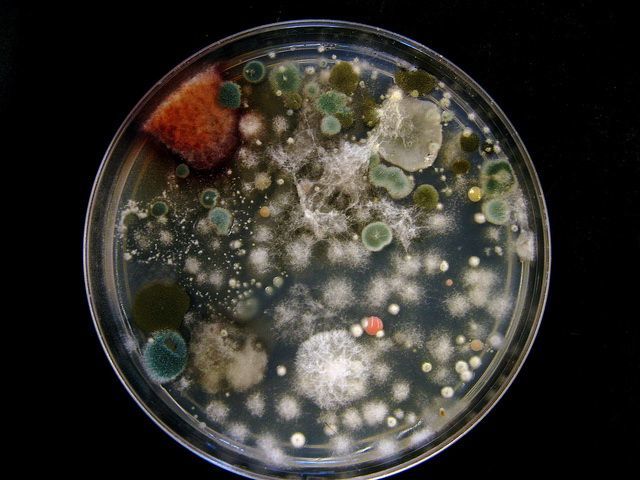
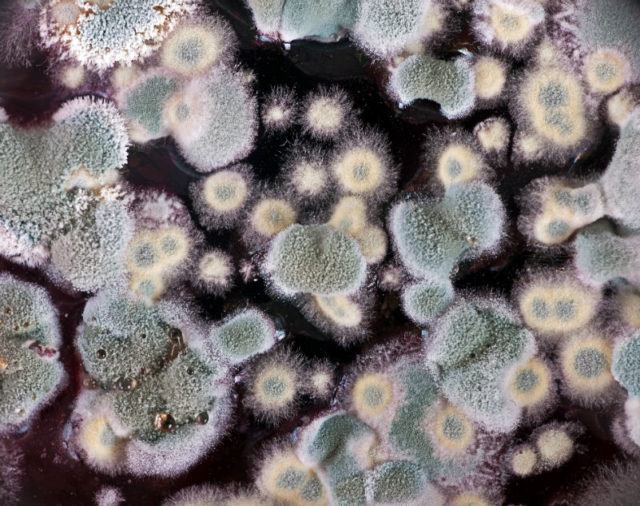
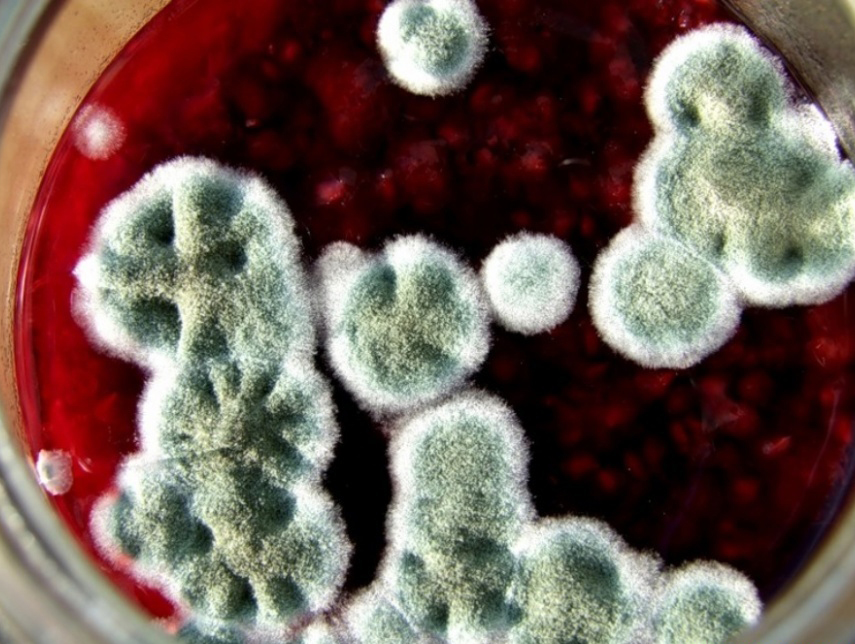
Ways to remove mold from wine
It's important not to skip the early stages of mold formation and take action right away. In this case, homemade wine can be saved.
Preparation and filtration
 The first thing to do is pour the wine into a clean vessel. To do this, a hole must be made very carefully in the film. You can use a sterile dropper tube to transfuse the fluid. In this case, the film should not get into the new container.
The first thing to do is pour the wine into a clean vessel. To do this, a hole must be made very carefully in the film. You can use a sterile dropper tube to transfuse the fluid. In this case, the film should not get into the new container.
The drained wine must be well filtered.
Surgical treatment at the initial stage makes it possible to save the drink without losing its taste and aroma.
Before corking such wine, you can add crushed activated carbon (it is sold in pharmacies) at the rate of a tablespoon per liter of product. Mix. As soon as the coal chips settle to the bottom, strain the wine through a paper filter.
Sulfur treatment
Sulfur is a strong, fast-acting poison for wine blossoms. It must be clean, free from impurities. If fumigation is done correctly, this operation will not significantly affect the taste of the wine.
It is recommended to handle sulfur and containers into which wine is planned to be poured. For fumigation, strips (wicks) are made of white cotton cloth 2–2.5 cm wide and dipped in melted sulfur. The lit wick is lowered into the container. Fumigation with sulfur must be done very carefully.
