Content
- 1 Greenhouse growing rules in Siberia
- 2 Varieties
- 3 Types of greenhouses and planting
- 4 Planting care
- 5 Greenhouse growing rules in the Moscow region
- 6 Why grow grapes in a greenhouse?
- 7 Choosing varieties
- 8 Features of the greenhouse for grapes
- 9 Do-it-yourself greenhouse trellis
- 10 Planting grape seedlings
- 11 Grape care and pollination
- 12 Watering and feeding
- 13 Preparing grapes for winter
- 14 Greenhouse growing rules in Siberia
- 15 Varieties
- 16 Types of greenhouses and planting
- 17 Planting care
- 18 Greenhouse growing rules in the Moscow region
- 19 Why grow grapes in a greenhouse?
- 20 Choosing varieties
- 21 Features of the greenhouse for grapes
- 22 Do-it-yourself greenhouse trellis
- 23 Planting grape seedlings
- 24 Grape care and pollination
- 25 Watering and feeding
- 26 Preparing grapes for winter
- 27 Pros of growing in a greenhouse
- 28 Selection of varieties
- 29 Greenhouse requirements
- 30 Preparatory work
- 31 Landing features
- 32 Pruning rules
- 33 Watering and feeding
- 34 Wintering grapes
- 35 Problems with fruiting
Unfortunately, many grape varieties cannot be grown in northern climates, since the plant is too thermophilic. In such cases, they resort to using greenhouse structures. Indoors, the culture can be provided with no less care than in the southern regions.
Greenhouse growing rules in Siberia
For northern latitudes, growing grapes in greenhouses has many advantages.
Growing grapes in a greenhouse makes it possible for the fruit to ripen earlier.
The grapes that grow in the greenhouse are practically immune to insects.
The vineyard is protected from frost in the greenhouse.
By growing grapes in a greenhouse, you can achieve high yields.
A vineyard growing in a greenhouse does not need to be treated with chemicals.
It should be noted right away that it is unprofitable to build a greenhouse only for your own use of grapes, since too high costs are ahead.
As a rule, growers resort to the greenhouse method in the case of industrial use of the crop, that is, they grow grapes for sale fresh, or they are going to use the berries for mass processing for wine or other food products, with the subsequent sale of finished products.

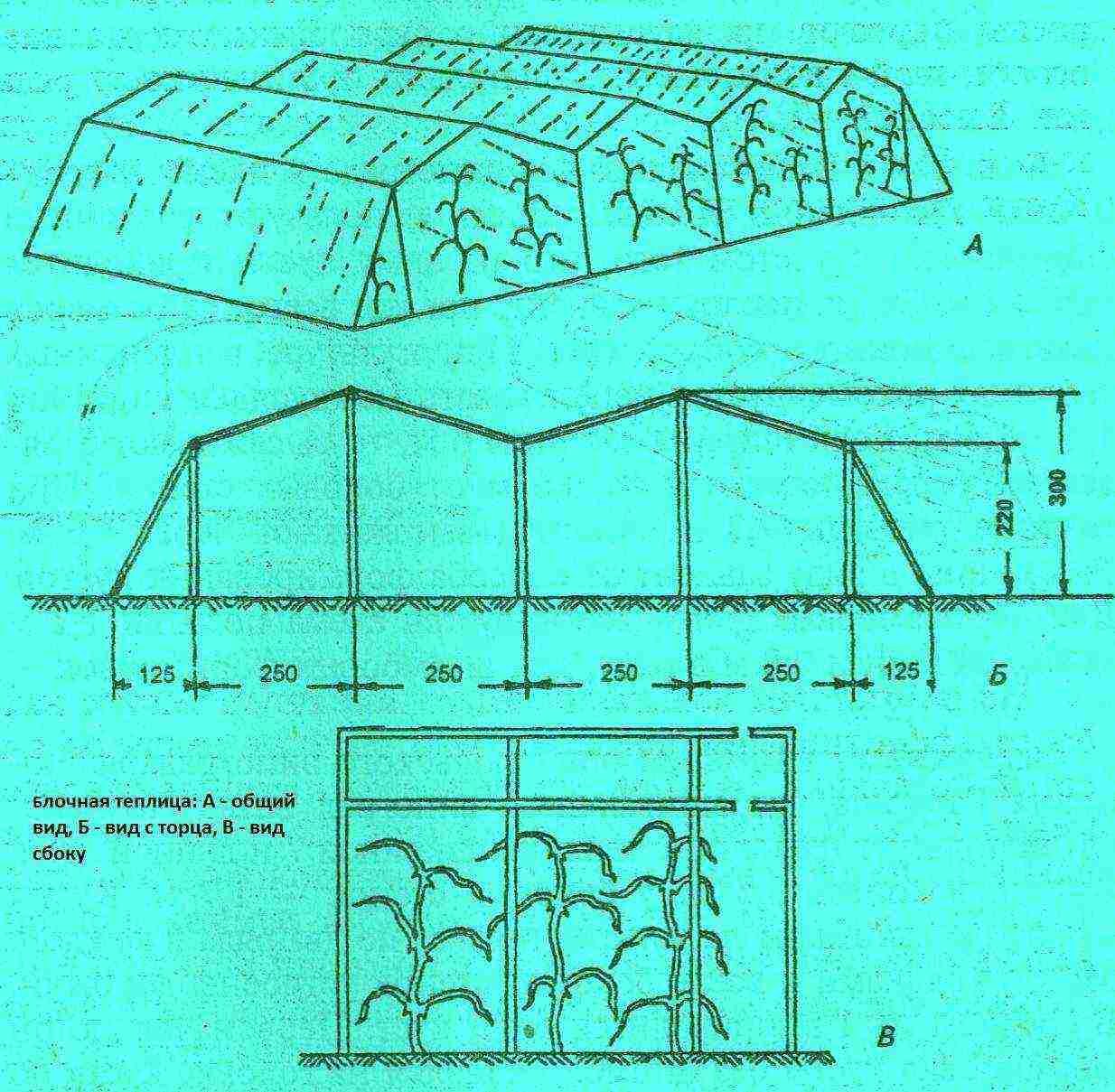
Greenhouse 3 by 6 meters.
It is noteworthy that not all varieties are suitable for growing inside closed soil.... In Siberia, Delight, December, Strashensky will not take root in such conditions.
Varieties

It is better to give preference to frost-resistant and early varieties.
However, they will give excellent results the following cultures:
- Arcadia.
- Transparent.
- Laura.
- Song.
- Kishmish.
- Irinka.
- Currant.
- Alyoshenka.
- Sidlis.
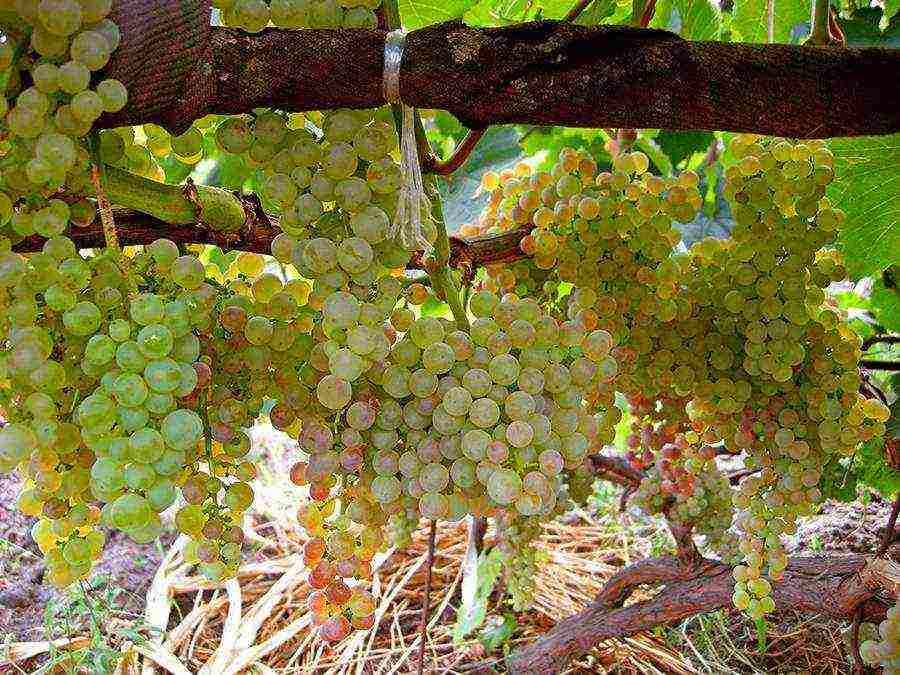
It is characteristic that Arcadia is able to bear fruit and bring record harvests in greenhouses - productivity is an order of magnitude higher than under normal conditions.
The same performance can be expected from Transparent. Laura will delight you with larger berries than in open soil.
Types of greenhouses and planting
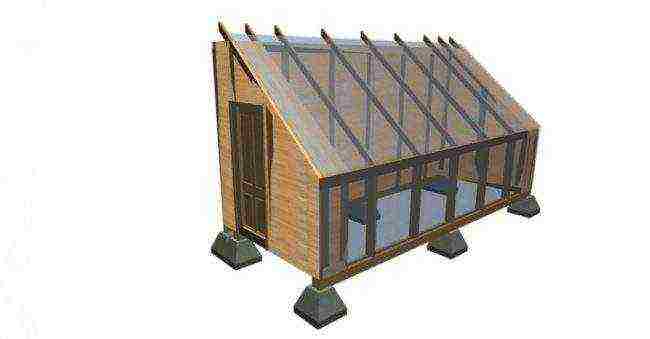
The greenhouse for growing grapes must be high enough.
Usually, gardeners use two types of structures - a wall-mounted and a stationary type.
- The wall method involves the use of a wall of a heated residential building as one of the walls of the structure.... Thus, this wall provides additional heat and maintains an optimal level of heat transfer. It is noteworthy that, using this method, during the summer season, you need to open the structure and properly ventilate. As a rule, an earlier harvest can be expected in this case.
- The second method is a stationary structure, which is recommended to be built on the south side of the garden area to receive a large amount of light.... The size depends on the desired amount of planting material. The only requirement is height. The entire building must be more than two and a half meters in height. This is necessary so that the bushes of crops can grow as well as possible without creating crowding.
Features of preparation

The greenhouse should have 50-60 cm of fruitful soil.
The first condition is proper soil preparation.
It should be noted that the roots of the plant are located in the upper layer, so it is necessary to create the most suitable conditions for their strengthening and further development. The soil layer should be composed of soil, sand and gravel, with sand and gravel usually making up about half of the potting mix.
Top dressing
Drainage channels must be made in the ground.
The mixed soil should be fertilized with mineral fertilizers.
For this, ready-made mineral complexes are chosen that have a beneficial effect on the development of the entire plant, participate in the formation of the green and woody part.
Technology

Grape bushes need to be fertilized throughout their growth and maturation.
- It is advisable to mulch the soil and cover with a special agrofibre to prevent the growth of weeds, as well as to control the level of moisture and retain heat.
- Holes are made for cuttings.
- Usually plants planted in three rows, while the distance should be at least one and a half meters between plant units.
Planting care

When planting, the distance between the bushes of grapes must be respected.
Care measures consist of several points that must be strictly observed in order to obtain high results:
- watering;
- pruning;
- top dressing with saltpeter;
- feeding with phosphorus;
- maintaining a constant temperature;
- airing;
- humidity control;
- prevention against diseases.
Since at first the plant requires a lot of moisture to harden, it should be watered regularly, but do not overdo it.
Water only if drying of the soil is noticed. Over time, weak, dense or damaged vines are removed - you cannot provoke excessive density in order to avoid peas, reduce productivity.
- As soon as the first buds appear, the new plants are fed with a solution of saltpeter four times a month, that is, every week..
- Next, you should make phosphorus fertilizing.
- At the same time, the varietal characteristics of the culture are taken into account - the most suitable feeding for this variety is selected. It is advisable to use a high-quality sprayer for this in order to apply the mixture to the branches as much as possible for normal absorption.
- After flowering, wood ash is added, since this agent acts not only as a fertilizer, but also serves as an excellent preventive measure against fungi.
Greenhouse growing rules in the Moscow region
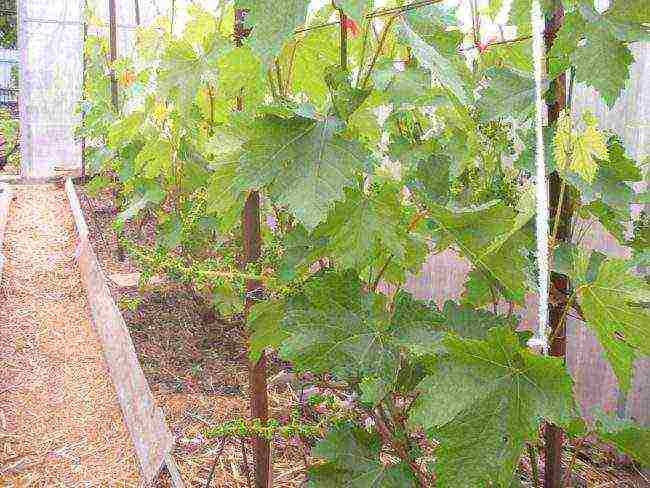

The grape bushes should be secured to the trellis.
Several facts speak in favor of growing grapes in a greenhouse.
In greenhouse conditions, in any weather, it is possible to create a comfortable microclimate for the normal development of culture, since the minimum temperature regime can be only five degrees Celsius.
At the same time, an acceleration of the activity of all growth phases is noted, as a result of which the beginning of fruiting is shifted earlier by about a month. Among other things, a greenhouse is a reliable shelter from drafts, sudden gusts of wind, dangerous precipitation. Recommended varieties for the Moscow region:
- Korinka Russian;
- Michurinsky;
- Moscow Stable;
- Irinka;
- Rylines Pink;
- Rusball;
- Agat Donskoy;
- Kay Gray;
- Alpha;
- Northern Early.
As in Siberia, it is better to use seedless varieties for greenhouse cultivation.... In addition, it is recommended to plant crops that are overly attractive to birds. Indoors, invasions of feathered pests are not terrible.
Types of greenhouses and planting
A greenhouse with one blank wall is the best option for northern locations.
In the Moscow region, a wall-mounted version of a greenhouse with one transparent wall facing the south or south-west side is most often used for greater access of light.
However, they often build a stationary greenhouse equipped with water heating, a drip irrigation system, artificial lighting, and special shelving. Arched or domed design. For construction, a metal frame with a polycarbonate coating is used.
Dimensions (edit)
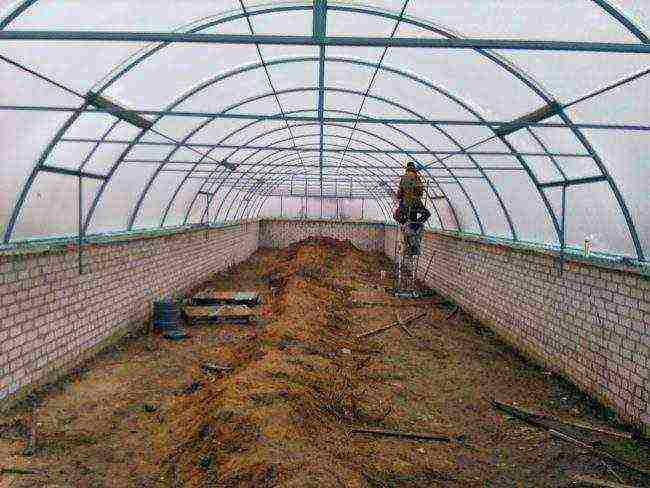

A spacious greenhouse is required to grow grapes.
The height of the arch is at least three meters, the total area depends on the amount of planting material - the purpose of growing... Classic dimensions: height - three meters, area - thirty squares. Before construction, it is necessary to make a drawing design of the structure, which takes into account: half-arcs of the sides and gaps, vertical posts, fasteners, horizontal ribs, the location of the vents, doors.
Fill
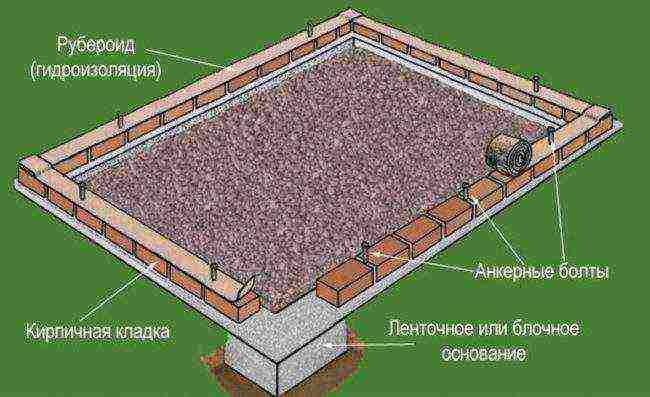
The foundation will be required to protect the soil from weeds.
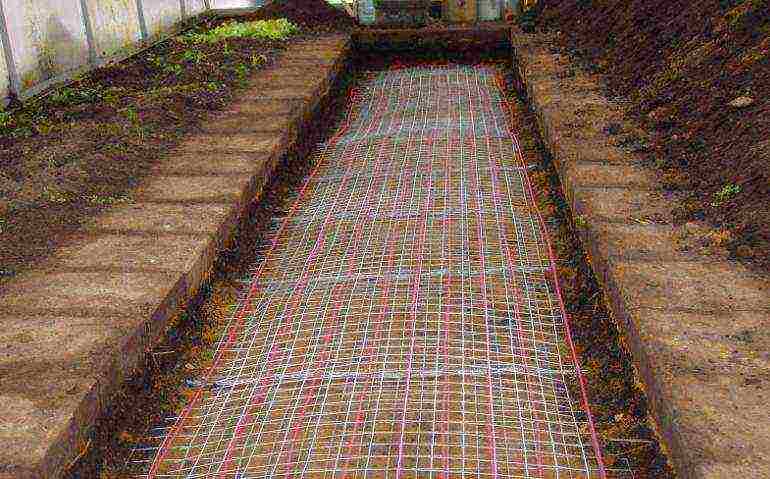
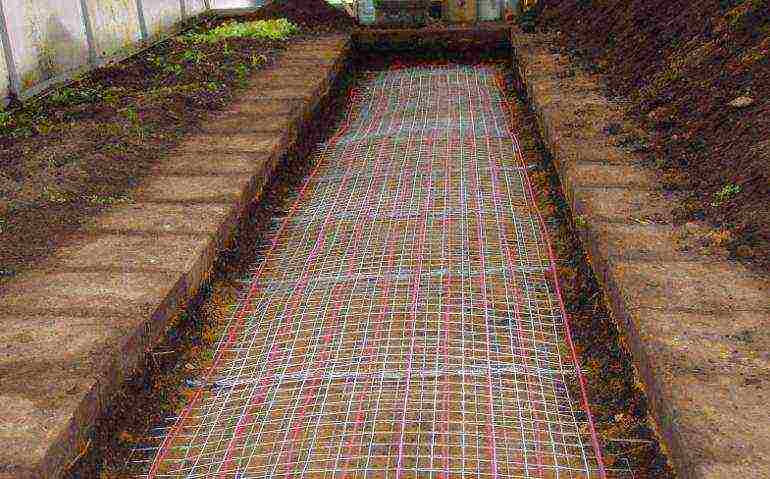
Further actions include digging a trench for the foundation, establishing formwork, embankment for a sand cushion, reinforcement with steel mesh or wire, concrete pouring.
- It is noteworthy that even at the stage of pouring the foundation, it is worth fixing the frame racks. For this, you can use pipes or metal corners.
- Distance between supports - 1 meter.
- After installing a solid frame, the surface is covered with polycarbonate.
Soil preparation

Before planting a vine, you need to prepare a hole for each seedling.
The first step is to prepare the soil for planting seedlings.
- First you need to decide on the location of the vine, that is, where it will be located - inside the greenhouse or outside, but regardless of where the vine will grow, the rhizome should only be in closed soil.
- The soil should be balanced with the necessary nutrients, while containing sufficient drainage mixture to filter air and water.
- Possible composition of the potting mix - earth, sand, loam, peat, chalk powder.

