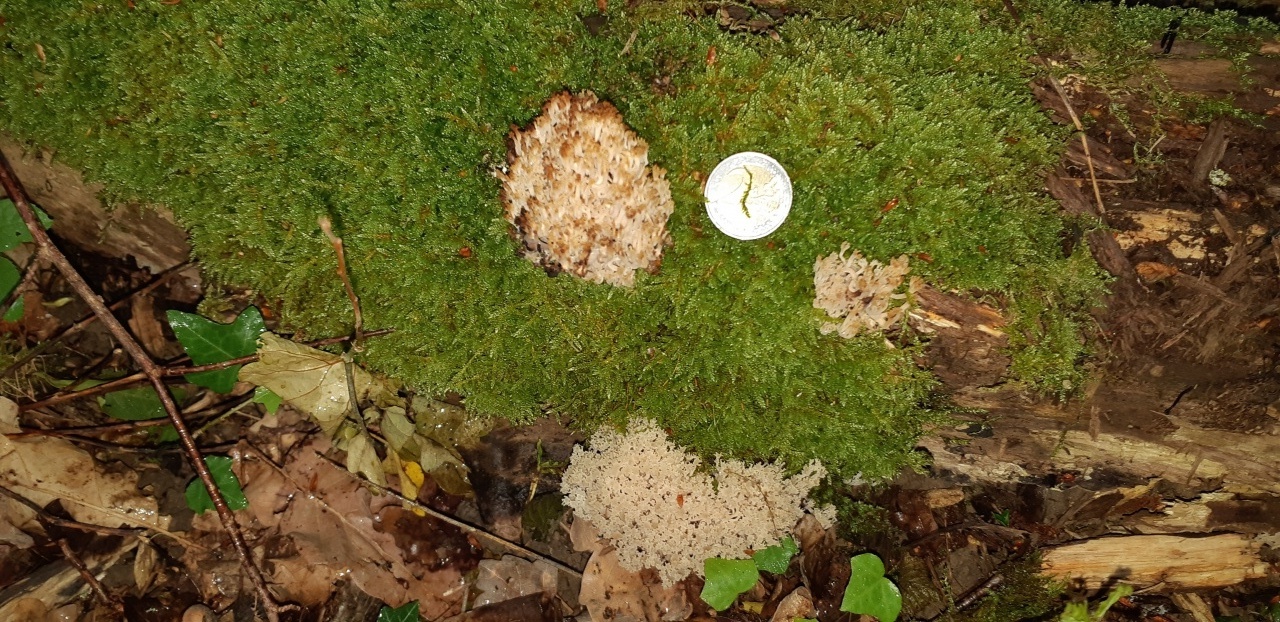
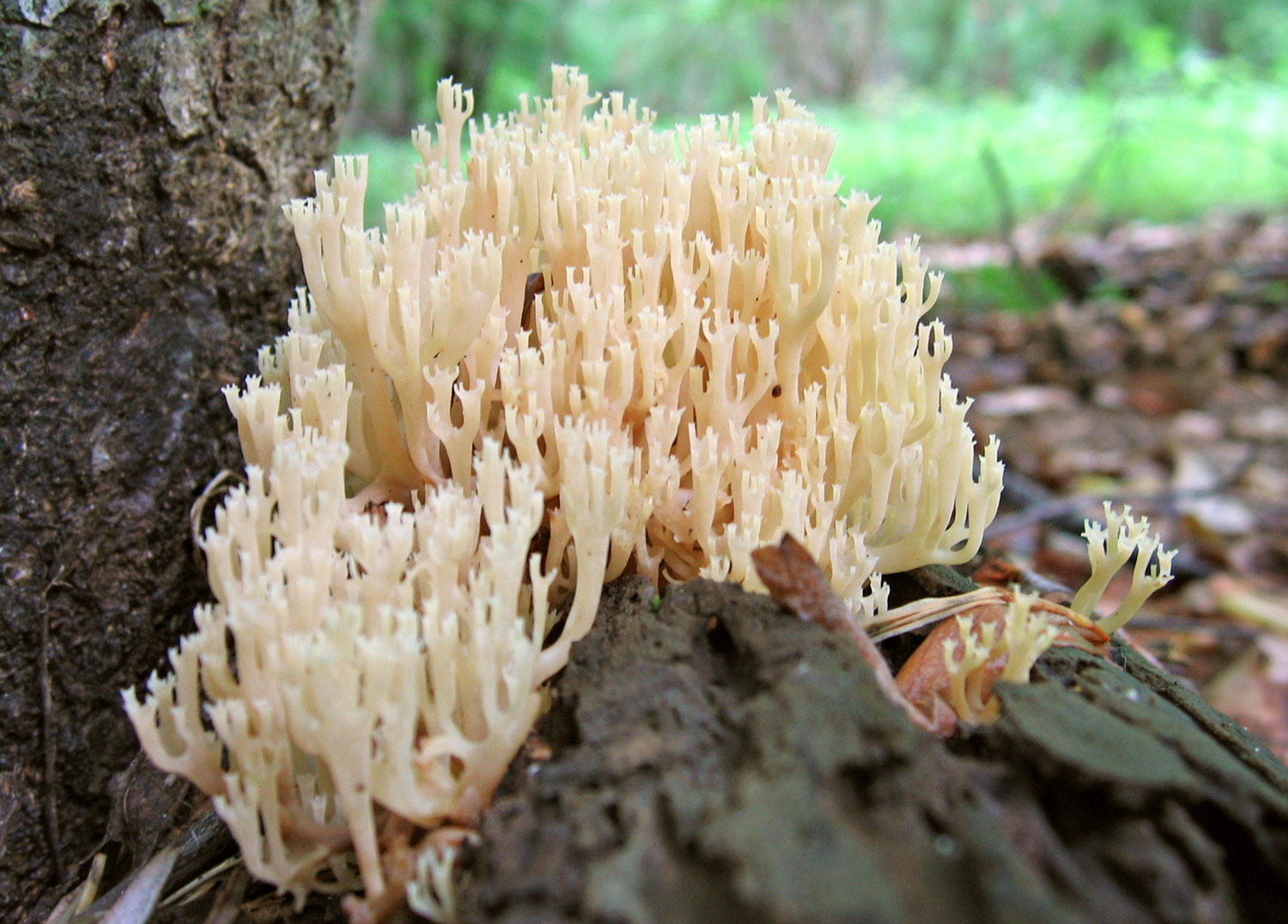
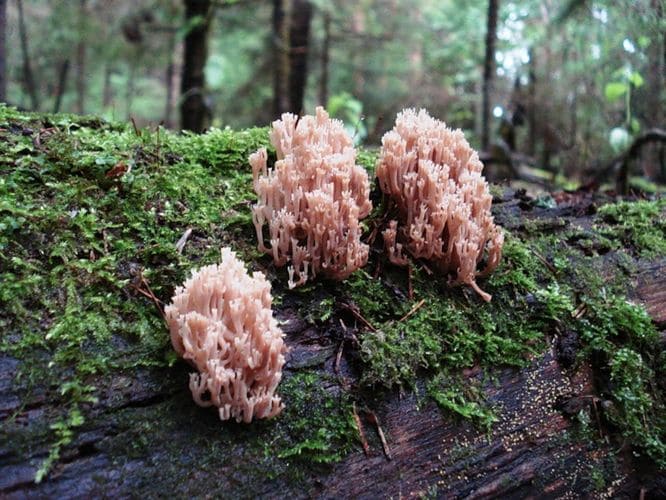
Mushroom exotic in the forest, or a bizarre forest dweller - Coral mushroom. What do you know about him?
Autumn is the best time of the year for mushroom picking. Many mushroom pickers are looking forward to the autumn rainy season when their favorite varieties of mushrooms begin to appear.
Often, many bypass plants, not even realizing that they also belong to the kingdom of mushrooms, and in fact many varieties are quite interesting and edible.
Others, on the contrary, really should not be touched. The most interesting, however, are the coral mushrooms, some of which can be eaten. But it's worth exploring which ones are truly safe.
Incredible Ramaria
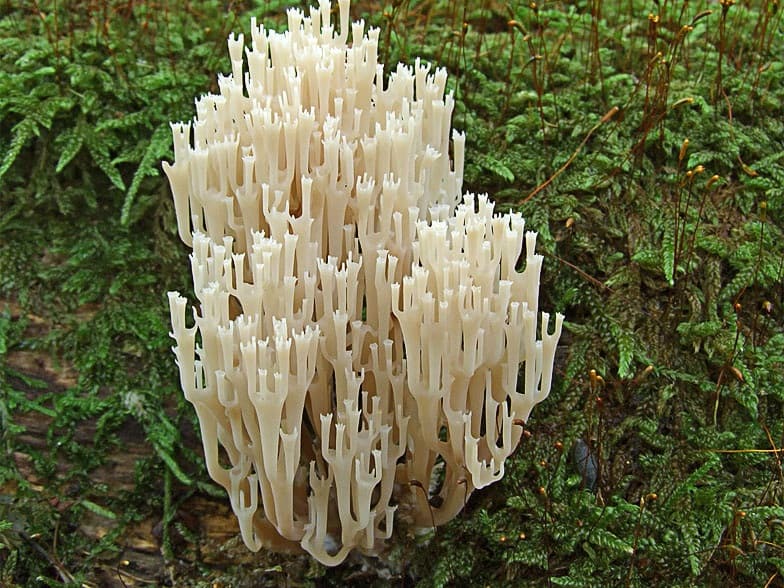
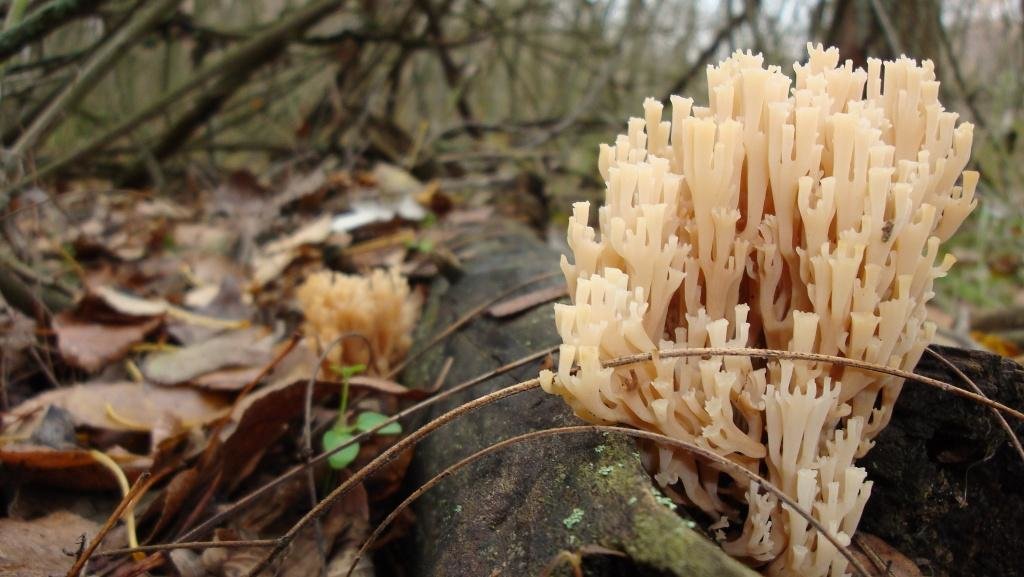
Very often on rotten trees you can find unusual beauties resembling corals from a distance. At first it may seem that they have sprouted completely inappropriately in such an area, but is this so?
