Symptoms and Signs
The initial stage can be detected within a few hours. The duration of the asymptomatic period depends on the type of mushroom that was eaten, the person's weight and age, the method of heat treatment and the fact of taking alcoholic beverages. Having poisoned with a pale toadstool, you will feel the initial ailments after 6-7 hours, and after eating a lepiot or a cobweb, signs of poisoning will be found after 2-3 weeks.
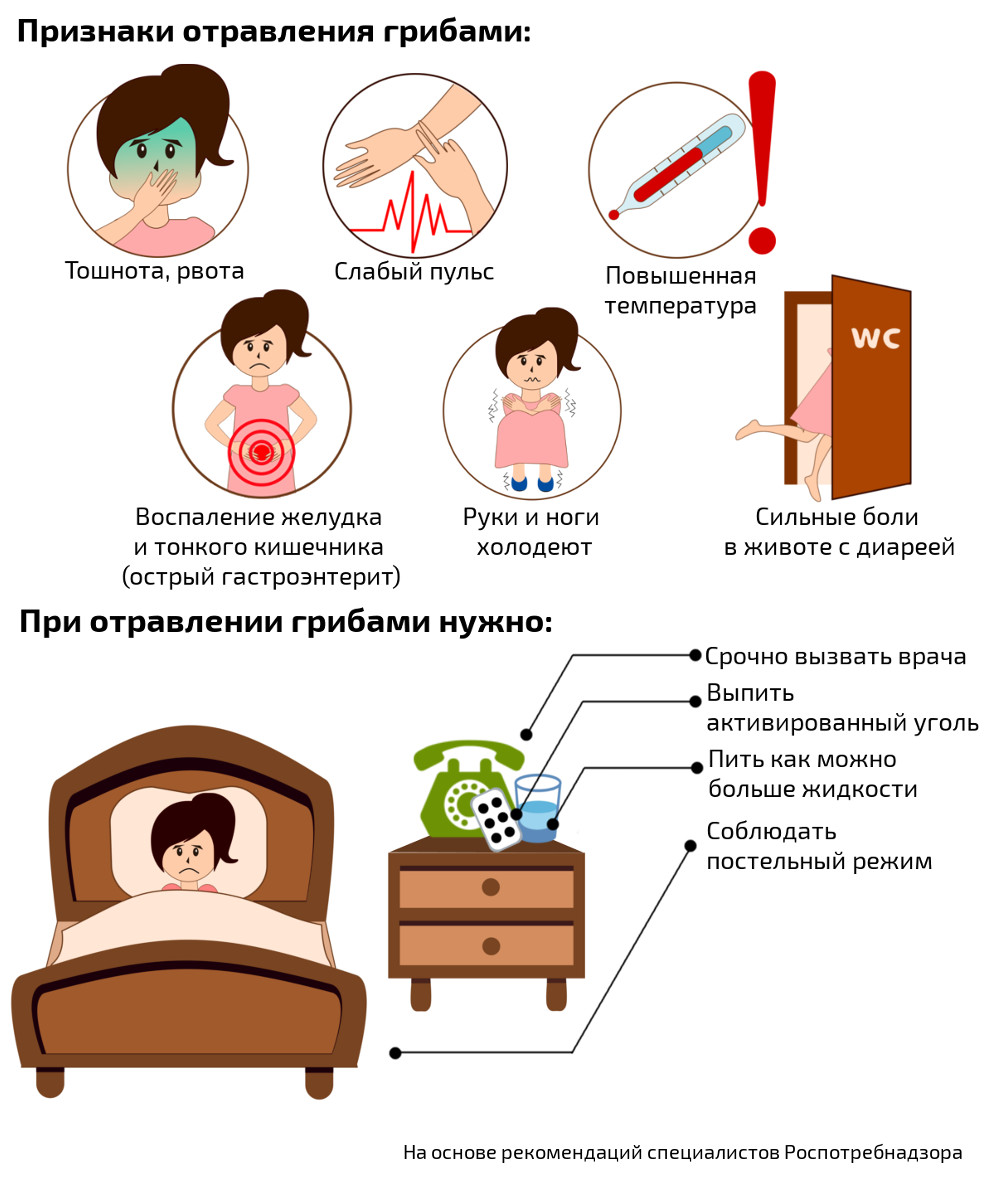
 In case of mushroom poisoning, there are the main signs of general intoxication:
In case of mushroom poisoning, there are the main signs of general intoxication:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Stomach pain;
- Frequent diarrhea
- Weak pulse;
- Low pressure;
- Cold extremities.
In addition, in case of poisoning, some specific signs appear:
- Gas formation;
- Belching with a bitter taste;
- Clouding of consciousness;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Decreased amount of urine;
- Pallor of the skin;
- Deterioration of vision.
Intoxication of the body after eating fly agaric, false mushrooms or satanic mushroom leads to hallucinations, delirium and clouding of mind.
In a patient who has eaten a pale toadstool, characteristic symptoms are distinguished: intense vomiting, with a frequency of up to 40 times in 24 hours. Blood is found in the feces, and it thickens, due to a violation of hemostasis. The patient starts having convulsions and heart failure. The liver and kidneys cease to function normally, which causes kidney failure, which flows into a coma, leading to the death of the patient.