Our editor-in-chief is at work!
Landing

Before planting, the lateral shoots must be removed and only strong shoots should be left.
Young seedlings should be planted in February.
- Directly disembarking is carried out in the same way as on the open ground - hole with a diameter and depth of fifty centimeters, where top dressing is applied, fertile soil, a mound is formed on which the roots are straightened.
- Compost, manure, humus are introduced into the pit.
- The root zone is covered with mulch and watered abundantly.
- The distance between the novosads should not be less than fifty centimeters. Most often they are planted at a distance of seventy centimeters from each other, but this is in case there is a lot of free space for planting.
Care

After planting, the vineyard bushes need watering and fertilization.
Further care consists of systematic watering, eliminating weeds, sanitary pruning, preventive measures against fungal and other diseases.
But timely normalization of the brushes is also necessary, since the most comfortable conditions are created inside the greenhouse in order to provoke possible overloads.
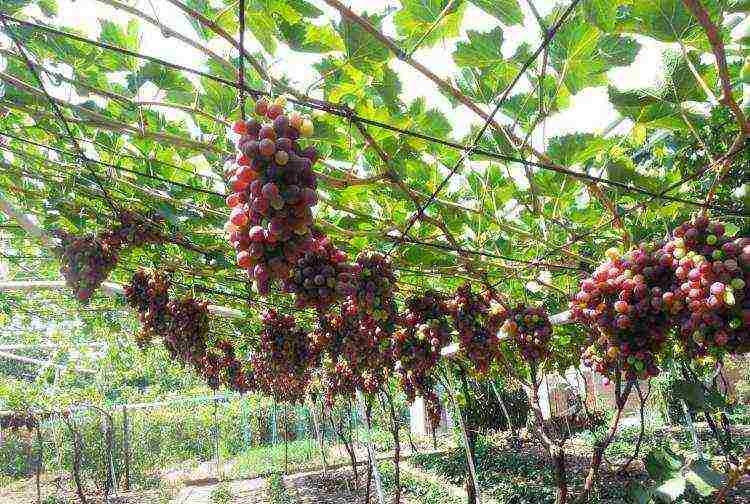
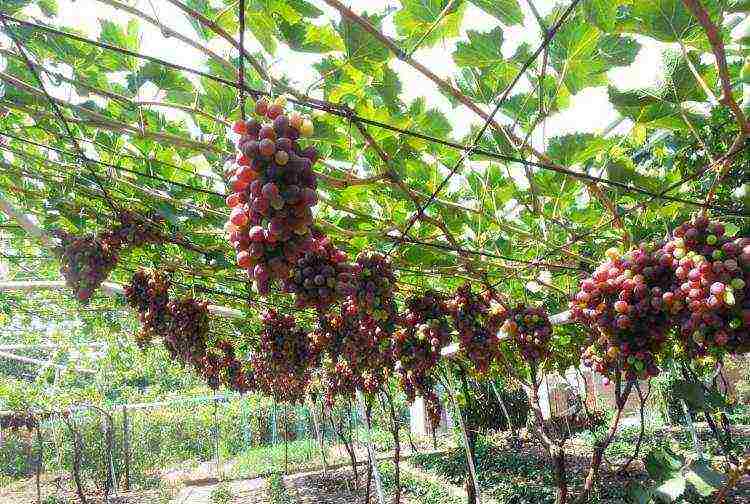
Do-it-yourself grapes will always find a place on your kitchen table - either as sweet, large and tasty berries, or as homemade wine. In addition, surplus grapes can always be sold or donated to your friends and acquaintances.But how to achieve a bountiful harvest of this crop in the middle lane, where light and heat may be lacking? The solution to this problem is to grow grapes in a greenhouse.

Growing grapes in a greenhouse
Why grow grapes in a greenhouse?
Compared to open ground, growing grapes in a greenhouse has many advantages. This is especially pronounced if your land plot is located in middle latitudes or slightly north of them.
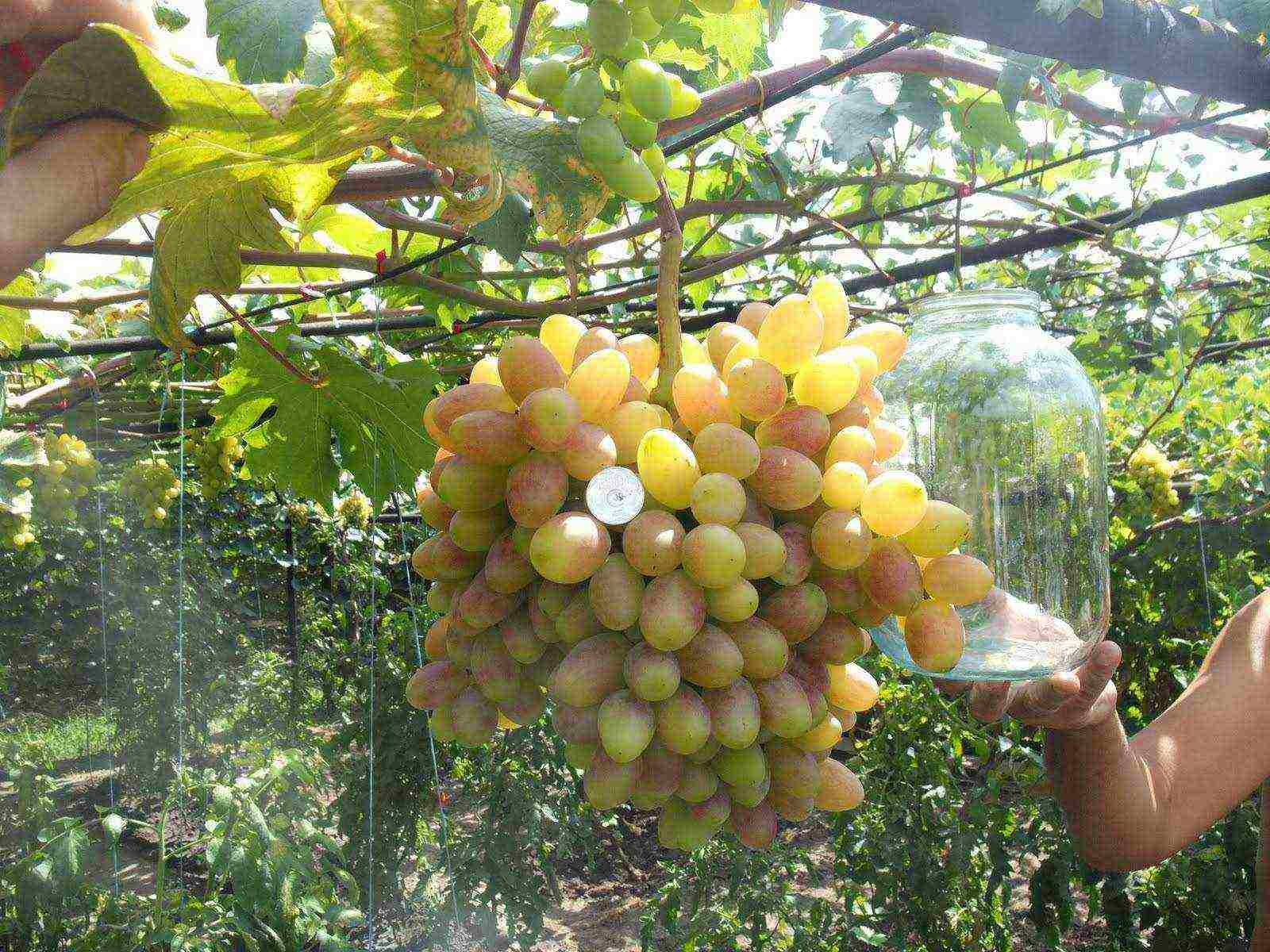
- Creation of favorable temperature conditions - even without artificial heating, the greenhouse will be 2-5 degrees hotter. To humans, this may seem insignificant, but for grapes it is very important.
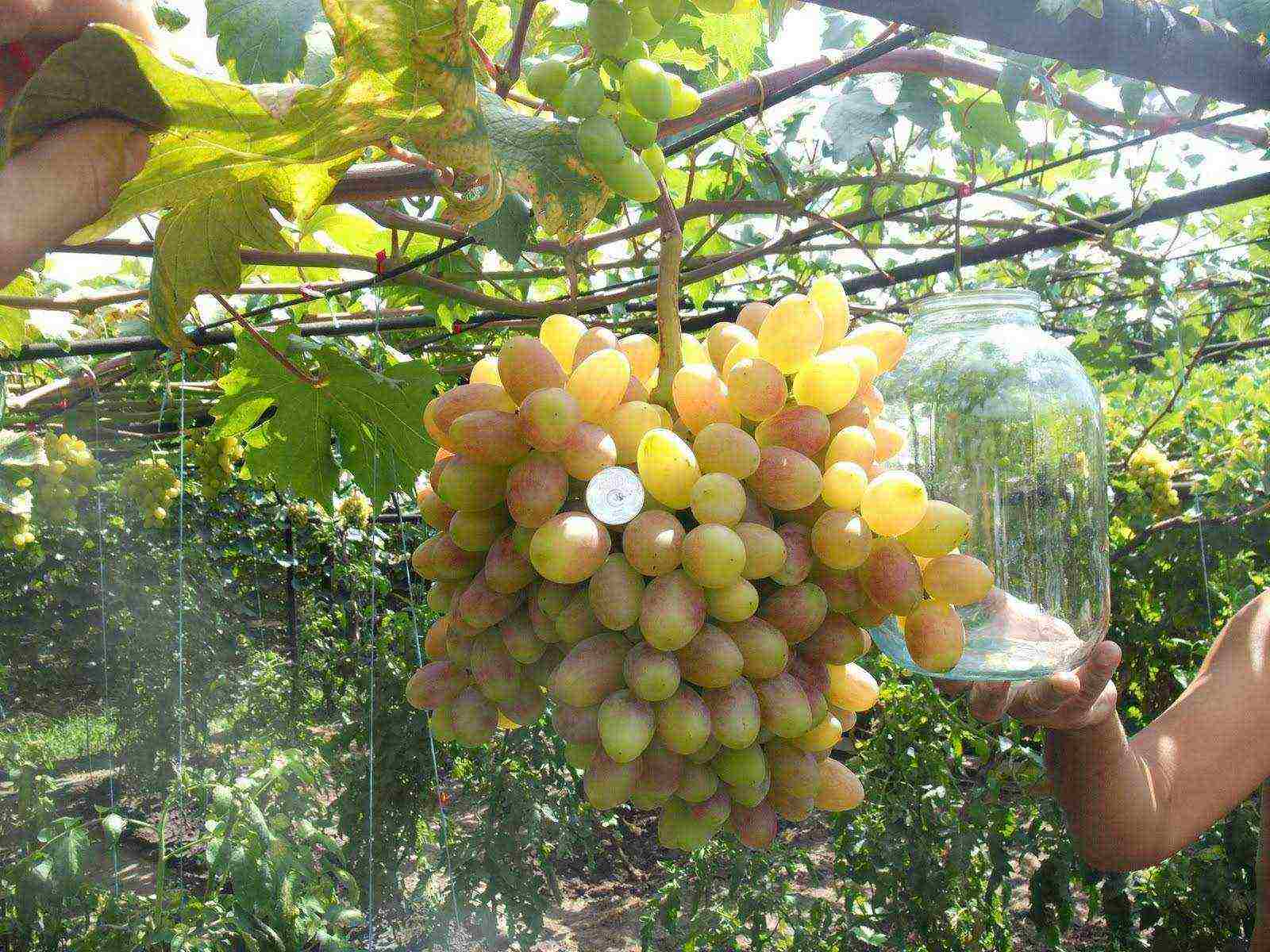

Greenhouse grape growing increases yields
- The ability to get the harvest earlier - with the correct cultivation technology and favorable conditions provided by the greenhouse, the harvest can be obtained 2-4 weeks earlier than in the open field. This is especially important for late grape varieties, which do not have enough warmth outside the greenhouse for this.
- No problems with insects and diseases - the greenhouse will partially solve the problem with wasps that damage and eat berries. In addition, mildew or powdery mildew are extremely rare indoors.
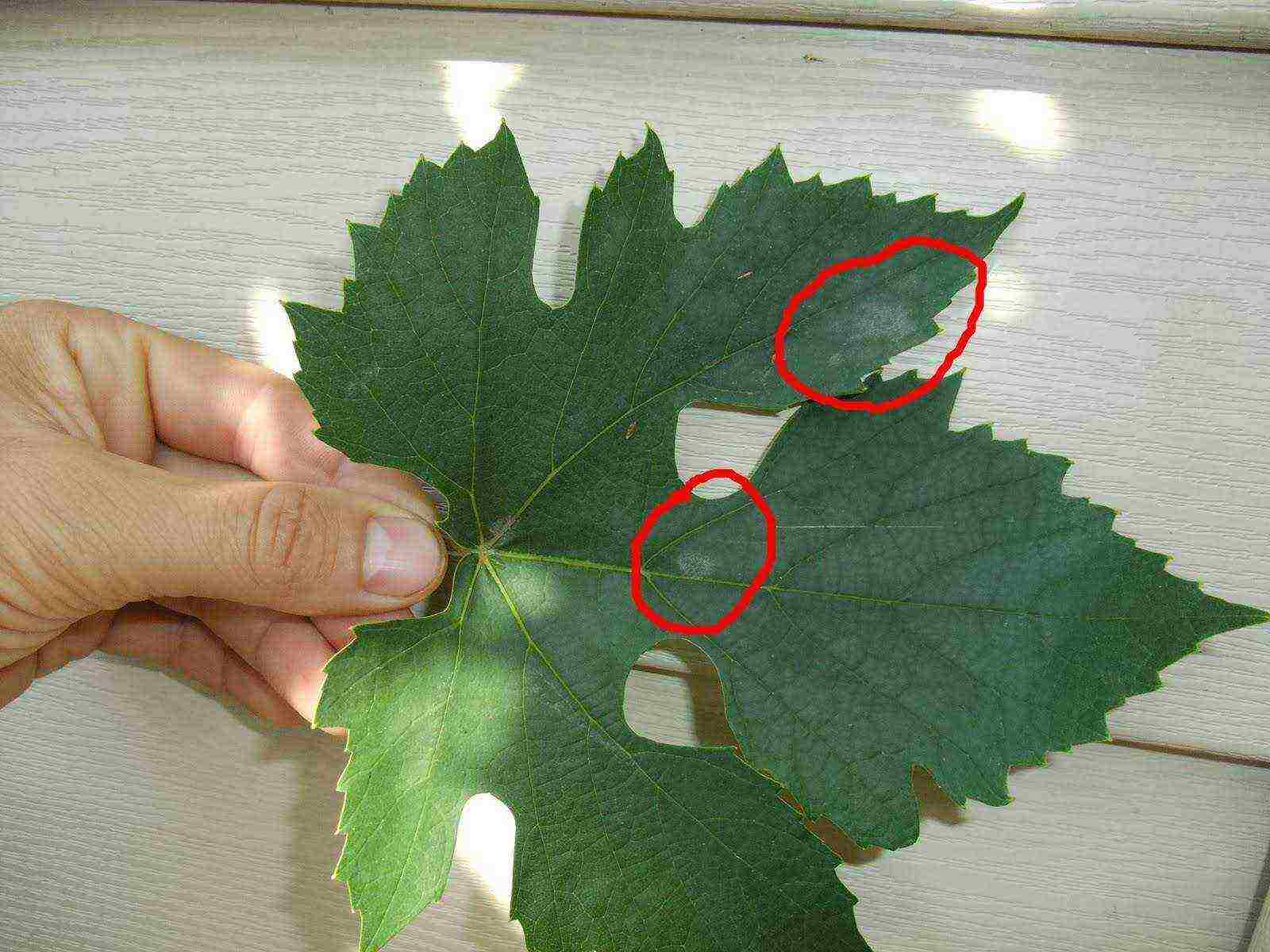
Oidium on a vine leaf
- No need for chemical treatment - since the grapes in the greenhouse are protected from diseases and plants, then they need to be processed much less often. As a result, the cost of berries is reduced, their safety and environmental friendliness increase.
- Frost protection - the casing and foundation of the greenhouse will protect the plants inside from sudden changes in temperature. This is especially important for those grape varieties that do not have sufficient cold resistance.
- No problems with berry cracking - there is no precipitation in the greenhouse, optimal values of temperature and humidity are maintained.
- High yield, which depends on the density of planting seedlings (from 4 to 8 kg of berries per square meter of the greenhouse).

Grapes in the greenhouse
- Convenient working conditions - there is no gusty wind in the greenhouse, it is not so cold in autumn or winter. And with proper arrangement of trellises, the harvesting process will be significantly simplified.
- The ability to use the greenhouse for growing other crops - Strawberries, garlic, spinach, onions or flowers can be grown in the space between the trellis.
It should be borne in mind that to start growing grapes, significant initial investments will be required - for the purchase of seedlings, the arrangement of the foundation and the construction of a greenhouse. Also, you will need to spend a lot of effort on caring for this agricultural crop, and at the same time it will not begin to produce crops immediately. But all the costs will more than pay off with a large number of tasty and nutritious berries that you can either consume yourself or sell or use to make wine.

When growing grapes, you will have to spend a lot of time and effort on care.
Choosing varieties
The process of growing grapes in a greenhouse begins with the selection of a variety. If you are a beginner and have not dealt with such a crop before, then give preference to early and frost-resistant varieties, which are guaranteed to give a plentiful and high-quality crop in the greenhouse. These include various types of raisins, Korinka Russkaya and Michurinsky. As soon as you successfully get a harvest from early and frost-resistant grape varieties, move on to its other varieties, designed for cultivation in the southern regions, in the Kuban or in Moldova.

