Recognition of edible and poisonous mushrooms
Mushrooms with a fruiting body are divided into:
- poisonous (pseudo-foam, common line, pale toadstool);
- inedible (toadstool-like fly agaric, common veselka);
- conditionally edible (pink wave, morel cap);
- edible (porcini mushroom, autumn honey fungus).

To recognize edible and inedible mushrooms, you need to be guided by appearance or have the experience of a mushroom picker. If you are not sure that the mushroom you see is edible, then it is better not to take it
When collecting, pay attention to external signs and carefully examine the fruiting bodies
The value of mushrooms in nature and in human life
|
In nature |
In human life |
|
Included in the process of circulation of substances. |
One of the power supplies. |
|
Participate in the formation of the soil layer. |
They are used in the baking industry. |
|
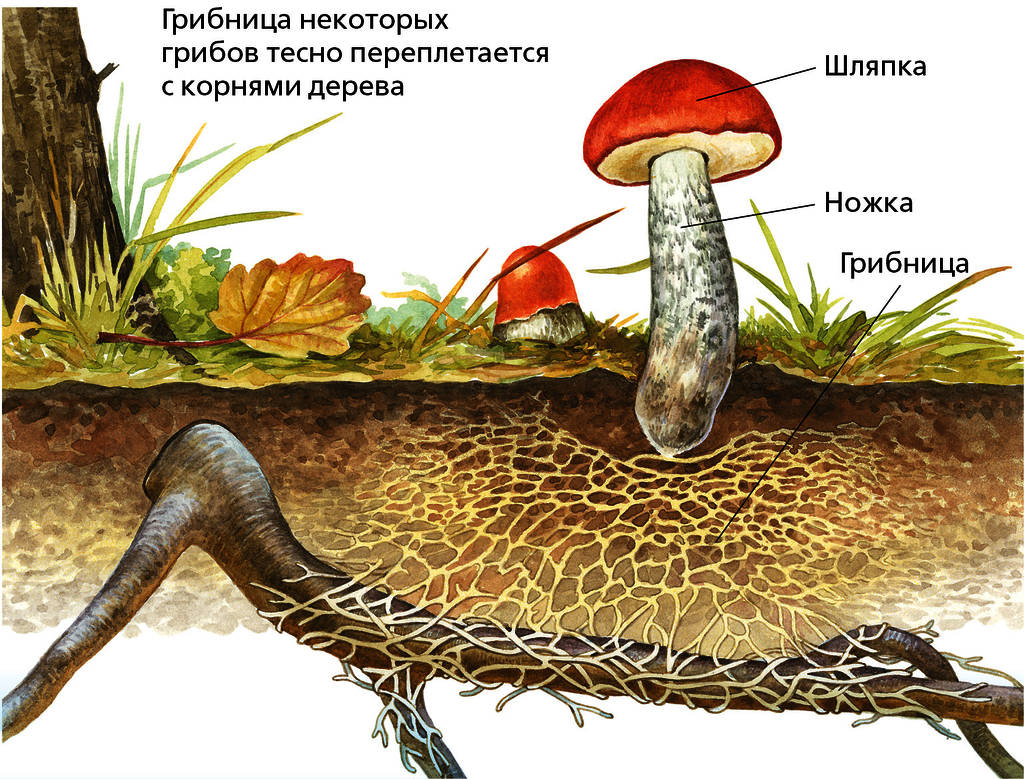
They form a symbiosis with plants (mycorrhiza). |
Used to create wine, alcohol-containing products. |
|
They are a source of food for birds, molluscs, insects, animals. |
|
 Rice. 4. Mold growth and spore formation
Rice. 4. Mold growth and spore formation
Many mushrooms cause serious harm to humans. They parasitize plants, animals, cause spoilage and decay of food, destroy leather, wood, and paper products. Old manuscripts and works of art suffer from them.
Features of the structure of mushrooms
Before talking about the methods of reproduction of mushrooms, you need to understand what these organisms are. They combine some characteristics of animals and plants, and therefore were united into a separate kingdom - Mushrooms. After a long debate, scientists, who could not decide which species they should be attributed to, assigned a separate kingdom to mushrooms.
