Primary processing and preparation
Bitters can be salted, pickled, sometimes even fried, although the latter method of preparation is rarely used. However, in order to properly prepare them and get rid of the characteristic bitterness present due to the milky juice, the mushrooms need soaking.
Usually only young bitters are pickled. They can be salted both hot and cold, but it is definitely best to do it with spices. Correctly cooked bitters, salted or pickled, can become a real decoration of the festive table.
Bitter is a gift of nature, which is not only good for food, but also used in medicine. Its tissues contain a substance that negatively affects some pathogenic bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus. So bitters can not only be used as food, but also prove to be beneficial to health.
Bitter

Path
Lactarius rufus
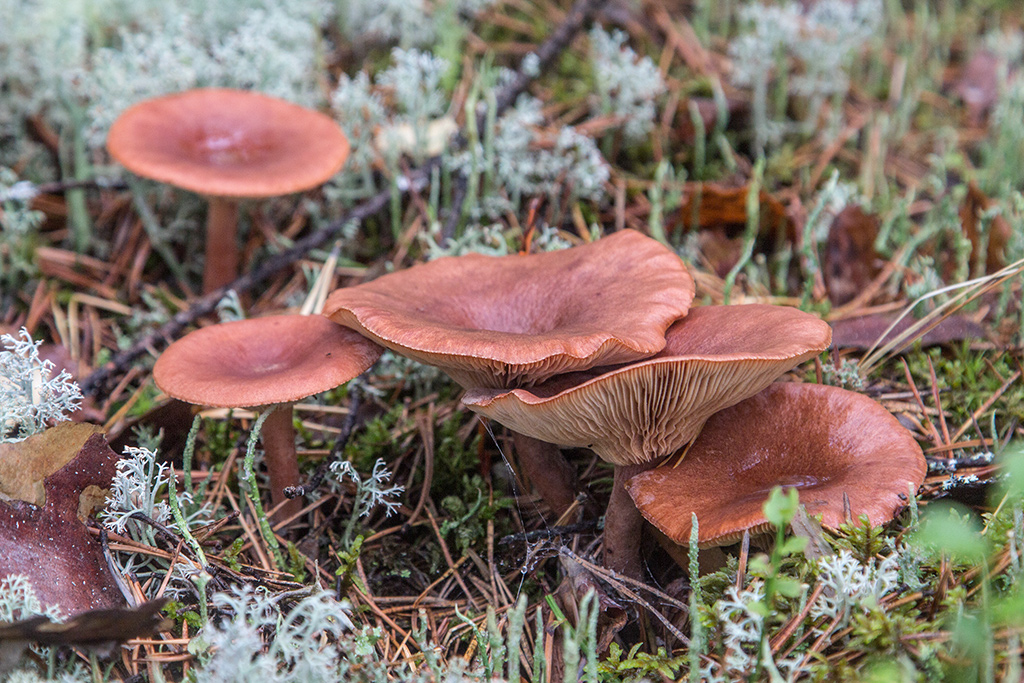
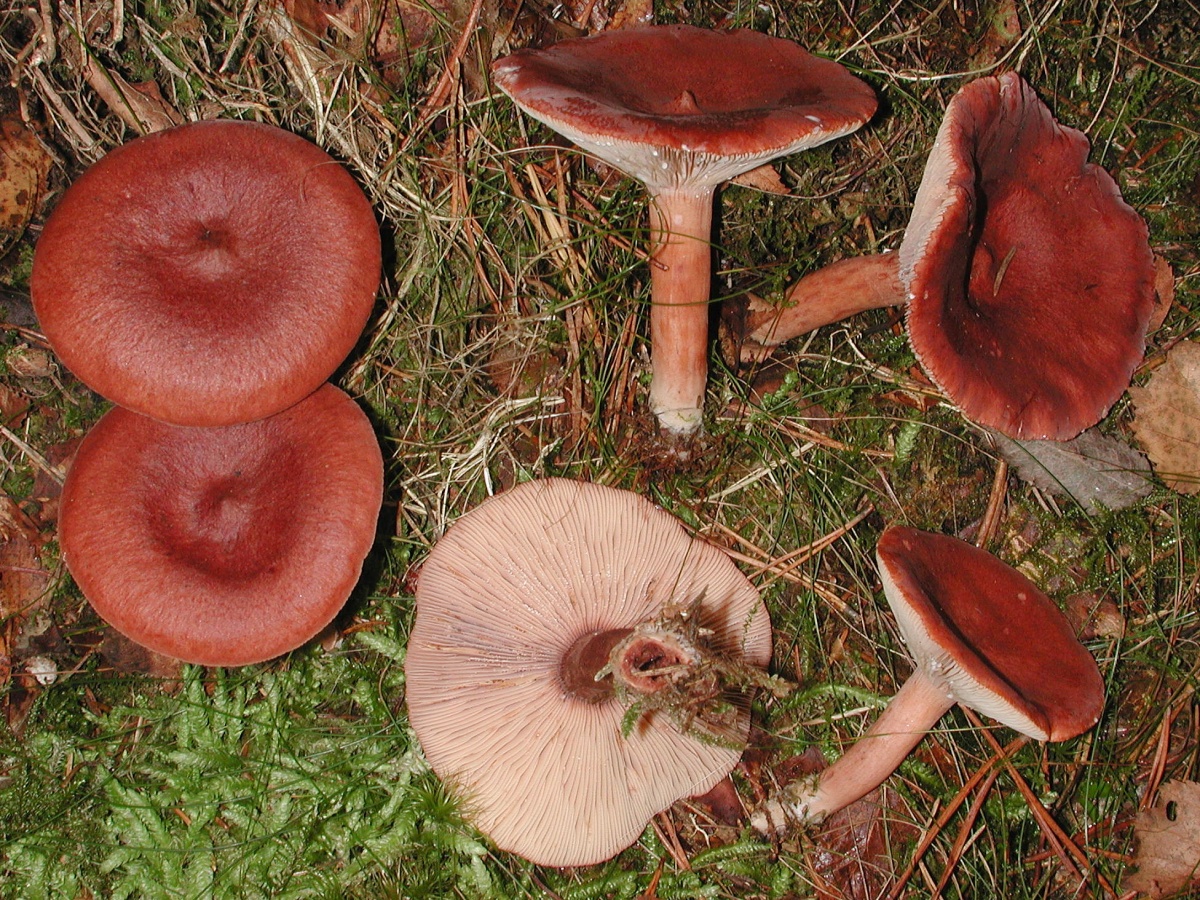
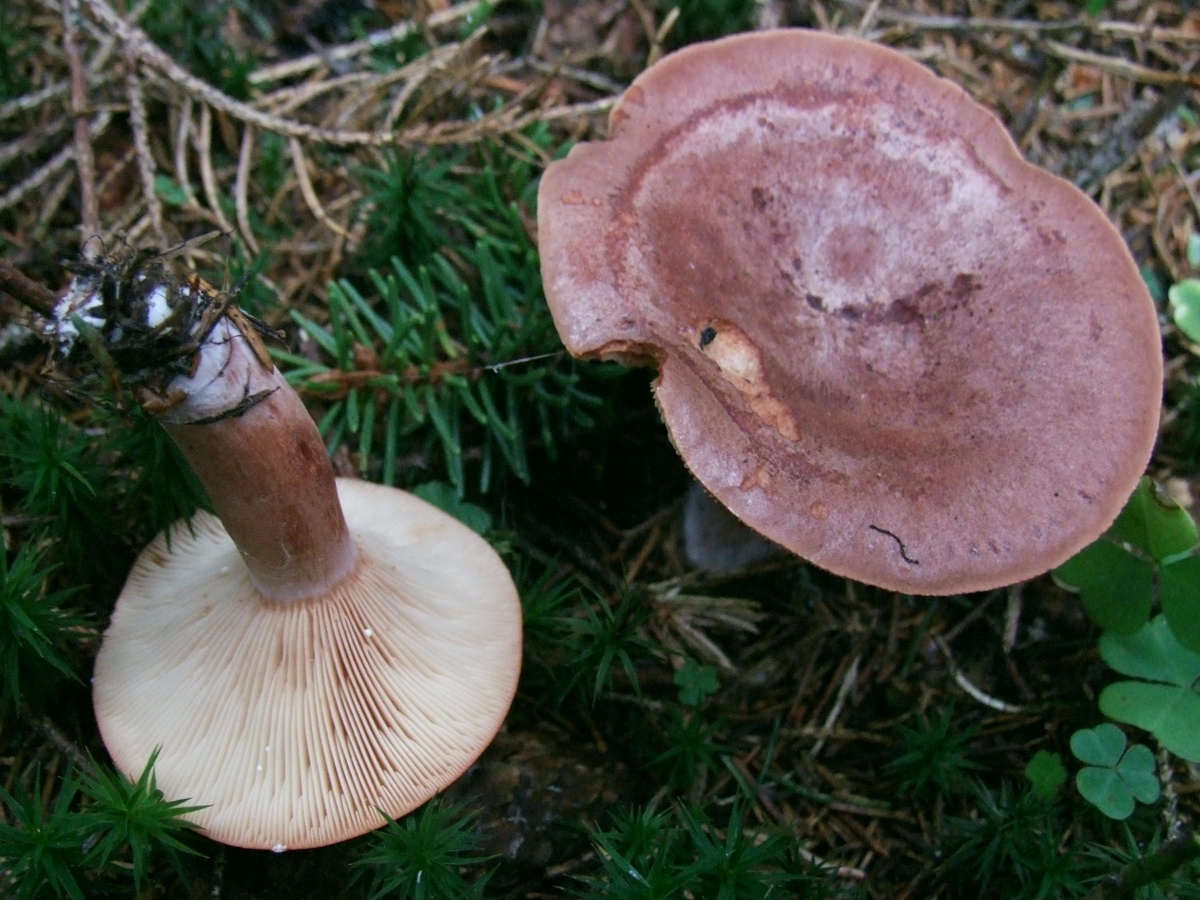
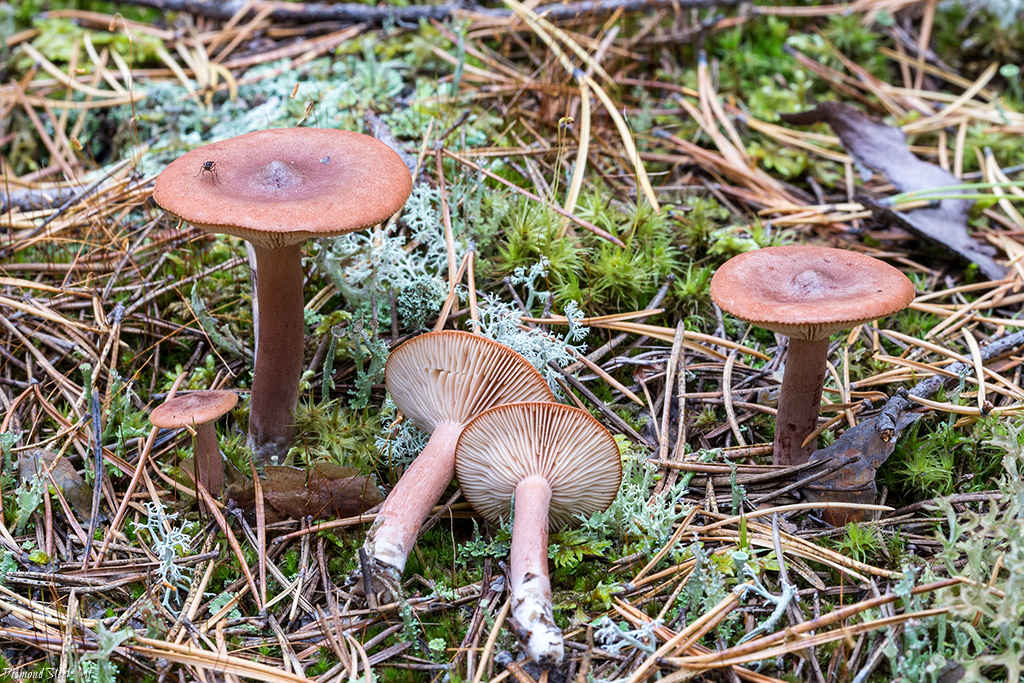
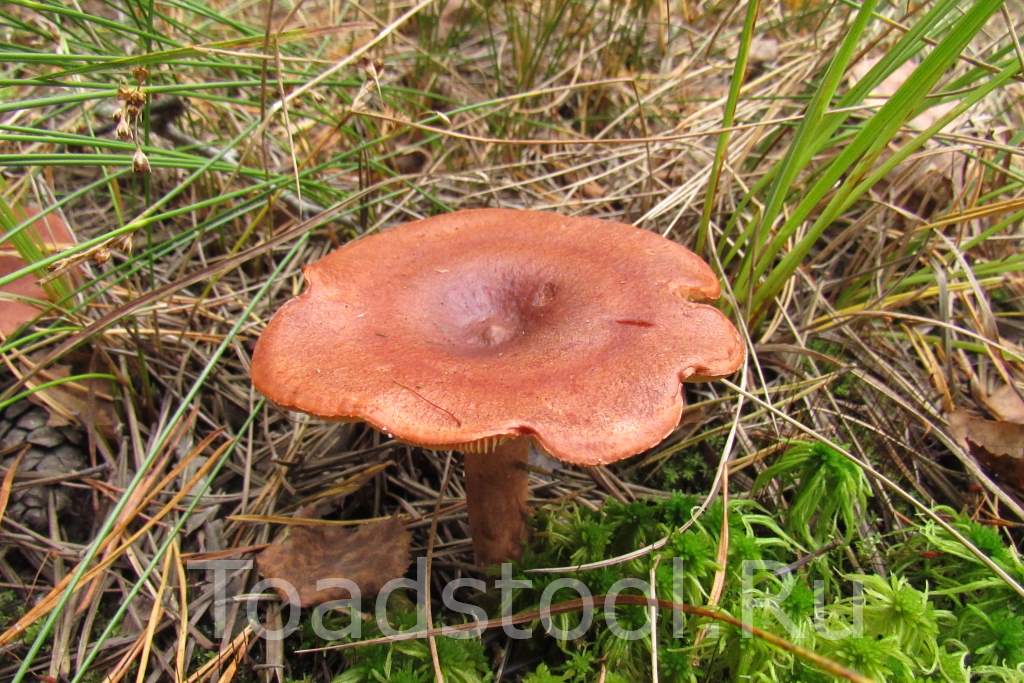
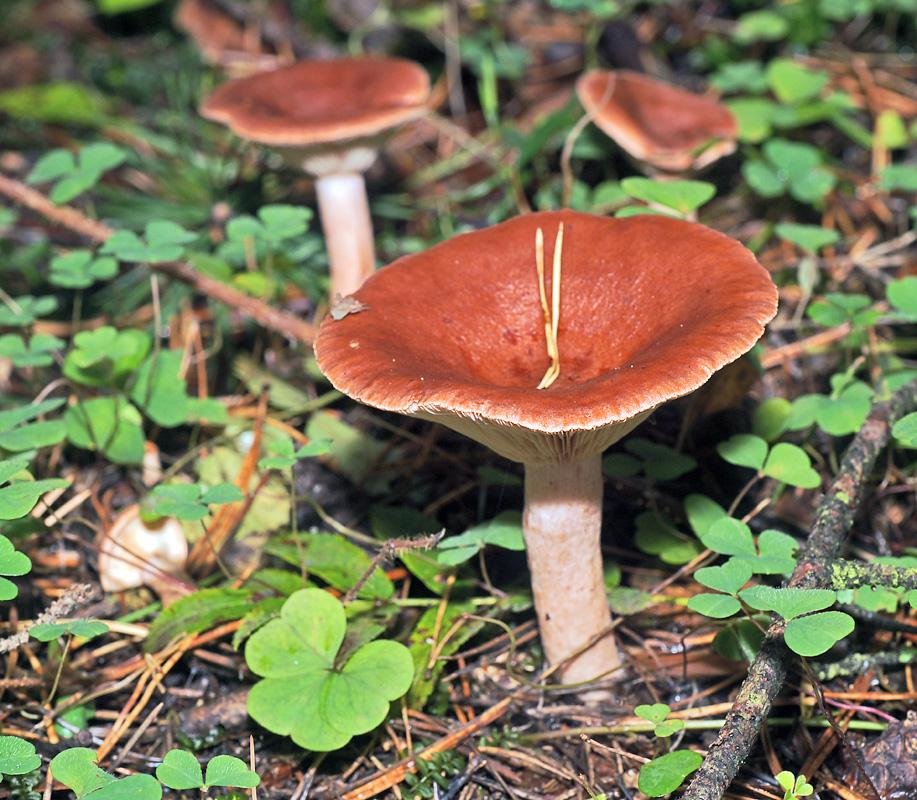
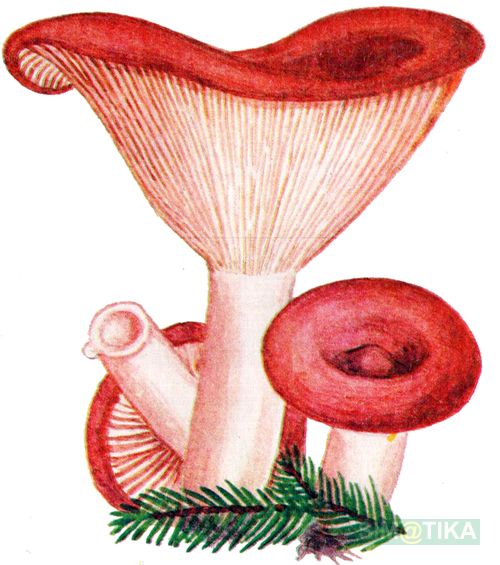
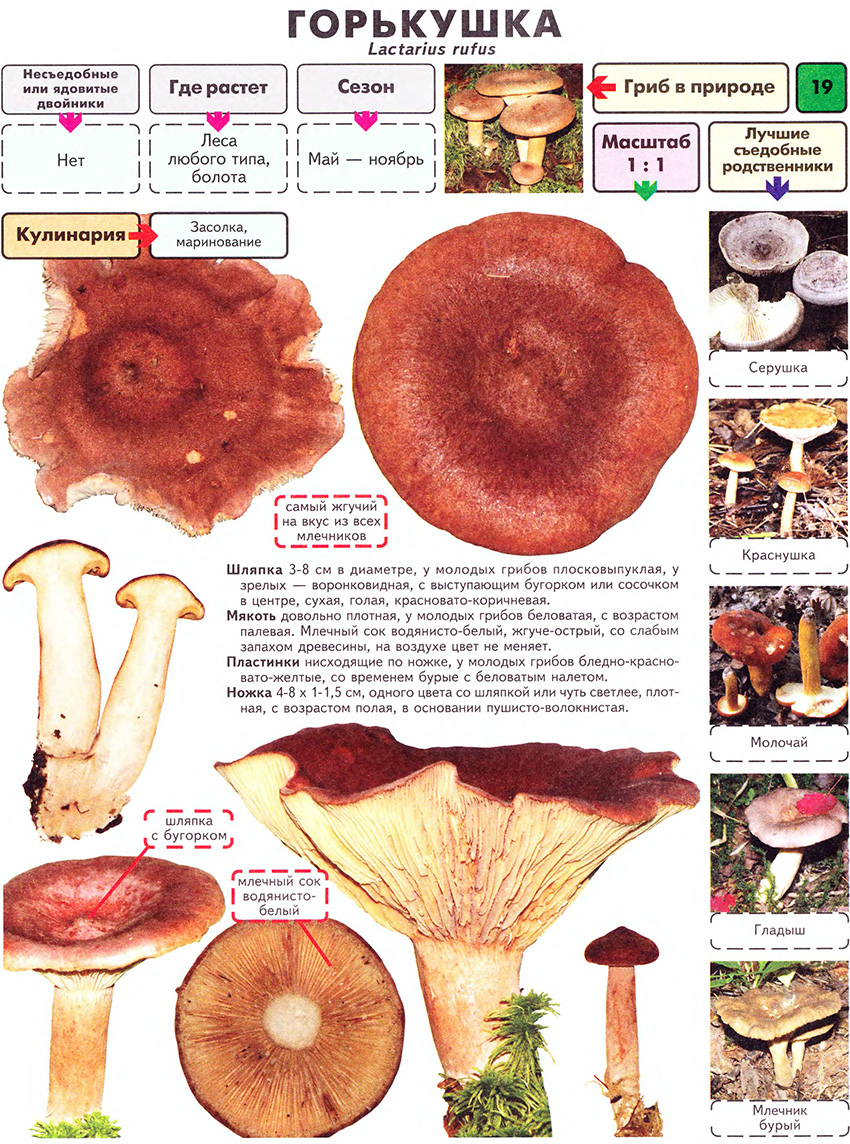
Description: A bitter hat with a diameter of up to 12 cm, flat-convex, funnel-shaped with age, fleshy, dry, red-brown, matte, with a sharp tubercle in the middle, around which it is depressed. It is characteristic that in mature specimens it is colored dark red or red-brown. Lighter circular areas are sometimes possible. The surface is finely grooved, has a cloudy matte color.
Bitter pulp is thin, with the smell of resinous wood. The milky juice is pungent, pungent, white, very plentiful. The plates are narrow, frequent, at first reddish-yellow, later reddish-brown, in old age with a whitish bloom, slightly descending along the stem. The spore powder is whitish.
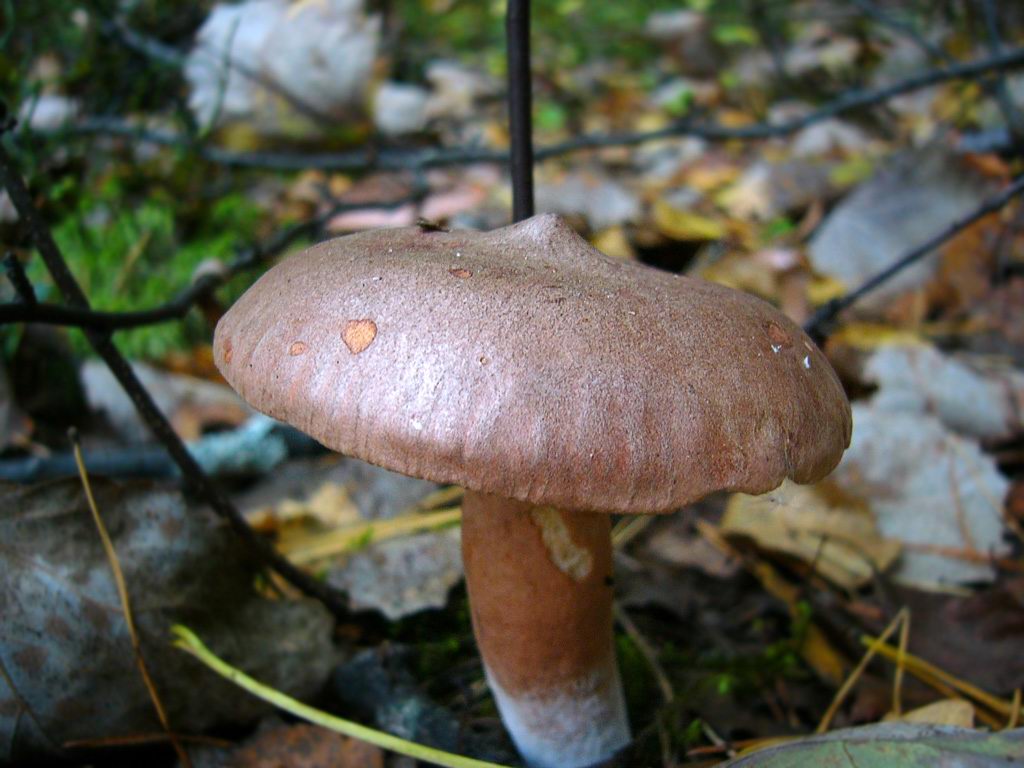
The leg of the Bitter is up to 10 cm long, up to 2 cm thick, cylindrical, white-tomentose, has pubescence at the base, solid at a young age, later hollow. Young mushrooms have a whitish surface, older ones are pinkish or rusty-red. The leg can be colored in the same way as the cap.
Doubles: Bitter is confused with the edible camphor mushroom (Lactarius camphoratus), which smells of dry roots, and the slightly bitter orange mushroom (Lactarius badiosanguineus), which has a strong red-chestnut hat with a dark center and a similarly colored stem. A similar marsh lump (Lactarius sphagneti), which is colored the same as bitter, grows in damp, swampy spruce-pine forests.
Note: The word rufus in the name of the mushroom means "redhead".
Edible: Bitter is a conditionally edible mushroom, often referred to the fourth category. It is used in salted and pickled form after pretreatment - thorough boiling or soaking. In saline it becomes dark brown.
In medicine, Bitter (Lactarius rufus) contains an antibiotic substance that negatively affects a number of bacteria, and also inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus cultures.
Where it grows and when to collect
There is no specific place where these mushrooms grow, since they are common almost everywhere - in forests of any type.
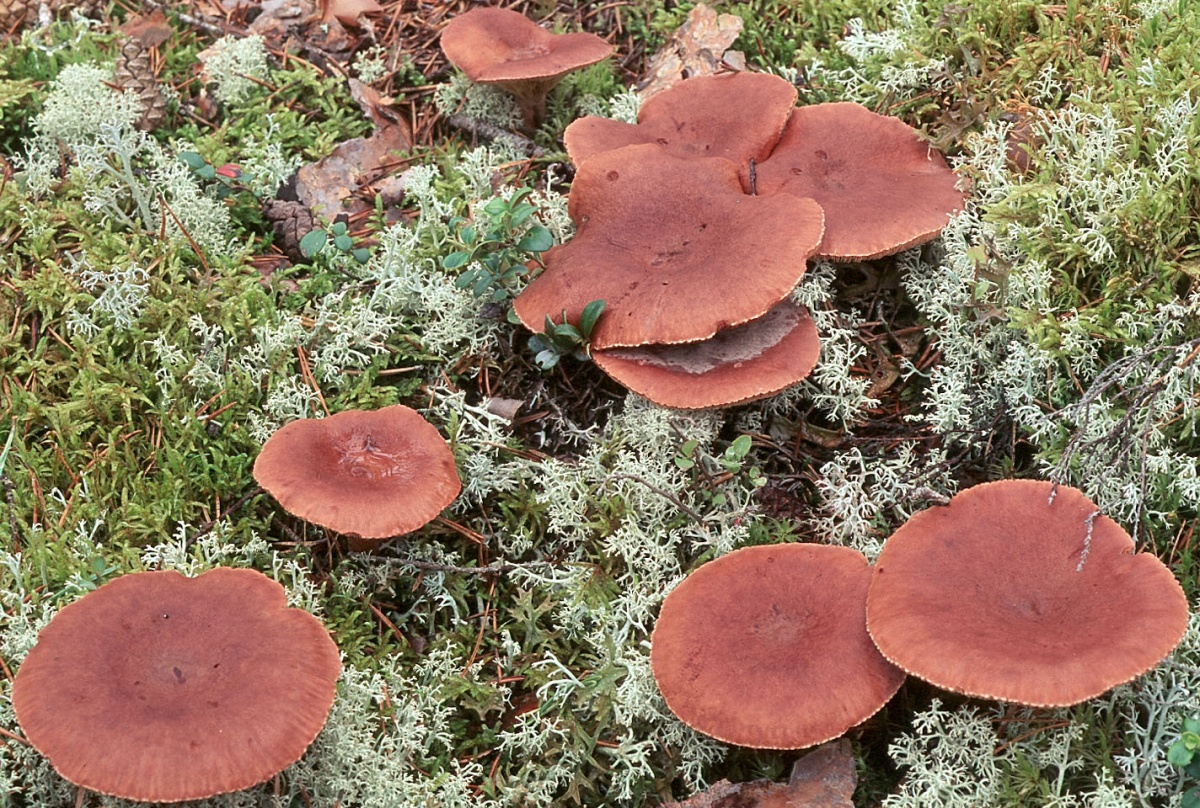
The largest accumulation of fruit bodies is observed under pines and birches in the northern half of the forest zone, in moist pine forests, where it forms mycorrhiza with these trees.
Also, the collection is carried out near lichens and mosses, where the soil is acidic and moist. Meet singly or in groups.
Fruit bodies can occasionally come across in parks or near detached trees, in the case of the introduction of mycelium with soil from the forest.
Collecting mushrooms begins in July. Fruiting lasts until mid-autumn - October. In some regions, they bear fruit before the first autumn frosts.
You should not harvest near roads, industrial and gas-polluted areas, because they are capable of accumulating toxic substances and become dangerous to human health and life.
Processing and preparation process
It is believed that bitter is not an edible mushroom, however, it should be noted that they can be salted, pickled, fried, only after preliminary heat treatment. In order to completely free the mushroom from bitterness and make it suitable for consumption, it is necessary to give it a sufficiently long soaking.
If you are going to pickle this type of mushroom, then you should make sure that only young mushrooms are selected for this process. When pickling, it is worth considering that it is necessary to use a lot of spices, this is necessary in order to kill the bitter unpleasant aftertaste as much as possible. If the salting process is done correctly, then bitters can become one of the best dishes on the festive table.
If you intend to fry these gifts of the forest, then you should not just soak them for a long time, but also take into account the peculiarity that the last water must be well salted so that the salt absorbs all the bitterness as much as possible. After that, the bitters are cut into small pieces and fried in butter with the addition of onions and various spices. If you fry the bitters yourself, without adding seasonings, then the bitter aftertaste may not completely go away. However, it should be borne in mind that bitters very rarely lend themselves to the frying process.
Bitter is an inhabitant of the forest, which can be eaten not only as food, but it is also widely used in folk medicine. A fairly large number of infusions and decoctions are prepared with the addition of this mushroom. Bitter pulp contains beneficial substances that can be useful in the treatment and prevention of many diseases. Bitter is recognized as a fairly effective remedy in the fight against bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Consequently, bitter can be used not only as food, but also to help maintain human health.
Similar species
Bitters are quite similar to many mushrooms of the genus Millechnik. The easiest way to identify the mushroom is by the tubercle in the center of the cap and the presence of caustic sap when it breaks. However, mushrooms can be distinguished by other signs.
It is important to know exactly which mushroom goes into the basket. The main similar types of mushrooms:
Liver Miller