Grapes raisins Korinka Russian
Important! When planning to grow grapes in the Urals, North-West or Siberia, equip a greenhouse heating system and artificial lighting. They will help plants to cope with the lack of sun and heat, which will be noticeable even taking into account the microclimate of the greenhouse.
Some of the varieties that are suitable for growing in a greenhouse located in the middle lane are shown in the table below.
Table. Frost-resistant grape varieties recommended for cultivation in greenhouses.
| Beauty of the North | Dining room | 14 to 17 | 250 to 900 | -26 | White |
| Ruslan | Dining room | 17.5 to 18 | 500 to 1200 | -21 | Dark |
| Kishmish Potapenko | Dining room | 25 | 500 | -25 | Dark |
| friendship | Technical | 19 to 21 | 280 | -23 | White |
| In memory of Shatilov | Universal | 17 | 600 to 1500 | -30 | White |
| Russian Early | Dining room | 17 to 21 | 200 to 600 | -23 | Dark |
| Delight | Dining room | 19 to 26 | 500 to 2000 | -25 | White |
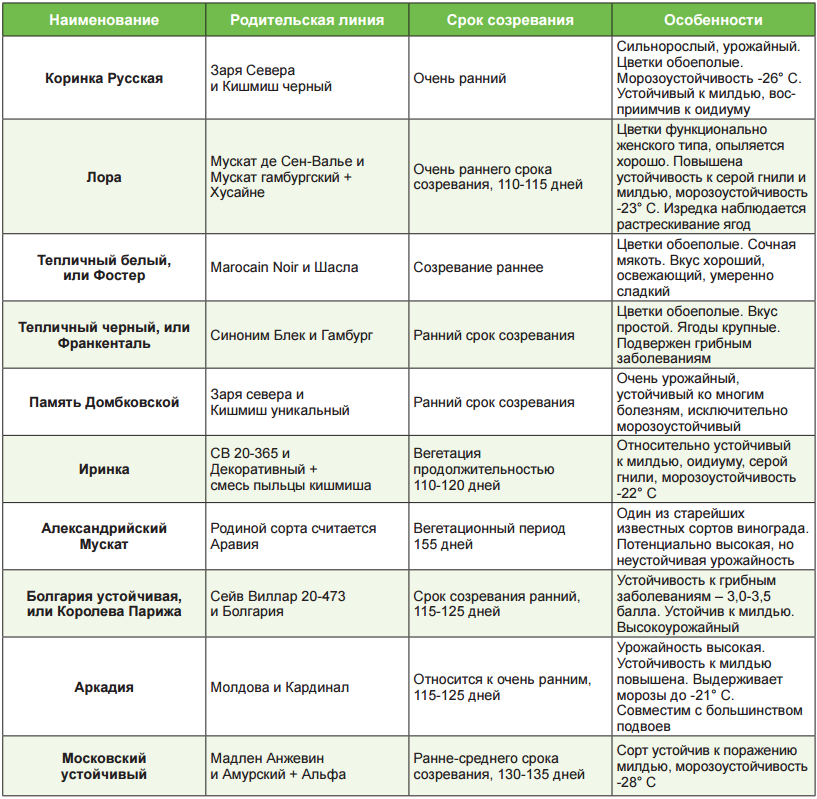
Some more suitable greenhouse grape varieties

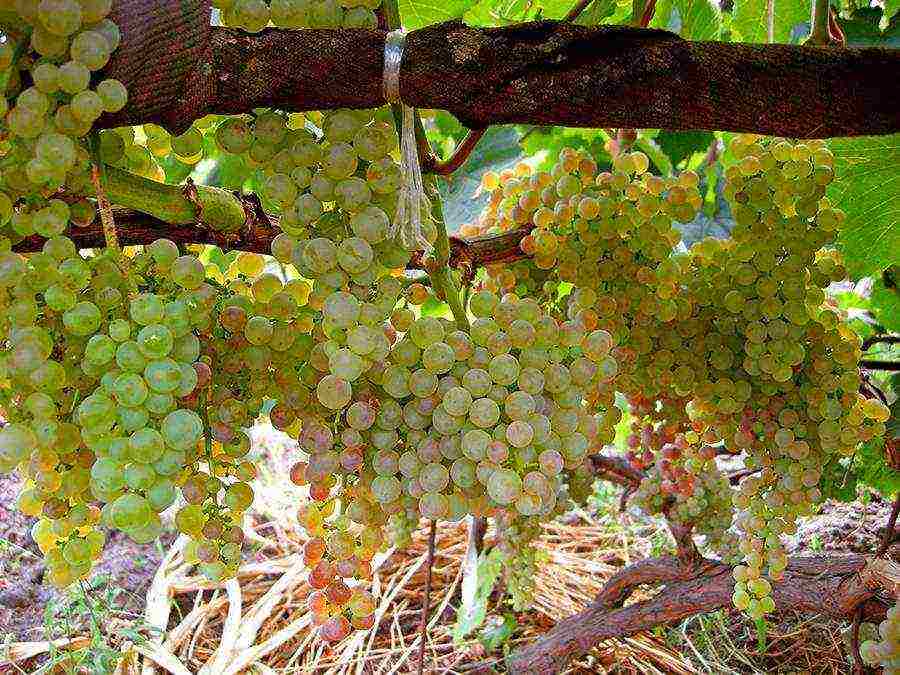
Arcadia grapes
Features of the greenhouse for grapes
A greenhouse designed for growing grapes has significant differences in its design from traditional greenhouses for tomatoes and cucumbers. Let's consider separately all the features that need to be taken into account during the construction.
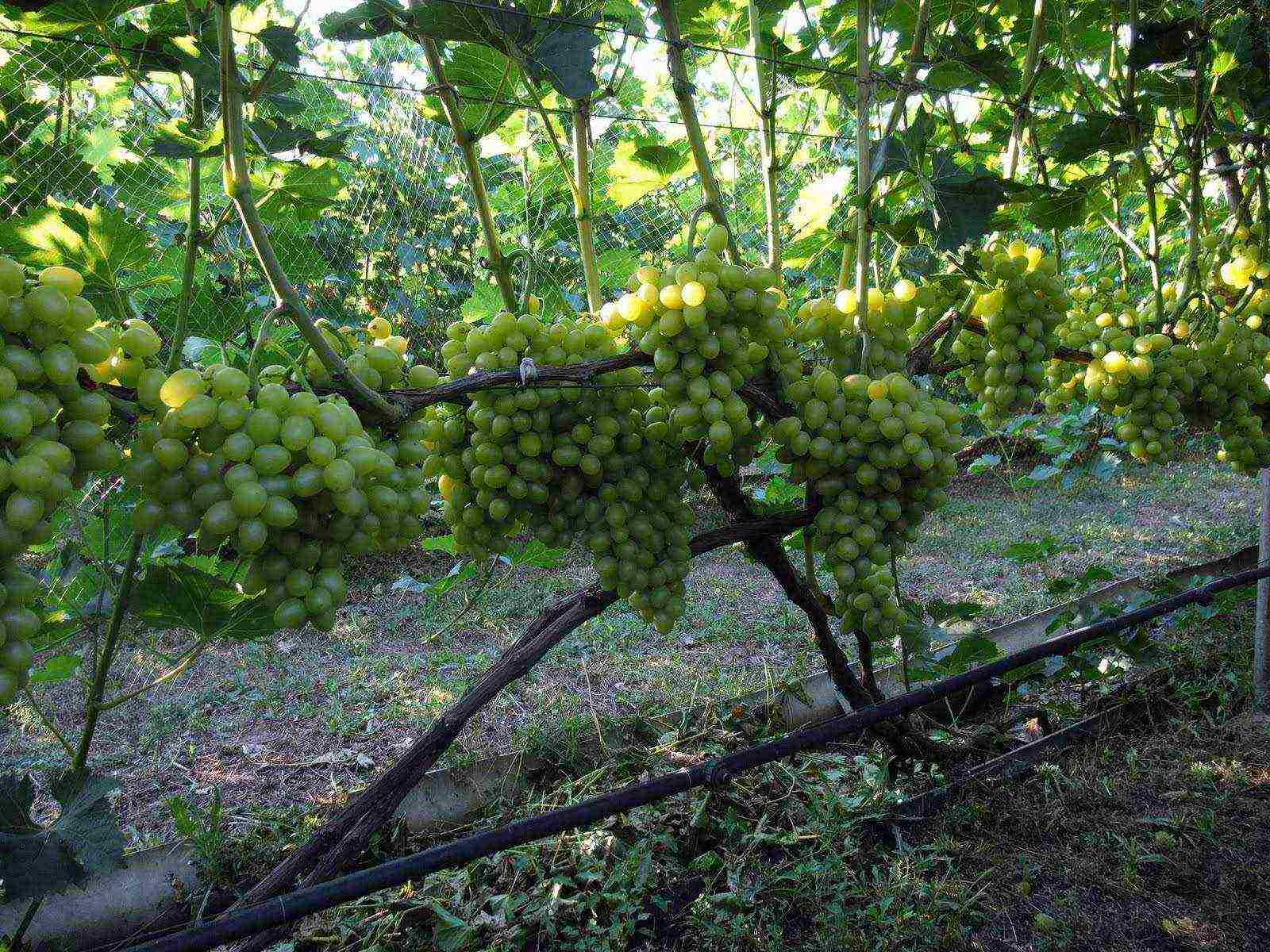
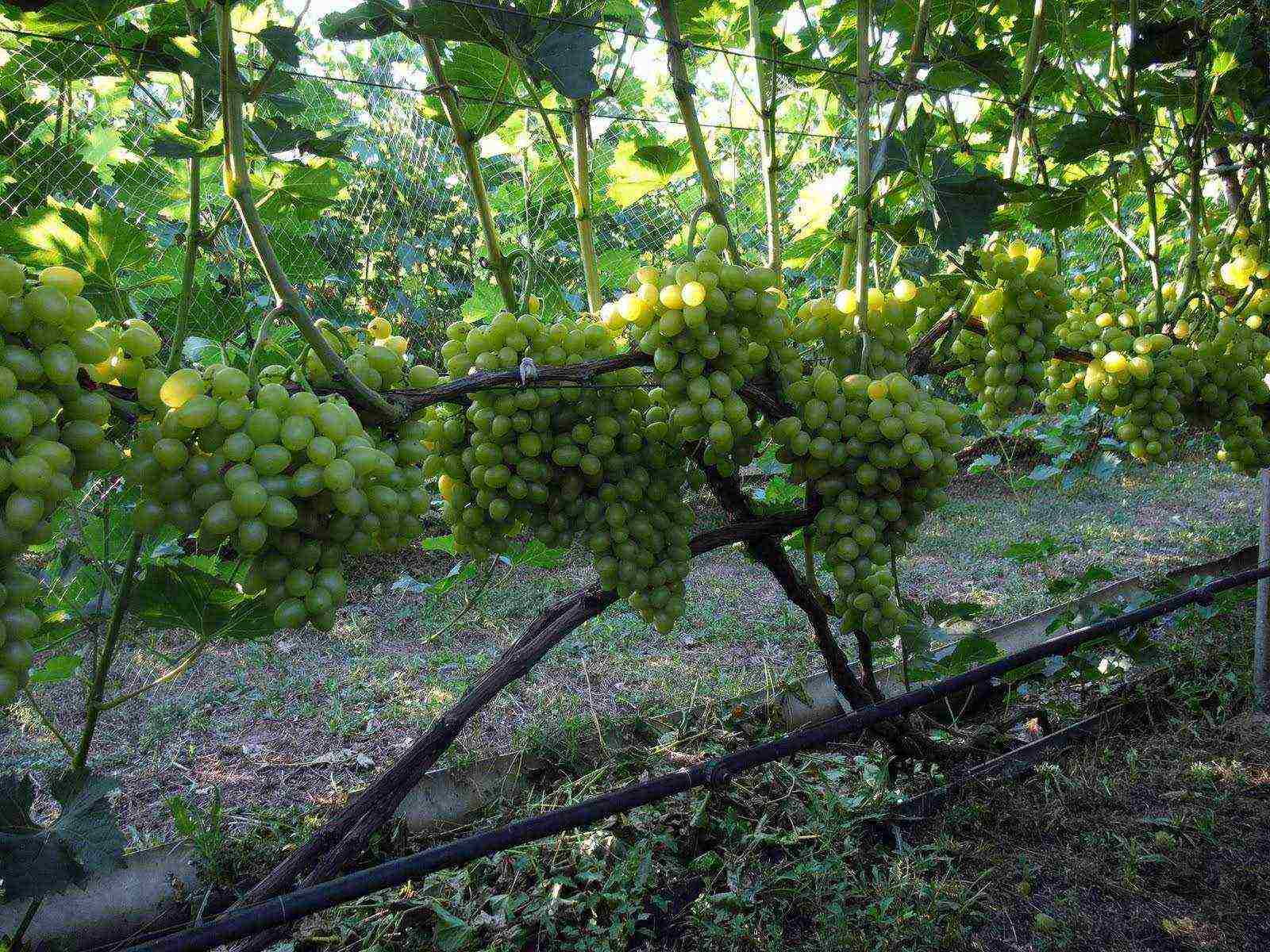
Dimensions. A greenhouse for growing grapes must have a considerable height - from 2.5 to 3 meters or more, depending on the design and size of the trellises. The optimal building area designed to meet your own need for grapes is 25-30 m2. Larger greenhouses can be used to grow berries for sale or to make wine.

Greenhouse for growing grapes
Foundation. The soil in the greenhouse for grapes must be reliably protected from freezing. In addition, without a foundation, weeds, pests and uncontrolled drafts will penetrate inside. Build a shallow concrete strip foundation.
Sheathing. For a greenhouse, it is desirable to use transparent cellular polycarbonate - a material with high light transmission and good thermal insulation properties. Plastic wrap is acceptable, but only for unheated structures.
Greenhouse example diagram
Frame. Grapes do not like haste and do not start producing a good harvest immediately, therefore the greenhouse must be durable and have a significant service life. And as a material for the frame, the optimal choice in such conditions would be a galvanized steel profiled pipe - it is strong enough, durable and easy to work with.
Heating. If it is planned to grow grape varieties that are not designed for cold weather, then the greenhouse will need heating. To do this, you can use infrared lamps suspended from the ceiling (in this case, you will need to significantly strengthen the frame of the building), or a heating cable brought under the ground of the greenhouse. For lovers of simple options, the arrangement of conventional heating radiators is suitable.
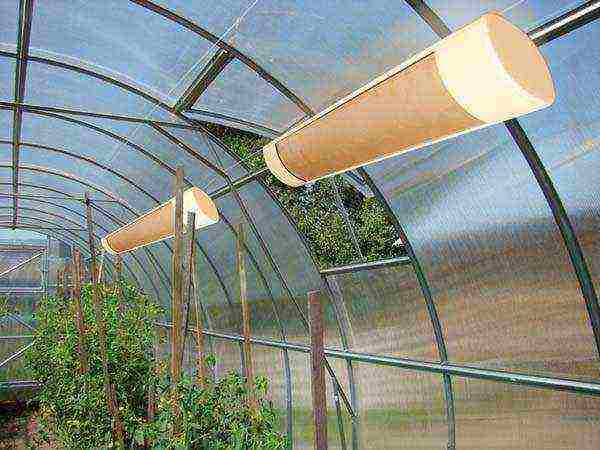

IR lamps for heating greenhouses

Heating cable installation
Lighting. Southern grape varieties in Siberia or the Northwest may lack sunlight. This deficiency can be corrected with the help of special fluorescent lamps. They are presented in luminescent, LED and sodium subtypes.
Ventilation. For a small greenhouse, designed for growing grapes for own consumption, two vents located in the gables of the building will be enough. If it is planned to produce berries or wine for sale, then the greenhouse should be larger, respectively, the number of transoms should increase. To ensure an optimal microclimate, equip all vents with thermocylinders that open and close the flaps at a certain air temperature inside.
Photo of a bimetallic element of automatic greenhouse ventilation
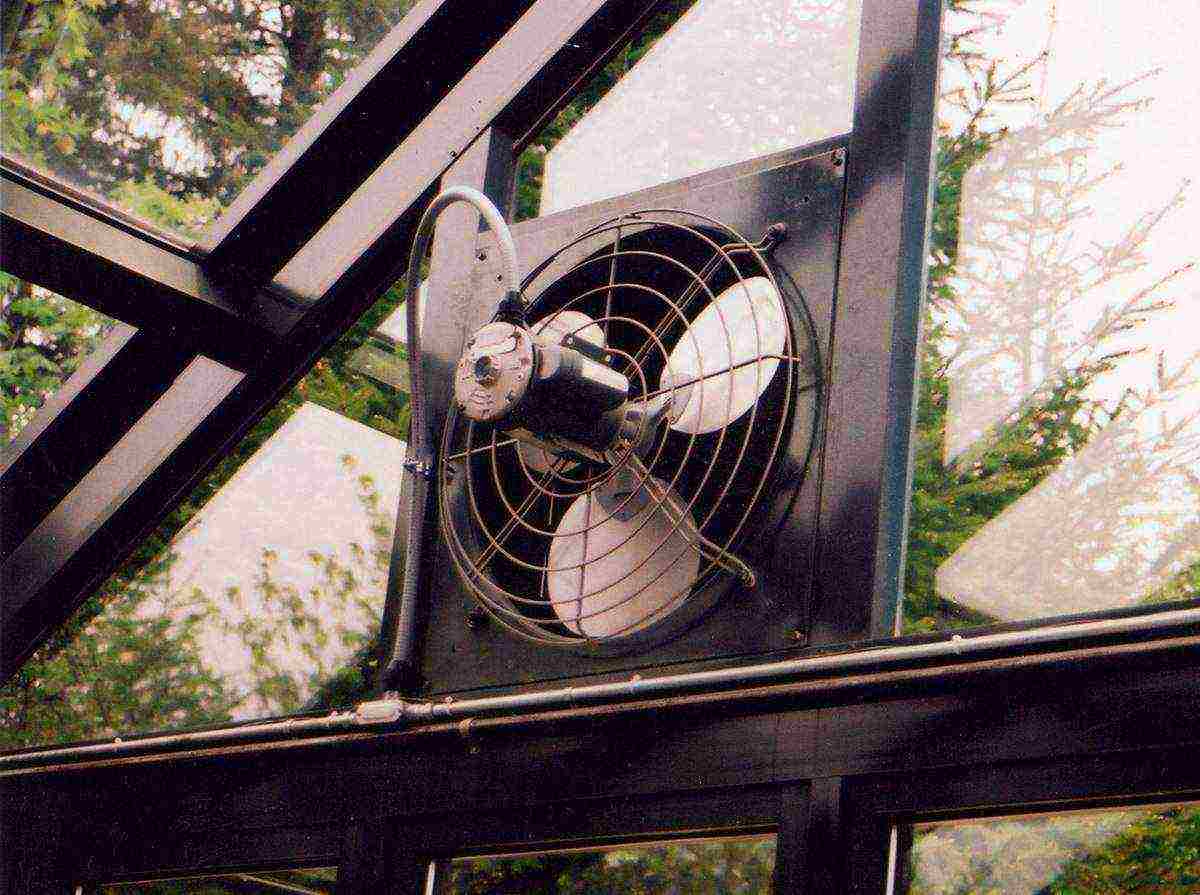