Pasteurization
If the disease has already led to the clouding of the drink, then after filtration it must be pasteurized. For this, the intoxicated drink is kept at a temperature of 60–65 ° C for 20 minutes.
Pour the filtered drink over the shoulders into clean, sterilized, gray-fired bottles (the liquid should not flow out when heated).
For home pasteurization, you can use a large saucepan. Put bottles of wine in it (on a towel or wooden lattice), fill with water. Its level should overlap the level of wine in bottles.
Heat water to the required temperature and maintain it for the specified time. To control the temperature, you can put a bottle with ordinary water and a water thermometer in the container.
After pasteurization, the bottles are topped up to the top and closed tightly with sterile stoppers. There should be as little air as possible between the cork and the wine.
Also, pasteurized wine is recommended to be blended. For the blended mixture, wines of similar quality are selected.
The pasteurized drink can be left until next summer to use the grapes of the new crop to improve its quality. White wines are corrected in the process of secondary fermentation with the addition of freshly squeezed juice, while red wines insist on fermented pulp.
If after the treatment the taste of the wine has changed slightly, then after pasteurization it can be fixed with high-quality vodka, brandy or pure alcohol. Fortified homemade wine (from 17%) does not grow moldy.
Mold in wine during fermentation - what to do
You can remove mold by heat treating the drink. The properties of Botrytis mold affect the taste and texture of the fruit infested with it. If you want to make sweet wines, a drying room is used, where moisture is evaporated from the grapes, leaving the acidic concentrate and sugar. The noble fungus, feeding on these residues, transforms and reveals new flavors for lovers of exotic.
True, the appearance of a harmful fungus can spoil the production procedure. As much as one would like, but there is no insurance against mold on the wort. When a white coating appears on the wine, you need to act. After all, the appearance of mold on the surface indicates a violation of the production of homemade wine and its infection with microorganisms that can destroy the creation.What is the danger of this fungus?
Multiplying in the wort, it converts it into water and carbon dioxide. You should not be upset, because with the correct and quick response to the problem, the drink can be saved.
First you need to establish the degree of damage to the wort: What is the reason for the appearance of mold, it is necessary to find out and protect yourself from repetitions, in order to preserve the product of your labors.
Users browsing this forum: Google and 0 guests. My profile.
Recommended reading - Is it true that mold is dangerous and leads to cancer? When bloom mold appeared on the wine, it is necessary to urgently start rescue work.
Causes and signs of moldy mash
After all, mold in homemade wine begins to eat up acid and sugar, converting the wort into water and carbon dioxide, as mentioned above, which spoils the drink created by yourself. The appearance of mold during fermentation in wine occurs in such cases: These two possible reasons are the main factors for the appearance of fungal microorganisms in alcoholic beverages.
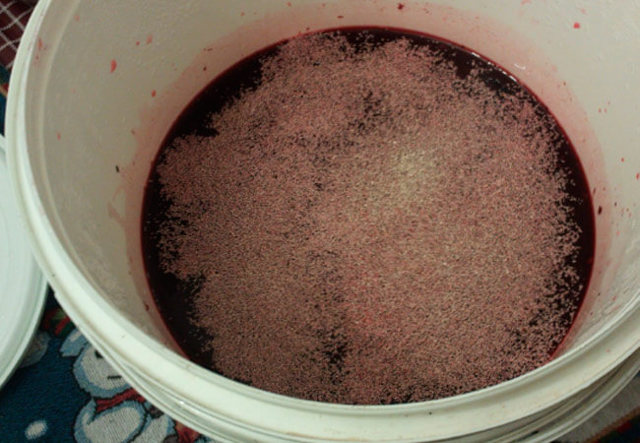

For the process of making wine and eliminating mold, there are rules that require them to be followed: Even when the wine has become moldy, don't panic. At the initial stage of its development, it is necessary to find out why homemade wine deteriorates and molds, to eliminate the cause and consequences of the disease.
The main symptoms that serve as a signal of wine disease: Therefore, in order to preserve the quality of the product, you need to know what to do if mold appears on homemade wine and how to save the drink.

We recommend that you read - Forewarned is forearmed! What is the most dangerous mold?

If the wine has started to grow moldy, it means that the technology of preparation and storage of wine must has been violated. In order to understand how to save wine from mold, it is necessary to identify the cause of its appearance.
How to get rid of mold
First of all, inspect the wine product and find out possible foci of fungal disease and the putrefactive state of the sediment. You can remove mold from homemade wine by following the recommendations: In the presence of fungal flora in the wort, a slight moldy smell appears. To remove mold odor from homemade wine, two options are used: It must be remembered that a high-quality product can only be obtained if the manufacturing technology is followed, hygiene standards are observed and the contributing items are sterilized.
In this case, you are not threatened with the disease of wine. Skip to content FUNGUS ON THE BODY Symptoms and treatment of ear fungus in humans The main forms of aspergillosis in adults and children and methods of treatment Methods for diagnosing and treating fungus in the intestine How to remove fungus from the body with folk remedies Essential oils from fungus on the feet selection, recommendations for use Why common nail extension can lead Iodine from fungus: the best remedy at the initial stage of the disease There is no better remedy for nail fungus than soda!
