False doubles: how to recognize
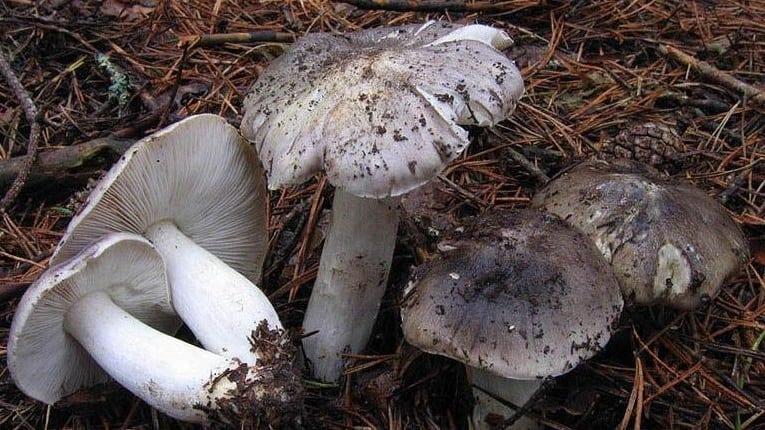
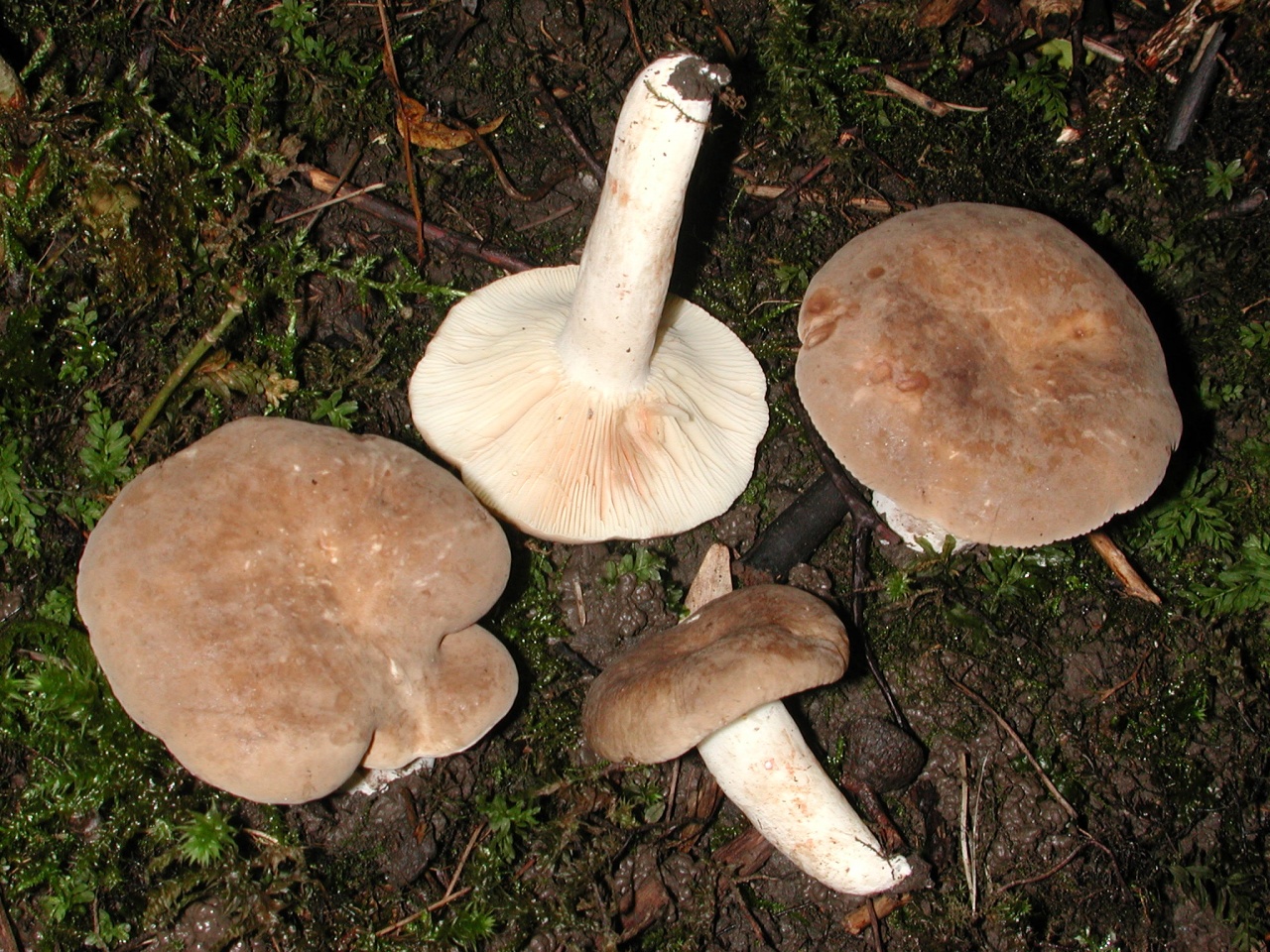
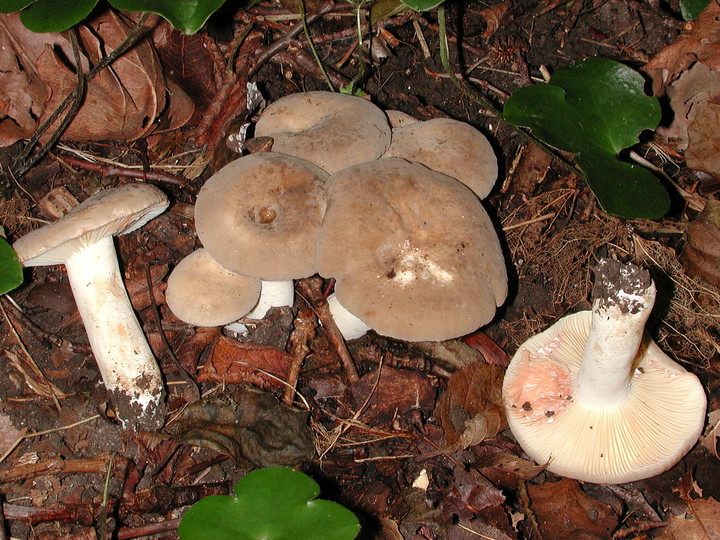
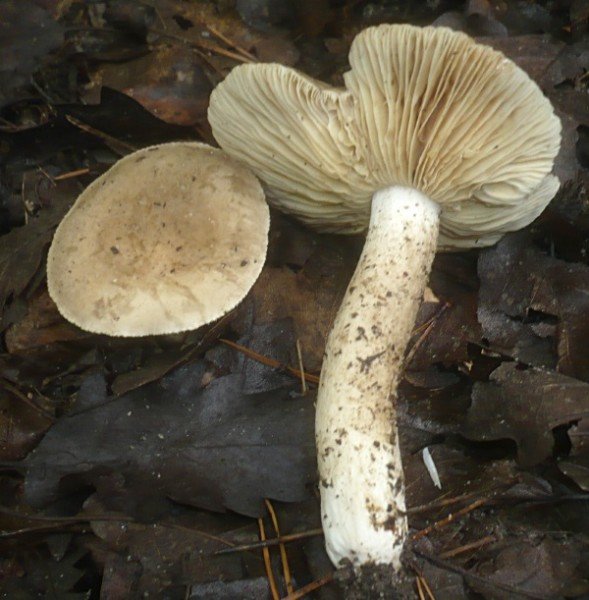
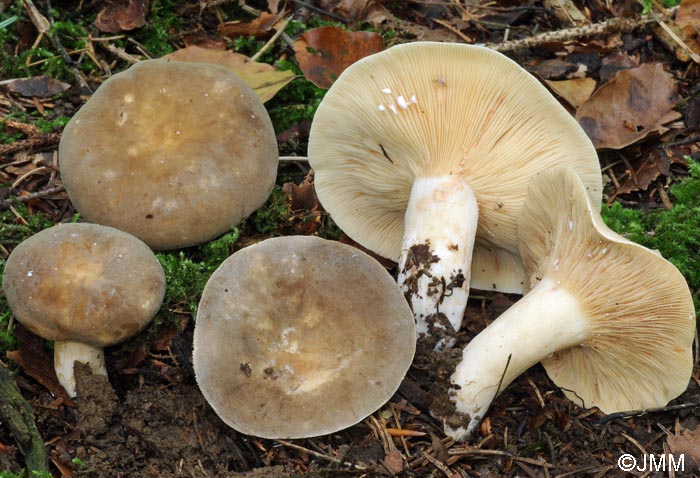
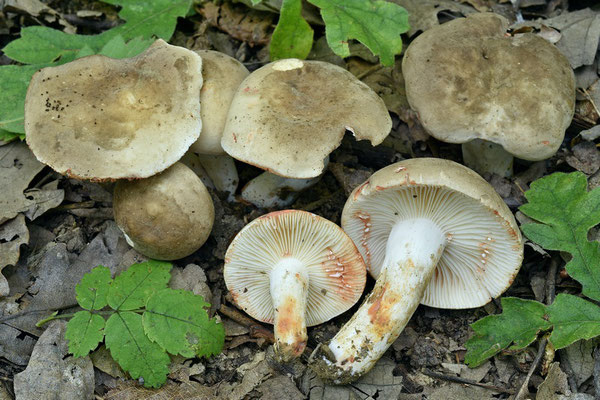
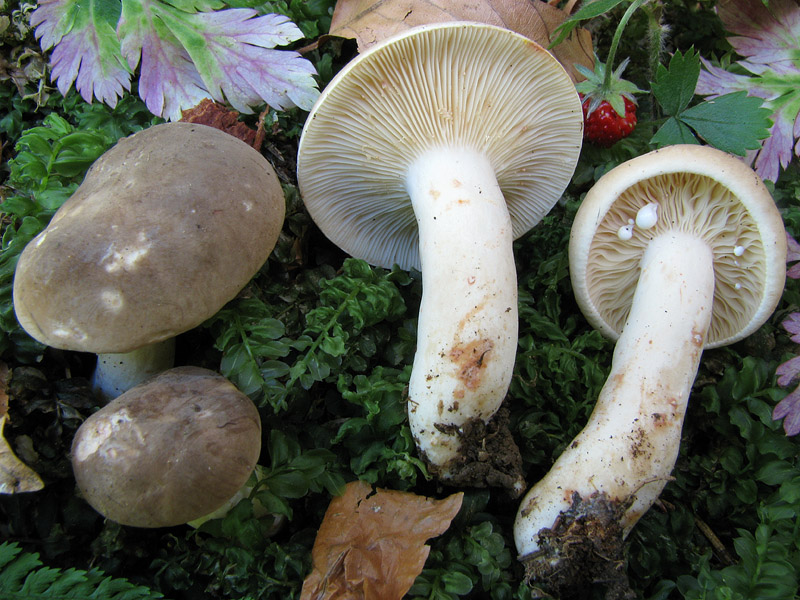
Two lactic acid plants are similar to plantain - zonal and zoneless. The first (Lactarius zonarius) has an ocher or cream cap, the second (Lactarius azonites) has a variably brown cap. They are also conditionally edible, suitable for salting.
