Description
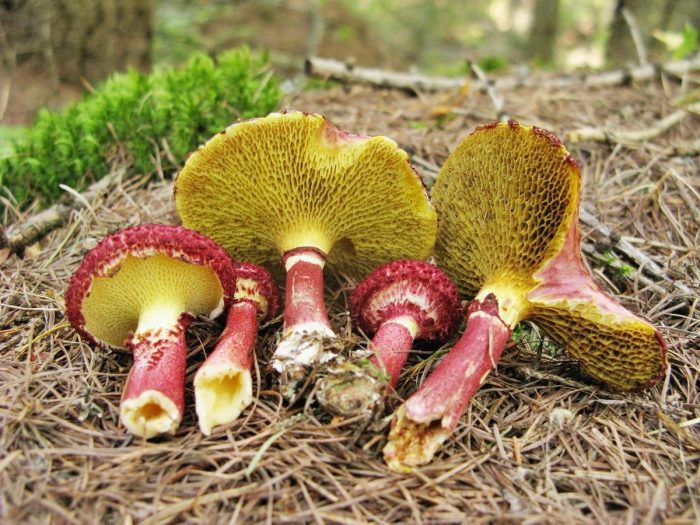
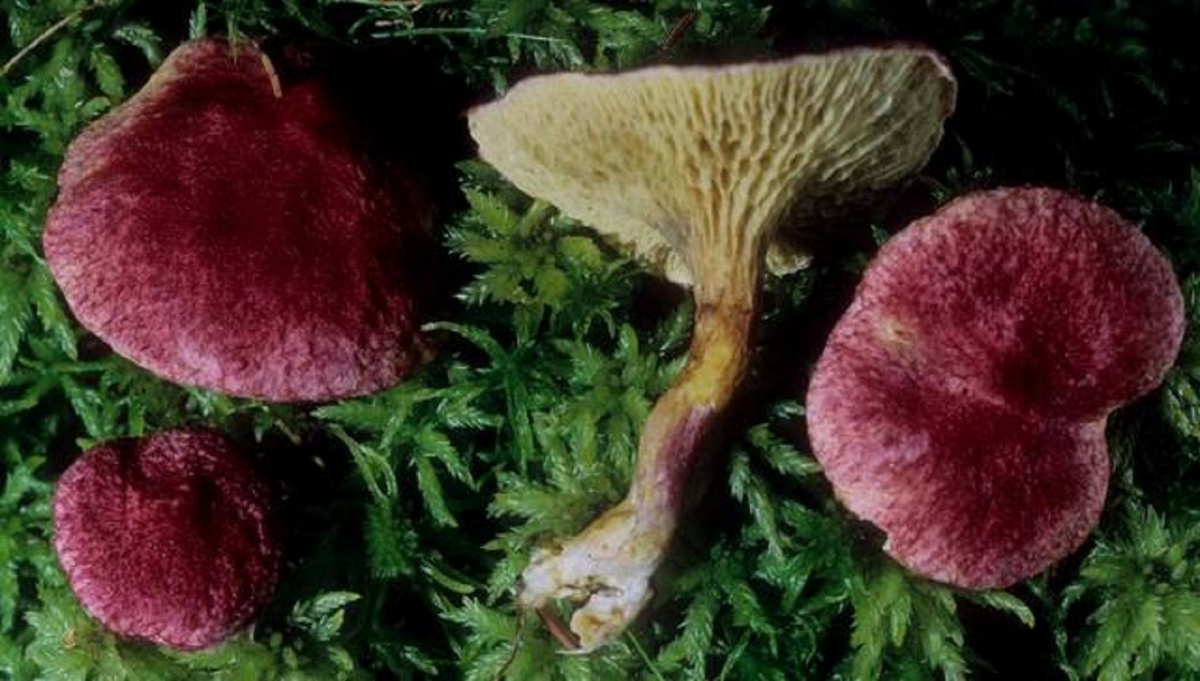
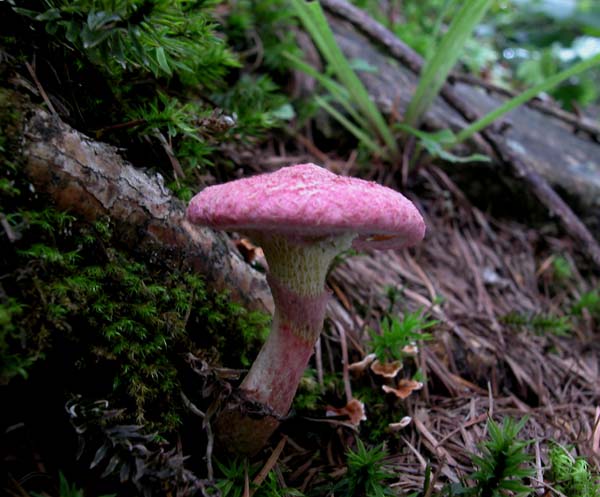
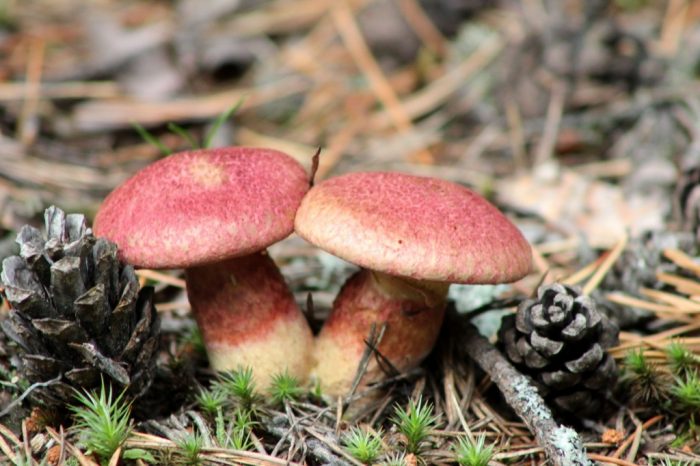
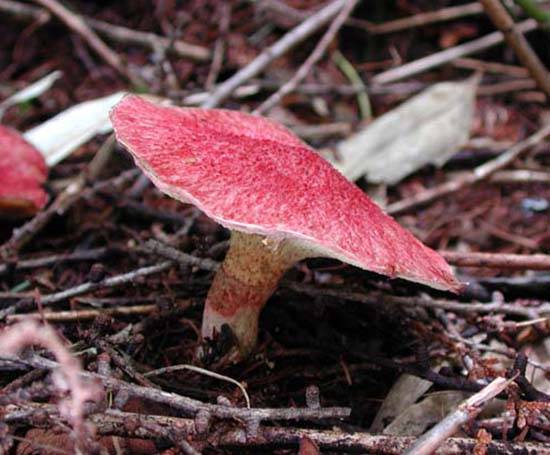
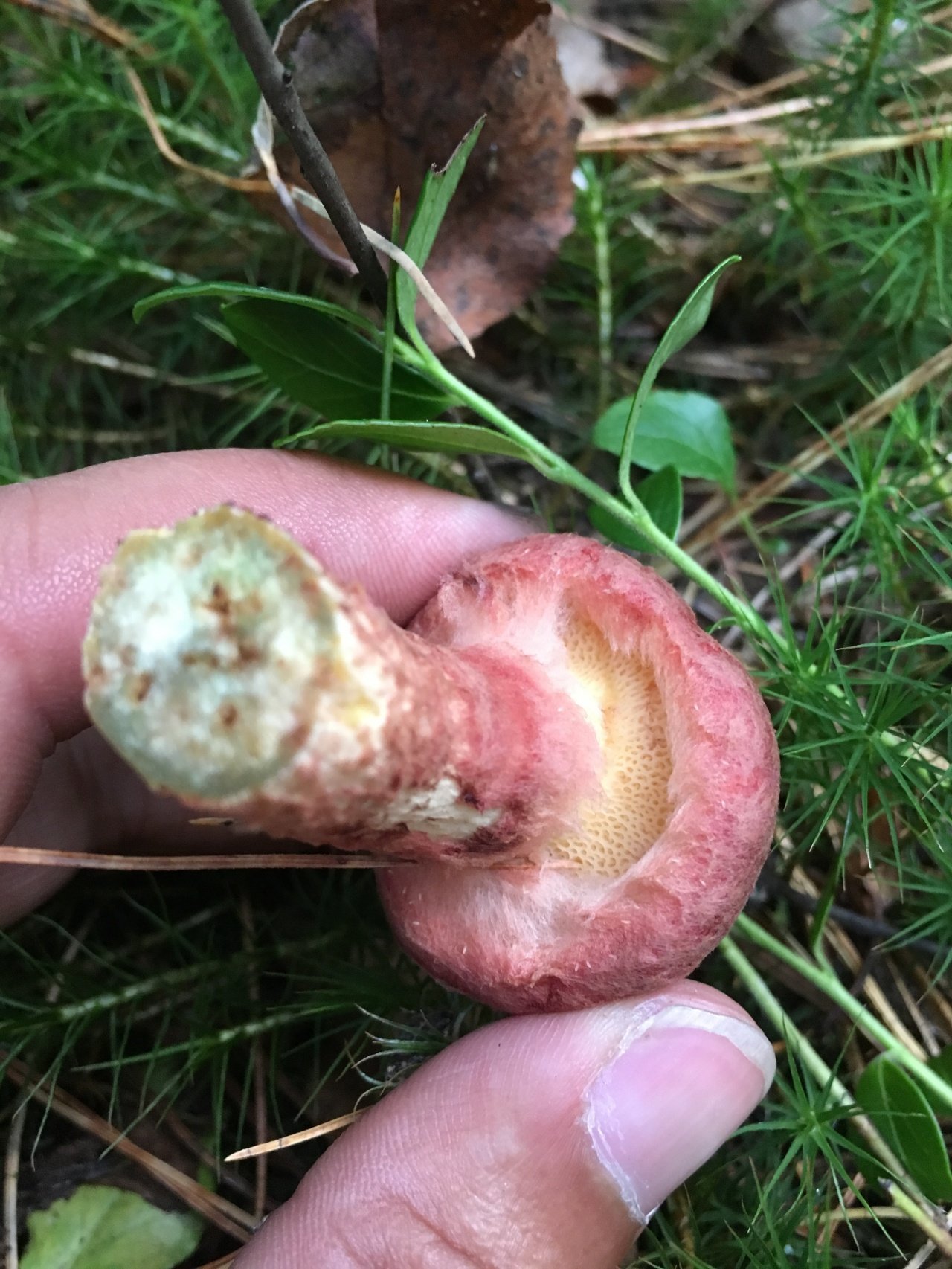
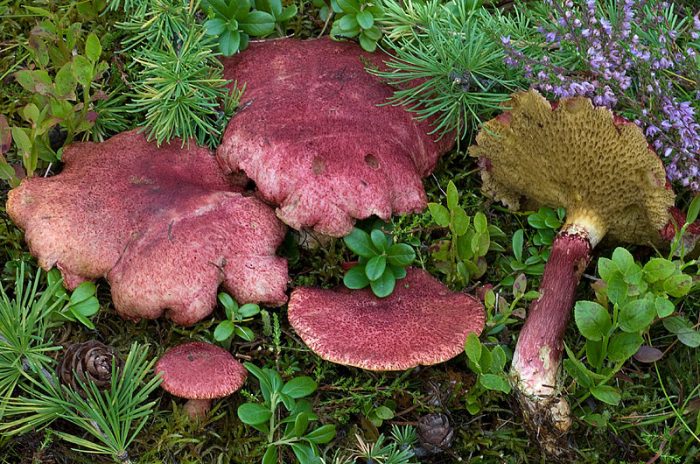
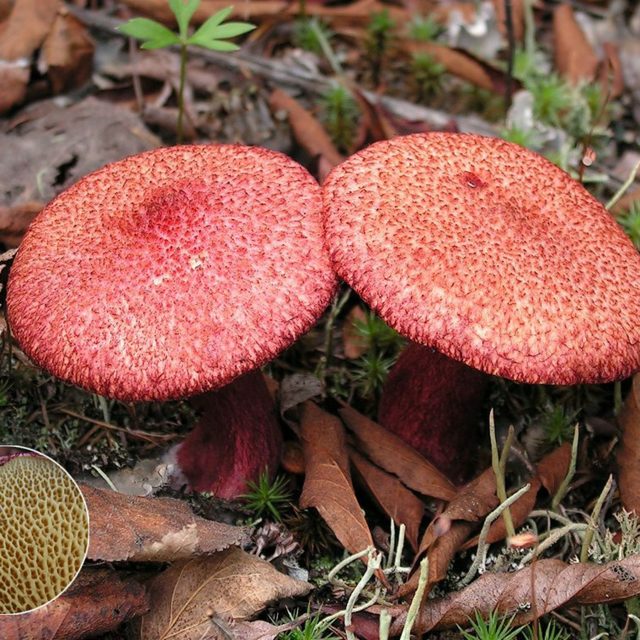
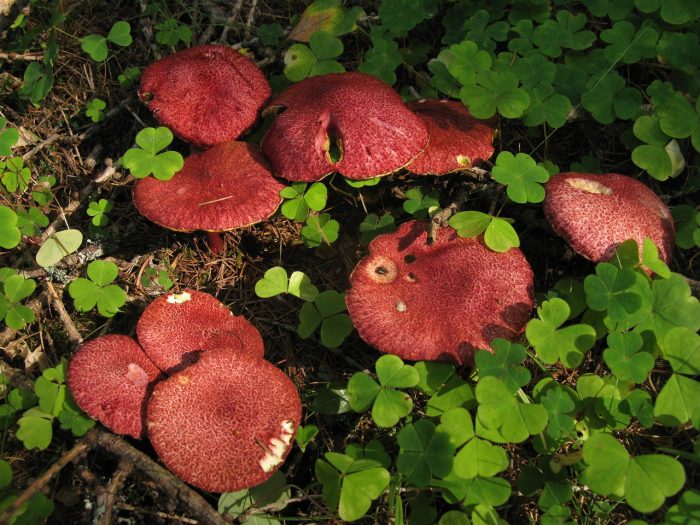
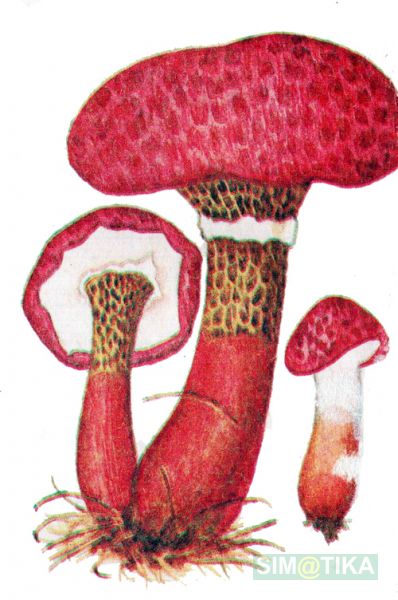
The cap grows up to 10 - 11 cm in diameter. It looks like a pillow, almost flat in shape, with a tubercle in the central part, covered with scales. The consistency is dry but rather fleshy. A characteristic feature of the cap is its color: in young mushrooms, it is bright burgundy, cherry or purple-red. In adult plants, it is paler, with a yellowish tinge. Sometimes you can see the remains of the bedspread along the edge.
