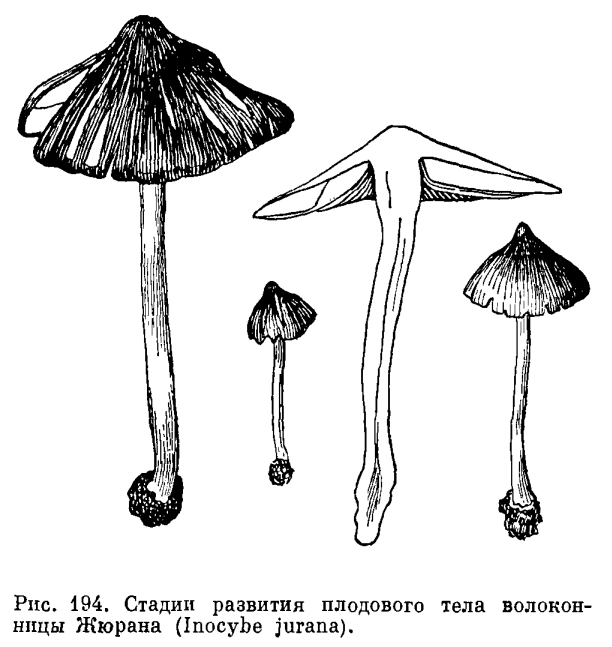
Description
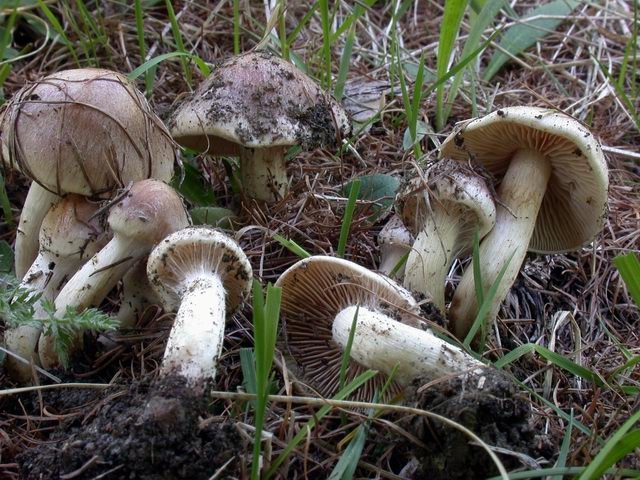
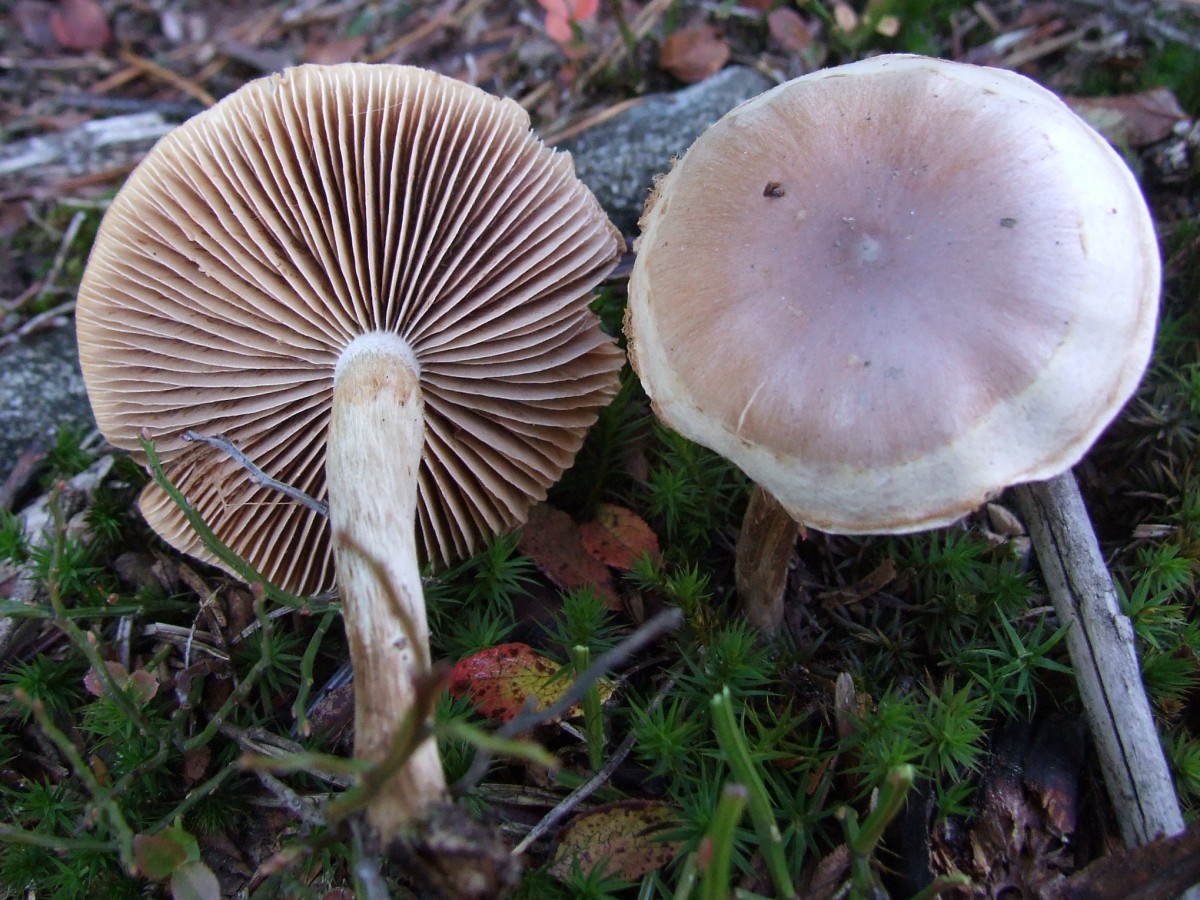
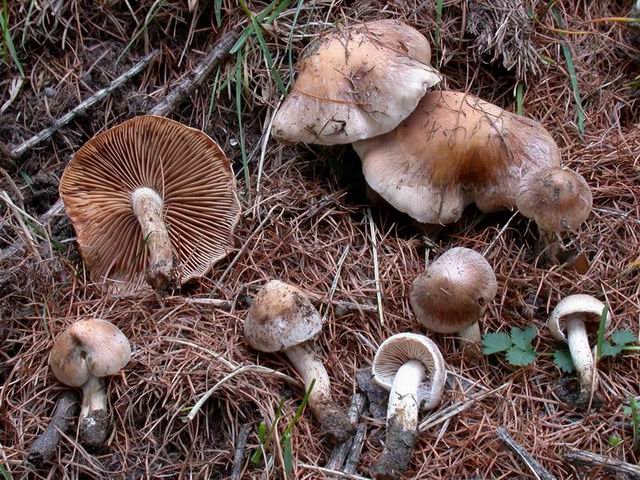
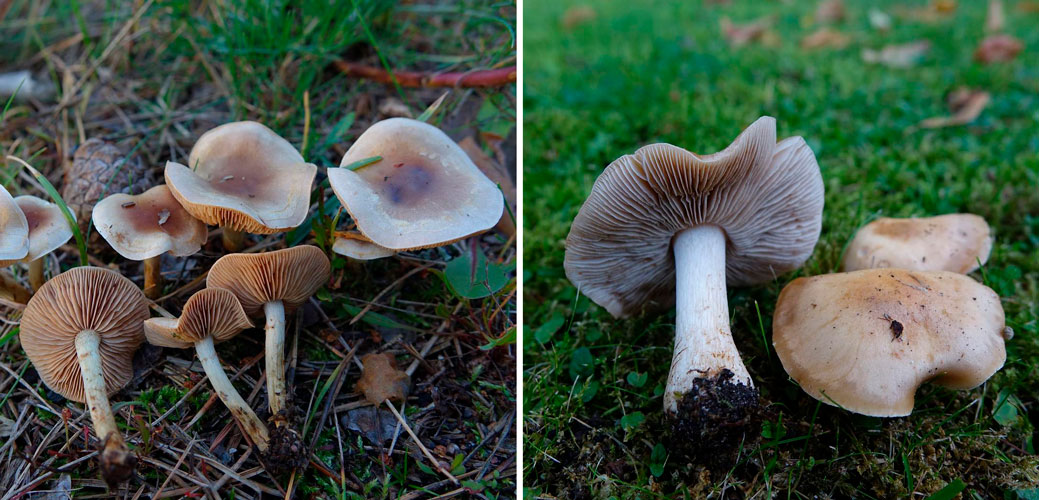
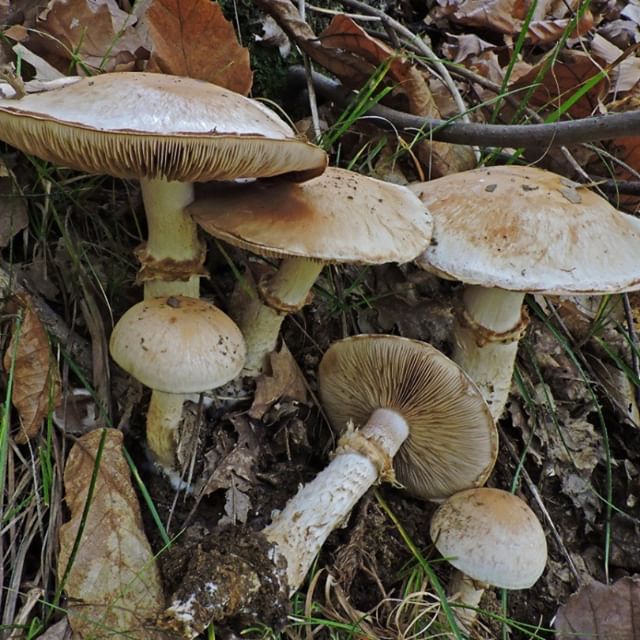
The hat is 4-9 cm in diameter, at first hemispherical or rounded-conical with a turned edge, then opens to a flat one with an uneven surface and a tubercle in the center. The skin is smooth and slightly sticky, light yellow or yellowish brown, lighter at the edges.
The pulp is compact, relatively soft, white, with a bitter taste and an unpleasant smell of radish or raw potatoes.
The leg is 3-8 cm high and 0.8-2 cm in diameter, cylindrical, sometimes with a thickening at the base, in mature mushrooms it is hollow, whitish or yellow-brown. Its upper part is covered with a powdery, easily washable coating.
