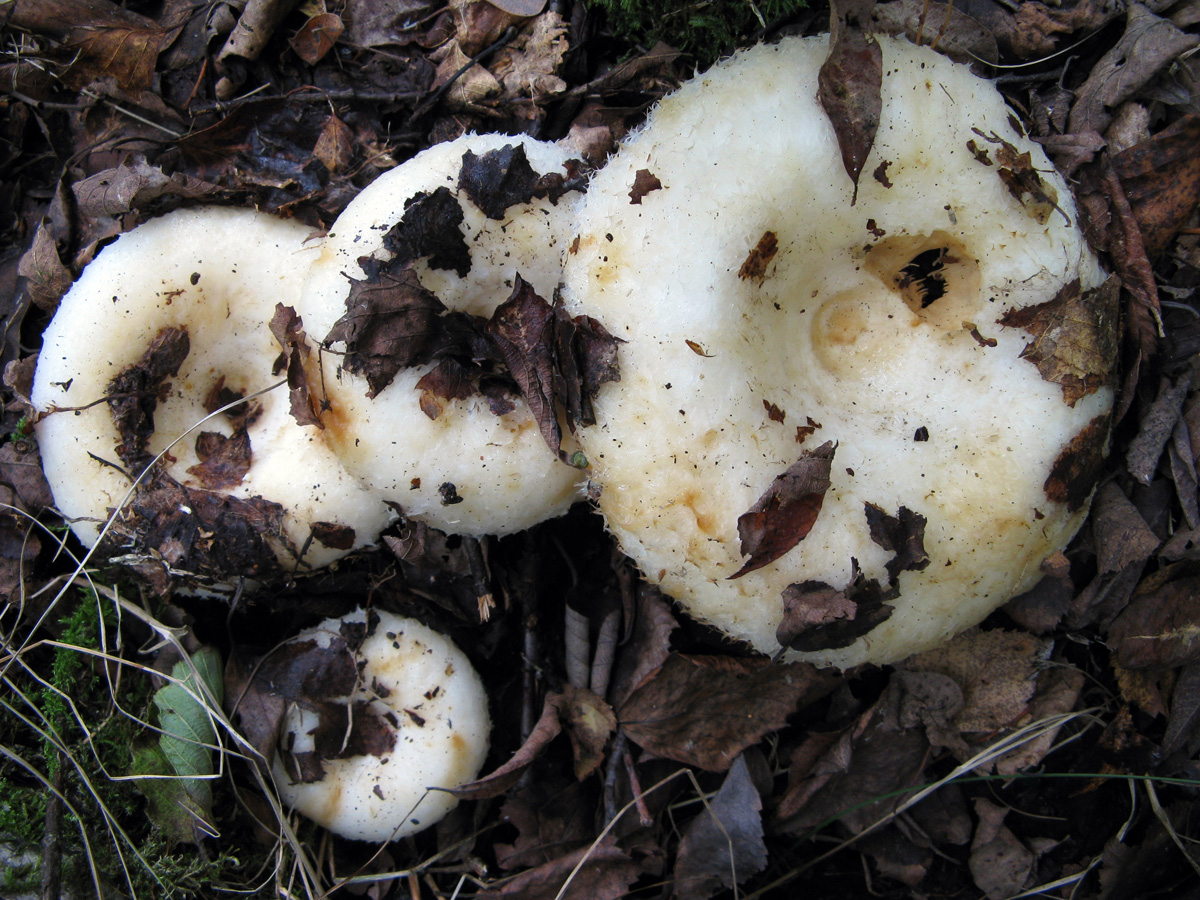
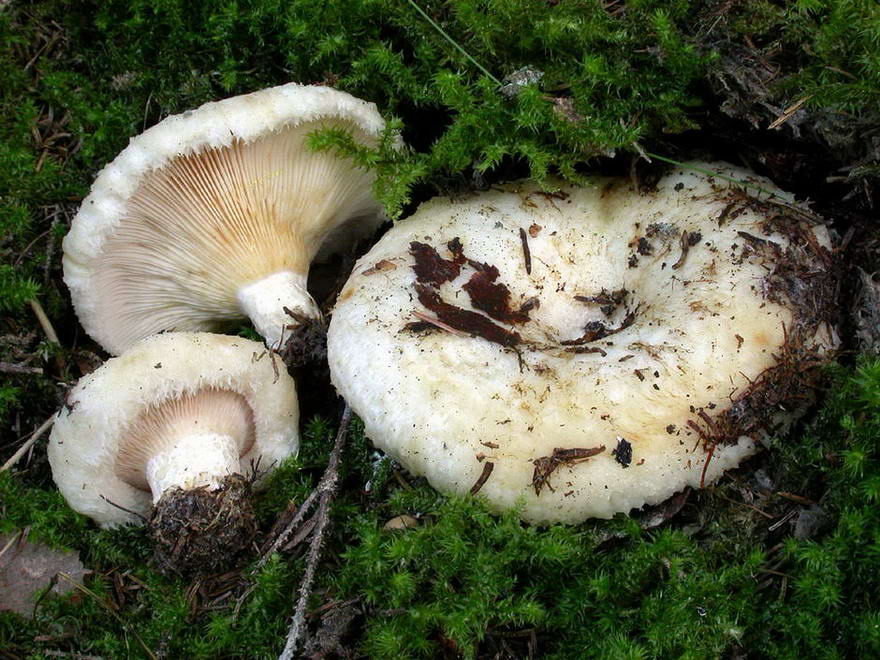
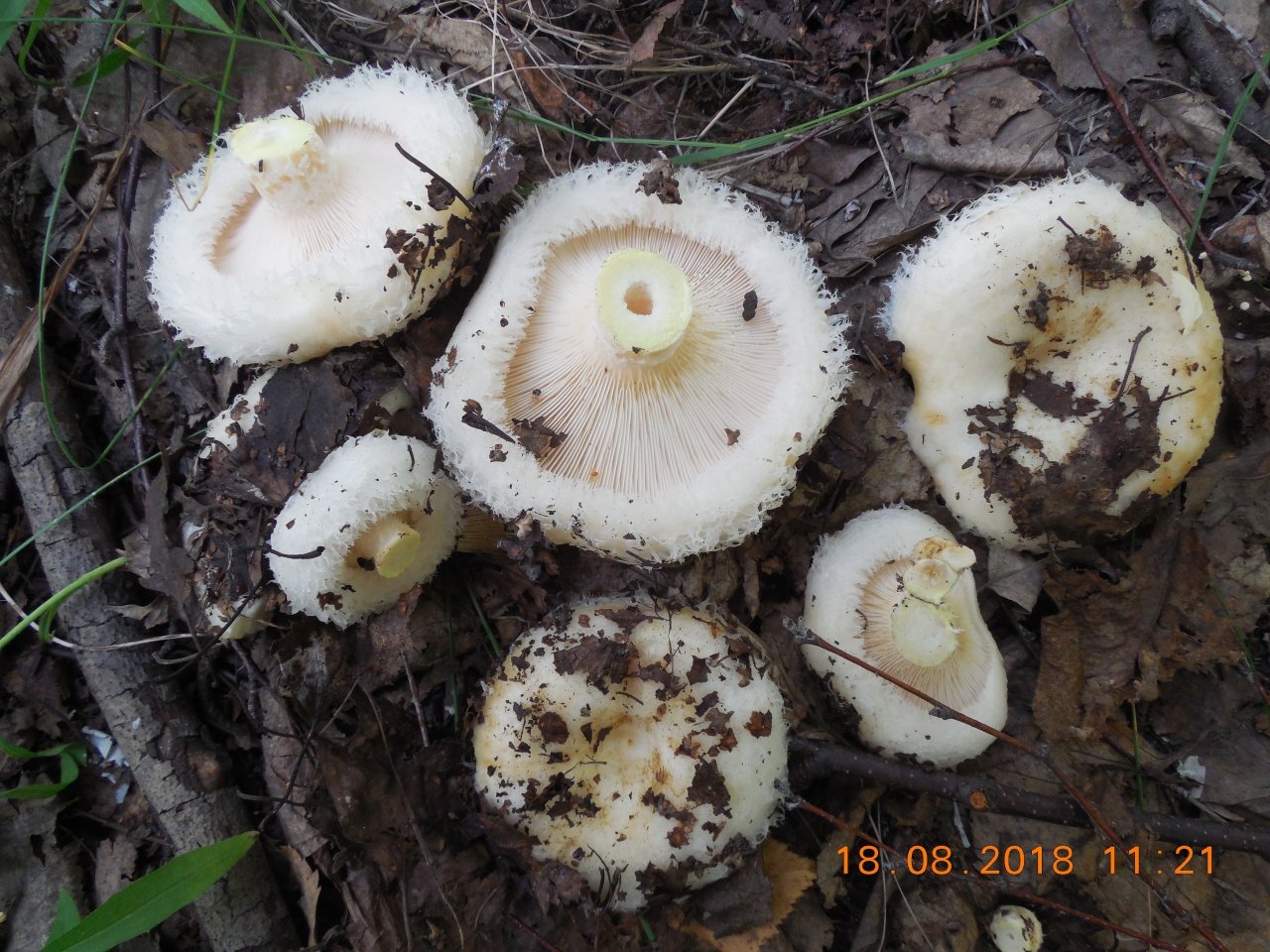
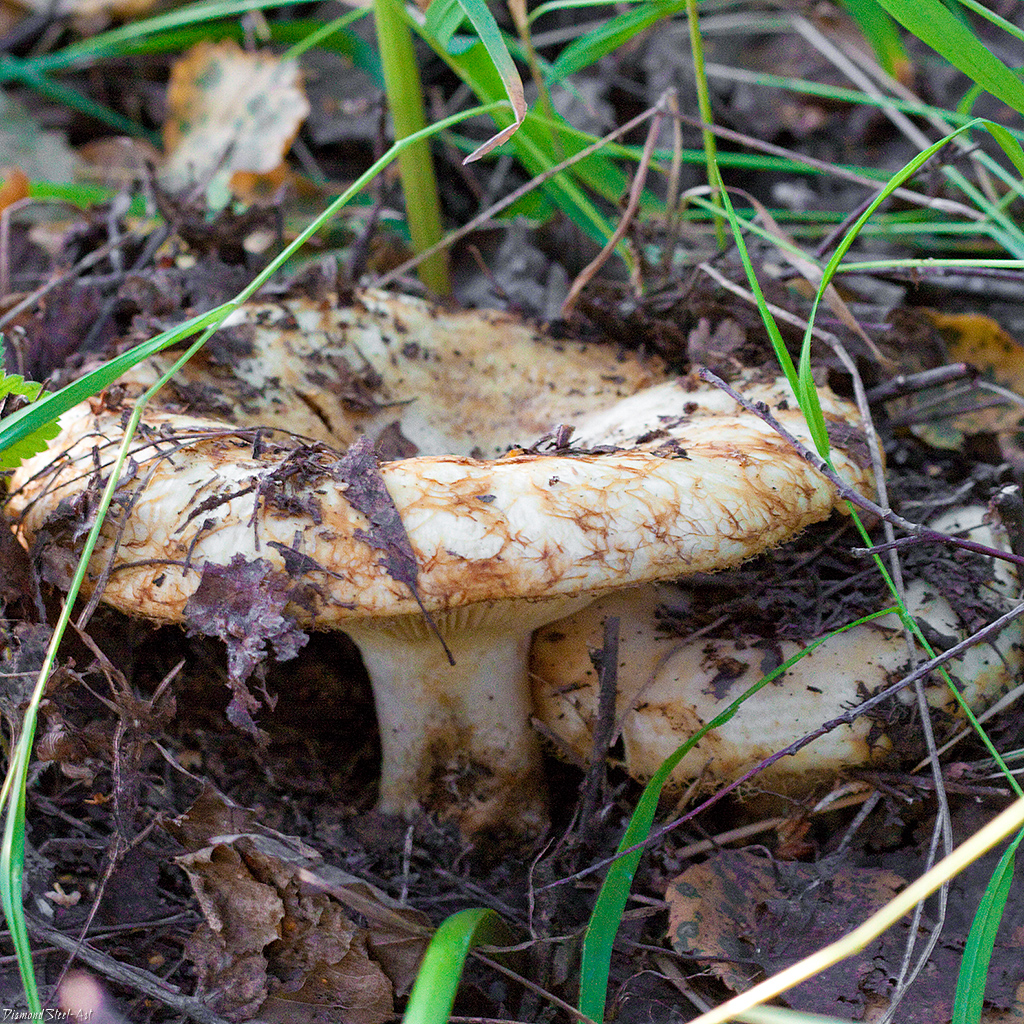
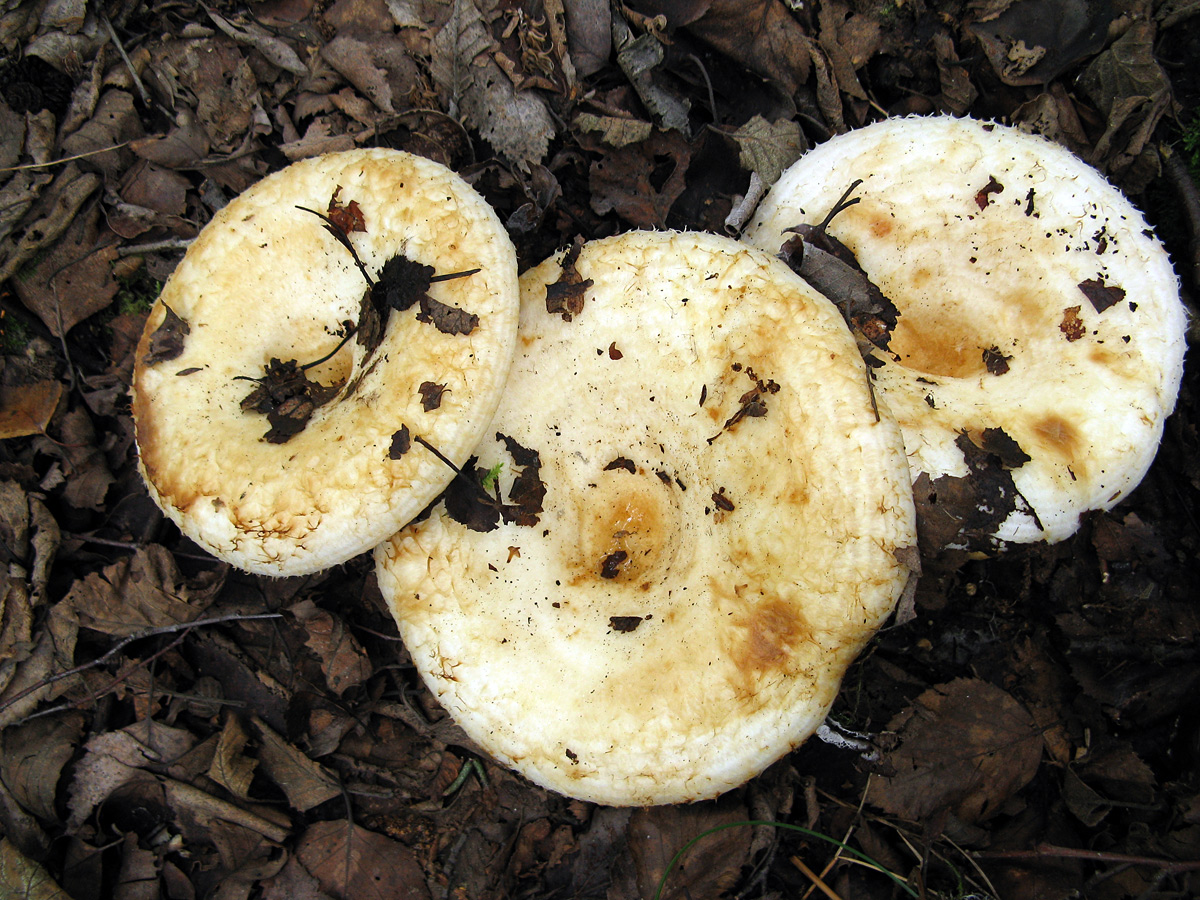