Ramaria golden
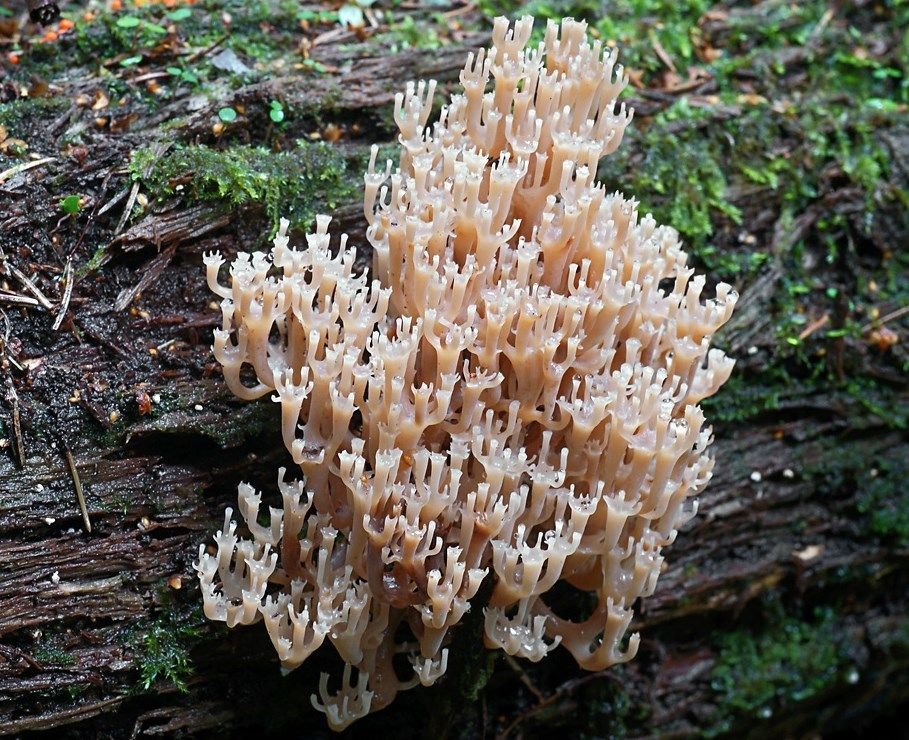
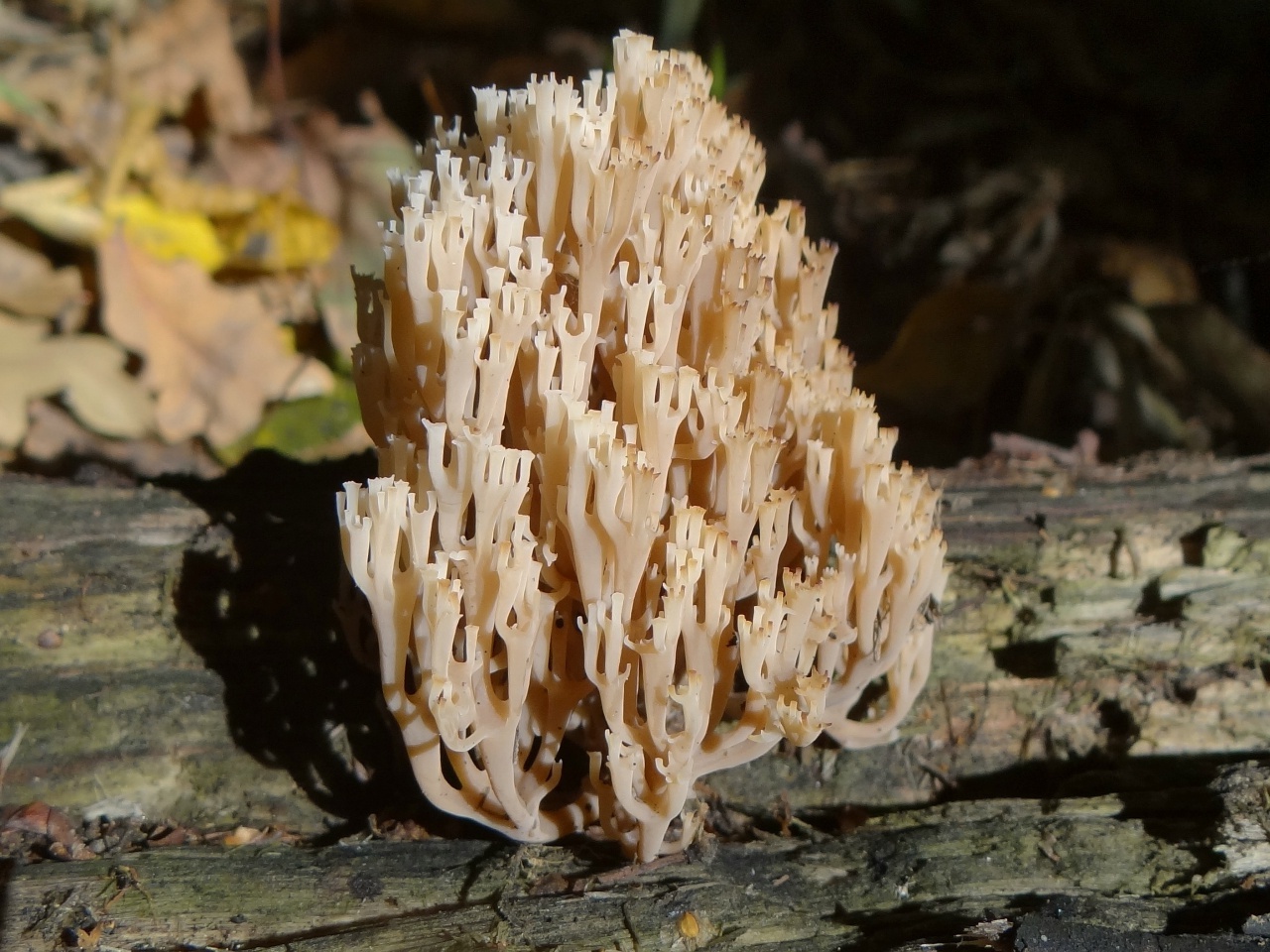
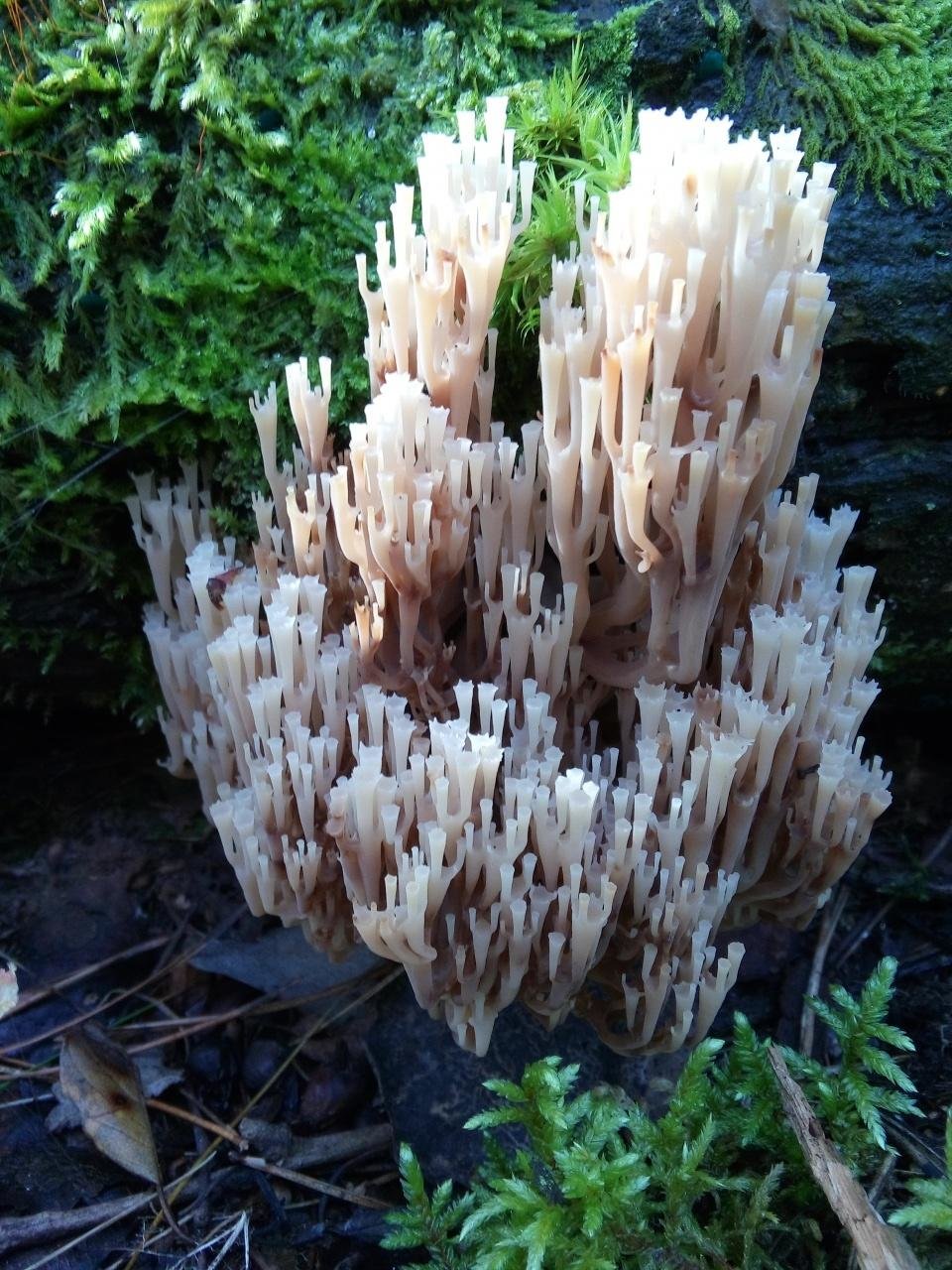
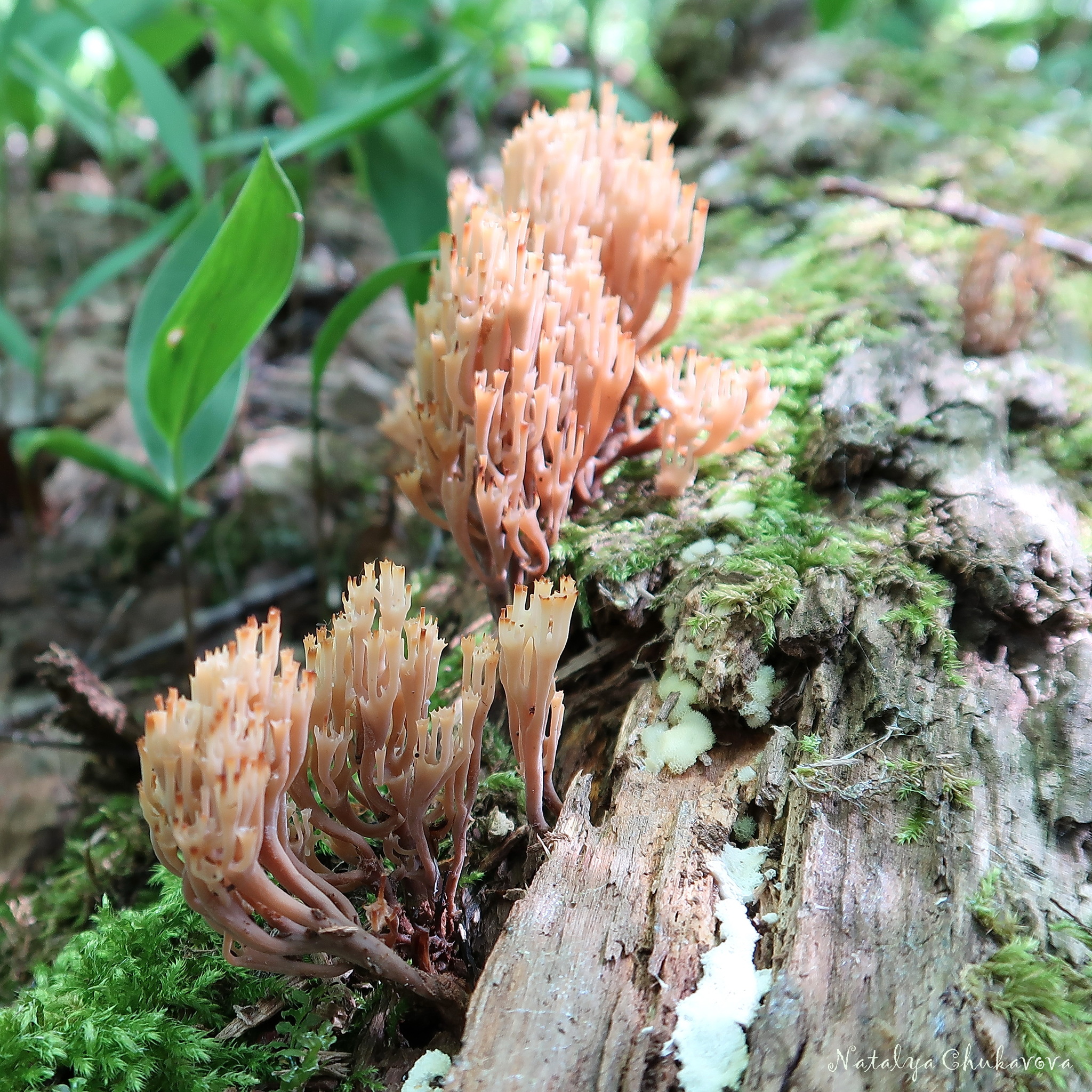
It is a mushroom in the form of a golden coral. It is worth remembering that the color of this variety changes with age. The darker the shade, the older the mushroom. Only young plants are tasty, older ones gain bitterness and become almost inedible.
Ramaria is beautiful
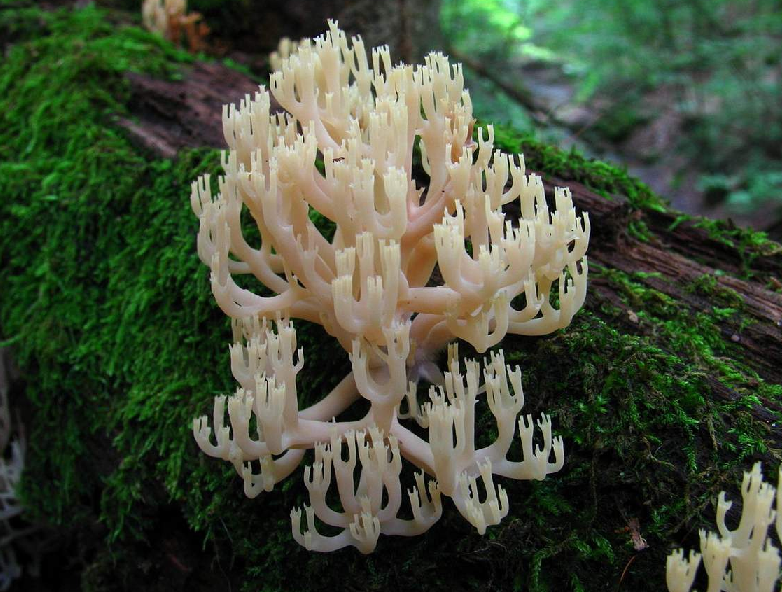
This attractive specimen often distracts mushroom pickers from looking for edible mushrooms. She beckons, causing the desire to rip it off. It itself looks pinkish, and if you touch the twig, it will become even more pink. However, you shouldn't pluck it, as this variety is inedible and can cause stomach upset.
