Real milk
Real photo
Systematics. Class - Basidiomycetes, order - Russulales, family russula - Russulaceae, genus Mlechnik - Lactarius.
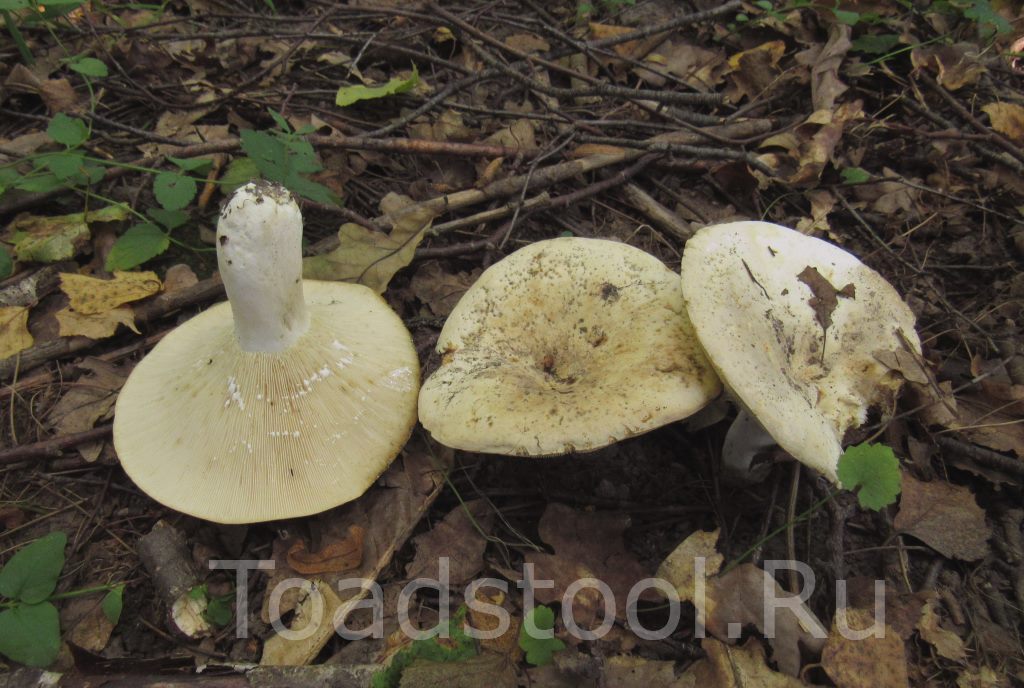
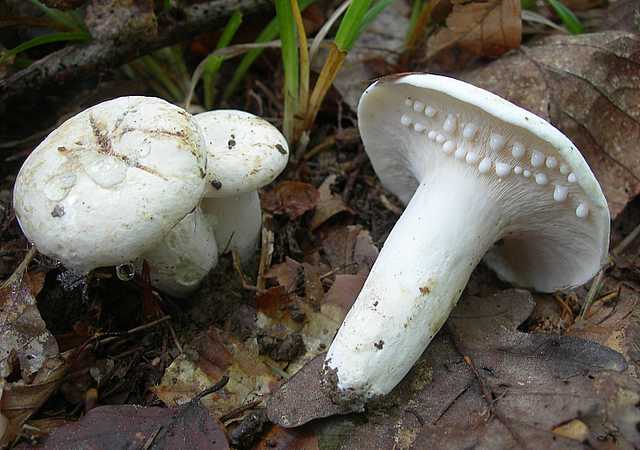
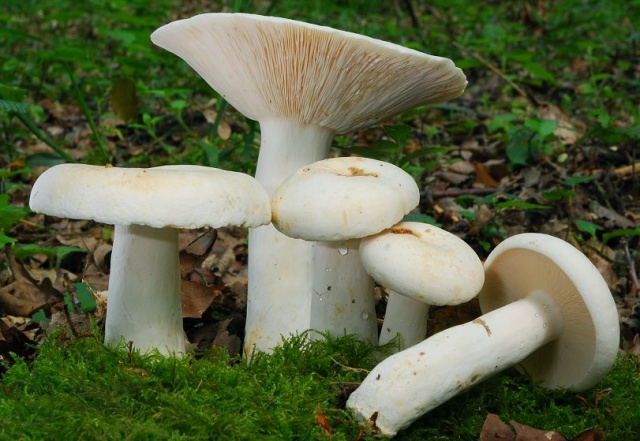
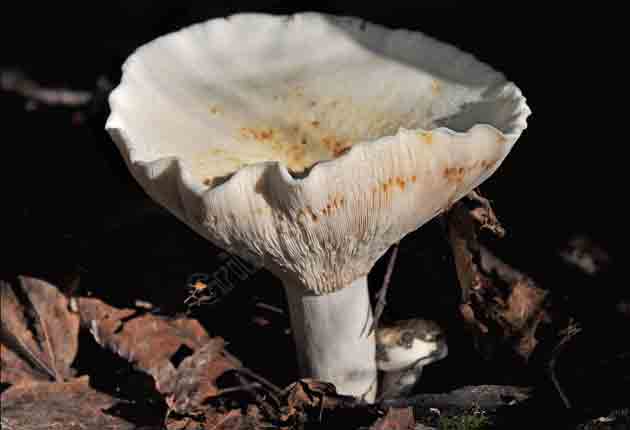
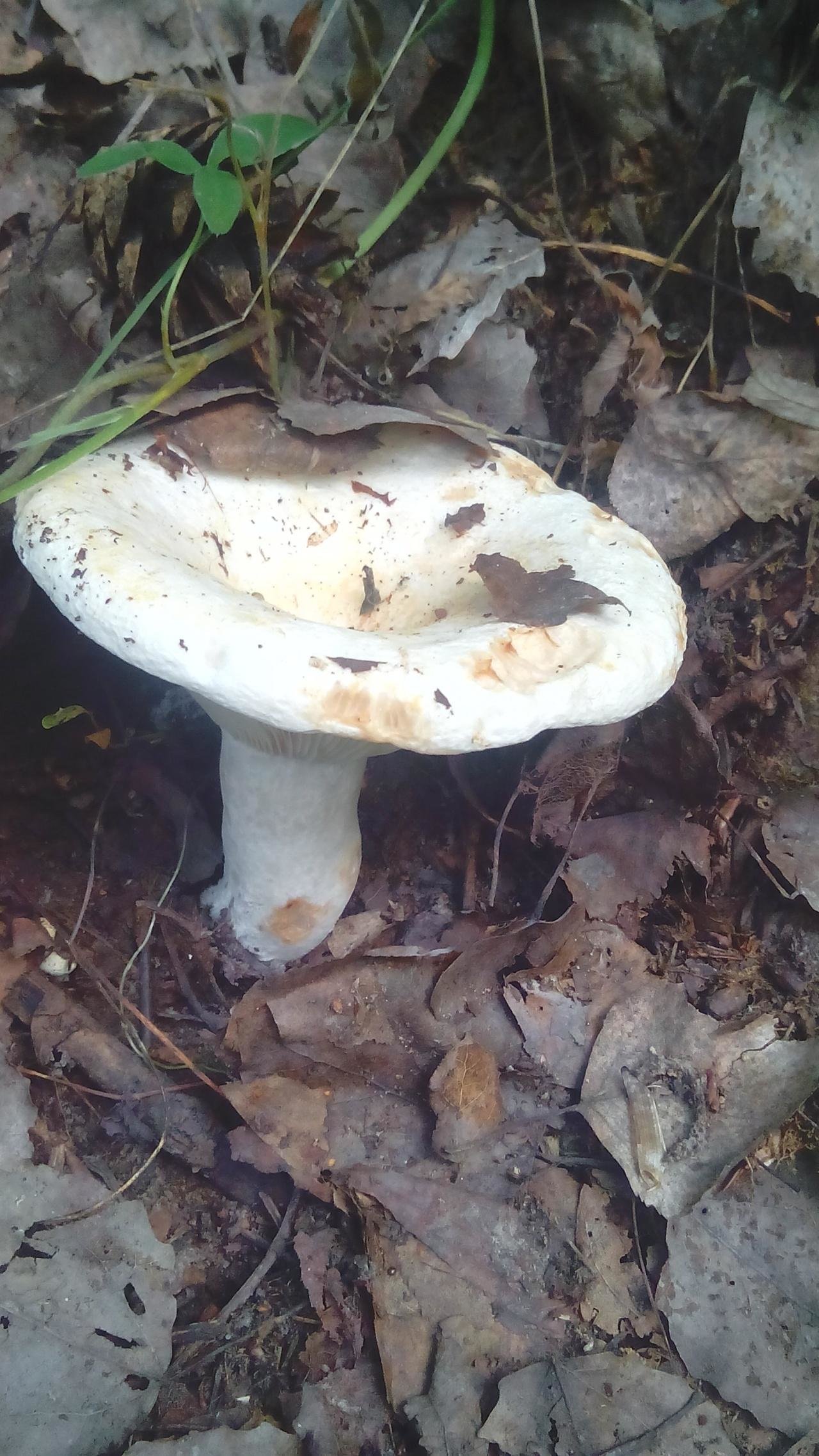
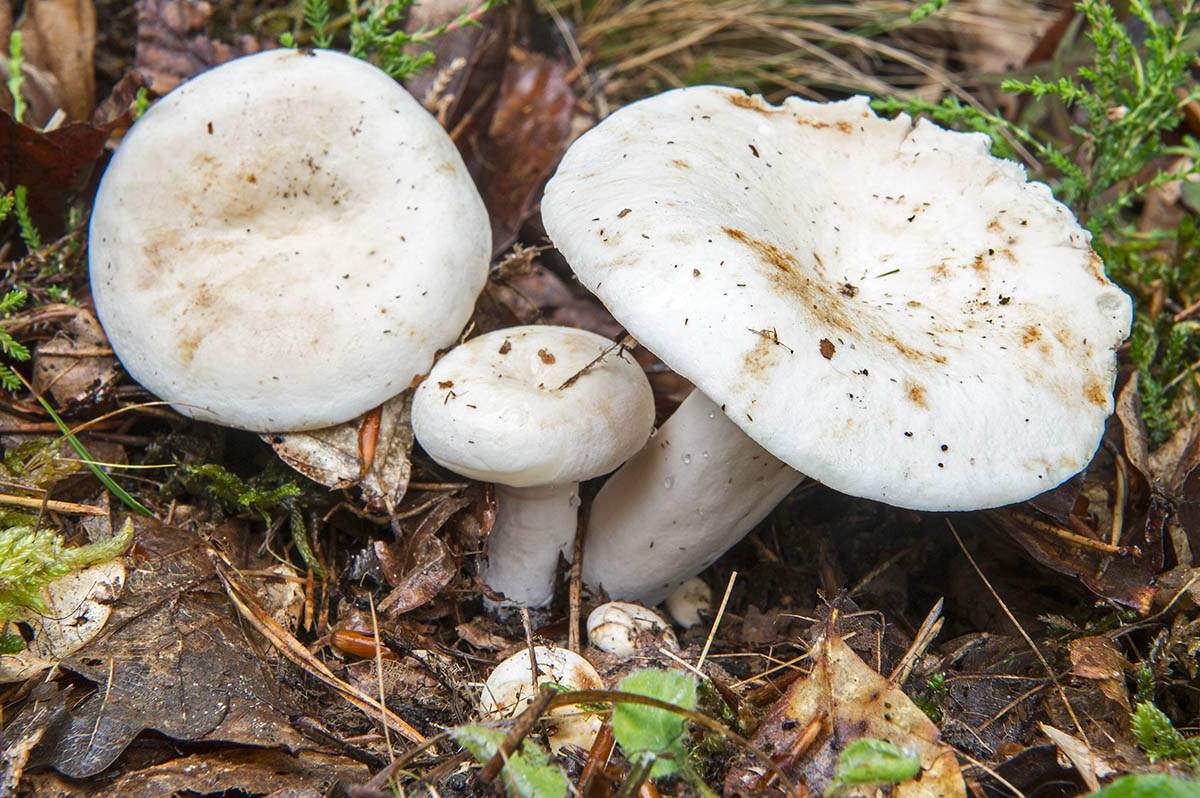
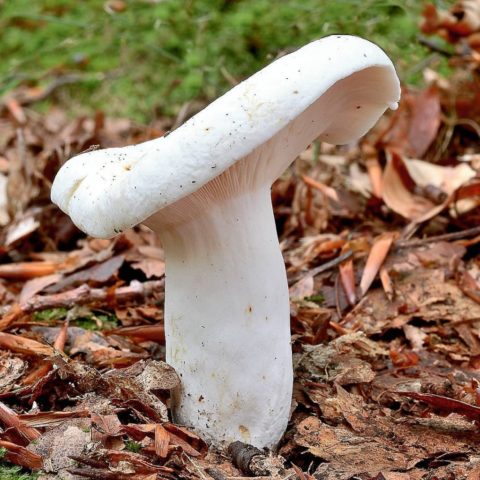
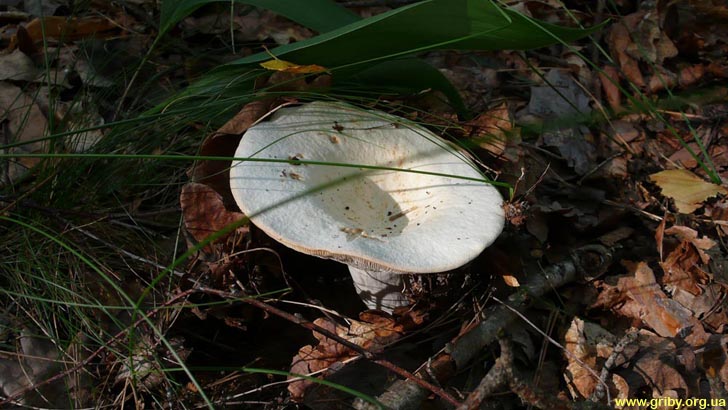
Real lactose - Lactarius resimus... Real milk mushroom is also called raw milk mushroom, white milk mushroom (Ural, Volga region), pravsky milk mushroom (Siberia), wet milk mushroom (Kazakhstan, Western Siberia).