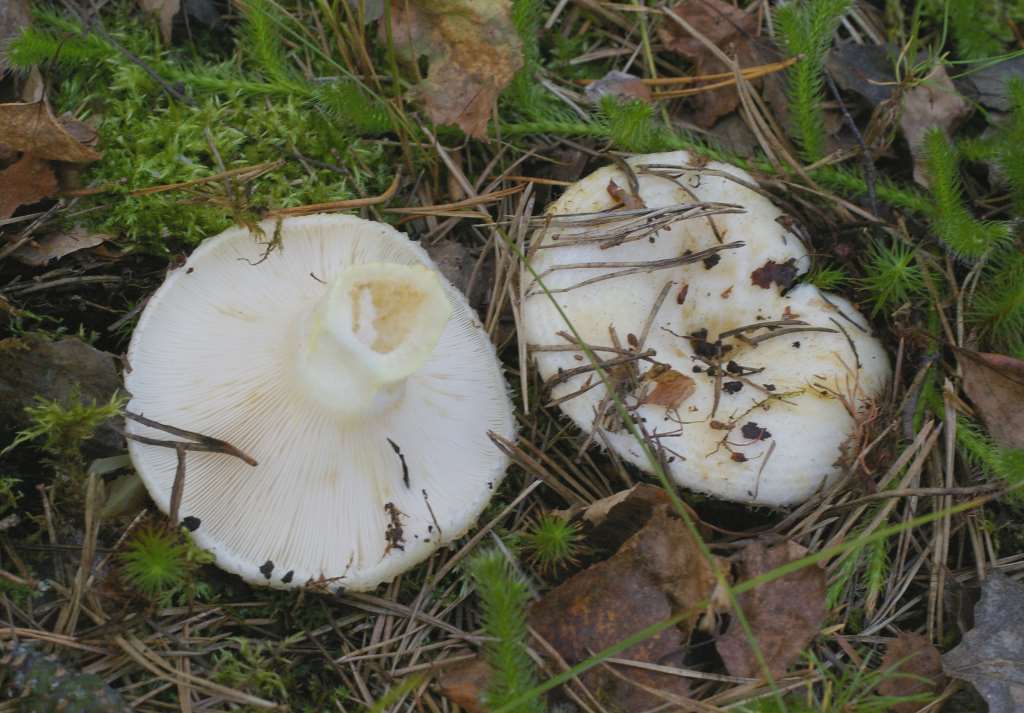
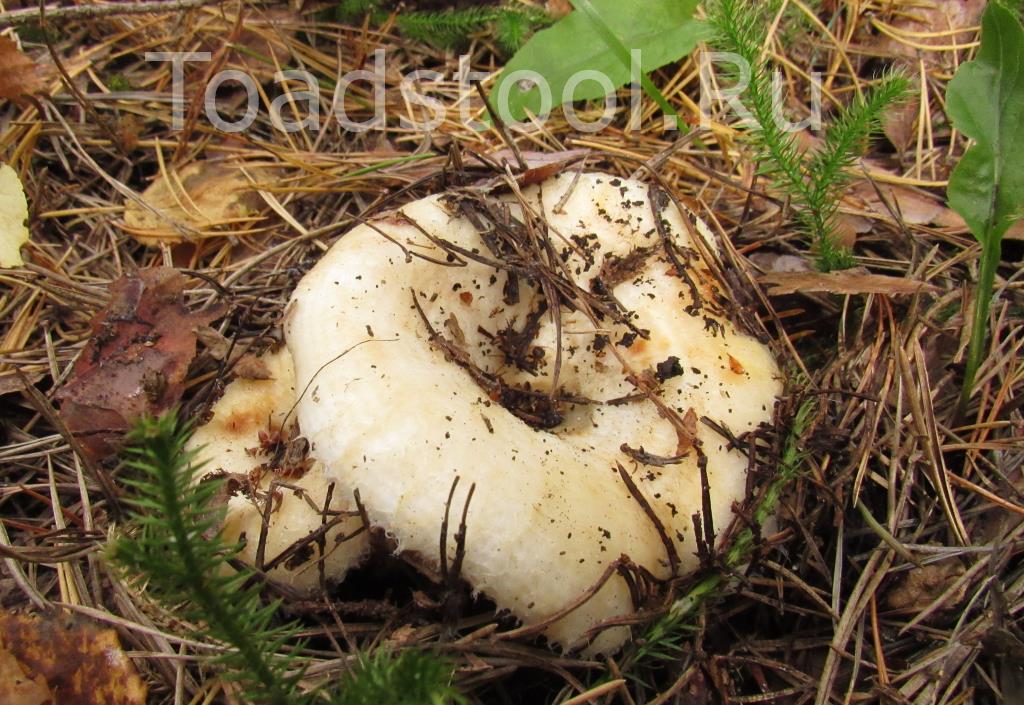
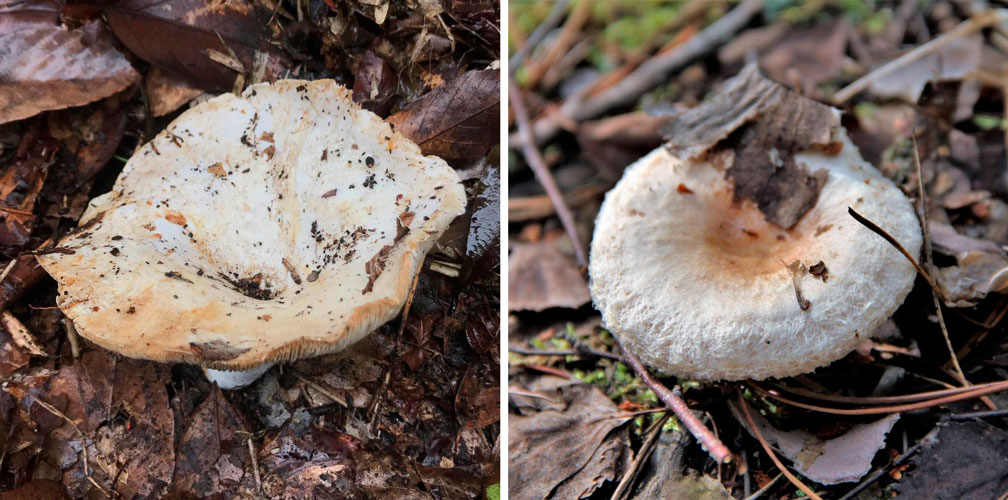
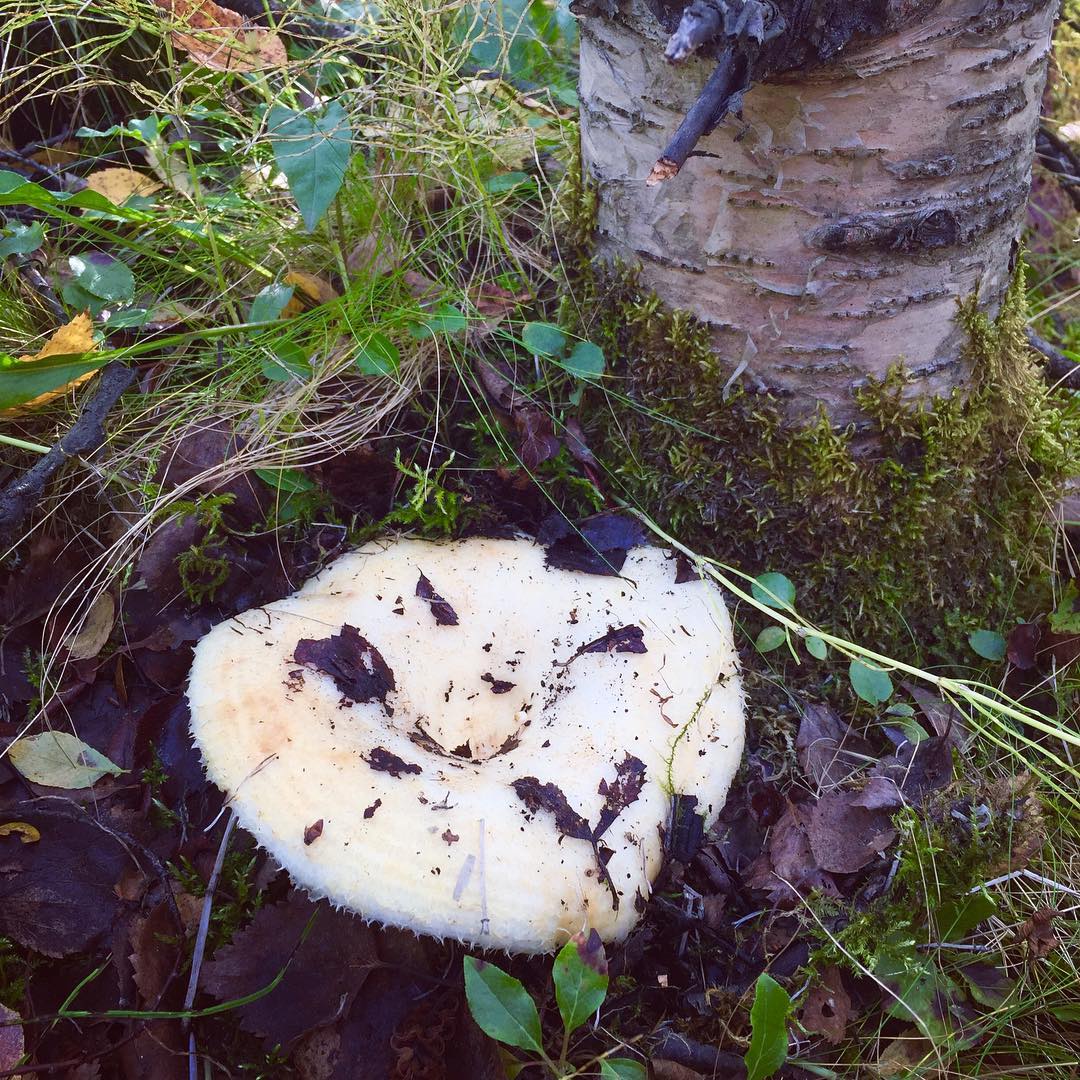
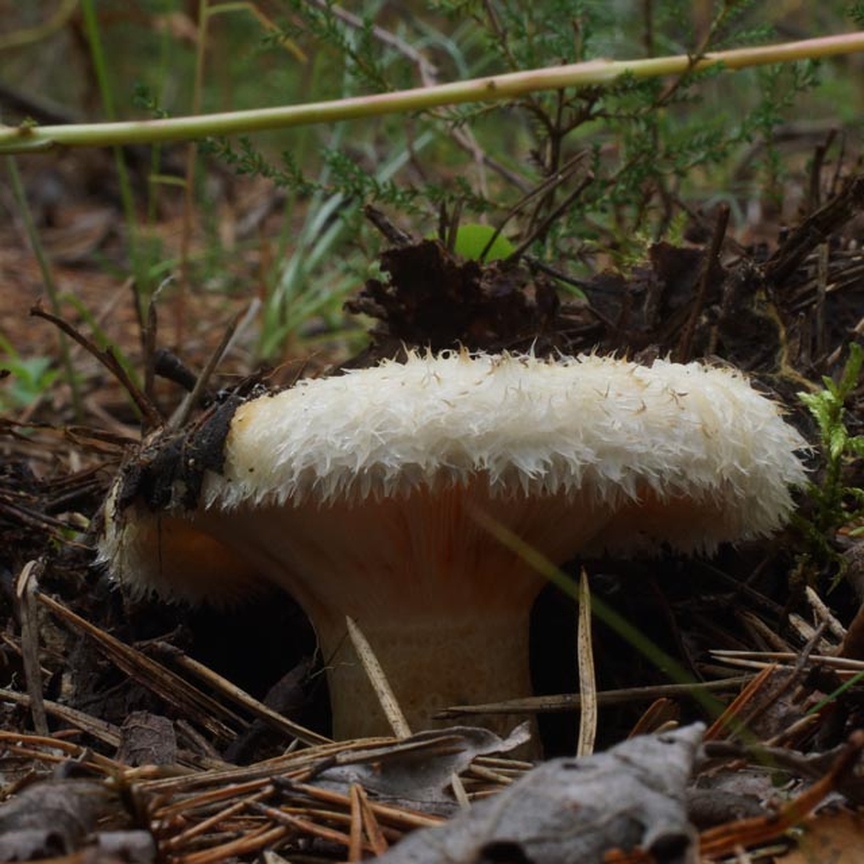