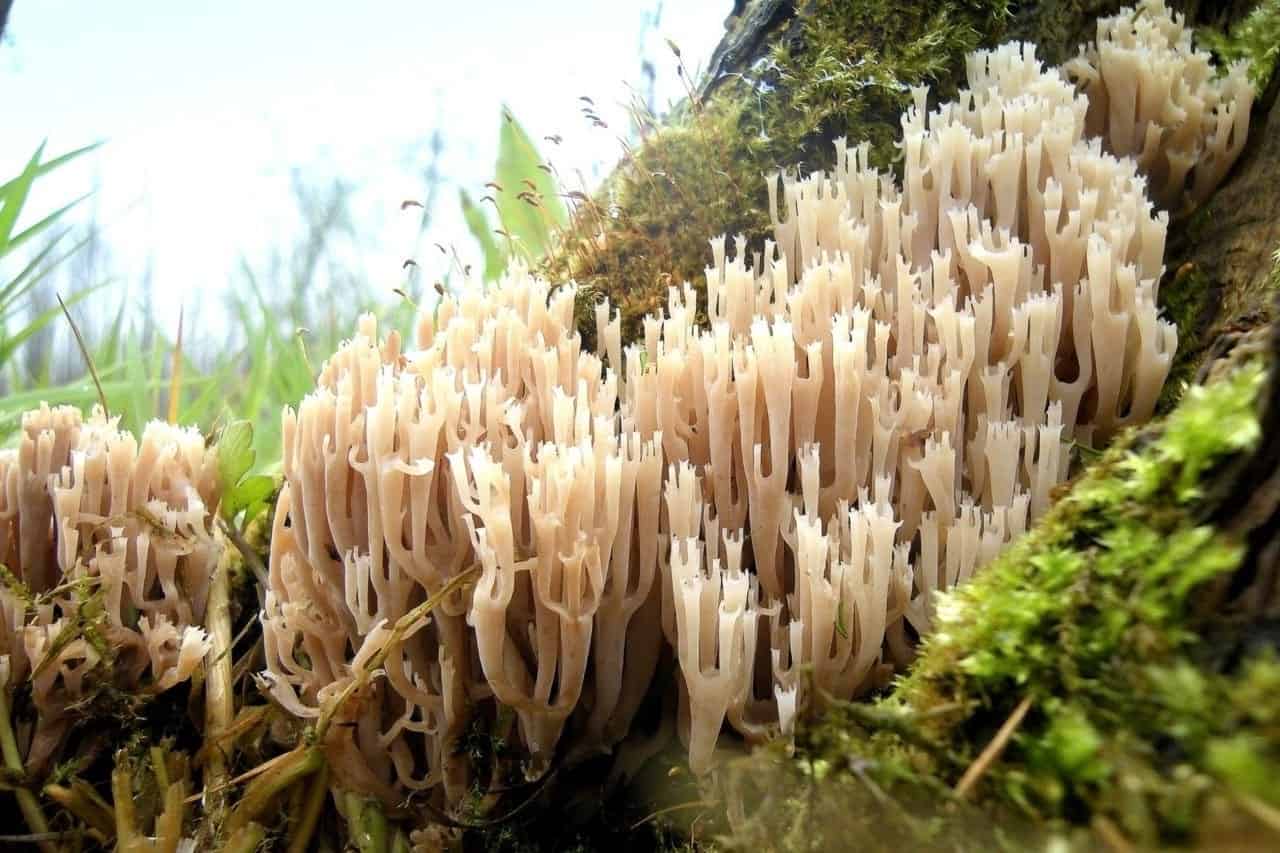
Common ramaria
This view looks much simpler than the others. When touched, it does not change shade and along the entire length of the same color.
However, it is worth considering that this variety also contains bitterness, therefore it is worth picking young mushrooms and infusing in water before cooking, changing it periodically for several days. You can find it in the coniferous zone, it grows quite abundantly, forming different geometric shapes in shape.
Bunched ramaria
This mushroom looks more like a cauliflower in appearance. It is pink in color and grows in small families. Finding her is quite difficult, because she loves warmth.
As long as this mushroom has pink-red twigs, it can be safely eaten without the need for soaking. When its color begins to turn brownish, it means that it should not be consumed, as it becomes inedible.
Ramarias that should not be consumed
These mushrooms have an incredibly photogenic appearance, which is why curiosity lovers and photographers will also be attracted by such varieties as: hard ramaria. It has slender twigs that, if pressed, will turn redder. However, this variety is bitter and should not be eaten.
Ocher-green ramaria - young shoots of a lime shade, although if damaged, they will almost immediately become darker shades. You can meet them in coniferous forests and they are very bitter.
