Collection rules
Collecting mushrooms is quite simple, since the risk of taking a poisonous mushroom instead of an edible mushroom is quite insignificant. Similar inedible species are easily identified, so at home, when parsing and processing the gifts of the forest, they are easy to reject. Do not take mushrooms with worms, especially if you have a long way home. During the time until the harvest reaches the processing point, the worms will not only spoil the wormy mushroom even more, but also infect the neighboring ones.
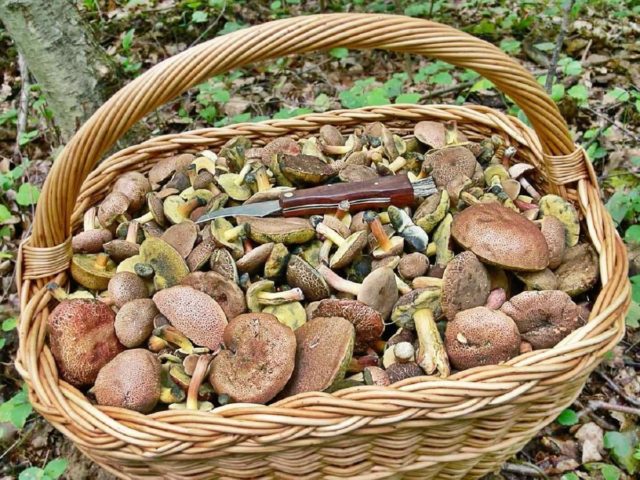

