Melanoleuca black and white
Melanoleuca black and white (lat.Melanoleuca melaleuca).
Other names:
- Melanoleuca cognata
- Melanoleuca vulgaris
- Common melanolevka
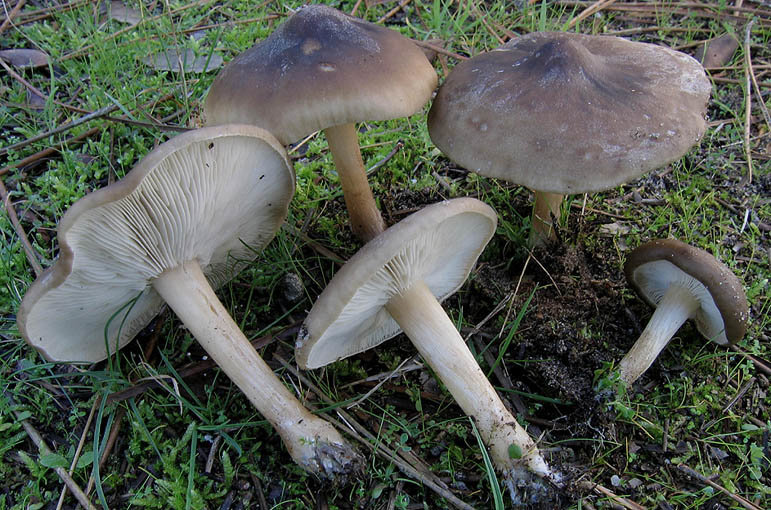
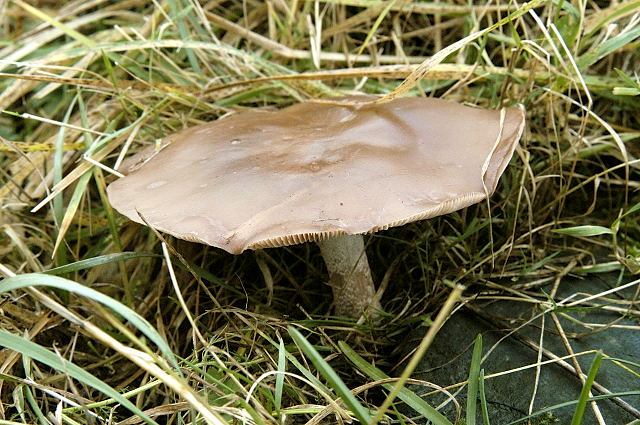
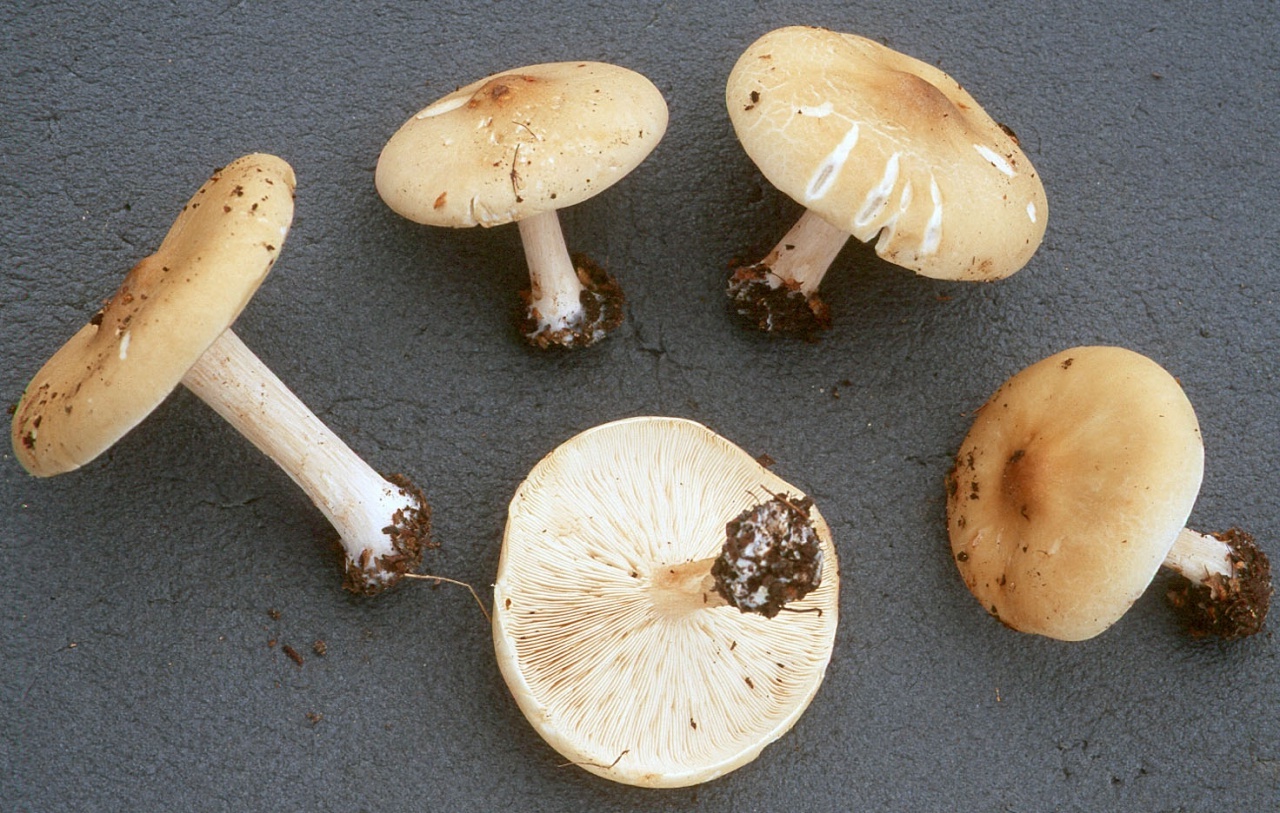
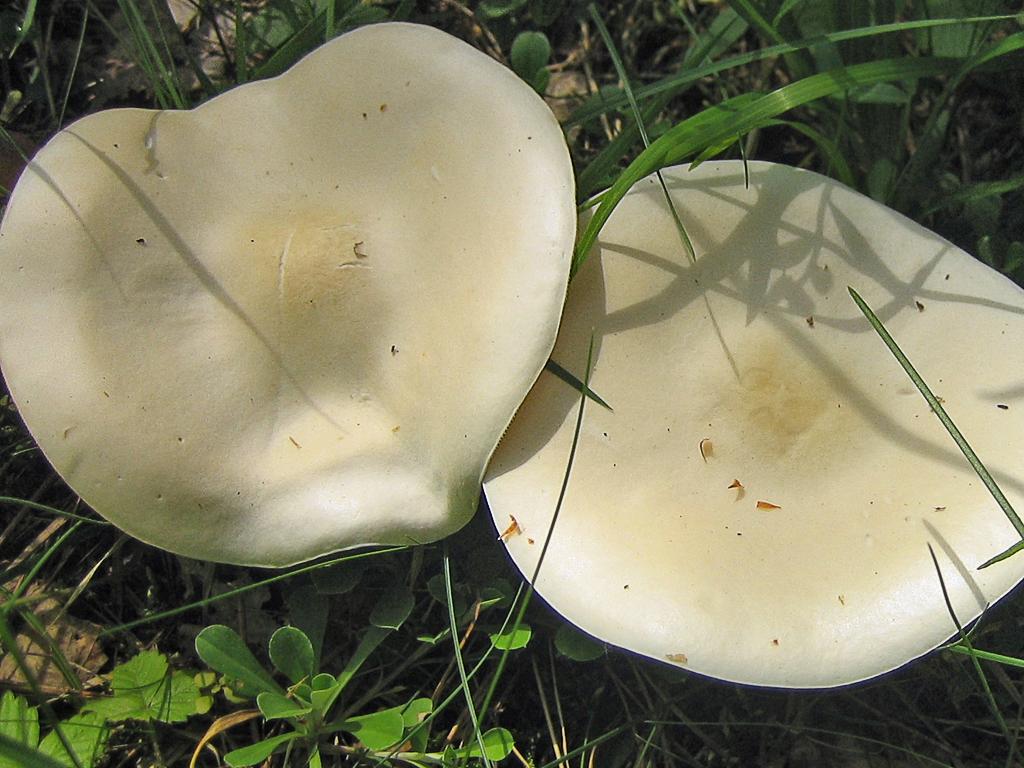
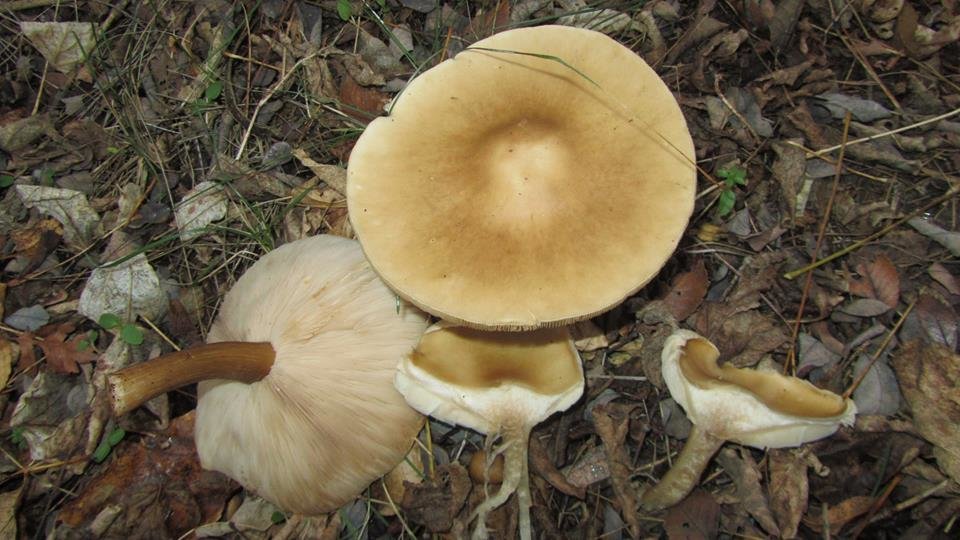
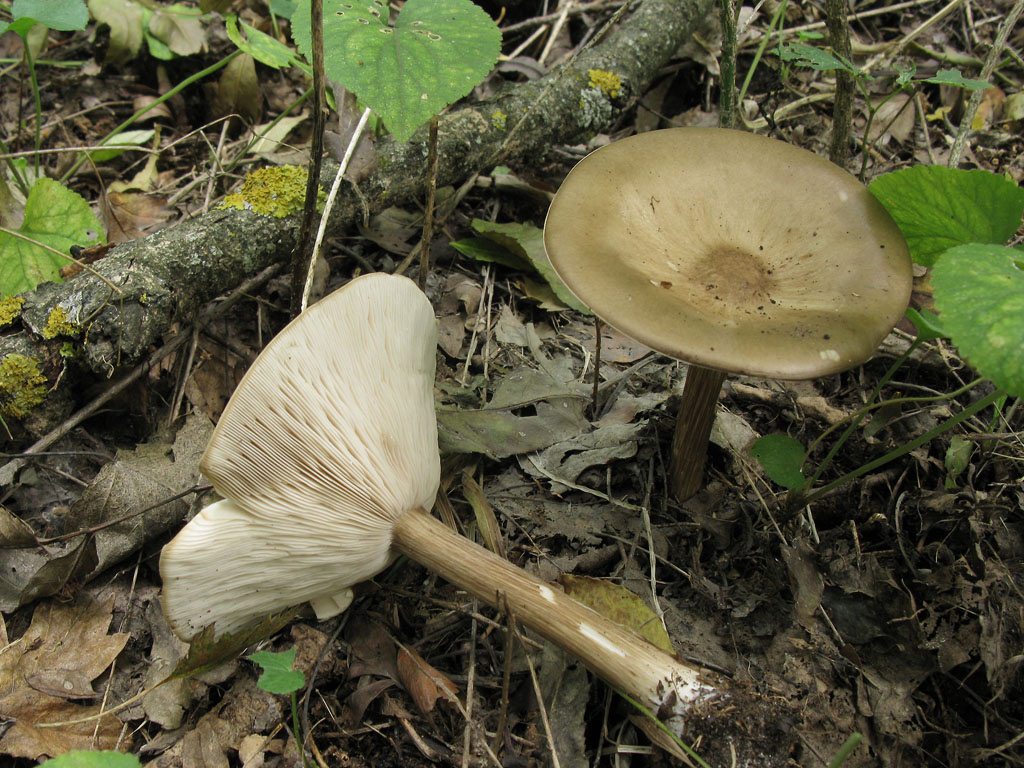
