Maintenance and care
Microsorum pteropus does not burden the owners in terms of maintenance and care.
For the normal functioning of aquatic ferns, it is recommended:
- avoid overheating by lighting fixtures;
- prevent a sharp drop in temperature in the tank;
- populate the aquarium with compatible fish species;
- monitor water quality;
- timely cut off withered and spoiled shoots with scissors.
With an acute deficiency of nutrients and insufficient lighting, the plant turns pale and slows down growth until a suitable microclimate is created.
Aquarium parameters
The growing tank is selected according to the height of the tropical plant. Bright greenery is suitable for decorating a deep and voluminous aquarium.
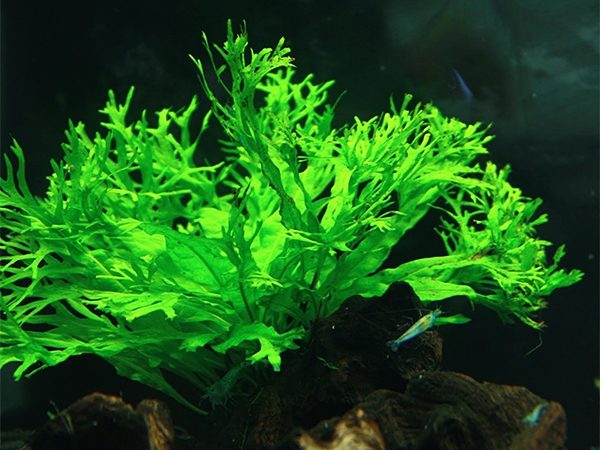

Fern Thai Vindelov.
Since the species prefers a calm atmosphere, it is recommended to grow it away from filtering equipment. Fragile shoots do not tolerate constant mechanical stress.
To provide each specimen with a sufficient amount of micro and macro elements, it is necessary to maintain a distance during landing - up to 20 cm from each other. Bushy bushes grow more slowly because their roots are intertwined, which inhibits the development of the entire population.
Water
The plant loves soft neutral water without sudden temperature fluctuations. A comfortable environment for the growth of most fern species is a tropical climate with a temperature of + 25 ... + 30 ° C. In cool water, the culture slows down development. A suitable hardness value is 0-6 ° dH, the acidity level (pH) is 4-6. It is recommended to replace 15-20% of the total water volume 1-2 times a month.
Lighting
Most varieties of Microsorum prefer dim artificial or natural diffused lighting. The plant slows down its growth with prolonged darkening. The recommended daylight hours are 10-12 hours. It is recommended to use incandescent lamps or fluorescent lamps with dim white light as lighting devices. The power is selected in accordance with the volume of the aquarium at the rate of 0.3-0.5 W per 1 liter.
An overabundance of illumination leads to the fact that the foliage becomes brown and transparent. When burned, the plates turn yellow and fall off. It is necessary to diffuse sunlight and reduce the intensity of artificial light.
Priming
Many varieties of Javanese fern do not require soil and do not need additional fertilizers (fine-grained silted sand is sufficient). Due to the undeveloped rhizome, which spreads over the substrate, the plant is attached to decorative elements, driftwood or coarse gravel.
The following means are used for fastening:
- glue;
- fishing line;
- thin silk thread;
- harness.
After weighting, the bush easily moves to any corner of the tank.
Top dressing
Intensive development and growth of representatives of Microsorum pteropus requires regular fertilization (at least 2 times a month). Fern receives all nutrients from water. For enrichment, liquid nitrogen fertilizer urea (urea) is used, which is applied at the rate of 10-12 granules per 100 liters. The supply of CO2 and universal mineral compositions when changing the water in the tank has a beneficial effect on the development and color saturation. Due to the lack of a developed root system, feeding in the form of sub-root tablets will not work.
Compatible with other inhabitants in the aquarium
The main advantage of the Microsorum family is the specific structure of the foliage (it is believed that the shoots are tough and bitter in taste). This discourages herbivorous species of fish and turtles from eating the fern, so they are suitable for the neighborhood.
The plant gets along well with cichlids, guppies, scalars, apistograms, swordtails and anubias, who love to feast on greens.
It is not recommended to populate fish digging soil into the tank. They easily damage thin roots, slowly destroying the bush.
These varieties include:
- gold fish;
- catfish;
- agamixis;
- corridor, etc.
Observing the main technical indicators and simple growing rules, the aquarist gets lush bushy thickets and bright decor.
To bookmarks
Main types
This genus unites about 50 plant species, but at the same time, as a rule, only 3 are grown at home.
Microsorum punctatum

The short rhizome of this plant is creeping. Short petiolate, very rigid leaves have a narrow elliptical shape. In height, the formed curtains reach only 30 centimeters and are outwardly similar to sorrel.
Banana microsorum (Microsorum musifolium)
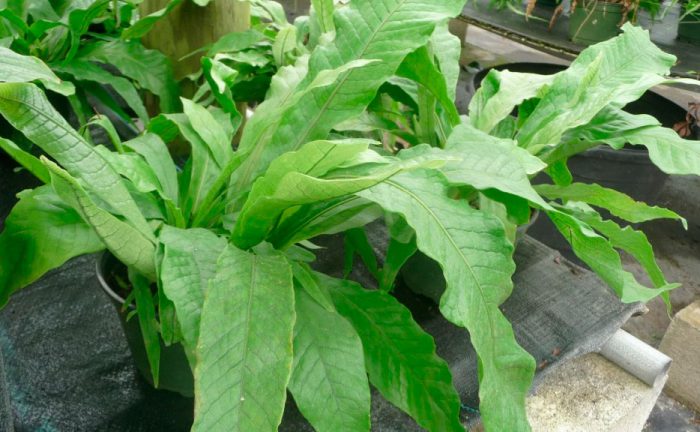

This type is not very popular. Over time, such a plant begins to release shoots that reach 1 meter in length. Its leathery leaves have an unusual appearance. On their surface there are mesh veins, and in this type of foliage, most of all resemble crocodile skin. Also, the leaves are outwardly very similar to banana leaves.
Microsorum diversifolium

The leaves of a rich color are divided into segments from 3 to 5 pieces, which have a wavy-oval shape. If you touch them, you can feel a very pleasant aroma.