Collecting mushrooms is like hunting. You need to get up early, at about six o'clock in the morning. Otherwise, the risk of finding cut legs increases.
The search for the fungus is carried out in birch forests, since the real milk mushroom forms mycorrhiza with it - a symbiosis of the mycelium of the fungus with the roots of the tree.
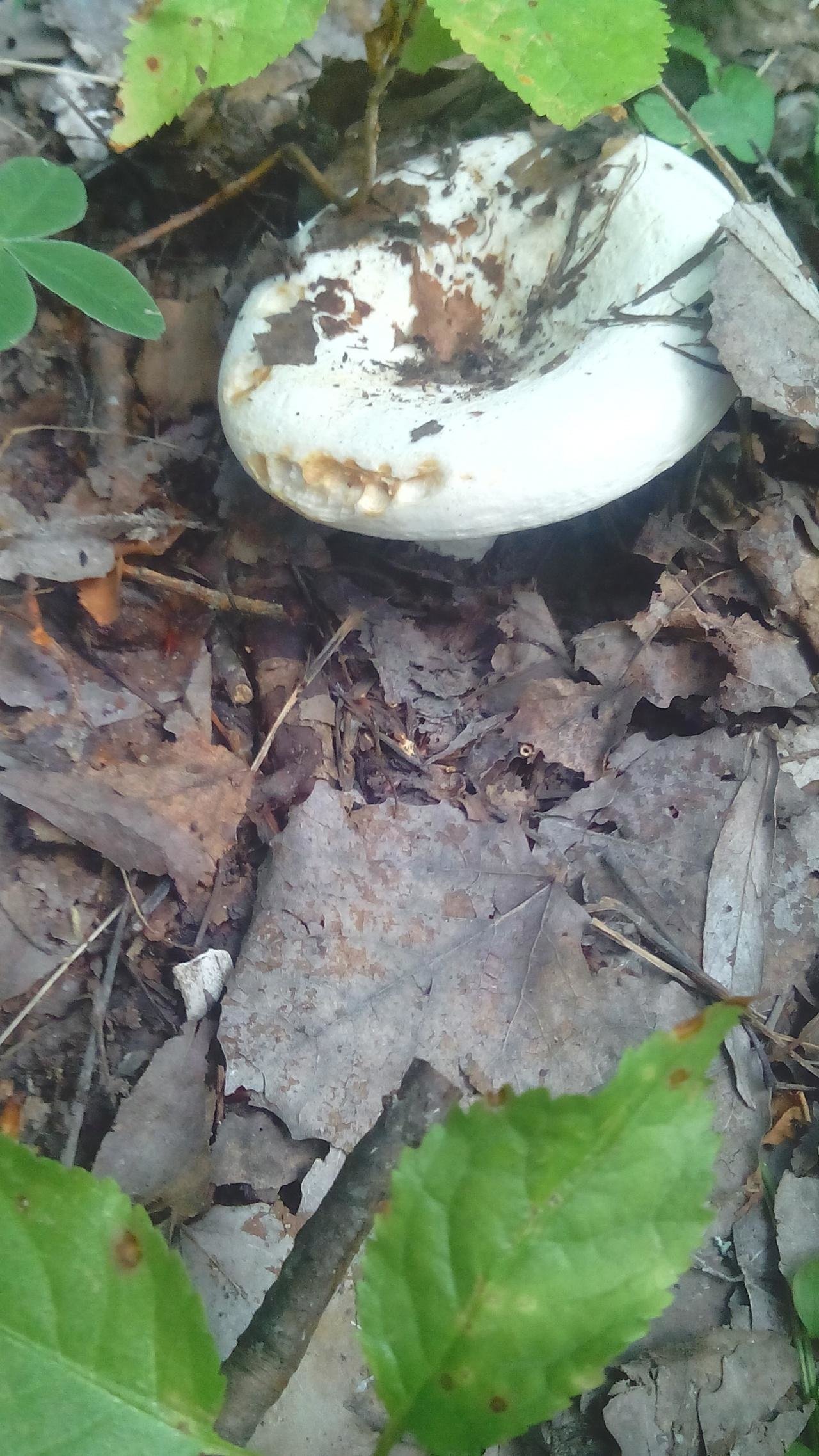
Walking through the forest, you need to look very carefully at all the irregularities and bumps of the soil, especially near the stumps and under the birches, since the cap may be completely hidden under the fallen leaves or needles. Milk mushrooms do not like light, therefore they grow