Home care
Irezine adapts well to any conditions. For example, during the heating period it can adapt to low humidity.
Illumination
It is better to place the flower on the south, southwest and southeast window. But, although the plant loves bright light.
In summer, it is better to shade it from direct rays, and in winter, the total exposure to the light should be at least 15 hours. This can be achieved with artificial lighting.
It can tolerate direct sunlight, but the irezine flower should get used to them gradually.
If the plant grows indoors and is illuminated only by fluorescent lamps, then they should be turned on for at least 14 hours a day.
Temperature regime
The plant grows quietly at home at room temperature. In summer, irezine can withstand temperature fluctuations within 15-25 ° C, and in winter - 15-22 ° C, but not lower than 13 ° C.
If the plant grows outside, then it should be kept there until the first frost.
Fertilizer
It is necessary to intensively fertilize irezine during the growth period, which takes place in the plant from spring to early autumn. It should be fed every week using mineral or organic fertilizers.
Since the plant has a dormant period in winter, it should be fertilized less often and less. Approximately once a month, reducing the concentration of the fertilizer used by 2 times.
Watering
In the period from spring to early autumn, it is necessary to water the plant at least once every 2 days. Or focusing on the topsoil - as soon as it has dried, the plant should be watered immediately. The soil must be constantly moistened.
In the cold season, the flower should be watered more moderately - about once a week. But in no case is the substrate allowed to dry out. If in winter the temperature in the room where the flower is located drops below 16 ° C, then watering irezine should be even less frequent. You should be guided in the same way as in the summer on the topsoil - it should not be dry.
For watering, you should take soft or infused water (at least a day). It is good to use rainwater for irrigation.
Planting and transplanting
If the flower will be grown as an indoor perennial plant, then it is better to transplant once every 2-3 years. It is better to transplant in the spring.
Transplanting can be done earlier if the pot no longer holds the plant.
The plant prefers slightly acidic soil. For example:
- Peat, sand, deciduous and sod land, humus - 1: 1: 4: 4: 2.
- Garden land, leaf, perlite, peat - 1: 1: 1: 1.
- Sod and deciduous land, humus, sand - 2: 2: 2: 1.
During the warm season, the plant can be planted outdoors.
The main condition for transplanting is the presence of a drainage layer in the pot. It can be expanded clay or broken bricks.
Cropping flowers
The flower should be trimmed and pinched every year. After these procedures, the plant grows more branched and lush. These manipulations are carried out over the apical shoots of irezine. Pruning and pinching can be done all year round, but it is better in February for plant development in spring.
Reproduction
Most often, flower reproduction is carried out by cuttings, since this method is faster. To do this, you should:
- In the spring and summer, cut off the apical stalk about 5-8 centimeters long with 2 knots.
- Plant him in moistened sand.
- Cover with plastic.
- Maintain the temperature within 17-21 ° C.
- After the roots appear (7-10 days), transplant into a small pot.
- For the plant to branch better, it should be pinched twice as it grows.