The Soviet way of getting rid of nail fungus with the help of tar There is in every home and it costs a penny! Main varieties Is the laser effective against fungus? Common cold or fungus in the nose: how to recognize? Allergic and unable to cure the fungus? What health problems does nail fungus indicate? These pills will cure the fungus! The juice is rather pink. I decided to do it through fermented pulp, kneaded it directly with cuttings, did not wash it, I decided on wild yeast, put it in a plastic bucket, covered with a cloth on top as advised in some kind of Internet recipes and in a stainless steel pressure cooker.
As ill luck would have it, the batteries were turned off at that time, the temperature in the apartment was about 20 C. It didn’t ferment, I was warming up by the oil heater. Today is the third day, fermented, but looking inside, with horror I saw islands of green mold on the surface of the mass. Both in the bucket and in the pressure cooker. He took it off, but of course everything was gone, right?
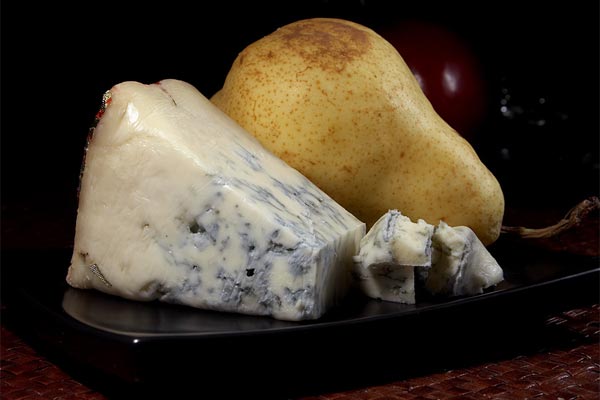
Blue mold
This type of mold, in contrast to the noble rot, has been known since time immemorial.With its help, marble cheeses are obtained or,
as they are now called blue. First of all, these are French Roquefort, Gorgonzola cheese from Northern Italy and Stilton from England. All these cheeses are characterized by a loose structure, a specific appearance (streaks and spots of bluish-green color) and a characteristic taste and aroma.
It is believed that blue cheese, like champagne and many other interesting and extravagant products, was "invented" by a fluke by the French. There are several legends. Once, in ancient times, near the town of Roquefort-sur-Soulzon in France, a shepherd accidentally left cheese and bread in a cave. When he returned two weeks later, the food looked unsightly, but one of them tasted quite good. Don't ask the French why the shepherd tasted it? Literary sources dating back to the 1st century, long before the French “invention” of blue cheese, mention blue cheese made and highly valued in Rome.
I do not think that the technology for the production of blue cheeses has fundamentally changed since that time. Until now, loaves of rye bread are completely destroyed by the fungus Penicillium roqueforti. The mold is then dried and powdered. It is added to the cheese only during the molding process. Subsequently, the cheese is aged in caves at low temperatures and high humidity, which contributes to the development of mold in the cheese dough. When Penicillium grows, it forms blue grooves or veins and gives the cheese a pungent flavor and distinctive aroma.
There is a huge variety of blue cheeses: rough, salty, spicy and fatty. Some may be of sheep
milk, others from cow or goat. They are made from raw or pasteurized milk. There is a whole army of large and small producers of these cheeses. Finally, blue cheese can be from France, Spain, Italy, England, Denmark, and the United States.
Blue cheeses made from sheep's milk, such as Roquefort, tend to be spicy, while those made from cow's milk tend to be sweet. But there are exceptions, such as Gorgonzola, the famous Italian blue cheese made from cow's milk, or the very specific Tanguy cheese made from goat's. Blue cheeses made from raw, unpasteurized milk tend to have a creamier, more oily and fresher meadow flavor.
The most famous Roquefort Pastourelle, Societe, La Papillion, Gabriel Coulet and Constans-Crouzatare are strong and impressive cheeses. Before buying Roquefort, be sure to make sure that it has a red sheep's mark, indicating its authenticity.
French blue cheeses made from cow's milk are no less tasty and famous: Bleu D'Auvergne, Fourme d'Ambert, Bleu de Bresse.
Like Roquefort, the name of Stilton, an English blue cheese made from cow's milk, is protected by Mr.
condemnation, although there are no small producers of this cheese in England now. The most exquisite of these, Colston Basset, with a rough taste and full aroma, is the most preferred by connoisseurs. Other celebrities include: Long Clawson Dairy, Cropwell Bishop, J.M. Nuttall, Millway Foods Ltd. and Tuxford & Tebbutt.
A quality Stilton should have a dry, rough, cream colored ring with numerous blue veins. It should be crumbly but moist enough to hold its shape.
Another cheese like Stilton Gorgonzola comes in two flavors: natural or mountainous and sweet. Mountain cheese has a very strong aroma and a pungent, deep taste. He's less well known than his mild, sweet version. In terms of taste, Gorgonzola is richer than Stilton.