Boletin marsh (Boletinus paluster) - description
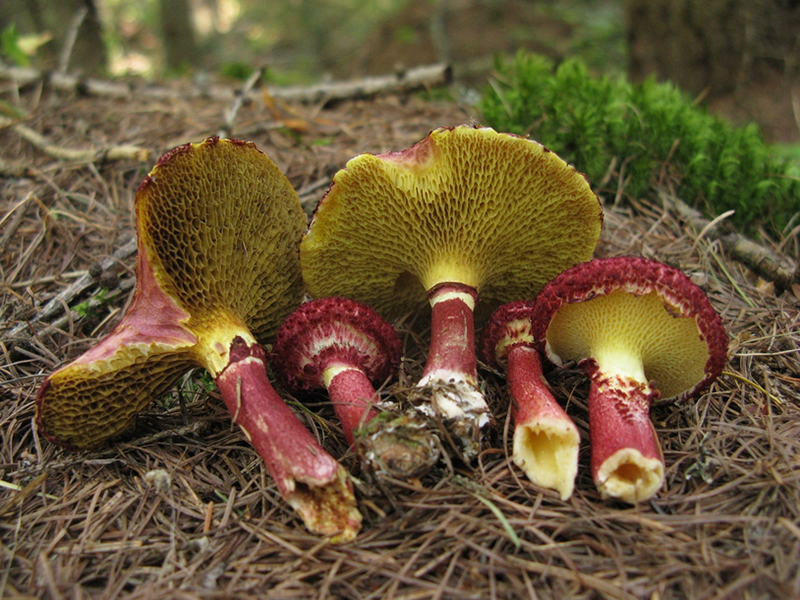
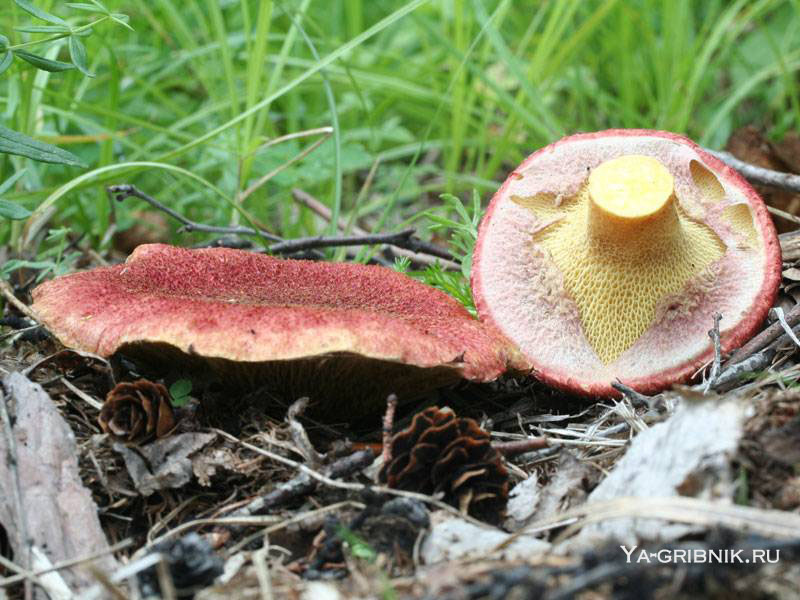
In boletin, the tubular layer descends strongly to the leg, has a yellowish color. While the mushroom is young, the underside of the cap is hidden under a gray-pink blanket. The pore diameter reaches 4 mm. Spore powder, unlike many other mushrooms, is pale brown in color. The leg is long (4-7 cm) and thin, up to 2 cm, slightly widening downward. In some cases, there are remnants of a ring on it. The pulp is yellow, sometimes with a blue, bitter taste and faint odor.
Description of Asian boletin
The diameter of the Asian boletin's cap reaches 12 centimeters. The hat is convex, dry. The color of the cap is purple-red, and the surface is covered with felt scales.