Pterygoid microsorum (Microsorum pteropus)

Also, a species called microsorum pteropus is gaining more and more popularity among aquarists. It is widely used to decorate aquariums, or rather their back or middle part.
Microsorum scolopendria
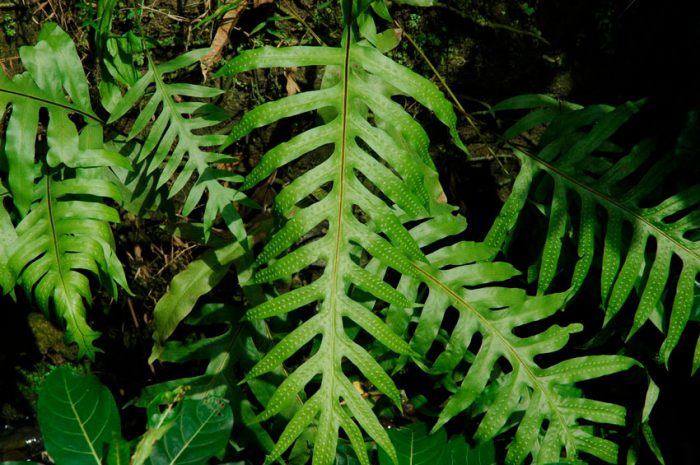

Not so long ago, the species Microsorum scolopendria was especially popular. However, today