This representative is inedible. It differs in a yellow tint of juice, which is released when it interacts with air. The flesh of the mushroom can be either yellow-brown or creamy.
Swamp milky

This edible species is found exclusively in swampy areas of coniferous forests, therefore, it can be distinguished from bitter by its habitat.
Camphor lactarius

It is a small edible mushroom with very specific flavor characteristics. It can be identified by its floral aroma, a very small bump on the cap and sweet milky juice.
Stunted milkman

This mushroom is conditionally edible and differs in that it secretes a yellow milky juice when cut and is covered with a lighter skin on the cap.
Gladysh

This representative is an edible mushroom. It is characterized by a more glossy cap without a tubercle. The color is chestnut red, and the leg is shortened.
While most mushrooms are edible, there are some that can be harmful to your health. Therefore, it is worth carefully studying false doubles before visiting the forest.
How to salt bitters at home?

Salting bitters at home is not at all difficult, but you need to know the features of their preparation. To eliminate the bitterness, the mushrooms need to be soaked in water for 5 days, changing the water every day. To store bitters at a time when they are salted, you need to in a cool place - a basement or cellar.
- salt - 2 tbsp. spoons;
- bitters - 1 kg;
- garlic, spices - to taste.
- The soaked bitters are washed and squeezed out.
- Spread in a container, season with salt, spices and garlic.
- Cover the mushrooms with water, put a load on top and leave for a month.
Marinade for bitters

Salting bitters for the winter is different. Sometimes only saline is used.And sometimes mushrooms are poured with marinade and vinegar. Then they turn out to be pickled and will have an interesting, slightly sour taste. After boiling, the mushrooms are poured over with cold water so that they have a denser structure.
- bitter mushrooms - 1 kg;
- water - 2 glasses;
- vinegar - 60 ml;
- salt - 1 tbsp. spoon;
- sugar - 1 tsp;
- black pepper - 10 peas;
- carnation buds - 5 pcs.;
- bay leaves - 2 pcs.;
- onions - 2 pcs.;
- carrots - 1 pc.
- The bitters are boiled for 20 minutes and squeezed out.
- Water is poured into a saucepan, sugar, salt, vegetables, spices are added and boiled until vegetables are cooked.
- Pour in vinegar, lay mushrooms and boil for 10 minutes.
- Mushrooms are placed in jars, poured with marinade and covered with lids.
How to pickle bitters quickly?

Pickled bitters, the quick preparation of which will be discussed below, turn out to be very appetizing with a light aroma of the spices used. In this case, it is not necessary to use the entire set of spices that are indicated in the recipe. If you don't like one of them, you can do without it.
- bitters - 2 kg;
- onions - 1 kg;
- vinegar essence - 3 tsp;
- black peppercorns - 9 pcs.;
- cloves - 3 pcs.;
- bay leaf - 2 pcs.;
- sugar, salt - 2 tbsp. spoons;
- water - 1 liter.
- Washed mushrooms are placed in a saucepan, poured with water, boiled for 10 minutes, thrown into a colander.
- The onions are chopped.
- A marinade is made from water, salt, sugar, cloves, pepper and vinegar.
- Place mushrooms in it and boil for 5 minutes.
- Mushrooms are placed in jars, shifting layers with onions.
- Pour boiling marinade and pour in 10 ml of oil and seal.
How to salt soaked bitters?

How to salt the collected bitters so that the taste of the finished product is pleasant, worries every housewife who is doing this for the first time. The first step is to soak the mushrooms well, changing the water several times. The process can take up to 5 days, but as a result the mushrooms will taste great.
- bitters - 1 kg;
- garlic - 4 cloves;
- salt - 1 tbsp. spoon;
- black and allspice pepper, dill, currant leaf.
- Mushrooms are poured with water, changing it 1-2 times a day.
- Soaking the bitters takes 4-5 days.
- The bitters are boiled for 20 minutes, the water is drained, and the mushrooms are cooled.
- Place mushrooms with garlic, salt and spices in a container, place oppression and leave for 3-4 days.
- Mushrooms are placed in jars, oil is poured in and removed in the cold.
How to salt bitters hot?

