Description of Limacella adhesive
Limacella sticky is a genus of mushrooms of the subgenus Agaricales of the amanita family. Although the limacella is sticky and belongs to the fly agaric, it is considered an edible species.
The cap is 2.5-8 cm, first in the form of a sphere, then convex, flat, often with irregular, wavy edges, with individual mucous flakes. The surface is smooth or fine-grained. The dark skin is reddish-brown in color, fading to pinkish over time. The middle is often darker.
The plates are multiple, free, snow-white in young and with a yellowish tint in old age.
The leg is cylindrical, 4-10 cm long and 5-10 cm in diameter, more or less even, with shaggy reddish-brown spots and scales with indeterminate patterns. Narrowed upwards, sometimes slightly thickened at the root, whole, the surface is corporal or beige, glossy above the ring, below it is covered with felt fragments in the form of flakes, which in small mushrooms are membranous or slimy after rain. Sometimes with an ephemeral annular zone, whitish under the cap.
A ring of uniform tone with a color of the leg, fibrous, in the form of a film with flakes, it can disappear or slide down the legs.
Volvo, as such, no.
The pulp is white, with a pink-brown color, fragile, smell and taste like flour.
Spores are oval, smooth, hyaline, 3.5-5 × 3.5-4.7 microns, almost transparent.
The color of limacells is highly dependent on the weather and growing conditions.
Limacella guttata
Limacella guttata @ Conoscere i funghi 10/29/2015
Limacella - fungi kingdom
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
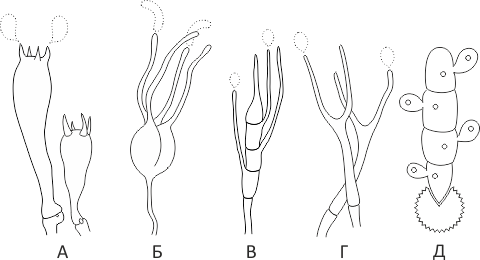
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
Cm.Agaricoid mushrooms, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Ixotrihoderma
-
Trichoderma, consisting of hyphae immersed in mucus. The surface of the cap is oily, slippery or slimy.
Lat. Ixotrichoderm.
See Trichoderma, Gifa.
Areas of growth of oily limacella.
Oily limacells grow on the soil. They can be found in mixed, deciduous forests and conifers. This species is very rare. Fruiting from August to October.

Oil limacells are common in the temperate zone of Europe. They can be found in the Baltics, Ukraine, Belarus, Transcaucasia, Primorsky Krai, Algeria and the USA.
Related species of oily limacella.
The steppe limacella has a thick-fleshed cap, which is at first hemispherical, and later becomes convexly prostrate. Its surface is naked, slimy or scaly. The color of the cap is brown-purple or brown-purple. Mucus is dark red, easy to wash off. The pulp with a strong flour smell, whitish color, turns pink when damaged. Central stem, one color with a hat.

The edibility of the steppe limacella has not been clarified. This is a rare species of mushrooms, it is listed in the Red Book of Ukraine and is endemic to the Khomutovskaya steppe reserve. These mushrooms settle in the virgin steppe. Fruiting is observed in May.