Poisonous ones are divided into several types:
- Death cap. After consumption, the poisons contained in it penetrate very quickly into the bloodstream, and then into the liver. The most toxic poisons are phalloin, amanitin and phalloidin. The ripening period for this pale toadstool is in late August and September.
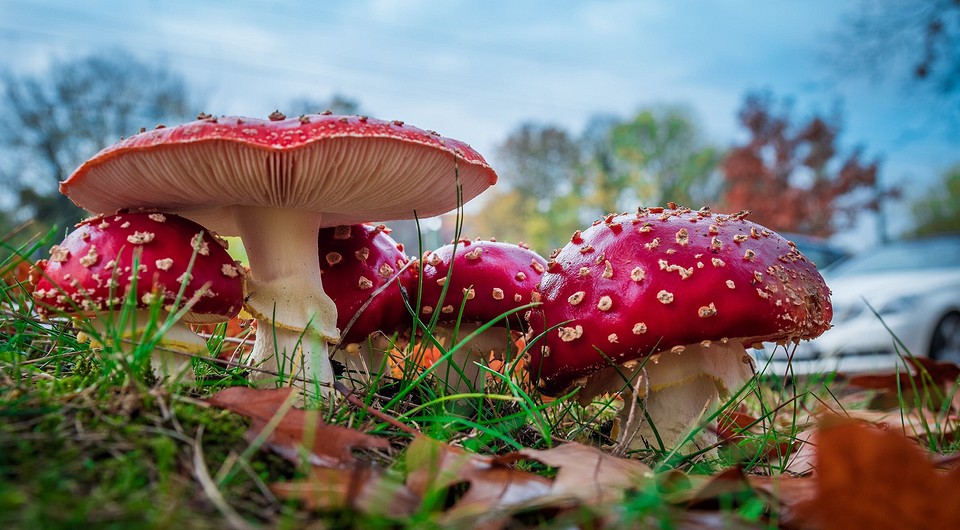
- Amanita. Distinguish between white and red types. Their poisoning affects the central nervous system. They are found in late summer and early autumn. Contains poisons muscarine and hyoscyamine.
- Outwardly, gall or satanic mushroom can be confused with boletus. Due to its similarity to the most popular mushroom, cases of poisoning are frequent. You can meet him in any forest of our Motherland. Poisoning affects the digestive system.
- Lines. Eating is not recommended as it can be fatal. Mushroom pickers mistakenly consider this mushroom edible.
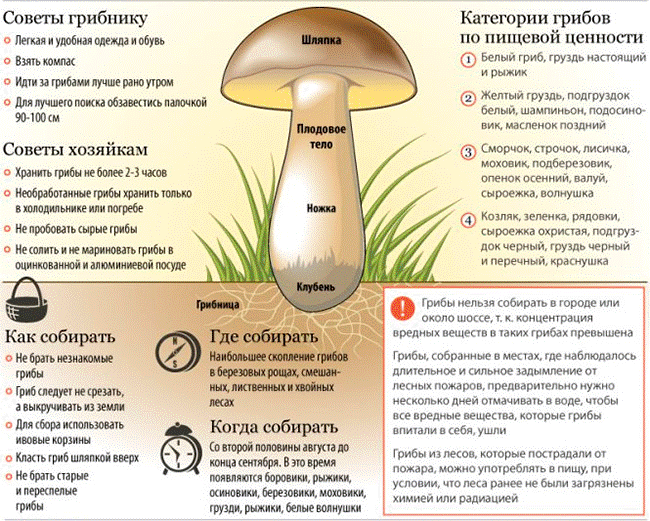
Types of mushrooms
There are 3 groups of mushrooms according to the degree of edibility. We are talking about such groups of mushrooms as:
- inedible, from which toxic substances are not excreted even after processing (gall mushroom, pale grebe, fly agaric and others);
- conditionally edible, which can be consumed, but only after proper preparation (preliminary soaking, prolonged cooking). These mushrooms include pigs, volnushki, milk mushrooms;
- edible mushrooms can be eaten even without prior preparation. Some of the species can be eaten raw. Certainly edible mushrooms include champignons, porcini mushrooms, boletus.