Silent hunting is quite an exciting experience. Communication with the forest, with wildlife always has a positive effect on the body. Plus, picking mushrooms is a great way to diversify your menu. However, one must also remember that the fruiting bodies of fungi are capable of accumulating heavy metals and radionuclides in themselves. Therefore, you should not collect them in the immediate vicinity of the sources of these harmful substances: highways, industrial zones, railways. And also, you should not take mushrooms if there is no 100% confidence in their edibility and safety.
How to recognize a flywheel
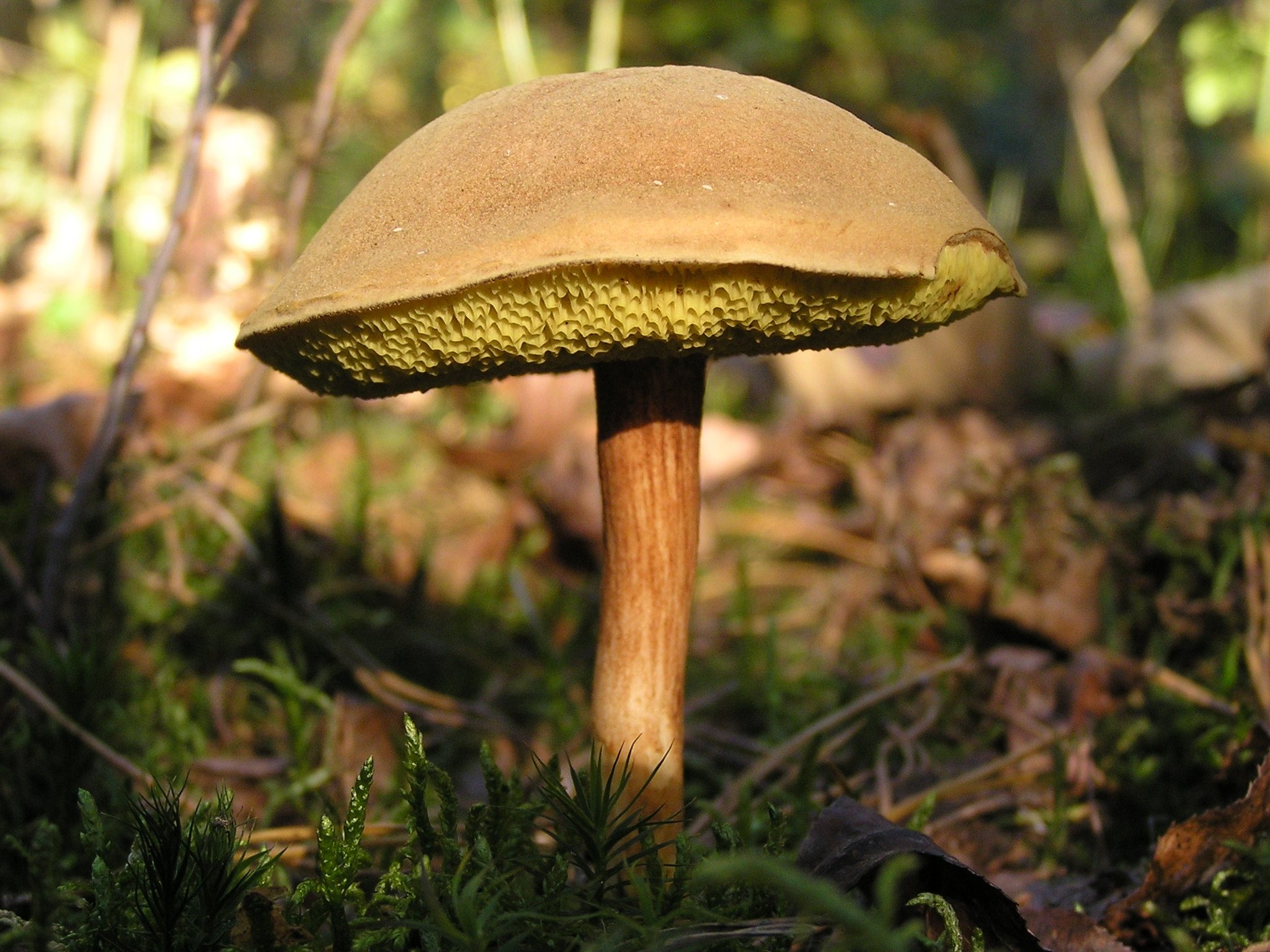
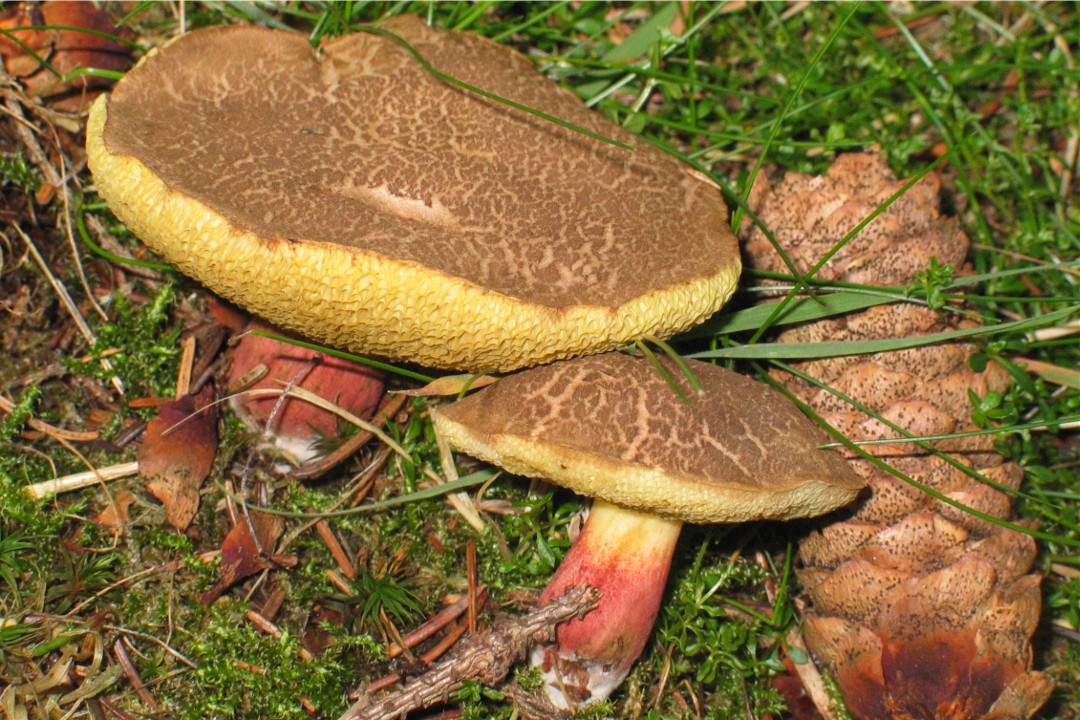
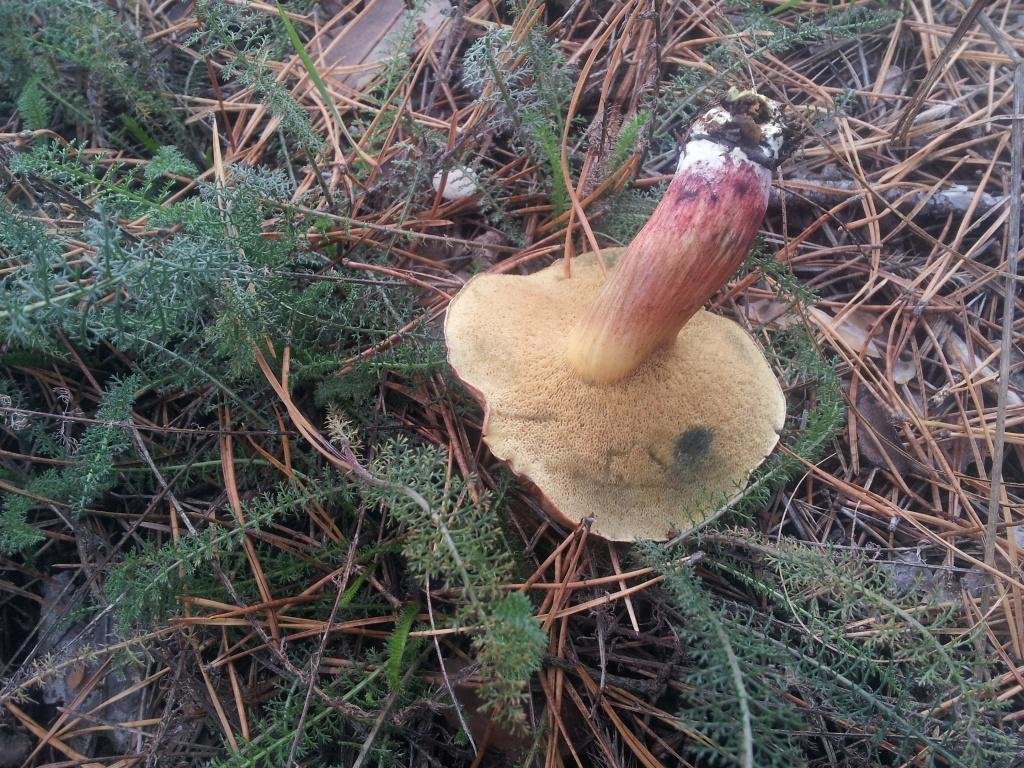
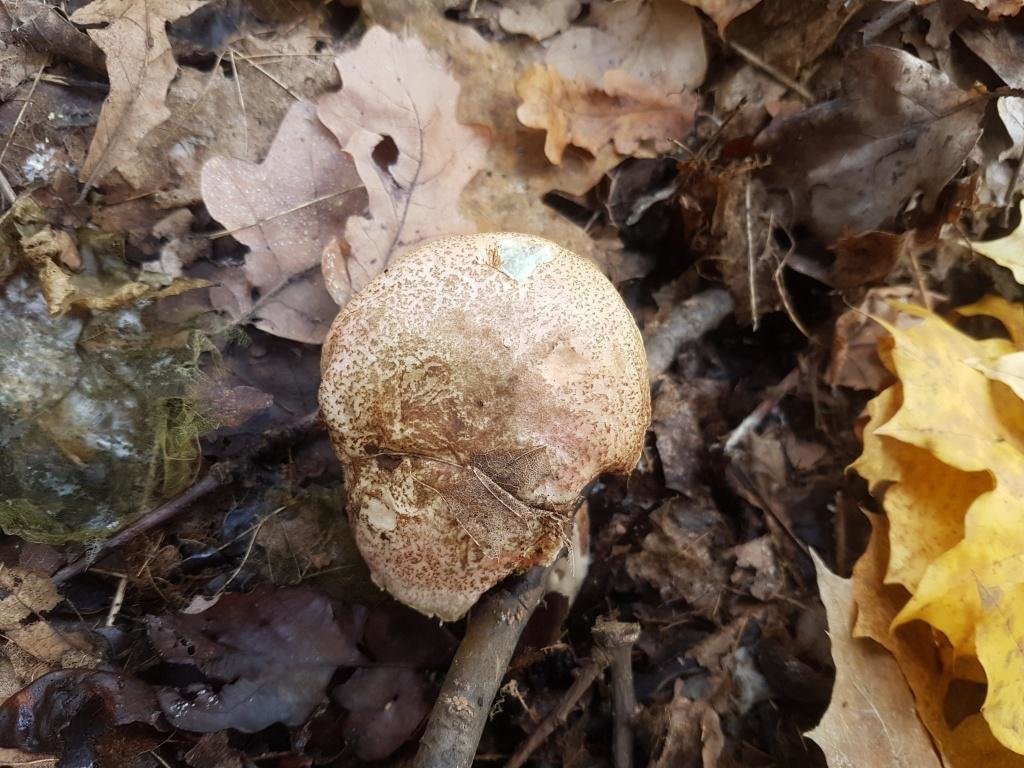
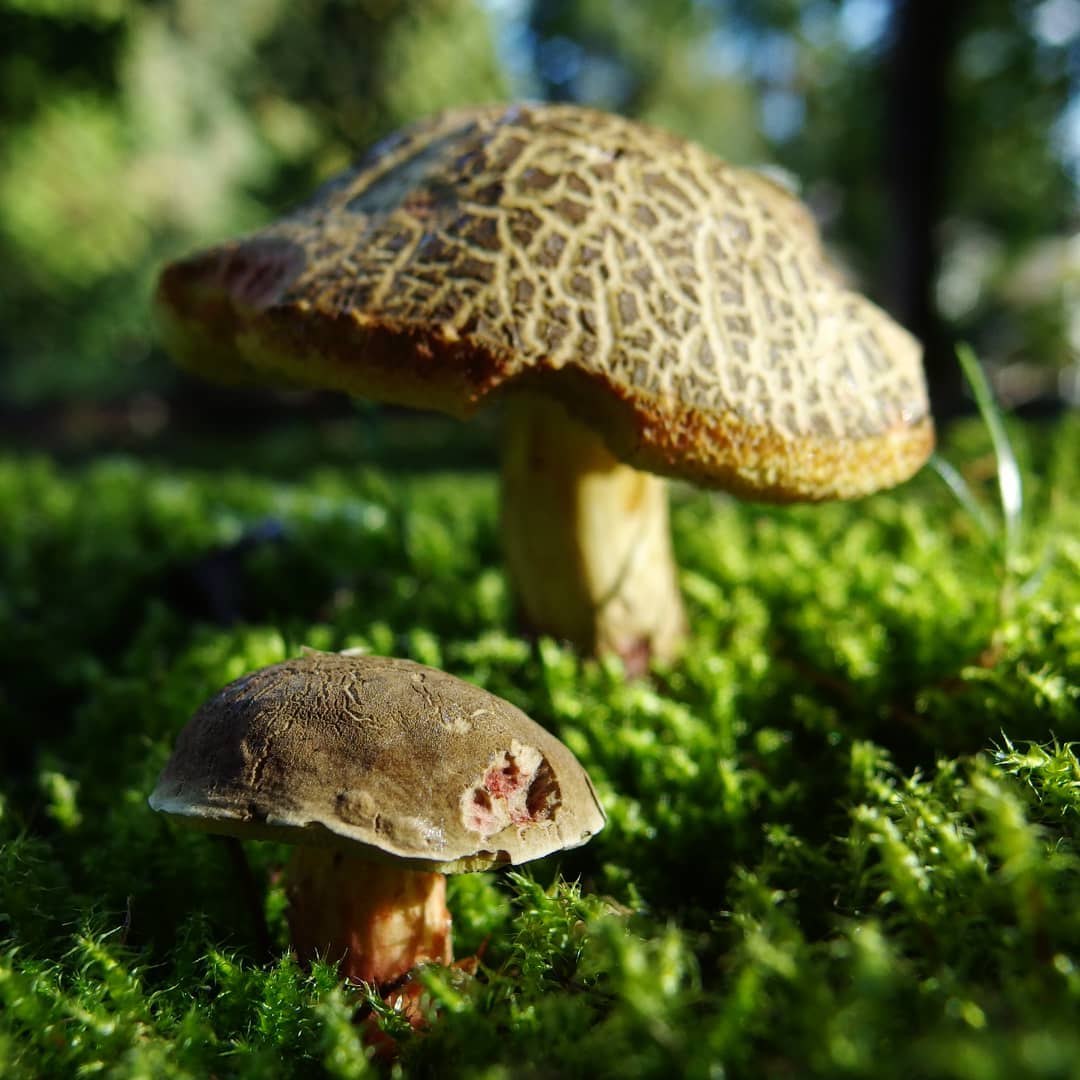
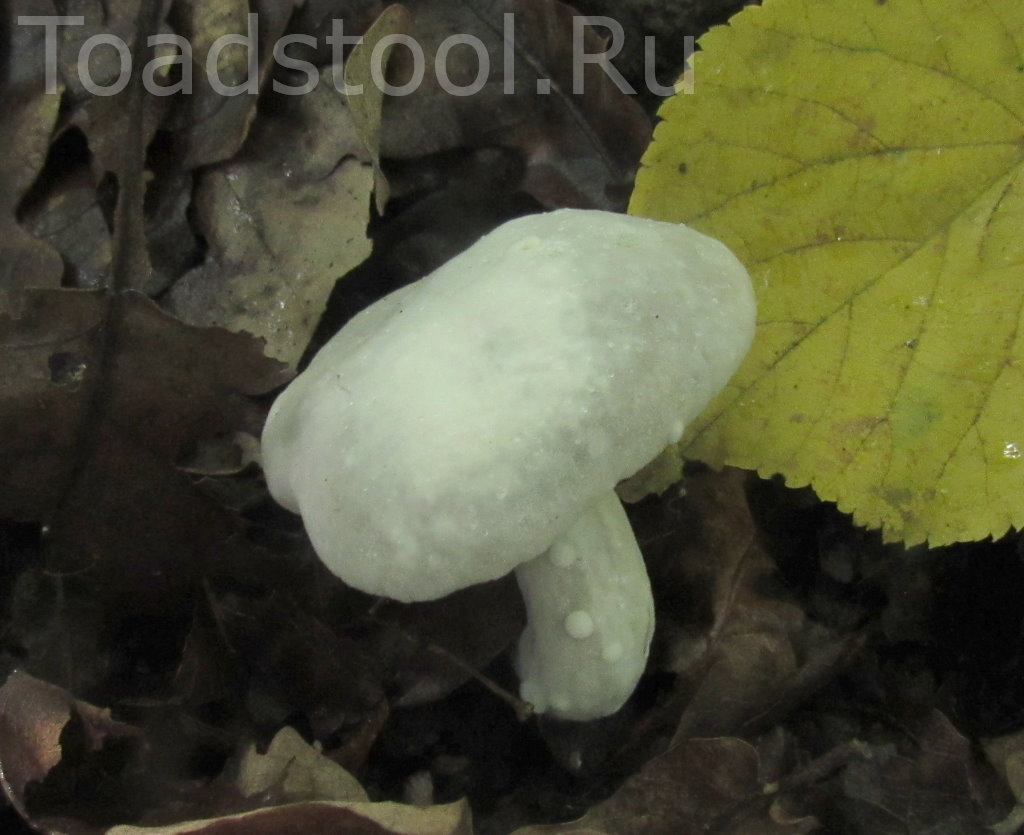
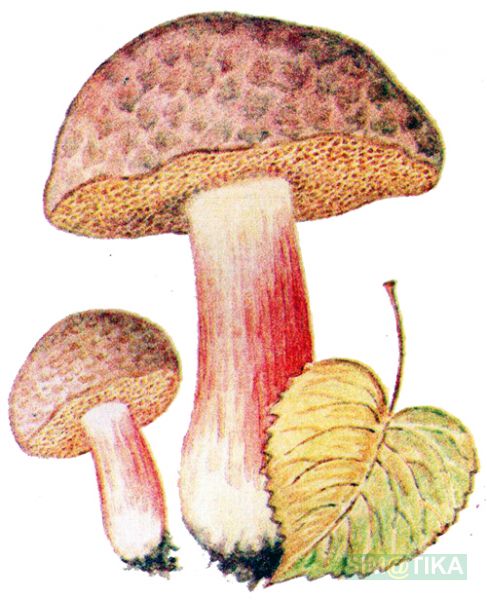
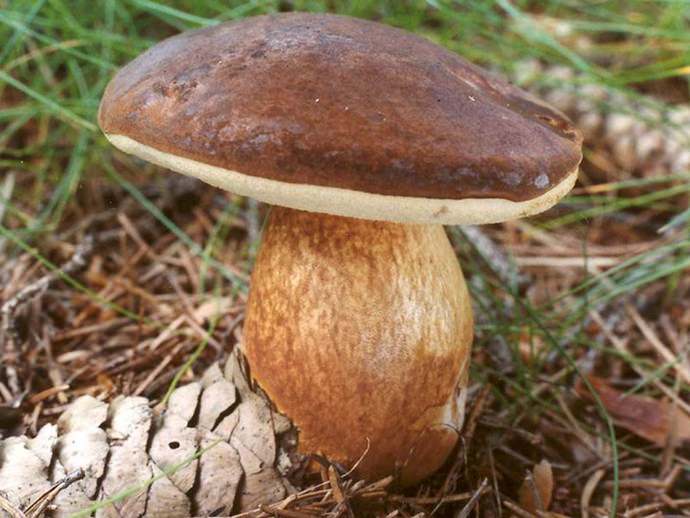
Mosswheel is a tubular representative of the Boletov family (to which the porcini mushroom also belongs - outwardly they are even slightly similar). Mushroom pickers recognize the flyworm by its massive hemispherical cap, which becomes flat in older specimens. The velvety dry cap, depending on the type of mushroom, can be brown-brown or olive-green, the stem is wrinkled, white and without a ring. The pulp is quite hard, yellowish, although after damage (on the cut) it quickly changes color - it turns blue. But such external transformations do not in any way affect the taste characteristics of the product.
Mycologists who have studied the huge family of moss plants have divided them into 18 species. Among them there are Polish, green, chestnut, red, powdered, semi-golden, woody, parasitic and others. Some of them may be conditionally edible, some have received the stigma of inedible. But in any case, there are no pronounced poisonous among them. This means that none of the representatives of the mushrooms (even inedible ones) can cause severe poisoning, since it does not contain toxic substances. And some mushroom pickers even believe that among the "moss family" there are no inedibles - they all go to the dining table, you just need to know how to cook correctly. True, not all mycologists can agree with this.
You can go to any forest in search of mossworms. They are found in deciduous, mixed and pine forests. The only requirement is the presence of moss. As the name implies, these forest dwellers simply adore the moss mat, on which they are comfortably accommodated either alone or in whole families.
Description and photo
Due to its incredible taste, this forest gift is very popular among mushroom pickers. Finding a basket of flywheels is a real success. But how to distinguish it from other representatives of the forest kingdom? Of course, for this you need to know what this mushroom looks like.