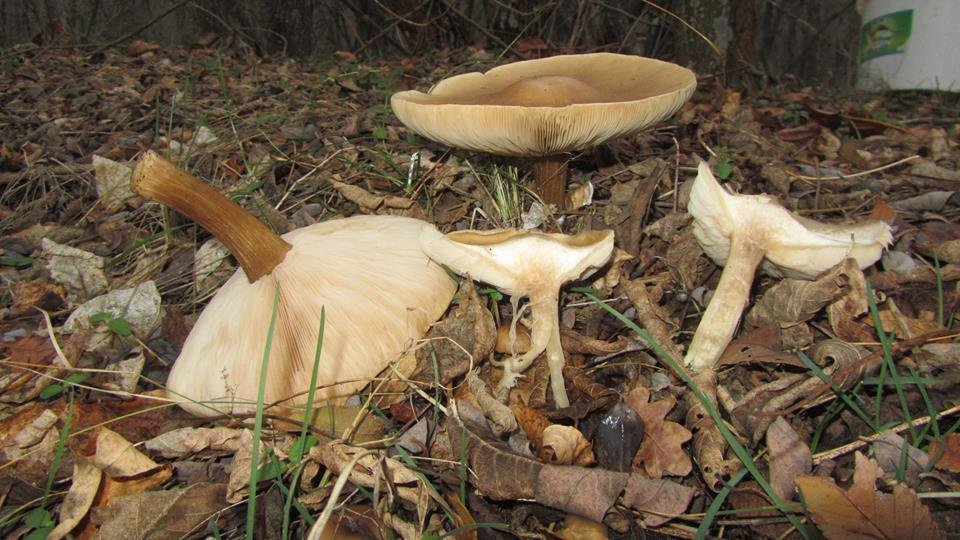
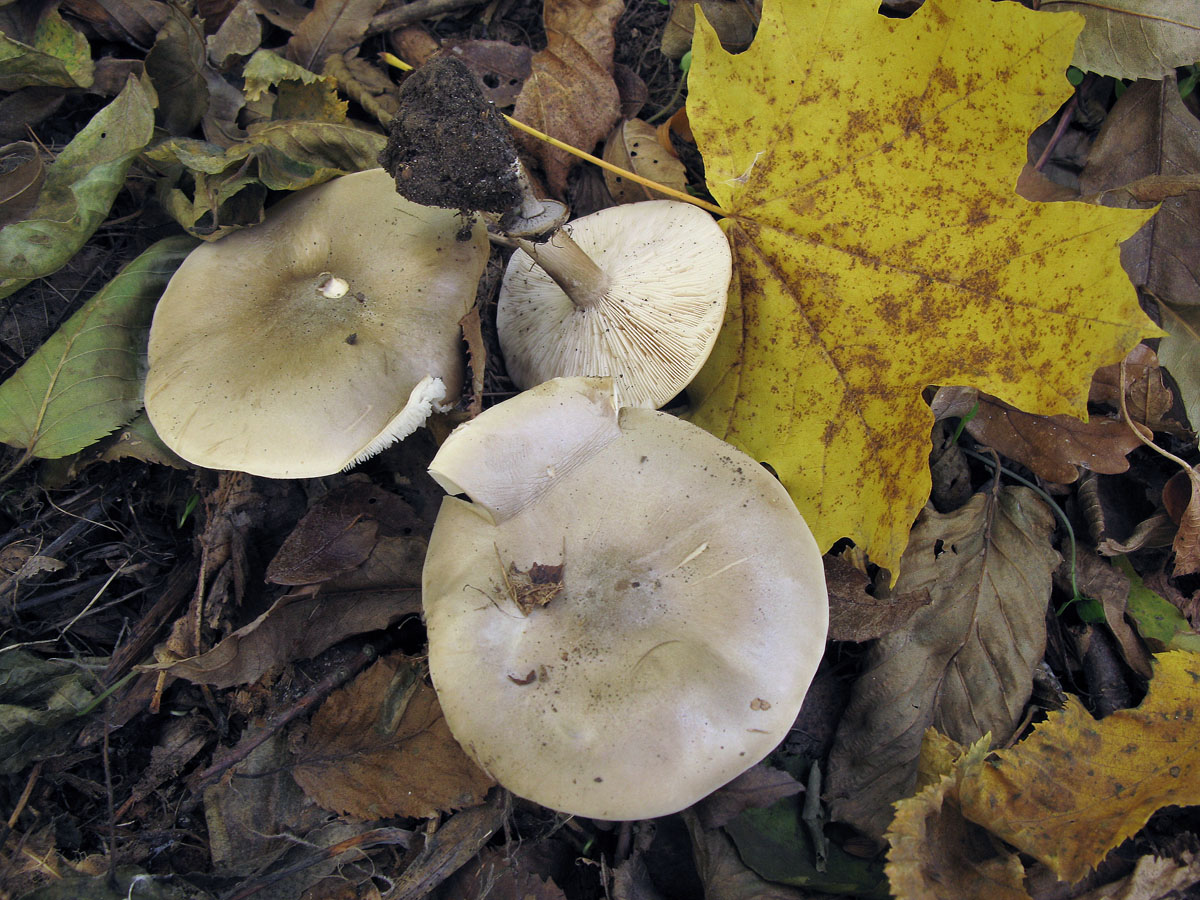
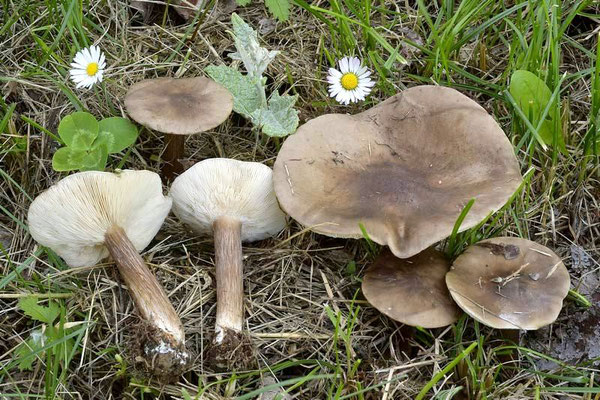
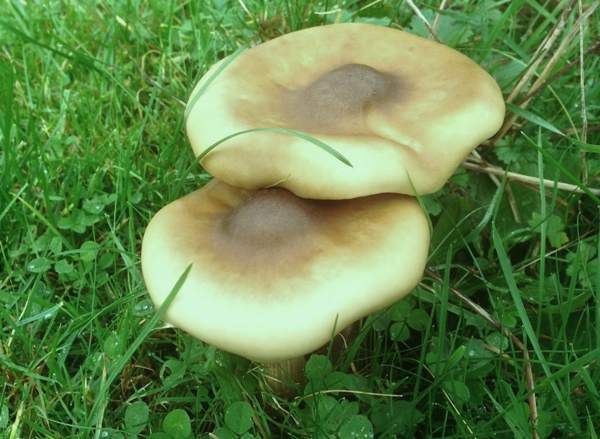
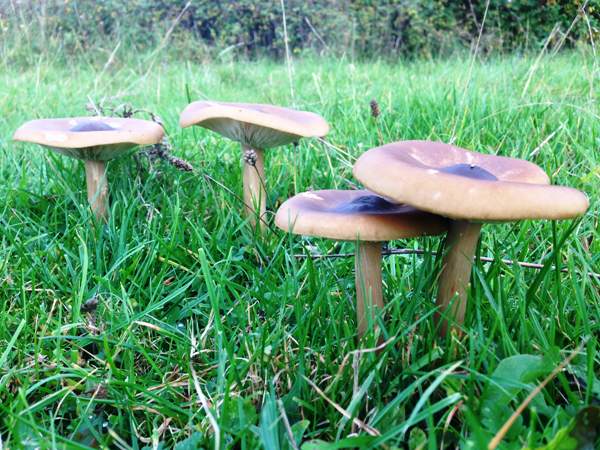
Melanoleuca black and white is an edible lamellar mushroom that grows singly from late July to mid September. Most often, it can be found in open areas of mixed and deciduous forests, in gardens, parks, meadows and along roadsides.