Roquefort is the most expensive blue cheese on the world market. Blue cheese is the perfect accompaniment to fruit. You can recommend red wines or sweet Sutterns, Tokay, port.
Noble wine mold - Botrytis cinerea
 The wines that inspire confidence, honey or shiny gold color, aromatic without satiety, vibrating and penetrating - these are the wines that are obtained from grapes affected by the noble mold. To distinguish this condition of grape bunches from harmful rotting, the ash-colored mold Botrytis cinerea is called "noble mold" or "noble rot".When it strikes healthy, fully ripe white grapes, it drains the flesh under the intact skin to a concentrated essence. If mold infects unripe berries damaged by insects or heavy rain, destroys the skin and allows harmful bacteria to enter the pulp, it is called gray mold, and it can pose a great danger to the crop. It also disrupts the pigmentation of bright red berries, imparting a dull grayish color to the wine.
The wines that inspire confidence, honey or shiny gold color, aromatic without satiety, vibrating and penetrating - these are the wines that are obtained from grapes affected by the noble mold. To distinguish this condition of grape bunches from harmful rotting, the ash-colored mold Botrytis cinerea is called "noble mold" or "noble rot".When it strikes healthy, fully ripe white grapes, it drains the flesh under the intact skin to a concentrated essence. If mold infects unripe berries damaged by insects or heavy rain, destroys the skin and allows harmful bacteria to enter the pulp, it is called gray mold, and it can pose a great danger to the crop. It also disrupts the pigmentation of bright red berries, imparting a dull grayish color to the wine.
The wines produced with Botrytis include French Sauternes, Hungarian Tokay and the famous German sweet wines. They cannot be obtained every year, since the growth of noble mold directly depends on the combination of heat and humidity in nature after the grapes have ripened. In a good year, early ripening grapes with thick skins may allow Botrytis to get the job done before bad weather sets in; at the same time, the skin will remain intact under the destructive influence of mold, and it will also protect the pulp of the berries from contact with air.
Noble mold invades vineyards from time to time, and even on individual clusters, its effect will be gradual. The same bunch may contain shriveled, moldy berries, while other berries may still be swollen with brown skin, softened by the initial attack of mold, and some berries may be firm, ripe and not in the least affected by green fungus.
In order for the noble mold to have its effect on the character of the wine, individual berries should be plucked from the bunch as soon as they are sufficiently wrinkled, but not yet completely dry. It is necessary to pick berries from the same vine several times - often five, six, seven times or more over a period that in some years stretches for months. Moreover, each time the harvested grapes are subjected to a separate fermentation.
Two special properties of noble mold affect the structure and taste of the wine and create a difference between wines with Botrytis and sweet wines obtained from grapes that are dried in conventional drying ovens. In this case, the concentration of acid and sugar occurs due to the loss of moisture, without changing the composition of the grape berries, while Botrytis, which feeds on acid with sugar, makes chemical changes in the grapes, creating new elements that change the bouquet of the wine. Since mold consumes more acid than sugar, the acidity of the wort decreases. In addition, Botrytis mold produces a special substance that prevents alcoholic fermentation. In the wort obtained from partially dried berries, whose chemical composition has remained unchanged, alcohol-resistant yeast bacteria are able to ferment sugar into alcohol up to 18 ° -20 °. But the high concentration of sugar in grapes with noble mold means a correspondingly high concentration of mold, which quickly inhibits fermentation. For example, in Sauternes wines, perfect balance is achieved due to sugar, which is able to turn into 20 ° alcohol. But thanks to the influence of mold, fermentation will stop earlier, and the wine will contain from 13.5 ° to 14 ° alcohol. If the harvested grapes contain even more sugar, fermentation will stop even faster, and the wine will be sweeter, with a low alcohol content. If grapes are harvested when they have an alcoholic potential of much less than 20 °, the balance of the wine will be disturbed due to the excessive alcohol content and the lack of sweetness.
Wine production processes are very different from each other. For example, the sweet Hungarian Tokaj wines are not pure wines with noble mold. They are obtained by adding a certain amount of noble mold grapes to must obtained from other white grapes.In Sauternes wines, the only difference in their production is that before fermentation begins, there is no way to separate the solid particles from the dense, thick must, so the juice is poured directly into the barrels. Its fermentation proceeds very slowly, as well as purification: the wine of Chateau Ikem takes three and a half years for the wine to be purified before being poured into bottles. And after that, it often absolutely calmly lives up to its centenary.
Prevention of the appearance of fungi in wine

To minimize the likelihood of mold in wine, you must:
- Observe the technology of making wine and use only clean (well washed, dried in the sun or sterilized) devices and containers.
- Carefully sort the raw materials for wine so that rotten and moldy berries do not get into the wort.
- Stir the pulp daily during the primary fermentation so that the top of the pulp cap does not become moldy from contact with air.
- Do not dilute wine too much with water, as the low acidity and low alcohol content of the wort leads to the multiplication of pathogenic microflora.
- Observe the temperature regime of the violent fermentation phase, it should be constant and not exceed 22 degrees (optimally 18-20 degrees Celsius).
- During quiet fermentation, the optimum room temperature with wine is around 16 degrees.