Edible and inedible mushrooms
When choosing mushrooms, you need to be very careful, because not only health, but also life is at stake. If you do not have any experience in picking mushrooms, then it is better to entrust this business to professionals.

Safety rules for picking mushrooms
Poisonous mushrooms that can be poisoned
Most inedible mushrooms can be fatal, so if you want to venture out into the woods, you need to familiarize yourself with them. Below are the most common types of mushrooms containing poisonous substances.
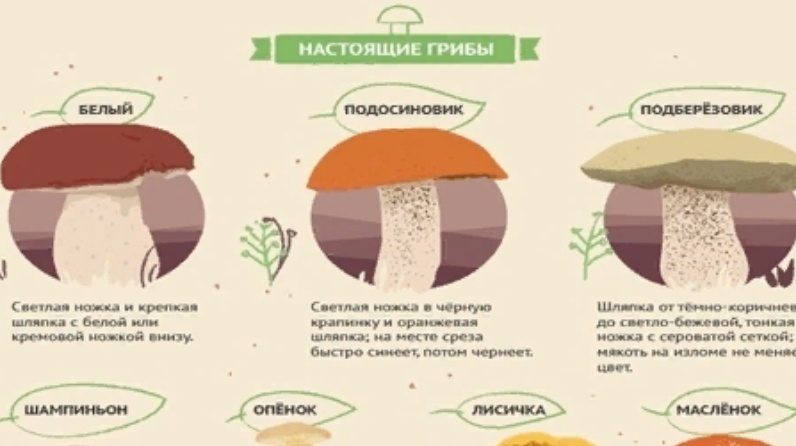
Table. The main types of poisonous mushrooms that can be found in the forest.
| Name of the mushroom, photo | Description |
|---|---|

False boletus |
Some people call this mushroom gall, but it looks more like a porcini mushroom. After entering the body, the false boletus, first of all, negatively affects the state of the digestive tract, and then on the entire digestive system. |

False chanterelles |
Based on the name, it is easy to guess that outwardly this mushroom is very similar to ordinary chanterelles. It causes irreparable damage to the kidneys, liver, and the organs of the digestive system. |

Whitish talker |
A poisonous type of talkers that affects not only the digestive, but also the nervous system. Therefore, if you suspect the use of a poisonous type of talker, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. |

Fly agaric |
There are several types of fly agarics, for example, white, red, smelly, and so on. If the fly agaric comes into contact with healthy mushrooms, then it is also necessary to get rid of the latter. This is all because of the poisonous surface of the fly agaric. After consumption, the poisonous mushroom affects the nervous system. |

Fiber |
Avoid all types of this mushroom as they are all poisonous. Outwardly, the fibrillas strongly resembles russula or champignons, but, unlike them, only 10-20 g of fibrillas can kill an adult. The first symptoms will appear 15 minutes after consumption. If first aid is not provided on time, it will be too late in 30-40 minutes. |

Gall mushroom |
It has a slightly yellowish tint, so inexperienced foresters may confuse it with porcini or boletus. The peculiarity of bile or, as they are also called, satanic mushrooms, is a negative effect on the digestive system. Symptoms appear almost immediately after poisoning, which makes it even more dangerous to health. |