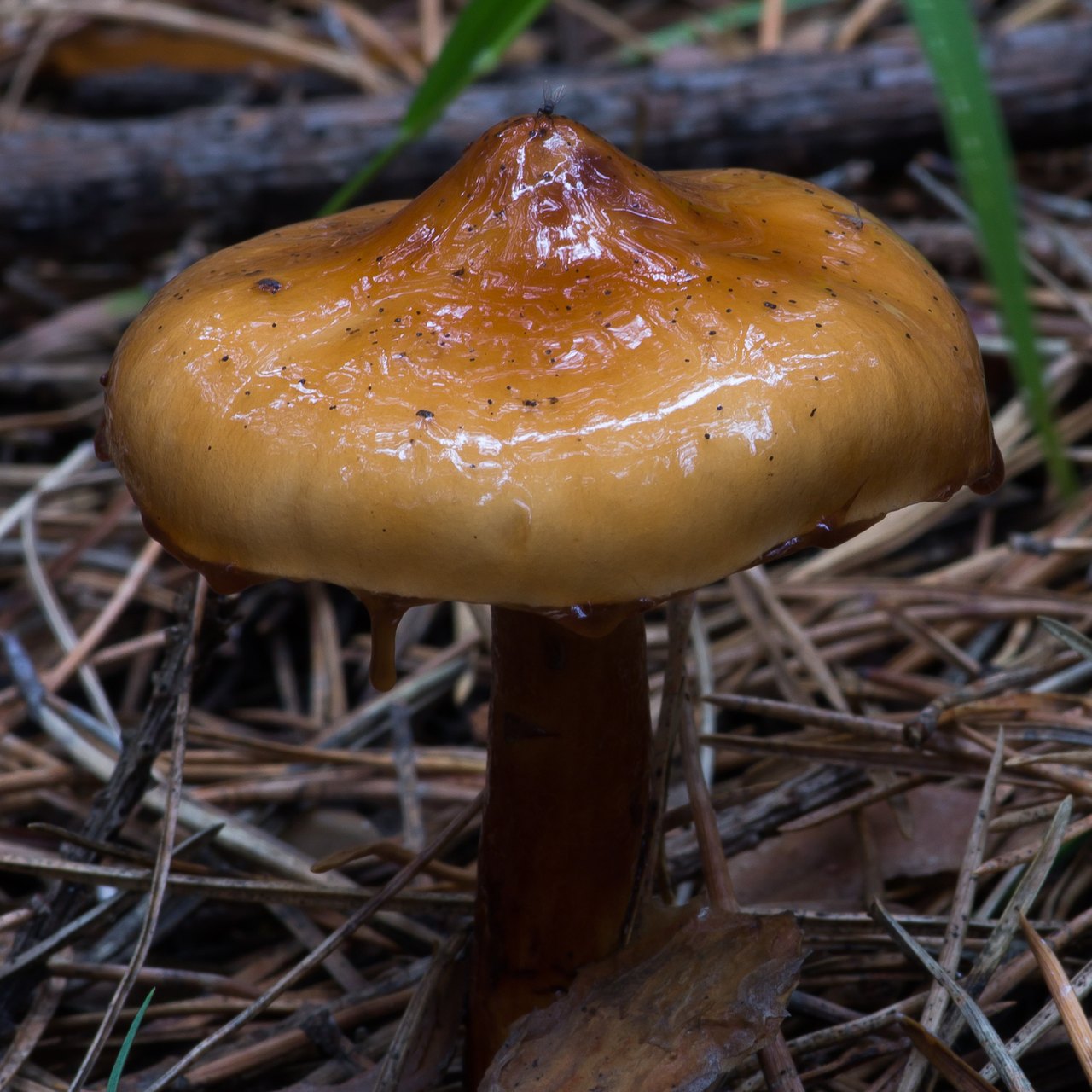
Limacella drip also has a thick cap. Its shape is bell-shaped at first, and then flat-convex with a central tubercle. The color is creamy ocher. The naked cap is covered with darker mucus. The pulp is thick, with a flour smell and taste, white color. The leg is cylindrical, thick at the base, white. Above the ring, the leg is dotted with transparent drops, when they dry out, gray spots are formed.

Drip limacella is considered an edible species in our country, but Western scientists do not recommend using it. Most often, drip limacells grow in pine forests, and also settle in moist mixed and deciduous forests. You can find them among moss and leaves, in rich soil. They are rare, in some places. They grow in groups. Fruiting is observed from July to October.
Morphology
Fruit bodies caps, central, small and medium-sized. The types of development are bivelangiocarpous or pileocarpous. From kind Amanita It differs mainly in the absence of volva and flakes on the cap, in the structure of the ring or in the presence of a mucous blanket.
Hat thick-fleshed, bell-shaped or hemispherical, later opens to a wide-conical, plano-convex or prostrate, smooth or toothed edge. A bump in the center may or may not be present. The surface is sticky or slimy.