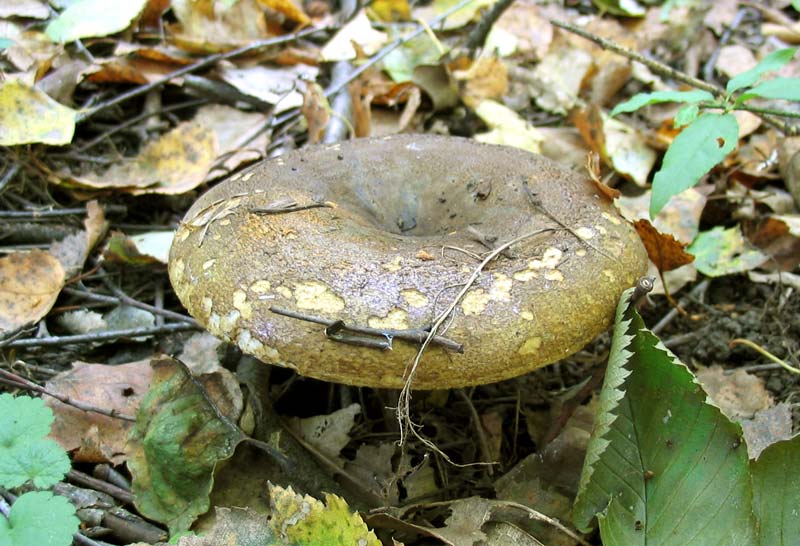
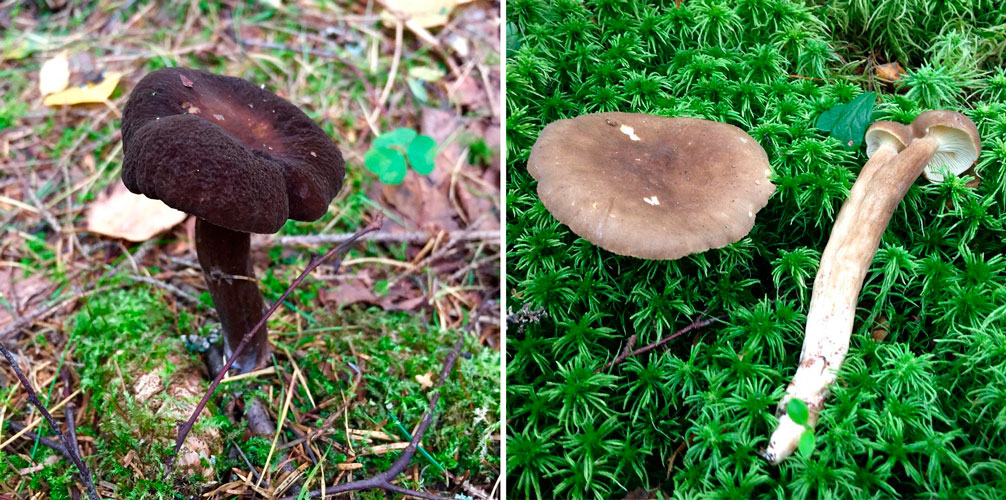
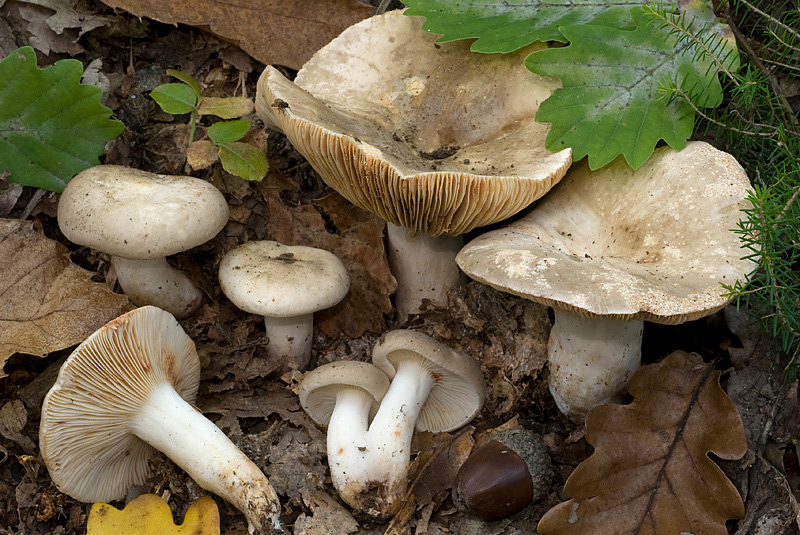
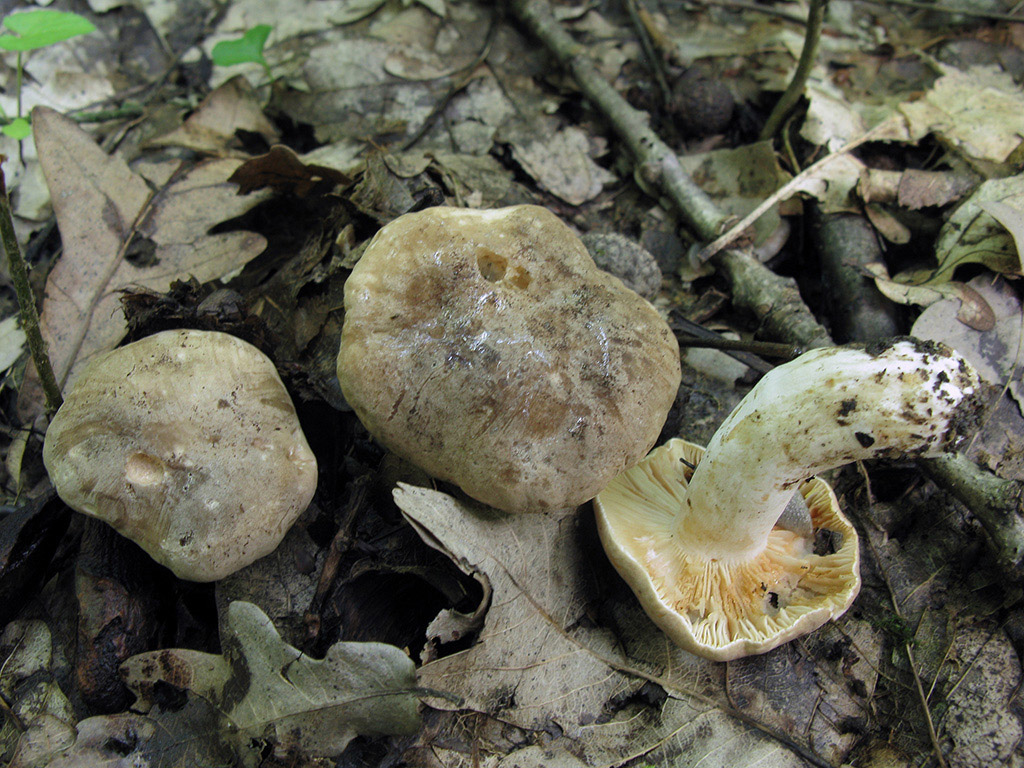
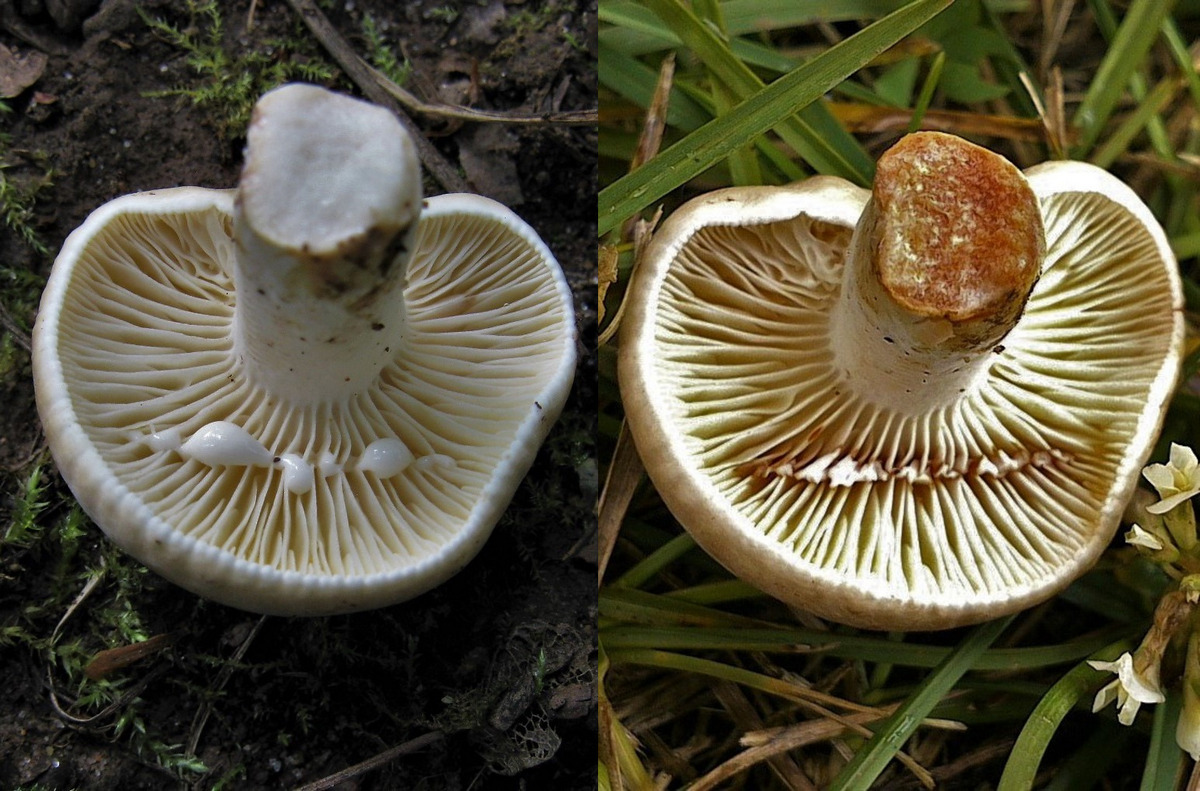
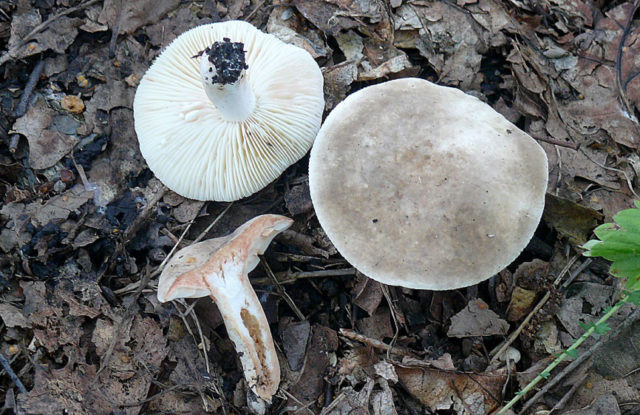
 Zoneless Miller (Lactarius azonites)
Zoneless Miller (Lactarius azonites)
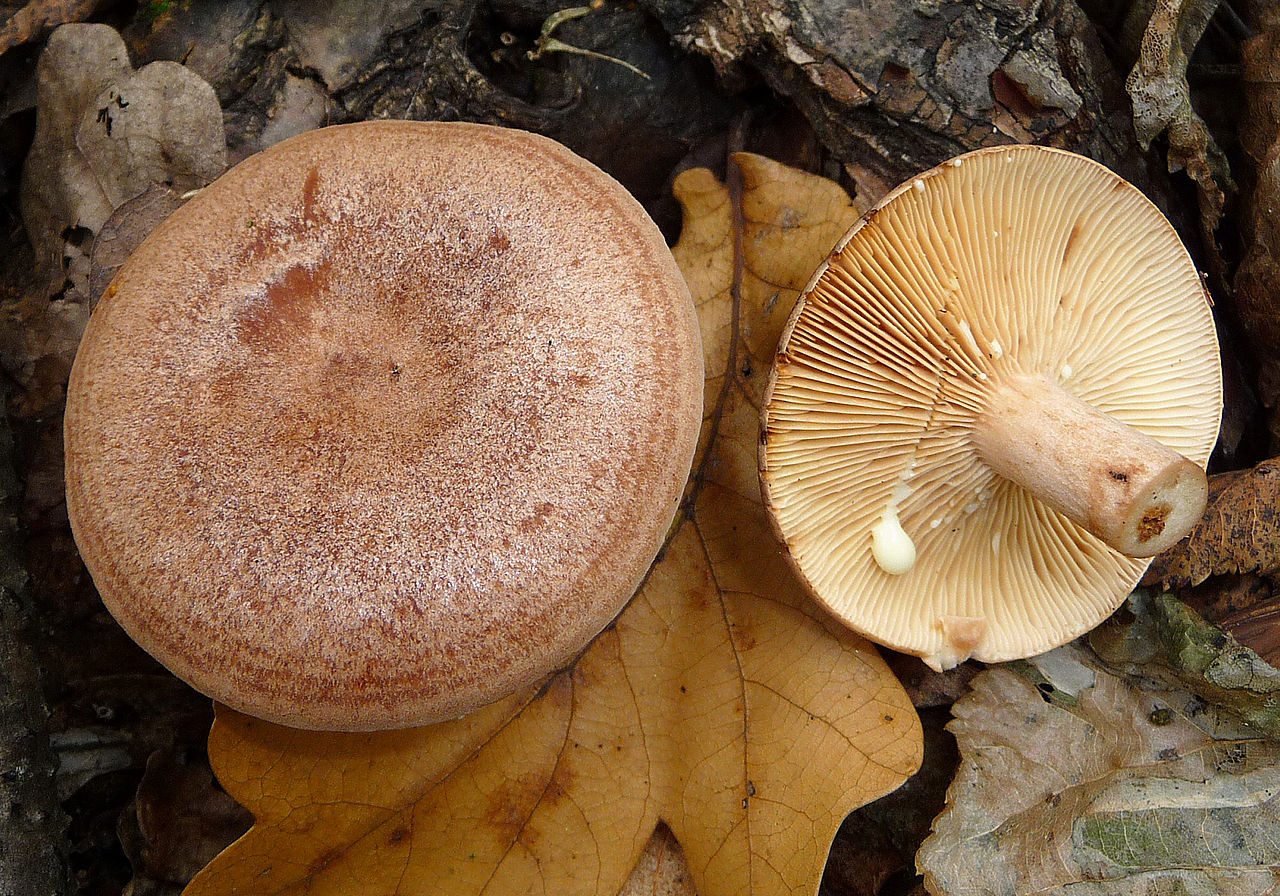
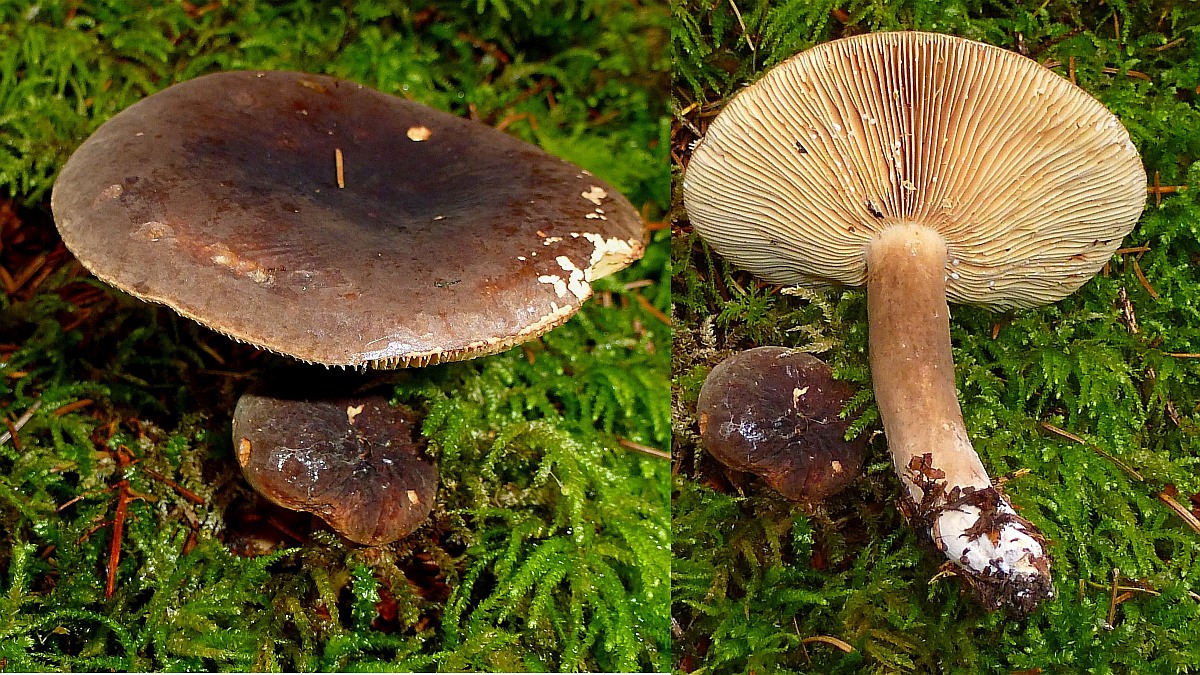
 Zonal Miller (Lactarius zonarius)
Zonal Miller (Lactarius zonarius)
In appearance, the Lubyanka is more similar to the smoothie (ordinary milkman) than to the milk mushrooms. But this is not dangerous, since the entire family of these mushrooms is edible, with the exception of only a few because of their excessive bitterness.