this plant belongs to the Phymatodes scolopendria family. And that's all, because fronds and the growth form of this plant are more like nephrolepsis, and not microorums.
Microporus yellow-pegged: photo and description
| Name: | Microporus yellow-pegged |
| Type of: | Inedible |
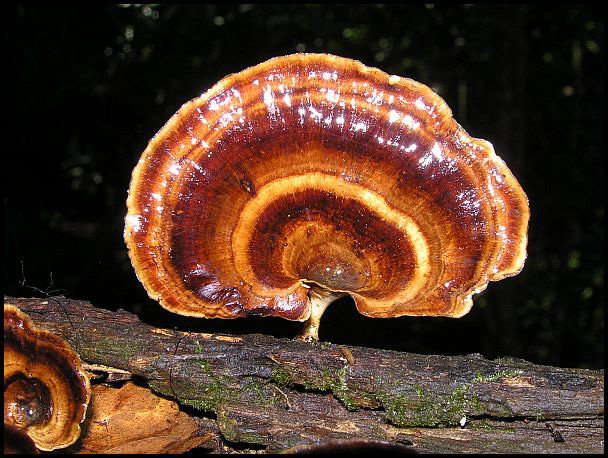
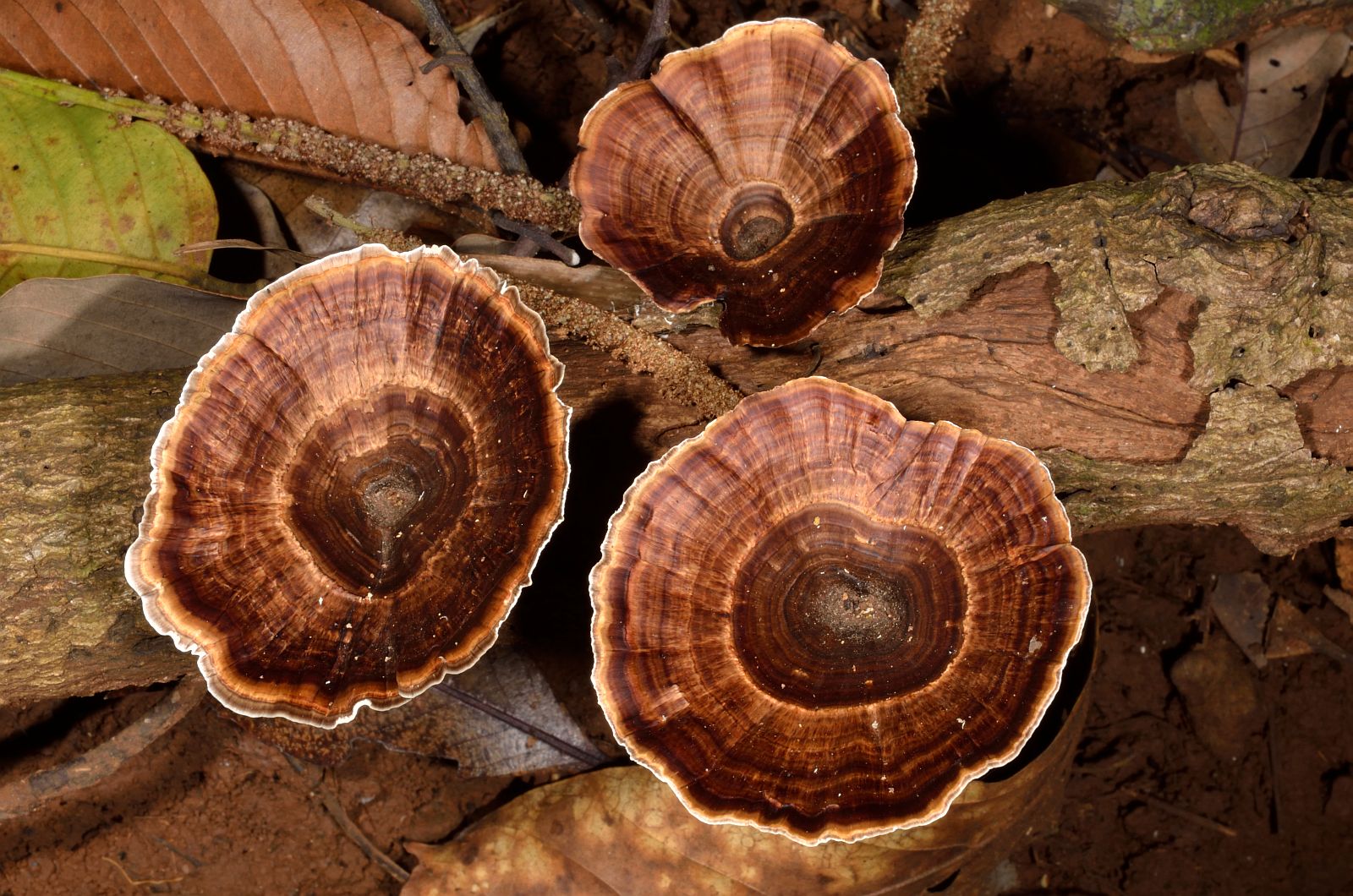
