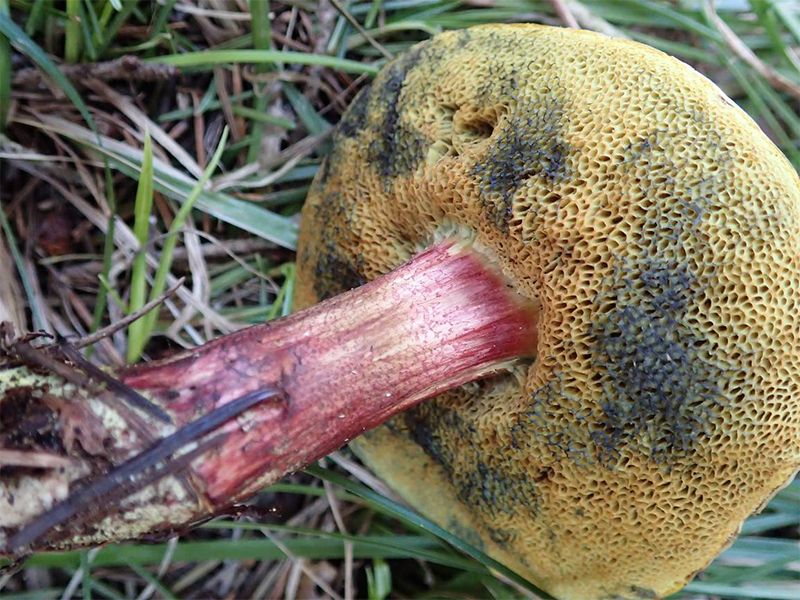
The tubular layer of young specimens is pale yellow, and in mature specimens it is greenish. The tubules can be gray or yellow, and over time they turn olive. The pores are wide enough, if you press on them, they will darken noticeably.
The pulp is loose, yellow-white, at the cut it first turns a little blue, and then turns red. At the base of the leg, the color of the flesh is purplish red. Her taste is sweet, pleasant, and the smell is fruity and delicate.
The length of the leg reaches 9 centimeters, its diameter is 1-1.5 centimeters. The shape of the leg is even, cylindrical, narrowed downward. The leg is solid in structure. The color of the leg is light yellow or yellow-brown, reddish at the base. If you press on the leg, bluish spots appear.
Areas of growth of variegated flyworms
Motley moss are found mainly in deciduous forests, especially in which lindens grow. They do not grow abundantly, but they come across often.
Taste qualities of motley moss
Motley moss is an edible mushroom belonging to the 4th category. These mushrooms are harvested from July to October. Young fruit bodies can be fried and pickled, and they are also suitable for drying.
Other mushrooms of this genus
Velvet moss is an edible mushroom. The diameter of its cap is 4-12 centimeters. At first, the shape of the cap is spherical, but gradually becomes flat. The skin of the cap is velvety, but in mature specimens it is naked and even wrinkled. The color of the cap is variable: brown, purple-brown, red-brown, deep brown, sometimes there may be a pink tint. The leg is 4-12 centimeters high and 0.5-2 centimeters thick. The color of the leg varies from yellow to yellow-red.
Velvety mushrooms grow in deciduous forests, mainly under beech and oak trees, in addition, they inhabit coniferous forests. They bear fruit actively from late summer to early autumn. They grow mainly in groups. Velvet moss is suitable for all types of culinary processing: it can be fried, salted, boiled and dried.
Moravian moss is an edible mushroom. These are reserved mushrooms, they are extremely rare, so their collection is prohibited. The fine for collecting Moravian moss is 50 thousand kroons.
The cap of the Moravian moravian is orange-brown in color, its diameter is 4-8 centimeters. The shape of the cap in young fruiting bodies is hemispherical, but becomes prostrate over time. The hats of old specimens are covered with cracks. The leg is fusiform with pronounced veins. The length of the leg is 5-10 centimeters, and its diameter does not exceed 1.5-2.5 centimeters. The color of the leg is slightly lighter than the cap.
Moravian mushrooms bear fruit from summer to autumn. They grow in deciduous forests, plantings and pond dams. They are distributed mainly in the southern parts of the country.
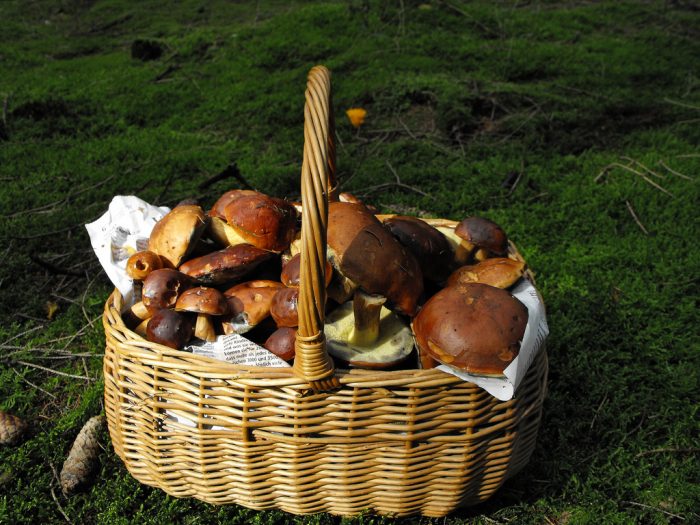
Basket with variegated mushrooms.