Toadstool is pale |
It is considered one of the most poisonous of all types of mushrooms that can be found. Outwardly, toadstool strongly resembles russula. Because of this similarity, many inexperienced mushroom pickers go to the hospital with poisoning. After consumption, the poisonous substances of this mushroom lead to the destruction of the liver, and this happens very quickly. Even a small dose of toadstool can be fatal. |
These are far from all types of poisonous mushrooms that can harm health or lead to death. But before going into the forest for mushrooms, you need to at least familiarize yourself with the most common of them.
How to cook mushrooms to avoid poisoning
In order not to get poisoned, it is important to properly cook the mushrooms. To do this, follow these guidelines:
- carefully examine all the collected mushrooms;
- clean and rinse thoroughly;
- soak mushrooms in cold water for 2 hours;
- rinse thoroughly again;
- cover with water and cook for an hour. Be sure to add the onion;
- Throw the cooked mushrooms in a colander and rinse well again with water;
- then it is recommended to boil the mushrooms and onion again for 15 minutes.
When boiling mushrooms, always add onions to the water. This vegetable changes color, turning blue if the mushrooms are poisoned. After double boiling, the mushrooms are ready for further cooking.
Prevention of mushroom poisoning
In order not to become a victim of poisoning, it is necessary to carry out high-quality prevention, the essence of which is to know the rules for collecting champignons in the forests and buying them in a store. It is best to pick mushrooms in the company of an experienced mushroom picker who will help you distinguish good mushrooms from false mushrooms and pale toadstools. It is not recommended to collect old and damaged mushrooms: it is in them that the most harmful substances that harm the human body accumulate. Also, do not pick mushrooms that grow along roads and near landfills, not far from enterprises and treatment facilities. Mushrooms perfectly absorb all the harmful substances that, when consumed by humans, settle in the body, sometimes causing even malignant tumors.
When choosing champignons in a store, it is important to remember that most of them are literally oversaturated with chitin, phosphorus and other harmful substances designed to increase shelf life of mushrooms and their pleasant appearance. Chitin in high concentration is dangerous for people with weakened immune systems and children
It is almost impossible to remove chitin from the body, but in general this substance cannot be called harmful. You can eat foods that contain no more than 150 grams of chitin per day.
Also, store-bought champignons have high acidity, so they are not recommended for people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. As soon as attacks such as heartburn or weakness in the body begin to occur, then you should immediately abandon the meal and drink some sorbents.
Perhaps the best type of champignons that can be eaten, are canned mushrooms. They contain a minimum of pathogens and harmful substances due to heat treatment. But even here there is a risk of getting an impressive dose of toxins, which are literally preserved in the body of the mushrooms. Another reason for poisoning can be insufficient adherence to the technology of conservation of mushrooms. In no case should you buy mushrooms in an uncorked jar, with a cloudy brine, and so on. It is also worth abandoning products that are stored in an inappropriate way.
Compliance with these simple rules will allow you to savor your favorite mushrooms and avoid poisoning at the same time.
Read also:
How to provide first aid

The provision of first aid to the victim must be carried out strictly according to the instructions. Treatment at home, before the arrival of an ambulance, should be as follows:
1. First you need to induce vomiting. Reliable and proven methods can help you with this:
- with two fingers or an ordinary spoon, you can press hard on the root of the tongue;
- 1% apomorphine solution, emetic syrup.
Inducing vomiting is necessary in order to stop the exposure and absorption of poisons and toxic substances into the blood. This method is prohibited for children under five years old, as well as for those persons who have an extremely serious condition.
2. The second stage is gastric lavage. The patient must drink a huge amount of warm boiled water, at least two liters. Then you need to induce vomiting. If possible, it is advisable to perform flushing using a probe. This is a special tube made of rubber. Procedure: insert one end into the stomach and pour in a special liquid with manganese into the other.
3. Cleansing the intestines. Give a special enema to the patient, and also give a good laxative. Carlsbad and Gauber salts are very good saline laxatives that would be appropriate in such a case. As for the enema, about two liters of warm water are taken. Then drink white coal, polysorb, enterosgel.
4. Reduce discomfort and soreness. To do this, you need to take the following medications:
- spazmalgon;
- no-shpa.
Then put the patient on his stomach, and it is advisable to apply heating pads on his legs to drain the blood.
5. Lots of liquid. It is necessary to drink more different liquids up to eight times a day. Perfect for this: lemon water, cold tea, preferably strong, a decoction of mountain ash or rose hips.
6. Dropper. Effective solutions that bind toxic substances and are excreted through the kidneys:
- hemodez 6%;
- gluconeodesis;
- neohemodesis.
Now you know how first aid is provided to patients who have been poisoned by mushrooms.
First aid
The further condition of the patient, and in rare cases, his life, will depend on the correctly provided medical care in case of mushroom poisoning. Therefore, you need to be guided by the following rules:
- do not panic. Panic will not help, but will only worsen the situation.At the slightest suspicion of mushroom poisoning, you need to call doctors;
- wrap the patient in a warm blanket or blanket. This promotes the evaporation of gelwellic acid and, as a result, relieves the victim's condition;
- try to find out more information from the patient (what kind of mushrooms he ate, when it was, and so on). The more information, the more chances for a quick recovery;
-
induce vomiting in the patient. To do this, prepare a special solution by mixing 200 ml of warm water with 1 tbsp. l. salt. While the victim is conscious, give him the prepared solution to drink. If there is no salt at hand, then the patient can be drunk with cool water. Apply pressure to the center of your tongue periodically. This will cause an attack of vomiting;
- give the patient activated charcoal. You need to drink at least 6 tablets of the drug and drink plenty of water;
- use medications to cleanse your bowels. A regular enema will cope well with this, but if it was not at hand, give the patient a little laxative;
- never give acidic food or alcoholic products to the victim. This will only aggravate the situation and toxic substances spread faster throughout the body.