If you are interested in how to salt bitters hot, this recipe is for you. It is believed that with this method of preparation, the mushrooms are especially tasty. First, the container with bitters is kept warm for about 10 days, and after that, for further salting, they are placed in a cold place.
- bitters - 1 kg;
- water - 1 liter;
- salt - 2 tbsp. spoons;
- dill, currant leaves, garlic.
- Hot salting of bitters begins by placing the mushrooms in a saucepan, pouring it over with water and boiling for 10 minutes.
- After that, they are thrown into a colander and poured over with cold water.
- A brine is boiled from water and salt, bitters are dipped into it and boiled for 15 minutes.
- Dill, currant leaves, garlic are placed at the bottom of the container.
- Chilled brine is poured in, a plate is placed on the mushrooms and the load is placed.
- In a couple of weeks, the bitters will be ready.
Description and photo of Bitter
As mentioned above, many mushroom pickers prefer to bypass the bitter side. And all because it is incredibly similar to a toadstool. However, it seems so only at first glance, if you do not know the nuances of the structure of the mushroom. Let's find out how to distinguish a bitter from other representatives of the forest. Indeed, in fact, it is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. Common names: Red Bitter, Bitter Milk, Gorchak, Goryanka, Putik, Sukharka.
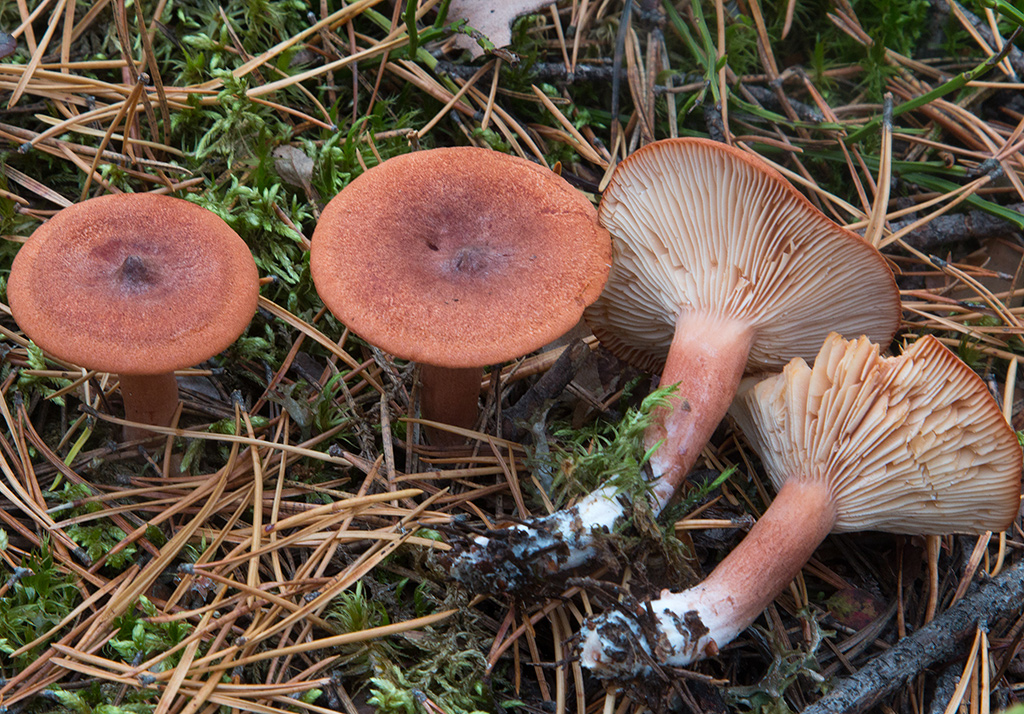
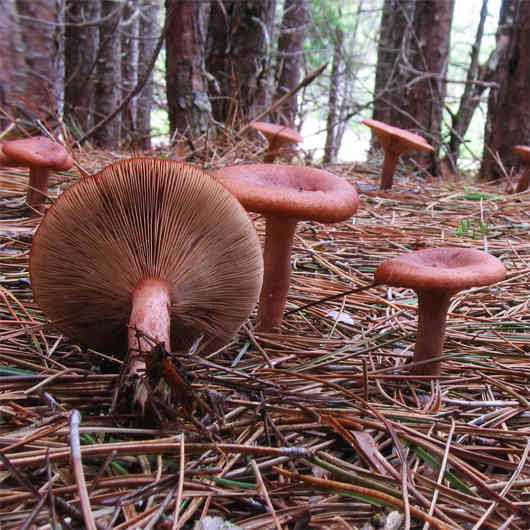
Hat
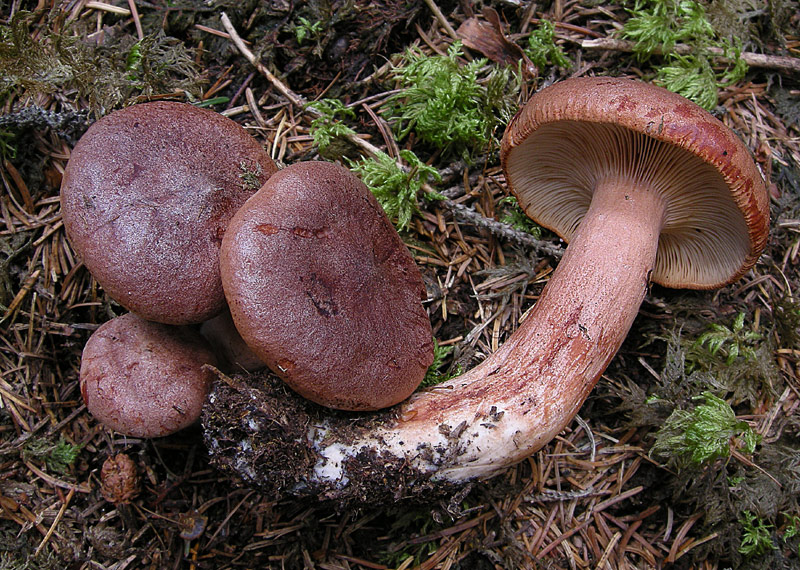
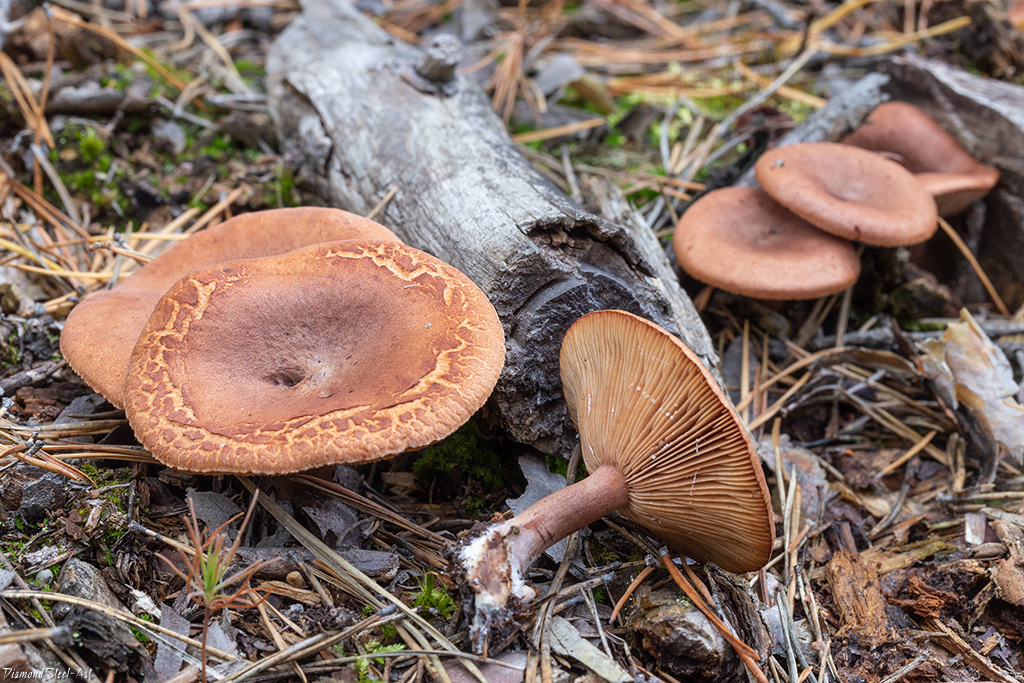
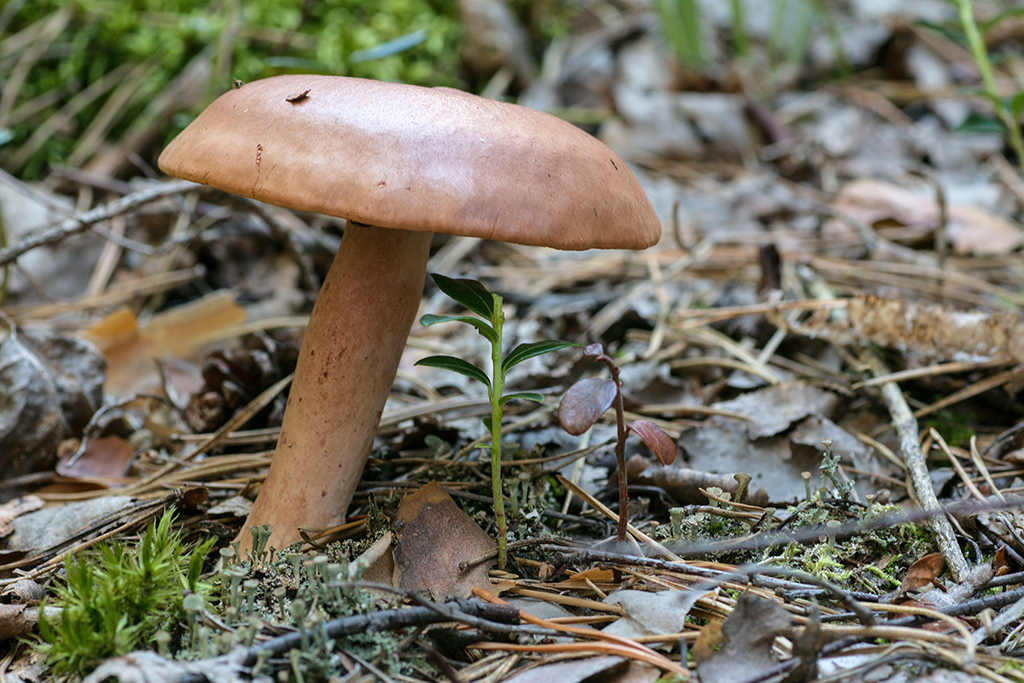
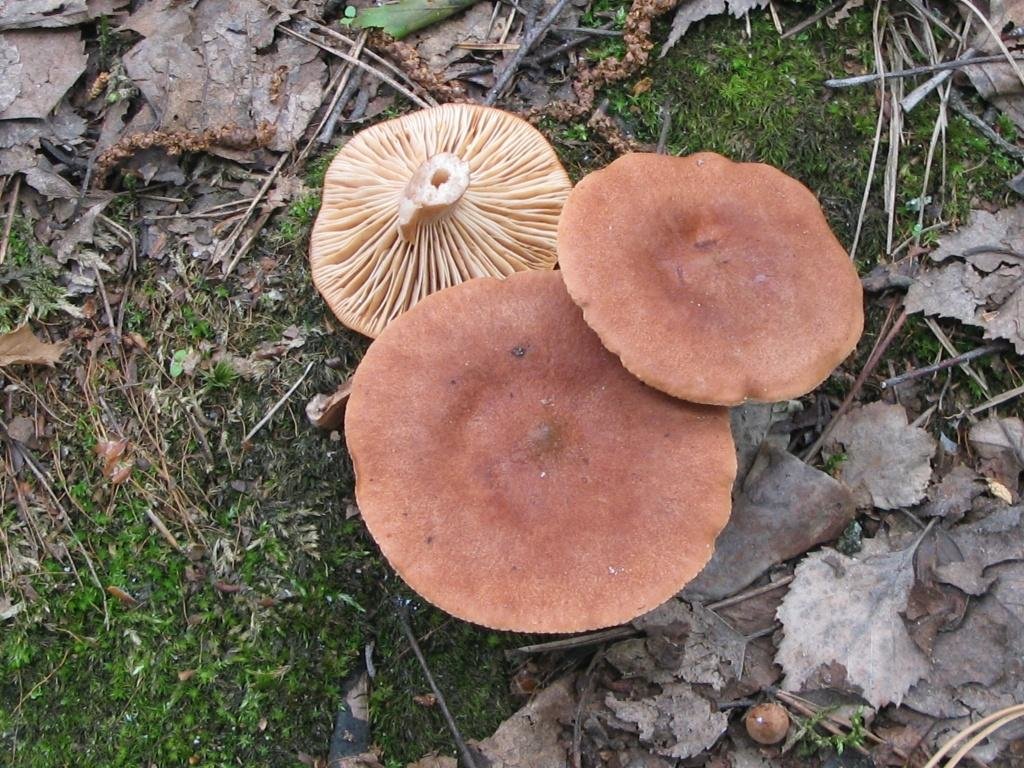
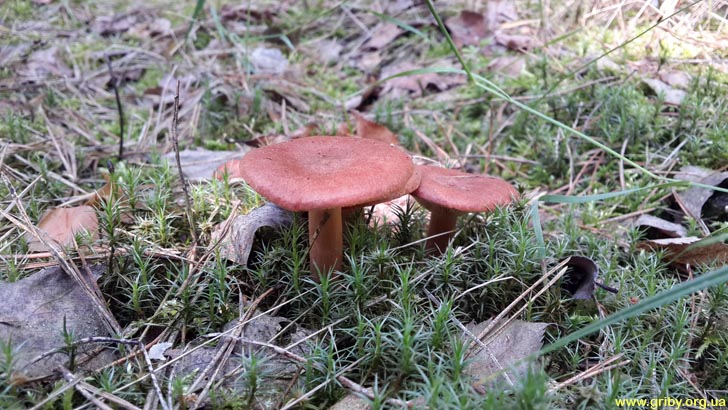
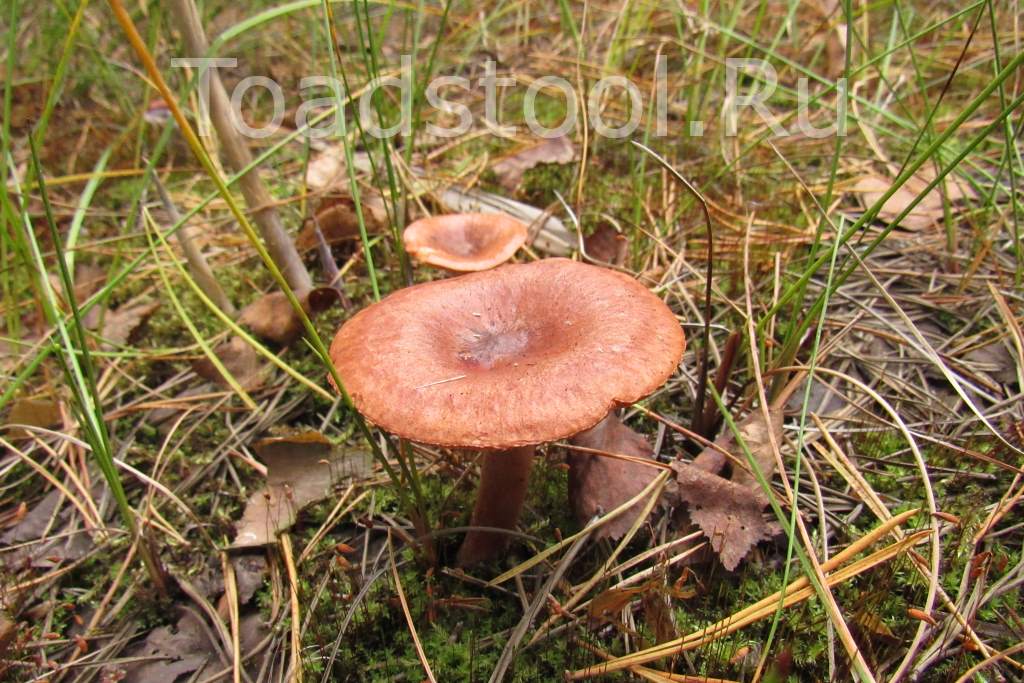
Bitter is a striking representative of the forest, and naturally, it is easy to spot it in the forest thicket. This mushroom has a very remarkable head. If you look at it carefully, you can see that it is bright enough. Most often it has shades of orange, brown or brown.In fact, it all depends on the soil in which the mushroom grows. If it is acidic, the mushroom becomes darker, if it is limestone, the cap of the mushroom is rather light.
As for the size of the cap, it can reach a maximum of 15 cm in diameter.However, most often there are specimens that are not so impressive in size. Average approximately 10, maximum 12 cm in diameter.
The hat is quite fleshy, if you touch it with both hands, you will feel elasticity and full of pulp. The hat smells pleasantly of mushroom champignon and other pleasant bouquet of aromas.
As for the skin of this forest dweller, it is quite dry and slightly slimy. However, if the mushroom does not grow in the shade, but prefers forest edges or clearings, then the cap becomes completely dry and cracks.
In general, the bitter has an umbrella-shaped hat with a pronounced dome. However, with age, its edges begin to rise, as a result of an uneven rise, the pulp begins to crack, and the mushroom does not look very presentable. Flies begin to settle inside.
However, this happens quite rarely and only under the direct influence of sunlight.
Leg
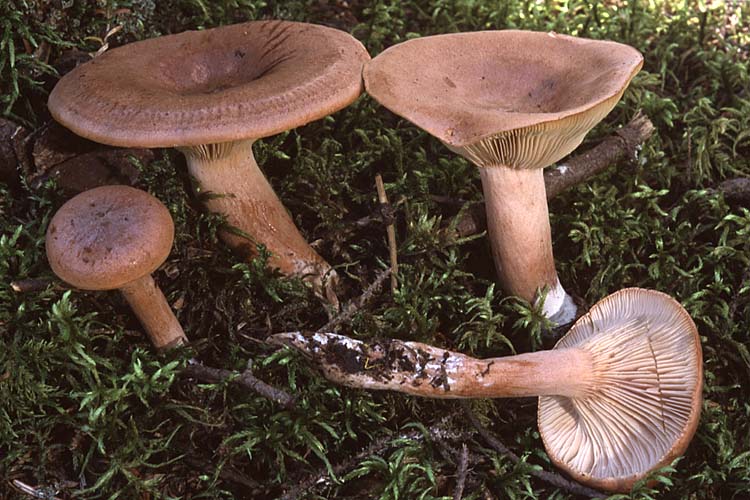
The stem of this mushroom is rather thin relative to the cap. And she hardly holds such a weighty mushroom. In length, it reaches about 8 cm. In diameter it rarely reaches 2 cm, usually from one to one and a half. The stalk is usually lighter than the cap, however, if the soil is very acidic, the stalk becomes darker.
It thickens slightly closer to the mycelium. With age, the leg becomes almost hollow, it can hardly withstand the cap. However, at a young age, it is very elastic and no less tasty. It also gives off a very pleasant smell.
Pulp
As for the pulp, it has a white tint, but when it interacts with oxygen, it quickly darkens and becomes beige and even orange. If you make a cut, then flies and other insects will quickly fly to the smell, because a bitter for them is a favorite delicacy.