In terms of its nutritional value, the leaflet is closer to the bitter (red milk). And her consumer-gustatory parameter corresponds to the third category, like that of a smoothie.
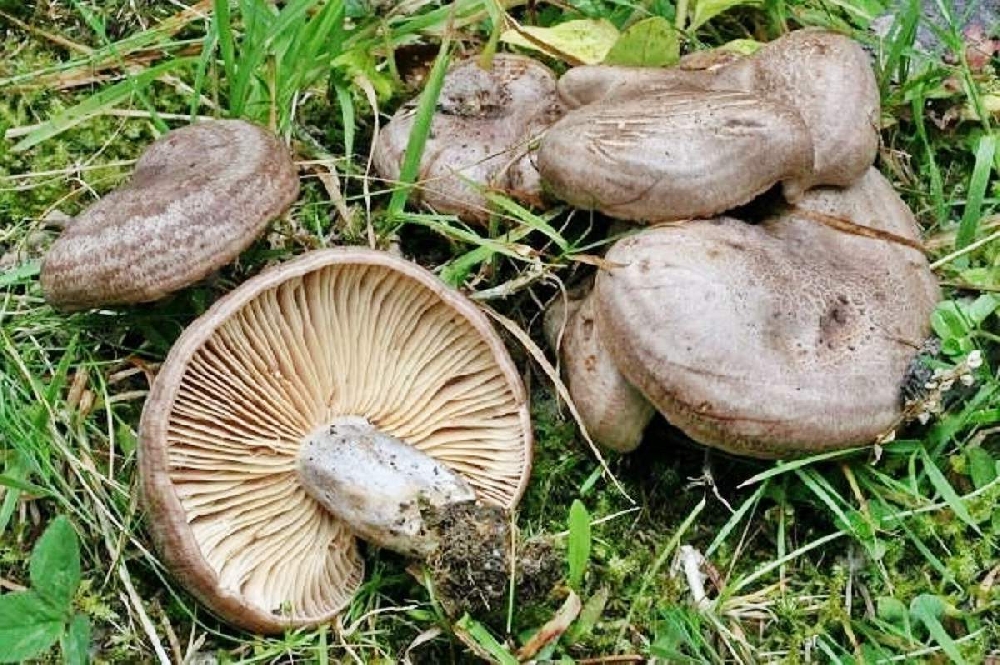
The photo shows the difference between the gray-lilac milk mushroom and its twins.
Pay attention to how the serushka mushroom looks like. A comparative table of species characteristics will help you correctly identify the varieties of mushrooms and distinguish between dangerous and edible:
| Mushroom names | Hat | Pulp | Leg | Hymenophore |
Serushka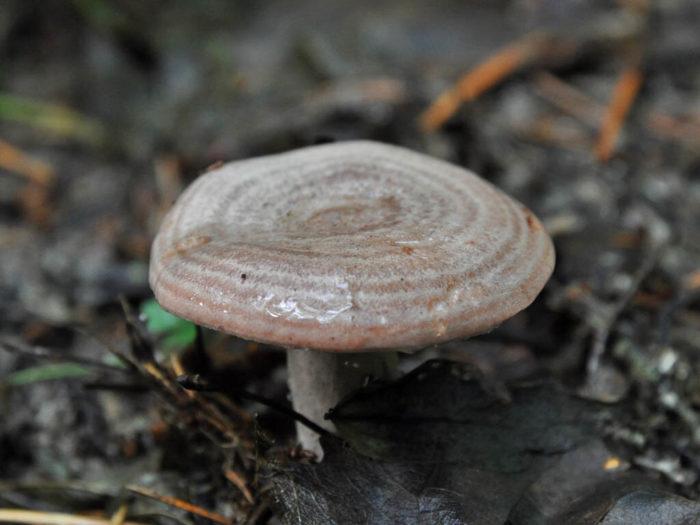 |
Gray-violet, ash-pinkish, lead-brown | Gives off bitter juice, has a fruity odor. Milk color does not change in air | Has a cap color | The plates are sparse, dirty yellowish |
Gladysh |
Light gray, lilac, lilac | Gives off bitter milk that changes color in the air | The colors are similar to those of the hat, but somewhat lighter | Pale cream-colored membranes |