Edible flywheel

Among the mushrooms there are both edible and inedible ones. Edible species are used for food without preliminary boiling for first courses, salting, pickling and drying. In cooking, the whole mushroom is used: both the cap and the leg. The skin is removed from the cap, and the leg is peeled. To improve the assimilation of mushrooms, they are thoroughly crushed. Dried mushrooms acquire a beautiful golden hue and pleasant smell.
Flywheels are rich in easily digestible proteins, sugars, enzymes and essential oils, they also contain vitamins A, B, B2, C, D and PP.
In addition, flywheels contain specific substances that quickly darken in air and spoil the appearance of the mushroom. Therefore, before cooking, the mushrooms need to be processed quickly so that they do not stay in the air for a long time in a purified form, they are immediately placed in water. When boiling, a teaspoon of salt and half a teaspoon of citric acid are added per liter of water.
How to collect and prepare flywheels?
Flywheels are harvested from mid-summer to mid-autumn. When collecting, you need to cut off only the fruit body, leaving the mycelium in the ground, so that the next year you can get a crop of moss. The collected mushrooms are sorted out, discarding the spoiled and wormy ones. Then they are thoroughly washed and various dishes are prepared from them. If there are a lot of mushrooms, you can store them in the refrigerator for some time, but not more than 2-3 days. It is better to freeze or dry the excess immediately. Before freezing, the mushrooms should be boiled in salted water for a while.
Flywheels can be pickled and salted. They are good because their caps do not need to be peeled off: it is enough to rinse and scrape the damaged areas with a knife. Marinades are prepared on the basis of vinegar with the addition of various ingredients. Boil the mushrooms before pickling. Mushrooms are salted hot and cold. In the first case, garlic is never added and boiled for a short time so that the mushrooms do not creep. Otherwise, the methods of salting mushrooms do not differ from other mushrooms.
Dishes made from mushrooms are very varied. It can be salads, soups, main courses, aspic. Mushrooms can be added to pizza, vegetable caviar, and pie filling. Dried mushrooms are used to add to various sauces. Cooked in any way, these mushrooms taste great.
Photo by: George Chernilevsky, public domain
Useful properties and contraindications
In their composition, mushrooms contain many healthy substances: enzymes that facilitate the digestion of food; natural sugars, thanks to which dishes made from them are considered low-calorie and suitable for dietary nutrition; vitamins PP, D and B; microelements, including molybdenum and calcium, according to the content of which, mushrooms occupy a leading position among mushrooms.
Mushrooms do not produce harmful effects on the body. Most mushrooms are perceived by the stomach as a heavy food, therefore people with chronic liver and gastrointestinal tract diseases are advised to refrain from eating mushroom dishes in large quantities. However, mushrooms do not create such a pronounced effect of gravity on the stomach as other mushrooms. Still, you should not offer them to children under 3 years old and, of course, those who are allergic to mushrooms.
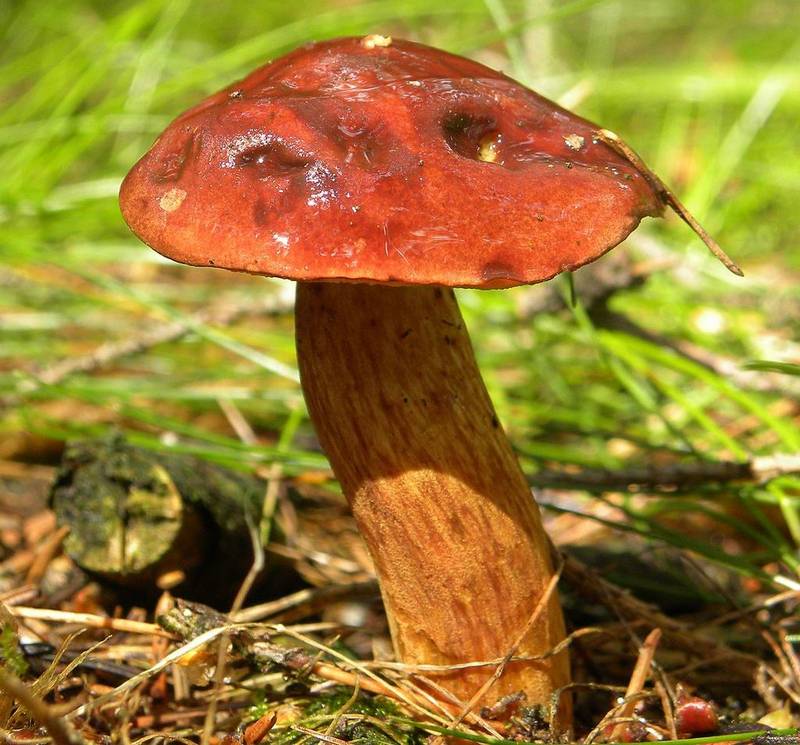
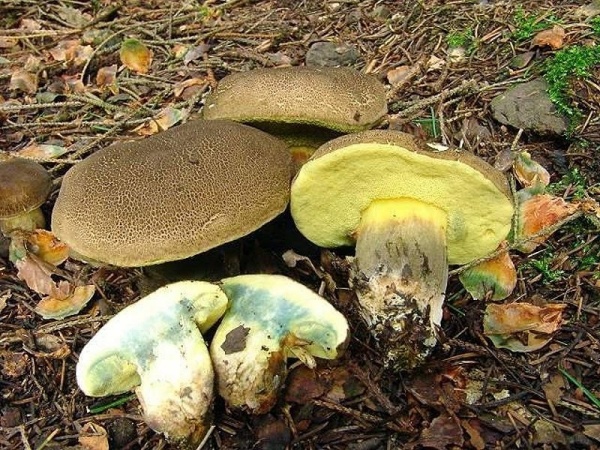
False doubles of a mushroom with a red cap and a red leg
Borovik blushing has false doubles that are poisonous. Outwardly, they are somewhat different. See photo.