From Latin - xerocomus subtomentosus.
Hat
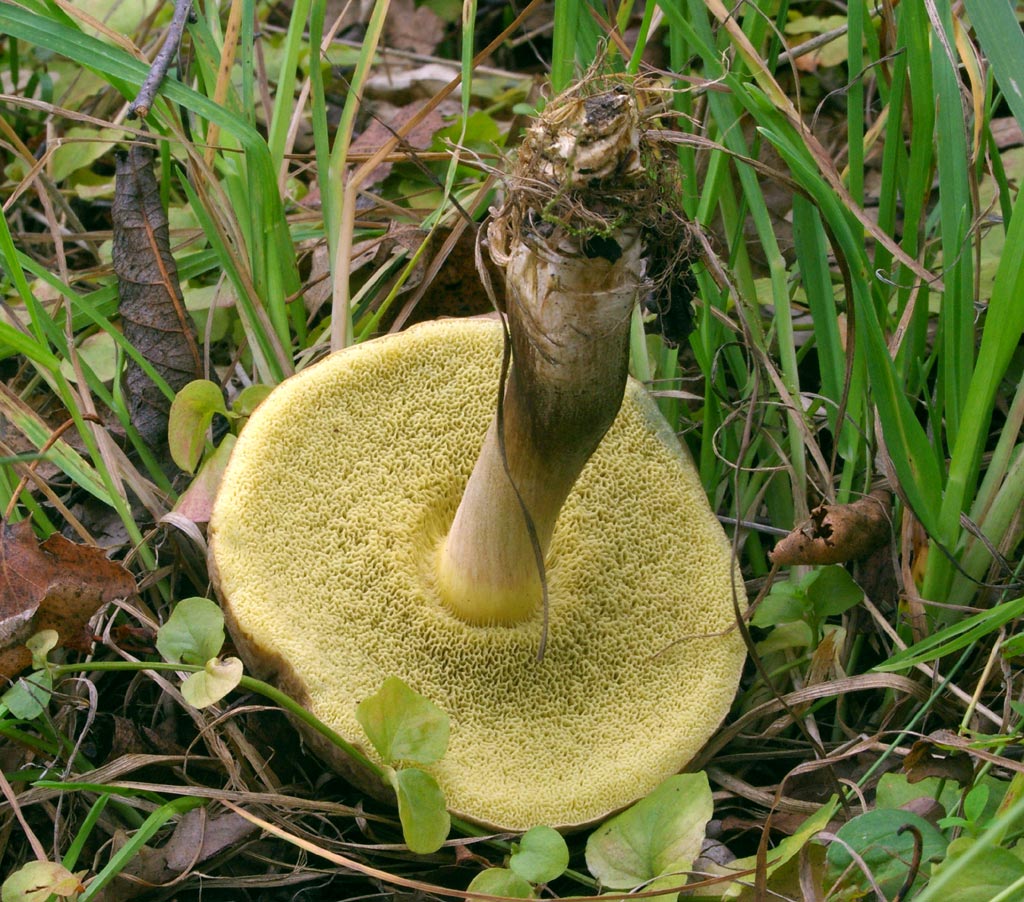
The cap of the flywheel is very dense and has a diameter of 4 to 12 cm. In many respects, it depends on the conditions in which the mushroom grows and what its age is. If we talk about color, then it can be called green at a stretch. It usually has a greenish gray or olive surface. Sometimes it is even brown, but this applies to old mushrooms. The shape is slightly convex. If you touch the mushroom from above, then it has a very velvety pleasant hat. However, every touch leaves a small mark and imprint on it.
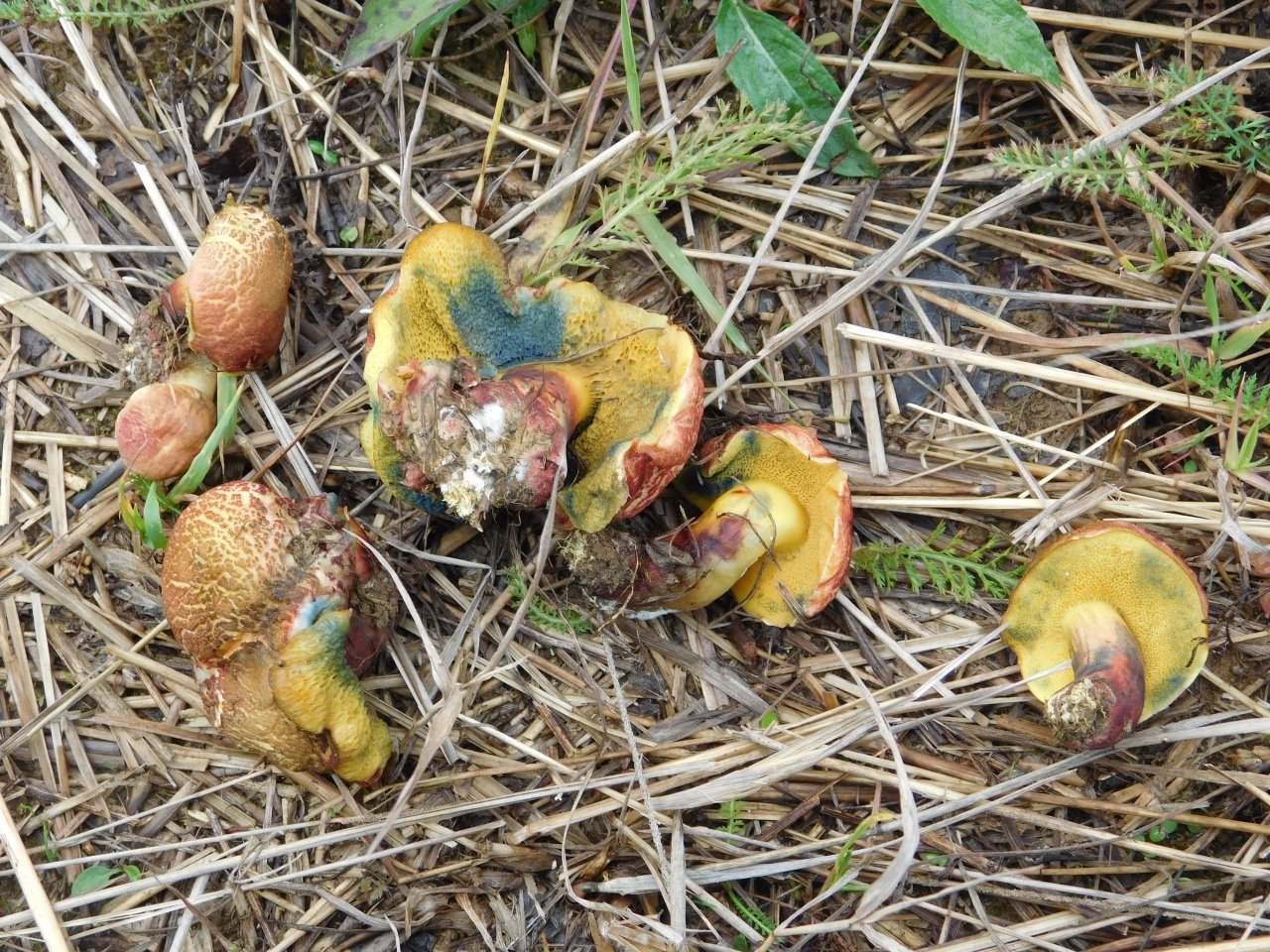
On the cut, the pulp is white and does not lose its hue when interacting with oxygen. Smells very tasty, also dense. There are small white tubes under the cap, from where the spores fall out. The tubular layer is yellow, has a greenish or olive base. If you press hard, then this mushroom will begin to turn blue.
Leg
The stem of the mushroom, on the other hand, has the shape of a cylinder. Stable, and its pulp is no less tasty than the cap. White when cut, turns blue when pressed.
Despite the fact that this fungus is edible, it still sometimes becomes covered with mold, which can be dangerous to humans. However, it can be cleaned off.
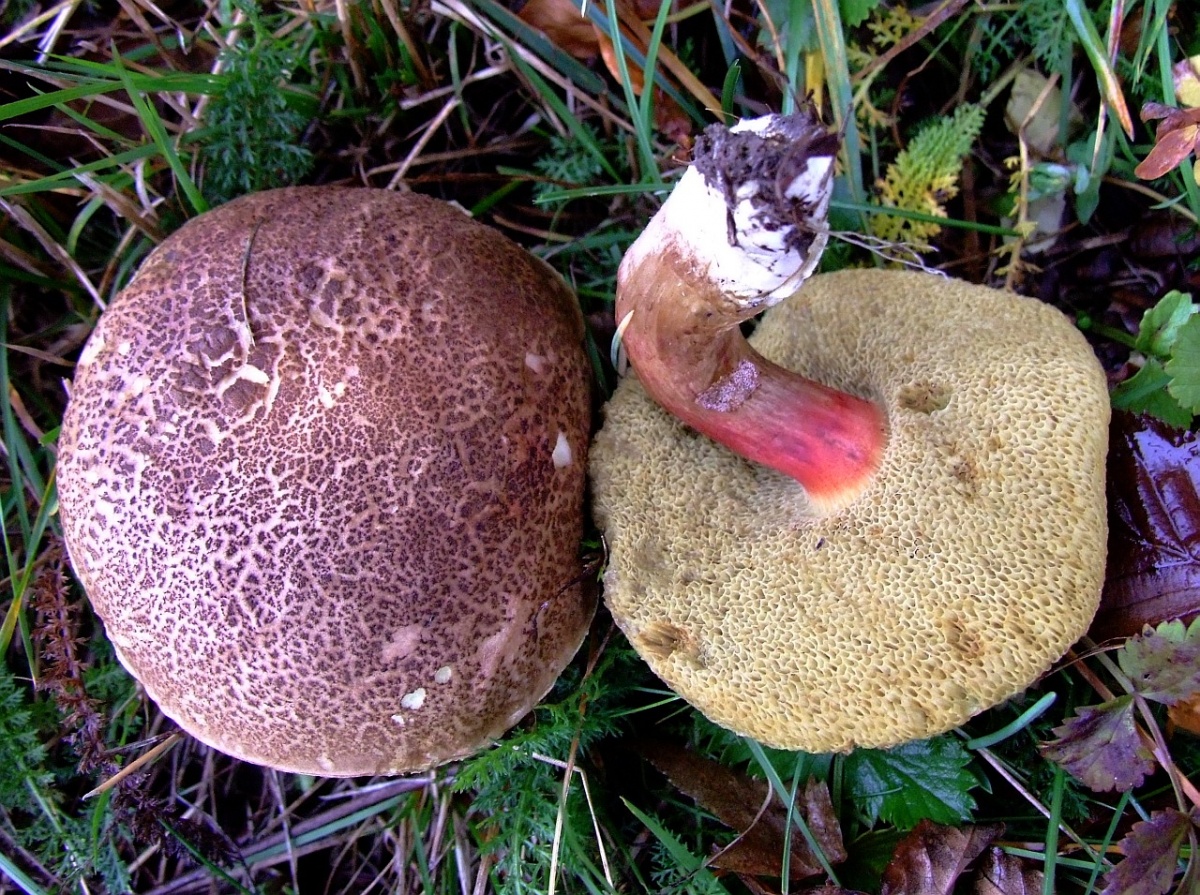
Why does the flywheel turn blue? This very much worries the people who collect it. Sometimes, seeing that blue is forming under the imprint, mushroom pickers refuse to collect. In fact, the pulp turns blue due to a special process. However, this is not at all a sign that the mushroom is poisonous. It contains substances that, if damaged, begin to react with oxygen. As a result, the oxidation process begins. It is because of him that the surface darkens. A dark film is formed during oxidation
Types of mushroom flywheel
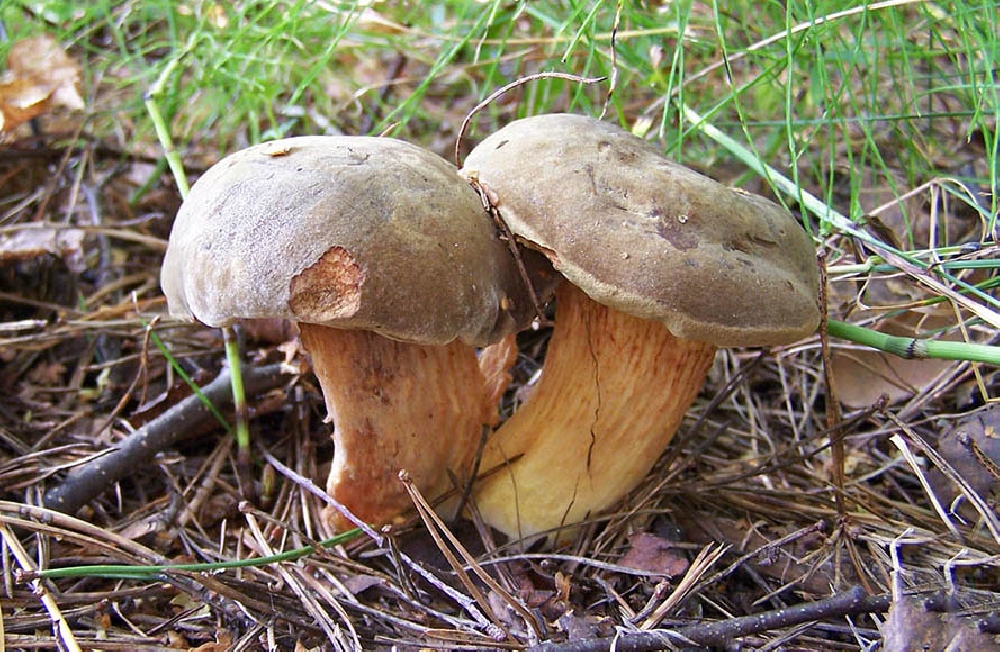
Pan mushroom or chestnut flywheel (Boletus badius)
Also known as brown or polish mushroom.
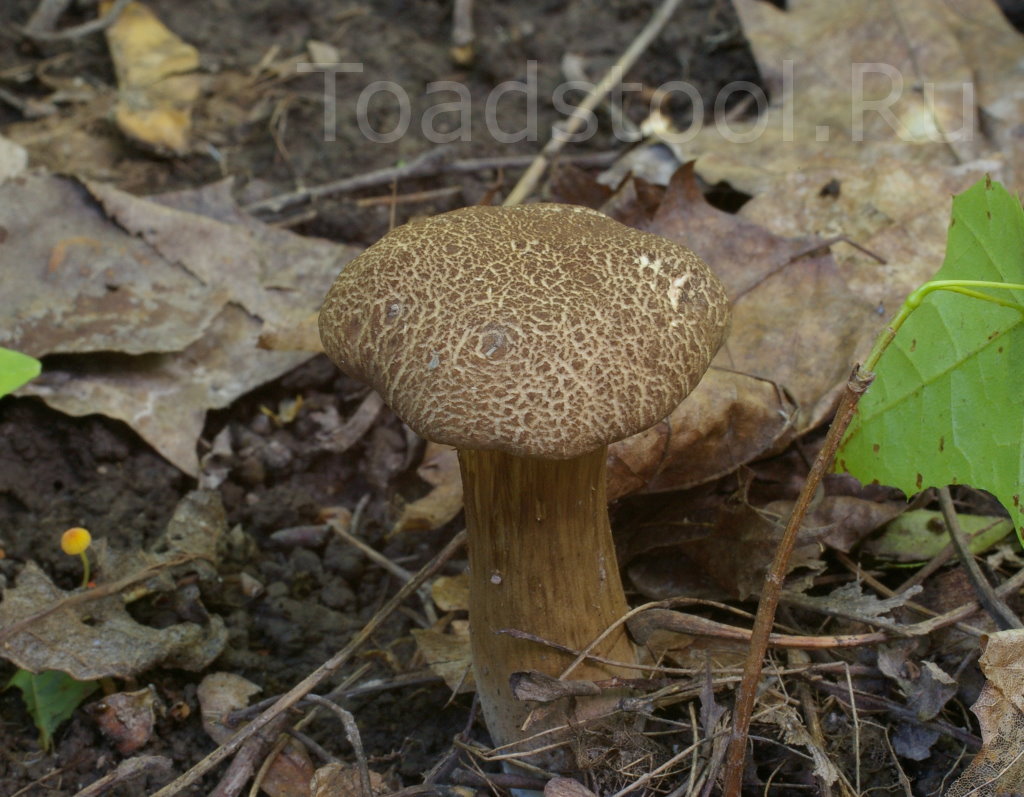
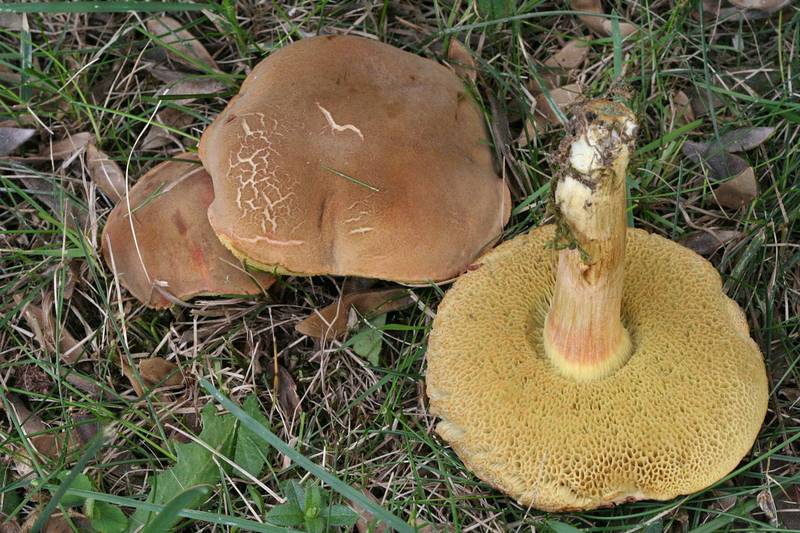
The hat is 4-12 cm in diameter, the shape is semicircular, convex, later becomes cushion and even flat. The skin does not separate, the surface is smooth, dry, becomes sticky in wet weather, matte in young mushrooms, shiny in mature ones. Colored chestnut brown or brown. The pulp is fleshy, dense, whitish or yellowish in color, turns blue on the cut. The aroma is pleasant, mushroom. The leg is 4-12 cm high, 1-4 cm thick, cylindrical, narrowing or widening downward, fibrous structure, light brown, brown or yellow with red-brown fibers.
The mushroom grows next to pines, spruces, beeches, oaks, chestnuts, in conifers, sometimes in deciduous forests, singly or in small groups. The species is distributed in the northern temperate zone of the European part of Russia, in the North Caucasus, in Siberia, in the Far East. The season runs from June to November.