Bitter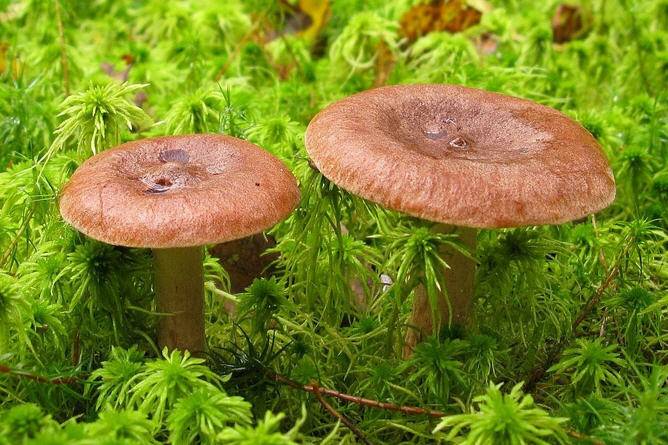 |
Comes in different colors | Gives off bitter juice that changes color on air | Slightly paler than the color of the hat | The tone of the pulp may be different, depending on the color of the juice of different subspecies of the mushroom |
Row gray (mice) |
Pale or dark gray | Does not emit milk | White with a yellowish-grayish tint at the bottom | The plates are white with a grayish or fawn tint |
Death cap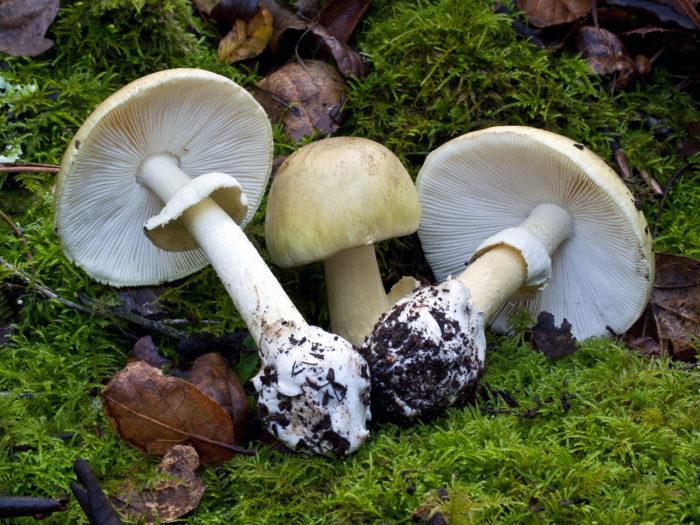 |
Greenish, grayish, olive | No milk | The color is whitish with a hat shade and a moire pattern. It has a fringed ring under the cap, a Volvo at the base | Free records, white |
Mushroom common lactarius and its photo
Category: conditionally edible.