Special fan for greenhouse
Important! Unlike other crops, grapes do not require frequent watering. But with its manual (watering) implementation, you have to spend a lot of labor and time. The arrangement of an automatic irrigation system controlled through a conventional valve or a special microcontroller will help to partially solve this problem.
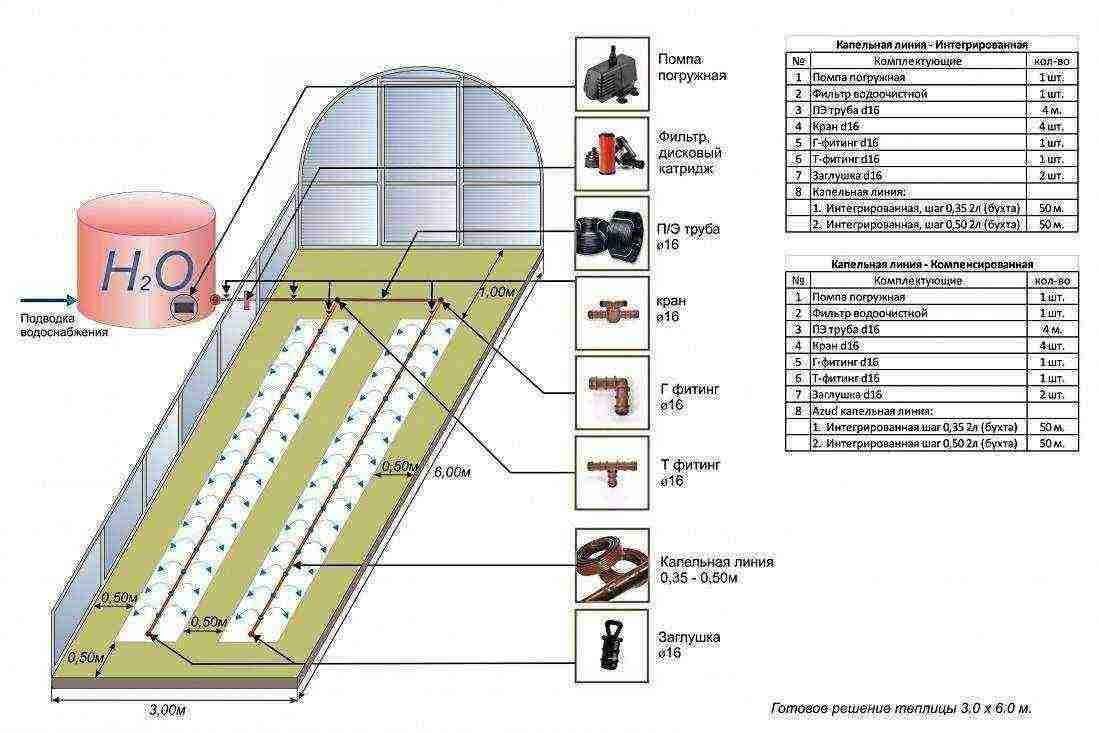
Drip irrigation in the greenhouse
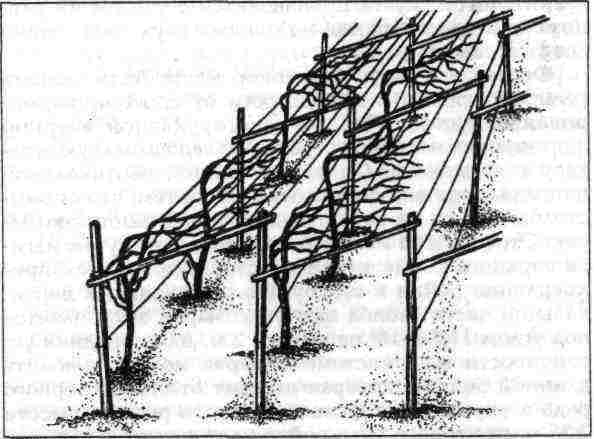
Do-it-yourself greenhouse trellis
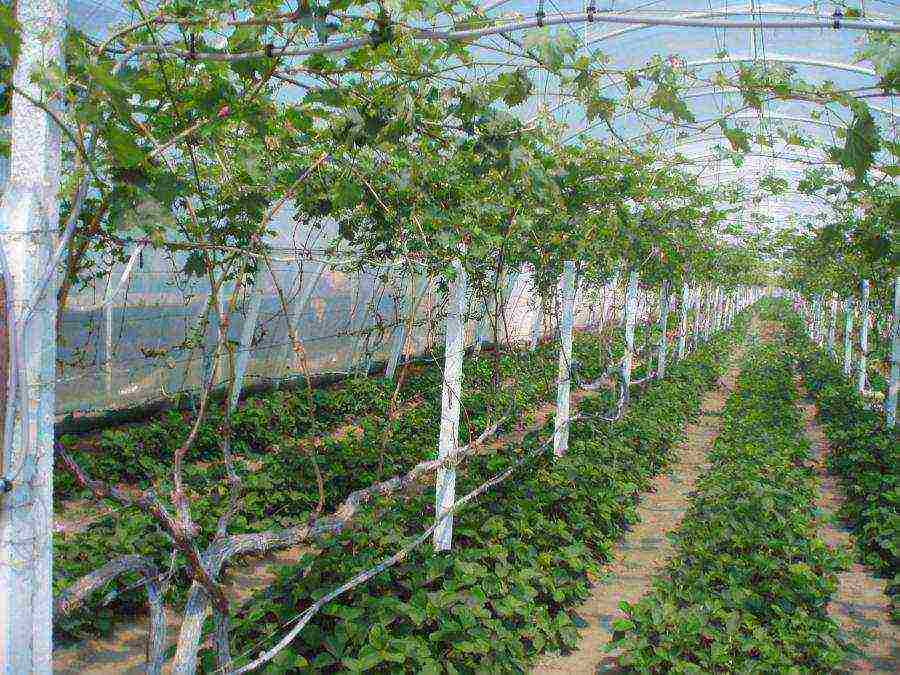
The main element of the greenhouse for growing grapes are trellises - trellises that serve as a support and a means of controlling the direction of growth of agricultural crops. There are many varieties of this design, vertical single-plane and horizontal T-shaped trellises are best suited for use in a greenhouse. Let's see how they are created.

Trellis for growing grapes in the greenhouse
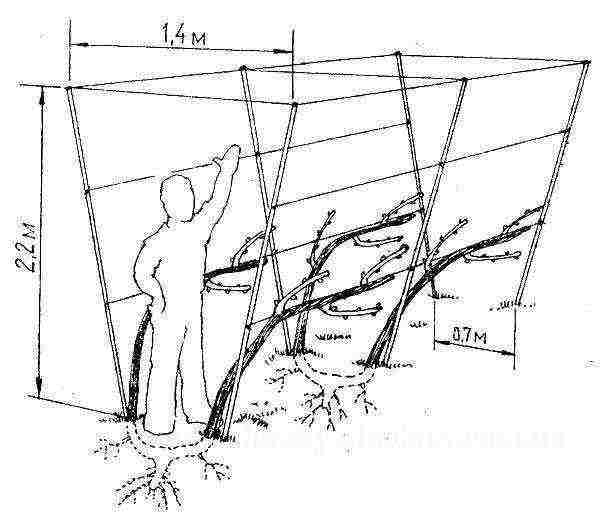
Roughly speaking, vertical single-plane trellises are a fence made of wooden pegs or metal pipes, between which a wire is stretched with a certain pitch. The vines are attached to the wire and shaped in a certain way.
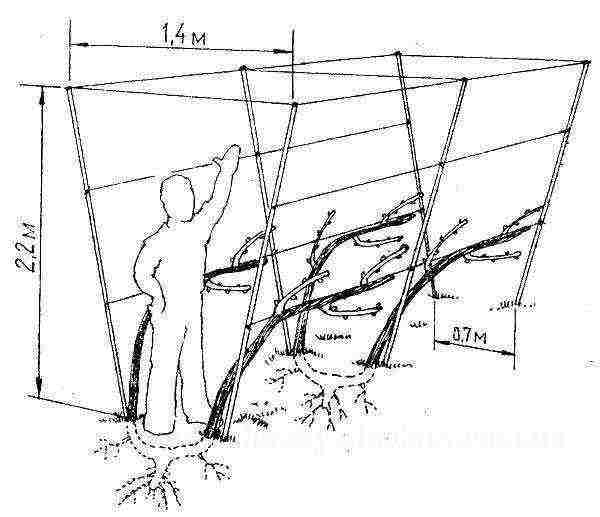
Scheme of an example of a trellis for grapes
As a result, it becomes possible to grow a larger number of bunches per unit area and, accordingly, to obtain bountiful harvests. You can equip vertical trellises as follows.
Step 1. Inside the greenhouse, mark out the places for the pegs.
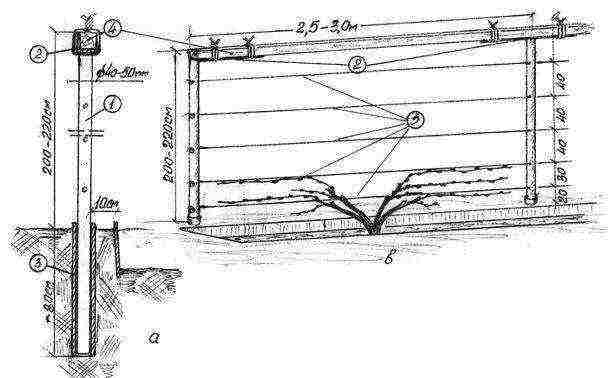
Step 2. Drive in stakes or pipes at the desired points. For the first, use a beam of 50x50 mm, for the second - steel pipes with a cross section of 7-10 cm.The depth into which they are driven is 1-1.5 m, the height of the trellis above the ground level is 3-3.5 m. The distance between the individual stakes or pipes - from up to 6 m.
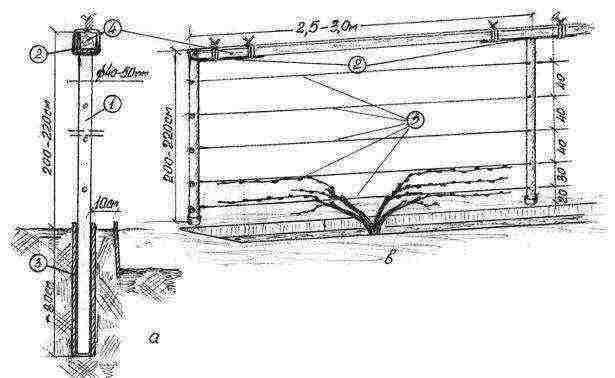
An example of a vertical trellis for grapes with a seedling in a trench
Important! Processing wooden stakes with protective compounds is undesirable - these compounds can subsequently harm the vine, leaves or berries. Copper sulfate is a safe alternative.
Step 3. At a height of 50 cm from the grape seedling, pull a wire with a cross section of 3 mm. Attach with wire loops, nails or metal staples.
Step 4. Pull the second one 35-40 cm above the first wire.
Step 5. Repeat step # 4 two to four more times (depending on the required height of the trellis).
Step 6. At a distance of at least 0.5-0.75 m, start installing a new trellis.
Advice! The arrangement of the cornice will help to increase the useful area of the vertical single-plane trellis, as in the image below.
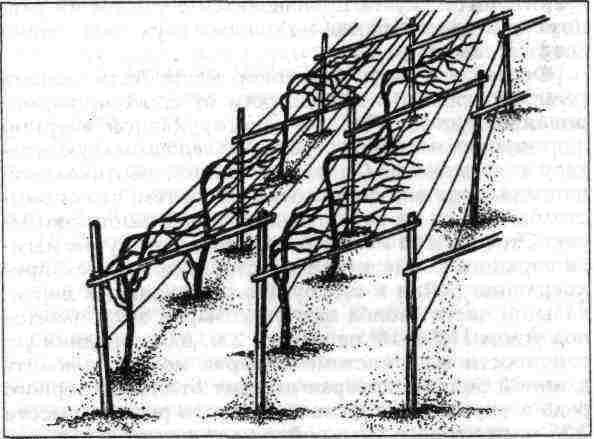
Vertical tapestries with cornice
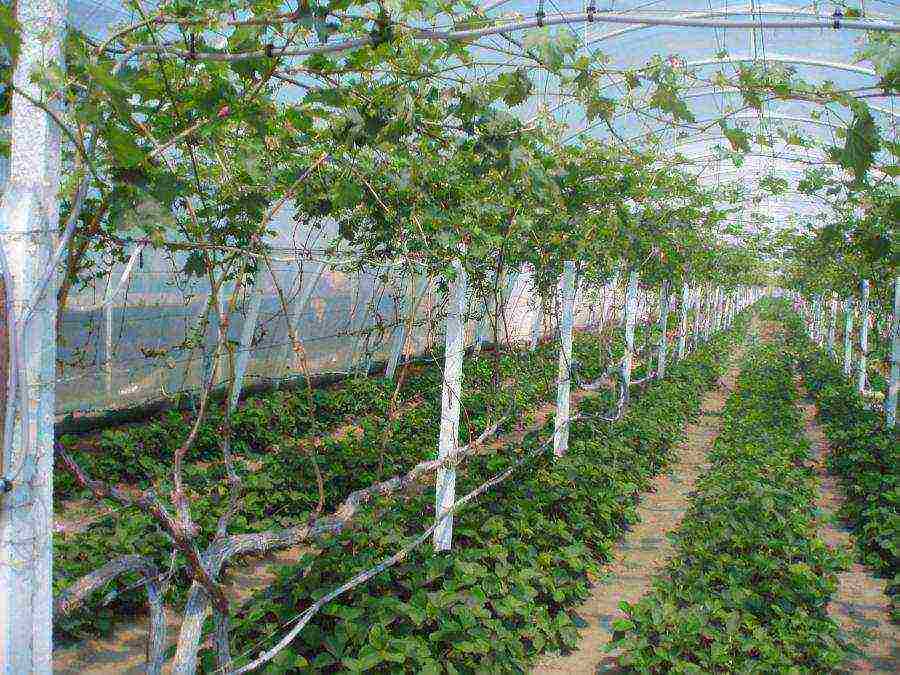
Horizontal trellises are arranged somewhat differently. They can be either T-shaped supports, between which a wire is stretched at intervals of 30-40 cm, or a lattice using thick metal pipes as a support. The latter design turns out to be quite complex and heavy, but at the same time very convenient for harvesting - bunches of berries hang at the level of the head of an average person and there are no problems with removal. In addition, strawberries or other similar crops can be grown under these horizontal trellises at the same time.

T-shaped trellis

An example of growing dark grapes on a horizontal trellis
Important! Regardless of the design, the upper rows of the trellis should not be closer to the greenhouse cladding than 30-40 cm. Otherwise, there will be a risk that the grapes will get sunburn.
The upper part of this vine bush is on the gazebo, the lower part is like a single-plane trellis
Planting grape seedlings
It is necessary to start planting seedlings in late winter or early spring, it all depends on the grape variety and its frost resistance, while the plant material must meet the following requirements:
- absence of fungus and diseases;
- strong and healthy roots;
- lack of mechanical damage;
- no traces of freezing.
The place for planting the seedling should be no less than 30-50 cm from the greenhouse sheathing. The interval between plants in a row depends on the specific variety and can reach from 0.5 to 1.5 m. The preparation and implementation of planting is carried out according to a certain technology.
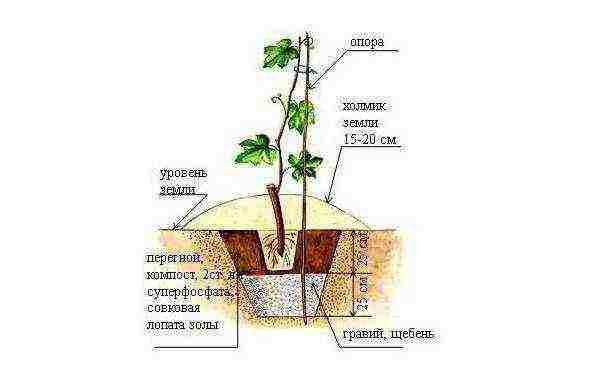
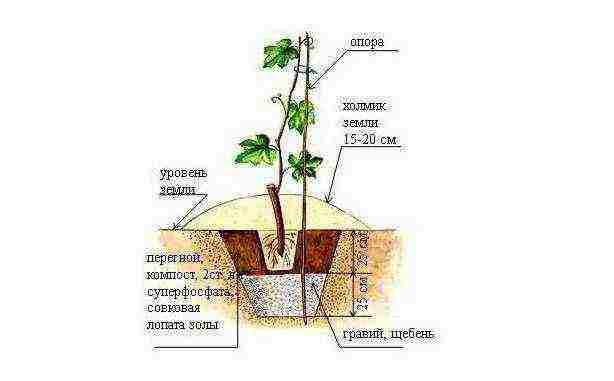
Step 1. Dig a hole 80x80 cm and a depth of 70 cm. It is advisable to equip the trellises at the same stage.
Scheme of a finished hole with a grape seedling
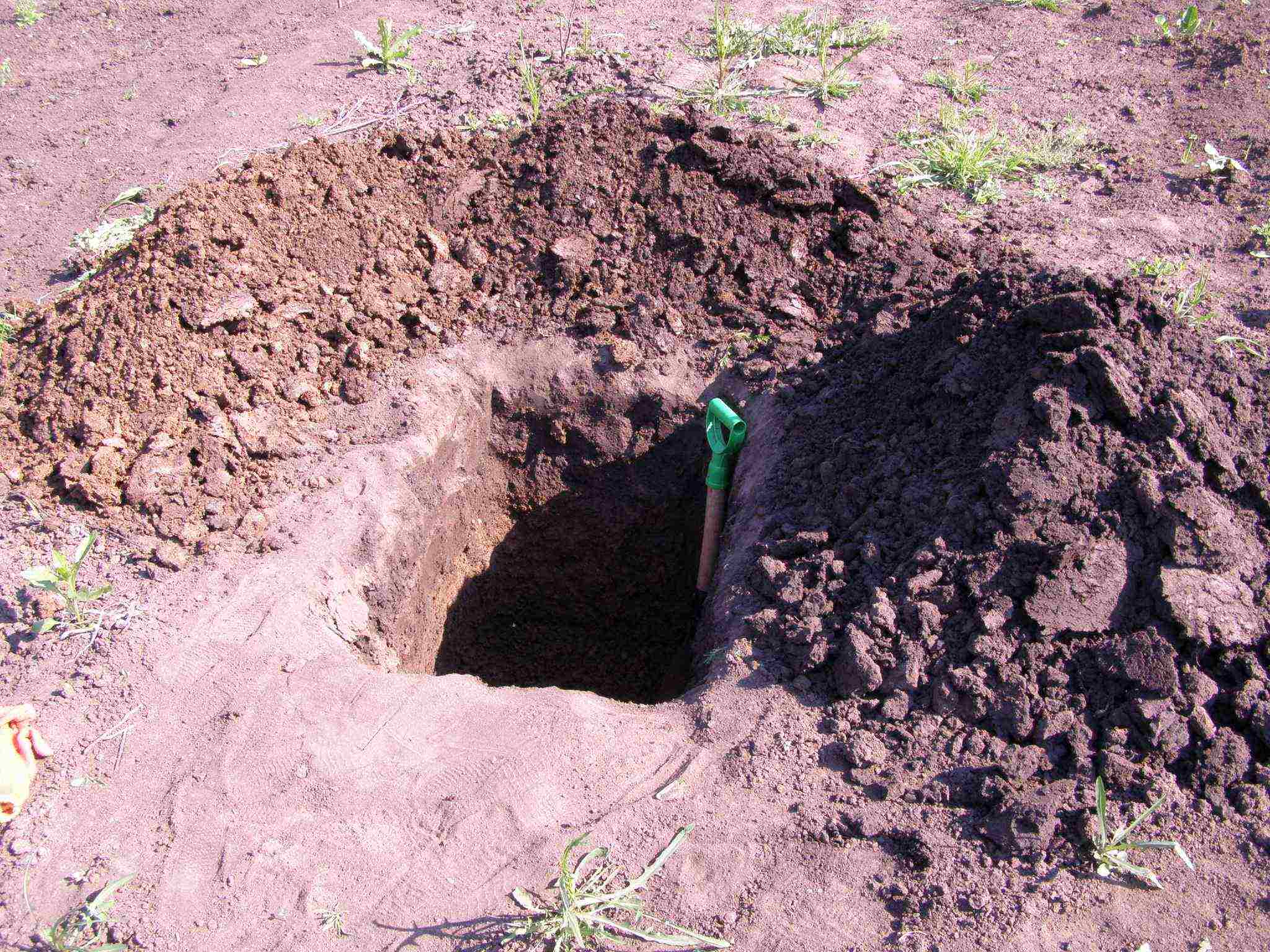