The tubular layer descends to the pedicle. The pores of the tubular layer are radially elongated, they are arranged in rows. The color of the spores is yellow at first, and then becomes dirty olive. The pulp is yellowish; at the break, its color does not change.
In shape, the Asiatic sieve is similar to other representatives of the genus, but differs in the purple-red color of the cap, and in the same color of the leg below the ring. The length of the stem is less than the diameter of the cap, its shape is cylindrical, the stem is hollow inside. Above the ring, the color of the leg is yellow, and below it is purple.
Places of growth and fruiting times of Asian sieve shafts
Asian boletins grow in Eastern and Western Siberia, in the Far East and also in the South Urals. Also found in Europe, Finland. They can be found among larch trees.
They bear fruit from August to September.

Other members of the genus
Boletin half-peg or sieve half-peg is a conditionally edible mushroom. His hat is thin, elastic, initially bell-shaped, and then flat. The surface of mature mushrooms is ribbed. The color of the cap varies from rusty red to yellow. Its diameter reaches 17 centimeters. The surface of the cap is dry with scales. There is a thin fluff on the skin. The leg is hollow, for which the mushroom got its name. There is an adhesive ring at the top of the leg.
Externally, boletin is similar to a flywheel, for which it is also called a half-legged flywheel. These mushrooms grow mainly in deciduous and cedar forests. Fruiting time is from August to October. They are found in lowlands and mountainous areas.
Boletin is a conditionally edible mushroom of the 4th category. The mushroom has no value due to its tough, rubbery pulp.
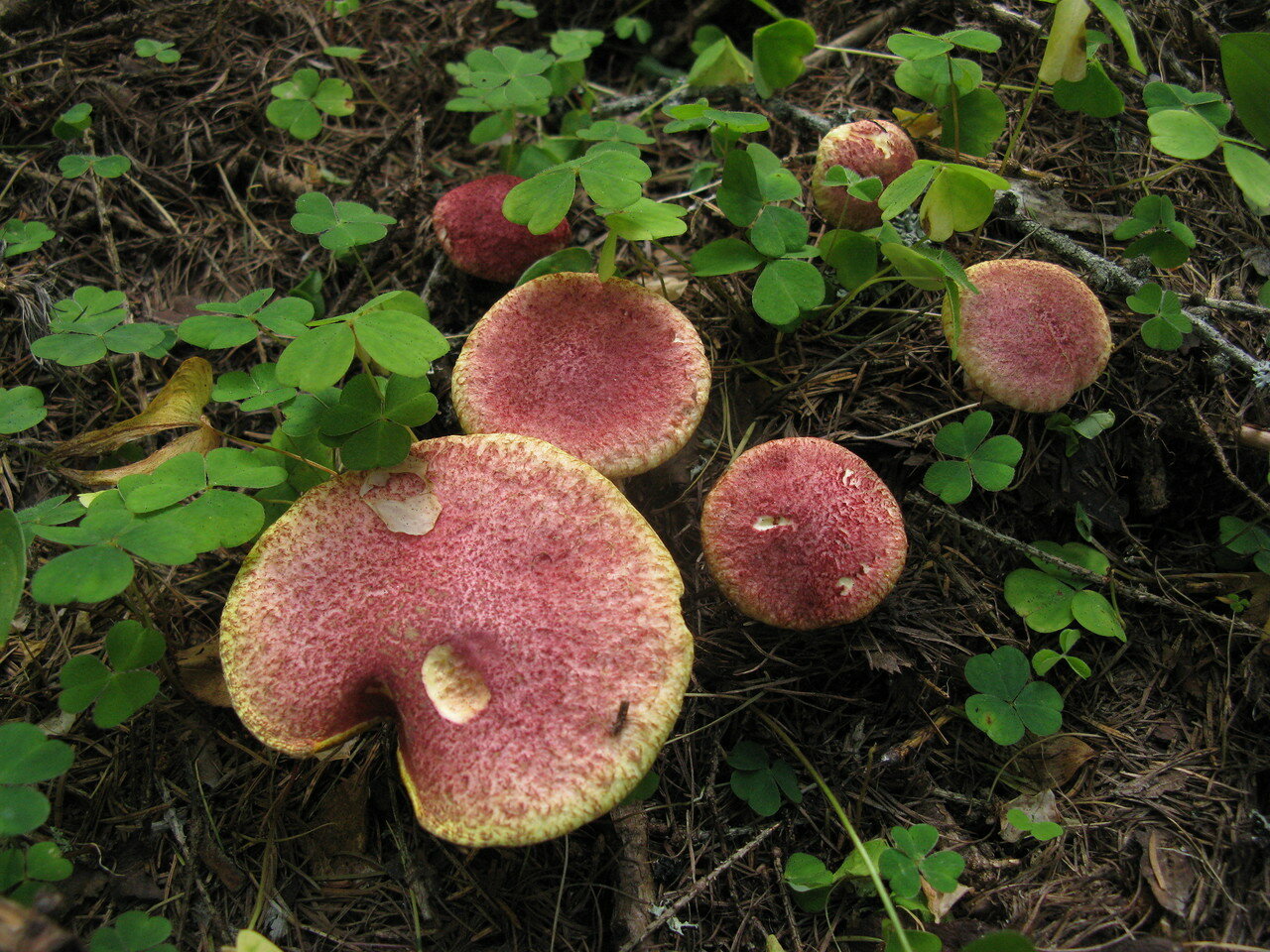
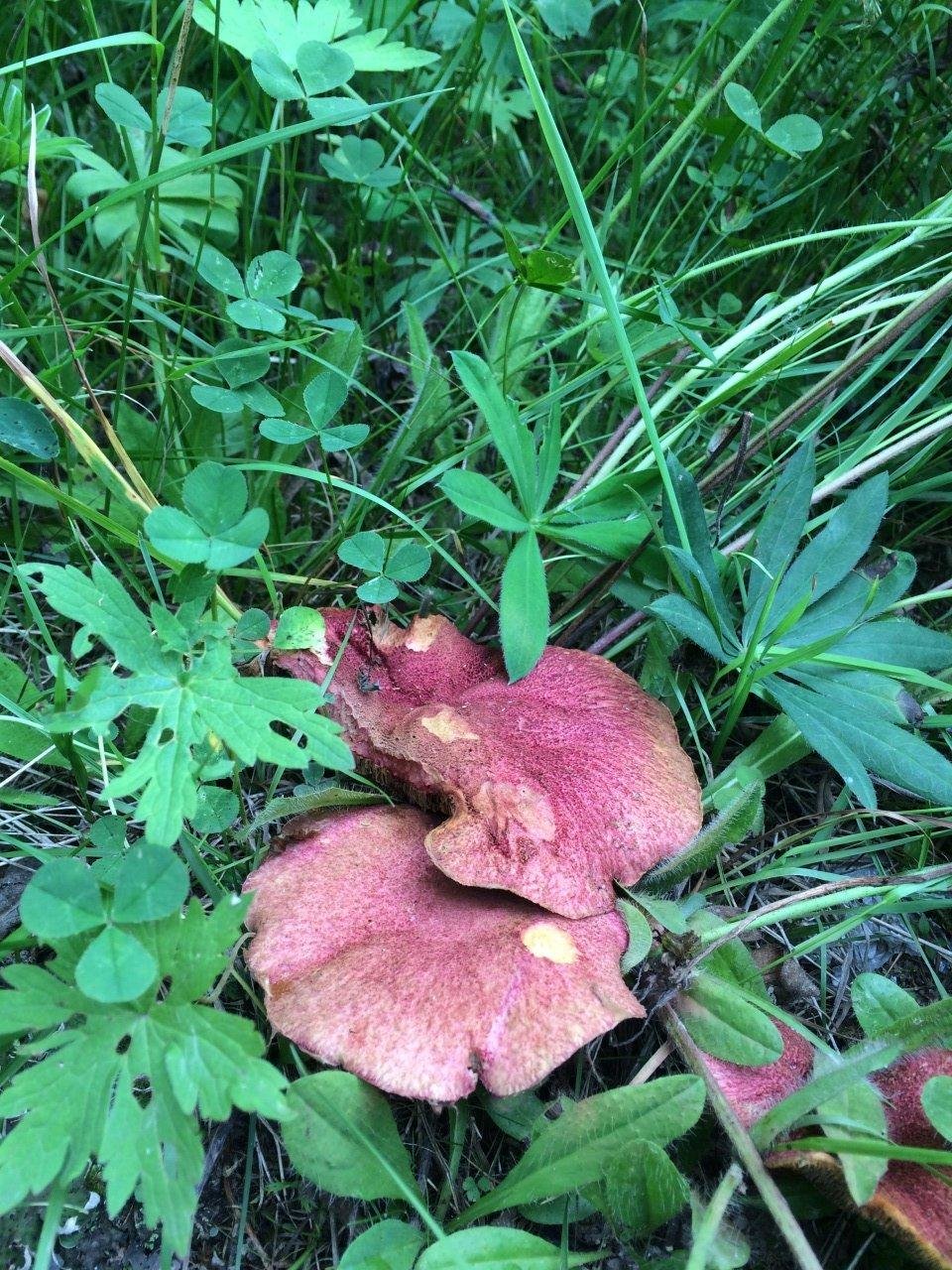
Marsh boletin, or yellow oiler or marsh sieve, is a conditionally edible mushroom. The diameter of its cap is 5-10 centimeters. The cap is convex with a tubercle in the center, fleshy, dry, scaly. The color of the hat in youth is very bright - burgundy red, purple red or cherry red, in older specimens the color becomes paler - red-ocher. Remnants of the bedspread are noticeable along the edges of the cap.

