Maintenance and care, arrangement of the aquarium
For a group of 3-4 fish, a tank with a volume of 60 liters or more will be sufficient. The design should provide for a large amount of aquatic vegetation, both floating on the surface and rooting, while maintaining open areas for swimming. Any substrate, selected based on the needs of plants
Various decorative elements are not very important and are placed at the discretion of the aquarist Please note that the aquarium should be equipped with a lid to prevent accidental jumping of the fish, and the equipment (primarily the filter) is adjusted so as not to create excessive internal flow, to which Afiosemion Gardner is not accustomed ... Otherwise, it is a very unpretentious species that does not require special personal care.
To maintain optimal living conditions, it is enough to replace part of the water (15–20% of the volume) with fresh water on a weekly basis and regularly clean the soil from organic waste.
Conditionally edible
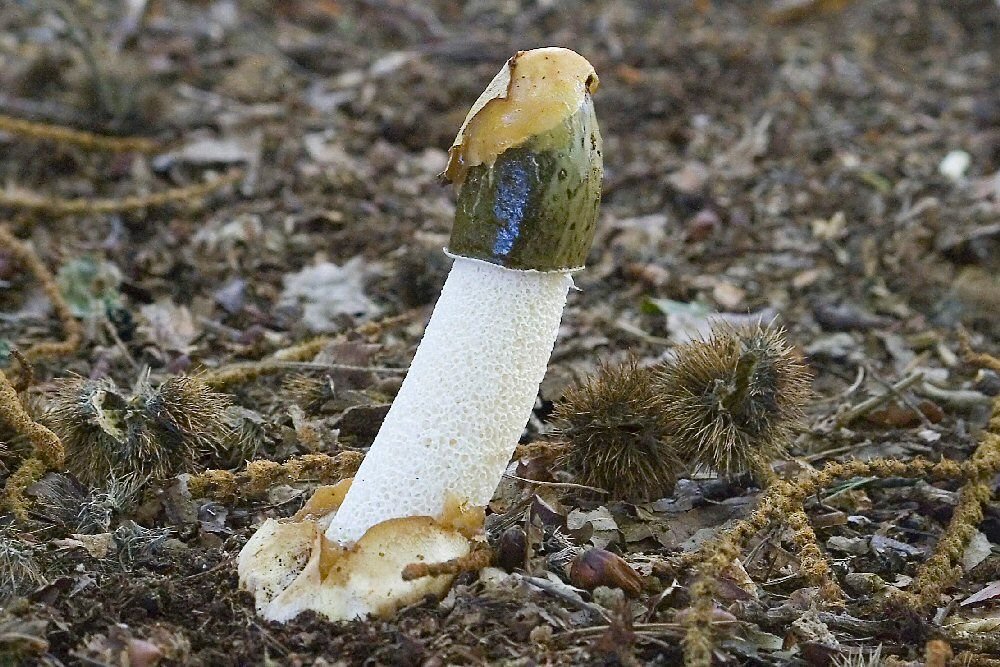
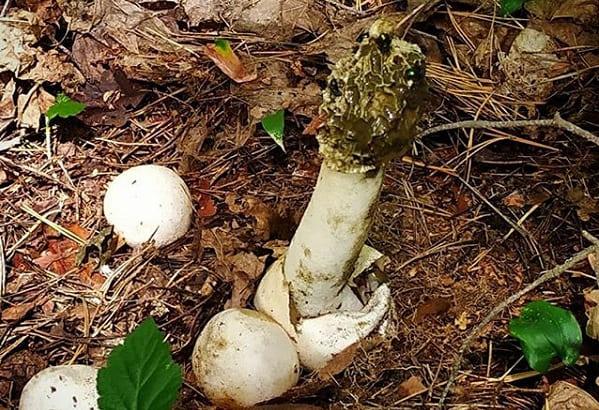
There are slightly fewer conditionally edible varieties, and they are suitable for consumption only after special heat treatment. Depending on the variety, you need to either cook it for a long time, periodically changing the water, or simply soak it in clean water, squeeze it and cook.
