Pepper Milk (Lactarius piperatus)
Synonyms:
Lactifluus piperatus
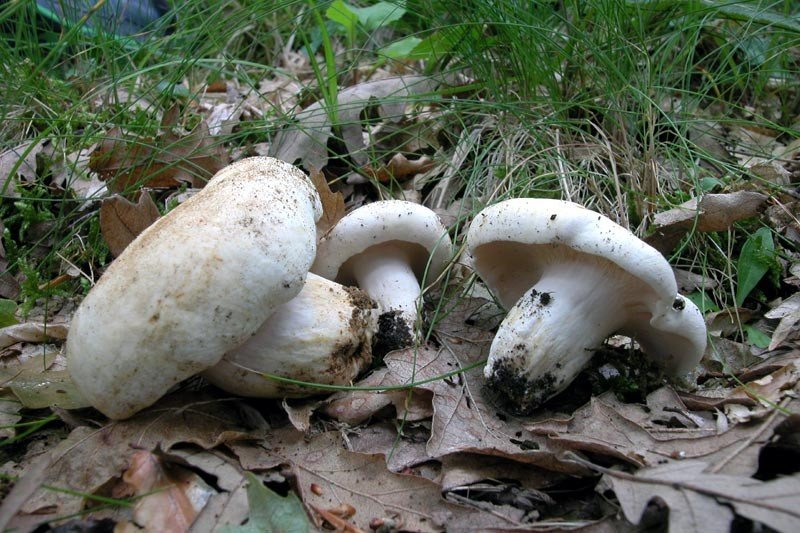

