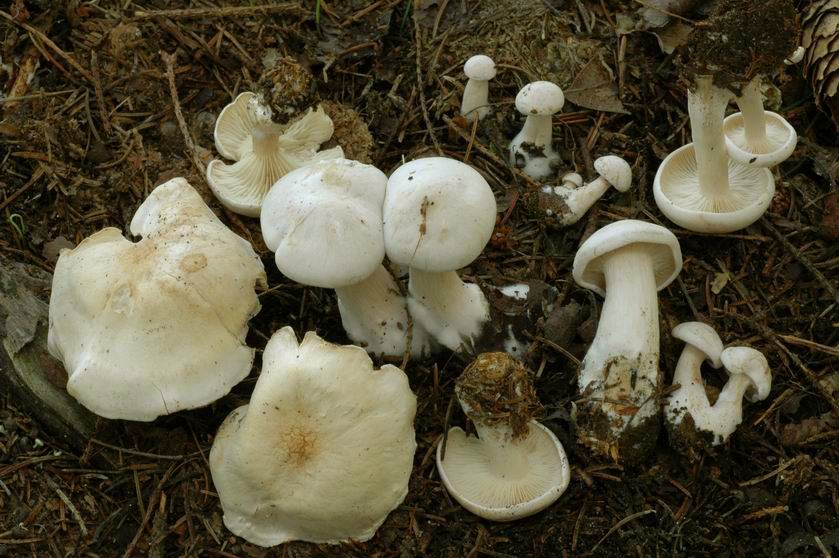
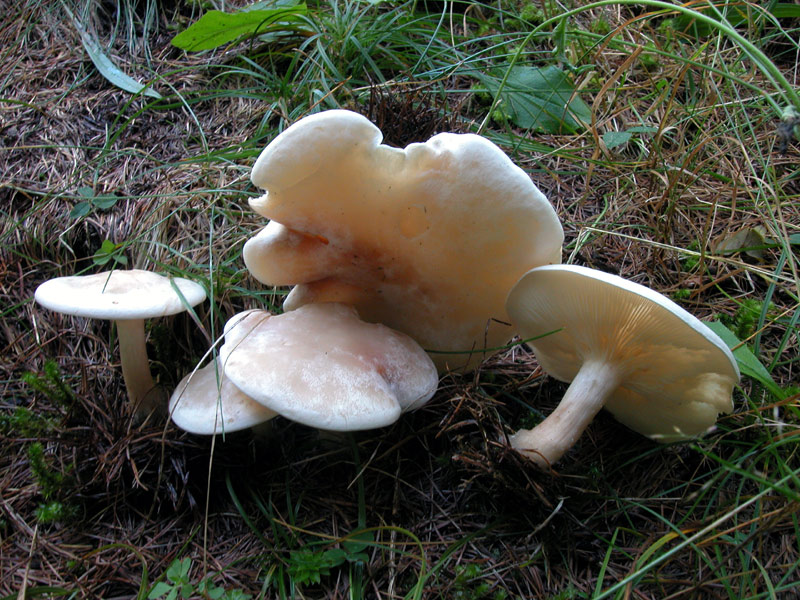
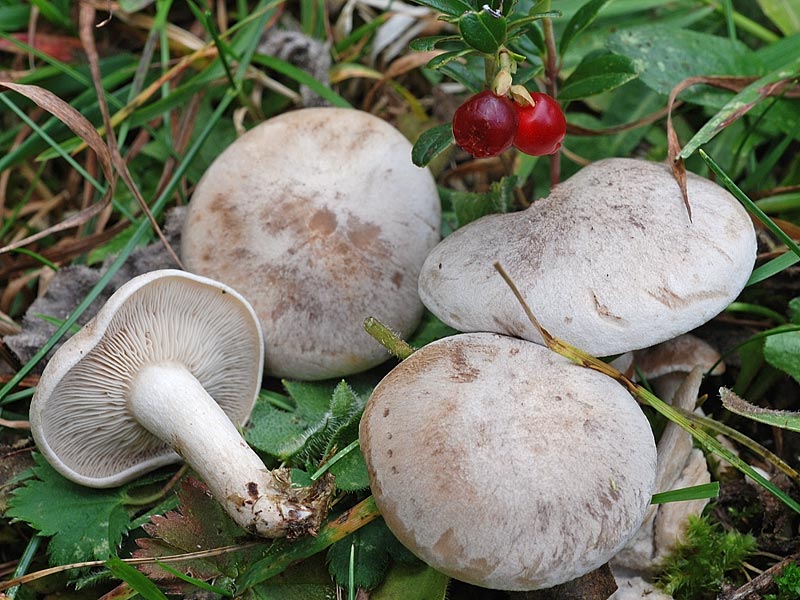
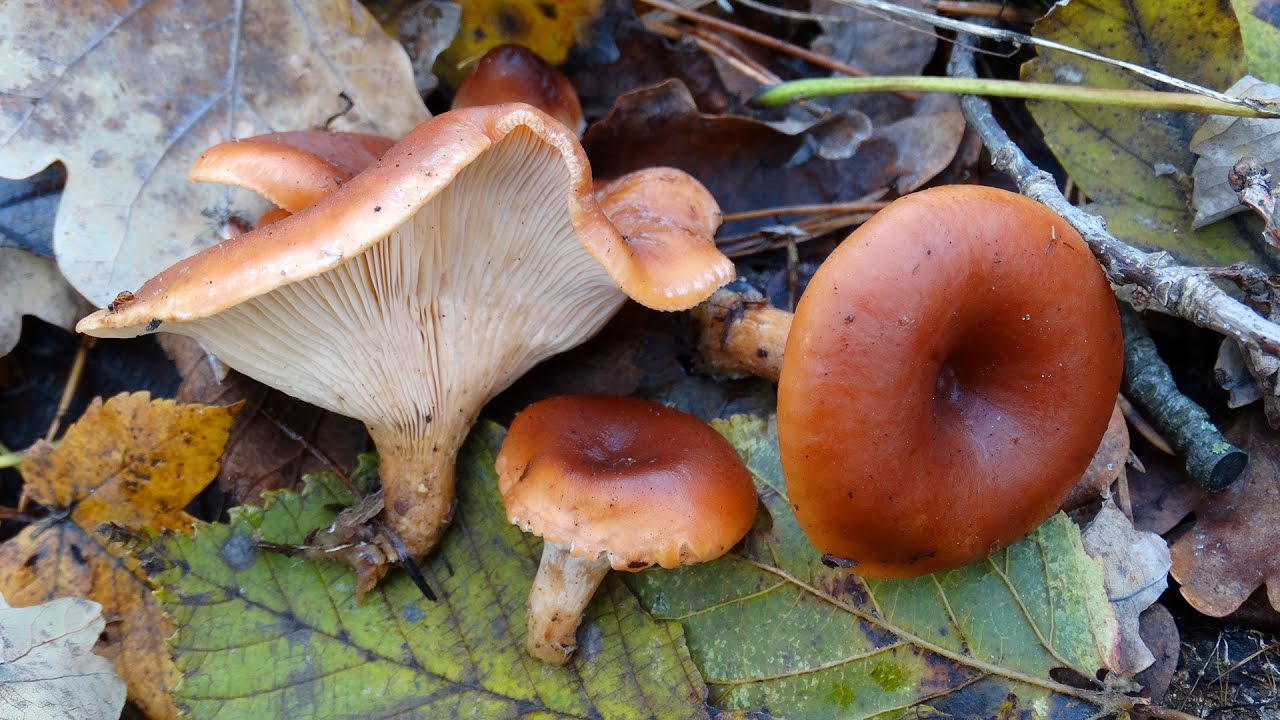
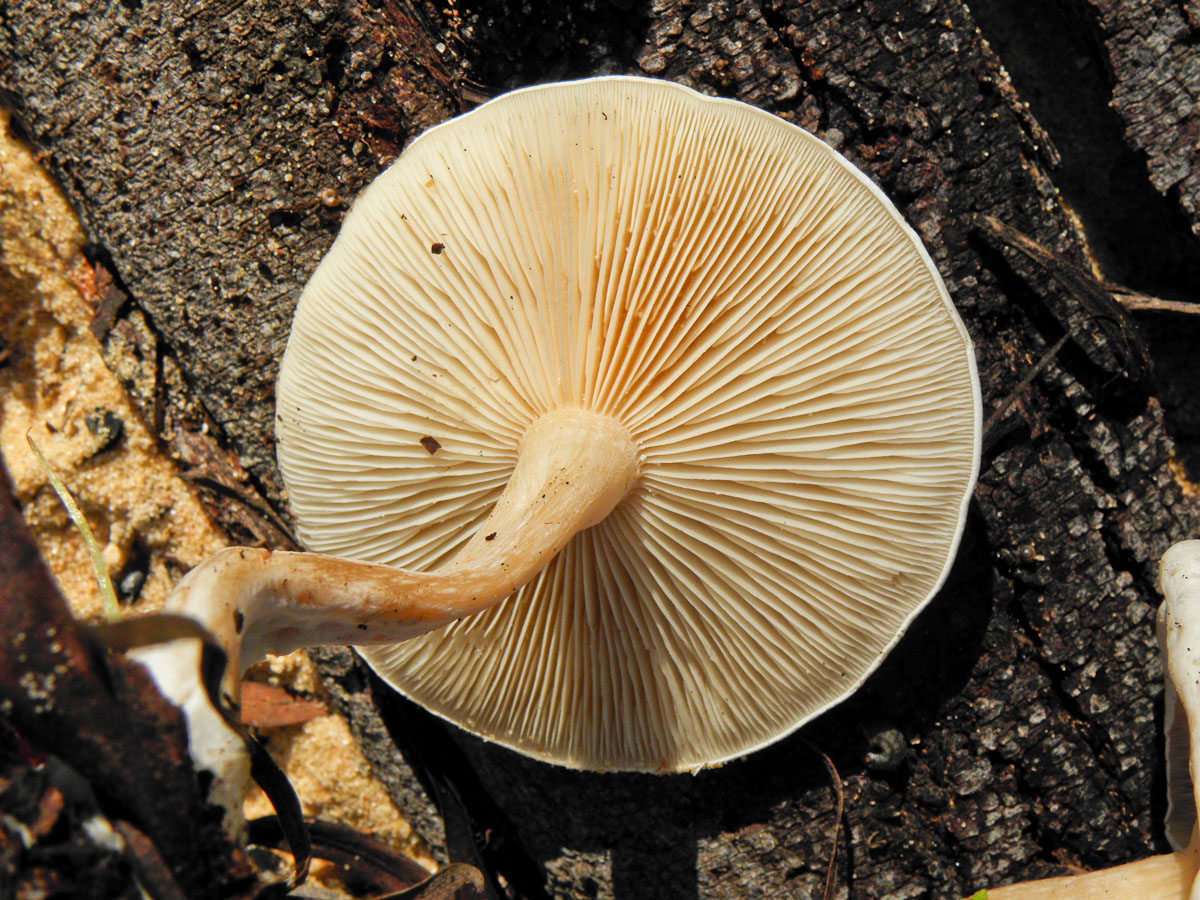
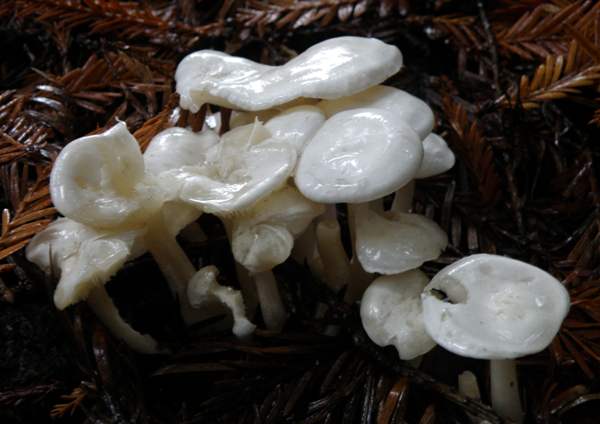
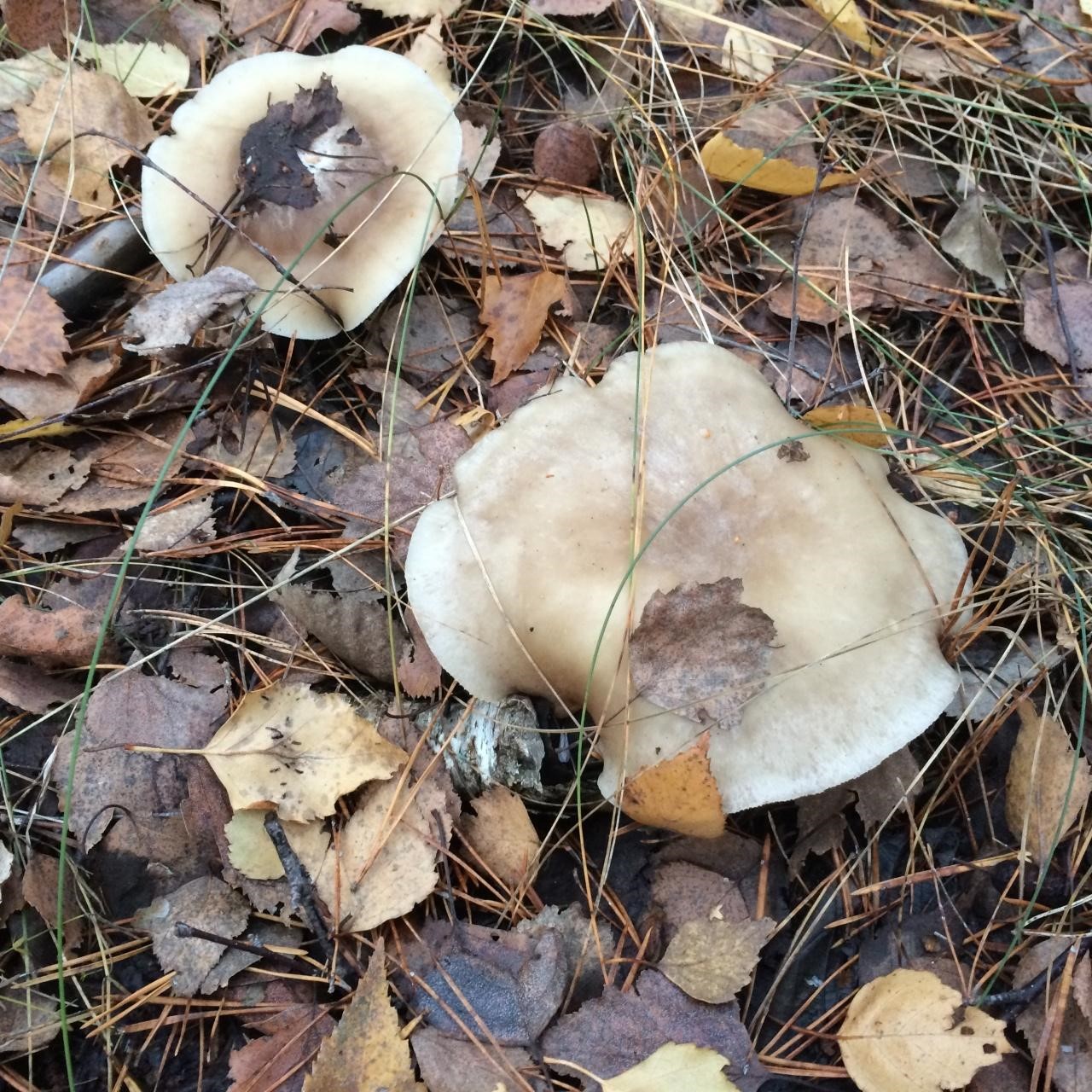
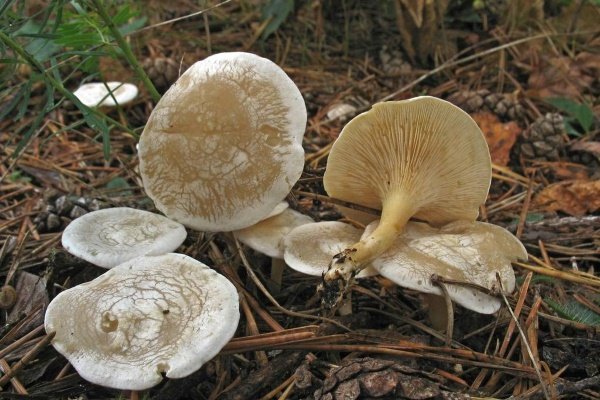
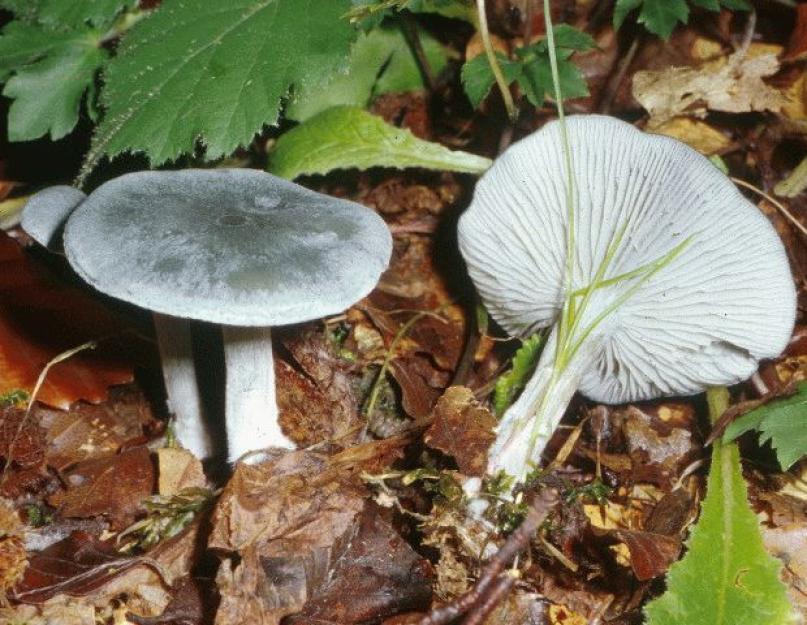
