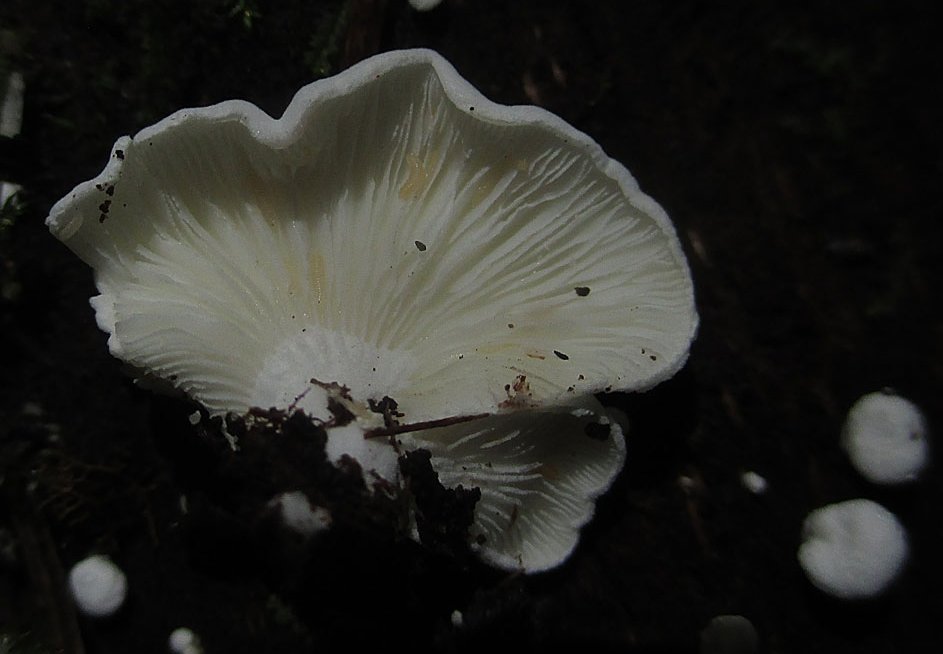
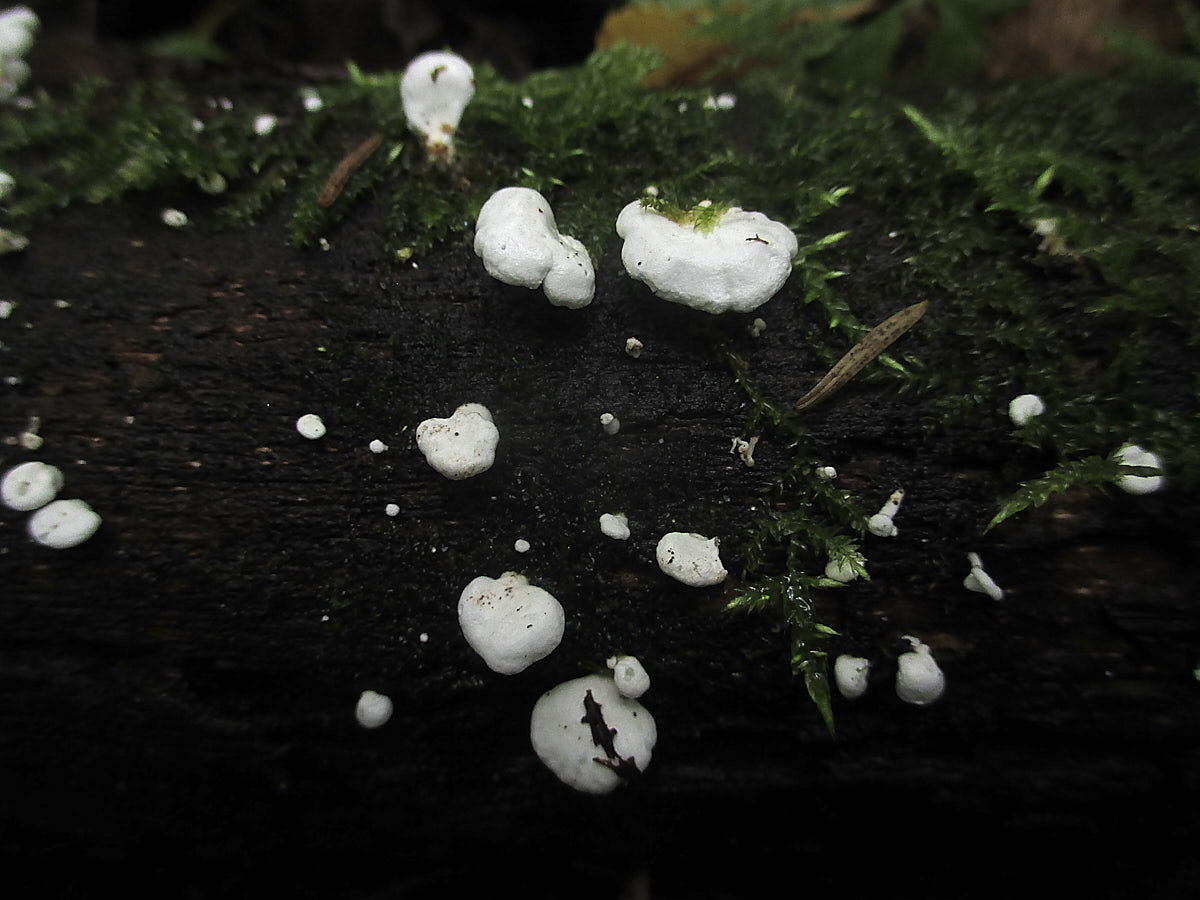
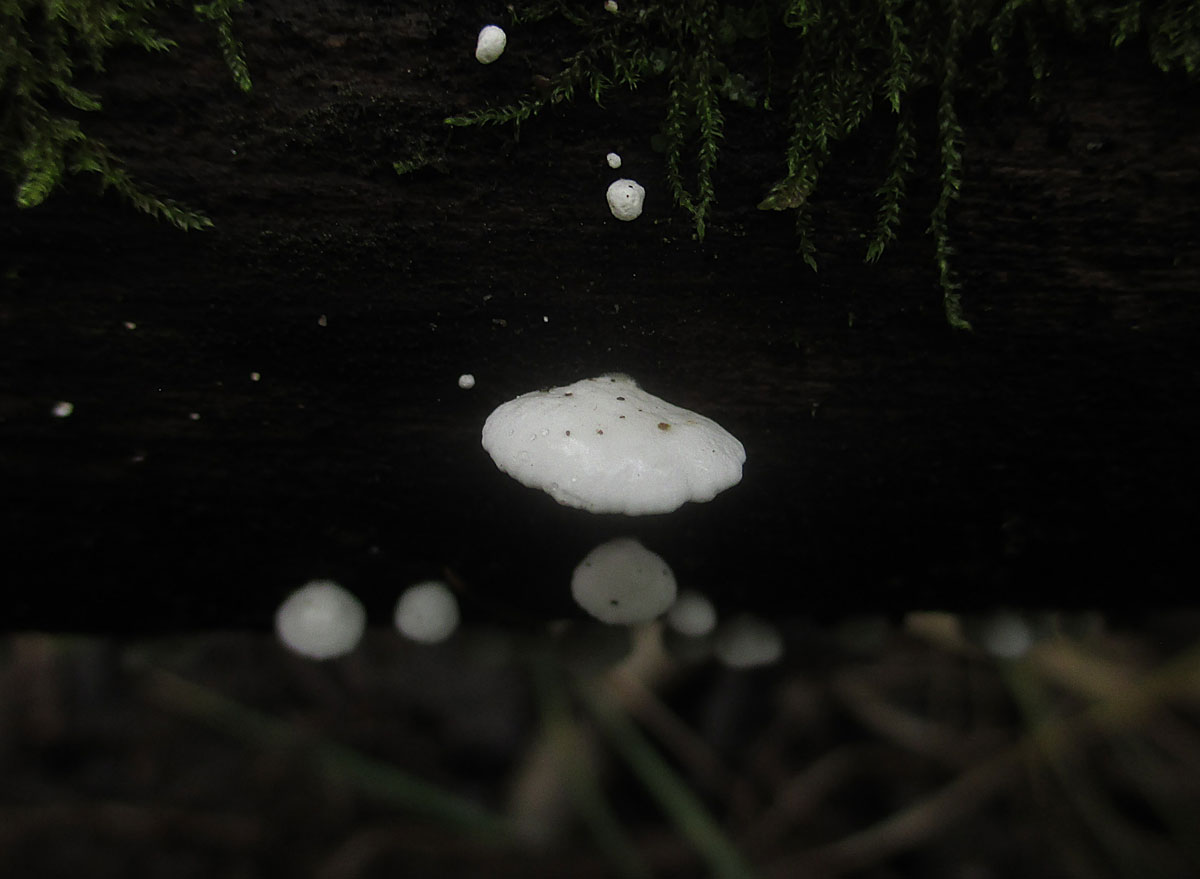
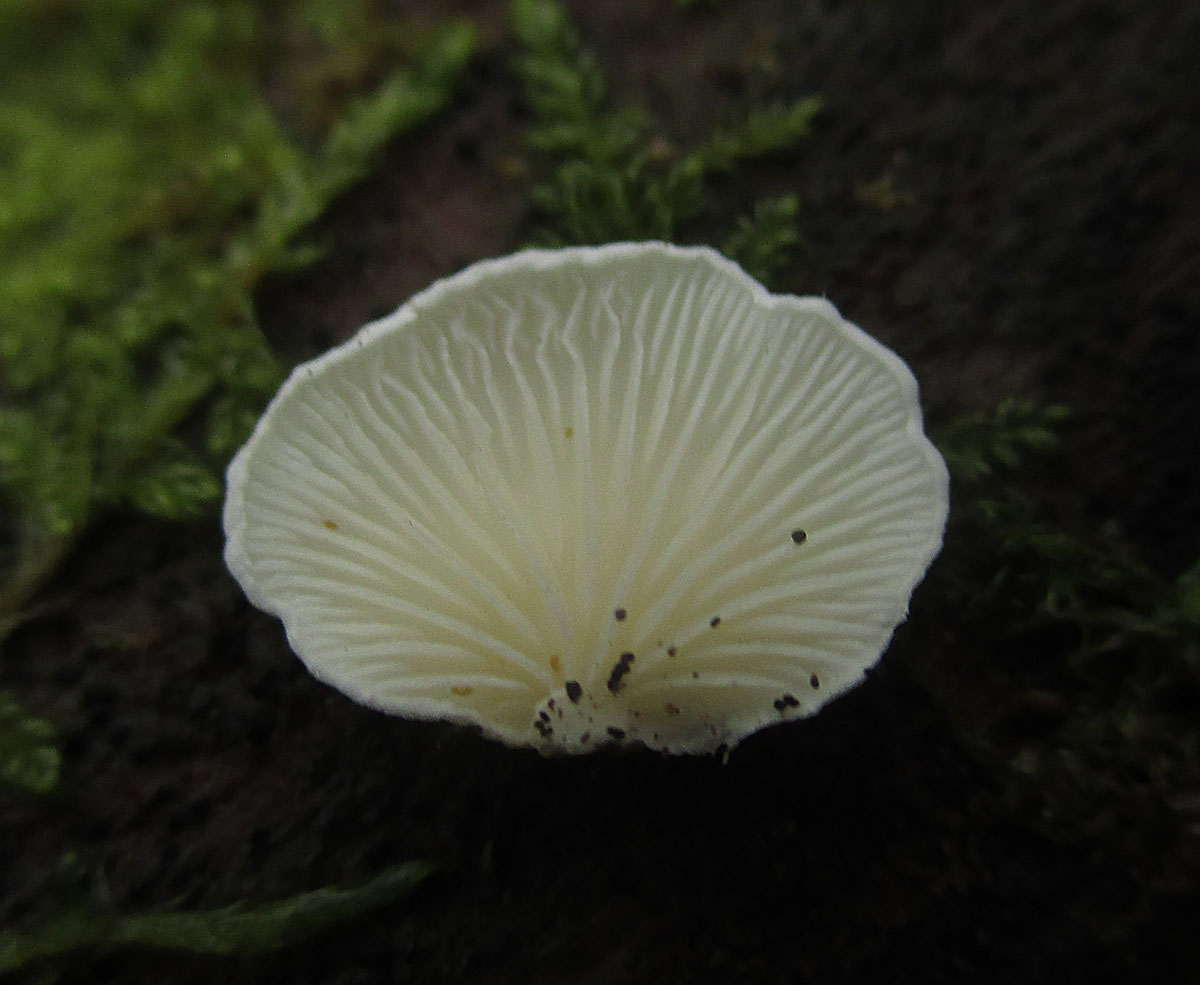
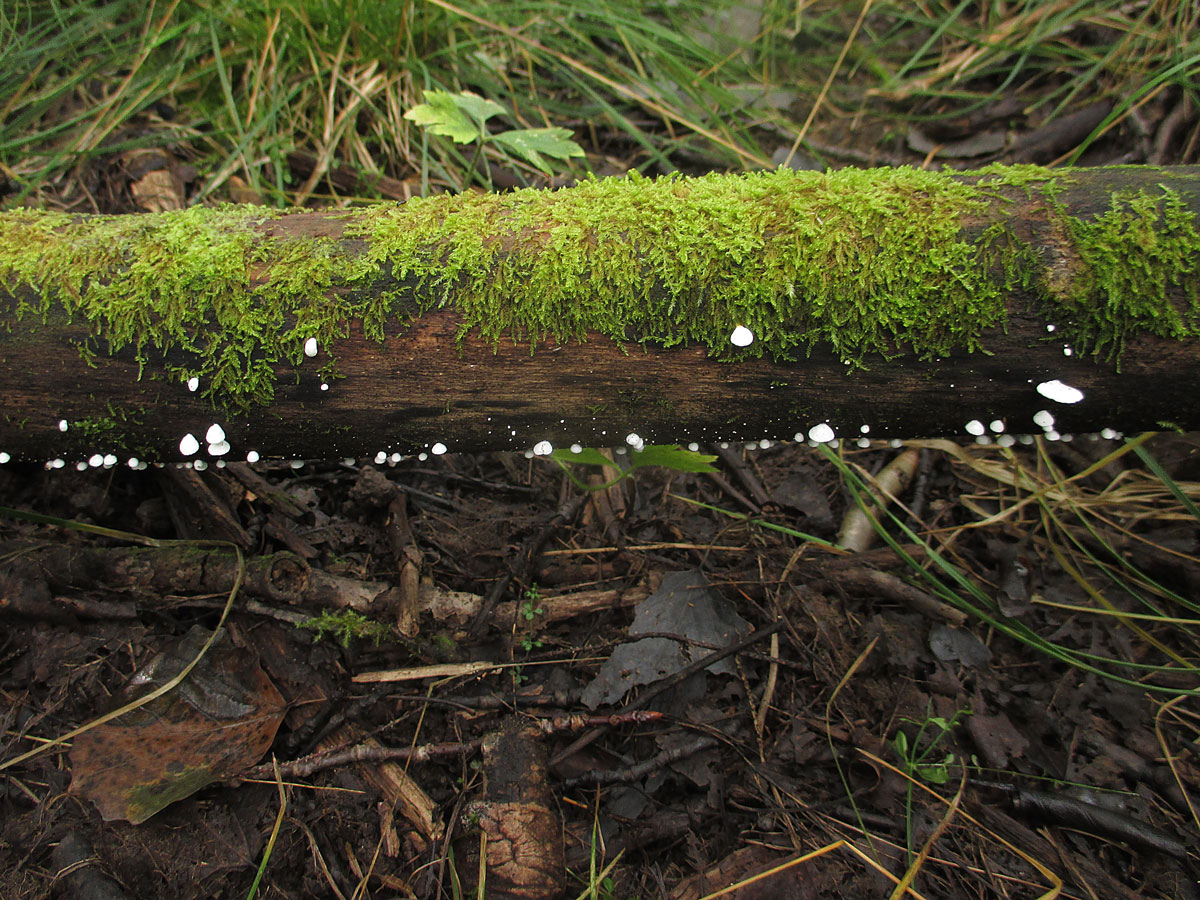
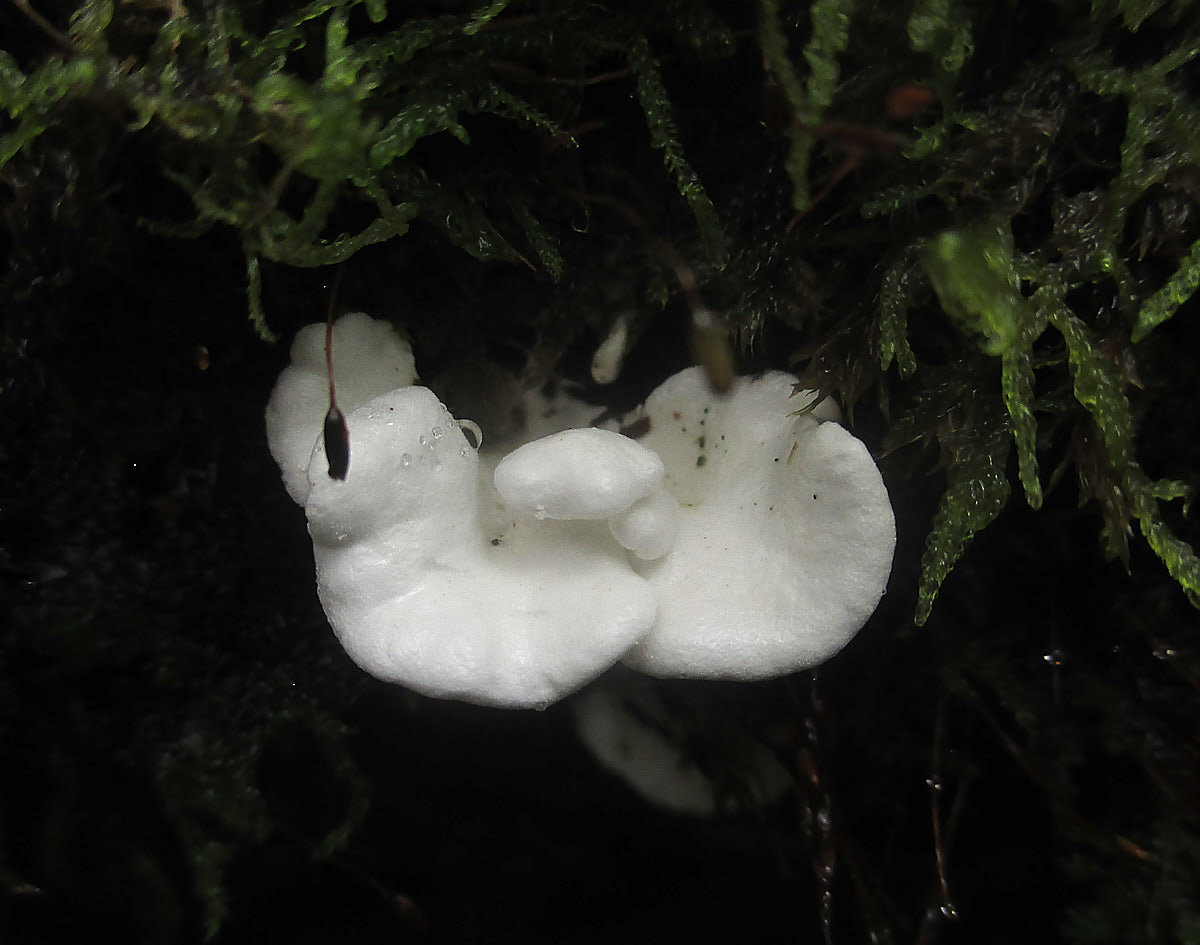
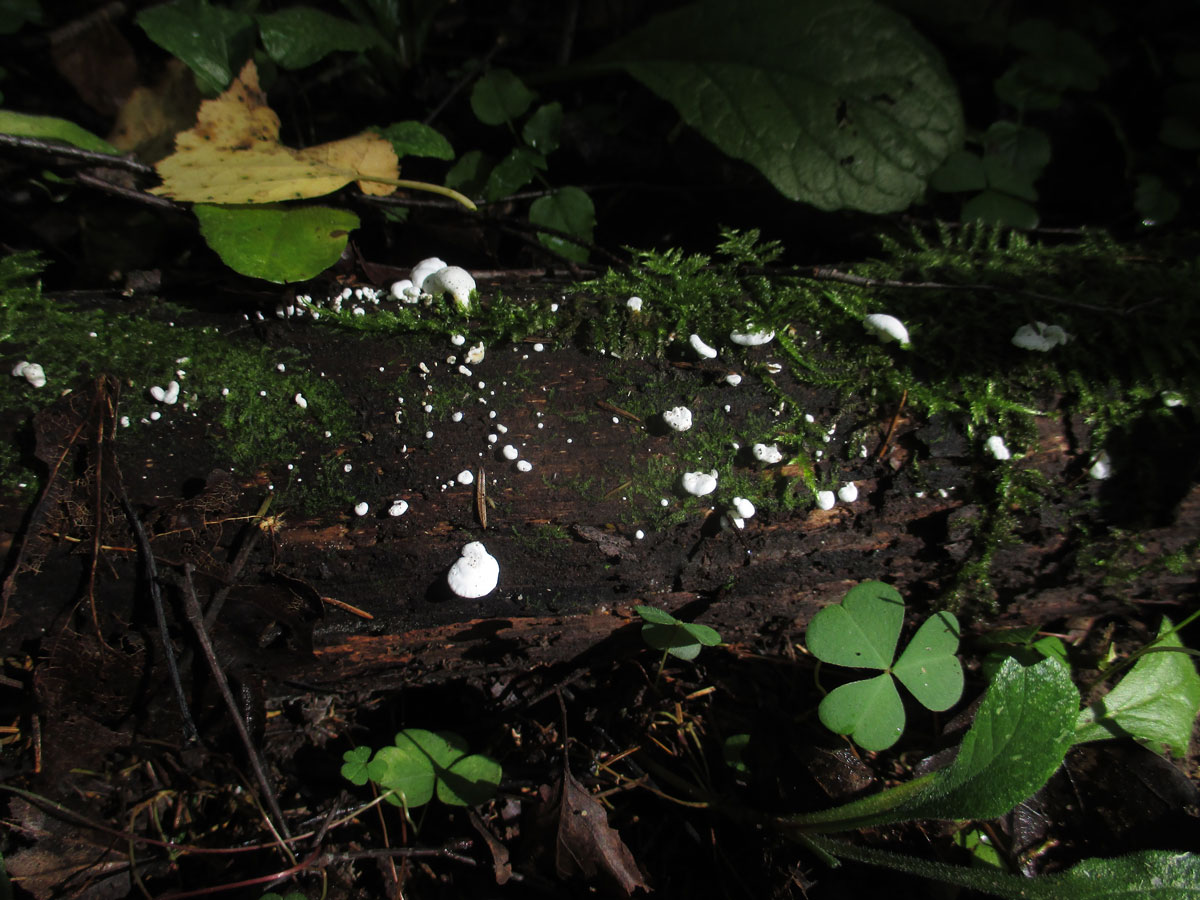
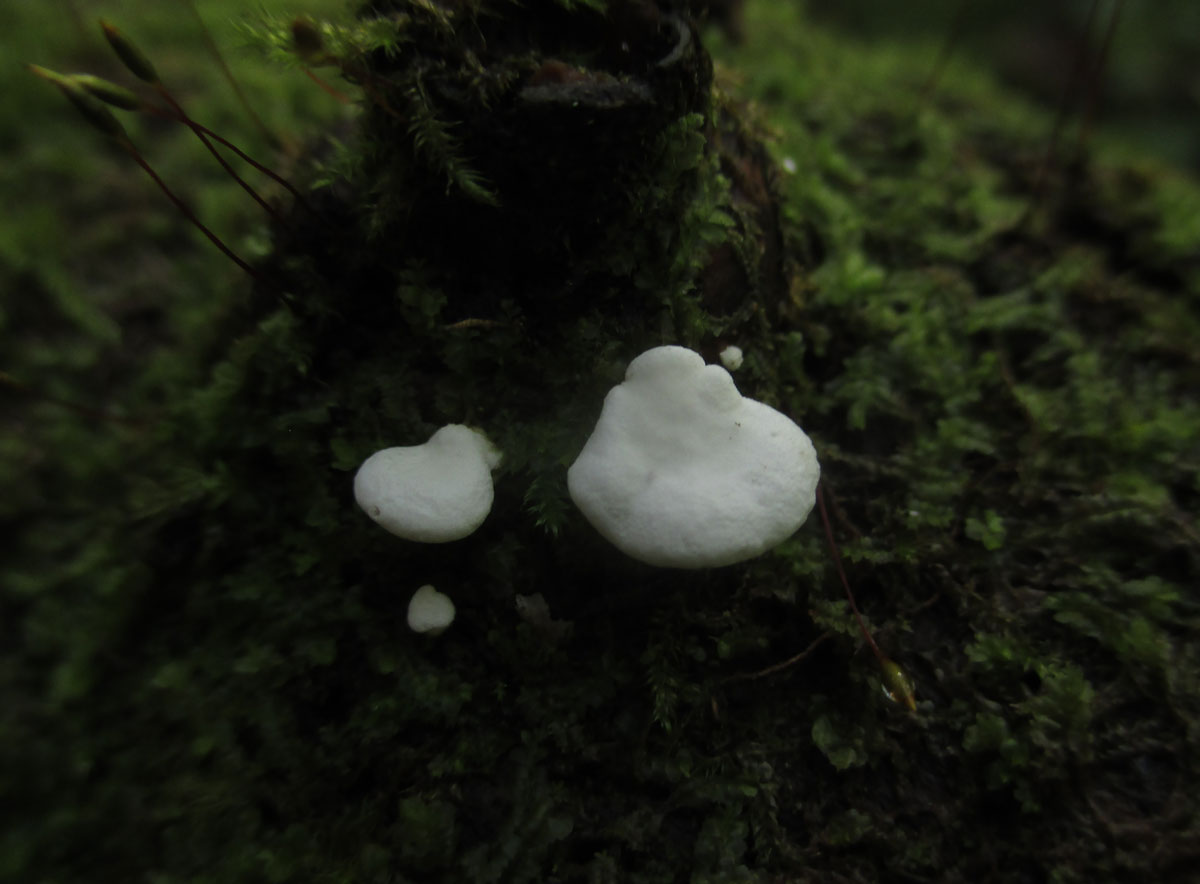
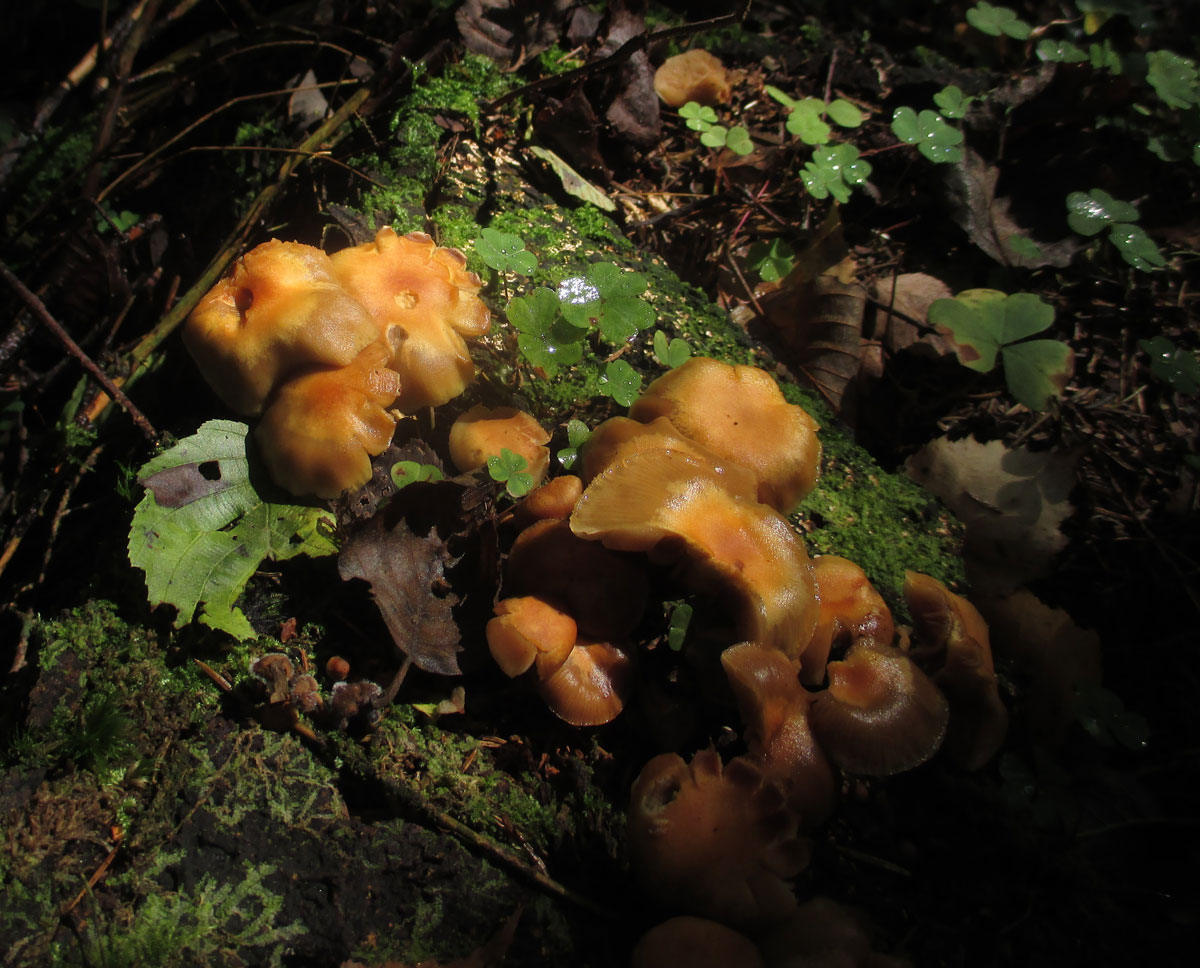
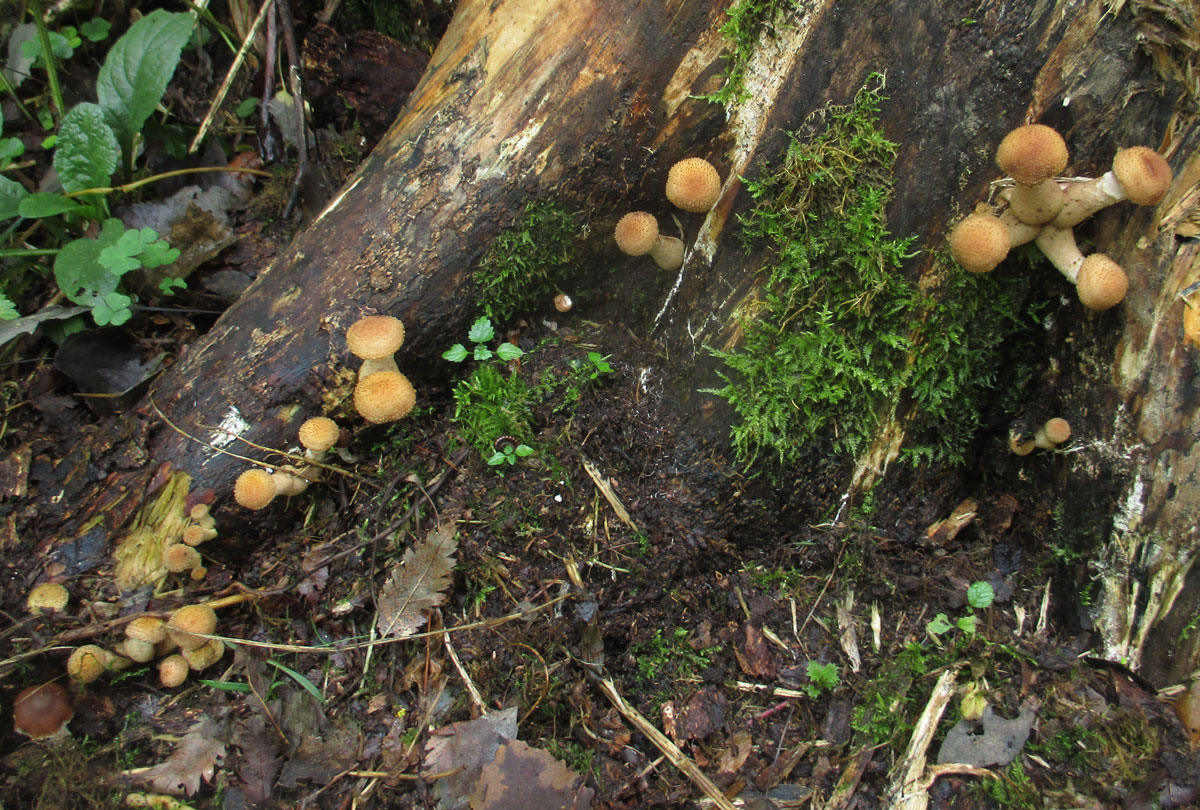
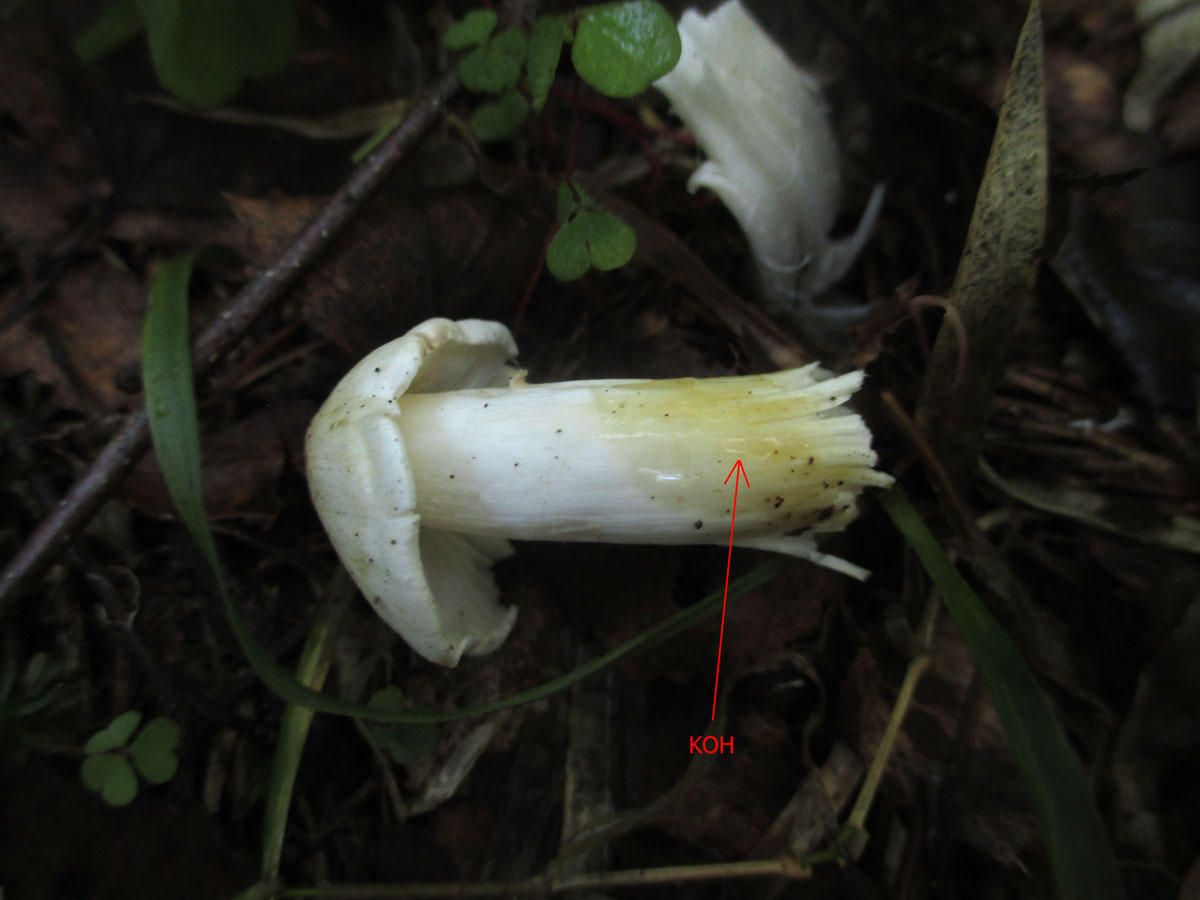
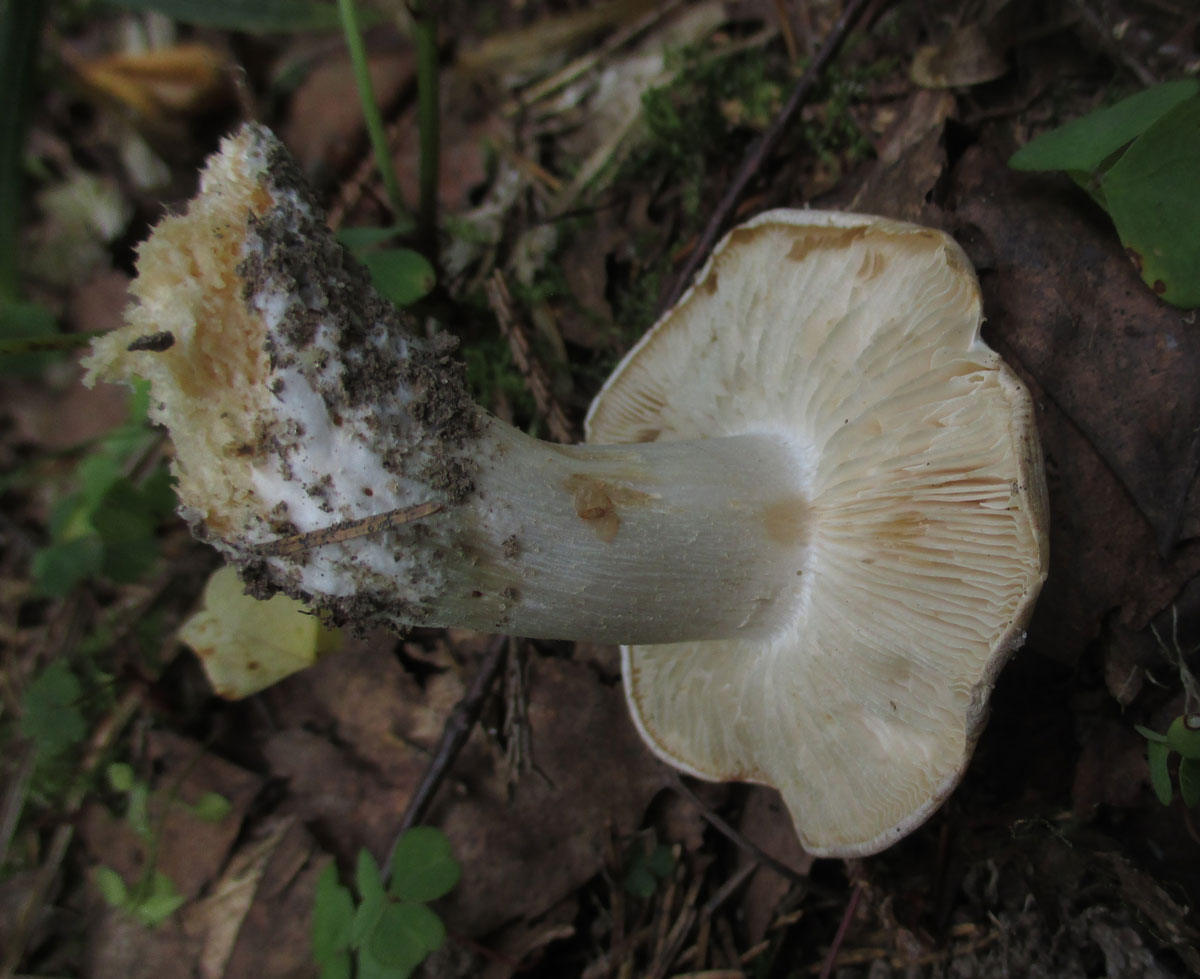
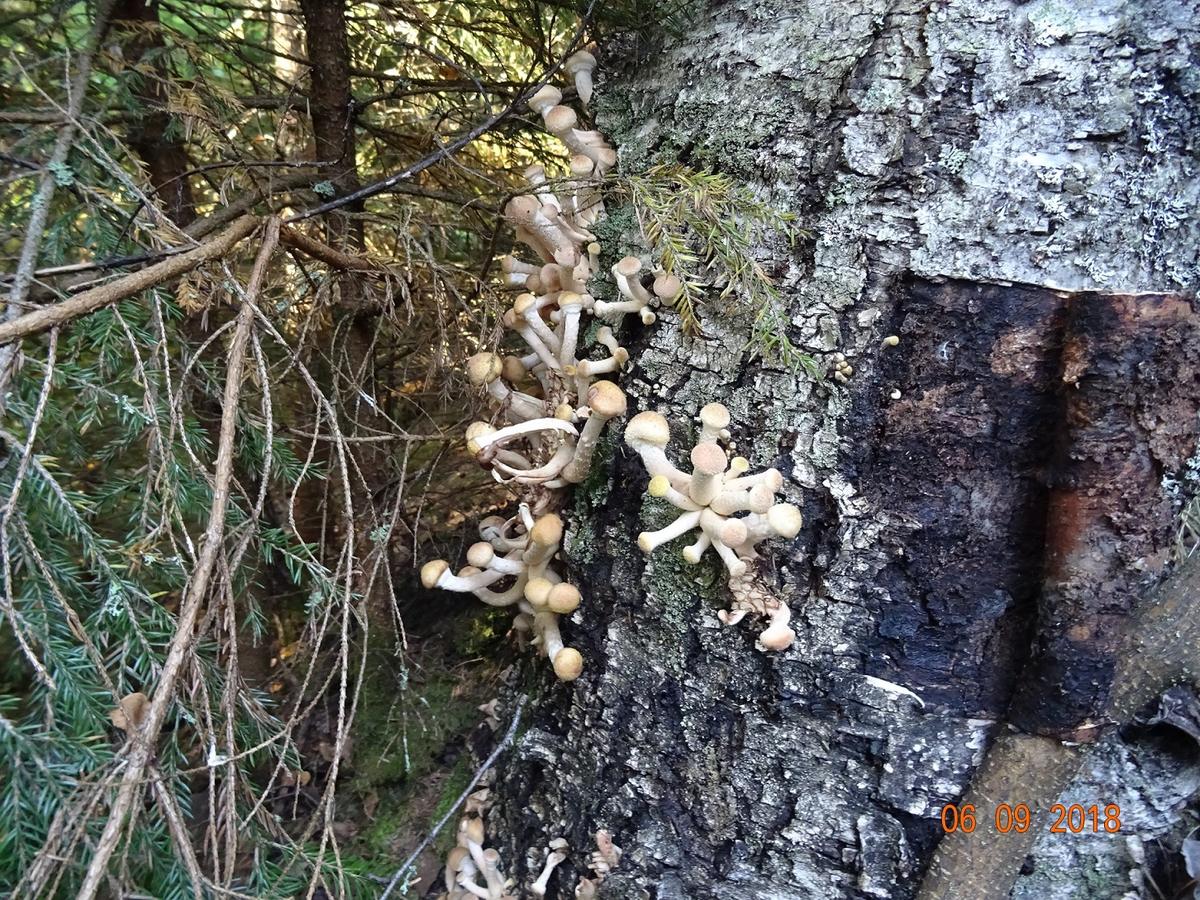
Diseases and pests
Hemantus has good immunity to diseases and pests. But, for example, overflow can lead to rotting of the root system and the bulb itself. The consequence is the development of fungal diseases, which are fought by removing the diseased part of the plant and treating it with fungicides.
Fortunately, the "deer's tongue" also has few insect pests, but it is imperative to fight them. All of them easily move from plant to plant, which means that soon all flowers may suffer.