- The best temperature for settling and storing wine is 10-12 degrees.
- The humidity of the room where wine is made and stored should also be low, since high temperature and humidity are the best conditions for the development of fungi.
 Winemakers regularly check the wine that is in storage. During the next inspection, you may find that the house wine has become moldy. This means that it is ill and requires urgent treatment.
Winemakers regularly check the wine that is in storage. During the next inspection, you may find that the house wine has become moldy. This means that it is ill and requires urgent treatment.
What to do if the wine is moldy? He needs to be treated urgently!
Mold (wine blossom) is a fairly common wine disease. It is caused by a huge accumulation of special microscopic filmy fungi - Mycoderma vini.
These microorganisms convert the nutrients that make up wines into carbon dioxide, water, and other components. This process significantly degrades the quality of the wine and can lead to spoilage.
The appearance of mold, as a rule, is the result of a violation of the technology for making a drink, neglect of temperature standards. For active growth of mushroom mycelium, oxygen is needed.
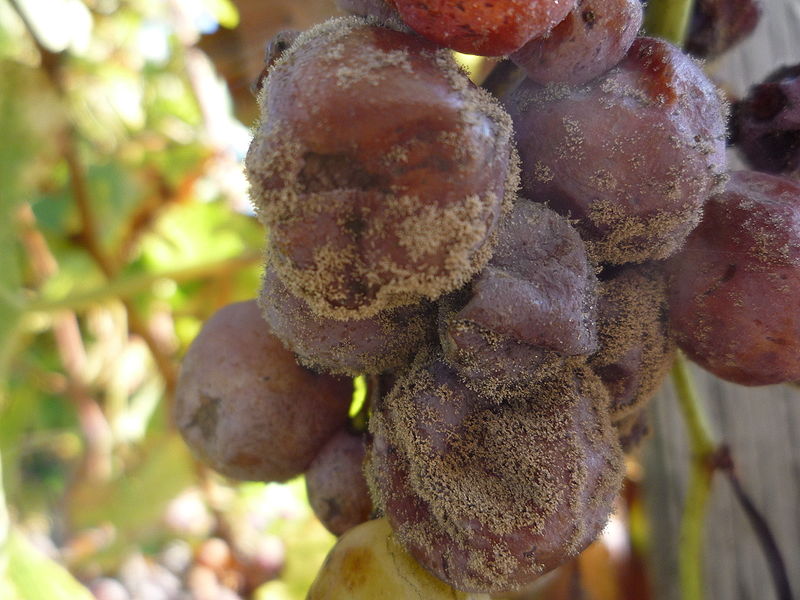
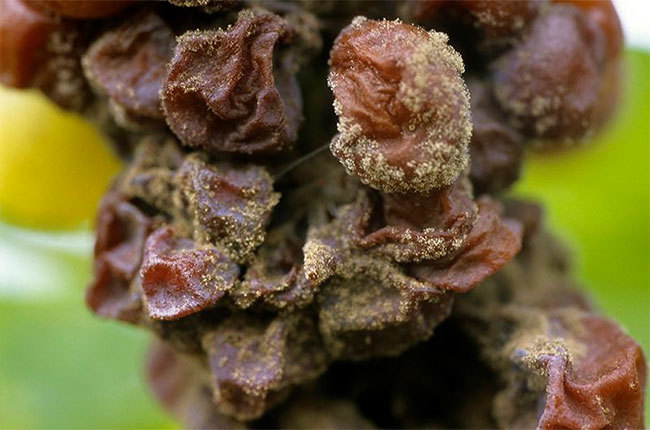
Noble mold on grapes
The berries, which are used to make a certain type of wine, mostly noble ones, are harvested a little later than the rest. If the fruits remain on the vine longer than the prescribed period, then the content of juice in them decreases, due to which the amount of sugar and acid is concentrated. With high humidity, mold (the fungus Bortrytis cinerea) can appear on such berries, which does not spoil the pulp of the berries and their skin, but only deprives them of moisture, which is a huge plus for the production of some varieties of wines. Such mold, unfortunately, appears very rarely - only during warm autumn, when there are wet fogs in the morning, and dry and sunny days allow the fruits to dry out from moisture, and it does not always affect grape berries. Wines made from such grapes have a bright, unique, refined taste and aroma. They are often referred to as "angel sweat" and the cost of such drinks is very high.

Sometimes, noble mold affects only individual fruits, in which case, the collection of these berries becomes a whole problem for winegrowers, since on one cluster there can be ripe and unripe berries at the same time, so the collection of fruits with such mold can take a long time.
The grape culture is mainly cultivated in warm and humid climates, and if there is not enough heat during the day with high humidity, then the development of the Bortrytis cinerea fungus occurs too soon, especially with heavy rainfall, which causes the death of the crop (the fruits rot right at the root). In this situation, the noble mold can develop into gray rot, with the development of which, the berries crack.

The problem that many winemakers have faced is mold appearing from nowhere, on the surface of the wine.Is it worth worrying about her appearance in wine and what to do if she appears? You will find answers to these and other related questions later in our article.