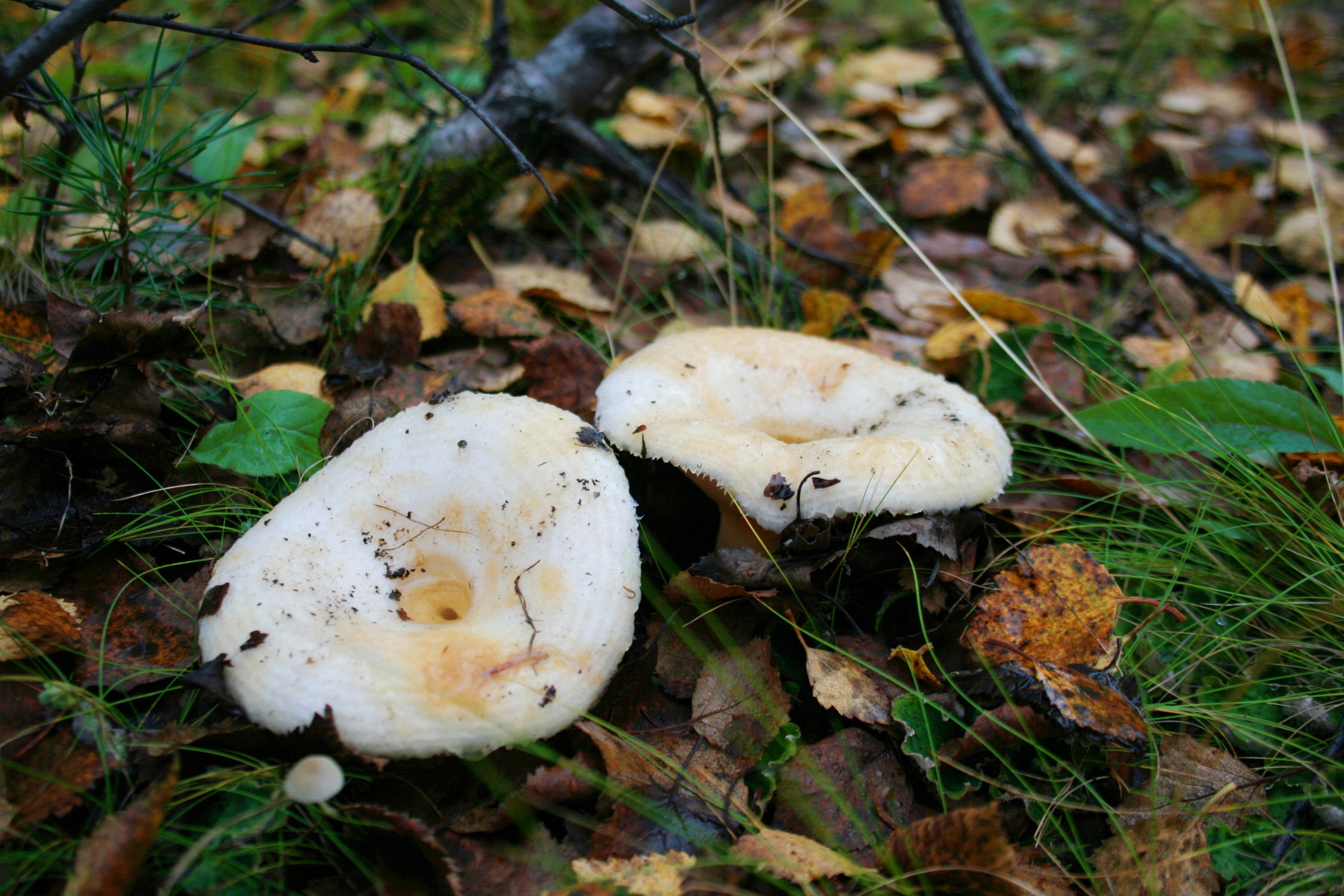
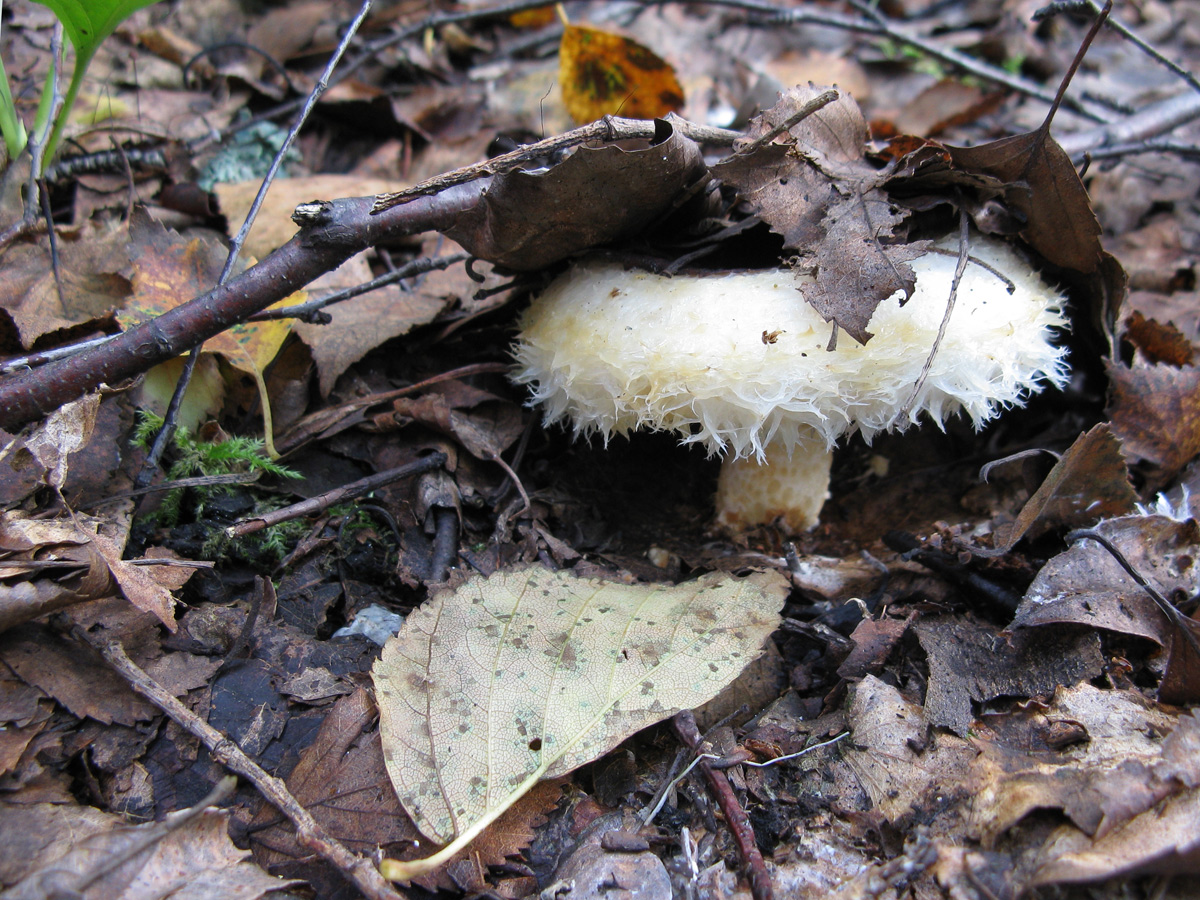
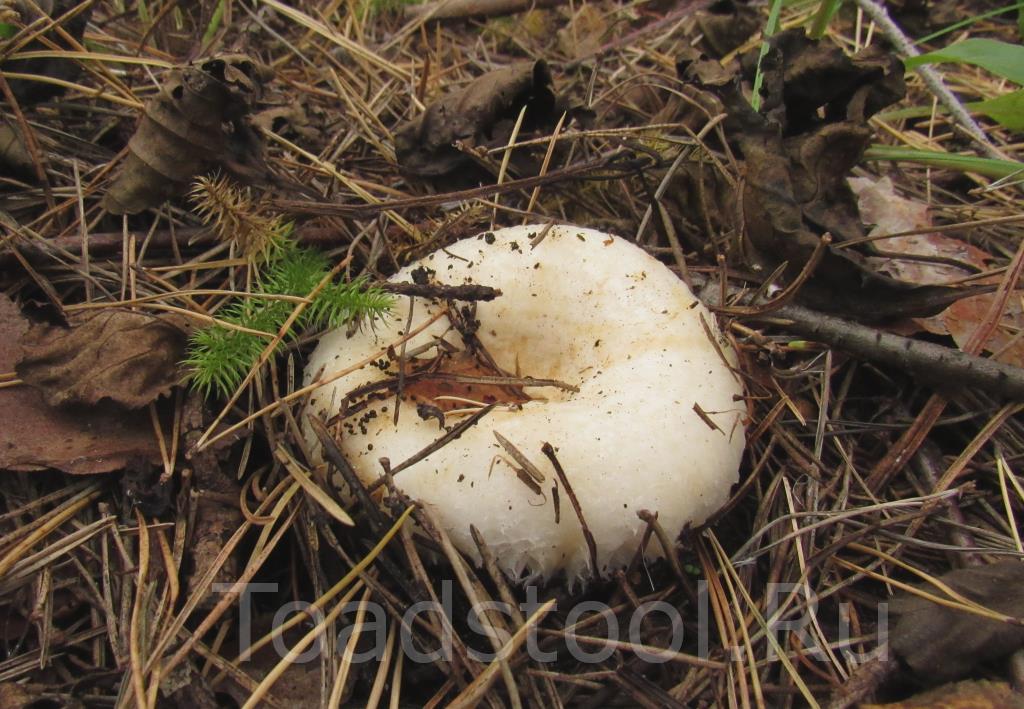
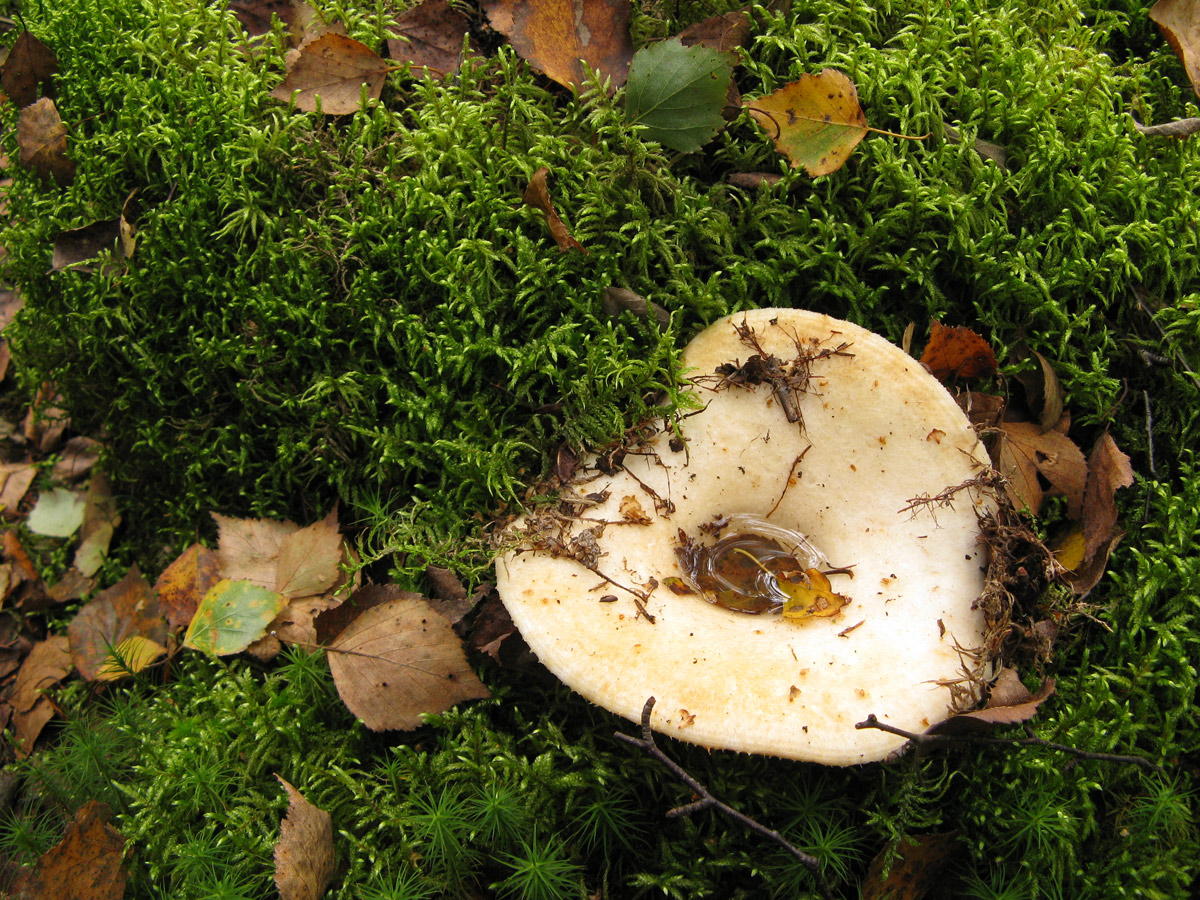
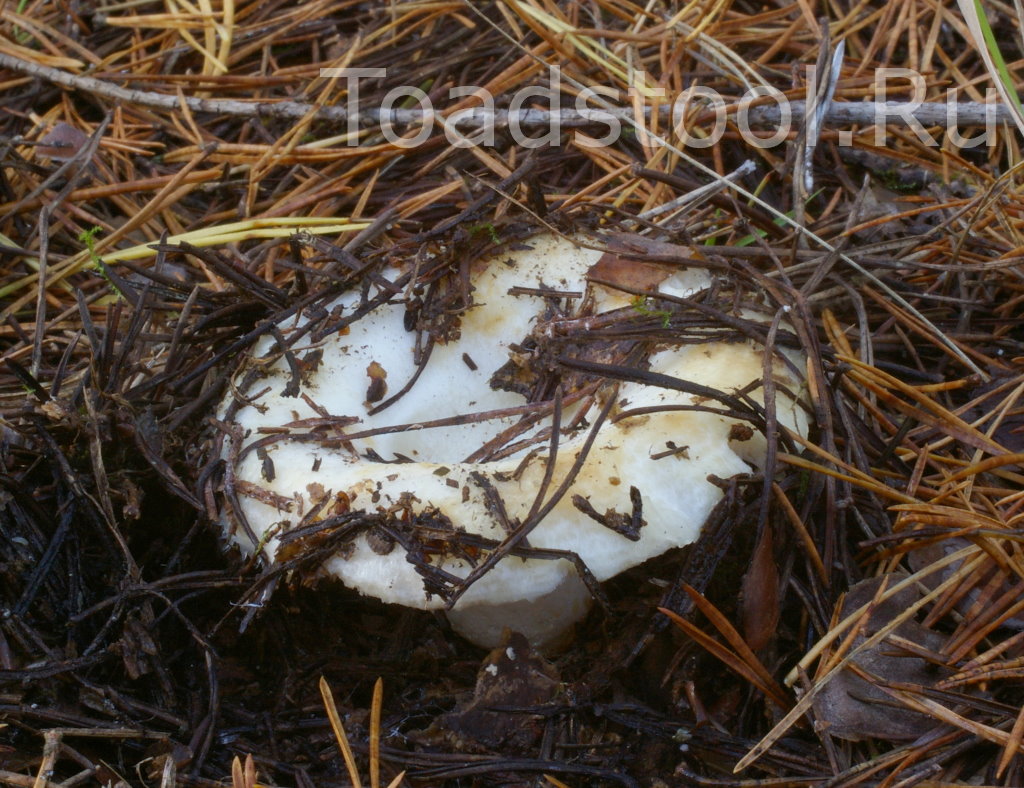
