Maintenance and care
Such a large fish will need a tank of about 500 liters. Such volumes are necessary for the fish to have somewhere to accelerate; in confined conditions, Dimidochromis quickly loses its tone. The design is quite simple, a substrate of sand or fine gravel with areas of small thickets of the Vallisneria plant, which are recommended to be located in any one zone, and not everywhere throughout the area. The quality and composition of the water is decisive. Acceptable conditions are the following parameters: pH - slightly alkaline, dH - medium hard. More information about the parameters and methods of changing them in the section "Hydrochemical composition of water". Large fish produces a lot of waste, which, together with a meat diet, leads to a rapid accumulation of dirt, so cleaning the soil with a siphon and renewing water by 20-50% should be carried out weekly. The amount of water to be replaced depends on the size of the tank, the number of fish and the capacity of the filtration system. The more efficient the filter, the less water will need to be refreshed. Other minimum required set of equipment includes heating, aeration and lighting systems.
Types and varieties of thyme
Thyme belongs to the Yasnotkov family; on the territory of the former Soviet Union there are more than 400 species of it. About 50 species of thyme grow in the European part alone. Siberia and the Caucasus are replete with another 40 species. It is a semi-shrub thyme, whose stems are half-recumbent, half-upright, and at the same time lignified. The most popular species are common thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and creeping thyme (Thymus serpyllum).
Thyme ordinary
The leaves of this species are small and slightly pubescent. The stems grow up to 15 centimeters in height. The plant has beneficial properties and is classified as medicinal. Collect them for use in traditional medicine. This type of thyme has several varieties that differ from each other not only in the color of the flowers, but also in the height of the stem. It should be noted such varieties as:
- Alba - white flowers;
- Splendens - deep red flower color;
- Coccineus - flowers are colored red;
- Elfin - grows only five centimeters, but at the same time forms a carpet with a diameter of up to fifteen centimeters.

Thyme ordinary
Creeping thyme
Everyone knows this plant as thyme. In Russia it is called "Bogorodskaya grass". This plant is perennial, with stems that intertwine with each other and have cylindrical leaves. On the ground, the plant forms a dense carpet. In varieties of this type of thyme, the leaves are variegated, and the color of the flowers is saturated. Among them are carmine, white and pink. The plant reaches a height of 15 centimeters.
Lemon-scented thyme
Latin name - Thymus x citriodorus (Pers.) Schreb
Particular attention should be paid to this particular type of thyme. It is a hybrid of two other species: pulegioides and vulgaris.
This type of plant loves warmth and does not tolerate cold, so it should be covered in winter. The height of the shoots can reach thirty centimeters. Thyme leaves are variegated, beautiful, have a rounded shape. The plant is perennial, it must be trimmed so that it does not lose its shape and density.
Famous varieties are:
- Silver Queen (Silver queen) - has leaves bordered in white;
- Golden Duarf - there are yellow spots on the leaves;
- Golden King - green leaves are surrounded by a yellow border;
- Archer Gold - differs in golden green leaves and pink flowers;
- Bertram Anderson - light green leaves with a yellow border;
- Doone valley - leaves have small yellow spots.
The peculiarity of this species is that it has a pleasant lemon scent.
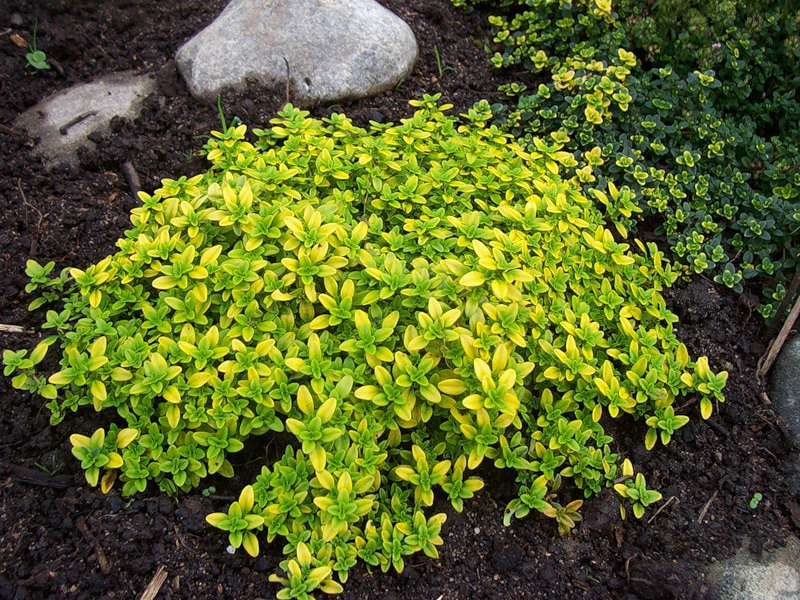

Lemon-scented thyme
Flea thyme
Lat. Thymus pulegioides. It is a small, but at the same time very dense bush, the height of which reaches no more than one centimeter. The color of the plant is lilac pink, the shade attracts the eye.Thyme begins to bloom in June.
In addition to the described types of thyme, there are many others, such as:
- Dorfler's thyme (Thymus doerfleri);
- Subarctic thyme (Thymus subarcticus);
- Early thyme (Thymus praecox Opiz);
- Thyme Aureus;
- Thyme variegated.
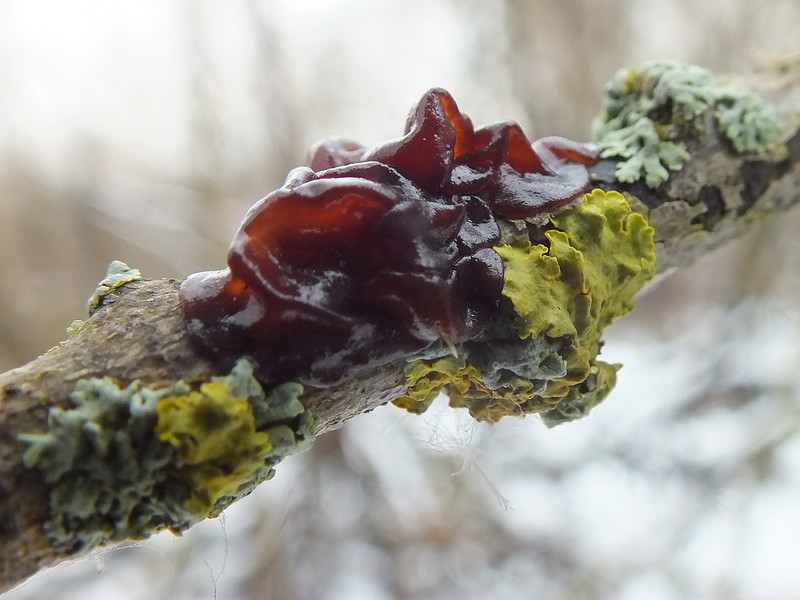
Chlorocyboria blue-greenish (Chlorociboria aeruginascens)
Synonyms:
- Chlorosplenium aeruginosum var. aeruginascens
- Peziza aeruginascens
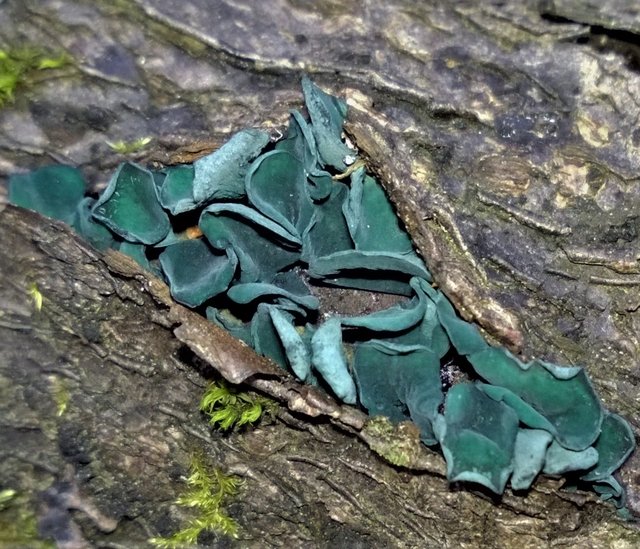