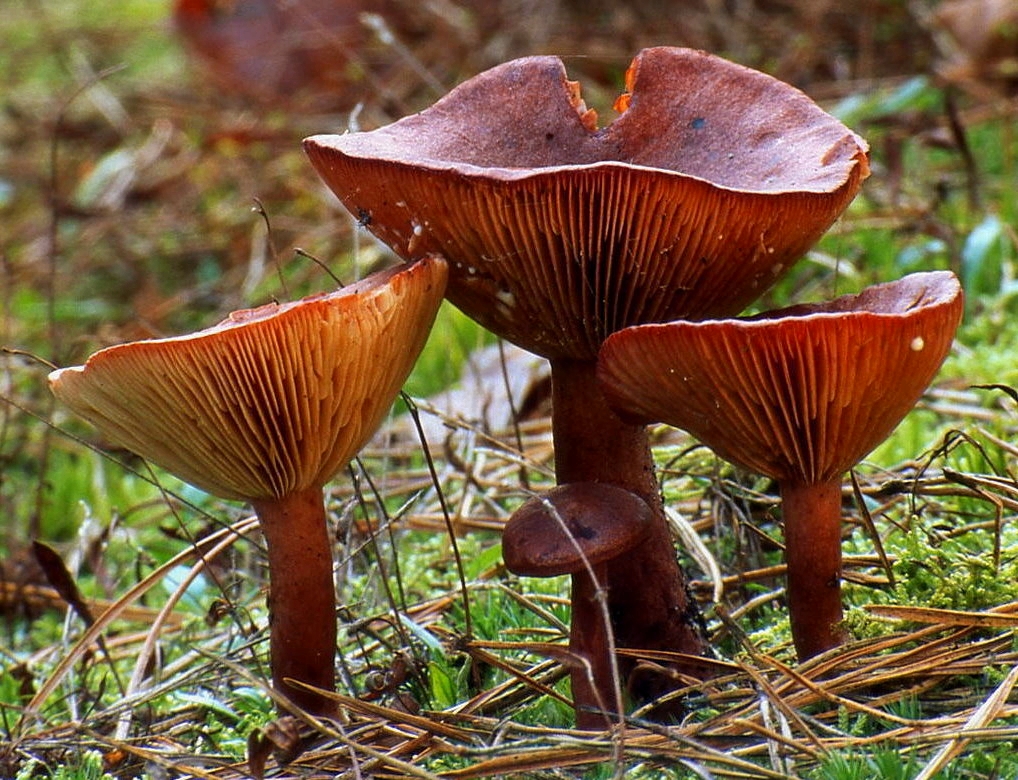
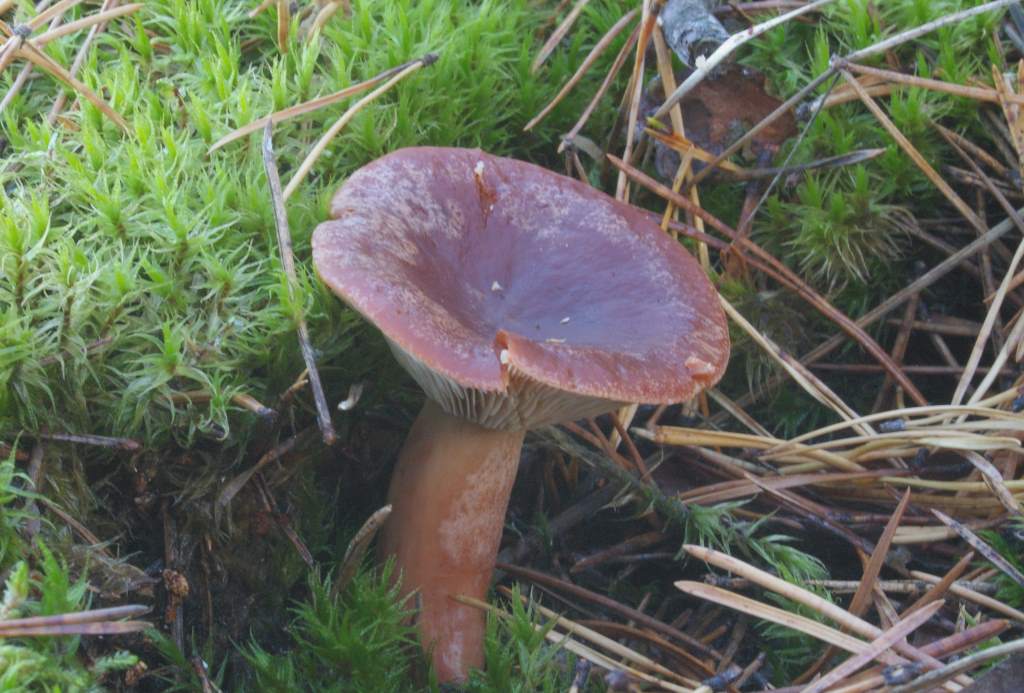
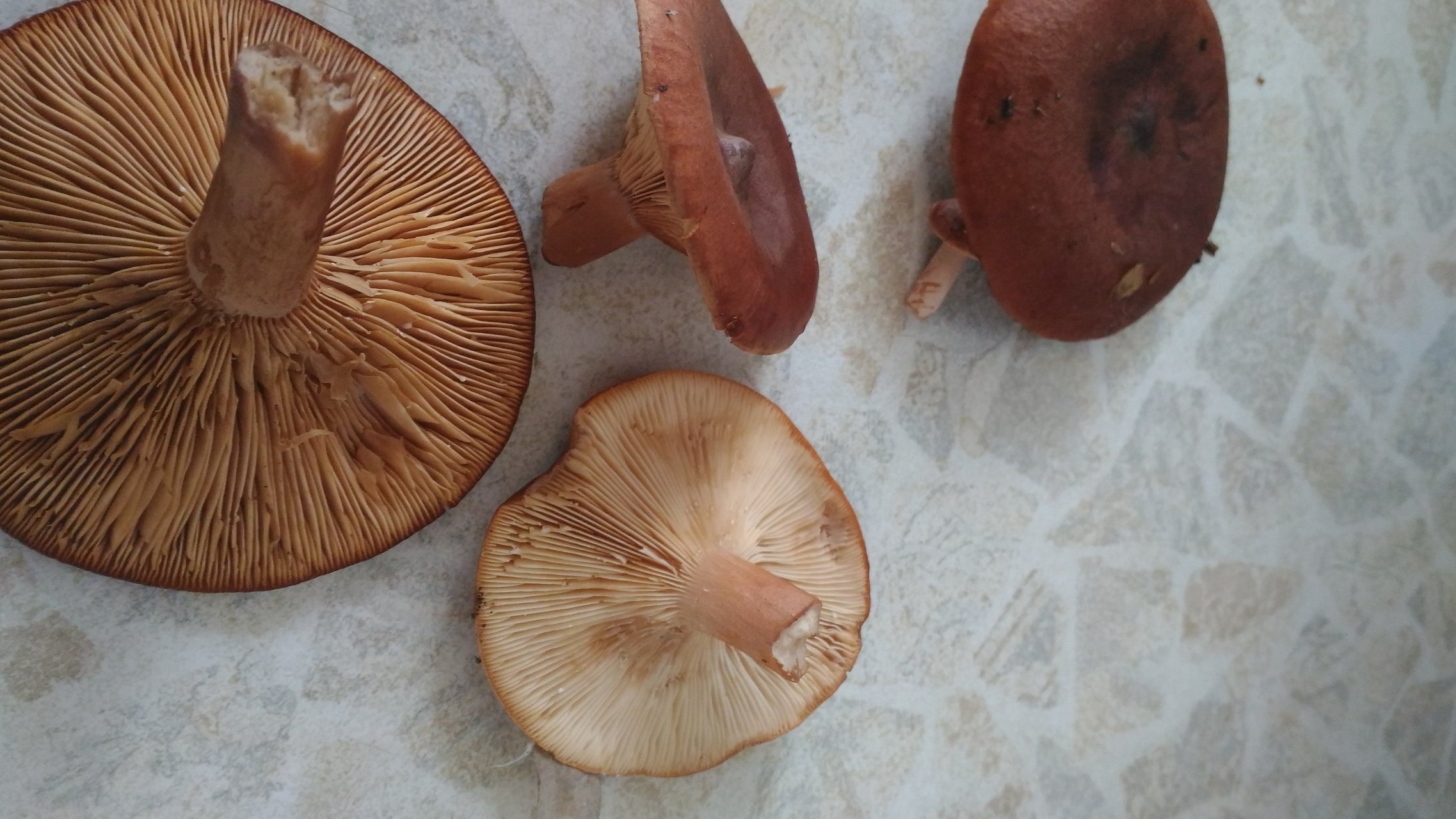
If you look under the hat, you can see very thin white and pink plates. Also, over time, these plates can also acquire a brown color. It is believed that the standard size of such plates is quite thin, however, depending on the nuances of growth, the plates can become wide. Spores of olive shade and spore powder are hidden there.
The mildness is bitter on the palate, but with proper home processing, it will become truly tasty, aromatic and nutritious.
Raw mushroom tastes hot, like you tasted pepper. Also, the pulp on the cut gives a milky white juice, and the smell is similar to wood.
Growth calendar
When should you go looking for a bitter taste?
In fact, this mushroom has a very clear framework for growth and development. It is believed that the bitter begins to grow actively from June, when a bright and active sun appears and is already warm enough. However, as it grows and develops, the bitter has a fairly large seasonality. It is believed that from June it grows to mid-September, after which this mushroom stops actively growing and begins to dry out.
However, if the spring is very warm, then the bitter can begin to grow from May.
The same applies to warm autumn, with a favorable development of events, the bitter can grow until the end of October.
It is believed that the optimal time to harvest this mushroom is from mid-August to mid-September. Then the mushrooms are already gaining their strength, have the best possible characteristics in terms of quality and composition. The same goes for taste characteristics. Therefore, you should go on a mushroom hunt at this time.
Difference from false doubles
Edible bitter has several siblings. Some of which are inedible, and some can be eaten.
In order not to confuse the desired mushroom with a "copy", often unsuitable for food, one should be guided by two signs: white milky juice secreted by the pulp during cutting, and a protruding tubercle in the center of the cap.But when collecting edible counterparts, you can be glad that you will be able to introduce your relatives to the new "participant" of the feast and continue collecting the fruit bodies of these mushrooms in the future.
To be sure, you can familiarize yourself with a more detailed description of species similar to bitter.
- Hepatic miller. An inedible mushroom (due to its extremely pungent taste), from which, when broken, a milky juice flows out, yellowing in air. The pulp is creamy or brown-yellow. The leg is upright in the same shade as the cap.
- Miller stunted (tender breast). A cap with a light surface, a tubercle in the center, surrounded by a depression. When cut, it produces a white milky sap that turns yellow in air. The species is classified as conditionally edible mushrooms.
- Swamp bush. Prefers to grow in wetlands in coniferous forests. The hat is brick-colored, the leg and plates are one tone lighter. Milky juice is whitish, in air it is gray with a yellowish tinge. Refers to edible mushrooms.
- Camphor milky (camphor milk). This double is edible, but due to its specific smell it is not in demand among mushroom pickers. Gives off copiously acrid white milky juice. The pulp is loose, fresh. A hat with a small tubercle and ribbed edges.
- Common miller (smooth). An edible mushroom with a glossy cap, concave inward in the center. The color of the cap is from brown to lilac. The leg is upright, short. The smell is practically absent. Milky juice is white, acrid, not very plentiful, slightly green in the air.
- The miller is reddish. An edible mushroom with a maple syrup flavor and scent. The cap is bright brown-red, up to 10 cm in diameter, the leg is up to 12 cm long and up to 3 cm thick. The hymenophore plates are closely spaced, the color is pinkish-yellow.
Composition and calorie content of bitter