Pulp usually white, dense, with a flour smell.
Lamellar hymenophore, plates are loose, poorly adherent or with colarium, frequent, white, there are plates.
Leg cylindrical, can be with an expanded or tuberous base, made or with cavities, with a mucous, sticky or dry surface.
Remains of bedspreads: Volvo is absent, the ring is fibrous, cortical, well pronounced or slimy, quickly disappears.
Spore powder White, disputes round to ovoid, smooth or slightly scabrous, non-amyloid or pseudo-amyloid, not cyanophilic.
Trama plates are initially bilateral, with age it becomes inverted or irregular. Pleuro- and cheilocystids are absent.
Characteristics of the fungus lyophyllum elm
Hat
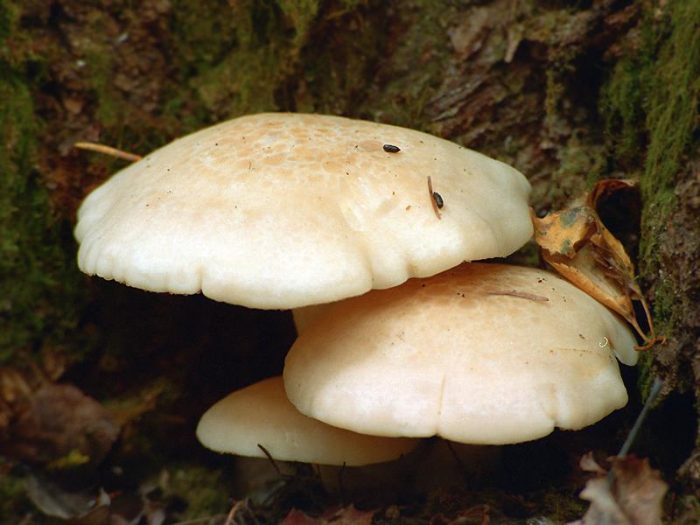

The cap of the mushroom is wide, 5-15 cm in diameter, sometimes up to 25 cm. The surface of the cap is dry, silky, decorated with a marble pattern, painted in a light gray or gray-ocher color. The shape of the cap in a young mushroom is convex, tuberous, the edge is curled up, with watery brown spots; with age, it gradually becomes convex-prostrate or prostrate, with a tubercle or depressed.
Pulp