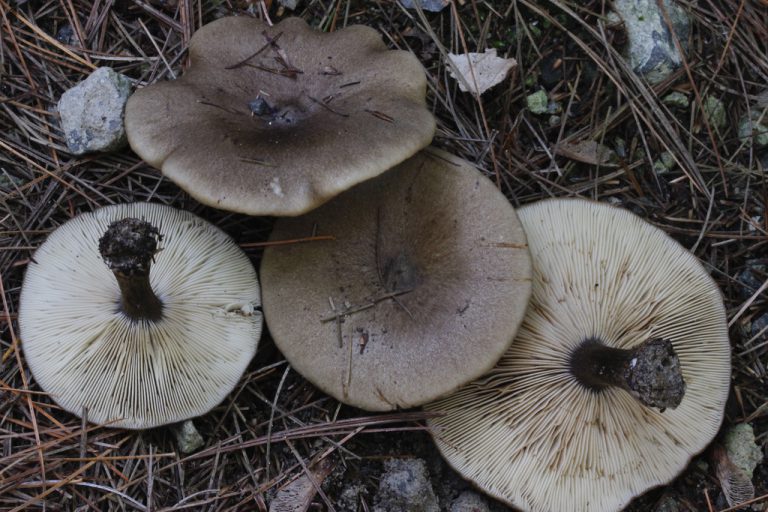
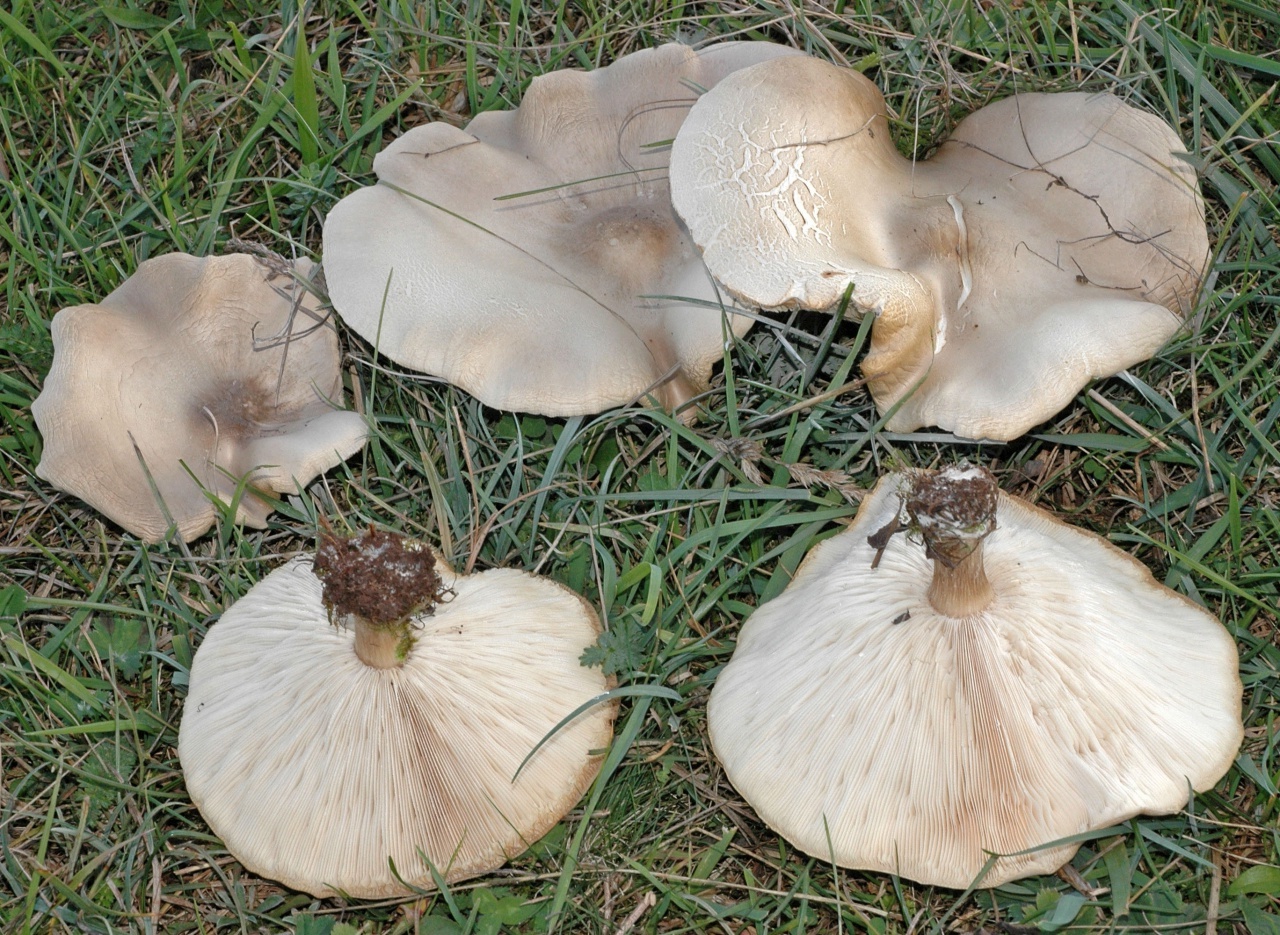
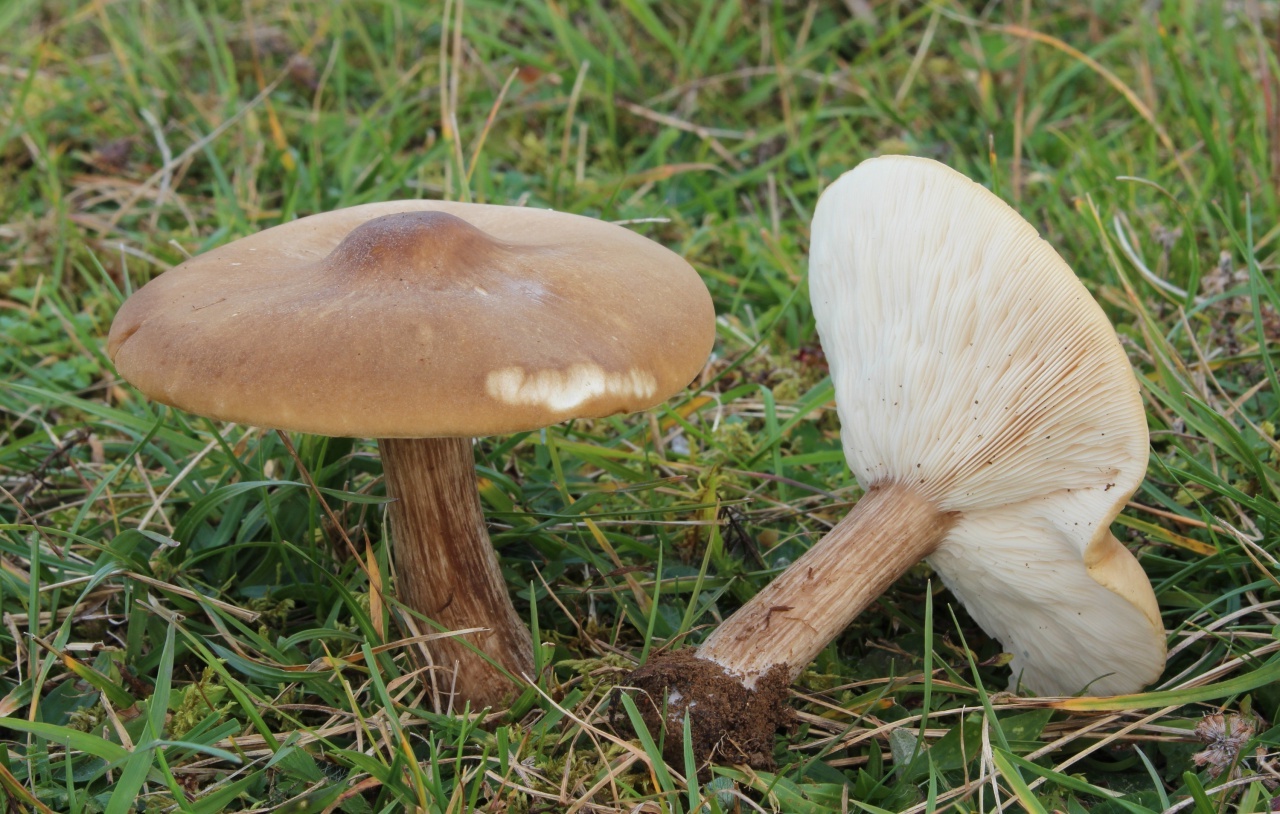
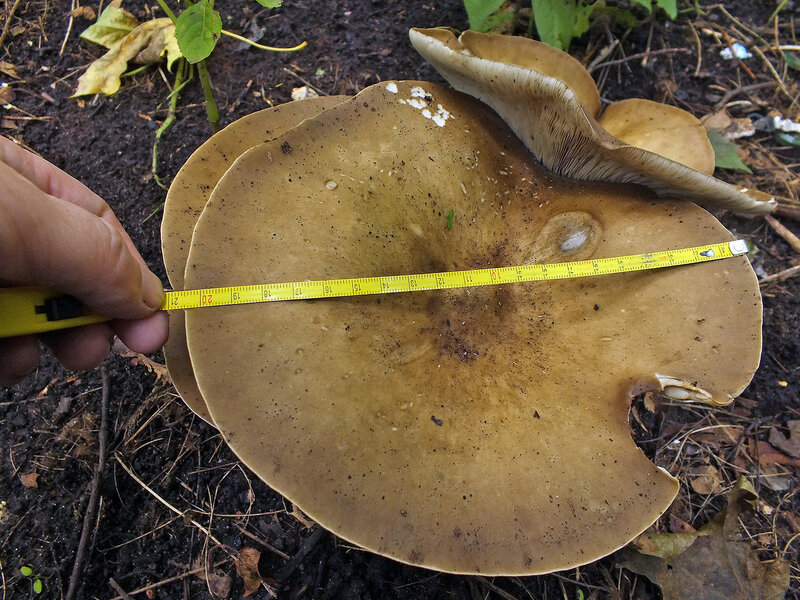
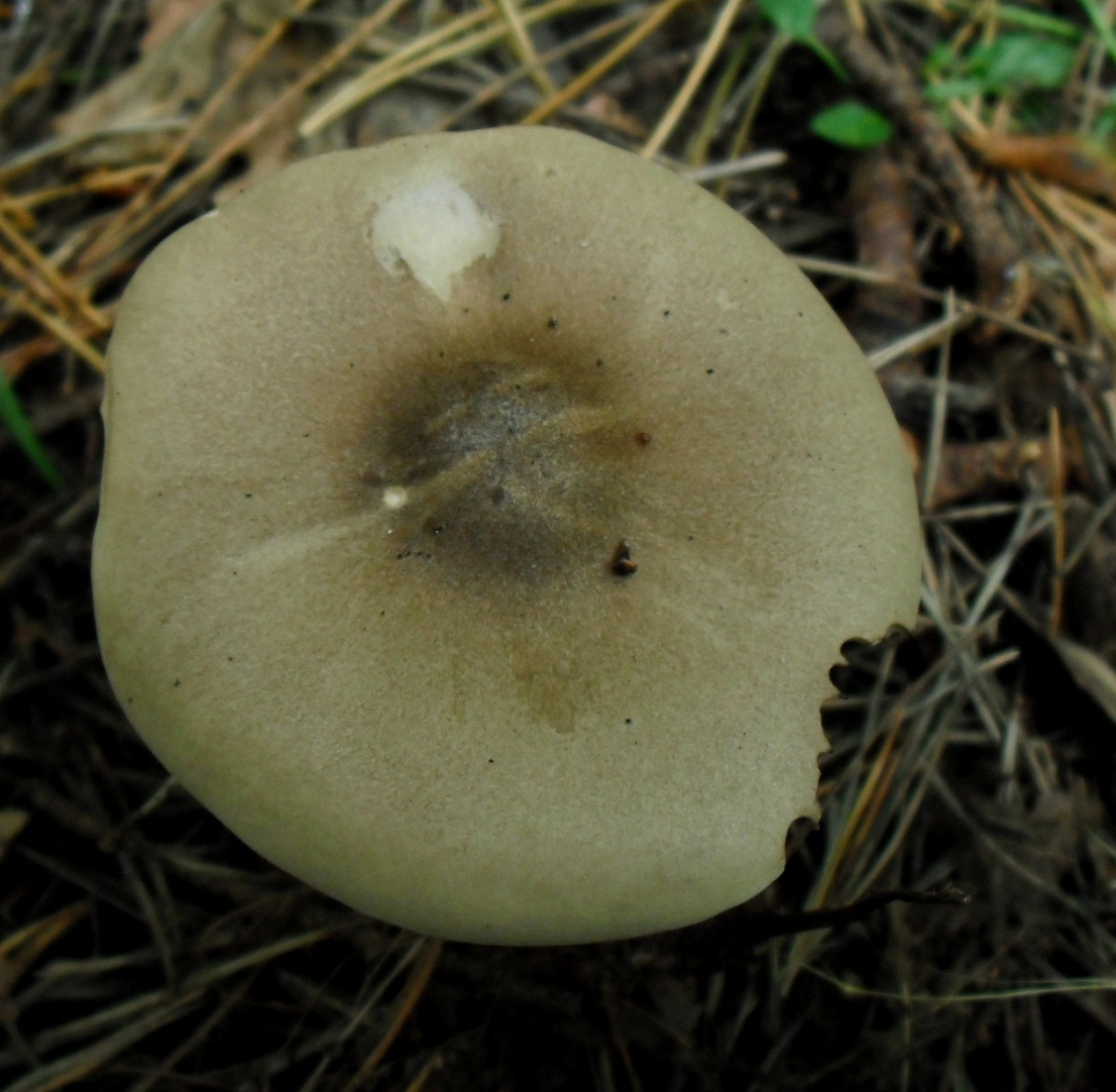
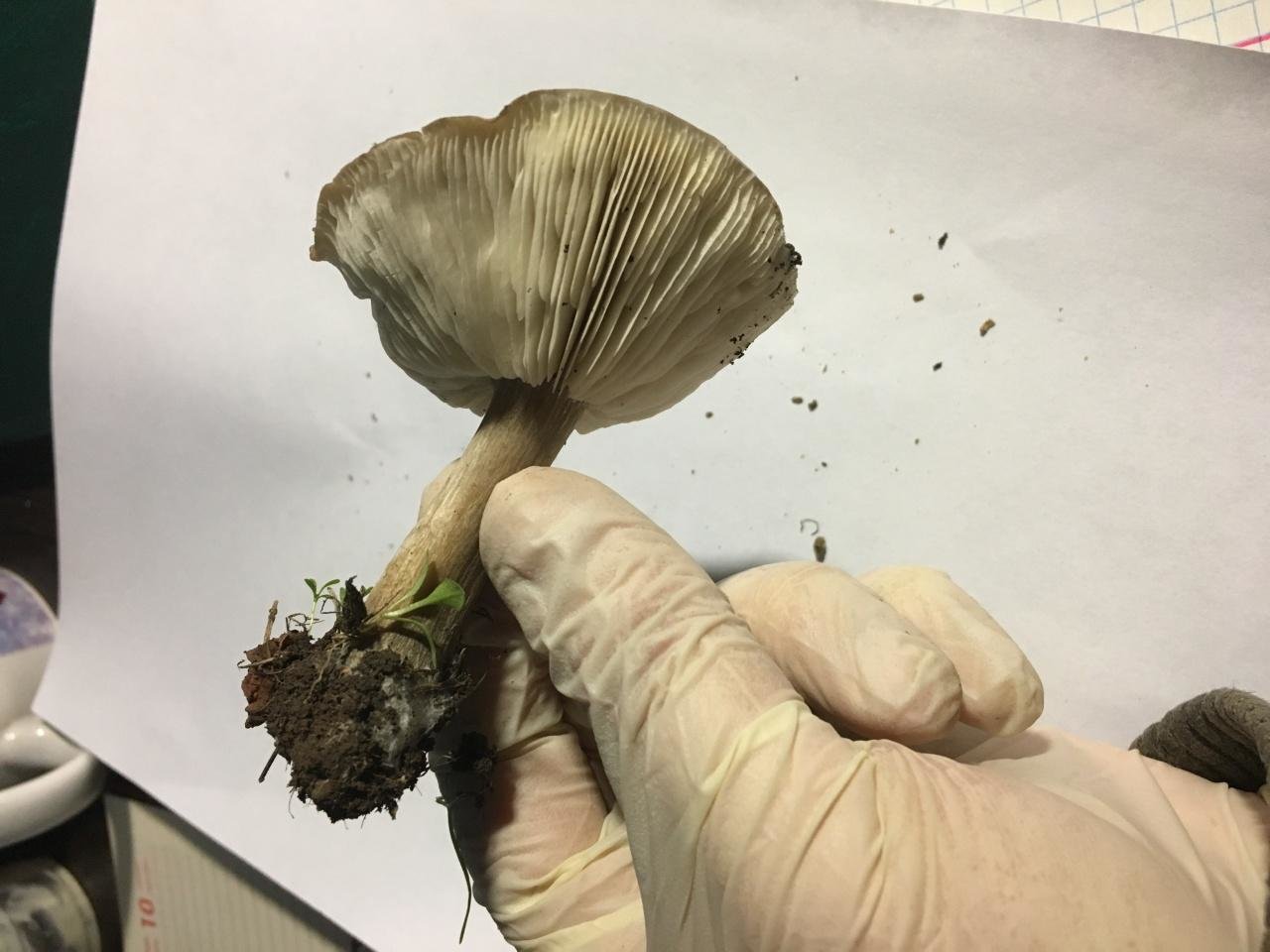
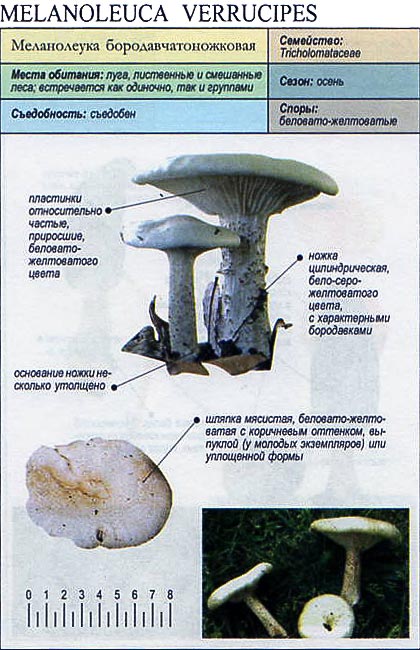
Hat
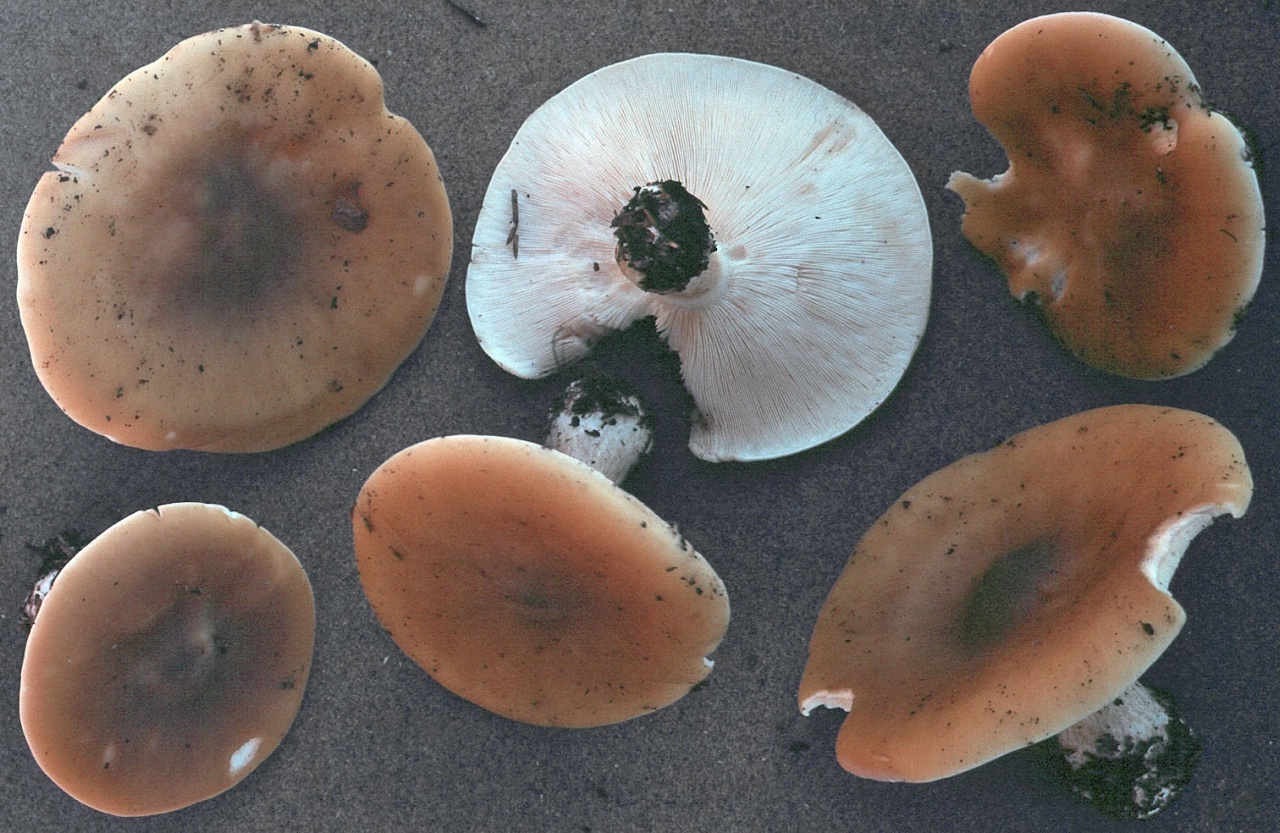
The cap of the mushroom is convex, in the process of growth it gradually flattens, becoming prostrate, with a slight bulge in the middle. Its diameter is about 10 cm. The surface of the cap is smooth, matte, with a slightly pubescent edge, painted in a grayish brown color. In hot dry summers it fade to a pale brown color, retaining its original color only in the center.
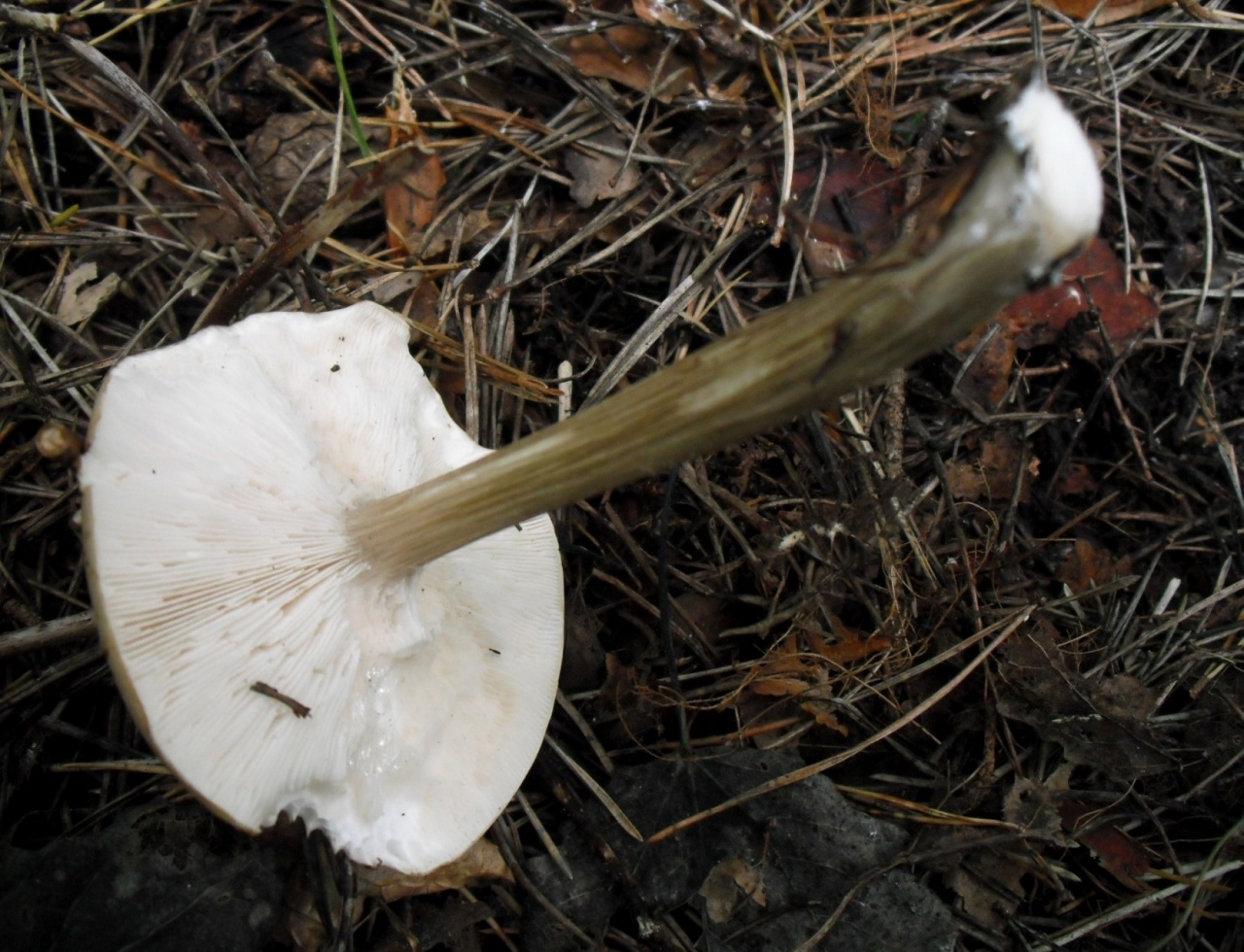
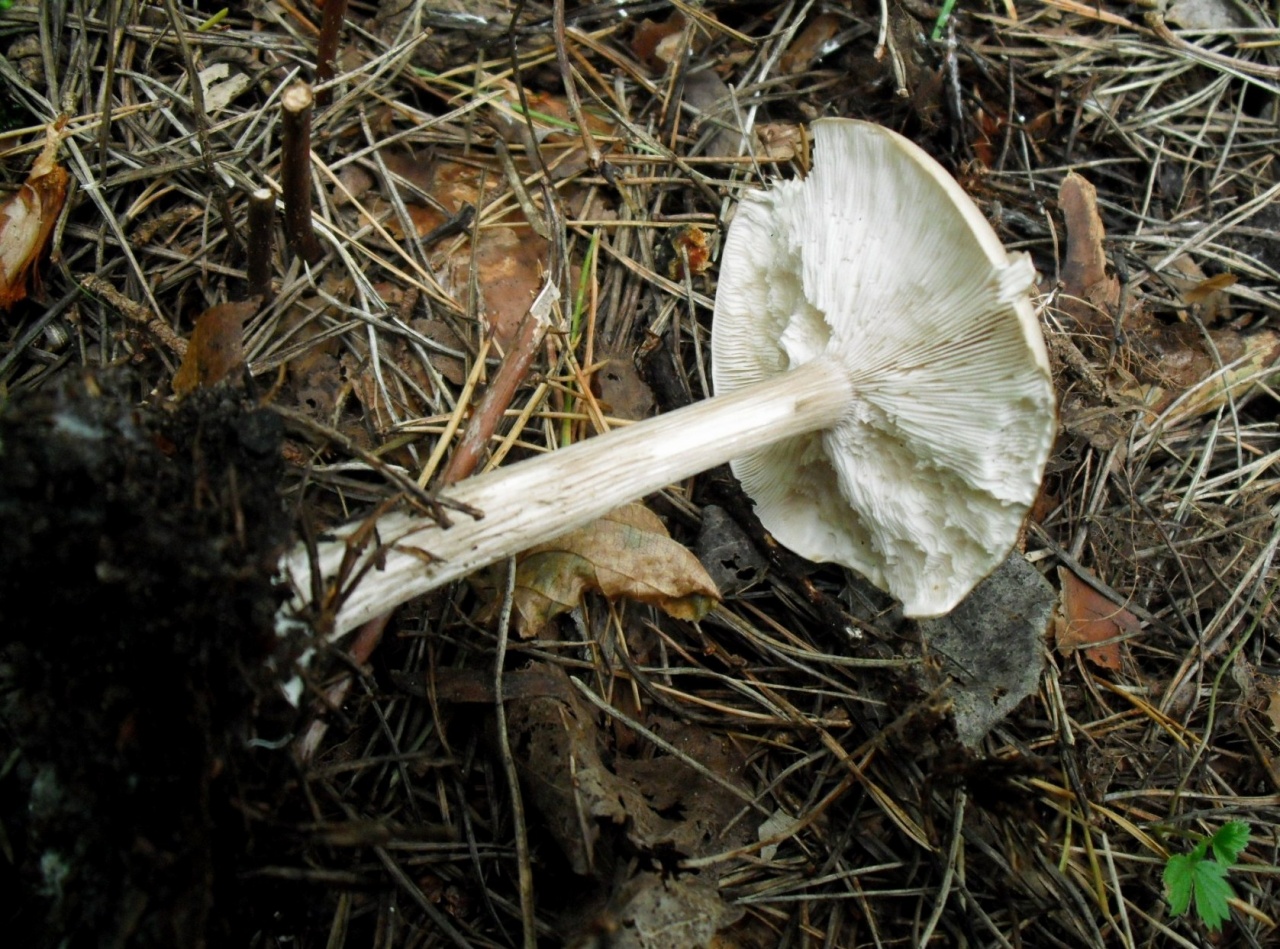
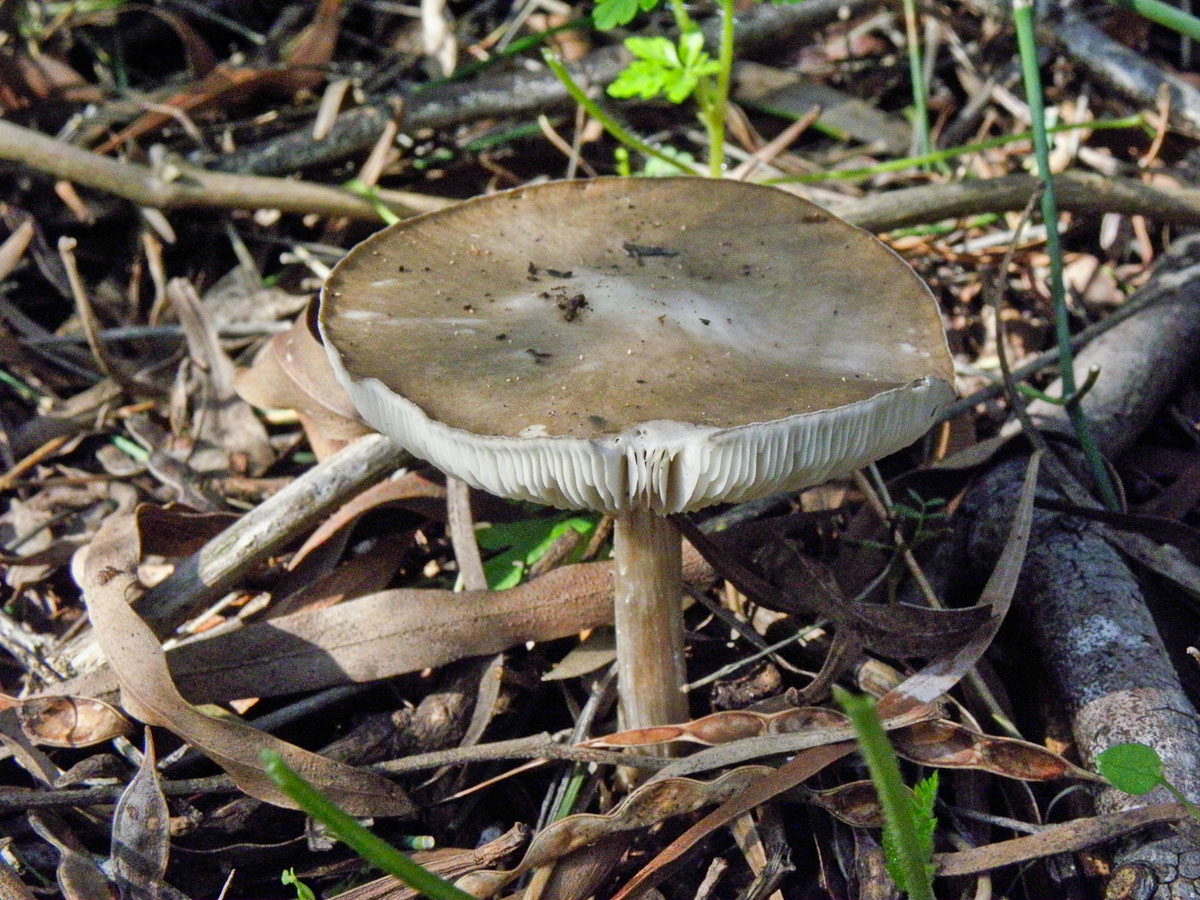
Leg
Stem thin, rounded, 5-7 cm long and about 0.5-1 cm in diameter, slightly widened, with a root nodule or curved to the side, dense, fibrous, longitudinally ribbed, with longitudinal black hair fibers, brownish-brownish. Its surface is matte, dry, brownish in color, on which longitudinal black furrows are clearly visible.
Pulp
The flesh in the cap is soft, loose, elastic in the stem, fibrous, initially light gray, brown in mature mushrooms. Has a subtle spicy scent.
Places and times of collection
Melanoleuca black and white most often settles on rotting brushwood and fallen trees in forests.
