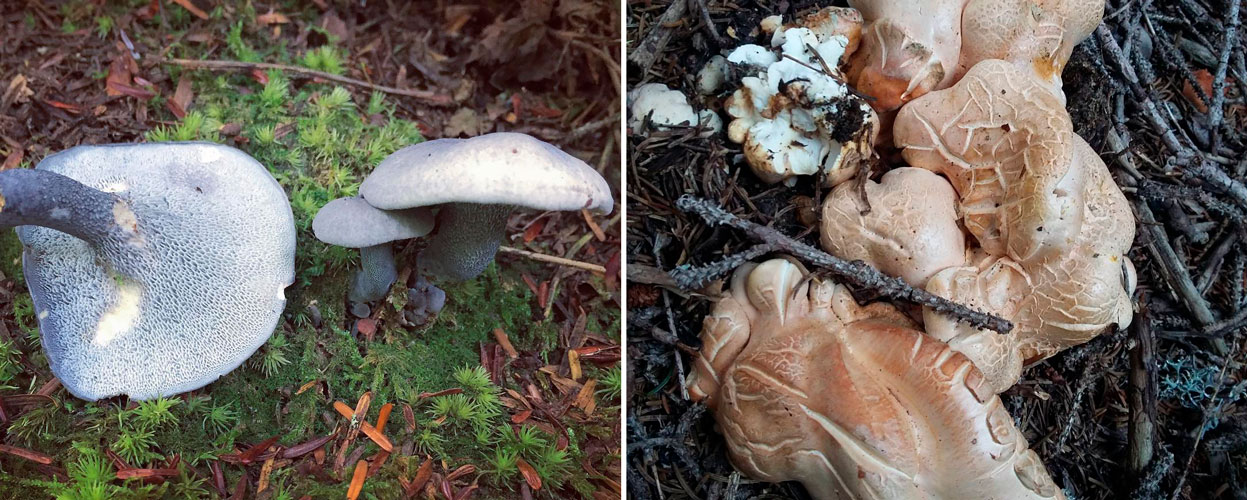
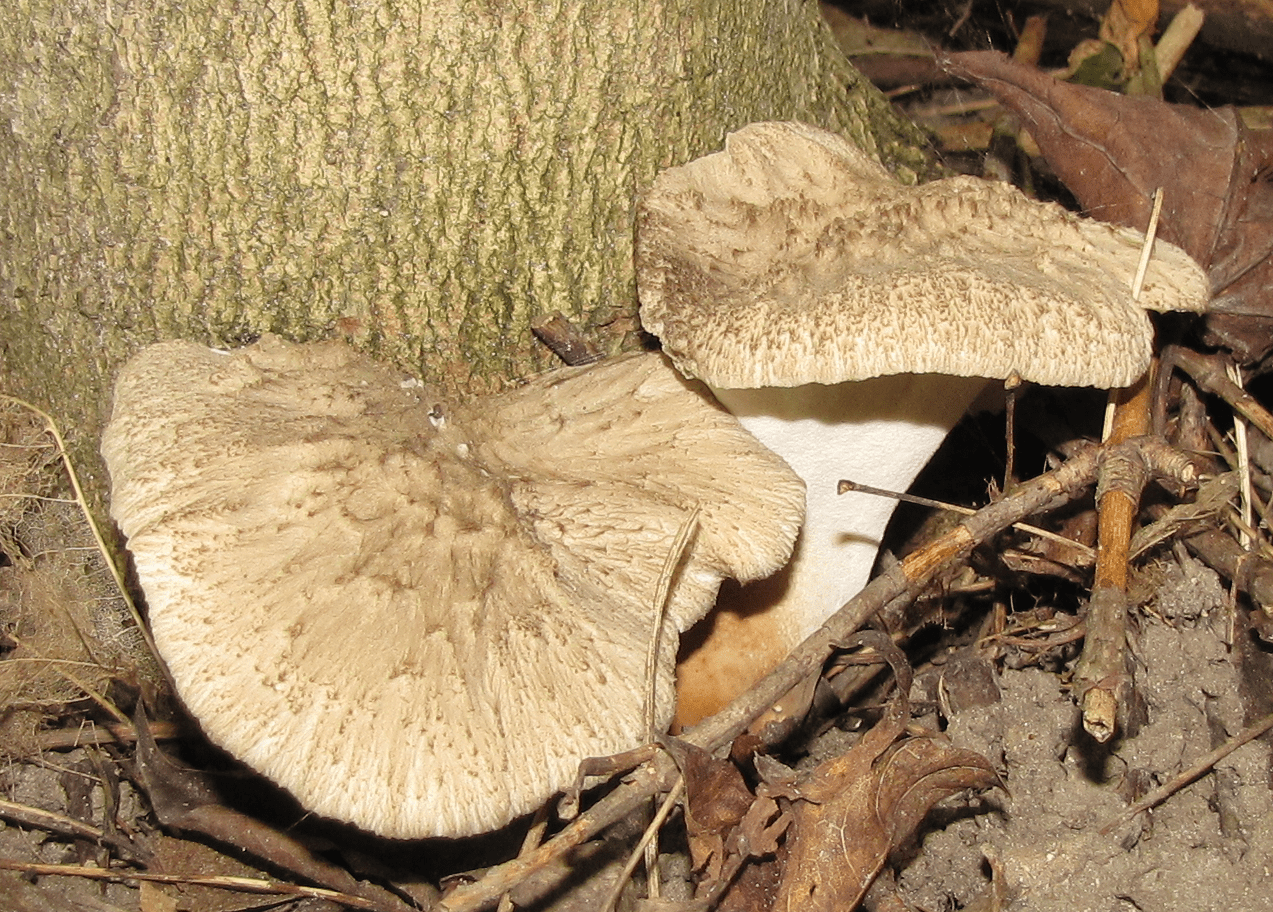
Albatrellus cristate (Laeticutis cristata)
Synonyms:
Albatrellus cristatus
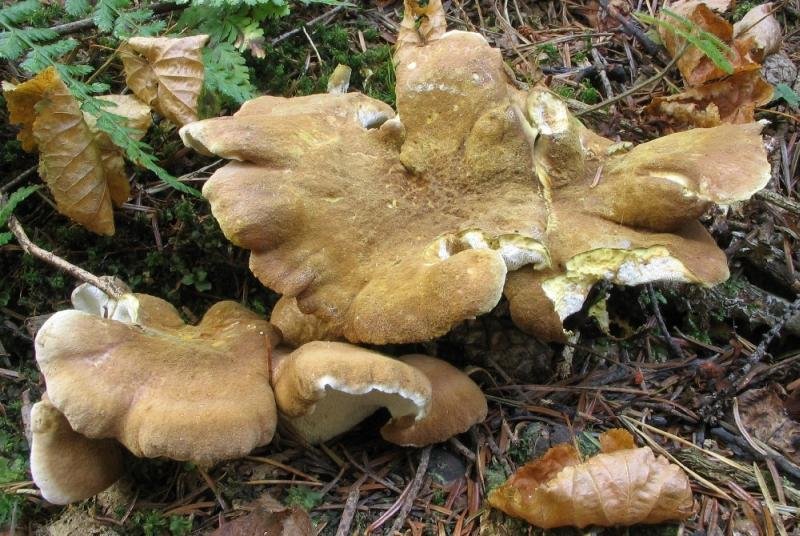