The depth of the pit should be 70 cm
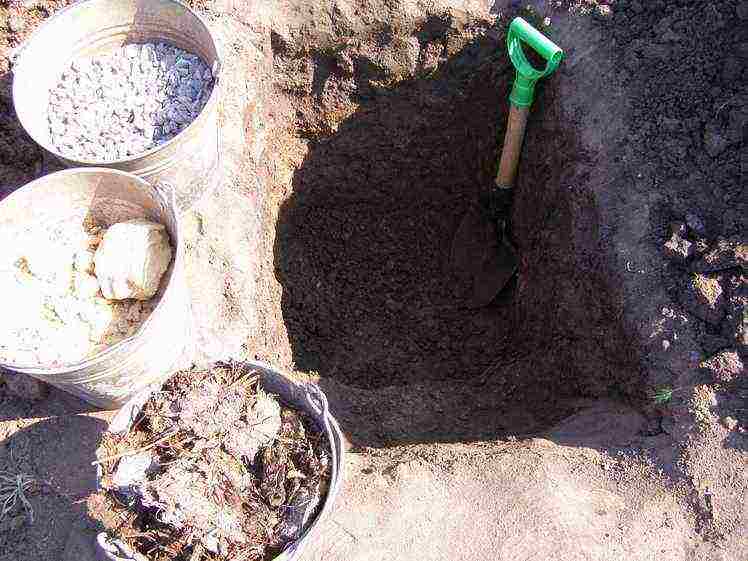

How to prepare a planting pit for grapes
Step 2. Place a quarter of a bucket of wood ash on the bottom.
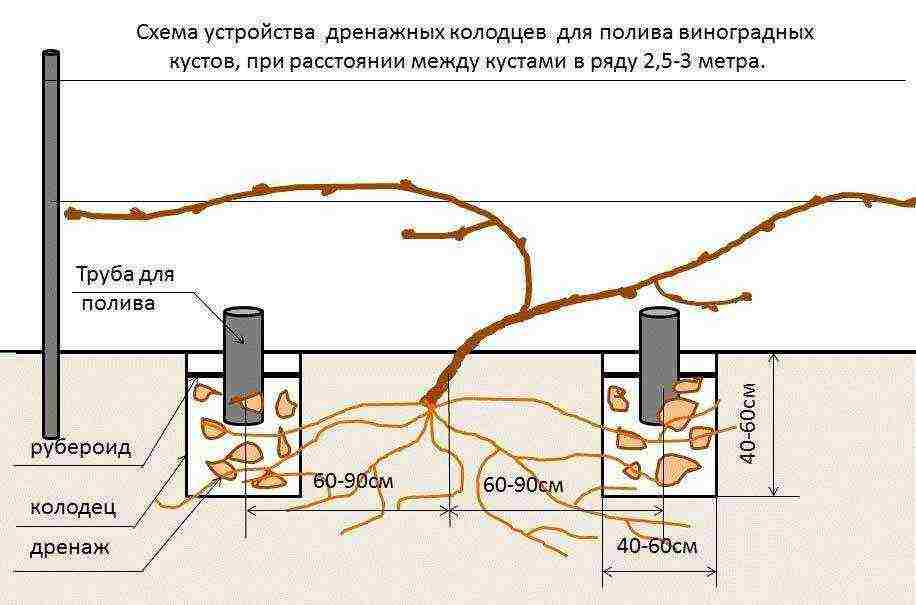
Step 3. Equip a drainage layer with a thickness of 20 cm. To do this, fill in expanded clay or gravel. Insert a 10-12 cm tube into the resulting layer, which will be used for watering. Its height above ground level should be at least 5-10 cm.
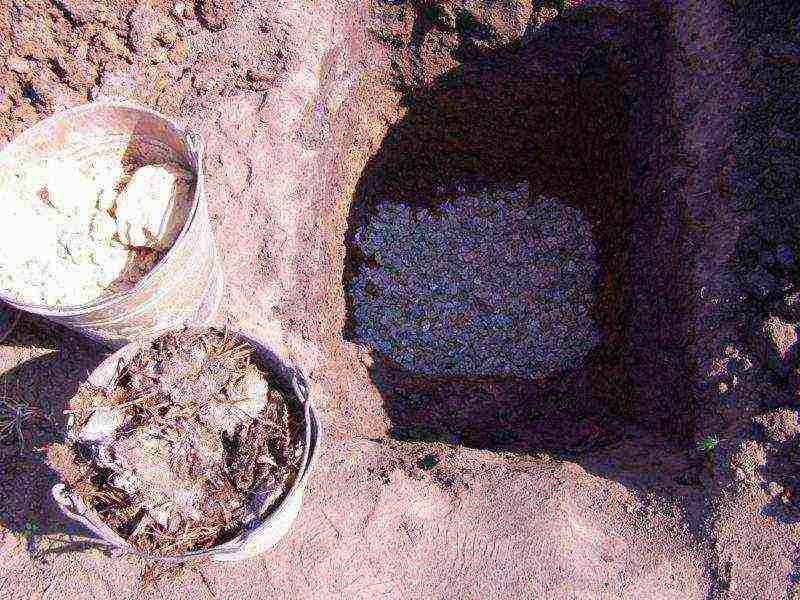

Drainage layer
Important! The drainage layer does not have to be arranged directly under the future seedling. It can be arranged nearby, at the entry point of the irrigation tube. In this case, the depth of the pit directly under the seedling is reduced to 50-60 cm.
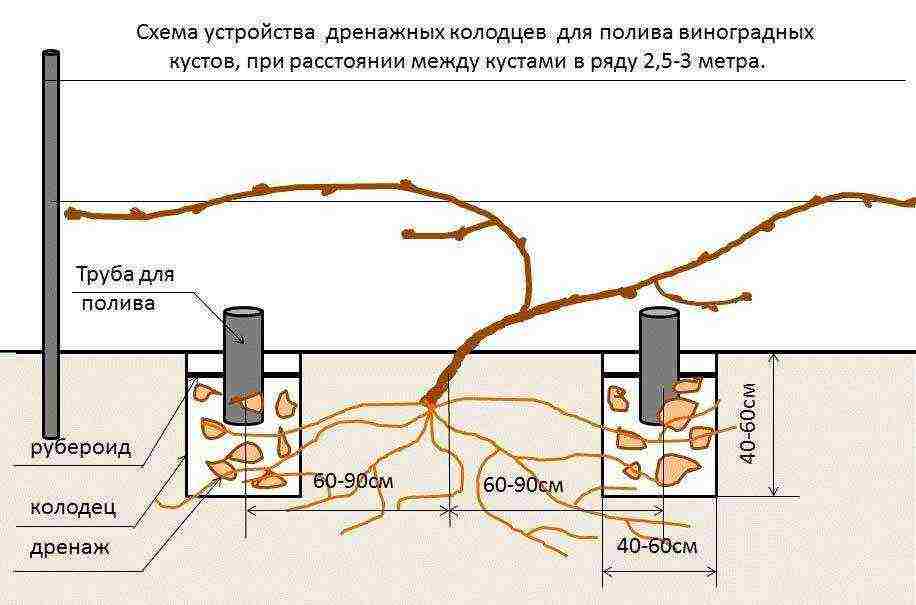
Arrangement of pipes for irrigation and drainage layer
Step 4. Prepare the seedling substrate. There are two recipes. In the first, 1 part of sand is used for 2 parts of humus and 5 parts of fertile soil. In the second recipe, for 1 unit of sand mass, 2 units of peat and 4 units of loam are taken. Add fertilizer or lime to the substrate (the latter is taken from a ratio of 100 g per bucket).
Step 5. Pour the substrate into the hole with a layer 20 cm thick and pour water over it. If the substrate has settled and decreased in volume, add more.

Backfilling of the substrate
Step 6. Plant the seedling in the soil, straighten the lower root system and add another 15-20 cm of substrate on top. As a result, the remaining depth of the hole should be 10-20 cm. Orient the seedling parallel to the greenhouse sheathing.

Planting a seedling
Planting scheme for seedlings
Advice! To plant a large number of seedlings, you can dig a trench of appropriate depth, width and length.
If you plan to plant a seedling not in spring, but in autumn, take care of it with the right shelter for the winter.
Grape care and pollination
The main principles of ensuring good conditions for grapes are the right temperature, access to sunlight and the formation of shoots.
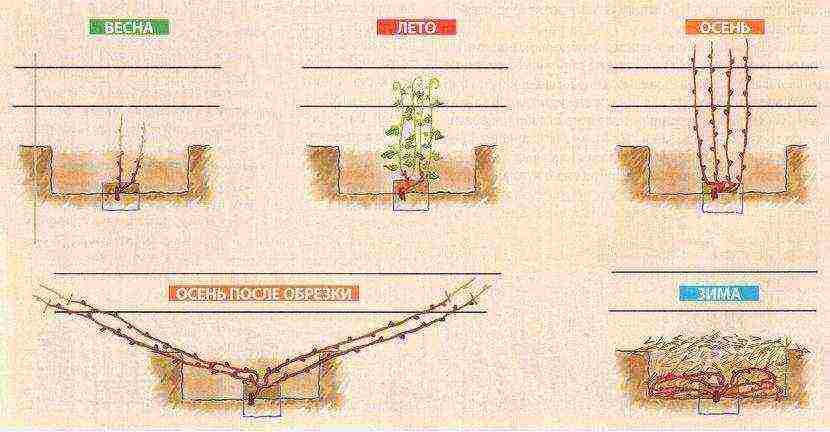
Diagram of the vine care cycle
The temperature is regulated by heating and ventilation. The optimal regimen for grapes depends on the stage of growth. So, in the spring, at the stage of bud formation, the plant needs + 10-20 ° C during the day, at least +8 ° C at night. During the flowering period, the optimum temperature during the day is + 25 ° С, at night + 15 ° С. And when the berries begin to ripen and fill with juice, it should be a little hotter in the greenhouse - + 30 ° С during the daytime and + 18-20 ° С in the dark. When using artificial heating, try to reproduce these cycles so that the plant is not stressed and produces the best yield.

The optimal temperature regime for grapes depends on the stage of growth.
Important! The above values for optimum temperatures are general. More accurate values depend on the specific grape variety, therefore, before choosing each of them, read in detail the description and experience of working with one or another species.
Providing access to sunlight is achieved through the correct design of the trellises and their correct location. In addition, make sure that the vines on the lower wires are not shaded; if necessary, it is permissible to cut a certain number of sheets in that place.
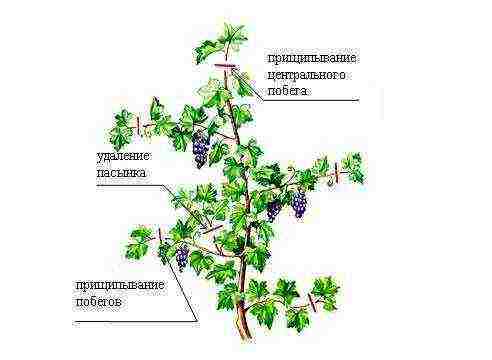
Shoot formation is a very important part of grape care. As a result, you should form strong branches with fruiting vines. Stepsons (also called second-order shoots) and weak branches should be cut to the first "eye". This way, you will not allow the plant's resources to be wasted on parts that will not yield crops. In addition, you need to trim the tops of the shoots several times each season. Forming grapes is a whole art, and for a better understanding of the process, one should consult specialists or reference literature on viticulture.
Grape care
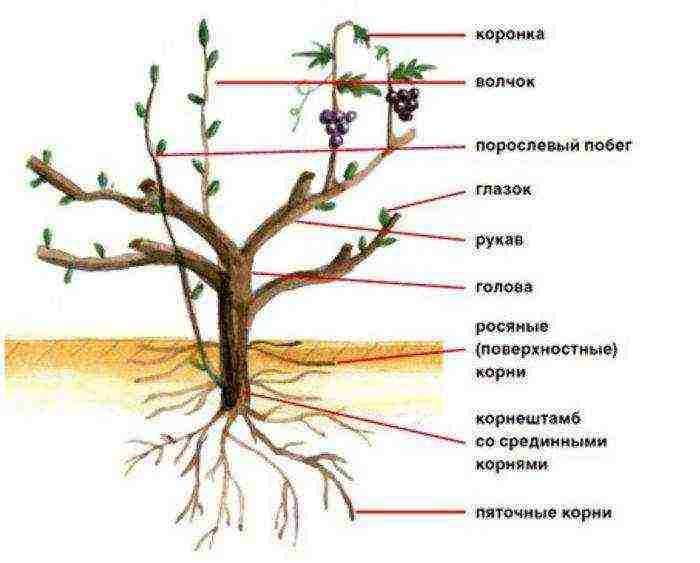
The structure of the grape bush
Inspect the bunches regularly. If damaged, rotten or diseased berries are found, cut them off immediately. In addition, sometimes it is necessary to thin out clusters of small fruits and weak branches in order to avoid overloading and “direct resources” to higher quality berries. The optimal distance between branches during ripening is from 6 to 8 mm. Carry out thinning carefully, using long and thin scissors, so as not to cause additional damage.

Thinning grapes in the greenhouse
Since in the greenhouse, most likely, there will be no bees, the pollination of the grapes must be carried out independently.Perform the event after the opening of the flowers of the plant. Everything is quite simple - light and quick blows are applied along the stem. An alternative way is to tap the flowers of one plant and then transfer the pollen on the hand to another.
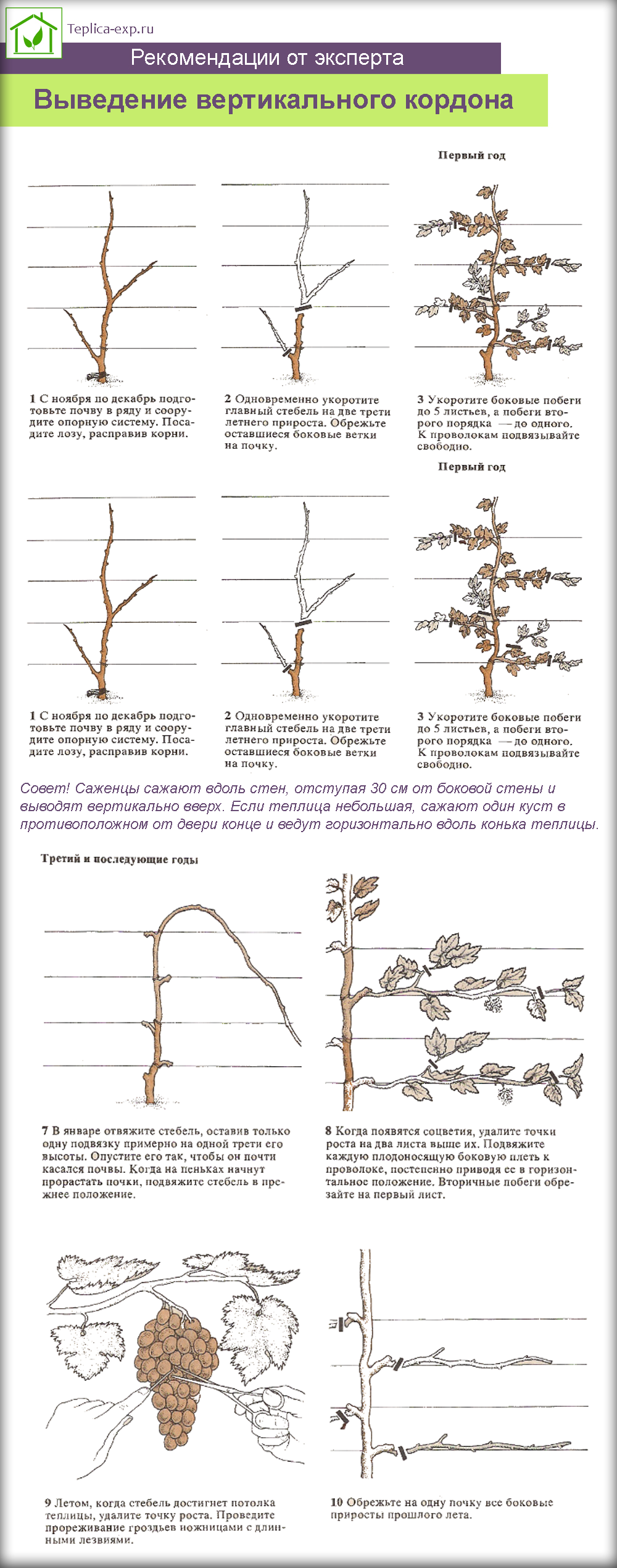
Removing a vertical cordon
Video - Growing grapes in the middle lane
Video - Caring for grapes
Watering and feeding
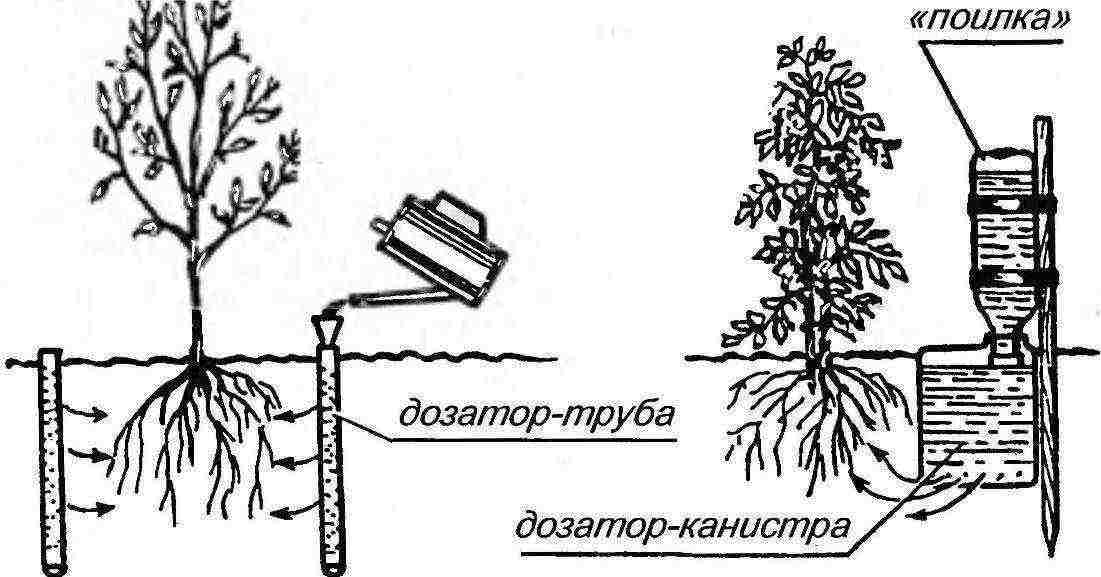
It is worth noting that the grapes do not require frequent watering. Excess moisture can damage the crop and cause the berries to crack. Perform the first watering even before planting the seedling, when forming a hole - 20 liters of warm water for each. Then the same amount - after planting, the place should be well saturated with water, but make sure that due to excess moisture the plant does not "drown" and does not start to rot.
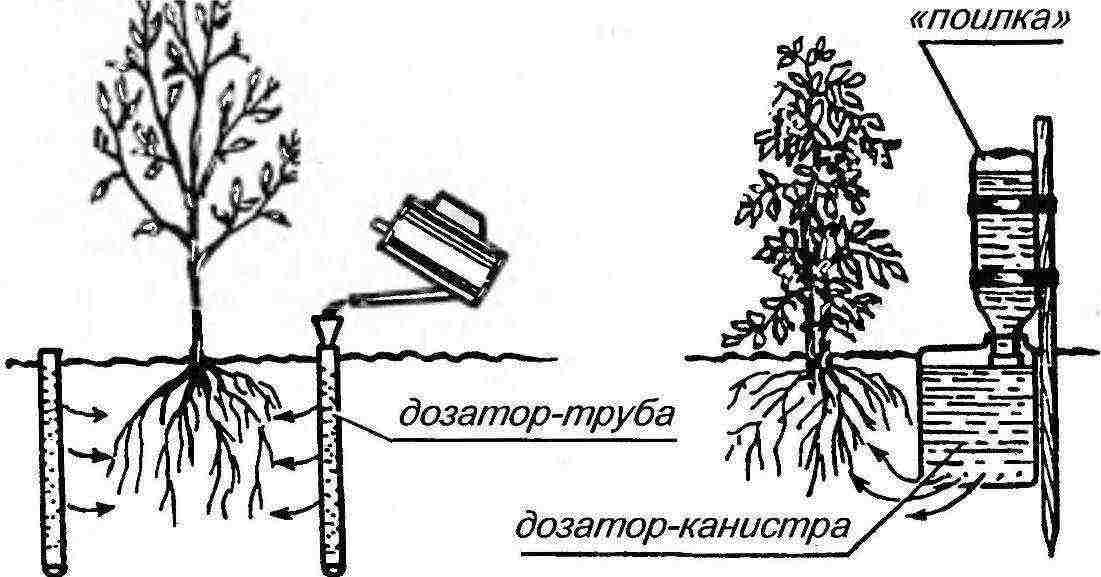
An example of a do-it-yourself subsoil irrigation scheme
After seven days, watering is repeated, while mulching the soil in the hole with the seedling is also performed. Further, in the summer, the grapes are supplied with water once a week, watering should be done either in specially dug holes and grooves, or in a tube inserted into the drainage layer - most of the moisture should go to the lower roots of the plant. During the ripening of the berries, the frequency of watering is reduced so that the fruits do not crack from an excess of moisture. In the future, plants with an age of several years are watered as needed, carefully controlling the level of moisture in the earth - the latter should not be overdried, but its transformation into sticky and wet mud is also undesirable.

