Appearance
Hat
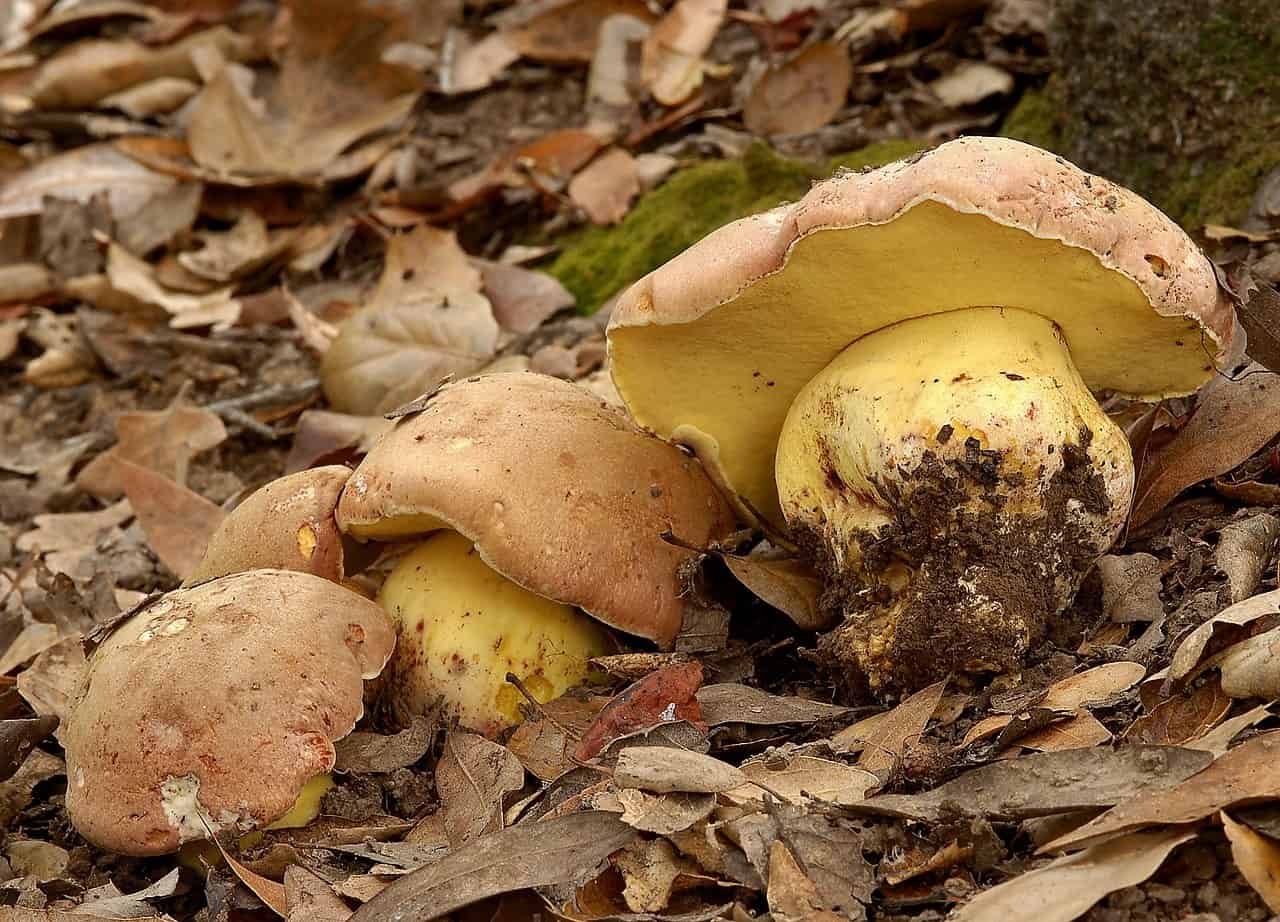
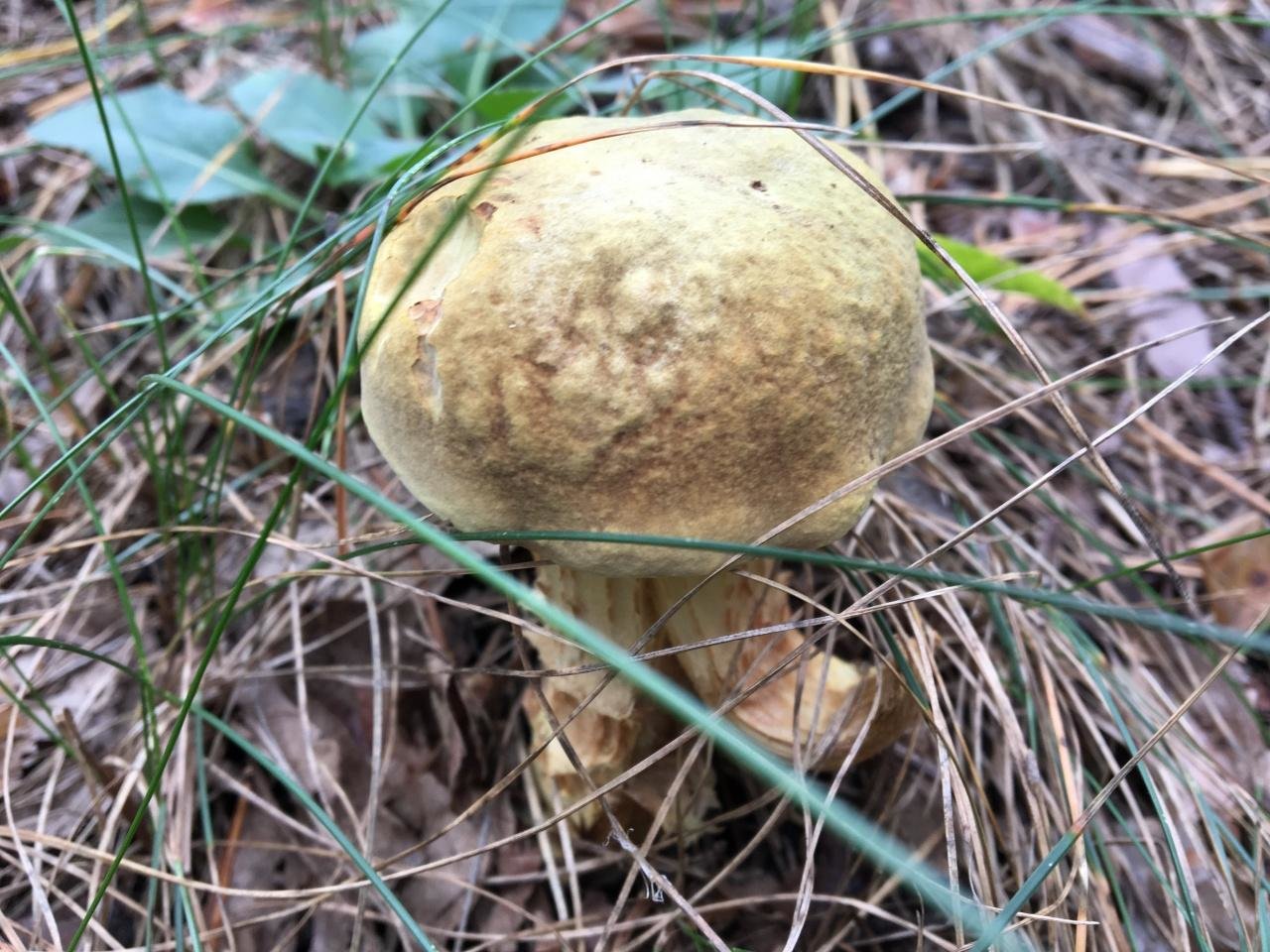
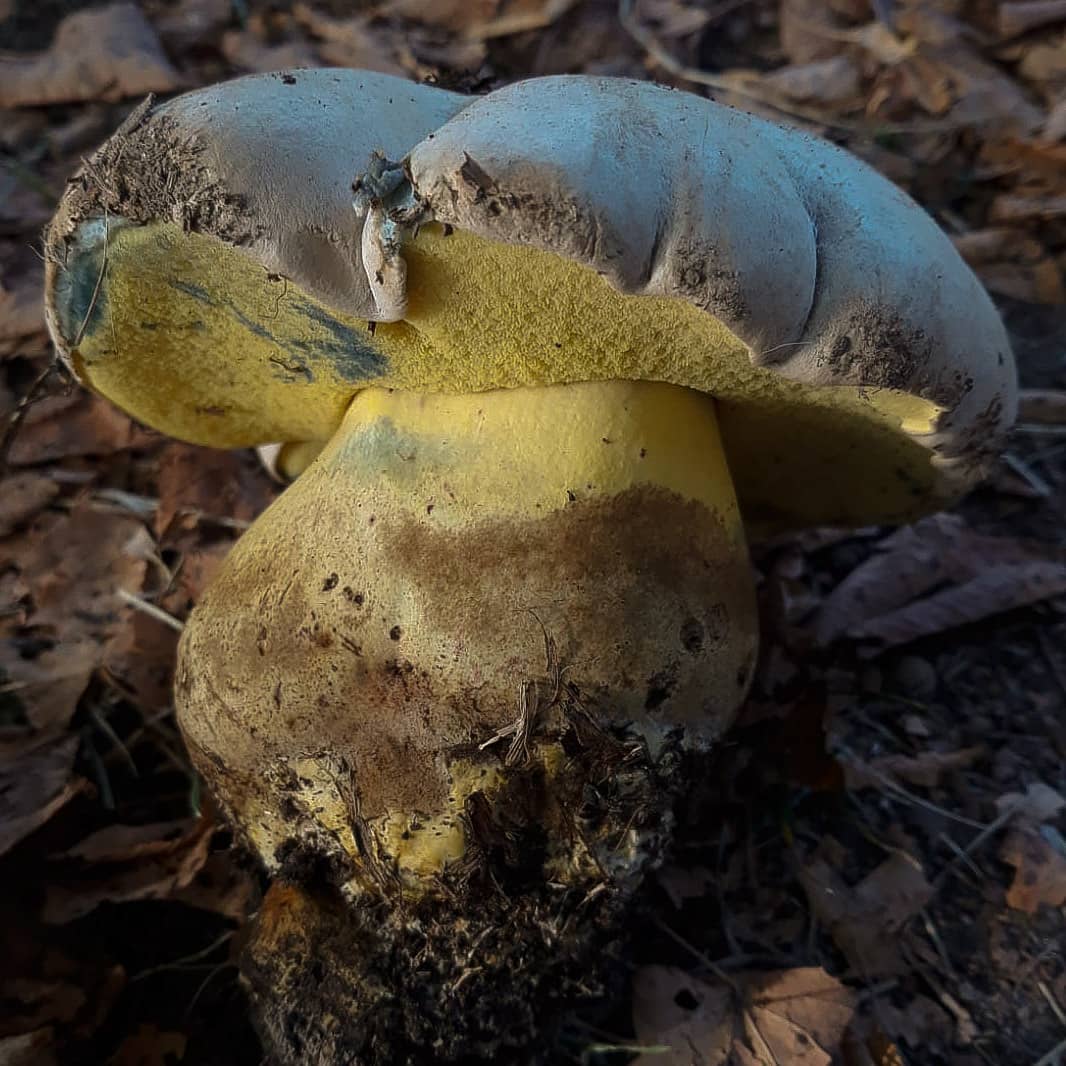
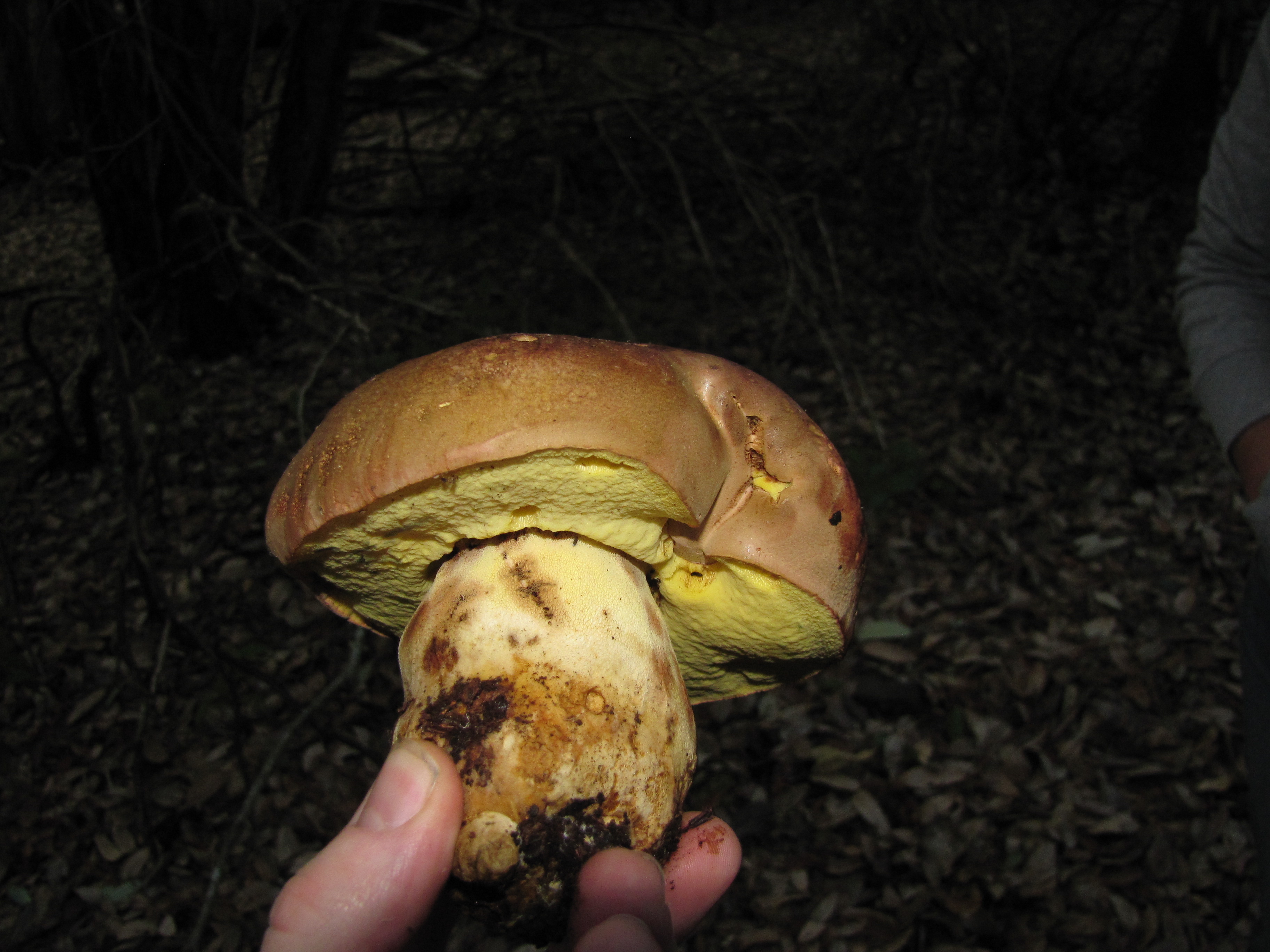
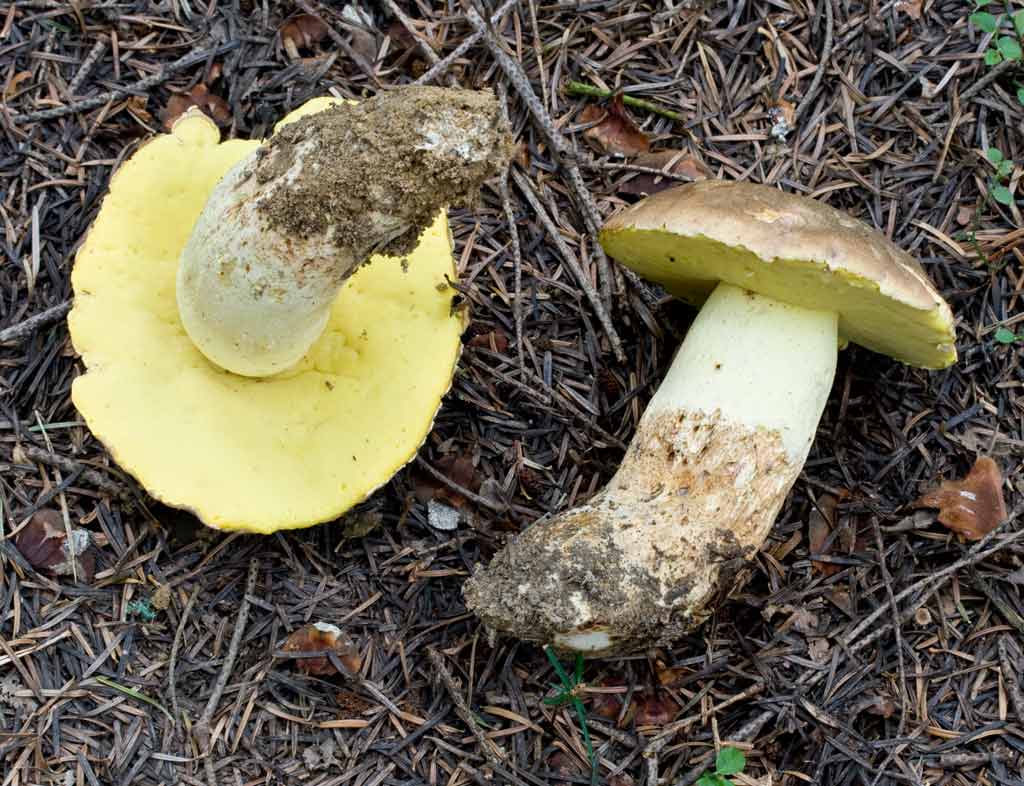
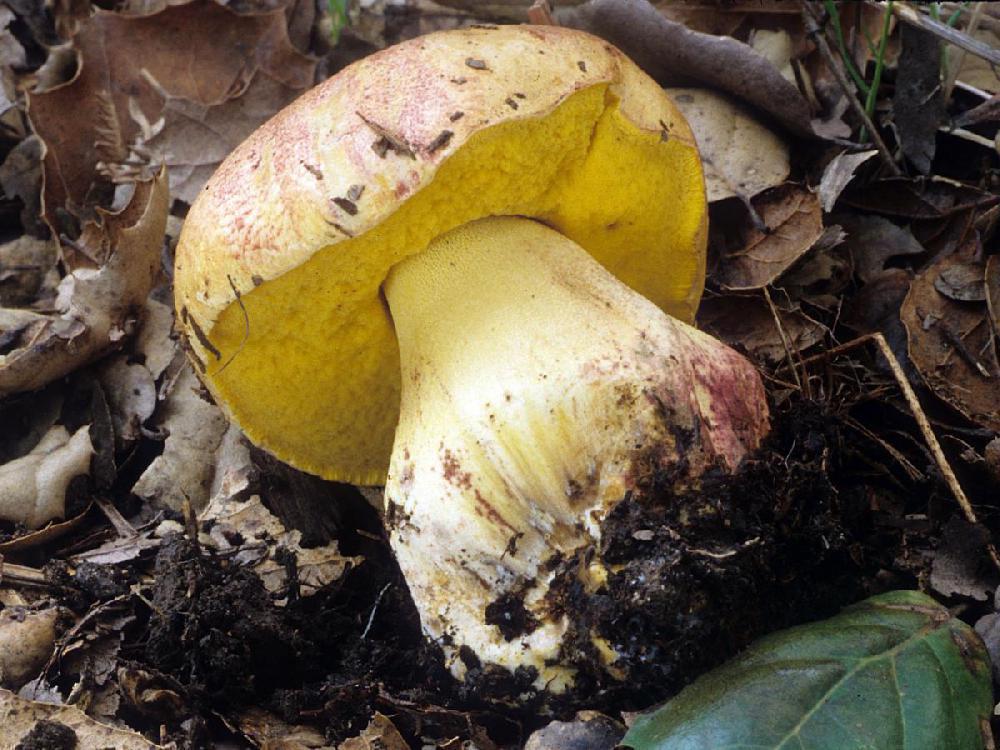
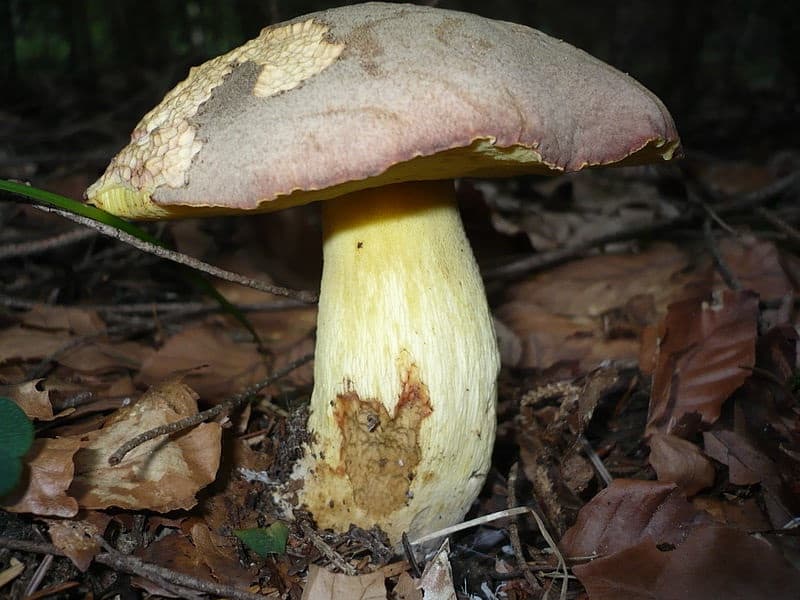
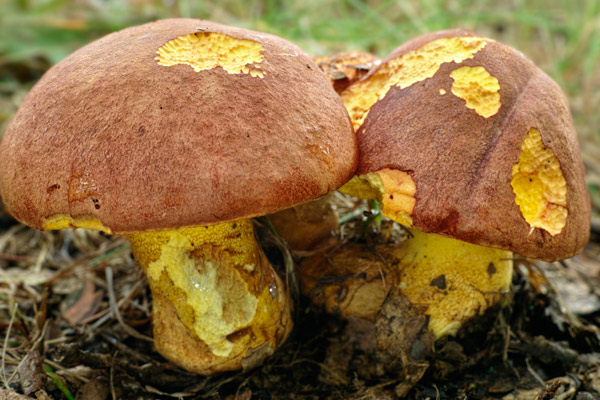
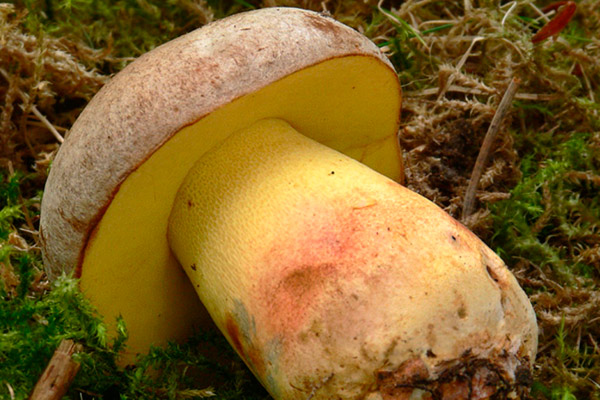