Lactarius trivialis cap (diameter 5-22 cm): shiny even in dry weather, with dark rings. Changes color and shape depending on the age of the fungus: in young mushrooms, it is dark and gray-gray, rather convex; in old ones, purple and brown, and then ocher or yellow, flatter and even depressed. Dense, maybe with small dimples. The edges are wavy, curved, often curled inward.
Stem (height 4-10 cm): pale gray or light ocher, cylindrical, sometimes swollen, but always hollow. A bit slimy and sticky.
Pay attention to the photo of an ordinary milkman: its plates are frequent, thin (occasionally wide), mostly yellow or cream in color, with rusty spots. Pulp: thick and fragile
Mostly white, but brownish under the skin itself, and red at the base. Milky sap is very bitter; when interacting with air, it changes color to yellow or slightly greenish. Has a peculiar smell reminiscent of fishy
Flesh: thick and fragile. Mostly white, but brownish under the skin itself, and red at the base. Milky sap is very bitter; when interacting with air, it changes color to yellow or slightly greenish. Has a peculiar smell reminiscent of fishy.
Doubles: none.
When it grows: from mid-July to late September.
Where to find it: In humid places and lowlands of all types of forests, most often near pines, spruces and birches. Hides in dense grass or moss. An ordinary milkman is not afraid of pests.
Eating: fresh or salted, subject to pre-soaking to remove bitterness. When cooking, it changes color to bright yellow or orange. It is very popular in preparations for housewives in Finland.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: gladysh, alder, nest, yellow nest, gray lump.
Faded milky: photo and application
Category: conditionally edible.
Faded lactarius cap (Lactarius vietus) (diameter 4-9 cm): gray, lilac, lilac or gray-brown, eventually fades to white or grayish. Slightly convex or outstretched. The center is slightly depressed, but with a slight tubercle and usually darker than the edges, which are curved towards the inner side. The surface is often uneven. Sticky and damp to the touch, with sticky twigs or leaves.
As you can see in the photo, the faded lactarius has an even, sometimes slightly curved leg. Its height is 5-9 cm. The color is white or light brown, lighter than the cap. The shape is cylindrical.
Plates: thin, narrow and very frequent. Cream or ocher in color, gray at the point of depression.
Flesh: white or gray, with a pungent milky juice. Thin, very fragile.
Doubles: none.
When it grows: from mid-August to early October.
Where to find: in deciduous and mixed forests, especially near birches. Prefers damp and swampy places.
The use of faded lactarius in cooking is limited - since the flesh of the mushroom is very thin, it is not very popular. Only the largest specimens are salted and pickled.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: sluggish milky, marsh wave.
Time and place of collection, distribution
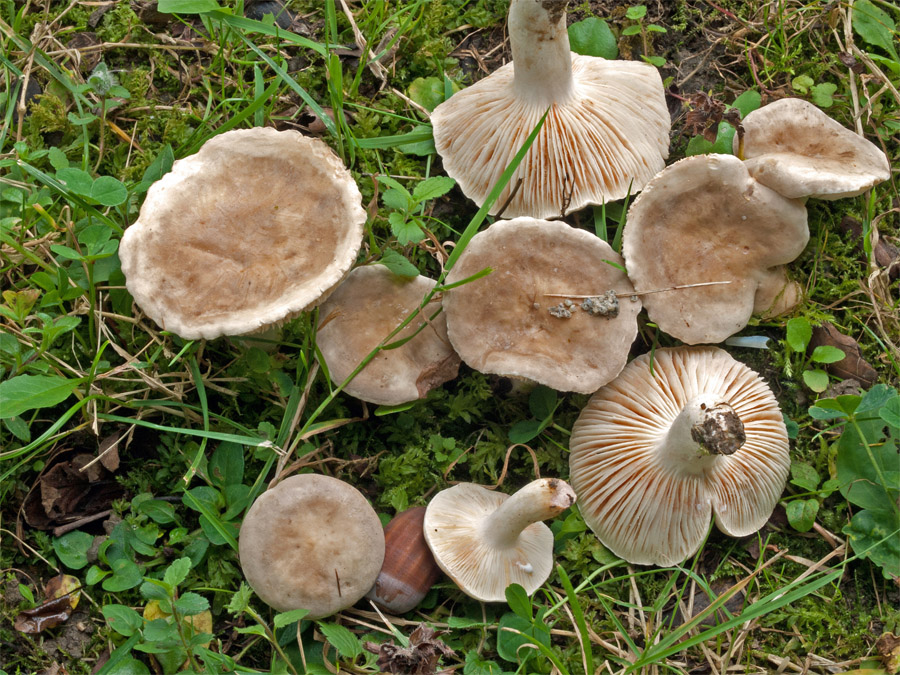
Lilac-gray mushroom grows mainly in deciduous and mixed, coniferous forests. It can be harvested in light wetlands. This is a fruitful species, often bears fruit abundantly after rains. Inhabits meadows, forest edges, along forest paths (not without reason it is called plantain). The first "swallows" appear in July. The seryanka reaches its peak yield in the autumn: it grows in September, but then a decline is observed in October. Before freezing, it disappears. Distributed in the fall in Russia, Moldova, Bulgaria, Austria, Macedonia, Great Britain, Portugal, Israel, Iran, Pakistan.
Description of mushrooms
Judging by some of the names, we can conclude that the gray-headed mushrooms have gray caps and are found in nature as mushrooms.
Why do they still refer to milk mushrooms? Because they also contain milky juice.
By its structure, the mushroom is most of all similar to a smoothie, and not to a lump. Many novice mushroom pickers confuse the seruha with the smoothie, but this is not important, because both are edible. The description of the traveler's mushroom refers to the fact that centric circles are visible on its hat, for this reason they can still be confused with waves. If you look closely, you can see that the earrings have gray or purple waves, while others have dark pink.
Traveler mushrooms have lamellar spores, the cap itself is smooth, and its edges are slightly rounded. On young mushrooms, the cap is slightly convex, but in mature ones it looks more like a funnel with a tubercle in the center. Usually the diameter of the head does not exceed 10-12 cm, but if the summer is rainy, then you can find a mushroom with a cap 20 cm in diameter.
The traveler's leg is of medium length, cylindrical in shape and with fine grooves along its entire length. Mature earrings have a hollow stem, the same color as the cap or slightly lighter in color. Due to the fact that the mushroom has a hollow leg, it is also called a nest box. Seruha has a dense white flesh with a fruity or slightly resinous odor.
Beneficial features
Mushrooms have a unique chemical composition. When consumed regularly, it contributes to:
- nutrition of the brain;
- increasing the immune properties of the body;
- strengthening of blood vessels;
- removal of heavy metals and salts.
Traditional healers use these mushrooms to treat stomach ailments and various skin problems.
It is worth noting that, despite the non-sounding and frightening name, serushki are very useful for the body. In addition to them, there are one more green mushrooms, which are distinguished by a green cap that does not change its color even after cooking.Seruha and greenback mushrooms sound low, but they have a rich vitamin composition that benefits the body.
Growing places
Most often, the traveler can be found in groves where aspen or birch trees grow, but they can also grow in mixed forests, on the edges, along paths or meadows. Gray mushrooms and greenfinches, as well as milk mushrooms, grow in heaps in lighted places. Why was he called a traveler? Because most often he is met by those mushroom pickers who hunt quietly.
In our country, it is found in regions with a temperate climate. Fruiting begins in mid-summer, given the fact that there will be plenty of moisture for it. This period lasts until the first frost.
If in the autumn there is white powder around the pile of serukha, then you should not collect it. These are disputes and their presence suggests that they are already overripe. Most mushroom pickers prefer young specimens for this very reason.