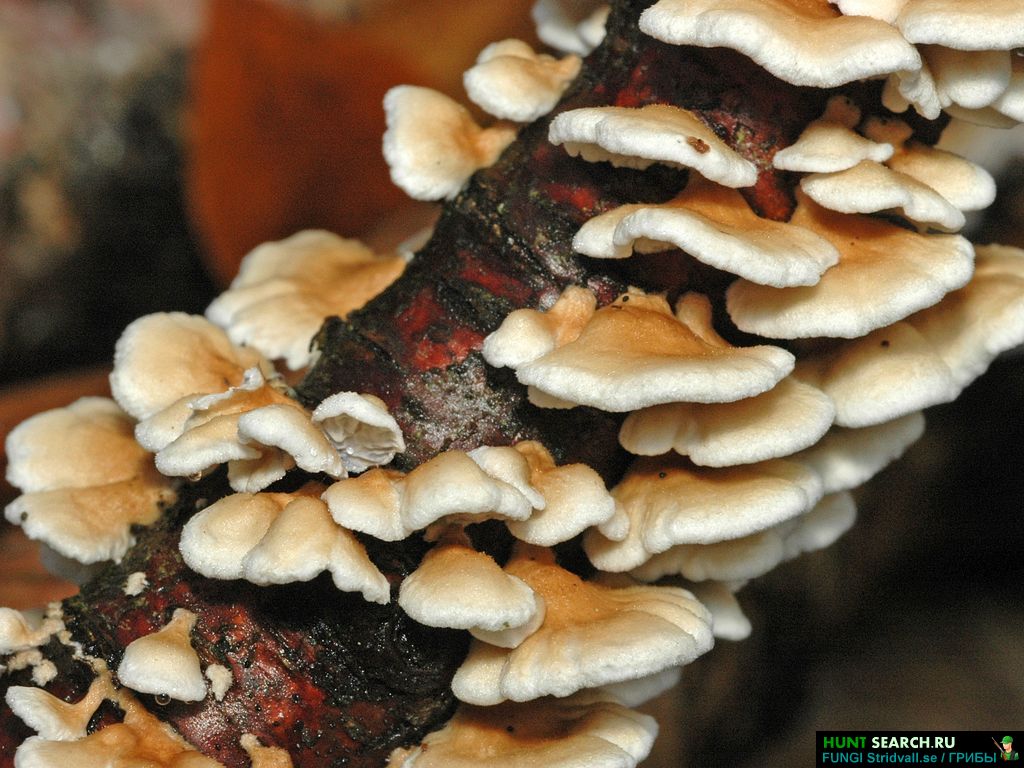
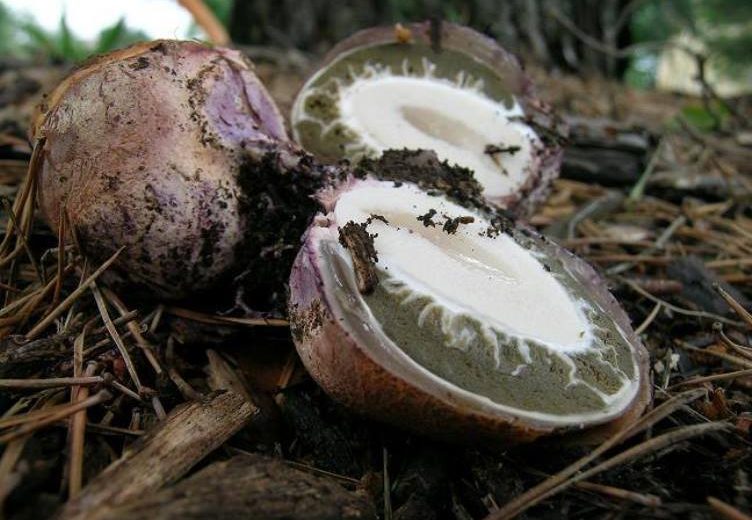
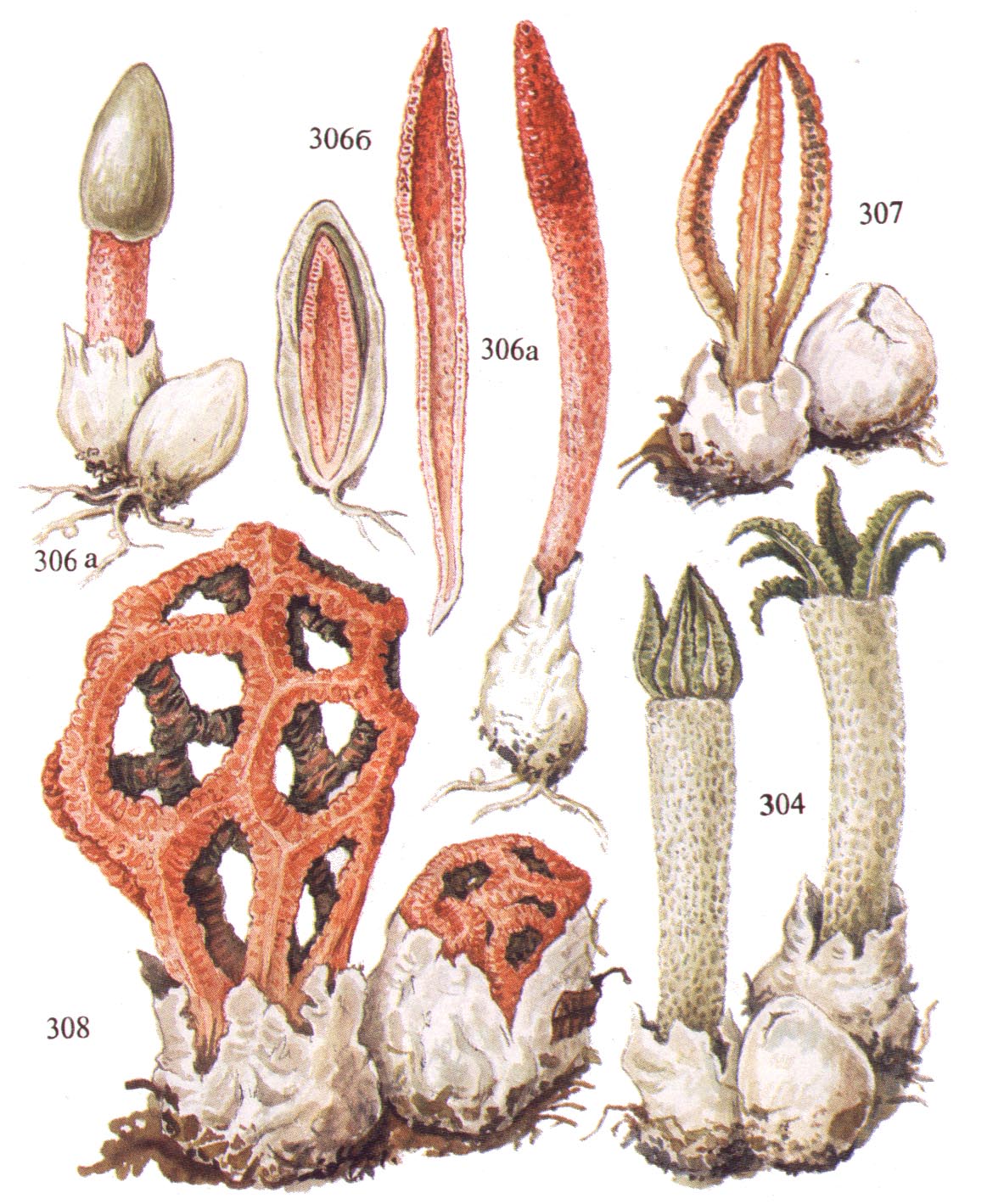
The most popular conditionally edible varieties include (Figure 4):
Some types of truffles, russula and fly agaric are also classified as conditionally edible.
But there is one important rule that you should adhere to when collecting any mushrooms, including conditionally edible ones: if you have even small doubts about edibility, it is better to leave the prey in the forest.
Inedible mushrooms: photos and names
Inedible species are those that are not eaten due to health hazards, poor taste, and too hard flesh. Many representatives of this category are completely toxic (fatal) to humans, others can cause hallucinations or mild discomfort.
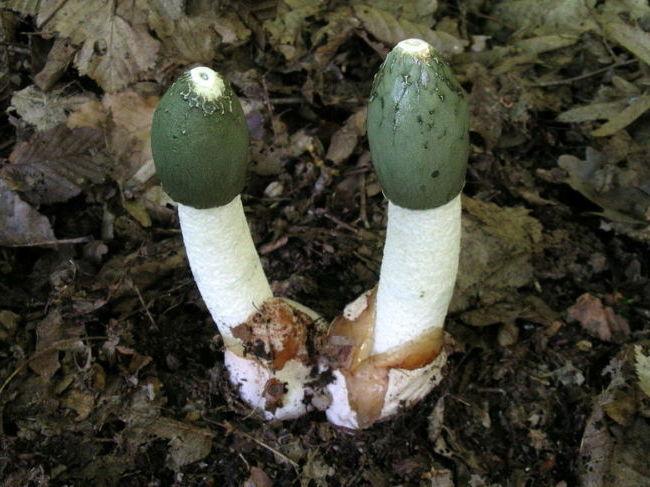
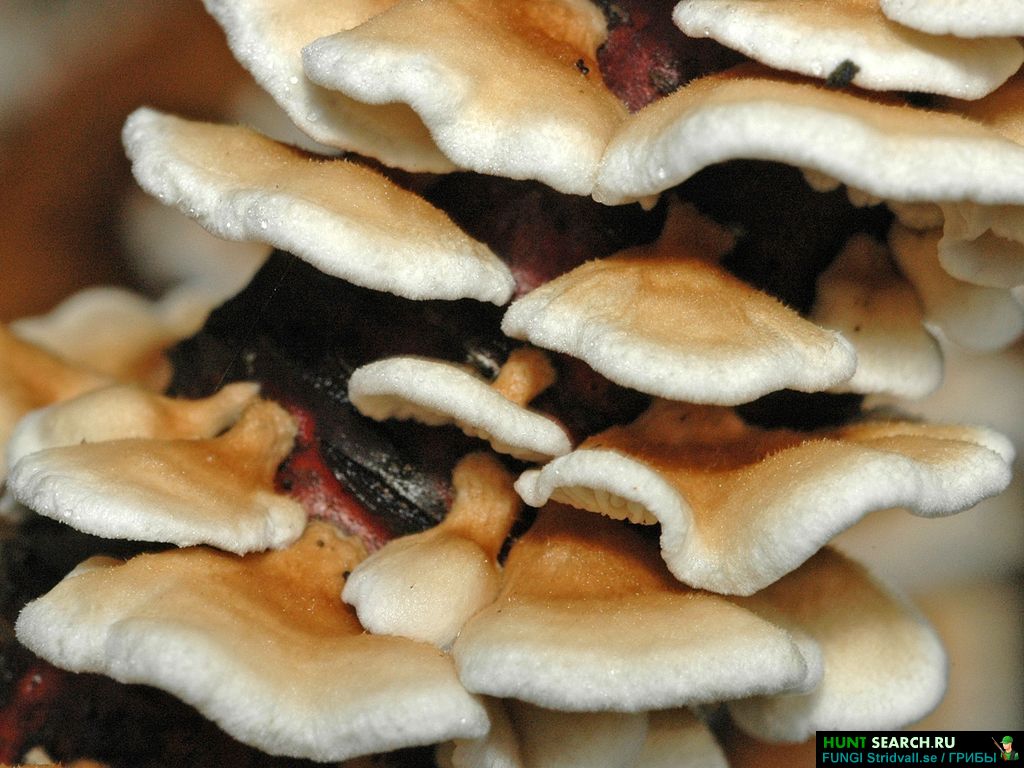
It is worth avoiding such inedible specimens (with photos and names in Figure 5):
In fact, every edible double has a false double that disguises itself as a real one and can end up in the basket of an inexperienced hunter of a quiet hunt. But, in fact, the greatest mortal danger is the pale grebe.