Photo Credit: Zygmunt Augustowski
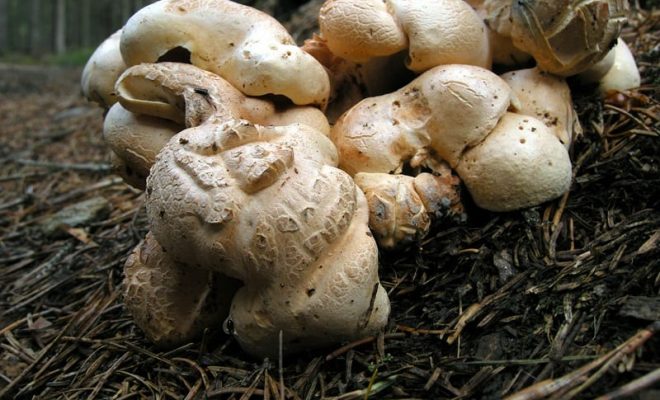
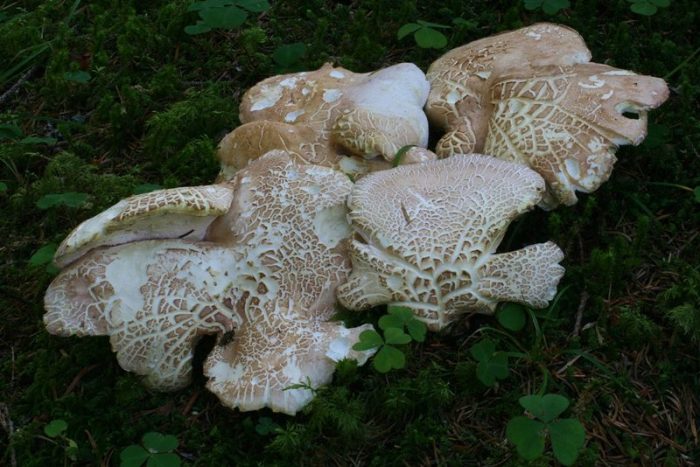
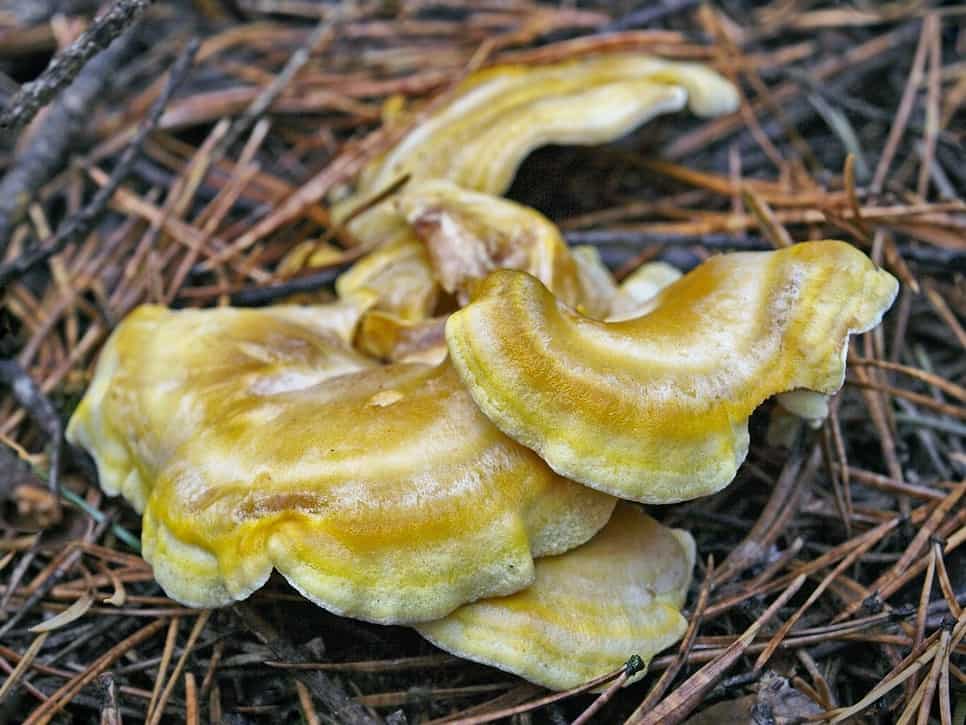
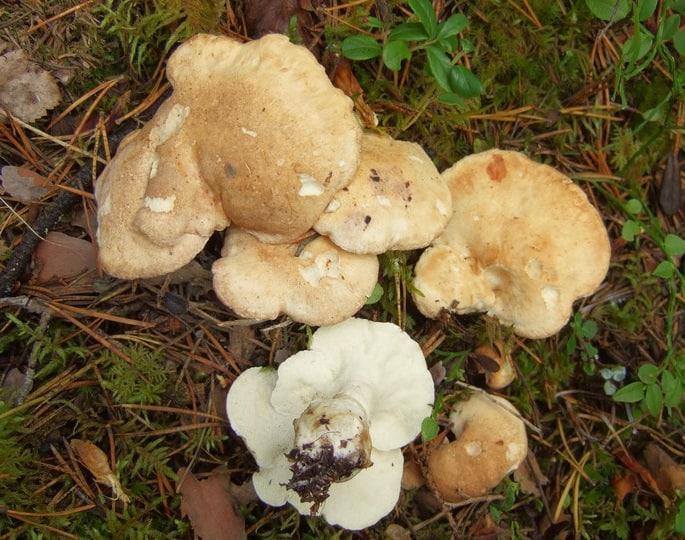
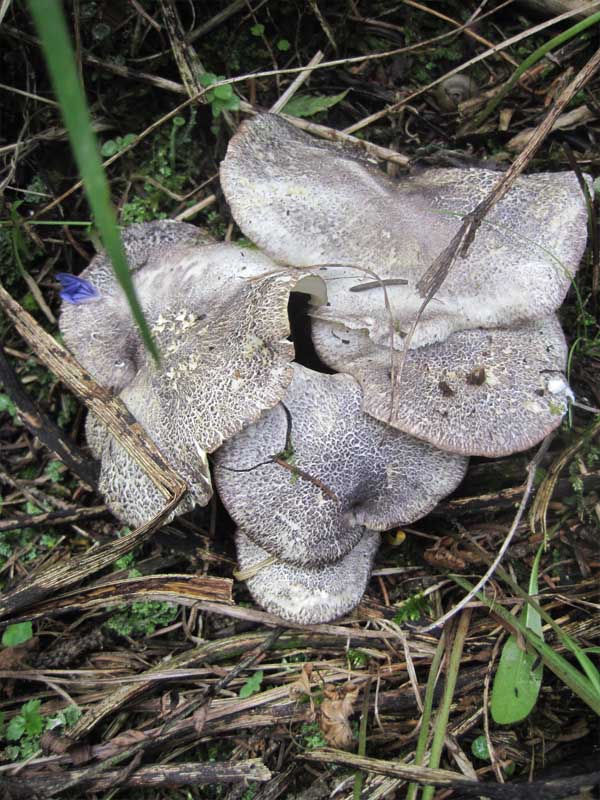
Basidiomas in this fungus are annual. Sometimes they are solitary, but it is much more common that they grow together at the base, and the edges of the caps remain free.
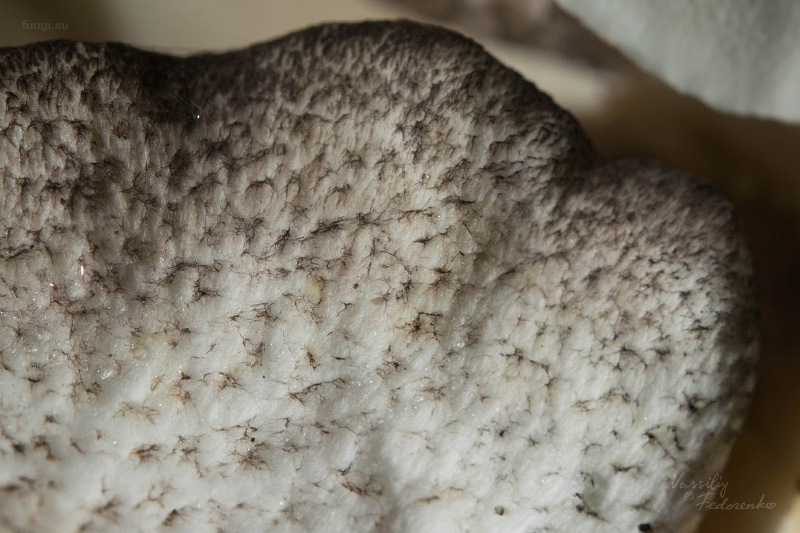
Faced with Albatrellus comb, you can see a hat with a diameter of 2-12 cm and a thickness of 3-15 mm. The shape is round, semi-round and kidney-shaped. Often mushrooms are irregular in shape and depressed towards the center. In old age and with dryness, they become very brittle.
The top is thinly pubescent. Later, it begins to become more and more rough, breaks and scales at the center become visible. The surface of the cap has an olive-brown, yellowish-green, less often red-brown bloom, with a greenish tint at the edges.
The edge itself is very flat and coarse. The fabric of this representative of Albatrell is white, but towards the middle it becomes noticeably yellow, even lemon. Differs in fragility and fragility. The smell is slightly sour, the taste is not particularly pungent. Thickness up to 1 cm.
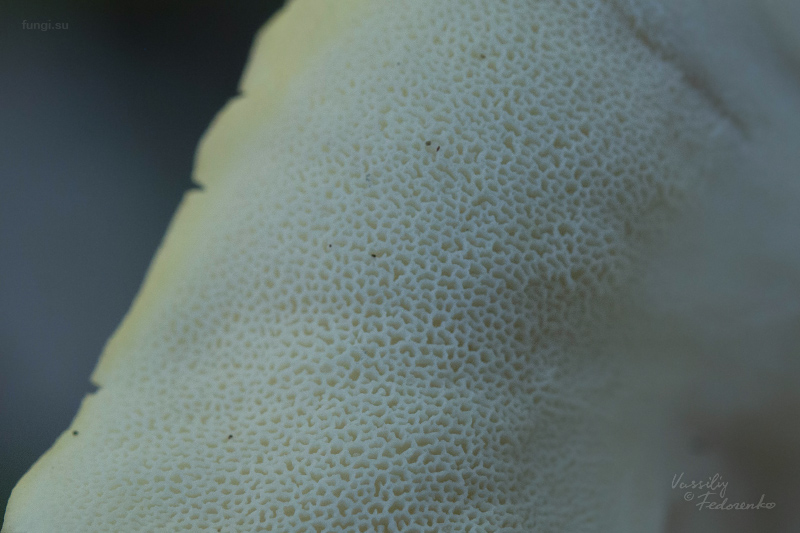
The tubes of this mushroom are rather short. only 1-5 mm in length. They are downhill and white. Like all mushroom breeds, they change their color when dried. It takes on a yellow, dirty yellow or red hue.
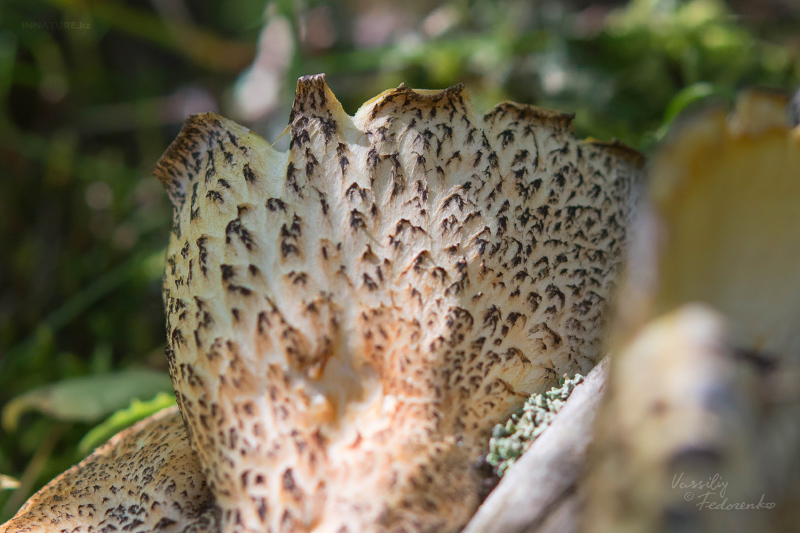
Pores tend to enlarge with age. Initially, they are small in size and round in shape. Placed with a density of 2-4 by 1mm. Over time, they not only increase in size, but also change shape, look more angular. The edges become scored.
The stem is central, eccentric, or nearly lateral. It has a white color, often set off by marble, lemon, yellow or olive colors. Leg length up to 10 cm and thickness up to 2 cm.
Albatrellus comb has a monomytic hyphal system. The tissues are wide with thin walls, the diameter varies (the diameter ranges from 5 to 10 microns). No buckles. The hyphae of the tubules are located rather consistently, have thin walls and are branched.
Basidia are club-shaped, and spores are elliptical, spherical, smooth, hyaline. They have thickened walls and are drawn obliquely near the base.
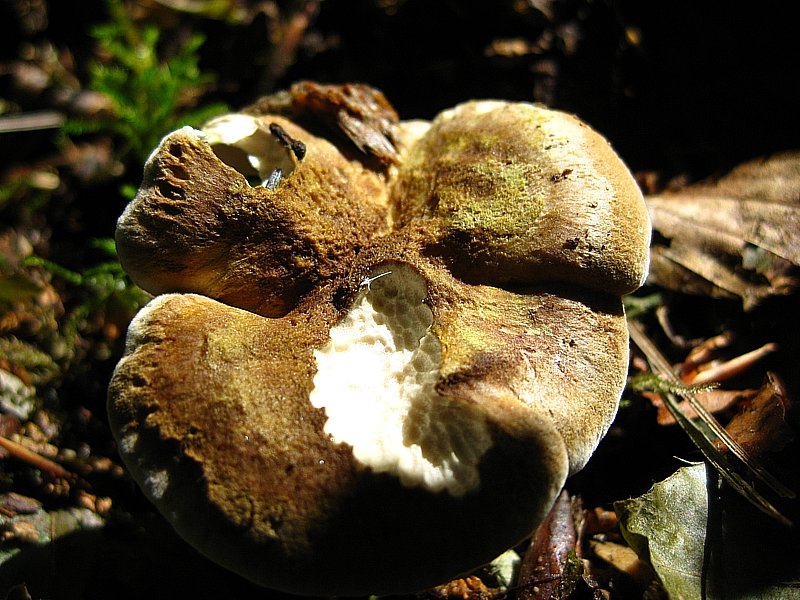