How to wash the stomach at home
By following these recommendations, you can prevent serious consequences in case of poisoning. You just need to remain calm throughout the entire time. Remember that the life of the affected person can depend on your actions.
Why are mushrooms poisonous
The ability of fungi to accumulate mycotoxins from the environment, poisons contained only in mushrooms, makes them potentially dangerous to humans.

- Amanitine is the most poisonous substance found in mushrooms. It blocks the work of cells, leading to their death. The cells of the liver and kidneys are most affected.
- Muscarine ─ acts selectively on nerve endings.
- Muscaridin is an alkaloid that disrupts the functionality of the digestive and nervous systems.
- Phallotoxins are a group of poisons that affect the plasma of cells. The most susceptible are hepatocytes (liver cells).
Poisonous mushrooms, depending on the type, have a different concentration of toxic substances and the strength of their effect on the human body.
1st category - poisons of local or local action. They affect the digestive tract, disrupting digestion. The effects of poisons begin 2 hours after ingestion. Symptoms: nausea, unexpressed pain in the epigastric region, general weakness. Edible mushrooms lead to this state if the technology of their preparation is violated.
2nd category ─ toxic substances that affect the central nervous system. Symptoms: impaired vision, coordination, speech. The victim has hallucinations, memory loss. Against the background of neurological disorders, nausea and increased sweating.
3rd category - deadly poisons, which are fatal in 90% of cases. The action of toxic substances begins several hours after their absorption in the stomach. Symptoms are acute. Since the brain is affected, the victim has a sharp decrease in all vital functions of the body against the background of paralytic effects on neurons: failure of the kidneys and liver, cardiac arrest and respiratory arrest.
First aid
When providing first aid, it is important to remain calm and take all the necessary steps. The first thing to do is call the medics
Then you need to try to induce vomiting in the patient, a saline solution will help with this. If there is no salt on hand, you can give him plenty of cool water and artificially induce vomiting. You can also induce vomiting by pressing on the center of the tongue. If possible, take activated charcoal (1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight). Then you can give an enema.
Before the arrival of an ambulance, it is necessary to find out from the patient what and when he ate.The poisoned person must be wrapped in a blanket to induce perspiration. Together with sweat, gelwellic acid, which is contained in mushrooms, will be released from the body. You can not give the victim alcohol and sour food, they only contribute to the spread of poison throughout the body.
First aid for mushroom poisoning
Anyone can be poisoned by mushrooms, so it is important to know what to do with the development of this dangerous condition, how to provide the victim with first aid, where to go for subsequent treatment

After calling the ambulance team, proceed to provide first aid to the victim. With mushroom poisoning, life can depend on it.
Below, we have described in detail the components of assistance that you can independently provide at home before the arrival of doctors from the emergency room.
Gastric lavage
Gastric lavage helps to cleanse it of the remnants of food eaten and poisons that have not had time to be absorbed into the blood. In order to clear the stomach, you should drink a liter of plain water in one gulp and pull it out. This procedure can be repeated several times in a row.
Purgation
An enema should be done using plain boiled water at room temperature. It should be carried out until clean and transparent wash water is obtained.
Sorbents