If you bring flexible hoses to the pipes, watering can be automated
Top dressing of grapes is carried out in four stages:
- in the spring when disembarking;
- 15-12 days before flowering;
- when forming berries with a diameter of a pea;
- at the beginning of ripening.
In all cases, superphosphates, potash and nitrogen fertilizers are used. It is allowed to use top dressing in liquid form, as well as slurry. The exact values of fertilizers that need to be applied to each plant depend on the specific variety, be sure to check this point when buying seedlings from a grower.
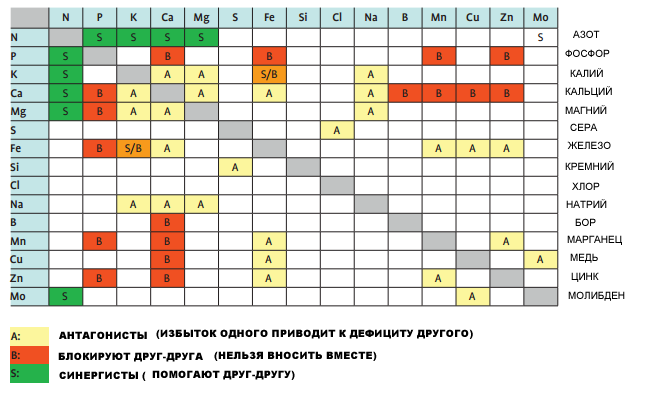
Table of mutual influence of fertilizers at combined application
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale is a profitable business, as the demand for the queen of flowers does not decrease even during the winter months. Depending on the region, the profitability can be 200% or more, and the payback period does not exceed two years.
Preparing grapes for winter
After harvesting, caring for the grapes does not end - you need to prepare for the winter. Shoots must be protected from hypothermia. To do this, they are removed from the trellis wires and laid on the ground. It is desirable that this is the bottom of the trench, which lies below ground level. Then the shoots are covered from above with straw, spruce branches or other similar materials. It makes sense to put poison from mice there as well, otherwise rodents in the greenhouse can cause significant harm to plants.

Reed for shelter

Grapes sheltered for the winter
If it is possible to temporarily dismantle the roof of the greenhouse - do it, the snow that has fallen will help protect the grapes from hypothermia. Also, do not forget to make a snow shaft around the walls of the greenhouse in December so that the soil inside does not freeze too quickly.
As mentioned above, growing grapes in a greenhouse is a complex, laborious and long process. But the reward for the effort expended is also appropriate. And for experienced gardeners, grapes from greenhouses can be a good source of income.
Unfortunately, many grape varieties cannot be grown in northern climates, since the plant is too thermophilic. In such cases, they resort to using greenhouse structures. Indoors, the culture can be provided with no less care than in the southern regions.
Greenhouse growing rules in Siberia
For northern latitudes, growing grapes in greenhouses has many advantages.
Growing grapes in a greenhouse makes it possible for the fruit to ripen earlier.
The grapes that grow in the greenhouse are practically immune to insects.
The vineyard is protected from frost in the greenhouse.
By growing grapes in a greenhouse, you can achieve high yields.
A vineyard growing in a greenhouse does not need to be treated with chemicals.
It should be noted right away that it is unprofitable to build a greenhouse only for your own use of grapes, since too high costs are ahead.
As a rule, growers resort to the greenhouse method in the case of industrial use of the crop, that is, they grow grapes for sale fresh, or they are going to use the berries for mass processing for wine or other food products, with the subsequent sale of finished products.

Greenhouse 3 by 6 meters.
It is noteworthy that not all varieties are suitable for growing inside closed soil.... In Siberia, Delight, December, Strashensky will not take root in such conditions.
Varieties

It is better to give preference to frost-resistant and early varieties.
However, they will give excellent results the following cultures:
- Arcadia.
- Transparent.
- Laura.
- Song.
- Kishmish.
- Irinka.
- Currant.
- Alyoshenka.
- Sidlis.
It is characteristic that Arcadia is able to bear fruit and bring record harvests in greenhouses - productivity is an order of magnitude higher than under normal conditions.
The same performance can be expected from Transparent. Laura will delight you with larger berries than in open soil.
Types of greenhouses and planting
The greenhouse for growing grapes must be high enough.
Usually, gardeners use two types of structures - a wall-mounted and a stationary type.
- The wall method involves the use of a wall of a heated residential building as one of the walls of the structure.... Thus, this wall provides additional heat and maintains an optimal level of heat transfer. It is noteworthy that, using this method, during the summer season, you need to open the structure and properly ventilate. As a rule, an earlier harvest can be expected in this case.
- The second method is a stationary structure, which is recommended to be built on the south side of the garden area to receive a large amount of light.... The size depends on the desired amount of planting material. The only requirement is height. The entire building must be more than two and a half meters in height. This is necessary so that the bushes of crops can grow as well as possible without creating crowding.
Features of preparation

The greenhouse should have 50-60 cm of fruitful soil.
The first condition is proper soil preparation.
It should be noted that the roots of the plant are located in the upper layer, therefore it is necessary to create the most suitable conditions for their strengthening and further development. The soil layer should be composed of soil, sand and gravel, with sand and gravel usually making up about half of the potting mix.
Top dressing
Drainage channels must be made in the ground.
The mixed soil should be fertilized with mineral fertilizers.
For this, ready-made mineral complexes are chosen that have a beneficial effect on the development of the entire plant, participate in the formation of the green and woody part.
Technology

Grape bushes need to be fertilized throughout their growth and maturation.
- It is advisable to mulch the soil and cover with a special agrofibre to prevent the growth of weeds, as well as to control the level of moisture and retain heat.
- Holes are made for cuttings.
- Usually plants planted in three rows, while the distance should be at least one and a half meters between plant units.
Planting care

When planting, the distance between the bushes of grapes must be respected.
Care measures consist of several points that must be strictly observed in order to obtain high results:
- watering;
- pruning;
- top dressing with saltpeter;
- feeding with phosphorus;
- maintaining a constant temperature;
- airing;
- humidity control;
- prevention against diseases.
Since at first the plant requires a lot of moisture to harden, it should be watered regularly, but do not overdo it.
Water only if drying of the soil is noticed. Over time, weak, dense or damaged vines are removed - you cannot provoke excessive density in order to avoid peas, reduce productivity.
- As soon as the first buds appear, the new plants are fed with a solution of saltpeter four times a month, that is, every week..
- Next, you should add phosphorus fertilizing.
- At the same time, the varietal characteristics of the culture are taken into account - the most suitable feeding for this variety is selected. It is advisable to use a high-quality sprayer for this in order to apply the mixture to the branches as much as possible for normal absorption.
- After flowering, wood ash is added, since this agent acts not only as a fertilizer, but also serves as an excellent preventive measure against fungi.
Greenhouse growing rules in the Moscow region

The grape bushes should be secured to the trellis.
Several facts speak in favor of growing grapes in a greenhouse.
In greenhouse conditions, in any weather, you can create a comfortable microclimate for the normal development of culture, since the minimum temperature regime can be only five degrees Celsius.
At the same time, an acceleration of the activity of all growth phases is noted, as a result of which the beginning of fruiting is shifted earlier by about a month. Among other things, a greenhouse is a reliable shelter from drafts, sudden gusts of wind, dangerous precipitation. Recommended varieties for the Moscow region:
- Korinka Russian;
- Michurinsky;
- Moscow Stable;
- Irinka;
- Rylines Pink;
- Rusball;
- Agat Donskoy;
- Kay Gray;
- Alpha;
- Northern Early.
As in Siberia, it is better to use seedless varieties for greenhouse cultivation.... In addition, it is recommended to plant crops that are overly attractive to birds. In closed ground, invasions of feathered pests are not terrible.
Types of greenhouses and planting
A greenhouse with one blank wall is the best option for northern locations.
In the Moscow region, a wall-mounted version of a greenhouse with one transparent wall facing the south or south-west side is most often used for greater access of light.
However, they often build a stationary greenhouse equipped with water heating, a drip irrigation system, artificial lighting, and special shelving. Arched or domed design. For construction, a metal frame with a polycarbonate coating is used.
Dimensions (edit)

A spacious greenhouse is required to grow grapes.
The height of the arch is at least three meters, the total area depends on the amount of planting material - the purpose of growing... Classic dimensions: height - three meters, area - thirty squares. Before construction, it is necessary to make a drawing design of the structure, which takes into account: half-arcs of the sides and gaps, vertical posts, fasteners, horizontal ribs, the location of the vents, doors.
Fill
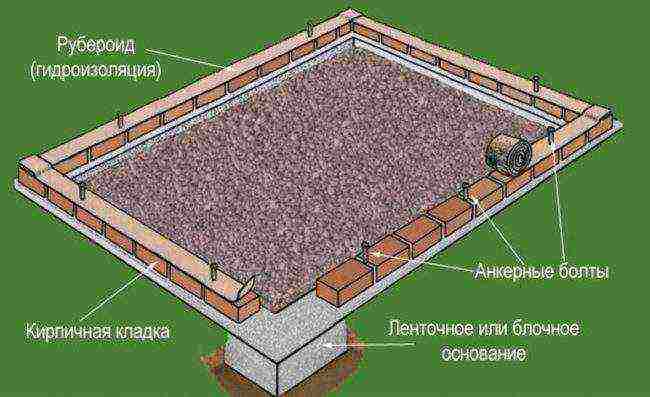
The foundation will be required to protect the soil from weeds.
Further actions include digging a trench for the foundation, establishing formwork, embankment for a sand cushion, reinforcement with steel mesh or wire, concrete pouring.
- It is noteworthy that even at the stage of pouring the foundation, it is worth fixing the frame racks. To do this, you can use pipes or metal corners.
- Distance between supports - 1 meter.
- After installing a solid frame, the surface is covered with polycarbonate.
Soil preparation

Before planting a vine, you need to prepare a hole for each seedling.
The first step is to prepare the soil for planting seedlings.
- First you need to decide on the location of the vine, that is, where it will be located - inside the greenhouse or outside, but regardless of where the vine will grow, the rhizome should only be in closed soil.
- The soil should be balanced with the addition of the necessary nutrients, while containing sufficient drainage mixture to filter air and water.
- Possible composition of the potting mix - earth, sand, loam, peat, chalk powder.

Our editor-in-chief is at work!
Landing

Before planting, the lateral shoots must be removed and only strong shoots should be left.
Young seedlings should be planted in February.
- Directly disembarking is carried out in the same way as on the open ground - hole with a diameter and depth of fifty centimeters, where top dressing is applied, fertile soil, a mound is formed on which the roots are straightened.
- Compost, manure, humus are introduced into the pit.
- The root zone is covered with mulch, watered abundantly.
- The distance between the novosads should not be less than fifty centimeters. Most often they are planted at a distance of seventy centimeters from each other, but this is in case there is a lot of free space for planting.
Care

After planting, the vineyard bushes need watering and fertilization.
Further care consists of systematic watering, eliminating weeds, sanitary pruning, preventive measures against fungal and other diseases.
But timely normalization of the brushes is also necessary, since the most comfortable conditions are created inside the greenhouse in order to provoke possible overloads.
Do-it-yourself grapes will always find a place on your kitchen table - either as sweet, large and tasty berries, or as homemade wine. In addition, surplus grapes can always be sold or donated to your friends and acquaintances. But how to achieve a bountiful harvest of this crop in the middle lane, where light and heat may be lacking? The solution to this problem is to grow grapes in a greenhouse.

Growing grapes in a greenhouse
Why grow grapes in a greenhouse?
Compared to open ground, growing grapes in a greenhouse has many advantages. This is especially pronounced if your land plot is located in the middle latitudes or slightly north of them.
- Creation of favorable temperature conditions - even without artificial heating, the greenhouse will be 2-5 degrees hotter. To humans, this may seem insignificant, but for grapes it is very important.

Greenhouse grape growing increases yields
- The ability to get the harvest earlier - with the correct cultivation technology and favorable conditions provided by the greenhouse, the crop can be obtained 2-4 weeks earlier than in the open field. This is especially important for late grape varieties, which do not have enough warmth outside the greenhouse for this.
- No problems with insects and diseases - the greenhouse will partially solve the problem with wasps that damage and eat berries. In addition, mildew or powdery mildew are extremely rare indoors.
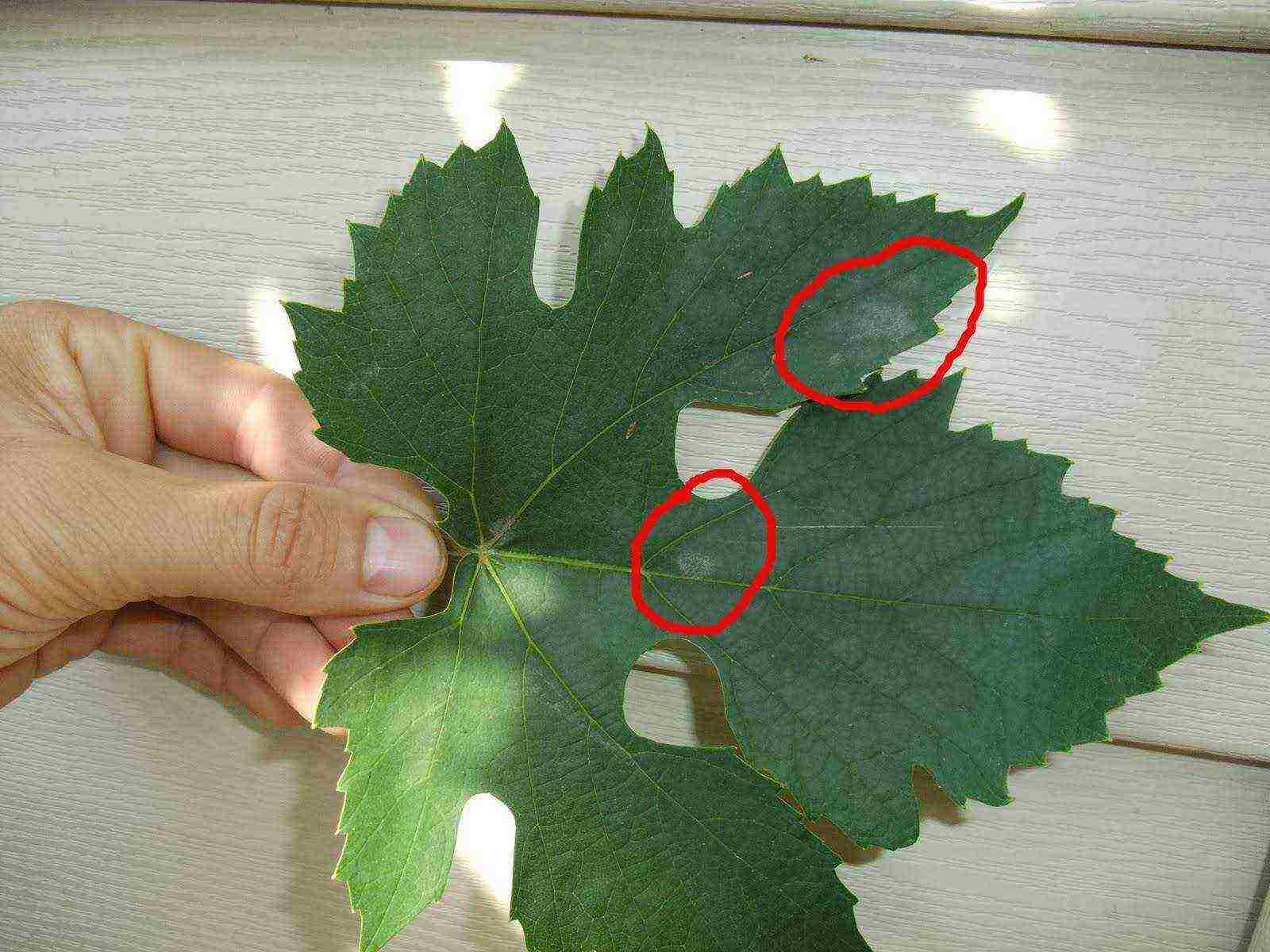
Oidium on a vine leaf
- No need for chemical treatment - since the grapes in the greenhouse are protected from diseases and plants, then they need to be processed much less often. As a result, the cost of berries is reduced, their safety and environmental friendliness increase.
- Frost protection - the casing and foundation of the greenhouse will protect the plants inside from sudden changes in temperature. This is especially important for those grape varieties that do not have sufficient cold resistance.
- No problems with berry cracking - there is no precipitation in the greenhouse, optimal values of temperature and humidity are maintained.
- High yield, which depends on the density of planting seedlings (from 4 to 8 kg of berries per square meter of the greenhouse).

Grapes in the greenhouse
- Convenient working conditions - there is no gusty wind in the greenhouse, it is not so cold in autumn or winter. And with proper arrangement of trellises, the harvesting process will be significantly simplified.
- The ability to use the greenhouse for growing other crops - Strawberries, garlic, spinach, onions or flowers can be grown in the space between the trellis.
At the same time, it should be borne in mind that to start growing grapes, significant initial investments will be required - for the purchase of seedlings, the arrangement of the foundation and the construction of a greenhouse. Also, you will need to spend a lot of effort on caring for this crop, and at the same time it will not begin to produce crops immediately. But all the costs will more than pay off with a large number of tasty and nutritious berries that you can either consume yourself or sell or use to make wine.

When growing grapes, you will have to spend a lot of time and effort on care.
Choosing varieties
The process of growing grapes in a greenhouse begins with the selection of a variety. If you are a beginner and have not dealt with such a crop before, then give preference to early and frost-resistant varieties, which are guaranteed to give a plentiful and high-quality crop in the greenhouse. These include various types of raisins, Korinka Russkaya and Michurinsky. As soon as you successfully get a harvest from early and frost-resistant grape varieties, move on to its other varieties, designed for cultivation in the southern regions, in the Kuban or in Moldova.