- Purchase seeds.
- Sow them into a container with suitable soil.
- Cover with glass or plastic.
- Ventilate and humidify.
- Remove the cap as soon as sprouts appear.
- Place in a well-lit place.
- As soon as 3 (or more) leaves appear on the sprout, plant it separately.
Pests and diseases
Pests:
Green aphid - requires treatment with an insecticide, which contains pyrethrum.
Scratch. Appears due to waterlogging of the soil.
Also, the irezin plant is susceptible to such pests as whitefly and spider mites.
The main causes of flower disease are improper living conditions.
So, if the flower lacks lighting, then:
- leaves become small and fade;
- the stem is pulled out;
- foliage falls.
The cause of foliage falling can also be if pruning has not been done. But if the plant is already adult, this phenomenon is considered normal.
Consequences associated with watering:
- leaf discharge (lack or excess of watering);
- drooping leaves (drying out of the soil).
If the temperature is below normal (12 ° C):
- soft and drooping leaves and stems;
- leaf discharge;
- rotting roots.
If the temperature is increased, then the leaves lose their elasticity and droop.
mushroom edible, tasty and aromatic
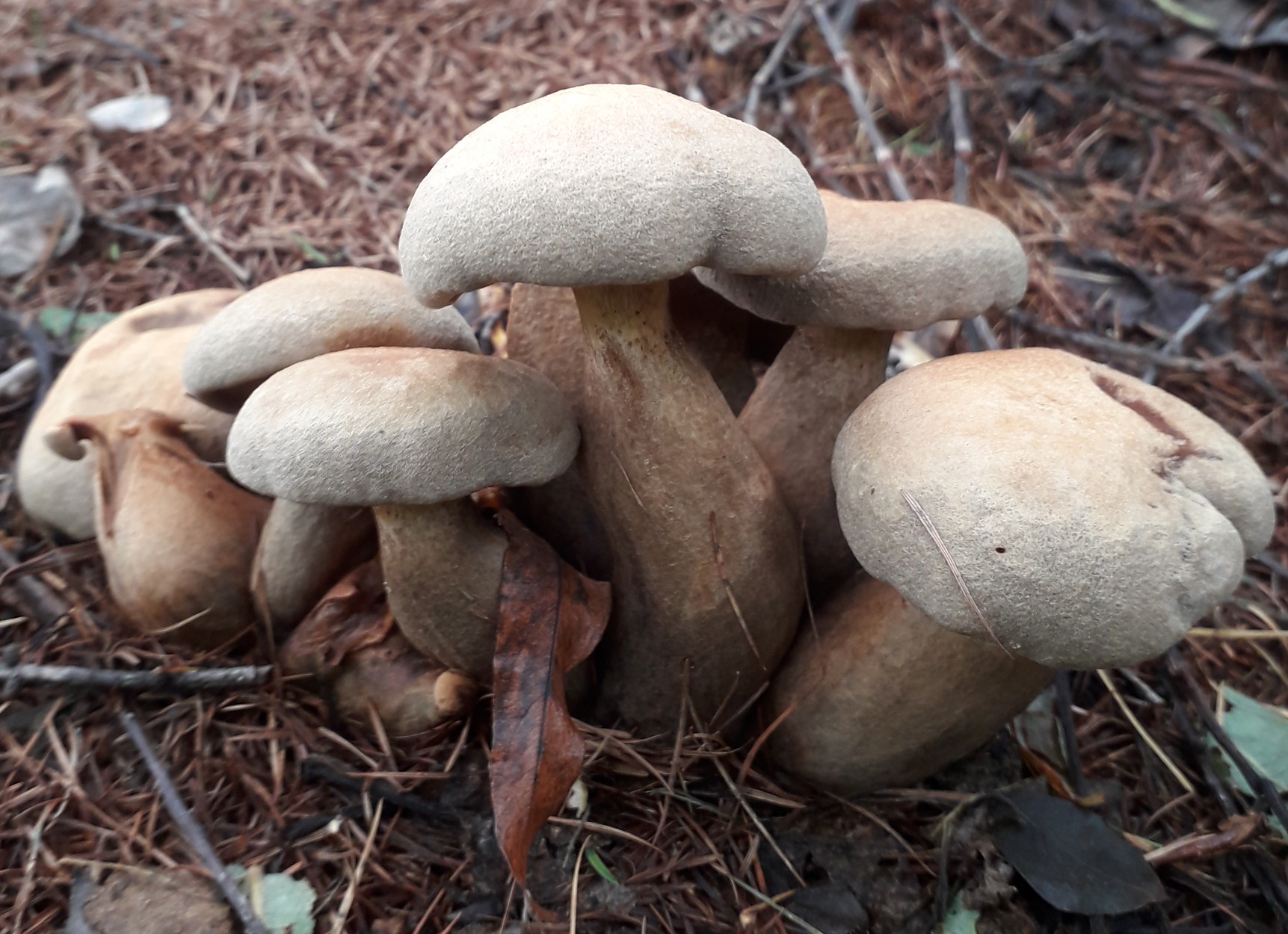
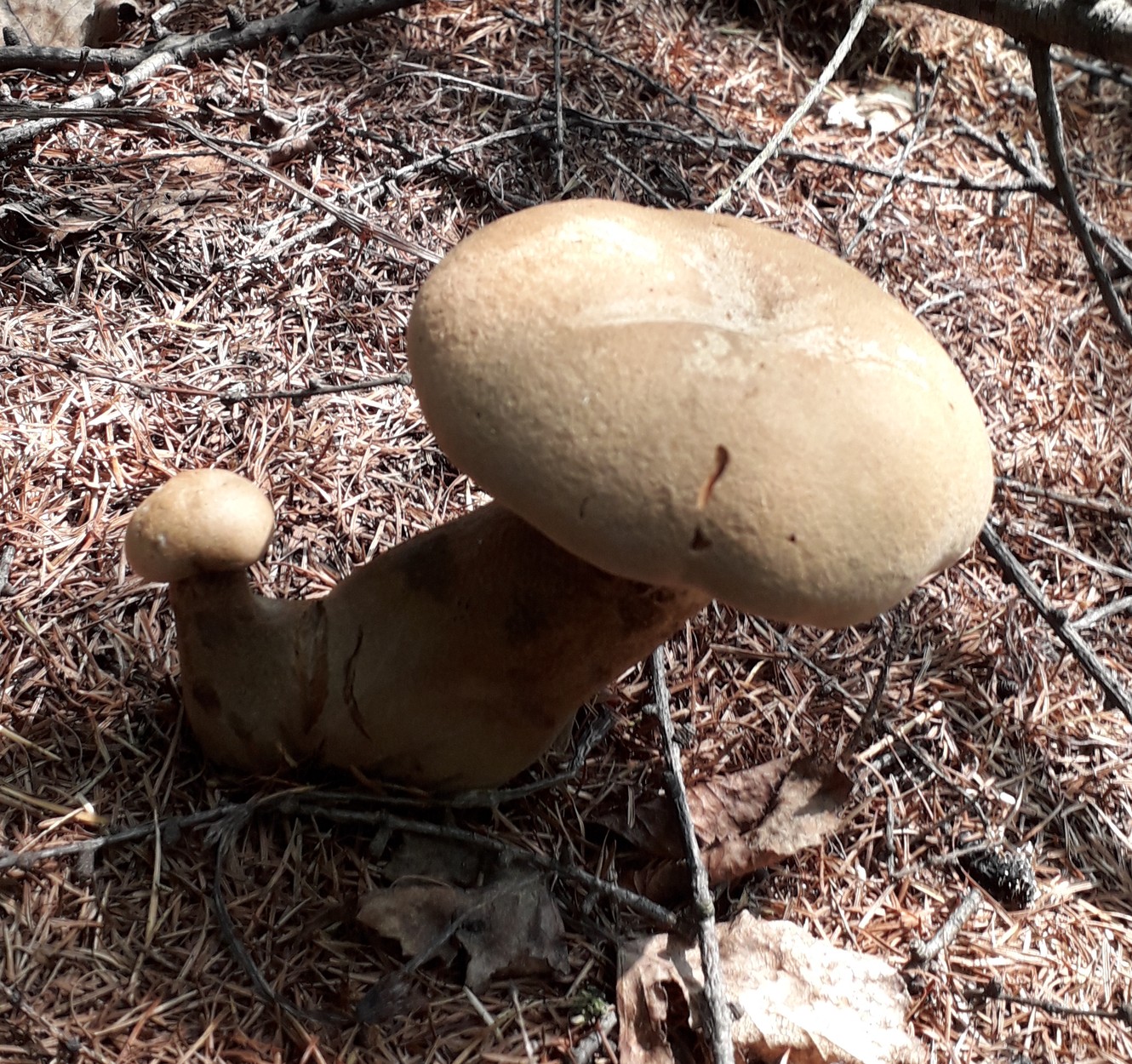
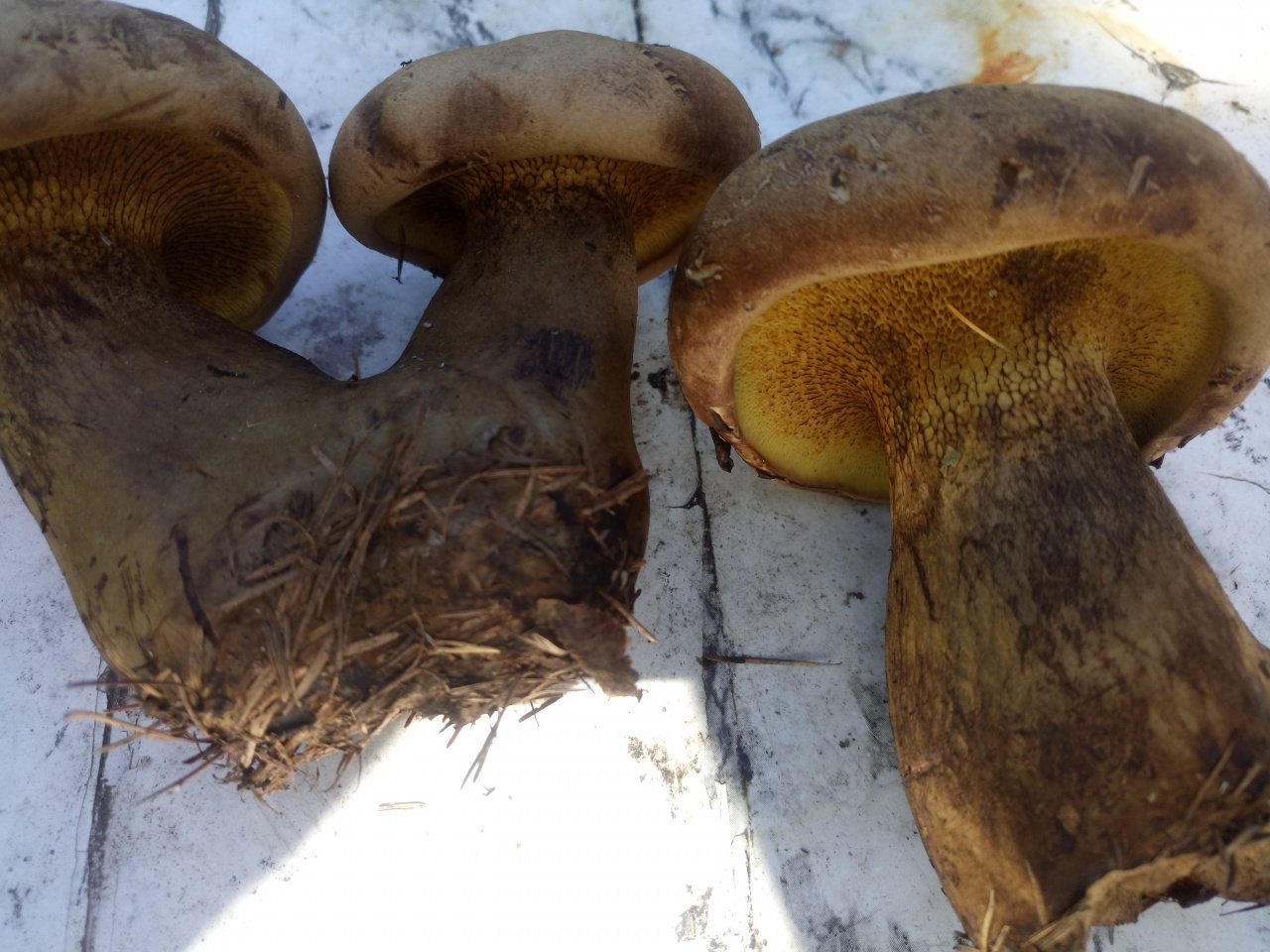
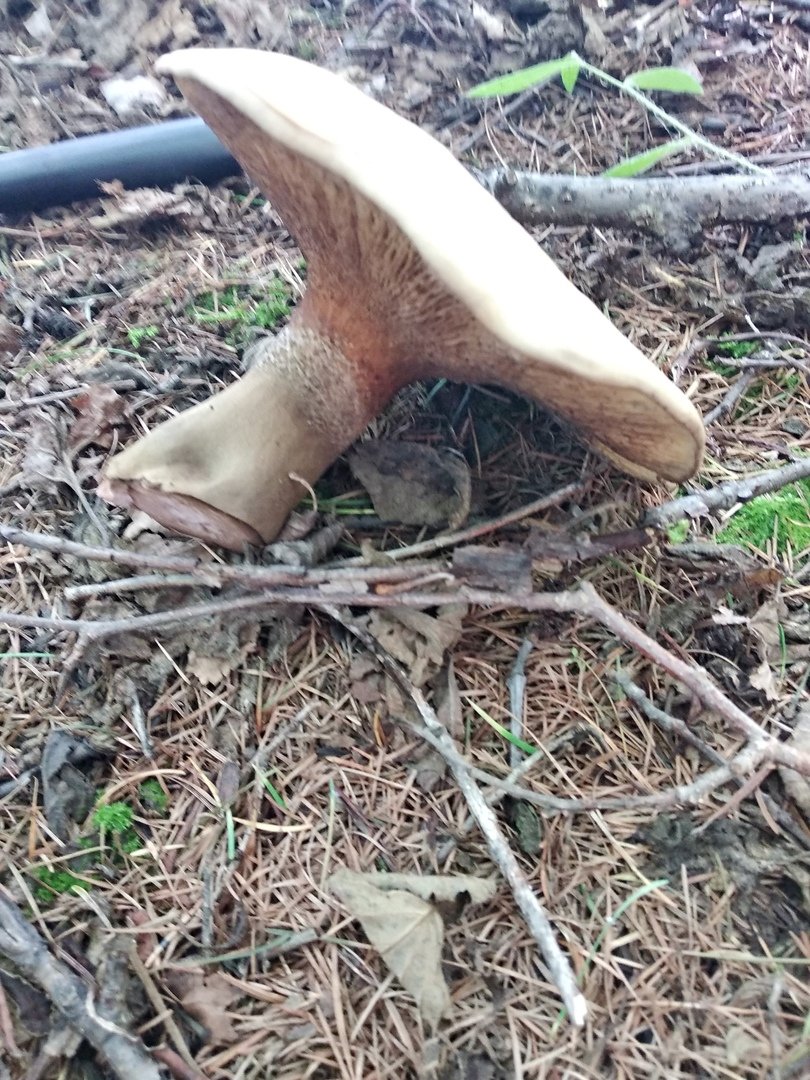
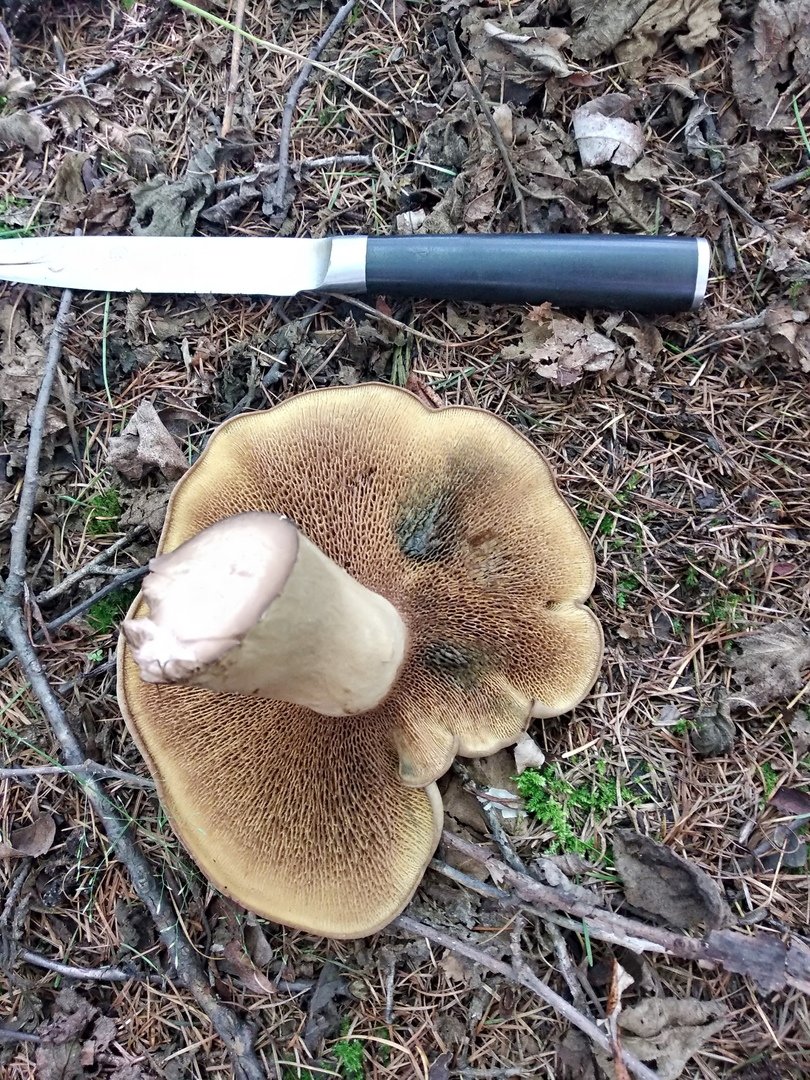
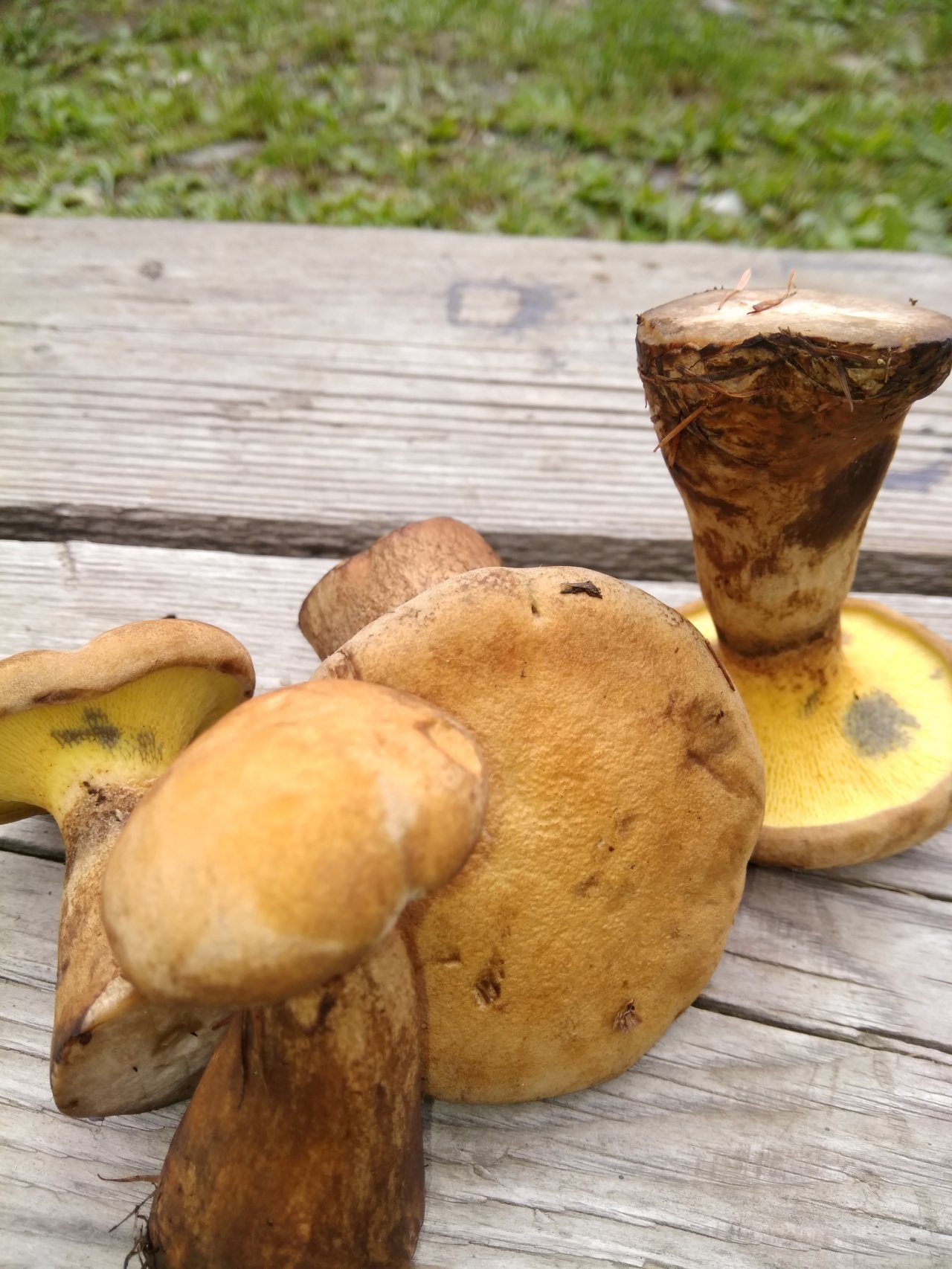
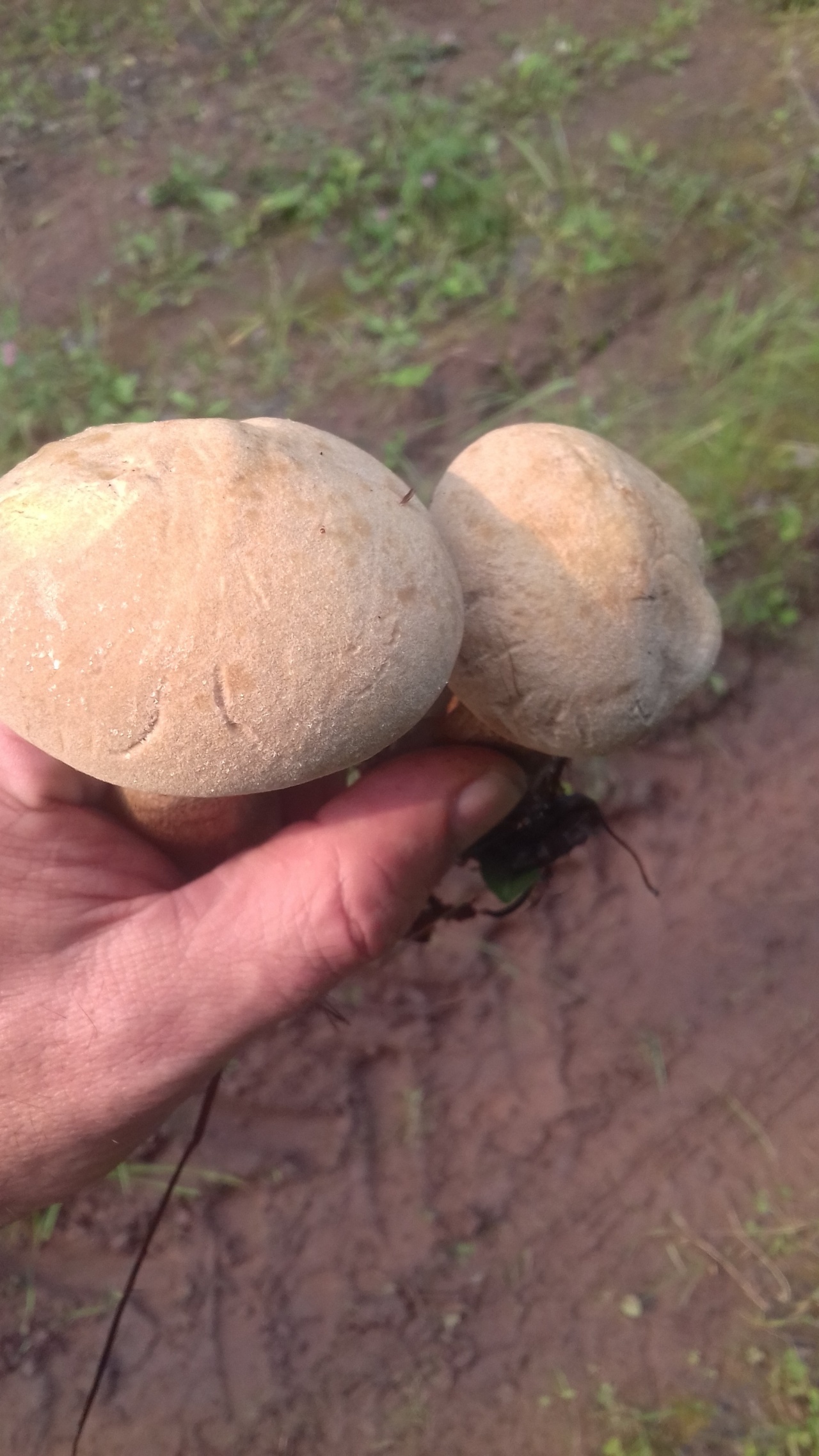
Among the edible tubular mushrooms, there is one, similar at the same time to boletus, boletus and boletus. This is a flywheel - a mushroom that grows in coniferous, deciduous and mixed forests. Moreover, its appearance depends on the place of distribution. That is why it is often confused with other edible cousins, and even more often they do not know about its taste at all, mistaking it for false or poisonous.

The flywheel mushroom can be harvested from June to October, it grows mainly in deciduous forests, often adjacent to oak, aspen, birch and conifers. It is usually eaten fried and dried, has an excellent taste, but during processing it changes its color, becoming dark. The hat is slightly irregular, matte, cushion-shaped, dry, with velvet hairs pleasant to the touch. The color can vary from light green to brown and bright yellow. The flywheel is a rather large and noticeable mushroom, the diameter of the cap is on average from 40 to 110 mm.
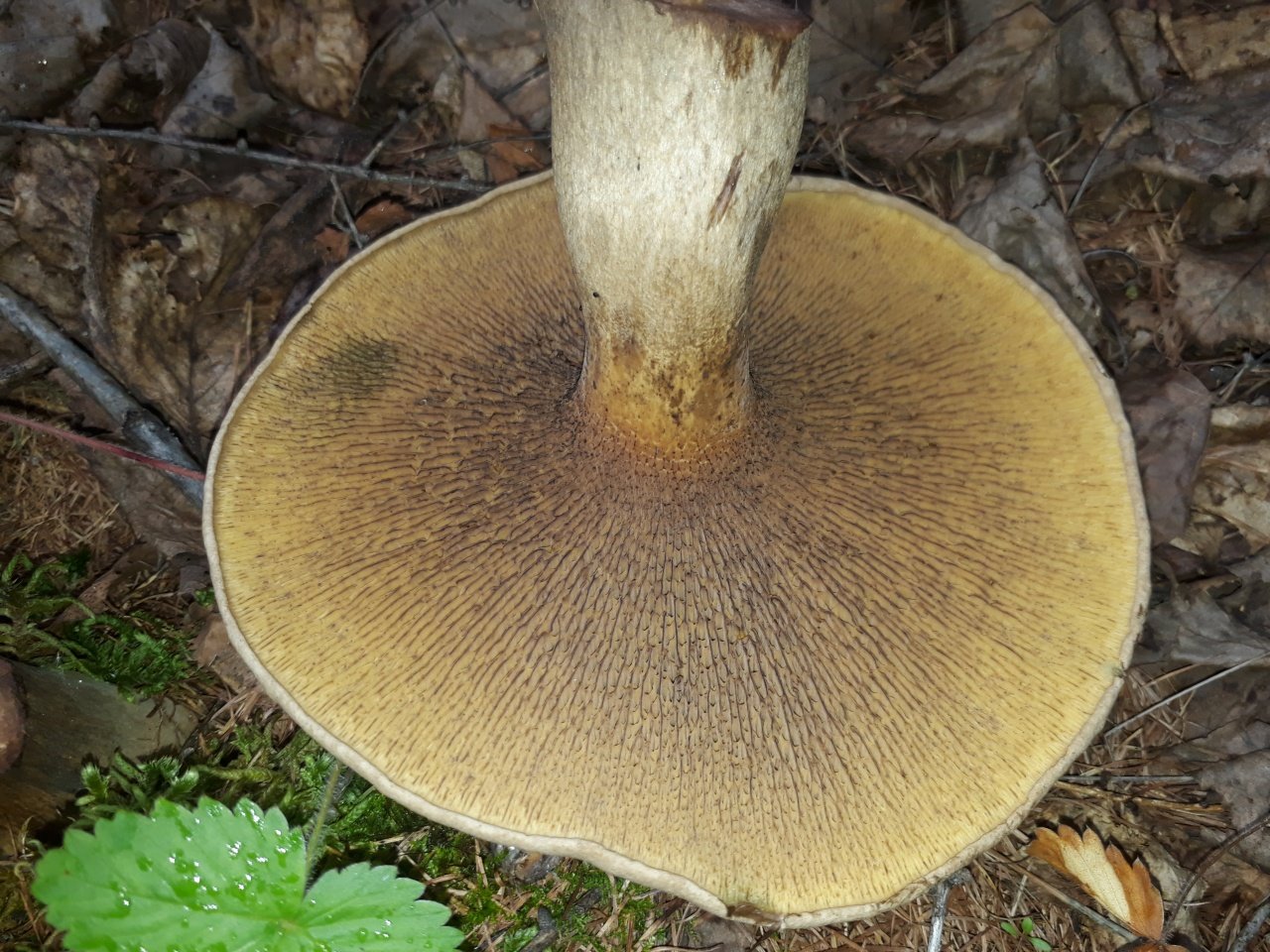
The tubes on the back are yellow (in young mushrooms, the thickness is from 5 mm, in older ones, up to 15 mm). At first, they are tightly pressed against the cap, as the flywheel matures, they become looser and change their color to olive. In old age, they acquire a chestnut or bluish tint; when pressed, dark traces remain on them.
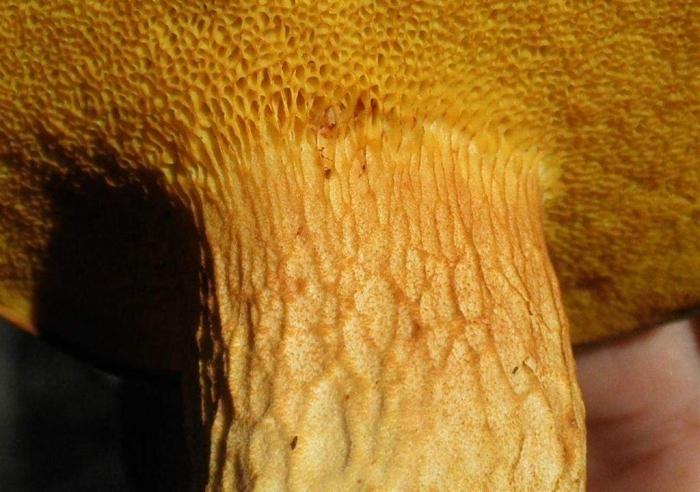
Flywheel is a mushroom with a pleasant, light scent reminiscent of a fruity aroma. The younger the mushroom, the more pleasant it tastes, so the best for assembly are young or slightly grown individuals. In a young flywheel, the cap is round, without breaks; in older ones, it is voluminous, thick, often curved. Overgrowths quickly deteriorate, sometimes the mushroom decomposes in a few hours. That is why it is advised to sort out and prepare the forest "harvest" during the same day when it was harvested, and eat only young specimens not spoiled by worms.

