Description of northern climacodon
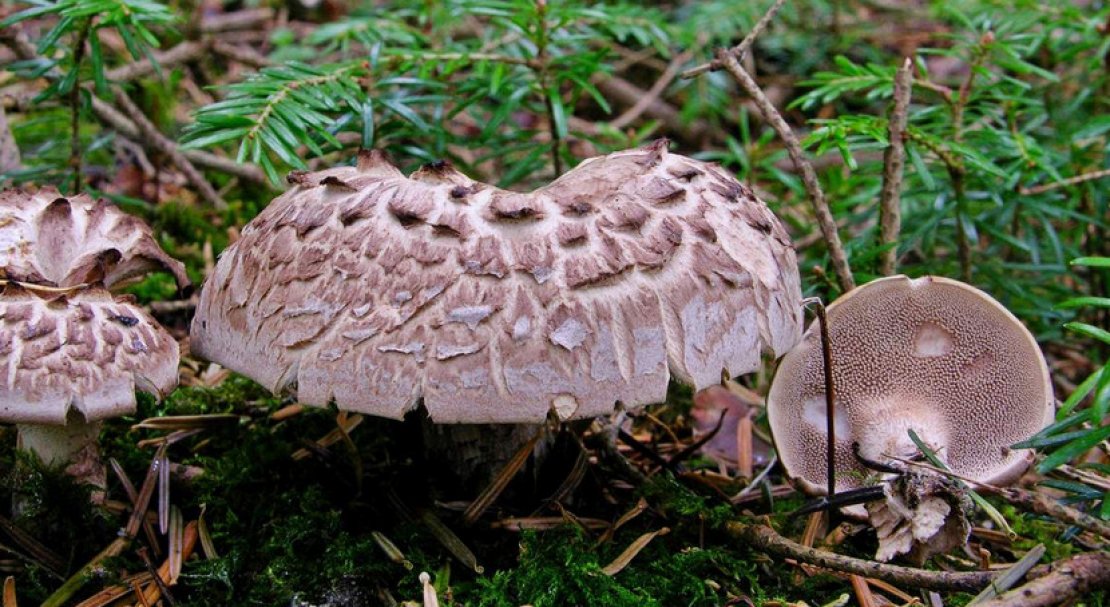
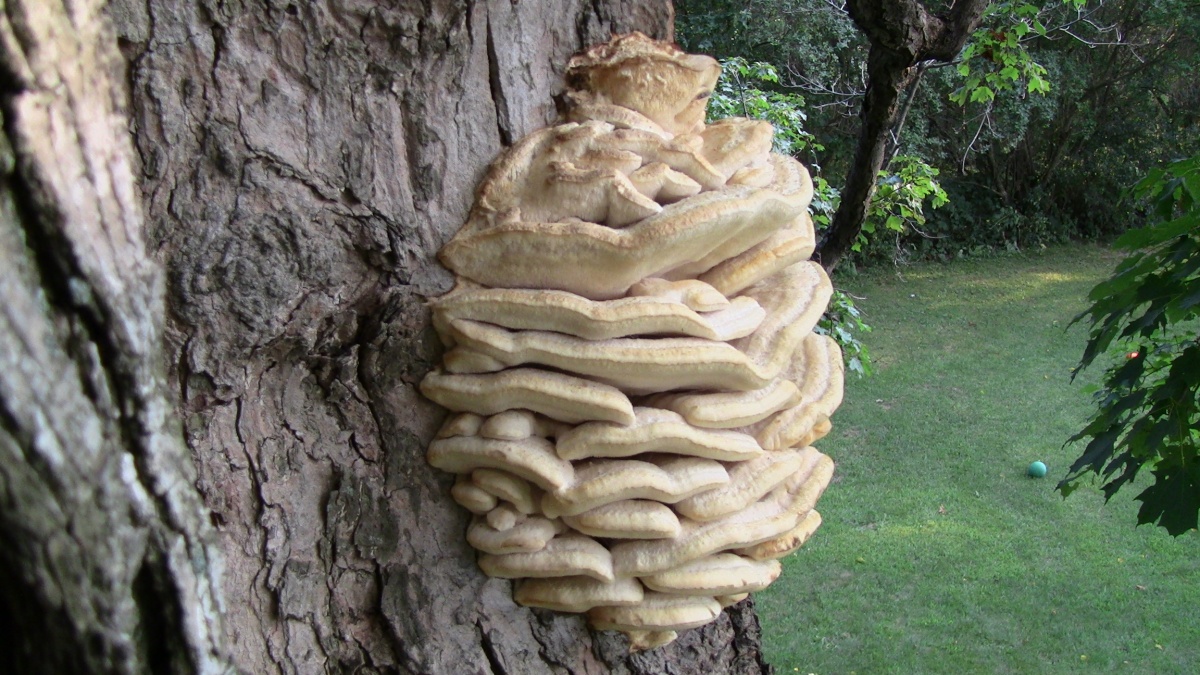
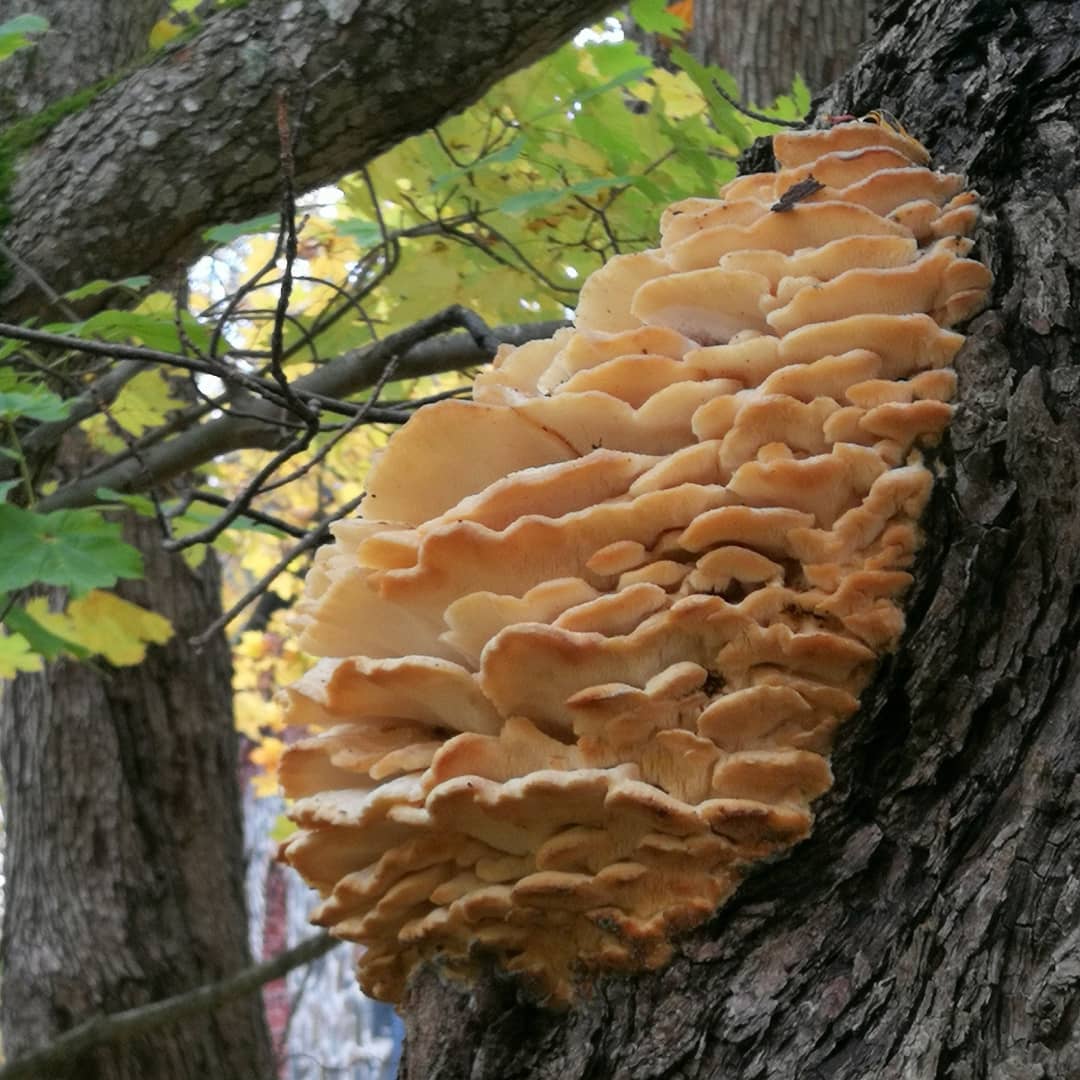
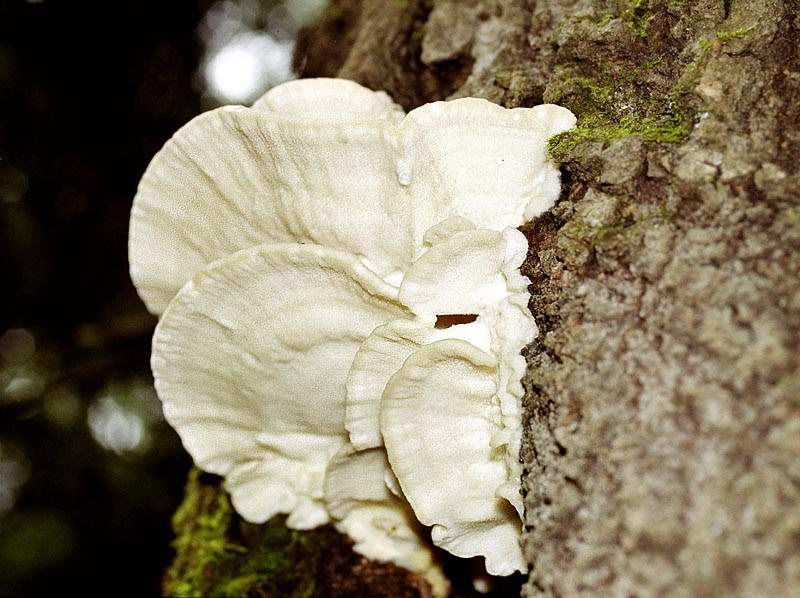
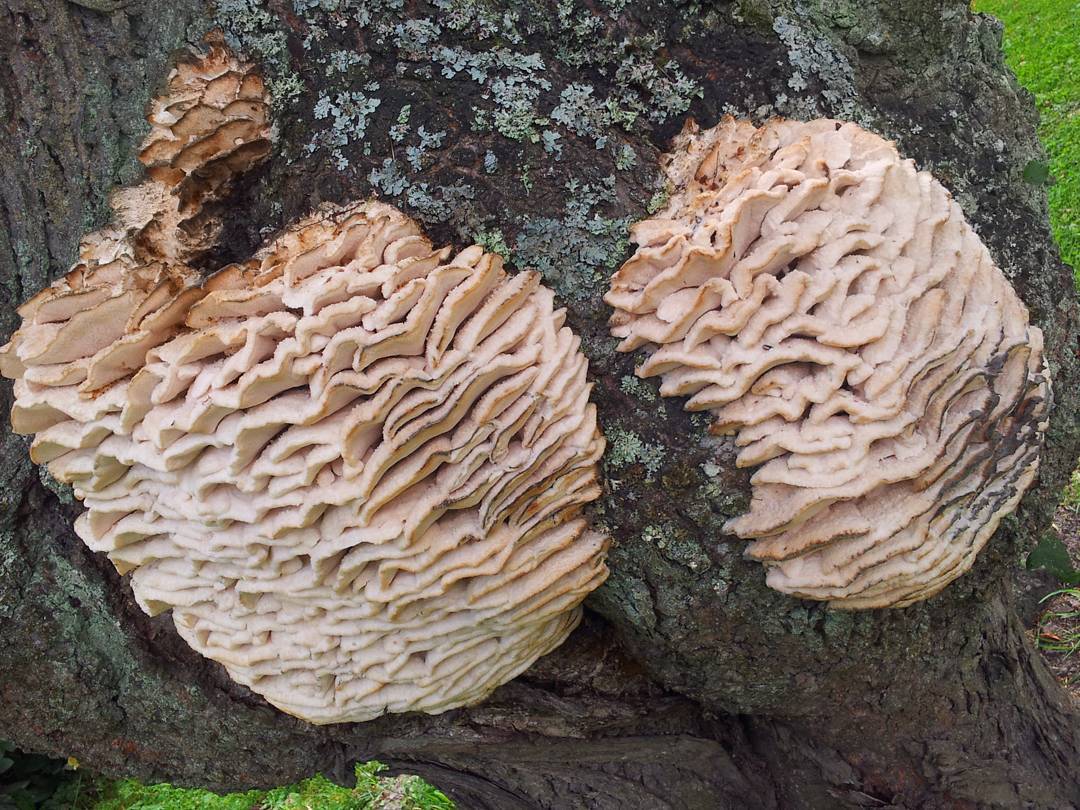