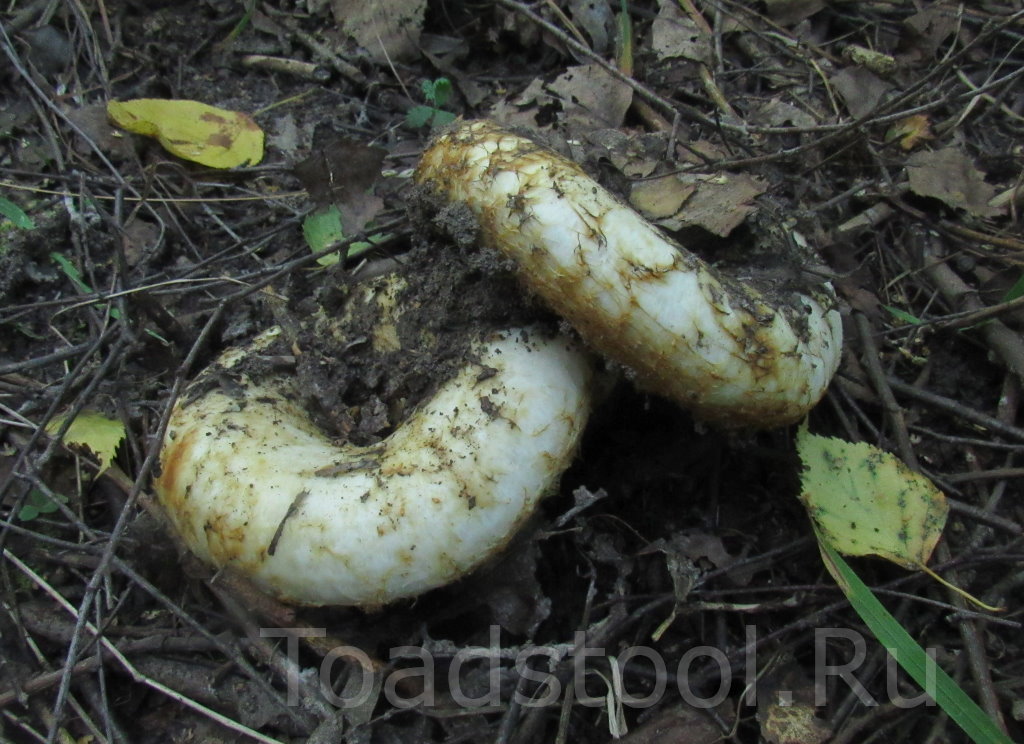
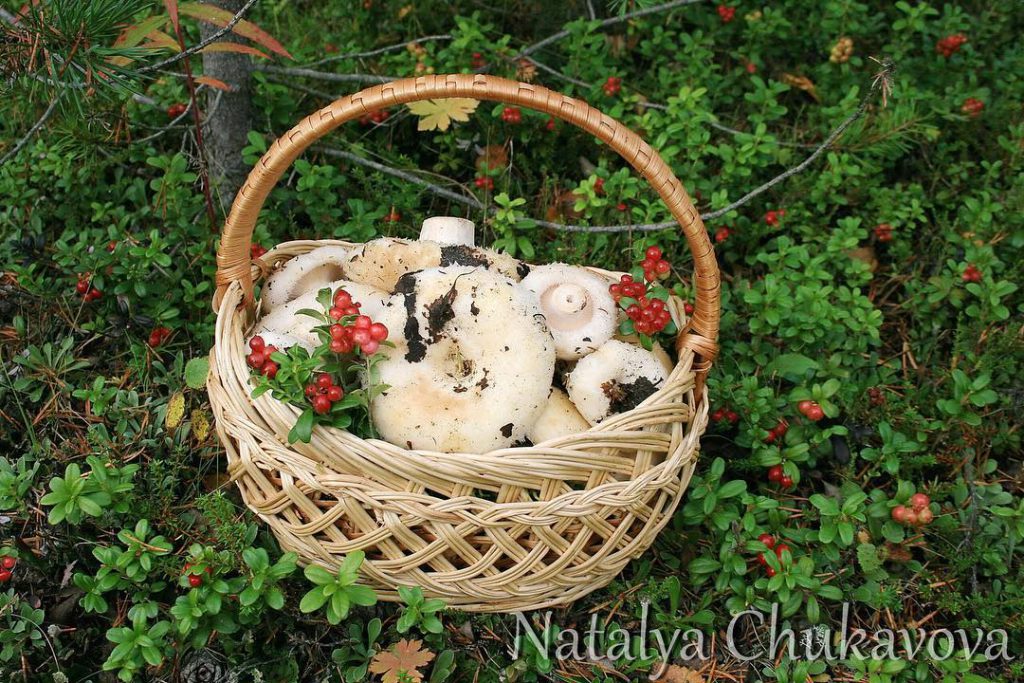
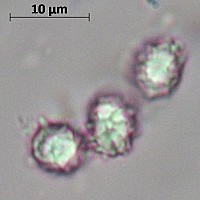
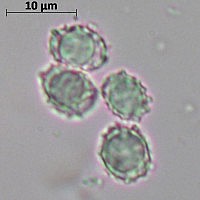
Description of the thick fringed.