Grapes raisins Korinka Russian
Important! When planning to grow grapes in the Urals, North-West or Siberia, equip a greenhouse heating system and artificial lighting. They will help plants to cope with the lack of sun and heat, which will be noticeable even taking into account the microclimate of the greenhouse.
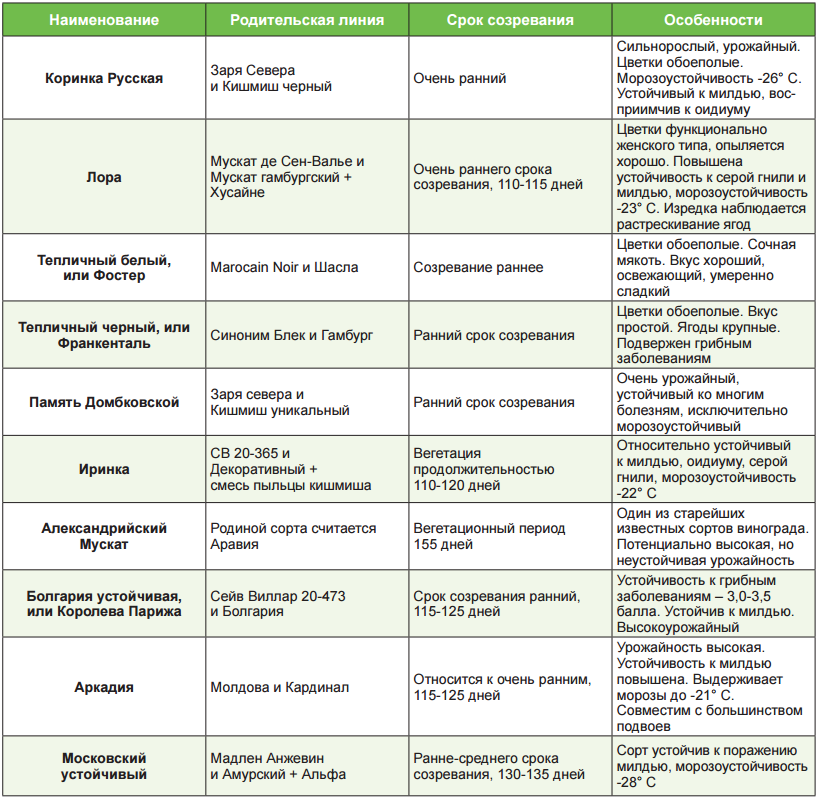
Some of the varieties that are suitable for growing in a greenhouse located in the middle lane are shown in the table below.
Table. Frost-resistant grape varieties recommended for cultivation in greenhouses.
| Beauty of the North | Dining room | 14 to 17 | 250 to 900 | -26 | White |
| Ruslan | Dining room | 17.5 to 18 | 500 to 1200 | -21 | Dark |
| Kishmish Potapenko | Dining room | 25 | 500 | -25 | Dark |
| friendship | Technical | 19 to 21 | 280 | -23 | White |
| In memory of Shatilov | Universal | 17 | 600 to 1500 | -30 | White |
| Russian Early | Dining room | 17 to 21 | 200 to 600 | -23 | Dark |
| Delight | Dining room | 19 to 26 | 500 to 2000 | -25 | White |
Some more suitable greenhouse grape varieties

Arcadia grapes
Features of the greenhouse for grapes
A greenhouse designed for growing grapes has significant differences in its design from traditional greenhouses for tomatoes and cucumbers. Let's consider separately all the features that need to be taken into account during the construction.
Dimensions. A greenhouse for growing grapes should have a considerable height - from 2.5 to 3 meters or more, depending on the design and size of the trellises. The optimal building area designed to meet your own need for grapes is 25-30 m2. Larger greenhouses can be used to grow berries for sale or to make wine.

Greenhouse for growing grapes
Foundation. The soil in the greenhouse for grapes must be reliably protected from freezing. In addition, without a foundation, weeds, pests and uncontrolled drafts will penetrate inside. Build a shallow concrete strip foundation.
Sheathing. For a greenhouse, it is desirable to use transparent cellular polycarbonate - a material with high light transmission and good thermal insulation properties. Plastic wrap is acceptable, but only for unheated structures.
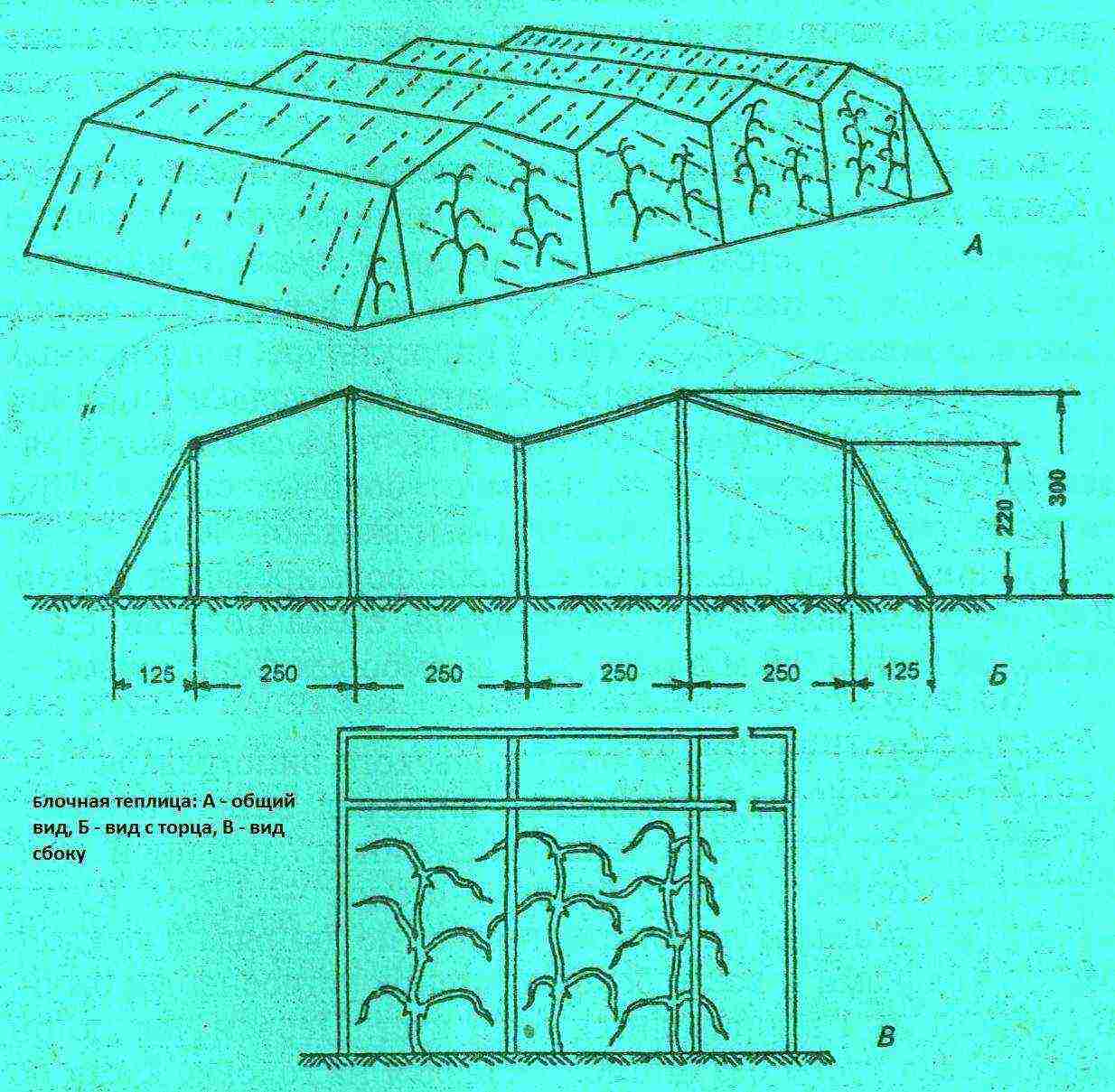
Greenhouse example diagram
Frame. Grapes do not like haste and do not start producing a good harvest immediately, therefore the greenhouse must be durable and have a significant service life.And as a material for the frame, the optimal choice in such conditions would be a galvanized steel profiled pipe - it is strong enough, durable and easy to work with.
Heating. If it is planned to grow grape varieties that are not designed for cold weather, then the greenhouse will need heating. To do this, you can use infrared lamps suspended from the ceiling (in this case, you will need to significantly strengthen the frame of the building), or a heating cable brought under the ground of the greenhouse. For lovers of simple options, the arrangement of conventional heating radiators is suitable.

IR lamps for heating greenhouses

Heating cable installation
Lighting. Southern grape varieties in Siberia or the Northwest may lack sunlight. This deficiency can be corrected with the help of special fluorescent lamps. They are presented in luminescent, LED and sodium subtypes.
Ventilation. For a small greenhouse, designed for growing grapes for own consumption, two vents located in the gables of the building will be enough. If it is planned to produce berries or wine for sale, then the greenhouse should be larger, respectively, the number of transoms should increase. To ensure an optimal microclimate, equip all vents with thermal cylinders that open and close the doors at a certain air temperature inside.
Photo of a bimetallic element of automatic greenhouse ventilation
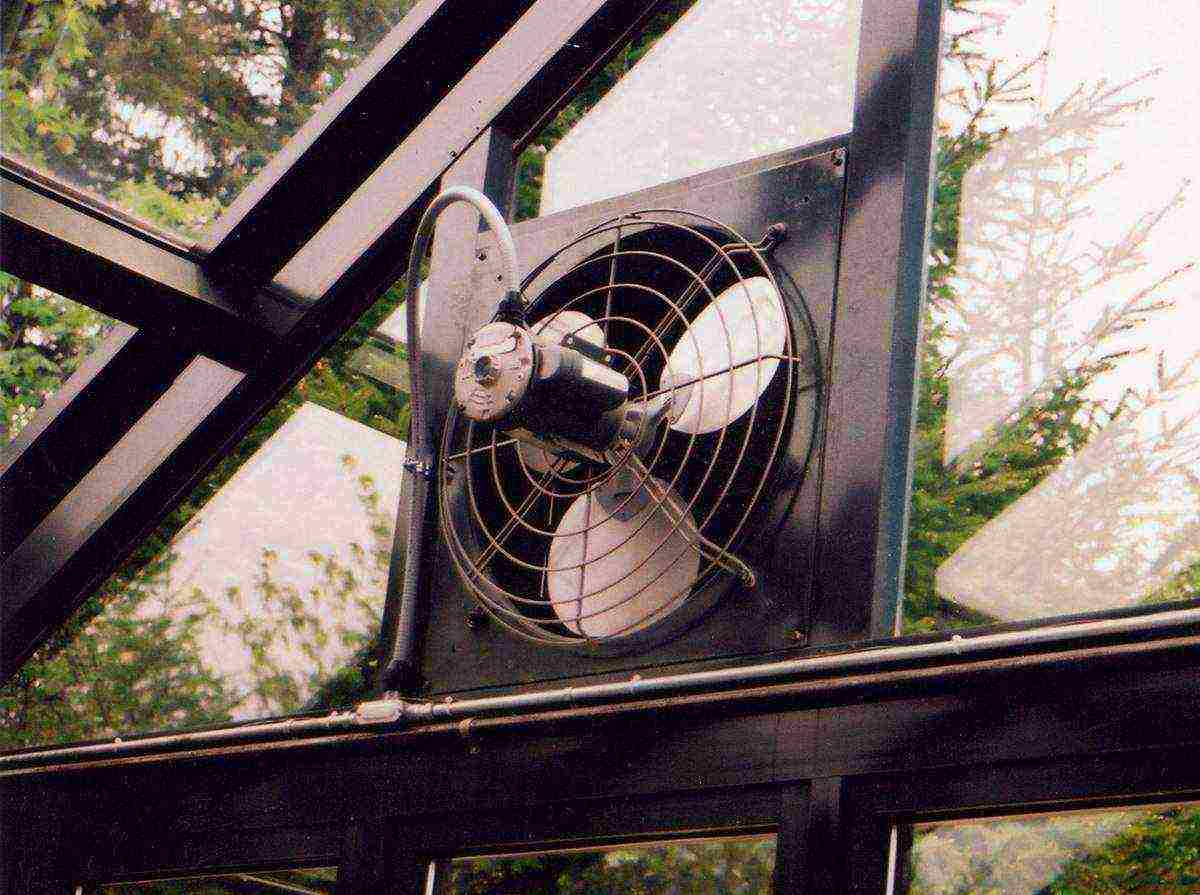

Special fan for greenhouse
Important! Unlike other crops, grapes do not require frequent watering. But with its manual (watering) implementation, you have to spend a lot of labor and time. The arrangement of an automatic irrigation system controlled through a conventional valve or a special microcontroller will help to partially solve this problem.
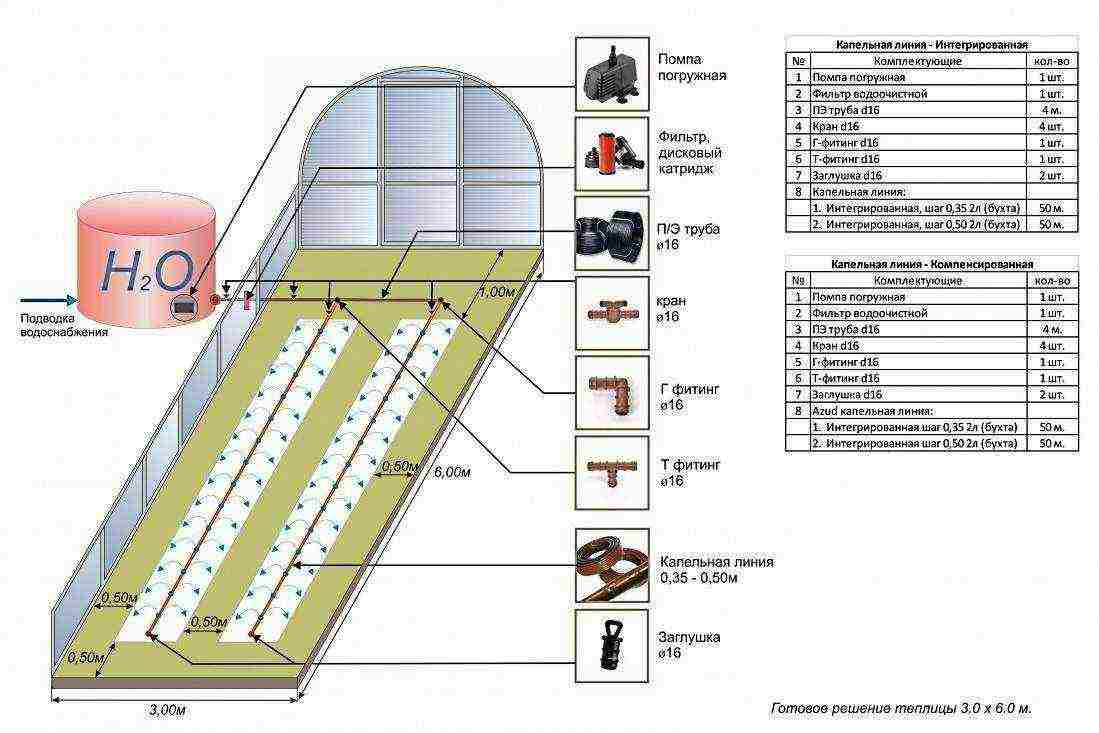
Drip irrigation in the greenhouse
Do-it-yourself greenhouse trellis
The main element of the greenhouse for growing grapes are trellises - trellises that serve as a support and a means of controlling the direction of growth of agricultural crops. There are many varieties of this design, vertical single-plane and horizontal T-shaped trellises are best suited for use in a greenhouse. Let's see how they are created.

Trellis for growing grapes in the greenhouse
Roughly speaking, vertical single-plane trellises are a fence made of wooden pegs or metal pipes, between which a wire is stretched with a certain pitch. The vines are attached to the wire and shaped in a certain way.
Scheme of an example of a trellis for grapes
As a result, it becomes possible to grow a larger number of bunches per unit area and, accordingly, to obtain bountiful harvests. You can equip vertical trellises as follows.
Step 1. Inside the greenhouse, mark out the places for the pegs.
Step 2. Drive in stakes or pipes at the desired points. For the first, use a beam of 50x50 mm, for the second - steel pipes with a cross section of 7-10 cm.The depth into which they are driven is 1-1.5 m, the height of the trellis above the ground level is 3-3.5 m. The distance between the individual stakes or pipes - from up to 6 m.
An example of a vertical trellis for grapes with a seedling in a trench
Important! Processing wooden stakes with protective compounds is undesirable - these compounds can subsequently harm the vine, leaves or berries. Copper sulfate is a safe alternative.
Step 3. At a height of 50 cm from the grape seedling, pull a wire with a cross section of 3 mm. Fasten with wire loops, nails or metal staples.
Step 4. Pull the second one 35-40 cm above the first wire.
Step 5. Repeat step # 4 two to four more times (depending on the required height of the trellis).
Step 6. At a distance of at least 0.5-0.75 m, start installing a new trellis.
Advice! The arrangement of the cornice will help to increase the useful area of the vertical single-plane trellis, as in the image below.
Vertical tapestries with cornice
Horizontal trellises are arranged somewhat differently. They can be either T-shaped supports, between which a wire is stretched at intervals of 30-40 cm, or a lattice using thick metal pipes as a support. The latter design turns out to be quite complex and heavy, but at the same time very convenient for harvesting - bunches of berries hang at the level of the head of an average person and there are no problems with removal. In addition, strawberries or other similar crops can be grown under these horizontal trellises at the same time.