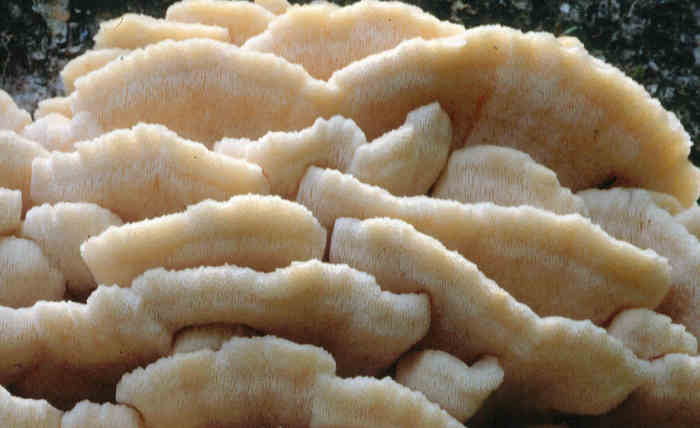
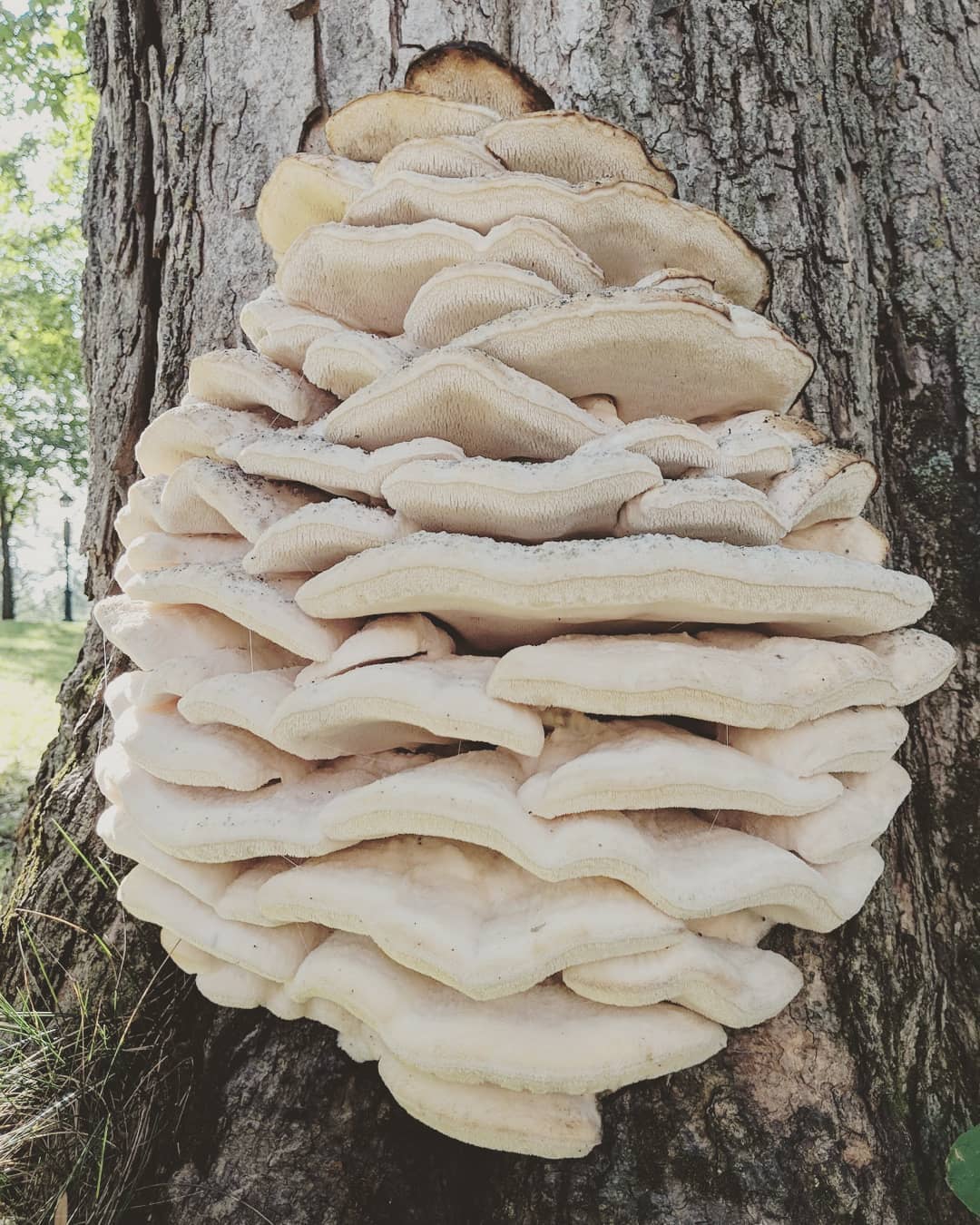
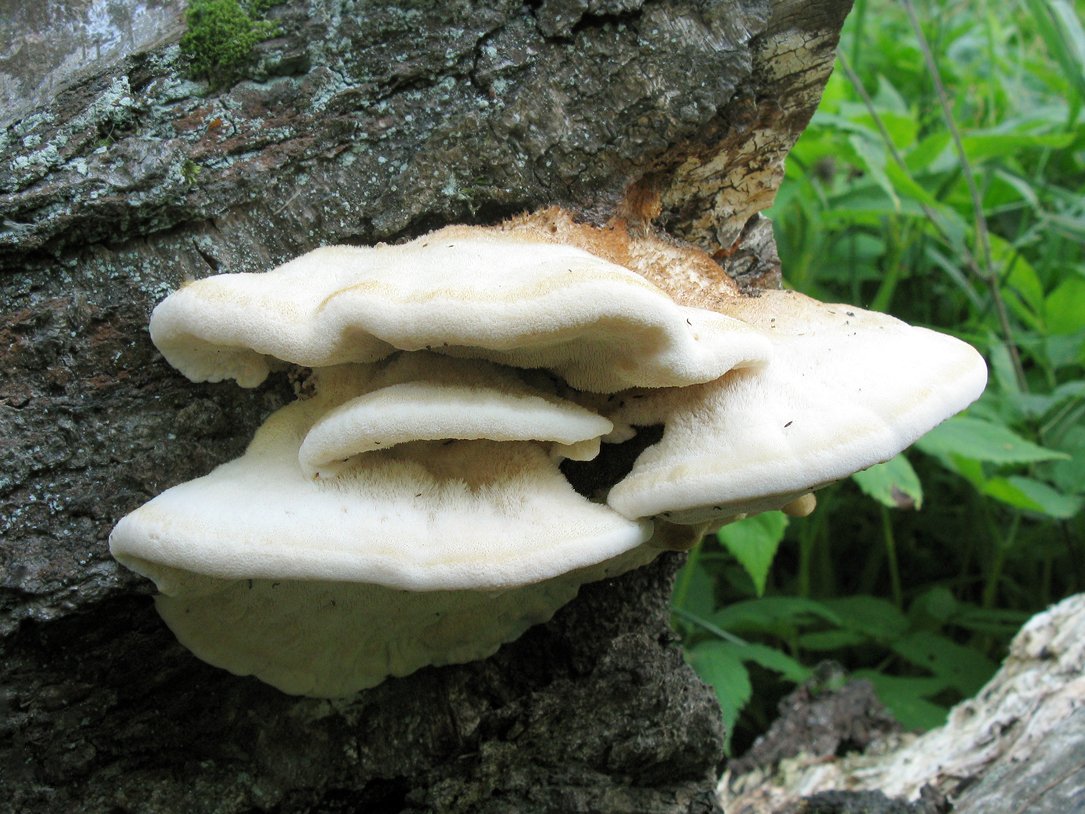
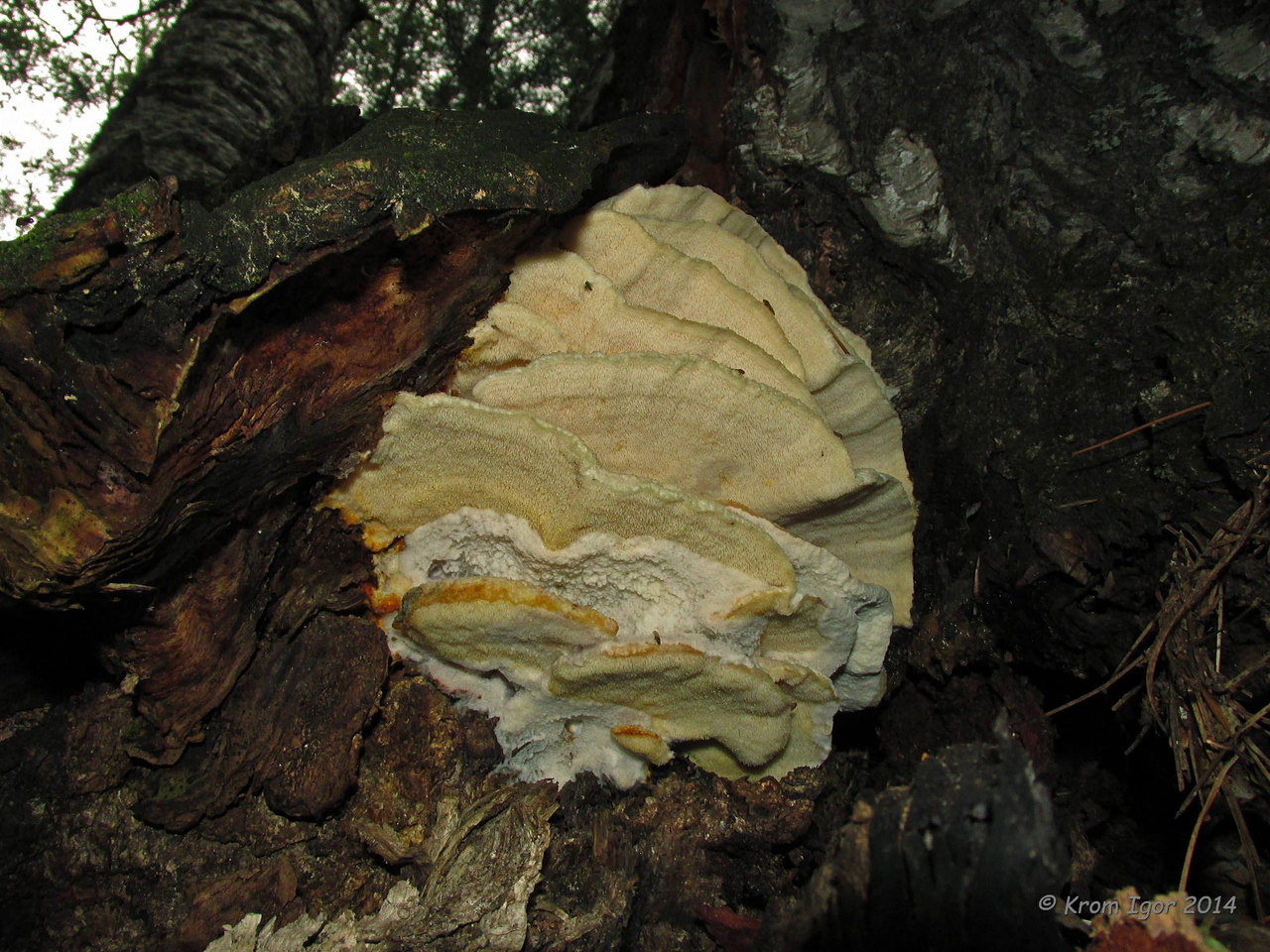
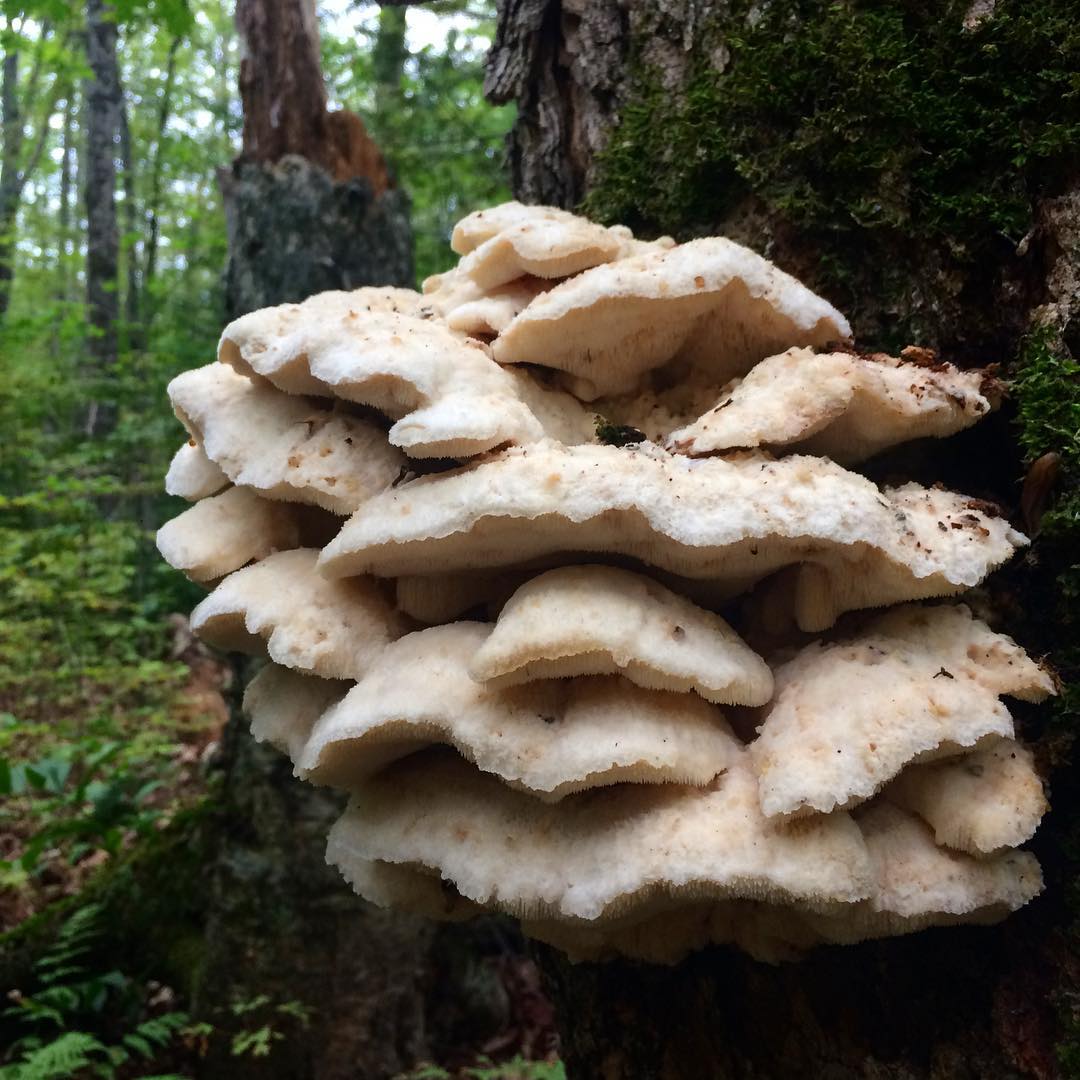
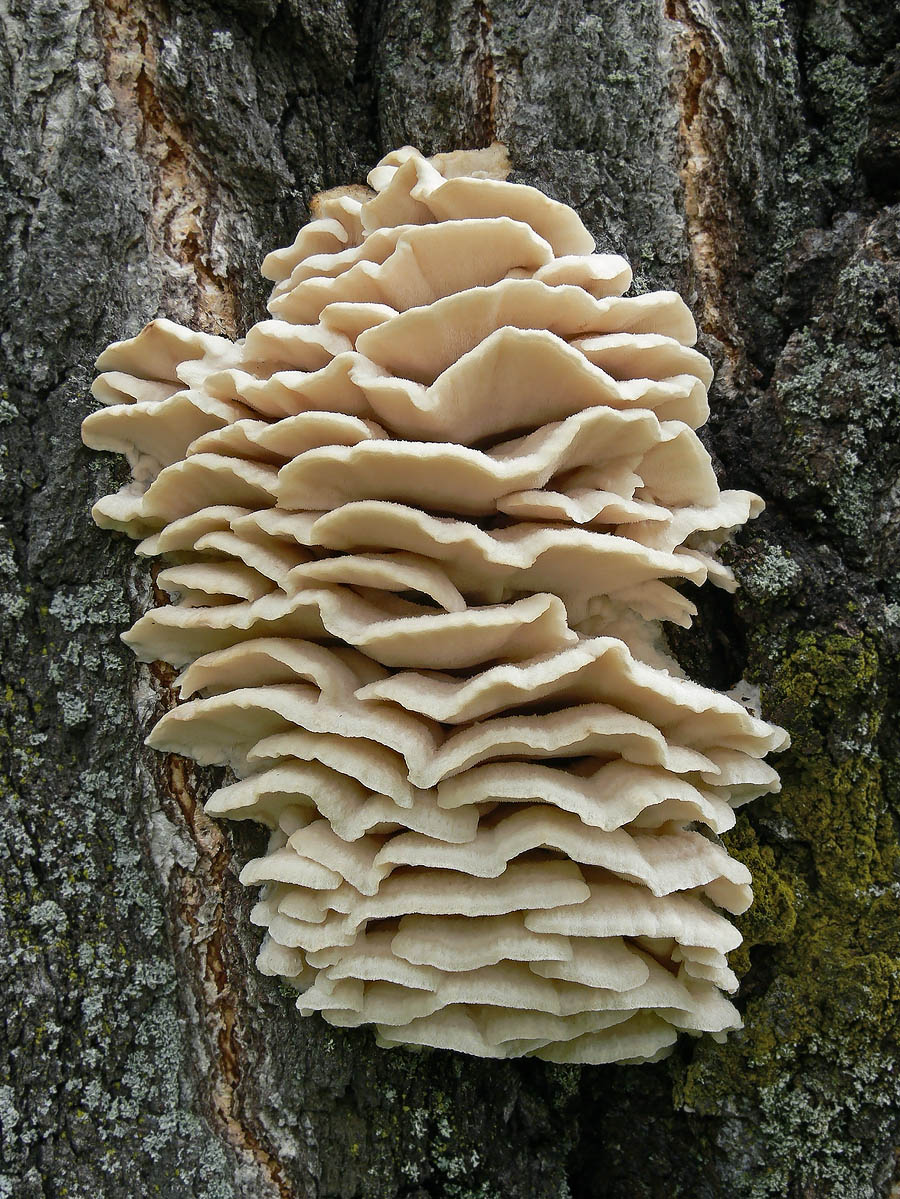