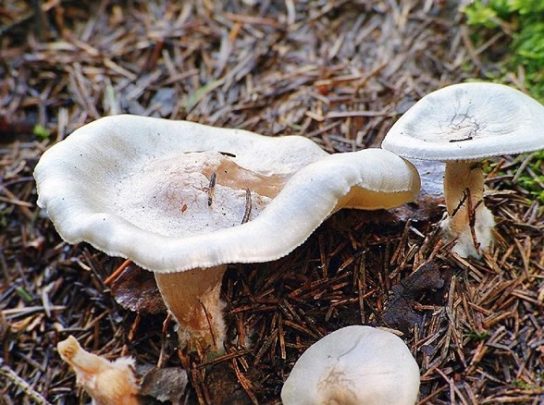
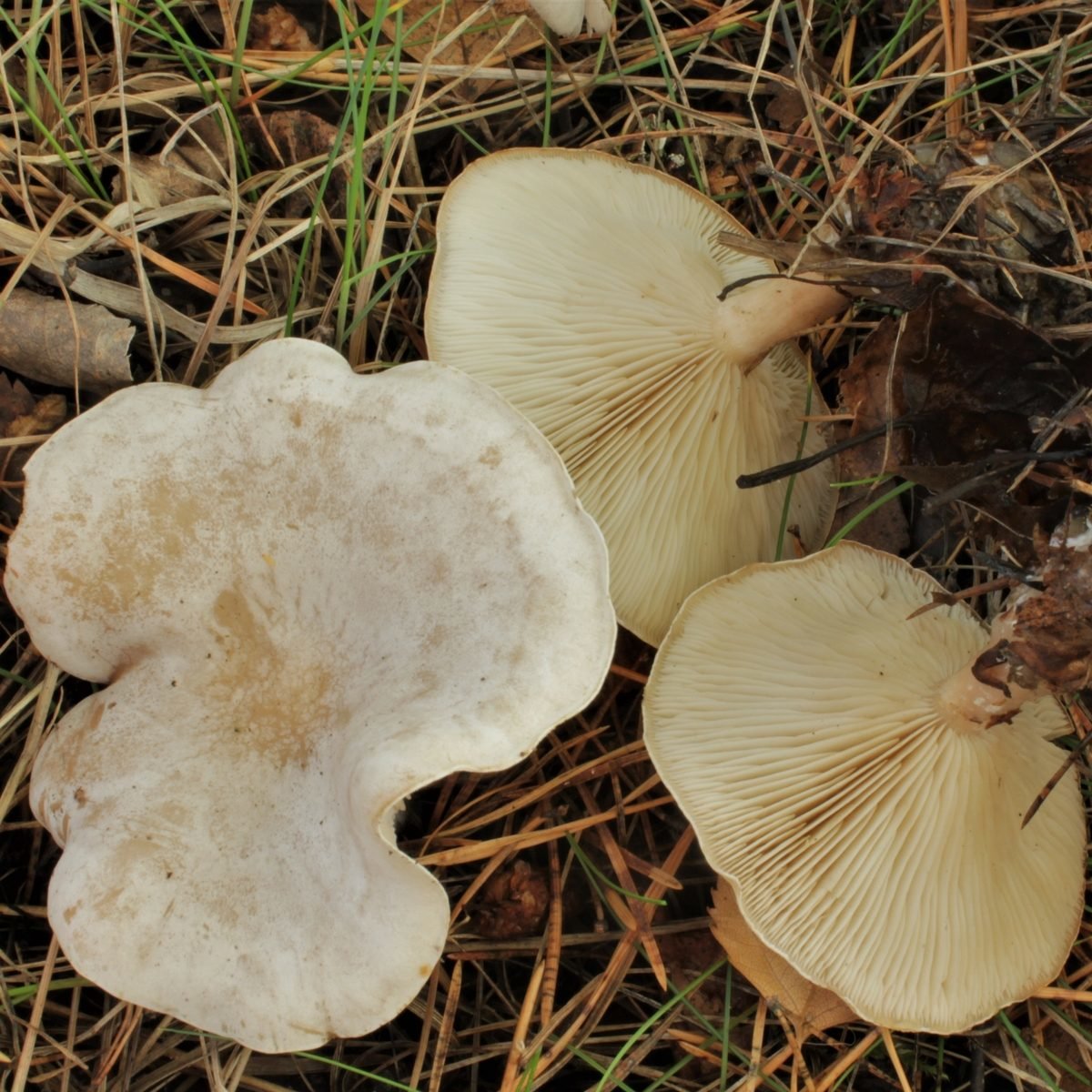
Talkers are whitish, whitish and reddish-brown
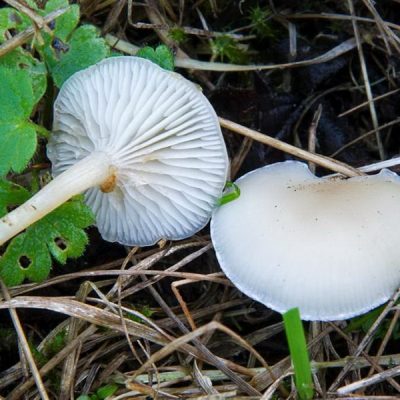
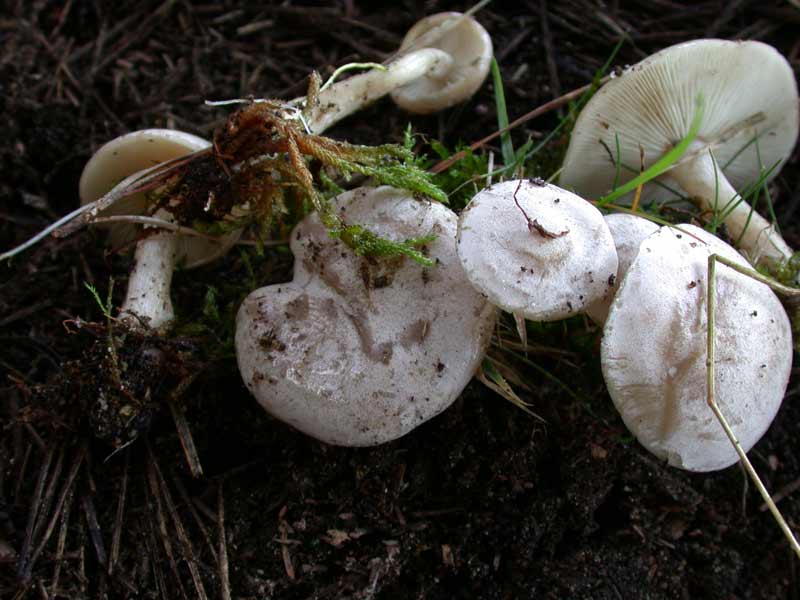
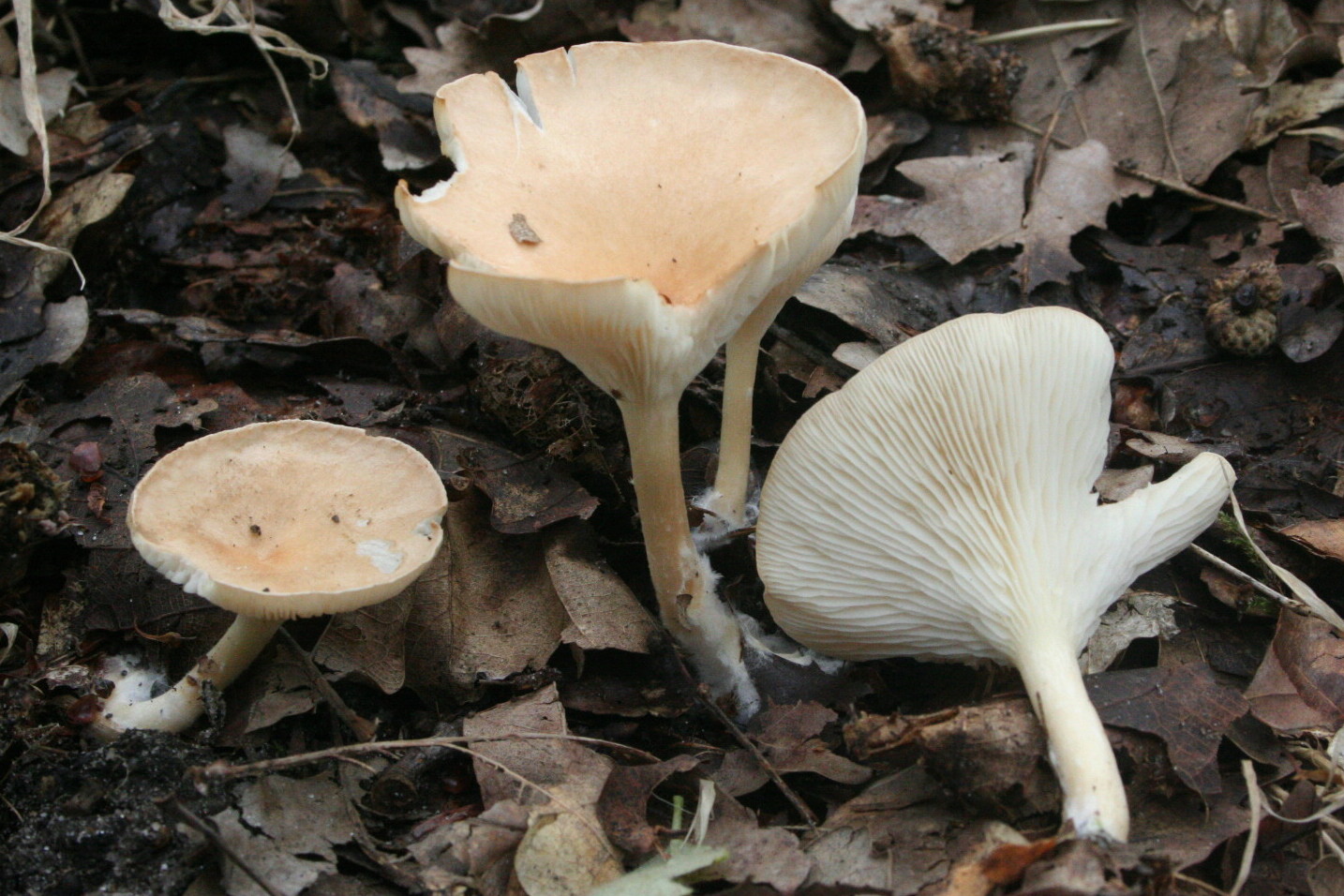
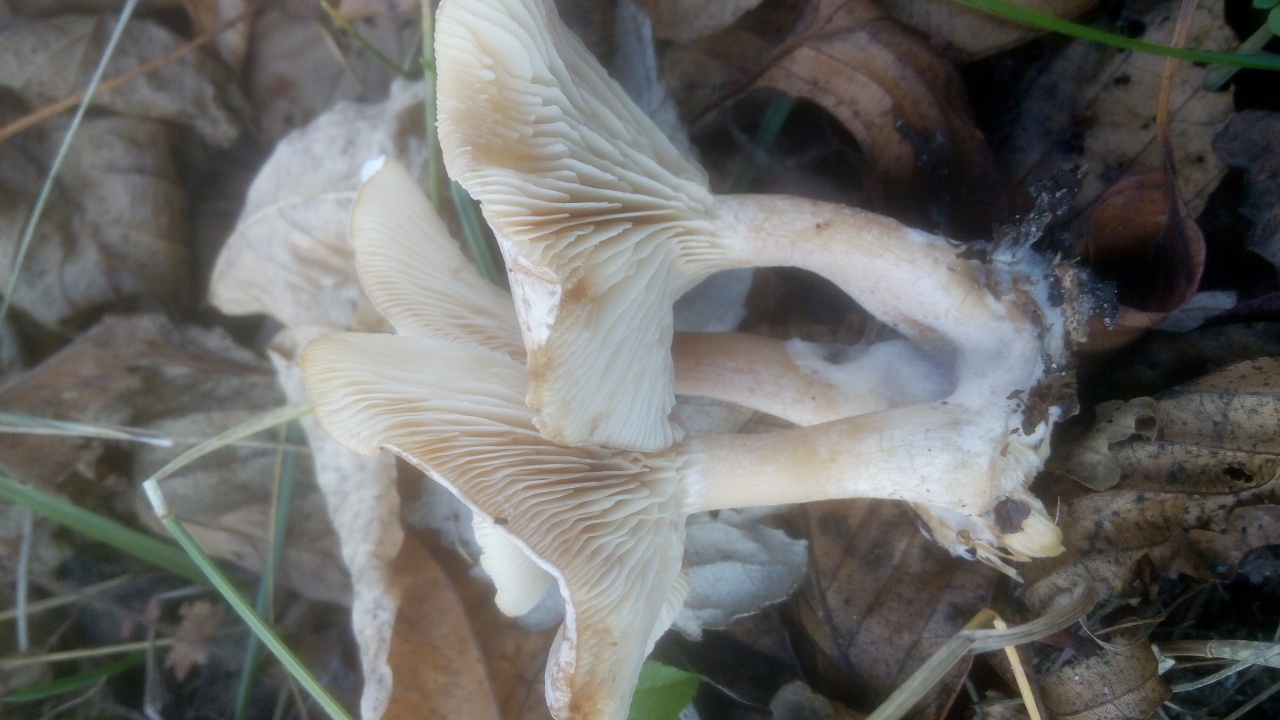
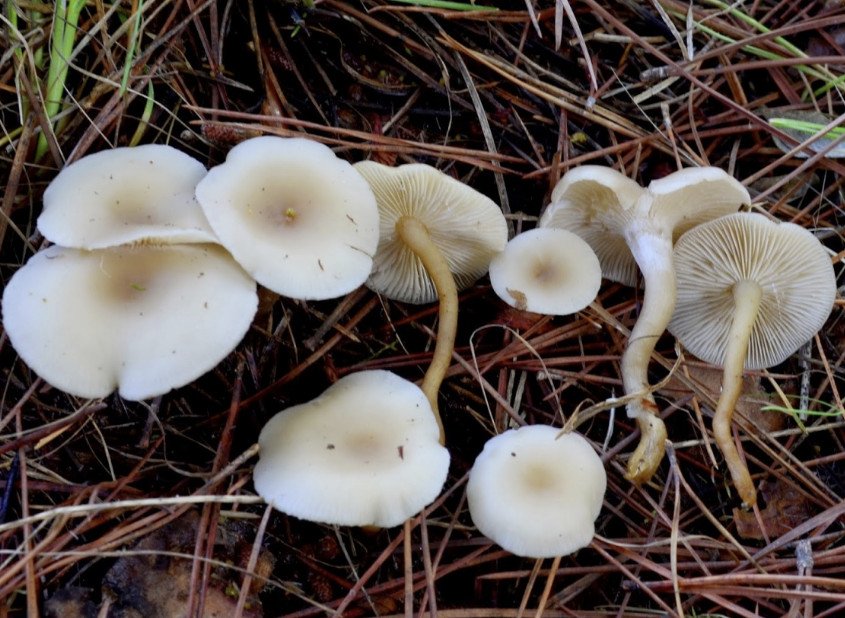
Whitish talker (Clitocybe candicans). The cap is 1.5–5 cm in diameter, initially convex, later flattened to a concave one, the edge is thin and lowered. The skin is slightly mealy at first, then shiny, smooth. The color is white, sometimes with a faint pink tint. The plates are frequent, weakly descending, white. The pulp is thin, white, the smell is expressionless, the taste is pleasant.