mainly in dark, humid places, slightly nestling on the ground. For convenience, you can take a long stick with you and use it to check the contents of the tubercles.
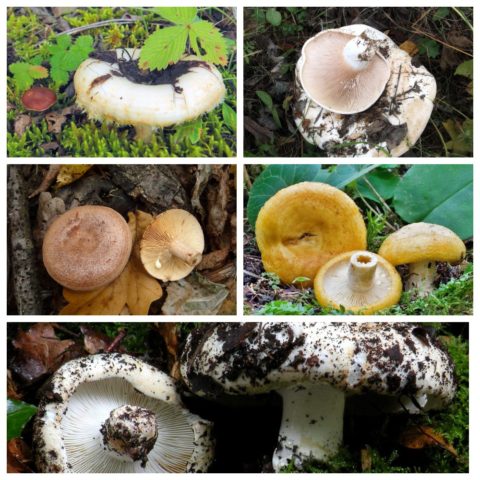
The real description
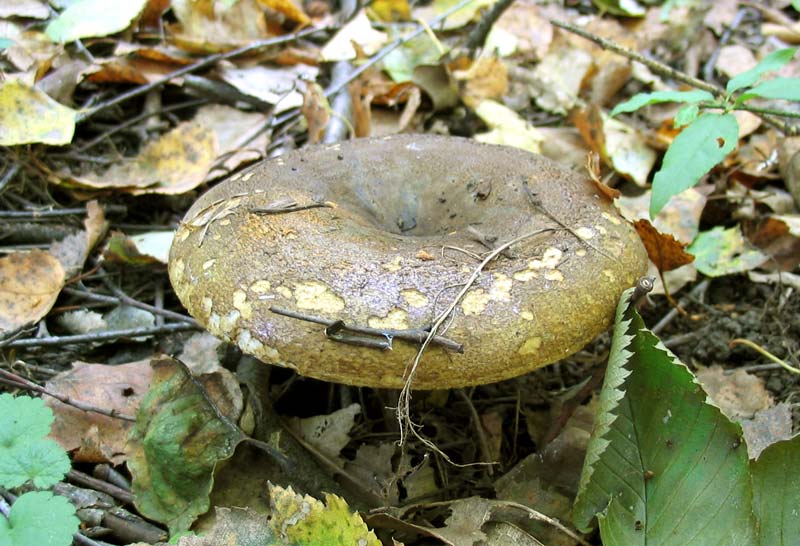
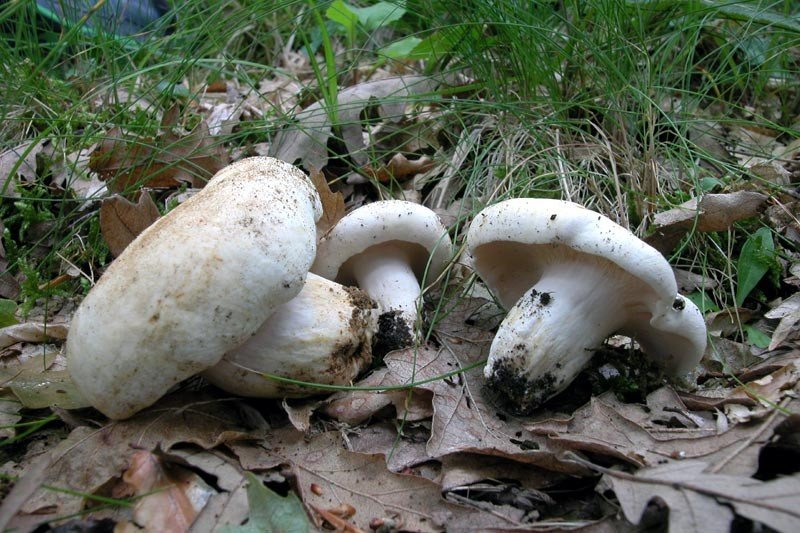
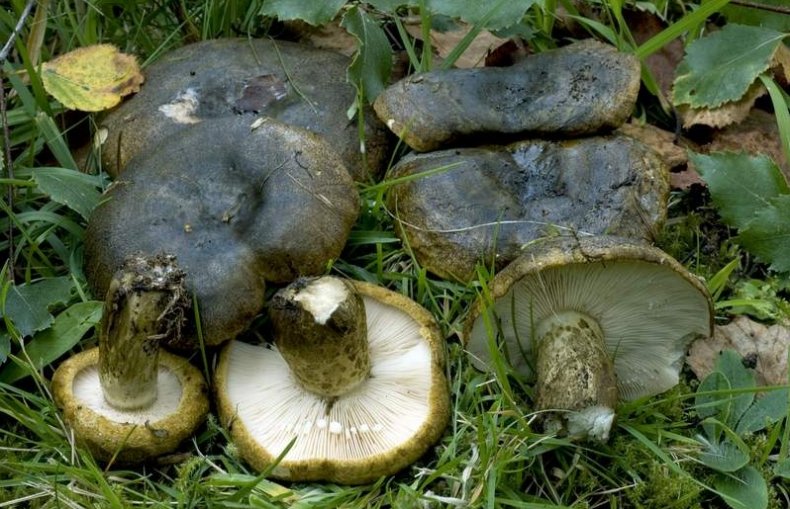
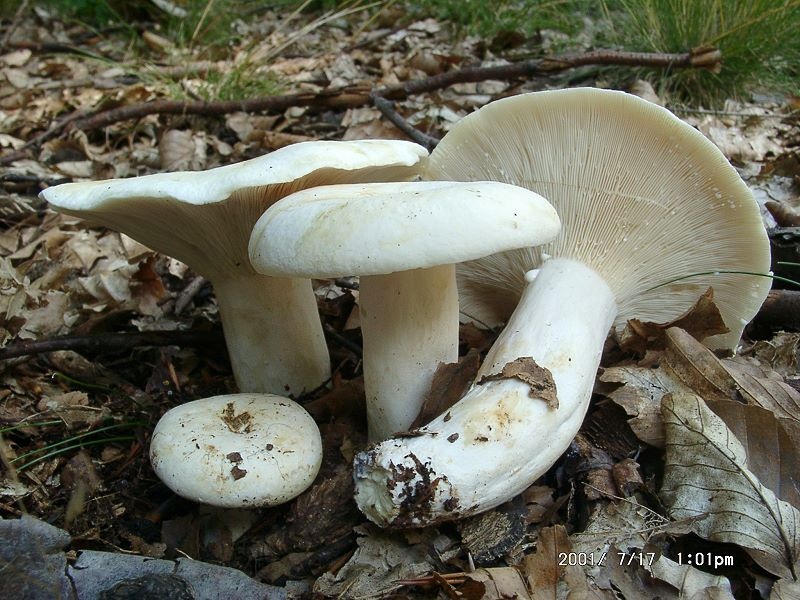
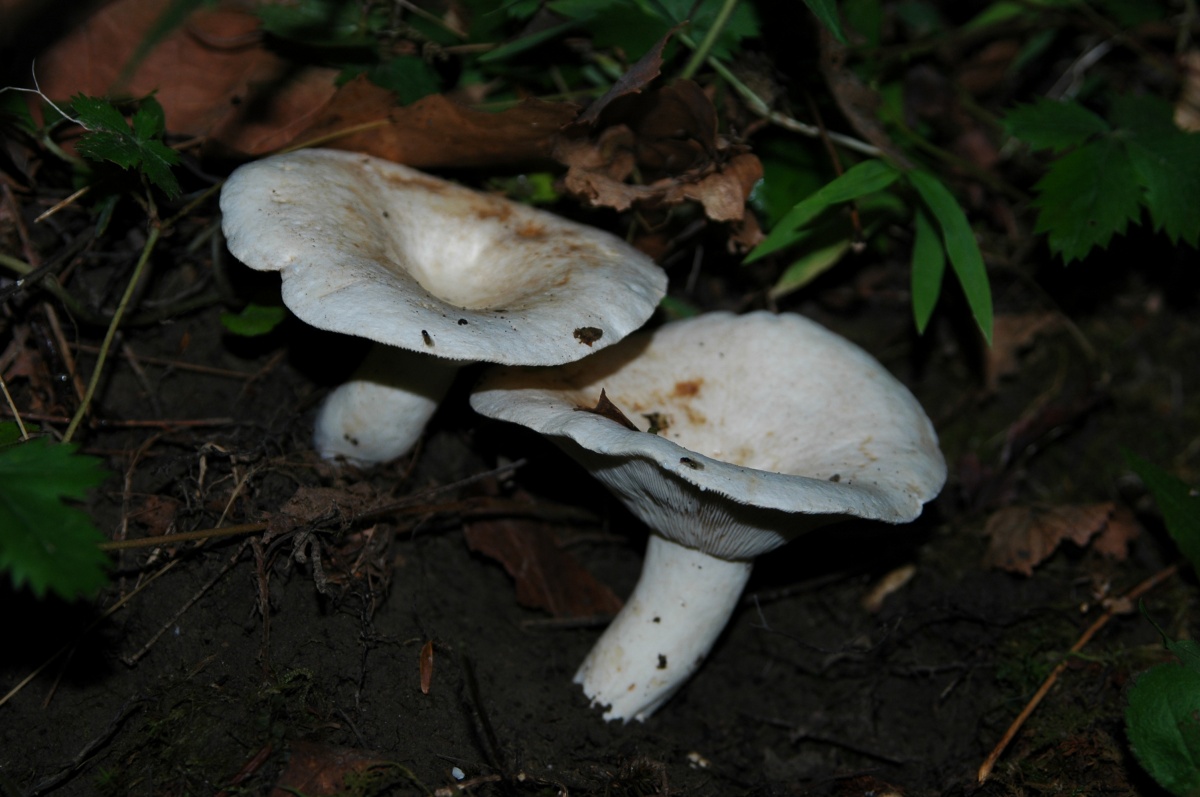
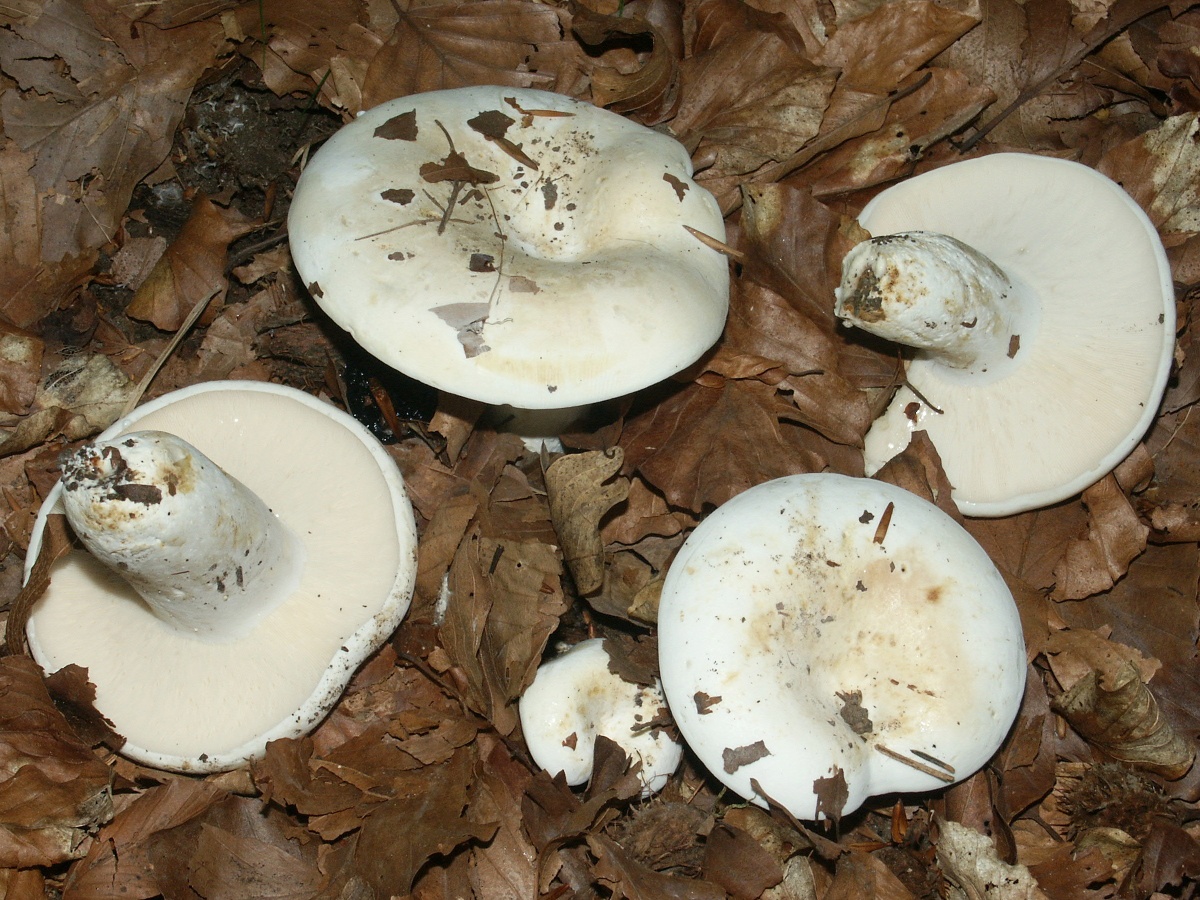
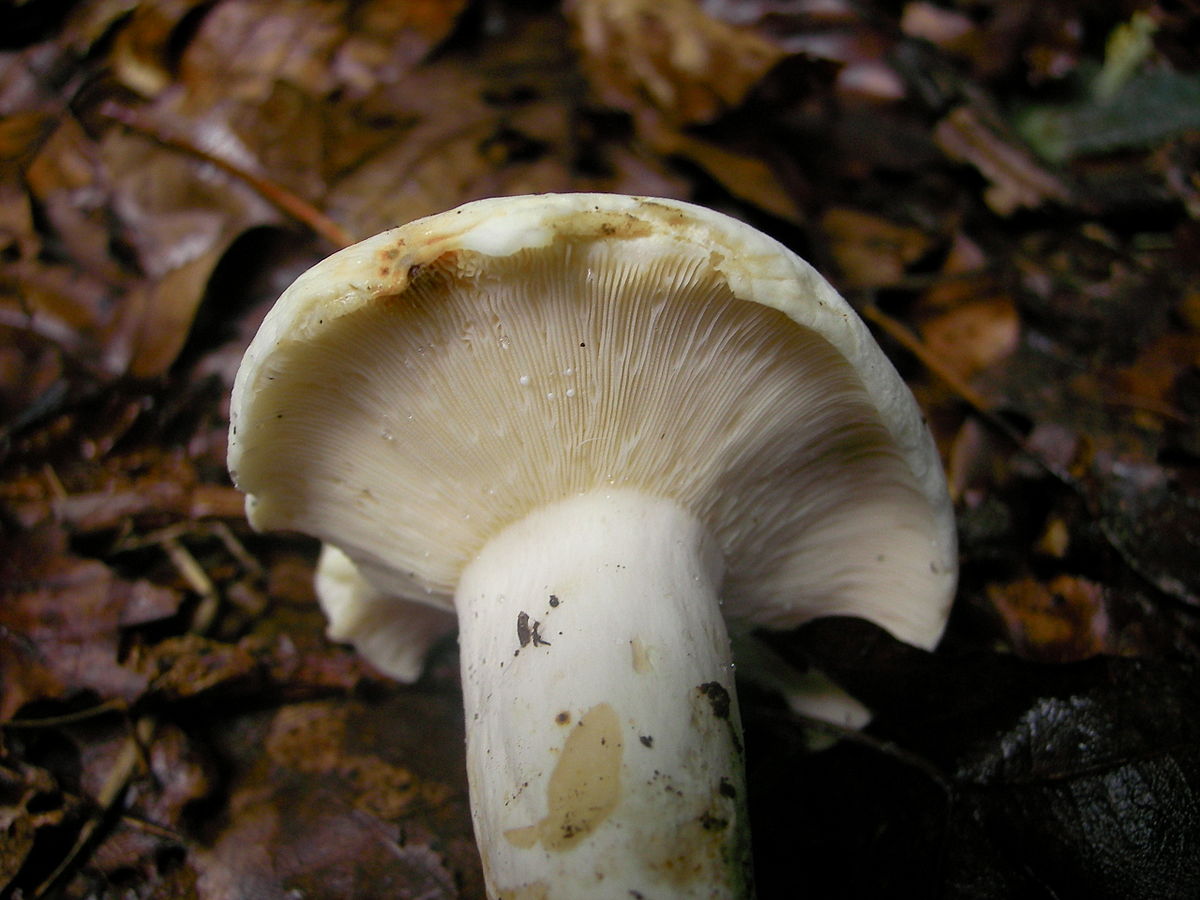
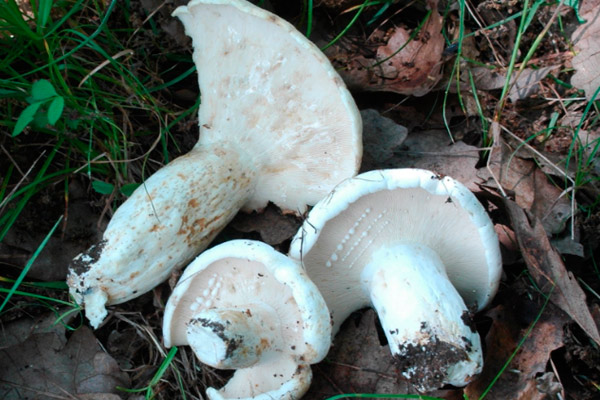
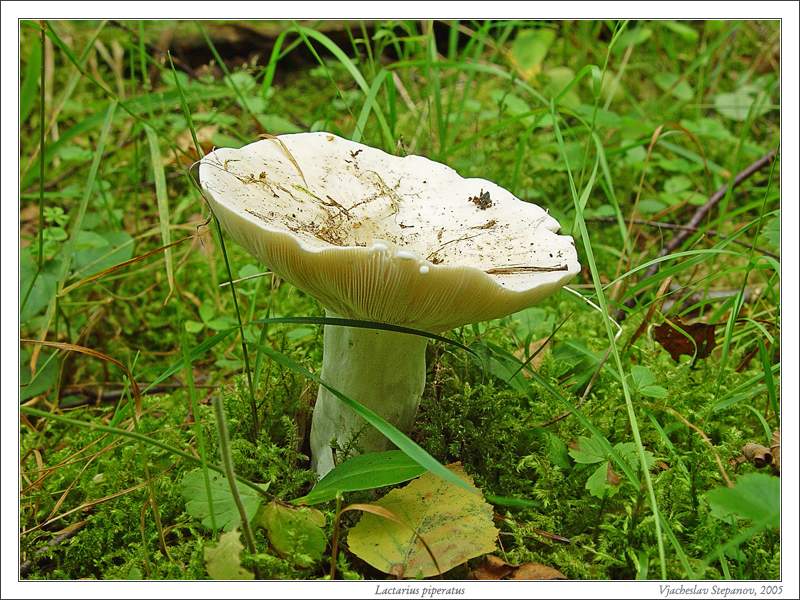
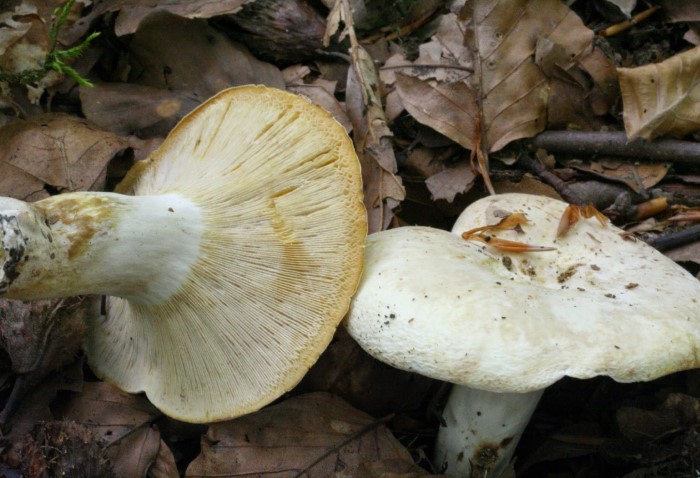
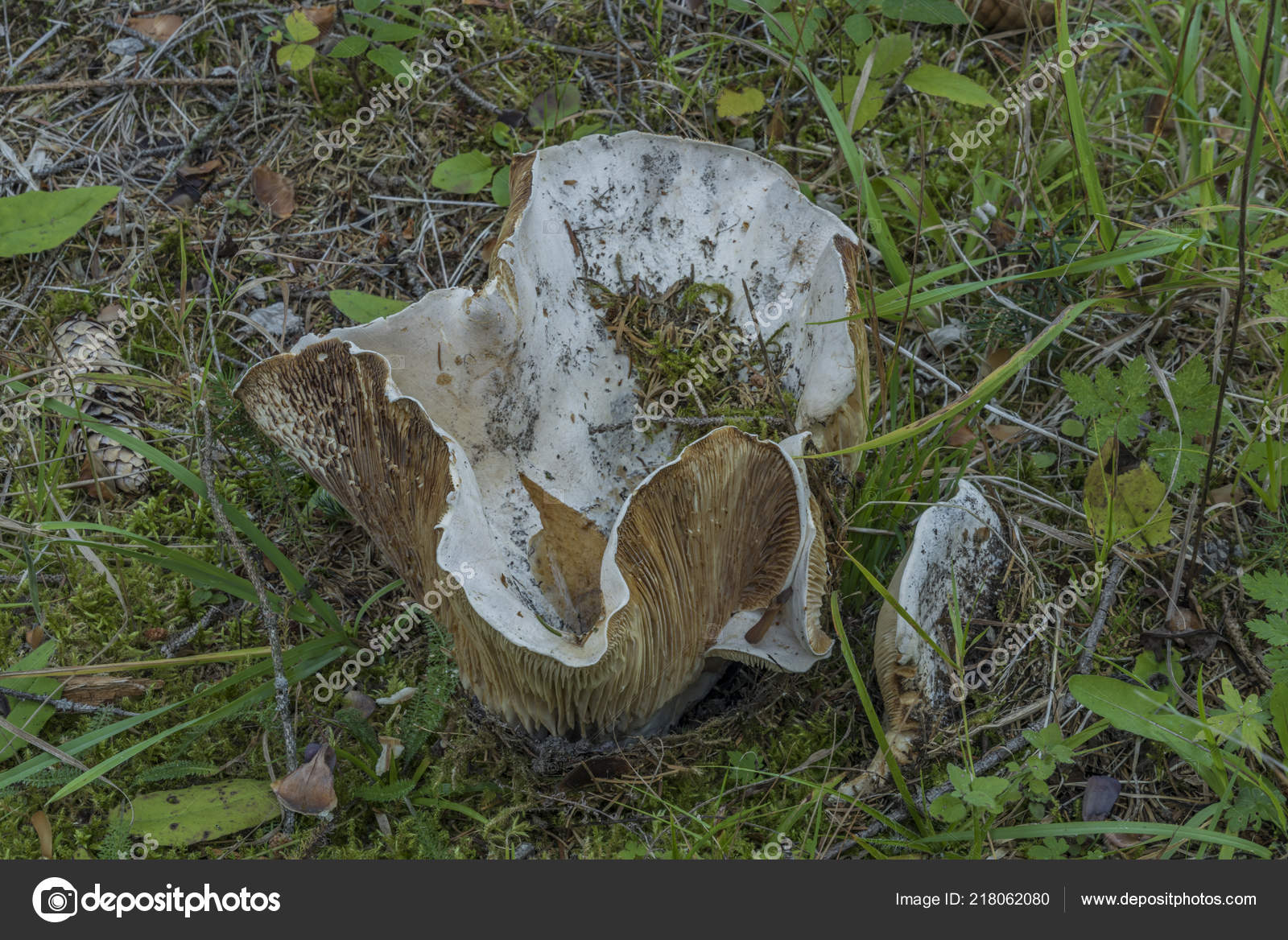