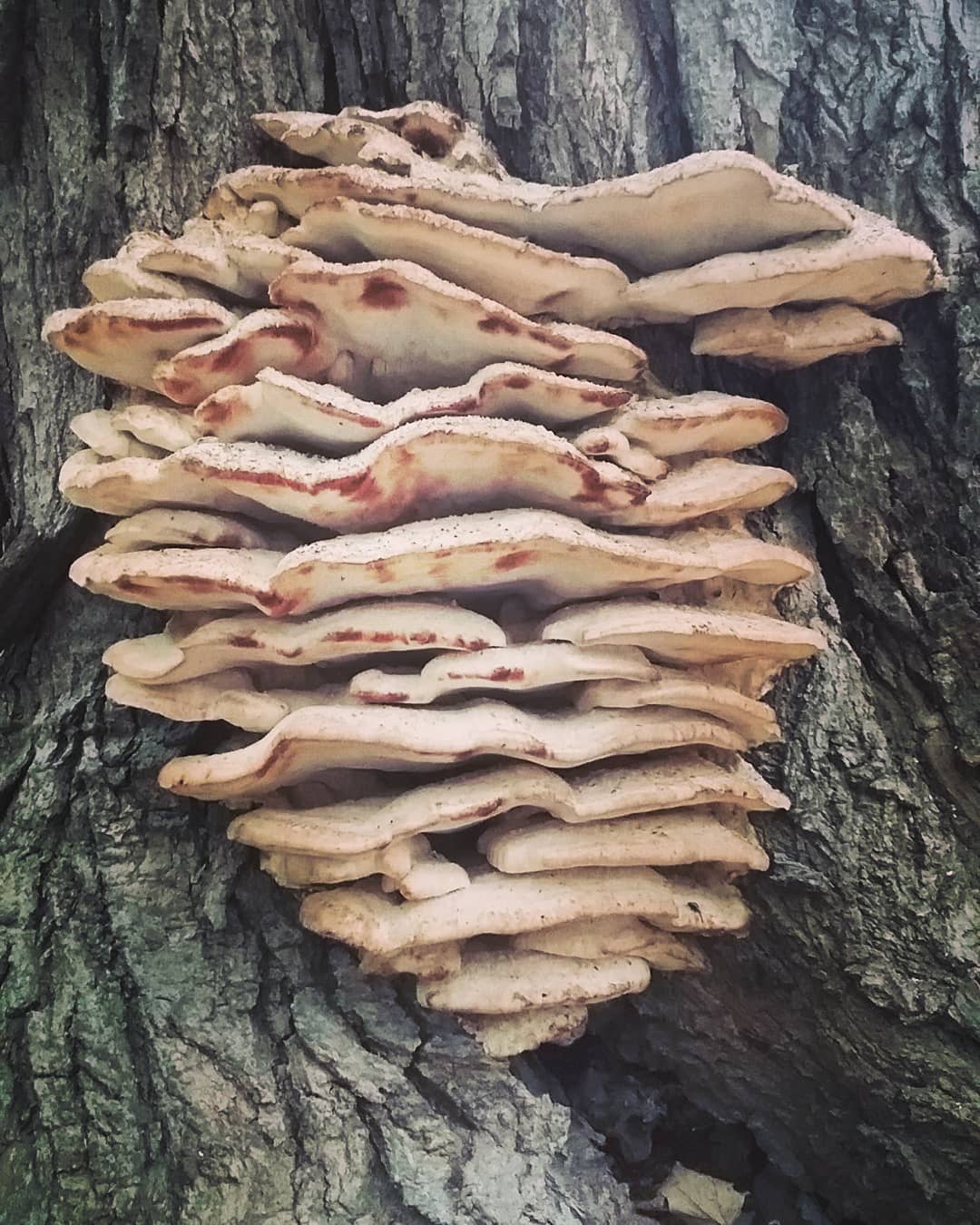
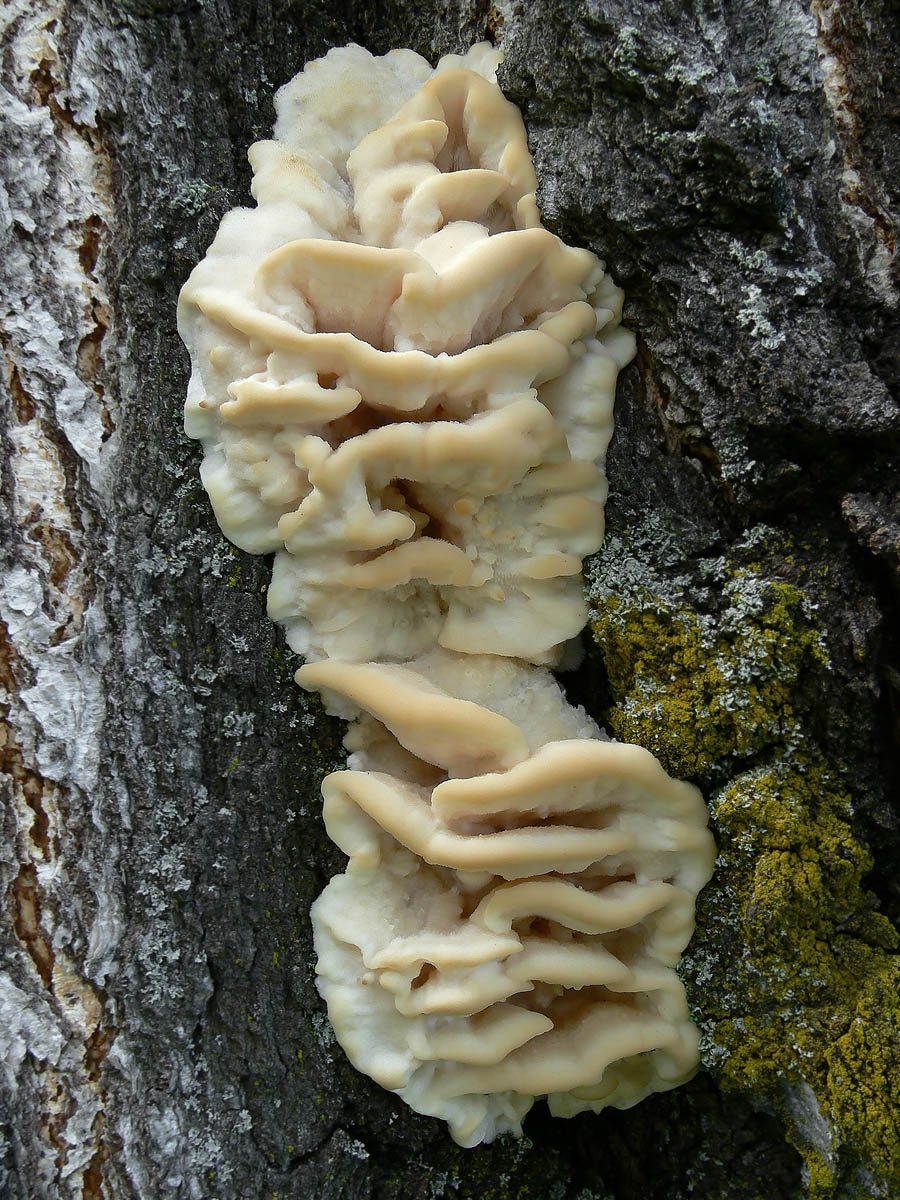
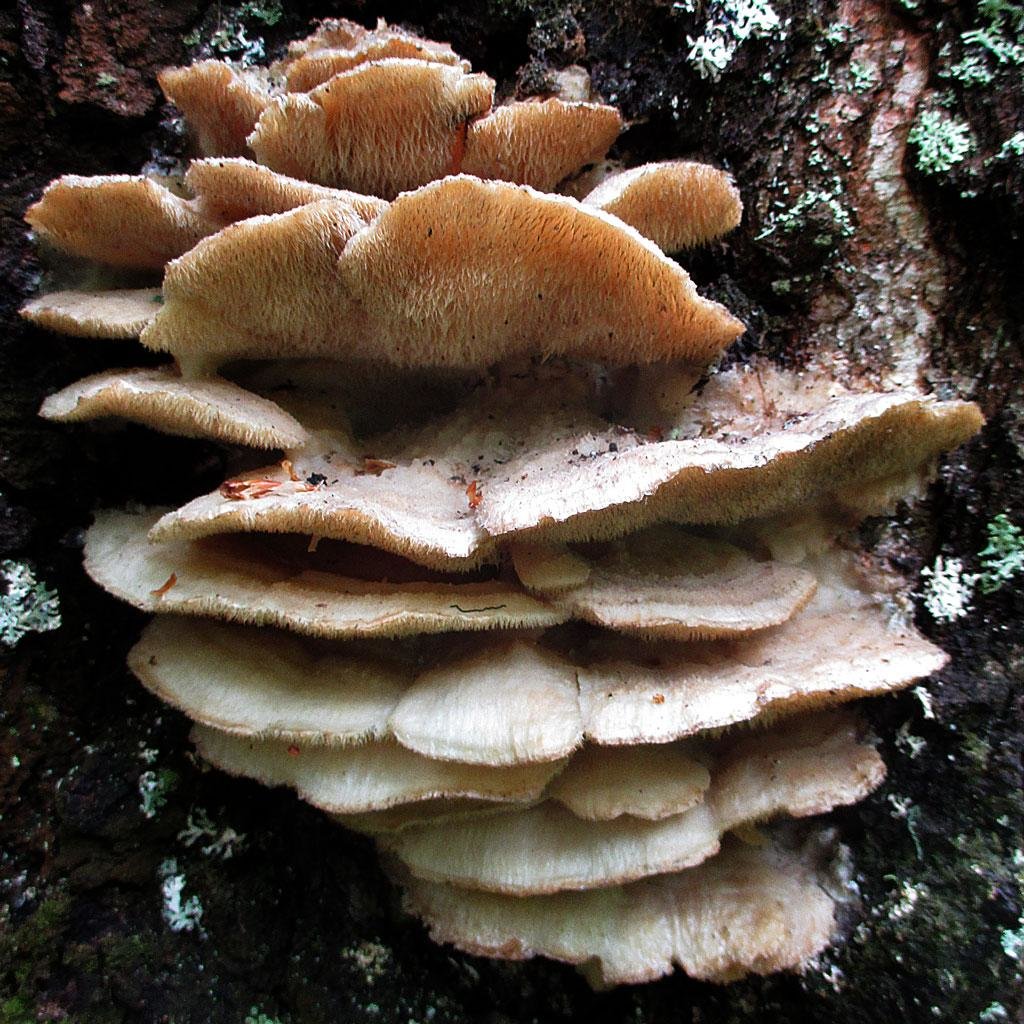
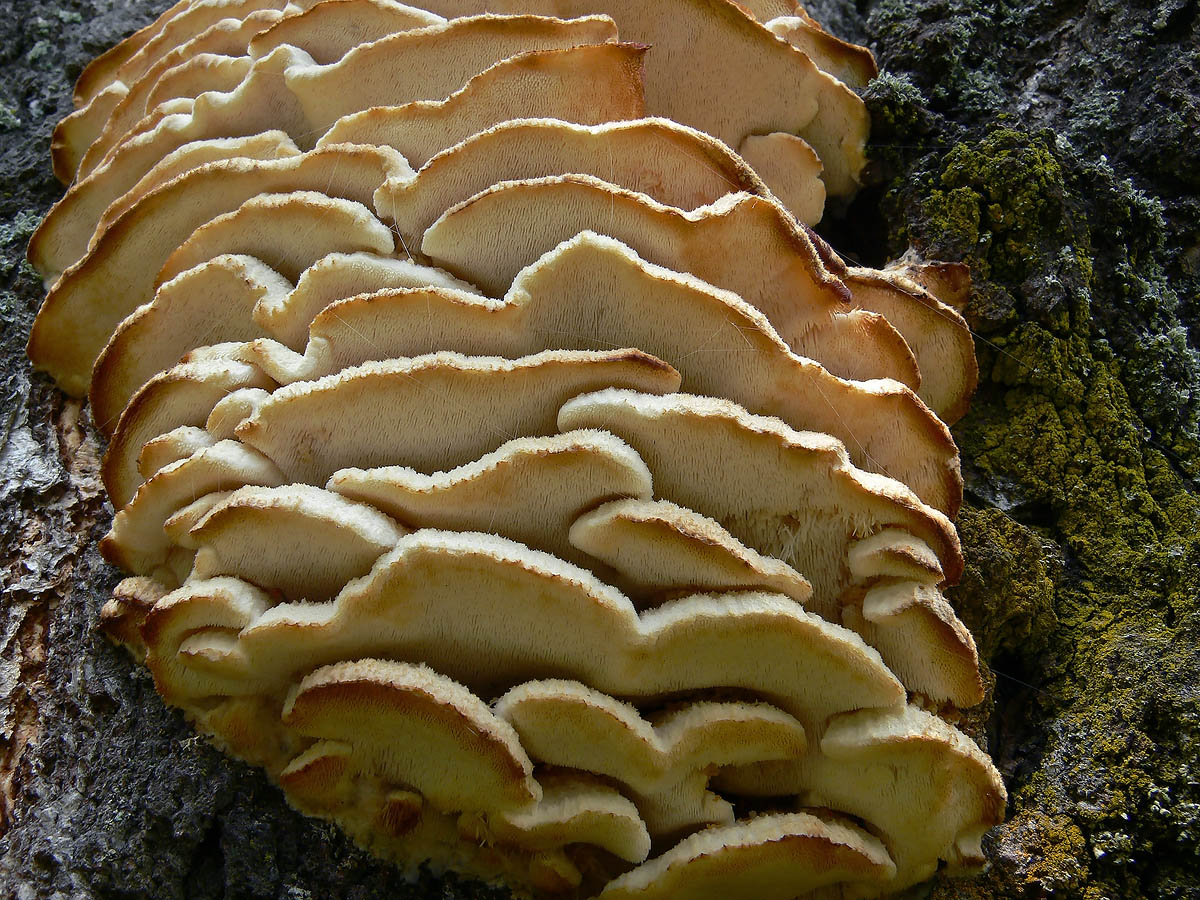
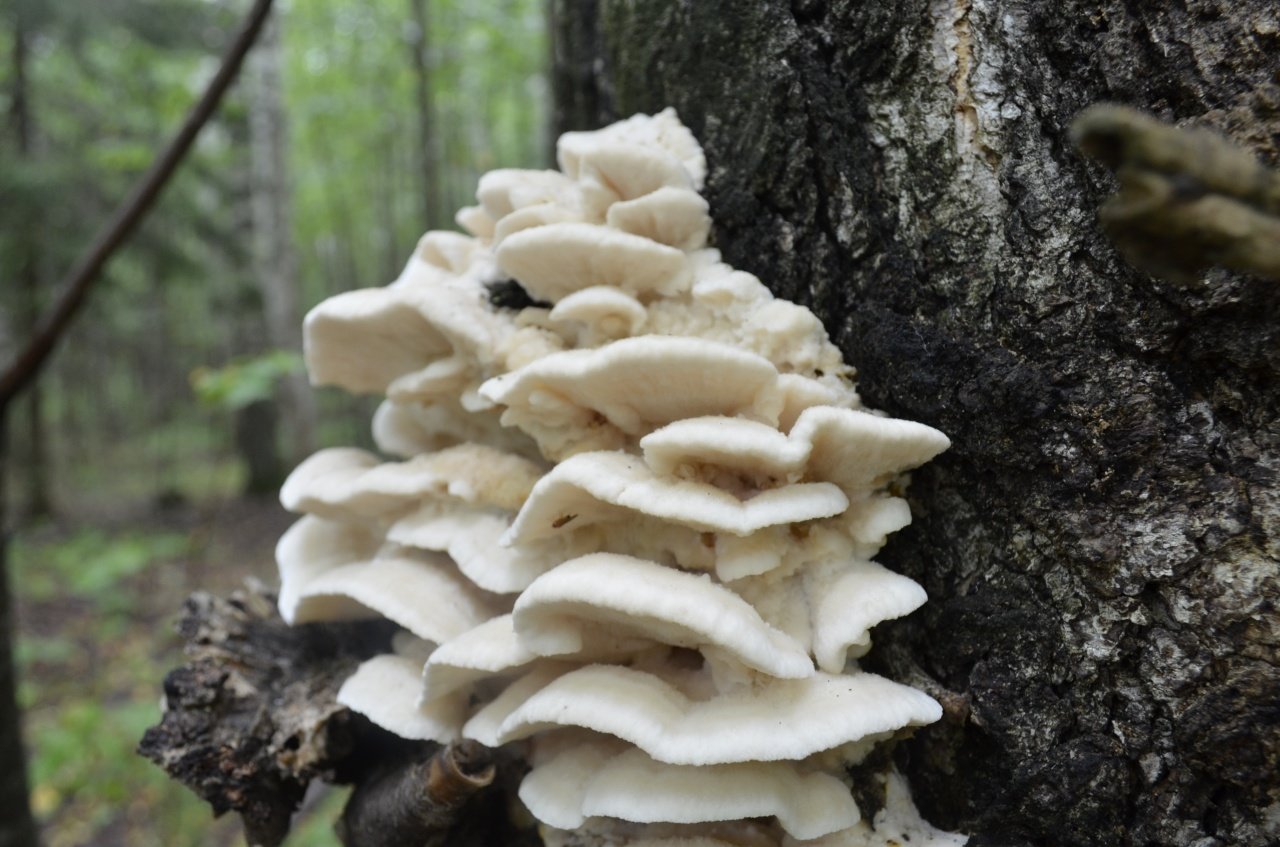
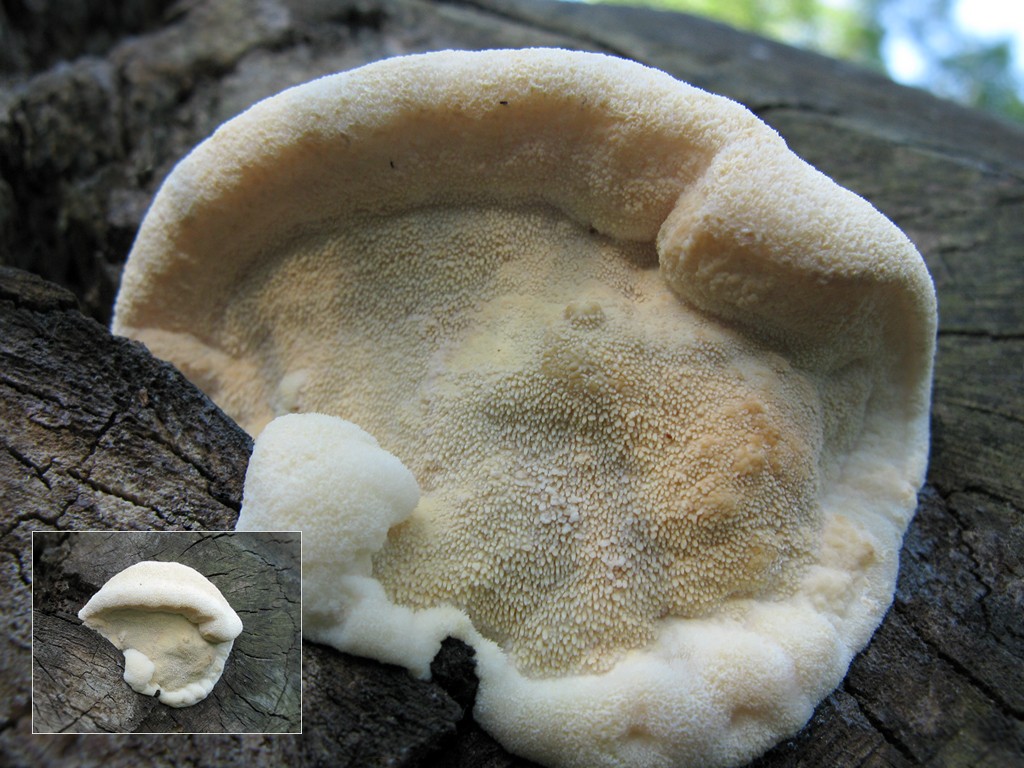