Fir pheoklavulina, was previously assigned to a different genus, but in the end it was decided to nevertheless refer it to the genus Ramaria.
Charming clavulins
Not only ramarias are admired, their brethren, which do not differ much in appearance, also cause a lot of delight.
Coral clavulina
In coniferous forests, you can often find this beauty that looks like white coral. As to whether or not it is edible, there are many different versions. However, among those who have ever tried it, it did not cause any particular delight.
Amethyst Clavulina
This beauty can not only be photographed, posted on all social networks, shown to relatives, friends and acquaintances, but even eat. This mushroom has nothing outstanding in terms of taste, but in combination with beauty, it’s nothing like that.
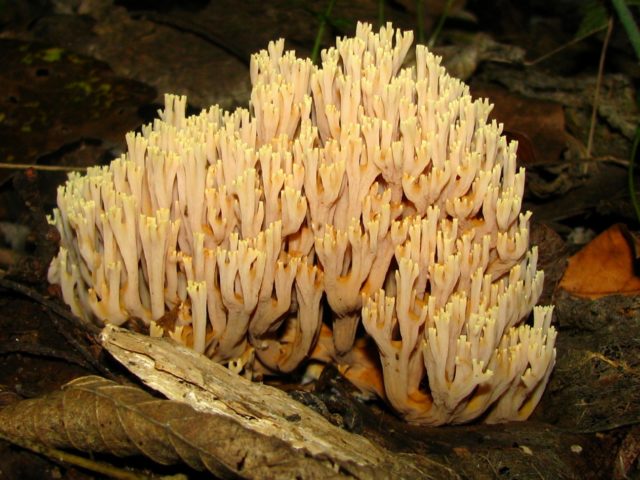
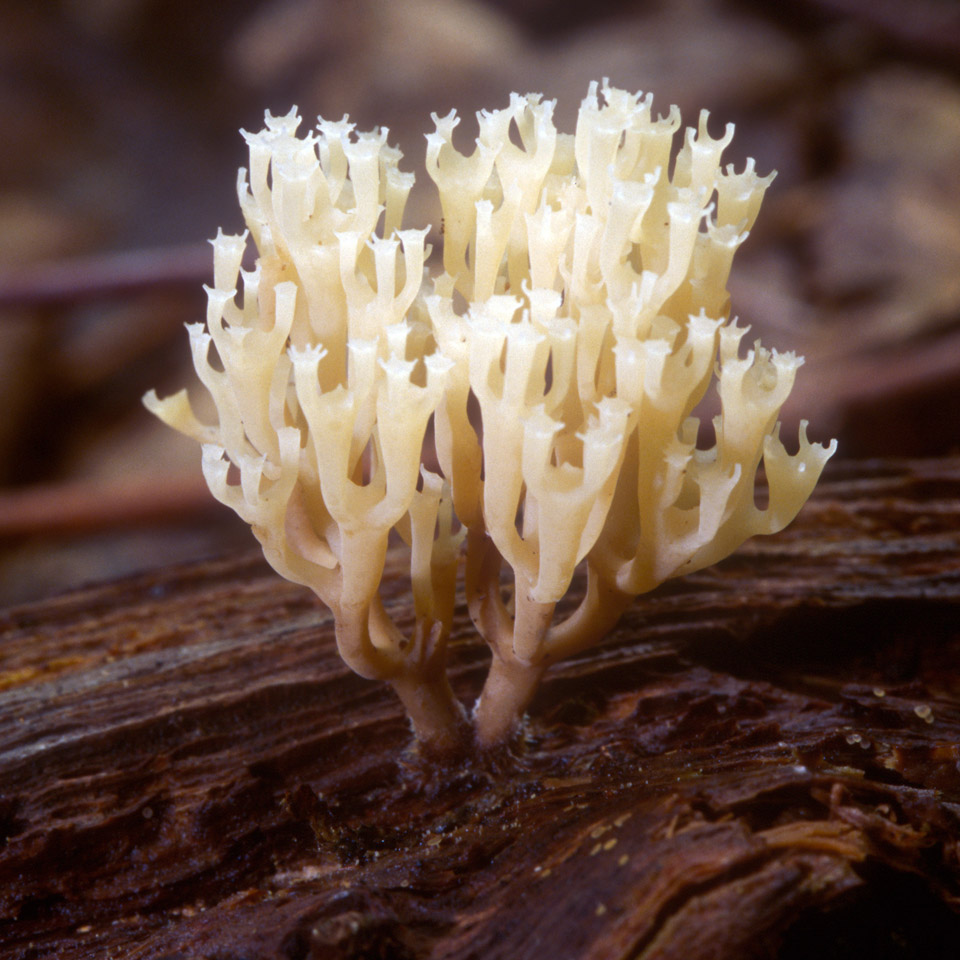
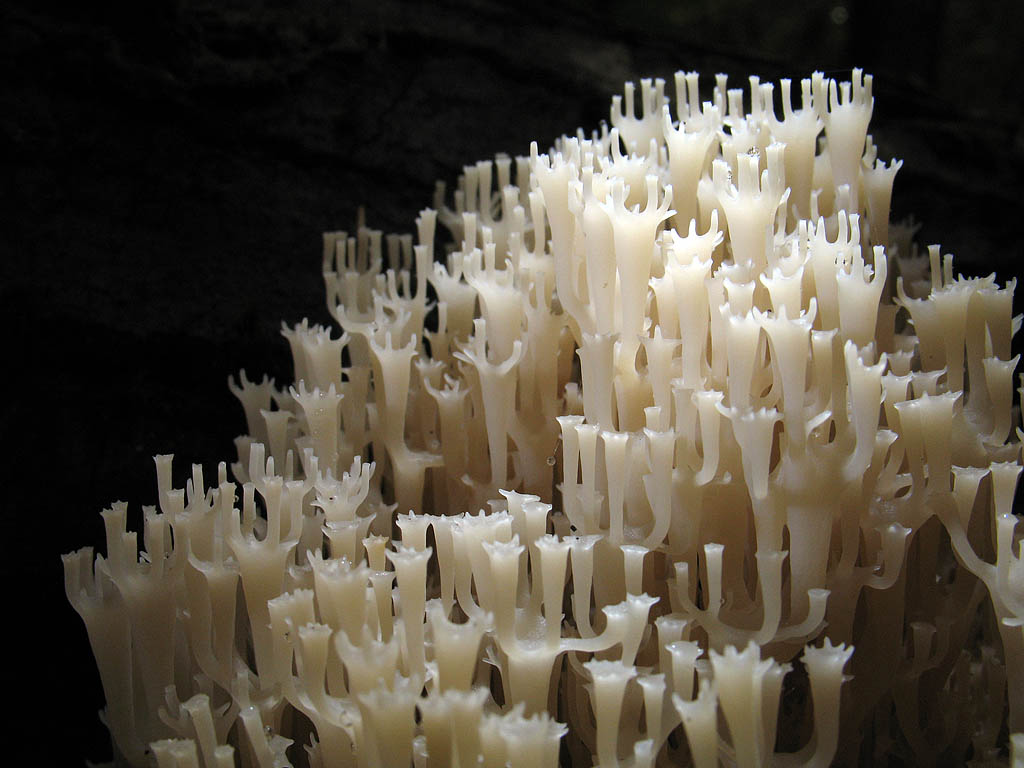
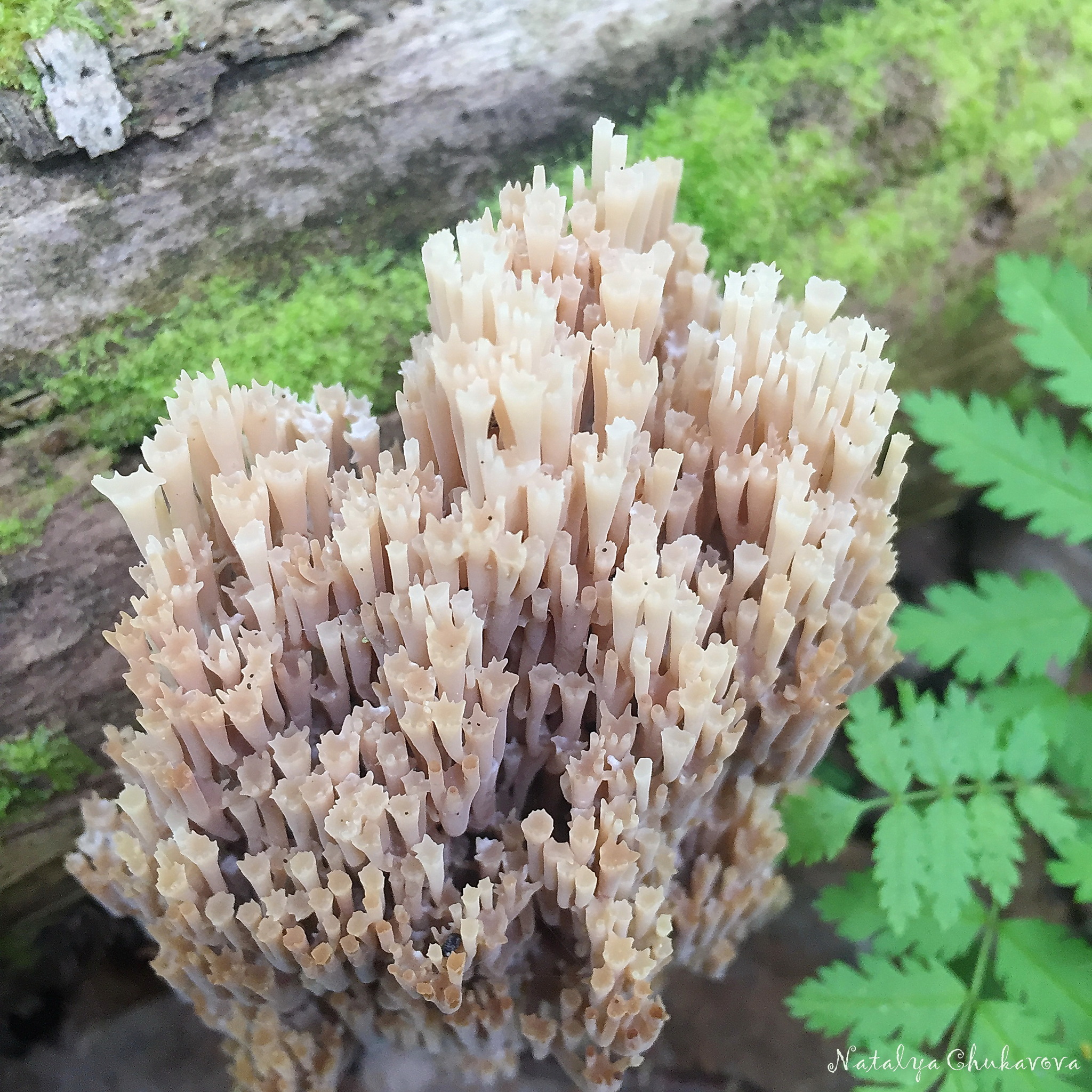
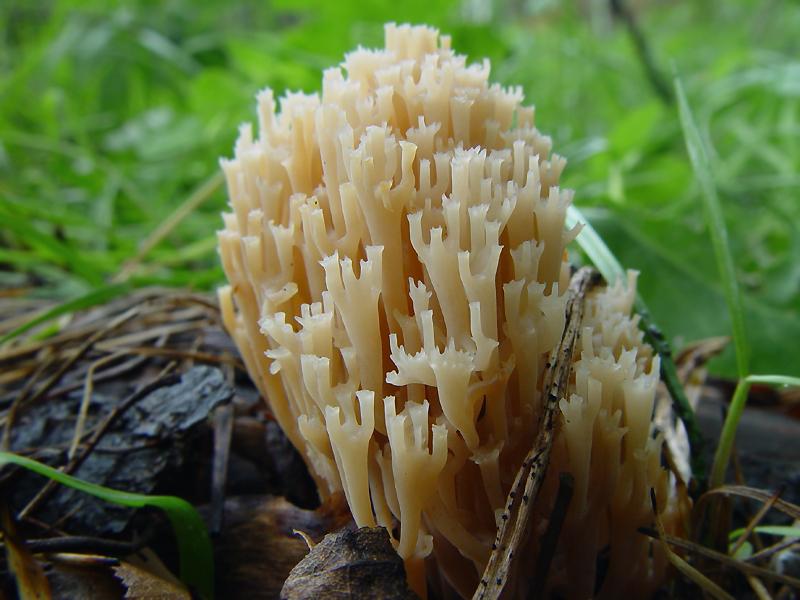
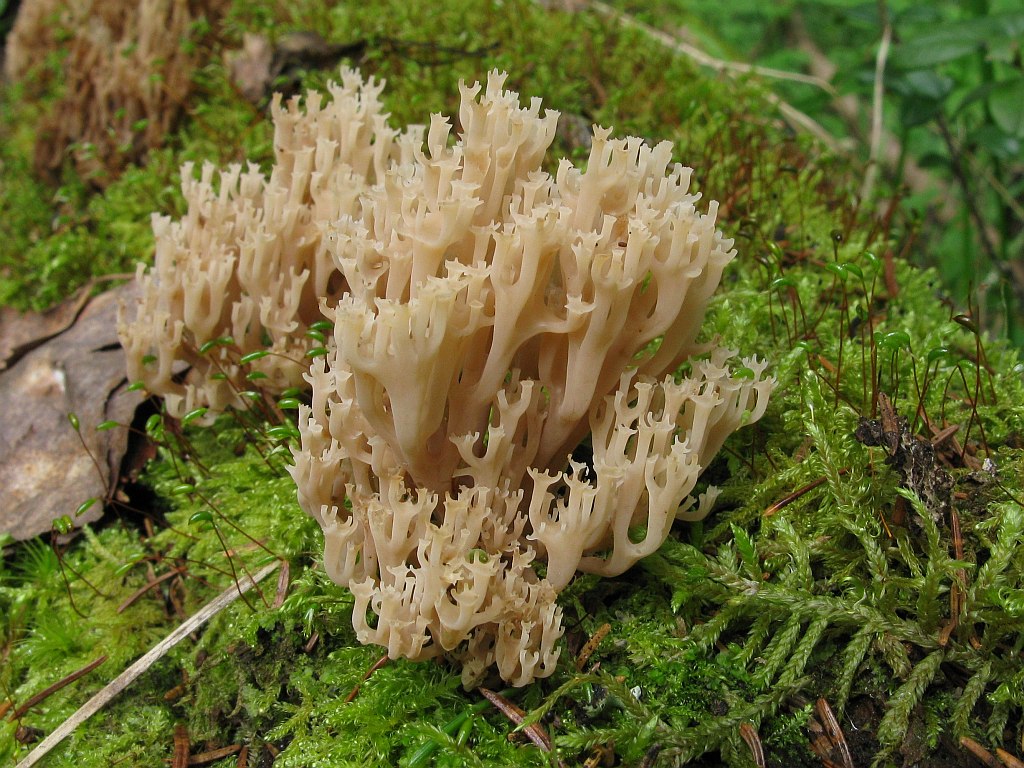
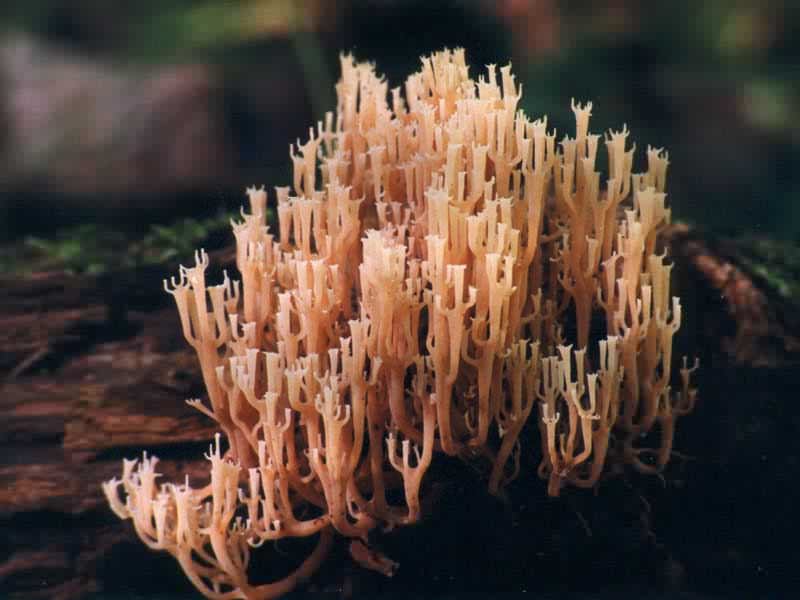
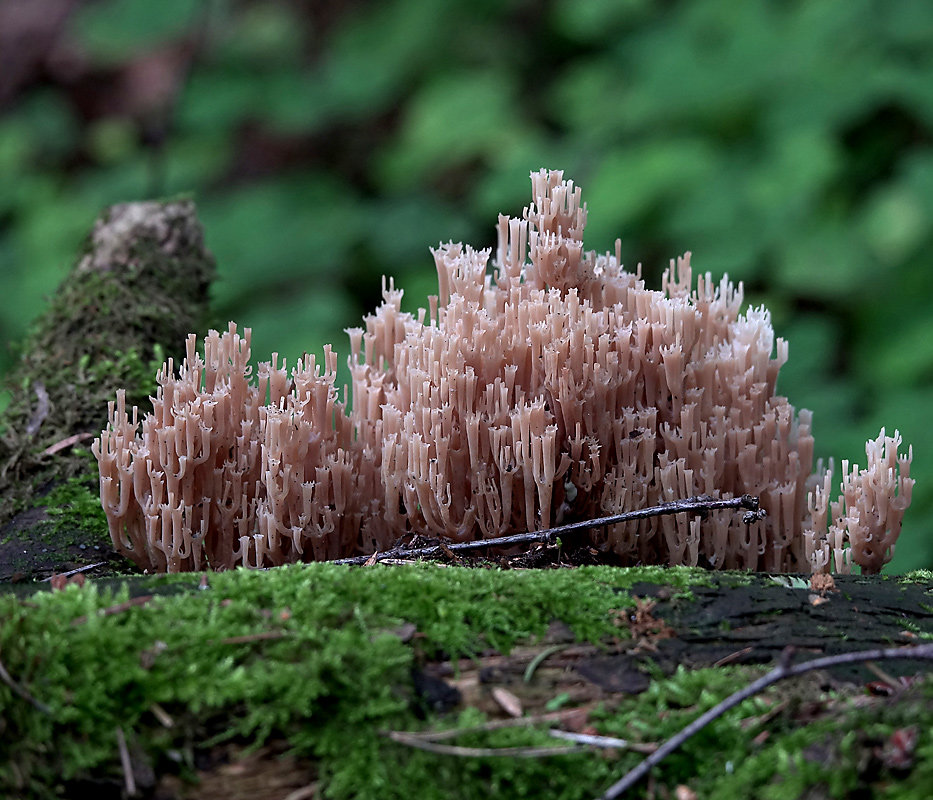
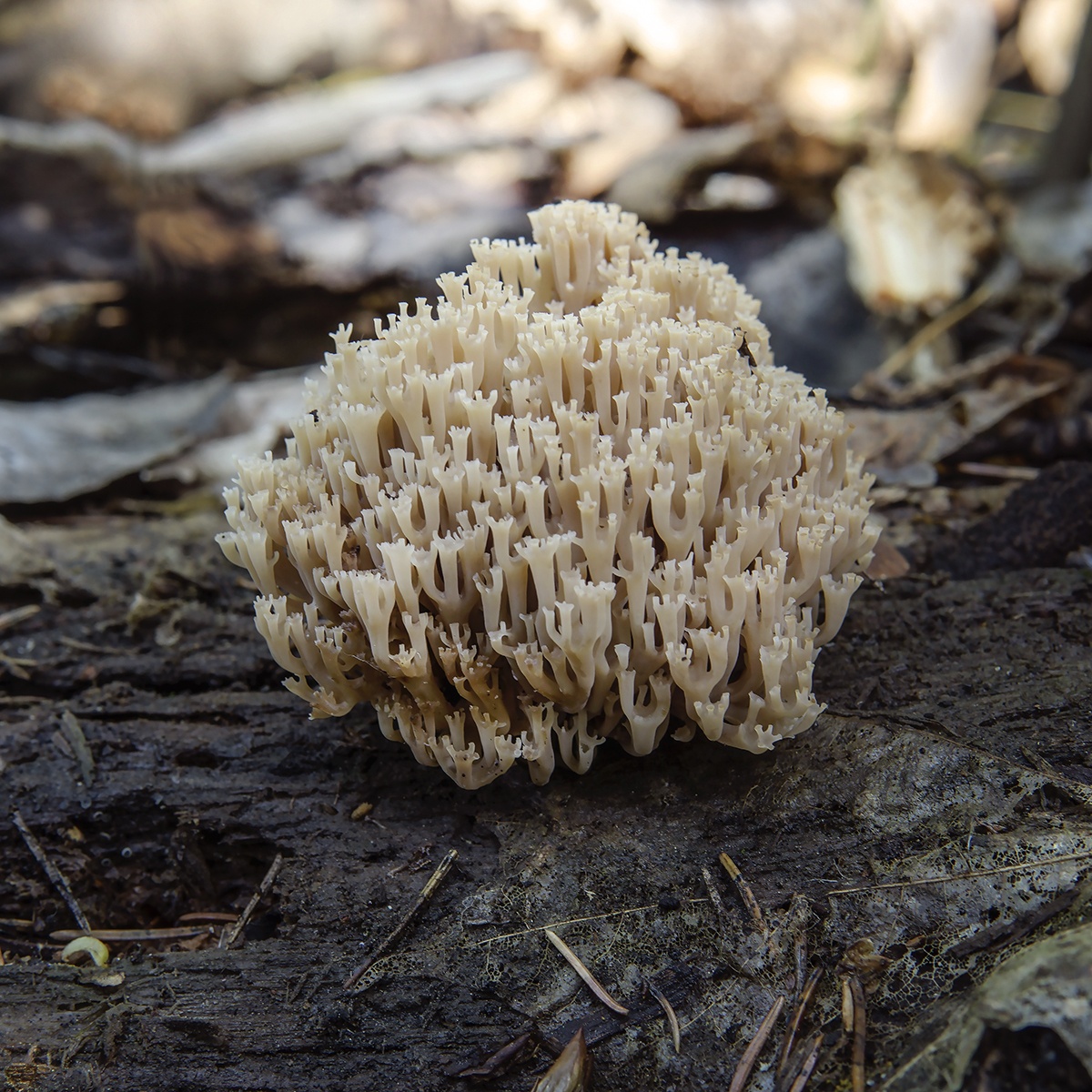
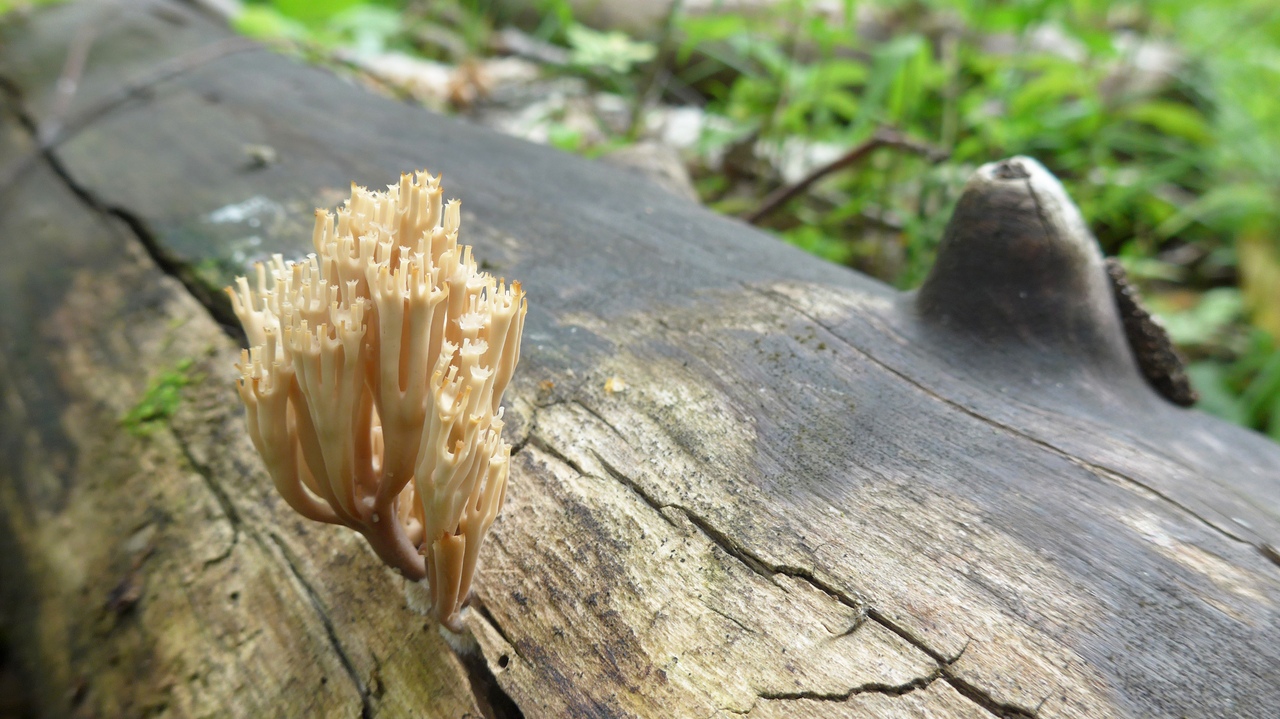
Crown-shaped clavicorona
This species has nice little cups on the tips. It grows mainly on rotten wood. Sand color with a slightly pinkish tinge. Young mushrooms can be eaten, but you will have to tinker a little with cooking, since they are a little island. The old mushroom is too rubbery.