How to distinguish mushrooms. Mushrooms mushrooms - photo and description of how to distinguish false mushrooms from real ones
- Miscellaneous
- Admin
Gingerbread is a delicious mushroom from the genus Lactarius. They grow in young spruce or pine plantations. Gingerbreads are edible mushrooms, have a leg up to 8 cm tall, cylindrical in shape. The plates of the mushroom are clean, acquire a greenish color when pressed.
Spruce mushroom - description, photo
The cap of the spruce mushroom (Lactarius deterrimus) can reach 8 cm in diameter, it is funnel-shaped, depressed, thin, fleshy. The skin is smooth, sticky, greenish-reddish or pale reddish in color.

The pulp of the mushroom is orange, the aroma is fruity, the taste is quite pleasant. The stem is about 4-6 cm in height, cylindrical, hollow, moist, brittle, pale orange.
Where to find: grow in dry pine forests, in July-September.
Gingerbreads are real - description and photo
True mushrooms (Lactarius deliciosus) are also called common mushroom, pine mushroom, noble mushroom, autumn mushroom.
The mushroom cap is 4-15 cm in diameter. The color is reddish or orangeish, shiny, sometimes dark yellow, ocher, brown. You can find white patches or rings. The shape is convex, but in adulthood it becomes flat or depressed. Slippery, smooth and sticky to the touch.

The leg of the common mushroom reaches a height of up to 10 cm. The color is the same as that of the cap. The mushroom plates are the same shade as the cap. If you press a little, they turn green.
The flesh of real saffron milk caps turns green when it interacts with air when cut, quite dense, the smell is slightly fruity. The color is orangeish, light pale.

Where to find and when it grows: can be found in coniferous forests next to spruce and pine trees, as a rule, they appear in July and until mid-September.
Red Camelina mushroom - information and description, photo
Red mushroom (Lactarius sanguifluus) has a flat-convex cap that reaches up to 17 cm in diameter. The color is orange, pink, light red, very dense, slightly depressed in the center, prostrate, as a rule, the edges are bent.
The leg of the mushroom can be up to 10 cm in height, the shape is cylindrical, too strong. Often it has a powdery coating or small pits.

The plates of red saffron milk cap are frequent, can bifurcate, sink deeply along the leg. The flesh is whitish, brittle, with red pits, dense.
Where to find and when it grows: The fungus is often seen on deciduous forest soils, appearing in early July to mid-September.
Read on the topic - Tubular chanterelle - photo, description, how to distinguish from false and where to find
How to distinguish false mushrooms from real ones
In total, there are the following main types of saffron milk caps:
- Pine / upland mushroom (Lactarius deliciosus);
- Spruce / spruce mushroom (Lactarius deterrimus);
- Red mushroom (Lactarius sanguifluus);
- Milky red mushroom (Lactarius semisanguifluus).
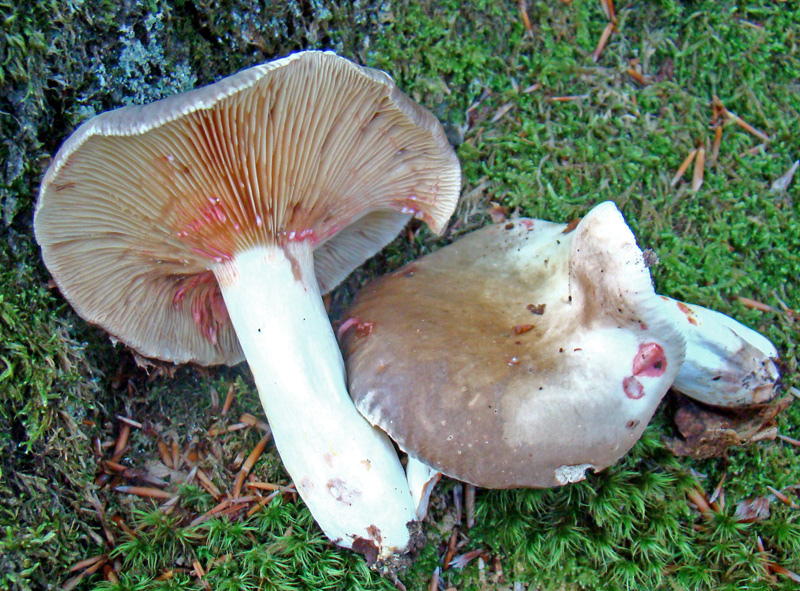
Pink wave (Lactarius torminosus)
False mushrooms include wavelets - these are such conditionally edible mushrooms
This mushroom can be salted or boiled, but it is important to know that if it is not enough to salt it (less than 40-50 days), then you can get problems with the work of the intestines and stomach

A real saffron milk cap differs from a wave in color. The wave by its name has a pink tint, and there are also frequent villi on the surface. The cap is usually about 11-12 cm, convex in shape. In adulthood, there is a small depression on the surface.
If you touch the skin, then it will be slightly slimy, with a white or slightly pinkish tint. If you press on the cap, then dark spots are formed.
The mushroom grows in places with high humidity or where there is moss. The leg of the mushroom can be up to 8 cm in height, and the diameter is not more than 2 cm. Young mushrooms have a solid leg, and then in adulthood it becomes completely hollow. Milky sap does not change when cut and remains white.
Large or papillary milky (Lactarius mammosus)
This mushroom can be used for food after prolonged salting and soaking. You can find it in coniferous forests. The main difference is the grayish-brown hat, white milky juiceand it does not darken when exposed to air.

The flesh of the mushroom is brittle, white, pleasant smell.
We also recommend that you read - False mushrooms and edible photos, how to distinguish real mushrooms from false ones
Fragrant Miller (Lactarius glyciosmus)
The mushroom has a cap with a diameter of no more than 6 cm, the color is usually ocher or beige, the edges are tucked up.

The pulp of the aromatic lactarius is light, the milky juice is white, does not change color, the smell is slightly coconut. It is used in a salted form and as a spicy additive in cooking.
Description of the mushroom serushka
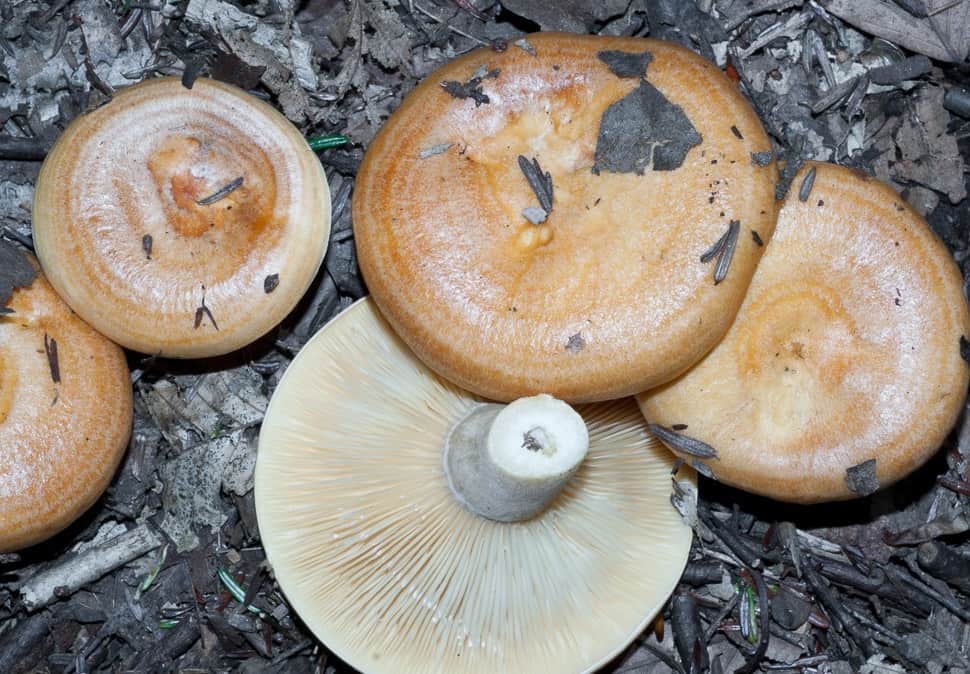
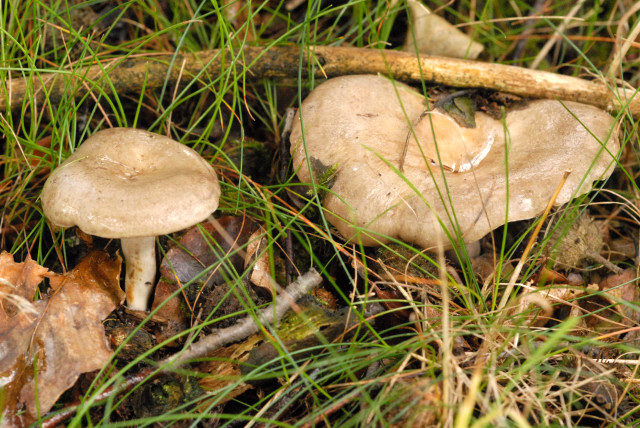
The serushka mushroom is one of the most popular among gourmets and amateurs. It is common in birch groves and in the north, including Siberia. Because of the caustic milky juice in the composition of the serushka, it is considered conditionally edible.