The mushroom is considered conditionally edible, it is not consumed raw.
The calorie content of bitter is 22 kcal per 100 g, of which:
- Proteins - 2.18-3.09 g, depending on the growth conditions;
- Fat - 0.34 g;
- Carbohydrates - 3.26 g;
- Fiber or dietary fiber - 1 g;
- Water - 92.45 g.
The bitter contains sugars - 1.98 g, of which dextrose 1.48 g and fructose 0.17 g.
The pulp of the mushroom contains vitamins and minerals, albeit in small quantities.
Vitamins per 100 g of product:
- Vitamin C - 2.1 mg;
- Thiamine - 0.081 mg;
- Riboflavin - 0.402 mg;
- Nicotinic acid - 3.607 mg;
- Pantothenic Acid - 1.497 mg;
- Vitamin B6 - 0.104 mg;
- Folate - 17 mcg;
- Choline - 17.3 mg;
- Betaine - 9.4 mg;
- Vitamin B12 - 0.04 mcg;
- Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) 0.01 mg
- Tocopherol, beta - 0.01 mg;
- Tocopherol, gamma - 0.01 mg;
- Tocopherol, delta - 0.01 mg;
- Tocotrienol, alpha - 0.05 mg;
- Vitamin D (D2 + D3) - 0.2 μg;
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) - 0.2 mcg;
- Vitamin D7 - IU;
- Vitamin K1 (as dihydrophilloquinone) 1 mcg
The amount of vitamin D varies: mushrooms that have grown on sunny fringes have more of it.
Mineral composition of pulp:
- Calcium, Ca - 3 mg;
- Iron, Fe - 0.5 mg;
- Magnesium, Mg - 9 mg;
- Phosphorus, P - 86 mg;
- Potassium, K - 318 mg;
- Sodium, Na - 5 mg;
- Zinc, Zn - 0.52 mg;
- Copper, Cu - 0.318 mg;
- Manganese, Mn - 0.047 mg;
- Selenium, Se - 9.3 μg.
It also contains amino acids and lipids.
There are a lot of mushroom pulp:
- Vitamin C, which is necessary for the body: stabilizes the hormonal system, supports hematopoiesis, neutralizes the development of allergic reactions.
Riboflavin, which improves the quality of hair and skin, prevents headaches and increases local immunity of the organ of vision and oral mucosa.
Folic acid, which normalizes digestion processes, participates in metabolic processes and stimulates the production of red blood cells. Another beneficial effect of folic acid is the production of serotonin, the pleasure hormone. With its lack, depression develops.
What mushrooms look like
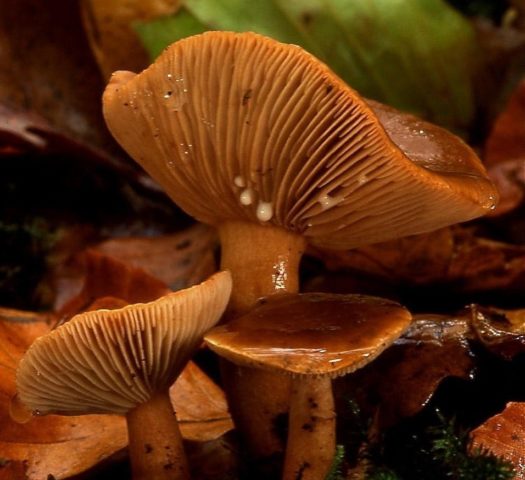