The pulp is dense, elastic, fibrous structure, light or grayish-brown in color, the smell is weak, flour, the taste is pleasant, weakly expressed.
Leg

The stem of the fungus has a fibrous structure, the color is whitish, pale fawn, with a light bloom, turns yellow from touch.The leg is 5-8 cm high, 1-1.5 cm thick. The structure is rigid, fibrous. Often three or more mushrooms grow together.
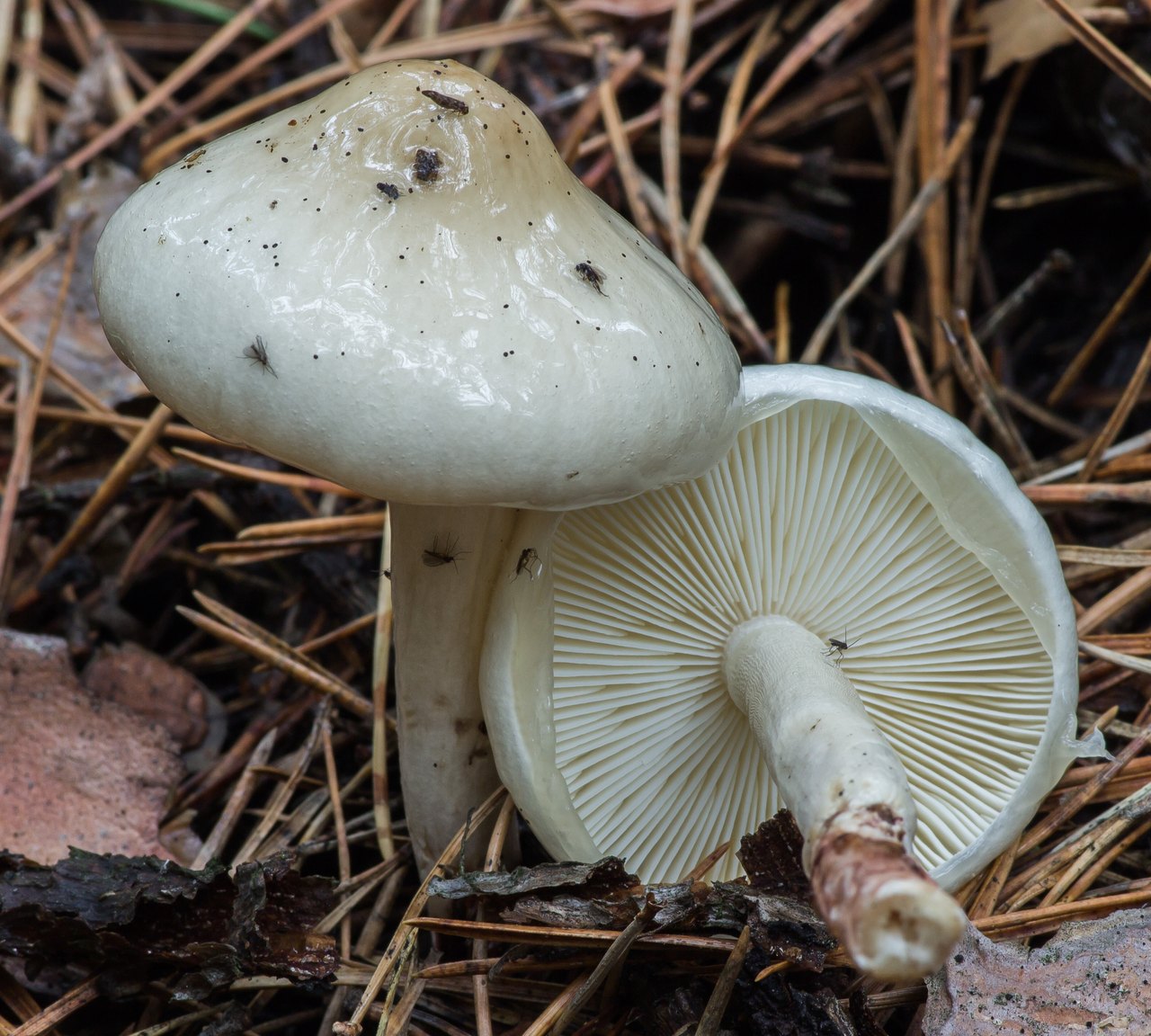
Limacella oozing
The cap is 4-12 cm in diameter, initially hemispherical, then convex or flat-spread, with a protruding tubercle, cream, light copper, light ocher-brownish, brownish-brown, grayish-reddish, sometimes yellowish in the center, with an uneven , often toothed, edge, densely thick-fleshy, smooth, naked, sticky, slimy. The plates are loose, thin, frequent, sometimes forked-branched, initially white, then light cream. Trama is wrong. Stem 7-12 x 1-2.5 cm, widening towards the base, whitish or with a brownish tinge, with a wide whitish ring hanging down. The ring and leg above it with small yellowish droplets, spotty when dry. The pulp is white, thick, with a mealy taste and smell. Spore powder is white.

The limacella oozing fungus grows mainly in spruce forests, it is found in July - September. Edible.