Diameter hats 5-20 cm, initially flat-convex, later acquires a funnel-shaped shape with a pubescent edge wrapped inward, dense.
Skin milky white or slightly yellowish, wet, slimy, has unclear concentric zones, most often with adhering particles of litter and soil.
Leg 3-7 cm high, 2-5 cm in diameter, smooth, cylindrical, white or slightly yellowish, sometimes with yellow pits or spots, hollow.
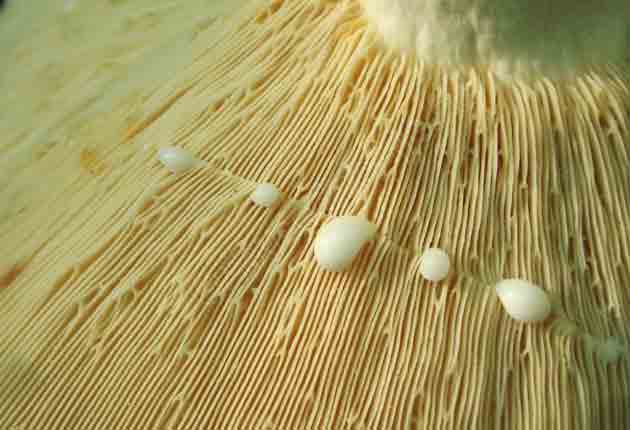
Pulp mushroom is strong, dense, white, with a characteristic odor that resembles that of fruit. Milky juice tastes pungent, white, turns sulfur-yellow in the air. The mushroom is moist to the touch, even in dry weather.