Found in deciduous and mixed forests, where there are oaks and beeches. Germinate on a sandy soil surface. Often found on roads that are overgrown with grass.
The geographical location of Albatrellus crested is Russia (Krasnodar, Moscow, Siberia), Europe, East Asia and North America.
Eating: Not edible mushroom, because it is tough enough and has an unpleasant taste.
Edible albatrellus sheep

Ovine albatrellus is an edible mushroom that is used fresh, dried, pickled, boiled, fried, stewed. It is a tasty mushroom, but its tough flesh is difficult to digest and can cause gastrointestinal upset.
They eat the caps of young mushrooms, which are boiled before use. When boiled, the flesh of the mushroom turns yellowish-green. Another cooking method is to fry raw albatrellus without boiling. Also, the mushroom is pickled with spices, which allows it to be stored for a long time.
Albatrellus is dried in the sun, in an oven, in an oven or on a gas stove. Drying outdoors requires sunny, dry weather to keep the mushrooms from spoiling. Fresh healthy mushrooms are cleaned, wiped with a damp cloth and sized. It is not necessary to wash the mushrooms, as they absorb moisture well and then dry out poorly. Then they are strung on a thread or hairpins. Albatrellus dries unevenly, so you need to monitor the process. An overdried mushroom will lose its taste, and an underdried mushroom will quickly deteriorate. When finished, dried albatrellus becomes light and dry, and tastes and smells like a fresh mushroom.Dried mushrooms are stored in dry, well-ventilated rooms, in sealed metal or glass jars.
Another way to store sheep's albatrellus is salting and pickling. Mushrooms are salted in a bowl made of wood, glass or enamel. Peeled and washed mushrooms are boiled in salted water for half an hour. The water is drained, the mushrooms are thrown into a colander and put in a container for salting. Salt is added at the rate of 50-60 g per 1 kg of mushrooms. Garlic, pepper, bay leaf are also added. Then they put him under oppression. A delicious dish is ready in a week. Salted albatrellus is stored in cool rooms. The brine should completely cover the mushrooms.
A delicious soup is made from albatrellus. 1 kg of fresh mushrooms is sorted out, peeled, legs removed and washed. Mushrooms are cut small, filled with water and boiled for 15–20 minutes. 4 onions are sautéed in vegetable oil. Add 350 g of any cereal, fried onion, chopped greens, seasonings to boiled mushrooms and bring to readiness.
Albatrellus is also used for preparing main courses and salads. For example, rolls made from these mushrooms are popular. Fresh mushrooms are boiled and fried, after which they are ground into minced meat with onions, garlic, salt and pepper. Chopped boiled eggs and mayonnaise are added to the finished minced meat. Sausages are formed from the mixture, which are wrapped in slices of ham. Rolls are laid out on a dish and poured with meat jelly, cooled.
Salads are prepared from pickled albatrellus: 1 kg of pickled mushrooms is cut and finely chopped green onions are added. Diced boiled potatoes (300 g) and a jar of green peas are added to the mixture. Dress the salad with mayonnaise, seasonings - salt and pepper.