Pepper milk mushroom (lat.Lactarius piperatus) is a mushroom of the genus Millechnik (lat.Lactarius) of the family
Description
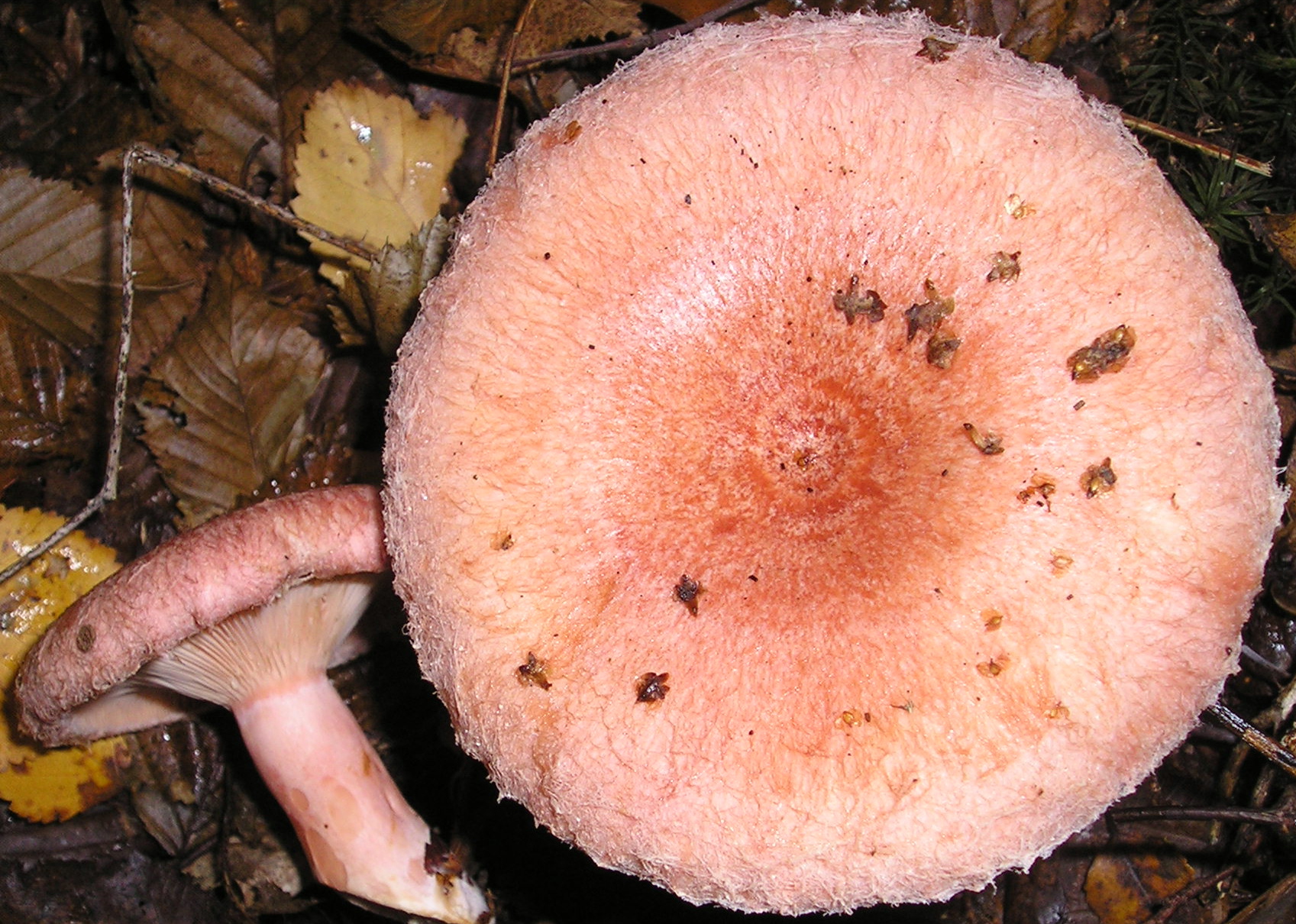
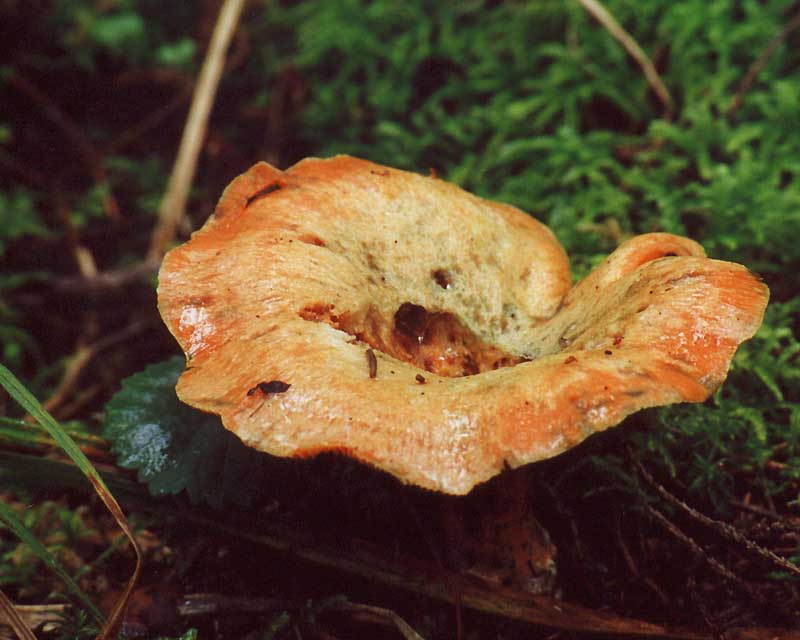
The cap ∅ 6-18 cm, at first slightly convex, then more and more funnel-shaped, in young specimens with bent edges, which then straighten and become wavy. The skin is creamy white, matte, often covered with reddish spots and cracks in the central part of the cap, smooth or slightly velvety.
The pulp is white, dense, brittle, very sharp in taste. When cut, it releases a caustic milky sap of white color, slightly yellowing or does not change color upon drying. The FeSO4 solution stains the pulp in a creamy pink color; under the action of alkalis (KOH), the color does not change.
Leg 4-8 cm in height, ∅ 1.2-3 cm, white, solid, very dense and with a narrowing at the base, its surface is smooth, slightly wrinkled.
The plates are narrow, frequent, descending along the pedicle, sometimes bifurcated, there are many short plates.
Spore powder white, spores 8.5 × 6.5 μm, ornamented, almost rounded, amyloid.
Variability
The color of the cap is completely white or creamy. The plates are first white, then cream. The leg is white, with time it often becomes covered with ocher spots.
Ecology and distribution
Peppermilk is a mycorrhizal forming agent with many trees. A common mushroom. Grows in rows or circles in damp and shaded deciduous and mixed forests, much less often in conifers. Prefers well-drained clay soils. Found in the middle lane, less common to the north.
The season is summer — autumn.
Similar species
- The violin (Lactarius vellereus) and the aspen milk mushroom (Lactarius controversus) are conditionally edible mushrooms with buffy plates.
- glaucous mushroom (Lactarius glaucescens) with white milky juice, when it dries, it becomes grayish-greenish. The milky juice of L. glaucescens turns yellow from a drop of KOH.
Nutritional quality
It is often considered inedible due to its very pungent taste, although it can be consumed as conditionally edible after careful processing to remove bitterness, it is only salted. Mushrooms can be eaten 1 month after pickling. It is also sometimes dried, ground into powder and used as a hot seasoning instead of pepper.
Healing properties
Peppermilk has a depressing effect on the tubercle bacillus. In folk medicine, this mushroom, slightly fried, was used to treat kidney stones. Pepper milk is also used in the treatment of cholelithiasis, blennorrhea, acute purulent conjunctivitis.
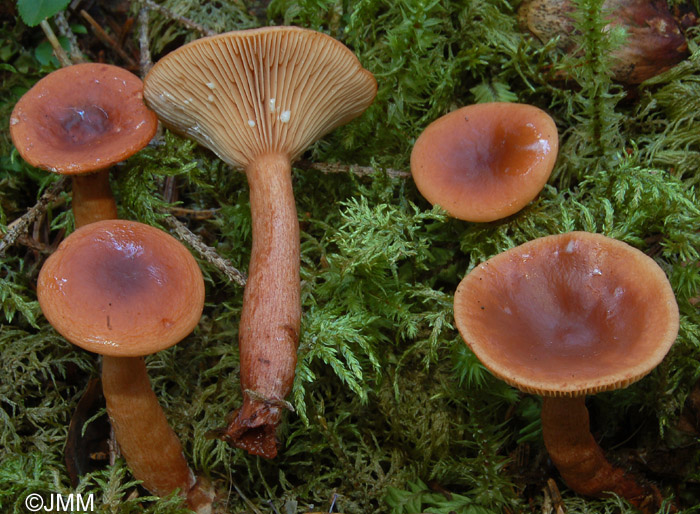
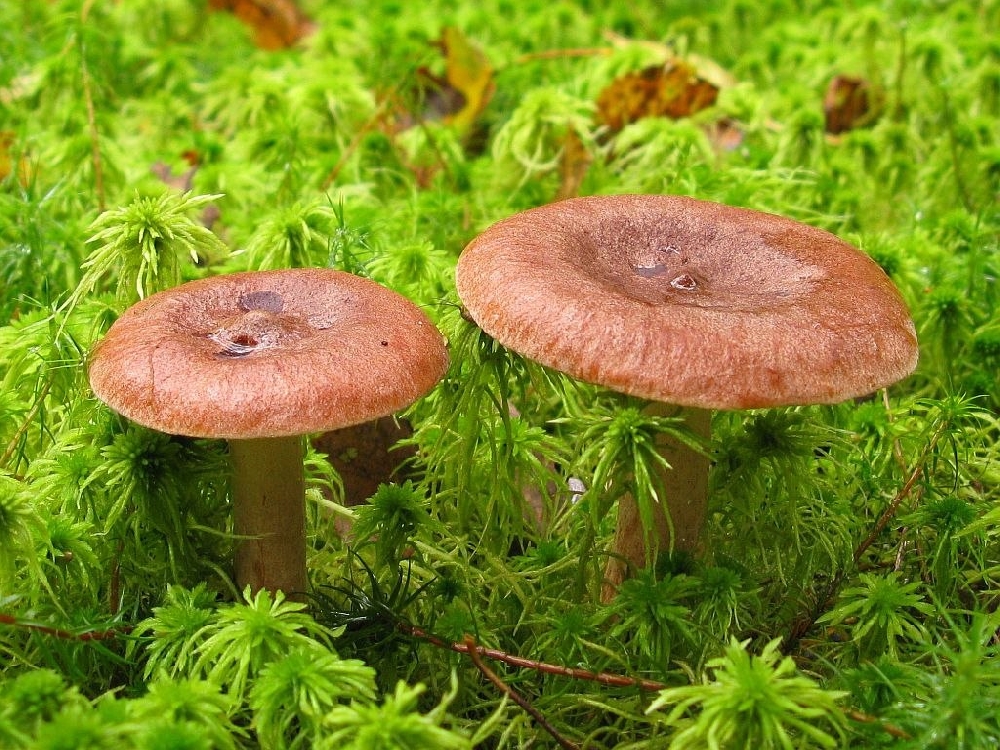
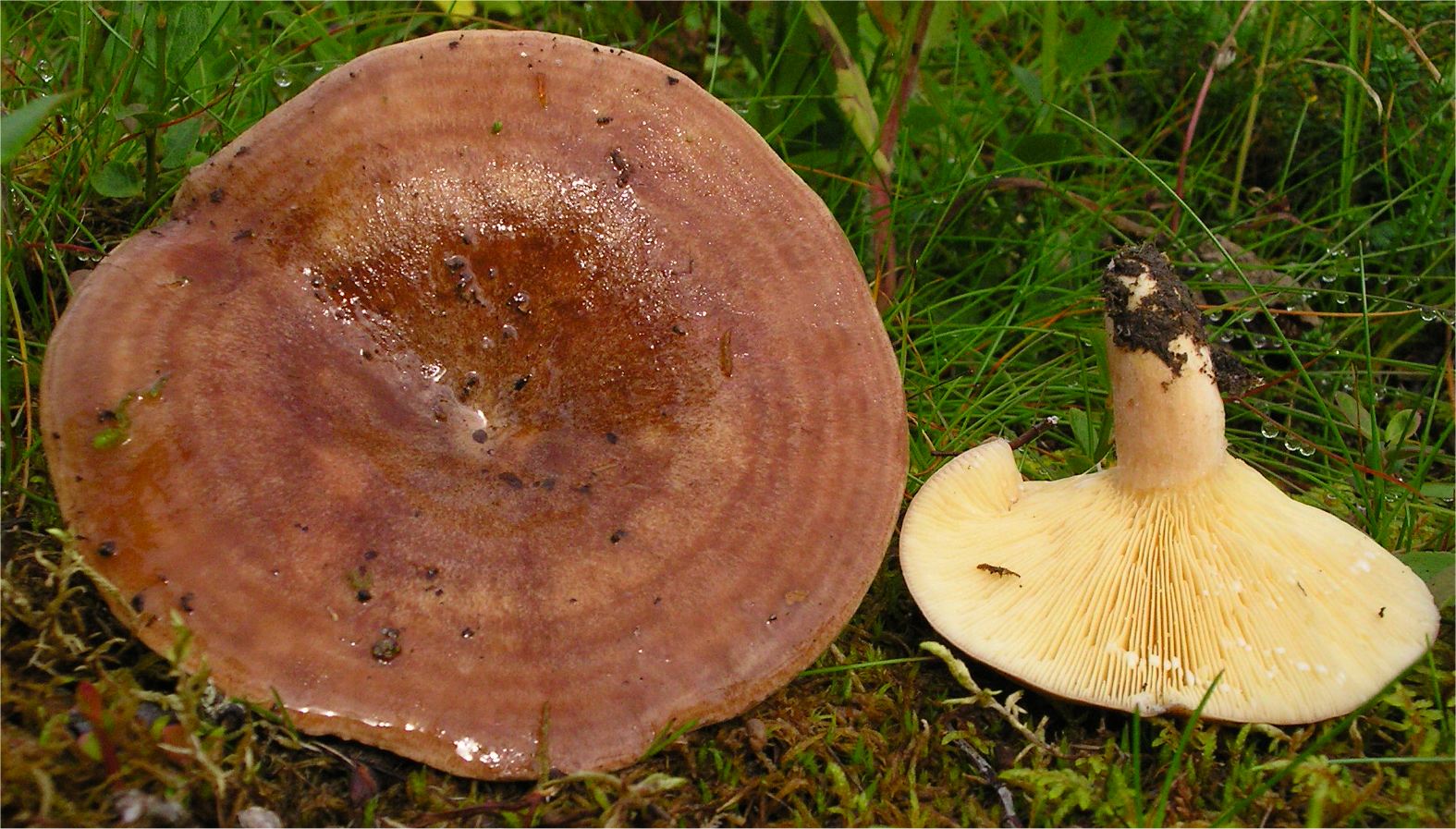
Red-brown Milk (Lactarius volemus)
Synonyms:
- Galorrheus volemus
- Lactifluus volemus
- Amanita lactiflua
- Lactarius lactifluus
- Lactifluus oedematopus
- Lactarius oedematopus
- Lactarius ichoratus
- Galorrheus ichoratus
- Lactifluus ichoratus
- Lactarius testaceus
- Millechnik is the best (by the way, the official Russian-language mycological name)
- Podoreshnik (Belarusian - Padareshnik)
Lactarius volemus (Fr.) Fr., Epicr. syst. mycol. (Upsaliae): 344 (1838)
Description
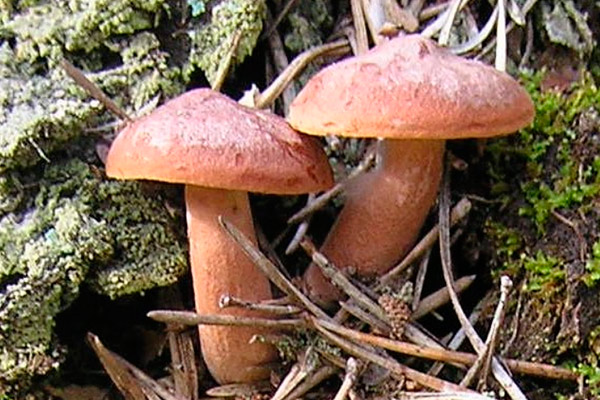
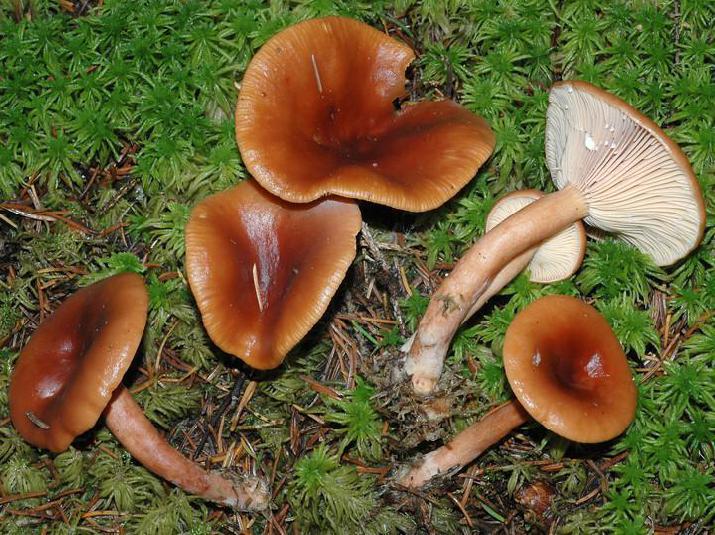
A hat with a diameter of 5-17 (up to 16) cm, convex in youth, then prostrate, possibly pressed in the center, and even up to concave. The edge of the cap is straight, thin, sharp, first tucked up, then straightened and even raised. The color is reddish-brown, brownish-brown, in rare cases, rusty or light buffy. The surface is velvety at first, then smooth and dry. Often cracked, especially in dry conditions. There is no zonal coloration.
Flesh: White, yellowish, very fleshy and firm. The smell is described in various ways, mainly as a herring (trimethylamine) smell that increases with age, but there are more interesting associations, for example with pear flowers, or not at all. The taste is soft, pleasant, sweetish.
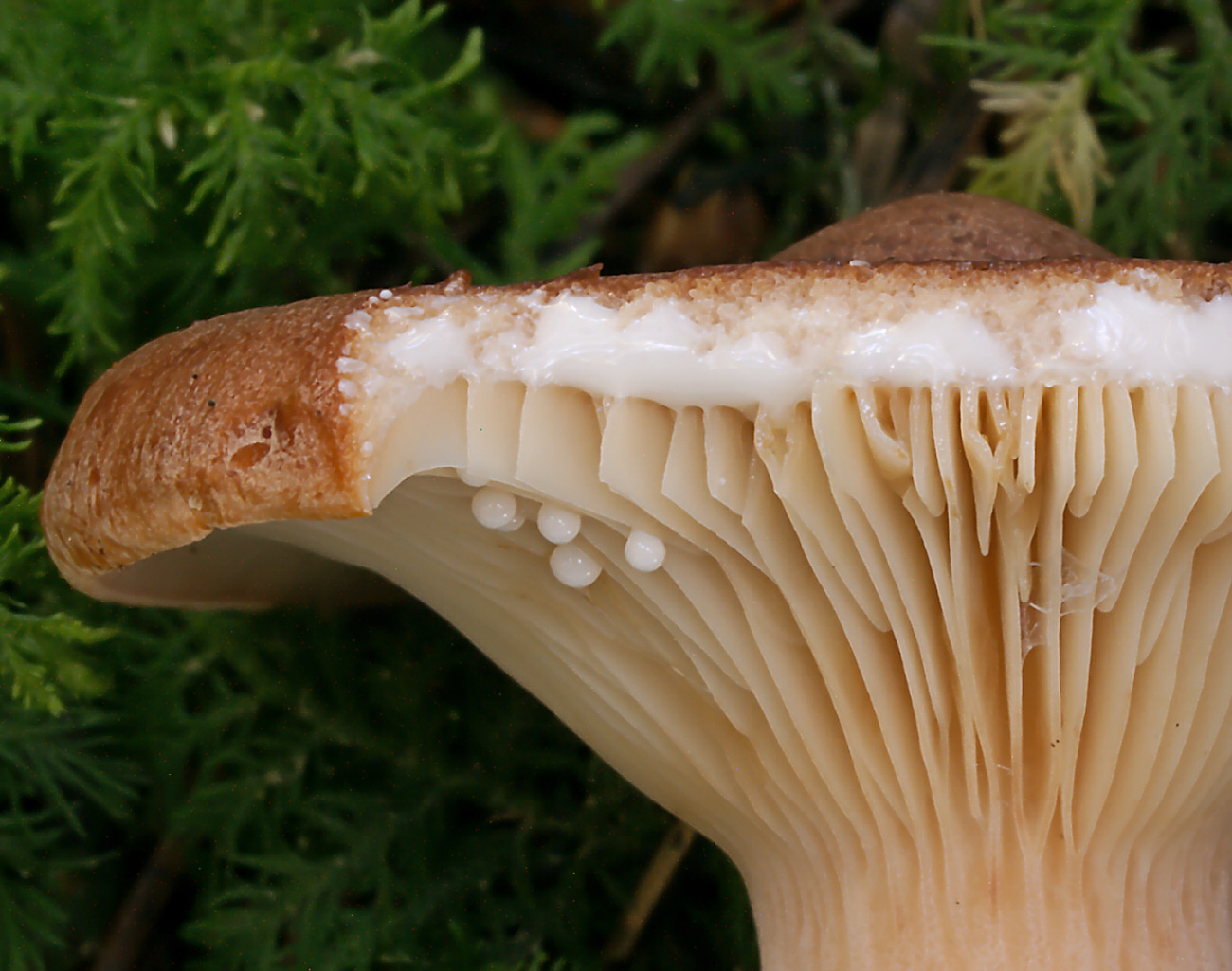
The plates are frequent, from adherent to weakly descending, creamy or warm skin shades, often forked at the leg. There are shortened plates (plates).
Milky sap is abundant, white, turning brown and thickening in the air. For this reason, this type of lactarius turns brown and everything else if damaged - pulp, plates.
The leg is 5-8 (up to 10) cm high, (1) 1.5-3 cm in diameter, hard, often full, the color of the cap, but slightly paler, smooth, may be covered with fine pubescence, which looks like frostiness, but not to the touch felt. Often tapered to the bottom.
The spore powder is white. The spores are close to spherical, according to the data 8.5-9 x 8 µm, 9-11 x 8.5-10.5 µm each. The ornamentation is ridged, up to 0.5 µm in height, forming an almost complete network.
Habitat
Occurs from July to October. One of the earliest milkmen. Grows in deciduous, mixed and spruce forests (in general, in all forests). According to the data, it forms mycorrhiza with oak (Quercus L.), common hazel (Corylus avellana L.) and spruce (Picea A. Dietr.).
Similar species
Given the "power" of this mushroom and the abundant brownish sweetish milky juice, perhaps, it has no similar species. The most similar lactic to him, perhaps, is the hygrophoroid lactarius - Lactarius hygrophoroides, but it is easily distinguished by non-brown milky juice and rare plates. Quite conditionally, rubella (Lactarius subdulcis) can be attributed to similar species, but it is thin-fleshed and slender. The same applies to the orange lactarius (Lactarius aurantiacus = L. mitissimus), it is not only small and thin, but also late, does not overlap in terms, although it grows in exactly the same biotopes with spruce.
Edibility
An edible mushroom that can be eaten raw. It is good in raw salted or pickled form, without any heat treatment. I don't like it in another form because of the "wooden" pulp, although, they say, mushroom caviar is good from it. I hunt him specifically and purposefully, for the sake of raw salting.
Literature Used 1) Verbeken, A. & Vesterholt, J. 2008. Lactarius. - In: Knudsen, H. & Vesterholt, J. (eds.): Funga Nordica, 82-107.2) Flora of Belarus. Mushrooms. In 7 volumes. Volume 1. O.S. Gapienko, Ya.A. Shaporova, 2012, Boletales. Amanitales. Russulales.
Video about the miller mushroom:
External description of the mushroom
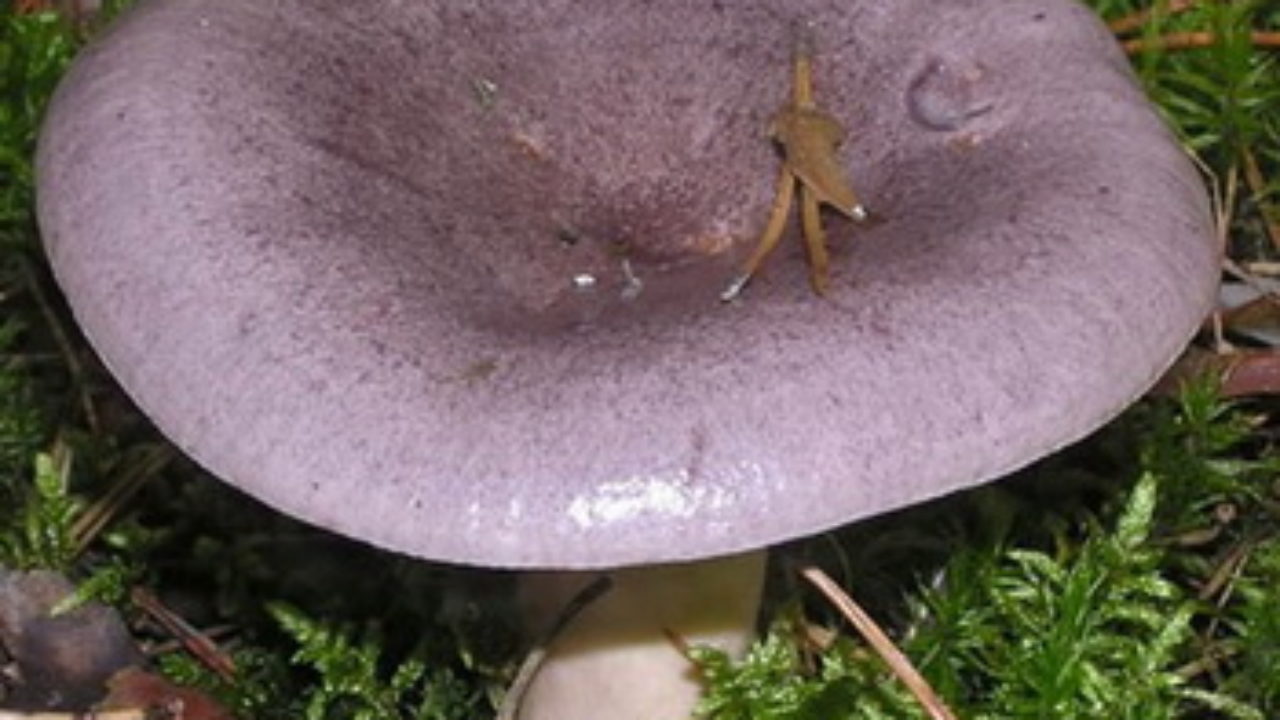
The fruiting body of a wet lactarius consists of a stem and a cap. The height of the leg is 4-7 cm, and the thickness is 1-2 cm. Its shape is cylindrical, slightly widening at the base. The structure at the foot is strong and durable, and the surface is sticky.
It is very rare to meet this type of mushroom, a distinctive feature can be called the color of the cap, which varies from grayish to gray-violet. Its diameter is 4-8 cm, in young mushrooms it has a convex shape, which becomes prostrate over time. On the surface of the cap of old, mature mushrooms, there is a depression, as well as a wide flattened tubercle. The edges of the cap are bordered with small villi and bent. From above, the cap is covered with a grayish-steel skin, with a slight shade of purple. It is wet, sticky and smooth to the touch. These characteristics are especially common in humid climates. A vaguely expressed zoning sometimes appears on the surface of the cap.
The hymenophore of the fungus is represented by plates containing white spore powder. The plates themselves have a small width, are often located, slightly descend along the stem, initially have a white color, but turn yellow over time. When pressed and damaged, purple spots appear on the plates. The milky juice of the fungus is characterized by a white color, but under the influence of air it acquires a purple hue, its release is very abundant.
The structure of the mushroom pulp is spongy and tender. It does not have a characteristic and pungent smell, but the taste of the pulp is distinguished by its sharpness. In color, the pulp of the wet lactarius is white or slightly yellowish; in case of damage to the structure of the fruiting body, a shade of purple is mixed with the main color.
Cracker doubles
Bitter has a lot of doubles. In order to distinguish it from them, you need to know the structural features of each. Fortunately, a bitter mushroom is a mushroom that does not have poisonous counterparts, which means you are safe. But still, it is necessary to distinguish it from other inhabitants of the forest. Let's find out who the bitter looks like and with whom it can still be confused.
Camphor milk
Bitter is very often confused with camphor mushrooms, largely because these two mushrooms have almost identical colors. However, there is still a significant difference. The lump has a darker cap, and at the same time, more slimy. If there is not much mucus on the bitter, then there is an excess of it on the pile.Therefore, many unconsciously confuse these mushrooms, and then wonder why this mushroom has become so peppery.
In order to distinguish between these mushrooms, it is enough to look at their pulp. The pulp has a light shade in the milkweed, and in the bitter, when interacting with oxygen, it becomes dark. This is the main difference.
Swamp lump
The swamp lump also partially repeats the bitter. It is believed that the swamp mushroom is very similar to this mushroom, but the difference is noticeable "on the face". Swamp milk mushroom has a pronounced strong aroma, for which it actually deserves its name. In addition, this mushroom is very slimy, and its cap also has a green tint. Therefore, only very inattentive people can confuse it with a bitter taste. As for the taste, they are identical.
Salting bitters at home
It is believed that bitter mushrooms are most delicious when salted. There are two basic options for salting these mushrooms, the so-called "cold" and "hot" methods.
Advice! For salting, it is best to choose young small bitters, which do not need to be cut into pieces.
It is believed that it is preferable to salt these mushrooms hot by boiling them in a brine with seasonings. In this case, they turn out to be elastic and break less.