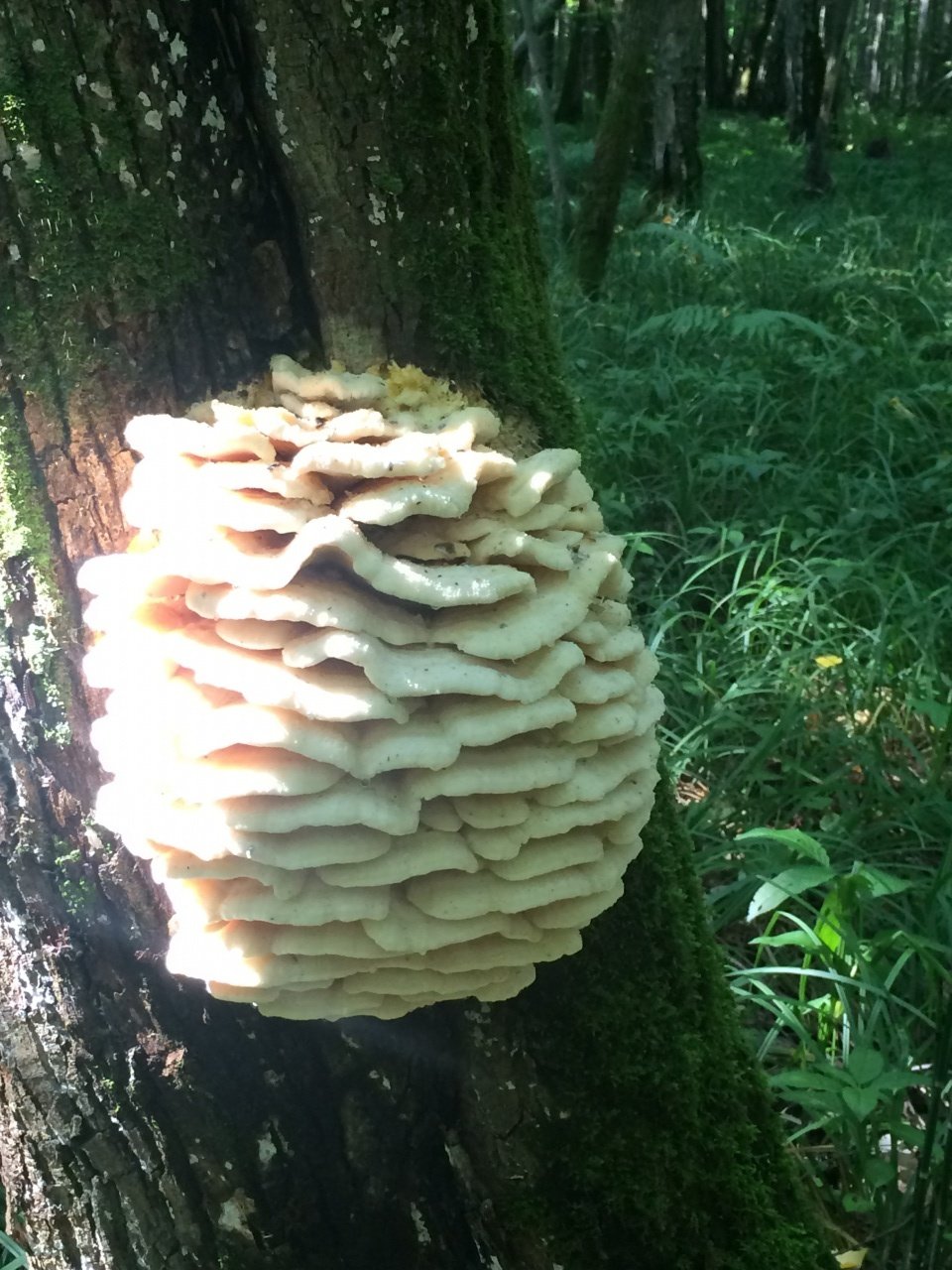
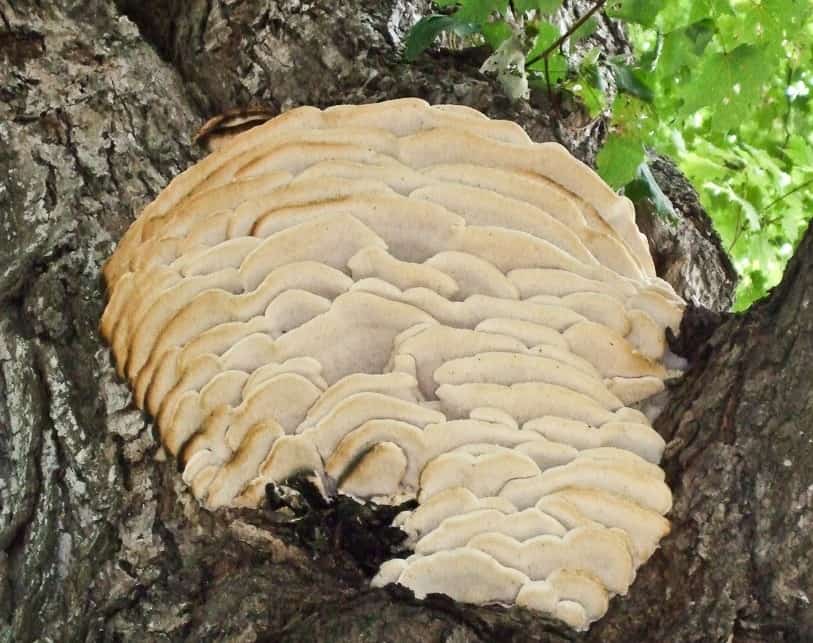
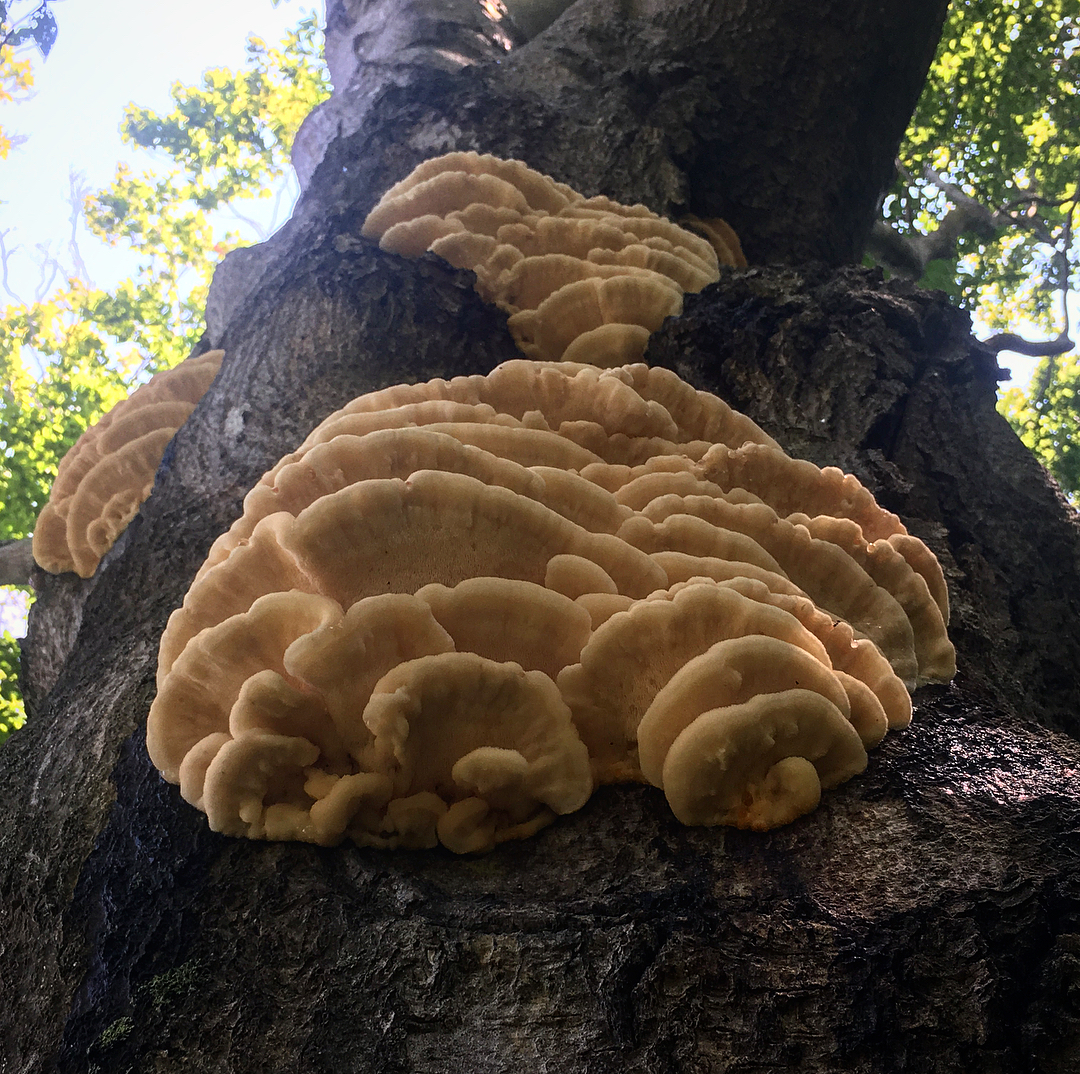
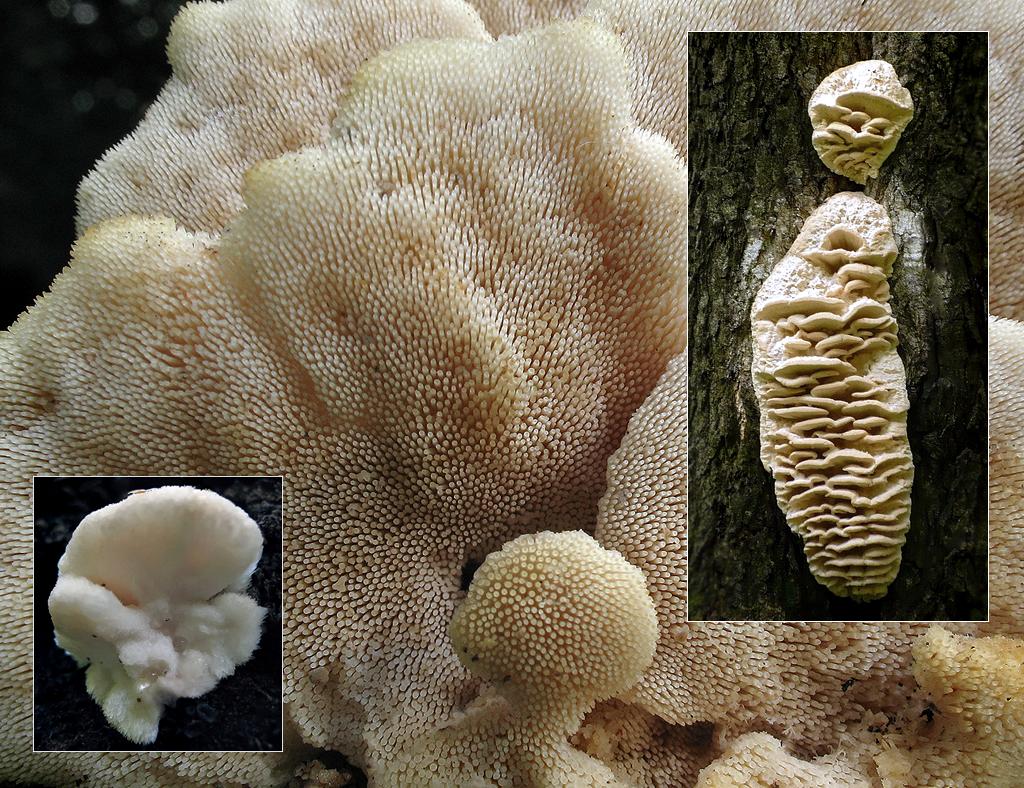
The fruit body of the northern hedgehog consists of large tongue-shaped or leaf-shaped caps. The hats grow together at the base, forming large formations that look like steps. Each hat is large in diameter from 10 to 30 centimeters. The thickness of the cap at the base is 3-5 centimeters.