Albatrellus ovinus (Albatrellus ovinus)
Other names:
- Scutiger ovinus
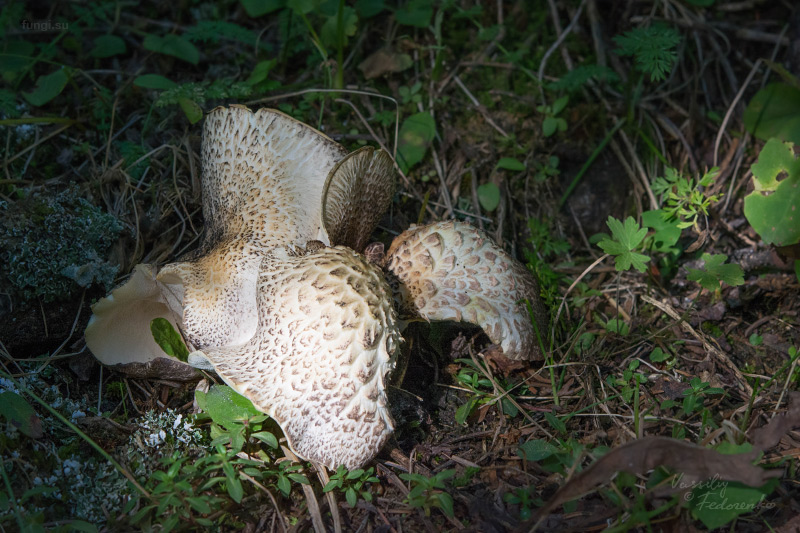
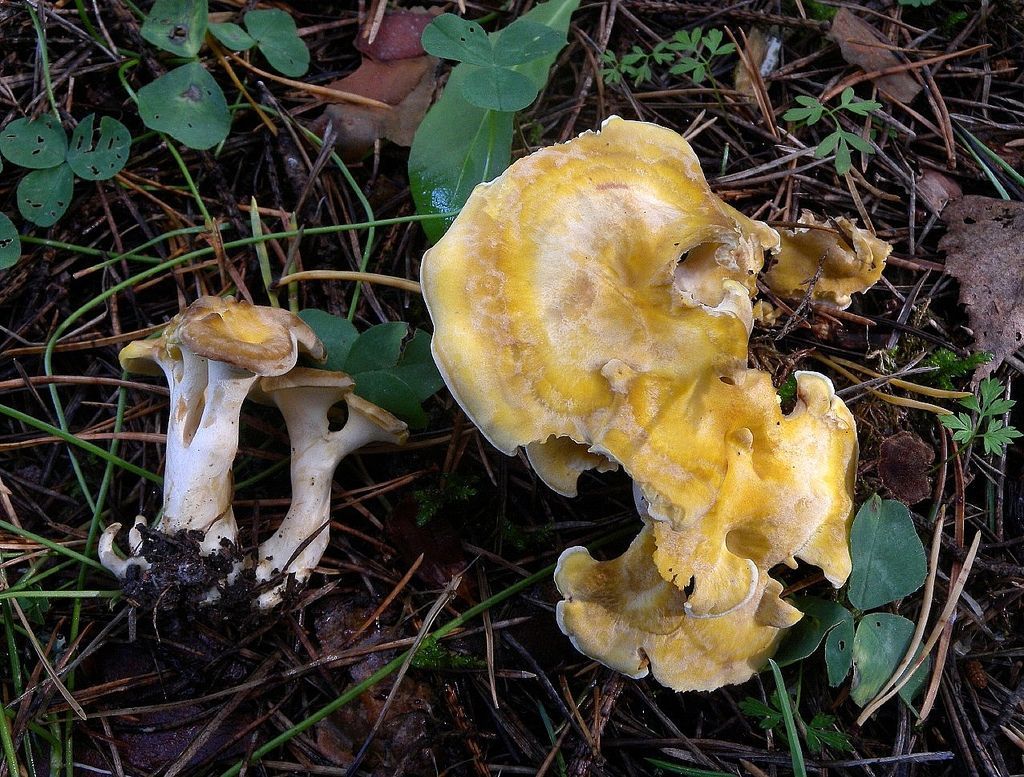
 Albatrellus ovine, ovine mushroom (Albatrellus ovinus) grows in dry pine and spruce forests. Belongs to the well-known mushroom family Tinder fungus.
Albatrellus ovine, ovine mushroom (Albatrellus ovinus) grows in dry pine and spruce forests. Belongs to the well-known mushroom family Tinder fungus.
Description:
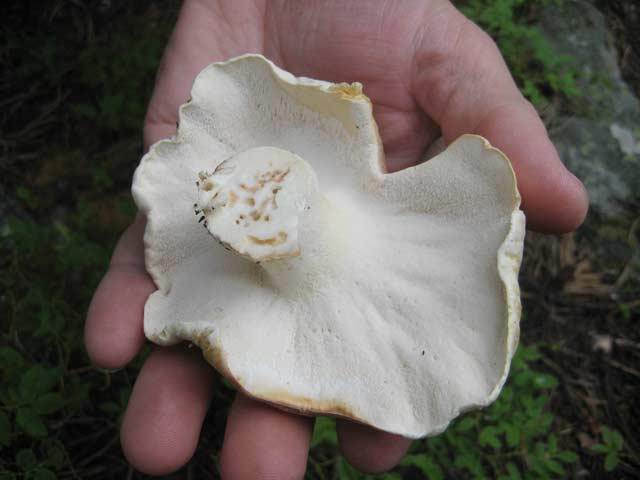
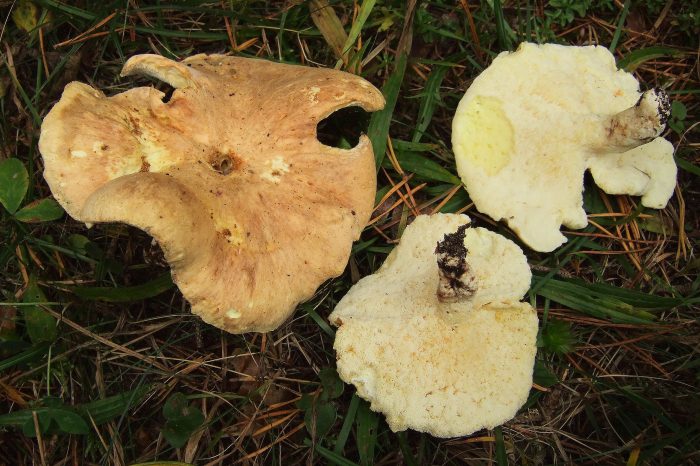
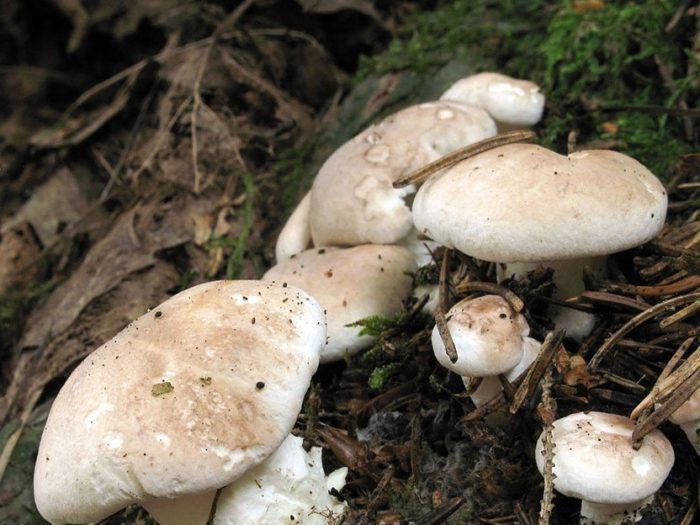
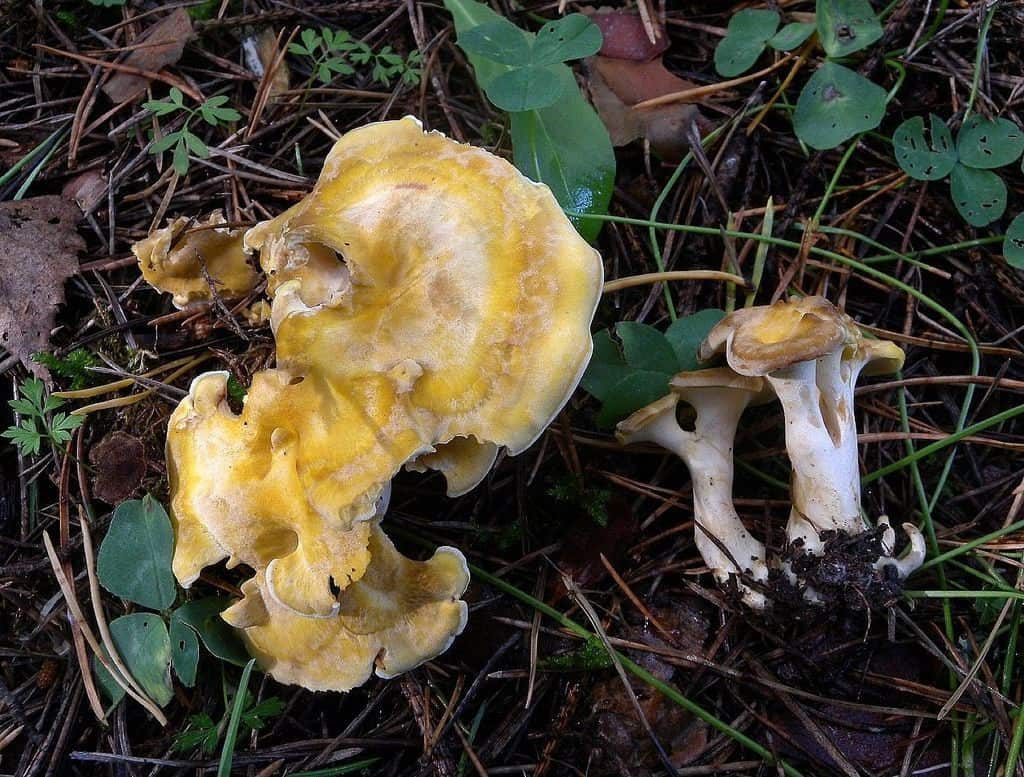
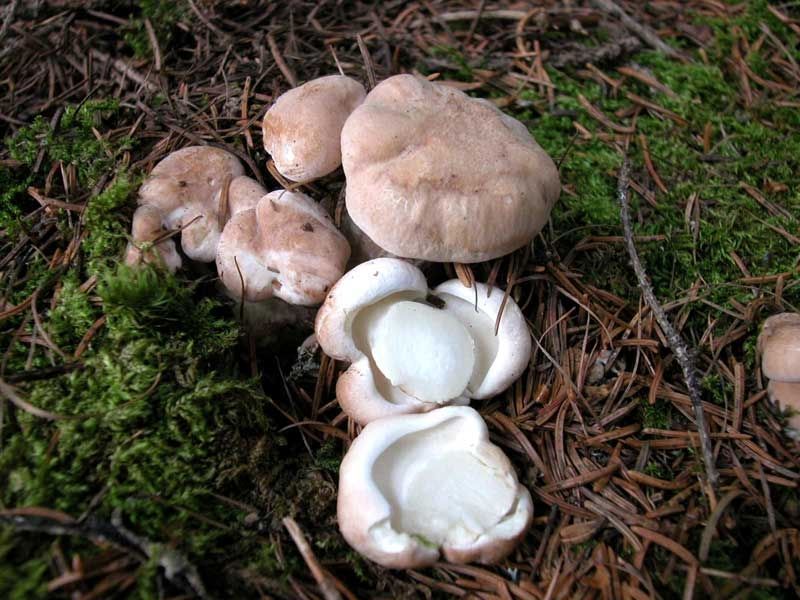
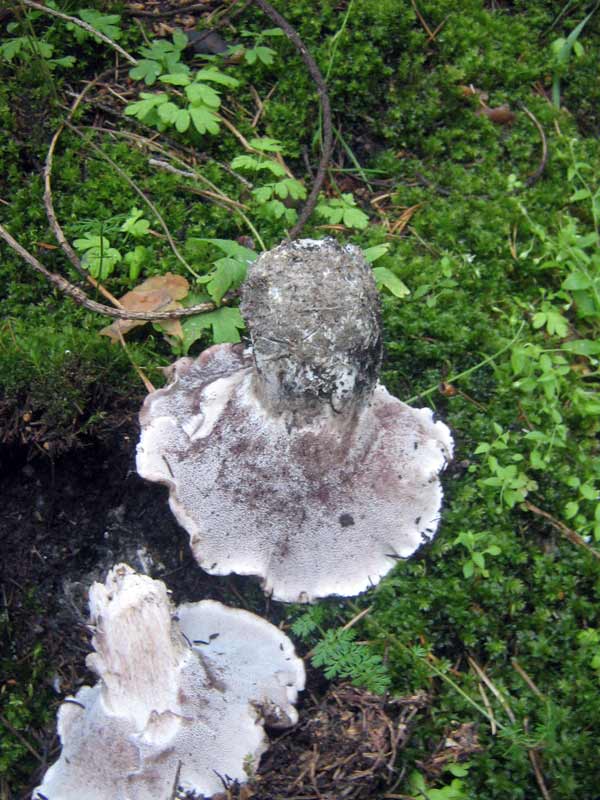
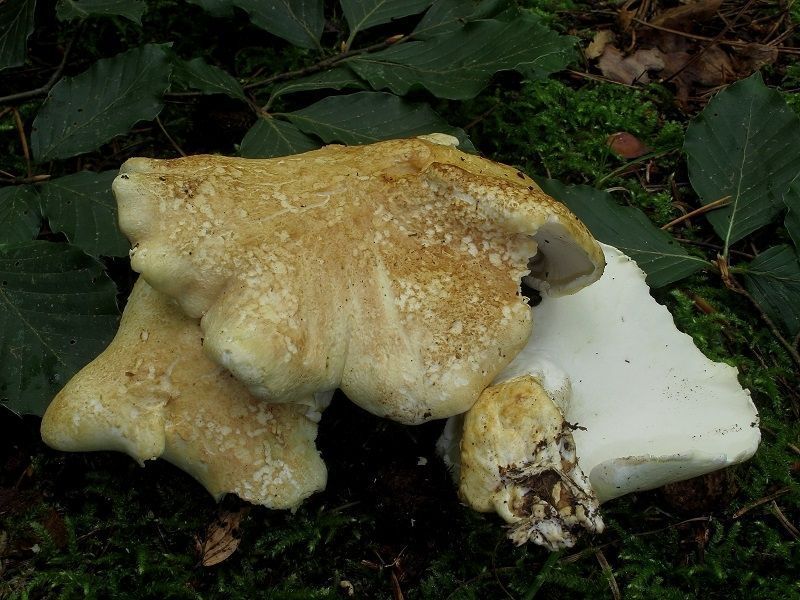
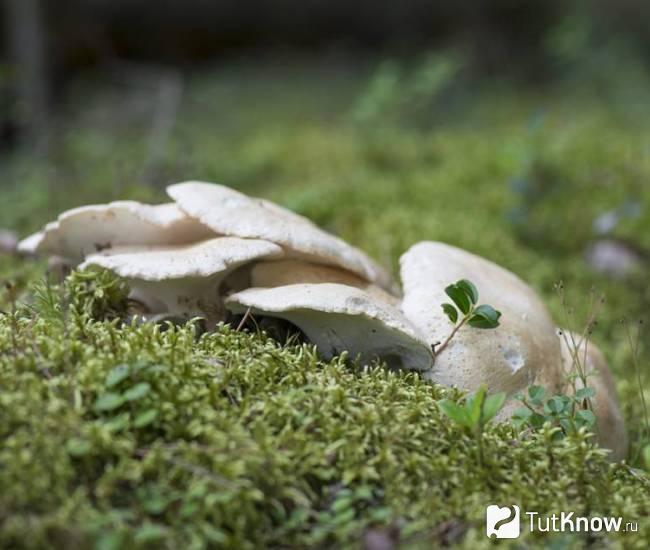
The round mushroom cap reaches ten centimeters in diameter. In an old mushroom, it cracks. The skin of the cap of the young mushroom is dry and silky to the touch. The lower surface of the mushroom cap is covered with a fairly dense layer of white-colored tubes, which are easily separated from the mushroom pulp. The surface of the cap is dry, naked, at first smooth, silky in appearance, then slightly scaly, cracking in old age (especially during dry periods). The edge of the cap is thin, sharp, sometimes pubescent, from slightly wavy to lobed.
Tubular layer strongly descending on the leg, the color varies from white or cream to yellow-lemon, greenish-yellow, turns yellow when pressed. The tubules are very short, 1–2 mm long, the pores are angular or rounded, 2–5 per 1 mm.
The stem is short, 3 - 7 cm long, thick (1 - 3 cm thick), strong, smooth, solid, central or eccentric, narrowed towards the base, sometimes slightly bent, from white (cream) to gray or light brown.
Spore powder is white. The spores are almost round or ovoid, transparent, smooth, amyloid, often with large drops of fat inside, 4 - 5 x 3 - 4 microns.
The pulp is dense, damp, brittle, white, yellow or yellowish-lemon when dry, often turns yellowish when pressed. The taste is pleasant, soft or slightly bitter (especially in old mushrooms). The smell is rather unpleasant, soapy, but according to some literary data, it can be both inexpressive and pleasant, almond or slightly mealy. A drop of FeSO4 stains the flesh gray, KOH stains the flesh a dirty golden yellow color.
Spreading:
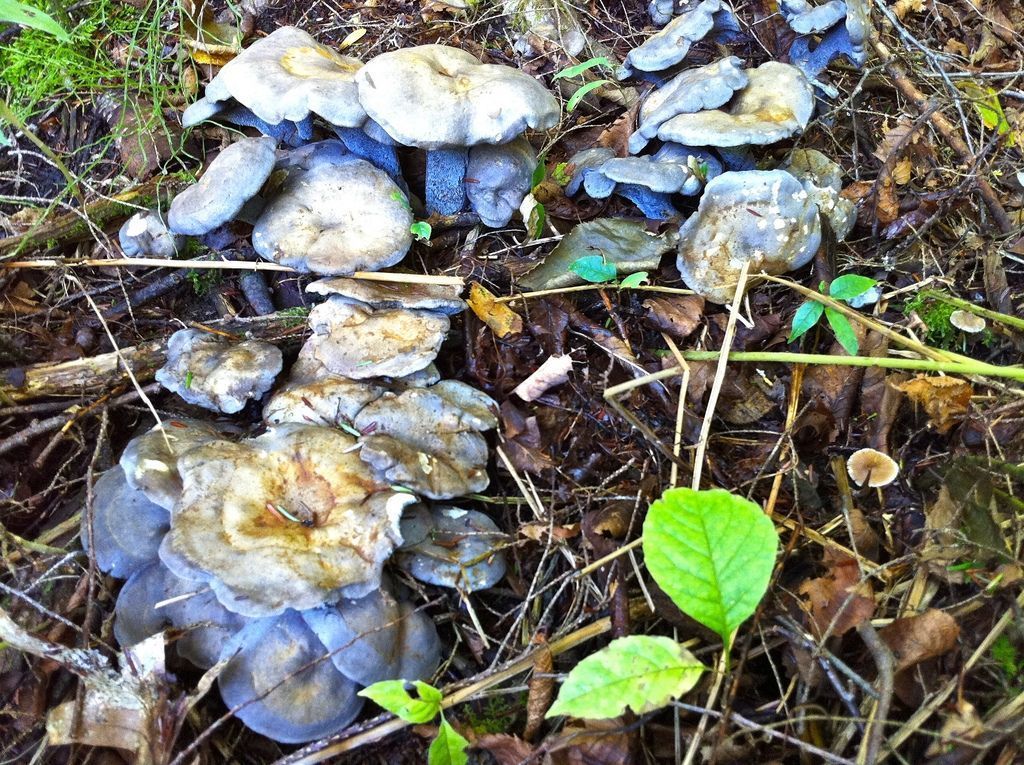
Albatrellus ovine occurs infrequently from July to October on the soil under spruces in dry coniferous and mixed forests in clearings, clearings, forest edges, along roads, and also in the mountains. Prefers neutral and alkaline soils, often grows in moss. Forms clusters and groups with closely adhered to each other, sometimes growing together, legs and edges of caps, fruit bodies. Single specimens are less common. The species is widespread in the northern temperate zone: it is recorded in Europe, Asia, North America, and also found in Australia.On the territory of Russia: in the European part, Siberia and the Far East. Moss cover is considered a favorite place for growth. Tinder fungus is a rather large mushroom. It grows singly or in groups, sometimes growing together with its legs.
Similarity:
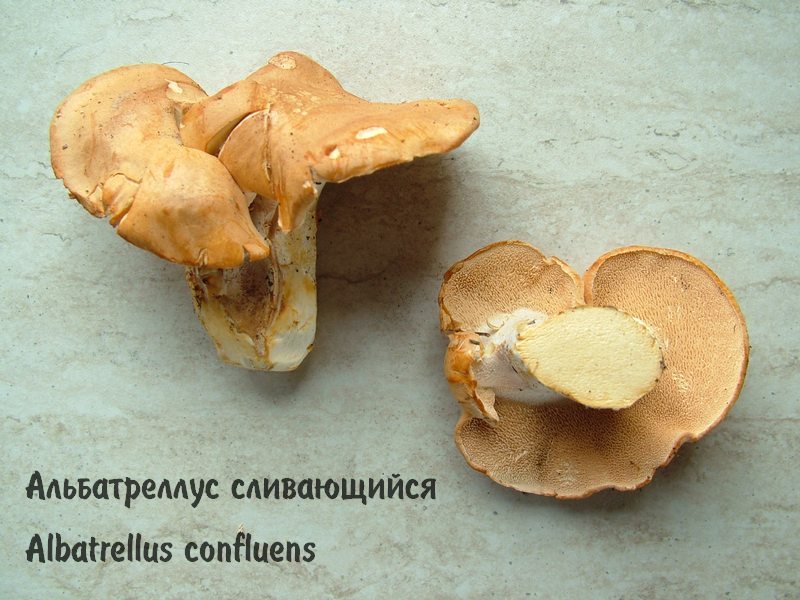
Ovine albatrellus in its appearance is similar to the confluent tinder fungus, which has a more brown color. Yellow blackberry (Hydnum repandum) is distinguished by a hymenophore, consisting of thick light creamy spines slightly descending on the leg. Albatrellus confluens is colored orange or yellow. brown tones, with a bitter or sour taste. It has accrete, usually uncracking caps, grows under various conifers. Albatrellus subrubescens is colored orange, light ocher or light brown, sometimes with a purple tint. The tubular layer is light orange. Grows under pine and spruce trees, has a bitter taste. Albatrellus cristatus has a brown-green or olive cap, grows in deciduous forests, most often in beech groves. Lilac albatrellus (Albatrellus syringae) is found in mixed forests, colored in golden yellow or yellowish brown tones. The hymenophore does not descend on the leg, the pulp is light yellow.
Grade:
Albatrellus ovine is a little-known edible mushroom of the fourth category. The mushroom is suitable for consumption only in an unripe form. Young caps of this mushroom are used fried and boiled, as well as stewed. Before use, the mushroom must be boiled with the preliminary removal of the lower part of its leg. In the process of boiling, the mushroom pulp acquires a yellowish-green color. The mushroom is considered especially tasty when fried raw without preliminary boiling and heat treatment. Ovine albatrellus can be pickled with spices for long-term storage.
The species is listed in the Red Book of the Moscow Region (category 3, a rare species).
Used in medicine: scutigeral, isolated from the fruiting bodies of ovine tinder fungus, has an affinity for dopamine D1 receptors in the brain and may act as an oral pain reliever.
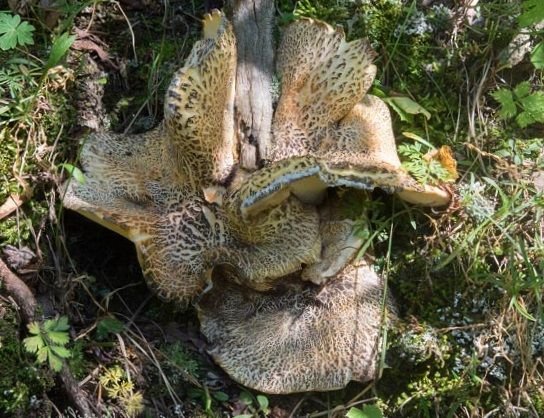
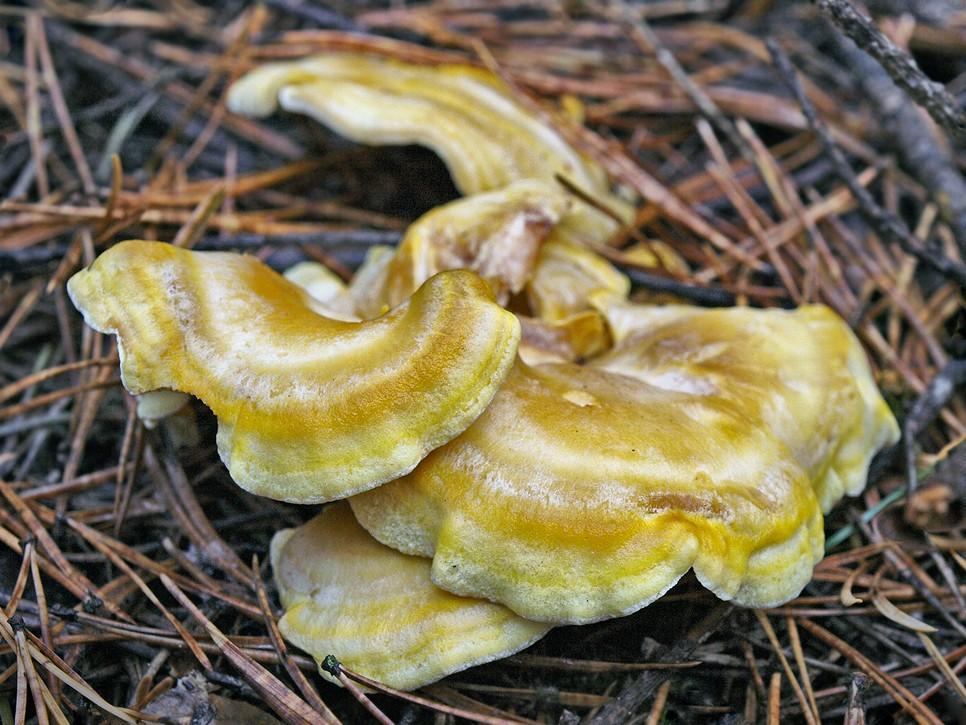
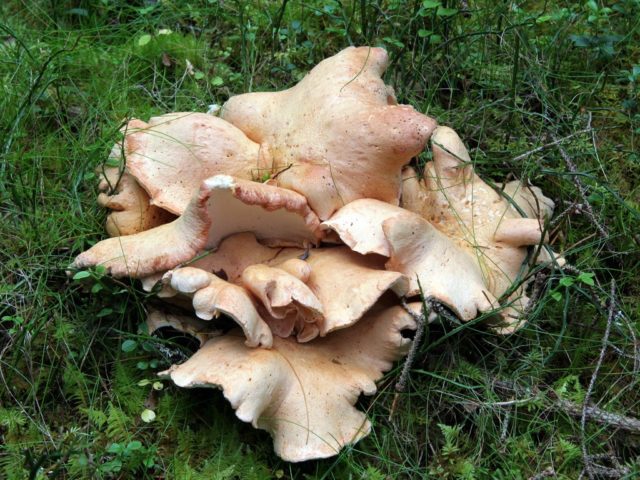
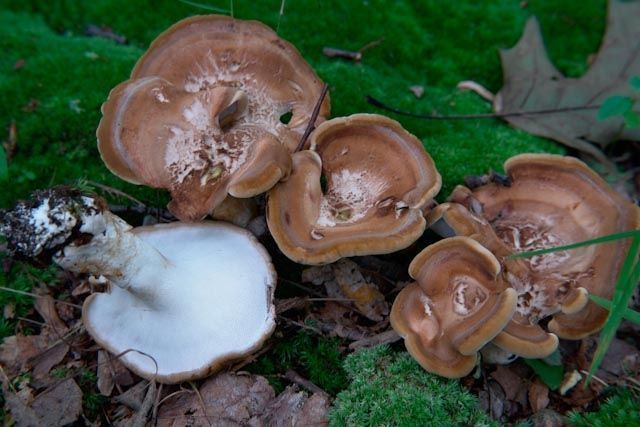
Description of albatrellus blushing
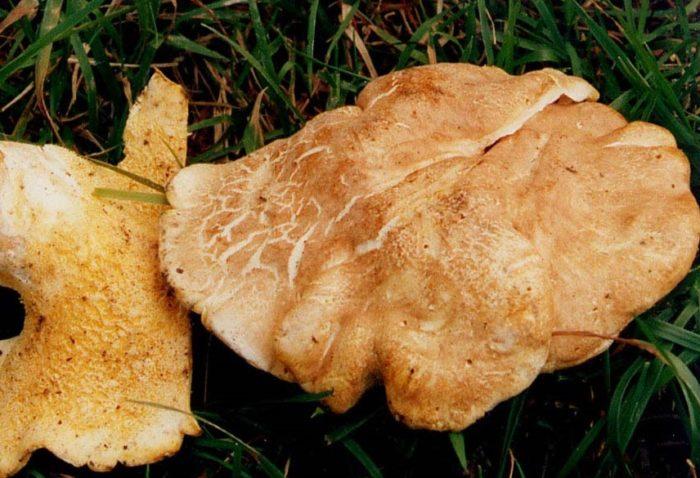
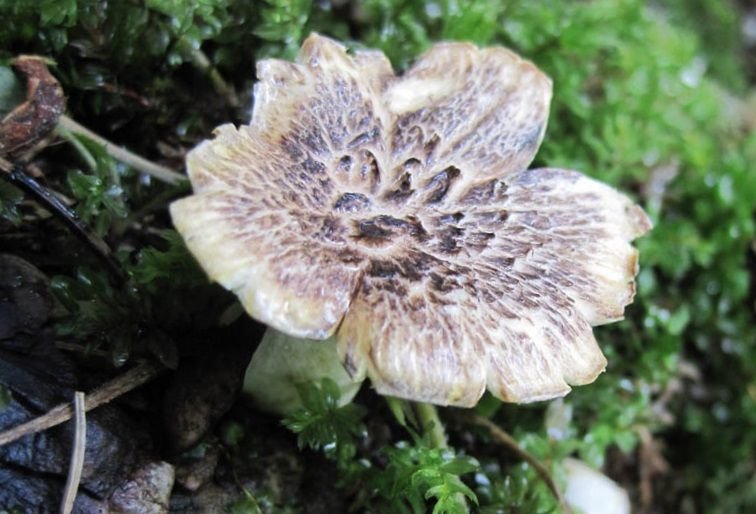
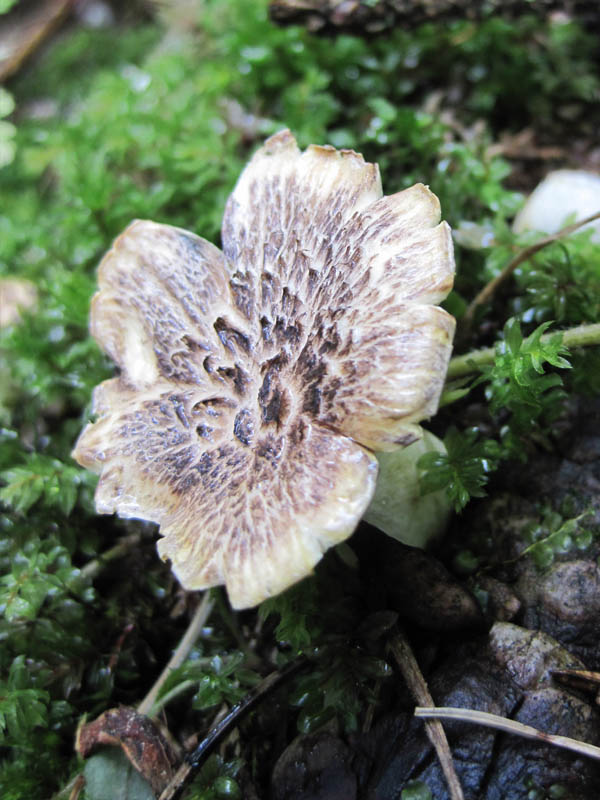
The fruit body of the blushing albatrellus is represented by a cap and a leg. The cap is scaly, in old specimens it can become cracking, with a diameter of 6-8 centimeters. The color of the cap is light brown, brown or dark orange with a purple tint.
The hymenophore is characterized by the presence of angular pores. The color of the tubular layer is yellowish, sometimes there is a green tint or there are pink spots. The tubules descend strongly on the pedicle. The pulp is damp, dense. The pulp tastes bitter.
Sometimes there are specimens with central legs, but mostly eccentric legs. The surface of the leg is covered with a small fluff. The color of the leg is pink. When dried, the stem turns bright pink, hence the name of the mushroom.
Distribution of albatrellus blushing
These mushrooms grow in the forests of European countries. And in Russia they are known in the Leningrad region, in addition, they grow in Karelia. There are no exact data on the habitat of these little-studied fungi, but it is known that they prefer pine forests. This is a saprotroph mushroom, that is, it uses decaying wood remains for food.