- The red spider mite braids the entire flower with cobwebs, and lays eggs in the ground. The problem is that they can be stored there for up to 5 years. The reason for the appearance is too low humidity and high temperature in the room. The way of prevention is bathing the foliage (but not the bulbs!), Preferably with soapy water. Control methods - insecticide treatment, preferably once a month for a quarter. If this method does not help, then the plant must be transplanted into a new pot with new soil.
- The scale insect is a pest that can harm all indoor plants. Florists are advised to first collect these oval insects from the leaves by hand or with a brush, and then treat them with insecticidal preparations.


The main thing is that when the first signs of a disease appear on any plant, it is immediately transferred to the quarantine zone so as not to infect other flowers.
For more information on Hemanthus, see the video below.
Types of ampel monsters
There are more than a hundred varieties and varieties of monsters that are grown at home as an ampelous plant. In Russia, only a few of them are especially popular:
- Friedrichstahl;
- gourmet;
- Karvinsky;
- Face;
- Adanson;
- pointed.
Each of the varieties listed above has a certain characteristic difference that makes it different from other varieties. As a rule, they differ in the shape, size and pattern of the leaf plates.
Friedrichstahl variety
Monstera Friedrichstahl
This species is most in demand in Russia and European countries. It can be argued that Friedrichstahl's monstera is the most famous and popular indoor cultivar. It is very easy to take care of the plant, which is its undoubted advantage.
The bush is quite tall, unlike other representatives of its kind, so it is more convenient to keep it in spacious rooms. It has large leaves with striped patterns in the form of cuts. Every year the shrub blooms with snow-white flowers, which gives it an even more decorative look.
The plant is very demanding on lighting, since its flowering depends on it. With a lack of light, the buds begin to shrink, and the leaves become dull and wither.
Note! In its natural environment, the Friedrichstahl monster survives under any conditions. The plant was nicknamed "the monster" because its vines twine around the support, like the tentacles of a monster.