The table clearly shows the features of the reddish edible Moss and its poisonous counterparts:
| Hat
(Colour) |
Hymenophore (color) | Pulp
(cut) |
Leg
(Colour) |
|
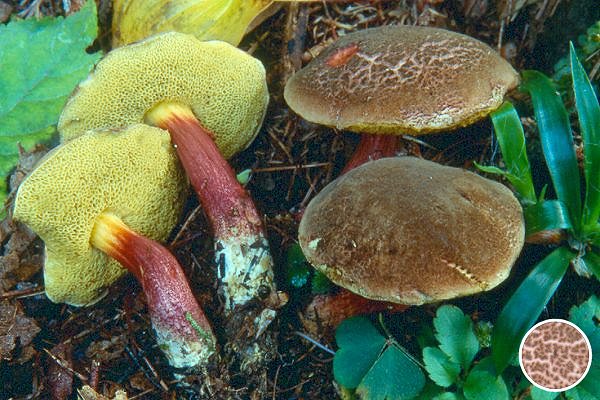
Flywheel red |
Red-brown | Yellow, turns blue quickly | Yellow, slowly turning blue | Top yellow, bottom red |
Boletus sensibilis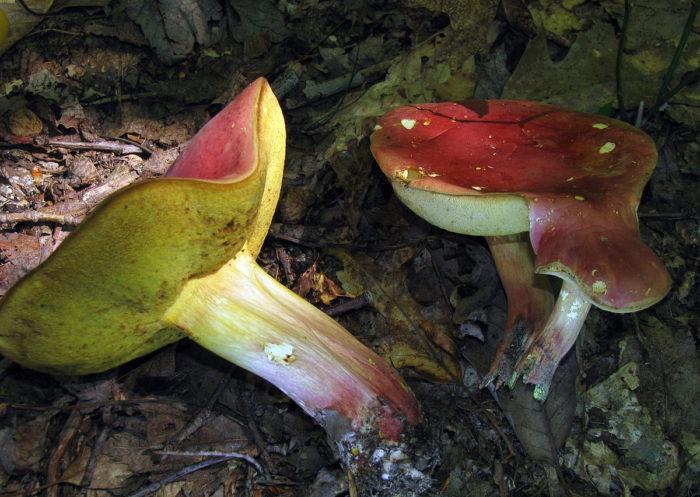 |
Brick red | Yellow | Yellow, turns blue quickly | Reddish |
Boletus calopus |
Gray, brown | Yellow | Yellow | Brown |
Wood flywheel |
Red brown | Red brown | Yellow | Red-brown |
Pepper mushroom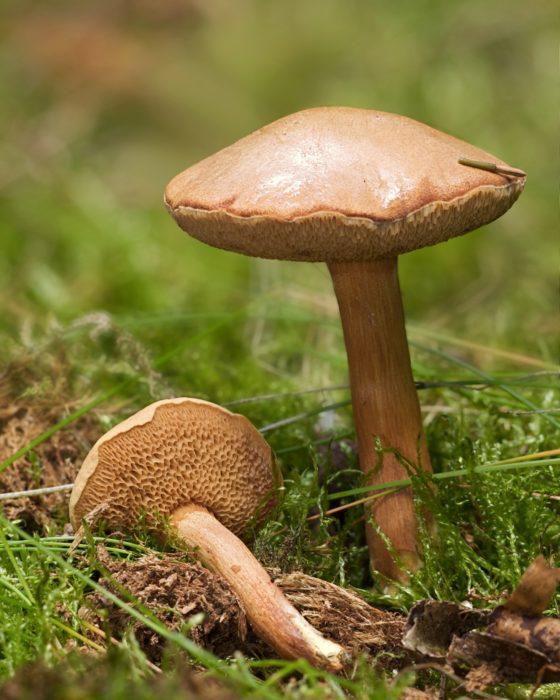 |
Light brown | Red brown | Yellow, reddens when cut | Brown |
Larch flywheel (Psiloboletinus lariceti)
Synonyms:
- Boletinus lariceti
- Larch boletin
Psiloboletinus is a genus of fungi of the Suillaceae family. It is a monotypic genus containing one species, Psiloboletinus lariceti. The species was first described by the mycologist Rolf Singer in 1938 as Phylloporus. Alexander H. Smith disagreed with Singer's general concept, concluding: “Regardless of which arrangement of the type species Psiloboletinus is ultimately made, it is clear that there are no clearly distinguishable characters by which the genus could be recognized. based on Singer's descriptions ”.