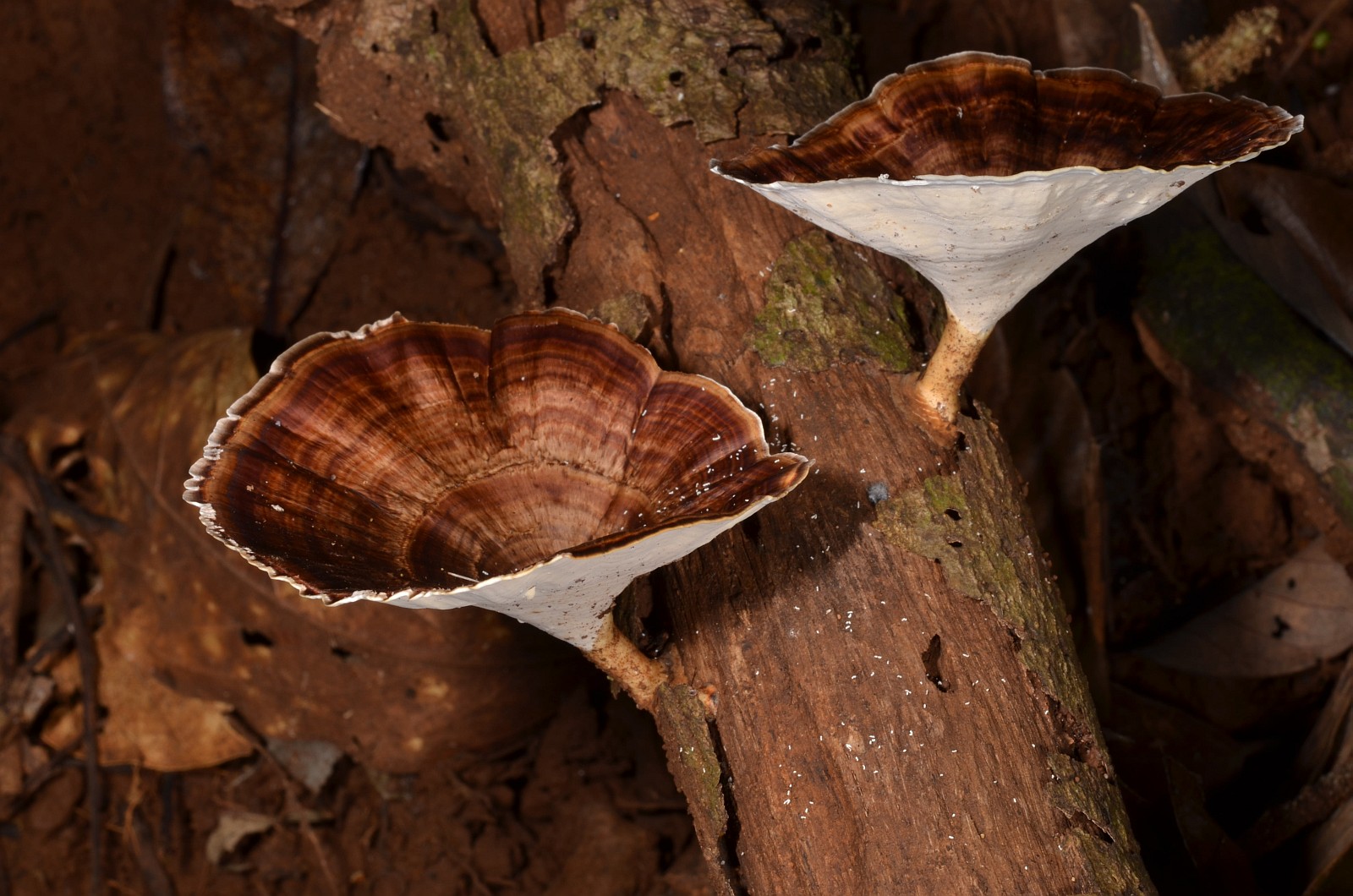
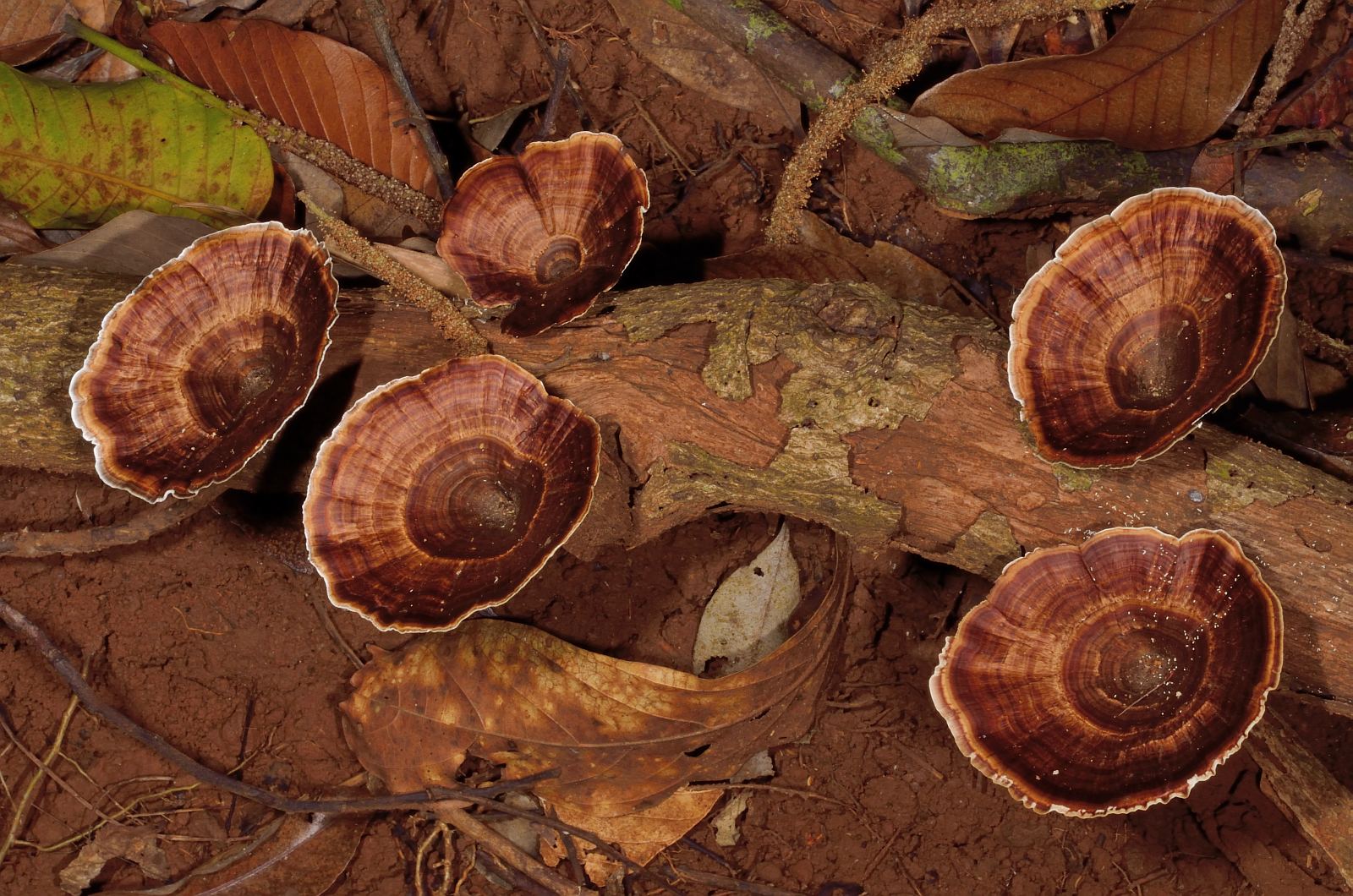
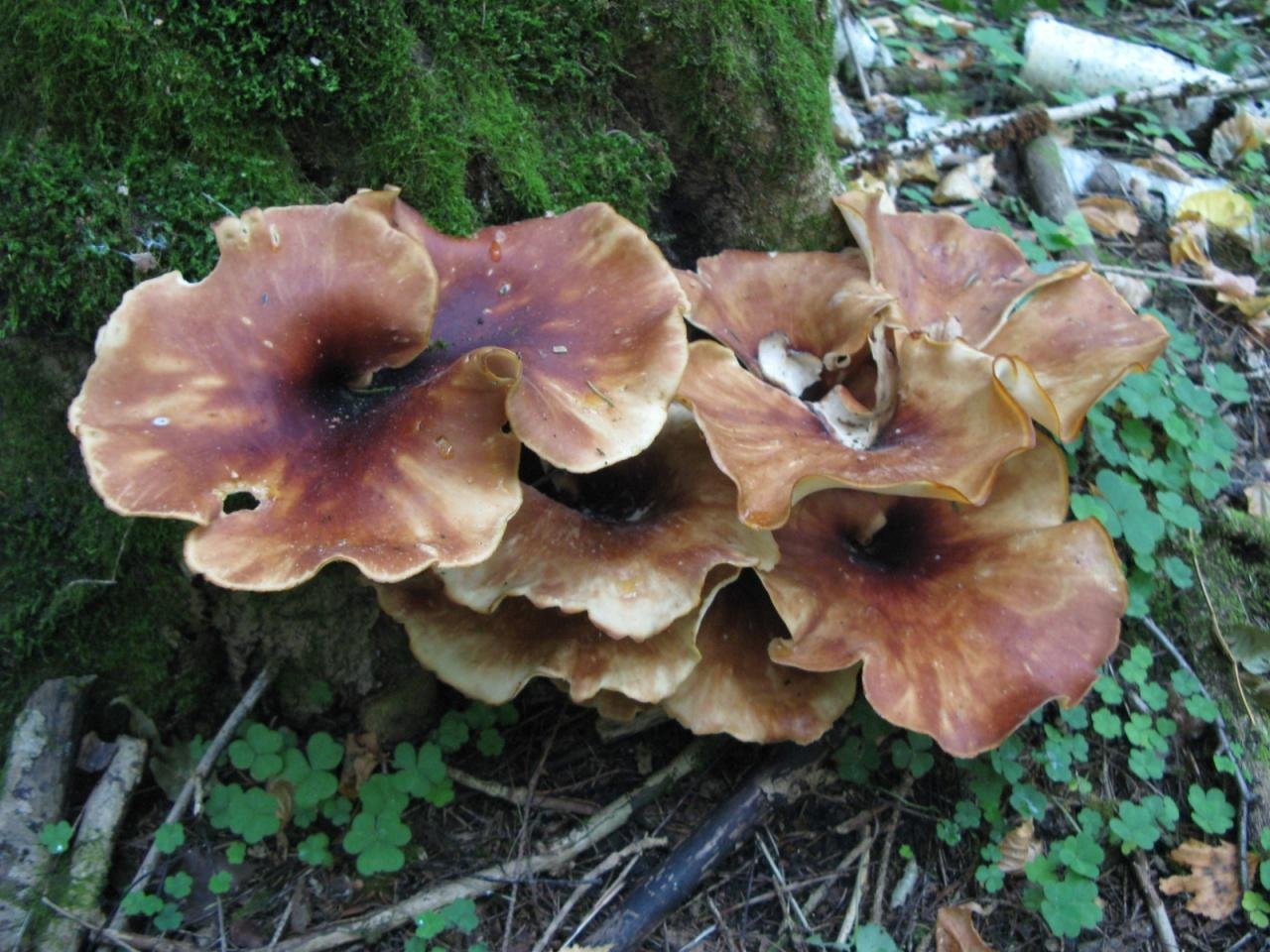
Microporus yellow-leg is a representative of the mushroom kingdom, belonging to the genus Microporos from the Polyporov family. Latin name - Microporus xanthopus, synonym - Polyporus xanthopus. This mushroom is native to Australia.