To prepare such salting, you should take:
| Bitter milk mushrooms | 1 kg |
| Table salt | 2 tbsp. l. |
| Water | 1 l |
| Condiments (dill umbrellas, cloves of garlic, currant leaves, horseradish, cherry) | Taste |
- Place the peeled and soaked milk mushrooms in a saucepan, add water and boil for 10 minutes.
- Place the mushrooms in a colander and rinse immediately with clean cold water (this will make them crispy).
- Prepare brine from water and salt. Boil it, put the mushrooms in there and boil for about 15 minutes.
- Place some of the seasonings on the bottom of the prepared container (enamel pot or bucket). It is advisable to pre-pour greens for pickling with boiling water. Layer the mushrooms, alternating with dill and garlic.
- Pour with cooled brine, cover with a flat plate on top and press down with pressure.
- Put in a cold place for a couple of weeks. Having sustained this time, the mushrooms can be served to the table.
Cold salting of mushrooms of bitters implies a longer period during which the mushrooms must be kept.
For this dish you will need:
| Bitter milk mushrooms | 1 kg |
| Coarse salt (pour mushrooms) | 50 g |
| Table salt (for brine) | 60 g |
| Water (for brine) | 1 l |
| Seasonings (dill, garlic) | Taste |
- Prepare and soak the mushrooms, then rinse thoroughly with clean water and squeeze lightly.
- Put the bitters into prepared containers (jars) with the caps down, sprinkling each layer with salt and shifting with seasonings.
- After filling the jar, put the herbs and garlic on the very top. If there is not enough liquid from the mushrooms, additionally prepare the brine and add to the container.
- Install a wooden circle on top and put oppression. Place jars in a cellar or refrigerator.
- You can try ready-made salting in two months.