Sorbents are the only drugs that can be drunk at the stage of first aid.
Before taking sorbents, you must carefully read the dosage rules. For some drugs, the dosage is calculated by weight, and for some, the dosage is based on age. In case of mushroom poisoning, any sorbents that are available in your home medicine cabinet will do. Examples of drugs:
- Activated carbon;
- white coal;
- sorbex;
- smecta;
- enterosgel;
- atoxil.
Drinking plenty of fluids
You can begin to replenish the body's water losses after cleansing the stomach. In order not to cause repeated vomiting, you should drink a little and often.
You can drink mineral water without gas, table water, sweet black tea.
What to do if the patient has lost consciousness

lay him on a flat, hard surface, lift his legs up, turn his head to one side and watch his breathing and heartbeat.
The pulse is best checked on the carotid artery. This vessel runs along the anterolateral cervical surface, under the skin.
To check for breathing, place your hand on the sick person's chest. When breathing is present, you will notice that your arm goes up and down during the chest excursion.
What to do with seizures
Cramps throughout the body are a common symptom of poisoning with poisonous mushrooms. They are similar to an epileptic seizure. During their appearance, you can hold the person's head, make sure that he does not hit the floor with it. After the attack is over, check your breathing and pulse.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
The absence of pulse and respiration indicates the onset of clinical death. You can do chest compressions on your own. You need to press on the lower third of the sternum with a frequency of 120 times per minute. In this case, the arms should be straight, not bent at the elbow joint.
According to the latest protocols, when performing self-resuscitation, it makes no sense to do mouth-to-mouth breathing, it is ineffective
More attention should be paid to indirect massage. His technique is taught even to schoolchildren in biology lessons.
First aid for mushroom poisoning: a scheme of action
Unfortunately, mushroom poisoning is not uncommon. It happens, as a rule, due to the inexperience of the people themselves, because not all species are suitable for eating, and some can even cause significant damage to health. First aid for mushroom poisoning is important information that all lovers of harvesting in the forest need to know.
Poisoning reasons
As mentioned above, the cause of the poisoning and intoxication of the body is the mistake of the mushroom picker himself.First of all, you need to know that mushrooms are divided into 3 large groups:
- Certainly edible. You can use them without preliminary processing;
- Conditionally edible. It is prohibited to eat them raw. They require preliminary cooking or soaking in water, depending on the further cooking mechanism;
- Inedible. It can be poisonous and non-poisonous mushrooms, but their use carries a great risk, both to health and human life.
Thus, eating an inedible species and not observing the rules for preparing conditionally edible mushrooms are precisely the reason for possible poisoning.
The toxins contained in these two groups of fungi, when ingested, begin to rapidly spread through the circulatory system. The mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and liver are primarily affected. Also, toxins can disrupt the functioning of the heart and central nervous system.
Botulism
Botulism is an acute infectious disease. Canned mushrooms are often the cause. The main causative agent of the disease is spore-bearing rods, localized mainly in the ground.
Accordingly, if the mushroom is poorly rinsed from soil residues, then harmful particles can enter the jar along with it. And the conditions of being in a hermetically sealed space even more affect their growth and development.
Improperly processed canned mushrooms are a source of botulism infection
If you eat such an infected mushroom, then the first signs will begin to appear after 12-72 hours. As a rule, they look like this:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Headache;
- Loose stools;
- Visual impairment, loss of clarity;
- Dry mouth;
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing
- Convulsions.
Botulism belongs to the category of serious diseases, therefore, at the first clinical signs, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor who can take the necessary measures and actions.
Prevention, how to avoid mushroom poisoning
It is very good to know how first aid is carried out in case of poisoning with poisonous mushrooms, but it is better not to allow this process at all
In order not to be poisoned by inedible mushrooms, you should pay attention to the following tips:
- Do not collect and, moreover, do not eat unfamiliar mushrooms or species that are in doubt;
- Overripe mushrooms, with signs of mold or lack of a leg, are prohibited to collect;
- It is necessary to rinse and clean them not superficially, but thoroughly;
- It is not worth picking mushrooms growing along roads, highways, not far from industrial plants, in areas with a high level of pollution;
- It is better to give preference to proven recipes for cooking and processing mushrooms, and not experiment with insufficient knowledge
- It is advisable to cook mushrooms immediately on the day of harvest;
- Do not keep them warm.
Due to the fact that mushrooms contain difficult-to-digest components, the intake of even non-dangerous species is not recommended for children under 14 years of age, pregnant women, deeply elderly people and people suffering from diseases of a serious nature.
Gall Fungus Poisoning - Main Signs and Symptoms
The false (bile) mushroom is popularly called bitter mushroom. The main toxic ingredient is bitterness. The substance cannot be processed by culinary procedures. Scientific research has identified hepatotropic poisons. The compounds destroy liver cells, which determines the time after which gall fungus poisoning occurs. With chronic intoxication, the first signs are observed after a few months. Poisoning factors persist even when pickled.
There is an opinion of foreign researchers that fungal toxins affect internal organs after tactile contact. The destructive effect of substances occurs gradually.With a test on the tongue, weakness, headache, dizziness are observed.
Gall fungus poisoning is associated not only with liver damage. Weakness, dizziness occurs due to the ingress of toxins into the blood.
Unfortunately, people very often eat gall fungus. Even forest animals do not feast on bitterness. Gorchak does not contain chemical compounds useful for humans, so you need to think about adding it to food.
Statistics note that the number of gall fungus poisoning increases annually. Polish scientists have doubts about the rationality of using this product in food. There are practically no useful substances in it, but there are many toxins.