"Larch" - from the word "larch" (a genus of woody plants of the pine family, one of the most common species of conifers), and not from the word "deciduous" (Deciduous forest - a forest consisting of deciduous trees and shrubs).
Description
Hat: 8-16 cm in diameter; under favorable conditions, specimens with caps of about 20 centimeters are possible. In youth it is convex, with a strongly tucked inward edge, then flat-convex; in very adult mushrooms, the edge of the cap is not tucked up, it may be slightly wavy or lobed. Dry, felted or tomentose-scaly, velvety to the touch. Brownish, ocher-brown, dirty brown. Flesh in the cap: dense (not loose), soft, up to 3-4 cm thick. Light yellowish, light buffy, very pale, almost white. Turns blue at a break or cut.
Hymenophore: tubular. The tubules are large, wide, with thickened side walls, and therefore visually form a semblance of plates. They run down strongly on the leg, where they become elongated, which is why their visual resemblance to the plates increases. The hymenophore is yellow, light in youth, then yellowish-brownish. When damaged, even minor, it turns blue, then turns brown.
Spores: 10-12X4 microns, cylindrical, fusiform, brown-yellow with drops.
Leg: 6-9 centimeters high and 2-4 cm thick, central, can be thickened at the bottom or in the middle, velvety. In the upper part it is light, in the color of the hymenophore, yellowish-brownish, below it is darker: brownish, brownish, dark brown. Turns blue when pressed. Whole, sometimes with a cavity. The flesh of the leg: dense, brownish, blue.
Ring, bedspread, volva: none.
Taste and smell: mild mushroom.
Ecology
It grows only in the presence of larch: in larch forests and mixed forests with the presence of birch, aspen, under larch.
Season and distribution
The peak of fruiting occurs in August-September. It is well known only on the territory of Russia, found in Western and Eastern Siberia, Amur region, Khabarovsk Territory, in the Far East, especially often and abundantly bears fruit on Sakhalin, where it is called "Larch moss" or simply "moss".
Edibility
The mushroom is edible, there is no data on poisoning. It is used for making soups, salads, main courses. Suitable for pickling.
Similar species
A slender pig in some growth stages can be mistaken for a larch flywheel. You should carefully look at the hymenophore: in the pig it is lamellar, in young specimens the plates are wavy, so that at a cursory glance they can be mistaken for large tubes
An important difference: the pig does not turn blue, but turns brown when tissue is damaged
Gyrodons are quite similar to Psiloboletinus lariceti, you should pay attention to the ecology (type of forest). Goat, it differs in the color of the flesh in the damaged areas, its flesh does not turn blue, but turns red
The goat, differs in the color of the flesh in the damaged areas, its flesh does not turn blue, but turns red.
Healing properties
Purposeful studies were carried out, there are works on the thrombolytic properties of enzymes of basidal fungi (Botanical Institute named after V. L. Komarov, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia), where there is a high fibrinolytic activity of enzymes isolated from Psiloboletinus lariceti. However, it is too early to talk about widespread use in pharmacology.
Note: The photographs from the questions in "Recognition" are used as illustrations in this article. If you have good photos of this mushroom, please share.
Types of mushroom flywheel
Pan mushroom or chestnut flywheel (Boletus badius)
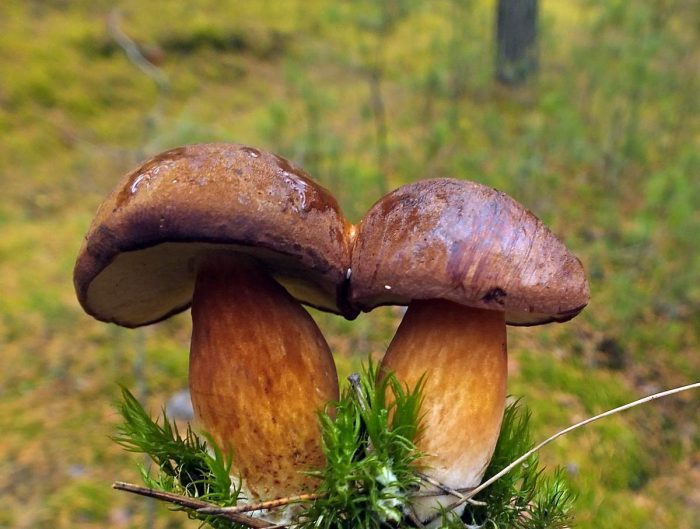

Also known as brown or polish mushroom.