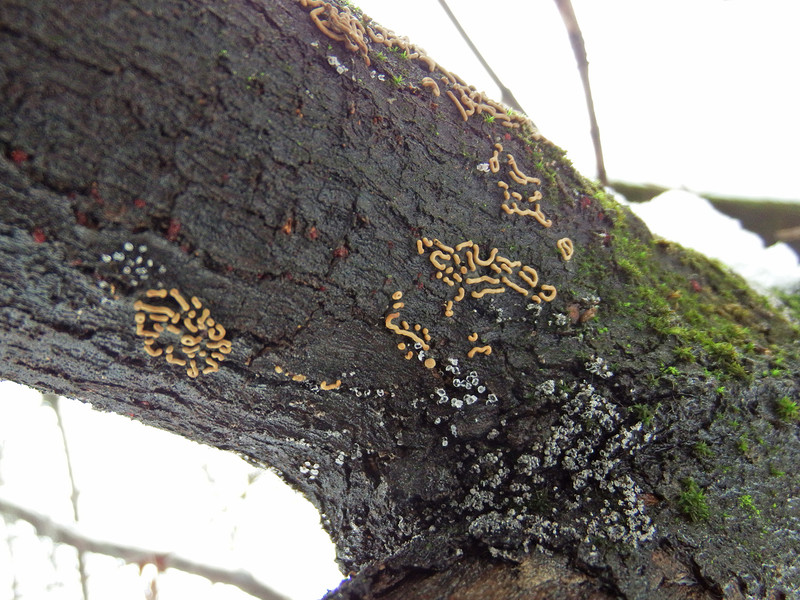
Evidence of the presence of chlorocyboria catches the eye much more often than she herself - these are areas of wood painted in beautiful blue-green tones. Responsible for this is xylidein, a pigment from the quinone group.
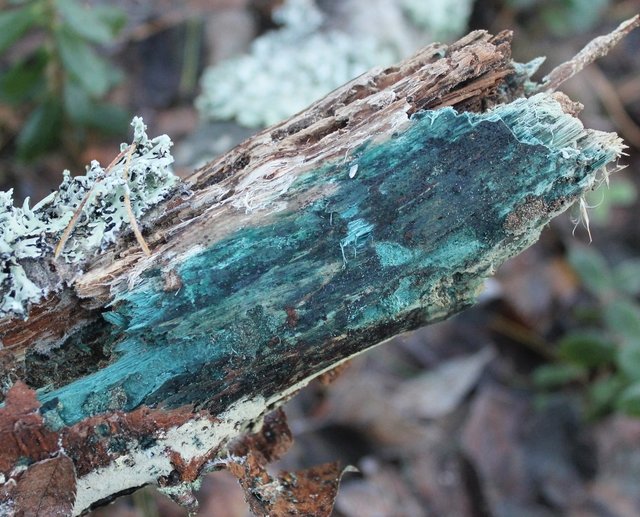

Wood dyed by him, the so-called "green oak", has been highly valued by woodcarvers since the Renaissance.
Fungi of the genus Chlorocyborium are not considered "real" wood-destroying fungi, which include the basidiomycetes that cause white and brown rot. It is possible that these ascomycetes cause only slight damage to the cell walls of wood cells. It is also possible that they do not destroy them at all, but simply populate wood that has already been sufficiently destroyed by other mushrooms.

External description
Chlorocyboria is blue-greenish - saprophyte, it grows on already rather rotten, barkless dead trunks, stumps and branches of deciduous trees. Blue-green colored wood can be seen throughout the year, but fruiting bodies are usually formed in summer and autumn. This is a fairly common species of the temperate zone, but fruiting bodies are rare - despite their bright color, they are very small.

Fruiting bodies are initially cup-shaped, with age they flatten, turning into "saucers" or discs of not quite regular shape, 2-5 mm in diameter, usually on a displaced or even lateral (less often on the central) leg 1-2 mm long. The upper spore-bearing (inner) surface is smooth, bright turquoise, darkens with age; lower sterile (outer) glabrous or slightly velvety, may be slightly lighter or darker. When dry, the edges of the fruiting body curl inward.
The pulp is thin, turquoise. The smell and taste are inexpressive. Due to its extremely small size, nutritional quality is not even discussed.