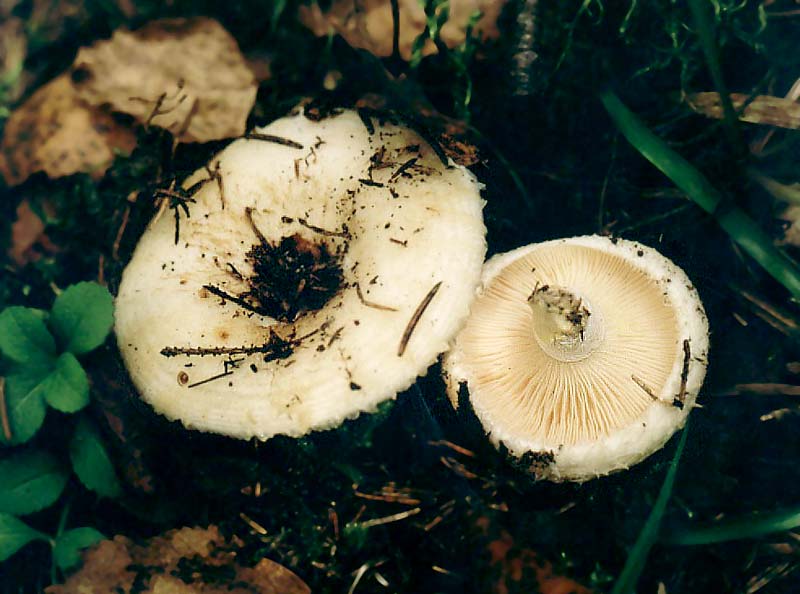
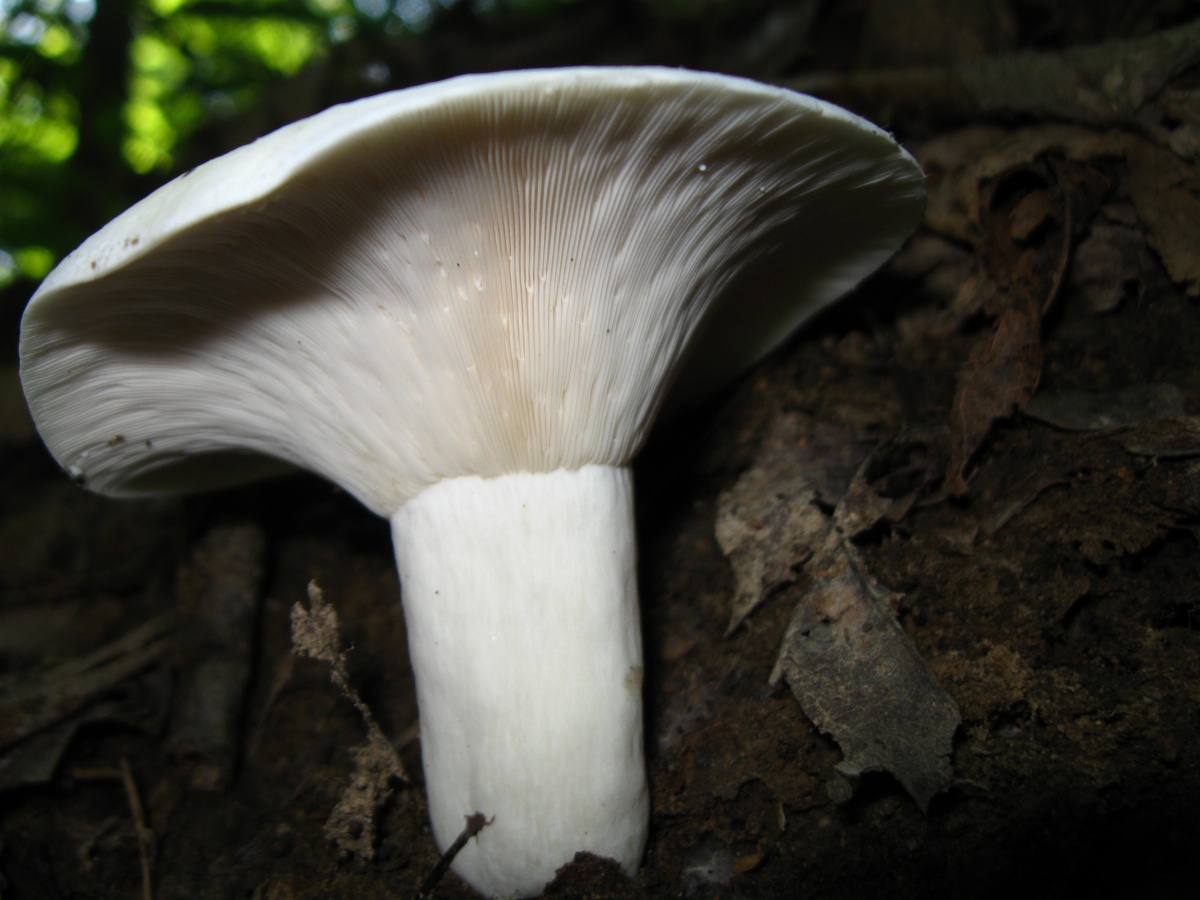
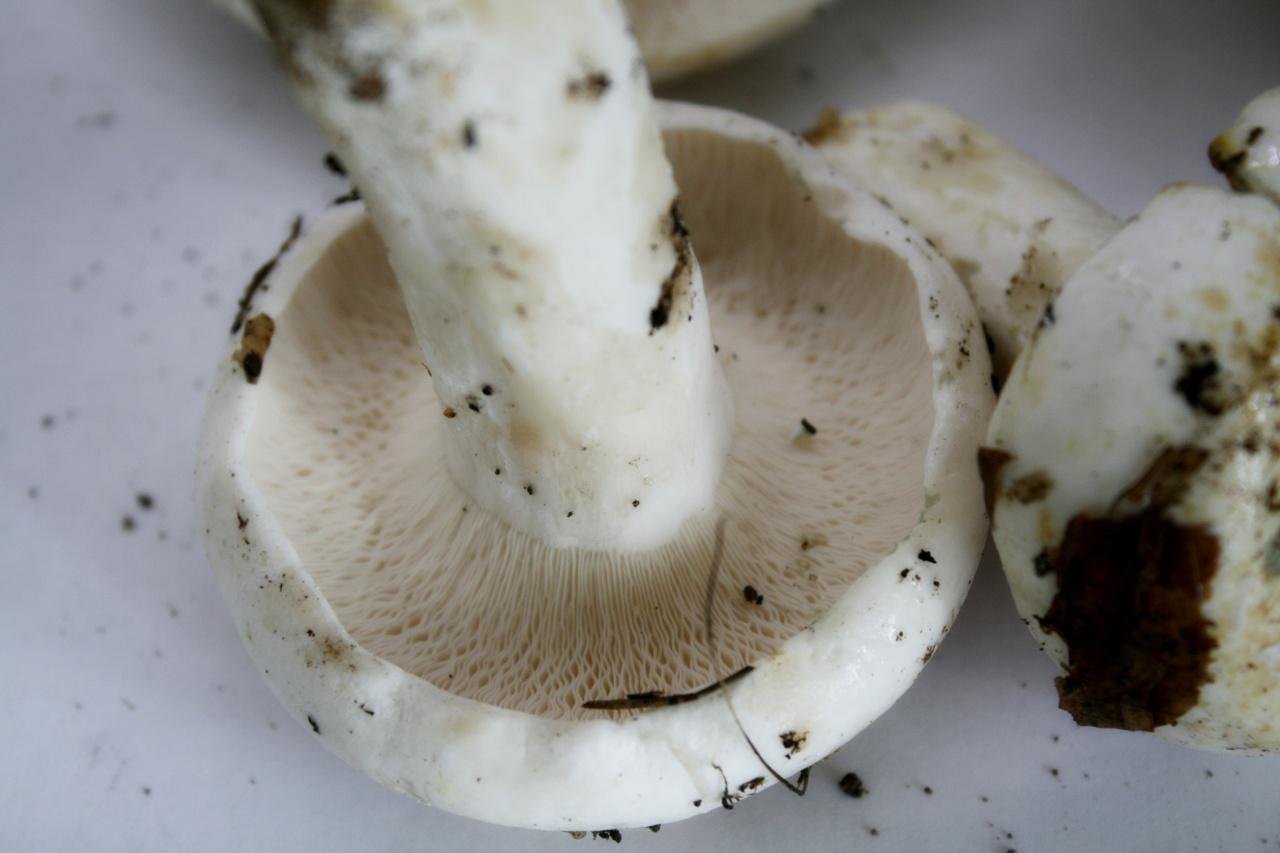
LPs fungus are quite frequent, slightly descending along the stem, wide, white with a yellowish tinge.
Spore powder yellowish in color.
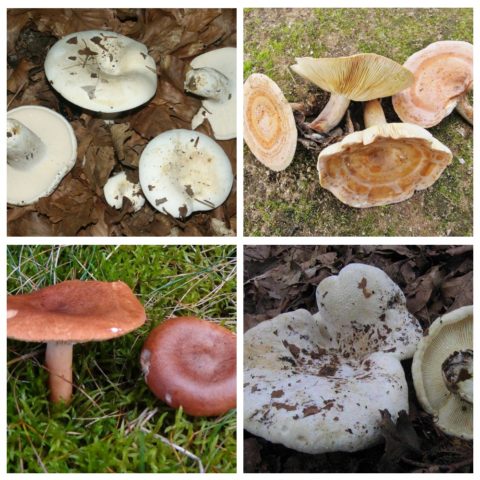
The variability of the mushroom is real
In old mushrooms, the plates turn yellow, the leg becomes hollow. There may be a brown spot on the cap. The color of the plates can vary from yellowish to cream in color.
Ecology and distribution of the fungus
Found in mixed and deciduous forests: pine-birch, with linden undergrowth, birch. Forms with birch mycorrhiza... Distributed in the North of Russia, in Western Siberia, in the Urals, in Belarus, in the Upper and Middle Volga regions. Grows in large groups. Not common.
For favorable fruiting, the optimum temperature is 8-10 ° C on the soil surface. Season - July-September, in the southern regions (Middle Volga region, Belarus), August-September.
The edibility of the mushroom is real
Milk is a real edible or conditionally edible mushroom of the 1st category.After collecting the mushrooms, they begin to process them. Mushrooms are cleaned, washed, cut off the legs with mycelium particles, put them in a container with water and sprinkle with salt. Salting milk mushrooms is a troublesome business. Soaking is carried out for at least three days. In this case, it is necessary to change the water three times a day. Thus, toxic compounds are removed from the mushroom, because of which it is considered conditionally edible.
Real photo:
Real photo
The classic cold way of pickling milk mushrooms
Before salting, the mushrooms are soaked in salted and acidified water (10 g of salt and 2 g of citric acid per 1 liter of water). Soaking is carried out for 2 days, while the water is changed in the morning and evening. Then the mushrooms are placed on the bottom, in prepared containers, caps down, sprinkling with salt at the rate of 40-50 g per 1 kg of mushrooms. When the container is filled, the mushrooms are covered with a clean cloth, a circle is placed on top and a small weight is placed on it.After 2-3 days, the mushrooms become denser and juice is released, a new portion of mushrooms is added to them, observing the same rules. This is done until the sediment of the mushrooms stops. Do not remove the load! The mushrooms must be covered with the formed brine. If it is not enough, then you can add salted boiled water and increase the weight. The filled containers are taken out in the cold for 35-40 days.
White Milk (Lactarius resimus)
Synonyms:
- Milk white
- Raw milk
- Wet breast
- The lump is right

Description
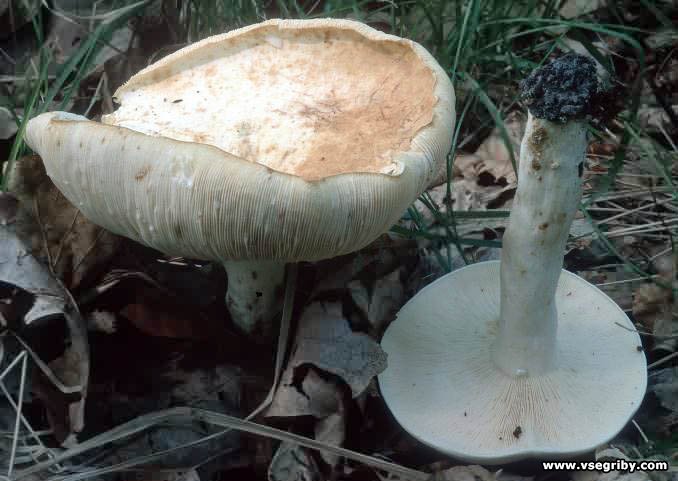
White milk mushroom (lat.Lactarius resimus) is a mushroom of the genus Millechnik (lat.Lactarius) of the russula family (lat.Russulaceae).
The hat is 5–20 cm, first flat-convex, then funnel-shaped with a pubescent edge turned inward, dense. The skin is slimy, wet, milky white or slightly yellowish with indistinct watery concentric zones, often with adhering particles of soil and litter.
Leg 3-7 cm in height, ∅ 2-5 cm, cylindrical, smooth, white or yellowish, sometimes with yellow spots or pits, hollow.
The pulp is brittle, dense, white, with a very characteristic odor, reminiscent of the smell of fruit. Milky sap is abundant, acrid, white, in the air it becomes sulfur-yellow.
The plates of the breast are rather frequent, wide, slightly descending along the stem, white with a yellowish tinge.