Folk remedies for mushroom poisoning
At home, it is allowed to use folk remedies to neutralize the poisons of the gastrointestinal tract only when combined with other procedures recommended by the doctor.
When vomiting, you should drink vodka with the addition of a large amount of salt. The hyper-concentrated solution draws fluid from the body, which promotes the elimination of toxic substances.
In case of poisoning with ptomain, foreign sources recommend cinnamon tea. According to the description, it eliminates all intoxication symptoms 3 days after the start of use.
To prepare the drug, you need to boil 2 cinnamon fingers for 5 minutes. Drink while the tea is hot.
We advise you to read:
Classification of kidney disease
Poisoning with metal poisons (lead, mercury) is eliminated by adding egg white to a mug of milk. After beating with a mixer, an effective medicine is obtained.

What to do in case of poisoning according to popular recommendations:
- Drink dill with honey (a spoonful of dill for a glass of honey);
- Drink fresh potato juice;
- Take 0.5 cups of valerian (chop the root, boil in 0.5 liters of water);
- Chopped coals of linden or pussy willow added to milk help with arsenic poisoning. Consume 5 tablespoons a day;
- Add 200 grams of magnesium carbonate to a glass of fresh milk. Give to a person three times a day. Fresh milk neutralizes toxins, reduces the severity of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
In conclusion, it should be added that poisoning is better prevented than cured. It is enough to correctly carry out the heat treatment of mushrooms, wash your hands before eating, and follow the rules for storing food.
Even edible mushrooms cause poisoning if they grow along highways, chemical plants. Radioactive substances gradually destroy organs. You should think about the rationality of collecting dubious mushrooms.
Four types of mushroom poisoning
Mushroom poisoning is divided into 4 types, depending on what types of product a person has consumed. Let's consider each type in more detail.
The first type of intoxication
The first type refers to poisoning with a pale toadstool, referred to as gastroenteritis. This type of mushroom is highly toxic, as a result of which death occurs in 90% of cases. The main reason for the high mortality rate is late seeking medical attention.
A pale toadstool has a number of similar external signs with champignon and russula. It is impossible to provide effective treatment at home. Often, the first symptomatology appears no earlier than 8 hours later and is expressed by the following symptoms:
- dizziness begins to disturb the person;
- the temperature rises;
- pulse quickens.

With an active intoxication, later signs of poisoning appear:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- hepatic and renal failure develops.
If poisoning is determined in a timely manner, you can avoid serious complications by seeking qualified medical help.
Such negative symptoms are observed if you eat a gall mushroom.At the same time, the concentration of toxic substances is several times higher and affects almost all internal organs and systems.
The risk to health, as well as to life, consists of the following signs:
- severe pain in the abdomen;
- gastroenterocolitis;
- incessant vomiting;
- cramps of all muscle groups;
- diarrhea and vomiting does not stop even on the second day.
As a rule, death in the absence of timely medical care occurs on the 3rd day.