frequent, adherent to the teeth, at first white, then become buffy or gray-brown with a light edge. On the plates, sometimes you can see small droplets of a milky or transparent liquid containing mature spores, when they dry, they leave dark spots.
Spore powder, ocher-brown, spores 11 × 6 μm, almond-shaped, folded.
Poisoning signs and first aid

The substances that are contained in the pulp of this mushroom are toxic to the human body, but they have not yet been identified and very poorly studied. But it is indisputable that their toxicity is very high.
The poisonous substances contained in the pulp of this mushroom have a significant negative effect on the human digestive system. The first symptoms of poisoning appear very quickly, after a short period of time after eating hebeloma:
- loose stools;
- nausea and vomiting;
- colic.
It is noted: respiratory failure, headaches, thirst, in severe cases - paralysis of the limbs. If a person feels at least one of the signs of mushroom poisoning, then immediately call an ambulance.
First aid to the victim is to cleanse the digestive tract of fungal toxins that have not yet been absorbed into the bloodstream. Usually, for this, the stomach is washed with boiled water or activated charcoal. And in any case, they call a team of doctors at home.
Sticky Gebeloma is a mushroom you shouldn't mess with. You can get to the hospital with poisoning by this "gift" of the forest very quickly. Fortunately, it is very easy to distinguish Gebeloma from other species due to its smell, so if the mushroom you cut has a sharp and unpleasant aroma, then it is better to throw it aside and move on.