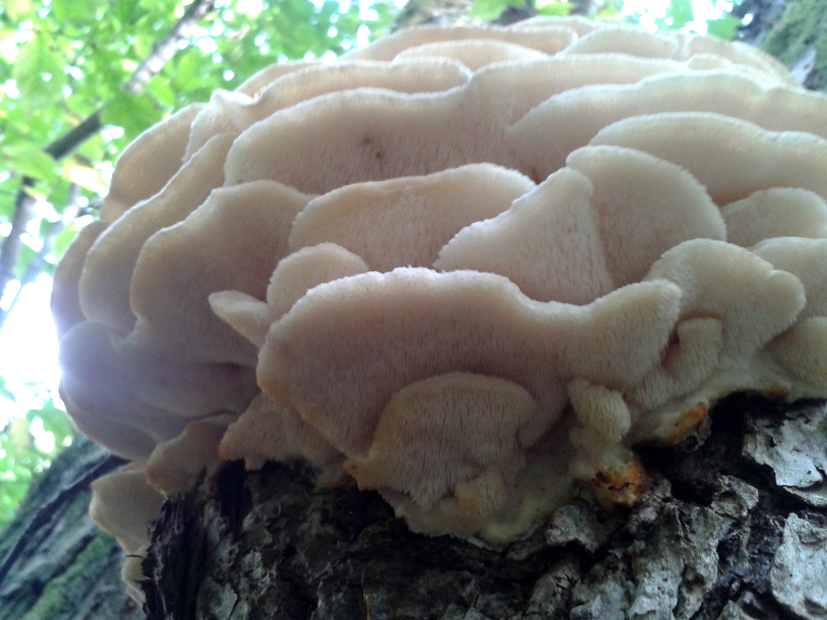
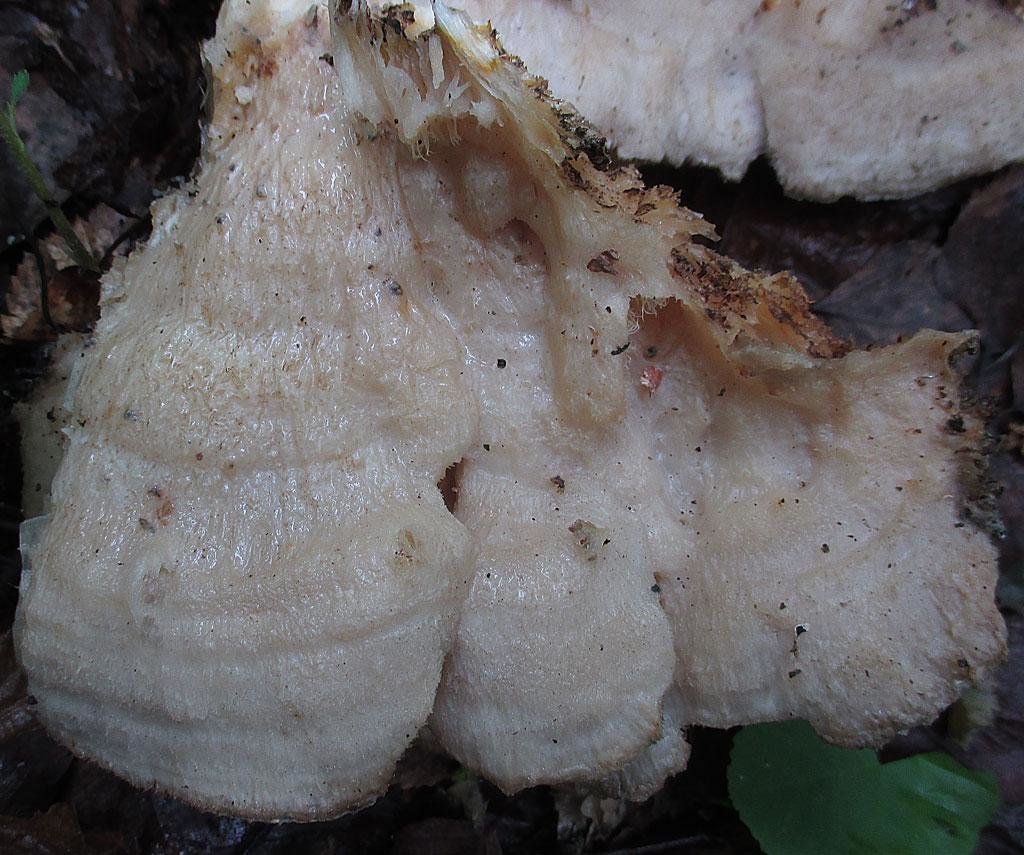
The color of the cap is gray-yellow. With age, these mushrooms fade and become whitish, and sometimes they, on the contrary, turn green from the mold covering them. The edges of the caps are wavy; at a young age, they can be very curved downward. The surface of the caps is smooth or slightly fluffed. The pulp is leathery, light, thick and dense. The smell of the pulp is quite strong and unpleasant.

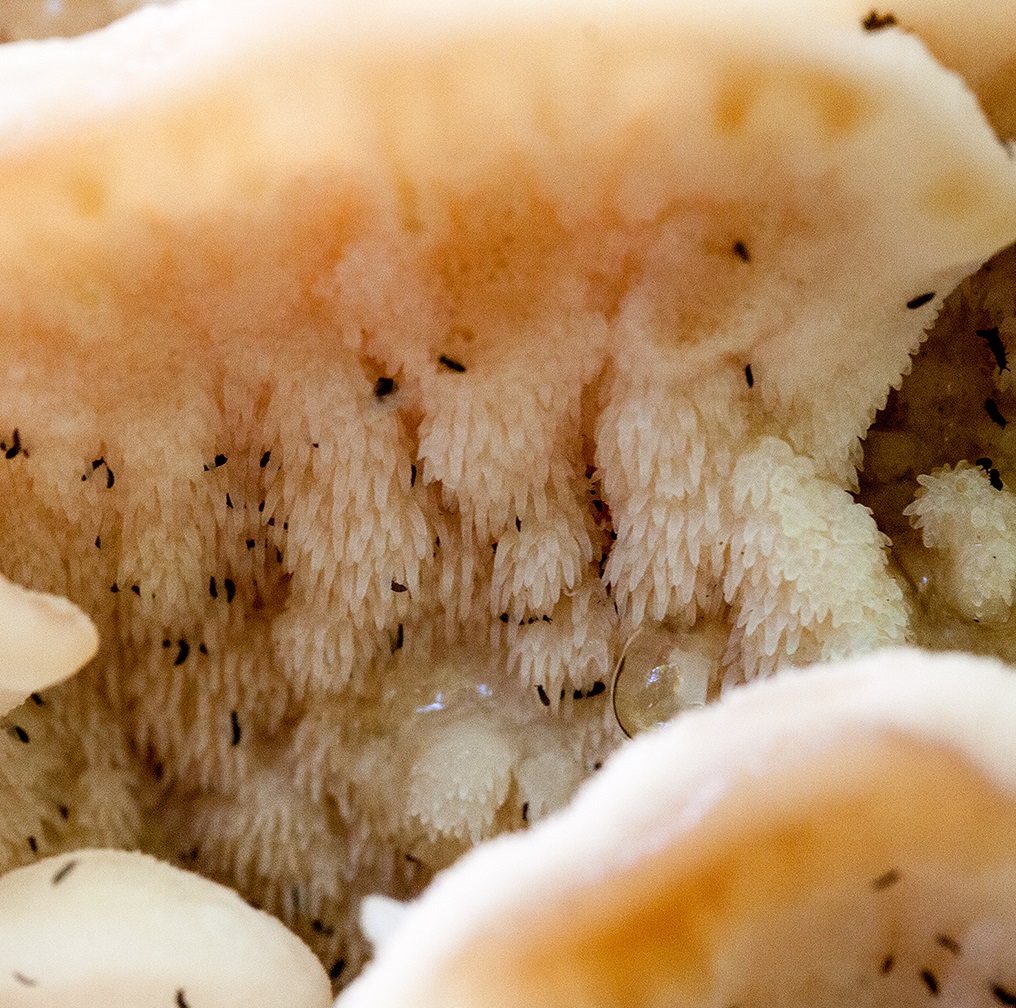
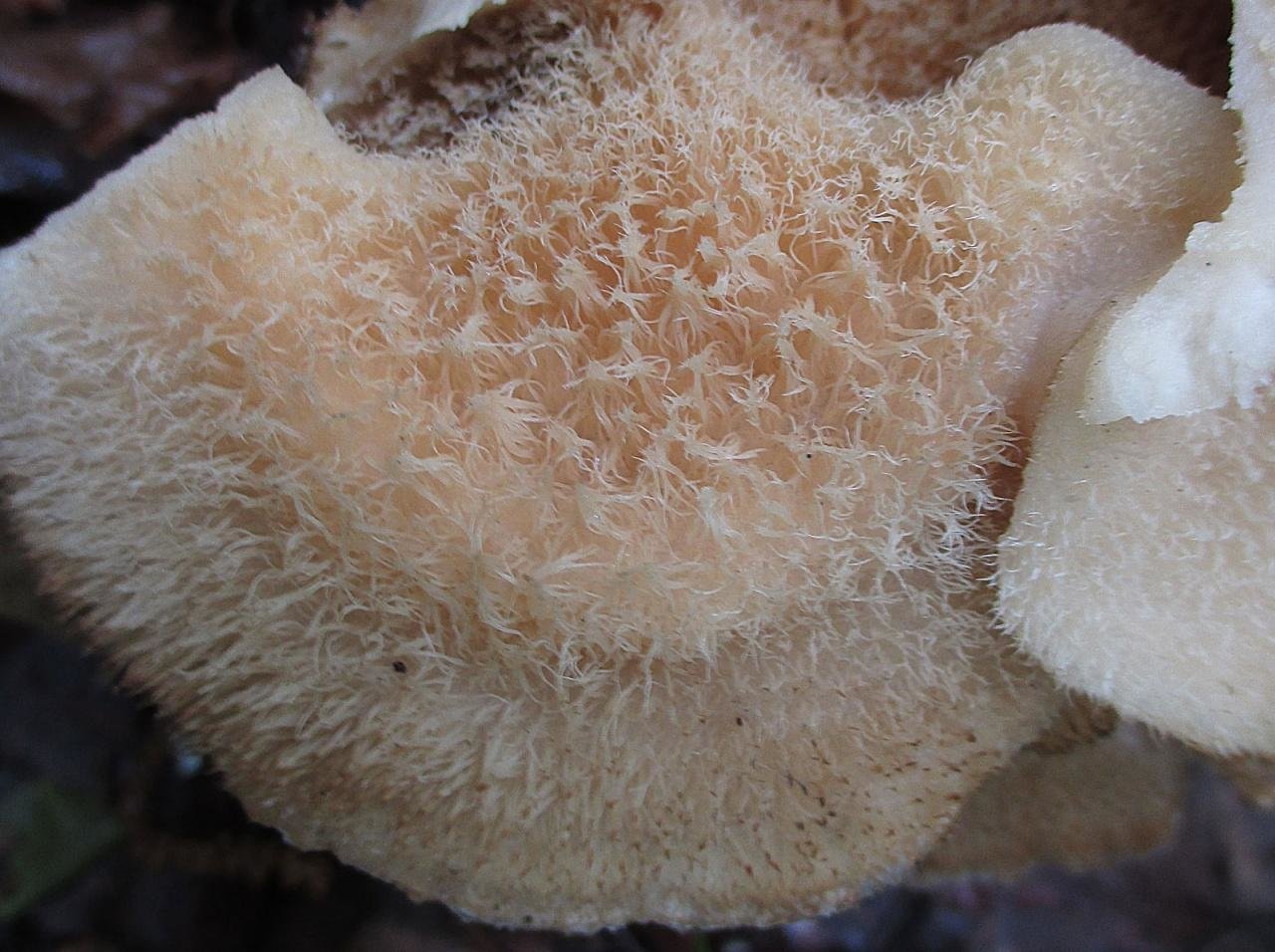
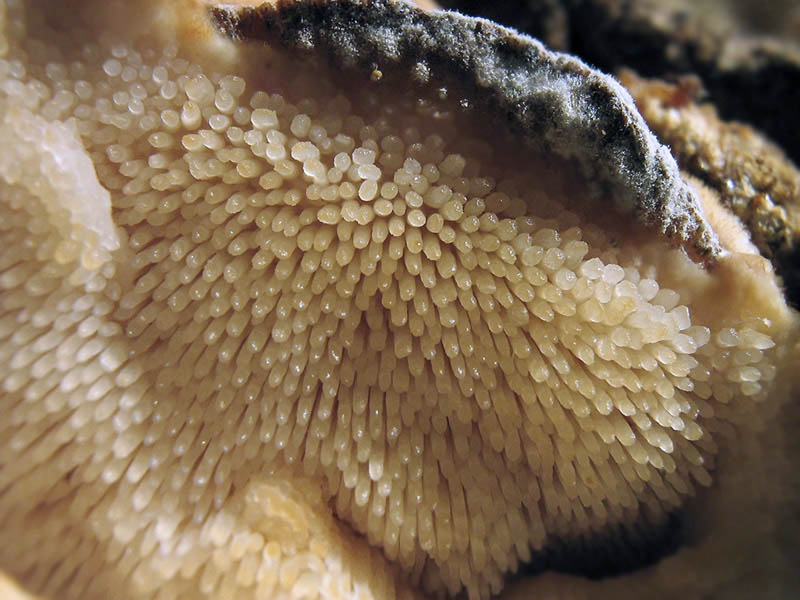
The hymenophore of the northern climacodon consists of spines. The thorns are long, thin, often located, rather brittle and soft. In young specimens, the thorns are white, and as they grow, their color, like the cap, changes. Spore white powder.