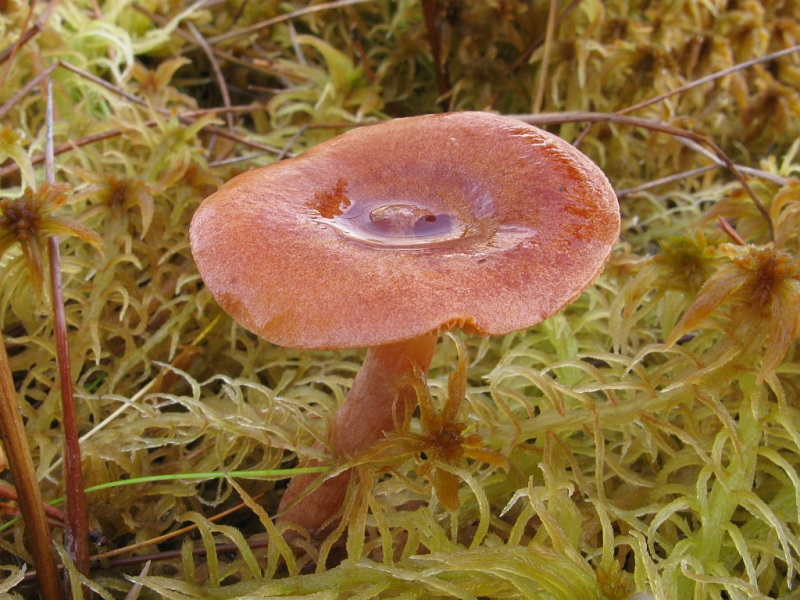
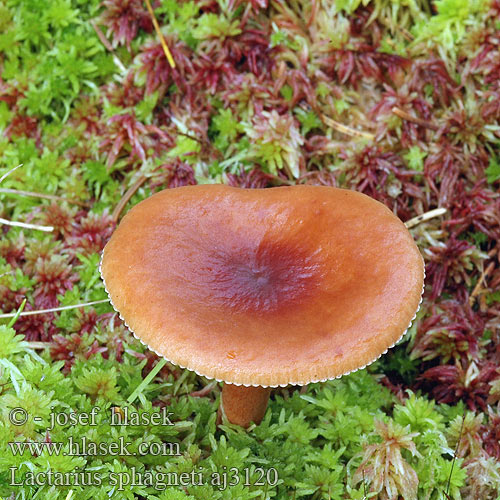
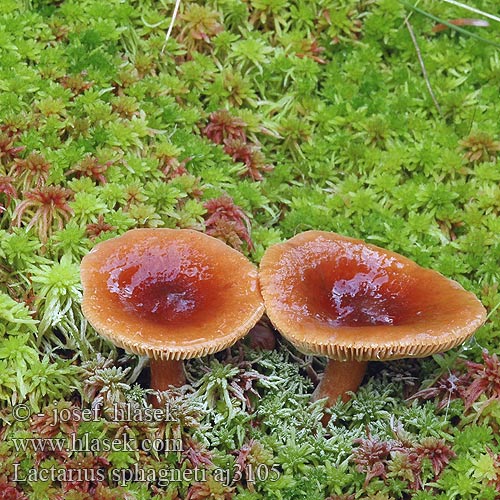
Marsh milk: photo and description of how to cook
| Name: | Swamp bush |
| Latin name: | Lactarius sphagneti |
| Type of: | Edible |
| Systematics: |
|
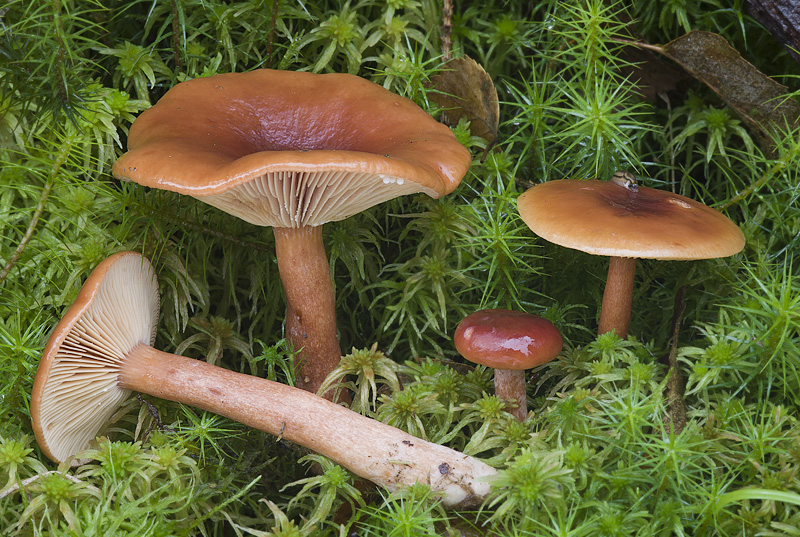
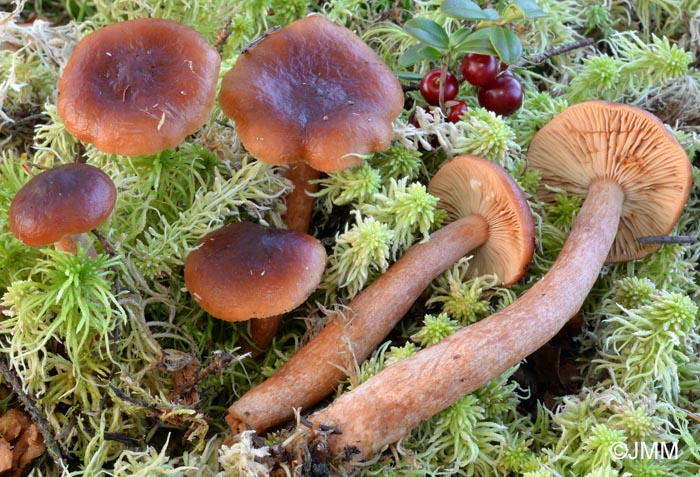
Swamp mushroom is an edible lamellar mushroom. Representative of the russula family, the genus Millechniki. Latin name: Lactarius sphagneti.