The leg is 2–4 cm high, up to 0.5 cm in diameter, cylindrical, often bent at the base, tomentose-pubescent. The color is white or yellowish.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. In forests of different types on litter and needles.
Season. August - November.
Similarity. With other small white talkers, which should be refrained from collecting.
Use. The mushroom is suspicious, in different sources it is designated as poisonous, inedible, non-poisonous. According to some reports, it contains muscarine.
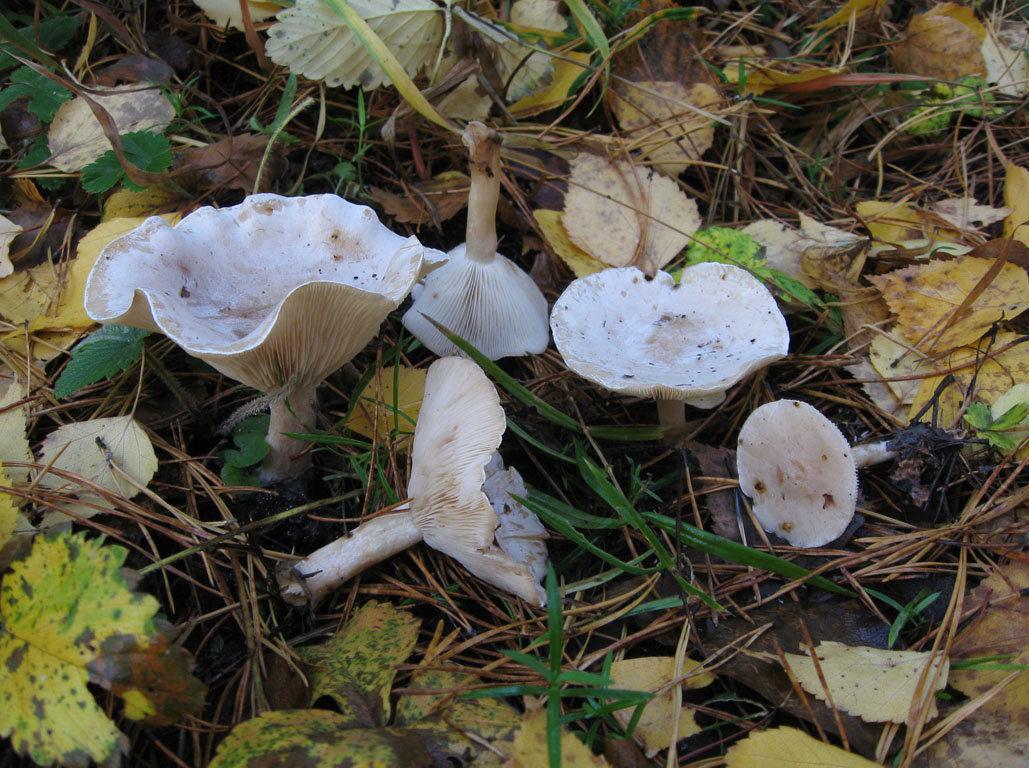
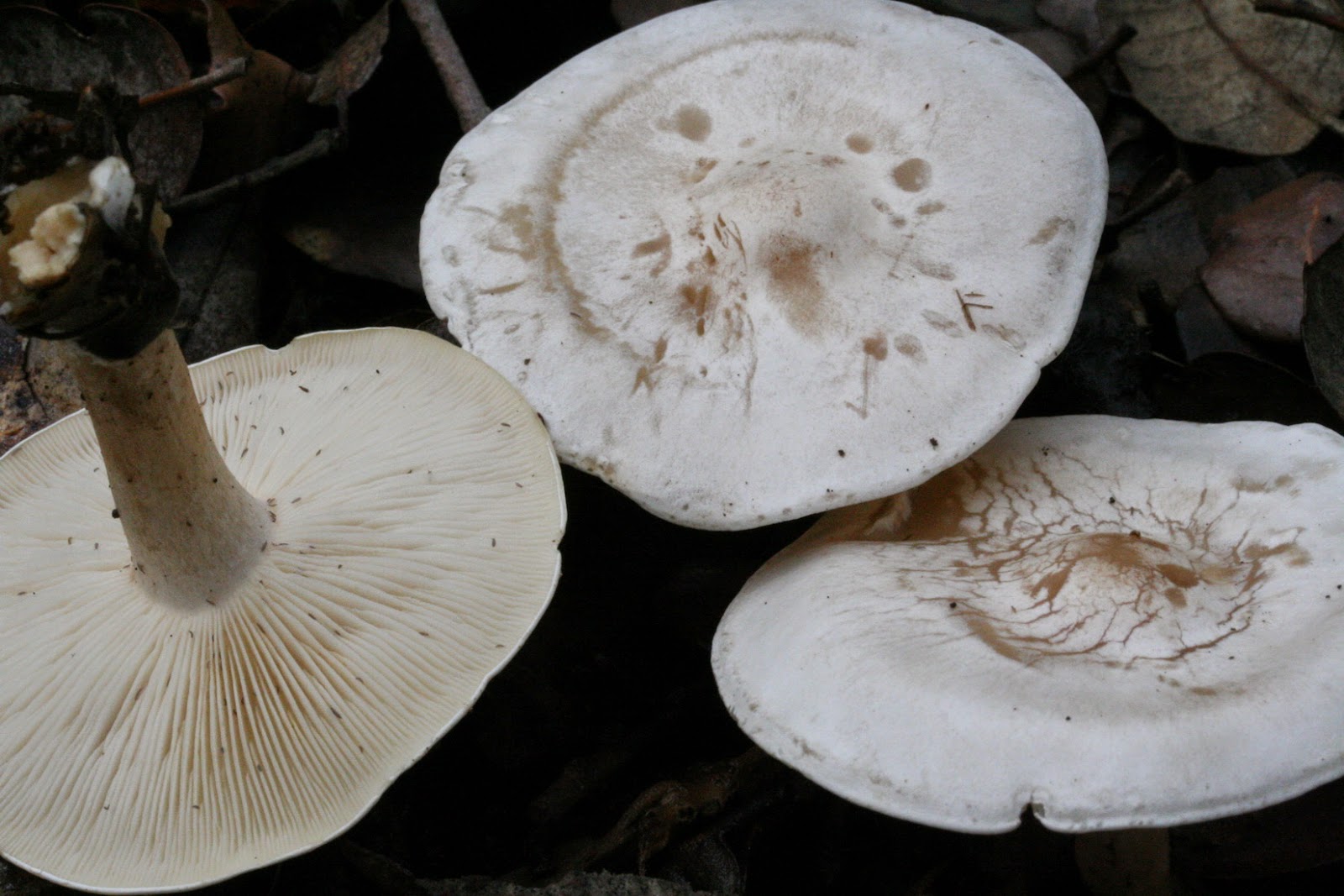
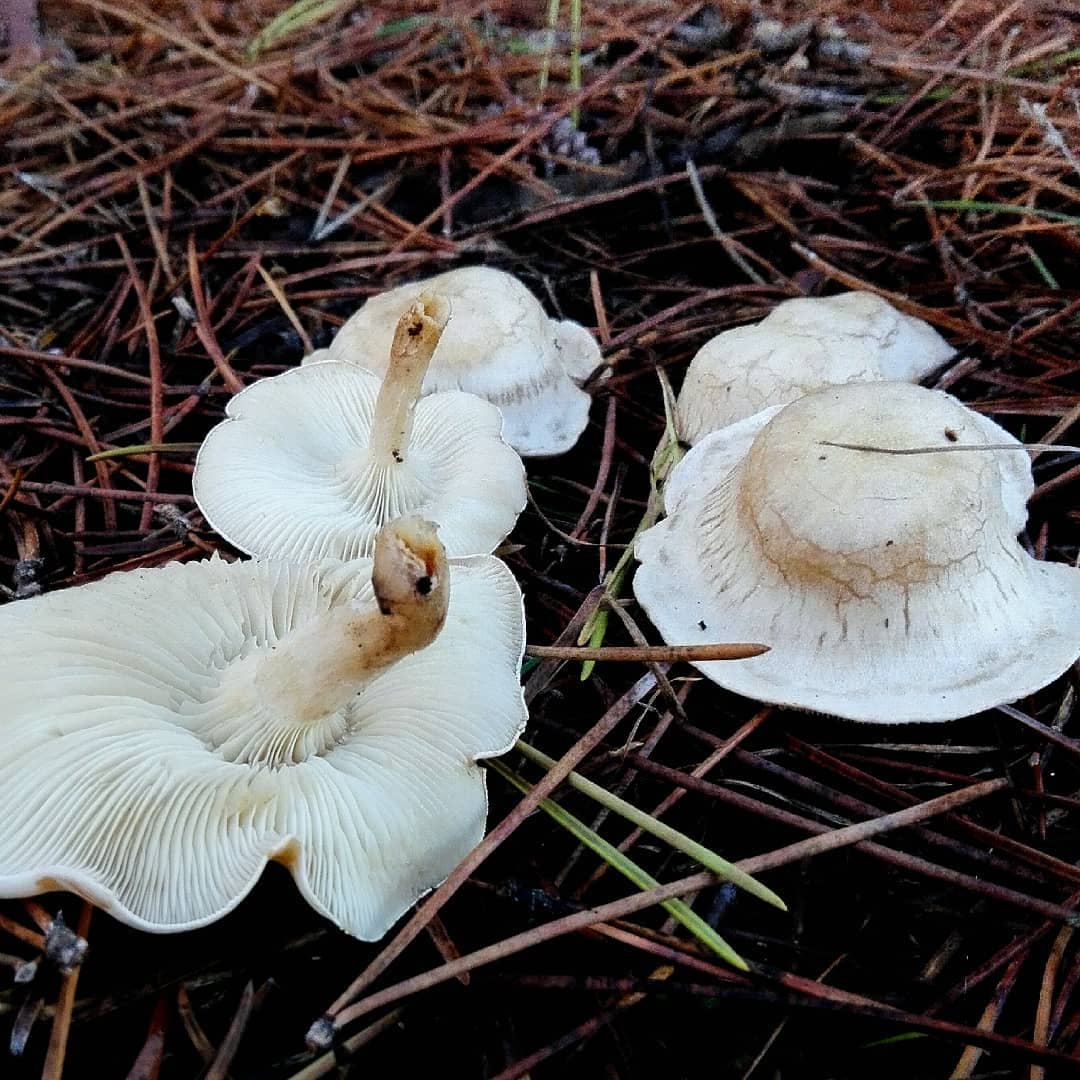
Whitish talker, whitewashed talker (Clitocybe dealbata). The cap is 2–4 cm in diameter, convex or flat, later funnel-shaped, often irregular in shape, with a winding, uneven edge. The skin is smooth, dry, with a light powdery bloom. The color is whitish, with faint grayish zones along the edge in the form of concentric circles formed by cracking of the plaque, at maturity with ocher spots. The plates are adherent or descending, white or grayish, then cream. The pulp is thin, white, the taste is expressionless, the smell is weak.