Spores 6-8 x 1-2 µ, from nearly cylindrical to fusiform, smooth, with oil droplets at both tips.
Similar species
Outwardly very similar, but rarer blue-green chlorocyboria (Chlorociboria aeruginosa) is distinguished by smaller and usually very regular fruit bodies on the central, sometimes almost completely absent, leg. It has a lighter (or lighter with age) upper (spore-bearing) surface, yellowish flesh and larger spores (8-15 x 2-4 µ). She paints the wood in the same turquoise tones.
Habitat
Originally from the eastern regions of Mexico. The natural habitat is limited by the Panuco Basin, which includes numerous lake systems in the lower reaches of the river.
Brief information:
- The volume of the aquarium is from 200 liters.
- Temperature - 20-33 ° C
- PH value - 6.0-7.5
- Water hardness - soft or medium hard (5-14 dGH)
- Substrate type - sandy or fine gravel
- Lighting - any
- Brackish water - no
- Water movement - weak or moderate
- The size of the fish is up to 20 cm.
- Nutrition - any sinking feed with herbal supplements
- Temperament - quarrelsome with benthic species
- Keeping alone or in a formed male / female pair
Disease Prevention and Pest Control
Thyme practically does not get sick, but in case of improper care, it is still attacked by insects such as:
- Meadow moth;
- Sandy linger;
- Aphid;
- Weevil.
The meadow moth is one of the most dangerous pests that infects the plant at night. If damaged stems are found, the plant is treated with insecticides.
The sandy beetle is a black beetle, 10 centimeters long, that damages the stems. To combat it, you need to use bait.
Important! If it is necessary to treat the plant with insecticides, drugs are selected that are harmless to the human body.If we talk about thyme diseases, then one of the most dangerous is fungus or rust.
A contraindication for breeding thyme is abundant watering, as a result of which diseases develop. To resist these diseases, it is necessary to properly care for the plant.
If we talk about thyme diseases, then one of the most dangerous is fungus or rust. A contraindication for breeding thyme is abundant watering, as a result of which diseases develop. To resist these diseases, it is necessary to properly care for the plant.
Interesting Facts
Snakehead is a poorly studied species and is of interest to the scientific world. To date, some interesting facts are known:
Double breathing allows fish to survive in the most adverse conditions. Having drawn air into the gill sacks and buried in the silt by almost a meter, it waits out a long drought.
The greed of the predator played a cruel joke on him, food quickly runs out in the reservoirs of his habitat
For survival, evolution has endowed the fish with the ability to move from one backwater to another, and on land it can safely move for up to 5 days without diving.
It is important for breeders to know that those species of Snakehead, which are bright and beautiful at a young age, turn into more gray and inconspicuous as adults, and there are varieties with directly opposite properties.
Red Book
Are you here:
Home - The Red Book of the Leningrad Region. Plants - Hemitrichia creeping
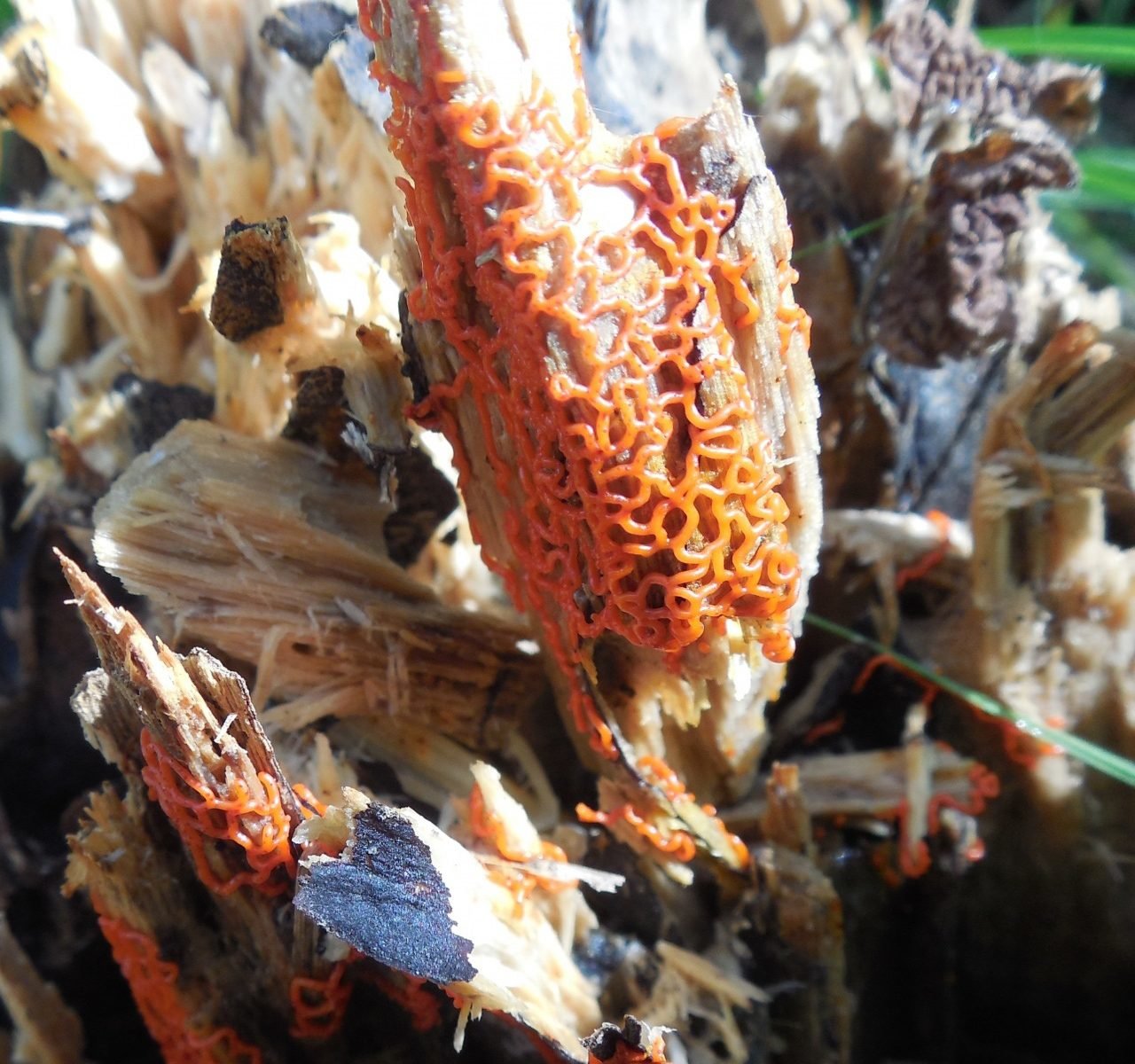
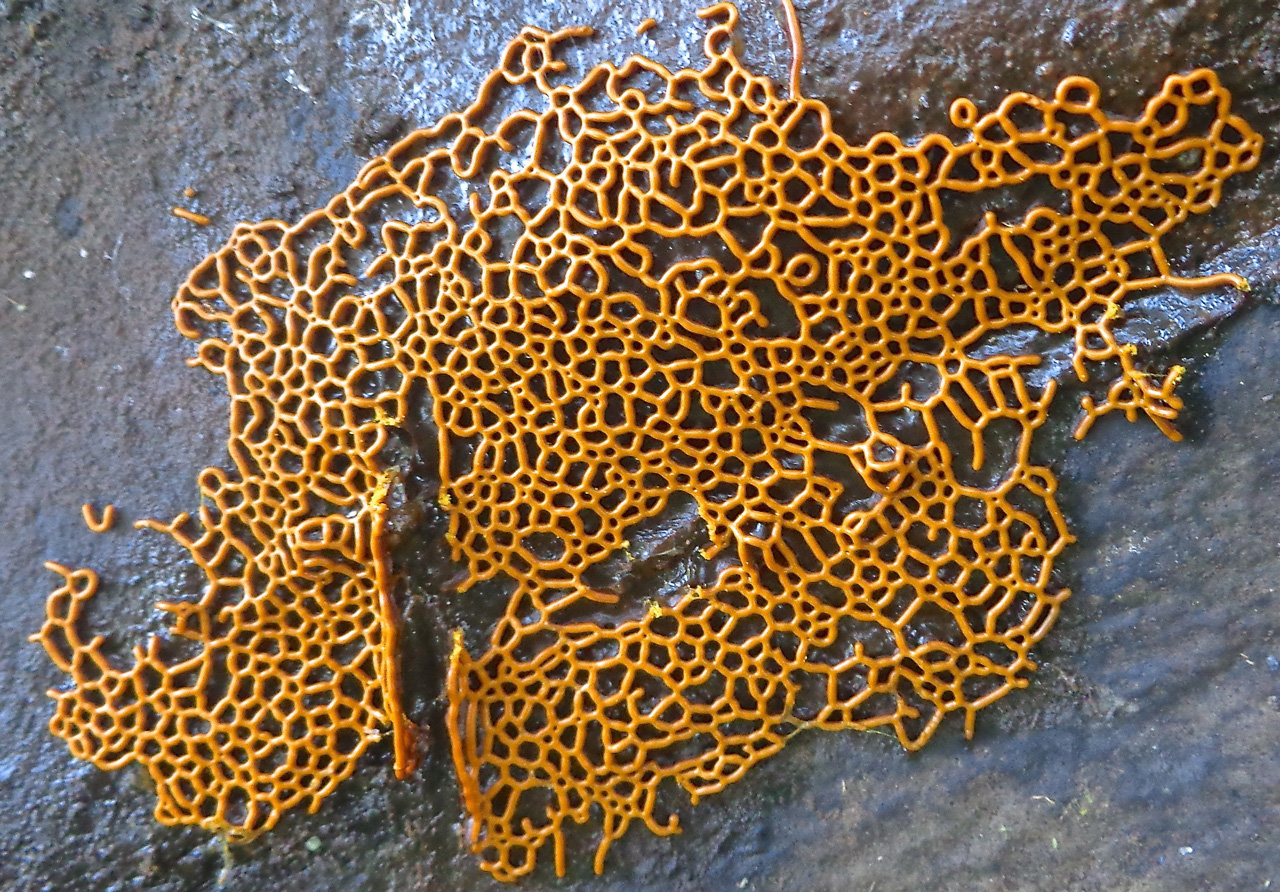
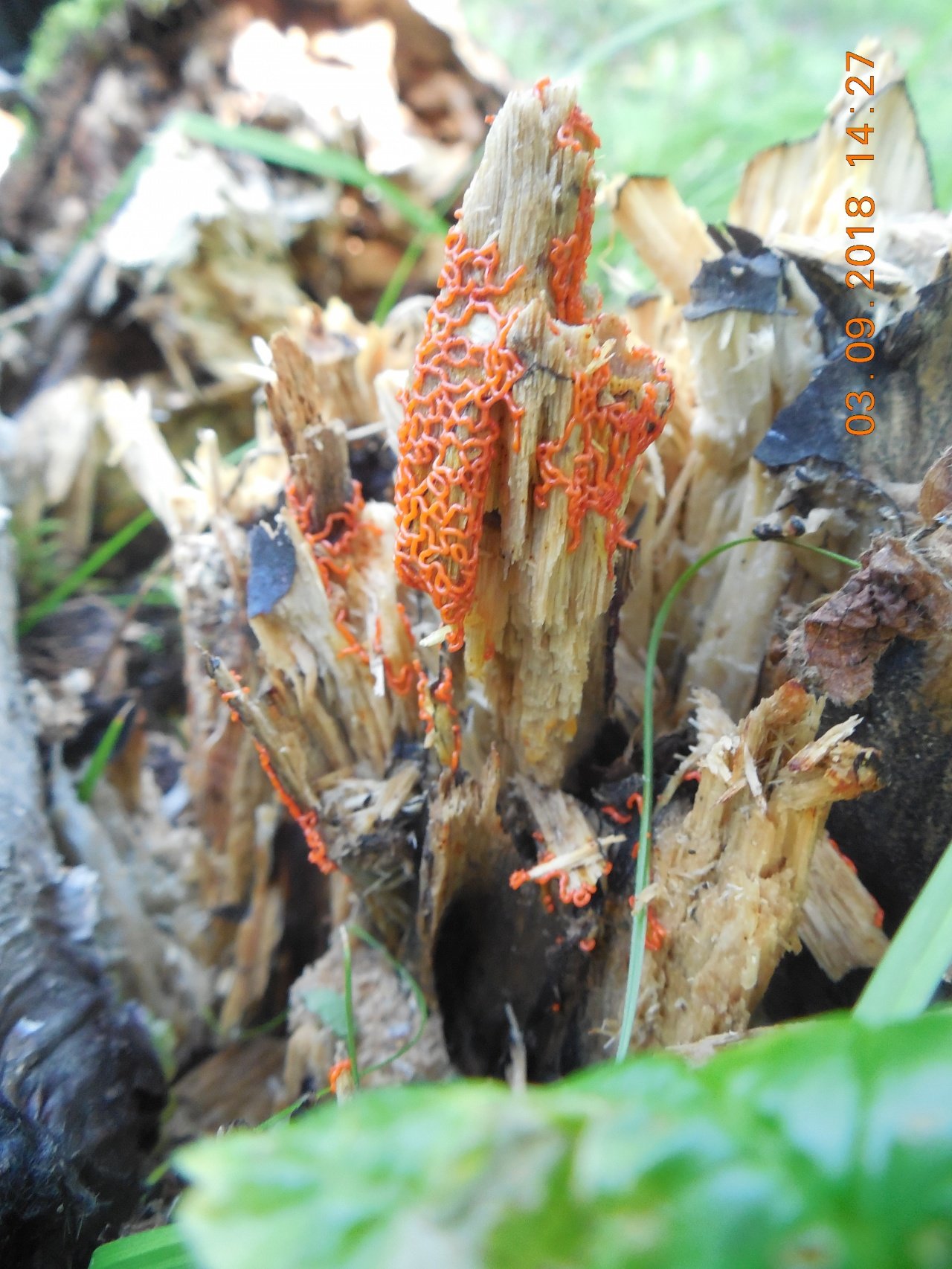
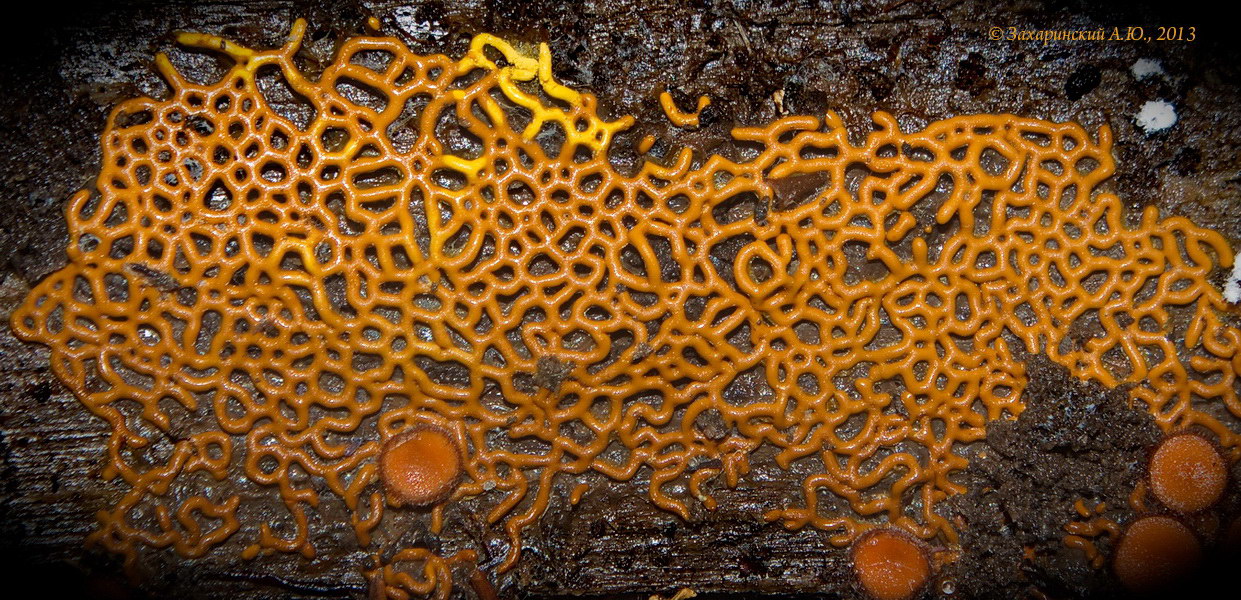
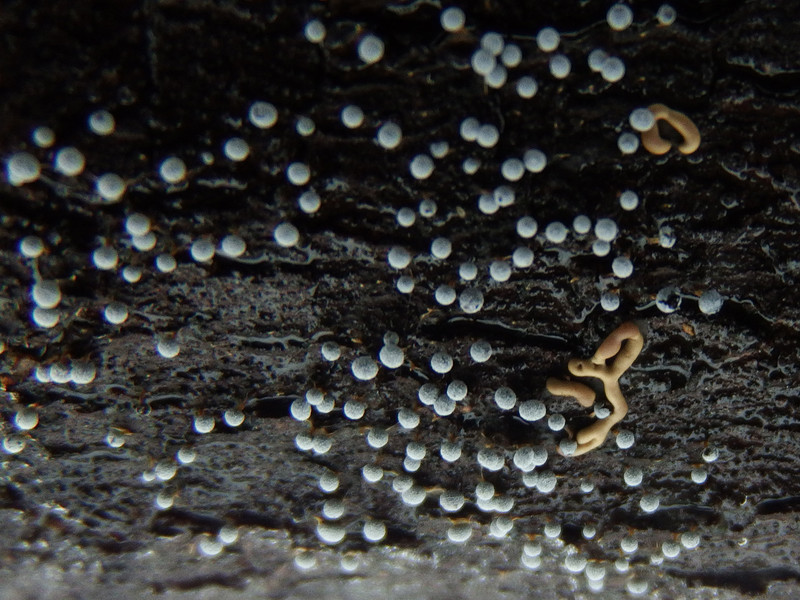
Hemitrichia creeping
Hemitrichia serpula (Scop.) Rostaf. (Myxomyeota. Trichiaceae) Status. 3 (R). Rare view.
Short description. Slime mold, forming bright yellow, often shiny, reticulate, cellular, fruiting bodies spread on the substrate in the form of plasmodiocarps up to several centimeters in length. The peridium is filmy, transparent, after maturation the sporangium cracks with a longitudinal slit, the capillium consists of threads entangled in a ball, ornamented with spines and spiral thickenings, yellow in transmitted light, 4-8 microns in diameter. From time to time in the mass yellow, 11-16 microns in diameter., Spherical, with mesh ornamentation.
Spreading. Found in env. the village of Kemka (Luga district) (1). In Russia, it was also noted in Western Siberia and the Dalny East (I). Found on all continents except Antarctica.
Ecology and biology. Found in an aspen forest on a large aspen log, under peeling bark.
Limiting factors. Not studied.
Security measures. Found in the proposed Kemka River Basin Wildlife Refuge. It is necessary to control the state of the known population and search for new locations.