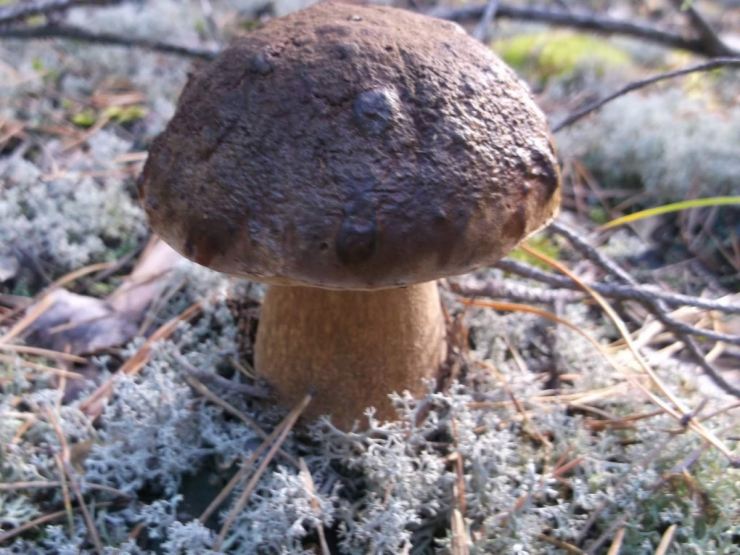
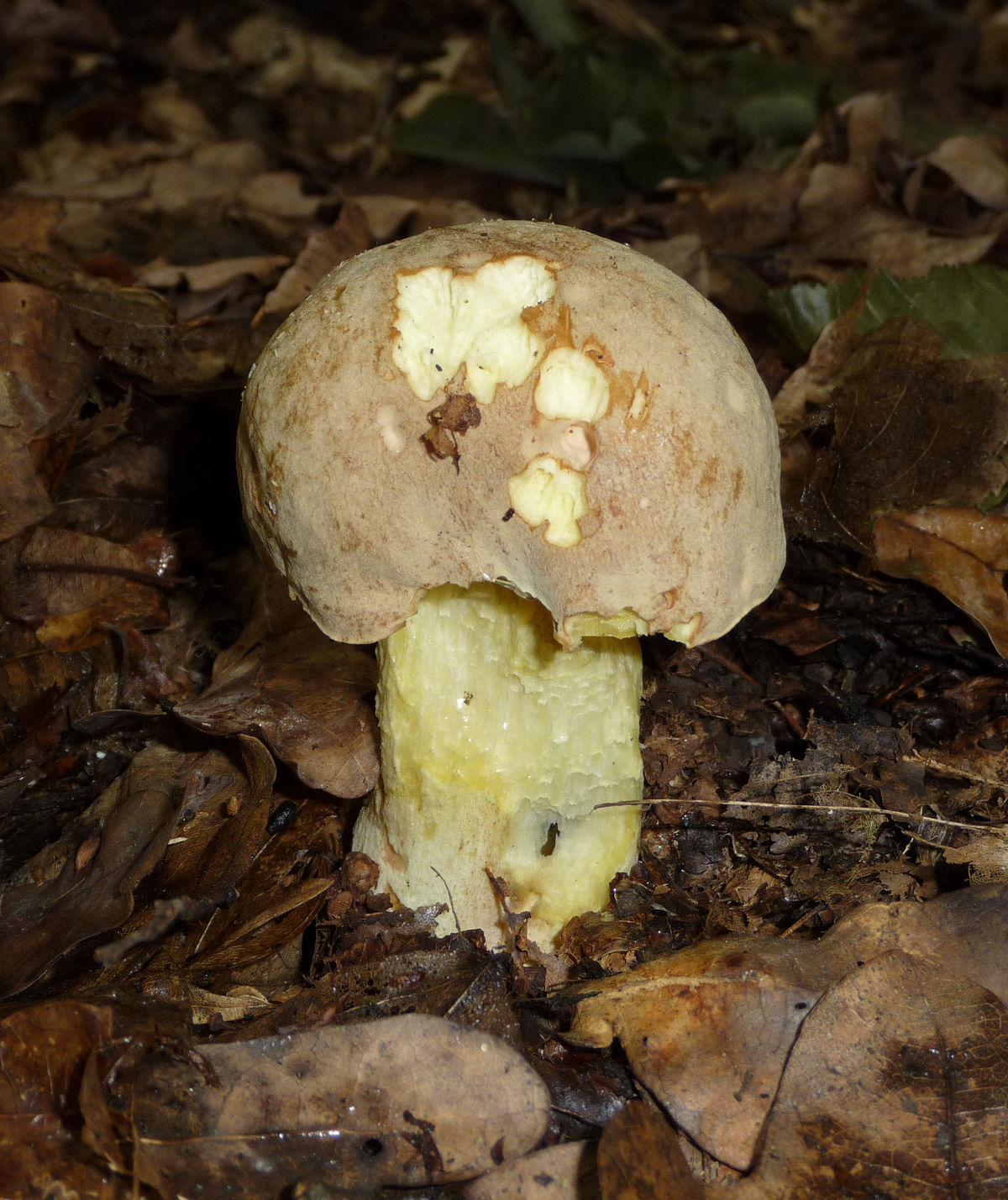
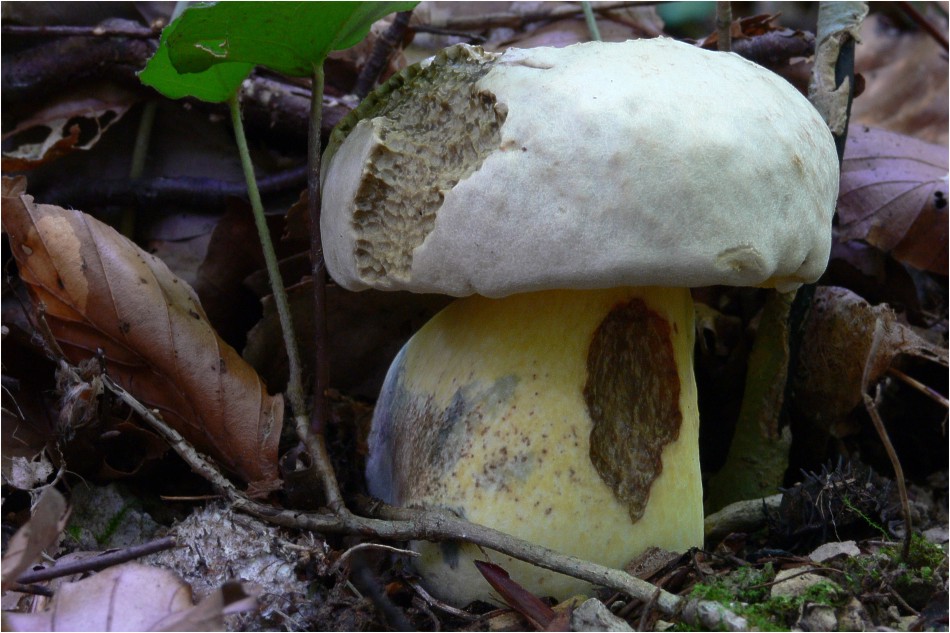
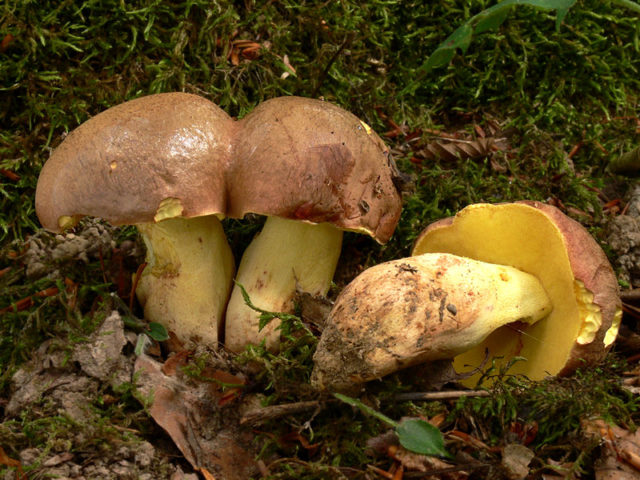
The appearance of a semi-white mushroom is represented by a large cap, the diameter of which can vary from 5 to 20 centimeters. In young semi-white mushrooms, the shape of the cap is convex and covered with a velvety skin. The color of the cap is beige with a red tint, it can also be gray with a greenish tint. The plates under the cap are loose with a golden tint, which turn yellowish with age.
Leg
The leg that holds the cap is up to 10 centimeters high, and its diameter does not exceed 6 centimeters. The color at the base is yellow or dark brown. The surface is slightly rough with dense fibers.