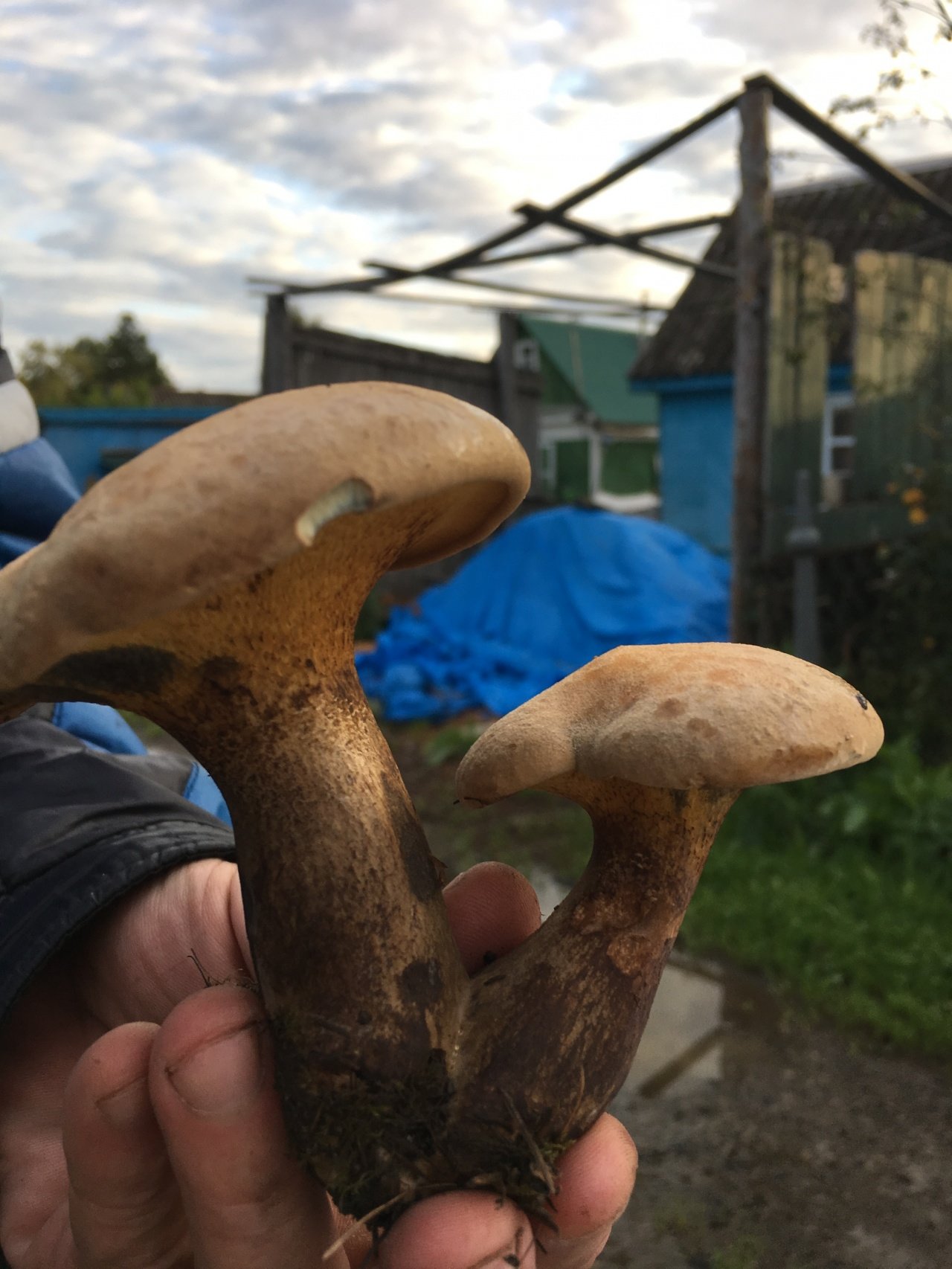
Due to the color of the cap, several subspecies of the flywheel are distinguished: yellow-brown, green, variegated and red. They all have a similar appearance, but grow in different forests. The yellow-brown mushroom flywheel (photo above) is one of the most common, always adjacent to a pine tree, and a green flywheel grows in deciduous forests. Often there are specimens with a variegated hat, they look original and tempting. Any of them are edible. They lend themselves well to drying, while the pulp retains its lemon shade and pronounced mushroom aroma. In addition to drying, you can also harvest fried mushrooms for future use, because they also have excellent taste, are well stored and are suitable for preparing various dishes: soups, pizza, fried potatoes.
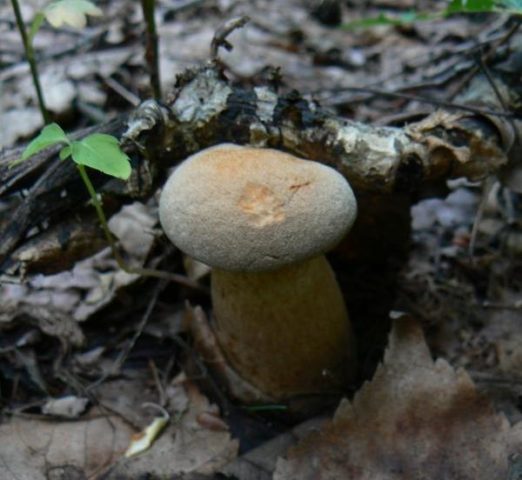
Larch flywheel (Psiloboletinus lariceti) photo and description
Larch flywheel (Psiloboletinus lariceti)
Systematics:
- Department: Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes)
- Subdivision: Agaricomycotina
- Class: Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes)
- Subclass: Agaricomycetidae
- Order: Boletales
- Family: Suillaceae (Oily)
- Genus: Psiloboletinus (Psiloboletins)
- Species: Psiloboletinus lariceti (Larch moss)
Synonyms:
- Boletinus lariceti
- Larch boletin