The hat is 4-12 cm in diameter, the shape is semicircular, convex, later becomes cushion and even flat. The skin does not separate, the surface is smooth, dry, becomes sticky in wet weather, matte in young mushrooms, shiny in mature ones. Colored chestnut brown or brown. The pulp is fleshy, dense, whitish or yellowish in color, turns blue on the cut. The aroma is pleasant, mushroom.The leg is 4-12 cm high, 1-4 cm thick, cylindrical, narrowing or widening downward, fibrous structure, light brown, brown or yellow with red-brown fibers.
The mushroom grows next to pines, spruces, beeches, oaks, chestnuts, in conifers, sometimes in deciduous forests, singly or in small groups. The species is distributed in the northern temperate zone of the European part of Russia, in the North Caucasus, in Siberia, in the Far East. The season runs from June to November.
Good quality edible mushroom. Used for freezing, drying and pickling.
Fractured flywheel (Xerocomellus chrysenteron)
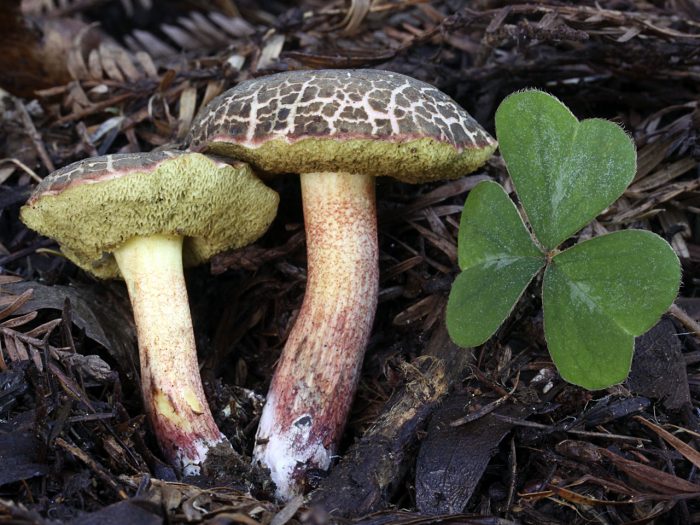

The diameter of the cap is 3-7 cm, the shape is convex or cushion-shaped, less often with a depression in the center, the surface is dry, matte, velvety or bare, burgundy-red, brown, olive-brown, brown, brown-red, ocher-gray. The hat cracks, forming a characteristic mesh. The pulp is white or with a yellow tinge, reddish at the base of the leg and under the cap, turns blue at the cut. Leg 4-10 cm in height and 1-2 cm in thickness, clavate, solid, smooth, fissured surface, light yellow with a red base.
The species is widespread in Europe, the North Caucasus, and the Far East. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests. Fruiting from July to September.
An edible mushroom that is eaten fresh and salted, and is also dried or frozen for use in fried and first courses.
Red flywheel (Xerocomellus rubellus)
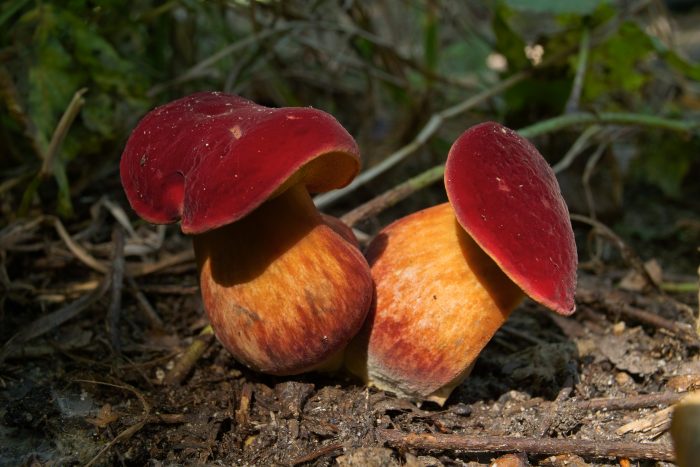

The cap is 2-5 cm in diameter, cushion-convex in shape, flattens with age. Colored bright red. The skin does not separate, the surface is velvety-felt, cracks in mature mushrooms. The leg is cylindrical, tapering towards the base, 3-10 cm in height, about 1 cm in diameter, solid, fibrous, fine-scaled. The color of the stem is yellow with a raspberry-pinkish, reddish or reddish-brown base. The pulp is dense, yellow, turns blue on the cut.
The mushroom grows in deciduous forests, often in oak forests of Europe, North Africa, Asia. The harvest season lasts from August to September. Does not bear fruit abundantly.
An edible mushroom with a pleasant aroma, the taste is not expressed. Used fresh. Darkens on drying.