Wine resuscitation options
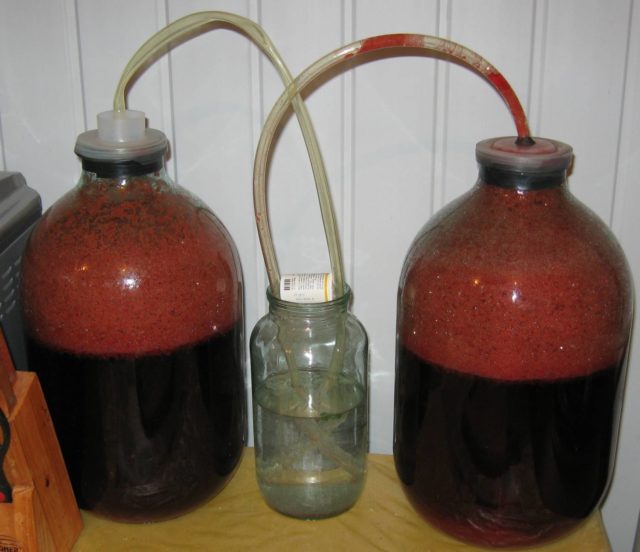

Treatment of wine from mold depends on the degree (stage) of its damage. In any case, the following methods of wine resuscitation can be used both independently and in combination with each other.
- Pouring is a method used in the first stage, when “greasy spots” have formed on the surface of the wine, that is, a thin film of fungi. For the transfusion method, you need to take a clean, sterilized container and a flexible hose. Gently destroying a section of the film with a stick, insert the hose into the liquid, without bringing it to the bottom of the container, and drain only healthy wine, and leave the sediment and the film from the fungi.
- Filtration - for this method of removing mold, both ordinary gauze and cotton wool are used, as well as in combination with activated carbon and white clay.
- Sterile medical gauze should be folded into 6 layers and the wine should be filtered through it, having previously removed the upper affected layer from it. It is advisable to filter only the middle portion of the wine liquid, therefore, the most effective filtration is carried out after pouring.
- The gauze-cotton filter is made in the following way: Medical sterile gauze is folded in two layers and cotton wool is put in the third layer. Two more layers of gauze are laid on top of the cotton wool. The filter is ready.
- In case of mold damage to wine with the appearance of a specific smell in it, filtration with activated carbon or white clay (bentonite) can help. For this manipulation, after pouring, add 1 tablespoon of activated (char) charcoal or bentonite to the wine for each liter of liquid. After mixing the mixture well, allow it to settle and then filter through a gauze-cotton filter. This method is also used to clarify wine and precipitate wine sediment.
Sulfur treatment (sulfitation). Many people know that sulfur dioxide is used in modern winemaking practically at all stages. Sulfur is the best preservative for wine. That is why disinfection of wine material and fumigation of the container with sulfuric anhydride is considered the most effective method of treating wine at the second stage of the disease. In addition to fumigation with sulfur wicks, the sulfitation of wines is carried out by adding sulfur to the wine material in the form of a powder or an aqueous solution. The sulfitation method is also effective in clouding wine.
Pasteurization is a method of treating wine material from fungi by heating the poured and filtered wine material. Wine bottles can be previously fumigated with sulfur sticks - the effect will be the best. Bottles of wine are lowered into cold water and heated to a temperature of 70-75 degrees C (no more). Thus, the bottles are heated for 1-2 minutes in a water bath. Then let the water cool completely (it takes 5-6 hours) and again the bottles with wine are heated in a water bath to 70-75 degrees Celsius. This method involves heating the wine material at least twice, but it is better to repeat the heating 3-5 times. This method will also clear cloudy wine, as when the wine is heated, flakes of sediment fall out and the wine is clarified.
Peculiarities
There is no single recipe for freezing zucchini. But on the other hand, there are some rules that should be followed so that the product does not lose a lot of vitamins as a result of such heat treatment and long-term storage. These rules relate to the selection of zucchini and preparation for storage.
In addition, it is important to choose the right container.
Any vegetables can be used for freezing, regardless of size and age. But it is still recommended to give preference to those fruits that are younger. Their seeds are small in size, and may even be absent altogether.
When choosing zucchini for freezing, it must be remembered that young fruits have a lot of water, and old ones have thick skin and large seeds.If it is decided to harvest overripe zucchini, then you will first have to remove the seeds and remove the skin.
Each copy must be carefully examined. If any damage or traces of rot are found on the surface, then such a product must be set aside. It is not suitable for freezing.