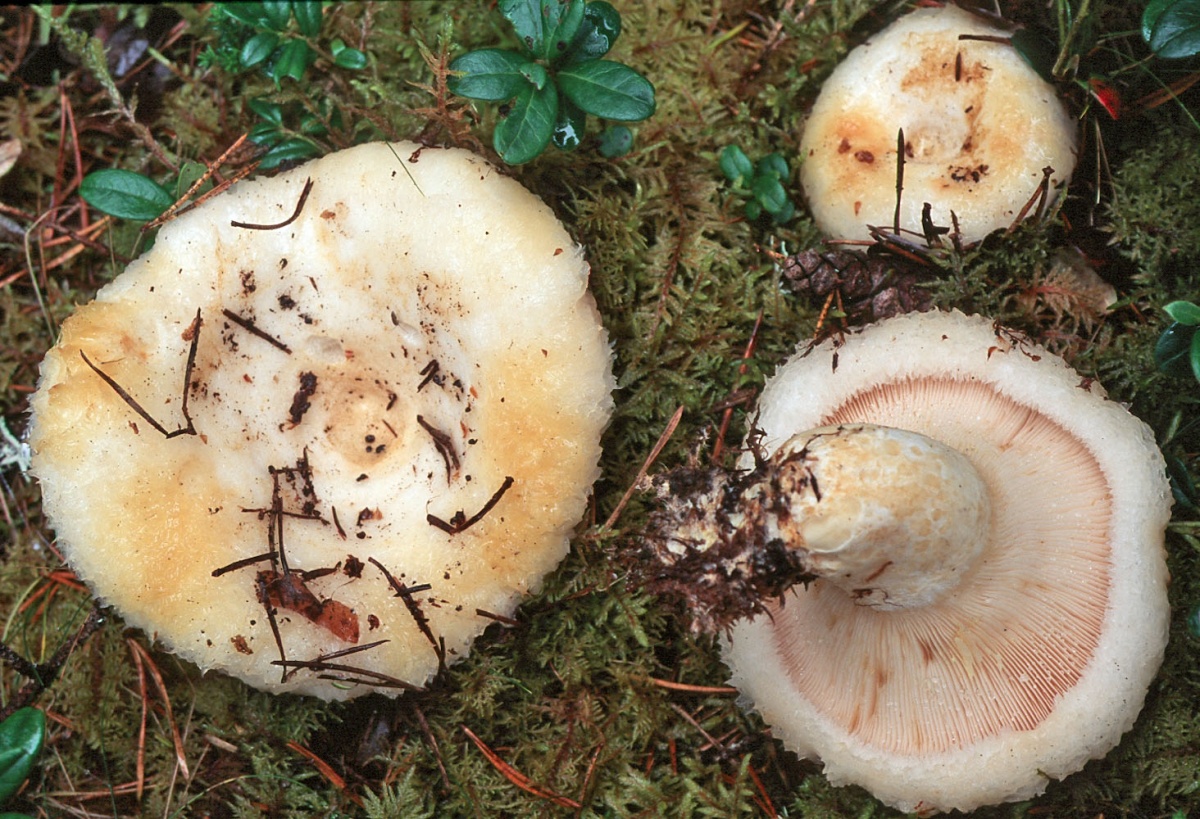
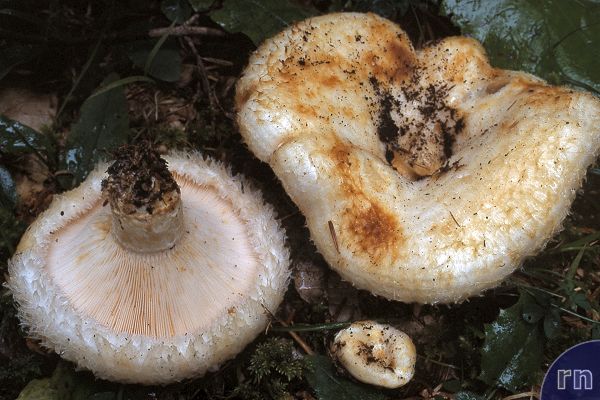
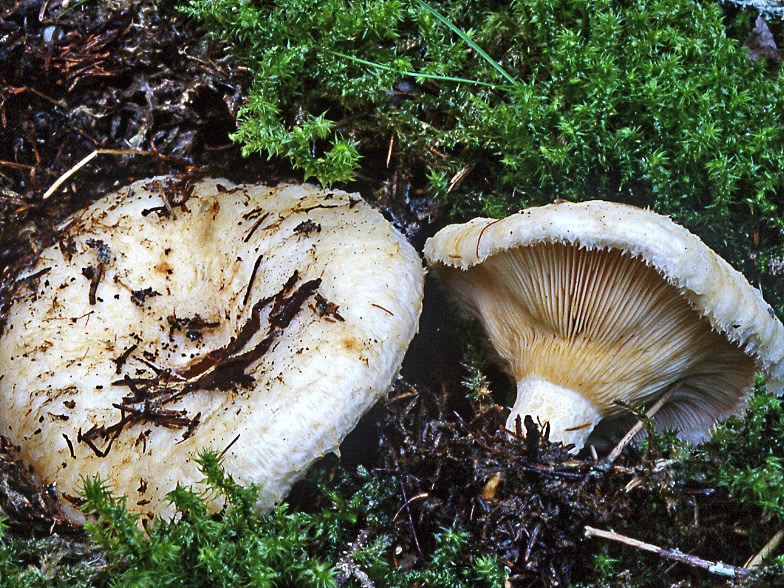
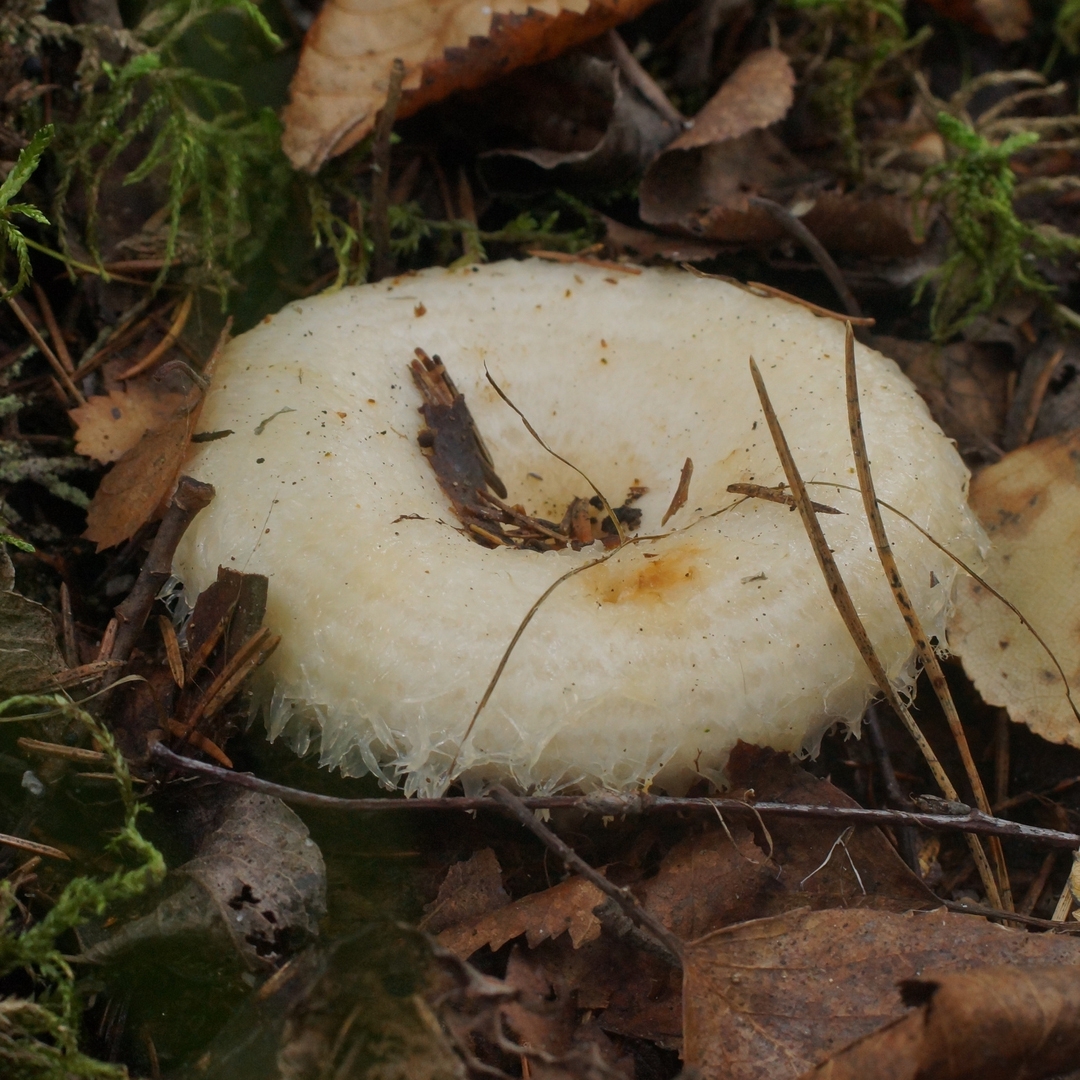
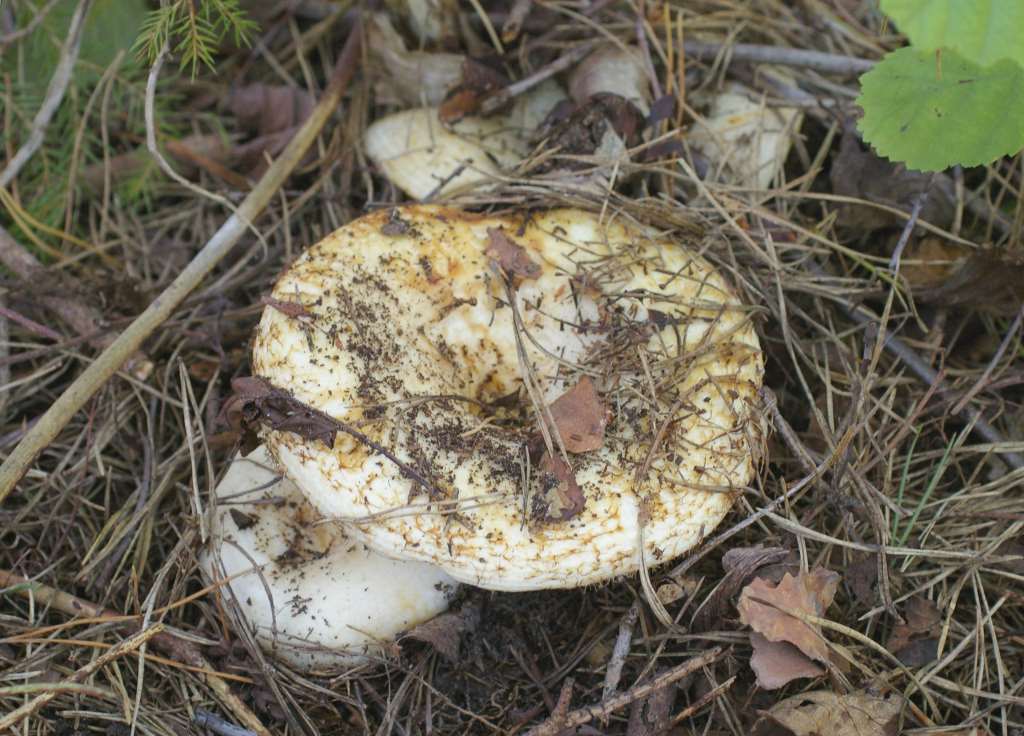
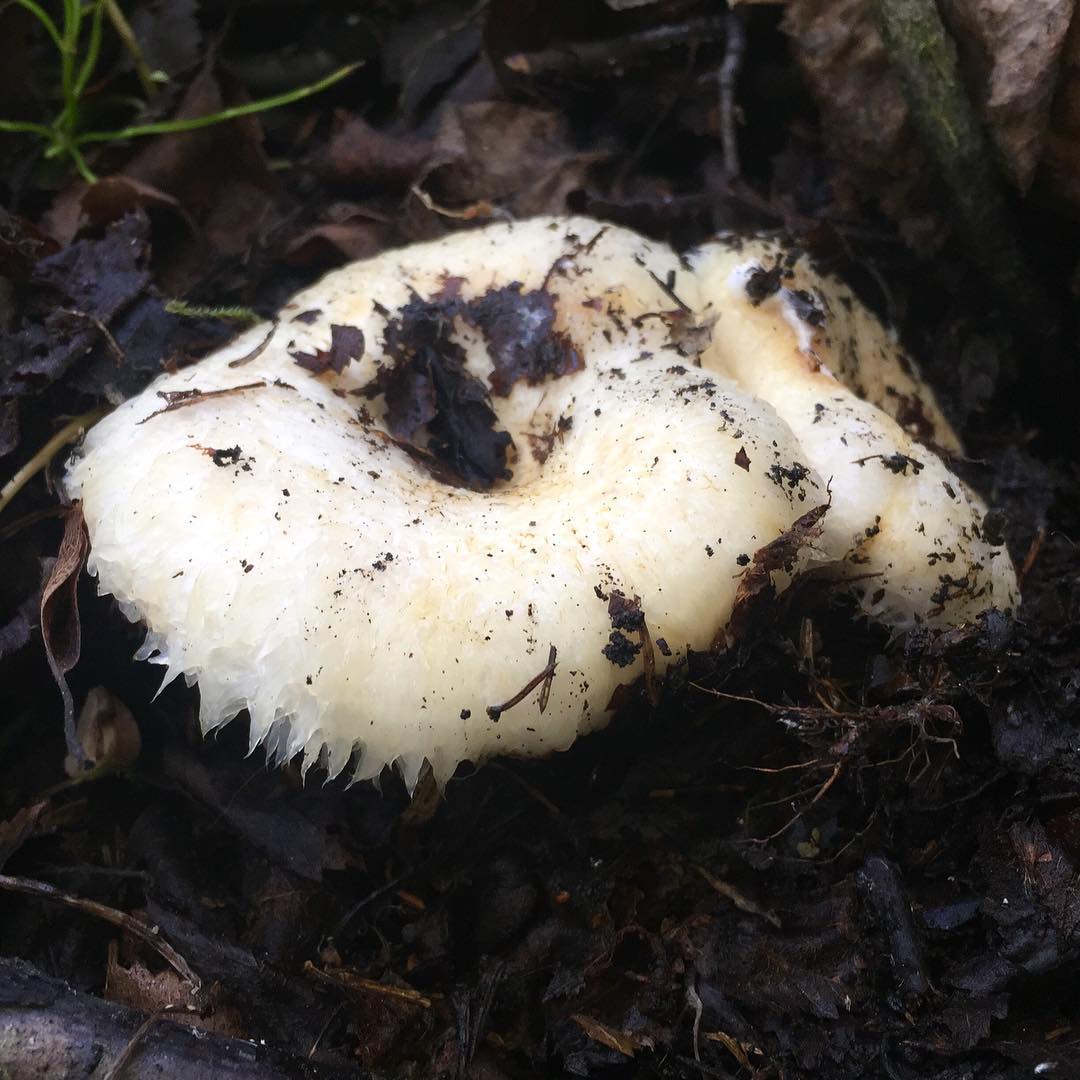
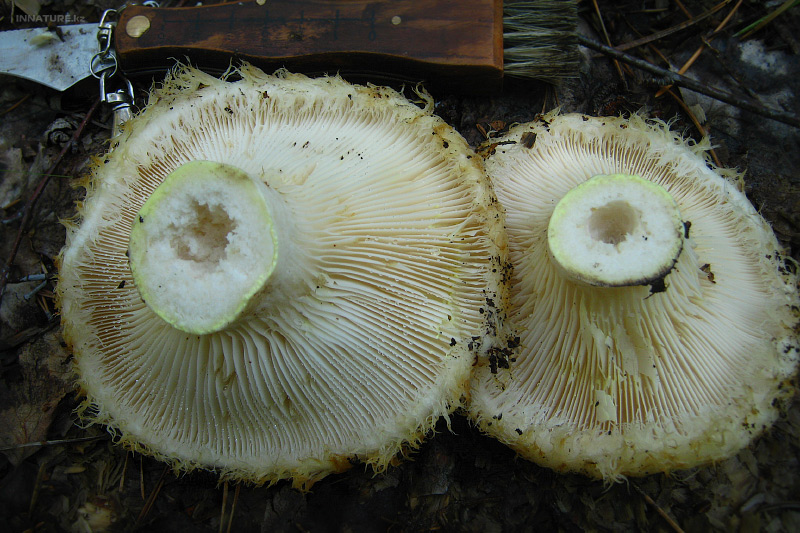
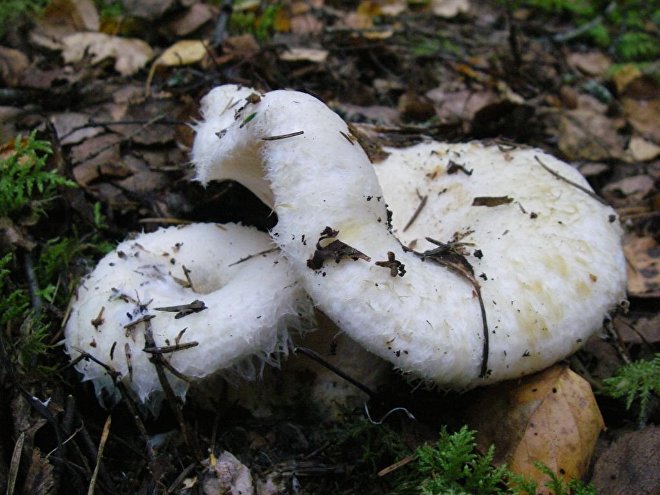
His hat is convex with a pronounced depression in the central part. Its adult diameter is 10-20 centimeters. The edges of the cap are first tucked up and later unfolded. The surface of the cap is fibrous, and there is a "fringe" along the edges, the length of which reaches 1 centimeter.

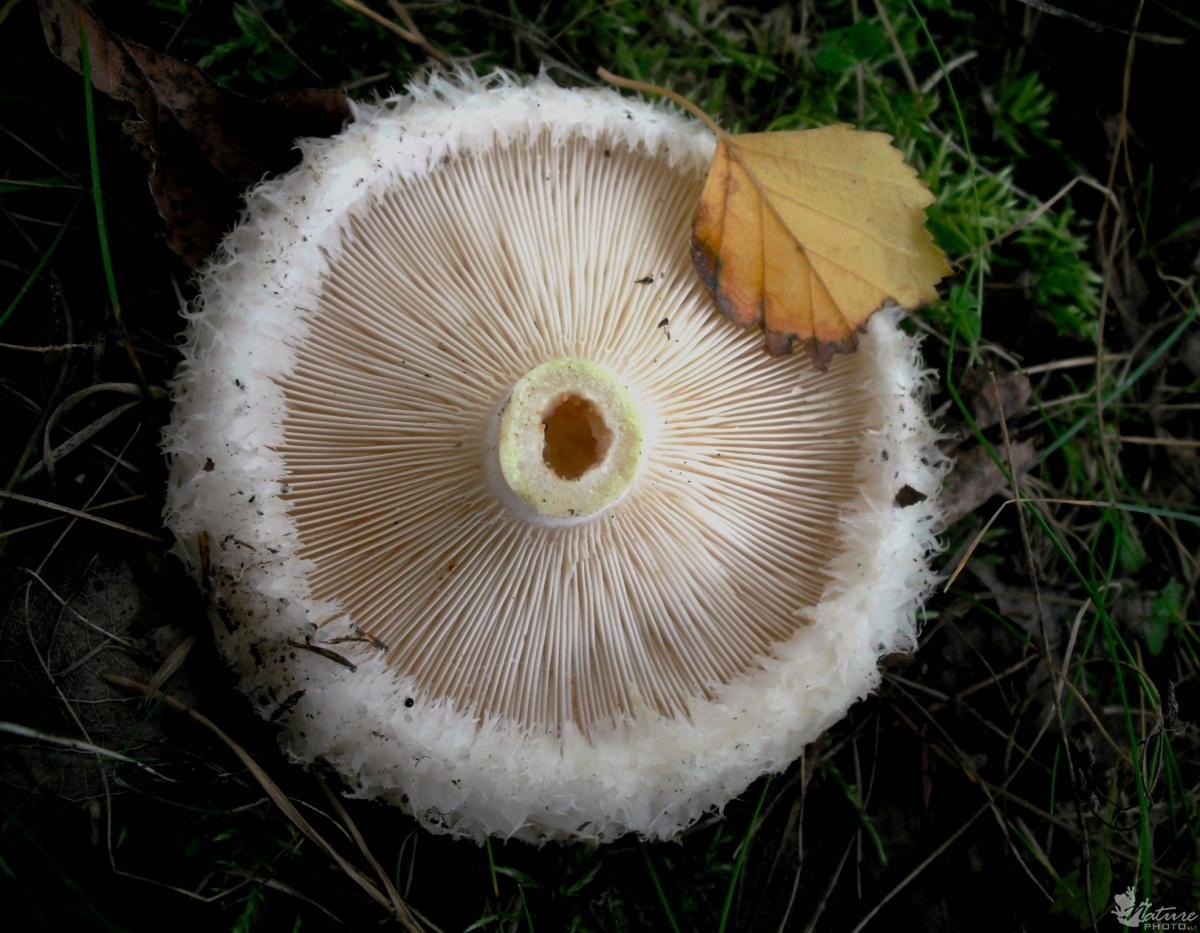
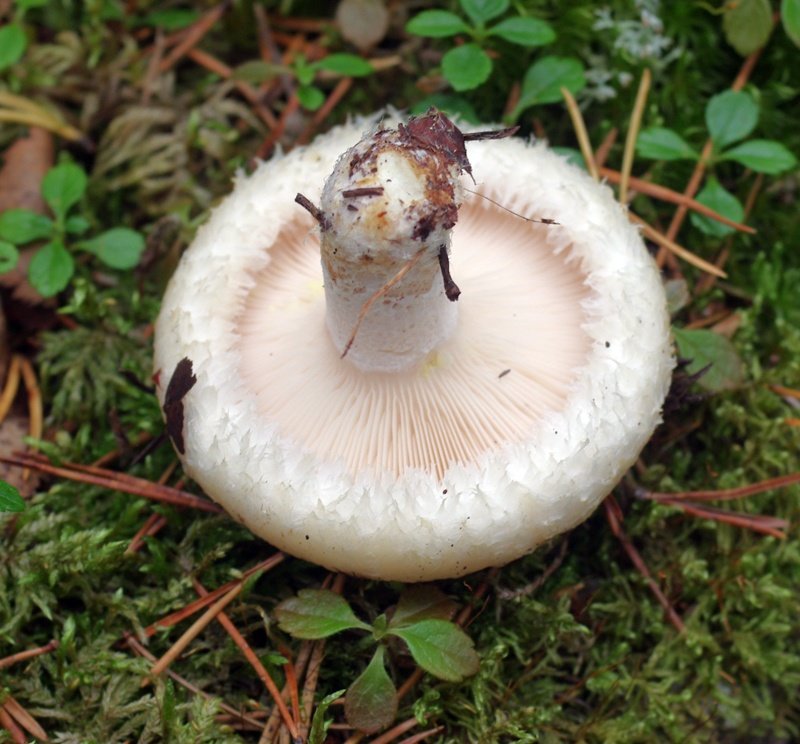
The central part of the cap becomes slimy after rain. The color of the cap is yellow-fawn or ocher-fawn, and the protruding fibers have a brighter color. Hymenophore plates are located under the cap. The plates come off the stem. The plates often branch around the peduncle. The color of the plates is pink-ocher.