Second type
Fly agaric poisoning is also considered dangerous, but with a lower mortality rate. Negative symptoms appear within 3 hours after eating mushrooms and are expressed by the following signs:
- incessant vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- increased salivation;
- pupils constrict;
- excessive sweating appears;
- shortness of breath;
- the pulse slows down.
With fly agaric poisoning, a person has a decrease in mental activity. In addition, hallucinatory syndrome occurs. In the absence of timely assistance, a coma occurs. Panic attacks and spasmodic constriction of the pharynx may also occur.

The probability of death after eating amanita is not high and amounts to 3%. But only if the person asked for help in a timely manner.
Third type
Stitching intoxication is extremely dangerous in the absence of adequate medical care. This mushroom variety contains a low concentration of Helvelic acid. Moreover, the content of the toxic substance may fluctuate depending on weather conditions. When direct sunlight hits the mushroom, the concentration decreases several times. But in wet weather, this substance becomes more.
After taking the lines, negative symptoms are formed after 6 hours:
- there is pain in the abdomen;
- weakness is felt in the body;
- nausea and persistent vomiting;
- upset stool;
- headache.

When poisoning with this mushroom variety, a person develops jaundice on the second day. This is due to the strong enlargement of the liver. In addition, the process of destruction of erythrocytes is observed. And if medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, hemolysis increases by 20%. As a result, brain hypoxia is formed.
To prevent such an intoxicating process from forming, it is recommended to boil the lines for 20 minutes. In addition, no more than 200 grams should be consumed at a time. of this mushroom variety.
Fourth type
This type of poisoning is inherent in the gall fungus, volushek, false honey agarics and russula. After using these varieties, negative symptoms appear after 1.5 hours.
The main signs are:
- the appearance of severe diarrhea;
- girdle pain in the abdomen;
- bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract;
- general weakness;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- the pulse quickens.
This symptomatology is caused by the relatively low toxicity of the considered types of mushrooms.
At the same time, in order not to aggravate the negative condition of the patient, it is important to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Overview of remedies for poisoning
It is possible to take medications only with an established cause of the disorder of the body and the phenomena of intoxication (vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, heartburn, headaches, weakness). The drugs are taken in order to avoid the development of severe complications - dehydration, disturbances in the water-salt balance, intestinal spasm, elimination of toxic poisons and restoration of the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. It should be taken strictly according to the instructions and prescriptions of the attending physician, in case of any side effects, you should immediately inform the doctor and discontinue the course of treatment before replacing the medicinal product, it is not recommended to arbitrarily make a replacement.
Groups of drugs at the first signs of poisoning with mushroom products can be divided into the following:
- Rehydrants (rehydron, humana-electrolyte, oralit). They help stop dehydration and replenish the deficiency of salts, trace elements and minerals.
- Adsorbents (smecta, white coal, polyphepan, activated carbon, lactofiltrum), which are the first line of help for any poisoning. Sorbents help to quickly remove toxic substances and toxins from the body, normalize metabolic processes, relieve vomiting, diarrhea, hyperthermia during intoxication. The most versatile and widely used is activated carbon, the spectrum of action reaches more than 200 poisonings, it is safe for use in the elderly and children. Smecta is most often used in pediatrics, in view of its mild action with an enveloping property.
- Enzymatic agents (mezim, festal, pancreatin) are used to reduce the load on the pancreas and protect the gastric mucosa.
- With indomitable vomiting, antiemetic drugs (cerucal, sturgeon, domrid) are used to inhibit the processes of peristalsis, relieve painful spasms.
- Antispasmodics (no-shpa, platifillin, papaverine) are used as adjuvant therapy in combination with antiemetic drugs for pain relief.
- A group of antibacterial drugs (fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, sulfonamides, nitrofurans). It is used if there is an admixture of blood in the vomit and stool, hyperthermic syndrome, or the addition of a bacterial infection.
- At the final stage of treatment, probiotics (linex, enterojermina, bifidumbacterin) are used to restore normal intestinal microflora.