The leg is 2–4 cm high, up to 1 cm in diameter, cylindrical, slightly thickened towards the base, whitish or creamy, at first solid, later hollow.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. In meadows, pastures, on forest grassy edges.
Season. Summer autumn.
Similarity. The mushroom is extremely similar to the willow (Clitopilus prunulus), which has a much stronger floury smell and in which the plates acquire a pinkish tinge at maturity.
Use. A very poisonous mushroom due to its high muscarine content.
Caution: in case of the slightest doubt, it is better to refuse to collect white talkers altogether.
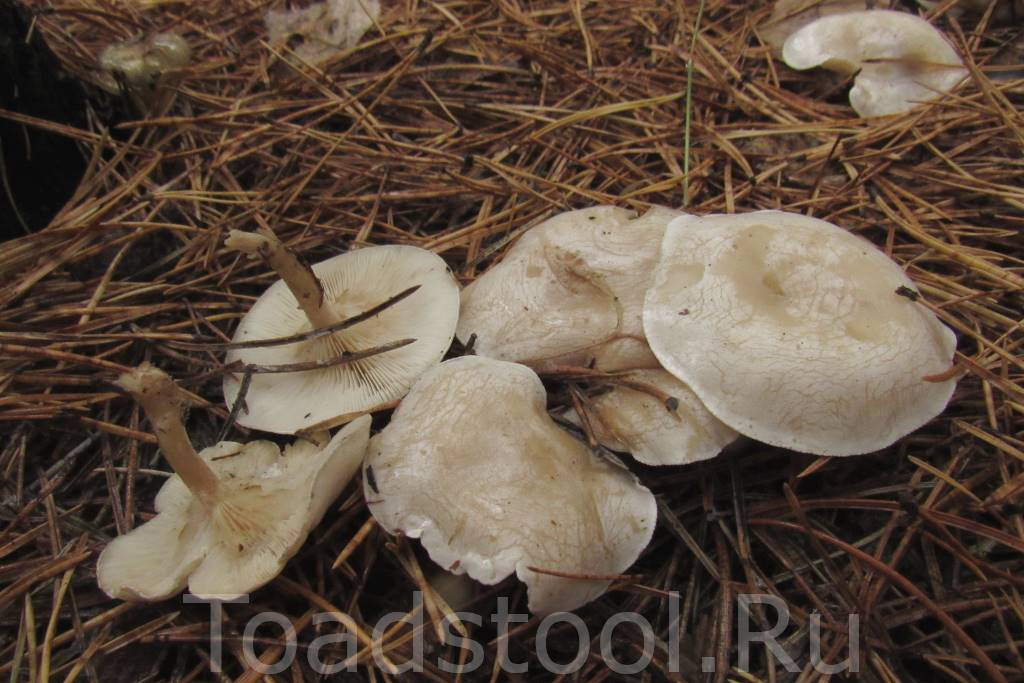
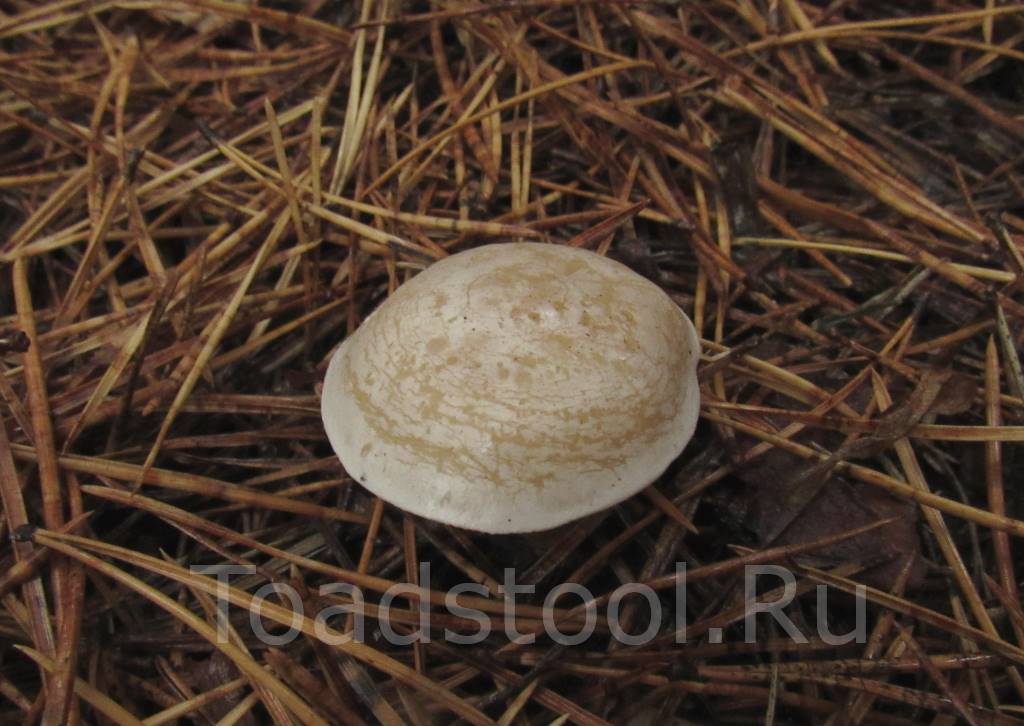
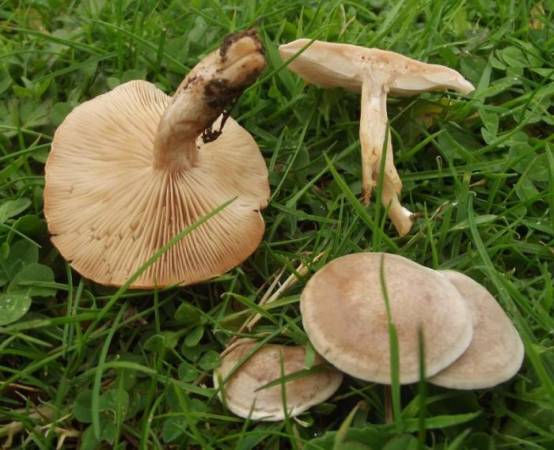
Cracking Talker, Reddish Talker (Clitocybe rivulosa). The cap is 2–5 cm in diameter, initially convex, later spreads out, depressed in the center, covered with a powdery white bloom, which cracks as the cap grows, revealing the main color - cream or reddish-reddish. As a result, the surface is covered with vague concentric zones. The plates are adherent, frequent, reddish-white, later cream. The pulp is thin, the taste is expressionless, the smell is inexpressive.
The leg is 2–4 cm high, 0.4–0.8 cm in diameter, of the same color with the cap, or reddish brown, slightly tomentose at the base.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. In forests, gardens, parks, often along paths, along the sides of ditches.
Season. From late summer to autumn.
Similarity. With other small white talkers, with edible willow (Clitopilus prunulus), which has a flour smell and pink plates.
Use. The mushroom is very poisonous.
Caution: do not collect small white talkers if you are not sure of the exact definition.