The pulp of this species gives off an abundant milky juice of a whitish color.
In this photo, you can see that the fruit body of the mushroom hitchhiking consists of a lamellar cap and a thin leg.The cap is convex or depressed with a small central tubercle and tucked edges inward. In diameter, it reaches up to 8 cm, painted in a reddish-red color. The surface is smooth or slightly wrinkled to the touch. On the inner side of the cap there are narrow, descending and frequent plates. Their color varies from whitish to light brown or pinkish. The spores are medium in size, spherical in shape with a mesh surface. Spore powder of creamy pinkish hue.
The leg is cylindrical, narrowed downwards, the thickness is 1.5 cm, and the length is 4-6 cm. It is characterized as straight, but in some specimens it may be slightly curved. Colored in lighter shades than the hat.
The flesh is firm and rather fragile, the color varies from white to nutty. When damaged, it secretes abundant milky juice, which remains unchanged in air. It is bitter in taste, exudes an unpleasant aroma, similar to the smell of rubber or bedbugs.
Application
The chemical composition of the species is different, so each of them has found its own niche for use. Some are used more for the preparation of gourmet dishes, and some are used in medicine, in pharmaceuticals or for cosmetic purposes.
Medicinal use
Some species are used to create medications that help stabilize blood pressure and reduce blood sugar and "bad" cholesterol levels.
- carbohydrates;
- proteins;
- fiber;
- vitamins (especially C and PP);
- microelements (phosphorus, potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium).
You can also talk about the following medicinal properties of bitter:
- normalization of heart rate and blood pressure;
- stimulation of metabolism and hematopoiesis;
- reducing the risk of the onset and development of cancer and infectious diseases;
- antioxidant, anti-inflammatory action;
- immunostimulation.
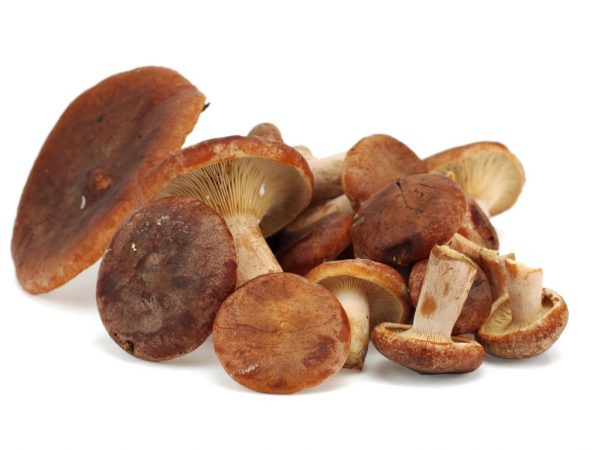