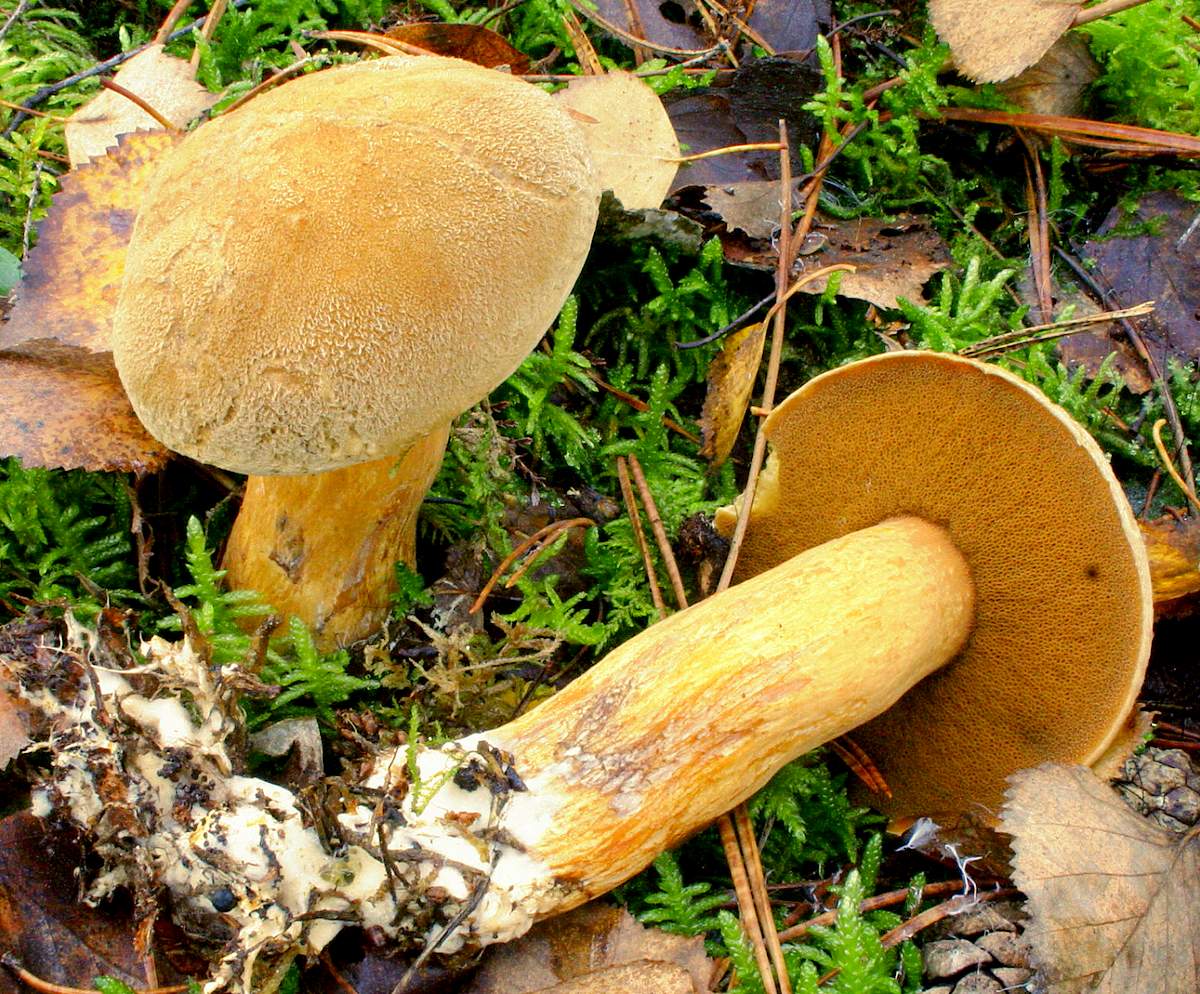
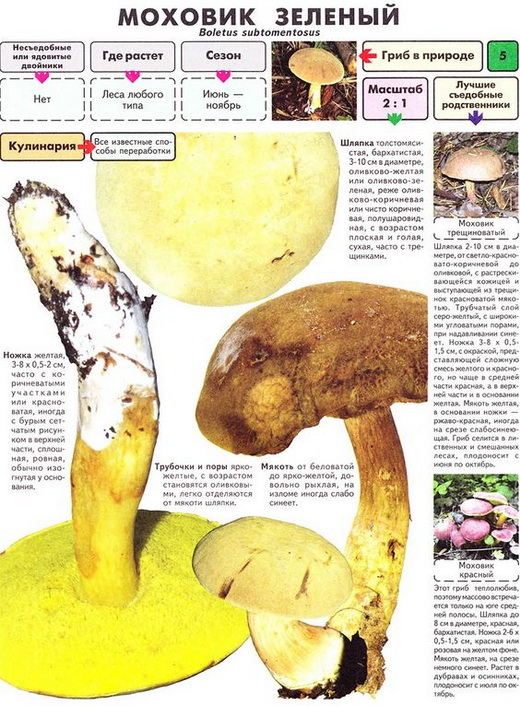
Green flywheel (Xerocomus subtomentosus)
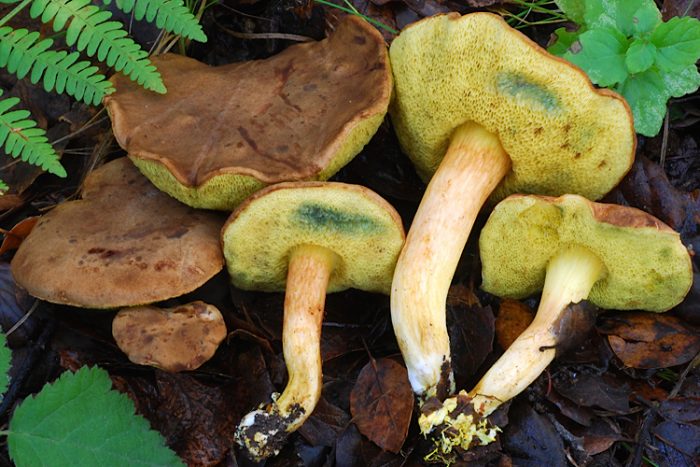

The diameter of the cap is 3-10 cm, the shape is pillow-convex, the surface is velvety, grayish or olive-brown in color. The pulp is white, turns blue on the cut. The leg is cylindrical, tapers towards the base, 4-10 cm in height, 1-2 cm in thickness, the surface is smooth, the structure is fibrous.
Grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, in clearings, along roads, singly or in groups. It is a cosmopolitan mushroom, as it is distributed on all continents. Fruiting occurs in May-October.
An edible mushroom, used fresh. Darkens on drying.
Mosswheel

Mosswheel. belongs to the genus of tubular fungi and grows from early summer to autumn in coniferous, deciduous and mixed forests singly or in small groups. The cap is hemispherical, with time it becomes convex and then flat. From above it is velvety, dark green or brown-brown, spongy layer is bright yellow. The flesh is firm, pale yellow, white in old mushrooms, turns blue at the break. Mosswheel fully justifies its name and grows, as a rule, in moss. Different forests are suitable for the flyworm, but more often he prefers to settle in conifers and, more specifically, in pine forests.
The genus Mokhovik unites 18 species that are widely found in the temperate zones of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Green flywheel - edible mushroom (3 categories), better at a young age. Chestnut moss is an edible mushroom. Red flywheel is an edible mushroom, although it is often damaged by larvae. Powdered flywheel is an edible mushroom. The Polish mushroom is a good edible mushroom. In central Europe, they say, it is valued on a par with white. Motley moss is one of the most popular mushrooms. Unfortunately, it is often damaged by larvae and quickly becomes moldy.Fried, boiled, dried, pickled. Semi-golden flywheel is a conditionally edible mushroom. Wood flywheel is a conditionally edible mushroom. Blunt-spore moss - conditionally edible mushroom Astraea moss is an inedible, non-toxic mushroom. The parasitic flywheel, the parasitic flywheel is an inedible non-toxic mushroom.
By nutritional value and taste, mushrooms are conventionally divided into four categories.
Category 1 includes the most valuable and delicious species that give excellent quality mushroom products (for example, white - birch, oak, pine, spruce; mushrooms - pine, spruce).
Category 2 includes good and rather valuable mushrooms that are not inferior in quality to the previous ones (aspen mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, blue mushrooms and aspen mushrooms).
The third category includes mushrooms that are collected only in the "mushroomless" (blue russula, autumn mushroom, flyworm).
Category 4 includes such mushrooms that most mushroom pickers usually bypass, and in rare cases only individual amateurs collect them. These are such mushrooms as oyster mushrooms - common, autumn, green russula, ram mushroom, marsh oil can.
Useful properties of a flywheel
Mosswheel is a first-class edible mushroom that can be used without prior boiling for cooking hot dishes, for pickling, pickling, and drying. The whole mushroom is used - the cap and the leg.
The flywheel contains a large amount of easily digestible proteins, sugars, various enzymes and essential oils. Mushrooms are very rich in extractive substances that give them a peculiar taste and smell, as well as enzymes that contribute to better digestibility and assimilation of food.
Almost all edible mushrooms contain vitamins A, B, B2, C, D and PP. Studies have shown that mushrooms are not inferior to grain products in terms of vitamin B content. Vitamin PP in them is the same as in yeast, liver, and vitamin D is not less than in butter.
To improve the digestibility and assimilation of the mushrooms, it is recommended to grind well.
It should not be forgotten that mushrooms contain easily oxidizing substances, which, when in contact with air, quickly darken and give such mushrooms an unattractive appearance. To avoid this, the processing of such mushrooms should be done as quickly as possible, trying not to allow the peeled mushrooms to stay in the air for a long time, but immediately immerse them in water. For one liter of water, be sure to add a teaspoon of salt and two grams of citric acid.
Dangerous properties of the flywheel
Like other types of mushrooms, mushrooms are considered to be a heavy food, therefore they are not advised to be used for chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal stroke.