The leg is 4-7 centimeters long and 1-2 centimeters thick. The base of the stem is slightly thickened. The remains of the ring are sometimes visible on the leg. The leg is red under the ring and yellow above the ring.
Marsh boletin is widespread in mixed and deciduous forests. They can grow in wet and dry places. Fruiting time is July - September. Marsh boletins grow in Siberia and the Far East; they can also be found in cultivated plantations of larch in the European part of our country.
These conditionally edible mushrooms can be eaten, but they do not have a high taste. They are very bitter, so they are only suitable for pickling and pickling.

Similar species
Asiatic boletin is very similar to representatives of its own species and some varieties of boletus.
Boletin is marsh. Conditionally edible. It is distinguished by a less pubescent cap, a dirty pinkish veil and a large-pored hymenophore.
The pulp of the fruit bodies is yellow, it can acquire a bluish tint
Boletin half-leg. Conditionally edible. Differs in chestnut color of the cap and brown-brown leg.
The hymenophore of these mushrooms is dirty olive, large pore
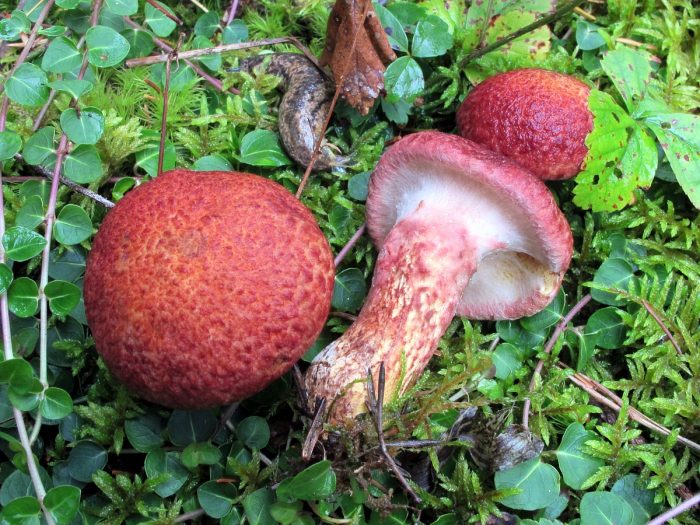
Sprague's Butter Dish. Edible. The hat is deep pink or reddish-brick shade. Loves damp, wetlands.
If the mushroom is broken, the flesh takes on a deep red color.
What does Asian boletin look like?
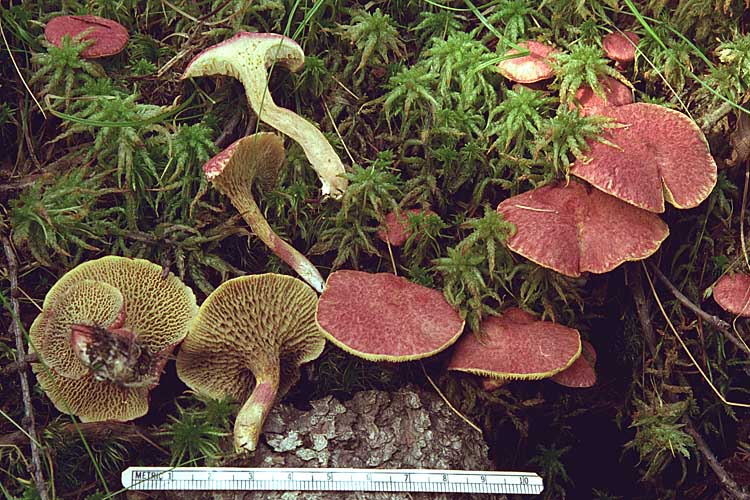
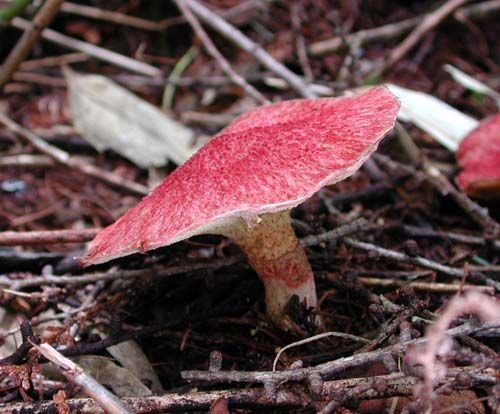
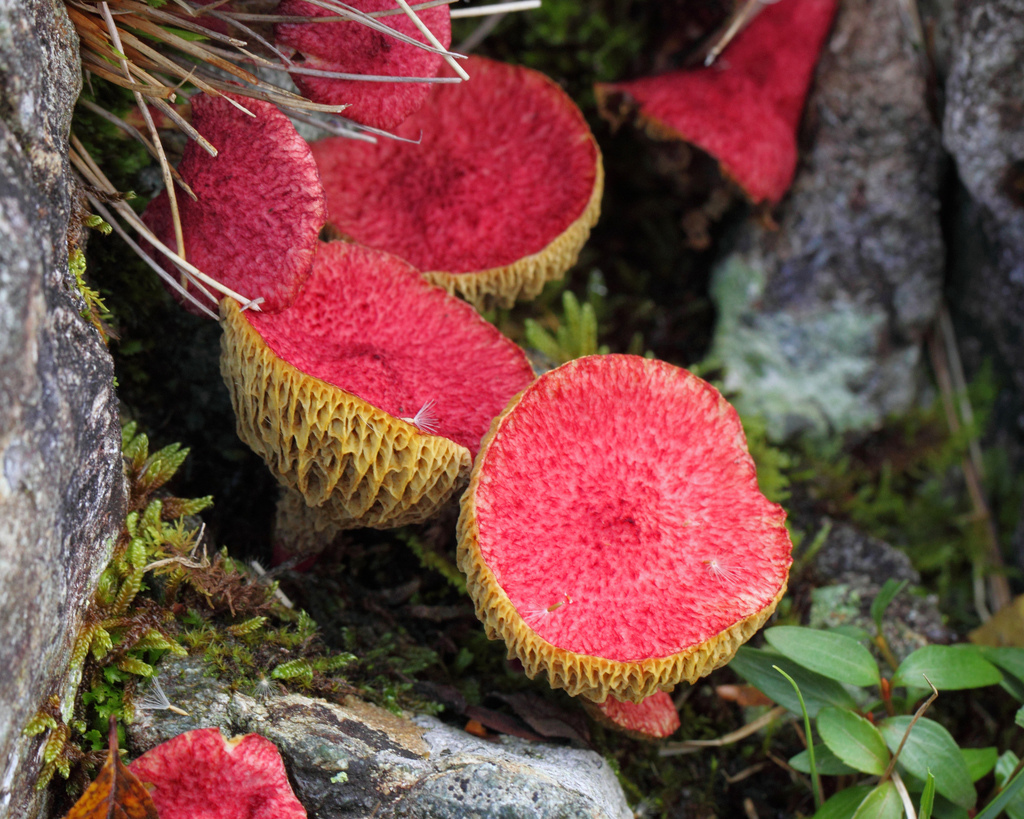
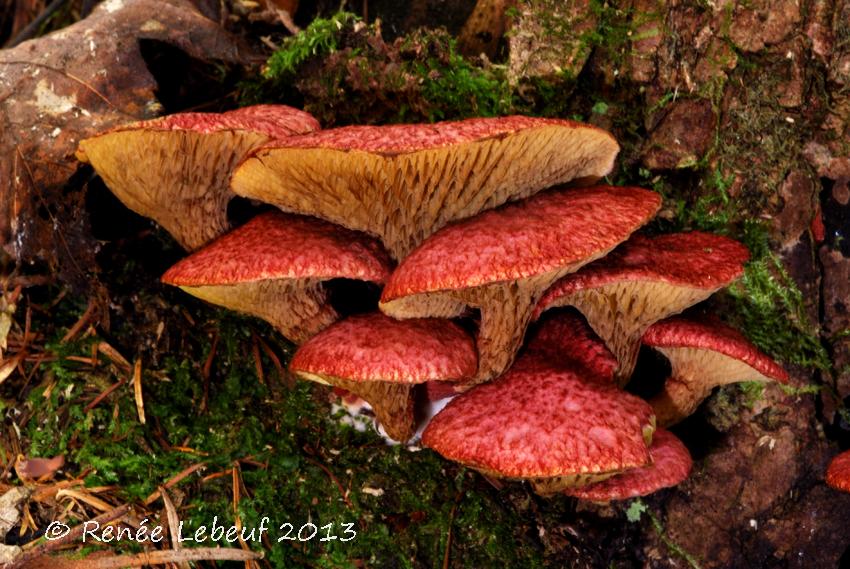
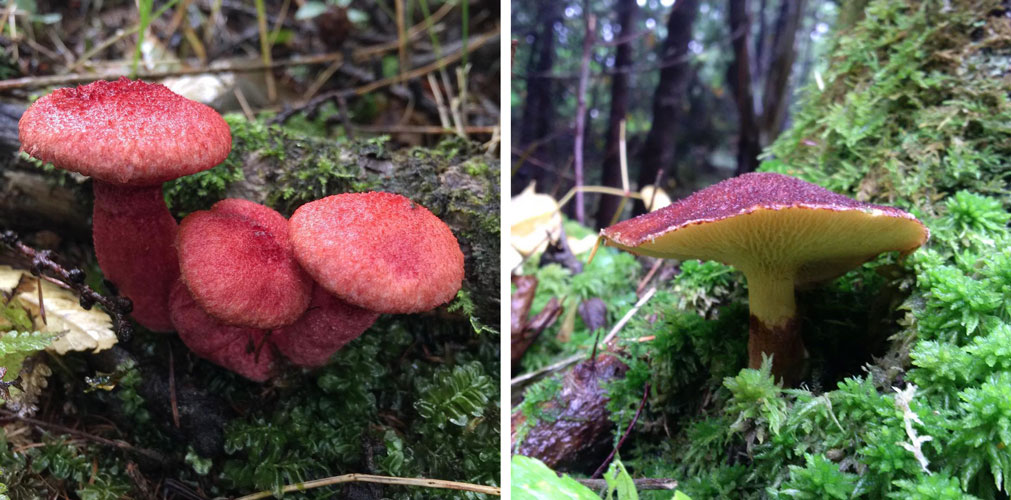
Asiatic boletin adorns the forest with its mere presence. Its caps are deep crimson, pinkish-purple, wine or carmine in color and are covered with soft scaly bristles, which gives them the appearance of elegant shaggy umbrellas. The surface is dry, matte, velvety to the touch. The shape of young mushrooms is rounded-toroidal, flat, with edges tucked inward with a thick roller. The hymenophore is covered with a dense snow-white or pinkish veil, which stretches with age, becomes openwork and remains on the edges of the cap and a ring on the leg.
As it grows, the cap straightens out, becoming umbrella-shaped, and then more and more raising the edges, first to a prostrate shape, and then to a slightly concave, dish-shaped one. The edge may have an ocher-yellowish narrow edging with the remnants of the bedspread. The diameter varies from 2-6 to 8-12.5 cm.
The hymenophore is tubular, accreted and slightly descending along the pedicle, rough. It can be up to 1 cm in thickness. Color from creamy yellow and lemon to beige, olive and cocoa with milk. The pores are medium-sized, oval-elongated, located in distinct radial lines. The pulp is firm, fleshy, whitish-yellow, the color does not change at the break, with a barely noticeable mushroom aroma. Overcooking can have an unpleasant fruity-bitter odor.
The leg is cylindrical, hollow inside, rigid-fibrous, can be curved. The surface is dry, with a distinct ring at the cap and longitudinal fibers. The color is uneven, lighter at the root, similar to the cap. Above the ring, the color of the stem changes to creamy yellow, lemon or light olive. Length from 3 to 9 cm, and the diameter is 0.6-2.4 cm.
There is a noticeable thickening in the lower part of the leg.
Moss is a favorite habitat
Galerina marsh chose fibrous areas where there is a large abundance of moss. It can be seen most often in wetland forest areas - coniferous or mixed - in Europe and North America. He chooses places that are warm, overgrown, but at the same time - with a lot of constant moisture.
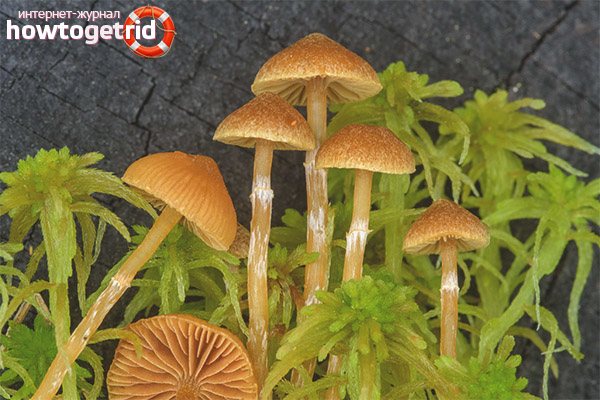