The mushroom is used both in medicine and in cooking.
Cooking applications
The fruiting bodies of bitterness are delicate and fragile. To preserve them better, they are laid out in one layer in the shade and in a cool place.
This condition is very important, because in direct sunlight they will oxidize and disappear. They start cooking no later than 4 hours after collection.
Preliminary primary treatment is required to release toxins, an unpleasant aftertaste of milky juice. The mushrooms are washed several times, it is better to do this in running water. After that, it is soaked for 3-8 hours.
The smoothie is excellent for salting: this treatment makes it possible to quickly go through the fermentation process. Before salting, they are soaked for 3 to 5 days with regular daily water changes. Then they are doused with boiling water and poured with brine. Both hot and cold salting methods are used.
The meatiness of this species is appreciated by gourmets. It is sometimes used for frying, after which the dish turns out to be spicy, with a peculiar pungent taste, although cooking takes place without the addition of hot spices.
But even after the most careful and correct processing, bitter is used almost only in salted and pickled form. You can serve the bitter milk as a separate dish, as well as including it in salads and cold appetizers from vegetables, poultry and meat.
Bitter helps out every year.
Salt bitter mushrooms at home - a simple recipe
Bitter mushrooms. Pickling and preserving
Bitter
Bitter - Latin Lactarius rufus
In a different way, this mushroom is called Goryanka, Putik, Pepper Millechnik, Red Bitter, Bitter Gruzd or Gorchak.
Description
Mushroom cap
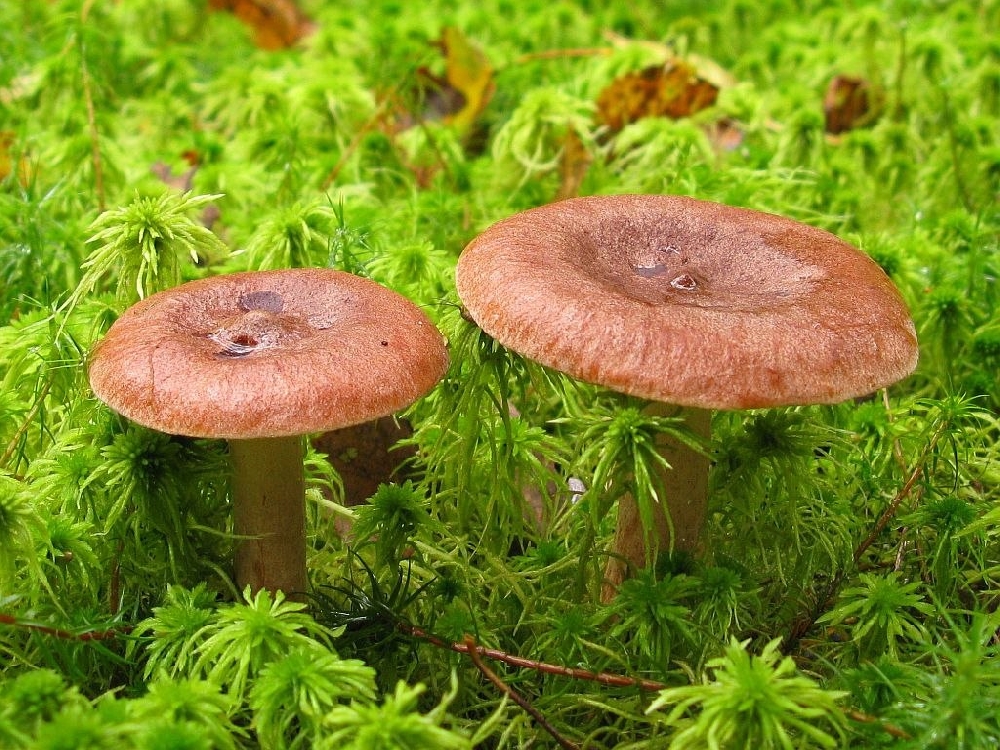
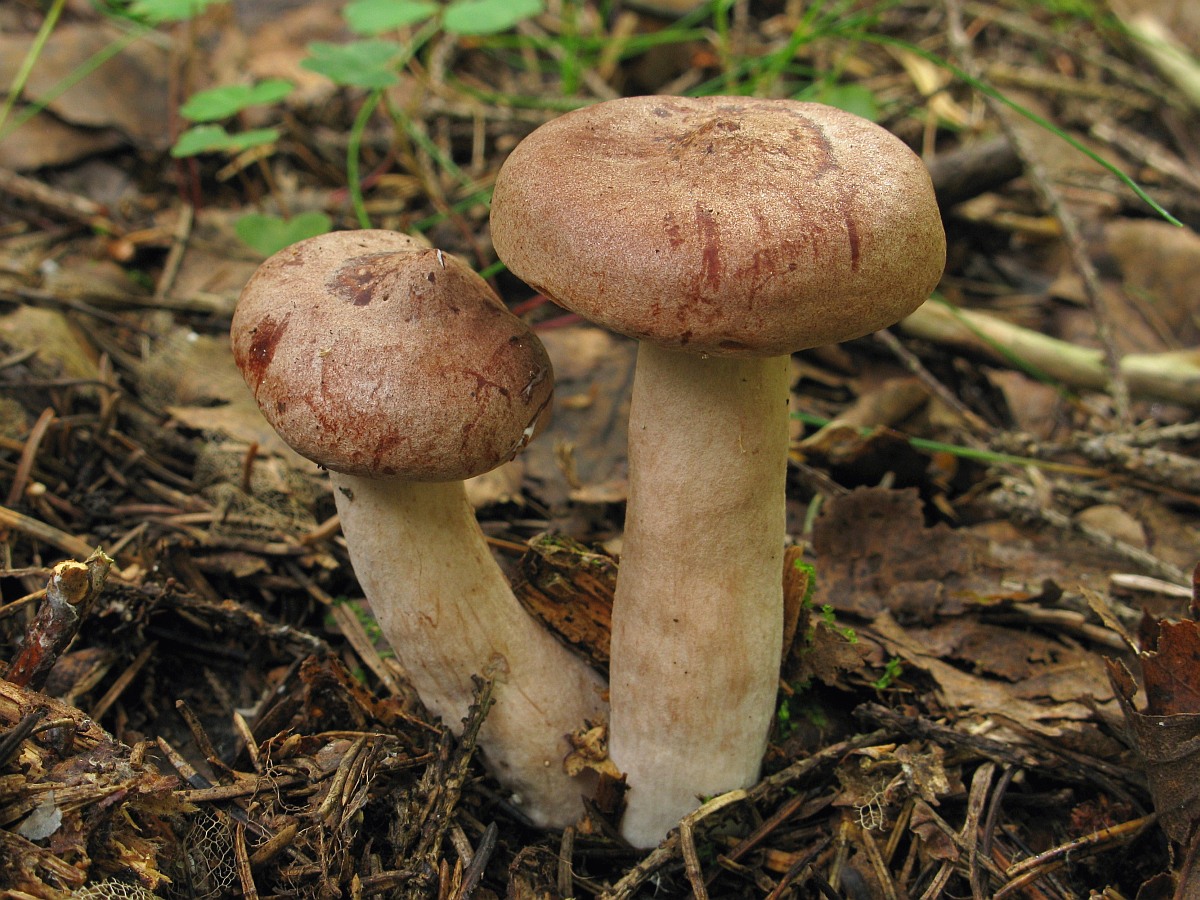
The diameter of Gorchak's cap reaches 10-12 cm. In young mushrooms, it grows convex - pointed, with a mound in the middle. The hats of the grown specimens become flat, the edges are bent inward, the mound remains, and the central part is slightly depressed.
The "headgear" is covered with a reddish-brown skin, shiny and sticky during rains and dry and dull on fine days.
The hats are filled with a tight, fragile white or pale brown flesh that darkens as the Pepper Miller ages.It is so juicy that if you break the mushroom, a lot of white, bitter-pungent juice will immediately stand out, which does not darken over time.
The hat bottom is decorated with narrow narrow plates slightly descending to the stem. Young mushrooms have reddish-yellow dull plates, mature ones are pale brown, old bitters are brown with a whitish bloom.
The fungus reproduces by whitish oval mesh spores contained in a white spore powder.
Stipe
Bitter is endowed with an almost smooth (with a barely noticeable fluff), not curved, cylindrical leg, the height of which reaches 80 mm, thickness - 15 mm. Adult mushrooms have legs with cavities inside.
The leg of a young mushroom is almost white, in an adult mushroom it is colored to match the cap, but it is somewhat paler - pinkish, reddish or slightly reddish.
Places of growth and fruiting
Millechnik grows well in any forest with a good bedding layer, but it is more common in pine forests with a mossy substrate and birch forests with lichens. The main thing is not to collect it near highways and near industrial facilities, since bitters can easily accumulate toxic substances.
The rarely wormy fungus is born in June and bears fruit until the end of September, since it is not afraid of frost.
Edibility
Red bitter is recognized as an edible mushroom belonging to the 4th category of edibility. The bitter pulp, slightly smelling of wood, becomes very tasty after cooking.
Before you salt or pickle the mushrooms, they must be soaked or boiled to remove the bitterness. After salting, the mushrooms turn dark brown. Only young mushrooms with tender pulp are pickled, spices are added to pickles and pickles.
Some gourmets fry Pepper Millechnik, but only after boiling.
Bitter - Latin Lactarius rufus
Similar types and differences from them
Edible
- Camphor milky. It differs in the smell of dry roots, while a woody aroma comes from the bitter.
- Swamp bush. There is no mound on its cap, and the mushroom itself chooses for growth exclusively spruce and pine forests located in the marshy area.
- The mushroom is orange. It differs in a slightly noticeable bitter aftertaste, has a tight hat of a reddish - chestnut shade with a darkish center and a leg of the same color.
Inedible
Hepatic miller. Unlike the juice of Bitter, which does not change color in air, the juice of the Liver Miller turns yellow.
Answers to common questions