Cooking methods
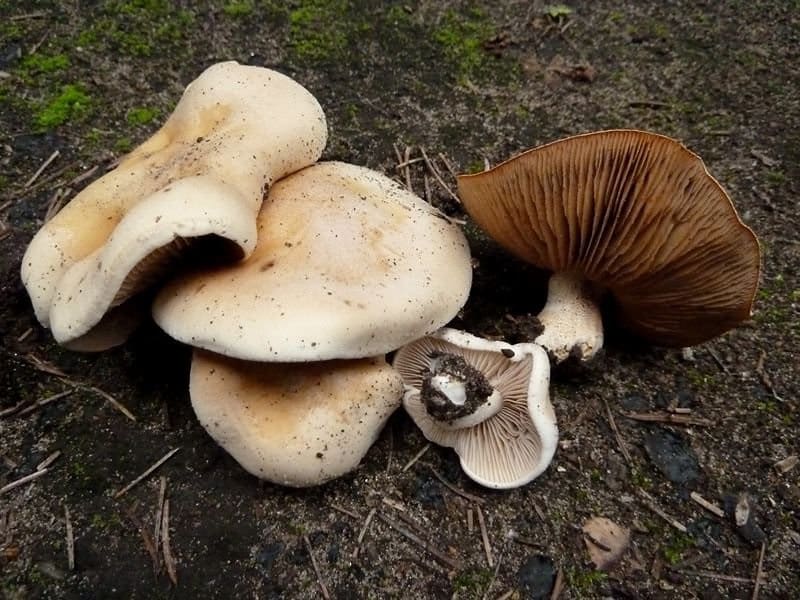
Valui should be cooked according to the established technology. Cooking should begin with the obligatory cleaning of plant debris and soil and involves obligatory soaking. Valui are traditionally pickled mushrooms and are used for cold pickling.
It should be borne in mind that only young mushrooms are subject to salting. At the stage of preparation, they must undergo prolonged and repeated soaking in cold water with its constant replacement with fresh water. Russula foetens can be used to make a very spicy and unusual pickled appetizer. Salting can be carried out not only cold, but also hot. After about a month and a half, the mushrooms will be ready to eat. Soaked valui are great for salads, vinaigrette, or stir-fry. Caviar from this type of mushroom is very popular.
The presence of a specific pungency and bitterness in the legs and caps of Russula foetens mushrooms suggests soaking and further use of only the caps (a specific taste in the legs remains even after processing). Valui must be kept in water for at least three to four days, with three water changes during the day. Then the soaked mushrooms are boiled for half an hour, after which they can be used for cooking or canning for the winter.
Description
Hebeloma sticky (Hebeloma crustuliniforme) belongs to the Strophariev family, the genus of the same name Gebeloma. This poisonous mushroom has several names that are common among the inhabitants of Russia: crusty gebeloma, false valui. Also, this dangerous beauty is called a horseradish mushroom, which is associated with the characteristic smell that its pulp emits. The British call Gebela a fairy cake or poisonous pie.