The mushroom also grows on stumps or on a rotten tree, especially conifers. A lot of mushrooms can be found in a place where there is a large accumulation of decaying wood. It does not grow in aggregates very often, mostly mushrooms are located side by side, but singly, the bases of their legs can rarely be found fused.
Fruiting of the mushroom is the period from June to September. Especially in August and September, mushroom pickers should be more careful, as this poisonous mushroom can be found in large quantities. And always remember that it is very poisonous.
Cooking use
Marsh boletin is an edible mushroom, but because of its bitter taste, it is not particularly popular. Some experts classify it as inedible and even poisonous. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully carry out the heat treatment of this mushroom. It is most often used for pickling and pickling. You need to use fresh, whole, ripe mushrooms.
Be sure to check that they are not wormy. Before processing, the mushroom is soaked for about two to three days, periodically changing the water.For brine, for every kilogram of mushrooms, half a glass of water, 2 tablespoons of salt, cloves, bay leaves, pepper, dill are taken. Mushrooms are placed in boiling salty water and cooked with spices, stirring occasionally, for half an hour. When the mushrooms settle to the bottom and the broth becomes almost transparent, you can turn off the heat and put them on a wide dish to cool them down faster.
After cooling down, we shift the grates into jars or barrels and fill with brine, the amount of which should not be more than a fifth of the weight of the mushrooms. You can eat such mushrooms in a month and a half. They need to be stored in a cool room with constant access to fresh air. The mushrooms should be covered with brine at all times. Salted mushrooms are used in various dishes.
Salad with salted mushrooms and chicken
Products:
- 100 g of salted mushrooms,
- 50 g boiled chicken fillet,
- 150 g boiled potatoes
- 1 pickled cucumber
- 1 tomato,
- boiled egg
- half an onion,
- sour cream or mayonnaise,
- salt,
- sugar,
- spices,
- greens.
Preparation:
Cut all products into equal pieces. Season with sour cream or mayonnaise. Add spices. When serving, sprinkle with finely chopped herbs.
Meat with mushrooms under a cheese crust
Products:
- 0.5 kg of pork or beef,
- large onion,
- clove of garlic,
- 250 gram tin of salted mushrooms,
- 150 g of hard cheese
- Bay leaf,
- salt,
- pepper.
Preparation:
Chop the onion and garlic and fry in sunflower oil. Add the meat cut into small pieces and fry until the meat is browned. Then put salted mushrooms, lavrushka, spices, except for salt in a pan. Add some water and simmer covered over low heat. Shortly before the meat is ready, add salt to taste. When the meat is ready, it needs to be put into a special form, sprinkled with grated cheese and baked in a hot oven for several minutes. Serve hot with boiled or fresh vegetables.
Salad "Fake Olivier"
Products:
- salted mushrooms - 400 g,
- 2 pcs. potatoes,
- onions - 2 pcs.,
- 100 g canned peas
- 100 g mayonnaise
- pepper,
- salt.
Preparation:
Boil the potatoes in their skins, then peel and chop finely. Chop the onion and mushrooms finely. Mix all the ingredients by adding the peas. Season with mayonnaise, salt and pepper. Put in a beautiful dish, garnish with sprigs of greenery and peas.
Boletin marsh - description, where it grows, the toxicity of the mushroom
Mushroom boletin marsh is included in the category of conditionally edible representatives of the kingdom of Mushrooms. Included in the ranking of the ten oldest mushrooms in the modern world. This species lives in deciduous or mixed forests. It can grow with both low and high moisture content. It occurs from mid-summer to mid-autumn. The most common in the forests of the Far East, in the east and west of Siberia, as well as in the Asian part of Eurasia and North America.
Basic information
The fungus comes from the department Basidiomycetes, Agaricomycetes class, Boletovye order, Oily family. Other names for marsh boletin: marsh sieve, false oiler, ivanchik. The people also call the mullein, the mushroom of the cows, the goat, the lamb, the flywheel.
The appearance of the mushroom
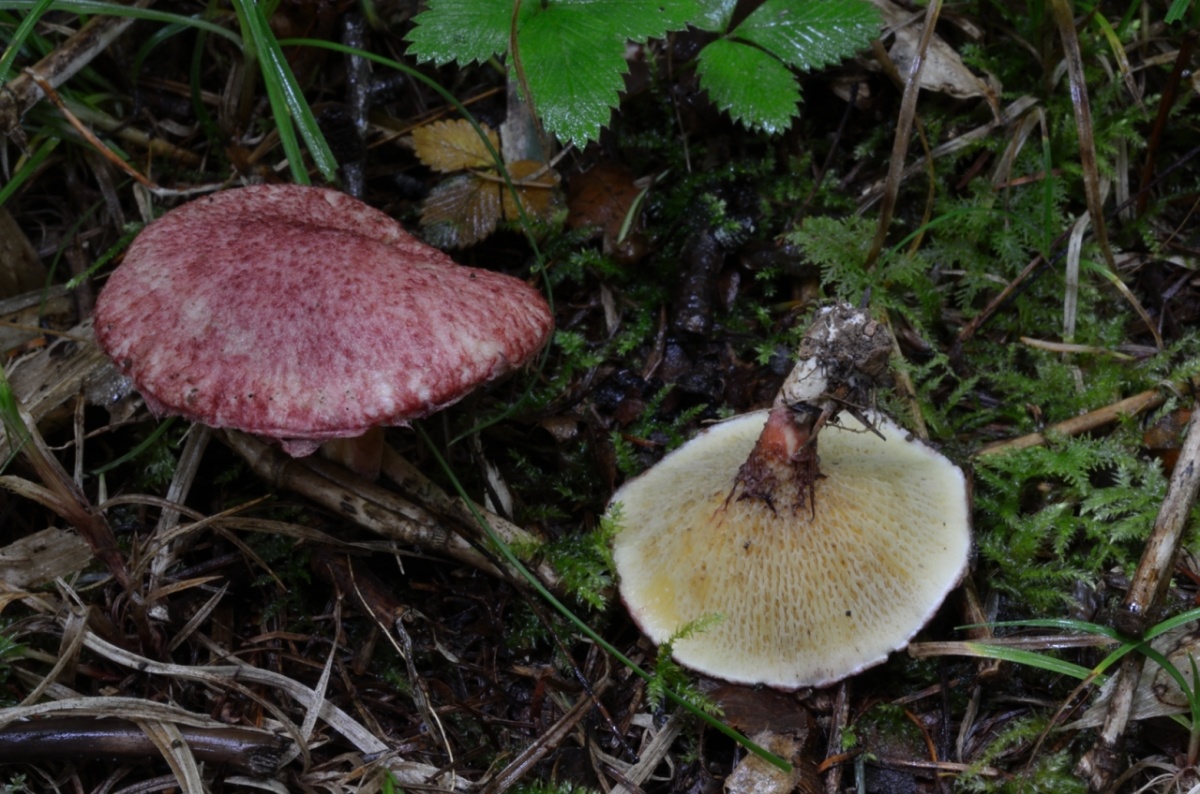
- Hat. The size of the cap in a circle is 5 to 10 centimeters. It has a flat, slightly convex shape, in the center there is a small bump, similar to a pillow. The cap itself is dryish and fleshy. Representatives of the species that have just appeared have a burgundy, ripe cherry or purple color. In the process of growth, the cap is set pale, with a yellow or ocher tint. A tubular layer is present, colored yellowish, later turning brownish. It descends along the leg, and at an early age has a coverlet of a dark pink hue on top. The tubes have radially elongated depressions, their size is up to 4 mm. The color of the spore powder is pale brown.
- Pulp. The pulp of the mushroom is inherent in a yellowish color, sometimes it casts a bluish color.Has a bitter taste. At an early age, boletin does not have a distinct smell; with age, it smells rather unpleasant.
- Leg. The leg of the mushroom can be from 4 to 7 centimeters in height, with a diameter of 1 to 2 centimeters. To the bottom, the leg begins to thicken. The top is yellowish, under the ring with a red color, but not darker than the mushroom cap itself.
Mushroom habitat
Boletin marsh chooses forests with larch and mixed forests for growth. It is found both in areas with low and high humidity. Widely distributed in Siberia, Asia, North America, found in the cultural landscapes of Russia.
Is it possible to eat a mushroom
This type of mushroom is considered conditionally edible. In ancient times, it was eaten in our territories, but today foreign experts consider it unsuitable for food.
The mushroom has a rich, bitter aftertaste, so no one really burns with the desire to eat it. Boletin is used for pickling and pickling, before which it must be well processed.
You can only eat whole, recently collected and mature representatives of the species. Before cooking, they are soaked for three days, periodically the water must be changed to fresh.
To make brine, you need to take half a glass of plain water, 2 tbsp. l. salt, dried carnation flower, dill for one kilogram of mushrooms. Boletins must be put in boiled water, add everything you need, and cook for half an hour, constantly stirring. After dipping the mushrooms on the bottom of the pan, turn off the stove and put the finished mushrooms on a large bowl to cool.