Literature
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what "Limacella" is in other dictionaries:
Limacella drip -? Limacella drip Lima ... Wikipedia
Limacella sticky -? Limacella sticky ... Wikipedia
Limacella tender -? Limacella tender Scientific classification Kingdom: Mushrooms Division: Basidiomycetes Class: Agaricomycetes… Wikipedia
Limacella oily -? Limacella oily ... Wikipedia
Limacella steppe -? Limacella steppe Scientific classification Kingdom: Mushrooms Division: Basidiomycetes Class: Agaricomycetes… Wikipedia
List of species included in the Red Data Book of Nature of the Leningrad Region - List of species included in the Red Data Book of Nature of the Leningrad Region, published in 1999 2002. The list is aligned with the second (animals) and third (plants) volumes. There are 1086 taxa in total, including 558 animals (120 vertebrates and ... ... Wikipedia
Amanitaceae family (Amanitaceae) - The amanitaceae family includes mushrooms in which fruit bodies have a well-developed central leg, free plates, white or pink spore powder. At the base of the leg, most genera of the family have a free or ... ... Biological encyclopedia
Amanite - Not to be confused with the Amish. Not to be confused with ammonites. ? Amanite ... Wikipedia
List of species included in the Red Data Book of St. Petersburg Nature - List of species included in the Red Data Book of St. Petersburg Nature, published in 2004. The publication includes 288 taxa of 164 animals (including 89 chordates (19 mammals, 55 birds, 2 amphibians, 3 reptiles, 1 cyclostomes, 9 ... Wikipedia
Similarity to other mushrooms
Limacella sticky is a rather unusual mushroom. Difficulties arise when determining the species, because outwardly the mushroom combines the features of various families - spiderwebs, lepiots, ryadovki and even hygrophors, and the hat is similar to an oil can. Most similar to gummy limacella:
- wine-red limacella - the same look, but with a rich burgundy note, without spots;
- tied rowing - a species tied to coniferous trees. It looks like a limacella with a sticky color of a cap with a reddish-pink tint, whitish plates and pulp. The flakes on the leg are the same as those of the limacella sticky. However, the ryadovka tied up is larger and more massive, the top of the head is strewn with large, tight membranous scales, and it cannot be slippery. The ryadovka has much denser and more elastic flesh and no orange spots on the legs;
- slimy cobweb is another, often found, representative of coniferous forests, it is easy to confuse it with sticky limacella. Mushrooms are of the same size, both have brownish-red and slimy tops of the heads. The edges of small cobwebs are snotty, like limacella sticky;
- belted webcap - differs in lilac color of the snotty top on the leg. Like limacella, it is a rare species.
Growing lyophillum elm at home

At home, elm lyophillum is grown from mycelium. For planting it, logs of birch, elm, elm, aspen are prepared at least 4-4.5 years old, about 30 cm in diameter, about 0.5 m long. The logs should be without branches, rot and other flaws.
Favorable period for sowing the mushroom: from April to October.Indoors, if it is possible to maintain the air temperature within 10-15 ° C, disembarkation is carried out all year round.
The logs are soaked in water for 2-3 days until the desired moisture level is obtained. After removing the logs from the water, the excess liquid is removed from them by keeping them for several days in a well-ventilated area.
In the logs prepared in this way, small holes are drilled with a drill (1 cm in diameter and 5-10 cm deep). They are staggered at a distance of 20 cm from each other.
Then, with cleanly washed hands or with gloves, special sticks with mycelium are placed into these holes. Further, the logs are packed in plastic bags, which prevents their infection and accelerates the development and growth of mycelium.
Logs with mycelium are placed in a shaded place with good ventilation and an ambient temperature of 20-25 ° C. The entire period of development of mycelium monitors the moisture content of the logs.
After 2-4 months, the mycelium completely fills the substrate. And six months later, the first harvest appears. The fruiting time depends on the hardness of the wood of the logs. For example, on soft woods, poplar, willow or birch, mushrooms are harvested for about four years. Hard varieties such as maple, mountain ash, beech bear fruit within 6-7 years. During the year, an average of 3-6 kg of mushrooms is harvested from each log.
Elm lyophyllum is an unpretentious mushroom. Even in dry summers, when other types of mushrooms practically do not grow, single lyophillums or clusters of mushrooms are found.
Limacella oil (Limacella illinita)
Category: edible.


Hat (diameter 3-10 cm): usually white, gray or light brown. In a young mushroom, it has the shape of a hemisphere, over time it changes to an almost extended one with thin and translucent edges and a weakly pronounced tubercle. Oily limacella is rather slippery to the touch.