Description of the mushroom serushka
Description
The mushroom has a rich gray color, which is reflected in its name. His other names:
- seruha;
- seryanka;
- the nest box is gray;
- gray milky (gray-lilac);
- backrest;
- plantain;
- greenfinch;
- traveler;
- the row is gray;
The row is found under some trees, often near roads and paths in the forest. Serushka mushroom russula, ranked among the genus of Milky.
According to the description of the autumn greenfinch, the color of its cap varies from pink and violet-gray to brown-lead. In all cases, prominent concentric zones are present on it. In the process of growth, the cap is convex over the entire area. In a mature representative, it has the shape of a funnel with a smooth tubercle in the middle. The edges are jagged and drooping. The row reaches 10 cm in diameter.
Other features of the plant's appearance:
- The plates are pale, yellowish in color. Rarely located. At first, they grow to the leg, but after a while they gain a wavy shape.
- Spores are yellowish in color. The leg is hollow, but only in mature seryanka. In a growing representative, it may be slightly swollen or, conversely, narrowed. Usually its thickness does not exceed 2 cm, and its length is 8 cm.
- The dense white flesh has a fruity smell.
- When cut or broken, a watery juice with a pungent taste is released.
Edibility
Mushrooms are only conditionally edible and belong to the 3rd food category, therefore, they should be soaked for several days before use. This will relieve them of the bitter-pungent taste and make them suitable for salting. Young seryanka with a hat no more than 7 cm are better suited.
It is possible to add serukha to the first courses during cooking. It is stewed, fried, while it goes well with other mushrooms, for example, in pickled form.
Spreading
The row can be found only in autumn
False ryadovka grows in loamy and sandy loam areas, wet but well lit. Usually, these mushrooms grow in groups, often inhabiting lowland (and not only) birch forests. They are found in areas where thawed waters stand for a long time, on ordinary forest edges and glades. The row is found only in August-October.
Beneficial features
In the Middle Ages, the stomach and related diseases were treated with a serush. It was even included in cholera medicines. The mushroom contains many vitamins and trace elements in suitable proportions. They are considered unique.
Seryanka is suitable for dietary nutrition, since it is surprisingly well absorbed by the body, and has the right effect on it. It is a wonderful immune stimulant and gastrointestinal tract support.
This mushroom has a positive effect on the brain, blood vessels and even the excretion of salts from the body.
Indications and contraindications for use
According to the description, green tea is not harmful to humans, so there are no strict contraindications
At the same time, soaking in water is important to get rid of the unpleasant aftertaste.
Serushki are edible even raw, but it is imperative to know when to stop, because overeating will have a bad effect on digestion, and in case of gastrointestinal diseases, mushrooms are best consumed in minimal doses.
Since September, spores have been encountered in the vicinity of mushrooms. They appear in case the mushroom is overripe, they look like a white powder.
Serushki have an excellent antiparasitic effect and are able to cope with many types of worms.
False doubles
| View | Morphology | Habitat | The main danger |
| Amanita regalis | The cap is from 7 to 16 cm, spherical in young mushrooms and almost flat in adults. The color is dark brown, olive-red, sometimes gray-yellow. The stem is slender, no more than 20 cm in length, with noticeable globular thickenings at the bottom. The pulp of the mushroom is yellowish-white, does not have a specific smell. | Prefers moist coniferous forests of the European part of Russia. Representatives have also been found in Korea and Alaska. | It is a poisonous and highly toxic representative of the kingdom due to the content of muscimol, which causes damage to the nerve endings. |
| Fly agaric, chunky fly agaric (Amanita excelsa) | The cap does not exceed a diameter of 12 cm, brown, silvery-brown with light gray remnants of the bedspread. The pulp has a faint turnip smell. | Drought tolerant and ubiquitous | The mushroom is considered conditionally edible, however, due to its similarity with other representatives of fly agarics, which are very poisonous, the collection and use of this type is not recommended. |
| Leopard or gray mushroom (Amanita pantherina) | In appearance, it is almost identical to Amanita rubescens | Found in all types of forests in the Northern Hemisphere | Despite the fact that this mushroom is included in the Red Book of Russia, it is dangerous. It contains muscarine, muscaridin, hyoscyamine. Because of this composition, the panther fly agaric is extremely toxic. Poisoning can be fatal. |
| Amanita phalloides | The cap rarely reaches 15 cm, mostly 10 cm. It has a silky skin, greenish-olive color. The cap, as the fungus ages, acquires a flat-convex, outstretched shape. The stem is thin and does not exceed 20 cm, with greenish veins and expansion in the lower part. | The pale grebe prefers moist forests. It is difficult to find it in arid regions. It is not whimsical to the type of soil and feels best in deciduous forests (it grows extremely rarely in conifers). | Extremely dangerous. The body and the leg contain a huge amount of phalloidin, which is a heavy toxin that affects the parenchymal organs. |
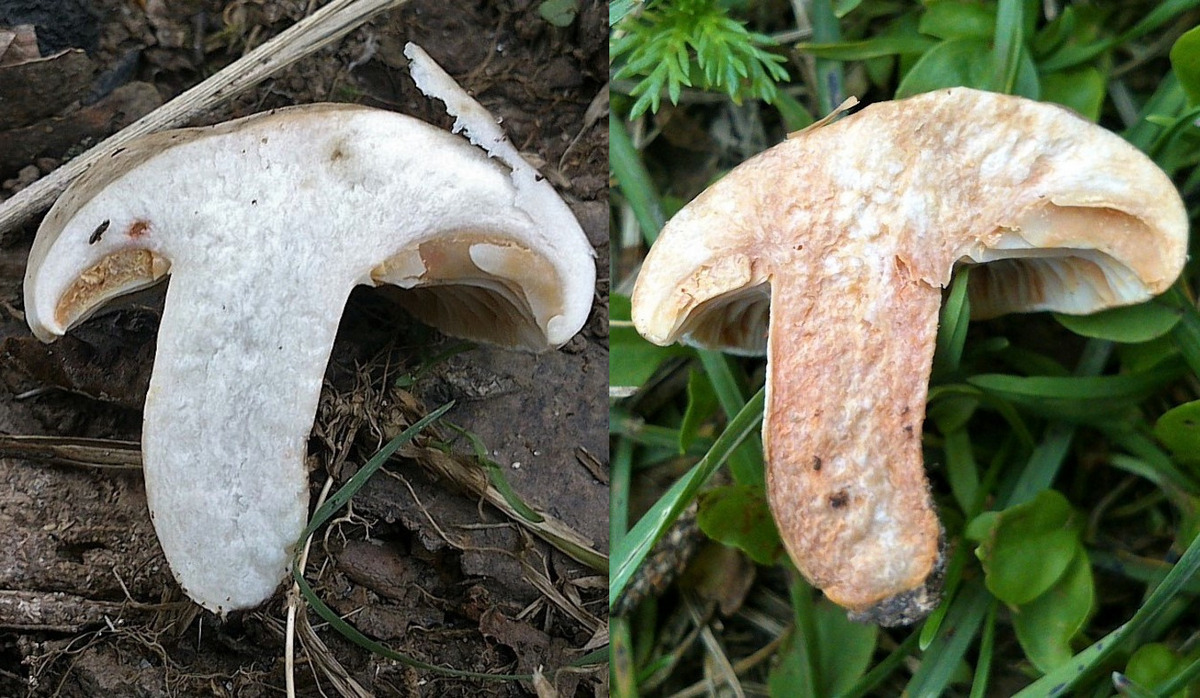
Below are photographs in which you can see that, despite the obvious similarity, the twins still have a number of differences from the pearl fly agaric.
Difference from the poisonous fly agaric panther
Distinguishing these two members of the genus from each other is not so difficult. Despite the almost identical appearance, the panther fly agaric never changes the color of the pulp when damaged (gray-pink always turns red).
Poisonous and inedible species of milky mushroom
Sticky Miller (Lactárius blénnius)
Inedible mushroom.
The diameter of the cap is 4-10 cm, the shape is convex, later extended, the edge is curved. The surface of the cap is shiny, sticky, gray-green in color with dark concentric zones. Leg 4-6 cm long, 2.5 cm in diameter, light. The pulp is white, odorless, the taste is sharp, peppery. Milky juice is thick, white.