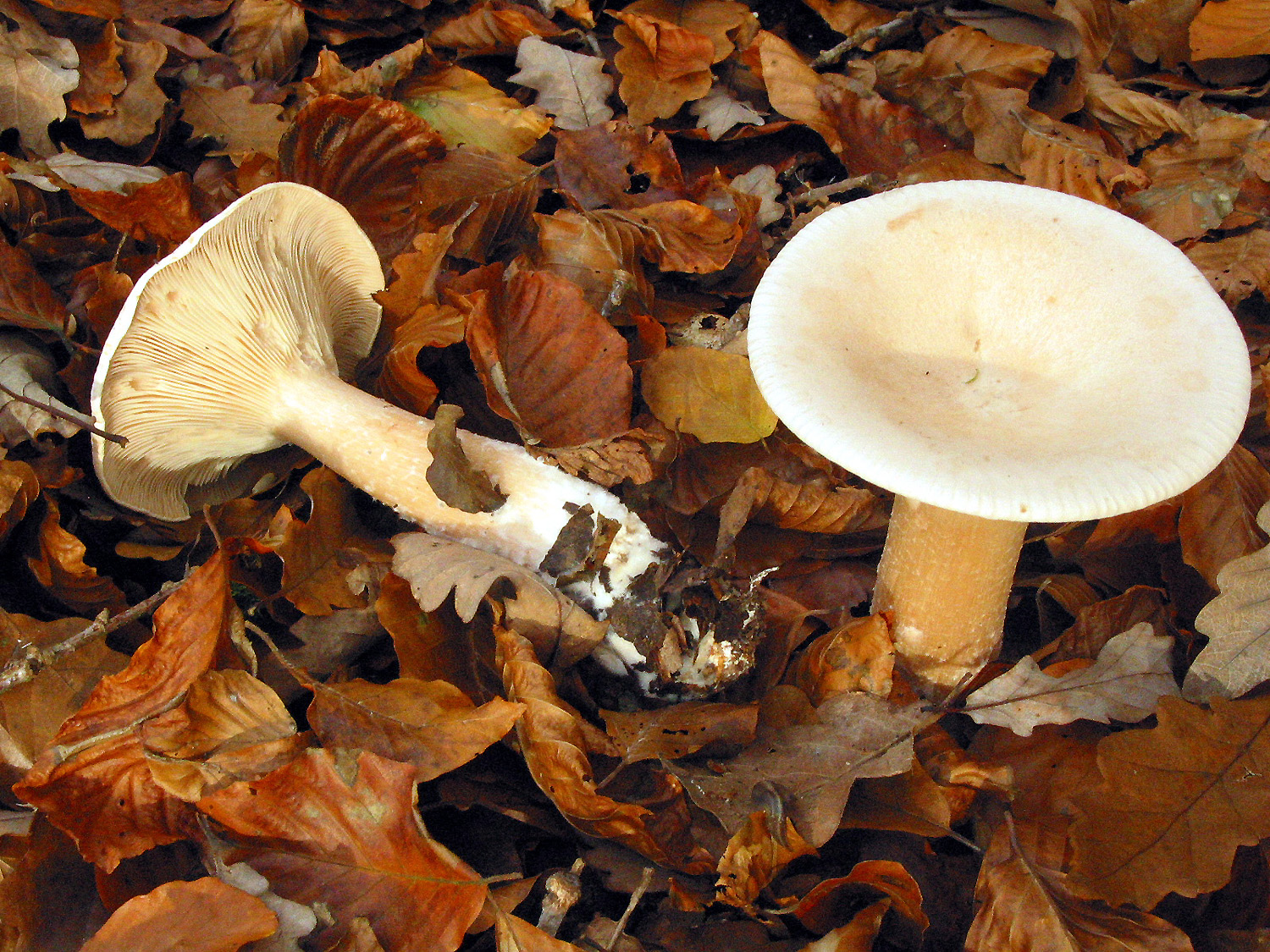
The talker is reddish-brown. The cap is 5–9 cm in diameter, wide-funnel-shaped, red-yellow, reddish-brown or rusty-spotted, often hygrophane. The plates are frequent, descending, cream or yellow-rusty. The pulp is thin, brittle, tough, reddish or pale yellow, sour smell, tart taste.
The leg is 3-5 cm high, up to 1 cm in diameter, reddish, lighter than the cap, tough.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. In coniferous, less often deciduous forests.
Season. It is an autumn species that grows until frost-resistant.
Similarity. It looks like a water-spotted talker (C. gilva) growing in deciduous and coniferous forests, lighter colored and having watery spots on the surface; on the edible funnel-shaped gossip (C.infundibuliformis), in which the plates are white.
Use. Previously, the red-brown talker and the water-spotted talker were considered edible, but later muscarine was found in them. The information in the literature about their edibility is very contradictory, moreover, their taste is mediocre, and therefore we do not recommend picking these mushrooms.
Look at the photo of the talker mushrooms, the description of which is presented on this page:
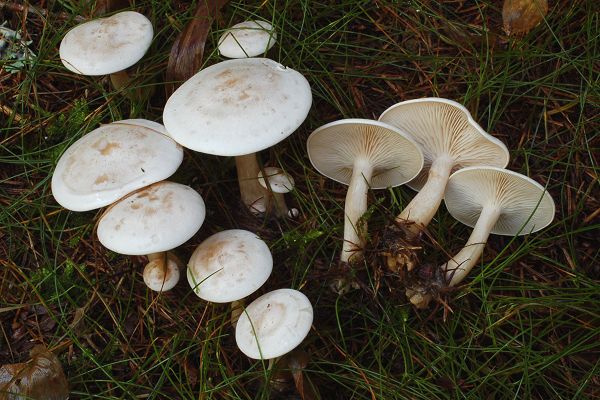
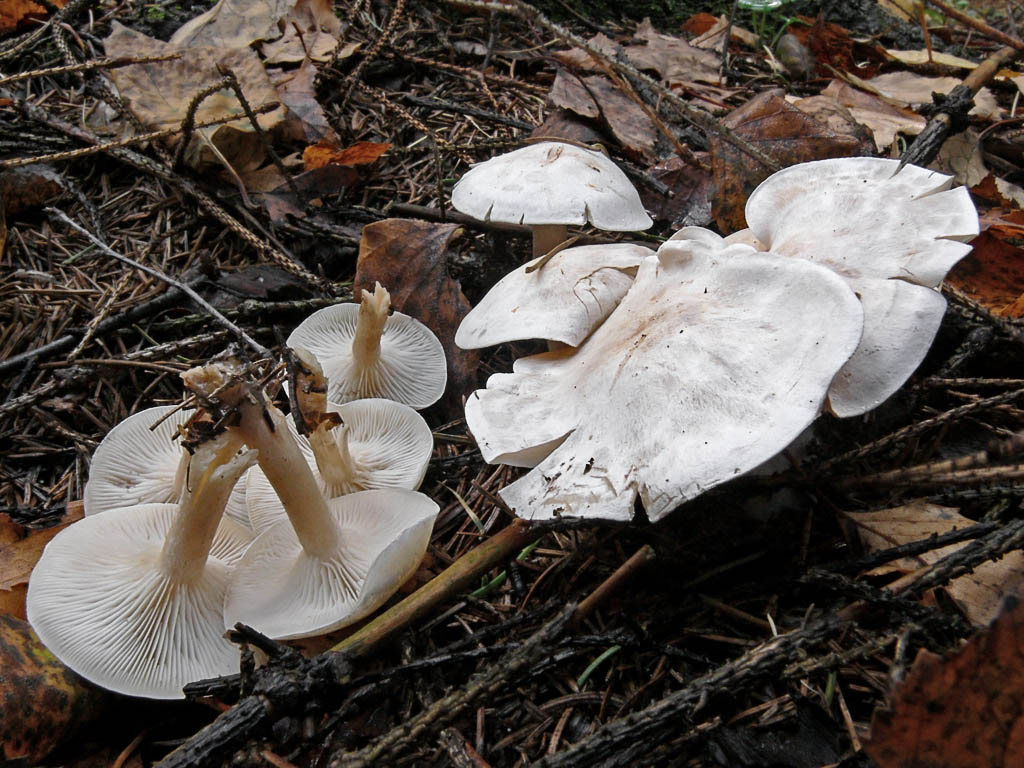
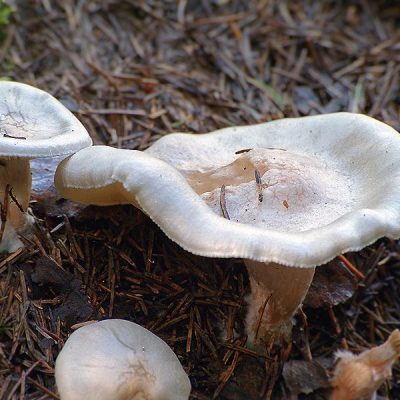
Large smooth bent talker in the photo
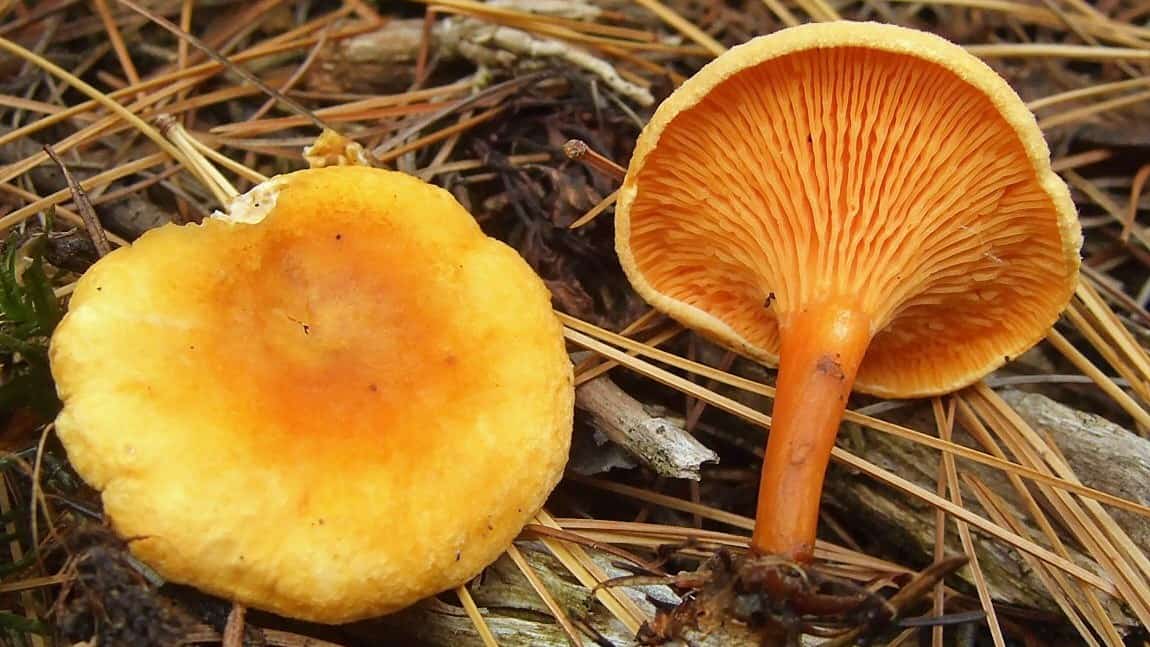
Rare edible mushroom Orange talker in the photo
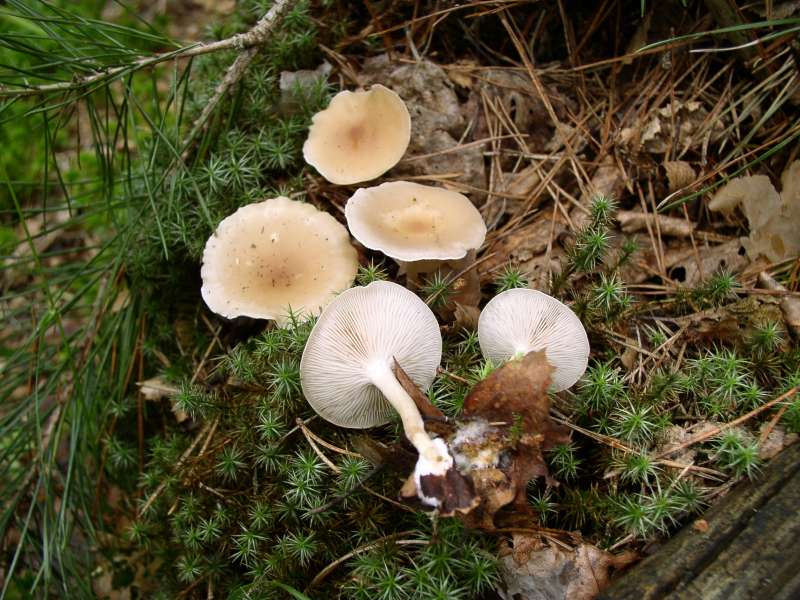
Whitish talker in the photo
Whitish talker (Clitocybe rivulosa)
Synonyms:
Whitish, bleached, or discolored (Latin Clitocybe dealbata), also reddish, or furrowed (Clitocybe rivulosa) - a type of mushroom included in the Clitocybe genus of the Tricholomataceae family.