Sources of information: I. Novozhilov. 1999. Yu. K. Novozhilov
Status. 3 (R). Rare.
Description. Slime mold forming bright yellow, often shiny, reticulate, alveolate fruit bodies, lying flat upon the substrate in the form of plasmodiocarps up to several centimeters long. Peridium membranous. transparent, splitting after maturing of the sporangium by a longitudinal slit. Capillitium of tangled threads ornamented by aciculae and spiral diickenings, yellow in transmitted light. 4-8 pm in diam. Spores yellow in mass, 1116 pm in diam .. globose, reticulate.
Distribution. In the Leningrad region has been found in the vicinity of Kemka (Luga district) (1). In Russia also recorded from Western Siberia and the Far East. Occurs over all continents excluding Antarctica.
Ecology and biology. Found in aspen forest on a large aspen log under flaking bark.
Limiting factors. Not studied.
Conservation measures. Occurs in The River Kemka Basin proposed sanctuary. Monitoring of the population and a search for new localities required.
Sources of information: I. Novozhilov. 1999. Yu. K. Novozhilov
|
25.11.2018 14:10:39
-
Menu
- home
- Photo gallery
-
Animals
- Mammals
- Birds
- Fishes
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Insects
- Crustaceans
- Worms
- Molluscs
-
Plants
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperms
- Ferns
- Mosses
- Seaweed
- Lichens
- Mushrooms
- Moscow
-
Moscow region
- Mammals
- Birds
- Invertebrates
- Pisces, presm., Terrestrial.
- Plants
- Mushrooms, mosses, lichens
-
Voronezh region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Republic of Crimea
- Plants
- Animals
-
Rostov region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Krasnodar Territory
- Plants
- Animals
-
Leningrad region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Pskov region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Sverdlovsk region
- Plants
- Animals
-
Saratov region
- Mushrooms
- Bryophytes
- Ferns
- Amur region
- Krasnoyarsk Territory
- Belgorod region
-
Chelyabinsk region
- Plants
- Animals
-
IUCN Red List
- Extinct mammals
- Rare birds of the world
- Cetaceans
- Carnivores
- Reserves of Russia
- Wild animals
- Birds of Russia
- Download the Red Book
- Basic documents
- Custom sog.
- .
Basics of keeping in an aquarium
Snakeheads are large and aggressive, so in artificial reservoirs they are kept alone or with pets that can fight back, and there are very few of them.
Requirements for the chemical parameters of water for each type are different, as mentioned above. As for the cleanliness of the environment, the filter is required, the predators litter heavily. Substitutions are done several times a week in small portions, up to 1/10 part.
Considering the possibility of movement on land, the aquarium should be tightly closed. It is also worth remembering that the pet needs air for breathing, therefore, a layer of at least 10 cm is left between the lid and the surface of the water.
The lighting should not be bright, in nature they like to hide in dark backwaters, in thickets of vegetation, under snags and in grottoes. It is recommended to create similar conditions in a container.
Landing
It is useful for those who want to have Lemon thyme in their garden: planting and caring for this plant does not require special conditions. You can plant Lemon thyme at any time, but you must take into account the fact that it needs to take root before severe frosts come. Therefore, in late autumn, it is better to refrain from planting.
It should be noted! The plant tolerates snowy winter well, it does not need to be covered. If a little snow fell in winter, then in order for the plant to endure this period well, it is better to cover it with spruce branches.
Before planting, you need to choose the place where the thyme will grow best. It should be a sunny area, while warm and low wind. If the plant is planted in the shade, then the stems will be tall, but will lose their attractiveness.
The soil that thyme loves should be light, well-drained, and fertile. On clay soils, the plant will rot and die. In this case, drainage is imperative. Mulch the soil with pebbles, gravel, crushed stone.
Mr. Tail recommends: varieties
For aquarists, Snakeheads of various colors and sizes have been bred. Consider the features of each type.
Golden Cobra
A beautiful fish, predominantly gray with orange stripes interspersed with black dots, the same markings on the fins. Came from India, aggressive, kept alone. Reaches 60 cm in length.
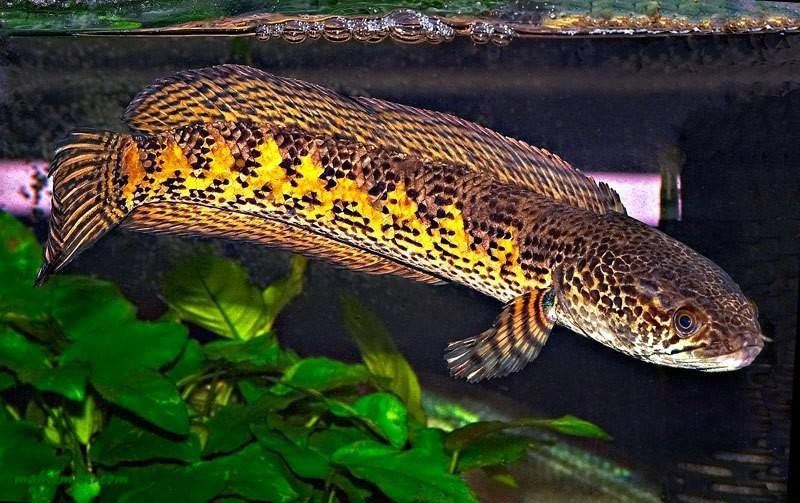