Kalocera
This mushroom sometimes looks like a yellow ramaria. From above it is covered with mucus, which distinguishes it from its relative. You can find a horned jellyfish on rotting needles. The mushroom itself is edible, but few people like the taste, since it is simply not there.
Of course, these are not all types of attractive coral mushrooms that can be found. However, you should not hope to go hunting to collect a whole basket.
Moreover, you need to be careful, their branches are very fragile, therefore it is difficult to preserve them. It is also worth remembering that not all ramarias are edible.
On the one hand, they are not deadly, but at the same time they can cause stomach upset. Therefore, it is worthwhile to study first from the reference books whether it is really possible to use these mushrooms, and how to cook them correctly.
How to cook?
The easiest way is to make a spice from clavicorona. To do this, you can take a clean, dry mushroom, finely chop its branches, put a thin layer on a clean surface in a dry warm room and cover with gauze. Due to the small volume, the pieces dry quickly. Grind dry fragments of twigs into powder.
Can be made from Artomyces salads. To do this, boil it in salted water for 20 minutes. Then they are thrown into a colander so that the water is glass, and it is better to taste the result after all: the taste, as they say, is not for everyone's liking, not everyone likes it. Then cut the mushroom finely enough, melt butter in a frying pan and fry for 5 minutes. Cut fresh cucumber into strips, mix with artomyces and Korean carrots, season with mayonnaise.
Kalocera - horned jellyfish
Sometimes a gummy calocera can look like a yellow ramaria. But this is outside. Feeling puts everything in its place - calocera is covered with mucus and somewhat sticky. And the pulp is gelatinous rubber. Not that inedible, rather, none. Grows on decaying coniferous wood.
These, of course, are not all "deer horns" that can be found in the forest, but the most bushy ones. There are also single sticks sticking out, there are beauties of clavaria, and there is a lot more, everything cannot be described at once. You should not touch or kick or knock unfamiliar mushrooms. Many fungi destroy wood - there is no need to spread them around the neighborhood.
Calocera viscosa. Living Planet
Description of the mushroom
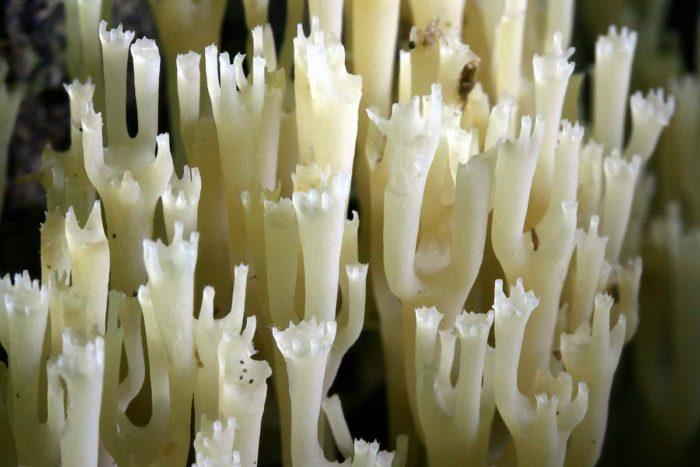
No wonder this species is compared with coral: twigs growing from one leg like a bush really resemble colonies of fossilized coelenterates.
Hat
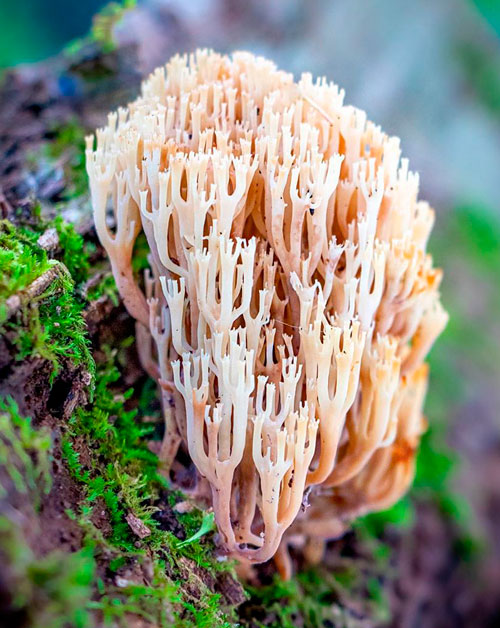 The deer horns do not have a hat in their usual form. Fruit bodies that can be related to the caps are bushy elongated twigs, whorled (that is, coming out of one point), usually collected in several similar "brooms".
The deer horns do not have a hat in their usual form. Fruit bodies that can be related to the caps are bushy elongated twigs, whorled (that is, coming out of one point), usually collected in several similar "brooms".
The height of the fruit bodies is from 2 to 13 cm, and the number in the bush is about five. Each of the branches can, in turn, branch out into several more stems. Each stem is crowned with a "crown" - a small thickening with very thin outgrowths diverging to the sides.
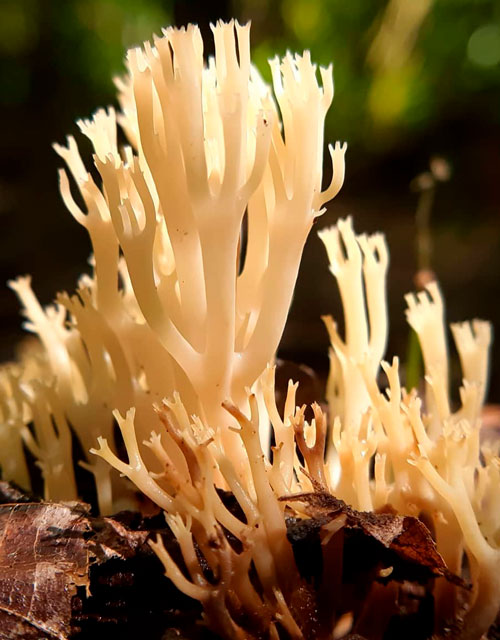 Pulp
Pulp
Quite soft, but at the same time has high elasticity, does not fall apart in the fingers, but retains its shape, slightly harsh on the tooth, "rubbery", has a neutral taste and smell, which some people compare to raw potato tuber. When chewing, a noticeable peppery taste is released, and pungency appears.
Controversy
Small ones, with small thorns, which can be seen under a microscope, contain starch, therefore, mycologists refer to amyloid ones (when they react with iodine, they give a blue color).
Interesting facts about the mushroom
The species Artomyces pyxidatus has a great genetic diversity.It has been suggested that these mushrooms, which grow in the northern and southern hemispheres, belong to different subspecies. However, when scientists collected dozens of specimens of these mushrooms from different parts of the world in the laboratory in order to study their genetic code, it turned out that they not only perfectly interbreed with each other, but also give fertile offspring. This means that, despite all the features of the genome of fungi from different countries and climatic zones, they all belong to the same biological species.
 This discovery prompted mycologists (researchers of fungi) to investigate deeper the genetic compatibility of isolated populations of Basidiomycetes. This detachment, to which the Clavicorona krynochkovidnaya belongs, is very extensive and unites both the well-known useful russula and the fungus that causes bread rust that threatened huge territories with hunger.
This discovery prompted mycologists (researchers of fungi) to investigate deeper the genetic compatibility of isolated populations of Basidiomycetes. This detachment, to which the Clavicorona krynochkovidnaya belongs, is very extensive and unites both the well-known useful russula and the fungus that causes bread rust that threatened huge territories with hunger.
It turned out that other representatives of the order of Basidiomycetes also have the same genetic feature that the Clavicorona is porciform. For example, edible Kollibia is les-loving, and more simply - Spring honey. This mushroom, like Artomyces porciformis, is also distributed throughout the world, and is also capable of producing offspring capable of reproducing. Several such species have already been discovered, and research continues. At the same time, geneticists are exploring the entire spectrum of DNA variability in representatives of disparate groups of fungi, despite which they still remain a single species.
Where is it found?
Arthomyces porciformis is distributed throughout the globe, excluding arctic and subarctic regions, where there are no trees that this fungus needs for nutrition. The only exception is the Pacific coast of North America, where these mushrooms have not yet been found. They are especially common in the Northern Hemisphere and Mexico.
You can find it on dead wood, tree stumps and even large branches. Sometimes it seems that the mushroom grows directly from the ground, but this is not the case for arthomyces. It's just that the branch he lives on is hidden in the topsoil. It can also be found on live weakened trees. Grows well both in the shade and in sunny areas. They grow in small groups or singly.
Edible and Eating
 Opinions vary widely regarding the edibility and nutritional value of mushroom noodles. Scientific mycology considers the mushroom edible, since it does not contain any substances that can harm the human body.
Opinions vary widely regarding the edibility and nutritional value of mushroom noodles. Scientific mycology considers the mushroom edible, since it does not contain any substances that can harm the human body.
At the same time, there are stories among mushroom pickers about how arthomyces led to disorders of the digestive system and even to poisoning. However, eating fruiting bodies did not bear any serious consequences.
Given the individual characteristics of assimilation, cases of gastrointestinal upset may well be caused by the presence of foreign microorganisms on the mushrooms, as well as individual sensitivity to the composition of the fungus.
Clavicorona cryoniform does not require mandatory heat treatment for elimination, and therefore cannot be attributed to conditionally edible mushrooms. However, many mushroom pickers still recommend boiling the fruit bodies for 20 minutes - just for more convenient use.
Despite these recommendations, the nutritional value of the mushroom is considered low. The reason for this is the specific taste and texture, which is significantly inferior to most classical mushrooms, where the fruiting body is divided into a stem and a cap.
The majority of those who ate "deer horns" agree that the mushroom is preferable raw, boiled or fried, but not very tasty when pickled.
However, there are also fans of this mycoid culture. They use box clavicorona as an addition to other dishes - it is in this capacity that the use of the mushroom is most justified.
Safety precautions when dealing with unfamiliar mushrooms
It is better to go for mushrooms, especially exotic ones, with knowledgeable people. They will show you edible ones and warn you against the suspicious. At the same time, they will share the recipes.
There are no deadly poisonous antlers among the deer. The use of beautiful ramaria can cause severe intestinal disorders, ramaria is tough and ocher-green - hard and bitter. They must be studied separately and not touched at all.
In the Red Book of Russia, there are no described horns. It is difficult to consider them as a specific object of "quiet hunting", since it is often problematic to collect a whole basket of young and edible ones. But if you really caught a ramaria, even one, you have to take it. And amethyst clavulin
At the same time, it is better to fold it separately and transport it carefully, since the very beauty - the twigs - are fragile and easily break
For those who set themselves the goal of independently studying unfamiliar horns, it is possible to advise taking no more than one characteristic mushroom and putting them in separate bags (otherwise, when the branches break off, you cannot tell where whose). And already at home, having laid out everything separately, start studying by reference books, by trustworthy sites. If in doubt, you can contact the experts of mushroom sites, providing high-quality photographs from all angles and in section.
Mushroom exotic in the forest, or Mushrooms-corals - tips and tricks for home and garden from.
Taste and color
If you taste the mushroom, you can feel its astringency, slightly “peppery”. Some scientists attribute Artomyces to edible mushrooms, because while it is young, it can be boiled and eaten. Others are referred to as "conditionally edible" - that is, theoretically, arthomyces crynociform can be eaten, but certain conditions must be met for this, since the old, hardened mushroom cannot be eaten even after preliminary cooking. Still others classify it as inedible due to its too hard and tough texture. At the moment, there is no consensus on the edibility or inedibility of Arthomyces cryniformis. Scientists agree on one opinion - the mushroom is not poisonous, although it is not recommended for consumption because of its not very pleasant taste. The bitterness of arthomyces only intensifies from cooking.
These mushrooms are slightly different in color, but they are united by one thing - no bright colors, the colors are exceptionally pale tones. Pale yellow, creamy mushrooms are common, but some other shades can be seen.