Psiloboletinus is a genus of fungi of the Suillaceae family. It is a monotypic genus containing one species, Psiloboletinus lariceti. The species was first described by the mycologist Rolf Singer in 1938 as Phylloporus. Alexander H. Smith disagreed with Singer's general concept, concluding: “Regardless of which arrangement of the type species Psiloboletinus is ultimately made, it is clear that there are no clearly distinguishable characters by which the genus could be recognized. based on Singer's descriptions ”.
"Larch" - from the word "larch" (a genus of woody plants of the pine family, one of the most common species of conifers), and not from the word "deciduous" (Deciduous forest - a forest consisting of deciduous trees and shrubs).
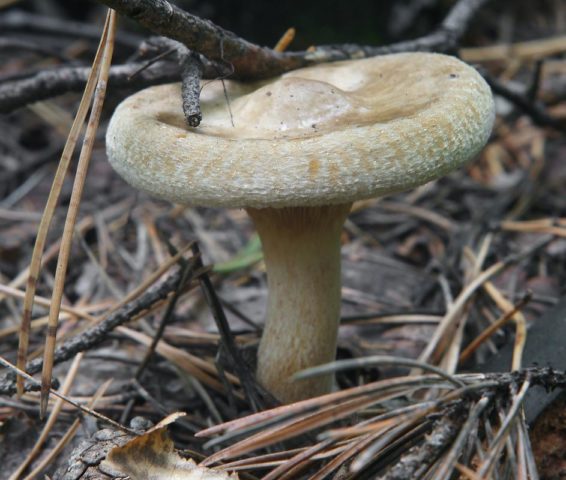
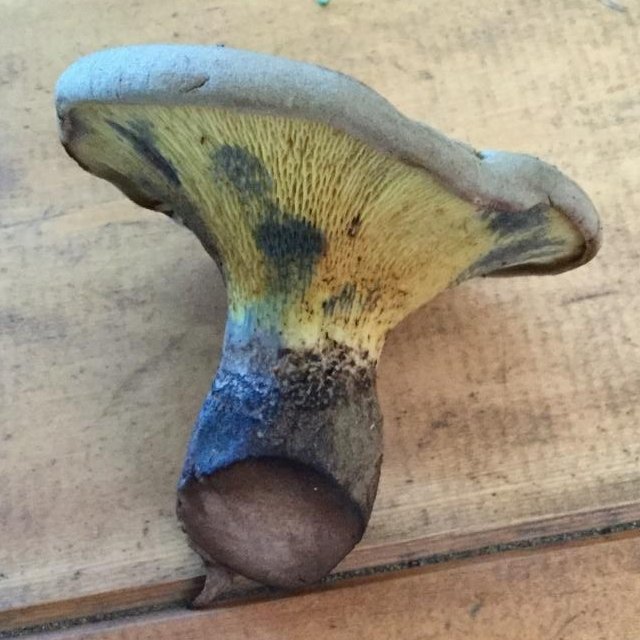
Description
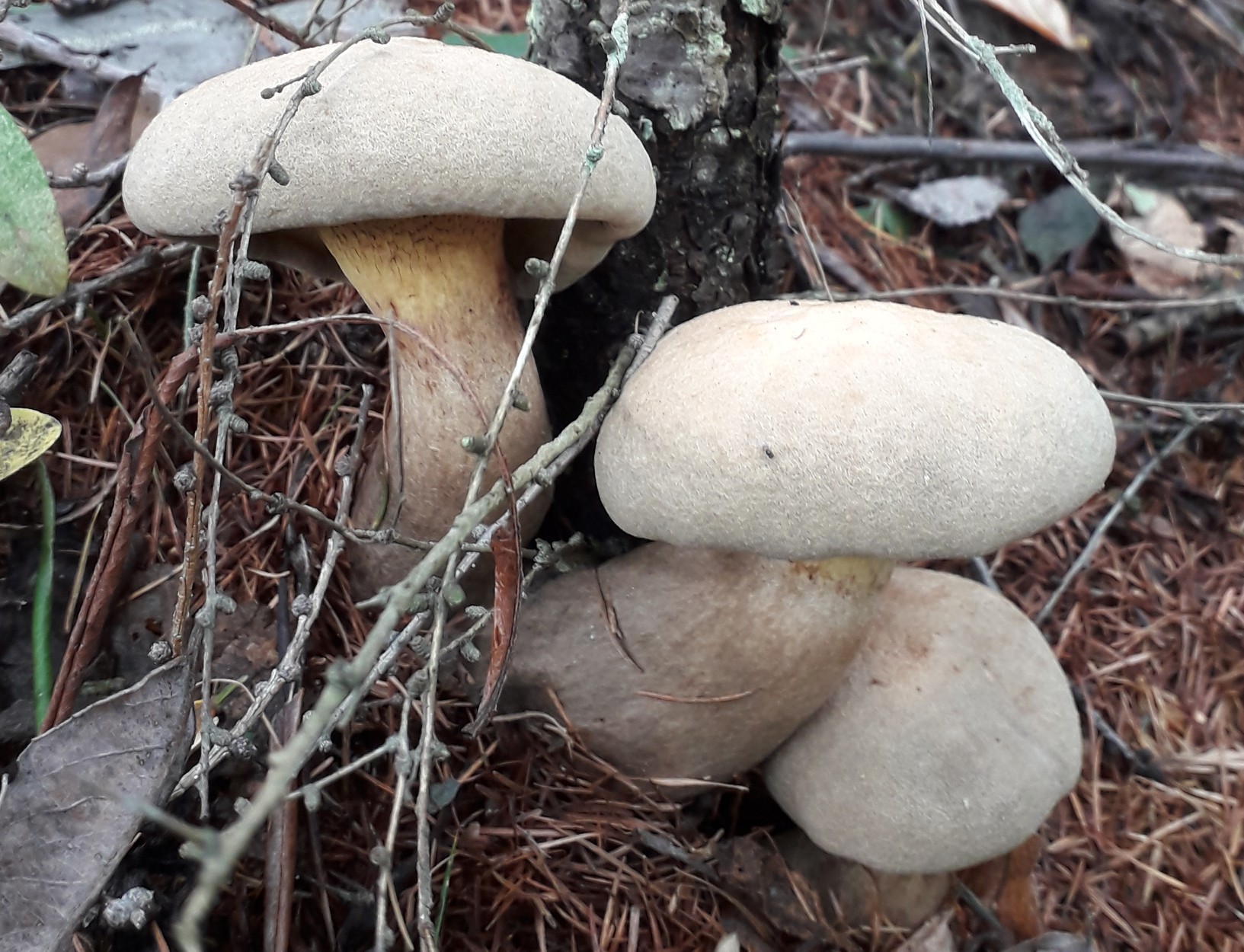
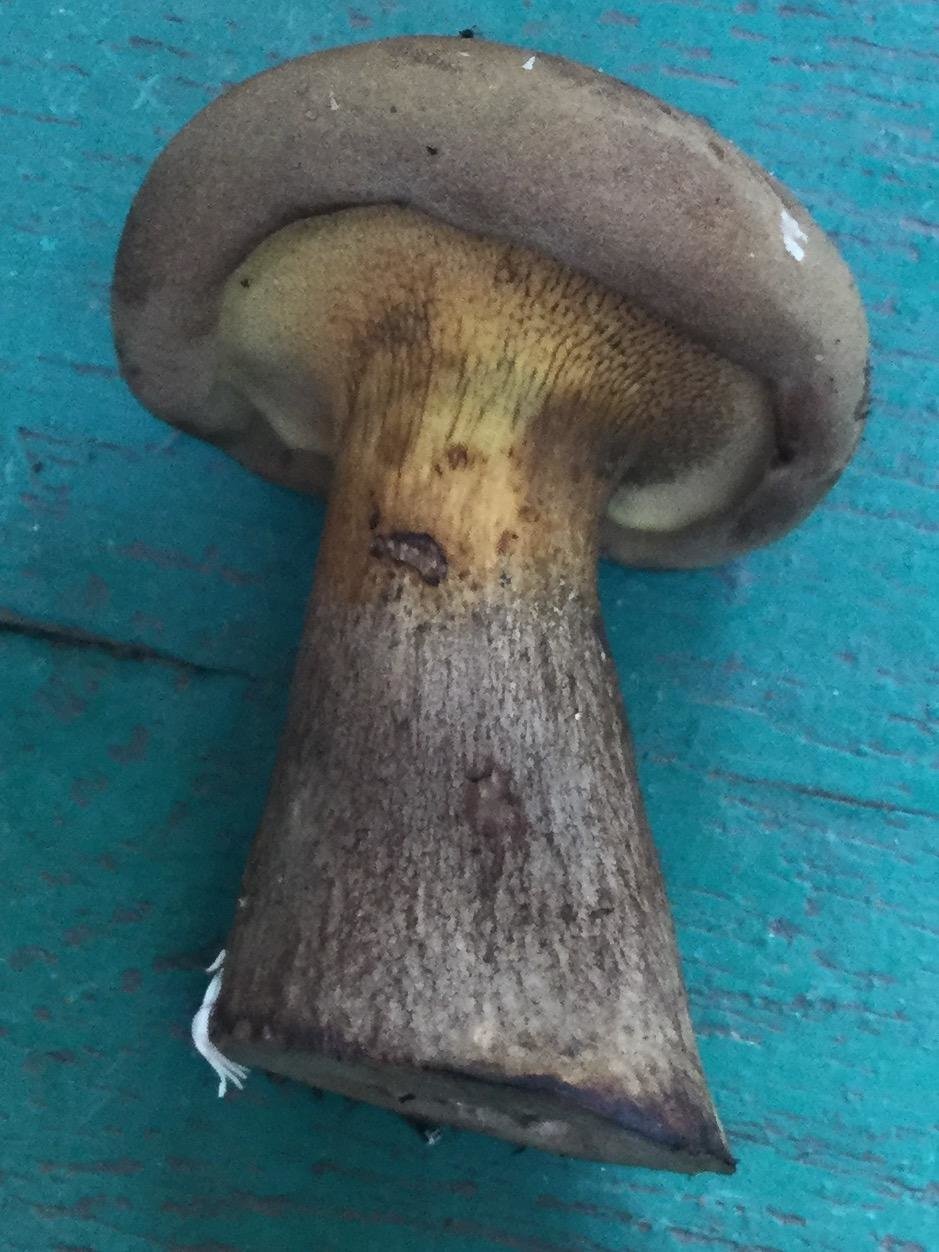
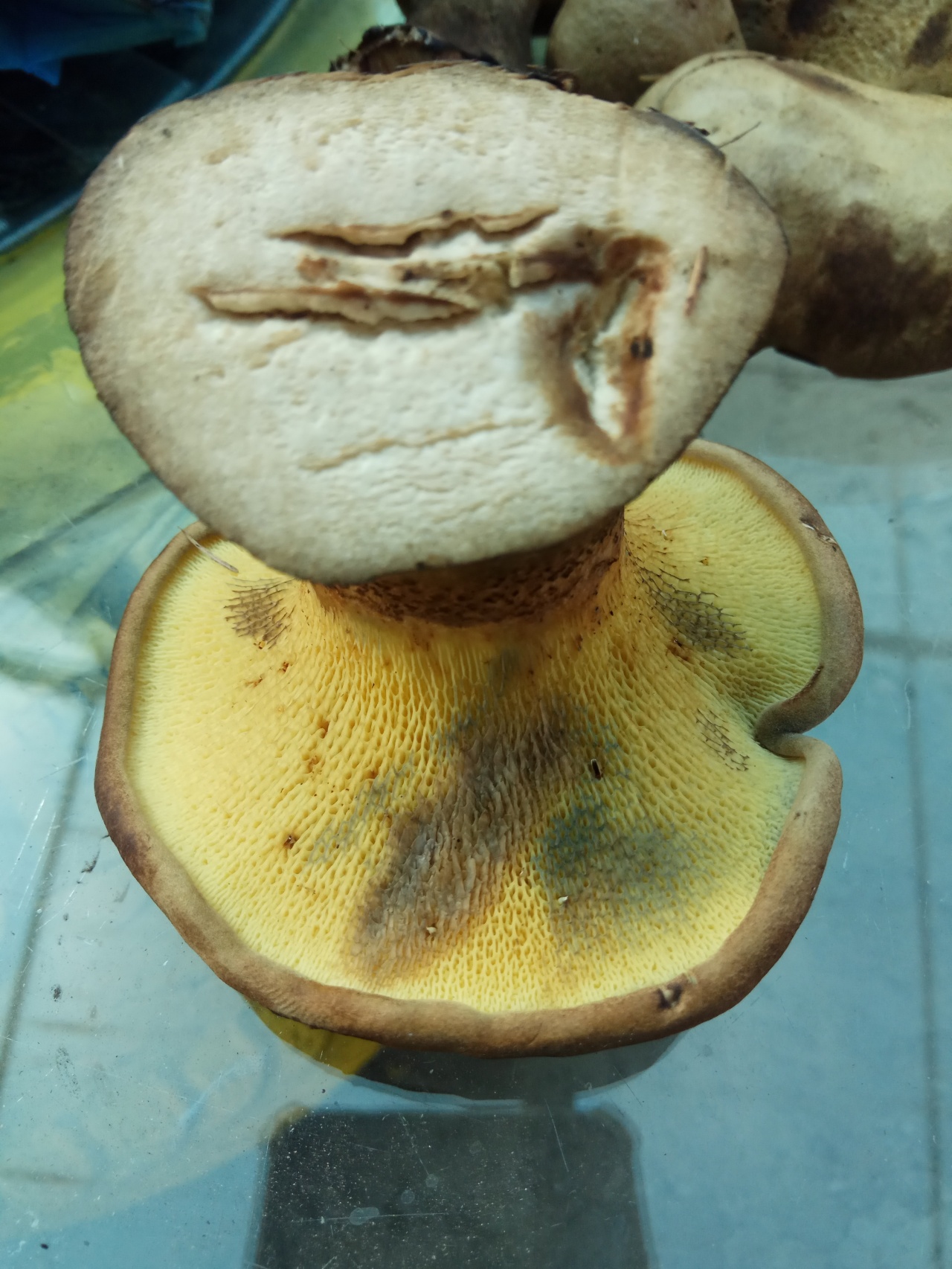
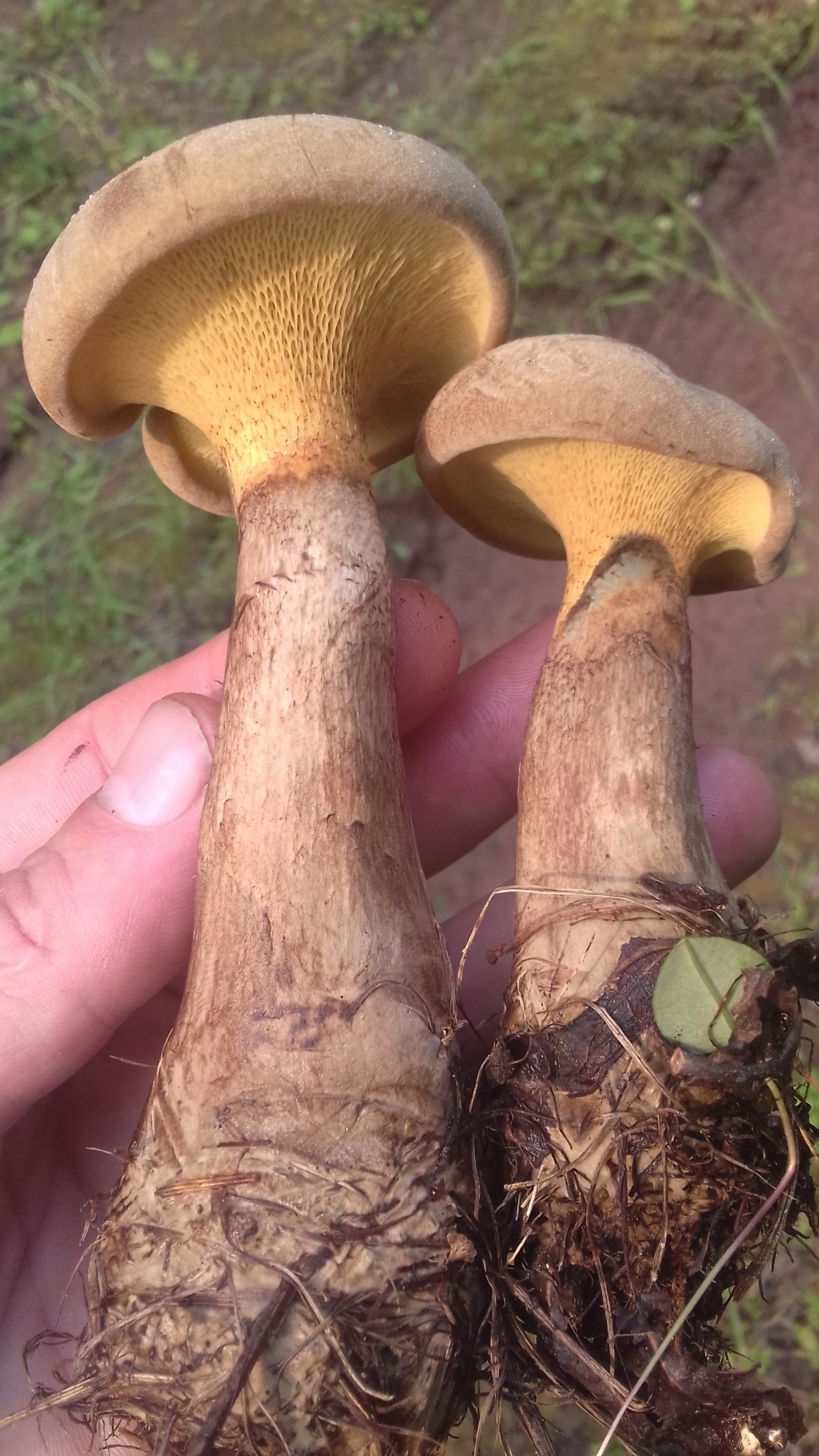
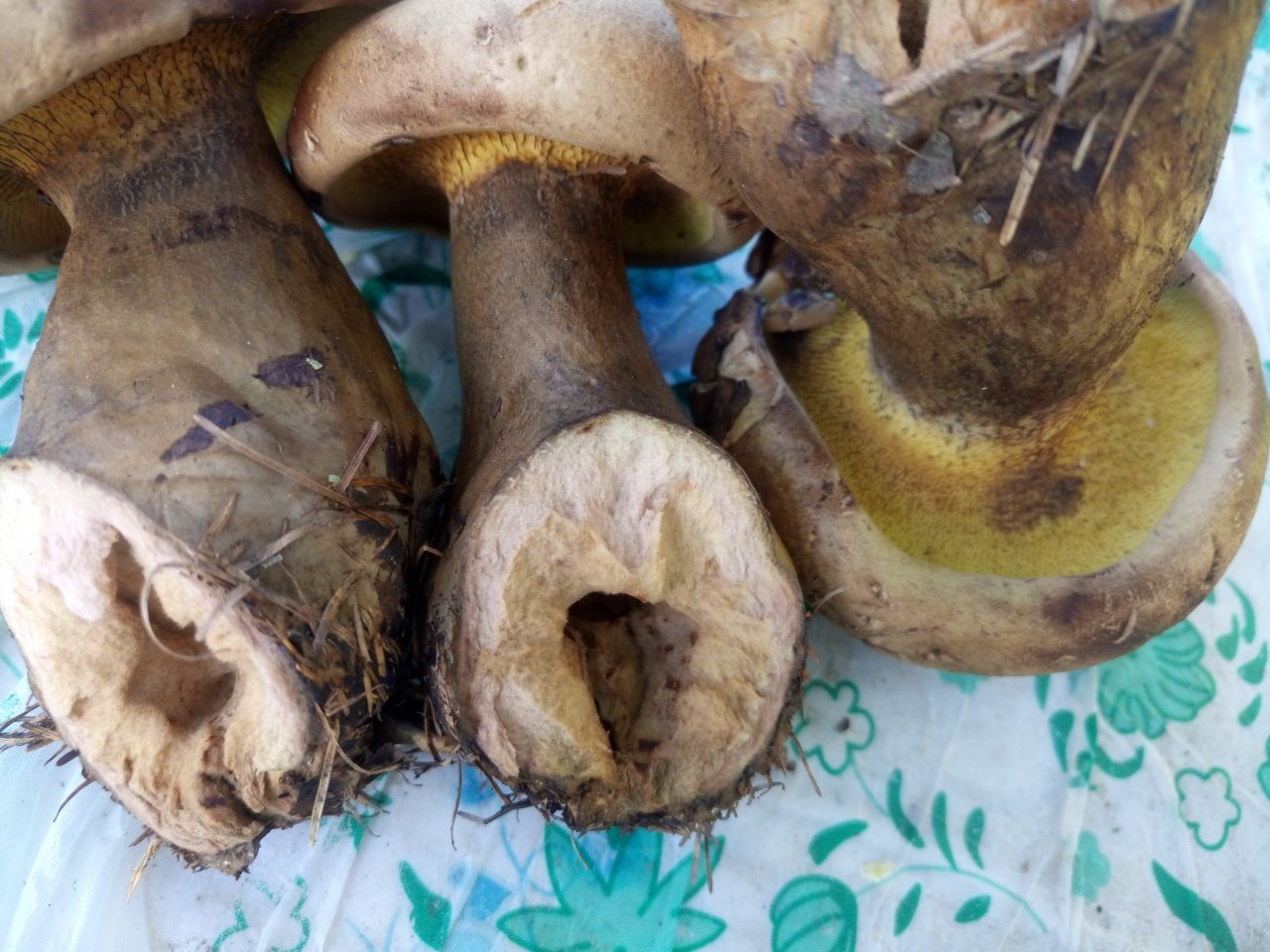
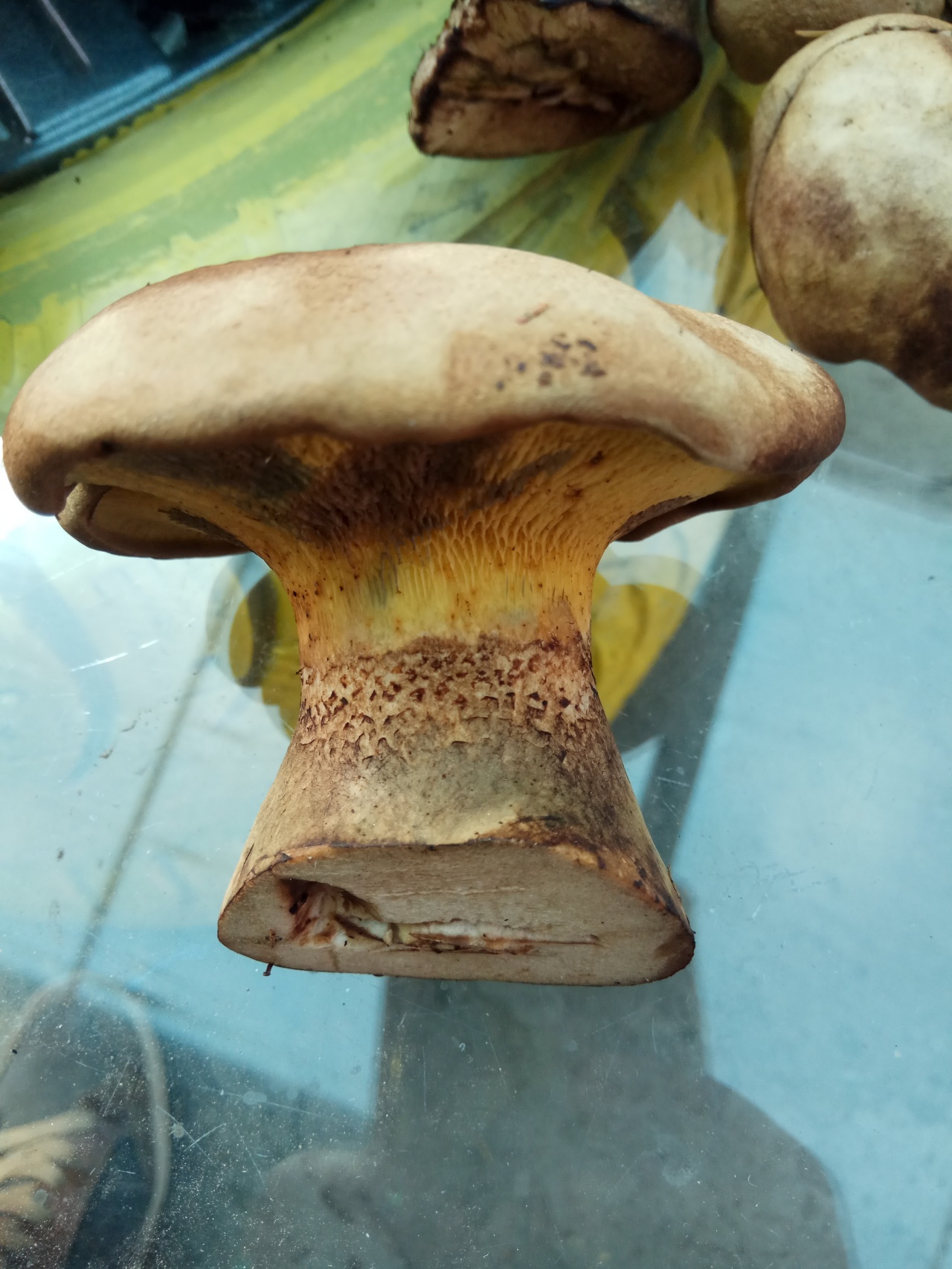
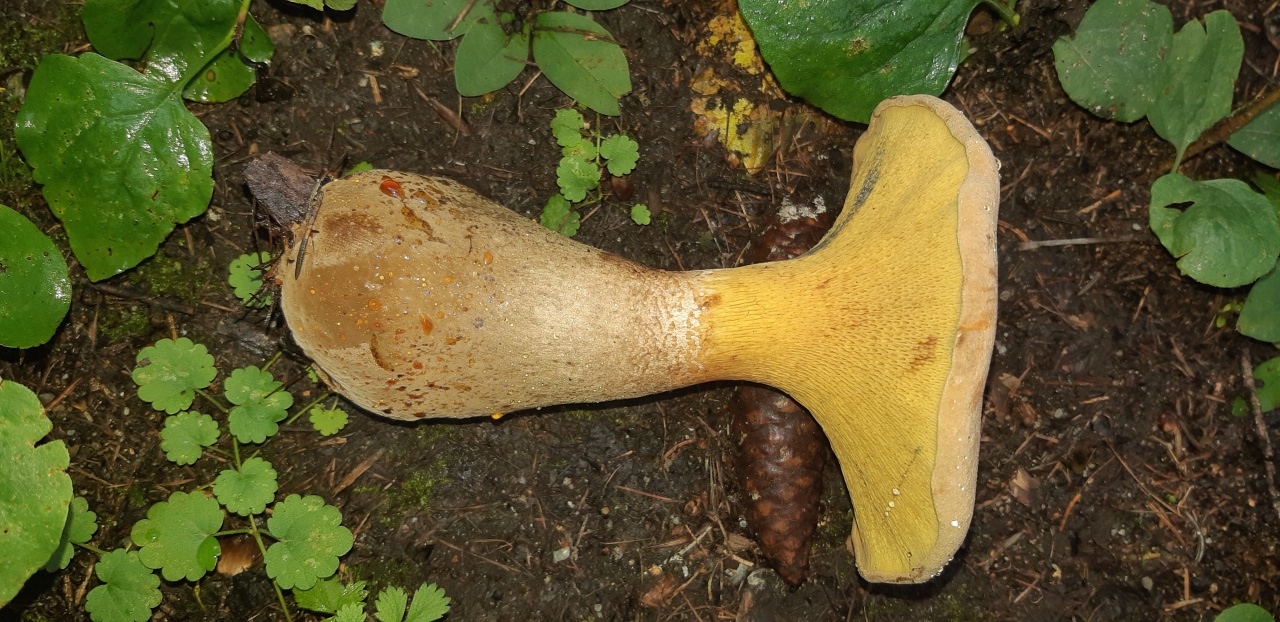
Hat: 8-16 cm in diameter; under favorable conditions, specimens with caps of about 20 centimeters are possible. In youth it is convex, with a strongly tucked inward edge, then flat-convex; in very adult mushrooms, the edge of the cap is not tucked up, it may be slightly wavy or lobed. Dry, felted or tomentose-scaly, velvety to the touch. Brownish, ocher-brown, dirty brown. Pulp in a hat