Good quality edible mushroom. Used for freezing, drying and pickling.
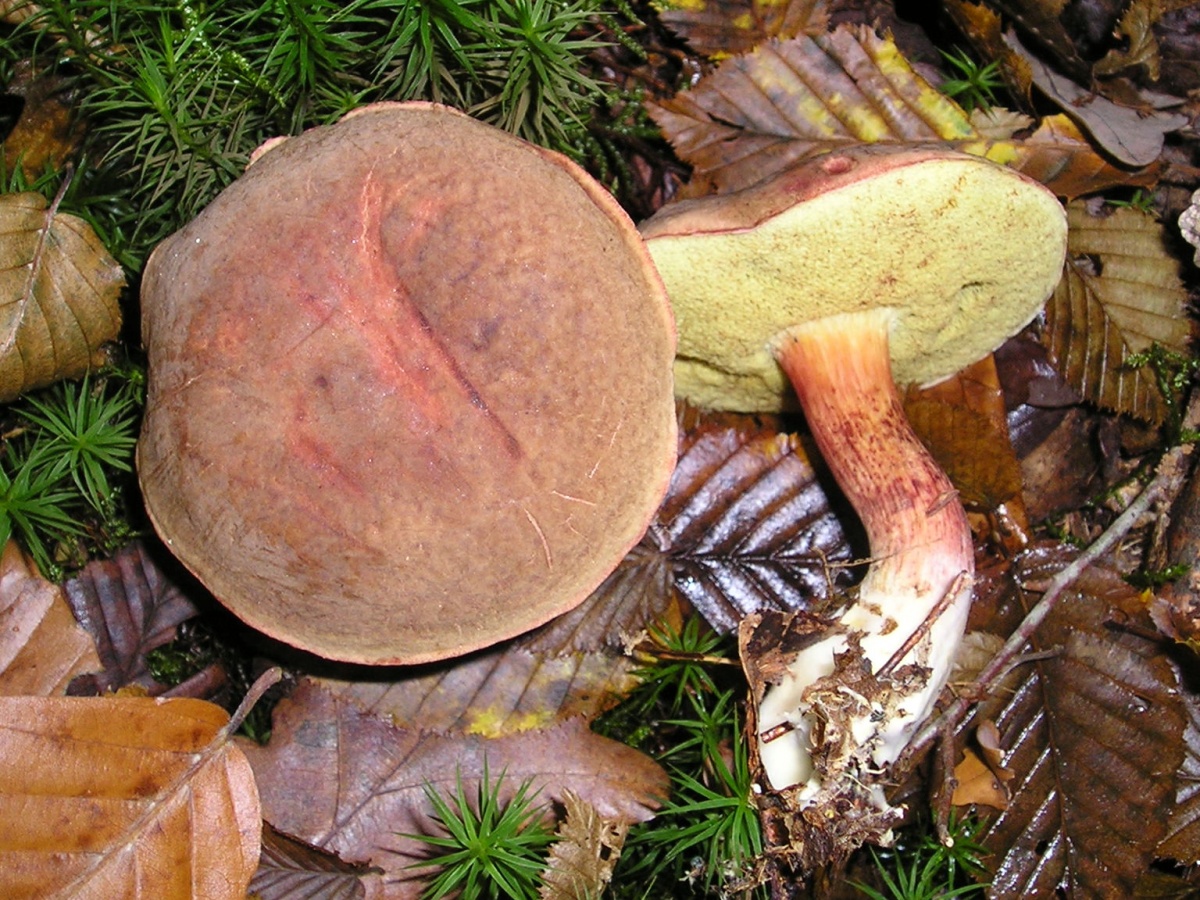
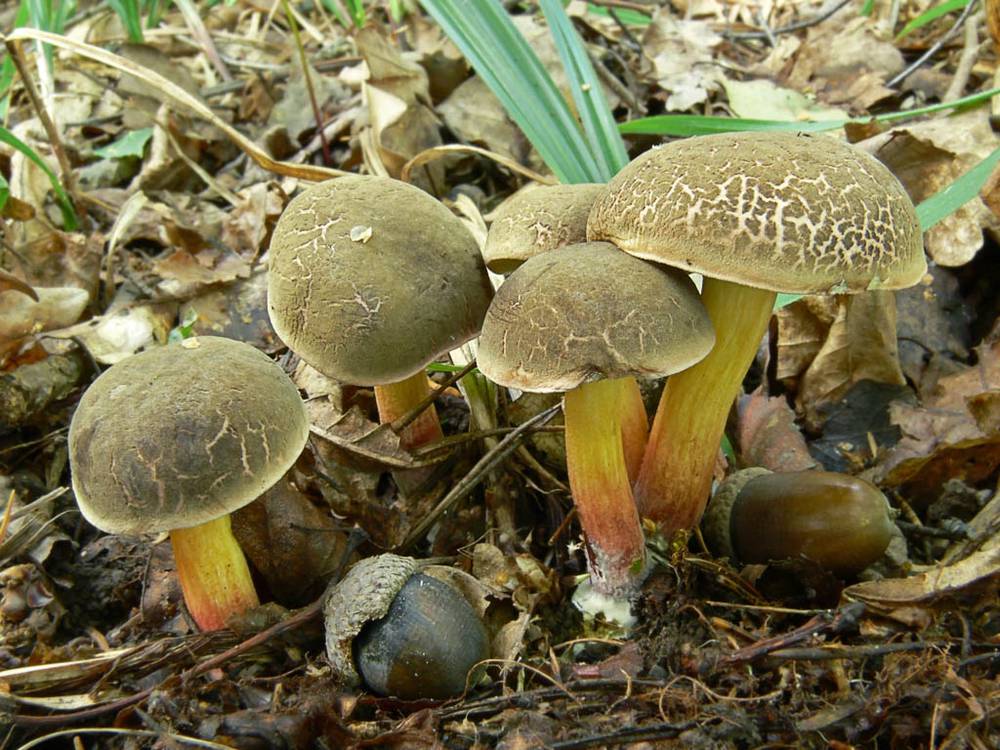
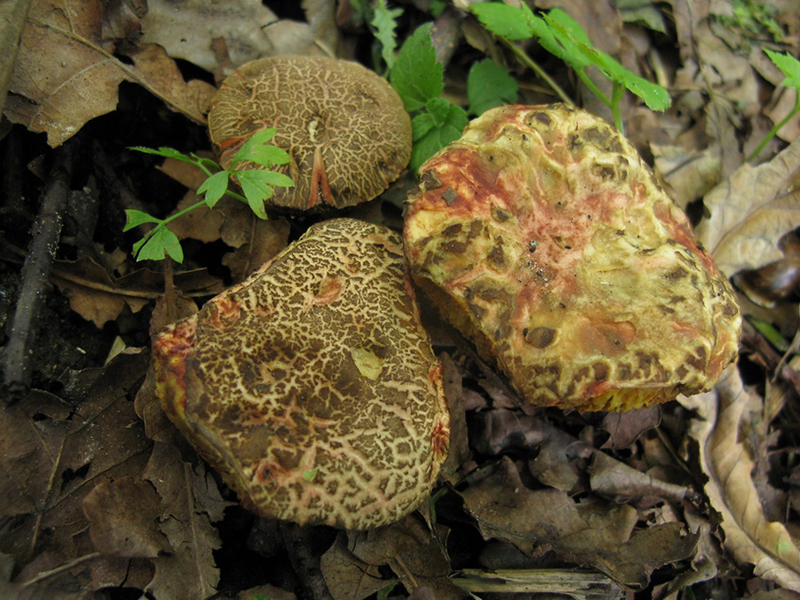
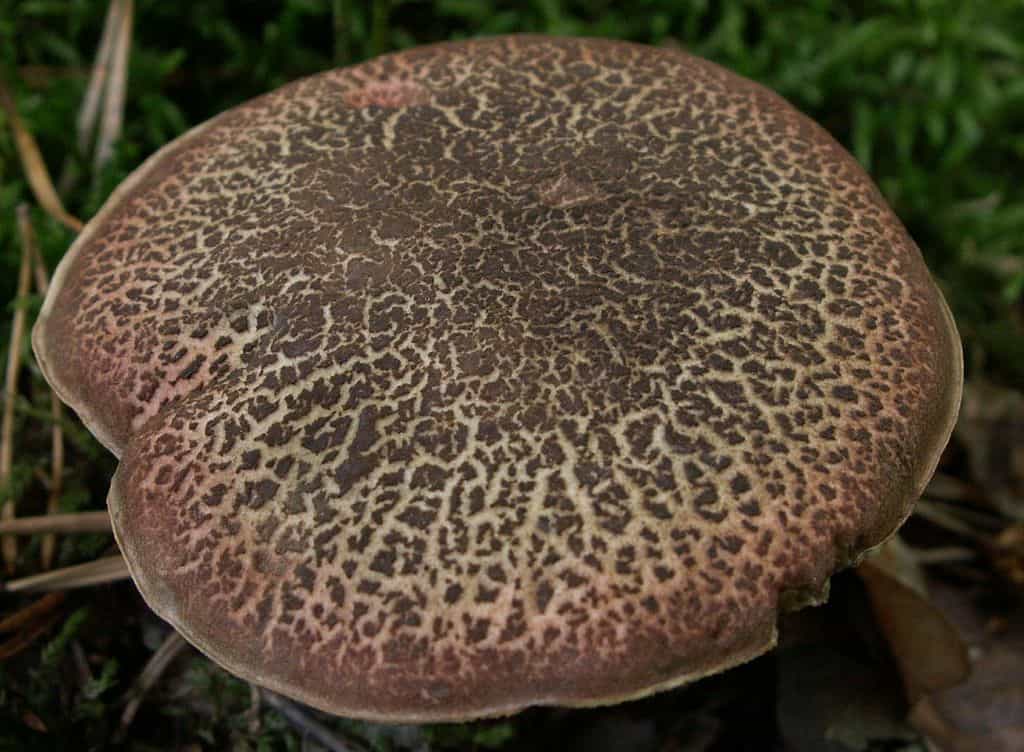
Fractured flywheel (Xerocomellus chrysenteron)
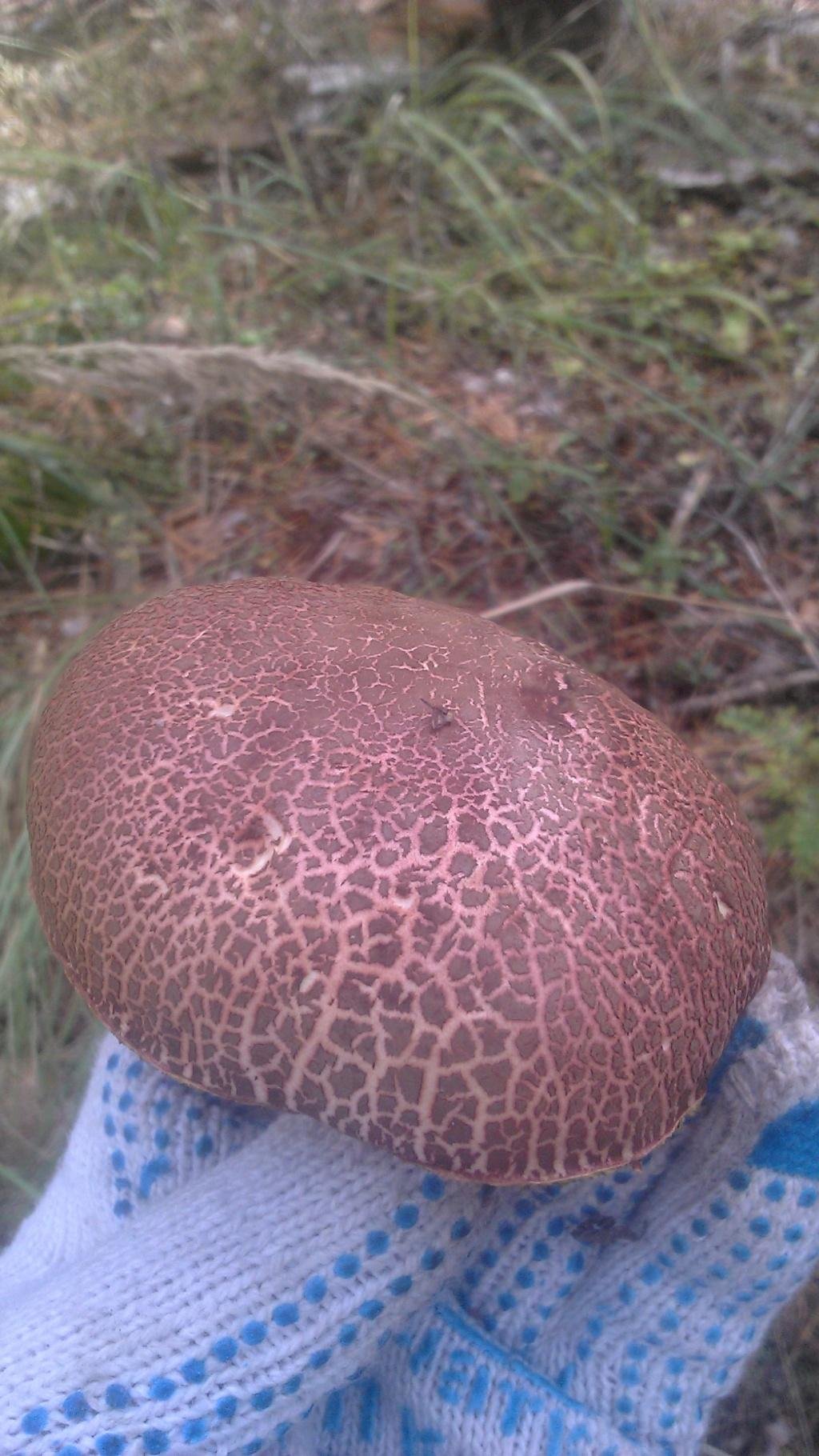
The diameter of the cap is 3-7 cm, the shape is convex or cushion-shaped, less often with a depression in the center, the surface is dry, matte, velvety or bare, burgundy-red, brown, olive-brown, brown, brown-red, ocher-gray. The hat cracks, forming a characteristic mesh. The pulp is white or with a yellow tinge, reddish at the base of the leg and under the cap, turns blue at the cut. Leg 4-10 cm in height and 1-2 cm in thickness, clavate, solid, smooth, fissured surface, light yellow with a red base.
The species is widespread in Europe, the North Caucasus, and the Far East. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests. Fruiting from July to September.
An edible mushroom that is eaten fresh and salted, and is also dried or frozen for use in fried and first courses.
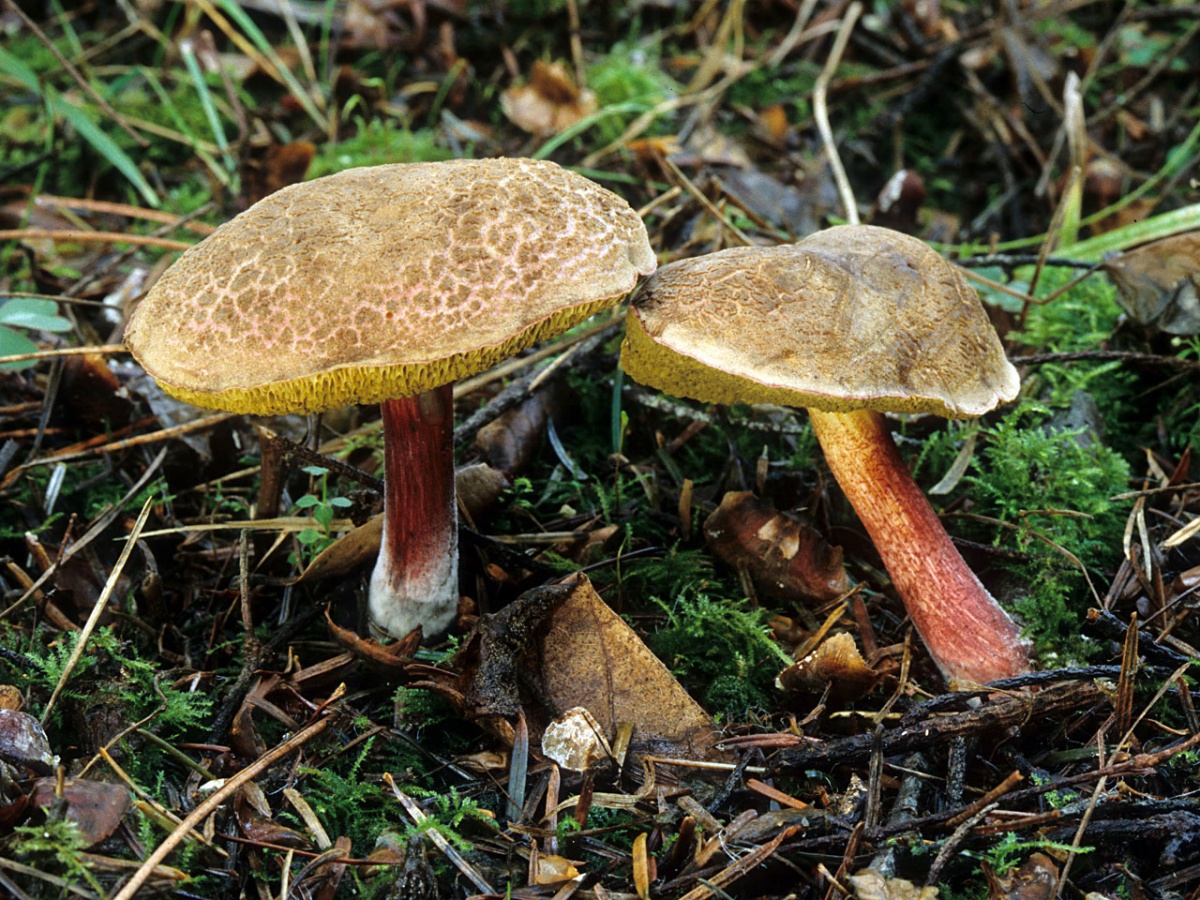
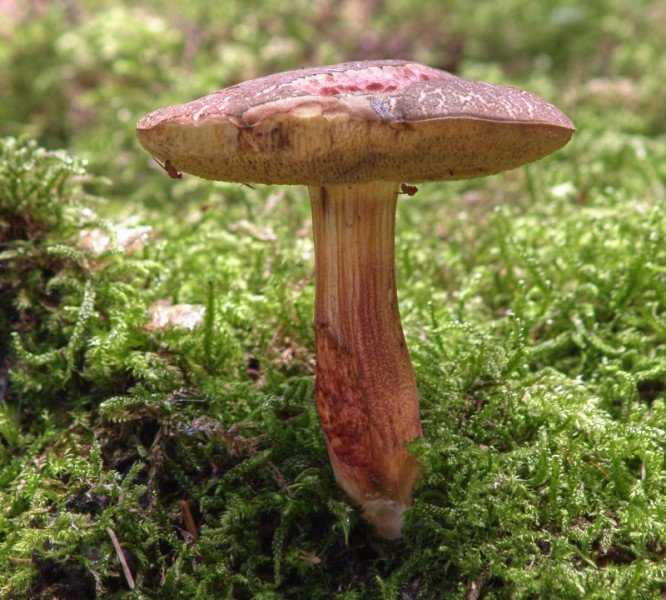
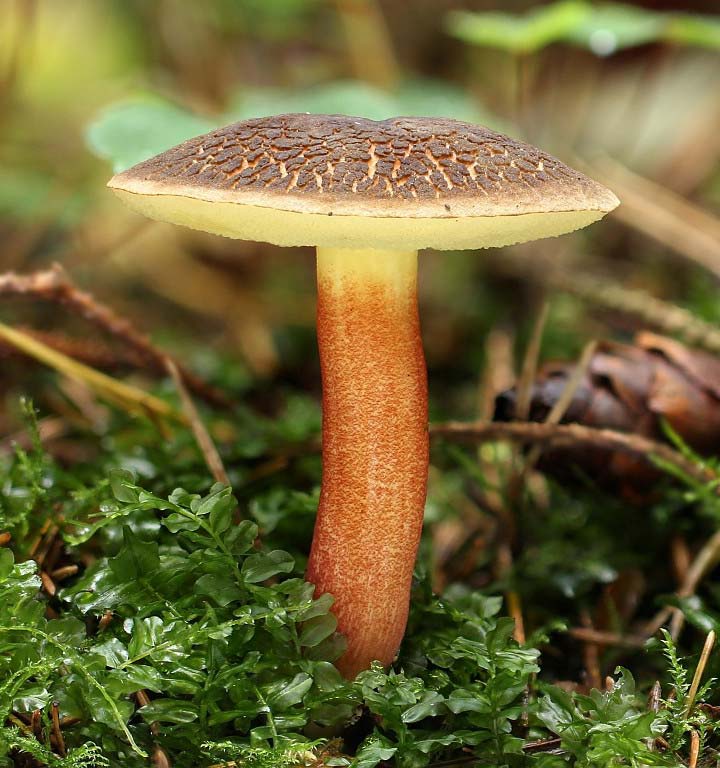
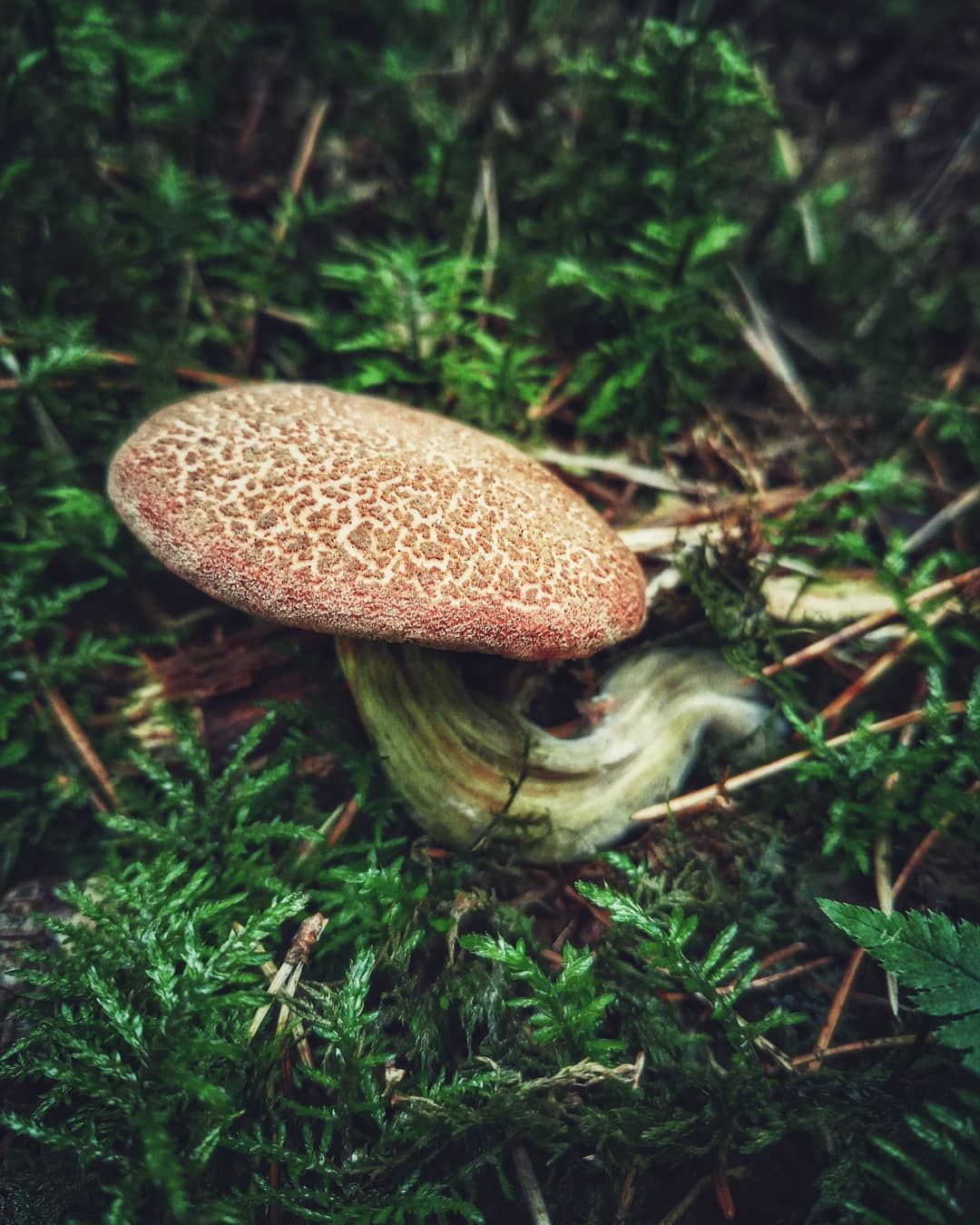
Red flywheel (Xerocomellus rubellus)
The cap is 2-5 cm in diameter, cushion-convex in shape, flattens with age. Colored bright red. The skin does not separate, the surface is velvety-felt, cracks in mature mushrooms. The leg is cylindrical, tapering towards the base, 3-10 cm in height, about 1 cm in diameter, solid, fibrous, fine-scaled. The color of the stem is yellow with a raspberry-pinkish, reddish or reddish-brown base. The pulp is dense, yellow, turns blue on the cut.
The mushroom grows in deciduous forests, often in oak forests of Europe, North Africa, Asia. The harvest season lasts from August to September. Does not bear fruit abundantly.
An edible mushroom with a pleasant aroma, the taste is not expressed. Used fresh. Darkens on drying.
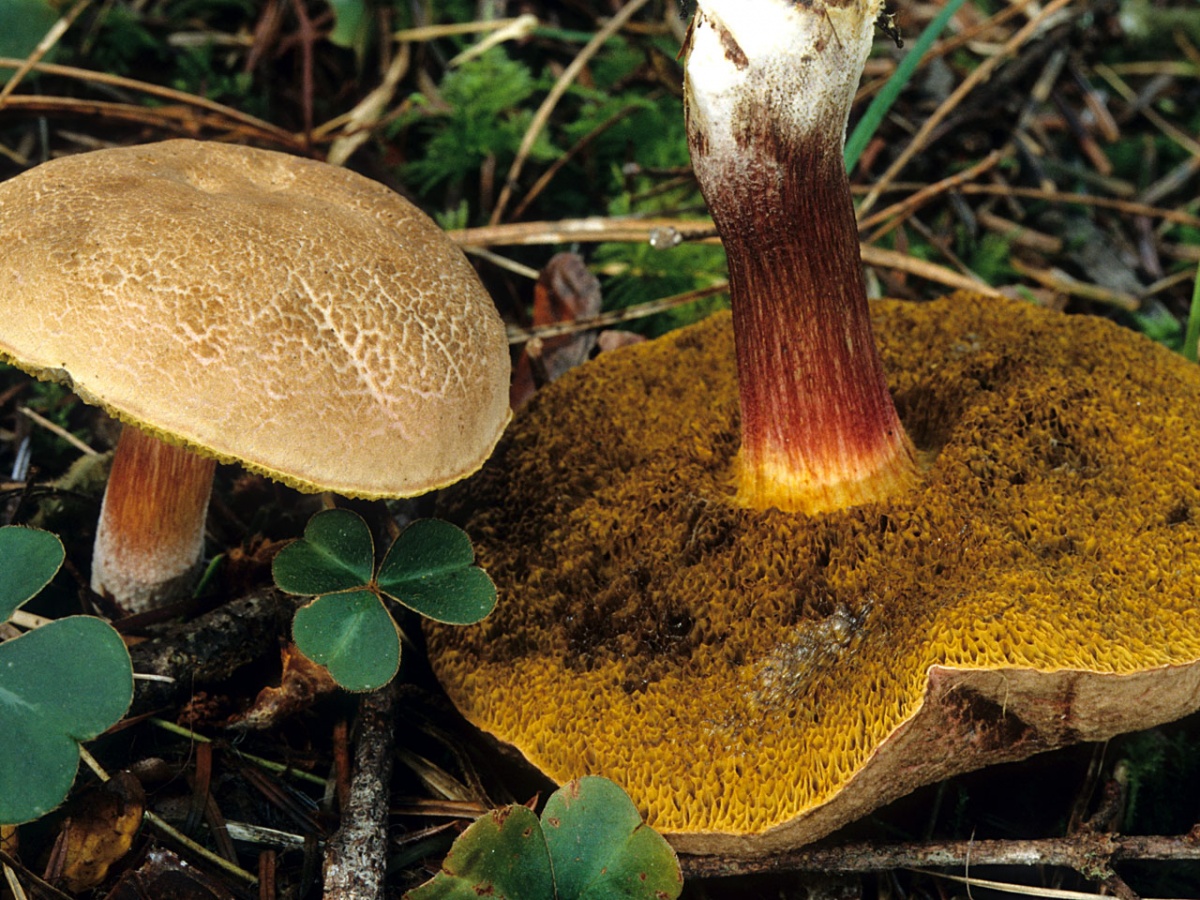
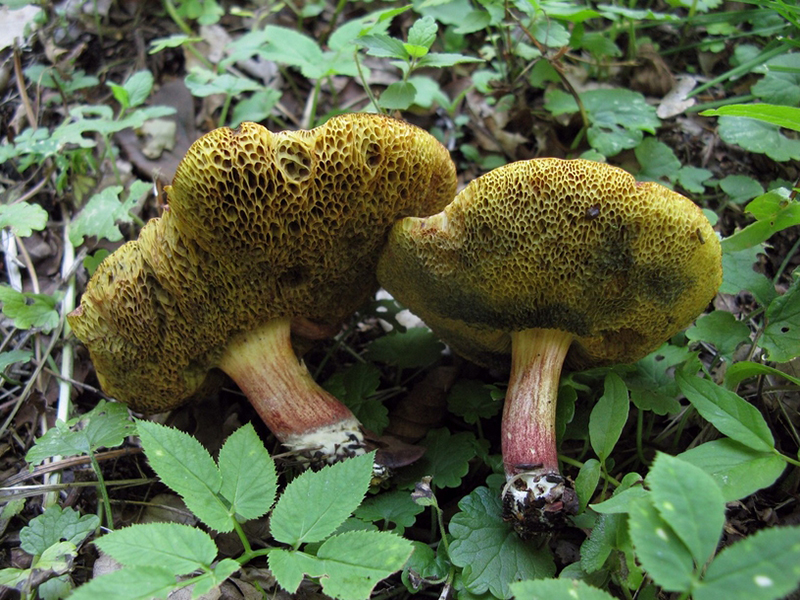
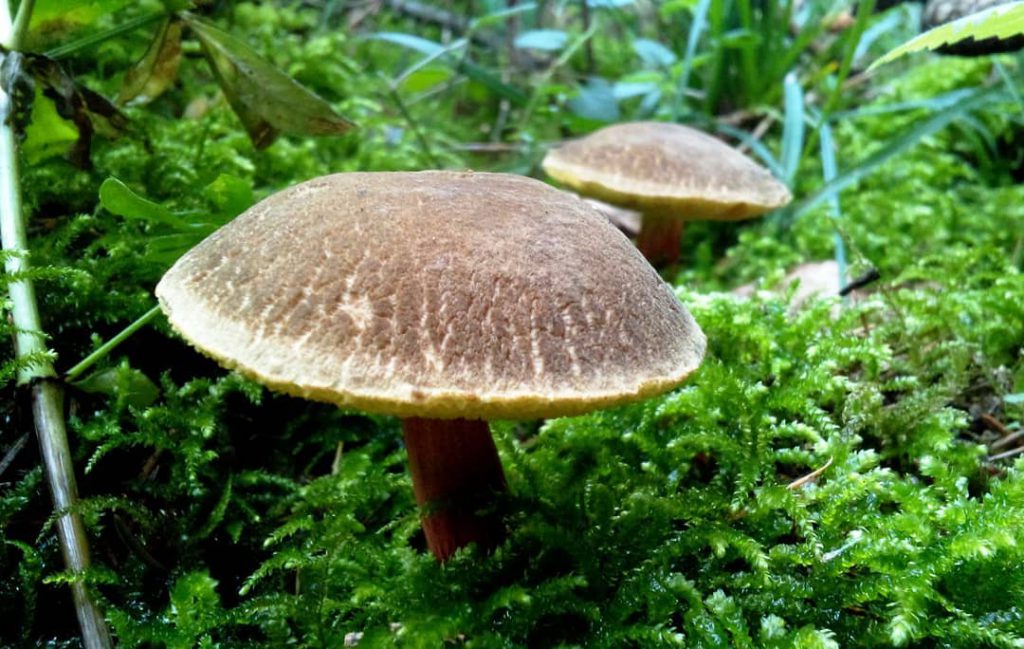
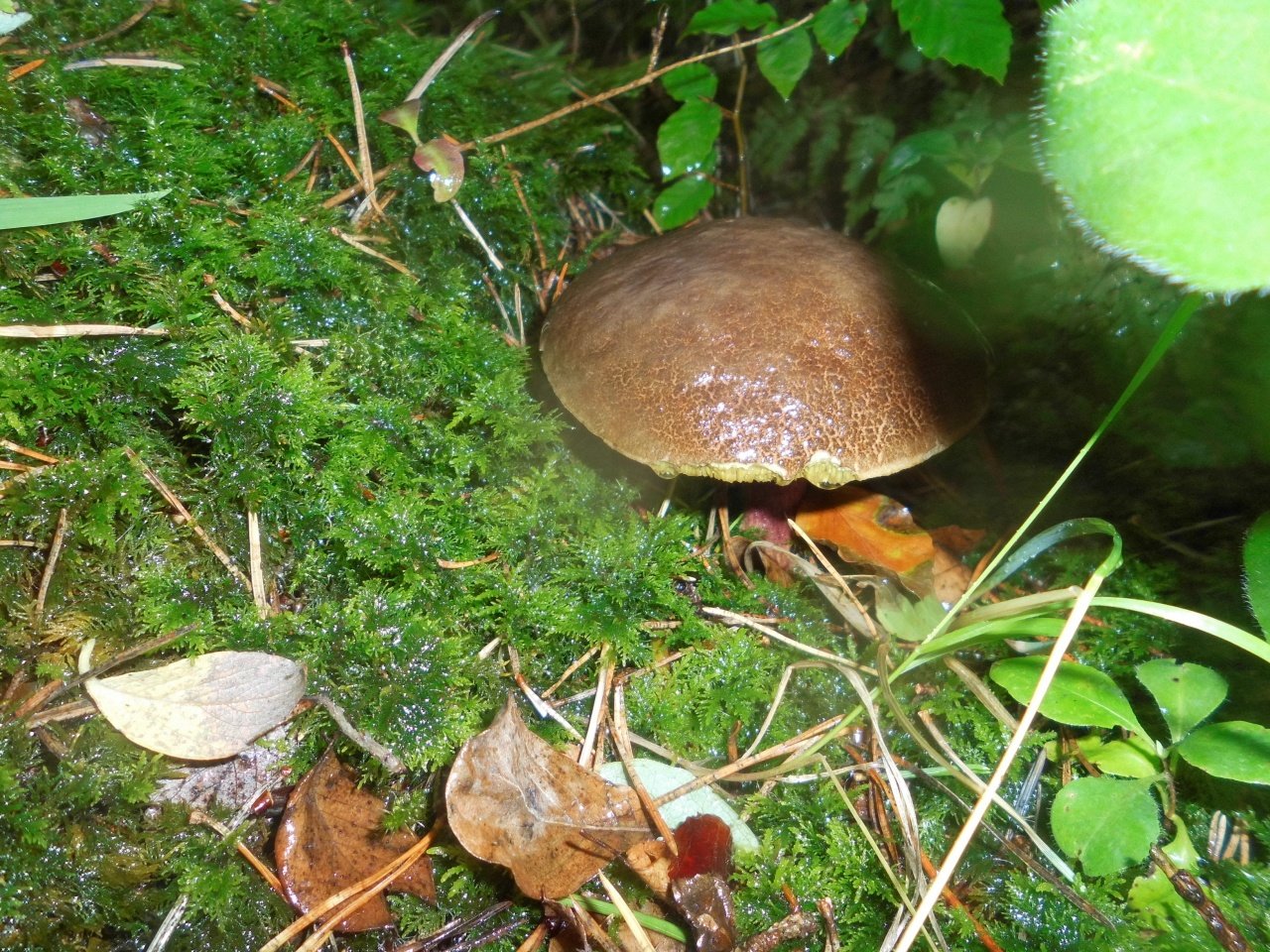
Green flywheel (Xerocomus subtomentosus)
The diameter of the cap is 3-10 cm, the shape is pillow-convex, the surface is velvety, grayish or olive-brown in color. The pulp is white, turns blue on the cut. The leg is cylindrical, tapers towards the base, 4-10 cm in height, 1-2 cm in thickness, the surface is smooth, the structure is fibrous.
Grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, in clearings, along roads, singly or in groups.It is a cosmopolitan mushroom, as it is distributed on all continents. Fruiting occurs in May-October.
An edible mushroom, used fresh. Darkens on drying.
Edible flywheel
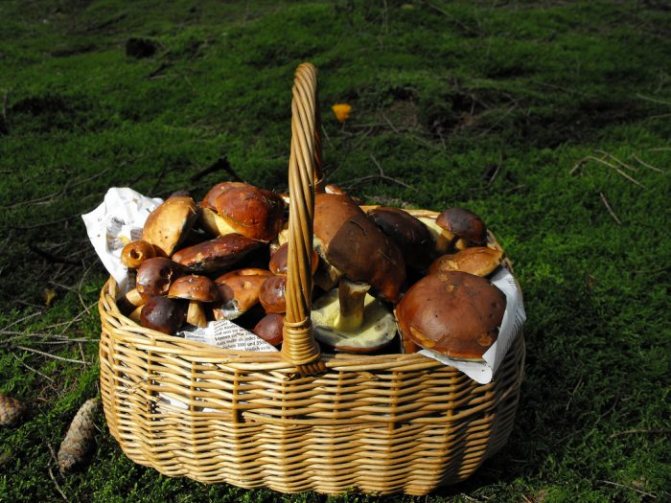