The similarity of the albatrellus blushing with congeners
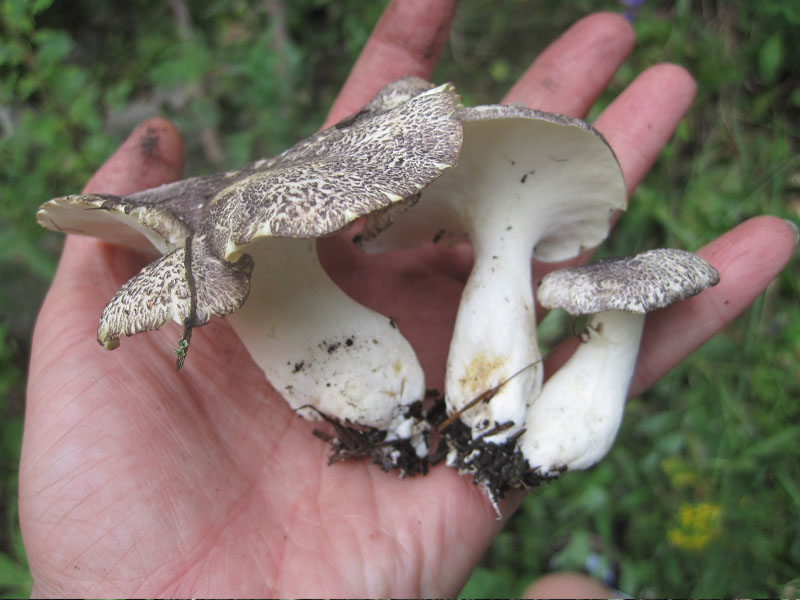
Albatrellus blushing has a great external resemblance to sheep's mushroom or sheep's albatrellus. The sheep mushroom is distinguished by greenish spots on the cap. Ovine albatrellus is an edible member of the family. His hat is dry, silky, rather large - up to 10 centimeters in diameter. The leg is thick, short and dense. The color of the leg is gray or light brown. The pulp is brittle, white with a bitter taste and a soapy smell.
Sheep mushrooms grow in spruce and pine forests. These mushrooms are rare. Fruiting is observed from July to October. They can grow in plains and mountains. They prefer neutral alkaline soils.Sheep mushrooms settle in dense clusters, closely snuggling, to each other, and single mushrooms are rare.