Note: Not only the fruit bodies of pale toadstools are considered poisonous, but even their mycelium and spores, therefore it is strictly forbidden to even put them in a basket.
Most of the inedible varieties cause abdominal pain and symptoms of severe poisoning, and it is enough for a person to receive medical attention. In addition, many inedible varieties are unattractive and low taste, so they can only be eaten by accident. However, you should always be aware of the danger of poisoning, and carefully review all the loot that you brought from the forest.
The most dangerous inedible mushrooms are described in detail in the video.
Types of hallucinogenic mushrooms
The main difference between hallucinogenic and other species is that they have a psychotropic effect. Their action is in many ways similar to narcotic substances, therefore their deliberate collection and use is punishable by criminal liability.
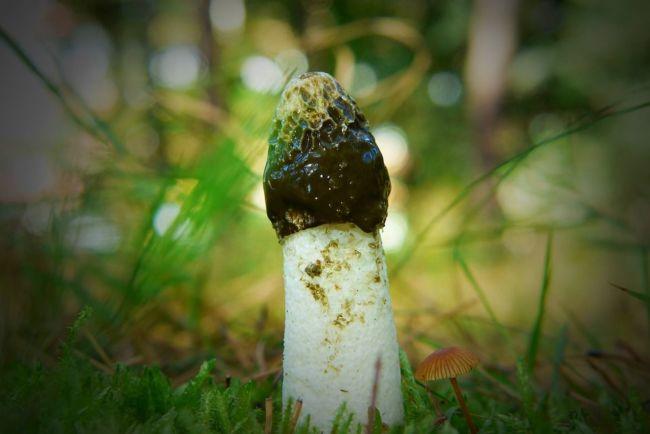
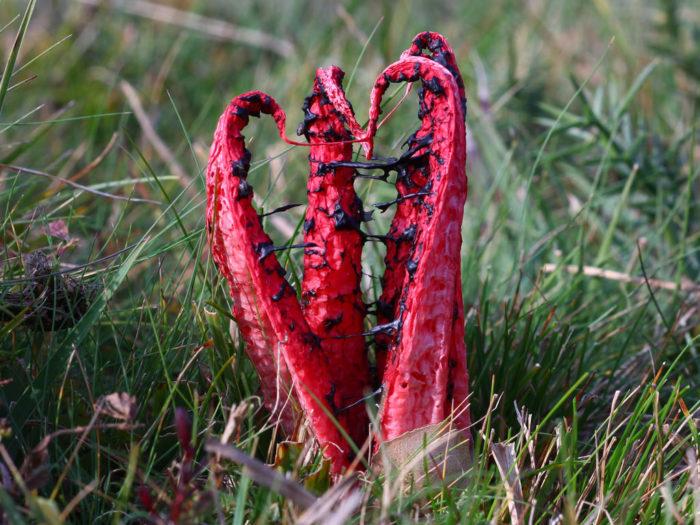
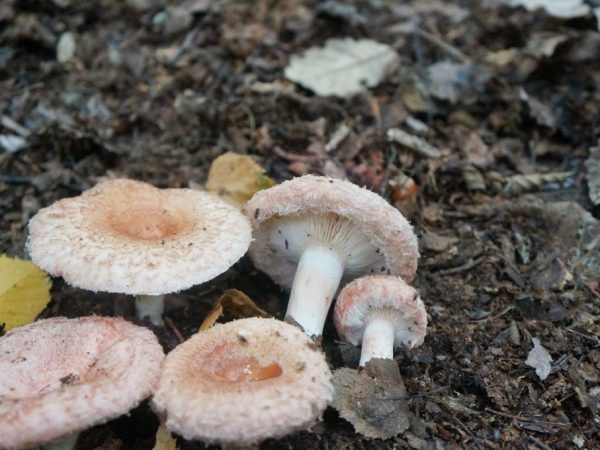
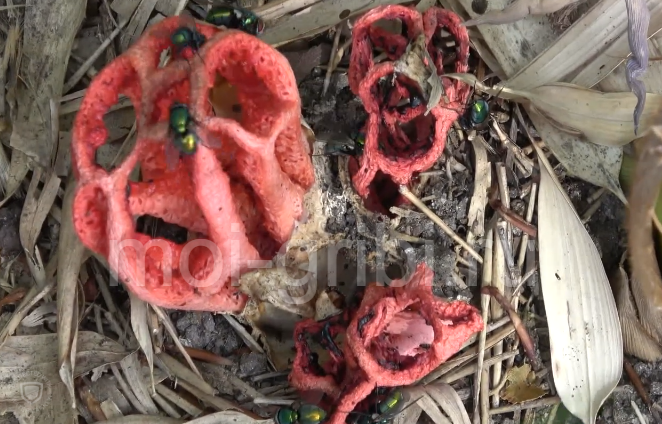
Common hallucinogenic varieties include (Figure 6):
Most hallucinogenic species grow in places where edibles simply won't take root (too swampy soils, completely rotten stumps and heaps of dung). In addition, they are small, mostly on thin legs, so it is difficult to confuse them with edible ones.
Poisonous mushrooms: photos and names
All poisonous varieties are somehow similar to edible ones (Figure 7).Even the deadly pale toadstool, especially young specimens, can be confused with russula.
For example, there are several boletus twins - boletus le gal, beautiful and purple, which differ from the real ones in too bright color of the leg or cap, as well as an unpleasant smell of pulp. There are also varieties that are easy to confuse with mushrooms or russula (for example, fiber and talker). Gall is similar to white, but its pulp has a very bitter taste.
Figure 7. Poisonous twins: 1 - purple boletus, 2 - bilious, 3 - royal fly agaric, 4 - yellow-skinned champignon
There are also poisonous twins of honey agarics, which differ from the real ones by the absence of a leathery skirt on the leg. Poisonous varieties include fly agarics: grebe, panther, red, royal, smelly and white. Cobwebs are easily disguised as russules, mushrooms or aspen mushrooms.
There are also several types of poisonous mushrooms. For example, yellow-skinned is easy to confuse with an ordinary edible specimen, but when heat treated, it gives off a pronounced unpleasant odor.
Edible, conditionally edible and poisonous mushrooms: how to distinguish
Many temptations lie in wait for the mushroom picker in the forest. Either a poisonous mushroom pretends to be edible, then suddenly it beckons a miracle mushroom with its enormous size, or it will lure into the forest mushroom pickers the mass appearance of a "harvest" after the first rains. In all cases, trouble cannot be avoided if you follow the lead of these insidious organisms.
Here are some of the more common temptations.
Into the forest for mushrooms: what to take with you, where to look for prey and how not to get lost
The classifications of poisonous mushrooms are different: either by the presence of poisonous compounds, or by the nature of the effect on the human body. According to the second criterion, three groups of poisonous mushrooms can be distinguished.
1. Deadly poisonous mushrooms with a pronounced plasmotoxic effect
They contain poisonous substances - phalloidin, phalloin, phallocin, phallisin, amanitins, amanin, orellanin, etc. These compounds are found in mushrooms such as pale toadstool, smelly fly agaric, plush cobweb, edged gallerina.
2. Mushrooms affecting the nerve centers
These mushrooms contain poisonous compounds such as muscarine, muscaridin and other neurotropic toxins. These are such species as red fly agaric, panther fly agaric, lemon fly agaric, white talker, whitewashed talker, Gornemann's stropharia, pink mycena, fiber plants and others.
The first signs of poisoning appear after 30 minutes, or even after 2 hours. They are expressed in palpitations, mild sweating, agitation, and a characteristic state that resembles alcohol intoxication. These phenomena disappear after 1–2 hours. There is no mortal danger.
3. Mushrooms with a local stimulating effect
These include the largest number of species, the use of which leads to mild poisoning, accompanied by gastric and intestinal disorders. These are such species, for example, as sulfur-yellow false honey fungus, brick-red false honey fungus, toad rowing and others.