Among the mushrooms there are both edible and inedible ones. Edible species are used for food without preliminary boiling for first courses, salting, pickling and drying. In cooking, the whole mushroom is used: both the cap and the leg. The skin is removed from the cap, and the leg is peeled. To improve the assimilation of mushrooms, they are thoroughly crushed. Dried mushrooms acquire a beautiful golden hue and pleasant smell.
Flywheels are rich in easily digestible proteins, sugars, enzymes and essential oils, they also contain vitamins A, B, B2, C, D and PP.
In addition, flywheels contain specific substances that quickly darken in air and spoil the appearance of the mushroom. Therefore, before cooking, the mushrooms need to be processed quickly so that they do not stay in the air for a long time in a purified form, they are immediately placed in water. When boiling, a teaspoon of salt and half a teaspoon of citric acid are added per liter of water.
Types of moss
In the genus Mokhovik (Xerocomus), there are 18 species, of which only seven are found in the vastness of Russia.
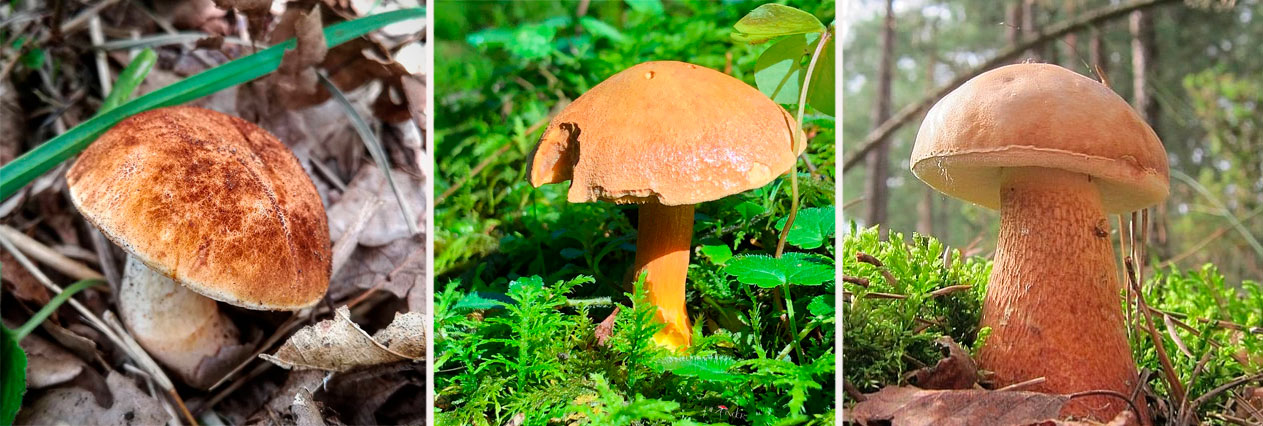
Polish mushroom (X. badius)