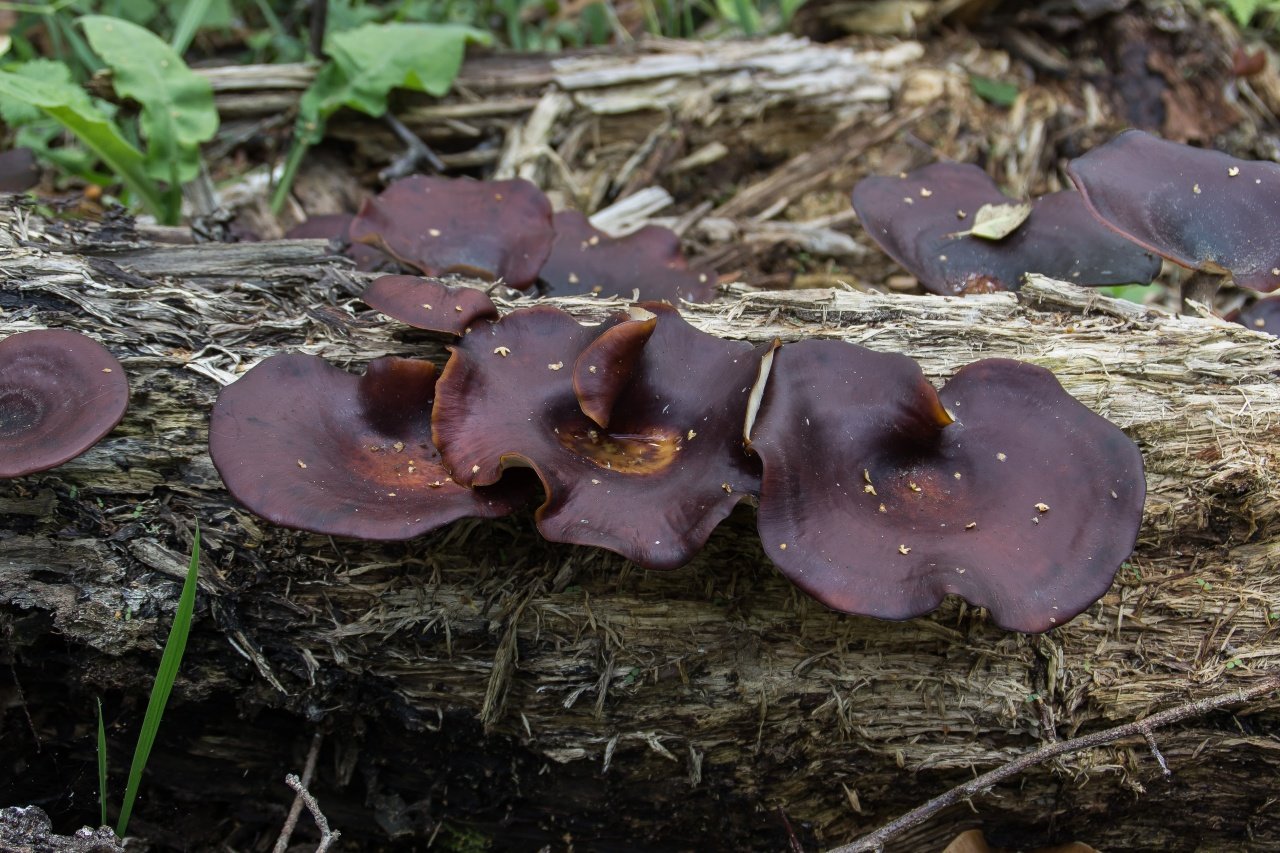
What does the yellow-pegged microporus look like?
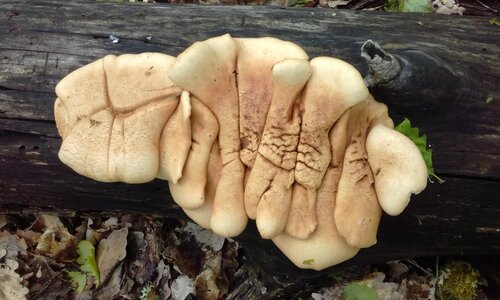
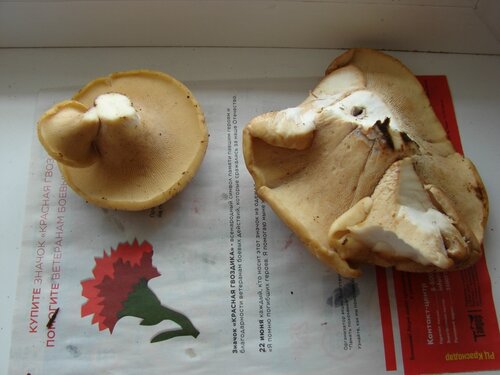
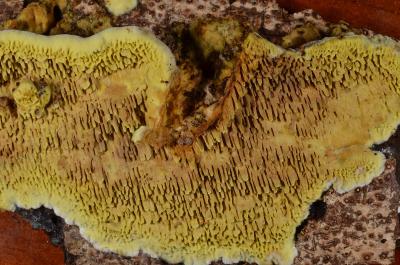
The hat of the fruiting body outwardly resembles an open umbrella. The yellow-pegged microporus consists of a spreading top and a refined leg. The outer surface is dotted with small pores, hence the interesting name - microporus.
This variety is characterized by several stages of development. A white spot appears on the wood, indicating the emergence of the fungus. Further, the size of the fruiting body increases, the stem is formed.
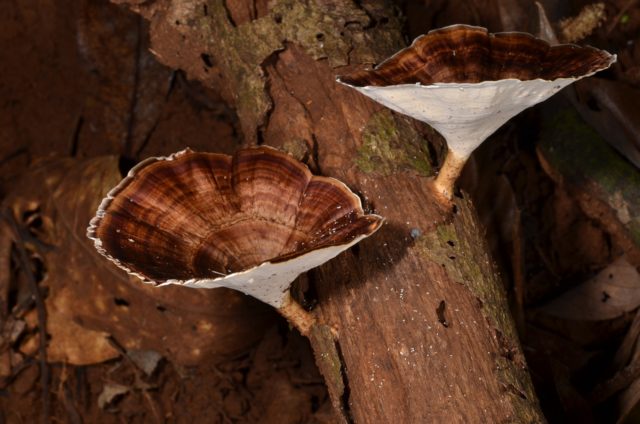

Due to the specific color of the leg, the variety received the second part of the name - yellow-pegged
The thickness of the cap of an adult specimen is 1-3 mm. The color ranges from brownish shades.