The flesh of the fringed mushroom is fragile, tough and fleshy, like the rest of the family. The color of the pulp is pale yellow, and in the stem it can be pink. The pulp secretes a white milky juice, which becomes noticeably yellower in air. The taste of the milky juice is hot and pungent, and the smell is fruity, sometimes they say that it smells like "overripe" lemon. After contact with K (OH) (Potassium hydroxide), the color of the flesh changes to egg yellow, and the milky juice turns orange.
The leg is cylindrical, strong, tapering downward. Its length is 4-8 centimeters, and the girth ranges from 2 to 4.5 centimeters. With age, the leg becomes hollow. The color of the leg is yellow-pale, and at the base, sometimes darker spots are noticeable. In young specimens, the legs are velvety-fibrous, while in mature mushrooms velvety remains only at the base.

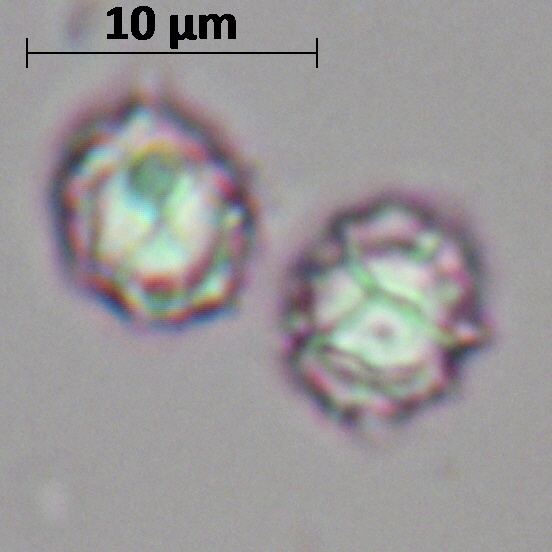
Spore powder of pale ocher or pale pinkish color. Spores are broadly elliptical or almost spherical, with a well-visible reticular pattern and sparse warts.