Some researchers classify so-called conditionally edible mushrooms in this group, for which preliminary processing is required - soaking, boiling. The first signs of poisoning appear in 0.5–2 hours. They are expressed in nausea, headache, stomach cramps, dizziness, vomiting and diarrhea. Such poisoning is extremely rarely fatal.
In conventionally edible mushrooms, toxic substances are destroyed during drying, salting, soaking, boiling. They can be divided into several groups:
Mushrooms with a bitter taste (pepper oil can, gall mushroom)
Pepper can be added to food in small quantities as a seasoning - instead of pepper. The gall mushroom looks like a porcini mushroom, but with pinkish tubules and a bitter taste. Even a small piece of it can spoil the taste of the whole dish. It is noticed that the mushroom loses its bitterness when dried. Therefore, in a number of localities it is collected, dried, and then used for food.
Mushrooms with a burning, pungent taste (some russula, volushkas, bitters, milkers)
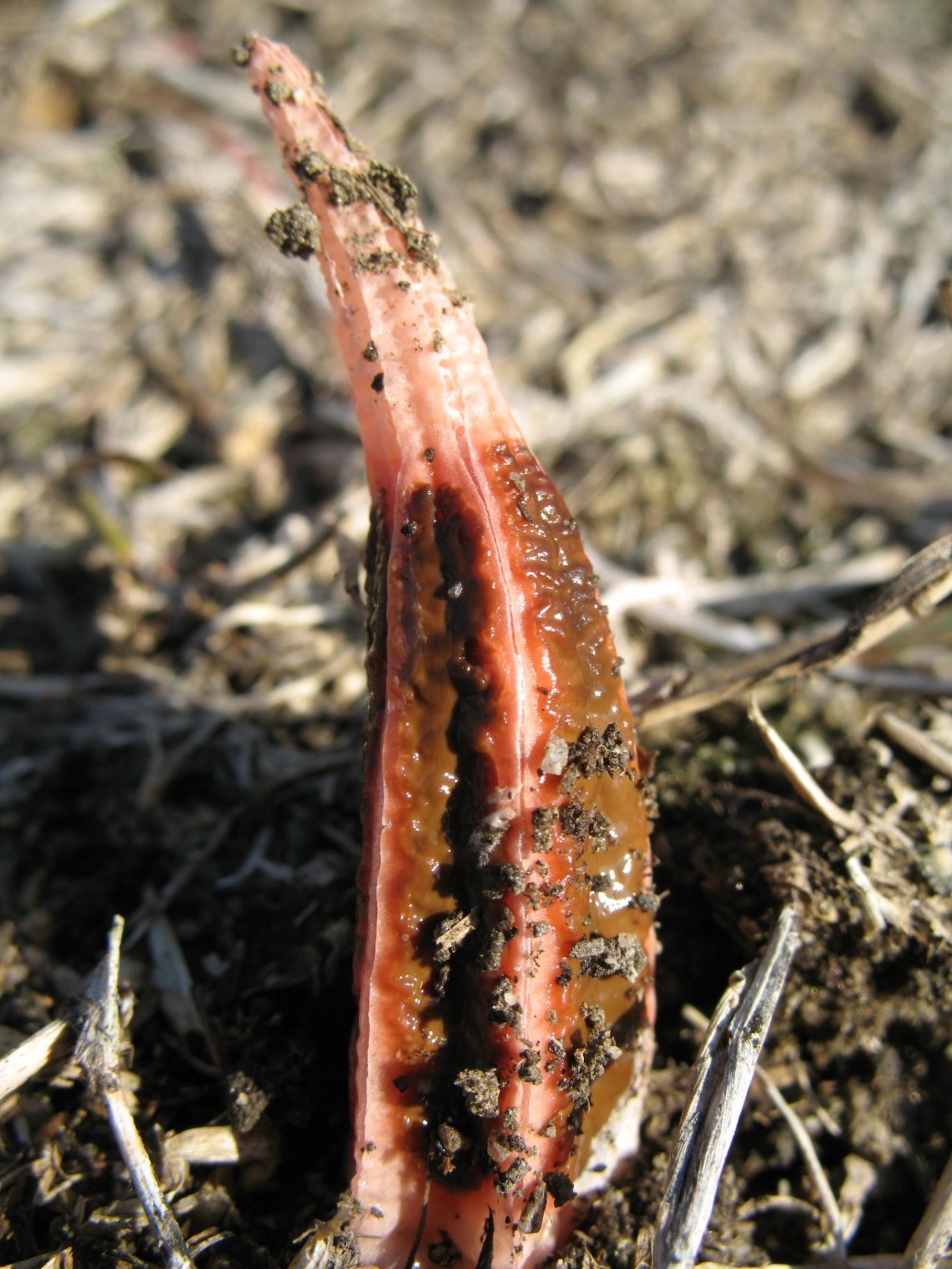
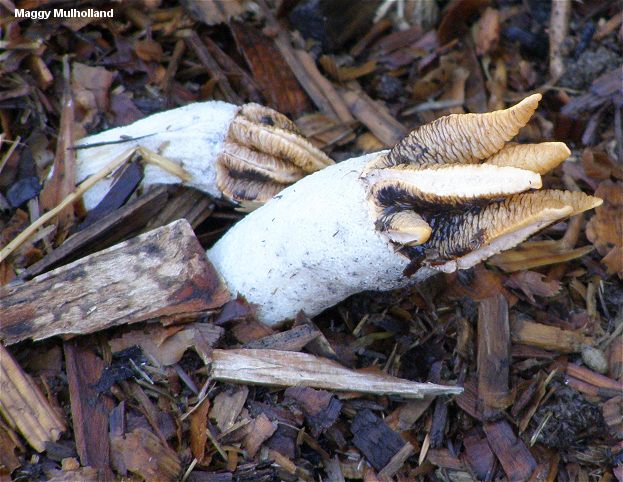
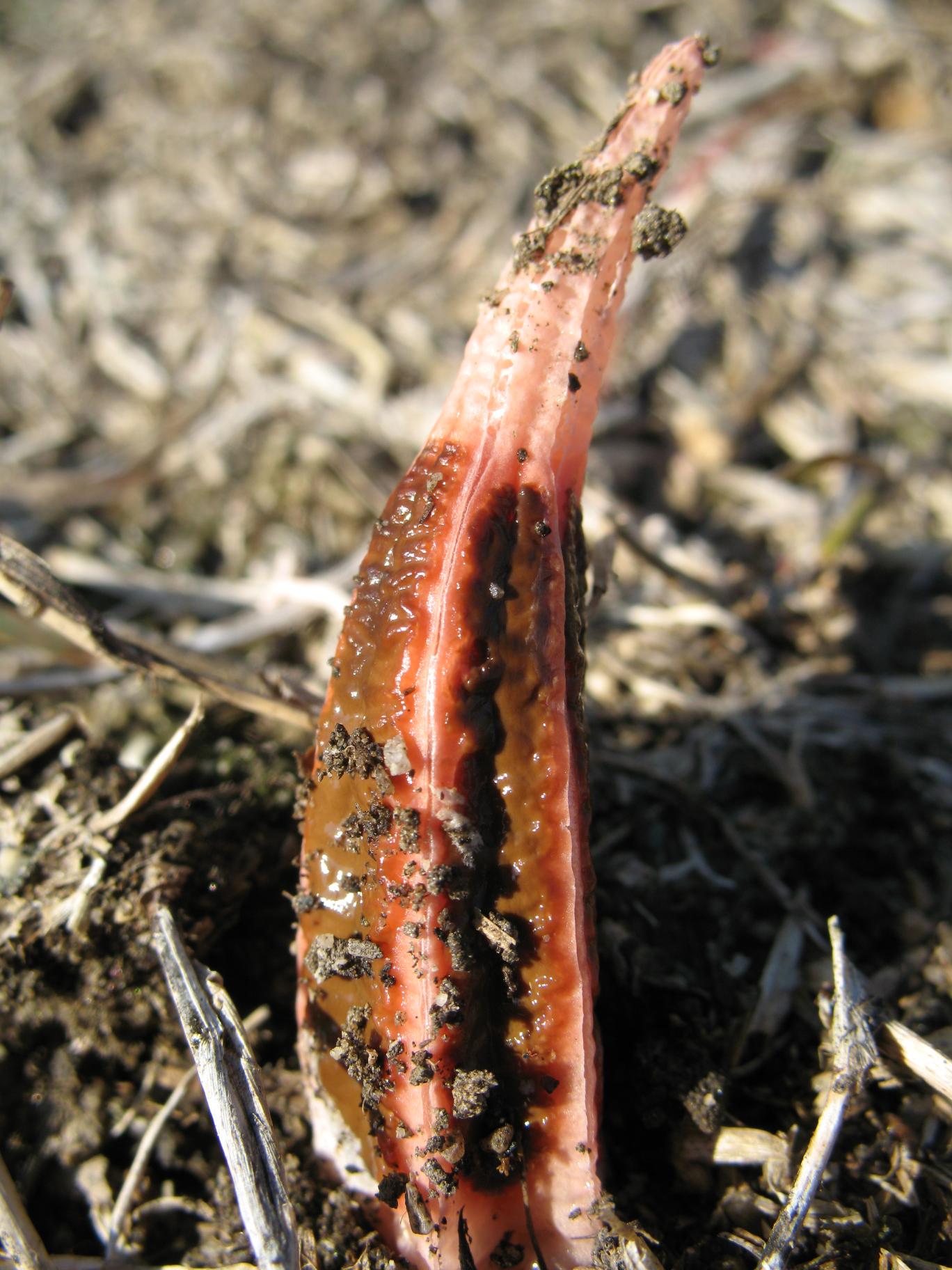
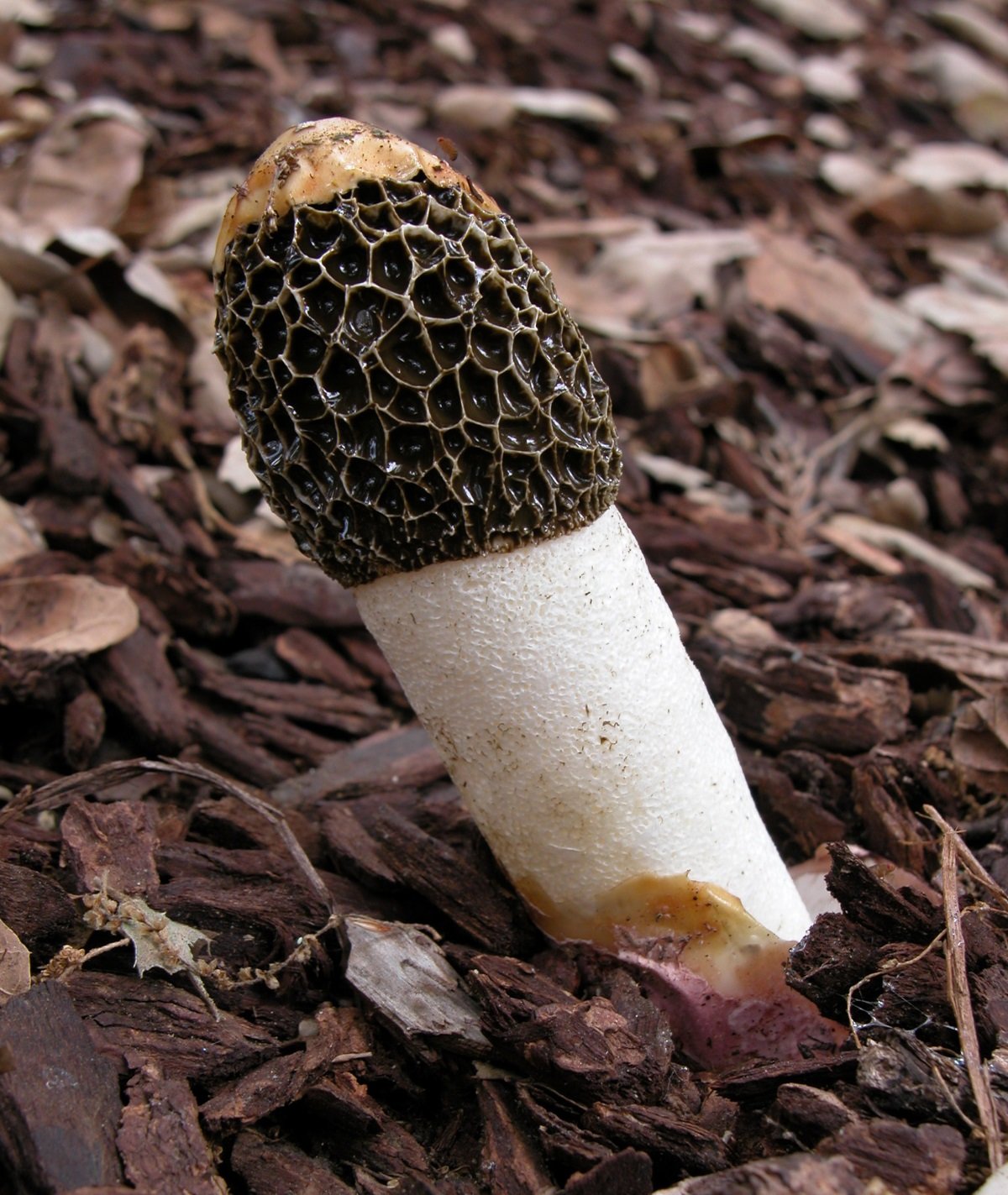
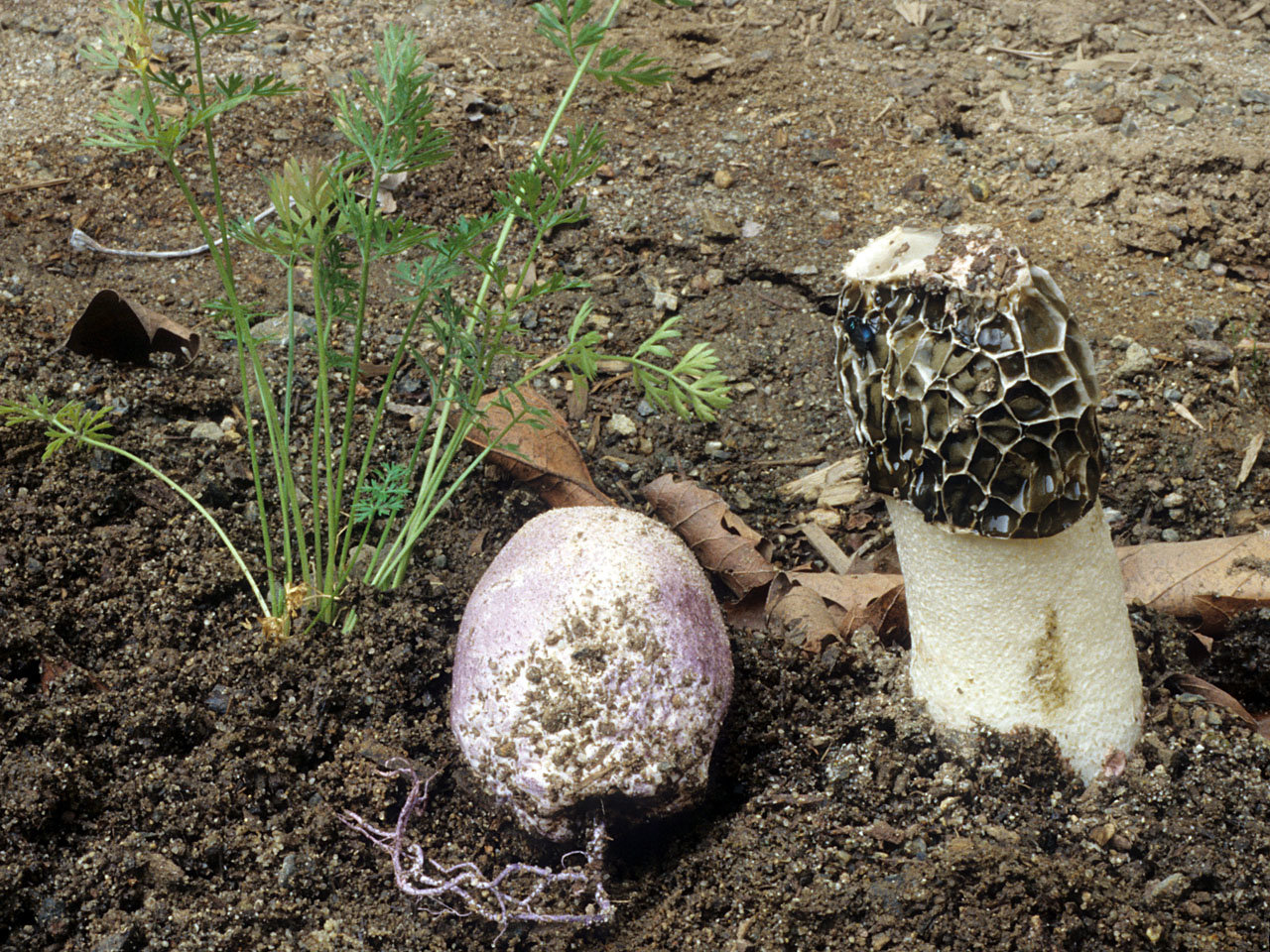
Mushrooms containing toxic substances that dissolve in water when boiled (morels, lines, morel caps)
These mushrooms are delicious, aromatic and healthy. But insidious! Before using for food, they are boiled for 20-30 minutes (morel caps need to be scalded with boiling water), the broth is poured out, the mushrooms are washed.