Whitish talker grows on soil or on a litter in places with a grass cover - in meadows and pastures or on forest edges, clearings and clearings in deciduous and mixed forests, as well as in parks. Fruit bodies appear in groups, sometimes very large; form "witch circles". Distributed in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere.
The season is from mid-July to November.
The cap of the talker is whitish ∅ 2-6 cm, in young mushrooms it is convex, with a turned-up edge, later it is spread, in old mushrooms it is flat or depressed, often with a wavy edge. The color of the cap varies from powdery white and whitish-grayish in young mushrooms to buffy in mature ones. Mature mushrooms have vague grayish spots on the cap. The surface of the cap is covered with a thin powdery coating, which can be easily removed; in wet weather it is slightly slimy, in dry weather it is silky and shiny; when dry, it cracks and becomes lighter.
The pulp is thin-fleshy (3-4 mm thick on the disc of the cap), elastic and fibrous, whitish, does not change color when cut. The taste is inexpressive; the smell is mealy.
The leg of the talker is whitish, 2-4 cm long and 0.4-0.6 cm ∅, cylindrical, slightly tapering towards the base, straight or curved, solid in young mushrooms, later hollow; the surface is whitish or grayish, in places covered with nut-colored spots, darkening when pressed, longitudinally fibrous.
Plates are frequent, whitish, later grayish-whitish, at maturity acquire a light yellow color, descending to the pedicle, 2 - 5 mm wide.
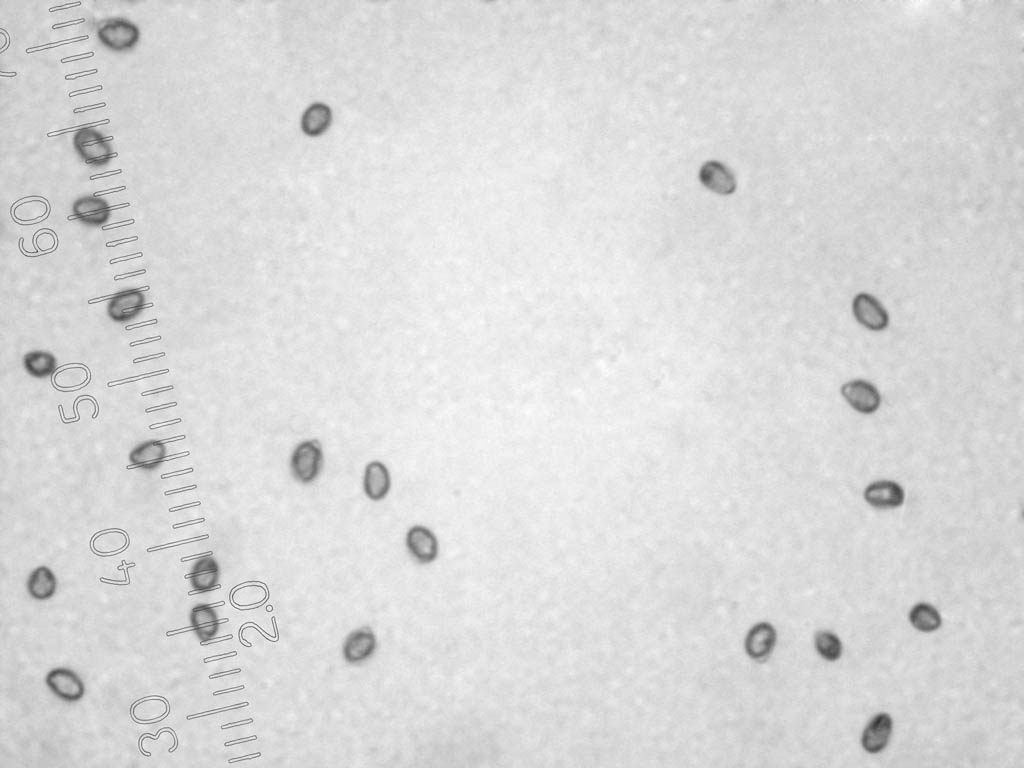
Spore powder is white. Spores 4–5.5 × 2–3 µm, ellipsoidal, smooth, colorless.
Deadly poisonous mushroom!
The content of muscarine in the whitish govorushka is higher than in the red fly agaric. Muscarine, contained in the fruiting bodies of the whitish talker (as well as in the fruiting bodies of related species, for example, Clitocybe phyllophila), can cause severe poisoning, which manifests itself 15-20 minutes after ingestion, increased secretion of saliva and tears, sweating, in large doses - weakening of the heart rate, a sharp drop in blood pressure, respiratory failure, severe vomiting and diarrhea. Poisoning symptoms usually begin to subside after two hours. Fatalities are rare. The antidote for muscarine poisoning is atropine and other M-anticholinergics.
It grows on soil or litter in places with grass cover - in meadows and pastures or on forest edges, clearings and clearings in deciduous and mixed forests, as well as in parks. Fruit bodies appear in groups, sometimes very large; form "witch circles". Distributed in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere.
The season is from mid-July to November.
In the literature, two species are often distinguished - Clitocybe rivulosa with a pinkish cap and blades and a short stalk and Clitocybe dealbata with a grayish coloration and a longer stalk. These factors turned out to be insufficient for separation, the color of hygrophonic talkers depends significantly on the degree of wetting. Molecular genetic studies have also come to the conclusion about one polymorphic species.
Mushroom diets
In order to go on a mushroom diet, in which the daily diet will consist of nutrients and talkers, you need to know in advance how to cook these mushrooms. The cooking method is simple. Fruit bodies must be cleaned of leaves, debris and other forest pollution.
Then you need to rinse the mushrooms under running cold water. Pour the required amount of water into a saucepan so that it completely covers the nutritious talkers and salt (1 teaspoon per 1 liter). When the water boils, you should mark for 25-30 minutes and cook over medium heat. After such processing and preparation, the mushroom can be used in any diet.
Nutritionists prescribe mushroom diets if there are no diseases of the kidneys, intestines, stomach or liver. This is due to the fact that the pulp contains a substance called chitin, which is difficult to assimilate. Therefore, it is best to consult with a specialist before starting testing a new diet.
A mushroom diet with vegetables will help you get rid of extra pounds in a short period of time. You need to eat 400 grams of talkers per day and the same amount of any vegetables. You need to eat mushrooms in three steps.
It is allowed to drink mineral water, juices, green tea and a glass of rye kvass. For a variety of tastes, it is allowed to enjoy one or two teaspoons of honey. The result of dietary nutrition will be noticeable after one and a half to two weeks.
A mushroom diet, in which mushrooms completely replace meat, and become the main ingredient in dishes.
Daily diet
Breakfast: 200 grams of mushroom salad and 100 grams of stewed vegetables, 200 milliliters of green tea.
Lunch: stewed vegetables, boiled talkers and 200 milliliters of rye kvass.
Dinner: salad from a mix of mushrooms, fresh vegetables, green tea with 1 teaspoon of honey.
Thanks to this diet, the body will be cleansed of toxins, toxins and begin to burn fats. This is an effective diet food, the amazing results of which can be seen in 2-3 weeks.
More fresh and relevant health information on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
Tags: talker, edible, poisonous
About the author: admin4ik
Distribution features in our country
Talker mushrooms of both edible species and poisonous varieties are widespread almost everywhere, but due to the difficulty of identification, fans of "quiet" hunting rarely collect such mushrooms.
Inexperienced mushroom pickers can confuse a poisonous talker with a hangover, which, unlike a dangerous double, has a white or slightly yellowish, and then gray, cap without watery circles, as well as white and then turning pink plates and pink spore powder.
Almost all edible varieties of govorushka belong to the fourth category, therefore, from the point of view of taste characteristics and nutritional qualities, they are low-value mushrooms. Before cooking, the collected Clitocybe mushrooms must be thoroughly cleaned of forest debris and soil particles, and also rinsed several times under running water.
Experienced mushroom pickers recommend subjecting the clean fruiting bodies of edible talkers to the obligatory double boiling in water with the addition of salt. As a result of such boiling, it is possible to obtain fruit bodies completely ready for further use in dishes, which can be used for making soups, fillings, cold mushroom snacks, stewing and frying.
Edible talkers
To distinguish the healthy and edible talker mushroom from the fake Clitocybe varieties, you need to know its main characteristics.
| Type of talker | Description of the hat | Leg characteristic | Mushroom pulp |
| Funnel or C. gibba | Flat, depressed and funnel-shaped, pinkish-buffy, prone to fading | Cylindrical, slightly widened at the base, ocher or whitish in color | Whitish, almond-scented, fresh |
| Bent or C. geotropa | Broadly bell-shaped, prostrate or wide-funnel-shaped with a tubercle in the central part, reddish color | Dense, with longitudinal fiber, cylindrical shape, with yellowish pubescence | Whitish-fawn color, with almond aroma and pleasant taste |
| Snowy or C. pruinosa | Flat-convex, depressed, fibrous type, with a whitish bloom on the surface, gray-brown with concentric rings of a darker color | Cylindrical or tapered, reddish-cream color, with a leathery surface | White or creamy color, with a pleasant taste and light mushroom aroma |
| Odorous or C. odora | Convex, flat or depressed, with wavy edges and a small tubercle in the central part, painted in a bluish-greenish color | Fairly dense, cylindrical or slightly widened at the base, bluish-greenish in color | Whitish in color, with a strong aniseed odor and a pleasant mushroom taste |
The deadly, poisonous govorushka mushroom does not have too pronounced, significant differences from the edible varieties of Clitocybe, so you should be extremely careful when collecting and be sure to read the description of the poisonous species.
Edible talkers include:
- clubfoot (it can be eaten, but not in combination with alcohol);
- odorous (aniseed);
- funnel-shaped;
- bent (redhead) and many others.