The flesh of this mushroom is very dense, pale yellow in color, which intensifies in the stem. The semi-white mushroom is distinguished by its pleasant taste and specific smell.
Inedible species

Poisonous mushrooms can cause severe poisoning
The genus Borovik includes a number of species that are unsuitable for human consumption. Among them there are toxic and even deadly poisonous. All of these varieties have specific characteristics. You should definitely familiarize yourself with them in order to understand the difference between the species, and not to put a poisonous mushroom in the basket.
Common poisonous and inedible species:
- beautiful-legged;
- rooted;
- Le Gal;
- beautiful;
- pink purple;
- pink-skinned;
- Satanic.
Beautiful-legged
Beautiful or beautiful-legged is an inedible, but not poisonous species either. His cap is olive or light brown, dry, fibrous in young specimens, the edge is wrapped with age. As the mushroom matures, the hymenophore changes its color from lemon yellow to olive. It is thin, the tubes are pink and turn blue when pressed. The leg first resembles a barrel, then a mace or cylinder. Above it is yellow, in the middle it is carmine-red, below it is reddish-brown, in aging fruit bodies it is almost colorless. The middle (pulp) is firm, creamy, with a bitter taste. It grows under fir trees, less often under deciduous trees.
Rooted
Rooted boletus, or stocky, loves warmth and prefers the root system of deciduous trees to create mycorrhiza. This boletus is inedible, but not toxic either. The cap sometimes grows up to 30 cm. The shape of a pillow or hemisphere, the edges are bent, in old mushrooms they are wavy. The color is light gray with a fawn or greenish tint, the surface is dry. The hymenophore is yellow-olive, turns blue when squeezed. The leg is lemon on top and olive on the bottom, with a fine delicate mesh, short. The middle is dense, has a pleasant aroma, but a bitter taste.
Le Gal
Borovik le Gal was discovered by the French scientist Marcel le Gal, after whom he got his name. The name "legal" is also found in the literature. Grows in deciduous forests, under oaks, hornbeams and beeches, it is poisonous. The hat is pink-orange, at first spherical, then convex and outstretched. The hymenophore is tubular, its constituents (tubules) are red, adherent to the peduncle with denticles. The middle smells like a mushroom, whitish or yellow, turns blue when cut. The leg of the same shade as the cap is covered with a red mesh, the shape is barrel-shaped.
Beautiful
Boletus is found on the west coast of the United States during the summer and fall. It is toxic, causes indigestion and diarrhea, but has not been fatally poisoned. The hat has a specific reddish tint, sometimes olive brown. The tubules of the spore-bearing layer are yellow-green, the pores are blood-red. The leg is swollen, reddish with a brown and characteristic purple or scarlet mesh.
The fruiting season begins in late summer and lasts until the end of autumn.
Pink-purple
Boletus purple, or pink-purple, has a characteristic cap color. On a gray background, there are spots of wine, purple, brown-red or pink shades.If the fruit body is turned over, blood-red pores are visible, while the hymenophore itself is olive yellow. The leg is clavate with a thickening at the bottom, covered with a reddish mesh. The middle (pulp) is firm, with a sour-fruity odor. On the cut, it first turns blue, then blackens, and over time becomes wine-red. The species grows on limestone soils, in deciduous forests.
Pink-skinned
Pink-skinned boletus is a rare species. It causes upset stomach, diarrhea, if the doses of the mushroom eaten are high - convulsions and loss of consciousness. The hat first takes the shape of a ball, then a pillow. The color is brown-gray with a reddish bloom at the edges, the surface is smooth or velvety. The pores are yellow at first, with time they acquire a scarlet hue or carmine color, the tubes are olive yellow. The leg is lemon on top, bright red below, covered with a reddish mesh. The middle is lemon yellow, turns blue when cut.
Satanic
The satanic mushroom, or the satanic mushroom, looks specific, it is difficult to confuse it with ordinary white. The hat is light gray, it can be olive or ocher-colored, pink stains are often visible on it. Upon closer examination of the hymenophore, it becomes noticeable that the tubules are yellow-green or yellow-olive. The pores change their color from yellowish to reddish, carmine and blood red. When pressed, they turn blue.
The leg is yellowish, carmine or orange on the cut. Top covered with a red mesh with rounded cells, tuberous shape, tapering at the top. If the mushroom is cut, it first turns red, then turns blue, old specimens smell unpleasant. The fungus causes damage to the liver, nervous system, spleen.
Where do boletus grow and what they look like
These mushrooms can be easily distinguished by a swollen stem, which has a thickening in the base area or in the middle, often covered with a kind of mesh. The mushroom cap has the shape of a hemisphere or pads. The hat has a dry and smooth surface and a little velvet to the touch. Each type of boletus has its own distinctive features.
Boletus are cosmopolitan mushrooms that are found on all continents except Antarctica and Australia. Certain species (for example, porcini mushroom) are not afraid of cold climates, and therefore grow on the borders of Iceland and Chukotka. Only boletus is more hardy to low air temperatures. This species was introduced to New Zealand, Africa and South America along with conifers. Northern Europe, Africa and America are natural habitats.
Certain types of mushrooms are listed in the Red Book. For example, the royal boletus is listed in the Red Book of Ukraine. Now this species is rare, like lipoviks and some other species.
How and where does boletus grow
Boletus can grow in almost any climatic conditions, anywhere in the world. It is possible to meet him alone and in small groups in coniferous and deciduous forests at the bases of trees. The porcini mushroom does not like wet covers and grows on lichen or moss, usually at the base of mature trees.