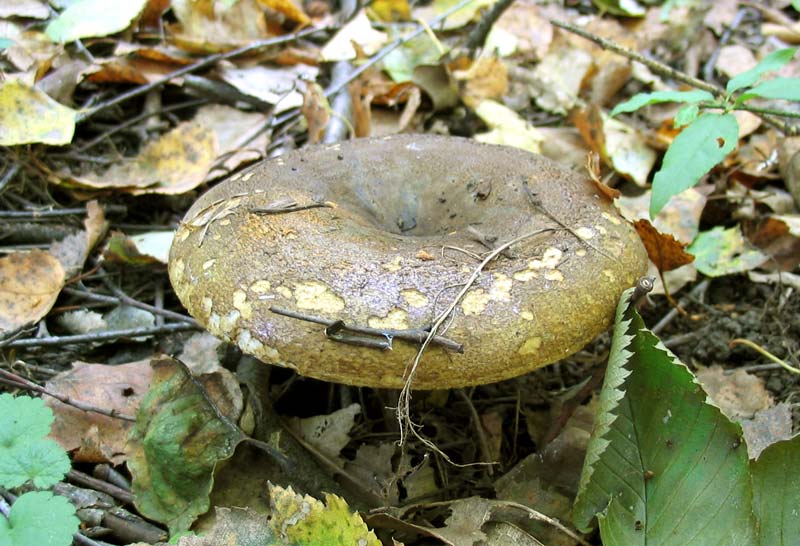
Description of the hat
Head width up to 55 mm. Appears convex, later opens, with a depression in the center, sometimes transforms into a funnel. Other characteristics:
- protruding tubercle in the center;
- in young specimens, the border is smooth, bent, and later drops;
- the skin is slightly wrinkled;
- chestnut color, brown-reddish to terracotta and ocher tone;
- with age, the top brightens.
Bottom narrow, densely spaced plates that descend to the leg. The lamellar layer and spore powder are reddish.
The swamp species has a creamy white flesh. Light brown under the skin, darker on the leg below. At the fracture, a whitish sap appears, which immediately darkens to yellow-gray.
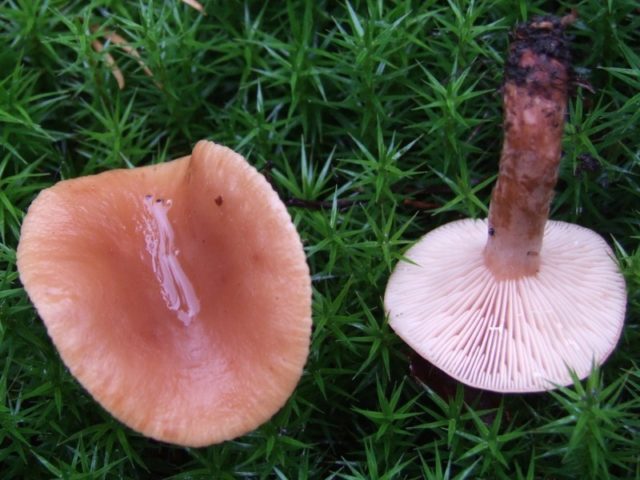

Leg description
Stem height up to 70 mm, width up to 10 mm, dense, hollow with age, pubescent near the ground. The surface color corresponds to the color of the cap or is lighter.
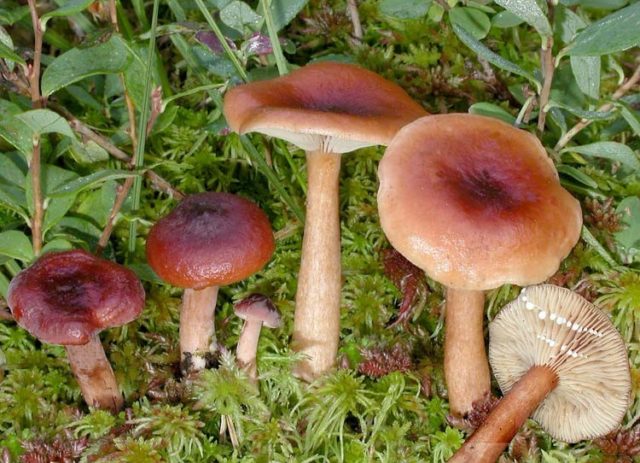

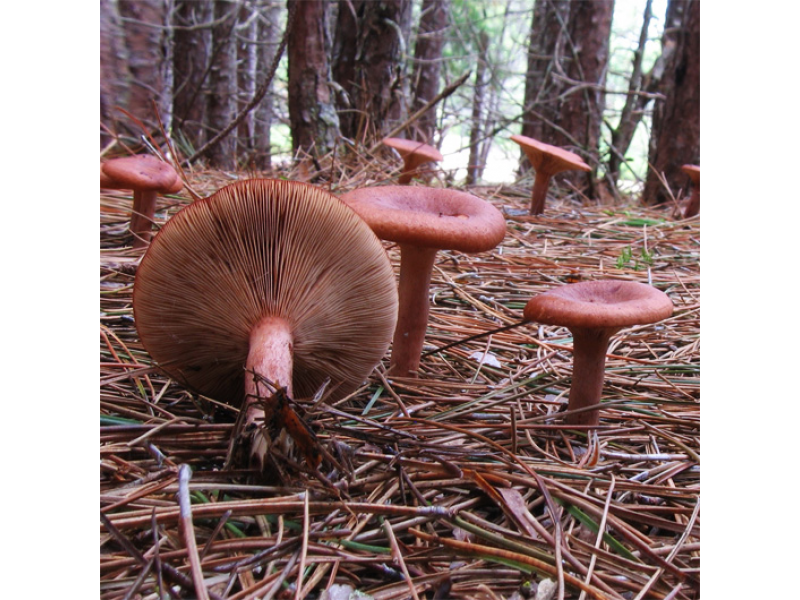
Where and how it grows
Marsh mushrooms grow in a forest zone of a temperate climate, in lowlands covered with moss, under birches, pines and lindens. The species is common in the Belarusian and Volga forests, in the Urals and in the West Siberian taiga. The mycelium is rarely seen, the family is large. Harvested from June or August to September-October, depending on the area.
How to cook swamp lump
The collected mushrooms are placed in water and soaked to extract the bitter juice for 6-60 hours. Then salted or pickled. Sometimes, after soaking, the fruit bodies are boiled for half an hour and salted hot or fried.
- the first water is poured out with bitterness, new is poured in and boiled;
- when soaking in the morning and evening, change the water;
- salted fruit bodies will be ready in 7 or 15-30 days, depending on the salt concentration.
Doubles and their differences
The conditionally edible papillary milk mushroom looks like a marsh lump, it is slightly larger, with a cap up to 90 mm. The skin color is brown, with an admixture of gray, bluish or purple tones. The height of the whitish leg is up to 75 mm. The species grows in forests on sandy soils.

The inedible double is the orange milk jug, which is considered poisonous by some scientists. The toxins are not strong enough to cause great harm to health, but they do upset the gastrointestinal tract. The cap of the lactarius is orange, 70 mm wide, young, convex, then depressed. The color of the smooth, slippery skin is orange. The leg is the same in tone. Millers grow in deciduous forests from the middle of summer.
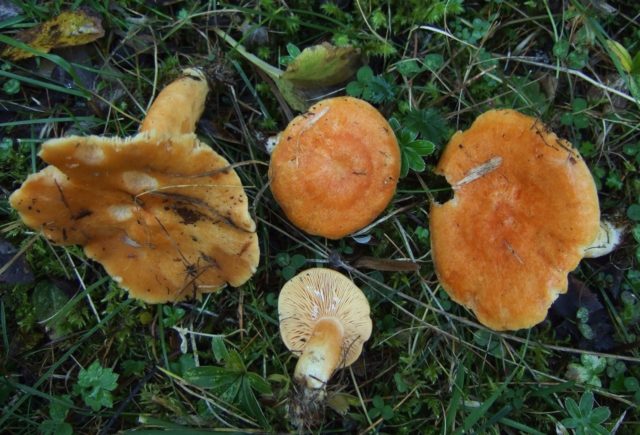

Conclusion
Swamp mushrooms are collected during a quiet hunt for salting, before cooking, the mushrooms are soaked. The species is rare, but appreciated by mushroom lovers.
Edible Bitters
Bitter is a conditionally edible mushroom. This means that it can be eaten, however, you will not always like the taste. It is believed that in order for the bitter to become tasty and not spoil the taste of other products, it must be properly cooked. But how to do it right?
In fact, everything is simple. To prepare bitters, several stages and approaches are used at once.
It is recommended to thoroughly clean the mushroom immediately after collection. It is necessary to remove all insects, as well as debris, needles and other foreign elements that you do not need for cooking.