Yellowish spore powder.
In old mushrooms, the leg becomes hollow, the plates turn yellow. The color of the plates can vary from yellowish to cream. There may be brown spots on the cap.
Spreading
Milk is found in deciduous and mixed forests (birch, pine-birch, with linden undergrowth). Distributed in the northern regions of Russia, in Belarus, in the Upper and Middle Volga regions, in the Urals, in Western Siberia. It is found infrequently, but abundantly, usually grows in large groups. The optimum average daily fruiting temperature is 8-10 ° C at the soil surface. Milk mushrooms form mycorrhiza with birch. Season July - September, in the southern parts of the range (Belarus, Middle Volga region) August - September.
Similar species:
- The fiddler (Lactarius vellereus) has a felt cap with not pubescent edges, found most often under beeches.
- Pepper milk (Lactarius piperatus) has a smooth or slightly velvety cap, the milky juice turns olive green in the air.
- Aspen milk mushroom (Lactarius controversus) grows in damp aspen and poplar forests.
- The white boll (Lactarius pubescens) is smaller, the cap is less slimy and more fluffy.
- White podgruzdok (Russula delica) is easily distinguished by the absence of milky juice.
All these mushrooms are conditionally edible.
Remarks
In the West, it is practically unknown or considered inedible, in Russia it is traditionally considered the best conditionally edible mushroom. After removing the bitterness, it is salted, the salted mushrooms acquire a bluish tint, fleshy, juicy, and have a special aroma. It is believed that milk mushrooms are superior in calories to meat. The dry matter of the mushroom contains 32% protein. According to the Siberian method, milk mushrooms are salted along with other mushrooms (saffron milk caps, volushki). The mushrooms are soaked for one day, periodically changing the water, then washed and poured with water for another day. Salted in barrels with spices. Milk mushrooms are usable in 40-50 days.
In the old days, White lump was considered the only mushroom suitable for pickling, it was called the "king of mushrooms". In the Kargopol district alone, up to 150 thousand poods of mushrooms and mushrooms were collected annually and exported to St. Petersburg with salted ones. A list of dishes at a dinner party on March 17, 1699 at Patriarch Adrian's is known: "... three long pies with mushrooms, two pies with milk mushrooms, cold mushrooms with horseradish, cold milk mushrooms with butter, warmed milk mushrooms with juice and butter ..." As you can see, during post, the main decoration of the table was all kinds of dishes from milk mushrooms.
Similar types and differences from them
Pepper is similar to its related milky mushrooms:
- aspen mushroom (Lactarius controversus). Its characteristic feature is orange-pink plates.The leg is grayish or pinkish in color.
- The violin (Lactarius vellereus), which is distinguished by the pile on the stem and cap, as well as more sparsely spaced plates.
- The parchment lump (Lactarius pergamenus) has a relatively elongated stem and wrinkled cap.
- Glaucous Milk (Lactarius glaucescens). Its description is close to the species characteristics of pepper, but the milky juice of this fungus, initially white, becomes gray-greenish when dried, and turns yellow under the influence of a KOH solution.
Description and distribution of aspen (poplar)
All milk mushrooms are outwardly similar to each other. Many people know these mushrooms by the proverb “he called himself a load - climb into the back”. But in it, rather, we are talking about a real mushroom - the most valuable conditionally edible mushroom, which has long been intensively collected by mushroom pickers. Other representatives of this genus are less known. One of them is the aspen milk mushroom, which is quite rare and less popular than the real one.
Description
Aspen milk mushroom (Lactarius controversus) is a mushroom of the Russulaceae family, of the Millechnik genus (Lactarius). In another way, it is called poplar mushroom.
- The cap is fleshy, whitish in color with light pink spots, at a young age it has edges strongly curved downwards and a depressed middle, later it straightens out, becomes widely funnel-shaped. The diameter reaches 7-20 cm. In wet weather, the surface becomes sticky and slimy, which is why it becomes covered with specks.
- On the back of the cap there are cream or light pink plates (an important identifying feature), weakly running down the stem.
- A short, thick leg - 2-7 cm in height and 1.5-4 cm in diameter - has the same color as the cap, or whitish, with yellowish spots. Dense, often narrowed at the base.
- The pulp is white, with a fruity odor and abundant acrid white milky juice, which does not change its color in the air.
The poplar mushroom belongs to conditionally edible - it can be eaten only with preliminary soaking, first of all in salted, less often - in fried and boiled form.
Spreading
Most often, poplar mushrooms can be found under poplars, aspens and willows, since with these trees they form mycorrhiza. They prefer moist warm temperate forests. In general, these mushrooms are quite rare. In Russia, you can find them in the Lower Volga region from July to October.
Similar species
Very often, aspen milk mushroom is confused with a white or whitewash (Lactarius pubescens). Distinguishing them is quite simple: the main difference is the pubescence of the cap. It is densely pubescent in the white beetle (“pubescens” means “pubescent”), but not in the poplar mushroom.
It can be distinguished from the real mushroom (Lactarius resimus), a more nutritious mushroom in terms of food, by its pubescence (the real one is pubescent at the edges) and the color of the underside of the cap (the real plate has white, not pink, like poplar).
Other lactarius (representatives of the genus Lactarius), such as the violin (Lactarius vellereus) or pepper milk mushroom (Lactarius piperatus) are also sometimes confused with the aspen milk mushroom, none of them has the underside of the cap painted pink, so it is not difficult to distinguish them.
Primary processing and preparation
As already mentioned, aspen milk mushrooms are conditionally edible, therefore they require special preparation before use. Most often they are salted. The correct cooking technology is very important: if you do not follow it, the mushrooms will be bitter due to the milky juice contained in their pulp.
Before cooking, aspen milk mushrooms should be soaked in cold water, changing it as often as possible to prevent fermentation and souring. The water should cover the whole mushrooms. With frequent water changes, one or two days of soaking is sufficient. After that, you need to rid the mushrooms of the wormholes, and then boil for 10 minutes. Less commonly, fried aspen milk mushrooms are used.
Nutritional qualities, benefits and harms
100 g contains:
- 1.8 g protein;
- 0.5 g fat;
- 0.8 g of carbohydrates.
Calorie content - 16 kcal.
Vitamins of group B, which are found in abundance in all milkmen, serve as the prevention of depression and neurosis. Other substances contained in them are useful for patients with tuberculosis - they neutralize the bacteria that excite it (which, of course, has found application in pharmaceuticals).
Also, milkmen help with kidney failure and urolithiasis, neutralize many toxins and serve as a diuretic. Due to the fact that, with a high nutritional value, they do not contain much glucose, they are often advised to be included in their diet for diabetics.
The poplar mushroom, however, also has a number of harmful properties. Firstly, when using an improperly prepared mushroom, you can get poisoning (this is due to the milky juice contained in its pulp). Secondly, even if the mushroom is cooked correctly, it is rather poorly digested. Therefore, in large quantities, milkmen, like other mushrooms, are not recommended to be consumed. It is especially harmful for those suffering from stomach ulcers, gastritis or other diseases of the digestive system.
As you can see, collecting aspen mushrooms is not devoid of sense: in salted form, they are edible and bring noticeable benefits to the body. They are also very nutritious, so vegetarians can eat them instead of meat.
Description and places of distribution of the mushroom peppers, photo
In the forest zone of the middle zone, by the beginning of autumn, various types of milky mushrooms with caustic sap bear fruit abundantly. They have been able to manage them on the territory of Russia for a long time, soaking and salting this crop as a winter harvest. Pepper milk is one of such milkmen.
Description
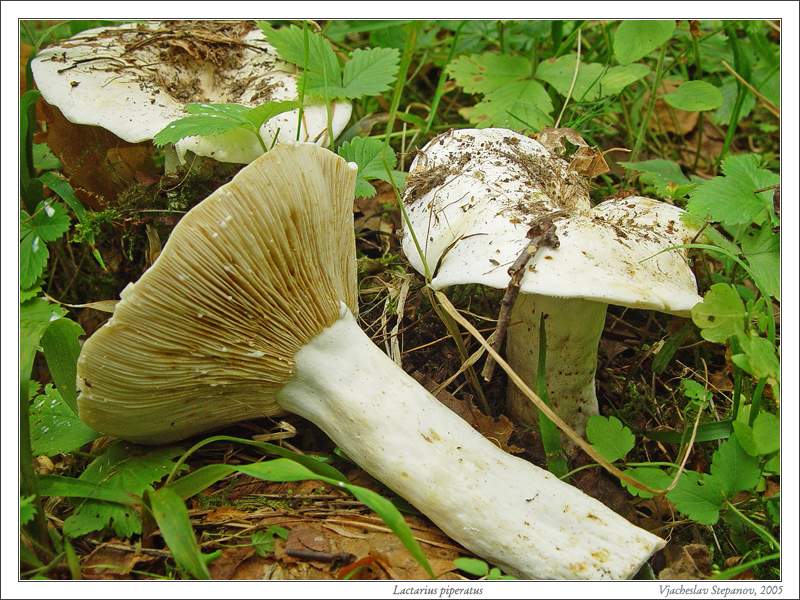
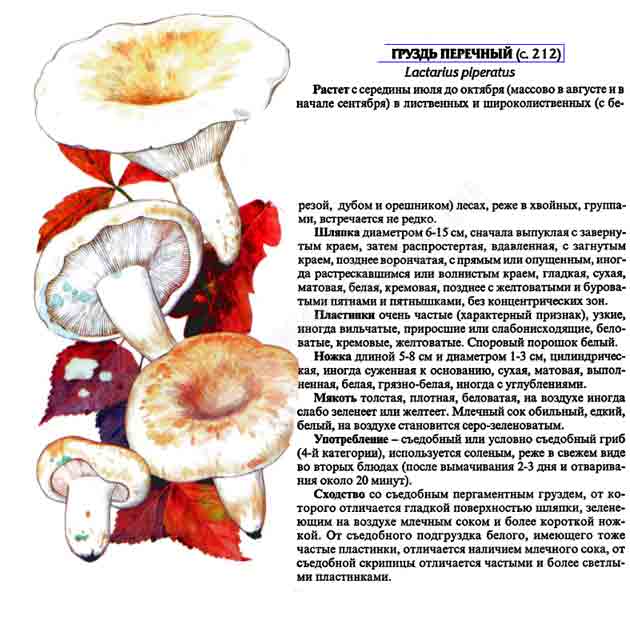
Pepper milk (Lactarius piperatus) belongs to the class of agaricomycetes, russula family, lactic acid genus.