Requires special aquarium water parameters:
|
Rigidity |
Acidity |
Temperature |
| 10 ° dH | 6.0-7.0 pH | + 20 ... + 26 ° С |
Red striped giant
In captivity, it grows up to a meter, requires a large reservoir. Usually take a capacity of at least 400 liters. The pet is so aggressive that it rushes at everything. Those whom he cannot swallow, he simply tears to pieces. Differs in the largest fangs of all types of snakeheads. Juveniles are attractively colored with bright orange stripes interspersed with cardinal blacks.

As they grow older, they turn pale and gradually turn dark blue. They are thermophilic and require an ambient temperature of + 26 ... + 28 ° С.
Dwarf (gaucha)
Gray body with slightly pronounced dark stripes, blue fins, red dot under the eyes. One of the most popular morphs. The homeland of the fish is India, several subspecies are known, slightly different from each other. The pet is peaceful, compatible with other underwater inhabitants of equal size. Adults reach 20 cm in length.
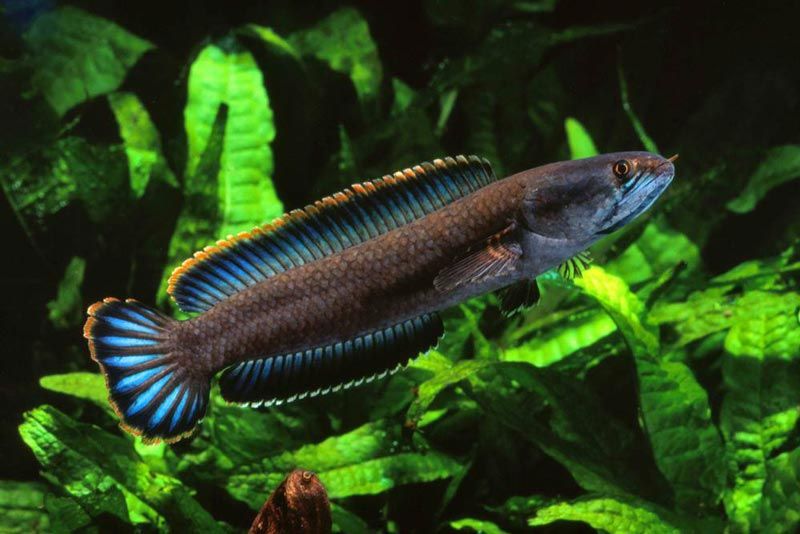