Initially, this group of organisms lived in the waters of the oceans. After some time, for unknown reasons, they changed their habitat, moving to the forest. They are united with the plant kingdom:
- the ability to reproduce by spores;
- absorptive way of eating;
- the presence of a cell wall;
- the presence of vacuoles in the cell;
- unlimited growth, etc.
With the kingdom of Animals they have in common:
- metabolic product - urea;
- lack of plastids (including chloroplasts);
- heterotrophic nutrition;
- the presence of chitin in the cell wall;
- reserve nutrient - glycogen, etc.
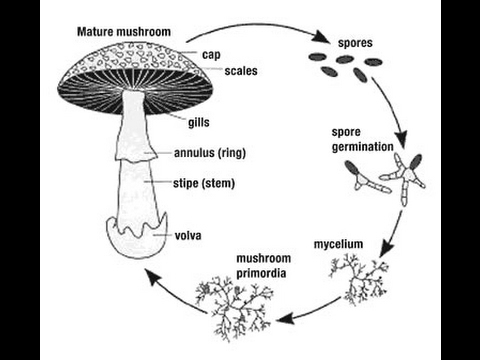
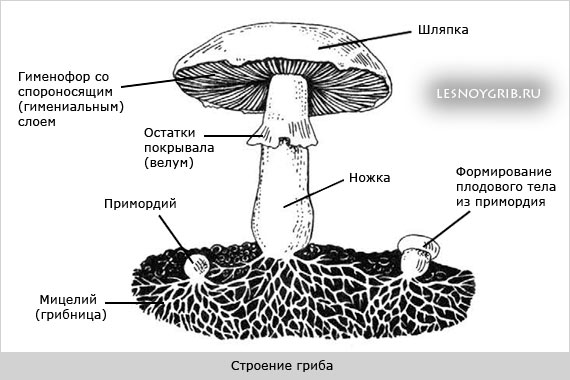
Not everyone has an idea about the structure of the fungus. It consists of mycelium (mycelium, or vegetative body), which plays an important role in the reproduction process, and directly reproductive organs. The mycelium is underground. It is a thin, colorless thread through which nutrition occurs.
Interesting Facts
The main role in reproduction in any way is played by the mycelium, which is located underground. If you harvest by cutting off the fruiting body, then the mycelium remains intact, because you left part of the leg in the soil. Within 14-20 days, he is able to grow a new fruiting body filled with spores.
If, during collection, the fruit body is pulled out of the ground (attention! Pulled out, not twisted), the integrity of the mycelium is violated. It will take a long time to restore this organ.
The duration of recovery depends on the area of the damaged part of the mycelium.
All methods of reproduction are characteristic of molds. Yeasts that do not use oxygen during respiration reproduce vegetatively and sexually, actinomycetes (radiant fungi) - vegetatively and asexually, imperfect ones - sexually.For parasitic fungi, sexual reproduction in the form of somatogamy is characteristic. The dicarion stage can last for years, and for tinder fungi even for decades. Each variety of the mushroom kingdom has properties that are unique to it.
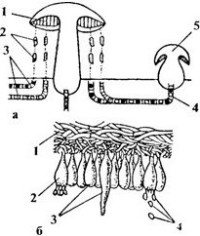
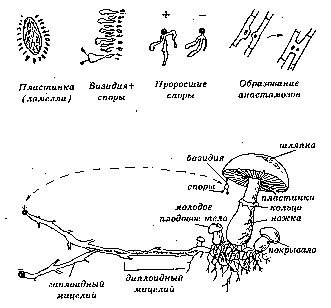
In cap mushrooms, the spores are under the cap (on the lower side of the cap). The part of the fruiting body where spores form is called the hymenophore. The spore layer can be tubular or lamellar. The tubular type of surface assumes the presence of many tubules tightly adjacent to each other, in which the spores are placed. It is impossible to see these tubes without a microscope, which is why the surface looks like a sponge. The people call them not tubular, but spongy. The lamellar hymenophore is clearly distinguishable without magnifying devices. In addition to the types of hymenophores that are familiar to us, there are several more, but we habitually use only two, known from school.