Varieties
Asian boletin
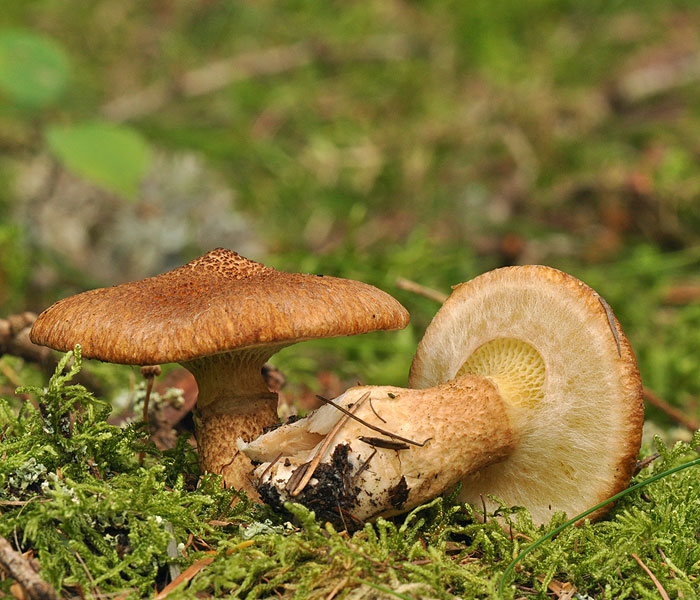
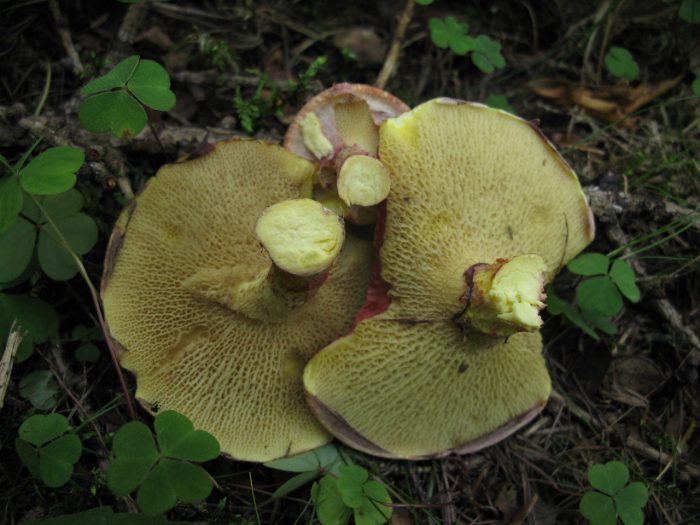
Boletin half-leg It looks like a marsh, sometimes called a half-peg flywheel. The hat is thin, up to 17 centimeters in size. At an early age, bell-shaped, later convex with tubercles. There are remnants of the bedspread on the edges of the cap. The color is brown at first, later becomes rusty or yellowish. The surface is dry, not sticky, there are dark-colored scales, there is a light fluff.
At the bottom, the leg has a root form, towards the center it becomes thicker. It can be watery in the rain. There is a sticky ring on top of it. The layer with the tubes is not long, the tubes themselves go down the stem, after which they join the cap. The shade of the tubules is light yellow later changes to brownish-brown, can give off green. Radical arrangement of tubules. Enlarged pores, pointed edges. A spore layer of olive shade, the spores themselves are in the form of ellipses.
Mushroom pulp is arranged in fibers, elastic to the touch, yellowish tint. The taste is acceptable, the aroma is not pronounced. Grows in forests of cedars and larch trees. The mushroom is harvested from late summer to mid-autumn. Boletin half-leg is conditionally edible. It is eaten fresh or dried.
Characteristics of marsh boletin
Boletin has a tubular structure. Its body consists of a cap and a leg.
Hat
The hat looks like a pillow. It has a flat-convex shape with a tubercle in the middle. Its diameter ranges from 5 to 10 cm. The upper part is dryish, when felt velvety, fleshy. The color depends on age: in young people it is bright red, burgundy or cherry, and in old ones, the cap begins to lose brightness, becomes pale, yellowish.
Tubular hymenophore - the part of the podbot, on which the hymenium is located - the layer where spores are stored. It is located at the bottom of the cap. Diverging in the radial direction, the hymenophore can pass directly into the plates. It has a yellow color that gradually turns brown. The tubular layer sinks noticeably onto the pedicle.
Pulp
The flesh of the podbolnik is painted in a marsh shade, sometimes a barely noticeable blue color is visible. The taste is clearly bitter. The smell of a young boletin is almost imperceptible, but the old one smells rather unpleasant.
Leg
The leg is in the center of the cap, sometimes it can be offset. Its width is about 2 cm, length is 5-7 cm. The leg is velvety in appearance. The upper part is yellow, the base is thickened. On it you can see the remnants of a light red ring.
Varieties
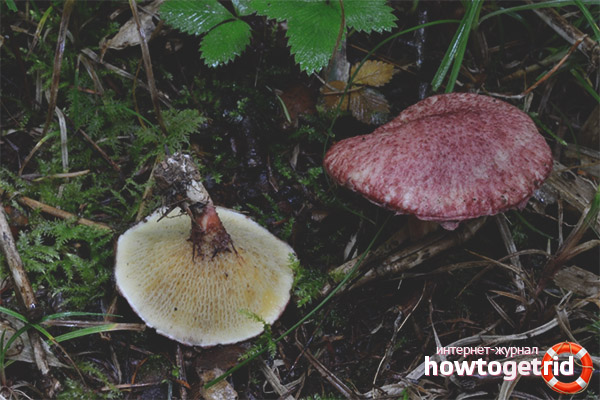 Asian boletin
Asian boletin
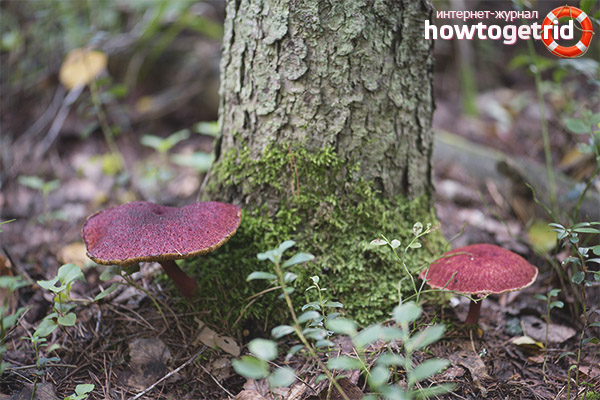
It grows in the west and east of Siberia, in the area of the Amur River, in the south of the Urals. Can be found next to larch trees. The hat can measure up to 12 centimeters. It is usually convex, dryish, covered with scales, purple hue. The pores of the tubular layer are yellow at an early age, then change to a dark green color. The pulp is yellowish, at the transition the shade remains the same. The leg is less than the size of the cap in length. It has the shape of a cylinder, a ring, yellowish on top, purple below. The mushroom is harvested from late summer to early autumn.
Boletin half-leg
It looks like a marsh, sometimes called a half-peg flywheel. The hat is thin, up to 17 centimeters in size. At an early age, bell-shaped, later convex with tubercles. There are remnants of the bedspread on the edges of the cap. The color is brown at first, later becomes rusty or yellowish. The surface is dry, not sticky, there are dark-colored scales, there is a light fluff.
At the bottom, the leg has a root form, towards the center it becomes thicker. It can be watery in the rain. There is a sticky ring on top of it. The layer with the tubes is not long, the tubes themselves go down the stem, after which they join the cap. The shade of the tubules is light yellow later changes to brownish-brown, can give off green. Radical arrangement of tubules. Enlarged pores, pointed edges. A spore layer of olive shade, the spores themselves are in the form of ellipses.
Mushroom pulp is arranged in fibers, elastic to the touch, yellowish tint. The taste is acceptable, the aroma is not pronounced. Grows in forests of cedars and larch trees. The mushroom is harvested from late summer to mid-autumn. Boletin half-leg is conditionally edible. It is eaten fresh or dried.
About the existence of false kids
Sometimes sieve shakers are confused with mushrooms or butter flies.
In general, false goat's rugs do not exist in nature. The kid's inedible counterpart is a pepper mushroom. Its pulp has a peppery flavor, it is neither edible nor poisonous. Dried goat is used as a seasoning for dishes. There are cases when pepper mushrooms were served as a spicy snack for vodka. If you cook it for a long time, it will lose its pepper flavor. Cooked together with other mushrooms, pepper pot will not spoil the dish.
Grilles are distinguished from butter by their skirt, the color of the bog can be yellow, dark and light brown. Young kids have a very neat hat that looks like a pillow. On old horns, it changes shape, cracks. You can distinguish a mushroom from butter and mushrooms by changing the shape as the cap grows.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores.Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
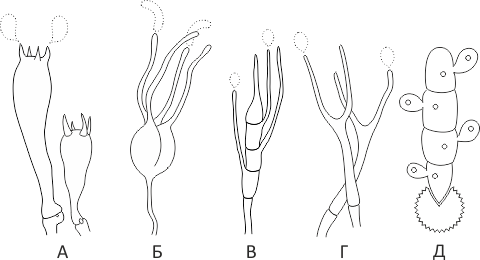
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
Where Asian Boletin grows
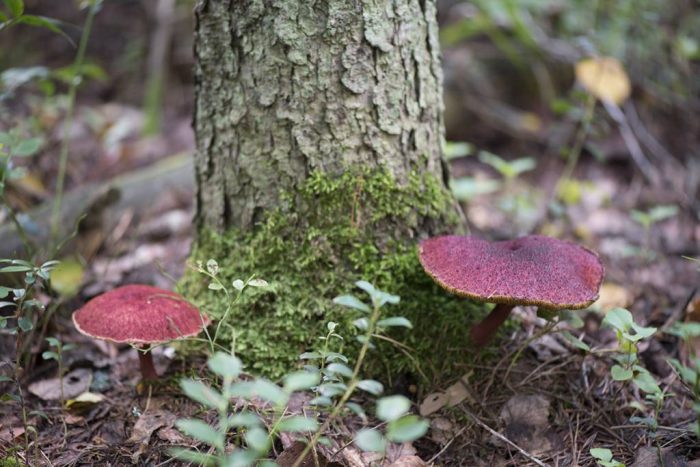
The mushroom is rare and protected by law. The distribution area is Siberia and the Far East. It is found in the Urals, in the Chelyabinsk region it can be seen in the Ilmensky reserve. It also grows in Kazakhstan, in Europe - in Finland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Germany.
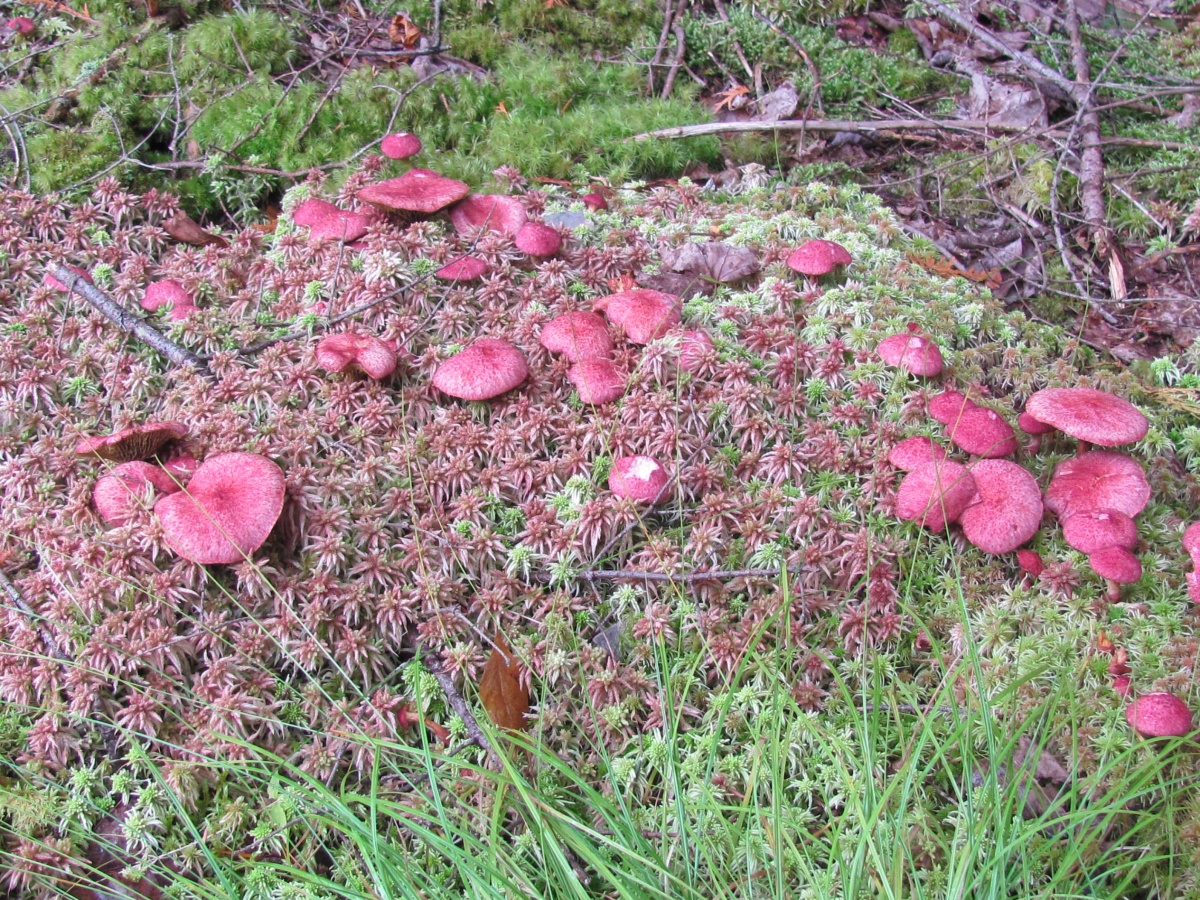
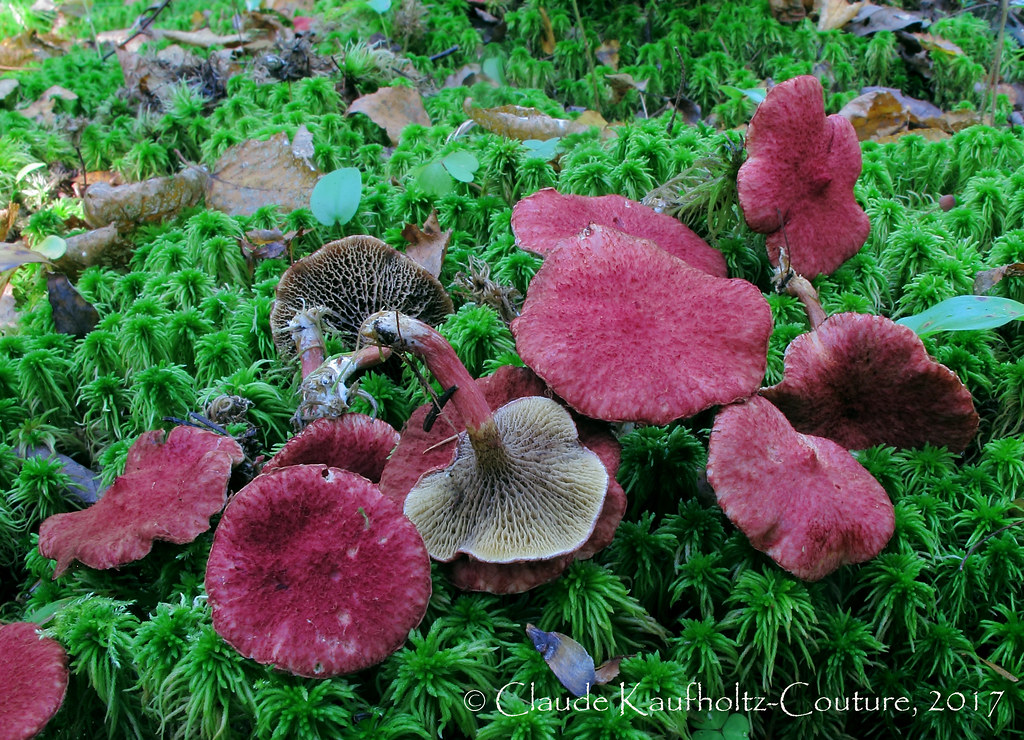
Asiatic boletin forms mycorrhiza with larch, it is found in coniferous forests where it grows. In mountainous areas, it prefers to settle in the lower parts of the slopes. The reason for the disappearance is uncontrolled deforestation. The mycelium bears fruit from mid to late summer to September. It grows on the forest floor, on the rotting remains of trees, in small groups. Sometimes two or more fruiting bodies grow from one root, forming picturesque groups.
Pink furry hats are visible on the forest floor from afar
Characteristics of marsh boletin
Hat
- Advertising -
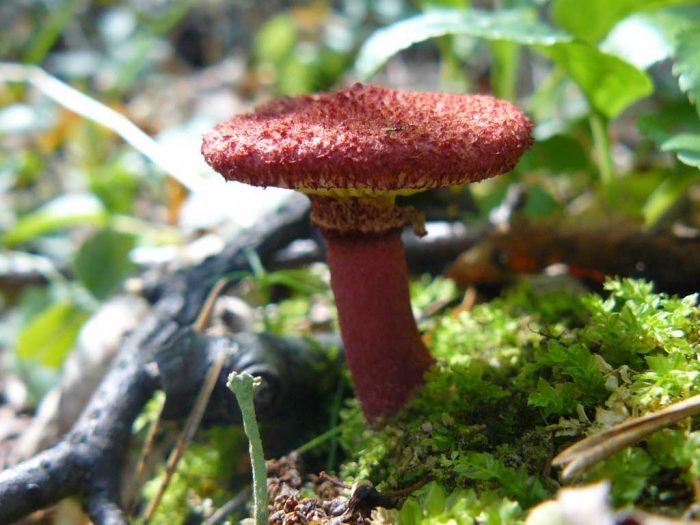