Loves cool water with indicators:
|
Rigidity |
Acidity |
Temperature |
| 6-8 ° dH | 6.0-7.5 pH | + 18 ... + 25 ° С |
Imperial
The belly is light, the back is brown with black equidistant rhombs. Reaches 65 cm in length, requires a large tank. Can only be combined with the same large pets. The conditions of detention are similar to those of the Golden Cobra.
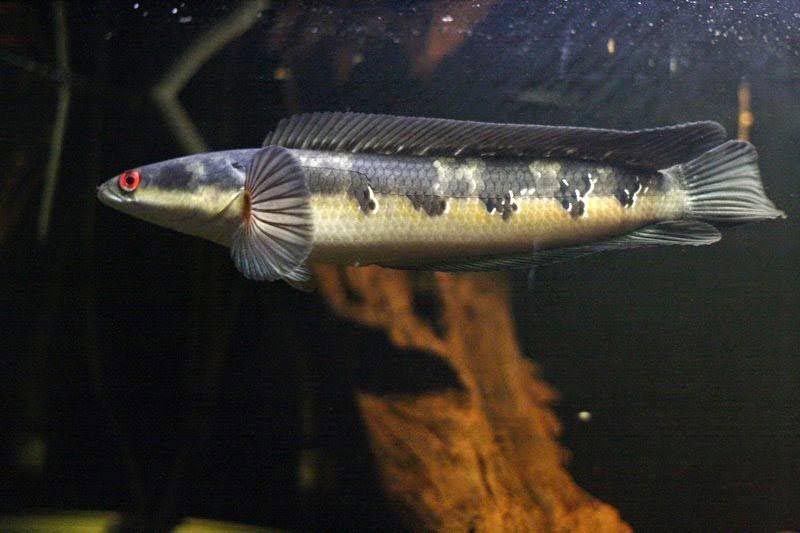