After that, the mushroom is washed under running cold water.
Then, you need to carefully remove the skin from it. This is done in order to protect yourself and your family from possible infection, because the fact is that a huge number of forest inhabitants, including dangerous insects, interact with the cap of this mushroom.
Then, fill a container with cold water and place the mushrooms there. It is advisable that they soak throughout the night. However, the preparation of the mushroom does not end there either.
The next step is to put a pot of cold water on fire. Bring it to a boil, then add the mushrooms there.
Cook for about 20 minutes, then carefully strain the resulting liquid. The mushrooms are ready, and in the future you can use them in your chosen recipes.
Bitter is believed to be a category 4 mushroom. This means that it is absolutely safe for humans, but at the same time, it does not have the best taste. However, proper preparation can correct this unfortunate misunderstanding.
Twin mushrooms
Gorchak, or bitter, has several doubles, some of which are edible, and some are not.They are cleverly disguised as the original. These include:
- lactic camphor;
- marsh lump;
- the milkman is meat-red;
- hepatic lactate.
The hot, scalding juice, which only the original bitter has, is the main distinguishing feature by which it is easy to recognize a real mushroom. This juice never changes its color.
Camphor milky
The camphor lactus (Lactarius camphoratus) belongs to the russula family, characterized by the lamellar structure of the cap's hymenophore. It belongs to the group of conditionally edible mushrooms; this species grows in North America and on the territory of Eurasia in coniferous or mixed forests, where it forms mycorrhiza with representatives of coniferous trees.
Prefers to live on decaying forest floor or wood. Prefers slightly acidic or acidic soils for development.
In Russia, the camphor milky is found throughout the European part and in the Far East. Its description:
- pleasant to the touch matte surface of the cap;
- the surface is red-brown;
- loose pulp;
- wide plates of the hymenophore are located close to each other;
- the color of the plates is red with dark spots;
- leg in the form of a cylinder;
- the structure of the leg is fragile;
- leg length - up to 5-8 cm;
- aroma medicinal, camphor;
- the taste is insipid;
- the juice is white, does not change color upon contact with air.
False mountain goats bear fruit for about 3 months, from July to early October. They are classified in a low, 4 flavor category: these are conditionally edible mushrooms. They require pre-processing, so they are usually used for salting or boiled.
Swamp bush
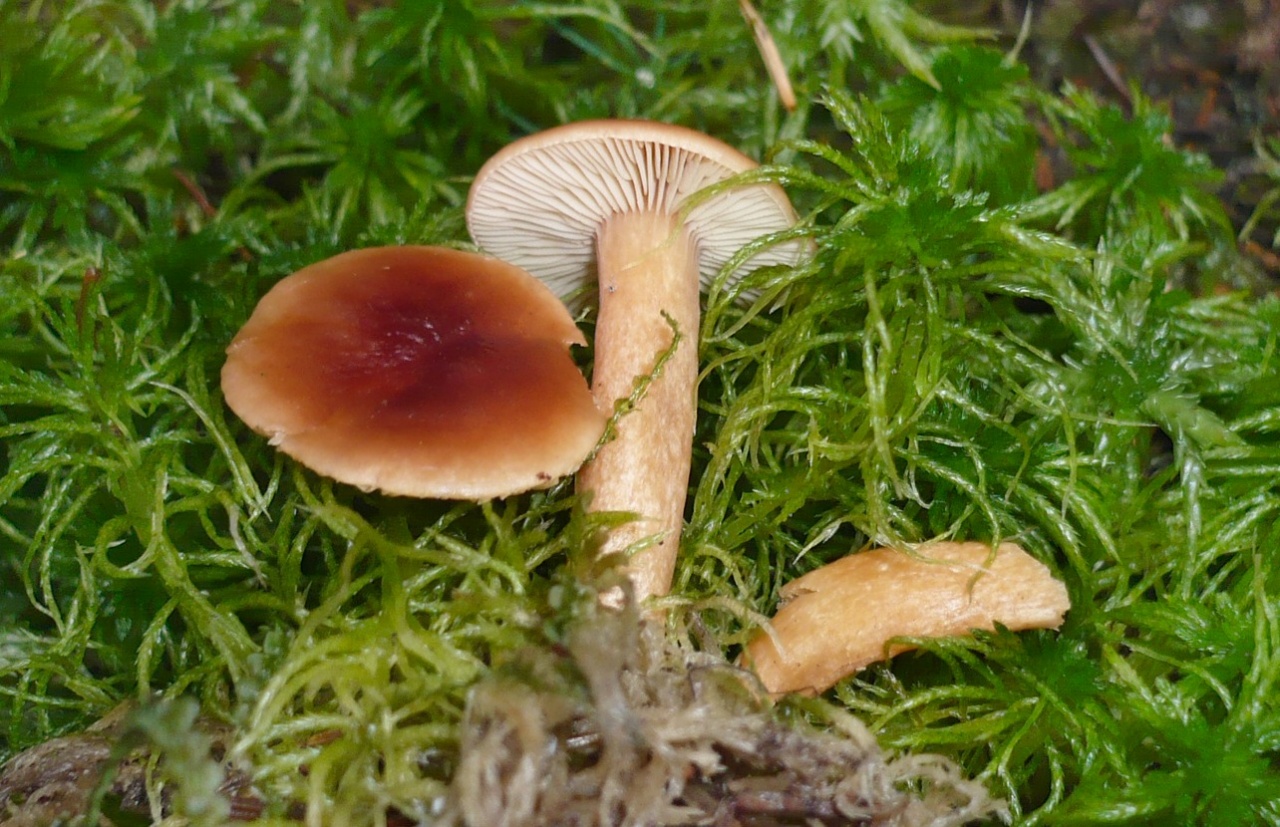
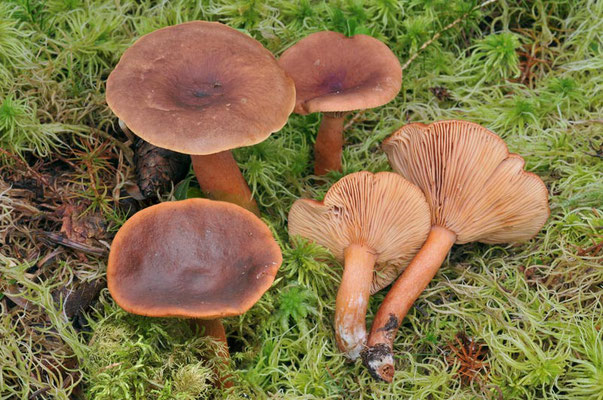
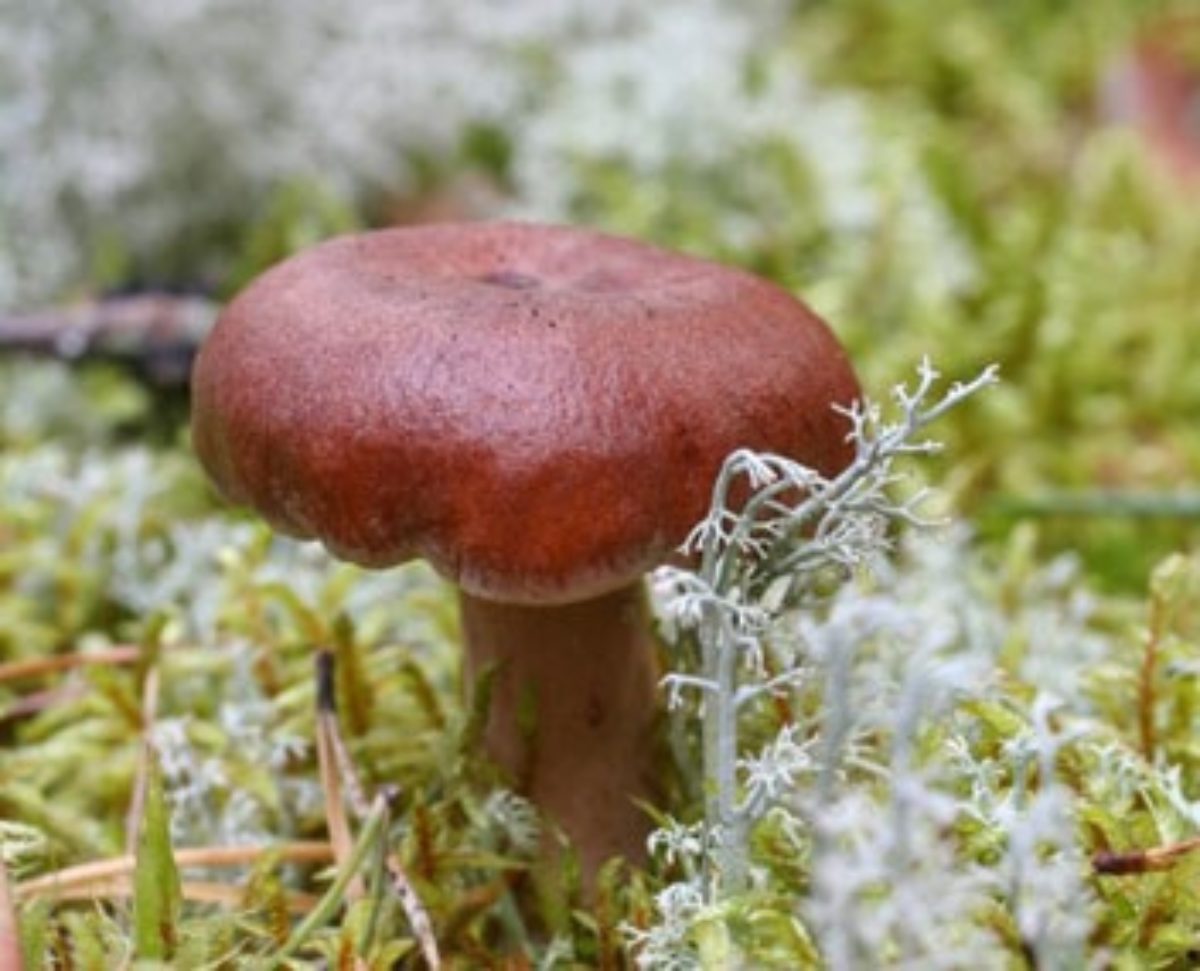
Swamp mushroom (Lactarius sphagneti) is an edible species of the russula family, belongs to the lamellar mushrooms. It is lamellar and brittle. Grows in clusters, on moist soils, in lowlands, from June to November. Its description:
- the body is dense, with a red skin of the cap;
- cap diameter - up to 5 cm;
- the shape of the cap is in the form of a funnel with a tubercle in the center;
- plates are frequent, descending to the leg;
- plates can be intertwined and form peculiar patterns;
- the color of the plates is reddish;
- the base of the leg with fibers, dense and fluffy;
- the pulp is creamy in color;
- the taste is unpleasant, sharp;
- the whitish milky sap interacts with oxygen and, being oxidized, changes color to gray with a yellow tint.
Old mushrooms are hollow inside.
The color of marsh mushrooms depends on the climate, soil and place of growth. The condition of the soil affects the taste and size of organisms. Prefers humid places, does not like heat. Found in all types of forests in Eurasia.
The marsh mushroom belongs to the group of edible mushrooms.
Liver Miller
Liver miller (Lactarius hepaticus) is not eaten because of the pungent taste and therefore it is classified as an inedible mushroom.
The cap is small, can reach a maximum diameter of 6 cm. The color resembles the color of a fresh liver, from which the specific name comes. There is a recess in the center of the cap, so they say that the cap is funnel-shaped. The leg is thin, cylindrical, up to 1 cm in diameter. The color of the leg matches the color of the cap. White milky juice turns yellow in air.
The flesh inside is usually creamy or beige.
More often the variety is found in pine forests, where it forms mycorrhiza with woody species. It grows best on acidic sandy soils.