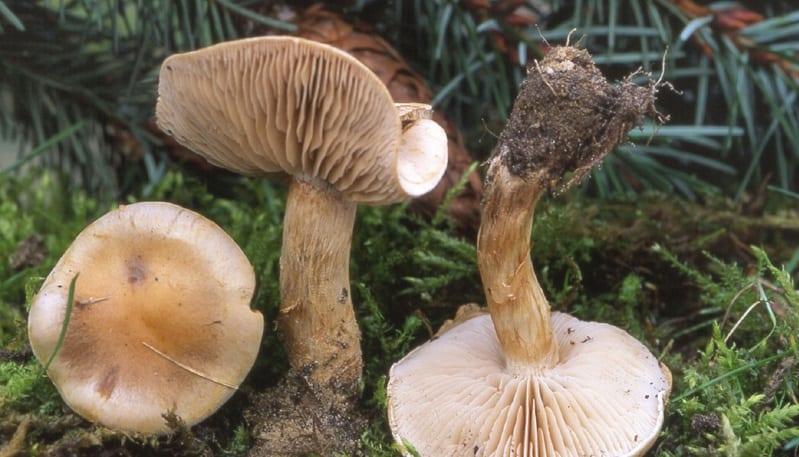
- the cap is soft, slightly convex in shape. In young gebelom it is rounded-convex, neat, with tucked edges; in adults, on the contrary, it flattens and even bends inward. There may be a small bump in the middle. The skin is sometimes sticky, slimy, smooth to the touch, and may be dry, which is usually observed in mature representatives of the species. The color of the cap is of various shades of yellow (from light to almost brown) with an almost white edge. Fruit bodies are also found with red, brick-colored caps. Diameter - up to 9 cm;
- the leg is white-fawn, covered with a powdery coating, cylindrical, thickening towards the bottom. In adult representatives of Gebelom, it is hollow inside. Its height is up to 8 cm, diameter is up to 2 cm;
- the pulp is quite dense, thick, bitter, with a bright characteristic unpleasant odor, strongly reminiscent of the smell of radish, potatoes. The color is whitish or creamy: the older the hebeloma, the darker the shade of the pulp;
- the plates are often located, adherent, whitish-gray in young fruiting bodies and a brown-gray, yellow-brown shade with light edges in adult mushrooms. On the outside of the plates, droplets of exudate are clearly visible, where the spores are located. When they dry, they darken and become almost black;
- spores are almond-shaped, reddish-brown in color.
Is a horseradish mushroom edible or not?
This type of Gebeloma, like most others of the same genus, is poisonous. In some sources, you can find information that the mushroom is not poisonous, but simply inedible, tasteless. This is due to the fact that the toxins contained in the pulp are still poorly understood.
Valuing toxicity is extremely high, cases of poisoning are not uncommon. Poisonous substances affect the digestive system, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and colic occur very quickly.
The use of Gebel can affect the musculoskeletal system, in severe cases, lead to paralysis, difficulty breathing and headache. First aid methods for poisoning with this fungus are not much different from others. It is necessary to flush the stomach from toxic substances, take any sorbent. You should immediately call a doctor and send the person to the hospital, because the earlier you seek help, the higher the chances of a full recovery.
Similar species
Similar mushrooms belonging to the same genus, they are all inedible or slightly poisonous, have a similar rare smell, sometimes the smell resembles cocoa:
- Gebeloma coal-loving (Hebeloma anthracophilum) is smaller and with a darker cap, with a soft stem, grows on burned-out areas.
- Gebeloma belted (Hebeloma mesophaeum) with a thin-fleshy chestnut brown hat and a thinner stem
- Mustard Hebeloma (Hebeloma sinapizans) are larger, with sparser plates and a not so slimy cap.
- Hebeloma edurum
- Hebeloma leucosarx
- Hebeloma pusillum with clay-brown plates, grows under willows.
- Hebeloma griseopruinatum recently described species of the genus, found in Denmark
Recipes for cooking dishes and preparations

Valui (bulls)
Valui, due to its bitterness, requires a long soaking or blanching before cooking. It is best to cook pickles from these mushrooms, in this form they turn out to be extremely tasty, satisfying and healthy.
Soaking and blanching
For soaking, the peeled fruit bodies are placed in a wooden or enamel container and poured with fresh, slightly salted water for a period of at least three days. From above, the mass is pressed down with a circle and oppression, the water is changed several times a day.
In order to better remove the bitter taste and preserve the crispy structure, you can acidify the brine, then 100 g of salt and 20 g of citric acid are taken for 10 liters of water, the value is soaked in the same way, changing the brine twice a day.
Blanching is used instead of soaking to speed up preparation. The mushrooms are immersed for 20 minutes in a boiling brine prepared at the rate of 100 g of salt per 10 liters of water, after which they are filtered and rinsed with cold water.
Valui in hot salting
For 5 kg of mushrooms, take: 10 tablespoons of salt, several bay leaves, black and allspice, dill seeds, black currant leaf, and other spices to taste.
Two and a half glasses of water are poured into the container, salt is added and brought to a boil, and then immersed chopped fruit bodiesthat will soon let the juice out. As soon as the brine boils, remove the foam, add spices and, stirring, boil for 20 minutes. External signs of readiness are the settling of all pieces to the bottom and clarification of the liquid. The workpiece is cooled and laid out in jars, poured with brine and closed. The snack is ready in 45-50 days. Store in a basement or refrigerator at a temperature not exceeding + 6 ° C.