In deciduous and mixed forests, parks, gardens, meadows, glades, forest edges, in light, usually grassy places, along the roadsides. Singles and in small groups, not often.
In the Moscow region, it is often found throughout the region from May to October.
Edibility
It is considered an edible mushroom, used fresh (boiled for about 15 minutes).
No poisonous species are found among representatives of the genus Melanoleuca
It is better to collect only caps that can be boiled or fried, the legs are fibrous-rubbery, inedible.
The mushroom is edible, little known. It is consumed fresh and salted.
Nutrition for melanoma
General description of the disease
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer that develops from pigment cells (melanocytes). Sometimes the disease affects not only the skin, but the retina, mucous membranes (vagina, oral cavity, rectum).
Prerequisites for the development of melanoma
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light of sensitive skin or radiation, the presence of a large number of freckles or moles, age over 50, nevus trauma, hormonal changes in the body, Dubreus melanosis, genetic predisposition, xeroderma pigmentosa, male sex.
Signs of melanoma are changes in the mole (nevus):
increased growth of a mole, a change in its surface, uneven compaction, weakening or increased color, the appearance of an erythematous border, hair loss in the area of the nevus, pinpoint pigmentation on the skin around the mole, bleeding of the nevus, burning, itching, soreness.
Varieties of melanoma:
- malignant lentig;
- superficially spreading melanoma;