Mushroom propagation
How mushrooms reproduce, www.grib.tv
Mushrooms. Botany educational film
How mushrooms multiply
For many, this will come as a surprise, but what we used to call a mushroom is actually just a part of a huge organism. And this part has its own function - the production of disputes. The main part of this organism is located underground, and is intertwined with thin threads called hyphae, which make up the mushroom mycelium. In some cases, hyphae can hang down in dense cords or fibrous formations that can be viewed in detail even with the naked eye. However, there are times when they can only be viewed through a microscope.

The fruiting body is born only when two primary mycelium, belonging to the same species, come into contact. The connection of the male and female mycelium occurs, as a result of which a secondary mycelium is formed, which, under favorable conditions, is able to reproduce the fruiting body, which, in turn, will become the place where a huge number of spores appear.
However, mushrooms have more than just a sexual reproduction mechanism. They are distinguished by the presence of "asexual" reproduction, which is based on the formation of special cells along the hyphae, which are called conidia. On such cells, a secondary mycelium develops, which also has the ability to bear fruit. There are also situations where the fungus grows as a result of a simple division of the original mycelium into a huge number of parts. Dispersion of spores occurs primarily due to the wind. Their low weight allows them to move with the help of the wind hundreds of kilometers in a relatively short period of time.

In addition, various fungi can spread as a result of "passive" transfer of spores, which is carried out by various insects, which can both parasitize on fungi and appear on them for a short period of time. Spores can also be spread by various mammals, such as wild boars, which may accidentally eat the mushroom. In this case, the spores are excreted together with the animal's excrement. Each fungus has a life cycle of a huge number of spores, but only a tiny amount of them get into an environment that would have a beneficial effect on their further germination.
Mushrooms are a huge group of organisms, numbering more than 100 thousand species, which are traditionally considered to be plants. To date, scientists have come to the conclusion that mushrooms are a special group that takes its place between plants and animals, since in the process of their life, features inherent in both animals and plants are visible. The main difference between fungi and plants is the complete absence of chlorophyll, the pigment that underlies photosynthesis.As a result, mushrooms are unable to produce the sugars and carbohydrates found in the atmosphere. Mushrooms, like animals, consume ready-made organic matter, which, for example, is released in rotting plants. Also, the membrane of fungal cells includes not only mycocellulose, but also chitin, which is characteristic of the outer skeletons of insects.
There are two classes of higher fungi - macromycetes: basidiomycetes and ascomycetes.
This division is based on various anatomical features characteristic of the formation of spores. In basidiomycetes, the spore-bearing hymenophore is based on plates and tubules, the connection between which is carried out using tiny pores. As a result of their activity, basidia are produced - characteristic formations that have a cylindrical or clavate shape. At the upper ends of the basidia, spores are formed, which are connected with hymenium using the finest threads.
For the growth of spores of ascomycetes, cylindrical or saccular formations are used, which are called bags. When such bags mature, they burst and the spores are pushed out.