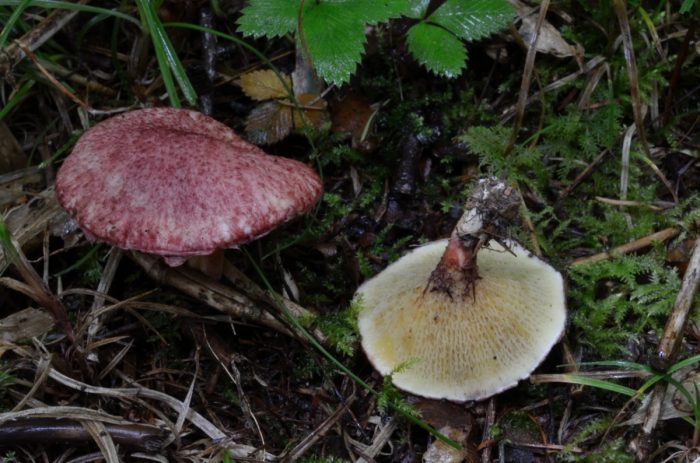
The diameter of the cap of the marsh boletin is 5-10 cm, its shape is flat-convex with a tubercle in the center, reminiscent of a pillow. The structure of the cap is tomentose-scaly, dry, fleshy. The color of young mushrooms is bright: burgundy, cherry or purple-red. With age, the cap turns pale, becomes yellowish or reddish-ocher. Remnants of the bedspread are visible along the edges of the cap.
Tubular layer of yellow color, which gradually turns into yellowish-buffy or brown. It is strongly lowered on a leg, and in young mushrooms it is covered with a filmy blanket of dirty pink color. The holes in the tubes are radially elongated. The pore diameter is about 4 mm. Pale brown spore powder.
Pulp