Albatrellus lilac also has an outward resemblance to albatrellus blushing, but its tubes do not run down to the stem, and its flesh is light yellow in color. The hat first looks like a funnel, and over time it becomes plano-convex. The color of the cap is egg-cream, the diameter is large - up to 12 centimeters. The surface of the cap is matte or with a slight fluff. If the fruiting bodies settle on the ground, then the legs can reach 6 centimeters in height, and in woody specimens they are very short.
Albatrellus lilacs can grow on soil and wood. These mushrooms grow in North America and Asia, and are rare in Russia. They bear fruit from spring to autumn. Fruiting bodies often grow together, but there are also solitary mushrooms. This is a conditionally edible type of mushroom.
Botanical description
Ovine albatrellus (Albatrellus ovinus) - This mushroom belongs to the genus Albatrellus from the Albatrell family. You can find other names for this mushroom: sheep tinder fungus or sheep mushroom. A possible reason for this name is the external similarity of this plant with a sheep. The tinder fungus colony resembles a flock. In addition, these animals love to eat this mushroom. It is a fairly large mushroom that usually grows in dry coniferous forests. It can be found under trees, on the outskirts of roads or on the edges. Forms families or entire colonies, but single fungi can also be found. Grows in areas with a temperate climate. A special feature is that the ripening period is from July to October. This mushroom can be found when the rest are no longer growing.
Sheep mushroom has a fleshy cap about two centimeters thick and 7-18 centimeters in diameter. It can be round or irregular. When the mushroom is young, the cap is convex in the center, and the edge is slightly bent. Over time, it becomes flat, cracks, scales and bumps form on it. Color also changes with age from white or cream to gray-yellow or gray-brown with yellow spots. The bottom of the mushroom cap is covered with a layer of white tubes that easily separate from the pulp. The tubular layer of the fungus descends low on the stem.
The length of the tubes is small, about 1–2 mm, the color can be white, cream, yellow with different shades. When pressed, a yellow spot appears at the point of impact. The stem of this mushroom is short, about 3-5 cm and thick - up to 3 cm. Quite dense and smooth. It can be located both in the center of the cap and eccentrically. The spores of this fungus are round or ovoid, transparent and smooth in structure. The spore powder is white. The pulp has a damp structure, dense, but brittle. The taste is pleasant and soft, but in the process of maturation the mushroom acquires a bitterness. Sometimes there is an unpleasant odor that resembles soap.
Synonyms
- Albatrellopsis confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Teixeira, 1993
- Boletus artemidorus Lenz, 1830
- Boletus aurantius Schaeff., 1774
- Boletus confluens Alb. & Schwein., 1805: Fr., 1821 basionym non Boletus confluens Schumach., 1803, q. e. Coltricia perennis (L.: Fr.) Murrill, 1903
- Boletus nitens J.F. Gmel., 1792
- Caloporus confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Quél., 1888
- Caloporus politus (Fr.) Quél., 1886
- Cladomeris confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Quél., 1886
- Merisma confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Gillet, 1878
- Polypilus confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) P. Karst., 1881
- Polyporus artemidorus (Lenz) Fr., 1838
- Polyporus confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Fr., 1821
- Polyporus laeticolor (Murrill) Sacc. & D. Sacc., 1905
- Polyporus pachypus Pers., 1825
- Polyporus politus Fr., 1836
- Polyporus whiteae (Murrill) Sacc. & D. Sacc., 1905
- Scutiger confluens (Alb. & Schwein.) Bondartsev & Singer, 1941
- Scutiger confluens f. politus (Fr.) Bondartsev, 1953
- Scutiger laeticolor Murrill, 1903
- Scutiger whiteae Murrill, 1903
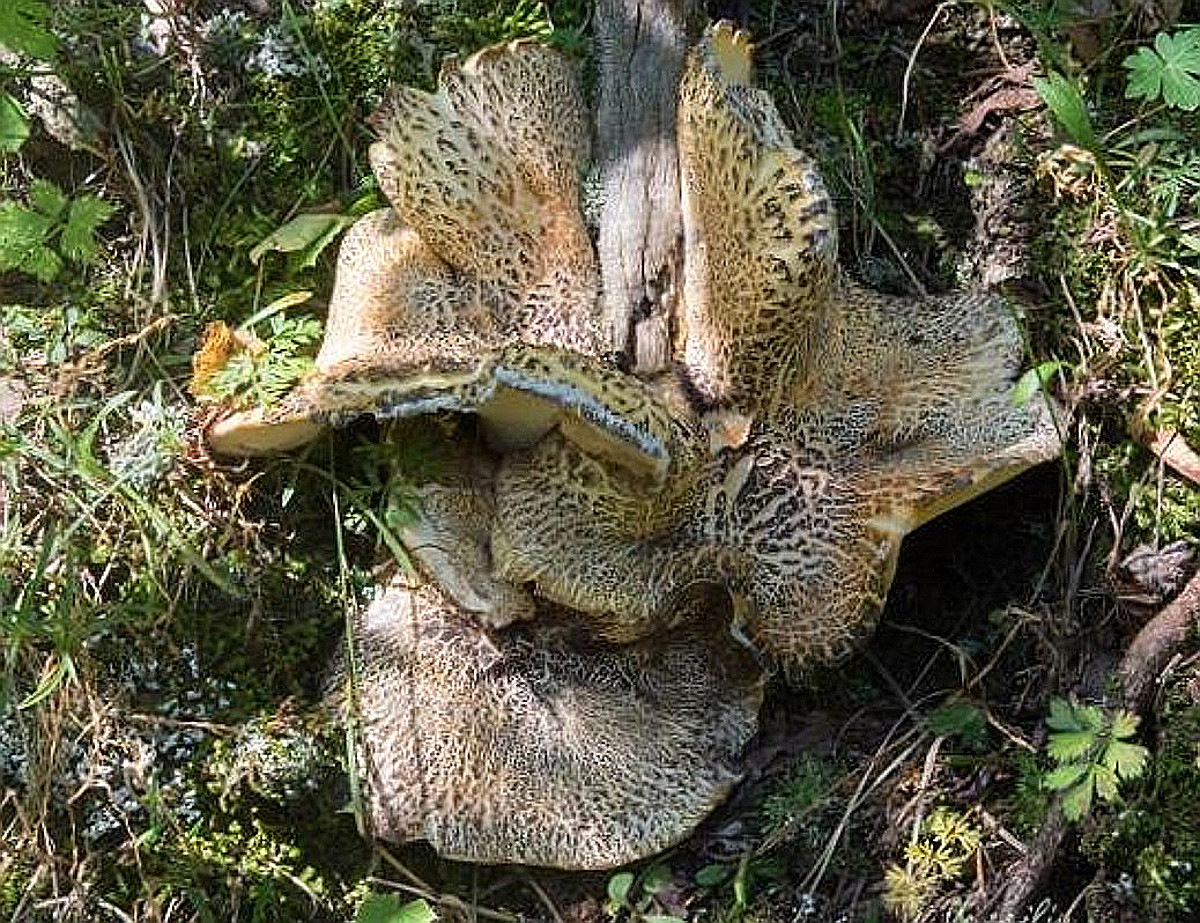
Description
Fruiting bodies are cap-stalk, annual, often in the form of several caps on a branched stalk. Caps are from rounded to fan-shaped or irregularly lobed, up to 11 cm in greatest dimension and up to 3 cm thick, the upper surface is pinkish-beige, salmon-pink when dry, often cracking into separate areas with age.
The hymenophore is tubular, cream-colored, when it dries, it becomes salmon pink. Pores from rounded to angular, 3-5 per millimeter, with thick septa.
The stem is central to lateral, cream or pinkish-beige, naked, when dry salmon-pink, wrinkled, up to 8.5 cm long.
The pulp is soft and fleshy, creamy, when dry it is pinkish-yellowish-brown, when it dries, it is tough, resinous, often with a pleasant smell, with a peculiar cabbage taste and a bitter aftertaste.
The hyphalous system is monomytic. Cystyds are absent. Basidia are tetrasporous, clavate, 20–30 × 6–7.5 µm. Spores ovoid or elliptical, uncolored, 4-5 × 2.5-3.5 µm.
How to cook?
There are many ways to prepare albatrellus ovinus for human consumption. Dried tinder fungi are especially appreciated, since in this form they retain their taste as much as possible. In addition, they are pickled, used for making soups and main courses, and salads are made.
How to dry a mushroom?
Polypores can be harvested for the winter by drying. To do this, fresh mushrooms are cleaned, wiped with a towel and strung on a thread. If weather permits, you can dry outdoors, but you need to constantly monitor this process. Tinder fungus quickly absorbs moisture, so any light rain or fog will backfire. A tinder fungus that has collected water will quickly grow moldy and deteriorate.
If the weather is humid, you can dry the mushrooms in an oven or oven. Do not overdry: a specimen that is too dry will lose its taste. If the sheep tinder fungus is dried correctly, it will smell and taste like a fresh mushroom. The finished product should be stored in sealed glass containers, where moisture does not get.
How to pickle?
A good way to preserve tinder fungus is to pickle it. This will require a glass or enamel container. You can use a wooden tub. Mushrooms need to be sorted out, peeled and boiled in salted water for 30 minutes. Then transfer to a prepared container and add 50 g of salt per 1 kg of mushrooms.
To taste, you can put a few cloves of garlic, bay leaves, black and allspice. Mix everything and put under oppression. The mushrooms will be ready in a week. Sheep tinder fungus can be stored for a long time in a cool room. The marinade must completely cover the mushrooms so that they do not spoil.
Best soup recipe