Mushrooms incompatible with alcohol (ink dung, olive oak, funnel talker)
Breeding / reproduction
The unpredictability of the natural habitat associated with frequent periods of drought has led to the emergence of a special adaptive mechanism in these fish, namely, eggs, in the event of a pond drying out, are able to maintain their viability for more than a month, being under a layer of dried silt or a layer of plants. In a home aquarium, growls will breed a couple of times a year. Spawning will require dense accumulations of low-growing plants or mosses, or their artificial counterparts, among which eggs will be laid. It is advisable to immediately transfer the fertilized eggs to a separate tank with identical water conditions in order to avoid being eaten by their own parents. The incubation period lasts from 14 to 21 days, depending on the temperature of the water.
Boletus
The closest neighbor of the boletus is the boletus. This mushroom is beautiful and strong only in its youth. His hat at this time has a dark color. At this time, he is strong and firm. It gets old a little - it loses its appearance. On the tenth day, on his leg, it was no longer a hat, but a hat. The flesh of this taiga mushroom is white at the break, but with further culinary processing it darkens, like in the boletus. It is no coincidence that both of these mushrooms are recognized as black.

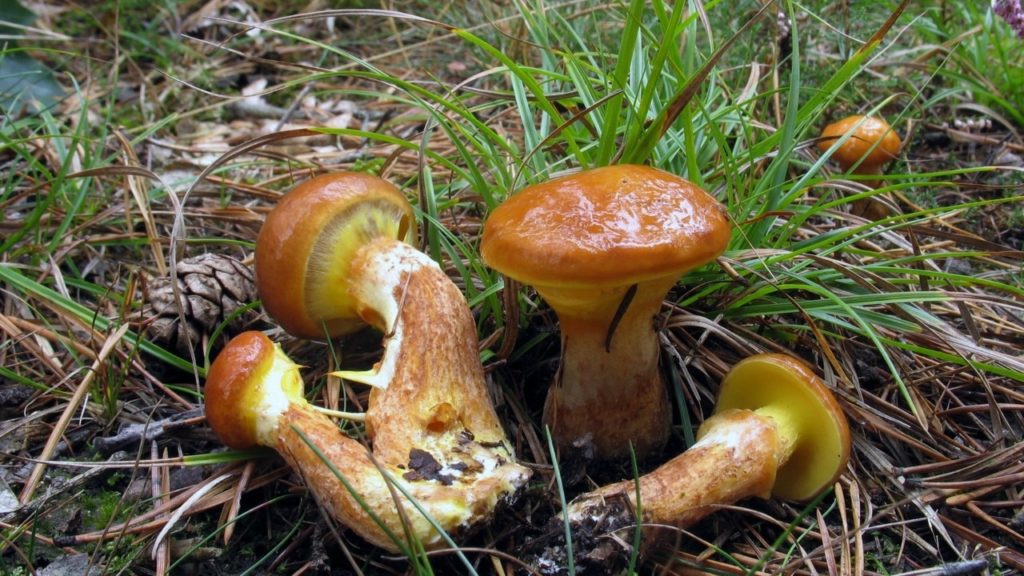
This mushroom rightfully belongs to the first category. The cap of the saffron milk cap is reddish-red on top with a depression in the center in the form of a funnel. The lower part of the cap looks like it is made up of orange plates. The leg is short, also orange, hollow, on a cut it looks like a ringlet. On the break of the mushroom, an orange-red juice is immediately released. You touch the orange plates, just take them in, they immediately turn green. Ginger, unlike other mushrooms, is incomparably fragrant.
And in terms of calorie content, he excelled. If we talk about the calorie content of 100 g of product, then salted mushrooms surpass marinated porcini mushrooms by 67 calories, dried boletus mushrooms - by 8 calories, chicken meat - by 75.7 calories. It used to be that the French were sent from Russia salty mushrooms of the Urals in bottles. In Paris, they were more valuable than champagne. Such are they - mushrooms.
The appearance of this mushroom looks like this. The hat is funnel-shaped, pink, with concentric circles. The surface of the cap is covered with a delicate fluff, especially at the edges. The leg is short, pinkish. At the break, the wave releases milky juice, pungent, bitter, which does not change color in the air.
How many are there? The name is one - russula, but differ greatly in color. There are many varieties. The cap of all russula is covered with a film, and this mushroom is distinguished by the color of the film. But whatever color the hat is, the russula flesh, like a porcini mushroom, always remains sugar-white. This is the most important difference and sign of a tender mushroom called russula. Another common name for the mushroom is bruise. In the Urals and Siberia, it grows everywhere.

Or a violinist. This mushroom got its name for the very creak that occurs when you rub the cap on the cap of just picked mushrooms. Few hunters take them to the basket, they do not want to interfere with other mushrooms. But in vain. This mushroom is not as bad as people think of it. Mainly there is a squeak in salting. First, the mushroom must be boiled well, in two waters.
Well, to recognize a violin among its relatives is as easy as shelling pears: break off a piece of the cap - and then, in large drops, milky juice, white as milk, will appear. If you lightly touch the tip of your tongue, it will burn with bitterness.
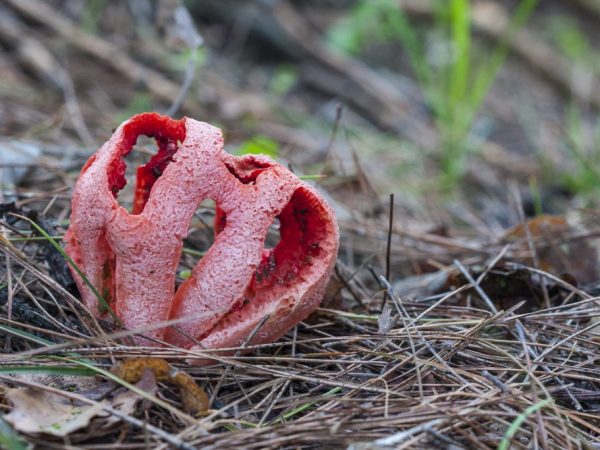
The people called him a comb.In Western Europe, and in some parts of our country, this mushroom is considered a delicious dish and is highly valued for its delicate taste and aroma. The body of the horned head can be yellow or white, with a pink tint. It is branched like coral, and a rare mushroom picker will decide to put the slingshot in the basket. But there is nothing to be afraid of the find, you just need to know that the slingshots are eaten only young and freshly cooked.