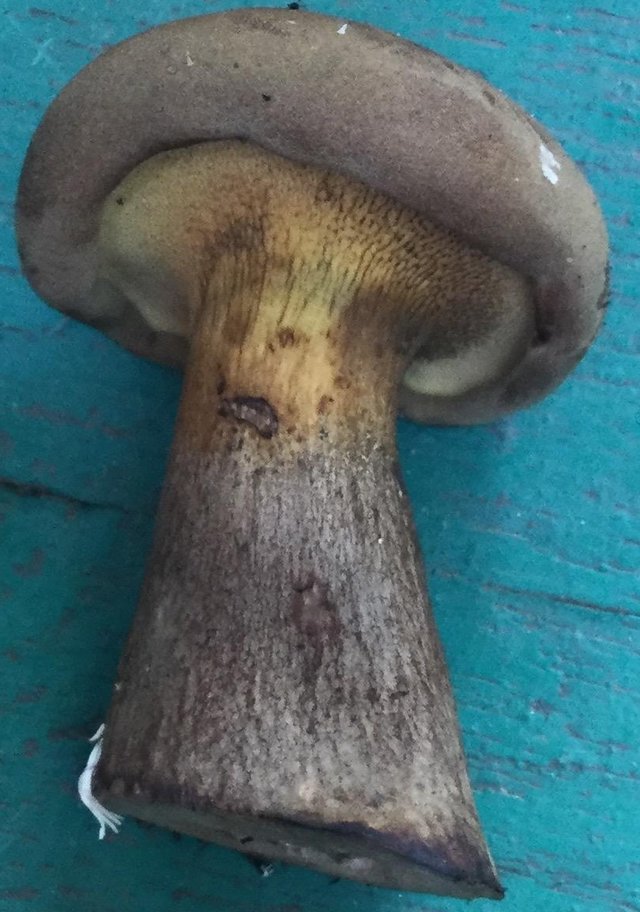

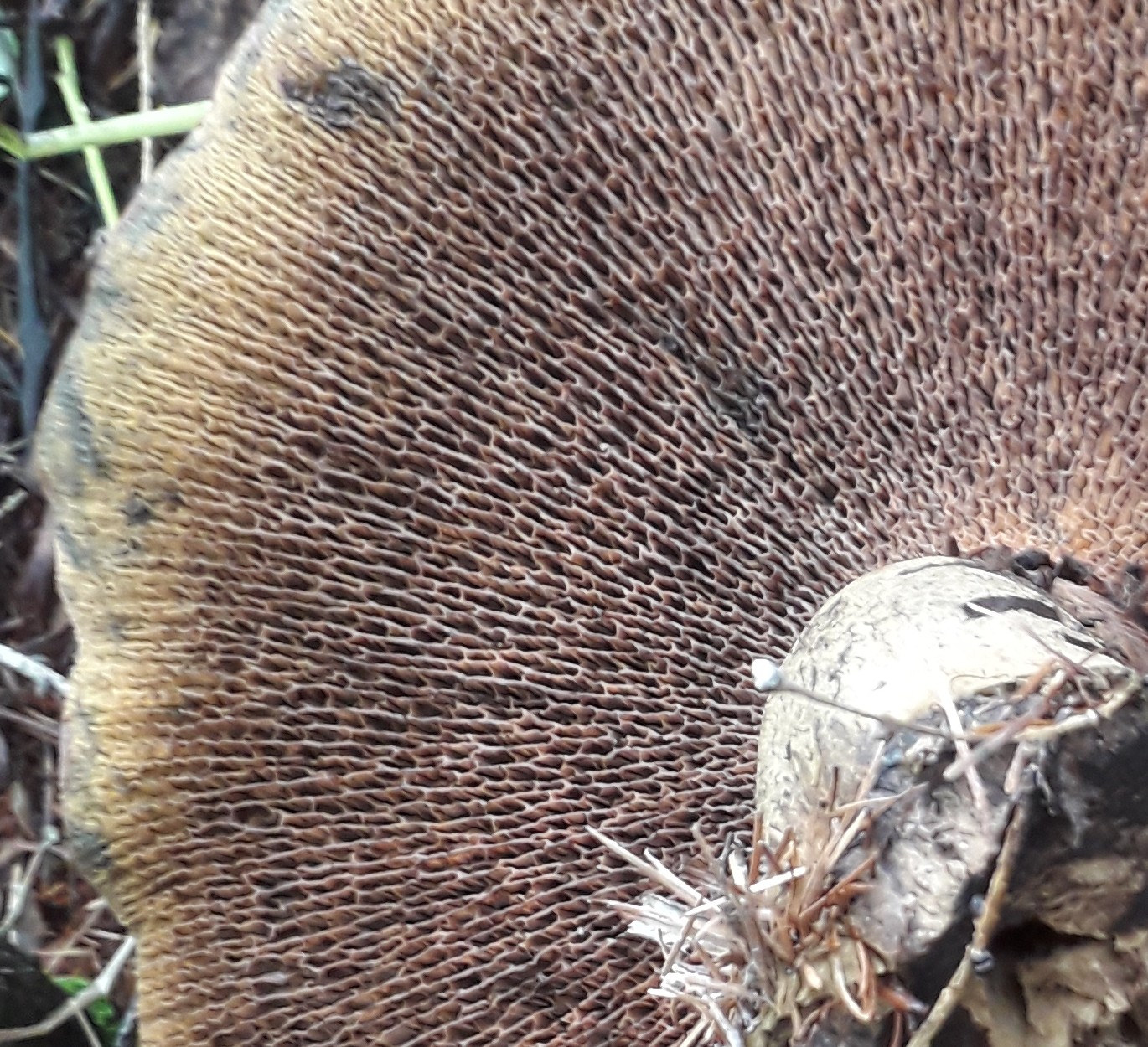
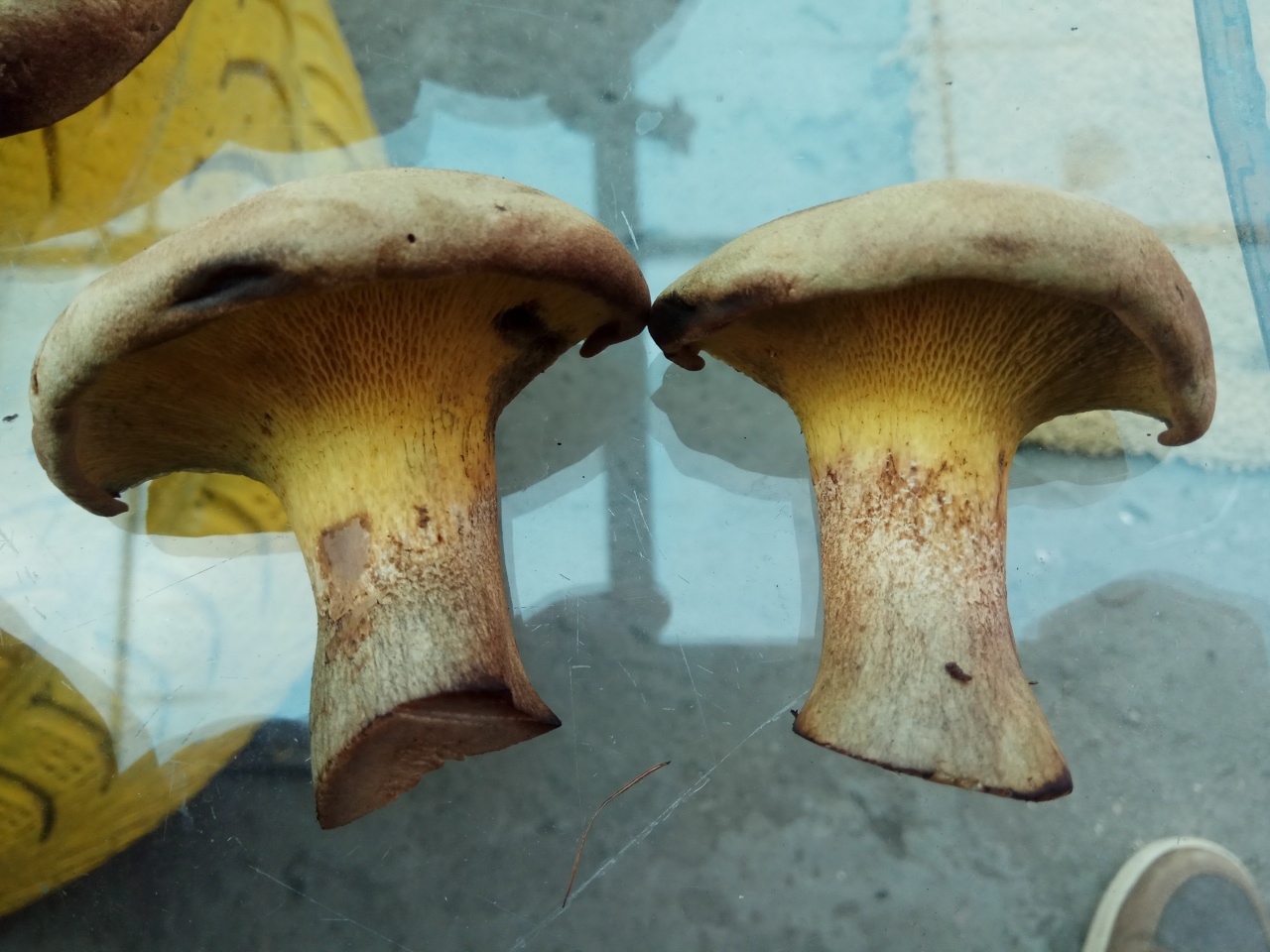
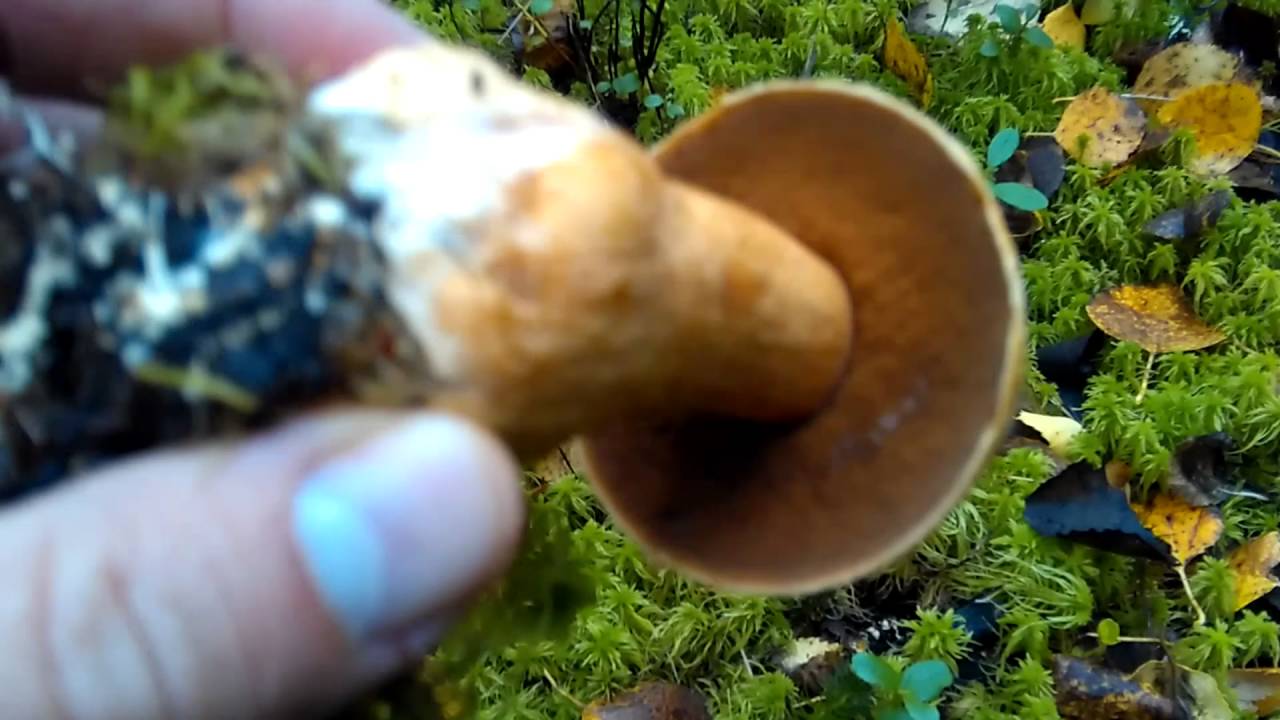
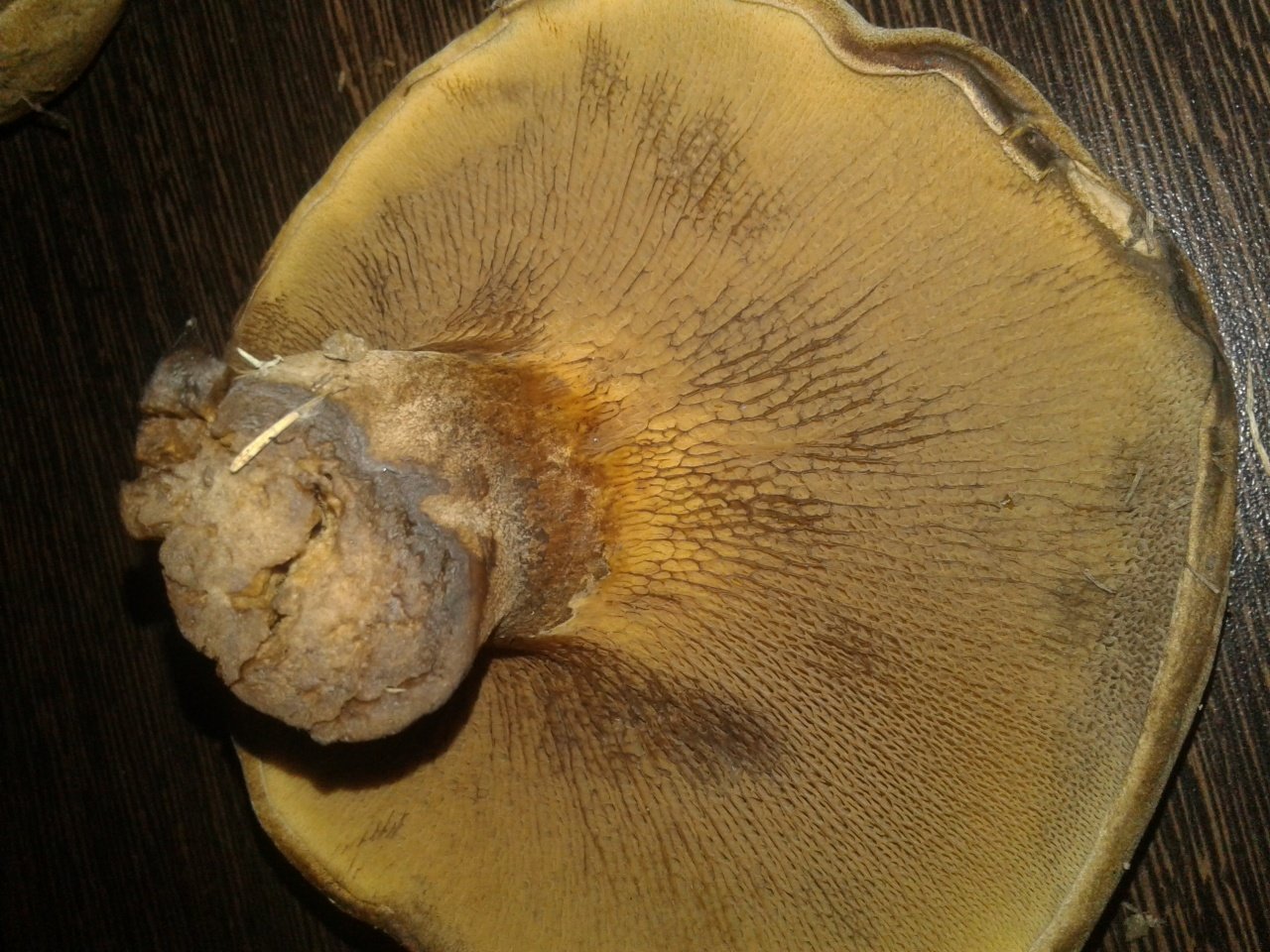
Hymenophore: tubular. The tubules are large, wide, with thickened side walls, and therefore visually form a semblance of plates. They run down strongly on the leg, where they become elongated, which is why their visual resemblance to the plates increases. The hymenophore is yellow, light in youth, then yellowish-brownish. When damaged, even minor, it turns blue, then turns brown.
Spores: 10-12X4 microns, cylindrical, fusiform, brown-yellow with drops.
Leg: 6-9 centimeters high and 2-4 cm thick, central, can be thickened at the bottom or in the middle, velvety. In the upper part it is light, in the color of the hymenophore, yellowish-brownish, below it is darker: brownish, brownish, dark brown. Turns blue when pressed. Solid, sometimes with a cavity.
Leg pulp
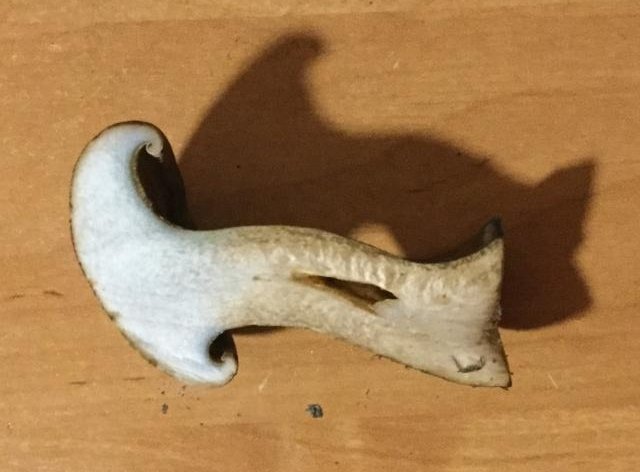

Ring, bedspread, volva: none.
Taste and smell: mild mushroom.
Ecology
It grows only in the presence of larch: in larch forests and mixed forests with the presence of birch, aspen, under larch.