Where and how it grows
Australia is considered to be the birthplace of the yellow-pegged micropore. A tropical climate, the presence of decaying wood - that's all it needs to develop.
Is the mushroom edible or not
In Russia, the yellow-pegged microporus is not used for food. Unofficial sources indicate that the indigenous people of Malaysia use the pulp to wean small children.
Due to its unusual appearance, the fruit body is popular with craft lovers. It is dried and used as a decorative element.
Doubles and their differences
The yellow-leg microporus has no similar species, so it is very difficult to confuse it with other representatives of the fungal kingdom. The unusual structure and bright colors are individual, which makes the microporus special.
Some external similarity is observed in the chestnut tinder fungus (Picipes badius). This mushroom also belongs to the Polyporov family, but belongs to the Pitsipes genus.
Grows on fallen deciduous trees and stumps. Appears in regions with damp soils.It can be found everywhere from the end of May to the third decade of October.
The average diameter of the mushroom cap is 5-15 cm, under favorable conditions it grows up to 25 cm. The funnel-shaped shape is the only similarity between the yellow-pegged micropore and the chestnut tinder fungus. The color of the cap in young specimens is light, with age it becomes deep brown. The central part of the cap is slightly darker, the shade is lighter towards the edges. The surface is smooth, shiny, reminiscent of varnished wood. During the rainy season, the cap feels oily to the touch. Creamy-white fine pores form under the cap, which acquire a yellow-brown tint with age.

The flesh of this mushroom is tough and overly elastic, so it is difficult to break it with your hands.
The leg grows up to 4 cm in length and up to 2 cm in diameter. The color is dark - brown or even black. The surface is velvety.
Due to its rigid elastic structure, the mushroom has no nutritional value. Polypores are harvested and dried to create crafts.
Conclusion
Microporus yellow-leg is an Australian mushroom that has practically no analogues. It is not used for food, but it is used in interior design.
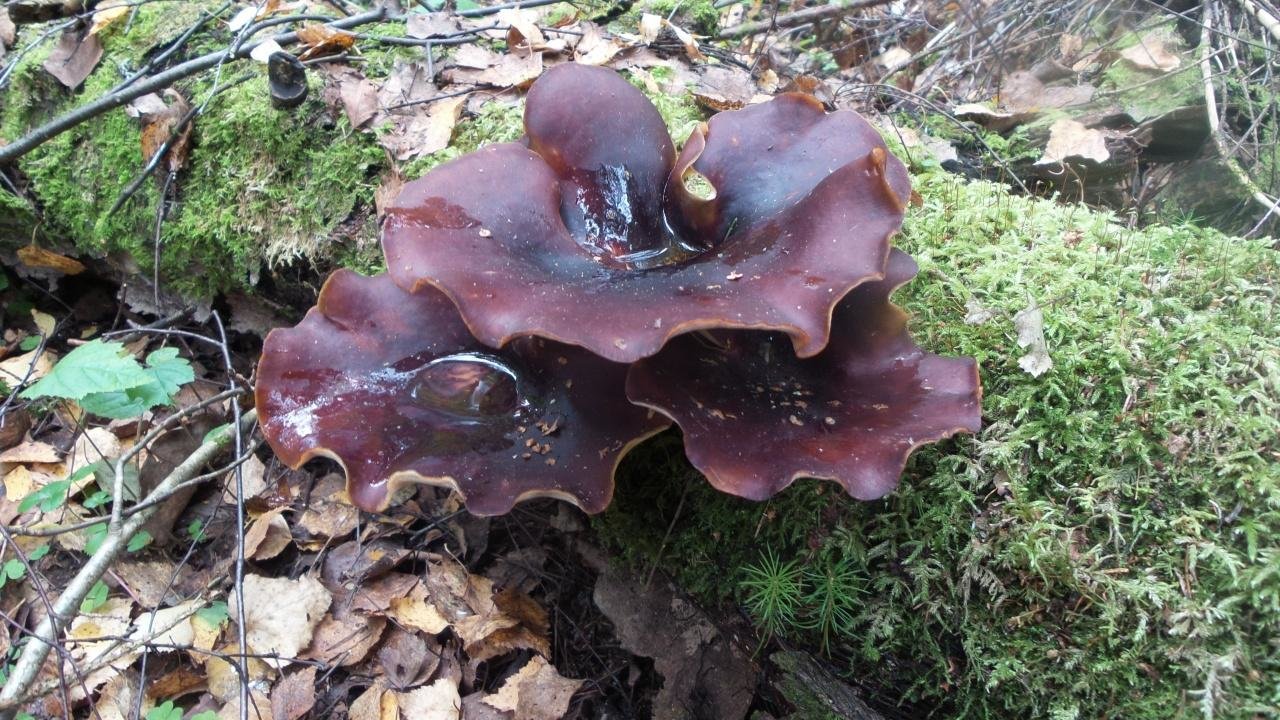
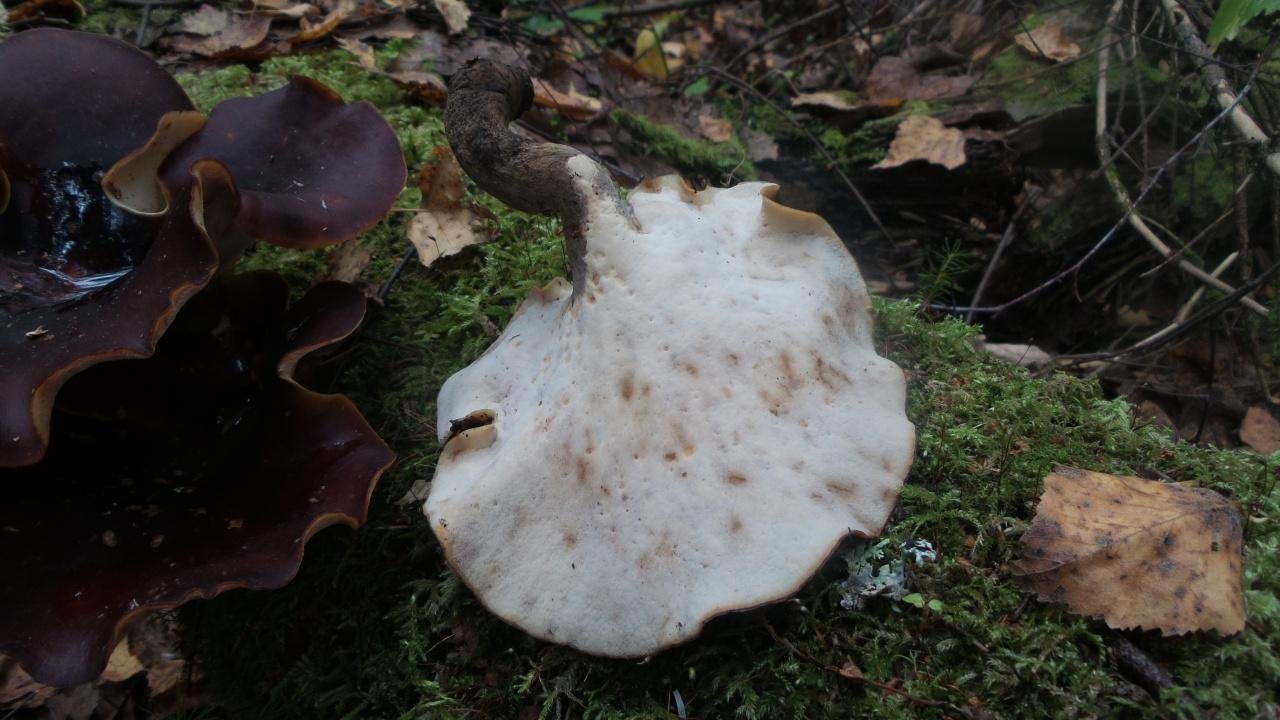
Melanogaster Bruma: edible or not, description and photo
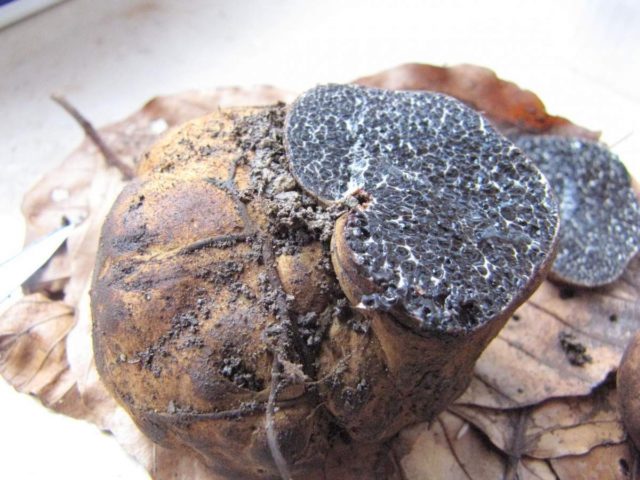