Related videos:
Reproduction
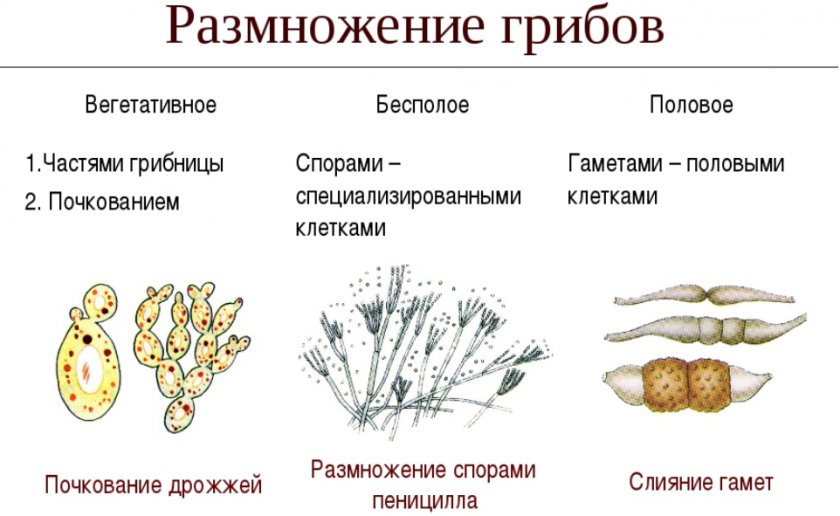
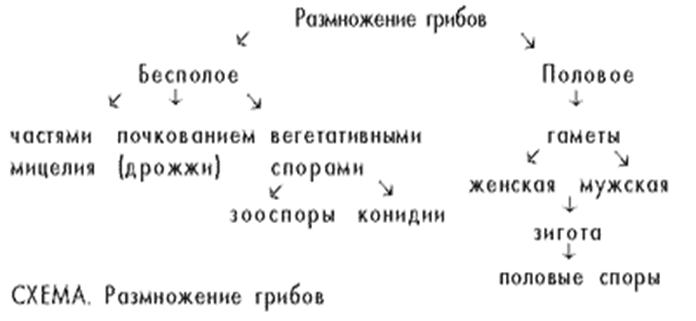
A separate kingdom of mushrooms has its own peculiarity of reproduction. It can be done in a variety of ways that may only be known. Each of them has its own nuances. The main ones are asexual and sexual reproduction. Let's take a look at what mushrooms are propagated by them.
Asexual fungi appear in the mycelium, since the filaments of the mycelium form a separate organism capable of creating processes. They will be the reproductive organ that appears during warm and humid seasons.
During vegetative propagation, part of the mycelium may separate. It will become a separate organism. An independent organism will emerge from the separated part.
Mushrooms reproduce by budding, which is referred to as a vegetative propagation method. The mycelium or its individual cells are budded. Kidneys are formed, which gradually increase in size, then they are separated from the mother's body and exist independently. Mushrooms that reproduce only by budding are vocal and smut species. The latter are parasites that can ruin the harvest of grain crops. Vocal mushrooms include a group of yeasts that we use to bake bakery products and taphrin fungi that parasitize fruit trees and shrubs. They infect the fruit, causing hypertrophy.
Certain types of fungi form oidia, which are light filaments. They will form a new organism. This whole process in natural conditions is not really visible to anyone, since it takes place at great depths.
Asexual reproduction can occur through spores. They are able to travel long distances by attaching themselves to animals and humans. Water can also carry them. Once in favorable environment, disputes begin to develop.
If we talk about the sexual mode of reproduction, then it is associated with the formation of a zygote. This occurs through hecatogamy, the fusion of two gametes, and somatogamy, the gradual fusion of the membranes, and then the nuclei, from which the future organism will develop in the future.

It is interesting
Scientists are very closely involved in the study of these living organisms. They are not just watched, many experiments are carried out with them. Some of which are shocking. So, it is known that Japanese researchers came to the conclusion about the intelligence of yellow yeast. They conducted an experiment in which they forced this organism to grow in a "maze" where sugar was hidden. It turned out that the yellow mold "remembers" the path it took to get to the treat. The scion taken from this organism grew straight to the place where the sugar was! But this is just the simplest mushroom that reproduces vegetatively.
Conclusion
Even scientists today do not give a complete description of the appearance on our planet of representatives of the kingdom of mushrooms. This process has been partially studied. But this knowledge is enough to understand the features of the process and reproduce it at home, creating conditions that most closely resemble the conditions for the growth of a particular species in nature.
When breeding at home, it is easiest to use the vegetative method. Some varieties or species can be propagated asexually. At the same time, the mycelium was growing independently, pouring water on the substrate in which the caps of the selected type of mushrooms were soaked. But it is better to get it in a specialized store. Its germination rate is 98%, while a self-prepared mixture does not always form a viable mycelium.