Spreading

The distribution area of this interesting fungus is almost the entire temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, that is, regions with a clear alternation of winter and summer seasons and sufficient humidity. "Mushroom cabbage" is a saprotroph, that is, it feeds on dead wood, actively grows on the trunks of fallen trees felled by a storm or old age.
There are clavicorona in North America, with the exception of the California coast. Although the species are geographically distant from each other, they hybridize quite successfully, which indicates a common species origin. Most often, the coral mushroom can be found in deciduous forests, almost never occurs in conifers, probably due to resinous wood. Of all the breeds, he prefers aspen.
Similar species
Our nature is so amazing that one can only wonder how wide variety of different types of living organisms can be found in this world. However, some species differ slightly and it can be very easy to confuse them. Artomyces cryoniformis is no exception; it has a fairly large number of similar fellows.
Artomyces has counterparts - mushrooms similar to it, such as ash horn, blood-red ramaria and many others, with which people can often confuse it. Indeed, having almost the same shape, some of these mushrooms outwardly only slightly differ in shades of color from arthomycese, often even the places of their growth coincide. However, upon closer inspection, you can find a completely different flesh, looking closer - you can see that the shape of the cap is slightly different. In order to see some of the differences, you need to know very well the features of the arthomyces cephalic.
Edibility, description and photo of Artomyces porciniiform
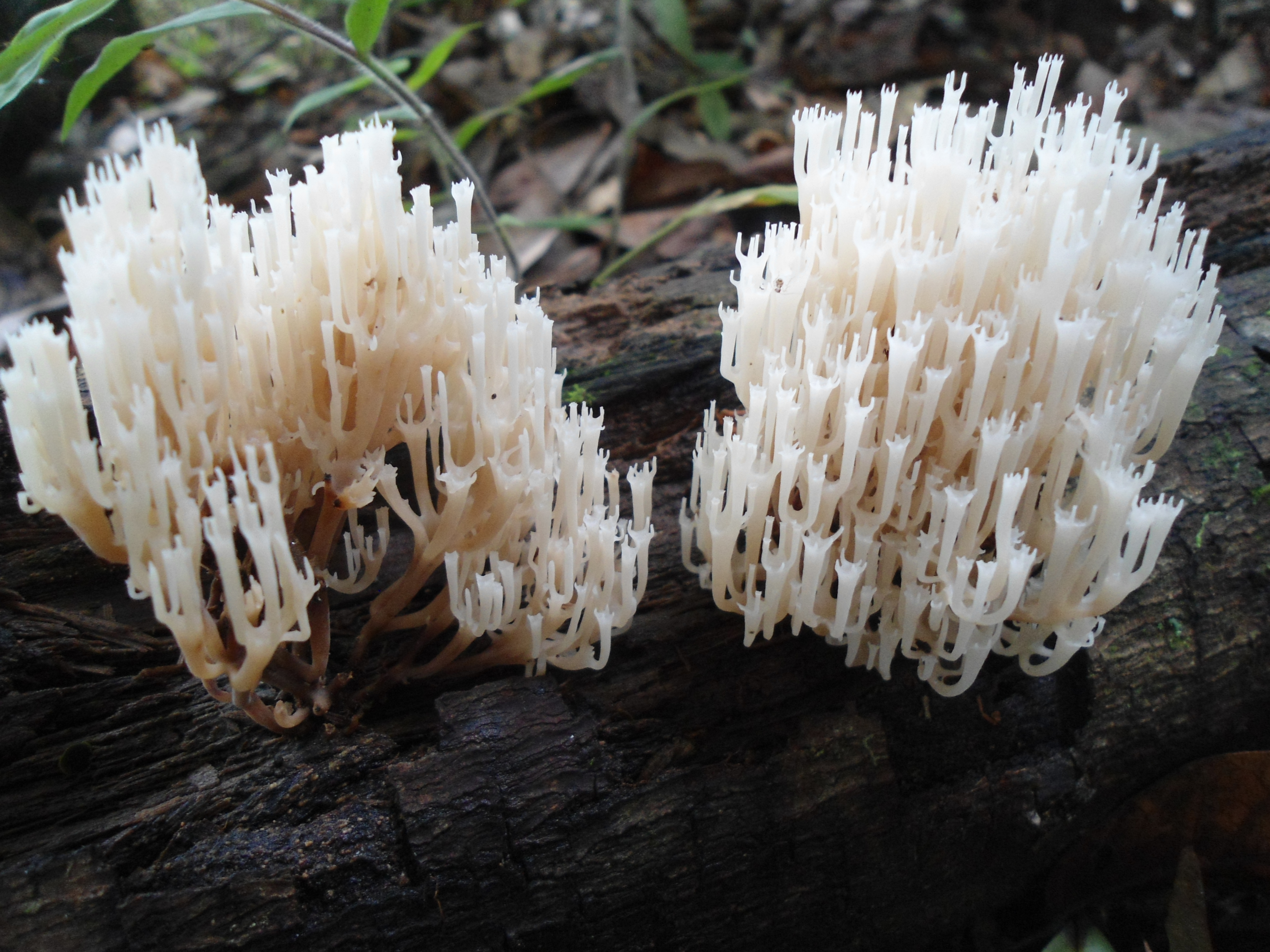
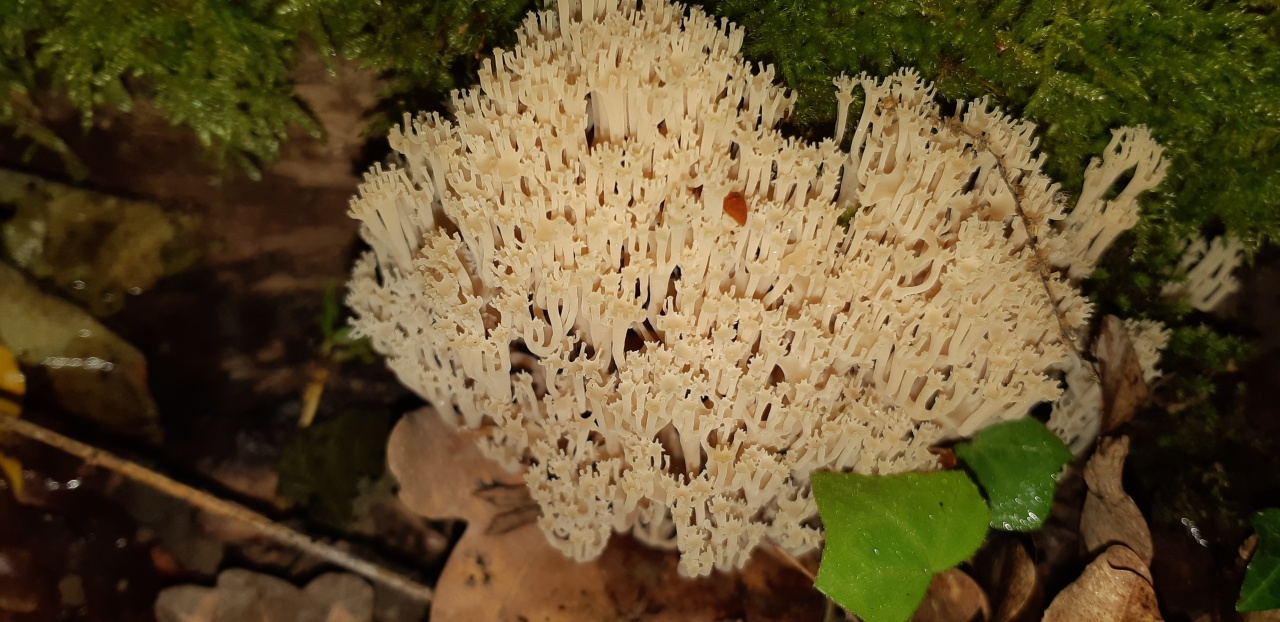
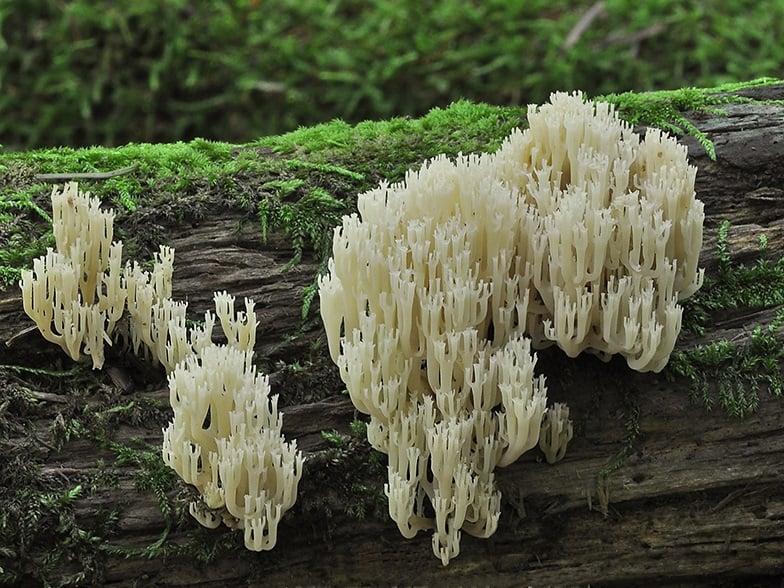
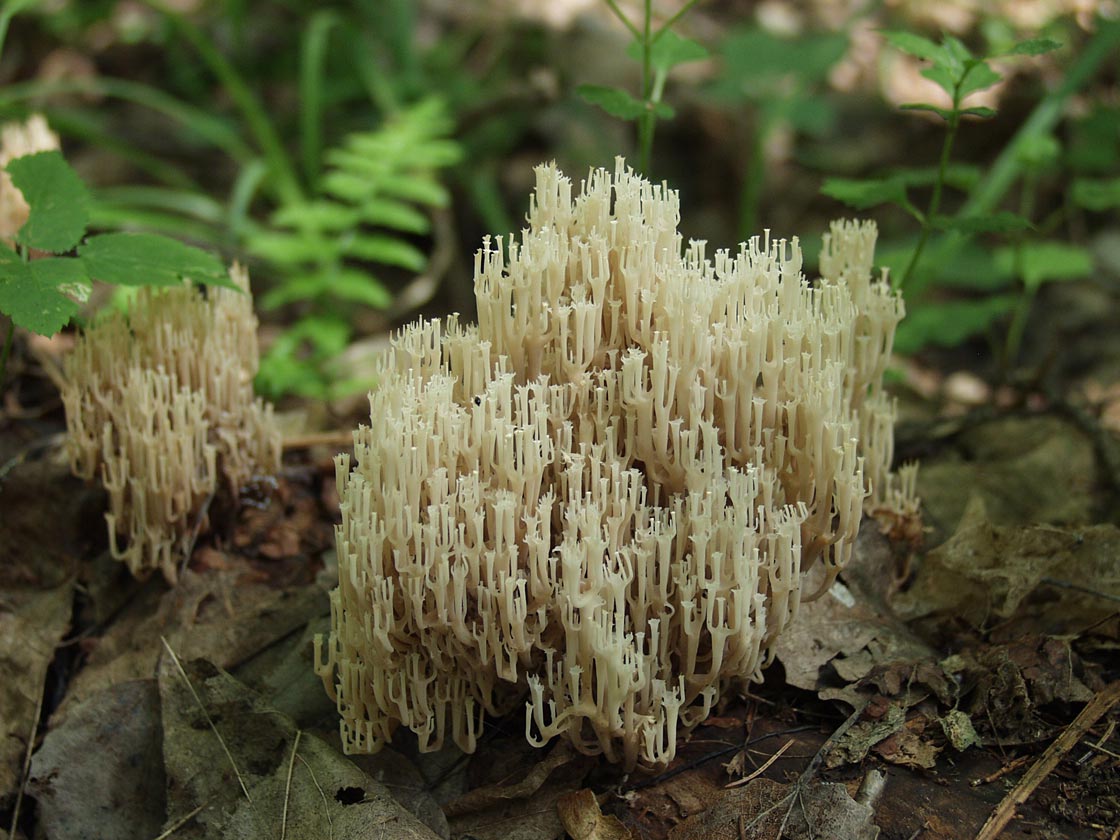
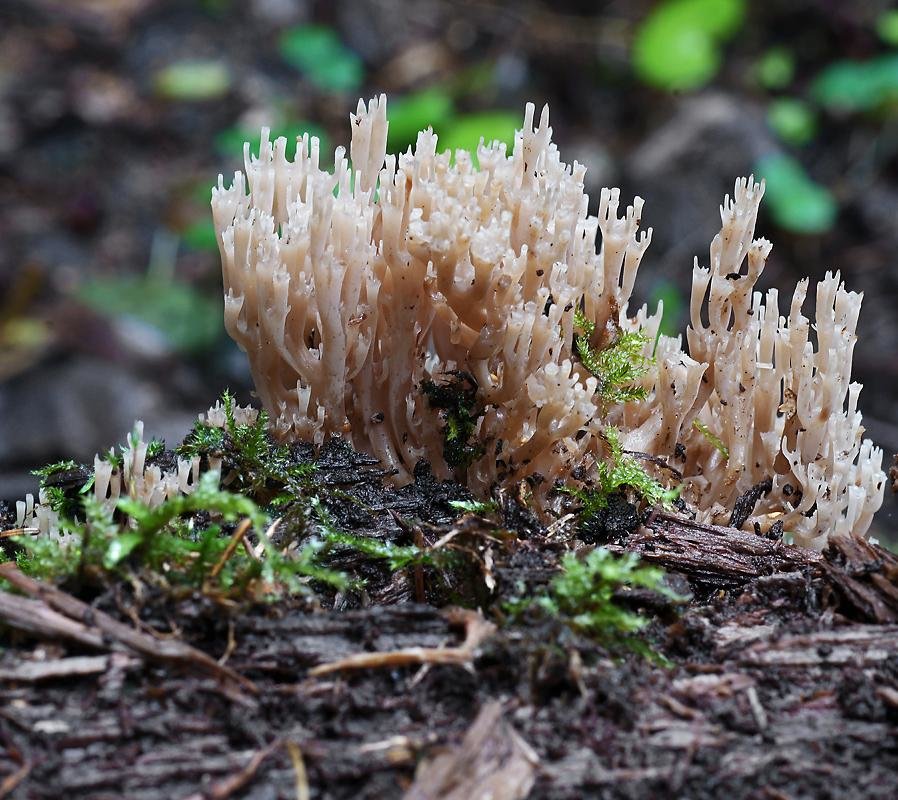
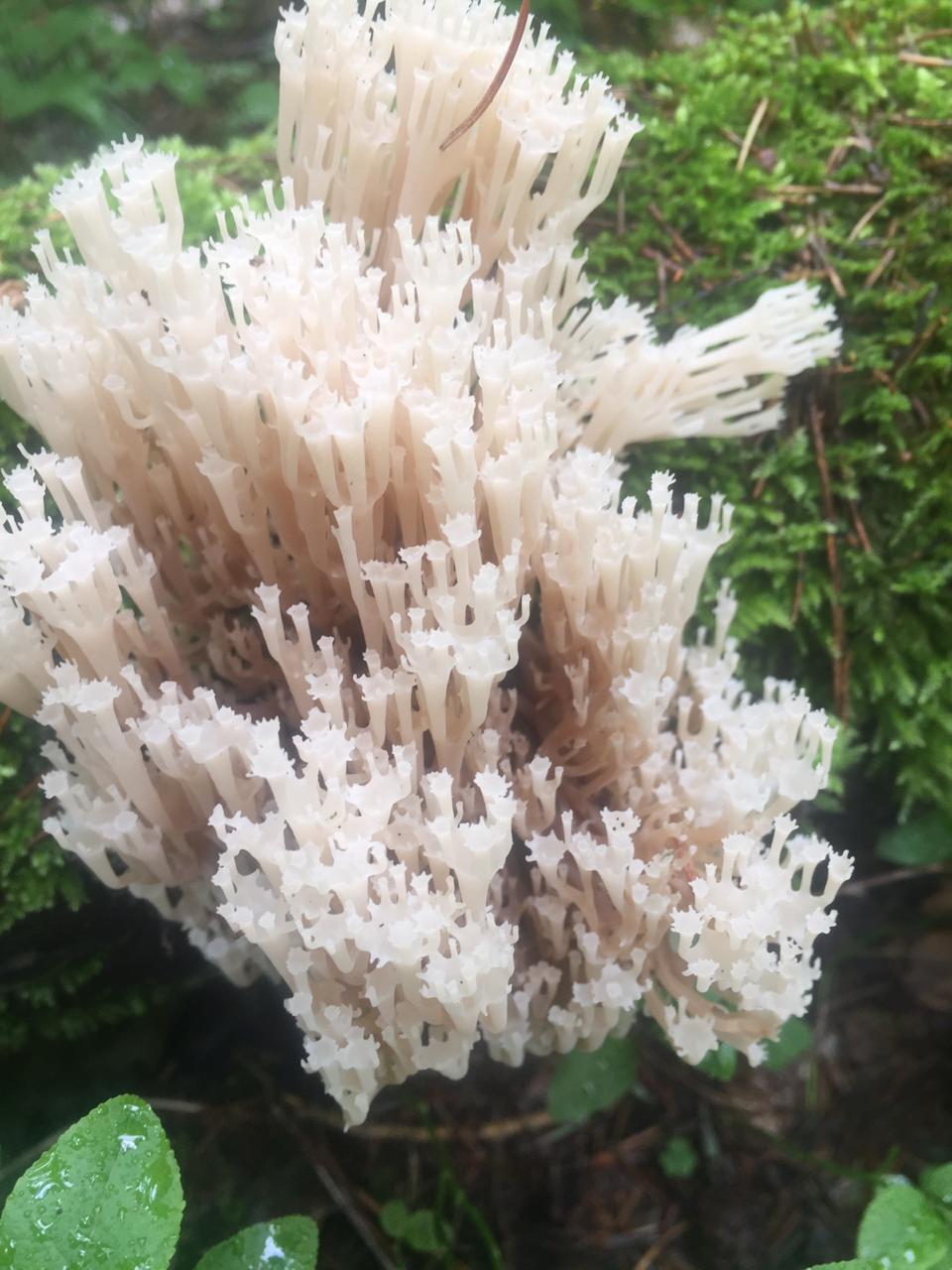
Mycologists also call the box clavicorona Clavicorona prynate or Artomyces prynate (in Latin Clavicorona pyxidata or Artomyces pyxidatus), and it is popularly known as "antlers".
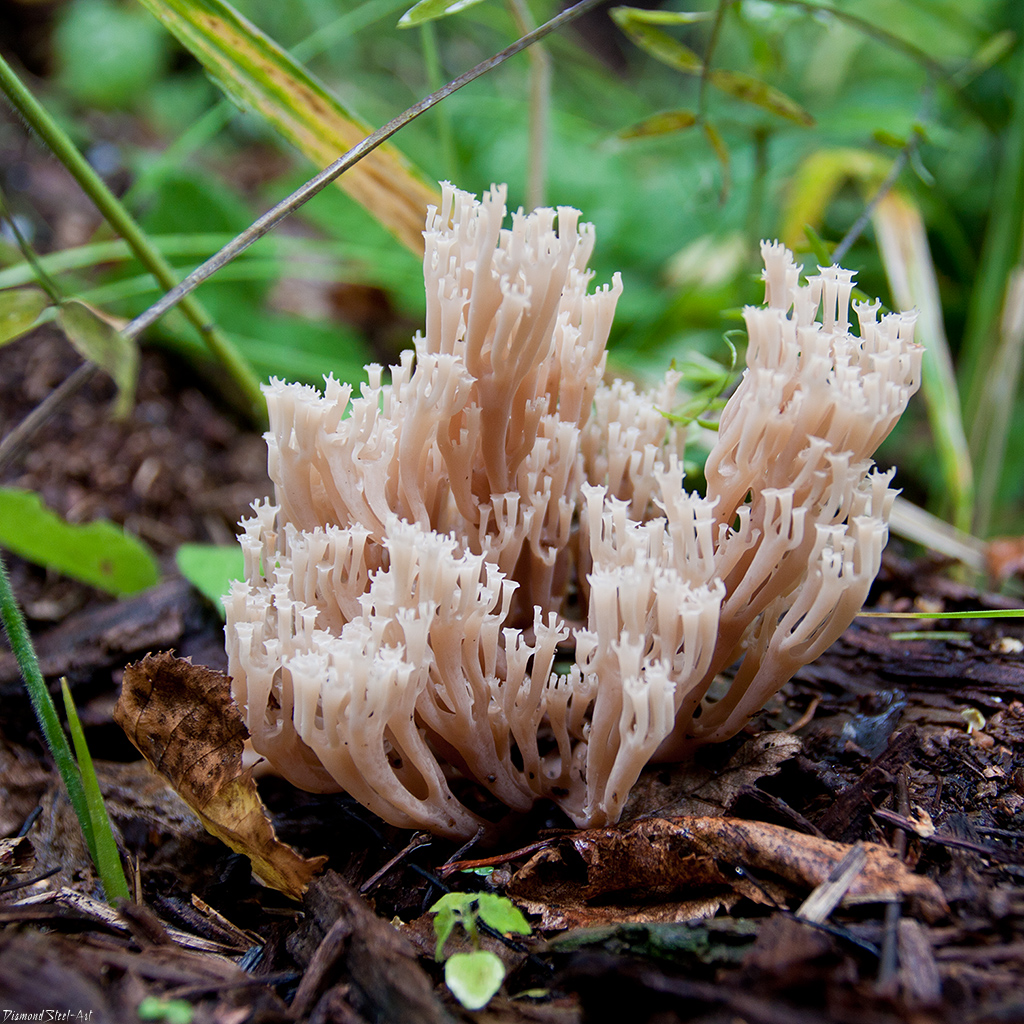
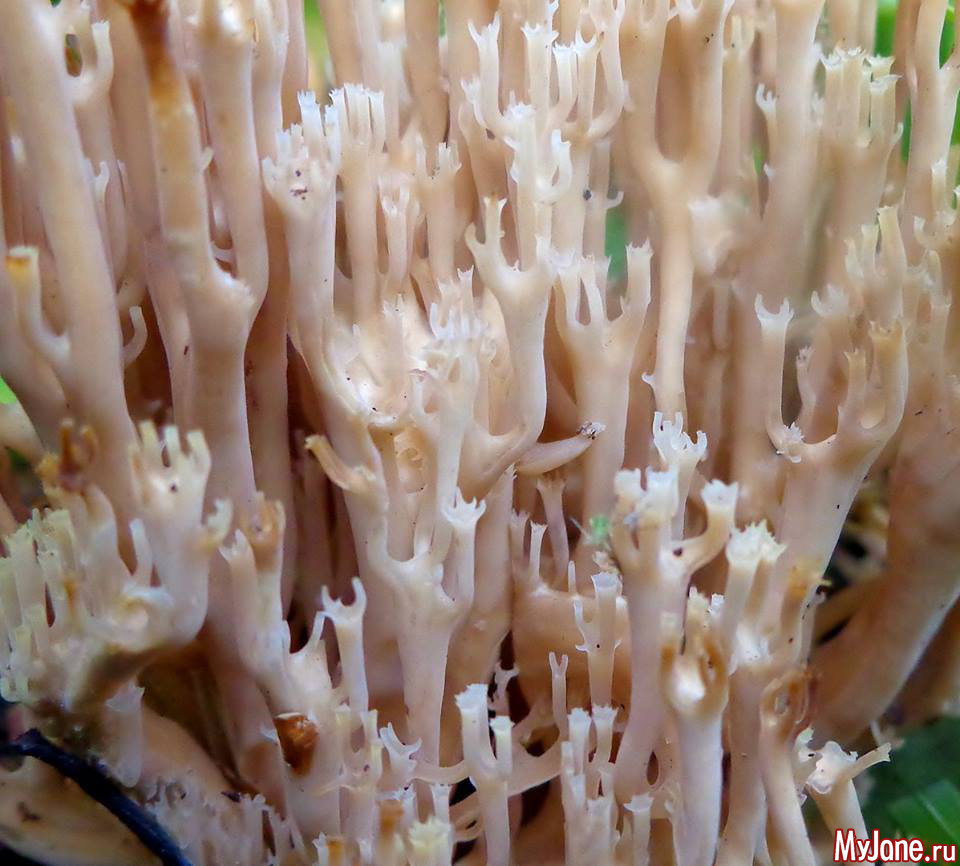
A cute, coral-like mushroom, Artomyces porciformis is very common in our country and in the world. It looks like a colony of individual fungi growing vertically, although in fact it is a single fruiting body. It's just very ramified. Each branch up to 1 cm thick, up to 3 cm long, re-branched, forming 4-6 processes, each of which ends in four teeth forming a crown (hence the second Latin name for the mushroom). The size of the fruit bodies of arthomyces is very different, from very small, 4x2 cm, to large, 20x15 cm.
The color of the fruit bodies ranges from whitish-yellowish to pinkish and brownish. "Crowns" the same color as the body, or slightly darker. The leg is missing or very short.
It seems that arthomyces is a very fragile mushroom. But this is not the case. The pulp of the mushroom is white, it is not fragile at all. On the contrary, elastic and tough. The smell is very subtle, earthy. The pulp tastes soft at first, and then gives a sharp, scalding taste, according to many, reminiscent of black pepper.