- acral-lentiginous form of melanoma;
- nodular melanoma;
- melanoma with a phase of radial growth that is not classified.
Depending on the causes of the occurrence:
- melanoma, which arises from precancerous melanosis or Hutchinson's melanotic spot;
- melanoma that arises from a blue nevus;
- melanoma that arises from a large pigmented nevus.
Healthy foods for melanoma
The diet for melanoma should be complete, with the required amount of protein, calories and a minimum amount of saturated fat.Try to cook food without fat (steam, in a special pot or in the oven), do not follow extreme diets and do not consume large doses of individual supplements, foods or vitamins. The diet should include:
- green tea;
- spices (camun, turmeric, cumin, saffron and rosemary);
- fish rich in omega-3 acid (salmon, sardine, mackerel, tuna);
- foods with unsaturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats (sunflower, soy, corn oil, fish oil, olives and peanuts);
- boiled or raw vegetables;
- fruits and fresh fruit juices (apples, cherries, blueberries);
- low-fat and natural dairy products (milk, yogurt, kefir and cheese);
- complex hydrocarbons (bran bread, durum pasta, brown rice, porridge);
- simple, purified water in large quantities;
- Selenium-containing foods (baked chicken breast, turkey, low-fat homemade cheese, selenium-fortified bread, cheddar cheese, Brazil nuts, pork and lamb kidneys, lobster, squid, mussels, oysters, shrimps);