Having found one specimen, you need to carefully examine the place where the boletus mushroom grows - most often, its brothers are nearby.


Beforehand, it is necessary to plant trees (spruce, birch or pine) on the site, since the boletus is closely related to their roots.

Breeding is available in the following ways:
- The caps of mature specimens are cut into medium-sized slices and mixed with wet soil, then laid out under a tree.
- Carefully dug out mycelium from the forest, place it in the recesses under the trees and cover it with forest soil on top. The planted mycelium should be regularly watered moderately.
- Chop the boletus finely and soak in water for 24 hours, then strain thoroughly. The remaining infusion, which contains the spores, is evenly poured under the roots of the trees.



Regular watering and competent planting will help to harvest the next year: first, the mushroom appears alone, then in groups of several at once.

Borovik: general characteristics
Boletus is a mushroom of the Boletaceae family (Latin Boletaceae). Experienced mushroom pickers and mycologists among themselves call all representatives of the species pains. Looking ahead, let's say that the boletus has enough relatives: in total, there are up to three hundred subspecies of the family.
They meet, as you know, by their clothes, so people have learned to identify the boletus mushroom by such key features as:
The size.
If you want to quickly fill your basket with mushrooms, then head to the pine forest. It is there that the most impressive in size individuals are found.
A mature boletus can weigh up to one kilogram. It is not difficult to notice this even under the fallen leaves. They love to grow in the company, therefore, having found at least one representative, you can expect to get on the trail of the whole "gang".
The style of the headdress of our hero is pillow-shaped or round. Boletus "wear" dry, velvety and smooth to the touch hats. The color of the crown differs from the type of pain and can vary from white to brown.
Boletus is a mushroom that has a large upper part, commensurate with the same large leg. The circumference of the mushroom hat can reach up to twenty centimeters in diameter.
Leg.
So that the boletus mushroom can hold its heavy cap, nature has awarded it with a powerful support. Considering the subspecies of pains, one can notice one common feature: the leg of the fungus is always thickened at the base, and sometimes in the middle, reticular or fibrous in structure, less often just smooth. The color palette varies here: white-yellow and red-brown.
Pulp.
The inside of the mushroom can also be different, but within certain limits. The pulp of the plant is light yellow with a lemon tint. To verify the authenticity of the mushroom, make a cut and observe. The cut should turn red or remain unpainted. Boletus has a dense flesh without cavities. Most species of spore powder are brown in color with various shades.
We have figured out how to recognize the boletus mushroom, and now we will "go to the individual." Consider the most popular types of pain relief among mushroom pickers:
- Bronze boletus.
- Boletus girlish.
- Yellow boletus.
- Mesh boletus.
- Boletus royal.
Bronze boletus loves to grow in deciduous forests under oak and beech trees. Differs in settlements in small groups of three or five individuals. The main habitat is Western and Eastern Europe.
Features of the view:
- Large fleshy cap, planted on a massive leg.
- The color is dark brown, close to black
- Hat diameter up to 17 cm.
Photo: wikipedia.org
The boletus maiden mushroom lives in mixed forests in the warm season, when the temperature does not drop below zero. The difference between the subspecies is its large size and high weight.
Features of this species:
- Headgear shape: from round to flat.
- The color is light brown with a snow-white leg.
- Hat diameter up to 20 cm.
Photo: wikipedia.org
Boletus yellow - a settler of the coniferous forests of Western Europe. Summer months and early autumn are the best times for mushroom hunting. They differ from other types of pains in their characteristic yellow color.
Features of the view are as follows:
- The hat is convex upwards and flattened towards the base.
- The tuberous stem is rather high and thick.
- Hat diameter up to 16 cm.
Photo: wikipedia.org
Boletus reticulated is also called white oak mushroom. The mushroom is not only healthy and tasty, but also holds the absolute record in hat size among the painters.
The features of the view are as follows:
- A hemispherical, convex hat with a velvety skin.
- The fleshy leg with a thickening, like the cap, is brownish in color.
- Hat diameter up to 30 cm.
Photo: wikipedia.org
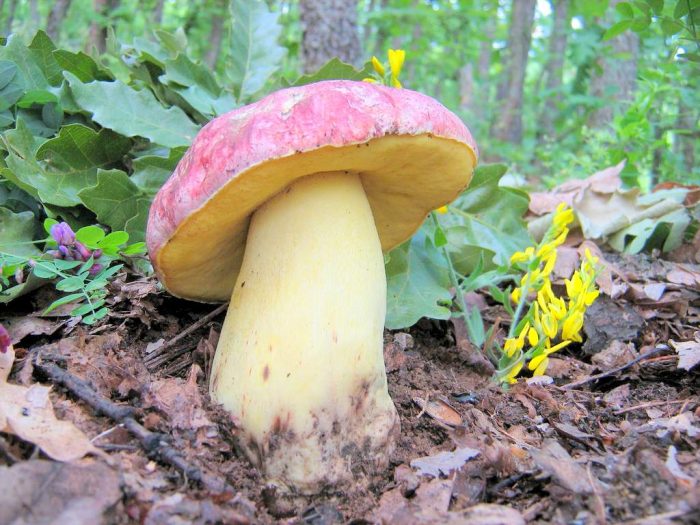
Royal boletus got its name because of the special color of the cap and leg. The clothes of the bolta resemble a court attire - a snow-white shirt and a velvet red cape.
The features of the view are as follows:
- The hat is pillow-shaped and unusually fleshy, with bizarre shades: red, pink, and even purple.
- The leg is large and high, reaching 15 cm in length and 6 cm in thickness.
- Hat diameter up to 15 cm.
Photo: wikipedia.org
Boletus mushroom - like a picture in the forest
To find boletus in the forest, you need to prepare: dress warmly and comfortably, take a basket or basket
Boletus must be plucked carefully so as not to damage the mycelium. Then next year it will be possible to return to this place again for mushrooms.
If you go to the forest after the rain, you can find a lot of Boroviks, but in hot dry weather all the mushrooms will hide.
You can meet the White Mushroom in the forest from June to October. They grow sometimes alone, and sometimes in large families. Most of all, Boroviks prefer the neighborhood of conifers, but they are also found in deciduous forests. Experienced mushroom pickers advise looking for Boletus in places where there are many anthills, under fallen leaves or dried pine needles. Both young specimens and rather large ones grow in the forest. The largest Borovik found was about 7 kilograms in weight and 50 cm high.
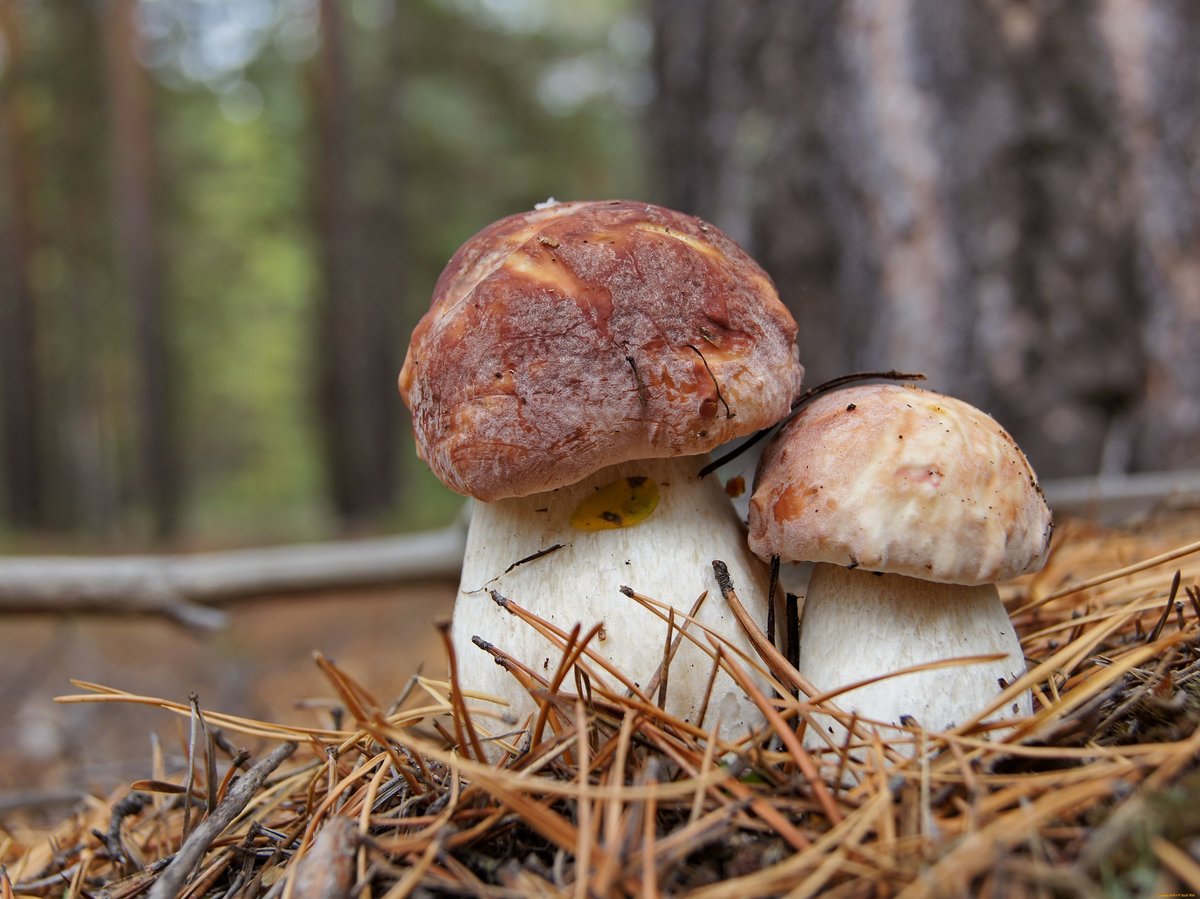


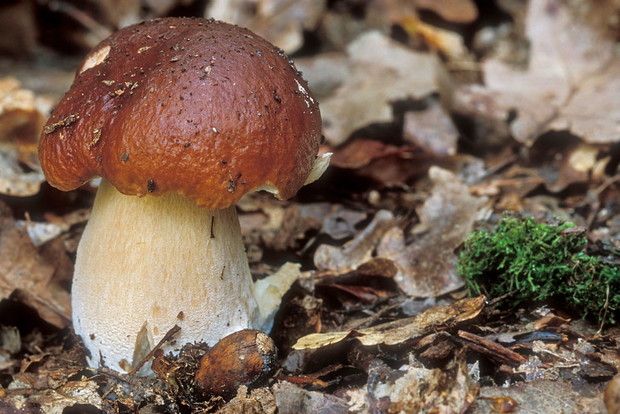
Description of boletus
Due to their large size and group growth, boletus mushrooms are noticeable even for beginner lovers of "quiet hunting". A fleshy brown cap with a slight gloss and an even more massive leg of a light brown shade make this mushroom not only noticeable, but also one of the most attractive in the forest.