A variety called Monstera Adanson
Monstera Adansona
This plant has a very high resistance to various types of diseases, including infectious ones, and is almost never affected by pests. The bush has oval and smooth leaf plates with large cuts. The home grown plant is very compact in size, but in its natural habitat it can reach 7-8 m.
The disadvantage of this type of monstera unequal can be considered the fact that it practically does not bloom at home, but only in the wild. The spike-shaped flowers have a pale yellow tint.

Oblikva is another well-known representative of the genus
Monstera Obliqua
The Latin name for this species is monstera obliqua. The plant is not capricious, therefore it does not require special care, but at the same time it has a very beautiful appearance. It has light green lance-shaped leaves with asymmetrical cuts. The length of the leaf plates does not exceed 30 cm. This ampelous type of dwarf monstera is grown in hanging pots or on special supports, as it tends to grow strongly.
Monstera Obliqua is very rarely affected by the spider mite, which winds a thin web on the stems and leaves. These parasites must be fought with acaricides.
Note! Since the branches of the bush have aerial roots, they must be periodically manually bent and guided into the soil.
Caring for the cellogin orchid at home
Illumination
All year round, such a plant needs bright lighting. So, its level should be at least 4000–6000 lux. The best place to place it is an east or west orientation window. At the same time, on the window on the north side, the flower will have little light, and on the south, it will need shading from the direct rays of the sun, which it cannot tolerate.
At the same time, do not forget that daylight hours should be no shorter than 12-14 hours throughout the year. In this regard, in the winter, he needs additional lighting.
Temperature regime
The temperature regime depends entirely on the type of orchid. In the warm season, almost all species need moderate temperatures from 20 to 25 degrees. In winter, the beautiful thermophilic cellogyne should be protected from low temperatures, so the room should not be colder than 10 degrees, while the cold-loving comb cellogyne needs coolness at this time (about 5 degrees).
Dormant period
It should be remembered that some species have a dormant period, while others do not. So, for example, the beautiful cellogyne does not have a dormant period, and therefore flowering can begin in any month, regardless of the season. In cellogyne fringed, the rest period is also absent, but at the same time this species blooms at a strictly defined time. A pronounced dormant period is present in the crested cellogyne, it begins at the end of the spring period and lasts 2-3 weeks. At this time, the growth of the root system is suspended, and the pseudobulbs become severely shriveled.
How to water
Watering is recommended by immersing the pot in a bowl filled with water. The pot should be removed after a few minutes. For irrigation, you need to use extremely soft water, which should be filtered or boiled. The fact is that such a plant reacts very badly to the salinity of the substrate (a whitish bloom forms on the surface).
During the dormant period, this orchid needs to be watered much less and only after the substrate has completely dried.