Distribution of northern black hairs
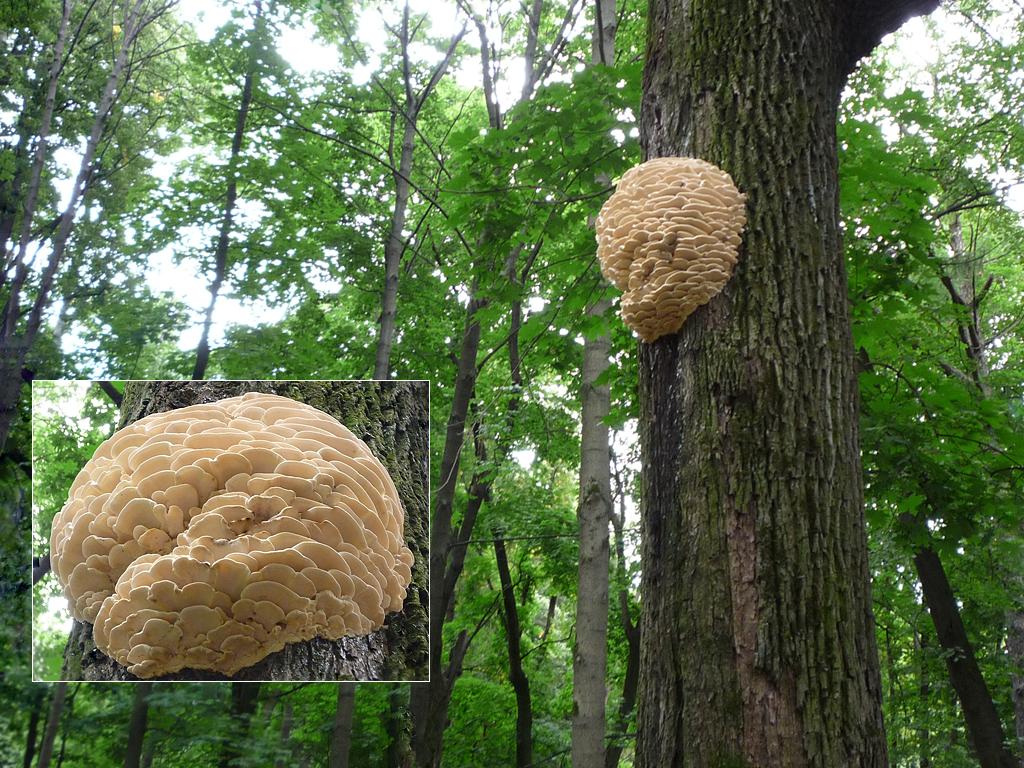
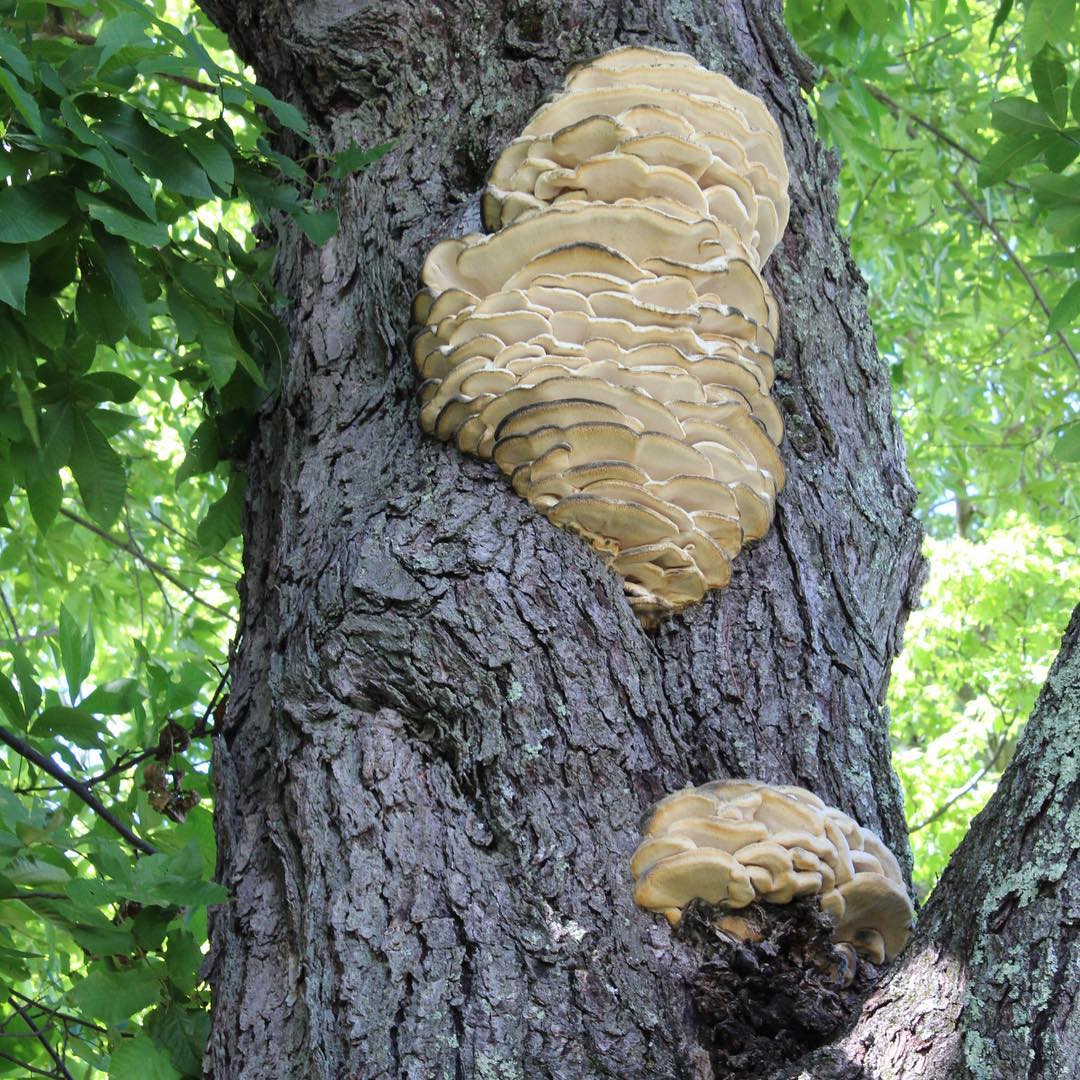
Northern Hericiums begin to bear fruit from the beginning of July, annual mushrooms can be found until autumn, but then insects eat them. You can find these hedgehogs in different types of forests, where they affect weak deciduous trees. Northern climacodons grow together in large groups, their aggregates can reach impressive sizes and weigh up to 30 kilograms.
Northern climacodons are dangerous parasites of the forest, but, despite this, there is little information about them.

Distinctive features of the northern black man's man
The northern Hericium is distinguished by a spiny hymenophore, in addition, the fruiting bodies are arranged in tiles, so it is difficult to confuse these mushrooms with other species

Other hedgehogs
Hericium Erinaceus is an edible mushroom. It is also called mushroom noodles. The fruit body is irregular in shape, without a leg, with long thorns, 2-5 centimeters in size. When dry, the thorns turn yellow. The pulp is white. The flesh tastes like shrimp meat.
Hericium erinaceans grow in China, the Amur region, in the Crimea and the Caucasus. These are rare mushrooms. They settle on the trunks of oak trees. In many countries, they are included in the Red Book.

Alpine Hericium is an edible member of the family. The width and height of the fruiting body is 5-30 centimeters. The color of the fruit body is white, and with aging it becomes light ocher. The fruiting body consists of numerous branches that diverge from the short stalk. At the ends of the branches there are hanging thorns about 2 centimeters long.
Alpine Hericiums live on fir, they can rarely come across other conifers. These mushrooms are common in the foothills and mountainous areas. Their fruiting occurs from summer to autumn.
Red Book
Are you here:
Home - Red Data Book of the Amur Region - Northern climacodon (Northern Blackberry)
North climacodon (northern black man's man)
Family Hericium - Hydnaceae
North climacodon - Climacodon septentrionalis (Fr.) P. Karst.
Category and status .. 3 b. A rare species with a significant range, within which they occur sporadically and with a small number of populations.
A brief description of. In the Amur region, the only known location of the northern climacodon is in the city of Blagoveshchensk (1). In Russia - the European part, the Caucasus, Siberia, the Far East. General distribution - Europe, North America, East and Central Asia.