Leg (height 3-11cm): cylindrical, slightly slippery.
Flesh: white and does not change when cut or broken. The aroma of oily limacella is similar to perfumery.
Plates: white or with a slight pink tint.
Doubles: none.
When it grows: From early August to mid-October in northern Europe, Asia, North America and Africa.
Where can you find it: on soils of all types of forests.
Eating: dried or fried.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Limacella coated (Limacella illinita)

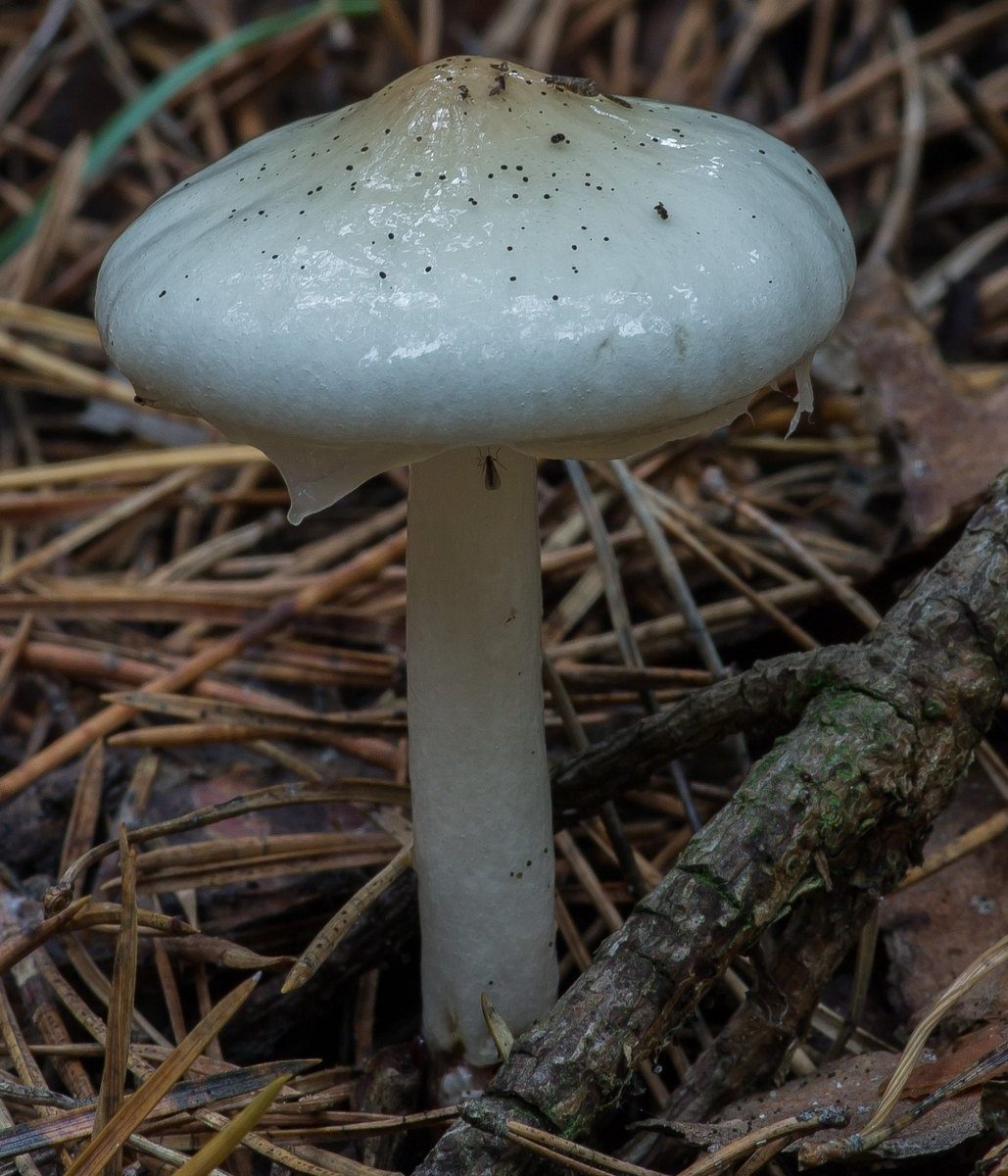
Actual name: Limacella illinita (Fr.) Maire (1933)
Description
Hat: average size 3-10 centimeters in diameter, variations from 2 to 15 cm are possible. Ovate, hemispherical in youth, conical, then almost prostrate, with a small tubercle. The edges of the cap are thin, almost translucent. Remnants of a mucous veil may hang along the edge. The color is white, gray, whitish, light brownish or light cream. It is darker in the central part. The surface of the cap of the smeared limacella is smooth, very sticky or slimy. Very slimy in wet weather.