Watery zone
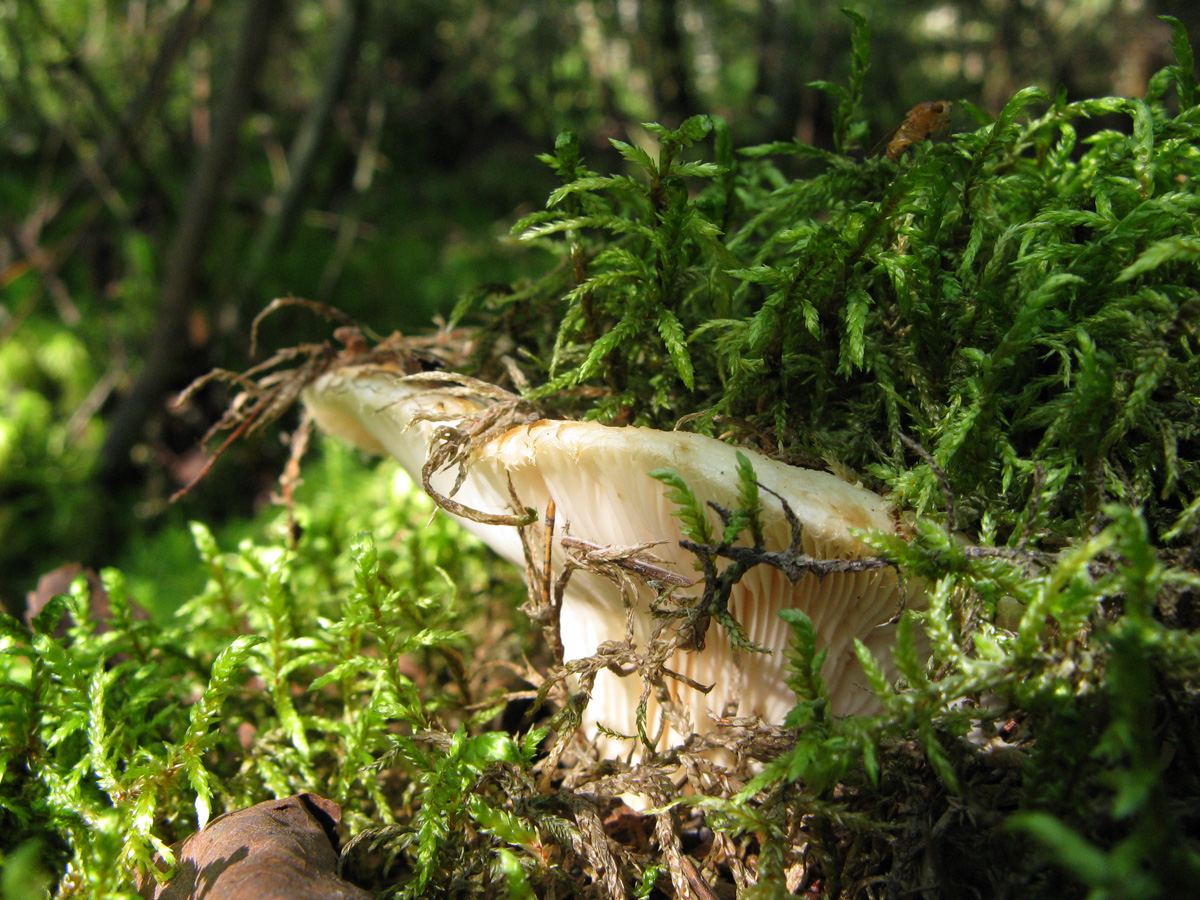
Watery-zone Milk (Lactarius aquizonatus)
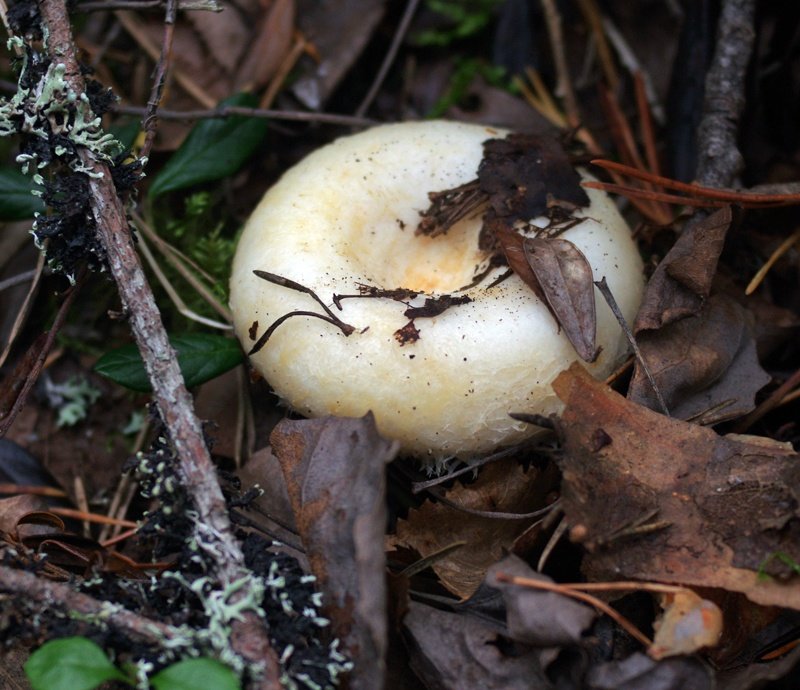
Description: A hat with a diameter of up to 20 cm, white with a yellowish tinge, slightly slimy, shaggy edges, rolled down. On the surface of the cap there are subtle concentric light, watery zones. With age, the cap becomes funnel-shaped.
The pulp is elastic, dense, white, does not change color at the break, with a specific, very pleasant mushroom smell. Milky sap is white, very pungent, instantly turns yellow in air. The plates are wide, sparse, adherent to the peduncle, white or cream, cream-colored spore powder.
The length of the leg of the watery-zone mushroom is about 6 cm, the thickness is about 3 cm, even, strong, hollow in adult mushrooms, the entire surface of the leg is covered with shallow yellowish depressions.
Doubles: Has some similarities with the white wave (lactarius pubescens), but much larger. It also looks like a white or dry milk mushroom (russula delica), which lacks white milky juice, a violin (lactarius vellereus), which is usually larger, with a felt surface of the cap and white milky juice, and a real milk mushroom (lactarius resimus), which, it seems that it does not grow on the territory of the Leningrad Region ... The most important obvious distinguishing feature is the stuck together yellowed fringe at the bottom of the cap. It has no poisonous counterparts, considering that all these mushrooms are conditionally edible and are considered toadstools in Western Europe.
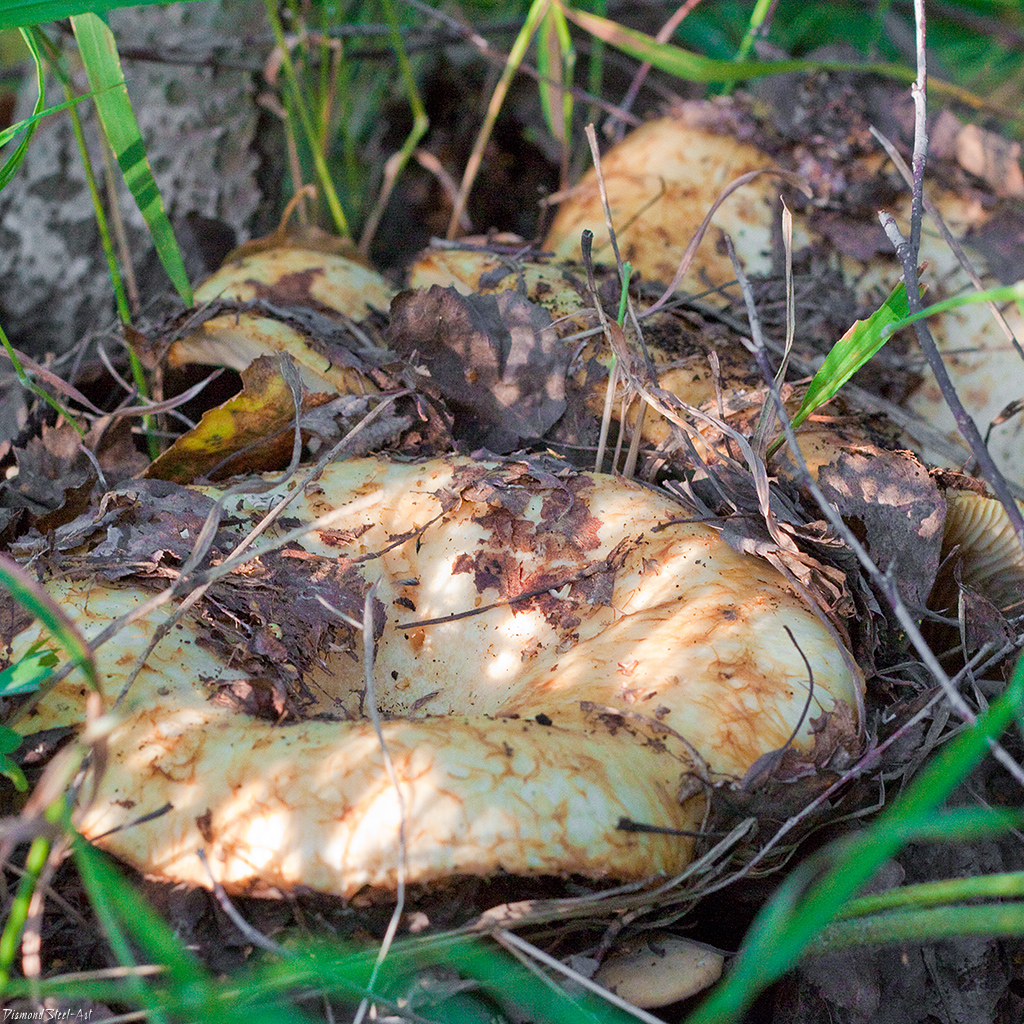
Note: Mushrooms grow in heaps, in piles, hence their name. Finding them is not so easy - the milk mushrooms are skillfully disguised in black fallen leaves. The best weather conditions for the growth of mushrooms are warm nights and fogs, then the mushrooms grow very abundantly. In rainy weather, it often rots at a young age, because completely hidden in last year's foliage.
Edible: Conditionally edible mushroom. Some find it possible to pickle young milk mushrooms, but the main taste of the mushroom is revealed in a salty form. Before salting, pre-treatment is necessary - boiling or soaking in order to remove the caustic juice.
Twin mushrooms
Gorchak, or bitter, has several doubles, some of which are edible, and some are not. They are cleverly disguised as the original. These include:
- lactic camphor;
- marsh lump;
- the milkman is meat-red;
- hepatic lactate.
The hot, scalding juice, which only the original bitter has, is the main distinguishing feature by which it is easy to recognize a real mushroom. This juice never changes its color.
Camphor milky
The camphor lactus (Lactarius camphoratus) belongs to the russula family, characterized by the lamellar structure of the cap hymenophore. It belongs to the group of conditionally edible mushrooms; this species grows in North America and on the territory of Eurasia in coniferous or mixed forests, where it forms mycorrhiza with representatives of coniferous trees.
Prefers to live on decaying forest floor or wood. Prefers slightly acidic or acidic soils for development.
In Russia, the camphor milky is found throughout the European part and in the Far East. Its description:
- pleasant to the touch matte surface of the cap;
- the surface is red-brown;
- loose pulp;
- wide plates of the hymenophore are located close to each other;
- the color of the plates is red with dark spots;
- leg in the form of a cylinder;
- the structure of the leg is fragile;
- leg length - up to 5-8 cm;
- aroma medicinal, camphor;
- the taste is insipid;
- the juice is white, does not change color upon contact with air.
False mountain goats bear fruit for about 3 months, from July to early October. They are classified in a low, 4 flavor category: these are conditionally edible mushrooms. They require pre-processing, so they are usually used for salting or boiled.
Swamp bush
Swamp milk mushroom (Lactarius sphagneti) is an edible species of the Russula family, belongs to the lamellar mushrooms. It is lamellar and brittle. Grows in clusters, on moist soils, in lowlands, from June to November. Its description:
- the body is dense, with a red skin of the cap;
- cap diameter - up to 5 cm;
- the shape of the cap is in the form of a funnel with a tubercle in the center;
- plates are frequent, descending to the leg;
- plates can be intertwined and form peculiar patterns;
- the color of the plates is reddish;
- the base of the leg with fibers, dense and fluffy;
- the pulp is creamy in color;
- the taste is unpleasant, sharp;
- the whitish milky sap interacts with oxygen and, being oxidized, changes color to gray with a yellow tint.
Old mushrooms are hollow inside.
The color of marsh mushrooms depends on the climate, soil and place of growth. The condition of the soil affects the taste and size of organisms. Prefers humid places, does not like heat. Found in all types of forests in Eurasia.
The marsh mushroom belongs to the group of edible mushrooms.
Liver Miller
Liver miller (Lactarius hepaticus) is not eaten because of the pungent taste and therefore it is classified as an inedible mushroom.
The cap is small, it can reach a maximum diameter of 6 cm. The color resembles the color of a fresh liver, from which the specific name comes. There is a recess in the center of the cap, so they say that the cap is funnel-shaped. The leg is thin, cylindrical, up to 1 cm in diameter. The color of the leg matches the color of the cap. White milky juice turns yellow in air.
The flesh inside is usually creamy or beige.
More often the variety is found in pine forests, where it forms mycorrhiza with woody species. It grows best on acidic sandy soils.
The bitter mushroom has several counterparts.