Rainbow
Brown with blue and orange splashes. The brightest of the varieties, reaches 20 cm in length. Quite compatible with other pets, relatively friendly. The conditions of detention are similar to those of Karlikov.
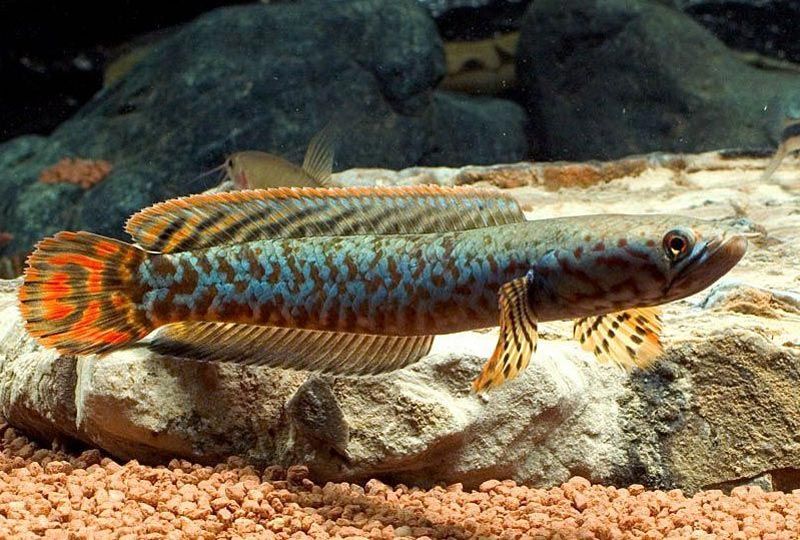

Bancanesis
The back is brown, the abdomen is white. All over the body there are small black blotches. Despite its small size, no more than 23 cm, it is extremely aggressive.
Also picky about the chemical indicators of water, the acidity level should not exceed 6.0. If the indicator is violated, the pet becomes prone to various diseases.

Lucius
Sandy-golden with chaotic black spots, large enough and requires a voluminous reservoir. Adults grow up to 40 cm, are aggressive, therefore, it is permissible to combine only with large neighbors, but for personal peace of mind it is better to keep it alone. Temperature up to +28 ° С.
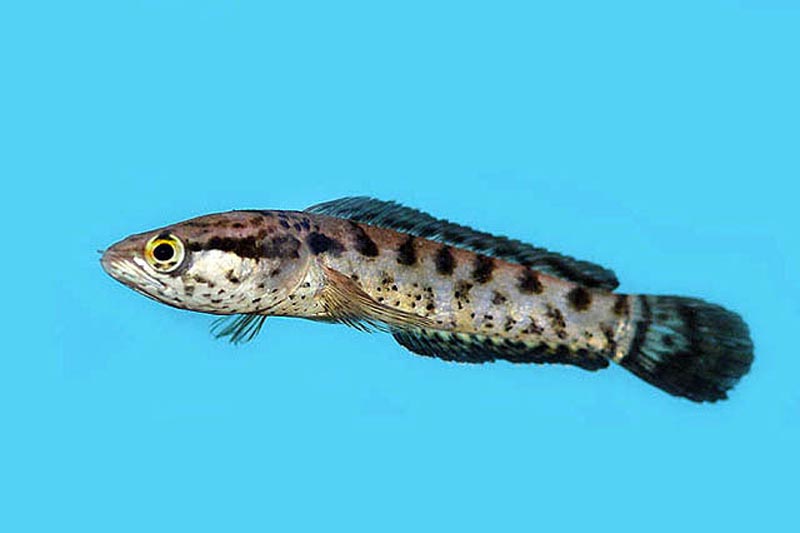

Three-point (speckled)
On the gray body there are large black spots, circled in gold (there is a resemblance to the eye), the same point is on the caudal fin. Large and strong, up to 45 cm in length. The throwing speed is so high that it allows the Snakehead to catch any prey. It welcomes water with low acidity, but also feels good in neutral water.

Spotted
Grayish-brown top and light belly; dark blotches are randomly scattered over the body, forming incomplete transverse stripes. Absolutely indifferent to the quality and temperature of the water, aggressive, kept alone. It can grow up to 30 cm.
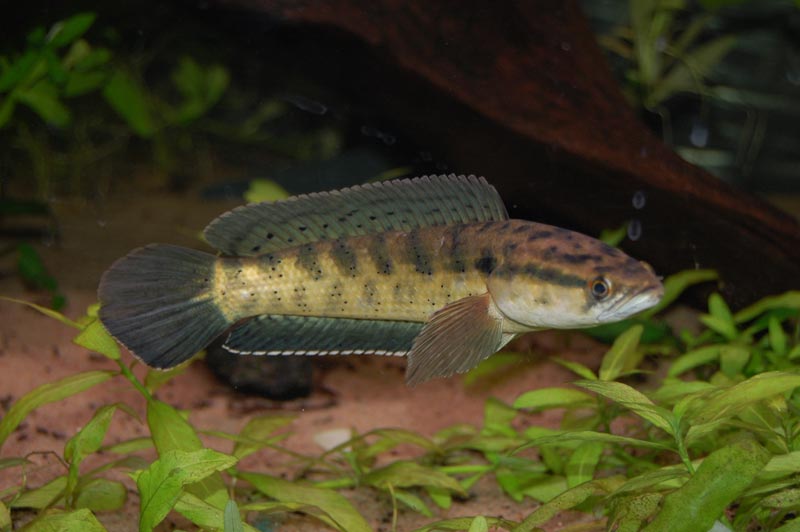

Chevron
The back is sandy brown, the belly is silver. Unpretentious look, indifferent to the conditions of detention. Grows up to 90 cm, requires a large reservoir.

African
Spotted, dark streaks on a light gray body. It differs from its counterparts in elongated tubular nostrils. It grows up to 40 cm, in terms of the chemical composition of the liquid, it is similar to Lucius.