Season and distribution
The peak of fruiting occurs in August-September. It is well known only on the territory of Russia, found in Western and Eastern Siberia, Amur region, Khabarovsk Territory, in the Far East, especially often and abundantly bears fruit on Sakhalin, where it is called "Larch moss" or simply "moss".
Edibility
The mushroom is edible, there is no data on poisoning. It is used for making soups, salads, main courses. Suitable for pickling.
Similar species
A slender pig in some growth stages can be mistaken for a larch flywheel. You should carefully look at the hymenophore: in the pig it is lamellar, in young specimens the plates are wavy, so that at a cursory glance they can be mistaken for large tubes
An important difference: the pig does not turn blue, but turns brown when tissue is damaged
Gyrodons are quite similar to Psiloboletinus lariceti, you should pay attention to the ecology (type of forest). Goat, it differs in the color of the flesh in the damaged areas, its flesh does not turn blue, but turns red
The goat, differs in the color of the flesh in the damaged areas, its flesh does not turn blue, but turns red.
Healing properties
Purposeful studies were carried out, there are works on the thrombolytic properties of enzymes of basidal fungi (Botanical Institute named after V. L. Komarov, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia), where there is a high fibrinolytic activity of enzymes isolated from Psiloboletinus lariceti. However, it is too early to talk about widespread use in pharmacology.
Note: The photographs from the questions in "Recognition" are used as illustrations in this article. If you have good photos of this mushroom, please share.
Preventive measures for the garden
It is possible to plant fruit crops only in those areas where plants susceptible to verticillosis have not been grown over the past 5 years. Strawberries, tomatoes, peppers, potatoes must not be planted in the aisles in the garden.
It is better to mulch or sow the soil in near-trunk circles with green manure. Alternatively, keep the soil under black steam (in a loose, dug up state).
When choosing the last option, you need to remember that during the cultivation of the land, mechanical damage to the root system of plants is unacceptable.
When watering, do not overmoisten the soil. A furrow irrigation system should not be used as the infection spreads rapidly from the source to the entire drain.
For irrigation, use only warm, settled water. In rainy weather, watering should be avoided altogether. For adult trees and grape bushes, 1-2 procedures per month are enough.
You need to be careful when applying fertilizers. The fungus actively develops on soils with a large amount of organic matter and nitrogen. Therefore, it is impossible to use fresh, not rotted manure as fertilizer. Nitrogen fertilizers can be applied only in early spring in small doses. 50-60 g of granular nitrogen fertilizer are applied under the bushes of grapes and large trees. During the season, plants need to be fertilized with phosphorus and potassium, which increase resistance to various diseases.
During pruning, do not shorten the shoots too much, as this stimulates their new growth, which reduces the resistance of plants to verticillosis.
If diseased trees are found in the garden, you need to remove the affected branches, cover the sections with garden pitch. Do not rush to remove them completely. With proper care, the likelihood of self-healing is high.
A completely dead bush or tree must be uprooted, and the hole must be disinfected. To do this, use the soil sterilizer Carbation at a concentration of 0.2 l per 1 sq. M.
Prevention for vegetable crops
With annual vegetables, of course, everything is much simpler. Grew up, reaped the harvest, ruthlessly uprooted and destroyed diseased bushes. The next year, in order not to step on the same rake, he planted disease-resistant crops.
If the infection has occurred in the greenhouse, diseased plants must be removed, the soil replaced, disinfected and preventive spraying.
Well, in order to prevent the spread of verticillium, before planting the seedlings in the greenhouse, the soil is disinfected and steamed to the depth of the roots.
The soil in the beds is dug up, treated with fungicides. In the fall, after harvesting, the beds are sown with green manure, and then they are plowed. In the process of decomposition of peas, rye, vetch, mustard, there is an accumulation of saprotrophic organisms that inhibit the pathogenic microflora.

After the seedlings are accepted, they must be regularly fertilized with a complex mineral fertilizer with a high potassium content and a minimum amount of nitrogen.
To reduce the amount of watering and thereby reduce the likelihood of spreading the disease, it is advisable to mulch the beds.
How to properly care for Echinopsis cacti at home
Echinopsis flower does not need complicated care. Minimal efforts on the part of the grower will allow you to get abundant flowering of the bush, as well as the unreal beauty of green thorns.
The plant should be placed on a windowsill where there is a lot of sunlight. It is best to orient yourself towards the south side. In summer, the bush is placed on the street, on an open terrace or loggia. But do not touch a plant that is actively forming a green mass. This will only harm the flower.