Miller meat-red
The meat-red miller (Lactarius trivialis) is sometimes also called smooth, alder, smooth or iron. It belongs to conditionally edible mushrooms from the russula family. The species is characterized by the following description:
- large surface of the cap (up to 20 cm);
- from the edge of it, a fold to the leg is noticeable;
- the center has a depression;
- the color can range from lilac to brown-pink;
- hymenophore type - lamellar;
- thin beige plates;
- the leg is cylindrical;
- the structure of the pulp is tender, brittle and light;
- weak aroma;
- the taste is pungent.
The change in the color of the liquid that stands out on the cut from white to yellowish is a feature of this species. Mycorrhiza with birch, pine or spruce is a natural state for this fungus. Fruiting begins in July, and continues until the last days of October on the fertile coniferous soils of Asia or Europe.
The benefits of fringed mushrooms.
The Russians figured out the benefits of milk mushrooms a long time ago. It seems that the composition of these mushrooms is rather poor, but the benefits from them are colossal. These mushrooms help to get rid of neuroses and depression, due to the content of vitamin B, which soothes the nervous system.
Milk mushrooms contain protein equivalent to the protein found in meat. With this protein replacement, the body does not get stress. In addition, the protein in mushrooms is absorbed more easily than other proteins.

Regular consumption of fringed milk mushrooms is beneficial for tuburculosis, since these mushrooms are active against the disease bacillus. They also help with urolithiasis and kidney failure. Milk mushrooms have a diuretic effect, due to which toxins, cholesterol and toxins are removed from the body. As a result, the risk of vascular blockage and plaque formation is reduced. Fringed milk mushrooms are natural antibiotics, as they contain vitamin C, riboflavin and thiamin.
Milk mushrooms have found their application in medicine, pharmaceuticals and cosmetology. From the substances that make up the milk mushrooms, they make medicines and medicines, for example, against the formation of stones in the bladder and kidneys.

The benefits of salted milk mushrooms are especially high, since in the process of fermentation, substances are formed that have an anti-sclerotic effect. Among other things, fringed milk mushrooms have a beneficial effect on the skin thanks to the vitamin D included in the composition. This vitamin is often called "solar", it is produced in the body when exposed to the sun. Vitamins D are found in animal products and milk mushrooms. This vitamin makes the skin firm, healthy and matte.
Contraindications to the use of milk mushrooms.
It should be borne in mind that fringed milk mushrooms have some contraindications:
- Mushrooms are heavy food, so milk mushrooms should be consumed in small quantities - no more than 250 grams, while taking a break for several days between their intake;
- Like any food, fringed milk mushrooms can cause individual allergic reactions;
- Milk mushrooms should be cooked correctly, otherwise poisoning may occur. Milk mushrooms are washed and cleaned. As noted, mushrooms are soaked in cold water for two days, while the water is periodically changed. Then they are salted and boiled for more than 20 minutes.
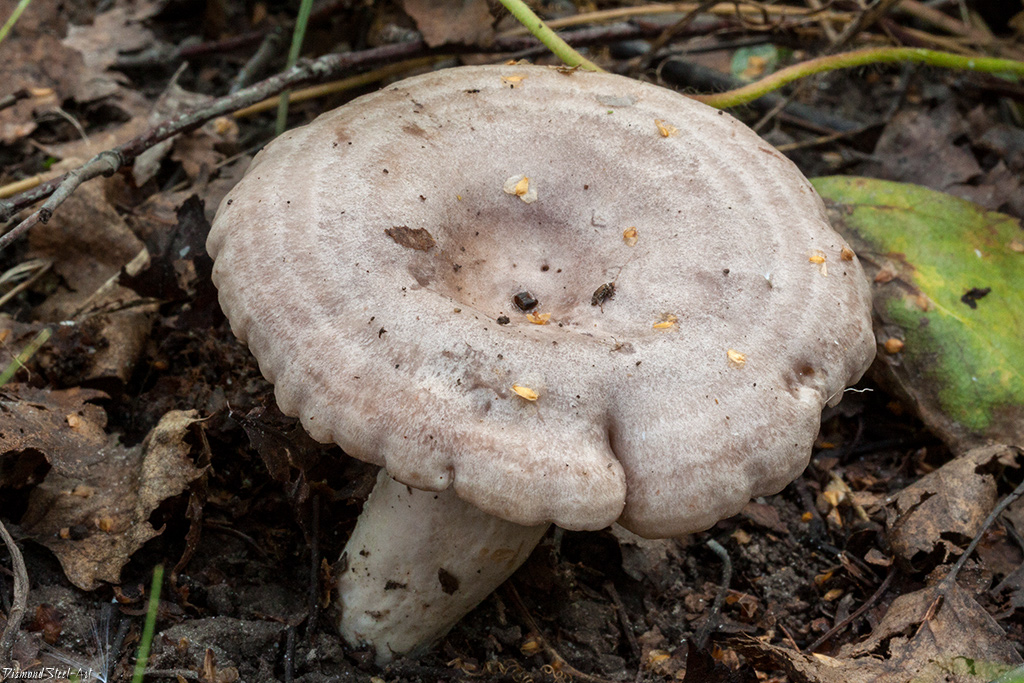
Similar species.
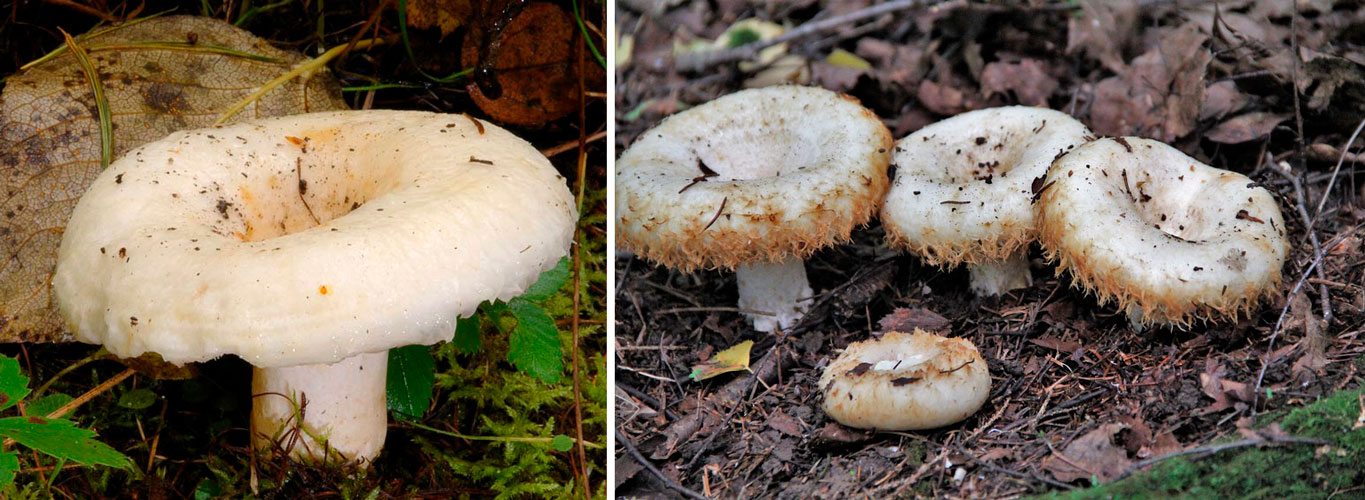
A distinctive feature of a fringed breast is a dry "fringe" along the edges of the cap, a hairy base of the leg and strong flesh. The most similar related species are the watery-zone mushroom, the real mushroom and the white wave.

- Watery-zone mushroom can be found in deciduous forests and conifers, which contain aspens, pines, birches and willows. A characteristic feature of this fungus is watery areas along the edges of the cap, fringed wet fibers on the slap, which sometimes disappear, spotting of the stem and absence of pubescence at the base;
- Real milk mushrooms will settle in forests with pines and birches. A distinctive feature of the present breast is the smooth, sticky skin of the cap, a long-lasting white color, a short "fringe" along the edges of the cap, which quickly disappears, and the absence of hairs at the base of the stem;
- White wolf grows under a birch. Its characteristic feature is milky juice that does not change on the air, a fibrous cap and edges, a white leg with a pinkish or orange zone.
Places of growth of fringed mushrooms.
In Europe, fringed milk mushrooms are widespread, but in the rest of the world they are quite rare. They grow in mixed forests. Fringed milk mushrooms form mutually beneficial alliances with beeches, oaks, birches, hazel, hornbeam.Fruiting occurs from July to October.

Evaluation of the edibility of the fringed lump.
The fringed milk mushroom, like many other milkmen, is considered a conditionally edible mushroom, since its pulp has a bitter taste. These mushrooms need long soaking.
In many Western countries, this type of mushroom is practically unknown. Mushroom pickers sometimes consider them inedible or poisonous. But in Russia, milk mushrooms are often found on dining tables.

Most often, fringed milk mushrooms are used for salting. After salting, they have a bluish tint. In consistency, these mushrooms are fleshy and juicy. Their taste is good, and the aroma is unique. In addition to salting, fringed milk mushrooms can be fried and dried. Before cooking, the bitterness should be removed from these mushrooms, otherwise it will be impossible to eat them.
The most common is the Siberian method of pickling milk mushrooms. They are soaked throughout the day, draining the water from time to time, then the mushrooms are washed and soaked again. After that, the milk mushrooms are salted in barrels or in jars with spices. After 40-50 days, the salted milk mushrooms are ready. Such milk mushrooms are very useful.
Earlier, milk mushrooms were considered one of the best mushrooms for pickling. It is known that only in Kargopol district, about 2.5 thousand kilograms of milk mushrooms were harvested every year. These mushrooms were salted and transported to St. Petersburg.

During the fast, milk mushrooms were considered one of the main dishes. This is evidenced by the menu for a dinner party organized by Patriarch Hadrian, held on March 17, 1699. This menu included pies with mushrooms, milk mushrooms in butter with horseradish, hot milk mushrooms with juice.
Chemical composition of fringed mushrooms.
Milk mushrooms, like cucumbers, contain a lot of water, but they also have many useful components. They are composed of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, ash, fiber and dietary fiber. In addition, the fringed milk mushrooms contain vitamins B1,2, C and D. This is a non-nutritive product - there are 16 kilocalories per 100 grams, therefore, fringed milk mushrooms are attractive for people who follow a diet, while the body is quickly saturated.

Shining like a starry sky - Milk golden yellow
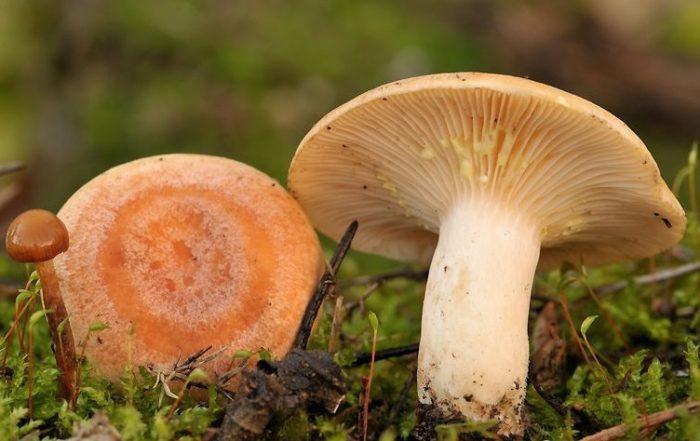

Description of the mushroom
The golden yellow mushroom belongs to the genus Millechnik, russula family.
This mushroom can be of different shades, from ocher-red and yellow to pinkish-brick, a distinctive feature will be spots and stripes on a matte smooth cap. The shape of the cap changes over time, initially it is strongly concave, and then gradually bends and expands upward, the edges are bent, its size varies from 3-7 centimeters.
The hymenophore (the lower part of the cap), like the cap itself, does not have one specific shade. Most often, mushrooms are found with creamy thick plates, which become reddish by adulthood and bifurcate at the ends.
The leg reaches 6-8 centimeters in height, smooth and light in color. The flesh of the mushroom is thick, white, turns yellow on the cut due to milky juice. There is no pronounced smell.

For the first time a golden yellow mushroom was noted by a member of the Royal Academy and a botanist from Sweden Elias Magnus Freis in 1838, this greatest man bore the title "father of mycology" and is considered one of the founders of the taxonomy of mushrooms and lichens.
Time and place of fruiting
This mushroom prefers deciduous forests, oak forests in a temperate climatic zone. Most often they are found under old oaks, beeches, chestnuts, it is with these trees that the golden yellow milk mushroom forms mycorrhiza (close, mutually beneficial relationship of the fungus with the plant roots).
This mushroom is widespread in the acidic soils of Britain and Ireland. Also found in North America and Africa. It can be found throughout Europe from Scandinavia to the Mediterranean.
It bears fruit from June until the end of autumn.