Admire the Clavicorona Cryotus in the places where it grows:
The existence of this species, at least for now, is not threatened. Perhaps this is due to the fact that scientists and culinary specialists cannot decide in any way whether it is edible. In different reference books, it is classified into different categories, from inedible (solely due to the hardness of the pulp) to edible. This type of mushroom does not relate to poisonous, although there is information about digestive disorders in people who have eaten this beautiful mushroom. Most researchers are inclined to the conditional edibility of this mushroom - it can be eaten if it is processed in a predetermined way. By the way, in the literature there is information that boiling enhances the sharpness of the taste of Artomyces pryniformis. But, since there is no dispute about tastes, some people like the taste of clavicorona so much that they come up with salads with it.
Edibility, description and photo of Artomyces porciniiform
Mycologists also call the box clavicorona Clavicorona prynate or Artomyces prynate (in Latin Clavicorona pyxidata or Artomyces pyxidatus), and it is popularly known as "antlers".
A cute, coral-like mushroom, Artomyces porciformis is very common in our country and in the world. It looks like a colony of individual fungi growing vertically, although in fact it is a single fruiting body. It's just very ramified. Each branch up to 1 cm thick, up to 3 cm long, re-branched, forming 4-6 processes, each of which ends in four teeth forming a crown (hence the second Latin name for the mushroom). The size of the fruit bodies of arthomyces is very different, from very small, 4x2 cm, to large, 20x15 cm.
The color of the fruit bodies ranges from whitish-yellowish to pinkish and brownish. "Crowns" the same color as the body, or slightly darker. The leg is missing or very short.
It seems that arthomyces is a very fragile mushroom. But this is not the case. The pulp of the mushroom is white, it is not fragile at all. On the contrary, elastic and tough. The smell is very subtle, earthy. The pulp tastes soft at first, and then gives a sharp, scalding taste, according to many, reminiscent of black pepper.
Admire the Clavicorona Cryotus in the places where it grows:
The existence of this species, at least for now, is not threatened. Perhaps this is due to the fact that scientists and culinary specialists cannot decide in any way whether it is edible. In different reference books, it is classified into different categories, from inedible (solely due to the hardness of the pulp) to edible. This type of mushroom does not relate to poisonous, although there is information about digestive disorders in people who have eaten this beautiful mushroom.Most researchers are inclined to the conditional edibility of this mushroom - it can be eaten if it is processed in a predetermined way. By the way, in the literature there is information that boiling enhances the sharpness of the taste of Artomyces pryniformis. But, since there is no dispute about tastes, some people like the taste of clavicorona so much that they come up with salads with it.