- cruciferous vegetables (Brussels sprouts and cabbage, cauliflower, kohlrabi, broccoli, Chinese cabbage, radish, turnip, horseradish and rutabaga);
- wasabi sauce;
- kelp (seaweed);
- lycopene (natural ketchup, tomato sauce, fresh tomatoes, tomato juice);
- leafy greens (parsley, dill, celery, spinach, green onions, rhubarb, watercress, parsnips, sorrel, wheat germ, edible seaweed);
- dietary fiber (components of plant cells, fiber).
Folk remedies for melanoma
- stone oil (five grams of stone oil per 0.5 liters of water, insist for three days, drain the resulting residue) to use for frequent lotions;
- kirkazon root (half a glass of crushed root, one teaspoon of sour cream, pour a glass of honey with 3 liters of water, insist warm for a week), take half a glass before meals for two months;
- Lycopodium pollen is used to dust the affected skin;
- decoction of lycopodium (boil one spoonful of pollen for fifteen minutes in a glass), take one glass a day;
- use juniper berries for compresses in gauze;
- use yeast (thick solution) for compresses, covering with a thin towel on top;
- marshmallow primark (in equal proportions, pour the flowers or root with water, boil for fifteen minutes, insist for two hours);
- freshly squeezed sea buckthorn juice.
Dangerous and harmful foods for melanoma
Exclude the following foods: fatty foods and foods high in trans fats (lard and fatty meats, butter and ghee, mayonnaise, pizza, burgers, sandwiches, fast food, fatty pork and beef, milk chocolate, sweets, fried foods, pastries, ice cream, coffee and milkshakes).