Melanogaster Bruma is an inedible representative of the Svinushkov family. The species got its name in honor of the English mycologist Christopher Broome. Also, in some sources, the mushroom is called "false truffle". Since it is not used for cooking, you need to know the external characteristics, view photos and videos.
What melanogaster Bruma looks like
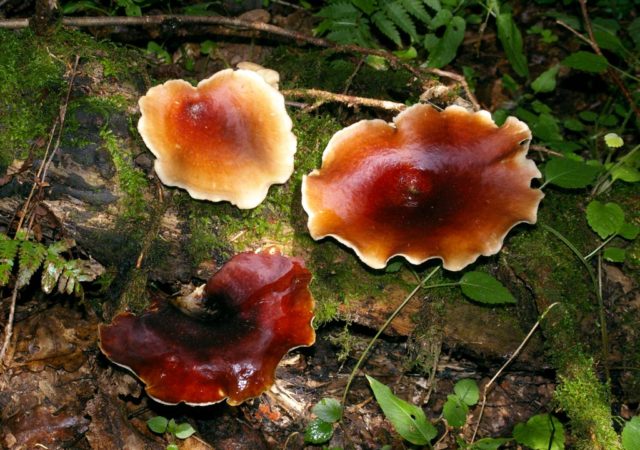
The spherical or tuberous fruiting body reaches up to 8 cm in size. In young specimens, a smooth or slightly velvety surface is painted in a light coffee color, with age it becomes dark chocolate.
The pulp is dense, gelatinous, initially brown, then becomes gray-black with pronounced light streaks. Reproduction occurs by microscopic spores, which are located in a dark powder.

Where melanogaster Bruma grows
Melanogaster Bruma grows shallow underground, under a thick layer of deciduous substrate. Prefers deciduous forests, begins bearing fruit from June to October.
This representative is a rare specimen, in the Novosibirsk region the mushroom is listed in the Red Book. Therefore, in order to increase the population, it is better to pass by this species.
Is it possible to eat melanogaster Bruma
This forest dweller is inedible, despite the fact that the pulp has a pleasant fruity aroma. May cause food poisoning if eaten. Therefore, in order not to harm the body, it is necessary to be able to recognize this instance and know the first signs of intoxication:
- nausea and vomiting;
- cold, clammy sweat;
- lowering blood pressure;
- pain in the epigastric region.
Melanogaster Bruma, like many forest dwellers, has similar brethren. These include:
- The Italian truffle is a delicious, edible species that prefers to grow in deciduous forests, on calcareous soil. It can be recognized by its tuberous fruiting body, with a whitish-yellow velvety skin. The gray-yellow pulp has a cheese-garlic smell and taste. Since the mushroom does not tolerate heat treatment, it is eaten fresh. It goes well with fish, vegetable and meat dishes, and is also used to flavor sauces and seasonings. Used fresh in cooking
- Summer truffle is a tasty and healthy forest dweller. The warty surface is gray-black. The light brown flesh has a nutty flavor and a strong aromatic odor. Grows on the territory of Russia, in deciduous forests.Fruiting occurs from July to November. To collect mushrooms, a specially trained dog is often taken as an assistant. Grows underground in deciduous forests
Conclusion
Melanogaster Bruma is a rare, inedible species that grows in deciduous forests. Since the species is not used in cooking, and it is listed in the Red Book, it is necessary to pass by the found specimen.