Has the following distinctive features:
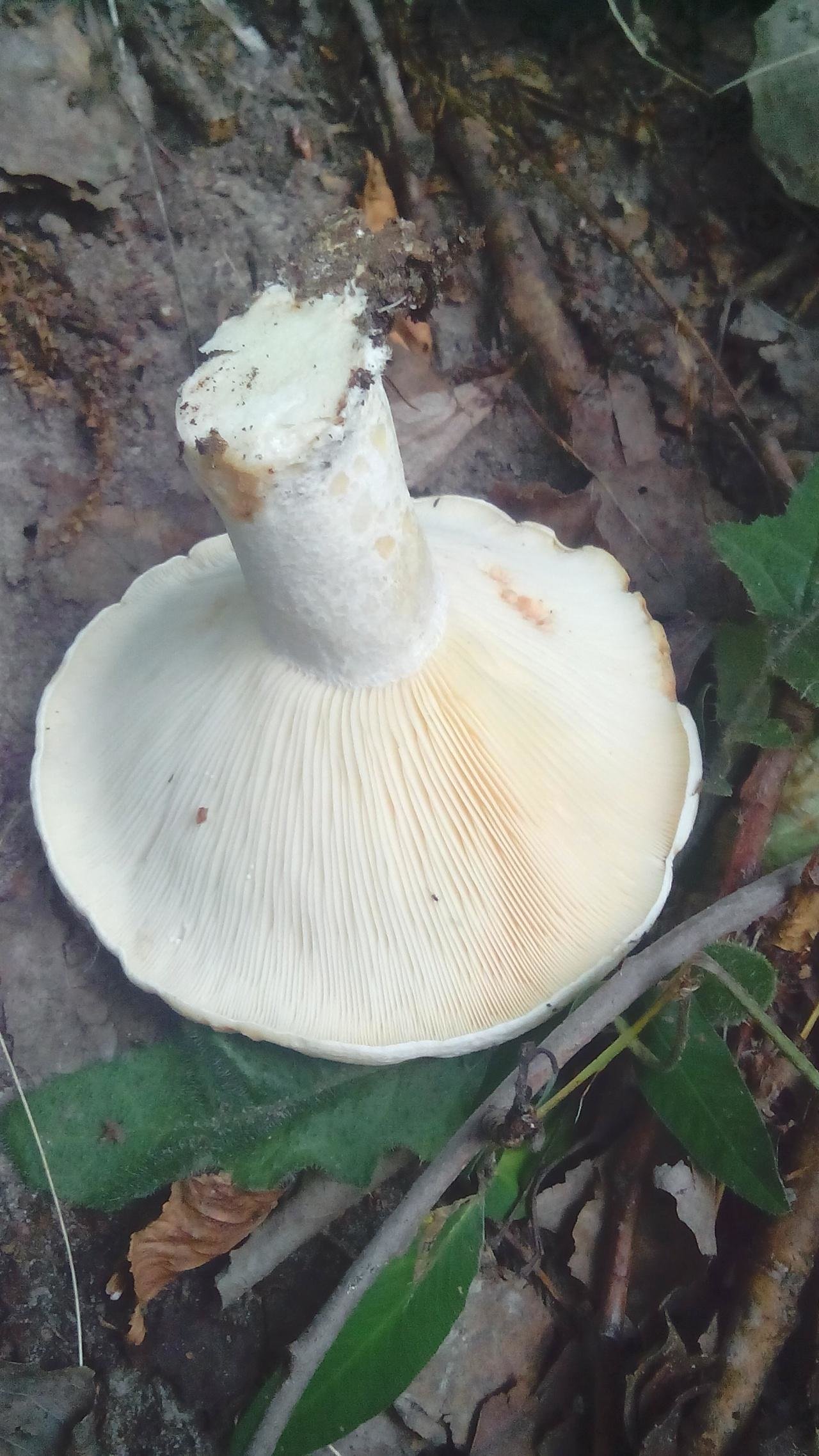
- the cap is white or with a cream shade, with a diameter of 5 to 20 cm. In the center it is covered with reddish spots and cracks. In young specimens, it has a slightly convex shape with tucked edges, later it becomes funnel-shaped, wavy along the edge. The surface is matte, smooth or slightly velvety;
- often located narrow plates are whitish at first, later cream. Descend to the leg, sometimes bifurcate;
- spores are whitish;
- the leg is white and dense, tapering towards the base, up to 8 cm high, up to 4 cm thick, solid, smooth or with slight wrinkles;
- the flesh is brittle, but at the same time dense, white in color. Pepper milk is considered conditionally edible because of the pronounced pungency of the white milky juice, acrid and thick. When in contact with air, it often acquires a greenish-olive or bluish tint.
Spreading
This milky grows both singly and in numerous groups, forming in rows and circles. Prefers sufficiently nutritious loams without moisture stagnation in deciduous, mixed, much less often coniferous forests. Refers to mycorrhizal - growing in symbiosis with tree roots.

Widely distributed in the temperate zone, tends to the northern, cool regions. There, the peppercorn appears in July and bears fruit until the first days of November. In the more southern parts of the range, this mushroom begins to grow a little later, from August.
Similar types and differences from them
Pepper is similar to its related milky mushrooms:
- aspen mushroom (Lactarius controversus). Its characteristic feature is orange-pink plates. The leg is grayish or pinkish in color.
- The violin (Lactarius vellereus), which is distinguished by the pile on the stem and cap, as well as more sparsely spaced plates.
- The parchment lump (Lactarius pergamenus) has a relatively elongated stem and wrinkled cap.
- Glaucous Milk (Lactarius glaucescens). Its description is close to the species characteristics of pepper, but the milky juice of this fungus, initially white, becomes gray-greenish when dried, and turns yellow under the influence of a KOH solution.
Cooking use

According to its taste characteristics, pepper milk is referred to the fourth category of nutritional value. Its preparation includes the obligatory soaking. This procedure will remove the excess pungency of the milky juice. This is followed by salting. A month later, the pepper milk mushrooms prepared in this way are ready for use.
Application
Sometimes these mushrooms are dried, ground into powder, and then used as a hot seasoning, which works as well as selected chili peppers.
In addition, pepper milk mushrooms suppress the development of Koch's bacillus, the causative agent of tuberculosis, and folk healers have long used these mushrooms, frying them, to heal kidney and cholelithiasis.
Since ancient times, milky mushrooms have been able to harvest and use them correctly in the Slavic lands. Pepper milk, which is not known in the West, or is classified as inedible, can also be salted for future use, used as a spicy seasoning, and even used as a medicine.
Types of edible milk mushrooms and their description with photos
The main edible species of milkmen:
- The real one, it is also white, has a snow-white cap of a typical shape for milk mushrooms, a short hollow leg and a pulp with a pleasant aroma, which turns yellow at the place of the break. Grows in groups. Fruiting period July-September. Real milk
- Yellow or yellow crow flies - this species is distinguished by its golden-colored hat, which often has small scales on the surface. The leg is small in size and dense in structure, the flesh is white, yellower when pressed. The plates have brown spots. Collection time July - early October. Milk yellow
- Bitter mushroom has a brown or reddish cap, concave in shape and small in diameter. The stem is cylindrical and thinner than other species. The pulp is brittle, and the milky juice is odorless, bitter in taste. Prefers acidic soils, grows in July-October. Bitter milk
- The red-brown appearance is distinguished by a large brown hat with a diameter of up to 20 cm, the edges of which are bent inward. The leg is velvety and strong, matching the color of the cap. The plates are light, slightly pinkish, darken when pressed. The pulp has an interesting aroma, similar to crab meat, it tastes sweet. It grows from early August to October. Milk red-brown
Characteristic features of conditionally edible milk mushrooms:
- Black mushroom or nigella got this name for the color of its cap. Its shape is rounded-funnel-shaped, with a diameter of 7 to 20 cm. The leg is narrowed at the bottom, smooth structure, up to 3 cm in diameter, low and dense. The plates are creamy in color, and the pulp secretes bitter juice, because of it, black milk mushrooms fell into the category of conditionally edible. It grows from July to October, but it can also occur after the first frost. Black milk
- The oak mushroom has a brown or reddish cap color, a small diameter and a solid cylindrical leg up to 7 cm high. The pulp is white and gives off a pleasant aroma. Harvested from July to September, mainly in deciduous forests. Oak lump
- Camphor mushroom with a matte brown cap, the stem is low and dense. The plates are small and frequent, and the flesh is of the same color as the cap; when broken, it emits the smell of camphor. Prefers acidic soils and grows in groups. Camphor milky
- Pepper milk is different in that the cap has a typical streaky shape of white or milky color, the shade is darker closer to the center. Dense and widened at the bottom, the leg reaches 10 cm. The milky juice is thick, and the pulp is sharp and bitter. The mushroom can be used as a seasoning dried. Pepper milk
- The purple mushroom got its name from the fact that the cap changes color to purple when pressed. The flesh is firm and fleshy, creamy in color, which becomes bluish when cut. Collect from August to October. Blue breast
Evaluation of the taste of peppermint milkers
Because of the bitter pulp, pepper mushrooms are not popular with mushroom pickers, they consider these mushrooms inedible. For the same reason, fruit bodies practically do not infect worms and various forest insects. But these milk mushrooms are quite edible.

Pepper milk mushrooms taste strikingly different from other milk mushrooms. According to their taste, they are referred to the 4th category. Young fruiting bodies are not as bitter as old ones, so it is recommended to collect only young mushrooms. Experienced mushroom pickers know that the taste of peppermint milkers depends on how they are prepared.
To remove the bitterness from the peppers, they are soaked for two days. After they are boiled for 20 minutes. In this case, the bitterness is completely gone. After salting, the lactarius becomes suitable for eating after a month. In some places, pepper mushrooms are dried and then ground into powder. This pungent powder is used in place of pepper.
The usefulness of pepper mushrooms
Pepper has been known to people for a long time. In China, these mushrooms are used to relax muscles. In Russia, the caustic juice of pepper mushrooms got rid of warts. They were also used to treat gallstone disease. It is believed that the lactarius peppers destroy the tubercle bacillus, but there has been no scientific research on this issue, and there is no information about the healing of tuberculosis with the help of these mushrooms.

Poisonous counterparts of the Pepper Milkers
Pepper millers bear a resemblance to a violin. The violin is also not poisonous, it is simply inedible, and there are no real poisonous counterparts in peppercorns.
Other milkmen
The miller is faded, it is also sluggish - a conditionally edible mushroom. The hat is thin fleshy. The color of the cap is wine-brown or gray-brown; when it dries, the cap brightens noticeably. The leg is pale brown, tapering towards the base. The pulp is fragile, its taste is spicy. Milky white juice is released from the pulp, burning in taste.
Faded millers are numerous in North America and Eurasia. These mushrooms are found in large groups, often. They settle in deciduous or mixed forests, next to birches.
The blue miller is an edible member of the genus. The shape of the cap is convex or funnel-shaped. Her color is blue.

The surface of the caps of young specimens is sticky. The leg is of medium length, thick, cylindrical in shape, also sticky in youth. The pulp is bluish in color, in the air it appears greenish. Milky juice is acrid, blue, odorless.
Blue lactaciers grow in Central and North America, in addition, they are found in Asia. Blue millers form mycorrhiza with deciduous and evergreen tree species.
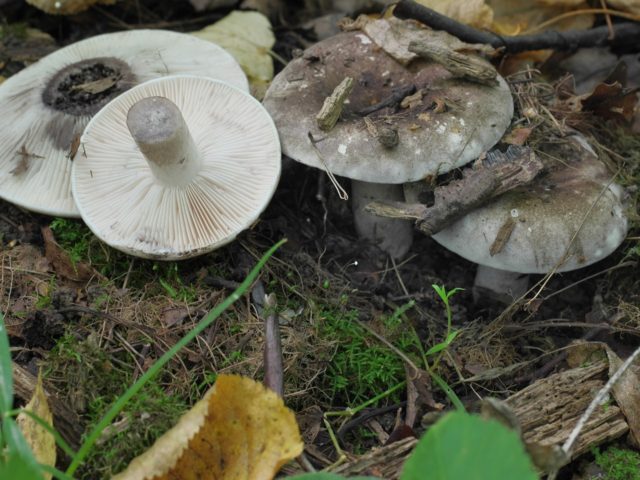
Black milk mushroom: photo and description
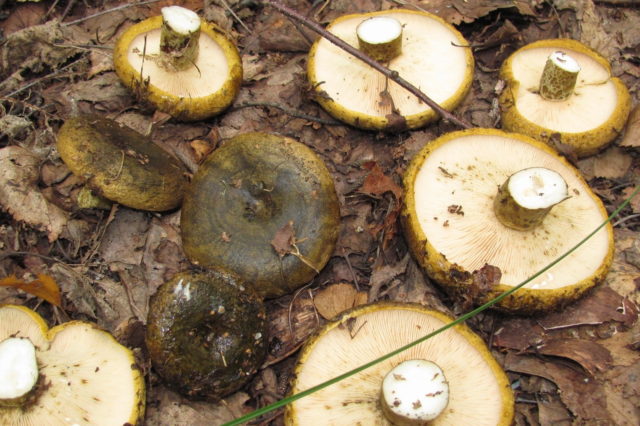

An experienced mushroom picker knows all the edible and poisonous mushrooms in their region. And beginners will need time to correctly recognize which mycelium he has come across. This is a conditionally edible mushroom belonging to the genus Millechnik and the russula family. Also received the names "Chernushka", "Gypsy".