White mushroom

Porcini mushrooms are good in marinade, mushroom sauce and mushroom soup. They are famous not only for their taste, but also for their appearance. “Colonel to all mushrooms,” they say about the porcini mushroom. The white has many synonyms: in different parts of Siberia and the Urals, he can be clicked by a grasshopper, a pechura, a capercaillie, a bear-bearer, a cow, a boletus, a belovik, a driller, a ladybug. And in the Urals, it has a strong and strict name - white.
If we talk about appearance, then the porcini mushroom cannot be confused with any other. The lower part of the cap is spongy, in a young mushroom it is white, in a more mature one it is slightly yellowish. The leg is thick, white at the break. In a word, if you see him once, you will not confuse him with any other. Be sure of this.
Types of mushrooms
The species diversity of fungi is very wide, therefore there is a strict classification of these forest dwellers (Figure 1).
So, according to their edibility, they are divided into:
- Edible (white, boletus, champignon, chanterelle, etc.);
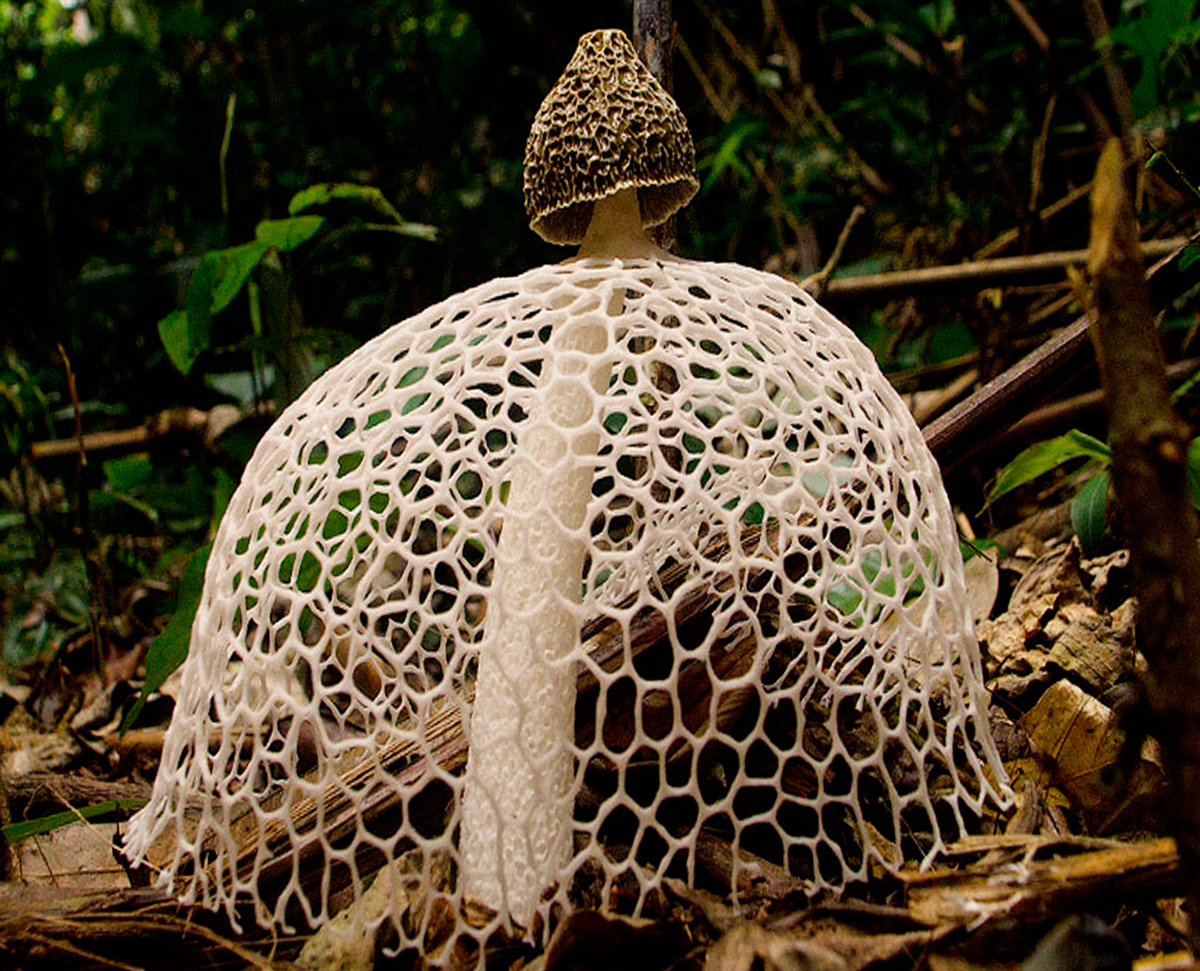
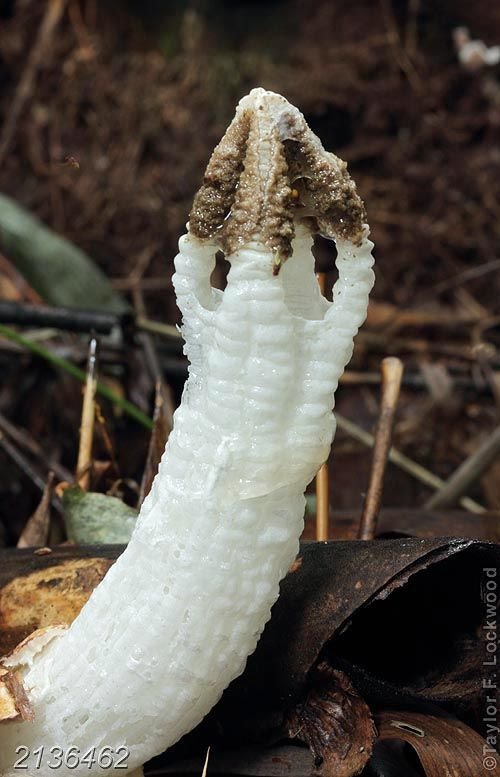
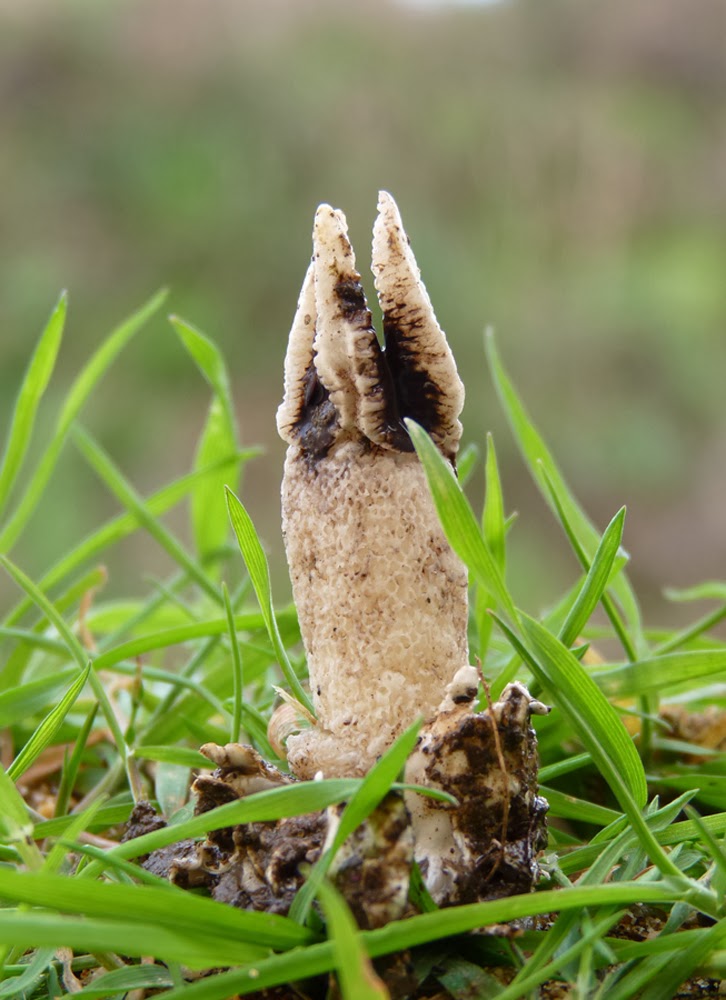
- Conditionally edible (oak, green leaves, veselka, milk mushrooms, lines);
- Poisonous (satanic, pale toadstool, fly agaric).