Thai fern species
There are dozens of varieties of Thai fern in specialized stores. The most popular are 9 varieties.
Narrow-leaved Microsorum pteropus Narrow
The subspecies has gained popularity among amateurs not so long ago. The length of the roots reaches 15 cm, and the foliage is 18-20 cm. The unpretentious plant is suitable for decorating small containers, narrow leaves adorn intricate driftwood. The price of a copy is 60-80 rubles.
Microsorum pteropus Undulata
The variety has delicate, wavy, light green foliage. The bush reaches 30-35 cm in height and 25 cm in width. Due to its wide leaves and volumes, it is suitable for aqua design in large aquariums. An exotic variety is rarely found on sale, so the price of a specimen is higher - 200-250 rubles.
Pterygoid Filipino pteropus Philippine

Fern Thai Tropica.
A bright representative of the fern native to the Philippines. Recently it has been in demand among aquarists. Long corrugated leaves grow up to 35-40 cm. The plant is attached with rhizoids to stones or planted in the ground.
Comfortable habitat - salty soft water with a pH level of at least 7 and dim lighting. The growth rate of the specimen is higher than that of other subspecies. Contained in large aquariums. Average price - 175 rubles.
Windelov
A feature of the subspecies is the extraordinary shape of the leaf plate, reminiscent of deer antlers. The length of the leaf dissected at the end reaches 12-15 cm, the width of the bush is 20 cm.
Interesting appearance and compactness make it possible to create beautiful compositions in small aquariums. Ease of maintenance and low cost (70-120 rubles) make the plant in demand among beginners and amateurs.
Tropica pteropus Tropica
It is considered one of the most hardy varieties. New foliage with even edges tapers as it grows, the plates are serrated. Old leaves fall apart, forming a sprawling bush 35-45 cm wide. Ideal for the background of a large aquarium. The price on the market is 80-100 rubles.
Fork-leaved Microsorum pteropus Fork Leaf
A decorative and undemanding fern with a soft green color, rarely found in home aquariums. "Horned" leaf plates grow up to 25 cm in length and up to 15-20 cm in width. A dense bush looks interesting anywhere in the aquarium. Contained in water of different hardness and temperature, does not require bright light and fertilizers. The average cost of a sample is 90-100 rubles.
True Narrow-leaved Real Narrow
The variety with the narrowest leaves 2-4 mm wide. Plates are painted in marsh color. Does not require special conditions for keeping. Grown on snags and gravel.
Small leaf
The variety with the smallest foliage - up to 7 cm. Green shoots develop in soft or hard water with a pH level of 4-7 and a water temperature of + 4… + 30 ° C. Suitable for the front of the vessel.
Red Microsorum Pteropus Red
Young fern leaves are colored red. Over time, they brighten, acquiring a light green hue. The bush reaches a height of 30 cm, in width - 20 cm. The leaf plates are wider than that of a simple Microsorum. Wide bushes are suitable for decorating the back wall of a volumetric aquarium. The price of a copy is 150-180 rubles.
Description of microorum
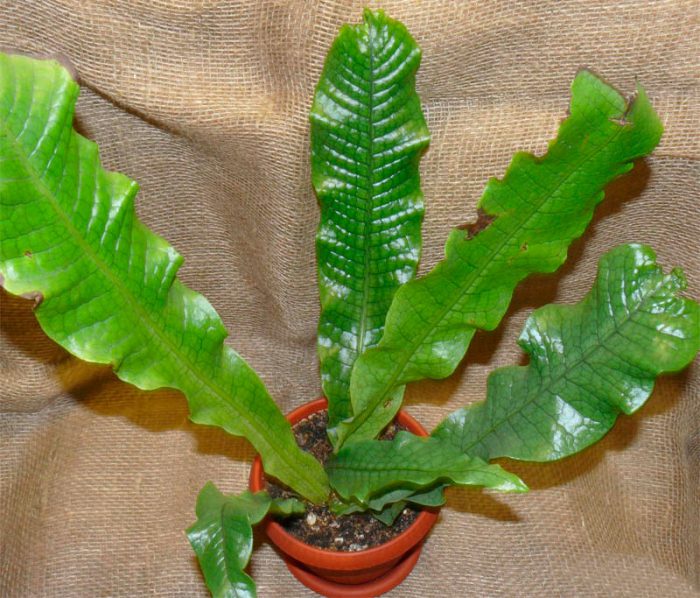

Having seen the microorum for the first time, everyone admires the density and curliness of its leaves, as well as its spectacular appearance. These plants are not capricious and undemanding to care for. Over the years, they acquire an increasingly spectacular appearance, so slender bushes become very lush and curly
Such a fern will perfectly complement any style of the apartment, while it can decorate almost every room and, importantly, its appearance always retains its uniqueness and individuality.These plants are popularly called "crocodiles", and all because on the surface of their unusual leaf plates there is a mesh vein, which gives a clear external resemblance to the skin of such predators
Such a fern is directly related to the family of the centipede (Polypodiaceae), and its homeland is Oceania, Australia, as well as Southeast Asia.
Compact plants such as Microsorum can be 25 to 50 centimeters tall and also have a creeping rhizome. It is not uncommon for the roots of this plant to crawl out of the soil onto its surface. In length, the leaf plates of microorums reach no more than 60 centimeters, but this is in room conditions. In a wild plant, the length of wai can reach 100 centimeters. Spectacular curtains are formed from sessile or petiolate leaves. Leaf plates can be simple, narrow-elliptical, as well as pinnate, dissected into fairly wide and large lobes (as a rule, there are from 3 to 5 segments).
Young (juvenile) frond outwardly have a great similarity with a plant such as sorrel. As they grow, the leaves change, while they become dissected, more delicate and spectacular. The surface of the sheet plates is wavy and uneven, while the edge is also unevenly wavy. Such leaves curl, curl, due to which the fern has an unusual curly appearance. Sori, which are reddish-brown spots on the surface of the leaves, are placed along the central vein in a row or on the seamy surface (unevenly). Uncovered sporangia represent the reproductive organ where spores form. They can be both unicellular (in a large number of lower plants and fungi) and multicellular (in higher plants). The word sporangia itself, translated from Greek, means "spóra" - "sowing, seed" and "angéion" - "vessel, receptacle."