Photo of Polish mushroom
Reputed to be an excellent edible mushroom, one of the most delicious in Europe. It has a rather large size: the brownish cap sometimes reaches 12–15 cm in circumference, and the leg rises by 10–13 cm. Its flesh is fleshy, with a pleasant taste and a pronounced mushroom odor, whitish or slightly creamy yellow. Tubular layer of golden, later - olive-yellowish color, light brown spores. In Russia, it grows more often in coniferous forests on sandy soils, it is found in the European part, in the North Caucasus, in Siberia and on the island of Kunashir.
For more information, see the article "Polish mushrooms."
Good edible mushrooms are: red flywheel, green flywheel and motley or fissured flywheel.
Red flywheel (X. rubellus)

Photo of a red flywheel
A medium-sized mushroom with a rich red cap up to 8 cm in circumference, velvety-felt to the touch. It rises on a thin, up to 1 cm thick, stalk about 10 cm high, at the base with a pinkish salmon tint. The tubular layer is dull yellow, the spores are brick-brown. The species is collected only in deciduous forests, more often in the oak forests of Europe, the Far East, the mushroom is found in North Africa, but it is not called ubiquitous growing.
Green flywheel (X. subtomentosus)

Photo of a green flywheel
A mushroom with an olive-brown or grayish cap up to 10 cm in diameter and a cylindrical, slightly narrowed downwards, smooth stem up to 2 cm thick and 4 to 10 cm high, white flesh and yellowish hymenophore. It grows everywhere, both in deciduous and coniferous forests, it is found even on anthills. The area of distribution is extensive.
Flywheel variegated or fractured (X. chrysenteron)
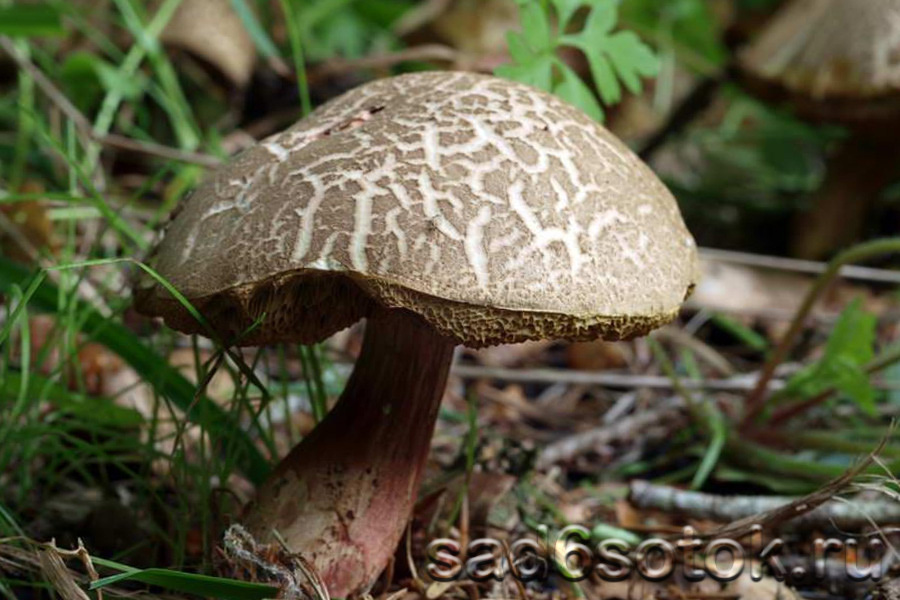