The bitter mushroom has several counterparts.
Miller meat-red
The meat-red miller (Lactarius trivialis) is sometimes also called smooth, alder, smooth or iron. It belongs to conditionally edible mushrooms from the russula family. The species is characterized by the following description:
- large surface of the cap (up to 20 cm);
- from the edge of it, a fold to the leg is noticeable;
- the center has a depression;
- the color can range from lilac to brown-pink;
- hymenophore type - lamellar;
- thin beige plates;
- the leg is cylindrical;
- the structure of the pulp is tender, brittle and light;
- weak aroma;
- the taste is pungent.
The change in the color of the liquid that stands out on the cut from white to yellowish is a feature of this species. Mycorrhiza with birch, pine or spruce is a natural state for this fungus. Fruiting begins in July, and continues until the last days of October on the fertile coniferous soils of Asia or Europe.
Salt
We figured out the soaking, and now we will learn how to salt the bitters. Let's consider both options:
- Hot ambassador.
- The salting is cold.
15 easy step-by-step recipes for pickling tomatoes for the winter in jarsRead
Hot salt
The mushrooms are soaked, there is no longer any bitterness in them. We start hot salting of bitters. We take an enamel pan, spread the mushrooms with the caps down. Add some salt to the water and pour it into a saucepan. Cook for 30 minutes. Stir occasionally so as not to burn.
You need to salt the mushrooms with dill, garlic. Before laying, put the dill in a basin, fill it with cold water, rinse and rinse. Peel the garlic. It can be sliced or used in whole cloves.
Suitable containers for salted mushrooms would be:
- Enamelled pan.
- Enameled bucket.
- Glass jars with a wide mouth.
Place the boiled mushrooms tightly in a prepared container, sprinkling them with salt and garlic. Salt per 1 kg takes 2 tablespoons. On top you need to put dill and cargo.

The brine should completely cover the corned beef. If not enough, add salt water.
Cold salting
Now let's try to prepare salted bitters according to the recipe for cold salting. Salt, as with the hot method, we will take 2 tbsp for 1 kg. l. From seasonings you will need:
- garlic;
- Dill;
- cherry leaves;
- peppercorns (black);
- caraway.
The mushrooms are already soaked, the jars (saucepan) are cleanly washed with baking soda and rinsed with water. The greens are sorted out, washed in running water, cut into pieces of a convenient size. Garlic is peeled.
We put the mushrooms down with their caps. Sprinkle the layers with salt and spices. We put a load on top so that the mushrooms are all covered with brine and do not darken. Cold-salted bitters will only be ready in two months.
The edibility of marsh mushrooms
Marsh milk mushrooms are edible mushrooms. In terms of taste, they are inferior to saturated milk mushrooms, but they are suitable for all types of culinary processing.
Other mushrooms of this genus
The orange milky is an inedible member of the family, and some mycologists consider it poisonous. These mushrooms do not pose a great danger to health, but after eating them, stomach upsets often occur.

The diameter of the cap of the orange lactarius ranges from 3 to 8 centimeters. Its shape is convex at first, then becomes depressed. Its color is orange, the surface is smooth, slippery. The leg height is 3-6 centimeters, and the thickness is 0.8-1.5 centimeters. The color of the noki is the same as the hat, but it can be a little darker.
Orange millers grow in deciduous forests. They live singly or in small groups. They bear fruit actively from summer to autumn. Form mycorrhiza with deciduous trees.
Milk papillary is a conditionally edible mushroom, which is most often consumed in a salted form. But in many foreign sources, these mushrooms are classified as inedible.
The diameter of the cap of this rather large mushroom is 3-9 centimeters. Its shape is concave-spread or flat-spread. There is a tubercle in the center of the cap. The edges of the caps in young specimens are bent, but over time they open up. The color of the cap is brown-gray, bluish-gray, gray-brown with a violet or pinkish tinge. In adulthood, the caps fade to yellow. The leg is 3-7 centimeters long and 0.8-2 centimeters thick. The color of the leg is whitish.

Papillary milk mushrooms bear fruit from August to September. They prefer coniferous and mixed forests. Papillary milk mushrooms settle on sandy soils. They grow singly or in groups. They are common in the temperate regions of the country.
What poisonous mushroom can be confused with a milk mushroom?
The miller, which has a gray-pink color, is very similar to the white lumps.It should not be eaten as it is considered fatal to the human body.
This mushroom has a cap up to 12 cm wide, dense, fleshy, convex or flat-spread in the form of a funnel. From the very beginning, the mushroom cap has bent edges, which eventually descend, dry out, and become covered with small scales. When the mushroom ages, its cap becomes bare, becomes red, pink or pink-brown, and after drying, blurry spots appear on the cap.
Millechnik
The leg of the lactarius is dense, up to 8 cm long and up to 4 cm wide. The shape is in the form of a cylinder. The pulp of the mushroom is yellow with a red tint. At the bottom, the leg is colored reddish brown. Milk grower grows from mid-summer to mid-autumn.
Useful properties of bitter
This is not to say that the benefits of eating bitter are pronounced. Because of the tart taste, mushrooms are soaked in 2 waters, boiled, the composition of nutrients is depleted by about a quarter.
But still, the following positive qualities should be noted:
- Antiseptic action. It is so pronounced that even old fungi are rarely colonized by parasitic worms.
- Antibacterial activity. The composition contains a substance that destroys a very dangerous microorganism for the child's body - Staphylococcus aureus. The same component stops the vital activity of Escherichia coli, Proteus.
- Increases the general immunity of the body, replenishing the reserve of ascorbic acid.
- It stabilizes blood pressure and improves blood formation due to the content of beneficial nutrients.
- Prevents the development of dermatological diseases, improves the quality of the skin when applied externally with fresh milk juice.
- Improves impulse conductivity due to the high content of magnesium, normalizes protein-carbohydrate metabolism.
- Selenium provides an antioxidant effect.
- Reduces blood sugar levels.
- Its high nutritional value promotes satiety and avoids weight gain. The calorie content is low, so when you introduce mushroom dishes from bitters into the diet, you will not have to feel hunger.
In the years of famine, bitter food provided healthy vital functions for the body, and prevented the development of dystrophy. The introduction of this mushroom into the diet allows you to work normally, maintain the growth and physiological development of children at the desired level, prevents rickets and lagging behind in height and weight.
Where, when and how it grows
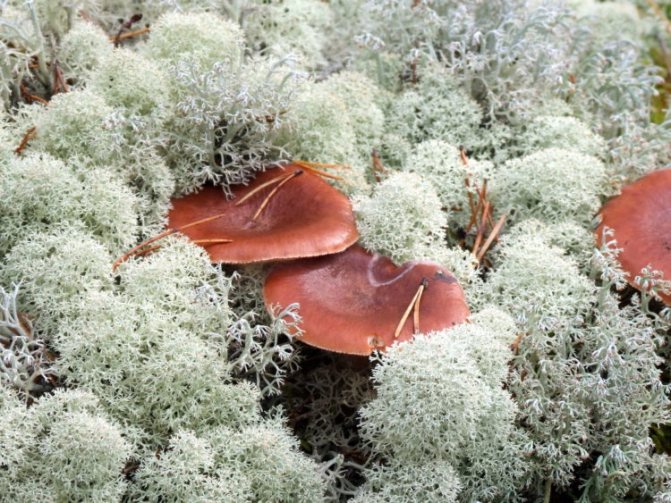

Bitter prefers to grow in mixed and coniferous forest belts. Especially favorite place is lichens, mossy ground and just good bedding. Very often, mustards enter into a symbiotic relationship with birch.
Mushrooms prefer to grow both in families and singly. The first crop appears in June, and the last one can be harvested until the end of October. Bitter is very resistant to frost, therefore it pleases mushroom pickers for a very long time. Experienced mushroom pickers say that bitter is very rarely wormy.
It should be remembered that mushrooms very quickly accumulate various harmful substances in themselves, so you should not harvest near any industrial enterprises, no matter how tempting it is.
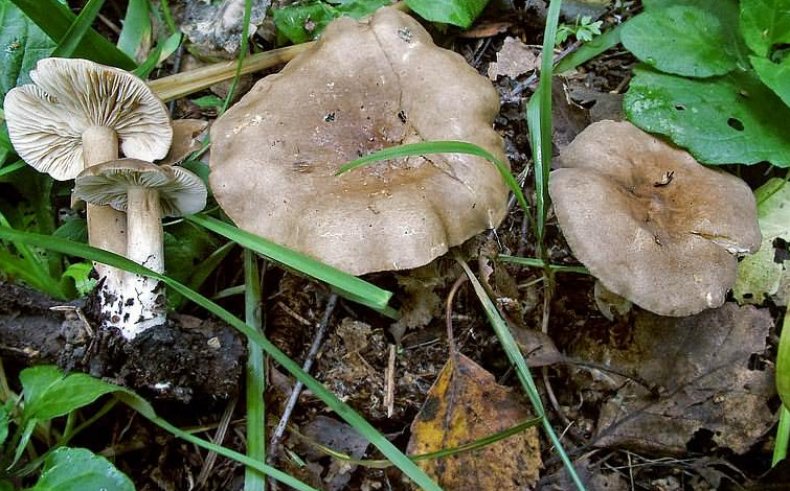
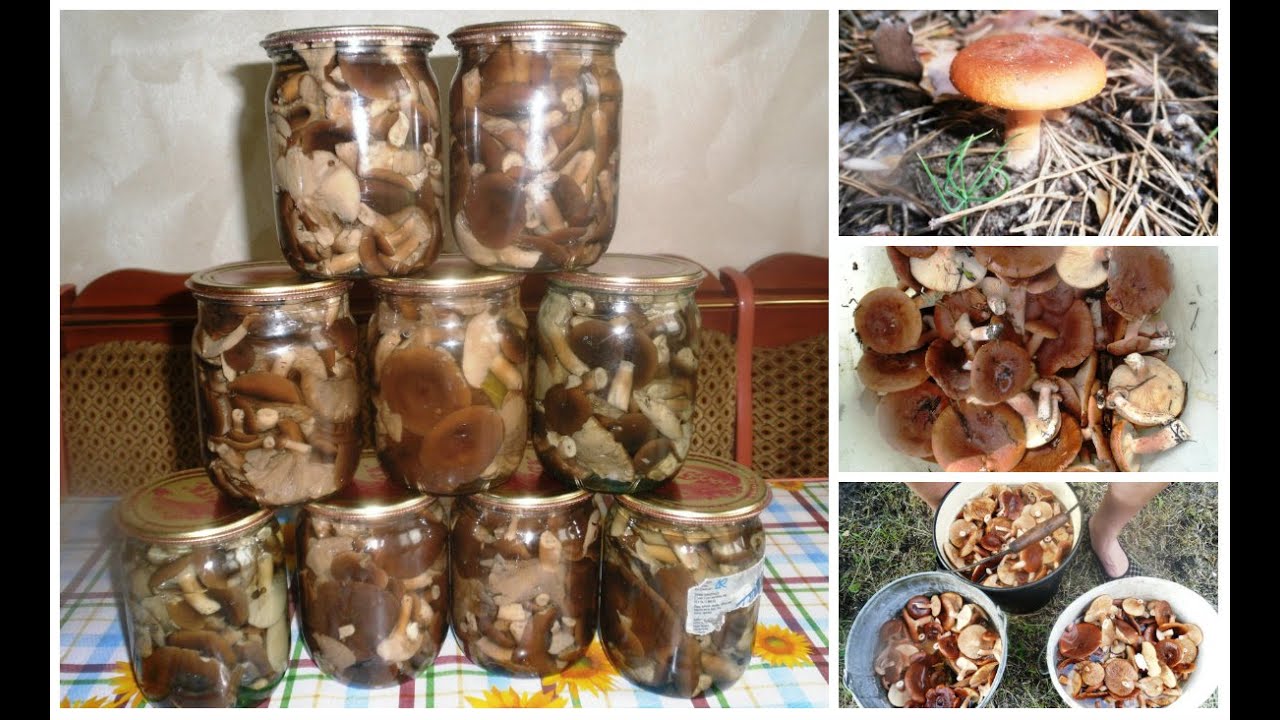
What edible types of milk mushrooms are suitable for salting: bitter milk mushroom