Valui in sour cream
For 1 kg of mushrooms take: 2 tablespoons of butter, 1 glass of sour cream, 1 small onion, dill, black pepper, salt.
Fruit bodies, previously soaked in acidified and salted water, are poured over with boiling water and cut. Put one tablespoon of butter in a container, add mushrooms, salt and simmer under a lid until they take in the liquid. Then they mix everything, put another spoonful of oil, finely chopped onion and, shaking and stirring, fry over medium heat. When the mushrooms reach readiness, add sour cream, dill, pepper, salt to the dish, bring to a boil and serve.
Morphology
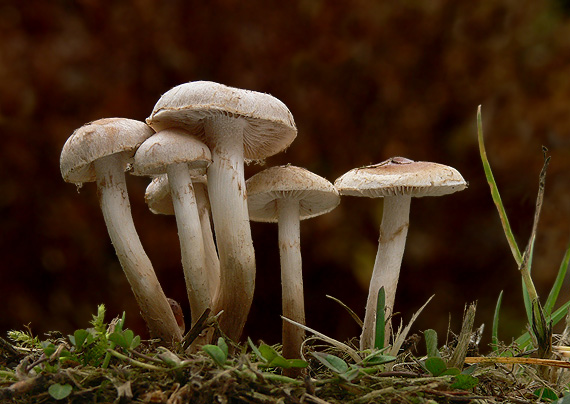
Fruiting bodies of cap-peduncles with a central position of the stem, usually of medium size.
The cap is from hemispherical to flat, possibly with a tubercle. The skin is slimy or sticky, less often dry, whitish or brown in color, usually light. The surface is smooth or fibrous, scaly.
The pulp is well developed, fleshy, soft or firm, compact or relatively thin, white or brownish, does not change on the cut, usually bitter and has a strong characteristic odor (sparse or otherwise).
The stem is cylindrical, fibrous, can be hollow, often with a scaly or mealy coating.
The plates are adherent, with a notch or free, at first pale, then light brown.
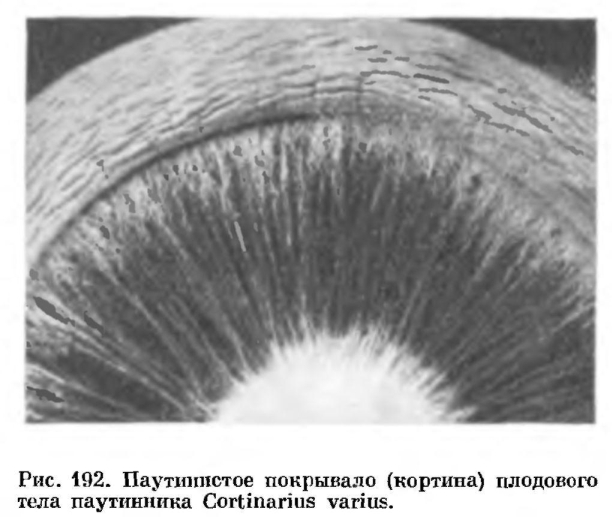
A private veil, cobweb or filmy, is found in the form of a ring or annular zone on the leg, hanging flakes along the edge of the cap, in many species these signs are vaguely expressed or completely invisible.
Spore powder of brownish-brown shades.
Distribution and fruiting season

Horseradish mushroom or sticky gebeloma is found both in deciduous and coniferous forests, on forest edges, meadows, meadows, fields, in gardens, along roadsides. Most often it can be found in the area of the northern temperate climatic zone, it is widespread in the European and Far Eastern parts of our country. It also grows in Central Asia and the Caucasus, in Australia.
Hebeloma of this species usually grows in groups or rings, best of all forms mycorrhiza with the roots of oak, aspen, birch. The fruiting season begins in summer and lasts until November, and where winters are mild and relatively warm, it occurs in the colder season.