A delicious soup is made from sheep's mushroom according to the following cooking recipe:
- fresh mushrooms - 1 kg;
- onions - 4 pcs.;
- any cereal - 350 g;
- vegetable oil;
- greens;
- seasonings to taste.
The tinder fungus is cleaned, the legs are removed, and cut into small pieces of the same size. Then it is poured over with water and boiled for 15 minutes. At this time, you need to chop the onion and fry it in vegetable oil. Fried onions, cereals, herbs and seasoning are added to a saucepan with mushrooms, and then boiled for about 5 minutes until cooked.
Second courses and salads
Sheep tinder fungus is well suited for preparing salads. You can use it both fresh and pickled. Finely chopped mushrooms are mixed with boiled potatoes and green peas, pickled cucumbers or pickled cabbage are added if desired. You can fill the salad with sour cream, mayonnaise or sunflower oil.
Mushroom rolls can be prepared as a second course.

- To do this, tinder fungi need to be fried, chopped, add onions and spices.
- Put finely chopped boiled eggs in the mushroom mince, cheese and mayonnaise if desired.
- Wrap the minced meat in lavash slices and serve beautifully, decorating with herbs.
Dishes from sheep's tinder fungus will not go unnoticed during a large feast.
Medicinal properties and use in medicine
Various useful substances for medical use are isolated from sheep tinder fungus. It contains griffolin, which has anti-inflammatory medicinal properties, and neogrypholine, which is a powerful antioxidant. And also sheep tinder fungus contains scutigeral. This substance is related to dopamine D1 in the brain receptors, which is why it is used as a pain reliever. Its action is similar to psaicin, which is obtained from red pepper.
For medicinal purposes, both young and mature specimens are collected. Requires the best medium sized mushrooms with a whole cap and an intact stem. Alcohol and water tinctures are prepared from them or dried and ground into powder. The tinder fungus is actively used in Chinese folk medicine, its beneficial properties have been used since ancient times.
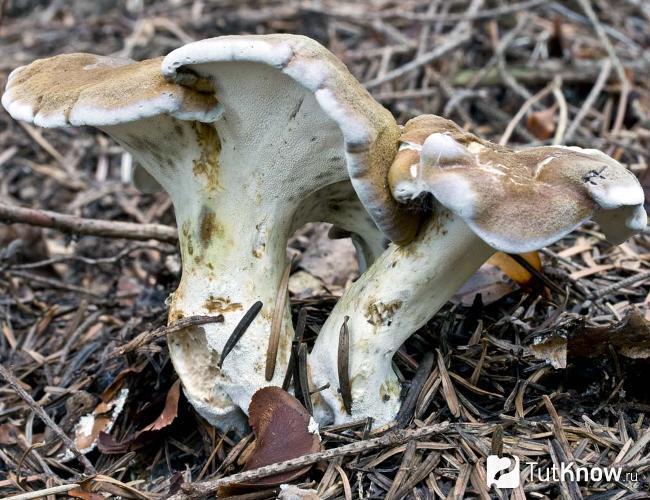
Description of albatrellus crested
The diameter of the mushroom cap can vary significantly from 2 to 12 centimeters, the thickness is also different - 3-15 millimeters. The shape is round or semicircular. Most often, the shape of the cap is irregular, in the center it is depressed. Above, the cap of the albatrellus comb is thinly pubescent, and with age it becomes more rough, grows, and noticeable scales form at the center.


The tubules of the crested albatrellus are short - their length is 1-5 millimeters. They are descending, white. The leg can be practically central as well as lateral. The stem is most often white with lemon, marble, olive or yellow tint. The leg can be up to 10 centimeters long and up to 2 centimeters thick.
How albatrellus comb grows and develops
Old mushrooms become dry and very brittle. These mushrooms have a slightly sour smell. When dry, crested albatrellus, like other mushrooms, change their color, they acquire a red or dirty yellow tint.

The pores increase in the process of growth, and at first they are small in size, round in shape. There are 2-4 pores per 1 millimeter of the fungus. Over time, mushrooms not only grow, but also change their shape, they become more angular. And the edges start to look jagged.
Distribution of crested albatrellus
These mushrooms are common in mixed and deciduous forests in which beech and oak trees grow. The habitat of crested albatrellus is sandy soil. They can often be found on grassy roads.

These mushrooms grow in Russia, for example, in Moscow, Siberia and the Krasnodar Territory, as well as in East Asia, Europe and North America.
Crested albatrellus are unsuitable for food because they are quite tough and have an unpleasant taste.

Related species
There are several species of albatrellus, most of them form symbiosis with conifers, and some of the members of the family are saprophages.
- Albatrellus lilac can grow both on soil and on wood, while it most often settles on deciduous trees;
- Albatrellus blushing is a poorly studied mushroom. This is a saprotroph mushroom, that is, it uses organic compounds of dead wood for nutrition;
- Albatrellus bluepore is considered conditionally edible, but the edibility of this mushroom has not been fully established;
- Albatrellus confluent - an edible annual mushroom;
- Albatrellus Tien Shan is edible at a young age, but over time it becomes tough;
Sheep tinder fungus or sheep mushroom is also edible only at a young age. The species is in the Red Book of the Moscow Region.
Sheep polypore - Albatrellus ovinus
Written by Nikolay Budnik and Elena Meck.
Sheep tinder is rarely found on Ulom Zheleznaya. It grows in dry pine forests in August - September. The confluent polypore (Albatrellus confluens) is very similar to it, which is distinguished by a yellow or brownish cap. We are not yet ready to distinguish between these mushrooms, so we call everything the Sheep Tinder.
Previously, we did not collect this mushroom, but once we decided to try it. We liked the sheep tinder - white, delicate, beautiful, tasty. This mushroom is especially good in drying.

1. This mushroom was not common to us.

2. We know only two places where it grows.

3. In both cases it is a dry pine forest.

4. Sheep tinder fungus, although called tinder fungus, grows on soil.

5. Often, mushrooms form whole drusen families.

6. Pleasant and tasty pulp only in young mushrooms.

7. Older specimens have slightly bitter taste, harder consistency.

8. However, the bitterness can be removed by preliminary boiling.

9. We met sheep tinder fungus in the middle of August - in September.

10. In our country, it appears only in pine forests.

11. The mushroom loves enough open spaces.

12. He can be seen among the moss.

13. Although the sheep tinder fungus can grow alone, whole families are more common.

14. It is a fairly large mushroom in size.

15.The sheep's tinder fungus hat can be of different colors - white-ocher.



18. The upper skin is sometimes cracked.

19. The hat has very uneven, winding edges, irregular shape.

20. The layer at the bottom of the cap can be called tubular.

21. These tubes are short and dense.

22. Here they can be examined more closely.

23. Tubular white layer, sometimes with yellow and cream shades.

24. The tubular layer is dense, the pores are small.

25. The stem of the mushroom is smooth, slightly tapering towards the base.

26. Sometimes it is white, but sometimes it is yellowish and creamy.

27. Inside, the leg is solid, dense.

28. Here you can see the attachment of the tubules to the stem.

29. The flesh of the mushroom on the cut is white and dense.

30. When dry, it turns yellow.

31. Some authors call the pulp of sheep tinder fungus cheese-like.

32. Sheep tinder is a good edible mushroom, especially at a young age.