What is the other name of the mushroom
Most people, answering the question about the second name for boletus, mention the well-known phrase "porcini mushroom", without even knowing that there is another name that has a more official status. This variety comes from the Boletov family, having received the appropriate name - Bolet.
What does boletus look like in the forest
The hallmark of the mushroom is its massive brown cap with a smooth surface and an even more voluminous stem with a fibrous structure. In the forest, there are both single specimens and whole groups of boletus, making their way through deadwood, foliage and sand. Strong fleshy fruits at maturity reach large sizes and weight (from 300 to 700 g).

The structure and features of the species
The mushroom is primarily notable for its cap and stem, both of which are edible. However, in nature, there is not only a brown head, but also its other shades, ranging from pale yellow to the darkest, brown. The size of the cap also changes, which may not exceed 5 cm in diameter or, conversely, reach 25 cm.
Having a cap-tubular structure, the surface of the fungus can be either convex or flat. Boletus pores also have a different shade - from milky to lemon and even red, which cannot be said about brown spore powder. The fruit is very pleasant to the touch, having a perfectly smooth or slightly velvety surface. The structure of its hymenophore is tubular, free or semi-free type.

The pulp of the mushroom has a dense, homogeneous consistency with a slight yellowish tint at the fracture, which in some varieties may turn blue or even redden over time. The size of the leg depends on the type of boletus, ranging from 3 to 18 cm. The surface of the leg can be even and smooth, but in the vast majority of cases it has a mesh or fibrous structure.
Similar species
What forest dwellers can you easily confuse boletus with? There can be many options, however, the answer is obvious. The boletus family includes a huge number of mushrooms and species that thrive in forests, moreover, they grow in abundance on the territory of Russia.
Let's get acquainted with the most common species that you can surely meet on your way.
Borovik girlish
This mushroom has a very interesting intricate name. It is edible, and also belongs to the family of paints.
It is a boletus.
Its appearance distantly resembles a semi-white mushroom. Its cap has a maximum diameter of 20 cm.The shape is predominantly convex, and the edges are bent inward. Itself seems quite thin, the hat has a golden hue, much less often red or brown.
The flesh itself is very dense, it also has a blue tint on the cut.
The leg reaches a maximum of 15 cm in height, very thick, up to 6 cm in diameter in thickness.
This species is widespread in southern Europe, however, such boletus cannot be found in large groups. Likes to grow alone. Mainly bears fruit during the early fall stage.
Root boletus
Another representative of the bolet family, the boletus genus. A mushroom that will surely not go unnoticed.
It is very large, the cap can reach a diameter of up to 30 cm. At the very beginning of growth, it has a conical shape, but then it acquires a flatter shape, the edges are bent inward.
The surface of such a cap is slightly woolly, and can often crack.
The pulp of this mushroom has a lemon-yellow hue, somewhat bluish. It does not have the most pleasant smell, but the taste is rather bitter.
The leg is thick, raises the mushroom to a height of 12 cm. It has a yellow tint.
This mushroom is widespread in Europe, and chooses only deciduous forests for its development. Loves calcareous and other neutral soils. He also prefers dryness. It grows from July to October.
Mosswheel green
A mushroom widespread in Russia.
Very beautiful, attracts attention. Despite the name, it belongs to the genus Boletus
This mushroom is easy to spot in the forest. Its cap is small, reaching a diameter of 10 cm. Individuals of 16 cm are very rare. It is somewhat convex and very velvety. The flesh is white, however, turns blue when cut.
The leg itself has a cylindrical shape, which tapers slightly towards the mycelium itself. It is about 10 cm high and up to 2 centimeters thick.
The spore powder is brown, frequent.
This mushroom chooses a variety of forests for its growth. In addition, he also prefers meadows and roads.
The fungus grows singly, and sometimes even in groups. Can form mycorrhiza with deciduous and coniferous trees. He is a cosmopolitan. It is equally often found both in North America and in Europe and Australia.
Boletus inedible
Inedible boletus can also be found in Russian forests. However, despite the fact that the name contains the word inedible, this mushroom is not poisonous. The fact is that it is unpleasant to cook mainly because of its taste, however, it does not carry any danger to the human body.
In order not to confuse this inedible species with a simple porcini mushroom, you need to carefully study the description.
The hat can be up to 15 cm in diameter. It has a conical shape. Sometimes, slightly convex, the edges curl inward or hang down in waves.
This hat is very smooth to the touch, somewhat matte and wrinkled. The skin has a light brown tint, however, at a young age it already has a brown or gray-brown color.
The flesh itself has a creamy or white tint, however, it can sometimes take on a blue tint at the cut. Bitter enough.
The leg rises 15 cm in height and is about 4 cm thick.
As for the tubular layer of this forest dweller, it has a lemon yellow tint, and a greenish tint predominates. The spore powder itself has a brown and olive color.
This mushroom is widespread in the south of the European part of Russia, most often it chooses the Kaliningrad region for its place of residence. It is also common in Europe, namely in warm countries, such as Italy or Spain. Mainly chooses coniferous forests, as well as oak and broad-leaved forests, prefers sandy and acidic soils, and also settles in places in parks and lawns.
Mushrooms grow from July to October.
Useful properties of boletus
Forest boletus is a natural and widely available storehouse of essential vitamins and many beneficial properties.The composition of the mushroom pulp is presented:
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- pantothenic acid;
- pyridoxine;
- folates;
- ascorbic acid;
- alpha tocopherol;
- vitamin PP;
- niacin;
- potassium;
- calcium;
- magnesium;
- sodium;
- gray;
- phosphorus;
- chlorine;
- iron;
- cobalt;
- manganese;
- rubidium;
- fluorine;
- chrome;
- zinc.
Useful properties are also due to the presence in the composition of a sufficiently large amount of digestible carbohydrates, essential and nonessential amino acids, which are involved in metabolic processes, oxidative and reduction reactions occurring in the human body. Vitamins "A", "B1", "C" and "D" promote the growth of nails and hair, and minerals are necessary for bones and joints, to prevent osteoporosis and anemia, to maintain normal functioning of the heart muscle.
Growing places
Boletus habitats are located in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere. The largest yields of these mushrooms are harvested in the forest zone and taiga, less often boletus grows in the forest-steppe. This representative of the genus Bolet does not grow on the territory of the tundra, forest-tundra and in the steppes. Boletus is also found in the forests of mountainous areas. The closer to alpine meadows, the less often this mushroom is found. At an altitude of 1500-2000 m above sea level, it does not grow.
The mycelium envelops the roots of trees, but the fungus is not a parasite, it forms a symbiosis - micrisa. Without it, Bolette will not grow, because nutrients enter the tree through the mycelium, and organic products go back to the mushroom. The mushroom also requires a certain type of soil, which is formed only in the forest. This makes it difficult to grow the species at home or on an industrial scale.