Limit the use of such products as: foods containing omega-6 (eel fat, vegetable oils (rapeseed, linseed, cottonseed, sunflower, soybean, hemp, safflower), pumpkin and sunflower seeds, nuts (pine nuts, pistachios), eggs, offal, animal fats and butter).
Diet for skin melanoma
The diet for melanoma should contain as little saturated fat as possible, contain the entire complex of vitamins and minerals. It is recommended to steam or bake or boil food. The following types of foods are recommended:
- Sea fish, squid, mussels, oysters, shrimps.
- Olives, olive oil, peanuts, soybeans, sunflower.
- Green tea.
- Boiled and baked vegetables.
- Raw vegetable salads.
- Fruit juices and fresh fruits.
- Low fat dairy products.
- Various types of cereals, durum pasta, bran bread.
- Various types of low-fat cheeses.
- Turkey meat, chicken.
- Seaweed salads.
- Cruciferous vegetables.
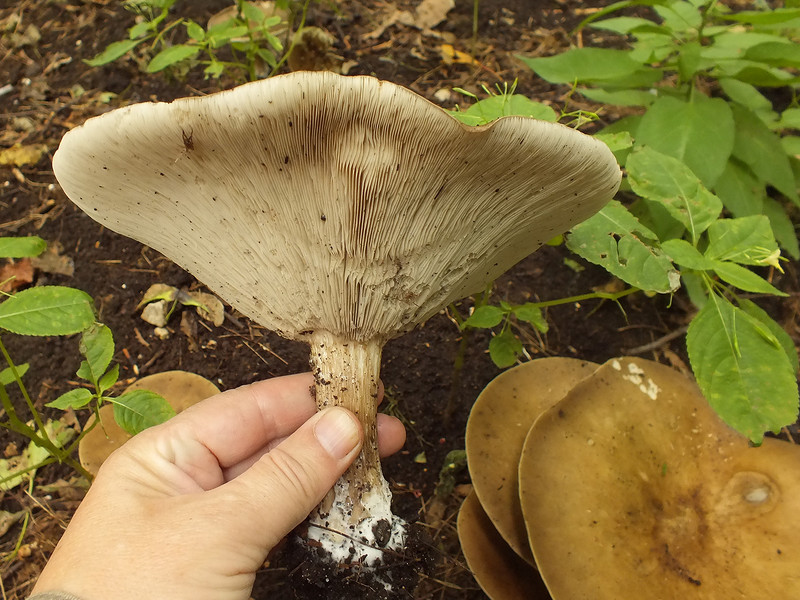
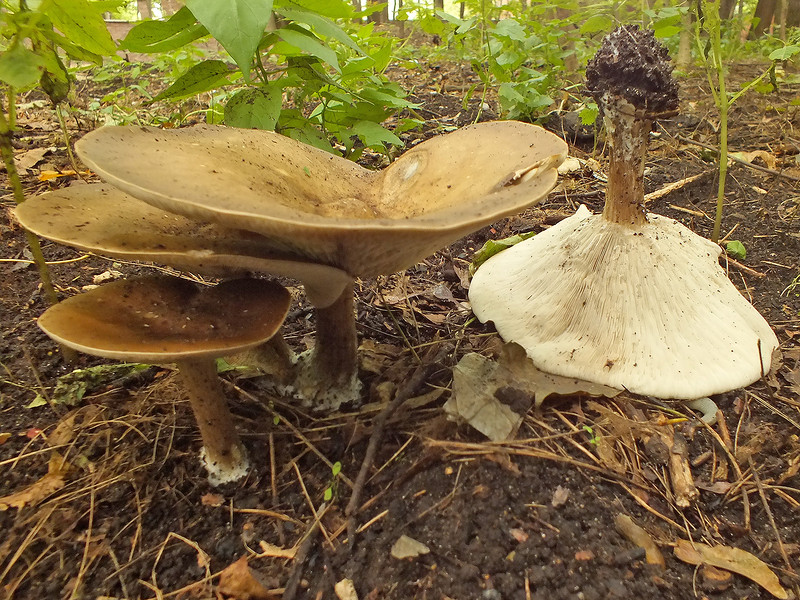
Description
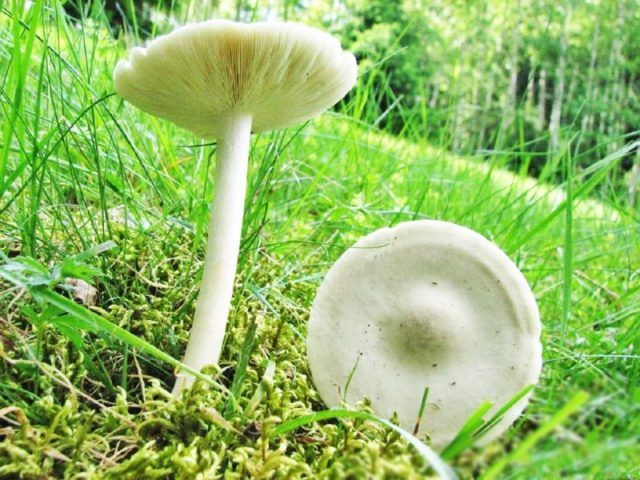
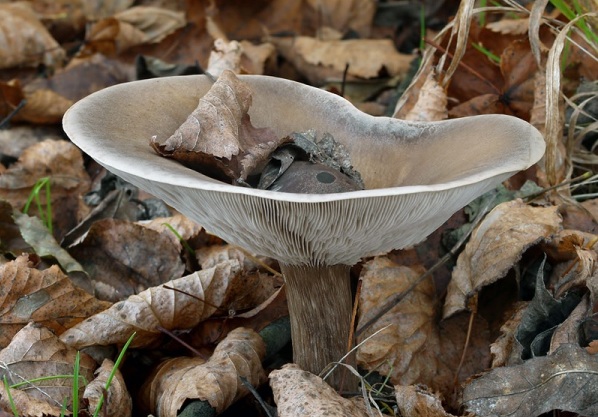
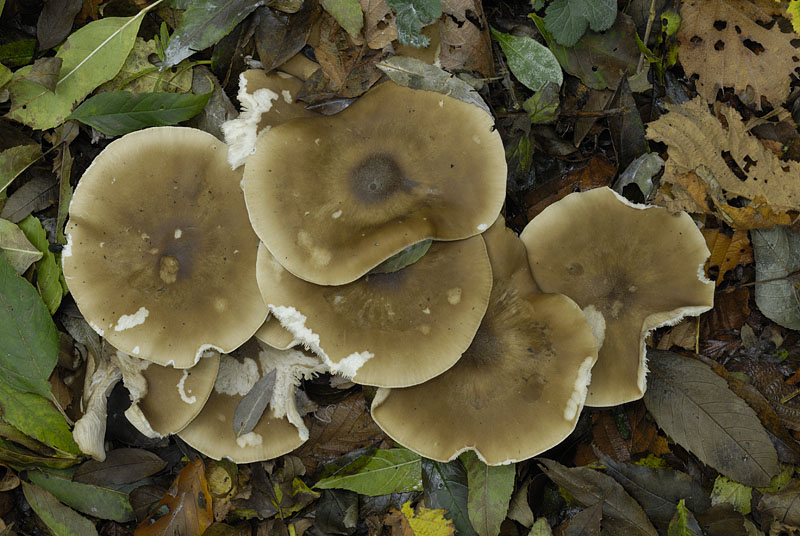
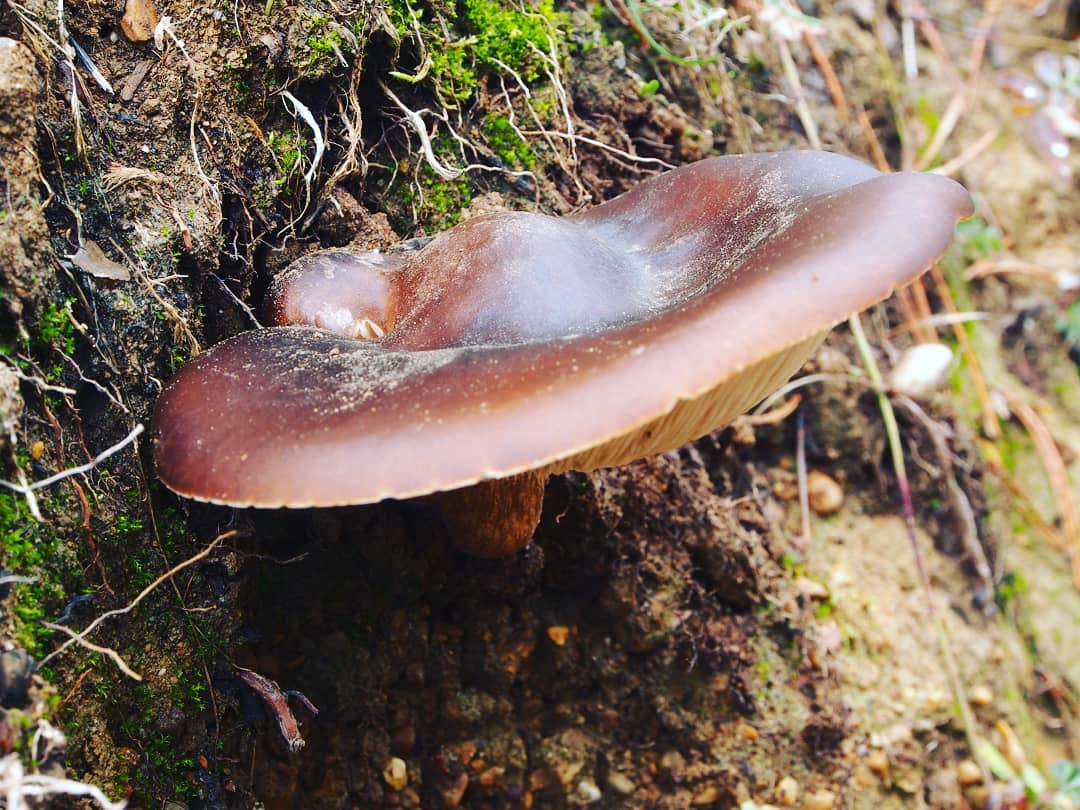
Hat
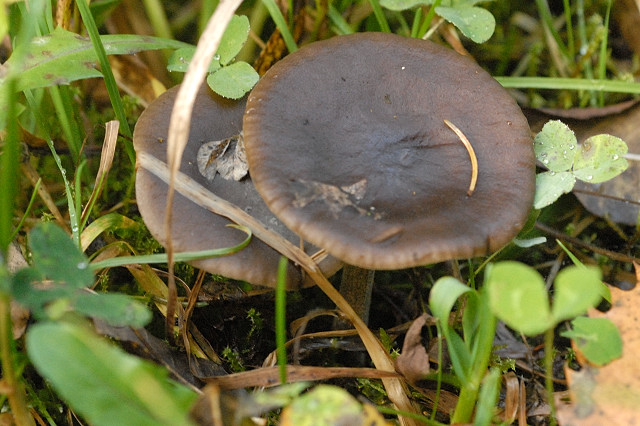
In a young mushroom, it has the shape of a hemisphere, then gradually straightens out, becoming almost flat, depressed in the center, with a small central tubercle. It grows in diameter about 10 cm, sometimes up to 14 cm.