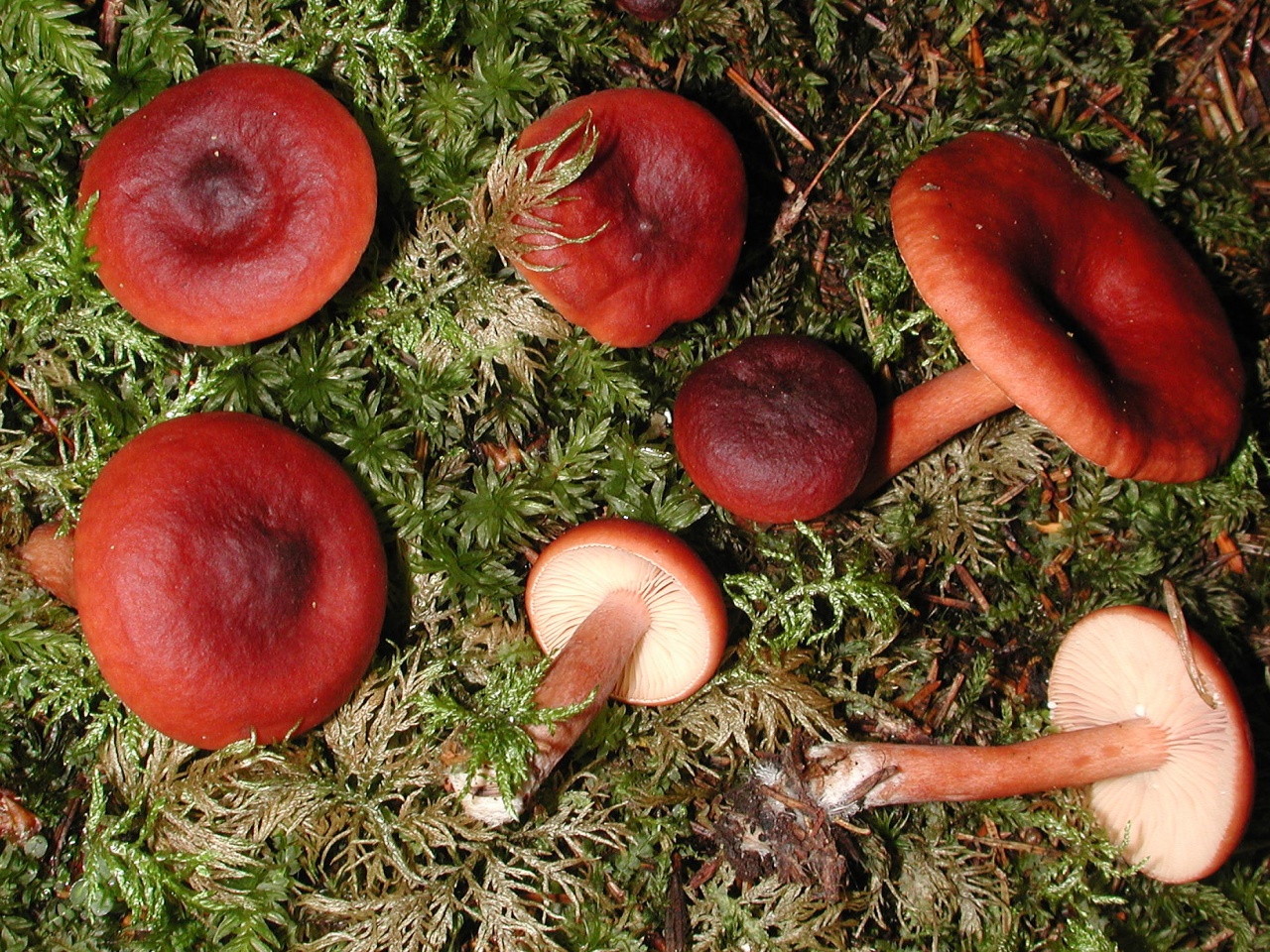
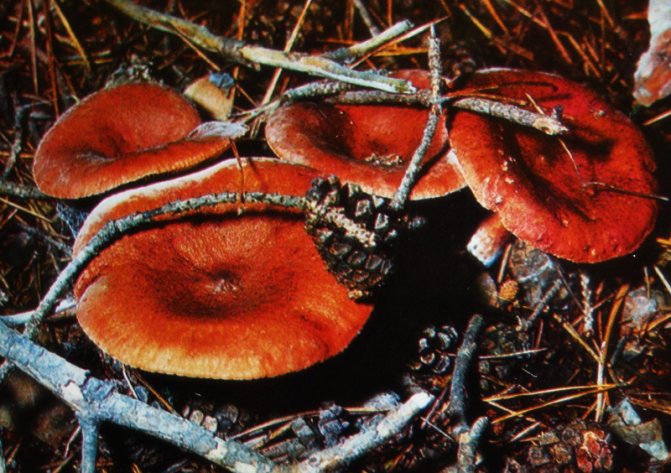
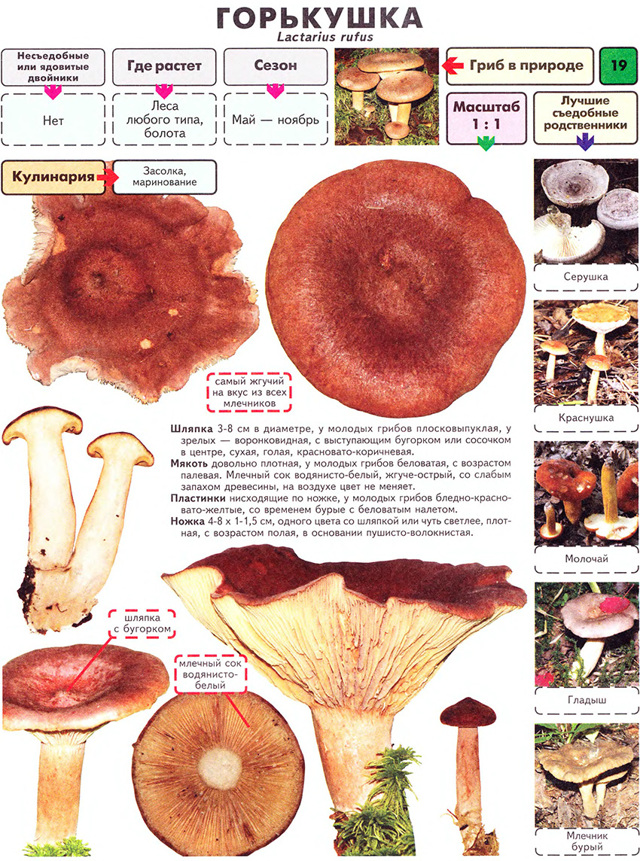
Above is a photo of what a bitter milk mushroom (Lactarius rufus) looks like. Its cap with a diameter of 3-12 cm, usually brown or reddish, has the shape of a bell, over time it becomes noticeably straightened, a small cone-shaped tubercle appears in the center. In mature mushrooms, it is depressed. Smooth to the touch, with slight pubescence, after rain or in damp weather it can be sticky and slippery. The edges, as a rule, are strongly curved towards the inner side and lighter than the center.
Leg (height 3-9 cm): relatively thin, cylindrical, similar in color to the cap. It is covered with light down and has a noticeable thickening at the base.
Plates: frequent and not wide.
Pulp: very brittle, gives off a thick, whitish milky juice on the cut. It does not emit practically any smell, and the mushroom got its name for its peppery, bitter taste.


According to the photo and description, this type of milk mushroom is similar to the inedible hepatic milkweed (Lactarius hepaticus), the milky juice of which turns yellow noticeably in air; the edible camphor lactarius (Lactarius camphoratus), which has a characteristic camphor smell, and the marsh lactarius (Lactarius sphagnei), which grows only in swampy areas.
When it grows: from mid-July to the end of September in almost all countries of the northern half of Europe and Asia.
Where can you find it: on acidic soils of coniferous forests, less often in dense birch forests.
Bitter milk is suitable only for salting, and only after thorough soaking with a constant change of water (10-12 hours). This is done to remove bitterness. When interacting with brine, this type of edible milk mushroom darkens noticeably.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable. However, scientists have learned to isolate from the bitter milkweed a substance that inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, hay and Escherichia coli.
Important! Bitter mushrooms can accumulate the radioactive nuclide cesium-137, which is deposited in the liver and muscles of humans and animals, so you should not collect this mushroom in areas of radioactive contamination. Other names: bitter, red bitter, mountain goat
Mushroom pickers call the bitter mushroom a traveler, as it is often found during the "quiet hunt"
Other names: bitter, red bitter, mountain goat. Mushroom pickers call the bitter mushroom a traveler, as it is often found during the "quiet hunt".