Motley or fractured flywheel
A mushroom with a characteristic network of cracks on a small (3–7 cm in diameter) cap, which differs in different shades: burgundy-cherry, olive-chocolate, terracotta-red, ocher-gray. An unusual clavate shape is observed at a leg that grows up to 10 cm. Below, the leg is reddish with barely noticeable grayish-fibrous belts. The hymenophore is large-pored, creamy yellow or light olive in color, the spores are yellow-brown. Distributed everywhere: in coniferous and mixed forests on loose sour soil throughout Europe and the European part of Russia, in the Far East and the North Caucasus.
The conditionally edible species include the following types of moss:
- blunt (X. truncatus),
- chestnut (X. spadiceus),
- powdered (X. pulverulentus),
- woody (X. lignicola),
- semi-golden (X. hemichrysus).
The parasitic flywheels (X. parasiticus) and asteraceae (X. astraeicolus) were identified as inedible non-toxic fungi.
Collection period and rules
Mushrooms bear fruit en masse from July to September inclusive, however, each species has its own dates for the beginning and end of ripening. So, the first fissured mosshogs appear in the last decade of June, and single specimens come across until the end of September, although they are collected in large quantities only from the second half of August to the tenth of the first month of autumn.
The harvesting period of the Polish mushroom is from June to November, it is often found when the rest of the tubular mushrooms can no longer be found.
The green flywheel in Russia is harvested from May to October, and the red one is not distinguished by abundant fruiting and falls into the baskets of mushroom pickers along the way with other flywheels in August and September.
When collecting mushrooms, they carefully monitor the appearance of blue on the cut or when pressing on the body of the mushroom - the main sign of its edibility.
What does a green flywheel mushroom look like?
Category: edible.
The name of the mushroom speaks for itself about what a green flywheel looks like. Hat (diameter 4-12 cm): usually greenish-gray or olive, maybe slightly brown. Slightly convex in shape, velvety to the touch.
Leg (height 3-11 cm): in the form of a cylinder, expands from bottom to top, can be with a brownish mesh.


Pay attention to the photo of the green flywheel pulp: it is white, and may turn slightly blue on the cut. Despite its rather noble description, the flywheel mushroom is very often covered with mold, which can be dangerous for humans.
Therefore, it is very important to pick mushrooms without mold.
Despite its rather noble description, the flywheel mushroom is very often covered with mold, which can be dangerous for humans.
Therefore, it is very important to pick mushrooms without mold.
When it grows: from mid-May to early October throughout Russia, as well as in European countries, North America and Australia.
Where to find it: in all types of forests.
Eating: a very tasty mushroom in boiled, fried and pickled form, however, it is not suitable for long-term storage (it turns black when dried). Best eaten immediately after preparation.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Mushroom red flywheel: photo and other names
Category: edible.
Xerocomus rubellus hat (diameter 3-9 cm): red, crimson or brown.


Look at the photo of what a red flywheel looks like at a young age: the cap of small mushrooms is convex, shiny. Over time, it almost straightens out. The peel is hardly separated from the pulp, after prolonged dry weather it can become covered with a network of small cracks.
Leg (height 4-12 cm): crimson, red or pinkish, slightly lighter than the cap, may be yellowish on top. Covered with small scales, expands from bottom to top, has the shape of a cylinder, solid.
Tubular layer: yellow or with a greenish or olive tint. Under strong pressure, it turns blue.


As you can see in the photo of the red flywheel, this mushroom has a very dense, yellow flesh, noticeably turning blue on the cut and when interacting with air.
When it grows: from the beginning of August to the end of September on the Eurasian continent and in Asia. Found in North America, but very rare.


Where to find it: On deciduous forest soils among low grass or moss, usually near oak trees.
Eating: a very tasty mushroom, but it darkens noticeably when dried, therefore it is recommended to use it pickled or fried.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names for the red flywheel: red boletus, red boletus, red ache, reddish boletus, reddening boletus.
Types of mushroom flywheel
Pan mushroom or chestnut flywheel (Boletus badius)
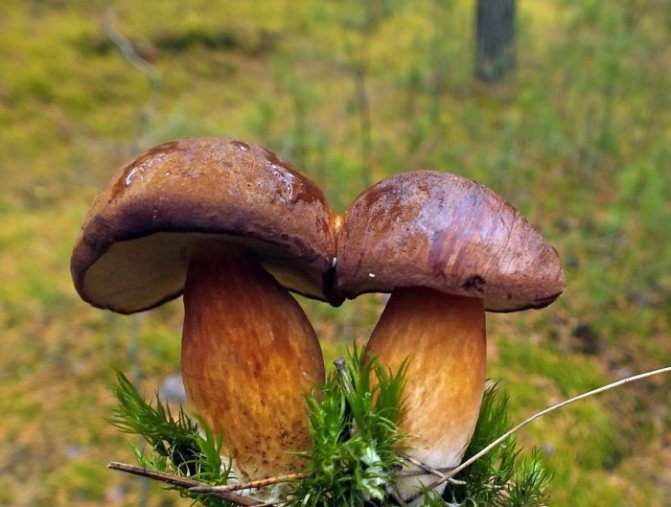

Also known as brown or polish mushroom.
The hat is 4-12 cm in diameter, the shape is semicircular, convex, later becomes cushion and even flat. The skin does not separate, the surface is smooth, dry, becomes sticky in wet weather, matte in young mushrooms, shiny in mature ones. Colored chestnut brown or brown.The pulp is fleshy, dense, whitish or yellowish in color, turns blue on the cut. The aroma is pleasant, mushroom. The leg is 4-12 cm high, 1-4 cm thick, cylindrical, narrowing or widening downward, fibrous structure, light brown, brown or yellow with red-brown fibers.
The mushroom grows next to pines, spruces, beeches, oaks, chestnuts, in conifers, sometimes in deciduous forests, singly or in small groups. The species is distributed in the northern temperate zone of the European part of Russia, in the North Caucasus, in Siberia, in the Far East. The season runs from June to November.
Good quality edible mushroom. Used for freezing, drying and pickling.
Fractured flywheel (Xerocomellus chrysenteron)
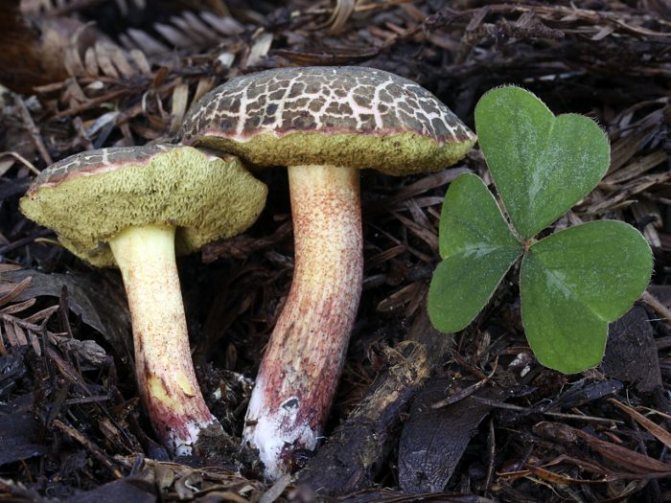

The diameter of the cap is 3-7 cm, the shape is convex or cushion-shaped, less often with a depression in the center, the surface is dry, matte, velvety or bare, burgundy-red, brown, olive-brown, brown, brown-red, ocher-gray. The hat cracks, forming a characteristic mesh. The pulp is white or with a yellow tinge, reddish at the base of the leg and under the cap, turns blue at the cut. Leg 4-10 cm in height and 1-2 cm in thickness, clavate, solid, smooth, fissured surface, light yellow with a red base.
The species is widespread in Europe, the North Caucasus, and the Far East. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests. Fruiting from July to September.
An edible mushroom that is eaten fresh and salted, and is also dried or frozen for use in fried and first courses.
Red flywheel (Xerocomellus rubellus)
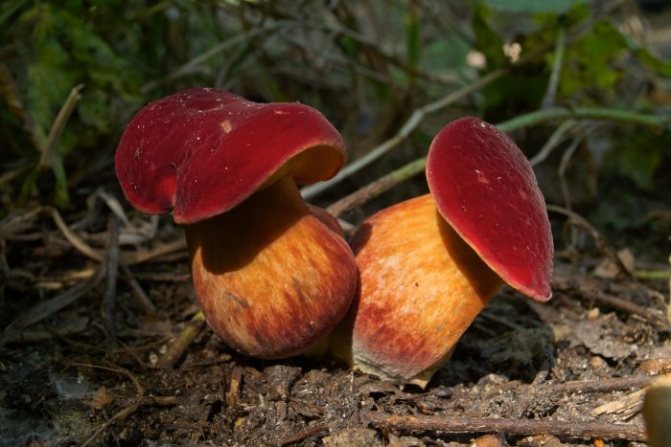

The cap is 2-5 cm in diameter, cushion-convex in shape, flattens with age. Colored bright red. The skin does not separate, the surface is velvety-felt, cracks in mature mushrooms. The leg is cylindrical, tapering towards the base, 3-10 cm in height, about 1 cm in diameter, solid, fibrous, fine-scaled. The color of the stem is yellow with a raspberry-pinkish, reddish or reddish-brown base. The pulp is dense, yellow, turns blue on the cut.
The mushroom grows in deciduous forests, often in oak forests of Europe, North Africa, Asia. The harvest season lasts from August to September. Does not bear fruit abundantly.
An edible mushroom with a pleasant aroma, the taste is not expressed. Used fresh. Darkens on drying.
Green flywheel (Xerocomus subtomentosus)
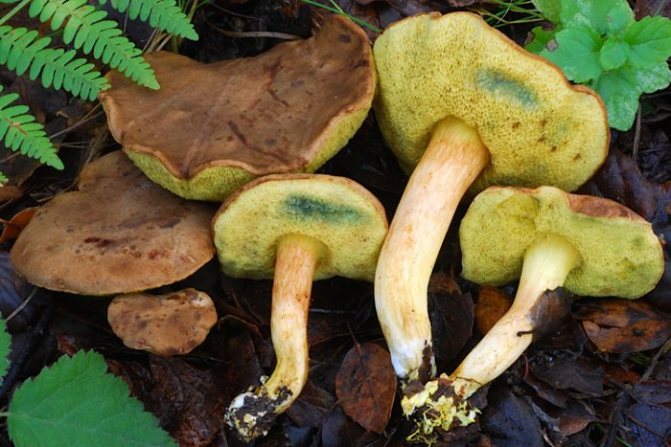

The diameter of the cap is 3-10 cm, the shape is pillow-convex, the surface is velvety, grayish or olive-brown in color. The pulp is white, turns blue on the cut. The leg is cylindrical, tapers towards the base, 4-10 cm in height, 1-2 cm in thickness, the surface is smooth, the structure is fibrous.
Grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, in clearings, along roads, singly or in groups. It is a cosmopolitan mushroom, as it is distributed on all continents. Fruiting occurs in May-October.
An edible mushroom, used fresh. Darkens on drying.
How and what to cook from the flywheels?
When starting to process the collected flywheels, it must be remembered that when cleaned, they darken upon contact with air. That is why they need to be immersed in water with citric acid dissolved in it (2 g per liter) and salt (teaspoon per liter).
Mosswheel goes well with meat, chicken, cabbage, pumpkin, cream.
Popular dishes made from these mushrooms are:
Pickled mushrooms
Mushrooms must be thoroughly peeled and rinsed. Put in a deep saucepan, add water, put on fire until boiling. Boil for 15 minutes over low heat, discard the mushrooms in a colander.
While the water is draining, prepare the marinade. To do this, pour a tablespoon of sugar and salt into a liter of water, add 2 bay leaves, a couple of cloves of garlic and a little clove. Put on fire, let it boil, add a tablespoon of vinegar.
Without turning off the heat, put the mushrooms in the marinade, boil for 5 minutes. Arrange the mushrooms in sterilized jars. The liquid should cover the mushrooms. Roll up the banks. Store pickled mushrooms in a cool place.
Stewed mushrooms
To prepare this fragrant dish, take a kilogram of mushrooms, an onion, 200 g of sour cream. Boil the mushrooms in a dish with a thick bottom for 1.5 hours, then fry.
A few minutes before the mushrooms are ready, add chopped onions, salt and pepper. Then add sour cream and a little water to the mushrooms.
When the sauce has thickened, the dish is ready. It can be served as a sauce for cereals or pasta.