During the active development of the bush, it is recommended to keep it under warm climatic conditions.
It is important that the room is at least + 20 ° C. Starting from October, temperature indicators decrease to + 9-10 ° С
But sunshine should always be enough. It is imperative that the bush does not suffer from through winds. But at the same time, be sure to ventilate the room where the flowerpot grows.
Photo of one of the Echinopsis species in the greenhouse
Echinopsis is irrigated regularly, from early spring to autumn. But it is recommended to perform this procedure only after the soil is completely dry. To regulate this moment, it is better to use a wooden stick, which is stuck into the container. The moisture content of the composition is determined by the amount of adhered soil.
For watering a cactus, it is recommended to use filtered or settled water at room temperature. In the fall, they begin to moisten the bush much less, the amount of liquid used is reduced. Spraying the plant is contraindicated, since the Echinopsis cactus feels great under normal room conditions. But for hygiene purposes, it is still recommended to wash the bush under shower water, while covering the substrate with cling film.
To see the blooming Echinopsis cacti, you should provide them with full-fledged fertilizer. It is recommended to start this process immediately after the start of the active development of culture. For such purposes, complex mineral dressings are used, suitable for succulents. Substances are applied once a month. Concentration is written on the packaging. In the dormant stage, the bush does not need to be fertilized, these procedures are resumed only with the arrival of spring.
Echinopsis cactus: diseases and pests
The plant is quite resistant to diseases. But, if it is wrong to water the bush, then stagnation of the liquid will occur, which will provoke rotting of the cactus. In this case, you will need to remove all damaged areas by treating the knife with alcohol. Further, the cut sites are disinfected with a fungicide.
A common pest of bushes is the spider mite. It damages the stem, sucks sap from plants. To combat the parasite, Actellik or Fitoverm is used. Spraying is best done outdoors, since the products are quite toxic.
How to transplant a cactus Echinopsis
Adult bushes do not need to be repotted often, this procedure applies only to young specimens. When you observe that the plant is getting cramped in the pot, you should choose a larger container for it.
Young representatives of the flora are planted in a soil mixture with a neutral reaction. If you wish, you can buy a ready-made substrate in the store. But often the composition is prepared by hand. This will require coarse sand, leafy, soddy soil, small gravel. The proportion is 2: 2: 4: 1. A little charcoal is also added to the mixture. With its help, it will be possible to reliably protect the rhizome from the development of rot.
It is recommended not to transplant adult bushes at all, but simply to replace the top layer of the soil with a fresh composition.
Pots are usually low, but wide enough for plants. At the bottom of the container, you will need to place a drainage layer; it is best to use expanded clay for such purposes. It is better to move the bush by the transshipment method so that there is a certain amount of soil on it. Formed voids must be filled with prepared soil mixture, thoroughly rammed. Immediately after transplanting, you will need to water the bush abundantly.
Pathogens and ways of spread
The disease is carried by the fungus Verticillium dahliae. It lives in the soil and feeds on plant debris. But as soon as it gets into the root system, it spreads throughout the aerial part, grows along the vascular system, clogs it and poisons it with toxins (waste products).
A colorless fungus that lives in the soil forms microsclerotia and conidial sporulation. Moreover, he produces both those and others only on the dead parts of plants. On living, albeit affected, conidial sporulation does not develop.
Micro sclerotia can be dormant in the soil for 8-10 years. They are not afraid of frost. They die only at temperatures above 60 ° C.Germinate at a temperature of 20-23 ° C and a humidity of 70-80%. They prefer soils with a pH of 6-7.
Most often, infection occurs through damage to the roots or shoots. The fungus primarily attacks young or weakened plants. Infection occurs especially often at the beginning of the growing season, when trees and shrubs are blooming and actively developing. At the same time, there is another negative factor contributing to the spread of the disease - tree pruning, as a result of which there are open wounds on the branches and shoots are actively beginning to grow.
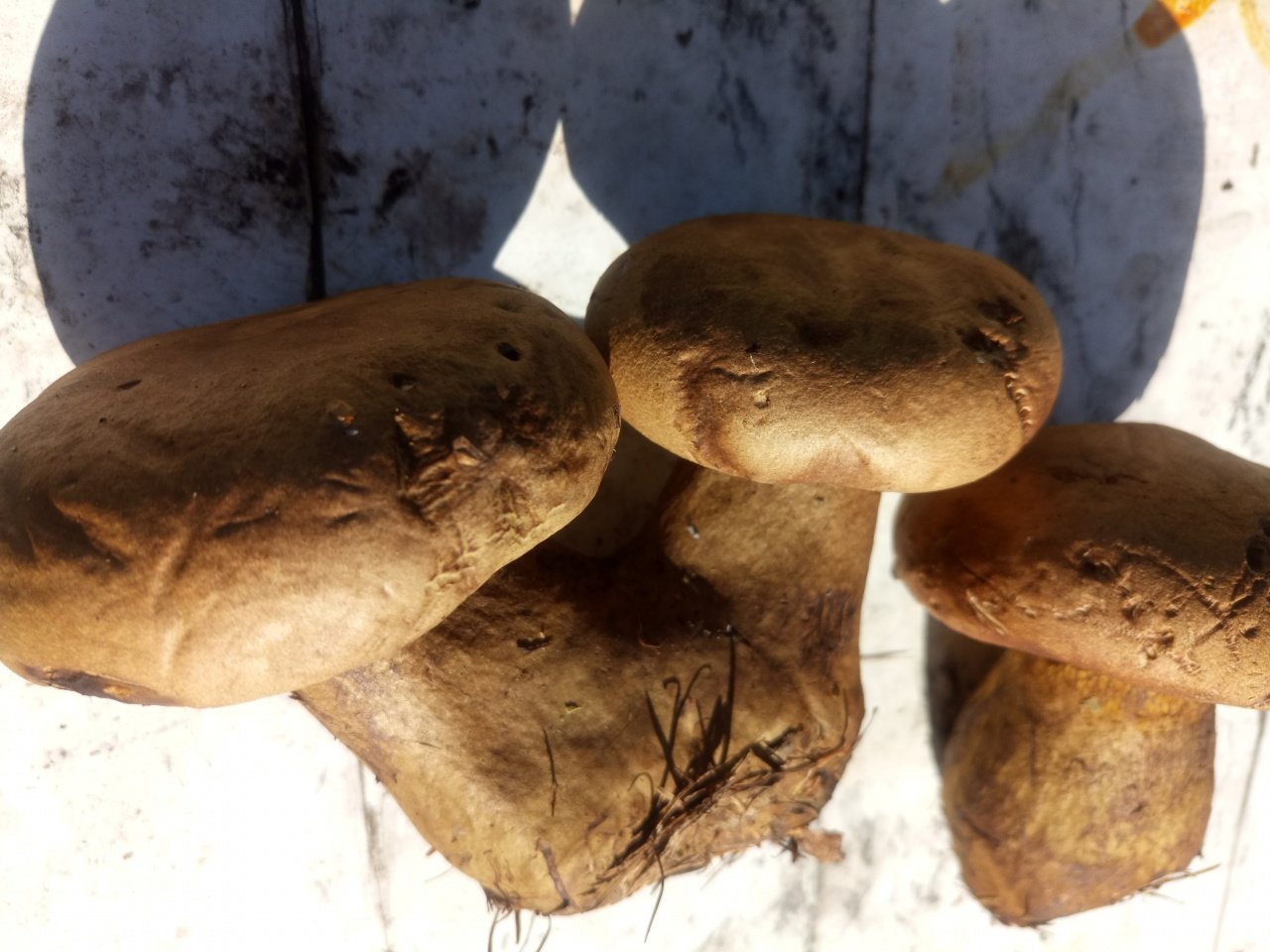
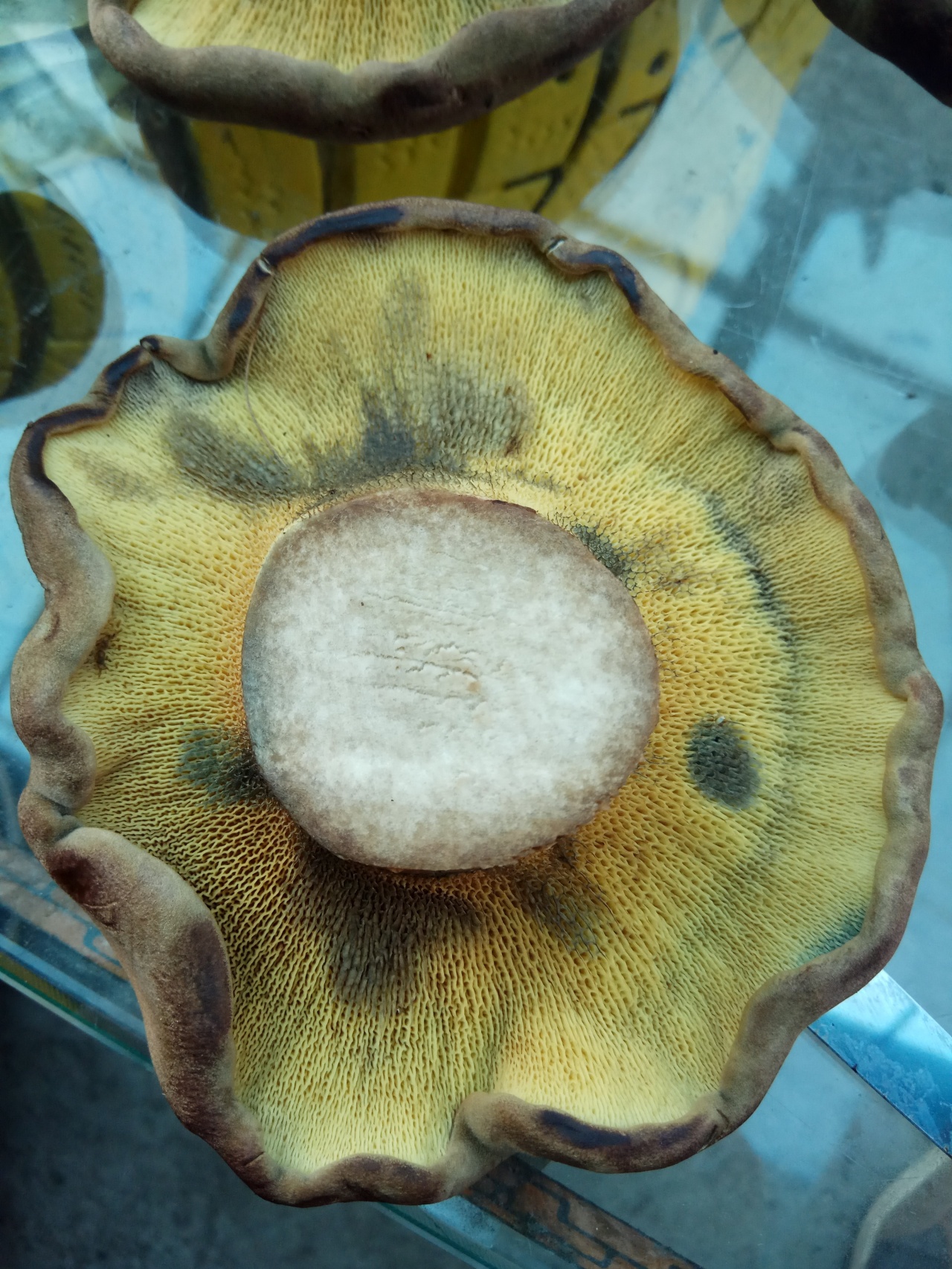
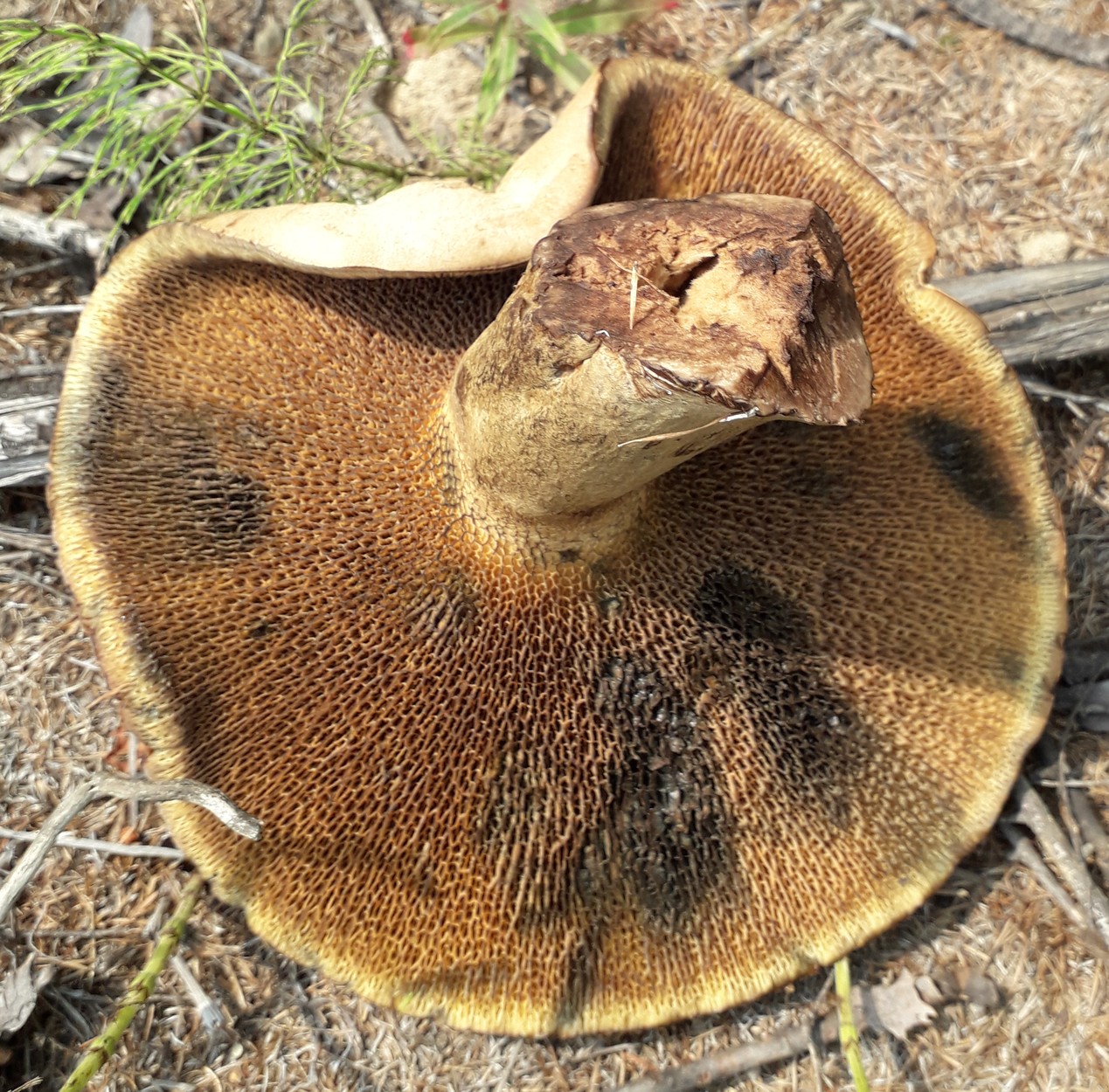
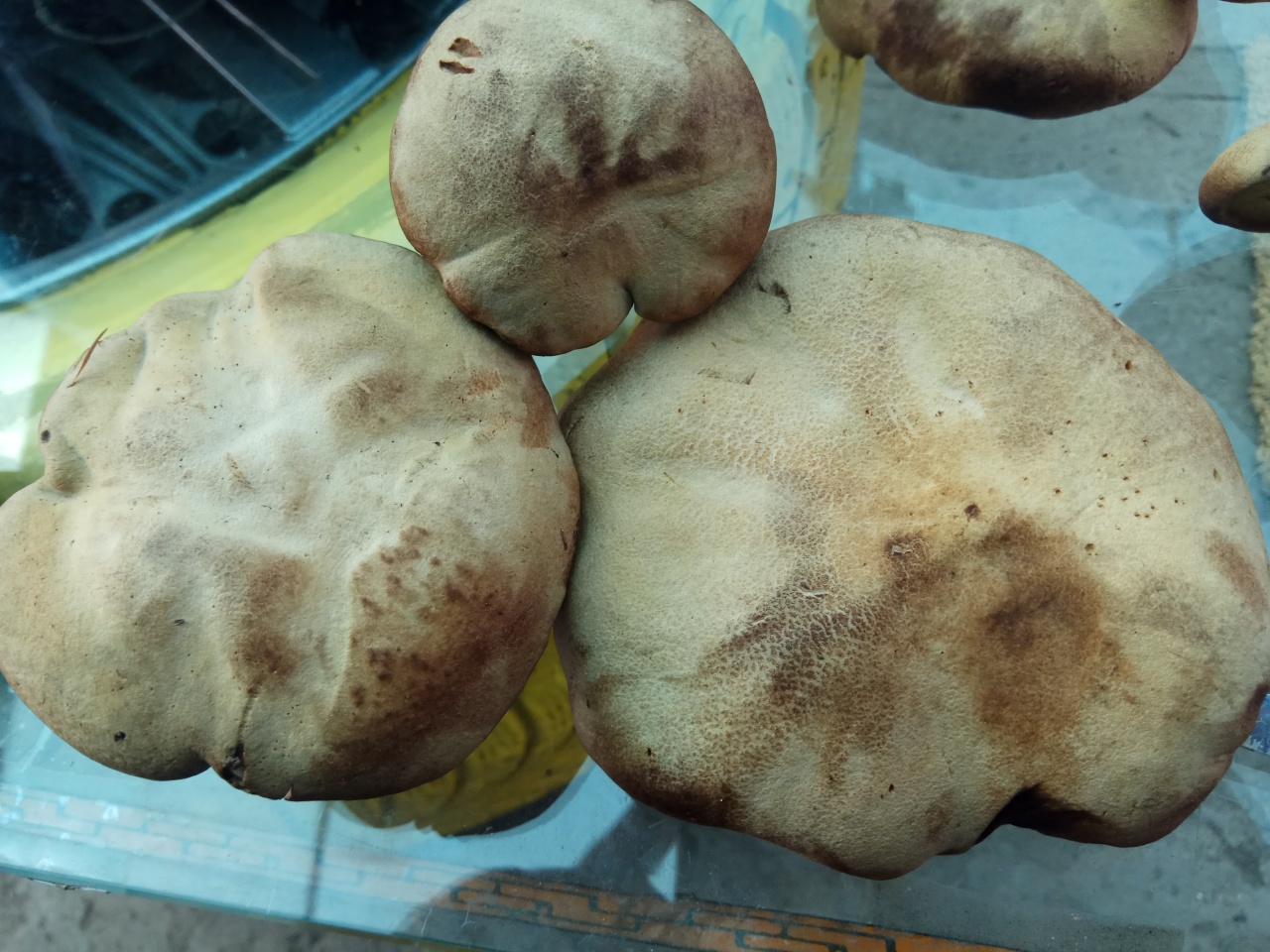
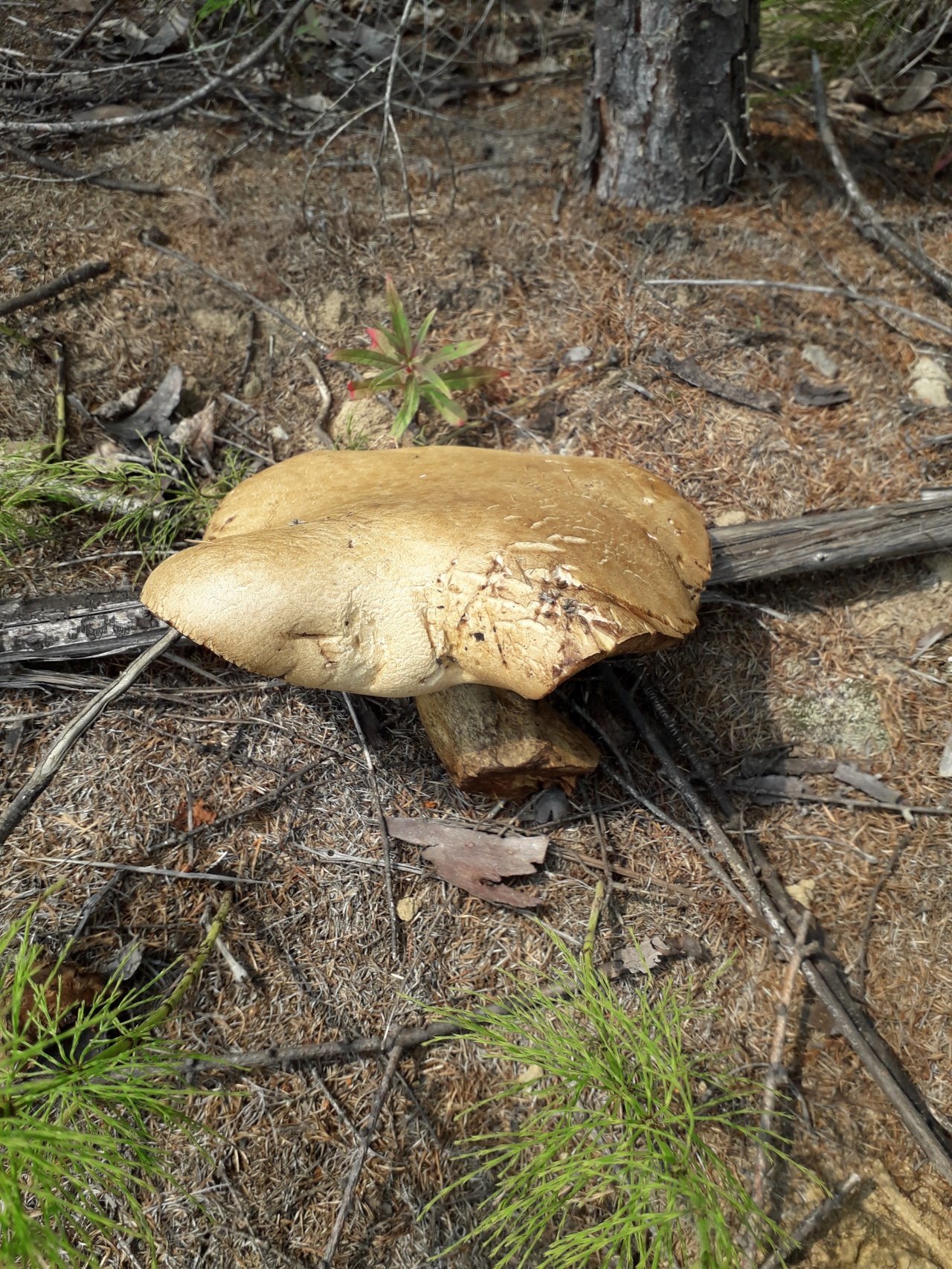
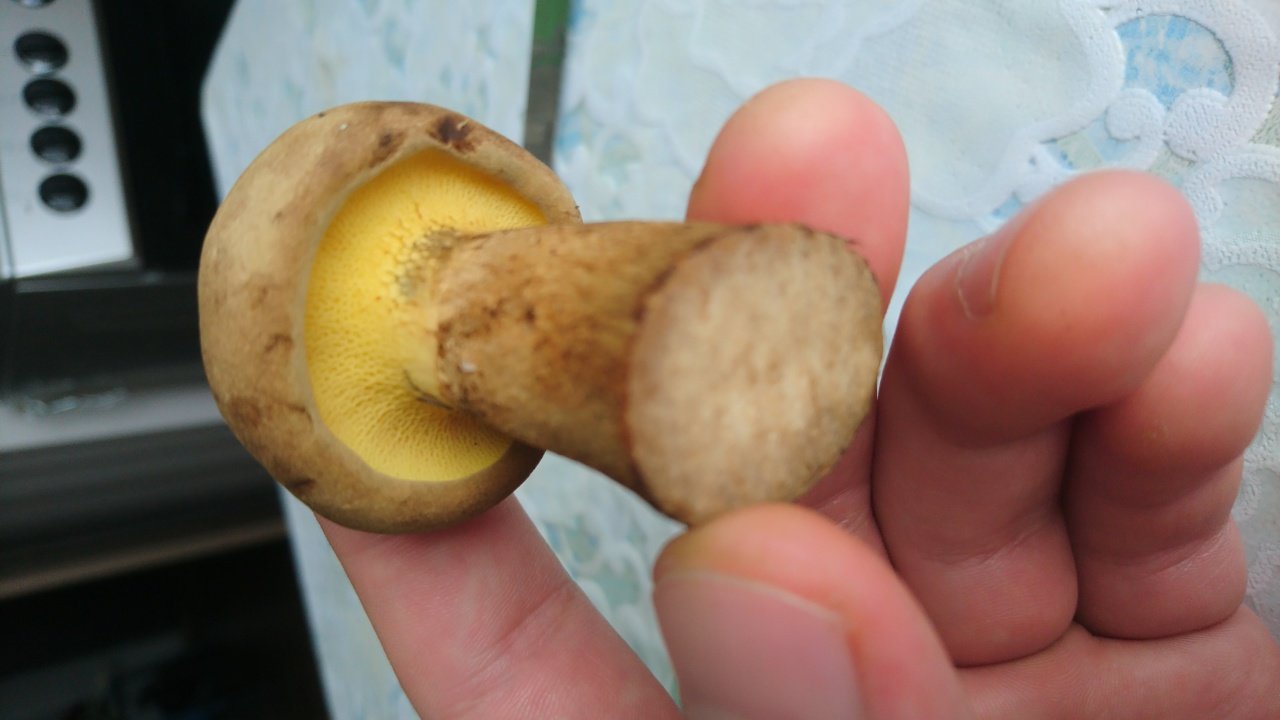
Description of the green flywheel
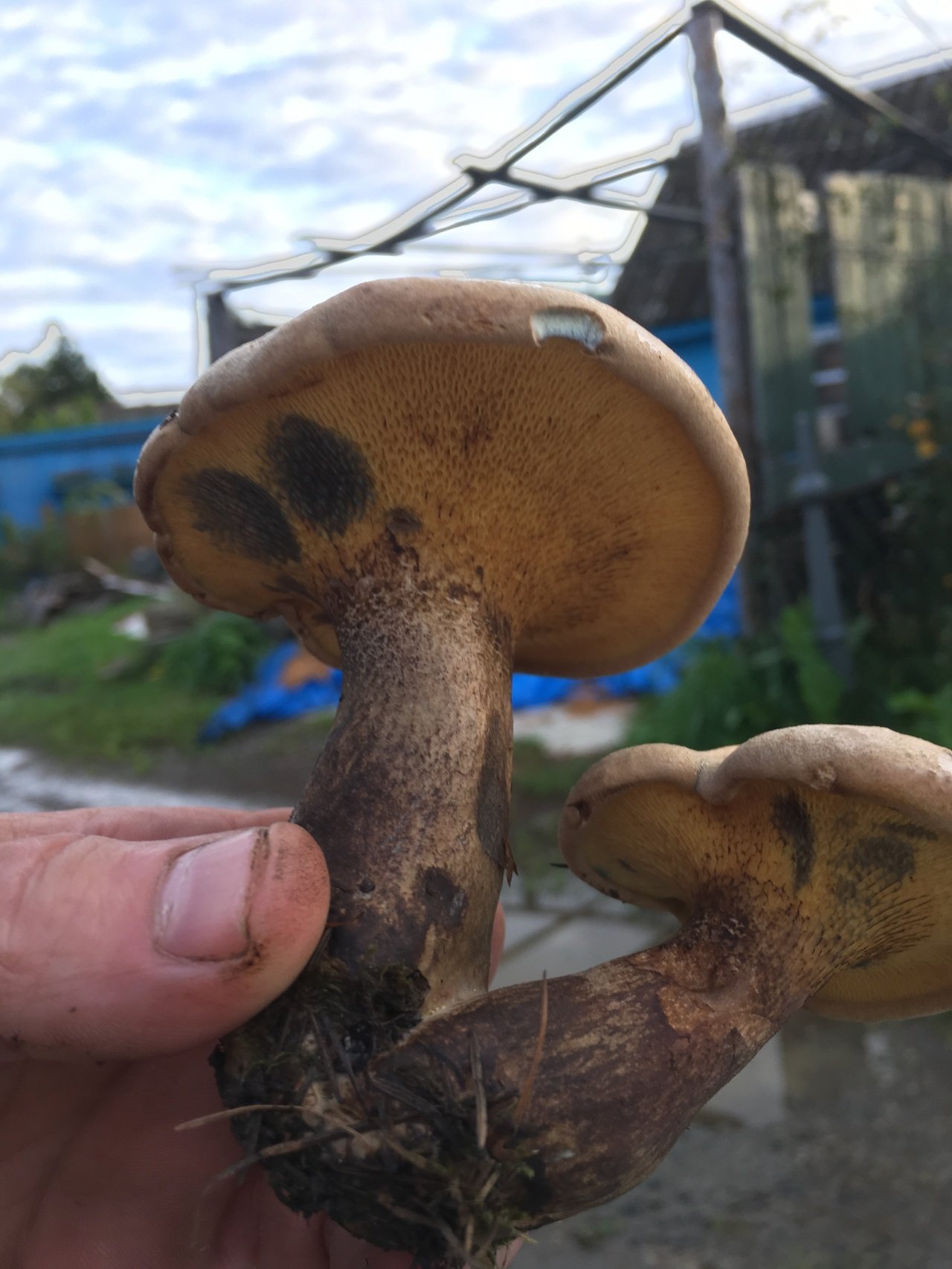
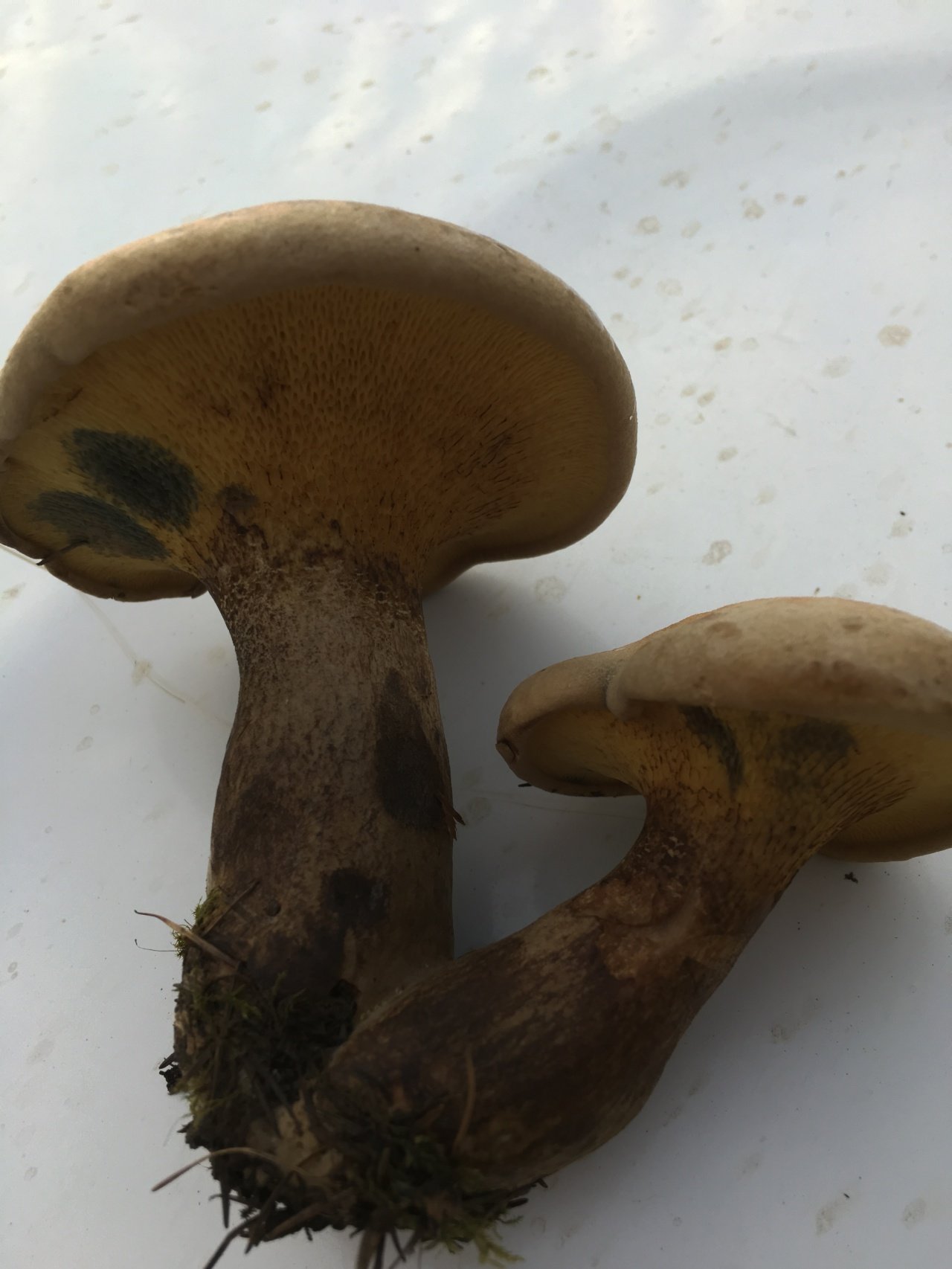
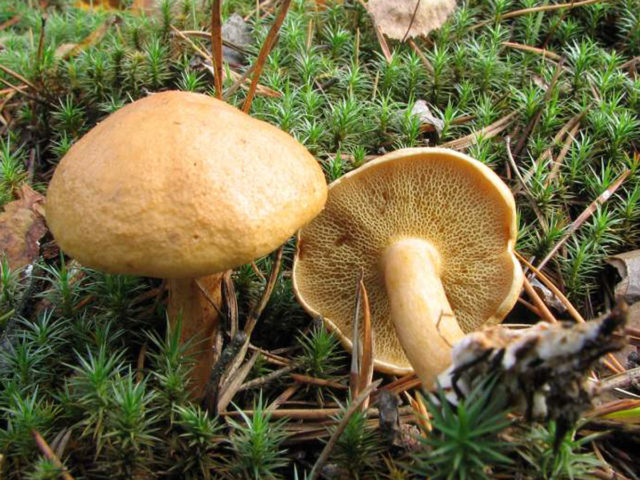
The diameter of the cap reaches 12 centimeters. The hat is thick-fleshed, at first its shape is hemispherical, but then it becomes flat and thin. The surface of the cap is velvety or chamois-fleecy, with age it becomes dry and almost bare, and can become covered with cracks.