Air humidity
High humidity is required. In order to raise it, expanded clay is poured into the pallet and a small amount of water is poured in. Also, the foliage must be moistened with a sprayer at least a couple of times a day (best in the morning and evening hours).
Earth mixture
For planting, a purchased ready-made soil mixture for orchids is quite suitable. It must be necessarily small-fraction and contain in its composition a small amount of decomposed leaf compost and small (up to 1 centimeter) pieces of pine bark. It should be borne in mind that the amount of bark from the entire volume of the substrate should be approximately half.
Those species that have long roots (for example, fringed cellogyne) are recommended to be grown on blocks of pine bark. The roots are fixed on the block surface with wire and covered with a layer of sphagnum. With this method of cultivation, you need to water more often, as well as spray.
Transplant features
The transplant is carried out in case of emergency. So, this is when a pot or block becomes too tight, while young growths go far beyond the container.
If the bush is large enough, then when replanting it, it should be remembered that it is imperative to put a weighting agent on the bottom (several large pieces of granite or pebbles). Thus, you will protect the flower from overturning.
Fertilizer
Top dressing is carried out during intensive growth once a week.And the plant also needs additional foliar feeding. To do this, use a ready-made fertilizer specially designed for orchids. When the plant blooms, the amount of dressing is reduced to 1 in 4 weeks.
Breeding features
The easiest way to propagate this kind of orchid is by division. An adult specimen with several mature pseudobulbs is suitable for this. It should be remembered that on each plot there should be several pieces of young and old pseudobulbs with a developed root system.
Pests and diseases
Most often, a spider mite settles on a plant. If pests are found, the flower needs to be given a warm shower, and its foliage should be rinsed with special care. An identical method of control is used when aphids or whiteflies are found.
Most often, the plant suffers from a variety of fungal diseases. If you start treatment with fungicides at an early stage, then you can heal cellogin quite quickly.
Nomaphila toothed
Much better known to aquarists is nomafila toothed. Its exact species identity has not yet been established and the plant is listed under the commercial name N.sp. "Densely leafed".
It differs from the previous species in wider leaves and a dark color of the leaf blade. A pronounced serration is visible along the edge of the leaf, which is well preserved in the emerging leaves. The whorls of leaves are located on the stem farther from each other than in previous species, which affects the decorative qualities of the plant. The conditions of detention are similar to those described above. It is not possible to grow this nomaphila in soft water for a long time, as it begins to shrink and shed old leaves.
Gradually, the tops of the plant die, the stems remain for quite a long time, but growth does not resume. In a tropical aquarium in water of medium hardness with sufficient light, this nomaphila develops quite satisfactorily, but it is completely uninteresting when it goes out into the air. Therefore, its stems, which have reached the surface of the water, must be cuttings - then the plant bushes and forms many shoots at the base of the stem. In some cases, long stems are pressed to the ground, but the top grows fastest, and there is almost no tillering. This nomaphila, like other species, is propagated by cuttings.
Pests and diseases of precious orchids
These plants cannot boast of great disease resistance. With excessive development of sphagnum, lack of control over moss, stem rot threatens precious orchids. You can only fight it with an emergency transplant with the obligatory scalding of the substrate. When fungal infections spread among precious orchids, at the first signs of damage, it is necessary to immediately remove the damaged leaves and process the sections with crushed coal.
Threatening precious orchids and pests. If the comfortable indicators of air humidity are violated, spider mites quickly appear on the greens. When using self-prepared substrates, variegated orchids can suffer from slugs and snails, as well as nematode contamination of the substrate. They usually result in severe stem damage. It is best to deal with this problem by pruning shoots and processing sections, followed by an emergency transplant.
 Goodyera bristly, or hispida (Goodyera hispida). Eric hunt
Goodyera bristly, or hispida (Goodyera hispida). Eric hunt
Nombres de este árbol
Al Calycophyllum candidissimum se le da el nombre de madroño en Nicaragua, de harino o alazano en Panamá, de urraca en Honduras, de camarón en México, de sálamo en Costa Rica (así también se le denomina en algunas regiones de Nicaragua), de dágame o dagame Cuba. Crece en México, Cuba, Centroamérica y hasta la parte norte de la América del Sur, con altura media de 15 a 20 metros; de ramas flexibles, color rojo marrón, lustrosas, generalmente con escamas. La madera es pesada, fuerte, de grano fino, elástica y fácil para ser elaborada; se emplea en mangos de herramientas, postes, leñas y carbón. En los Estados Unidos se fabrican arcos con ella.
Small-leaved monsters
Small-leaved species are referred to dwarf or oblique monsters. These shrubs are very demanding for abundant and regular watering and cannot tolerate direct sunlight. In their natural environment they live in tropical forests, in partial shade of trees.Therefore, in indoor conditions, it is recommended to plant a small-leaved monster on the western or eastern windows. Another criterion for the correct cultivation of a room monstera is humid indoor air, otherwise the leaves of the bush will begin to turn brown and dry.
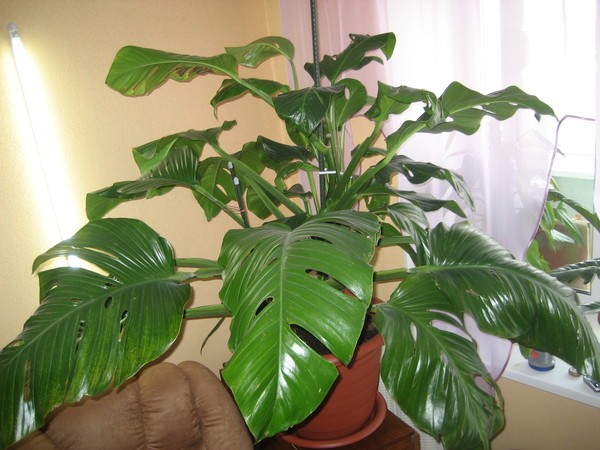

Monstera Karvinsky belongs to small-leaved varieties, but is large in size
Monstera Karvinsky
This type of monstera is most often used to decorate living rooms and dining rooms. Often, a shrub with a pot is placed in the office and in other work areas. In addition to its decorative appearance, Monstera Karvinsky has the ability to destroy harmful impurities in the air and purify it. This is very useful for those who spend a long time in a stuffy room.
The height of the bush can reach 3 meters, but in an apartment its size is half and three times less. This variety is characterized by very beautiful lace patterns in the form of cuts on the leaves. However, before such patterns appear, you have to wait a certain time until the plant matures and grows to a certain size. During this period, it is especially necessary to provide the bush with proper care:
- watering 2-3 times a week during the active period;
- spraying to clean the foliage and increase the humidity in the room;
- moderate lighting;
- feeding three times a year;
- loosening the soil and forming a bush.
This species is very sensitive to water stagnation in the ground. In such cases, the likelihood of the appearance of fungus and rotting of the stems at the base increases. Therefore, it is highly recommended to loosen the soil and use drainage material when planting. The drainage is covered at the very bottom of the pot and only on top of it is a nutritious soil substrate poured. It is better to buy it in specialized stores. A potting mix for vines or palms will work.
Note! The first three years, transplants are carried out annually, then they are carried out every 3-5 years. Many different superstitions are associated with this exotic plant, predicting various diseases and even death.
Despite this, monstera has a surprisingly beautiful appearance and has many beneficial properties. She is unpretentious in care and takes root well in apartment conditions.
Many different superstitions are associated with this exotic plant, predicting various diseases and even death. Despite this, monstera has a surprisingly beautiful appearance and has many beneficial properties. She is unpretentious in care and takes root well in apartment conditions.
Orchid care
For abundant flowering and growth of an orchid, it is necessary to satisfy not only the basic needs of the flower. The orchid needs additional care - feeding.
Fertilizer
Orchid feeding is carried out through watering, that is, during every second watering, the plant is fertilized.
The following fertilizers are used as top dressing:
Mineral - special formulations purchased in the store. You should choose those that are intended for orchids. This will allow for a balanced feeding without unnecessary trace elements that the orchid cannot absorb.
Organic - rotted horse manure
When using organic fertilizers, it is important not to oversaturate the soil with nitrogen. Otherwise, the substrate quickly becomes unusable - the soil acidifies, its air permeability deteriorates
For orchids, such growing conditions are destructive.