What to do if the wine gets moldy during fermentation
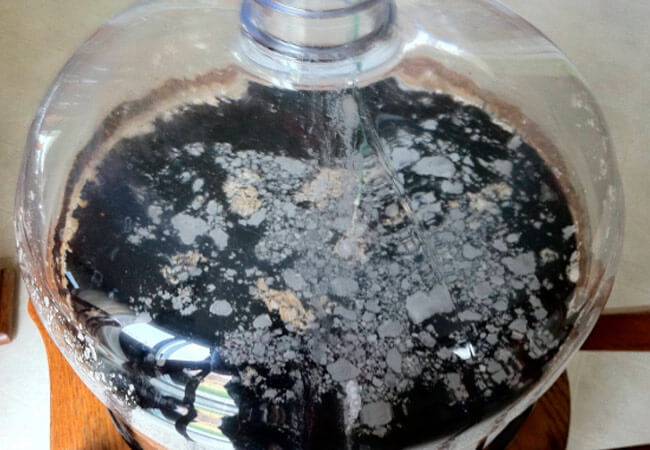
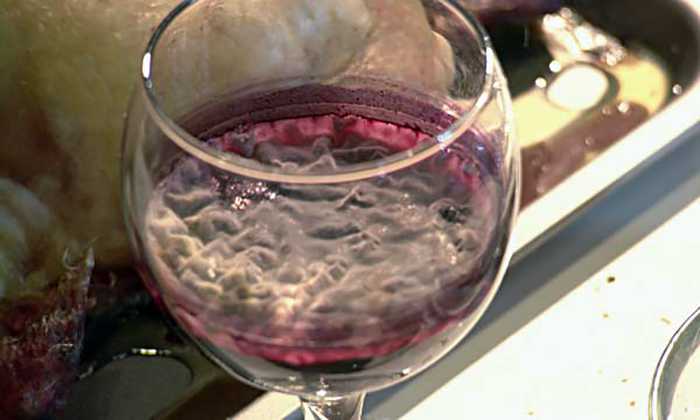
So, you have noticed a whitish film on the surface of your wine. What to do?
The first step is to get rid of the bulk of the mold. This can be done gently with a clean spoon or slotted spoon, or you can use a rubber hose.
Having created a vacuum inside it, carefully collect the colonies of fungi from the surface of the wort, at the same time capturing part of the liquid.
Next, we need to re-release our wort. This should be done at a temperature not higher than 75 degrees Celsius.
In no case should you boil the liquid, since this will adversely affect the taste of the drink. After keeping the future wine on fire for a couple of minutes, remove it and let it cool to room temperature.
Finally, we activate the fermentation process again - we add a small amount of sugar and wine yeast or the main raw material to the wort. We carry out anew the process of infusion of wine, and then follow the previous instructions indicated in the recipe.
To be completely sure that all pathogenic fungi are destroyed and do not pose a danger, you can also fix the drink with alcohol or vodka. This is done after the fermentation of young wine is complete.
Mold in wine during fermentation, what to do
Mold damage
Mold on the surface of the liquid
Moldy spoiled cheese
Danger to humans
Mycotoxins and antibiotics
Many molds produce secondary metabolites - antibiotics and mycotoxins, depressing or toxic to other living organisms. The following substances are best known:
- Mycotoxins:
- Aflatoxin,
- T-2;
- Antibiotics:
- Penicillin,
- Cephalosporins,
- Cyclosporine.
Many antibiotics are forcedly used in concentrations close to toxic. So, antibiotics gentamicin, streptomycin, dihydrostreptomycin, kanamycin and others can have nephro- and ototoxic effects.
Pathogens
Some molds can cause diseases of animals and humans - aspergillosis, onychomycosis and others.
Molds and agriculture
Some molds can have adverse health effects on livestock.
Mushrooms infect grain supplies, forage, straw and hay. Sometimes products become unusable due to the toxicity of the fungus metabolites.
Some molds are pests and pathogens
Fusarium
Danger to building and finishing materials
The development of mold fungi on the surface of building and finishing materials leads to the physical destruction of the latter. Mold has a particularly harmful effect on wooden structures. It is a wood defect from the group of fungal infections. Mold is one of the main participants in the processes of biocorrosion and biodegradation of materials.
Infection of documents with molds in archives and storages is the main cause of damage to documents and a threat to their safety. Mold develops most actively in conditions of high humidity, little or no ventilation or ventilation. When germinated in paper, it leads to the decomposition of cellulose and glue in the spines of books.
The causes of mold in wine
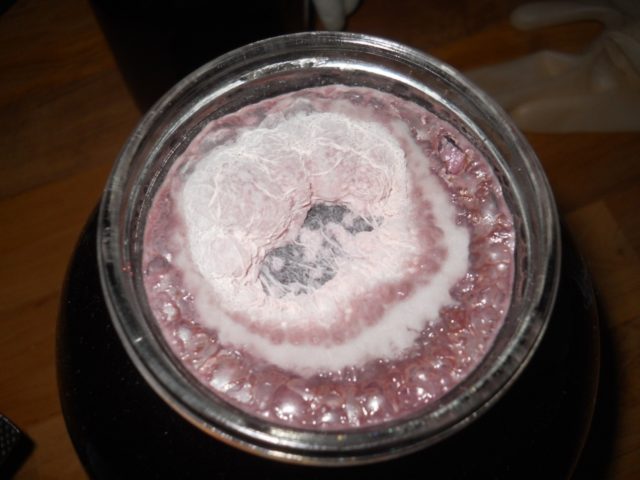

Let's list the most common causes of mold in wines:
- Dirty or poorly washed and undried crushers and containers for preparing, pouring and storing wine.
- Use of unsterilized (dirty) hoses, watering cans, a water seal and other auxiliary equipment.
- Ingestion of spoiled grapes infected with mold fungi into the wort.