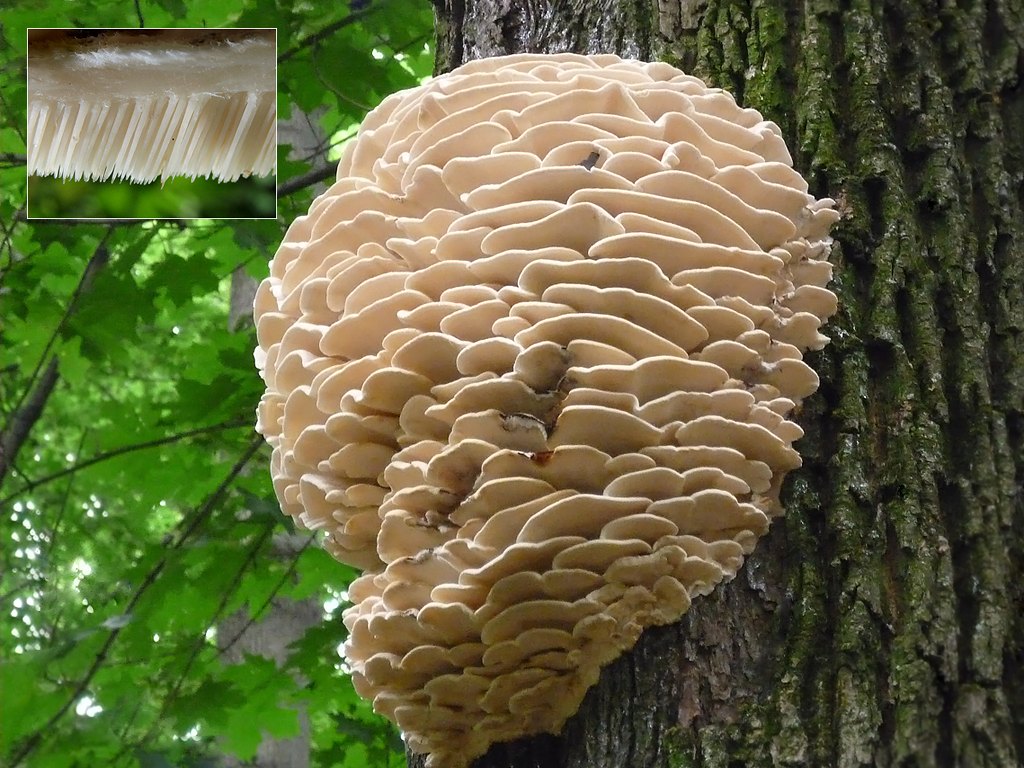
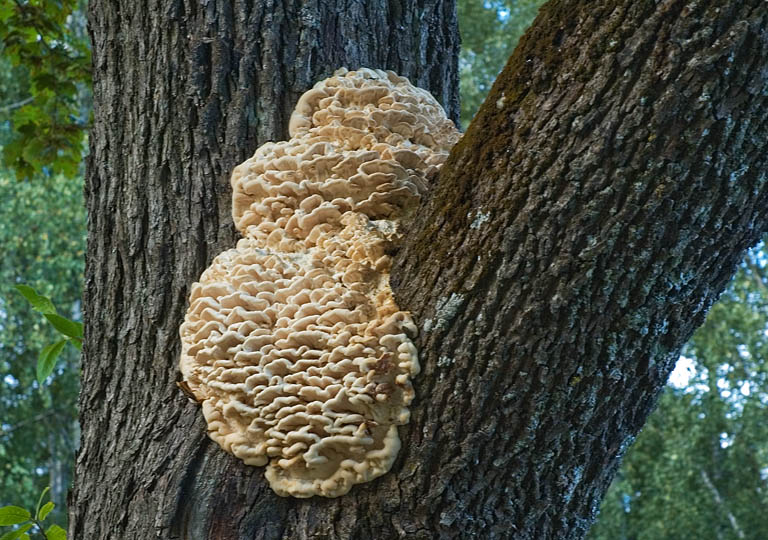
A brief description of. The fruiting body reaches 40 cm in height and width and consists of numerous accrete, usually tiled, fan-shaped, rounded, sessile, laterally attached caps 8-15 (20) cm long and 6-10 cm wide with a thin, later slightly wavy edge.
The surface of the caps is rough, felt-fibrous or with short white villi, with or without weak yellowish concentric zones, light, whitish, pale yellowish; when dry and from touch, the edge turns yellow.
The hymenophore is thorny, consists of dense, soft, about 0.2-0.3 (0.5) cm long, even conical white, later yellowish, spines. Spore powder is white. Spores 3.5-5 x 2-2.5 microns, ellipsoidal. Flesh: thin, dense, later firm, fibrous, white, with a pungent specific fishy odor.
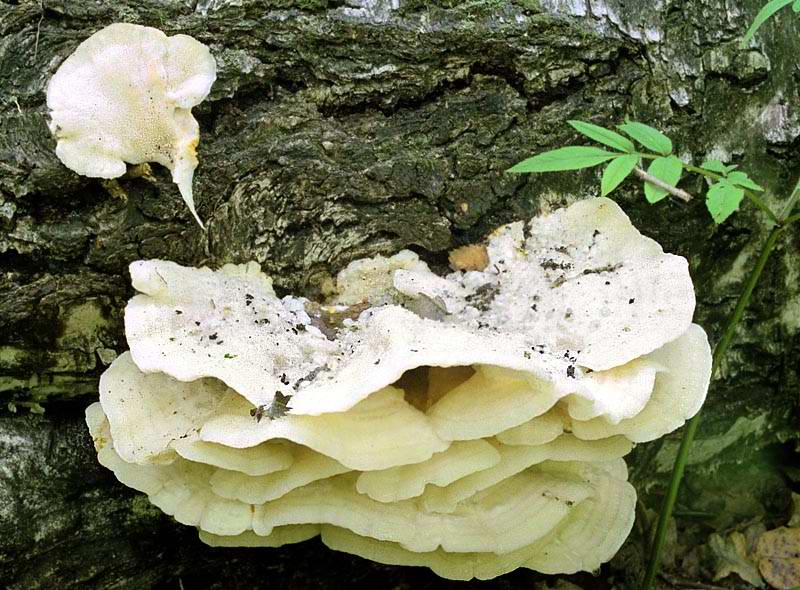
Features of ecology and phytocenology.Xylotroph on dead and living deciduous wood (birch, maple, elm, aspen), in deciduous and mixed forests, parks, dense tiled
in groups from mid-July to mid-September. Marked as a maple parasite in the area.
Limiting factors. Not studied. Necessary security measures. Search for new locations of the species.
Sources of information. 1. Compiler's data. 2. Nikolaev, 1961. Compiled by. ON. Kochunov.
|
20.10.2015 20:08:09
Back forward
-
Menu
- home
- Photo gallery
-
Animals
- Mammals
- Birds
- Fishes
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Insects
- Crustaceans
- Worms
- Molluscs
-
Plants
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperms
- Ferns
- Mosses
- Seaweed
- Lichens
- Mushrooms
- Moscow
-
Moscow region
- Mammals
- Birds
- Invertebrates
- Pisces, presm., Terrestrial.
- Plants
- Mushrooms, mosses, lichens
-
Voronezh region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Republic of Crimea
- Plants
- Animals
-
Rostov region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Krasnodar Territory
- Plants
- Animals
-
Leningrad region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Pskov region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Sverdlovsk region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Saratov region
- Mushrooms
- Bryophytes
- Ferns
- Amur region
- Krasnoyarsk Territory
- Belgorod region
-
Chelyabinsk region
- Plants
- Animals
-
IUCN Red List
- Extinct mammals
- Rare birds of the world
- Cetaceans
- Carnivores
- Reserves of Russia
- Wild animals
- Birds of Russia
- Download the Red Book
- Basic documents
- Custom sog.
- .
Cooking recipes
Young fruiting bodies of sulfur-yellow tinder fungus are tasty and are used in salads, fried, stewed (roast with potatoes), for making snacks and pie fillings. You can even make cutlets from them, dry them, cook salted, marinate them.
Primary processing
For safety reasons, a heat treatment of 40045 minutes is recommended. If there is complete confidence that the mushroom is real and not false, then 20-30 minutes is enough.
Cooking
Boiling mushrooms is one of the main operations before further cooking. The washed fruit bodies of the tinder fungus are placed in a saucepan with salted water and boiled for 40 minutes. After cooking, the water must be drained; it must not be used for food.
Frying
Fried mushrooms are one of the most delicious dishes. The sulfur-yellow tinder fungus must first be boiled, and then cut and fried.
Ingredients:
- 0.5 kg of boiled mushrooms;
- 2 onions;
- 4 tablespoons sunflower oil;
- 4 tablespoons tomato paste;
- salt and pepper to taste.
How to cook a sulfur-yellow tinder fungus:
- Cut the boiled tinder fungus into strips, the onion into half rings.
- Fry onions and mushrooms for 10 minutes in a skillet with sunflower oil.
- Add tomato paste, spices and simmer for another 5-10 minutes, stirring gently.
Pickling
Juicy pickled tinder fungi retain their useful and nutritious qualities and have a wonderful taste.
Ingredients:
- 1 mushroom (about 2 kg);
- 300 g of water;
- 2 tbsp salt;
- 1 tbsp. l. Sahara;
- 100 ml of 9% vinegar;
- bay leaf - 3 pcs.;
- ground black pepper to taste.
How to pickle a chicken mushroom:
- Rinse the mushroom, cut into slices and place in a large saucepan.
- Add water, place over medium heat and bring to a boil.
- Add salt, sugar, spices (except vinegar) and simmer for 20 minutes.
- Add vinegar and leave for 10-12 hours at room temperature.
- When serving, sprinkle with unrefined sunflower oil, sprinkle with herbs.
- Store in the refrigerator for up to 2 weeks.
Canning for the winter
For long-term storage, put boiled hot pickled mushrooms according to the recipe described above in glass jars, add 1 tablespoon of 70% vinegar per 1 liter and close hermetically with an iron lid. If you have a large freezer, tinder fungi can be frozen.
Stewed mushroom
This method of cooking gives the mushroom pieces a more delicate soft consistency, the stewed tinder fungus can be used as a gravy for side dishes. Cooking will not take long:
- Take 0.5 kg of boiled tinder fungus and two onions, cut them into thin slices.
- Put chopped food in a frying pan with heated vegetable oil, add 3-4 tbsp. tablespoons of sour cream and sauté for 7-10 minutes, stirring occasionally.
- Close the lid and simmer over low heat for another 3-5 minutes.
Mushroom pate
It is easy to make a pate; such a dish can even be canned for the winter, but for this you need to slightly change the recipe by adding vinegar to the list of components.
Ingredients:
- 1 kg of mushrooms;
- 0.5 - 0.7 kg of onions;
- salt and pepper to taste.
Cooking step by step:
- Wash the mushrooms, cut into large pieces, put them in boiling water and cook for 40 minutes.
- Drain the water and leave the boiled tinder fungus to cool.
- Chop the onion and mix with the mushrooms, add salt and pepper.
- Fry in a large amount of sunflower oil, stirring regularly, until tender (10-15 minutes).
- Cover and simmer for another 5 minutes.
- The cooled mass must be ground in a blender until smooth.
Tinder fungus pate is perfect for making breakfast sandwiches. Spread the slices of bread with mayonnaise and put the pate on top.
- Peel 500 g of mushrooms, cut into large pieces and boil in salted water for 40 minutes. Drain the water, wait until it drains and the slices dry a little.
- Season with salt and pepper, squeeze out the juice of half a lemon, pour over with vegetable oil and stir.
- Place the mushrooms on a baking sheet and bake in the oven at 180 ° C for 15-20 minutes.
- Sprinkle with finely chopped parsley before serving.
Scaly and varnished tinder fungi: photo and description
Scaly tinder fungus, motley, hare. The cap is 5-50 cm in diameter, 0.5-10 cm thick, whitish or creamy, with large pressed brown scales, making it variegated. The edge is usually more or less thin, often bent inward. Stem 4-8 × 1-4 cm, whitish-cream, almost black at the base. The tubular layer is white. The pulp is whitish, with a pleasant mealy smell and taste. Spore powder is white. Spores 10-14 × 4-5 (6) µm, oblong-ellipsoidal, smooth, colorless.
Growth. It grows on living and dead trunks and branches of fruit and broad-leaved trees.
Fruiting. June to September. Wound parasite. Having penetrated into the inner layers of the wood, the mycelium causes a yellowish-white internal rot.
Usage. Conditionally edible mushroom only at a young age (old mushrooms are tough).
Lacquered polypore. Basidiomas are annual or 2-3 years old with a cap and a leg. The cap is up to 25 cm in diameter and 1–3 cm thick, semicircular or kidney-shaped, covered with a shiny, lacquered, reddish, then reddish-purple, dark red or chestnut-brown and, finally, almost black crust. Leg up to 15 × 1–2 cm, sometimes short, eccentric, less often lateral, covered with the same crust as the cap, one color with the cap or almost black. The tubules are 0.5–2 cm long, ocher, with small and rounded pores.
As you can see in the photo, in the lacquered tinder fungus, the surface of the tubular layer is whitish, creamy, then turns brown, when pressed, it darkens:
The pulp is spongy-corky, hardening, white or light reddish. The hyphalous system is trimic. Spores 8-13x5.5-7.5 µm, ovoid or almost oval, truncated at the apex, warty.
The area where this tinder fungus grows in Russia is very wide. It is distributed in the Far East (Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territories, Jewish Autonomous, Amur, Sakhalin, Magadan and Kamchatka Regions), in the European part, in the Urals, in Siberia; outside Russia - in Europe, Asia, North Africa, North America.
Grows in deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests on stumps and deadwood of spruce, fir, larch, birch, in July - August, in small groups and singularly. The mushroom has medicinal properties. Grown in culture for food and medicinal purposes, maintained in pure culture in collections in many countries of the world, as well as in Russia.
Limiting factors. Human economic activity, leading to the removal of deadwood, deforestation, forest fires.
Below is another selection of photos of tinder fungi with a description.