Safety precautions when dealing with unfamiliar mushrooms
It is better to go for mushrooms, especially exotic ones, with knowledgeable people. They will show you edible ones and warn you against the suspicious. At the same time, they will share the recipes.
There are no deadly poisonous antlers among the deer. The use of beautiful ramaria can cause severe intestinal disorders, ramaria is tough and ocher-green - hard and bitter. They must be studied separately and not touched at all.
In the Red Book of Russia, there are no described horns. It is difficult to consider them as a specific object of "quiet hunting", since it is often problematic to collect a whole basket of young and edible ones. But if you really caught a ramaria, even one, you have to take it. And amethyst clavulin
At the same time, it is better to fold it separately and transport it carefully, since the very beauty - the twigs - are fragile and easily break
For those who set themselves the goal of independently studying unfamiliar horns, it is possible to advise taking no more than one characteristic mushroom and putting them in separate bags (otherwise, when the branches break off, you cannot tell where whose). And already at home, having laid out everything separately, start studying by reference books, by trustworthy sites. If in doubt, you can contact the experts of mushroom sites, providing high-quality photographs from all angles and in section.
Amazing ramaria
On a rotten tree, which is not particularly pleasant to look at, one finds amazingly beautiful corals - fragile and photogenic. It would seem completely inappropriate on these rotten ones. The words of Anna Akhmatova are immediately remembered: "If only you knew from what rubbish poetry grows without knowing shame!"
Ramaria golden
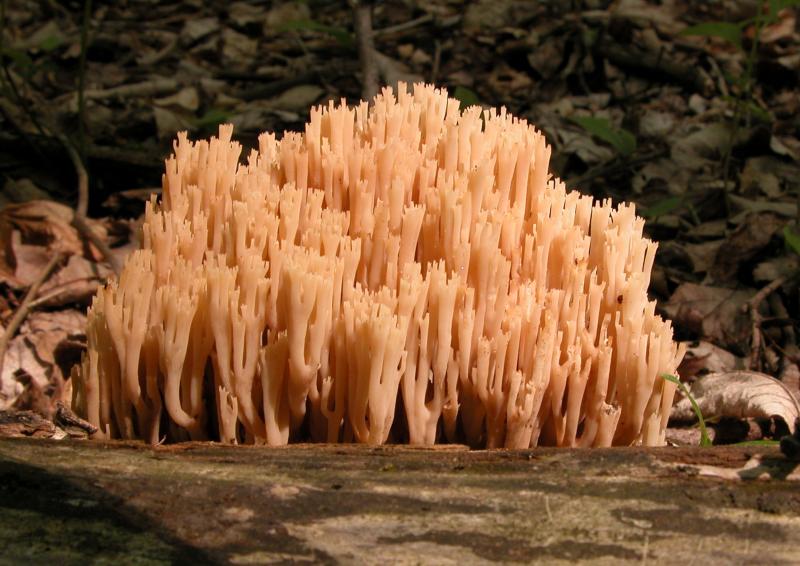
Beauty is born from dust, the living from the dead, fragile from the gross. But if you digress from poetry and philosophy and look at this miracle from a culinary point of view, you can see a delicious conditionally edible mushroom, popularly called yellow coral, mushroom cabbage or deer horns, and in science - golden ramaria.
If you come across a young mushroom of golden color, you can safely put it in the basket: in the marinade, in the soup, and as a roast - a very tasty mushroom. The main "stump" of a young mushroom (it is white) after boiling seemed to me even sweetish.
The older the mushroom, the more bitterness it contains. Starting with twigs. Perhaps that is why there are references to the conditional edibility of this mushroom and the need for boiling with a drain of water.
A mushroom of numerous branches growing from one base can weigh more than 2 kilograms. I, however, did not come across more than 0.5 kg. But often the mushroom is found in heaps. With age, it becomes bitter, "rubbery" and inedible.
The age is indicated by a change in color in a fairly wide palette: from grayish-yellow to brown-orange. Either golden ramaria or yellow ramaria can be found throughout the forest zone. Only mycologists can see the difference. And even then under a microscope.
 Ramaria golden (Ramaria aurea). Tatiana Nikolina
Ramaria golden (Ramaria aurea). Tatiana Nikolina
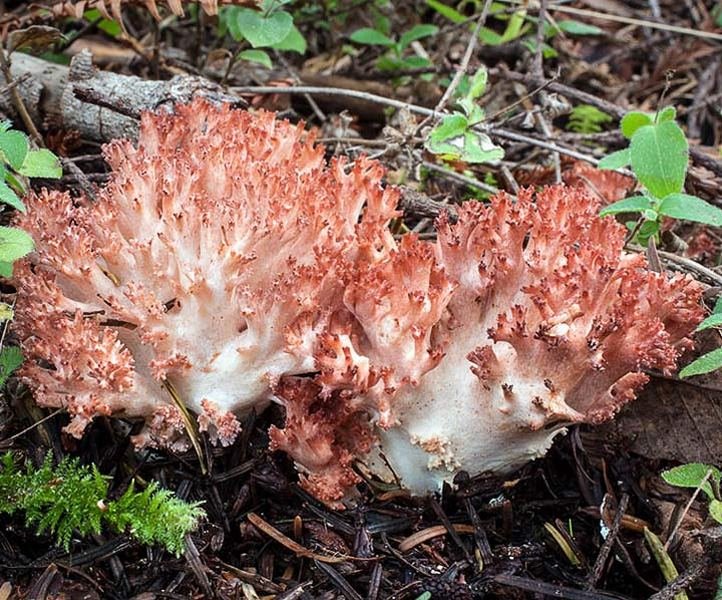
Ramaria is beautiful
In pursuit of edible horns, a beautiful ramaria, even more attractive, more rare, but inedible due to bitterness and unpleasant gastrointestinal consequences, can insidiously fall under the arm.
It has pink tones, the base, branches and branches at the tips are colored differently. A kind of design approach with a hint of a photo shoot. Glamorous beauty. Turns pink when palpated. It is better not to rip off, but to limit yourself to groping and photographing.
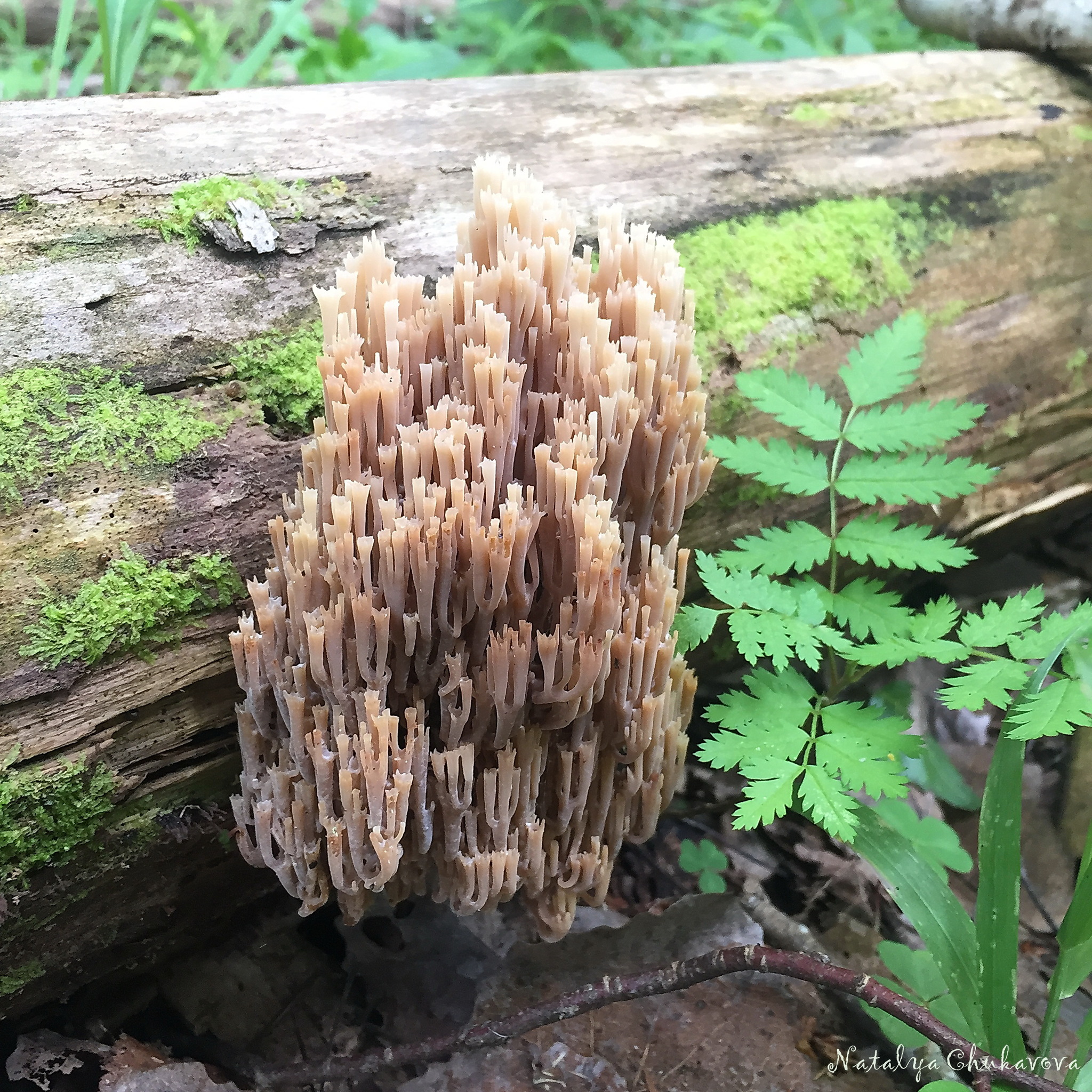
Ramaria ordinary
The simplest ramaria is simply called ordinary. In comparison with the previous ones, it is really simpler.But it is found in the temperate zone more often mainly on coniferous litter and is very abundant. Sometimes not just a family, but a whole diaspora.
Moreover, it grows, at times, in the form of a braid, or in an arc, or in a row, or a complete "witch's ring". He dabbles in geometry.
It is difficult to confuse it with other mushrooms, its branches are straight, without any frills at the tips. And the color from root to crown is the same, not changing when damaged.
It is necessary to collect young specimens. To remove bitterness, soak for a day with 2-time change of water or boil, drain the water. Bitterness, just like in golden and yellow horned horns, is gained with age, but, unlike them, there is a starting bitterness.
Ramaria uviform
But not everything is so arbitrary with edibility in the ramaria family, there are also representatives there with outstanding culinary properties, for example, ramaria uviform.
Also very beautiful, with pink-colored twigs. Only the twigs are shorter, thicker and have a very massive base. A sort of donut. The structure of the twigs is similar to cauliflower. Pleasant smell and pleasant taste, no need to suffer with soaking and preliminary boiling, you can immediately fry or cook without draining the water.
Edible, while the twigs are pink-red, browning indicates the onset of inedible old age.
Unfortunately, it is less common, loves warmth (both in terms of degrees and in terms of regions), an individualist - she does not grow up in large families.
 Ramaria uviform (Ramaria botrytis). Michael wood
Ramaria uviform (Ramaria botrytis). Michael wood Ramaria is beautiful (Ramaria formosa). Punkufer
Ramaria is beautiful (Ramaria formosa). Punkufer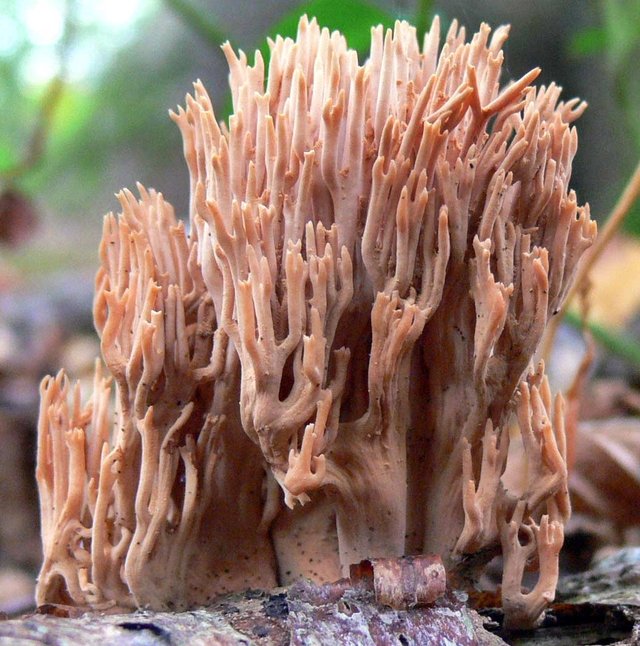 Ramaria stricta. wikigrib
Ramaria stricta. wikigrib
Inedible ramaria
There are still inedible representatives in this family, but deserving attention and photographing: ramaria is stiff, slender and straightforward, with parallel growing branches and turns red / brown when pressed. Initially bitter.
Ramaria is ocher-green in lime shades in youth, rapidly blue / green when damaged. It is rarely found, mainly on litter in coniferous forests. Bitter.
This mushroom, strictly speaking, is not particularly ramaria. At first, the mushroom was attributed to the genus Clavaria, then to the Ramaria, and now it is called Theoklavulina fir. A slingshot walking through the sections.
 Feoklavulina fir, or Ramaria ocher-green (Phaeoclavulina abietina). H. Krisp
Feoklavulina fir, or Ramaria ocher-green (Phaeoclavulina abietina). H. Krisp





















