Mycorrhiza forms with deciduous trees, grows in summer and autumn in small groups in deciduous forests of Europe and Asia.
Gray-pink Miller (Lactárius hélvus)
Inedible mushroom.
The cap is 6-12 cm in diameter, the shape is flat, later funnel-shaped, the edge is curled up. The color is pinkish brown. The leg is 9 cm high, 1.5-2 cm thick, cylindrical in shape, the color matches the cap. The pulp is light yellow in color. The smell is strong, spicy, unpleasant. The taste is bitter. Milky sap is watery white.
Grows in coniferous forests in the northern temperate zone. The fruiting season is from July to September.
Liver miller (Lactárius hepáticus)
Inedible mushroom.
Hat 3-6 cm in diameter, liver-brown color, smooth surface. The leg is 3-6 cm in height, 0.6-1 cm in thickness, cylindrical in shape, color like a cap. The flesh is thin, creamy or light brown in color, acrid.
Forms mycorrhiza with pine.
Dark Miller (Lactárius obscurátus)
Inedible mushroom.
The cap is 1.5-3 cm in diameter, in a young fungus it is flat, later goblet, the edge is wrinkled, the surface is matte, the color is ocher-brown. The leg is 0.5 cm in diameter, 2-3 cm in height, cylindrical in shape, color like a cap. The pulp is brittle, brown in color. Milky juice is white.
Grows in mixed and deciduous forests, from mid-July to September.
Resinous black miller (Lactárius pícinus)
Inedible mushroom.
The hat is 4-10 cm in diameter, the shape is convex, later spread out. The surface is velvety, brownish brown. The leg is 3-6 cm high, 1-1.5 cm thick, cylindrical in shape, tapering towards the base. The pulp is white, dense, the smell is weak, fruity, the taste is sharp, peppery, turns pink in the air. The milky juice is thick, white, turns red in air.
Grows in small groups or singly in coniferous and mixed forests. The season starts in mid-August and lasts until the end of September.
Orange Miller (Lactárius pornínsis)
Inedible mushroom.
The hat is 3-8 cm in diameter, the shape is convex. Orange color, smooth surface.
The leg is 3-6 cm long, 0.8-1.5 cm in diameter, cylindrical in shape, tapering towards the base, in a young mushroom it is solid, later hollow, the color coincides with the cap. The pulp is dense, fibrous, the smell is orange. Milky juice is thick, sticky, white.
Grows in deciduous forests, in small groups, in summer and autumn.
Wet Miller (Lactárius úvidus)
Inedible mushroom.
The diameter of the cap is 4-8 cm; in a young mushroom, the shape is convex, later prostrate. The edge is bent. The color is grayish-steel with a violet tinge, the surface is smooth and damp. The pulp is odorless, the taste is pungent, white or yellowish, turns purple on the cut. Milky juice is abundant, white, turns purple in air. The leg is 4-7 cm high, 1-2 cm thick, strong, cylindrical.
A rare mushroom that grows in damp deciduous and mixed forests, from early August to late September.
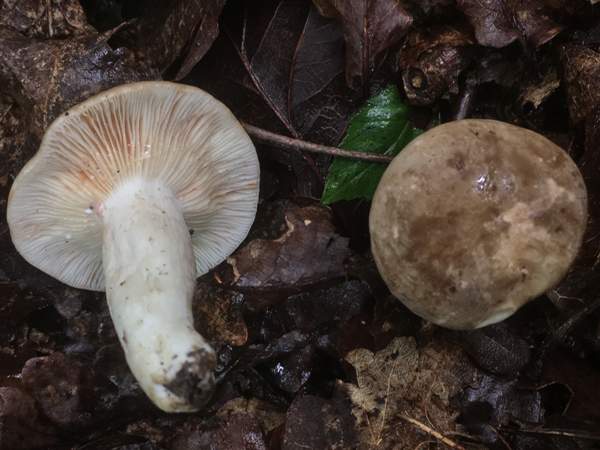
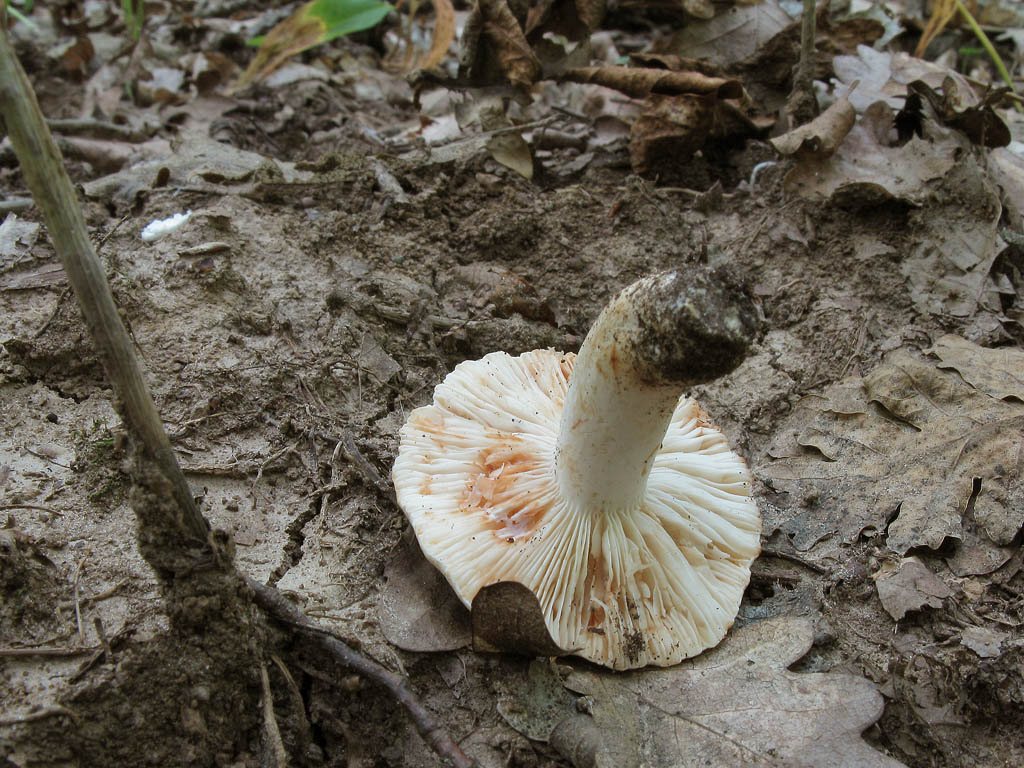
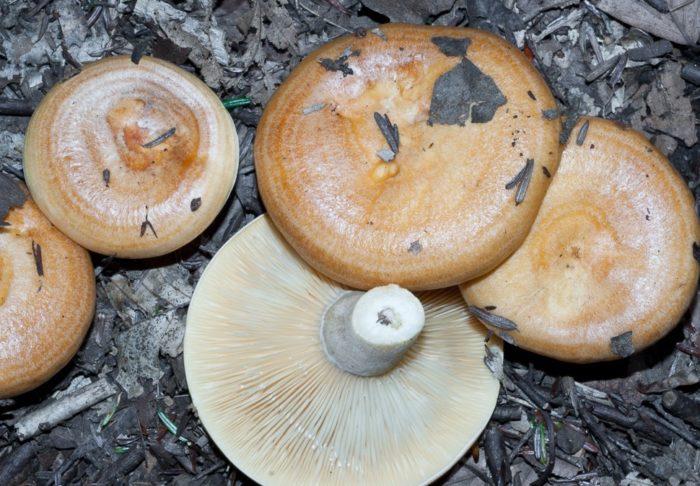
Description of zoneless milkmen
The fruiting body of the zoneless lactarius consists of a cap and a leg. The cap is flat, depressed or with a tubercle in the middle. The edges of the cap are even. The surface of the cap is velvety and dry. The color of the cap is sandy, brown, pale or dark brown. The size of the cap is 9-11 centimeters. It is very dense in structure.

His plates are narrow, going down the leg. The pulp is dense, snow-white in color. The pulp has a bland taste. Mature milkers develop an unexpressed pleasant aroma. A colorless juice is released from the pulp; in the air it quickly turns orange.
The leg is cylindrical, dense, 7-9 centimeters high. The color of the leg matches the cap. In young milkers, the legs are usually dense, and over time they become hollow.
Areas of growth of zoneless milkmen
These mushrooms grow in Eurasia. Moreover, they prefer deciduous forests. In Russia, they are found in the European part and in the southern regions, for example, in the Krasnodar Territory. You can find zoneless milkmen in the forests in which oaks grow, since it is with these trees that they form symbiotic alliances.

Fruiting bodies can occur singly or in not too numerous groups. Zoneless milkmen bear fruit from July to September. There are lean years in which the milkmen do not bear fruit at all.