- Advertising -
The pulp of the boletin is marsh yellow, sometimes with a blue tint. It tastes bitter. The aroma of a young mushroom is inexpressive; in old mushrooms it is a little unpleasant.
Leg

The length of the stem of the mushroom is 4-7 cm, thickness is 1-2 cm. The base of the stem is slightly thickened, the remains of the ring can be visible on it. The top of the leg is yellow, under the ring it is reddish, but lighter than the cap.
Cooking recipes
Delicious dishes can be prepared from young specimens of the bog, but they are not used for pickling, since the pulp is boiled too quickly.
Primary processing
She should be exposed to a fresh product, on the day of collection, at least within a day after going to the forest. Since mushrooms grow in dampness, before cooking, it is necessary to inspect each of them for worminess and spoilage. It is necessary to remove all forest debris, it is not worth soaking the swamp in water, it is already wet enough, just remove the plaque. Better to clean the cap with a soft brush. Cut off the leg at the bottom or remove it altogether, since it is rather stiff.
Cooking

To boil the mushrooms, you only need water (2 l) and salt (1 tbsp. L.). More or less salt solution is used depending on the amount of fruit.
- Bring water and salt to a boil.
- Place mushrooms in a saucepan.
- Continuously skim off the resulting foam.
- Cook for about 30 minutes, but the main sign of readiness will be the settling of the fruit to the bottom of the container.
If the mushrooms were used young, then they will remain dense and will not boil over.
Frying
Before frying white boletus boletus, you need to peel and remove the rotten and wormy fruits, then they are cut into pieces. Usually the hat is divided in half or in 4 parts. To fry 1 kg of mushrooms you will need:
- vegetable oil for frying;
- finely chopped onion - 300 g;
- chopped garlic - 3-4 cloves;
- salt, black pepper to taste.
Heat the oil in a frying pan, then:
- Add the garlic and bring to a golden color, remove with a slotted spoon and discard.
- Pour the boletus and fry until the moisture evaporates.
- Add chopped onion, bring until soft, season with salt and pepper.
You can add other favorite spices if you wish, but mushrooms will be delicious without them, especially if served with boiled potatoes.
Salting

Salting a white birch tree for the winter or just to the table for a holiday is not difficult, for this you need to collect 1 kg of young specimens with dense pulp. And also take:
- salt 40 g;
- allspice 5 peas;
- 4 laurel leaves;
- 2 carnation buds;
- some dill.
Before salting, the peeled mushrooms should be boiled for 15 minutes in salted water and allowed to drain. Then:
- Lay in layers in a prepared pan, preferably enamel.
- Sprinkle each bookmark with salt, spices and seasonings.
- Put a cloth on top and press down with a load.
You will have to wait about a month. Mushrooms are very juicy, and therefore you do not need to add liquid to them, they themselves will emit a lot of juice. The fabric should be rinsed regularly to prevent souring and mildew.
Stewed mushrooms

If you add sour cream to the fried boletus, then such a dish will be called stew. To improve the taste of this dish, some subtleties should be taken into account. To cook 1 kg of bogs, you will need:
- 250 g sour cream;
- 250 g of onions;
- 25 g flour;
- salt, pepper to taste;
- 30 g butter.
Pre-peeled fruits are fried in a dry frying pan and low heat until the moisture has completely evaporated. After that:
- Add oil and onions, it is better to finely chop it.
- In 10 minutes. add flour and continue frying over low heat.
- After 1-2 minutes. add sour cream, salt, pepper. Cook for another 5 minutes.
Now you can serve mushrooms with any side dish, they will be tender and tasty.
Russula
The most common family in the Primorsky Territory. On this territory you can find such subspecies as:
- Swamp russula.
- Brown russula, herring.
- The russula is comb.
- The russula is burning.
- The russula is yellow.
- The russula is green.
- Kele russula.
- Russula kidney.
- The russula is blue-yellow.
- Edible russula.
Some subspecies have a bitter taste, but it disappears with prolonged soaking and heat treatment. An interesting fact is that russules include the whole range of colors of the rainbow.

Marsh russula

Brown russula

Russula comb

Pungent russula

Russula yellow

Russula green

Russula Kele

Russula kidney

Russula blue-yellow

Edible russula