In winter, when the flower is at rest, feeding is excluded from the usual care. They resume with the transition of the orchid to the growing season - in the spring. At this time, Phalaenopsis is fertilized once every one to two weeks. During the growing season, only mineral fertilizers intended for orchids are used. The concentration of their dose is reduced 2, 3 or 4 times from the dose recommended on the package.
Descripción
Este árbol puede llegar a medir 15 a 20 m de altura con un DAP (diámetro a la altura del pecho) de 3 dm. Su corteza rojiza exfoliante (se despega del tronco en láminas delgadas) es muy característica de esta especie. La madera es dura y de un grano muy fino. En Panamá es utilizada como carbón. Las hojas son de forma obovada y llegan a medir hasta 15 cm de largo. Son glabras (sin pelos). Las estípulas son caducas (no son permanentes). Las flores son blancas y muy llamativas porque el lóbulo del cáliz es muy expandido. Emana una fragancia dulce. Los frutos son cápsulas pequeñas oblongas que se abren desde el ápice.
Reproduction of variegated orchids
Precious orchids are considered one of the easiest species to reproduce. All plants belonging to the variegated group are distinguished by the ability to root shoots. As soon as the shoots release more than five leaves (four full-fledged internodes are formed on them), a high-quality root is formed under one of the first leaves.
It is possible to cut off the shoot for rooting only if there are two leaves under the root release site, and at least two internodes above it (the cut must be carried out a few centimeters below the root, but not reaching the first lower leaf). Such a stalk takes root very simply. After sprinkling the cut with charcoal and planting it in a substrate suitable for the orchid, it takes root very quickly and starts growing.
You can also divide adult, powerful plants, provided that in each division there will be 2-3 full-fledged shoots with several leaves.
Reproduction
One of the features of this epiphyte is the frequent appearance of a large number of "children". The orchid forms them on an old peduncle after flowering, if favorable conditions have been prepared. For this, the humidity should be maintained at a level of 70-80%, the temperature should be at least 28-30 ° С.
"Babies" are formed on plants not younger than 2 years old, which have at least 4 leaves. They can germinate on faded peduncles, if they are not older than one and a half years.
Caring for the "kids" after their formation for the reproduction of the orchid is as follows:
- The mother plant should be helped by spraying the roots of the “babies” with a spray bottle.
- After the formation of roots 4-5 cm long and 3-4 leaves in the "children", they are disconnected from the mother plant along with a part of the peduncle. Places of cuts are treated with crushed coal, potassium permanganate or brilliant green.
- The separated "babies" are seated in small containers with a diameter of 6 to 9 cm, depending on the size of the new orchid.
After transplanting, the separated orchids are often sprayed to help them get used to independent living more quickly.
Control measures
Agrotechnical:
- thorough processing of row spacings and weeding in rows until the cultivated plants are completely closed in the aisles;
- obligatory removal of weeds from the field;
- deep autumn plowing in the early stages;
- control of weeds outside the fields by mowing before the flowering phase. (Maltsev A.I., 1939)
Chemical
Herbicide treatment. There are no herbicides registered from small petals in the "List of pesticides and agrochemicals", however, theoretically, preparations of the group of sulfonylureas, aryloxyalkane carboxylic acids, pyridine derivatives and other substances can be effective against this weed. (Fisyunov A.V., Handbook, 1984)
Chemical pesticides:
Spraying during the growing season:
- Monolith, EDG
- Grand Prix, EDC
- Referee, VGR
- Herbix, VRK
- Rapier, CE
- Megalith, BP
- Cicero, EDC
(State catalog, 2017)
Compiled by: P.I. Grigorovskaya, T.V. Zharyokhina
El madroño: el "Árbol Nacional de Nicaragua"

El Madroño en Managua, Nicaragua.
El madroño es el árbol nacional de Nicaragua desde. En La Gaceta, Diario Oficial de la República de Nicaragua, número 194, del viernes 27 de agosto de ese año, aparece reproducido el Decreto Legislativo No. 1891 por el cual se declara al madroño ÁRBOL NACIONAL DE NICARAGUA, y se dispone que el Día del Árbol, el último viernes de junio, sea plantado en parques, plazas, aceras y autopistas de todo el país y en el patio de cada centro de enseñanza de la Nación. Al momento de su publicación, el 27 de agosto de 1971, era Presidente de la República el dictador General Anastasio Somoza Debayle; el texto completo del Decreto es el siguiente:
Hybrid Phalaenopsis
Phalaenopsis belong to the orchid family. This type of orchid was first discovered in 1825 on the islands of the Malay Archipelago. After that, these extraordinary plants of various species were found in Southeast Indonesia and the tropical region of Australia. They gave rise to many hybrids and varieties of phalaenopsis.
Standard
The first phalaenopsis hybrids had large white or pink flowers and tall peduncles. They are called standard. Further interspecific selection continued in various directions:
- breeding plants with large flowers;
- brightly colored or variegated petals;
- miniature phalaenopsis, etc.
An example of a Maki Watanabe ‘Kingfisher Orchids’ hybrid (Romance Miki X Otohime)
Mini
In the middle of the last century, miniature phalaenopsis came into fashion. This is a fairly large group of varieties that share common characteristics:
- small flowering arrow;
- small classic-shaped flowers.
Phalaenopsis mini. The size is relative to the size of the lighter.
Taiwanese
Nowadays, Singapore is the trendsetter in the field of orchid breeding, as a result of which plants with pure petals of bright colors or spotted patterns have appeared, for which they were called "harlequins".
Taiwanese phalaenopsis Harlequin.
Novelty
These hybrids include plants with non-dying peduncles. After flowering, they have a dormant period, after which old peduncles grow and new ones form at the same time.
An adult novelty can have several dozen inflorescences that bloom up to 5 times a year. The petals of small flowers are covered with a tiger or leopard pattern, ripples or dots of different sizes.
Novelty I-Нsin Salmon Copper Star.
Peloriki
Phalaenopsis pelorics are of particular interest to orchid collectors. Peloric is a mutated plant, as a result of which its flowers have an atypical shape for their variety, and the petals and sepals take the shape of a flower lip, which gives the flower an unusual appearance.
Philadelphia Peloric.
Primary
The breeding of numerous phalaenopsis varieties and hybrids began with interspecific hybridization:
- the first hybrid of Phalaenopsis was obtained in 1875 by John Seden as a result of hybridization of Phal. aphrodite and Phal. equestris. And by 1900 there were already thirteen such hybrids;
- an extraordinary hybrid was developed in 1940 and registered under the name Phal.Doris. It is characterized by multi-flowered peduncles and huge, pure white flattened flowers, about 14 cm in diameter;
- a striking representative of miniature hybrid phalaenopsis is Phal. Mini Mark "Maria Teresa", reaching a height of 25 cm. A large number of branched peduncles are covered with small flowers with an ivory color, dotted with the smallest red-yellow specks;
-
spotted hybrid phalaenopsis is represented by phalaenopsis of French selection and Taiwanese "harlequins". One of the common varieties is Phal. "Paradise", a sophisticated variety with medium-sized flowers and elongated petals of a light greenish-yellow shade, dotted with pink-brown specks.
Interesting! Currently, more than 5 thousand phalaenopsis hybrids have been registered.
Intergeneric
A further impetus for obtaining new forms and colors of phalaenopsis was their hybridization with related genera of orchids:
- Doritis;
- Renanthera;
- Ascocentrum;
- Rhynchostylis, etc.
The first intergeneric hybrid called Doritaenopsis with an unusual scarlet color of flowers was obtained in 1923 as a result of crossing a phalaenopsis with an orchid of the genus Doritis. Further selection led to the creation of flowers of other, more complex shades: purple, orange, etc.
Often these orchids are confused, selling one variety after another. But both the appearance and the conditions of their maintenance are identical.
The appearance of the Doritaenopsis Liu's Sakura hybrid was especially delightful. Its flowers of exquisite shape with pearlescent pinkish petals give the inflorescence an amazing tenderness.
Doritaenopsis Liu's Sakura.
The best intergeneric hybrids of the modern direction of breeding are blue orchids varieties Doritaenopsis Siam Treasure "Blue", Doritaenopsis Kenneth Schubert "Blue Angel".
Doritaenopsis Siam Treasure 'Blue'.
Doritaenopsis Kenneth Schubert "Blue Angel".