Plates: adherent with a tooth or loose, frequent, wide, white or pinkish, with plates.
Leg: 5 - 9 centimeters high and up to 1 cm in diameter. Looks a bit disproportionately tall compared to the hat. Central, even or slightly tapering towards the cap. Whole, becomes loose, hollow with age. The color of the leg is whitish, brownish, the same color as the cap or slightly darker, the surface is sticky or slimy.
Ring: a pronounced ring, customary, in the form of a "skirt", no. There is a weakly expressed mucous "annular zone", more distinguishable in young specimens. Above the annular zone, the leg is dry, below it is mucous.
Flesh: thin, soft, white.
Taste: not different (no particular taste). Smell: perfumery, sometimes powdery is indicated.
Spore powder: white Spores: 3.5-5 (6) x 2.9 (4) -3.8 (5) microns, ovoid, broadly ellipsoid or nearly round, smooth, colorless.
Ecology
Limacella oily (coated) grows in forests of all types, it is found in fields, on lawns or on roadsides, swamps, meadows and sand dunes. Grows on the ground or litter, scattered or in groups, not infrequently.

Season and distribution
Occurs in summer and autumn, from June-July to the end of October. The peak of fruiting occurs in August - September.Smeared limacella is widespread in North America, European countries, and Russia. In some regions, the species is considered quite rare, in some it is found often, but does not attract special attention of mushroom pickers.
Edibility
Information is extremely contradictory, from "inedible" to "edible mushroom category 4". According to literary sources, it can be eaten fried, after preliminary boiling. Suitable for drying
We will carefully place this limacella in the category of conditionally edible and remind our dear readers: take care of yourself, do not experiment with mushrooms about the edibility of which there is no reliable information
Variability
Smeared limacella is a rather variable species. 7 varieties are indicated:
- Limacella illinita f. illinita
- Limacella illinita f. ochracea - with a predominance of brownish shades
- Limacella illinita var. argillacea
- Limacella illinita var. illinita
- Limacella illinita var. ochraceolutea
- Limacella illinita var. ochraceorosea
- Limacella illinita var. rubescens - "Reddening" - in places of damage, with a simple touch to the cap or leg, on the break and cut, the flesh turns red. At the base of the stem, the color turns reddish.
news
In the Collection "Flora and Vegetation of the Central Black Earth Region - 2020. Proceedings of the Interregional Scientific Conference dedicated to the 85th anniversary of the Central Black Earth State Natural Biosphere Reserve named after Professor V.V. Alekhine ”published an article on Kondukov's bryoflora.
The updated List of flora objects included in the Red River was approved book of the Tula region... Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of the Tula Region dated April 21, 2020 No. 193 was published on the official Internet portal of legal information.
The Tula Region will host a bird photography competition for the seventh time. Dedicated this year to the 75th anniversary of Victory in the Great Patriotic War and the 500th anniversary of the Tula Kremlin and the Great Zasechnaya Line, the competition was named “On the Wings of Victory. Defensive Frontiers of Russia ”and will be held in a new format for him and almost familiar to us # TogetherHome.




