The cap of the fly agaric is similar to the cap of the so-called panther fly agaric, which is one of the most poisonous mushrooms. Therefore, you need to look carefully at the back of the cap - in the fly agarics it is tubular, and in the fly agaric it is lamellar.
Flyworms can also harm those who are diagnosed with chronic liver or stomach diseases or allergies to mushrooms.
Carefully they should be given to children, not including babies under 3 years old in the diet. Also, remember that you should not collect mushrooms near roads and in forest belts from enterprises, as they accumulate harmful substances.
Also remember that you do not need to collect mushrooms from the roads and in forest belts from enterprises, as they accumulate harmful substances.
In this video, you can see the flywheel, as well as learn about its characteristic features. This information will be especially useful for mushroom pickers.
Description of the false flywheel.
The listed types of mushrooms are quite similar to a real flywheel. But each species is characterized by certain differences:
- The parasitic flywheel is characterized by its small size, its cap in diameter does not exceed 5 centimeters, and in edible flywheels, the caps most often reach up to 10 centimeters in girth. In addition, a parasitic flywheel can be recognized by its growing areas.If common flyworms are found on moss, then parasitic flyworms prefer to settle on other mushrooms - raincoats,
- Gall and pepper fungus can be recognized by the white, pinkish or dirty brown cut of the flesh, which later turns red.
- The chestnut mushroom is characterized by a red-brown color of the cap, which sometimes cracks in hot weather. The cut of the chestnut mushroom is yellowish, it does not change in air.

Gyroporus chestnut Gyroporus castaneus
What to do if you ate a false flywheel.
It is worth noting that none of the false flyworms are poisonous, therefore, you can not poison yourself with either a pepper, bilious, chestnut mushroom, or a parasitic flywheel. Basically, all of these species are classified as inedible because of their bitter taste.

Flywheel parasitic Pseudoboletus parasiticus
The gall mushroom is very bitter, and with heat treatment, the bitterness becomes even stronger. Some mushroom pickers recommend soaking the mushroom in salt water to remove the bitterness, and then cook.

Flywheel parasitic Pseudoboletus parasiticus
Pepper mushroom has a pungent peppery taste, but compared to the gall mushroom, this bitterness is even pleasant. And with prolonged heat treatment, the bitterness disappears completely.

Pepper mushroom chalciporus piperatus
After boiling, the chestnut mushroom is rather bitter, so it is used mainly for drying, in this case the bitterness disappears.

Flywheel parasitic Pseudoboletus parasiticus
The parasitic flywheel is edible, but there are few people who want to taste this mushroom, since it has an unpleasant taste.
Conclusion
Flywheels are not the last in the hierarchy of mushroom pickers' preferences. To get the maximum benefit and pleasure from the harvested crop, you should carefully consider their collection and remember the main feature: the false mushroom that is not edible on the cut does not turn blue.
Systematics:
- Department: Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes)
- Subdivision: Agaricomycotina
- Class: Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes)
- Subclass: Agaricomycetidae
- Order: Boletales
- Family: Boletaceae
- Genus: Boletus (Borovik)
- View: Boletus subtomentosus (Green moss)
Synonyms:
Xerocomus subtomentosus
Despite the classic "mossy", so to speak, appearance, this species is currently referred to the genus Borovik (Boletus).
Collection points:
Green moss is found in deciduous, coniferous forests and shrubs, usually in well-lit places (along the sides of paths, ditches, on the edges), sometimes grows on rotten wood, anthills. It settles more often singly, sometimes in groups.
Description:
The cap is up to 15 cm in diameter, convex, fleshy, velvety, dry, sometimes cracked, olive-brown or yellowish-olive. The tubular layer is adherent or slightly descending to the pedicle. The color is bright yellow, later greenish-yellow with large angular uneven pores, when pressed, they turn bluish-green. The flesh is loose, whitish or light yellow, slightly blue on the cut. Smells like dried fruit.
The leg is up to 12 cm, up to 2 cm thick, thickened at the top, narrowed downward, often curved, solid. The color is yellowish-brown or red-brownish.
Differences:
Green flywheel is similar to and, but differs from them in large pores of the tubular layer. The green flywheel should not be confused with the conditionally edible one, which has a yellowish-red color of the tubular layer and the pungent bitterness of the pulp.
Usage:Green moss is considered an edible mushroom of the 2nd category. For cooking, the whole body of the mushroom is used, consisting of a cap and a leg. Hot dishes are prepared from it without preliminary boiling, but with the obligatory peeling of the skin. Also, the mushroom is salted and pickled for longer storage.
Eating an old mushroom that has begun to break down protein can lead to severe food poisoning. Therefore, only young mushrooms are collected for consumption.
The mushroom is well known both to experienced mushroom pickers and to novice lovers of quiet mushroom hunting. According to its taste, it is highly rated.
This material presents the types of moss that can be found in almost any forest. A photo and description of the mushroom mushrooms are offered, which are accompanied by full botanical characteristics. What edible and inedible varieties of the flywheel have, you can read in the characteristics.
The description of the mushroom mushroom of each variety includes an indication of the possibility / impossibility of eating it.