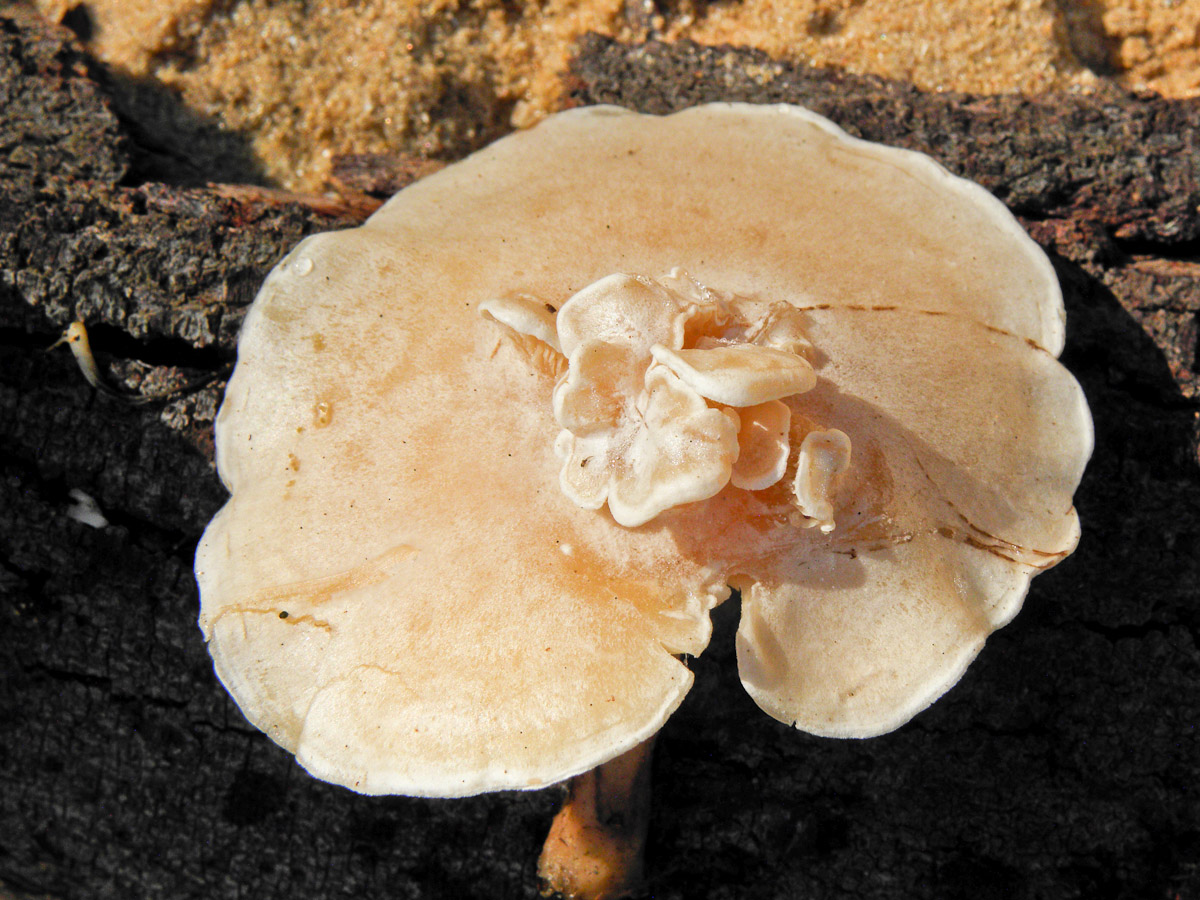
During the mushroom season, many mushroom pickers are looking for a giant and orange talker, since they are 100 percent edible and the dishes from them are delicious and nutritious.
The height of the leg is 4-7 centimeters, its shape is a cylinder. The pulp is firm, white in color, and has no distinctive aroma or taste. You can find a giant talker in North America, Europe and the Russian Federation.
The orange talker is considered a poor quality edible mushroom. Only fresh fruit bodies are used for food, which are boiled for 15-20 minutes, then marinated according to their preferences. Mushroom pickers collect only the hats of young talkers, their legs are tough, and their mature fruiting bodies are completely tasteless.
Clitocybe smoky (gray or smoky gray) refers to the conditionally edible species of mushrooms. In order to safely eat a smoky govorushka, it is necessary to boil it, it is undesirable to use the broth for the further preparation of any dish. Improper preparation can lead to shortness of breath and food poisoning.
This mushroom surprises with its ability to boil, but for the floral aroma of the pulp, you can forgive the fruit for a small amount of it after cooking. It is not difficult to find a smoky species in forest plantations, the period of mushroom picking begins in late summer and ends in late autumn.
Waxy talker (Clitocybe phyllophila)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Deciduous talker
- Leaf-loving talker
Synonyms:
- Waxy talker
- Greyish talker
- Lepista phyllophila
- Clitocybe pseudonebularis
- Clitocybe cerussata
- Clitocybe difformis
- Clitocybe obtexta
- Clitocybe dilatata
- Clitocybe pithyophila

Description
A hat with a diameter of 5-11 cm, in youth it is convex with a tubercle and a marginal zone tucked inward; later flat, with a turned-up edge and a barely noticeable elevation in the center; and, ultimately, funnel-shaped with a wavy edge; marginal zone without radial banding (i.e., the plates do not shine through the cap under any conditions); unhygropic. The cap is covered with a white waxy layer, under which the surface of a flesh-colored or brownish shade, sometimes with ocher spots, shines through; in the marginal zone of older fruiting bodies, watery spots are visible. Sometimes this waxy coating cracks to form a "marble" surface. The peel from the cap is removed to the very center.
The plates are adherent or slightly descending, with additional plates, 5 mm wide, not very frequent - but also not very rare, about 6 plates per 5 mm in the middle part of the radius, covering the lower surface of the cap, extremely rarely bifurcating, at first white, later ocher -cream.The spore powder is not pure white, but rather a dirty flesh-colored or pinkish-cream shade.
Stem 5-8 cm high and 1-2 cm thick, cylindrical or flattened, often slightly widened at the base, less often tapering, at first white, later dirty-ocher. The surface is longitudinally fibrous, in the upper part it is covered with silky hairs and a whitish “frosty” coating, at the base with woolly mycelium and a ball of mycelium and litter components.
The flesh in the cap is thin, 1-2 mm thick, spongy, soft, white; stiff in the stalk, pale ocher. The taste is soft, with an astringent aftertaste. The smell is spicy, strong, not quite mushroomy, but pleasant.
Spores often stick together in two or four, size (4) 4.5-5.5 (6) x (2.6) 3-4 microns, colorless, hyaline, smooth, ellipsoid or ovoid, cyanophilic. Hyphae of the cortical layer 1.5-3.5 µm thick, in deeper layers up to 6 µm, septa with buckles.
Ecology and distribution
Waxy talker grows in forests, more often on deciduous litter, sometimes on coniferous (spruce, pine), in groups. Active fruiting season from September to late autumn. It is a species common in the northern temperate zone and is found in mainland Europe, Great Britain and North America.

Poisoning symptoms
Before the first symptoms of poisoning appear, it takes from half an hour to 2-6 hours. Begins nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, profuse sweating, sometimes drooling, pupils constrict. In more severe cases, severe shortness of breath appears, the secretion of bronchial secretions increases, blood pressure drops and the pulse decreases. The victim is either agitated or depressed. Dizziness, confusion, delirium, hallucinations and, ultimately, coma develop. Mortality occurs in 2-3% of cases and occurs after 6-12 hours with large quantities of eaten mushroom. Fatalities are rare among healthy people, but for people with heart and respiratory problems, as well as for the elderly and children, it is a serious danger.
We remind you: at the first symptoms of poisoning, you should immediately consult a doctor!
How to distinguish a deciduous talker from other mushrooms
Under certain conditions, a conditionally edible saucer-shaped govorushka (Clitocybe catinus) can be taken for a deciduous gossip, but the latter has a matte surface of the cap and more descending plates. In addition, the saucer-shaped spores are of a different shape and larger, 7-8.5 x 5-6 microns.
The bent beetle (Clitocybe geotropa) is usually twice as large, and its cap has a pronounced tubercle, so it is usually quite easy to distinguish between these two species. Well, the spores of the bent talker are somewhat larger, 6-8.5 x 4-6 microns.
It is much more unpleasant to confuse edible sub-cherry (Clitopilus prunulus) with a vernacular gossip, but it has a strong flour smell (for some, however, quite unpleasant, reminiscent of the smell of spoiled flour, forest bugs or overgrown cilantro), and pinkish plates in mature mushrooms are easily separated from the cap with a fingernail. In addition, the spores are larger in the sub-cherry.
Talkers: benefit and harm
This type of mushroom has many beneficial properties because it combines vegetable and animal proteins. Fiber, vitamins, active minerals, amino acids - an incomplete list of what mushrooms are rich in.
You can cleanse and renew the entire body (remove toxins, heavy metal salts) with the help of Clitocybe. For vegetarians, these mushrooms are an irreplaceable product of the diet, because in terms of the total amount of nutrients and nutrients, they are in no way inferior to meat products.
Govorushka is a low-calorie product, the energy value of which is only 30 kilocalories (in one hundred grams).
| Composition | Gram |
|---|---|
| Protein | 3,7 |
| Fats | 1,7 |
| Carbohydrates | 1,1 |
Almost all types of mushrooms are low-calorie, for example, in 100 grams of champignons - 27 kilocalories, in 100 grams of butter - 9 kilocalories, but in 100 grams of dried porcini mushrooms - 152 kilocalories.

General description of talkers
Clithocybe is a genus of cap mushrooms, which belongs to the family of ordinary mushrooms. This species is very often confused in appearance with the genus Lepista or Leucopaxillus. People eat only safe varieties of the mushroom, they can be calculated primarily by their color and aroma. They are bright in color and with a less pronounced tart odor.
Talker mushrooms have small and medium-sized caps, the diameter of which varies from 3 to 6 centimeters. It happens that there are specimens in which the cap reaches 15 centimeters. The hemispherical shape of the cap is inherent in young mushrooms, but when they grow up, it becomes more even. Mature clitocybe have caps depressed in shape, somewhat like a funnel.
If the climate is right for the mushrooms, their caps will be dry and smooth. They are found in different colors: whitish, gray-brown, pink-brown, ocher. The color of the cap is uneven, becoming lighter from the center to the edge during the growth period.
The plates are located on the underside of the mushroom cap, they are white in color, but turn yellow as the talker ages. The height of the leg depends entirely on the type of clitocybe, the maximum figure is 8 centimeters.
Clitocybe has a huge genus, which includes about 250 types of fruit chalk. Some of them are very popular and are used for preparing various dishes for the purpose of rapid weight loss and in medicine.