They begin to collect boletus already in June, but the peak season is in August and September. If the fall is cold, the mushrooms disappear quickly. In the southern regions, the first forest boletuses appear in May and grow until the end of October. Fruit bodies grow in humid and warm weather, they live no more than a week.
When searching, it is worth carefully examining the litter under the pines, fir trees, hornbeams, oaks and beeches, places near anthills. Young specimens are small, hiding under leaves. Boletus rarely grow alone, if you draw a circle with a diameter of 10-15 m around the found specimen, then you will find a whole family within it.
Cooking recipes
There are many delicious and healthy recipes, the ingredients of which will be an umbrella mushroom.
Breaded mushrooms
- You will need 500 g of mushrooms.
- Two eggs.
- Onion 2 pieces.
- Three tablespoons of flour.
- Hard cheese 300 g.
- A little vegetable oil, salt, ground black pepper.
- A bunch of parsley and dill.
First, prepare the mushrooms. Remove the legs and clean and rinse the caps well.
Beat eggs and flour until smooth. Season well with salt and pepper. Chop the onion finely.
Place the mushrooms in a baking sheet and sprinkle with onions. Top with flour and eggs. Sprinkle with hard cheese, and then put in the oven for 30 minutes at 200 degrees. Wait for the cheese to melt. Decorate the stewed mushrooms with herbs.
Mushroom caviar
Caviar is very tasty when cooked correctly. To prepare it you will need:
- 1 kg of mushrooms;
- 4 pieces of onions;
- vegetable oil;
- lemon juice in the amount of 40 ml;
- garlic;
- salt;
- sour cream 100 ml;
- 2 tablespoons tomato paste.
Peel the mushrooms, finely chop the onion and fry in a skillet.
Then add the mushrooms to the pan and fry until the onion has a golden hue. Then add sour cream and simmer for about 10 minutes over low heat. Mix everything well, add salt, pepper and other favorite spices.
Simmer for 20 minutes. Season the resulting caviar with tomato paste in the specified amount. Serve spread over a baguette or toast.
Umbrella mushrooms in the microwave
If you are hungry, the umbrella mushrooms can be cooked very quickly in the microwave.
- To do this, separate the caps from the legs. You don't need legs.
- Add 200 ml mayonnaise.
- Season with black pepper and salt.
- Add coriander and a pinch of nutmeg.
- The mushrooms must be pre-prepared and pickled in the specified mixture. Leave it on for 30 minutes.
- Later, place the mushrooms on a plate, cover and microwave for 15 minutes.
The dish must be hot when served. It is recommended to decorate it with dill and parsley.
Umbrella filling
The French love to use this mushroom as a filling for buns, croissants or pancakes. But in order to prepare a truly delicious filling, you need to follow the recipe.
You will need 500 g of mushrooms.
- They need to be rinsed and cleaned well.
- The leg is detached from the cap.
- All mushrooms need to be chopped well with a knife to make a brown mass.
- Finely chop onion, garlic, herbs. It is recommended to use basil, parsley, dill, oregano.
- All ingredients are prepared. Put a frying pan on the fire, heat the vegetable oil.
- Add the onion first. Fry it until golden brown.
- Next, add the mushrooms. Fry with the onion for a short time, just a couple of minutes.
- Then add finely chopped herbs and garlic.
- Fry everything together for a few more minutes.
- Then add heavy cream. Pour in about 80 ml gently.
- Continue stirring the mixture.
- Then add some dry white wine. Approximately 30-40 ml.
- Continue to simmer. Finally, add salt and pepper to taste, as well as your other favorite seasonings.
Cool down well before adding the filling to pancakes or rolls.
The cool filling will have a slightly nutty flavor, it goes well with airy yeast dough.
If you want to stuff pancakes, then you can add fried minced chicken to this mixture. It turns out very tasty, and most importantly, interesting. New line with
Cream can be replaced with fatty sour cream. Manages to achieve the same effect.
Description
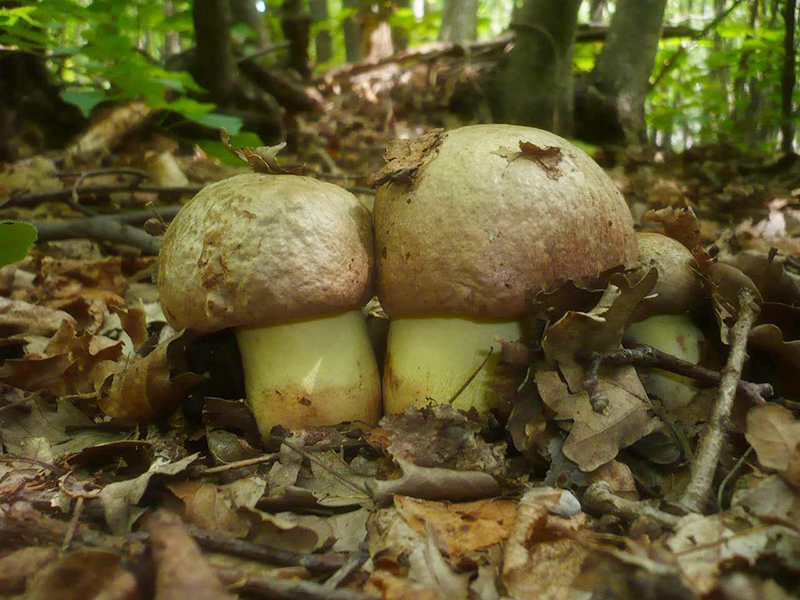
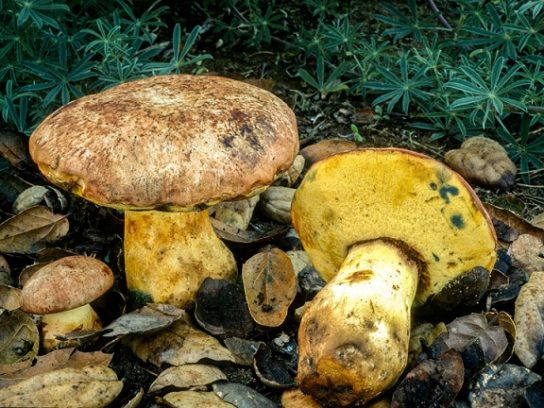
Boletus mushrooms are considered one of the largest cap varieties. They weigh 200-300 g, sometimes they reach a kilogram. The record holders grow up to 2-3 kg. These fruits look like this:
- the fruit body is massive, dense;
- the leg is thick and dense, with a characteristic thickening at the base or in the center, sometimes it has a barrel-shaped shape;
- leg height - 3-20 cm;
- the shade of the leg is light, sometimes reddish or brown, with a characteristic mesh;
- the surface of the leg is rough, sometimes smooth;
- the hat is wide, flat, or resembles a pillow, with a diameter of 5 cm to 25 cm;
- the color varies from light yellow and beige to dark brown and almost black;
- the surface of the cap is velvety or smooth, after rain it becomes slippery;
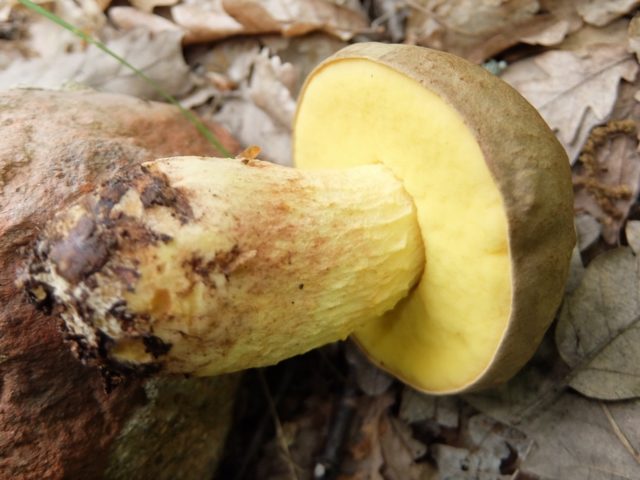
- hymenophore tubular, dense, color from yellow to olive, sometimes reddish, rarely white (in young specimens);
- spores are yellowish, brown or olive-brown;
- the flesh is white, dense, crunchy with a pleasant mushroom smell.
Edible boletus mushrooms are delicious, they belong to the 1-2 category in terms of culinary value. Many species remain light colored after processing. The pulp exudes a strong mushroom aroma, which intensifies when dried.
Mushrooms are prepared in different ways: boiled, pickled, dried, salted and frozen. They contain many beneficial substances. They are eaten for anemia, problems with bone tissue and joints. But this food is hard on the digestive tract.
Botanical description of boletus mushrooms
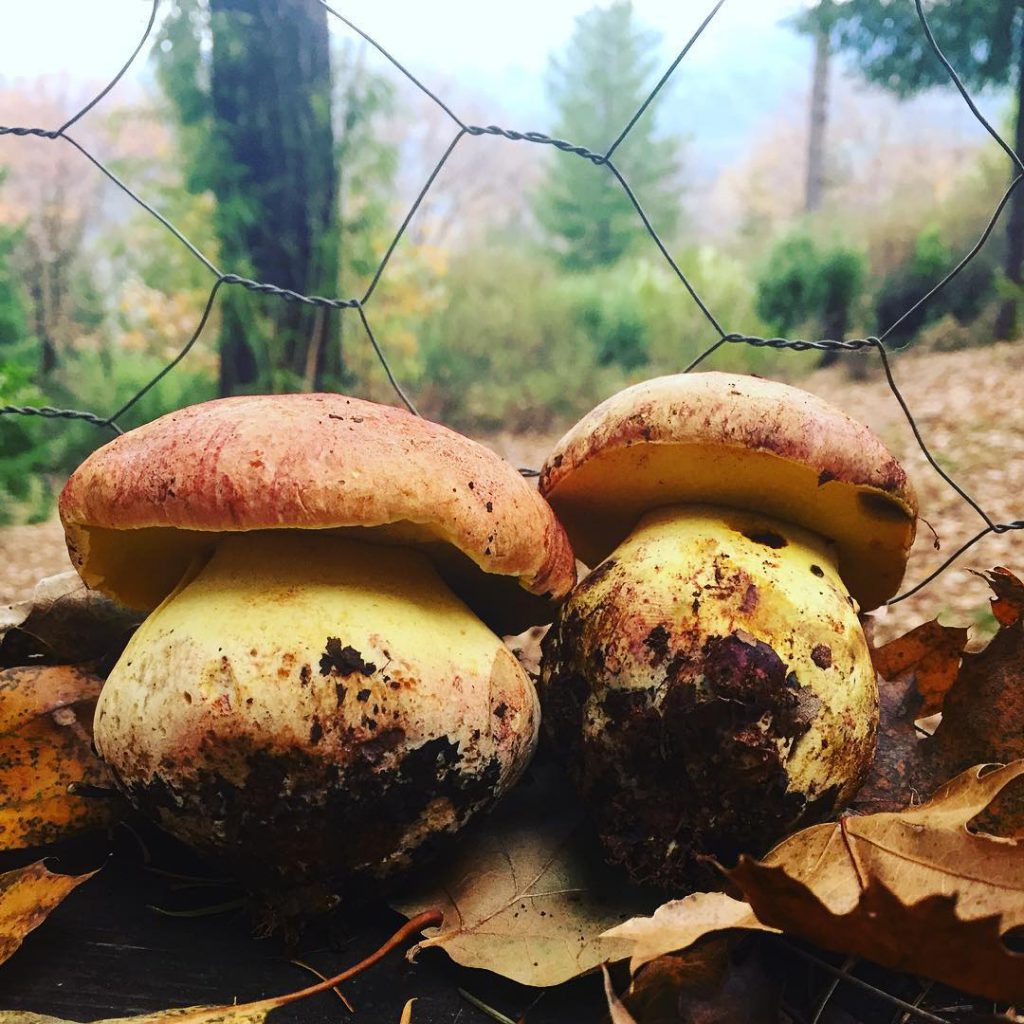
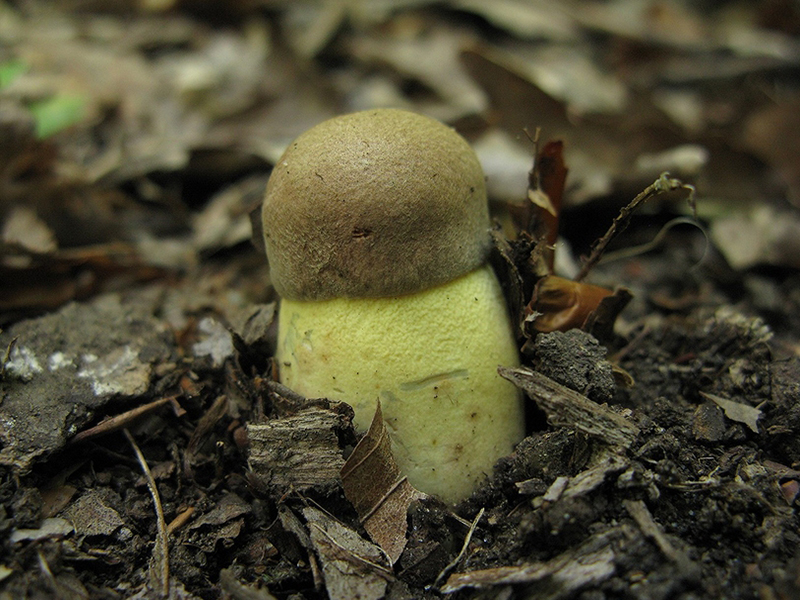
A mature fungus has a convex, flat-convex, sometimes spreading cap with a smooth or wrinkled, rarely cracking, bare or finely felt surface. The skin is adherent, can vary in color from red-brown to almost white.
The stem is massive, barrel-shaped or clavate, with a whitish, brownish, rarely reddish surface covered with a light mesh pattern. The shape of the leg can change with age. Tubular layer under the cap, easily separated from the pulp, light in color with yellow or olive-green tint. Spores are olive-brown, fusiform.
 The appearance of the porcini mushroom is significantly influenced by its origin or the so-called growing conditions
The appearance of the porcini mushroom is significantly influenced by its origin or the so-called growing conditions
Useful properties and application
Semi-white mushrooms have been considered extremely useful since ancient times. They are loaded with various antioxidants that prevent the development of serious cancers and other diseases. Strongly affect the functioning of the entire immune system. They cope well with viral diseases. Quite a common ingredient in traditional medicine. Various broths and tinctures of semi-white mushroom are used to help cope with nervous disorders and insomnia. Also, these miracle mushrooms activate the work of the brain and renew the body from old cells.
In addition to medicine, the semi-white mushroom is endowed with excellent taste and is used in cooking. These mushrooms can be dried or fried, pickled and salted. Also, many culinary experts use it as an additive to sauces or separately as a main course. Pickled semi-white mushrooms are not much different from porcini mushrooms. However, you should not pick half-white mushrooms that grow near roads and large settlements. Mushrooms are capable of accumulating dangerous toxins that are in the soil.