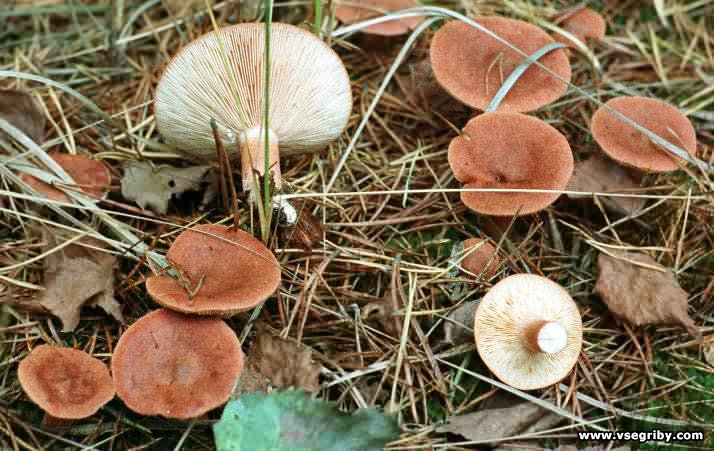
Bitter is the mushroom that is said to grow in any forest. It is especially abundant where there are pines, the ground is covered with moss, and the trees are lichen. They love bitters and mixed forests, especially wet ones. Bitter is found singly or in families. The mushroom bears abundant fruit from June to October, continues to grow even after autumn frosts.
Bitter has its own twin mushrooms. For example, edible milkman meat-red (smooth). The main differences between the milkman: a slimy wet cap without a tubercle. There are other differences, for example, subtle dark circles on the cap, shorter stems, less bitter taste, etc.
Reminiscent of the bitter and camphor milky. This small edible mushroom has a reddish-brown cap with wavy edges. The cap has a small tubercle, which is smaller than that of the bitter. Milky juice is more watery and sweetish. The smell of the mushroom is pleasant, it is compared to a flower one.
Other lactarius, edible and inedible, also bear some similarities to bitter. But there are much more differences.
Since bitters are most often found in coniferous and mixed forests, you need to look for them there. Grow singly or in groups
Experienced mushroom pickers recommend paying attention to places with dry forest litter near pine trees and birches - it is in these places that bitters grow and form mycorrhiza with trees. The collection is carried out from late summer to early autumn inclusive
Remember!
It is necessary to choose only young mushrooms, since the old bitters are more bitter and have time to accumulate harmful environmental substances.
The cut mushroom is carefully inspected, cleaned of soil, leaves or debris and placed in a basket with the cap down in order for them to be better stored. Arriving home, it is necessary to carefully examine each fruit part again in order to make sure that the species is definitely edible. Before eating, the bitters are boiled in boiling water for 40 minutes.

The most common questions are questions about edibility, cooking rules and heat treatment.
What happens if the bitter is not soaked before cooking?
If the fruit body is not soaked or processed, then the bitterness from the juice and an unpleasant pungent aroma will remain in its taste. This can provoke disorders of the digestive system.
Can you get poisoned with bitters?
Bitters can be poisoned if they are not soaked and processed in boiling water before use.
What to do if bitterness remains after cooking?
Bitterness after cooking remains only with old mushrooms. Experts do not recommend using such fruiting bodies. If, after careful processing, the bitterness has not gone away, then it is better not to eat such fruit parts.
Tourist Saratov
New on the site


Saratov water parks and swimming pools

Swimming pool FOK Yuzhny

Water sports complex "RECORD"

Swimming pool SGYuA

Swimming pool FOK "Yubileiny"

Swimming pool FOK "Zavodskoy"

Pool of the family club "Friends"

Swimming pool of the hotel and recreation complex "Dream"

Sports complex "Limkor"

Tent rest in Engelsky district

Places to rest with a tent on the Medveditsa River

Rest with tents in Marksovsky district


Places at the White Steep

Shcherbinovskie places for camping

Tent rest in Voskresensky district


Church of the Nativity


Places for recreation with tents in the Krasnoarmeysky district

Prison Ravine Beach

Abandoned German churches in the Saratov region

The touching zoo "Zootopia"

Physical culture and recreation complex "Kristallik"

Open winter public ice rinks

Nomad "Fox Balka"

Paleontological and archaeological sites of the Saratov region

Monument to A.N. Tolstoy




Ethnic tourism and crafts

Active and sports tourism

Festivals and events

Saratov region guides

Interesting places near the Saratov region
Contraindications
In some cases, the bitter taste can aggravate the sick person's condition. Contraindications include:
- gastritis, increased and decreased acidity of the stomach;
- peptic ulcer;
- pancreatitis;
- various liver diseases - hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver failure.
It is also forbidden to eat mushrooms for children under 7 years old, pregnant and lactating mothers. There is a contraindication in case of individual intolerance.
If you have at least one of these problems about the desire and possibility of eating even occasionally bitters, like other mushrooms, you need to consult your doctor.
Recipes and cooking features
Bitters belong to the genus Millechnikov and the Syroezhkov family. Very often there are other names of this species - red bitter, bitter milk mushroom, bitter mushroom, mountain goat, pathik. Also, this species has certain specific features.
Appearance and photos
In appearance, the mushroom has a medium-sized fruit part. The leg is narrow and high, and the cap is flat, with a notch in the center and edges curved outward.
 Description of the mushroom
Description of the mushroom
Morphology
The hat can reach 12 cm in diameter, it is flat in shape with bulges, over time it becomes funnel-shaped, fleshy and dry to the touch. Already mature representatives may develop light concentric zones. Also, the surface of the bitter is covered with small grooves. The color is dominated by brown, with a red tint. The surface of the cap is matte; there is a tubercle in the center.
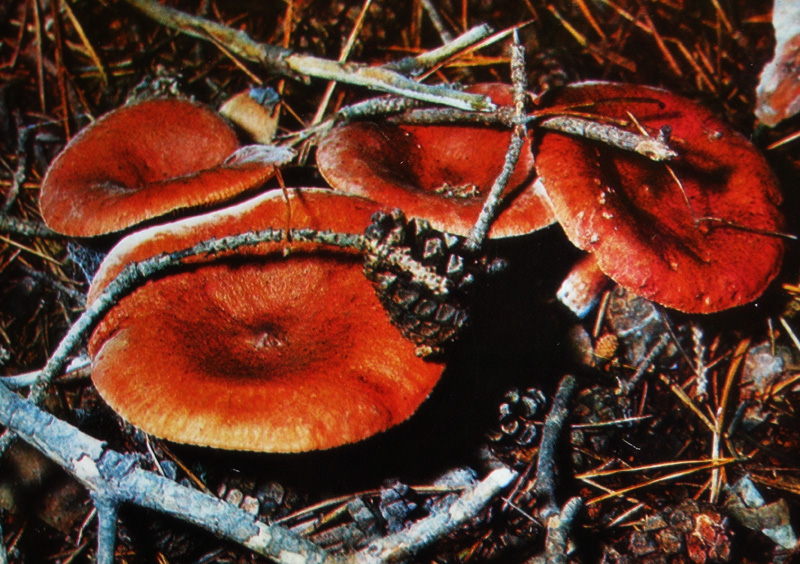

The pulp is thin in consistency and has a specific aroma that resembles the smell of wood with resin. The pulp secretes milky juice, which is distinguished by its pungency and acridity, it is white, thick in color. On the back of the cap there are narrow, often spaced plates. Their color varies from light red with a shade of yellow to deep red with a brown shade. The spore powder is beige or white in color.
The height of the leg does not exceed 10 cm, and its average diameter is 3 cm. The shape of the leg is cylindrical, in the lower part there are a small number of villi, with age it becomes hollow. The color of the legs of young representatives is closer to beige or white, and becomes pinkish with age. In most cases, the stem is the same color as the caps.
Most often, bitters are found in coniferous or mixed forests. They are characterized by the formation of mycorrhiza with pine trees and birches.
Yields peak in late summer and early autumn. Even in lean years, the fertility of bitters is high, which is why they are often used instead of other common mushrooms.
"Mushroom experts" from different countries have different opinions about whether this mushroom is edible or not. In Russia, bitters are conditionally edible and can be eaten after thorough heat treatment. In Western literature, this variety is classified as inedible due to the release of milk juice, which has a very pungent odor and gives off bitterness in the taste. But, since the species does not contain any poisons, it is quite possible to include it in your diet.
Since this variety is conditionally edible, it must be processed before eating and cooking. To do this, pour water into a saucepan and bring to a boil. Washed bitters are thrown into boiling water and continue to boil over medium heat for 40 minutes. After that, the mushrooms are cleaned and used in dishes.
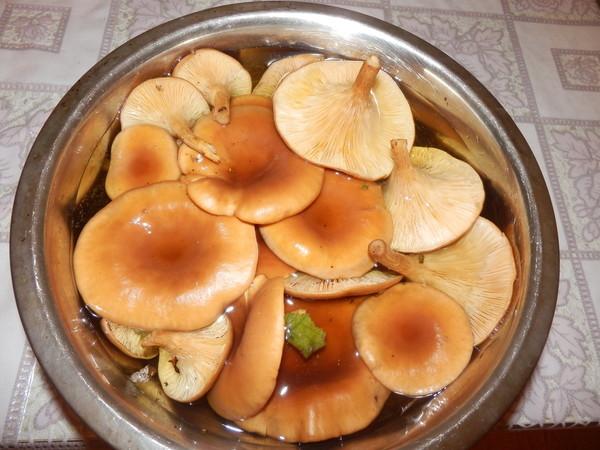 Cooking bitters
Cooking bitters
Bitters are boiled in order to get rid of the bitterness in the taste and the specific smell that they exude. In old mushrooms, bitterness can remain even after heat treatment, therefore experienced mushroom pickers recommend using only young specimens.
Cracker doubles
Bitter has a lot of doubles. In order to distinguish it from them, you need to know the structural features of each. Fortunately, a bitter mushroom is a mushroom that does not have poisonous counterparts, which means you are safe. But still, it is necessary to distinguish it from other inhabitants of the forest. Let's find out who the bitter looks like and with whom it can still be confused.
Camphor milk
Bitter is very often confused with camphor mushrooms, largely because these two mushrooms have almost identical colors. However, there is still a significant difference. The lump has a darker cap, and at the same time, more slimy. If there is not much mucus on the bitter, then there is an excess of it on the pile. Therefore, many unconsciously confuse these mushrooms, and then wonder why this mushroom has become so peppery.
In order to distinguish between these mushrooms, it is enough to look at their pulp. The pulp has a light shade in the milkweed, and in the bitter, when interacting with oxygen, it becomes dark. This is the main difference.
Swamp lump
The swamp lump also partially repeats the bitter. It is believed that the swamp mushroom is very similar to this mushroom, but the difference is noticeable "on the face". Swamp milk mushroom has a pronounced strong aroma, for which it actually deserves its name. In addition, this mushroom is very slimy, and its cap also has a green tint. Therefore, only very inattentive people can confuse it with a bitter taste. As for the taste, they are identical.