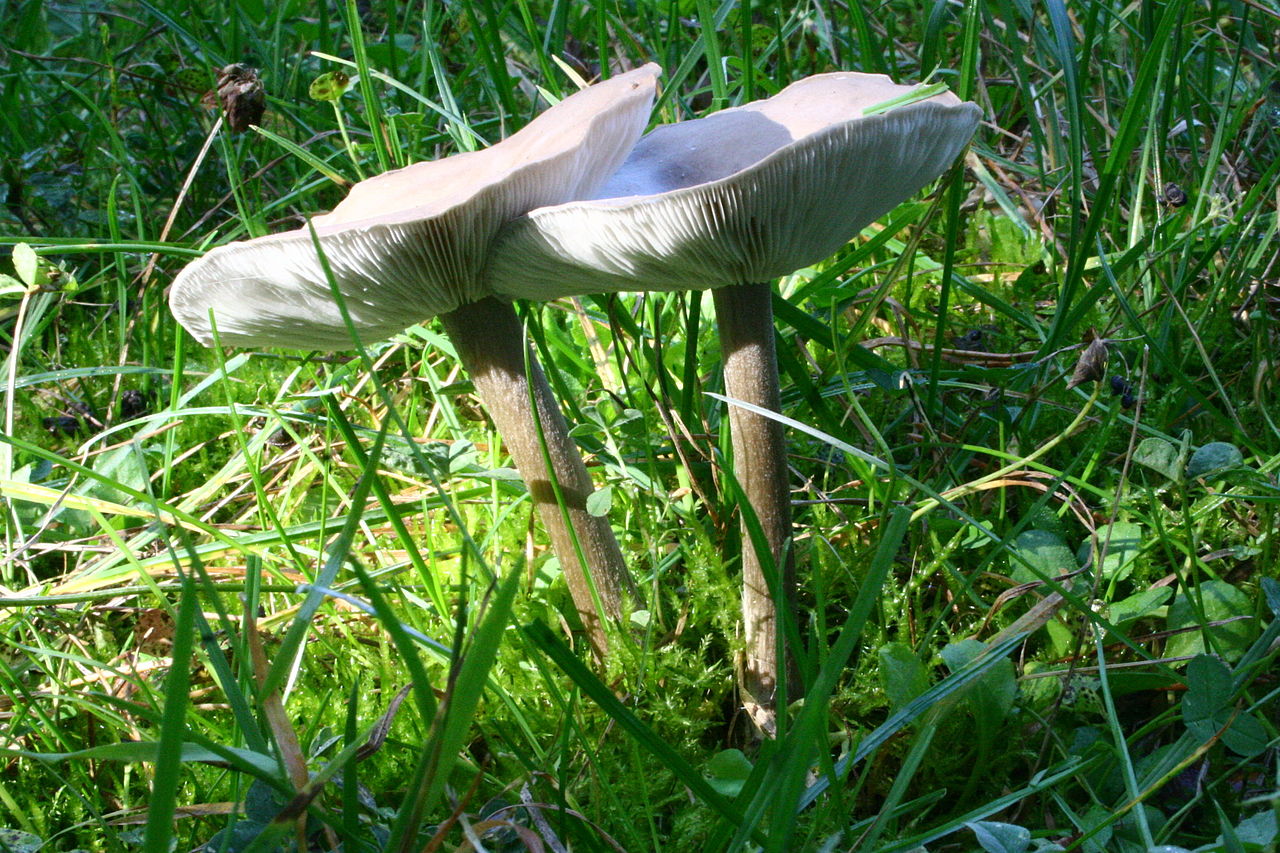
The structure of the cap is dense, elastic.The outer edge is almost always curled inward. The surface of the cap is smooth, matte, dry. The color of the young mushroom is deep gray, almost black. As it grows and ages, the cap gradually lightens, becoming light gray or gray-brown at the end of its life cycle.
Spore-bearing layer
Lamellar. It is colored grayish-white; it darkens a little by old age. The arrangement of the plates is frequent, the plates themselves are wide, adhered to the pedicle by a tooth. Spore white powder, ellipsoidal spores.
Leg
It grows in length only up to 3-4 cm, in diameter about 1 cm. The structure of the leg is dense, with longitudinal fibers, rather hard. The pulp is solid, without voids and cavities. Sometimes, especially in young mushrooms, it has an irregular shape, twisted or bent. Colored a tone darker than the cap.
Pulp
The hat is white, elastic. If damaged, it does not change color, does not emit milky juice. In the leg it is colored brown in different intensities, solid. Has a neutral taste and a weak flour aroma.
Distribution and collection
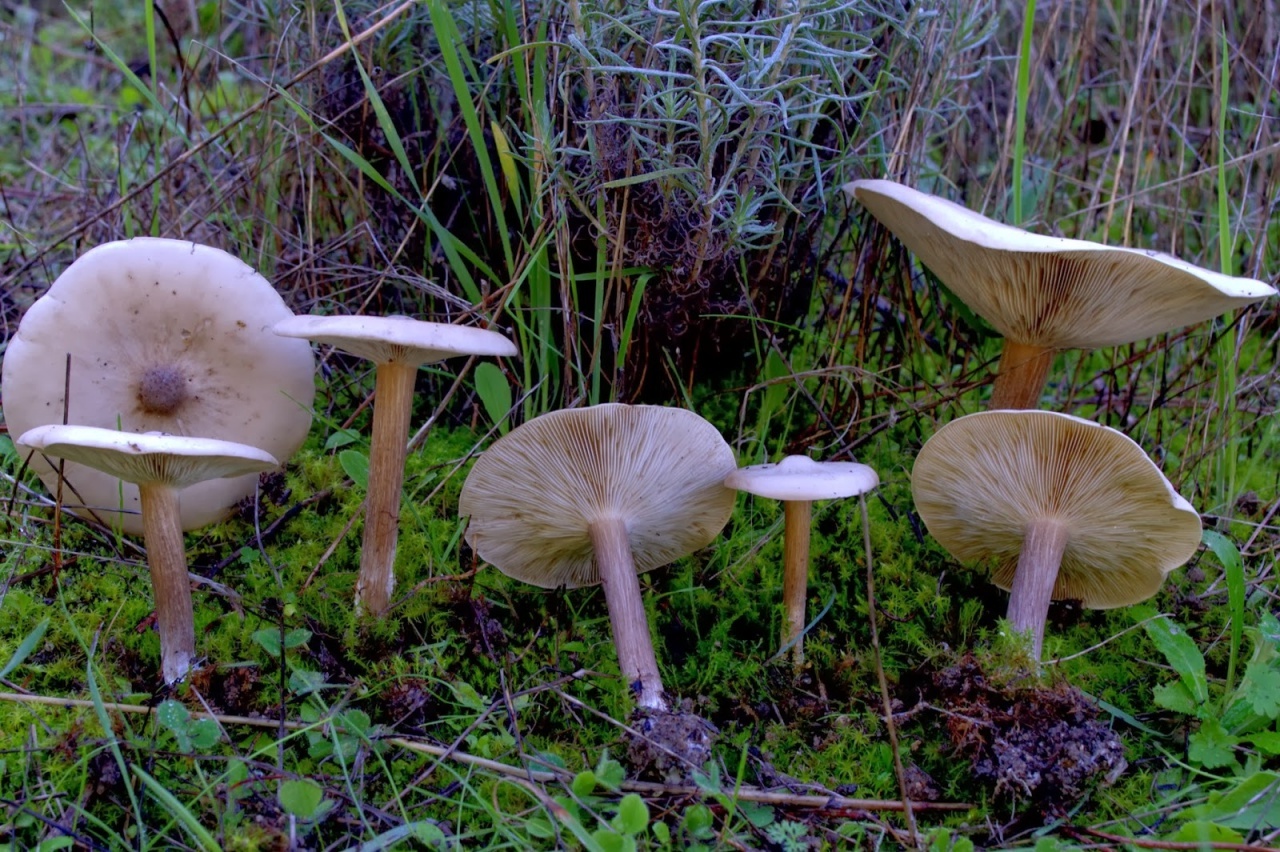
Melanoleuca short-legged often settles near human habitation. Prefers open grassy terrain, often grows on abandoned agricultural land, on pastures and pastures, on the side of roads and paths, in parks and squares. It grows most often in small groups. The geography of distribution is quite wide, this mushroom can be found throughout the temperate forest belt of Russia. It is rare.