- When preparing wine, the upper layers of the pulp can grow moldy, so you need to mix the pulp thoroughly for even fermentation.
- Wines with low acidity and alcoholic content, as well as highly diluted with water, are most often subject to mold infestation.
- Wines that have stopped fermentation ahead of time are also covered with zelem. This can be due to both very low and very high temperatures in the room where the wine is fermented.
- Young wine grows moldy when it comes into contact with air, so containers for settling and storing wines are filled to the top and carefully sealed with sterilized lids and corks.
Can wine be made from moldy grapes?
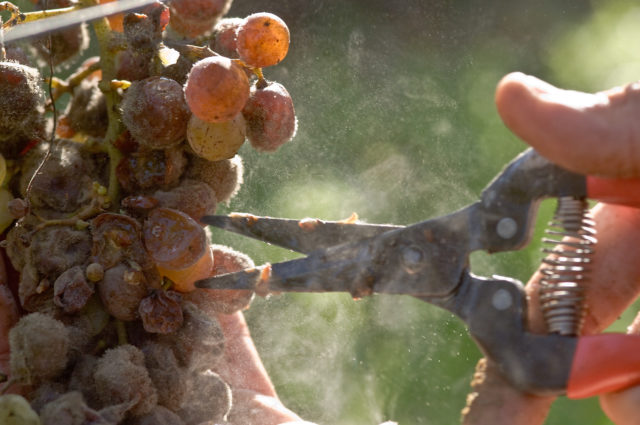

Of course, ordinary grapes, spoiled by mold, will not make wine. It is almost impossible to make botrytized wine from moldy grapes at home. And this wine is prepared using a very specific technology. Very few wineries in the world undertake the production of botrytized wines. The technology involves enormous risks and is complicated by an almost unpredictable result. The reason for this is the very specific conditions for the development of noble mold on grapes. Should fit together favorably
- natural growing conditions (vineyards are located in cool regions in close proximity to water bodies);
- temperature and humidity during ripening (the summer should be rainy, and the last two to three weeks before picking berries should be dry, sunny weather);
- features of the variety (white grape varieties are more successfully exposed to Botrytis cinerea, and red ones lose tannins a lot and lose very much in taste);
- the possibilities of the economy (the yield of botrytized wine, in comparison with traditional methods for white, is only 20%);
- sophisticated technology of preparation and aging of wine.
Special climatic conditions
Gray mold appears only in places where grapes are cultivated with a temperate climate, and even then only under certain conditions: when the warm autumn air causes humid morning fogs, and during the day the berries can dry out. Such conditions are quite rare. In Sauternes, the Girona River provides humidity and the Bordeaux sun for warmth. In Germany, the Rhine, Moselle, Saar and Ruwer flow, over which the morning fog forms. The required temperature is provided by the intense autumn sun and warmth emanating from the earth and water. In Austria, one-of-a-kind wines are born from the combination of heat coming from Hungary and the moisture of Neusiedler See, in Hungarian Tokay the necessary conditions are created by the combination of moisture from Tisza and Bodrog with the warmth of the Carpathians.
Sauternes combines sweetness and a high percentage of alcohol (14-15% by volume). On the other hand, selected German wines impress with their combination of sweetness and high acidity. The alcohol content is very low (about 7 vol.%)
The main causes of mold
- violation of sanitary standards in the process of wine production (tools and utensils that are used in the process of obtaining wine);
- oxygen access;
- increased temperature during production and storage (above 22 0 С);
- high humidity (over 85%);
- low strength of the drink (less than 12% alcohol);
- low acidity of the drink (red grape wines suffer from mold more often than white ones).
At first, the wine under such a film is completely transparent, its taste and aroma correspond to the norm.
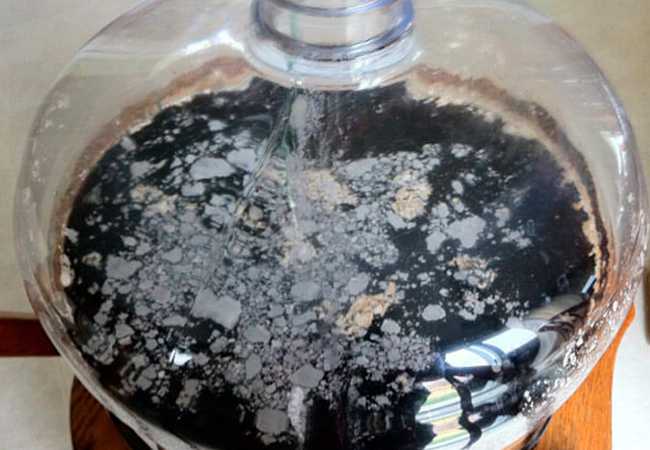
However, the volume of mold rapidly increases, the film becomes denser, becomes thicker, and sticks to the walls of the container. The mold layer begins to darken, wrinkle, and the drink develops an unpleasant rotten smell, it becomes cloudy.
A colony of fungi grows and sinks to the bottom. The wine is hopelessly spoiled.
If measures are taken in time, then the intoxicated drink, in which a lot of work has been invested, can be saved.