In addition, it is customary to divide them according to the type of the bottom of the hat. According to this classification, they are tubular (externally resembles a porous sponge) and lamellar (plates are clearly visible on the inner side of the cap). The first group includes boletus, white, boletus and boletus. To the second - mushrooms, milk mushrooms, chanterelles, honey mushrooms and russula. Morels are considered a separate group, which include morels and truffles.
 Figure 1. Classification of edible varieties
Figure 1. Classification of edible varieties
It is also customary to divide them according to their nutritional value. According to this classification, they are of four types:
- With high taste: mushroom, milk mushroom and white;
- The second category: boletus, aspen mushrooms, mushrooms and aspen mushrooms.
- The third group is the most numerous and includes boletus boletus, chanterelle mushrooms, russula and honey mushrooms.
- The fourth includes the species with the lowest palatability: black milk mushrooms, ocher russula, goat and rubella.
Since there are so many species, we will give the names of the most popular with their pictures. The best edible mushrooms with photos and names are shown in the video.
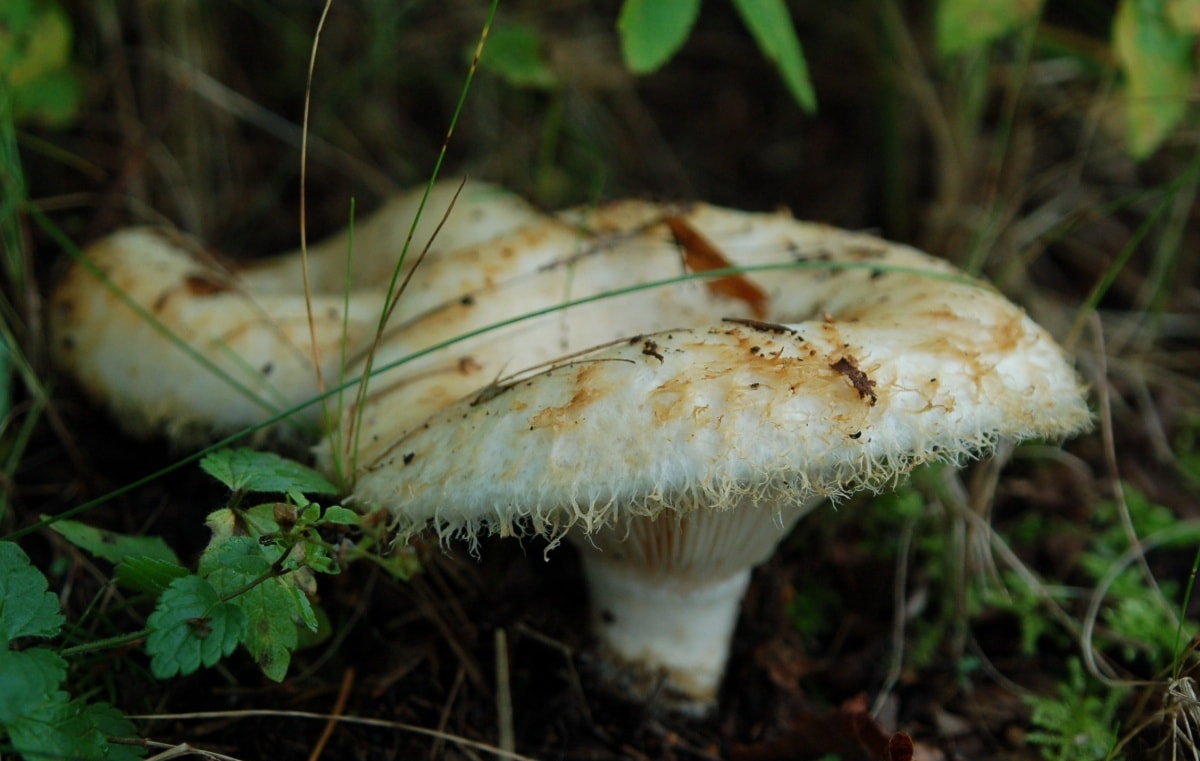
Two-ring type of champignons: photo and description
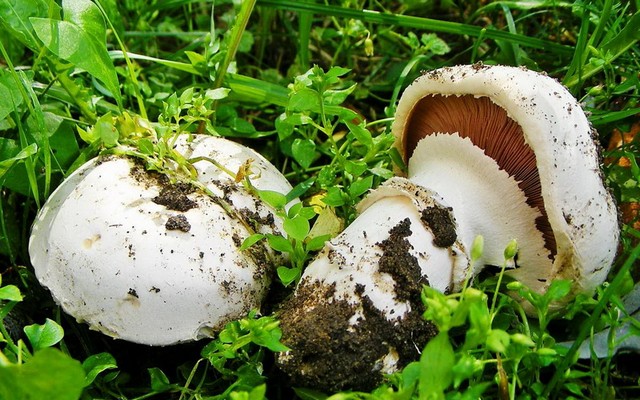

Two-ring view of champignons in the photo
The two-ring champignon is edible. Description of the species of this champignon: the cap is 6-15 cm in diameter, in young specimens it is convex, then almost flat with a turned edge, smooth or with radial cracks, white or brownish. The plates are loose, narrow, frequent pink, then chocolate brown. The leg is cylindrical, 4-9 cm long, smooth, white. Double ring in the middle of the leg. Volvo is missing. The pulp is firm at the cut or when pressed slowly turns pink.
Take a look this kind of champignons in the photo, which illustrates the growth and development of the fungus:

Two-ring champignon in the photo
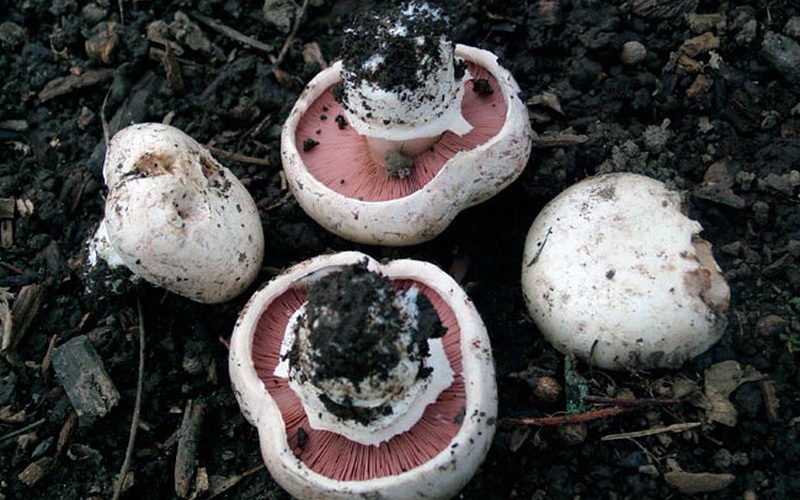

Two-ring champignon in the photo
Grows in organic-rich soil. Grows in large numbers on urban lawns, on dense soil along sidewalks. Sometimes it grows under the sidewalk, raising the asphalt or pushing apart a crack in the road surface. It is called sidewalk champignon.
Fruiting from July to October.
It looks like a poisonous yellow-skinned champignon (Agaricus xanhodermus), the flesh of which turns pink when cut and smells like carbolic.