There are several similar species in the forests:
Mushrooms that look like black milk mushrooms
The Millennium family includes several types of mushrooms, all of them differ in color, so it is very difficult to confuse them with each other. The most similar to him is the black one. But he's not that dark
It is important to distinguish a black milk mushroom from a lactarius or other double, or a false mushroom, so as not to collect excess and not put health at risk

The following similar mushrooms can be found in the forest:
How to distinguish black milk from other mushrooms
Mushroom pickers notice that poisonous mushrooms eventually mimic their edible counterparts.
Poisoning is becoming more frequent, so it is very important to be able to recognize a poisonous mushroom. Most often, mushroom pickers try to distinguish between a black mushroom or a pig, a false brother

There are three ways to identify an edible mushroom:
- They only grow straight.
- The plates are evenly attached to the leg.
- Plates are only light in color.
The most difficult thing is to distinguish it from its poisonous counterparts.Dangerous mushrooms look like this:
Where black milk mushrooms grow
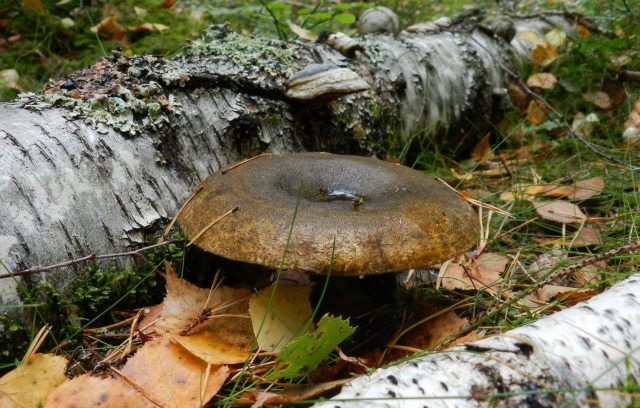

The mycelium lives in symbiosis with the roots of birches and other higher plants. They prefer to grow in birch groves, spruce forests and mixed forests. It is not easy to find black milk mushrooms from the photo in the forest. They settle in large groups on a bed of grass or moss. They are found near old forest roads, in clearings, mountain slopes. Choose well-lit places.
They blend well with the environment. They can be covered from above with fallen leaves, earth and grass.
Black Burger Harvesting Season
The first mushrooms are picked in July. And the last ones - in mid-October, when there will be first frosts. They grow most massively in the period from August to September.
Collect black milk after light rains. At other times, old wormy mushrooms can be found. After heavy rain, it is also not recommended to collect them, as they are less tasty. They put them in a basket, carefully cutting off so as not to damage the mycelium. Do not ram, as they are brittle and fragile.
Edible black lump or not
Research by scientists has determined that there is non-catorin in the composition - this is a toxic mutagen. Its concentration in the raw product is up to 20 mg / kg. Heat treatment destroys the substance by 75%. For this reason, there is a question: is the black lump edible. Some sources claim that it should not be eaten.
There are no signs of poisoning. It is believed that non-catorin accumulates in the body and can last for a long time. However, there are studies that did not confirm the mutagenicity of non-catorin and did not recognize this substance as harmful.
Characteristic features of mushrooms
Milk mushrooms are called different species of the genus Mlechnik; sometimes they also include several species of russula. Lactarius is the Latin name for this species, which in translation means "milk", "giving milk".
There are both edible and inedible fruiting bodies of this genus. The Slavic word "lump" means "hill, heap" and gives an explanation of how mushrooms prefer to grow. White and black milk mushrooms are considered to be the best in terms of their gastronomic value.
Appearance
Regardless of their color and type, mushrooms have similar external signs. A wide-brimmed concave hat with curved edges is a distinctive feature of the weight. The color gamut is quite wide - from white to black. The legs look dense and reach a height of up to 10 cm.
Structure and species differences
Depending on the place of growth and soil, millers have different colors, but in general, all mushrooms are similar in their morphology.
Description of the main characteristics of the mushrooms:
- The cap is round in shape, reaches 20 cm in diameter, in some fruits - 28 cm. It is usually convex in young representatives of the species and becomes chalk in adults. The hat has shaggy edges, rolled down. At high humidity, the surface becomes slimy. The structure of the cap is fleshy. Its color ranges from white, gray, shades of yellow to dark gray and brown (depending on the variety).
- The leg is short, reaches 10-12 cm, cylindrical, dense and thick, without pimples or other formations on it. The shade of the leg directly depends on the color of the mushroom cap and is as similar to it as possible.
- The plates are rather small and frequent, light, milky and pale brown in color.
- The pulp of the fruit has a light shade, which becomes yellow when pressed and interacted with air. Milk juice flows out of it, which has a pleasant mushroom aroma. The pulp is firm and fleshy. The red-brown and bitter milk jug has a brittle and friable flesh that distinguishes them from other species.
Mushrooms always grow in clusters and this makes it easier to find them in the forest.
Place of distribution
Areola of growth of milkmen - countries with temperate climates of the Eurasian continent, grow on the territory of Russia almost everywhere, while different varieties of mushrooms prefer certain zones and areas:
- white milk mushroom - the Volga region, Siberia and the Urals;
- bitter - northern Europe and Asia;
- red-brown - in almost every country in Europe, Asia with a temperate climate;
- yellow - many European countries, mainly northern ones;
- poplar - a rare species today, grows in the mouth of the Volga;
- black - the Urals, Siberia and other territories of Russia.
Since milkmen prefer different types of forests and soils, they can often be found
Beginners should pay attention to the fact that the fruits are hidden in leaves, moss and needles. The short leg allows them to be almost invisible, so you need to bend down and look more closely
All species love fairly light glades, hillocks and grow in middle-aged forests with low grass cover.
You may be interested in:
How to recognize a mushroom with a cap and a white leg: names and types (32 photos) Mushrooms are a wonderful culinary product that is successfully used to prepare various dishes. The most ... Read more ...
Eating
For many years, on the territory of Russia, it was the milk mushroom that was the main industrial type of representatives of their kingdom, it was appreciated and used both for personal needs and for sale.
Note!
It should be noted that not all species are edible, but there are no poisonous ones among them.
Practical use
Pepper milk is used in cooking and medicine.
Cooking
The mushroom belongs to the 4th category of gastronomic value. Due to the specific pungent-bitter taste, pepper milk is considered inedible or conditionally edible, but only after prolonged preliminary soaking, prolonged heat exposure and salting, which allows you to remove the stinging taste of milky juice.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
Although pepper milk mushrooms are not in great demand among Russian fans of mushroom dishes because of their specific taste, however, everyone who cooked them is sure that properly processed mushrooms can compete in taste with species that have a higher gastronomic characteristic.
The collected pepper mushrooms must be soaked in cold water for 1-2 hours immediately upon returning from the forest (this will make them more resistant to mechanical stress) and you can process them thoroughly and without problems. The processing is as follows:
- Remove the skin from the cap with a knife.
- Remove the plates (they do this for large mushrooms, but do not touch the small ones).
- Cut off the leg, leaving the "stump" flush with the cap and remove the outer layer from it. By the way. If the leg is "gnawed" by slugs, it is removed completely.
After that, the mushrooms are thoroughly washed and sent for a long soaking - 3 or more days. Having folded it into a deep dish, place the container in a cold place, fill it with water. The water is changed several times a day to completely remove the bitterness. The peppermill is then ready to use.
Advice. Wear rubber gloves to prevent the milky juice from staining your hands and causing irritation.
In some cases, lactarius is dried by grinding into a powdery mixture and used as a seasoning instead of hot pepper in cooking.
Medicine
Pepper milk is used for medicinal purposes. It has a neutralizing and destructive effect on the tubercle bacillus (Koch's bacillus). Traditional healing uses peppermint to treat kidney and cholelithiasis. Mushroom pulp is pre-fried.
Description of the mushroom peppercorn
The pepperoni is a member of the genus of lamellar mushrooms from the russula family of the genus Agaricomycetes. It is conditionally edible.
Description of the mushroom peppercorn
Botanical characteristic
According to the description. the peppercorn has a mushroom cap in diameter from 6 to 30 cm.It changes appearance as the mushroom matures:
- at the initial stage in young specimens it is convex, the cap edges are bent towards the mushroom leg,
- over time, it becomes funnel-shaped, the edges straighten and become wavy.
The surface is in shades of white, sometimes milky, matte, smooth to the touch or velvety. The central part of the mushroom cap is noticeably darker than the edges. Under mechanical stress, the cap cracks, and it is covered with specks of a yellow-brown hue.
Fungal plates are often planted, narrow in width, descend along the mushroom stem, in some cases split in two. They have multiple short plates. The initial white color of the plates changes over time to milky cream.
The mushroom leg grows up to 4-8 cm in length, up to 1.2-3 cm in diameter. It is closer to white in color. The structure is solid and dense, it can be smooth or slightly wrinkled. It narrows closer to the base.
The mushroom pulp is whitish, dense, but brittle.
Similar varieties
Pepper milkman has varieties similar in appearance, including:
- violin, characterized by the pubescent surface of the cap and leg, as well as less often planted plates,
- a bluish lump, the milky juice of which, during the drying process, changes color from white to gray-green,
- a parchment milkman with a mushroom leg of a greater height and a wrinkled cap.
Growing geography
Mushrooms begin to grow in the second half of summer.
The most preferred places for the growth of peppermint are damp shaded areas among deciduous trees, mixed forests. Less often, it can be found in the plantings of conifers. It is mycorrhizal and grows in symbiosis with tree roots.
Milk mushrooms grow both singly and in rows, or arrange colonies in the form of a circle. They love drained clay soil. They are common. The geography of distribution covers the regions of central Russia, less often this mushroom is found in the northern regions.
Cooking
The mushroom belongs to the 4th category of gastronomic value. Due to the specific pungent-bitter taste, pepper milk is considered inedible or conditionally edible after prolonged preliminary soaking, prolonged heat exposure and salting, which allows you to remove the burning taste of milky juice.
In some cases, lactarius is dried by grinding into a powdery mixture and used as a seasoning instead of hot pepper in cooking.
Medicine
Milk is used for medicinal purposes. It has a neutralizing and destructive effect on Koch's tubercle bacillus. Traditional healing uses peppermint to treat kidney and cholelithiasis. Mushroom pulp is pre-fried.
Conclusion
A member of the russula family from the genus of the lactarius, the peppermint, according to the description, is a conditionally edible mushroom. It is limited for food use due to its specific pungent bitter taste. Its use in cooking is permissible in the form of a dried spice substitute. It is also used for medical purposes in the treatment of tuberculosis. It is used in folk healing to treat certain diseases.