Boletus cooking rules
It is recommended to soak the harvested porcini mushrooms in cold water for 60 minutes to separate unnecessary forest debris. Then thoroughly clean them from dirt and cut off possible damaged areas. It is better to immediately cut the boletus into slices to check the internal cleanliness and rot.

Usually, mushroom pickers dry boletus, since during this procedure all the beneficial properties are maximally preserved, which are successfully used in the prevention and treatment of many diseases.

You can dry the crop:
In the traditional way - in the oven at + 50 degrees, putting their slices on parchment, for about 7 hours.






In a microwave oven, which is set at a power of up to 180 W for 20 minutes. This procedure should be repeated three times, with an interval of mixing and airing the product.

They are stored for quite a long time and, unlike their counterparts, retain their color and aroma. The photo shows a dry boletus.

For storing dry mushrooms, it is better to choose a dry, ventilated place where one constant temperature is maintained in order to avoid mold and moisture in the product. It is best to keep them in a cardboard box or paper bag throughout the entire year of storage.

Cooking and pickling recipes
Boletus is used in various dishes. They do not lose their taste during boiling, frying and salting. In some countries, they are eaten raw. Porcini mushrooms do not require long cooking or steeping. When boiled, Borovik does not darken, which allows you to cook soup with light broth from them. Aromatic mushroom soup is prepared according to the following recipe:
Ingredients:
- 1 glass of pearl barley.
- 3 medium potatoes.
- 2 carrots.
- 1 onion.
- 300g of mushrooms.
Pearl barley is cooked over low heat until the broth thickens. Mushrooms are fried with onions, and, together with chopped potatoes and carrots, are sent to the barley pan. You can add herbs, bay leaf or pepper to taste. After removing from heat, pour in a spoonful of butter and let it brew for 20 minutes.
Fried mushrooms
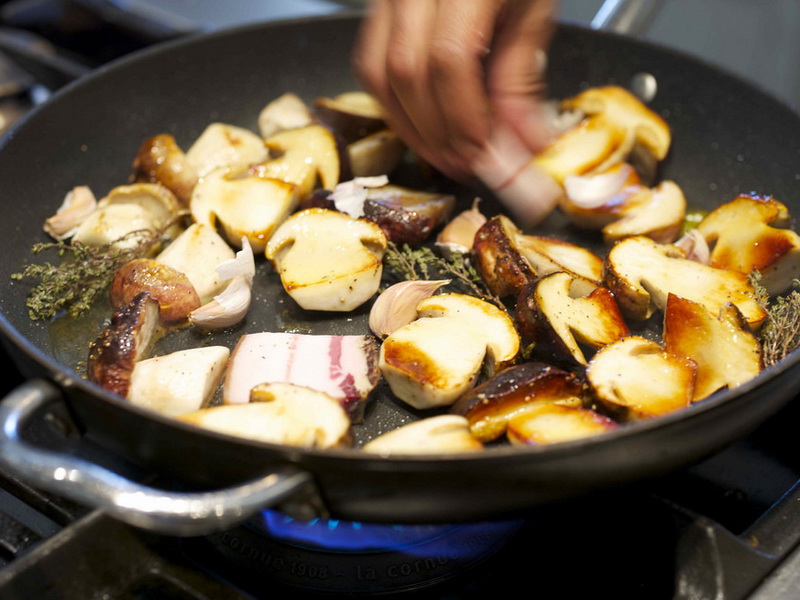
Fresh boletus does not lose its flavor when fried. There are many such dishes not only in Russian cuisine. For example, you can make fried mushrooms following an old Italian recipe.
Ingredients: fresh boletus, flour, oil (preferably olive) Chop the mushrooms and roll in flour. To create crispy mushrooms, place the mushrooms in cold water before frying. After frying in a hot skillet, blot them with absorbent paper. Sprinkle with salt or other seasonings on top and serve hot.

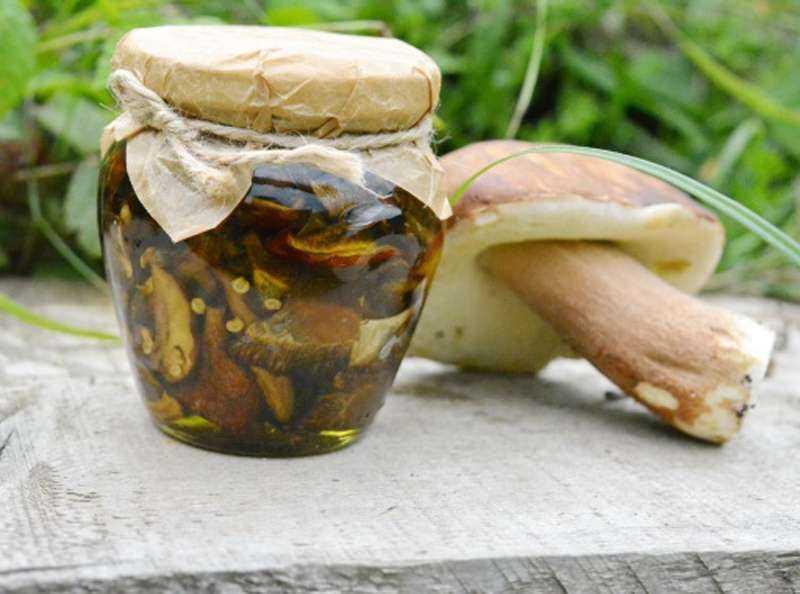
Marinated mushrooms
To store Boletus for a long time, they are dried, frozen, salted. In cold winter, you can enjoy delicious pickled mushrooms. This will require mushrooms, water, vinegar, salt, peppercorns, bay leaves, garlic, cloves.
Rinse and chop the mushrooms before cooking. Put Boroviki in a saucepan with salted water. Bring to a boil, drain and cook again. Drain the water, and rinse the mushrooms with water. For the marinade, boil 1 liter of water with 1 tablespoon of salt and a little less sugar. Add mushrooms, garlic, bay leaf, pepper, 1 tablespoon of vinegar. Let it boil for a while and pour it into the jars.


Not only people love to harvest Boroviks, but also “forest dwellers”. Squirrels dry them by putting them on twigs and branches. Thus, she can prepare almost a kilogram of mushrooms.
























