Fried mushrooms for the winter
This is a blank, different from the usual pickled or salted mushrooms. For cooking, you need to take a kilogram of mushrooms, 250 ml of vegetable oil, salt and pepper to taste.
Peel and wash the mushrooms, boil 2 times for 15 minutes, after each time changing the water and washing them again. Heat a frying pan with vegetable oil, place the chopped mushrooms there, cover and simmer for half an hour. After that, remove the lid and simmer for another 15 minutes until the liquid has completely evaporated, add salt and pepper.
Put the ready-made mushrooms in sterilized jars, pour the remaining oil from frying 2 cm on top, roll up. Store the mushrooms harvested in this way for 6 months.
Flywheels with honey
This is a very unusual dish with a pleasant sweet and sour taste. For cooking, you need 1.5 kg of mushrooms, 2 tablespoons of honey, 2 cloves of garlic, 2 tablespoons of mustard and the same amount of vinegar, 50 g of vegetable oil, parsley.
You need to peel and wash the mushrooms, cut into cubes. Chop the greens, pass the garlic through a press, add honey, vinegar, mustard and chopped mushrooms here. Mix everything thoroughly, refrigerate, stand for 3 hours.
Heat vegetable oil in a frying pan, add the whole mass along with the marinade. Simmer over low heat for 45 minutes. This dish goes well with boiled potatoes.
Mushroom soup
It can be cooked both in meat broth and vegetables. Process the mushrooms (300 g), cut off the legs. Chop the mushrooms. Peel and chop the onion and 3 potatoes, a bunch of green onions.
Fry the mushrooms for 8-10 minutes, then add onions to them, fry for another 4-5 minutes. Dip the contents of the pan into boiling water or broth, add salt, add 2 tablespoons of pearl barley, cook for 10 minutes over medium heat. After that, add potatoes to all the ingredients, cook for 15 minutes.
Then add the chopped greens, turn off the heat, let the soup brew under the lid for 10 minutes. Serve with sour cream.
Mushroom salad
To prepare a salad, you need to take 3-4 potatoes, boil them in their uniforms, and chop them. Also chop an apple, 300 g of pickled mushrooms and 150 g of ham. Mix, add chopped celery and parsley. Season with vegetable oil and vinegar, salt if desired and add black pepper.
The flywheel mushroom is common on all continents. It is represented by several species, most of which are edible. From the flywheel, you can prepare various dishes, as well as prepare them as canned food for the winter. It is easy to grow a mosswheel on your own in a summer cottage.
Distribution area
Boletus badius forms mycorrhiza with conifers and is often found under fir, beech and oak trees. Gives preference to sandy soils of coniferous plantings. The species that are quite common in our country include the flywheel Xerocomellus chrysenteron, which bears fruit en masse on acidic and loose soils from the second decade of August to mid-September.
Fruiting bodies of Xerocomellus rubellus are formed in the period from August to the first decade of September. The species Xerocomus subtomentosus is characterized by the formation of mycorrhiza not only with conifers, but also with deciduous trees. This cosmopolitan mushroom bears fruit en masse from May to the first decade of October and grows both in forest zones and on glades or roadsides.

Homemade mushroom noodles
Ingredients: a handful of dry mushrooms, onions, carrots, herbs. For noodles: half a glass of sour cream, one egg, half a spoonful of salt, one hundred and fifty grams of flour.
Before cooking the mushroom mushroom, it is poured with boiling water and steamed under the lid for twenty minutes. Then the mushrooms are cut into pieces, transferred to a bowl, where they were steamed, poured with boiling water and boiled for one hour, after which fried onions and carrots are added.

Next, prepare the noodle dough. To do this, mix all the ingredients, roll out the layer and cut it into wide strips, each of which is rolled in flour. The noodles are placed in the prepared mushroom broth and boiled for twenty minutes, then the herbs are added. Mushroom noodles with sour cream are served.
Cooking features and answers to common questions
This product can be stewed and boiled, fried and dried, pickled and salted - in any form it is very tasty.
But it needs to be properly prepared:
- rinse with running water;
- separate the caps and legs;
- clean all parts of the mushroom from dust and earth with a stiff brush;
- cut out dark spots and hard areas with a sharp knife;
- get rid of the spore layer under the cap;
Mushroom preparation rules
- pour cold water for 10 minutes (to remove dirt residues);
- place in a colander until the water drains;
- dry with a paper towel.
You need to cook for at least 30 minutes. Before the cooking process, they need to be divided into pieces and covered with boiling water for 10 minutes. Boiled mushrooms can be fried. The maximum time is 10 minutes. The cover is not needed. The fire is minimal.

You may be interested in:
Marinating butter - which recipe is the most delicious Butters are distinguished by their sticky and moist brown cap, on which forest debris is firmly fixed ... .Read more ...

Fried mushrooms
Before frying, the caps of raw mushrooms should be separated from the stems and soaked for 1 hour in cold water. Then they must be rolled in flour and sent to a frying pan with a small amount of sunflower oil. Cooking time over low heat is about 40 minutes.
All species of the genus Mohovichok:
| Motley flywheel (Xerocomellus chrysenteron) | Blunt flywheel (Xerocomellus truncatus) | Velvet flywheel (Xerocomellus pruinatus) |
If you are in doubt about the edibility of the mushrooms you find, do not take them. The site administration does not bear any responsibility for the actions of people taken on the basis of the information received on the site. Some types of poisonous mushrooms cannot be identified without special equipment and can be confused with edible ones.
What diseases can be cured by mushrooms
As already mentioned, mushrooms are a natural antibiotic. And all because of the substance boletol, which is part of the chemical composition of the product. This compound has anti-inflammatory effects and helps in the treatment of many diseases. It is known that mushroom extract is useful for people with liver cirrhosis, atherosclerosis, nervous disorders, anemia, reduced immunity, depression, chronic fatigue. This product improves blood circulation, heals inflammation and suppuration on the skin (powder from dried mushrooms is used). In alternative medicine, it is used as a treatment for cancer.
False flyworms, description and photo. How to distinguish from edible?
Among real mushrooms there are no mushrooms that can be poisoned, but they can still be confused with other inedible or poisonous mushrooms: for example, pepper mushroom or gall mushroom
That is why it is very important to know the signs by which you can distinguish false flyworms from edible ones. Below is a description of mushrooms that look like moss
Pepper Mushroom (aka Pepper Butter) (Chalciporus piperatus)
It has a cap with a diameter of up to 7 cm and a leg up to 8 cm high. The color of the cap varies from light brown to yellow-brown and orange-rusty. The pulp is yellow in the stem, lighter in the cap. When cut, the flesh turns pink. The taste of the pepper mushroom is spicy and pungent. The mushroom is considered inedible, although in the cuisines of some countries the powder from this "false flywheel" is added to dishes to spice them up.

Photo Credit: H. Krisp, CC BY 3.0

Photo by: Jean-Pol GRANDMONT, CC BY 3.0
Gall mushroom (Tylopilus felleus)
It has a hat up to 15 cm in diameter and a leg up to 12.5 cm high and up to 3 cm thick.There is a brown mesh on the leg. The color of the cap can be different: light brown, yellow-brown, with a grayish tint or darker, chestnut. The white tubular layer of the inedible gall fungus turns pink over time. The flesh also turns pink when cut and tastes bitter.
Sometimes bile mushrooms are confused with porcini mushrooms, boletus and boletus mushrooms.
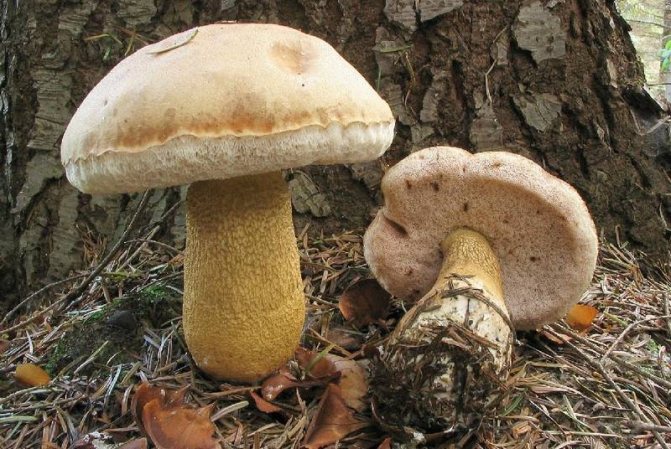

Photo Credit: Pumber, CC BY-SA 3.0
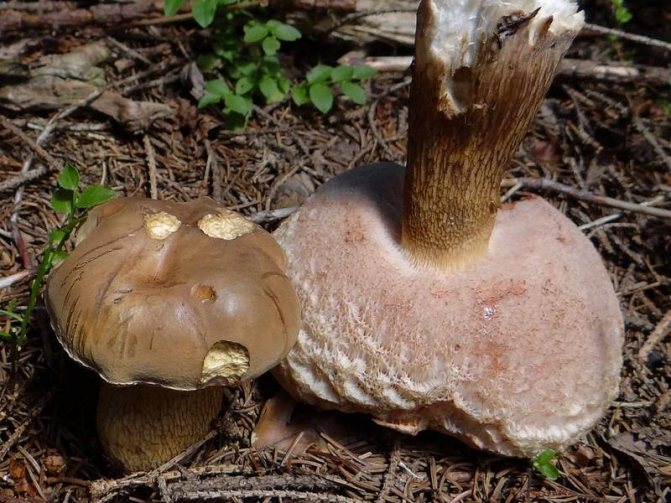

Photo by: Jerzy Opioła, GFDL
What is useful
Speaking about the beneficial properties of mushrooms, first of all, it is customary to remember the rich content of proteins. The flywheel, like its relatives, is also generous with proteins, the chemical composition of which is very similar to meat. This protein product is useful for restoring physical strength, during periods of intense growth and muscle building. Protein is essential for those involved in mental activity, as well as for the strengthening and regeneration of almost all tissues in the body. In addition, the proteins contained in the product are a set of amino acids essential for humans, without which healthy activity is impossible. By the way, some sources claim that the flywheel is the leader in the amino acid content of other mushrooms.
The second plus of this delicacy is its rich vitamin composition. Flywheels are a storehouse of vitamins A, C, D, as well as many vitamins from the B group. You can almost completely restore the daily intake of copper and zinc from one serving of these mushrooms. In addition, they are rich in molybdenum, calcium and chitin.
The unique characteristics of the moss mushroom include the special essential oils and enzymes contained in the caps. The rate of food digestion depends on these substances. This means that the flywheel improves the functioning of the digestive system and the quality of absorption of nutrients from food.
It also has natural antibiotic properties, strengthens the immune system and is beneficial for increasing hemoglobin. In folk medicine, it is known as a product with diuretic, tonic and anti-inflammatory properties. It was used to quickly heal wounds, as a natural antiseptic. And due to the presence of molybdenum, it is useful for treating the thyroid gland. The rich vitamin composition of mushrooms is a guarantee of good vision, healthy hair and beautiful skin. The ability to speed up metabolism has given the flywheel the glory of an anti-obesity fungus. The unique chemical composition of moss mushrooms makes them useful for the nervous system, brain function, kidneys, as well as for the rapid restoration of bone and muscle tissue.
Blunt flywheel (lat.Xerocomellus truncatus)
Name The moss is blunt-spore.Latin name: Xerocomellus truncatus.Other names: Blunt boletus, Pink-footed Mokhovik.Department: Basidiomycota.Class: Agaricomycetes.Order: Boletovye.Family: Boletovye.Genus: Mokhovichek.Conditionally edible mushroom.
Name The moss is blunt-spore.Latin name: Xerocomellus truncatus.Other names: Blunt boletus, Pink-footed Mokhovik.Department: Basidiomycota.Class: Agaricomycetes.Order: Boletovye.Family: Boletovye.Genus: Mokhovichek.Conditionally edible mushroom.
Leg
50–100 mm high, 15–25 mm thick, not hollow, cylindrical, sometimes slightly narrowed at the base, smooth, yellow, reddish at the base and above the middle.
Hat
50–120 mm in diameter, in young fruiting bodies it is cushion-convex, then becomes cushion-shaped. The skin is dry, felt, brown or chestnut brown, a characteristic feature of this species is the cracking of the skin, forming an almost reticular pattern. Cracks often turn pinkish.
Hymenophore
Tubular, adherent or slightly descending at the leg. The tubules are 10–15 mm long, yellow, later becoming greenish. The pores are large, wide-angular, of the same color as the tubules; they turn a little blue when pressed.
Pulp
A little loose, white or yellowish, at the base of the leg and under the skin of the cap it has a pinkish color, turns blue on the cut, the taste is slightly sour, the smell is not pronounced.
Habitat
Grows on soil in deciduous and mixed forests, singly or in groups, prefers saturated, acidic soils. It forms mycorrhiza with some deciduous trees, is thermophilic and grows in relatively warm regions, it is not so common.
Similarity
Blunt flywheel (Xerocomellus truncatus) has a direct resemblance to related species, such as Motley moss (Xerocomellus chrysenteron), some sources argue that the blunt moss does not pinkish cracks on the cap, there is a yellowish mycelium at the base and not the flesh, but lame intensively, but all these statements are controversial and undoubtedly, in order to determine a particular species, a microscopic examination of each specimen is required.
|
December |
January |
February |
|
March |
April |
May |
|
June |
July |
August |
|
September |
October |
November |
The nutritional value
Due to the slimy consistency in dishes and the mediocre taste, it is considered a conditionally edible mushroom of little value, but it is used in a variety of dishes.
Fractured flywheel mushroom: photo and description
Category: edible.
Hat Xerocomus chrysenteron (diameter 3-11 cm): matte, olive, burgundy or brown.


If you look closely at the photo of a fissured flywheel, you will notice a barely noticeable mesh pattern and a network of wrinkles. Because of this, the mushroom got its name. In a mature mushroom, it has the shape of a swollen pillow, but it may also be slightly depressed in the center. Velvety to the touch.
Leg (height 5-12 cm): yellowish above, and red-burgundy below, covered with small scales, solid (in old mushrooms it can be hollow), has the shape of a club.
Tubular layer: cream, yellow or olive, turns blue at the point of pressure.
Flesh: white or yellowish, strongly blue when cut or broken. Does not have a pronounced smell and taste.
When it grows: from early July to mid-September in Europe and the Far East.
Where to find it: On acidic soils of all types of forests, especially near beeches and oak trees.
Eating: salted and dried.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: yellow moss, yellow-meat moss, perennial boletus.