Stewart
A beautiful gray-blue fish of small size, up to 25 cm. Fearful, spends most of the time in shelter. She will not touch her neighbors if they do not climb into her house or take away food.
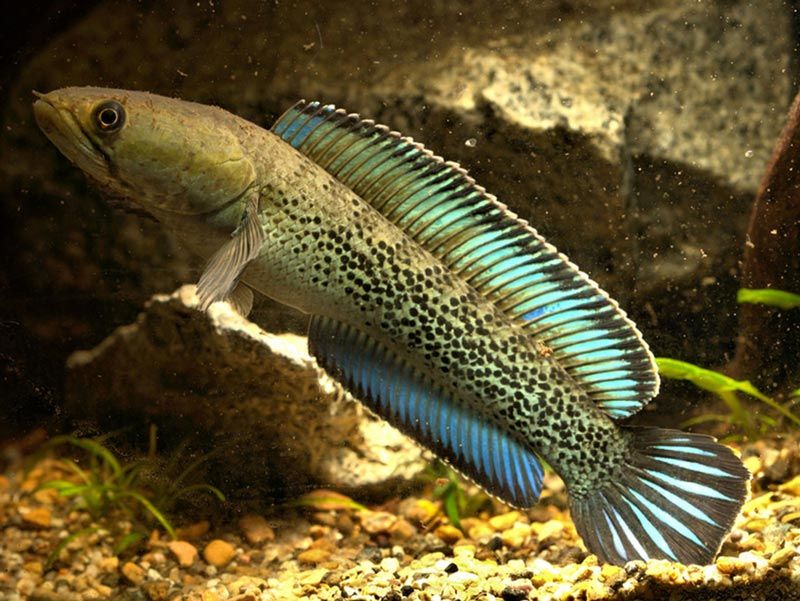

Pulchera
The blue and blue body is decorated with orange and black peas, the pectoral fins in black and white stripes effectively complement the image, the abdomen is slightly lighter than the main tone. Up to 35 cm in size, non-aggressive, omnivorous. Do not hide
There are 2 large canines on the lower jaw, move with care, bite.

Description and characteristics of the plant
Lemon-scented thyme is a perennial plant that emits a spicy aroma with hints of lemon scent. Its leaves are small and oval in shape. Their color is dark green, with small spots of yellow. The plant blooms from June to July in purple. Prefers to grow in an open, fully lit area. But it is found in places partially shaded. The soil for growing thyme should be well-drained, neutral or slightly alkaline, fertile. The plant tolerates drought well, does not like long stagnation of water. It is recommended to plant from nine to eleven bushes per square meter.
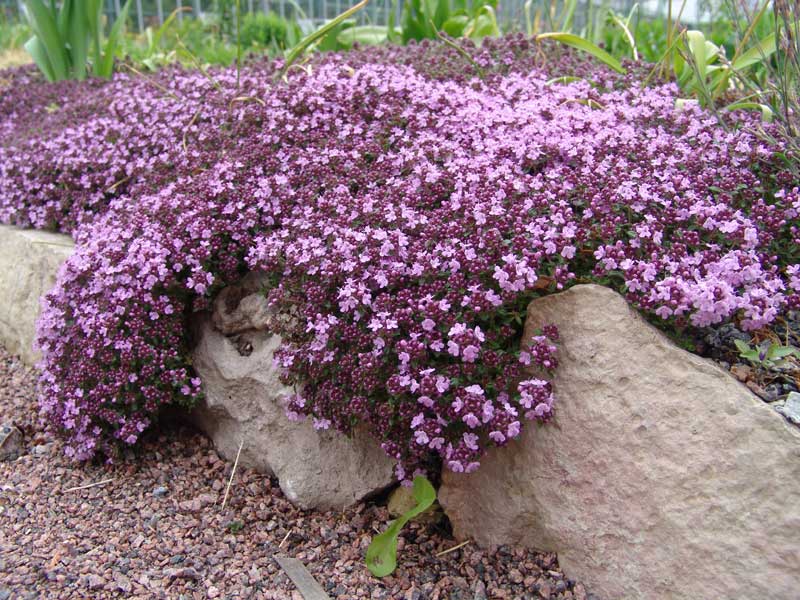

Thyme
Behavior and compatibility
Fish do not have a simple disposition. Males are aggressive in defending their territory, attacking relatives and representatives of other species that have violated the border. Females are also not very friendly to neighbors in the aquarium, which is especially evident during the breeding season, when the couple is guarding their offspring.
In small aquariums, it is recommended to purchase only one formed pair, and the male and female should grow together from a young age. If you put together an adult male and a female, who until this moment lived in different reservoirs, then there is a high probability that the fish will be hostile to each other.
Compatible only with large species and those who can defend themselves, such as catfish such as plecostomus.
Breeding / Reproduction
There are examples of successful breeding of Dimidochromis in an artificial environment. Females prefer to lay eggs on some hard, even surface, for example, a flat stone. They are then immediately placed in the mouth - this is an evolutionary defense mechanism inherent in most cichlids. The entire incubation period (21–28 days) is spent in the female's mouth. All this time, food intake is impossible, so if feeding before spawning was not regular or insufficient, she can release eggs ahead of time. The fertilization process looks no less interesting. Each male has a characteristic pattern of several bright dots on the anal fin, reminiscent of the shape and color of an egg.The female, mistaking the drawing for real eggs, tries to pick them up, at this moment the male releases seminal fluid and the fertilization process takes place.
Reproduction
Thyme reproduces in several ways.
Seminal
In this case, you will need a pot filled with a light mixture of peat and sand. Seed is sown into it and brought into the house. For good shoots, dishes with seeds are placed on the windowsill. After the seedlings have risen, they are transferred to the shade and periodically sprayed. This should be done only if the top layer of the earth is completely dry.
If mass sowing is planned, then seedlings can be grown directly in the garden bed or in a greenhouse. In this case, it is necessary to constantly remove weeds that can interfere with the growth of young shoots. If thyme is planted on open ground in early spring, then this year it will delight with the first flowers.
Cuttings
In this case, you need to cut off the stalk and plant in the place where you plan to grow the thyme. Alternatively, it can be grown initially in a greenhouse. This method is good because it can be used throughout the growing season. It should be noted that for undersized bushes it is best to use cultivation with cuttings no more than 5 centimeters. First of all, they are planted in a jar and the soil is slightly moistened. After a few weeks, the rooted sprout can be planted in a permanent place.

Thyme seed shoots
By dividing the bush
This is the easiest way to grow, because in this case the bush is completely dug up, the roots are divided and planted in the right places.
Reproduction
Pets are ready to breed when they reach 2 years of age. By this time, they are already quite large and reach 35 cm. Spawning takes place in the summer at a water temperature of + 18 ... + 20 ° С.
First, the male builds a large nest of plants, up to a meter in diameter. In it, the female lays eggs, which have their own particles of fat, which help to float to the surface and stay in the upper layers until the fry appears. During the season, a sexually mature individual is capable of sweeping up to 30,000 babies. Larvae hatch 5 days after spawning.
Parents carefully protect the nest and the area around it. The mother carefully winds her offspring with fins, creating a small current. After the appearance of juveniles, the parents do not abandon them, but continue to protect them jealously. This is why fish reproduce so quickly.