The color of the cap is olive-brown. In damp weather, the cap becomes covered with white mold, which is characteristic of other tubular mushrooms.
The tubular layer is adherent, it is easily separated from the pulp. This layer is spongy with coarse, irregular, angular pores. At first, the pores are bright yellow, and then they turn greenish-yellow. The tubules are adherent, adherent to the peduncle.
The flesh of the green flywheel is rather loose; when broken, it turns slightly blue. The pulp has a mild fruity odor and a pleasant taste. The skin does not separate from the pulp. In young specimens, the flesh is very tough, but with age it becomes soft. Spore powder of olive brown color.
The length of the green flywheel leg reaches 10 centimeters, and the thickness is 2 centimeters. The leg is cylindrical, solid, most often curved, slightly narrowed in the lower part. The surface of the peduncle is granular fibrous or bare. The color is yellowish, but can be reddish. In the upper part of the leg there is a brown mesh pattern. The flesh at the stem is fibrous and firm.
Growing places of green flywheel
These mushrooms are found in coniferous and deciduous forests, among shrubs. Most often, green mushrooms can be seen in well-lit places: on the edges, paths, along the sides of ditches. Sometimes these fungi can grow on ant hills and rotten wood. They grow, as a rule, singly, but sometimes they are found in groups.
Green moss in cooking
This mushroom is considered edible, according to its taste, it belongs to the second category. All parts of the mushroom are suitable for food, that is, both the cap and the leg.
Green flywheel is prepared without preliminary boiling, but it is imperative to peel off the skin. Also, green mushrooms can be pickled and salted, they are well stored.
It is impossible to eat old green mushrooms, since they already begin to break down protein, which leads to severe food poisoning. That is, only young specimens are used for cooking.
Green flywheels are well known to both professionals and novice mushroom pickers. The taste qualities of these mushrooms are quite high.
Similar species
Green flywheel has external similarities with the Polish mushroom and the yellow-brown flywheel, which are edible, as well as the pepper mushroom, which is classified as conditionally edible mushroom, since its pulp has a pungent bitterness.
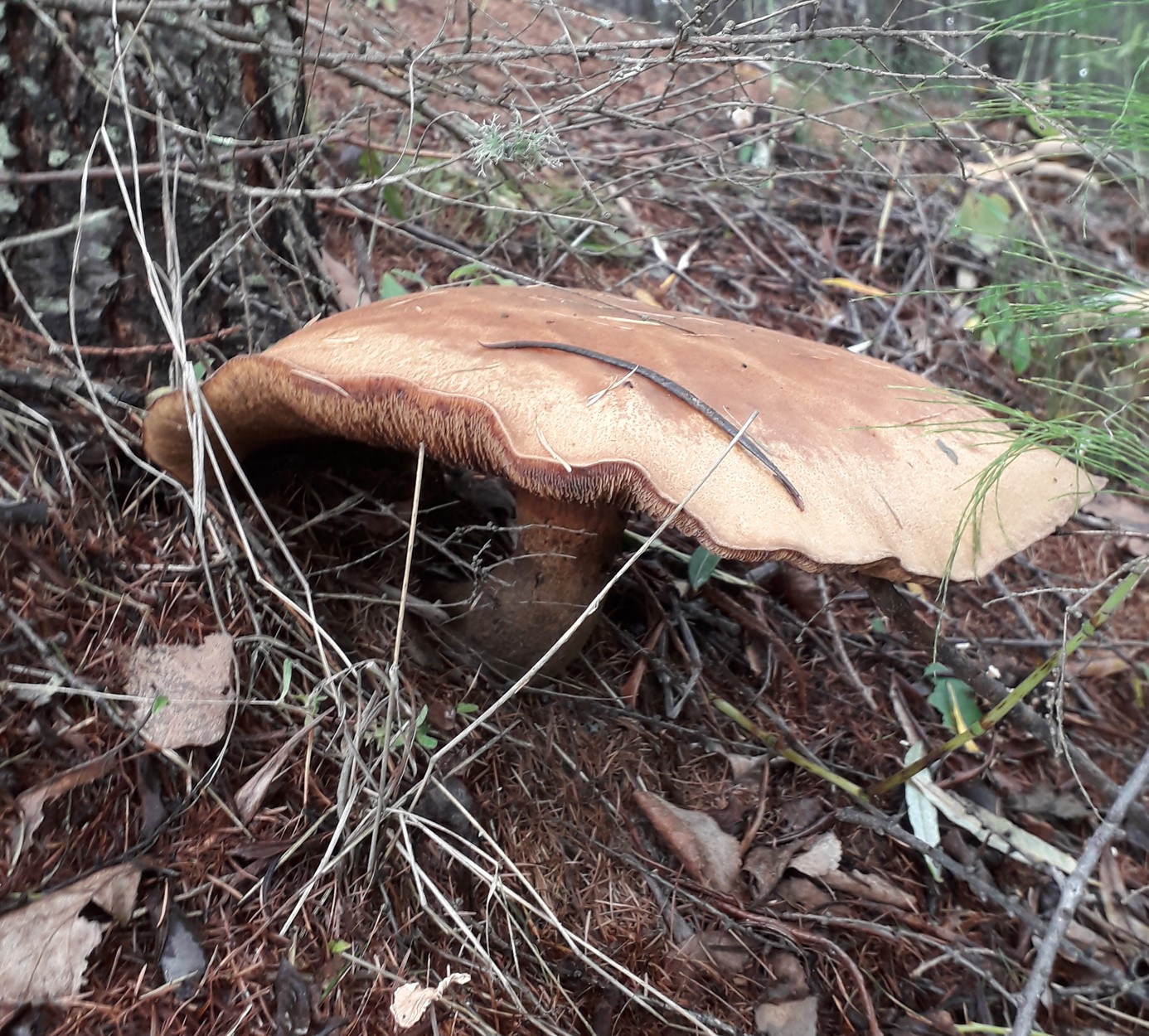
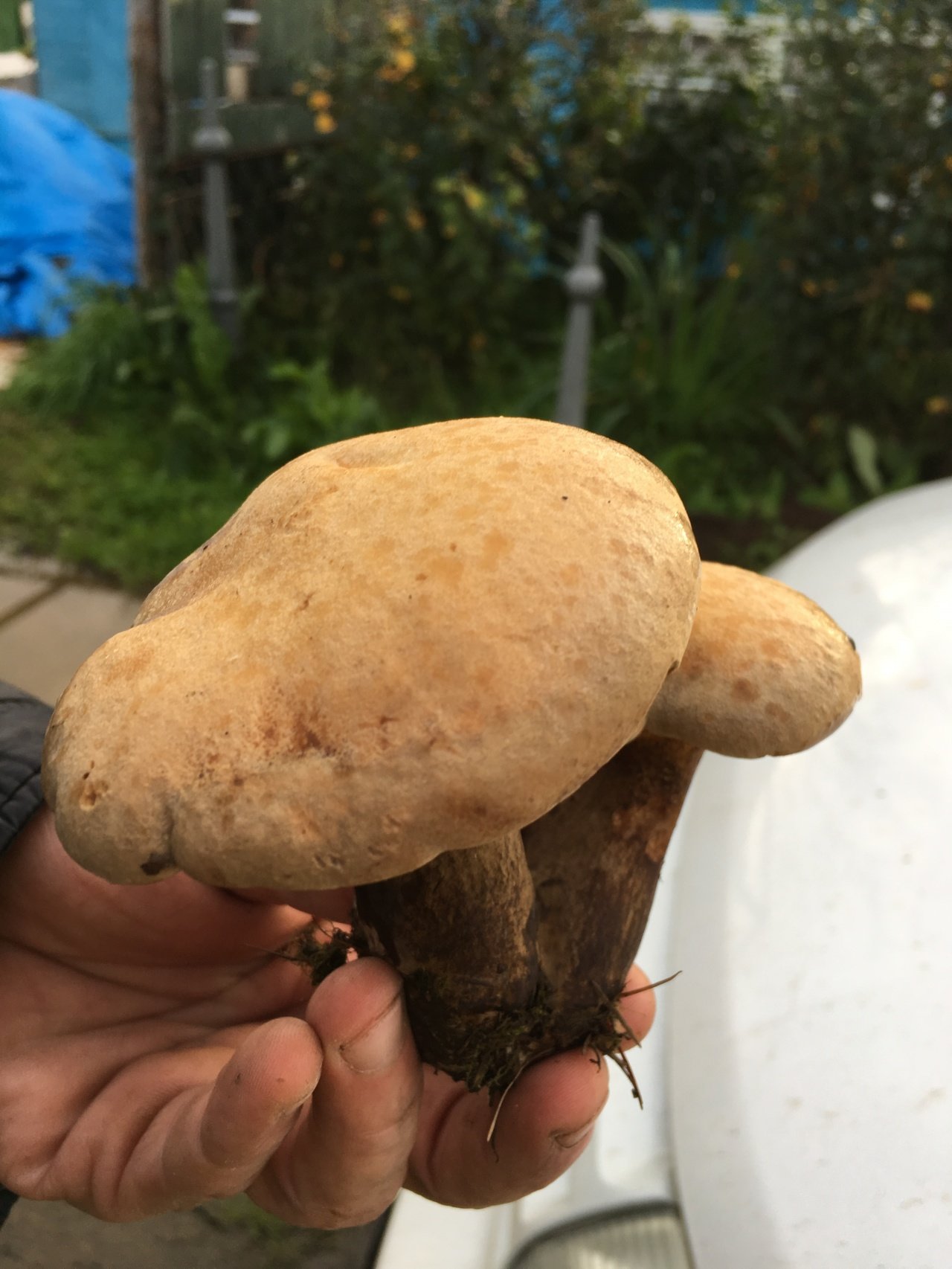
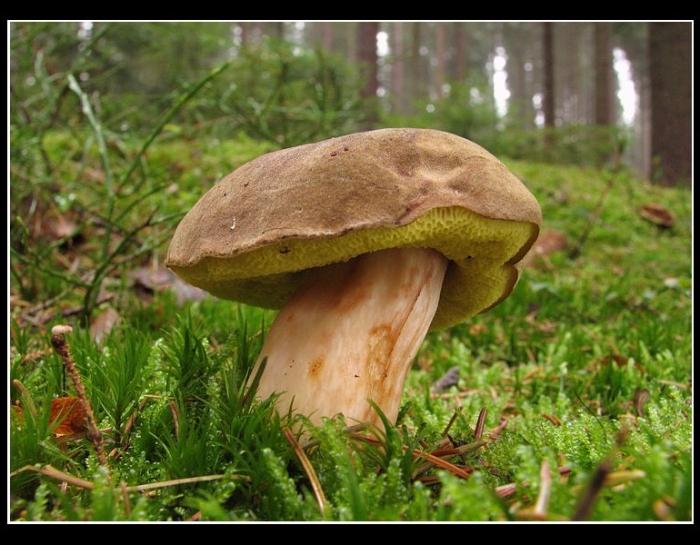
A yellow-brown flywheel or a yellow-brown oiler has first a semicircular and then a pillow-shaped cap, with a diameter of 5 to 14 centimeters. The color is first gray-orange or olive, and then becomes brown-red. These mushrooms grow on sandy soils, meeting from June to November. They grow in Europe and Russia.
In terms of taste, they are classified as edible mushrooms of the 3rd category. These mushrooms are best suited for pickling.
The Polish mushroom grows in mixed and acidic soils. They can often be found in coniferous forests, in litter, in moss, under beeches, oaks and chestnuts. Grow singly or in large groups. The season is from July to November. Polish mushrooms grow in Western Europe and in our country.
The diameter of the cap of the Polish mushroom ranges from 3 to 12 centimeters. At first, the shape is hemispherical, and then it becomes flat. The color of the cap is reddish, brownish, chestnut, dark brown, olive and even black-brown. In wet weather, the cap of the Polish mushroom becomes covered with mucus. The pulp of the mushroom gives off a pleasant fruity aroma; it is dense and fleshy to the touch.
The pepper mushroom is definitely not poisonous. Many people claim that pepper mushrooms have a bitter taste. But this is a controversial statement, for example, the gall mushroom is very tasteless, and the pepper mushroom has a spicy taste, while pleasant. The diameter of the cap ranges from 2 to 6 centimeters. Its surface is dry and velvety. The mushroom has a faint peppery smell and a rather pungent peppery taste.
These mushrooms are most commonly found in coniferous forests from summer to autumn. In addition, pepper fungi can form mycorrhiza with young birches and deciduous trees.
Special features: description and photo
Depending on the type of plant and its age, the disease can manifest itself in different ways. In general, the first noticeable signs are wilting or curling leaves on the underside of the stem. At the same time, brown or yellow spots appear on them. In the future, the leaves dry out and fall off.

A distinctive feature of verticillosis is that on the affected plant, signs of the disease can appear only on one branch or shoot. If you cut it off, then inside you can find brown spots that appear due to blockage of the capillaries. Fruits on infected bushes and trees may lag behind in development, growth, or even mummify. Often, instead of the affected and dying shoots, new ones actively begin to grow, but they are sterile.
Verticillosis can be in a sluggish or active form. The first option leads to the fact that the tree is sick for many years, partially dries out, does not bear fruit, and as a result recovers or dies. In the second case, it can happen that within 10 days, a seemingly healthy tree or shrub completely sheds its foliage and dries up.
























