T-shaped trellis

An example of growing dark grapes on a horizontal trellis
Important! Regardless of the design, the top rows of the trellis should not be closer to the greenhouse cladding than 30-40 cm. Otherwise, there will be a risk that the grapes will get sunburn.
The upper part of this vine bush is on the gazebo, the lower part is like a single-plane trellis
Planting grape seedlings
It is necessary to start planting seedlings in late winter or early spring, it all depends on the grape variety and its frost resistance, while the plant material must meet the following requirements:
- absence of fungus and diseases;
- strong and healthy roots;
- lack of mechanical damage;
- no traces of freezing.
The place for planting a seedling should be no less than 30-50 cm from the greenhouse sheathing. The interval between plants in a row depends on the specific variety and can reach from 0.5 to 1.5 m. The preparation and implementation of planting is carried out according to a certain technology.
Step 1. Dig a hole 80x80 cm and a depth of 70 cm. It is advisable to equip the trellises at the same stage.
Scheme of a finished hole with a grape seedling
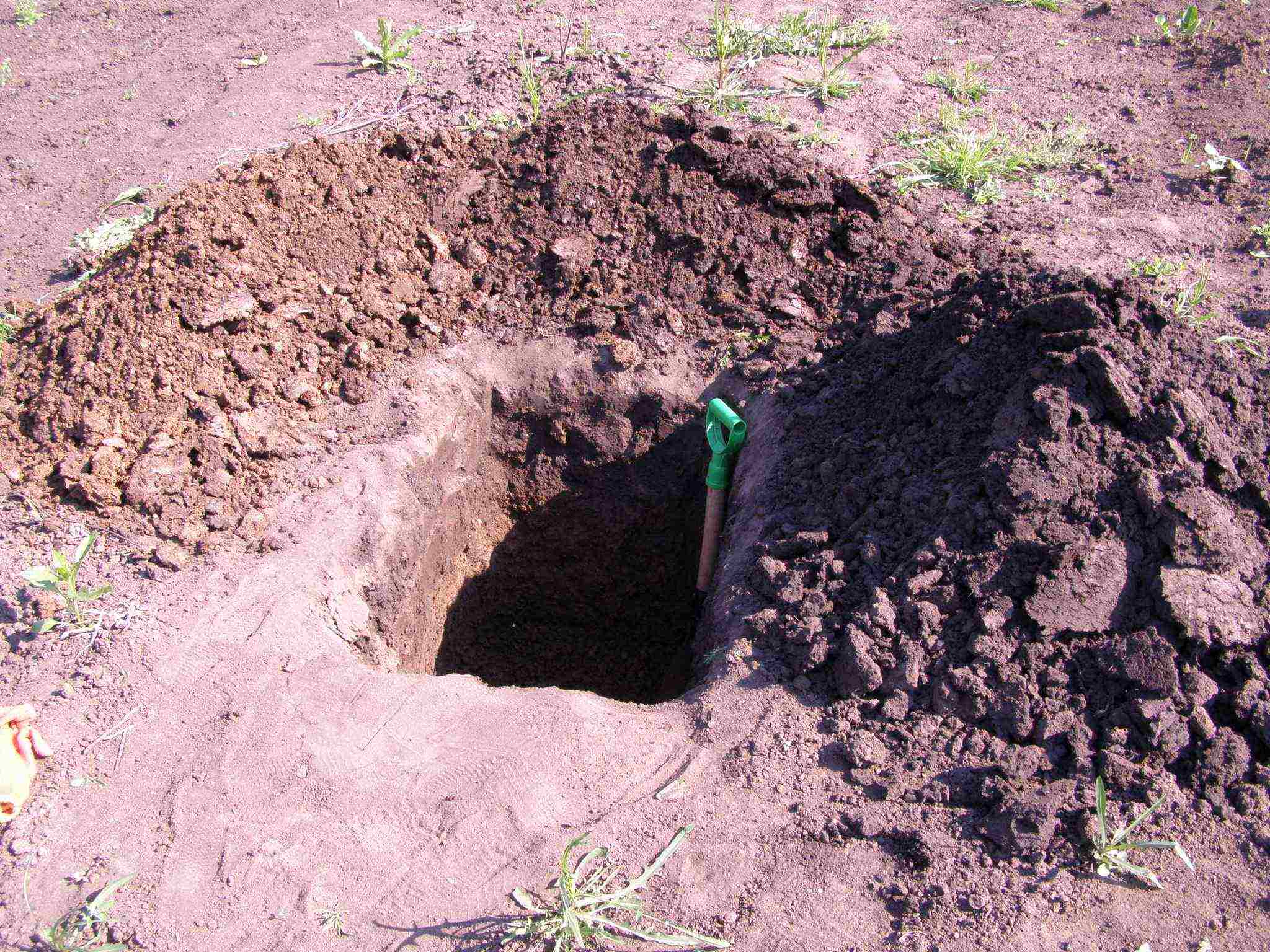

The depth of the pit should be 70 cm

How to prepare a planting pit for grapes
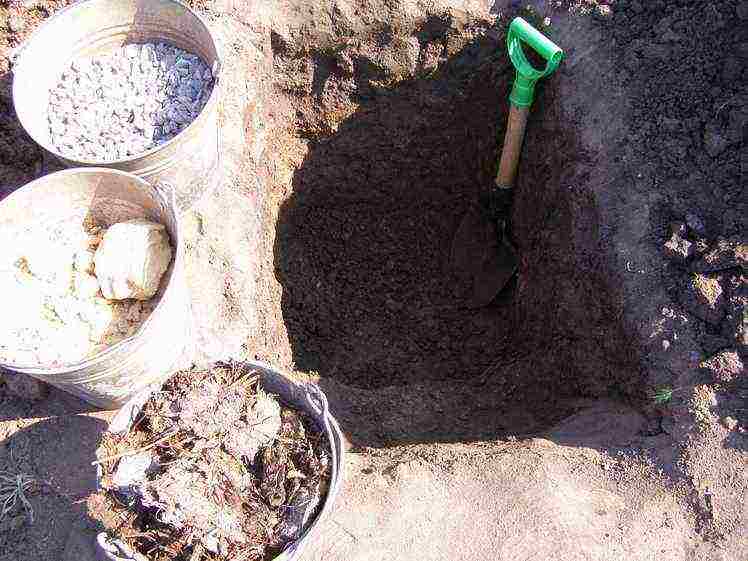
Step 2. Place a quarter of a bucket of wood ash on the bottom.
Step 3. Equip a drainage layer with a thickness of 20 cm. To do this, fill in expanded clay or gravel. Insert a 10-12 cm tube into the resulting layer, which will be used for watering. Its height above ground level should be at least 5-10 cm.
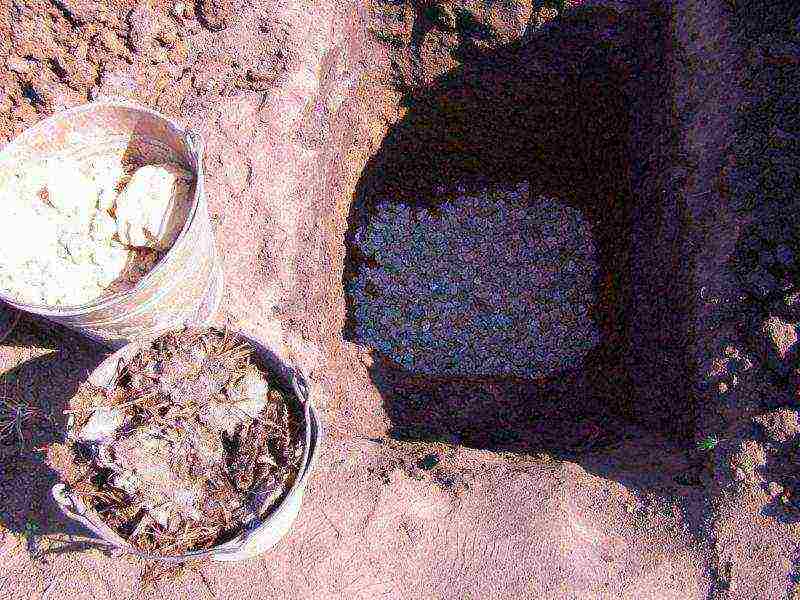

Drainage layer
Important! The drainage layer does not have to be arranged directly under the future seedling. It can be arranged nearby, at the entry point of the irrigation tube. In this case, the depth of the pit directly under the seedling is reduced to 50-60 cm.
Arrangement of pipes for irrigation and drainage layer
Step 4. Prepare the seedling substrate. There are two recipes. In the first, 1 part of sand is used for 2 parts of humus and 5 parts of fertile soil. In the second recipe, for 1 unit of sand mass, 2 units of peat and 4 units of loam are taken. Add fertilizer or lime to the substrate (the latter is taken from a ratio of 100 g per bucket).
Step 5. Pour the substrate into the hole with a layer of 20 cm thick and pour it over with water. If the substrate has settled and decreased in volume, add more.

Backfilling of the substrate
Step 6. Plant the seedling in the soil, straighten the lower root system and add another 15-20 cm of substrate on top. As a result, the remaining depth of the hole should be 10-20 cm. Orient the seedling parallel to the greenhouse sheathing.

Planting a seedling
Seedling planting scheme
Advice! To plant a large number of seedlings, you can dig a trench of appropriate depth, width and length.
If you plan to plant a seedling not in spring, but in autumn, take care of it with the right shelter for the winter.
Grape care and pollination
The main principles of ensuring good conditions for grapes are the right temperature, access to sunlight and the formation of shoots.
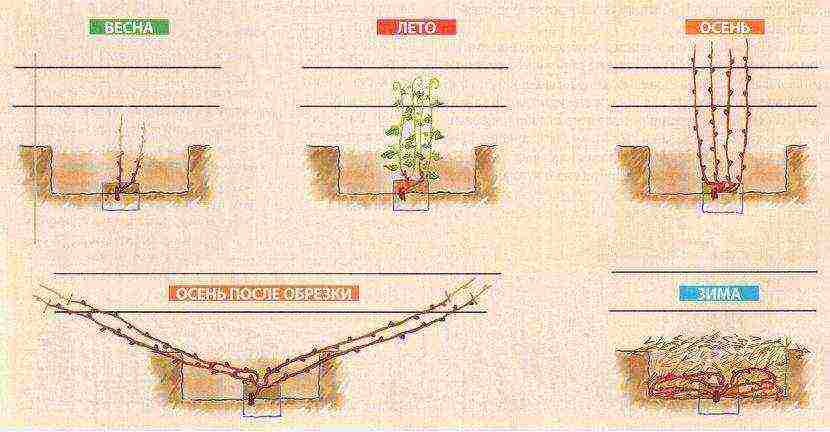
Diagram of the vine care cycle
The temperature is regulated by heating and ventilation. The optimal regime for grapes depends on the stage of growth.So, in the spring, at the stage of bud formation, the plant needs + 10-20 ° C during the day, at least +8 ° C at night. During the flowering period, the optimum temperature during the day is + 25 ° С, at night + 15 ° С. And when the berries begin to ripen and fill with juice, it should be a little hotter in the greenhouse - + 30 ° С during the daytime and + 18-20 ° С in the dark. When using artificial heating, try to reproduce these cycles so that the plant is not stressed and produces the best yield.

The optimal temperature regime for grapes depends on the stage of growth.
Important! The above values for optimum temperatures are general. More accurate values depend on the specific grape variety, therefore, before choosing each of them, read in detail the description and experience of working with one or another species.
Providing access to sunlight is achieved through the correct design of the trellises and their correct location. In addition, make sure that the vines on the lower wires are not shaded; if necessary, it is permissible to cut a certain number of sheets in that place.
Shoot formation is a very important part of grape care. As a result, you should form strong branches with fruiting vines. Stepsons (also called shoots of the second order) and weak branches should be cut to the first "eye". This way, you will not allow the plant's resources to be wasted on parts that will not yield crops. In addition, you need to trim the tops of the shoots several times each season. Forming grapes is a whole art, and for a better understanding of the process, one should consult specialists or reference literature on viticulture.
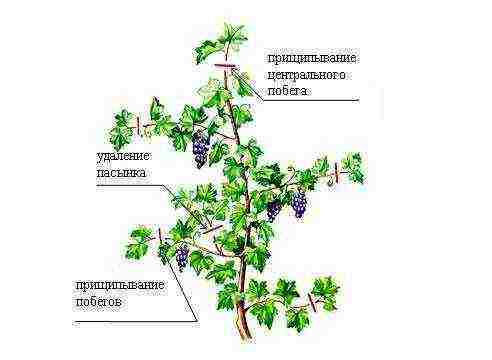
Grape care
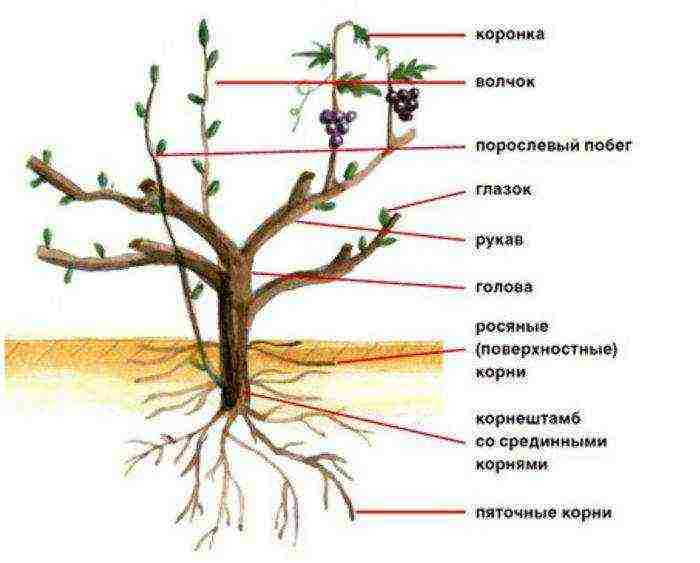
The structure of the grape bush
Inspect the bunches regularly. If damaged, rotten or diseased berries are found, cut them off immediately. In addition, sometimes it is necessary to thin out clusters of small fruits and weak branches in order to avoid overloading and “direct resources” to higher quality berries. The optimal distance between branches during the ripening period is from 6 to 8 mm. Carry out thinning carefully, using long and thin scissors, so as not to cause additional damage.

Thinning grapes in the greenhouse
Since in the greenhouse, most likely, there will be no bees, the pollination of the grapes must be carried out independently. Perform the event after the opening of the flowers of the plant. Everything is quite simple - light and quick blows are applied along the stem. An alternative way is to tap the flowers of one plant and then transfer the pollen on the hand to another.
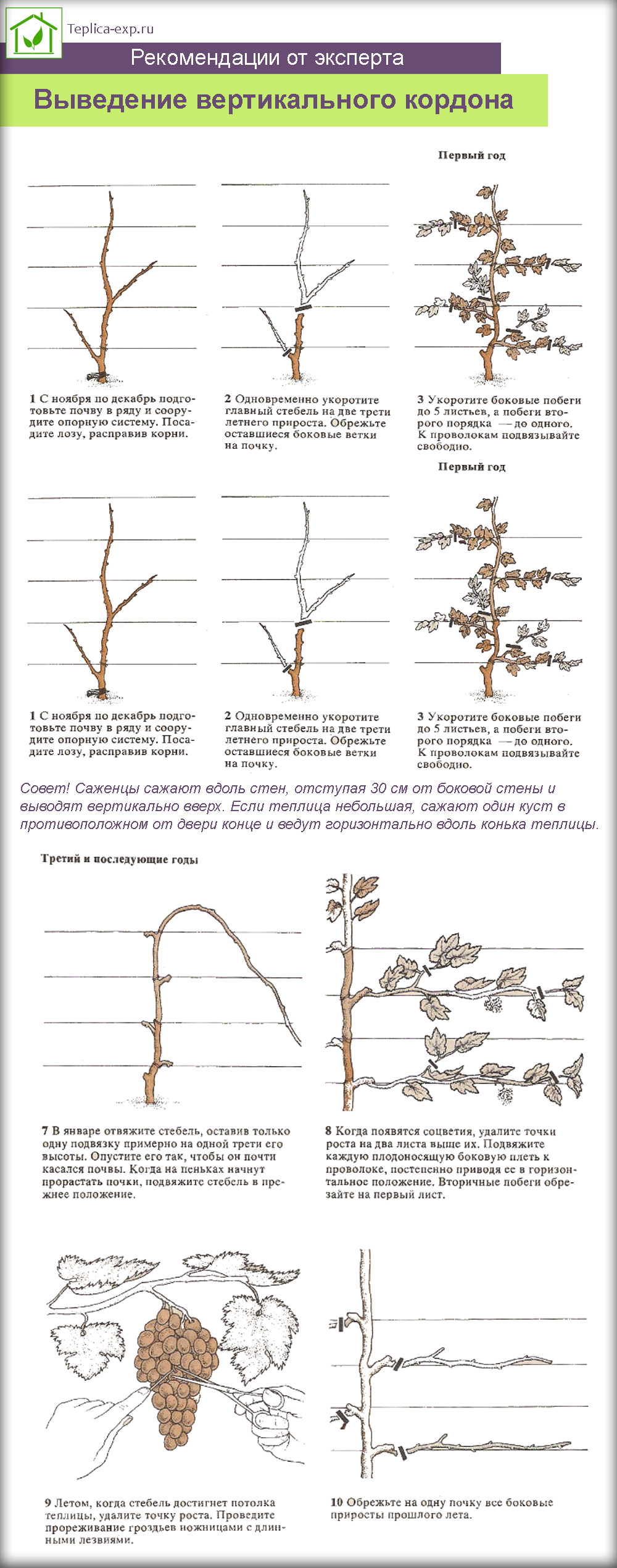
Removing a vertical cordon
Video - Growing grapes in the middle lane
Video - Caring for grapes
Watering and feeding
It is worth noting that the grapes do not require frequent watering. Excess moisture can damage the crop and cause the berries to crack. Perform the first watering even before planting the seedling, when forming a hole - 20 liters of warm water for each. Then the same amount - after planting, the place should be well saturated with water, but make sure that due to excess moisture the plant does not "drown" and does not start to rot.
An example of a do-it-yourself subsoil irrigation scheme
After seven days, watering is repeated, while mulching the soil in the hole with the seedling is also performed. Further, in the summer, the grapes are supplied with water once a week, watering should be done either in specially dug holes and grooves, or in a tube inserted into the drainage layer - most of the moisture should go to the lower roots of the plant. During the ripening of the berries, the frequency of watering is reduced so that the fruits do not crack from an excess of moisture. In the future, plants with an age of several years are watered as necessary, carefully controlling the level of moisture in the earth - the latter should not be overdried, but its transformation into sticky and wet mud is also undesirable.
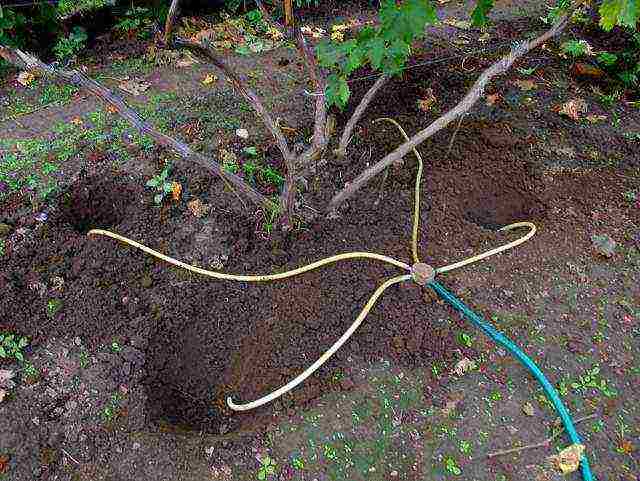

If you bring flexible hoses to the pipes, watering can be automated
Top dressing of grapes is carried out in four stages:
- in the spring when disembarking;
- 15-12 days before flowering;
- when forming berries with a diameter of a pea;
- at the beginning of ripening.
In all cases, superphosphates, potash and nitrogen fertilizers are used. It is allowed to use top dressing in liquid form, as well as slurry. The exact values of fertilizers that need to be applied to each plant depend on the specific variety, be sure to check this point when buying seedlings from a grower.
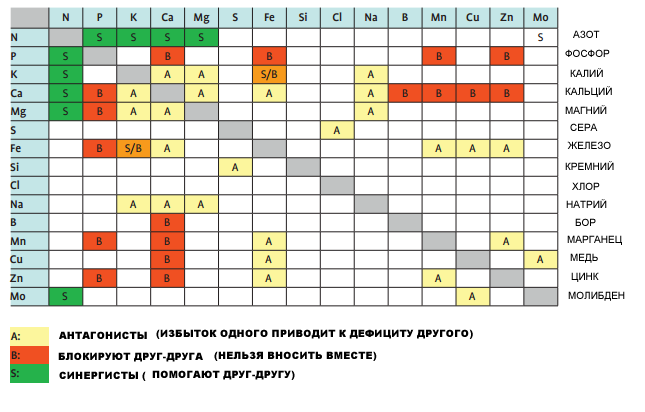
Table of mutual influence of fertilizers at combined application
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale is a profitable business, as the demand for the queen of flowers does not decrease even during the winter months. Depending on the region, the profitability can be 200% or more, and the payback period does not exceed two years.
Preparing grapes for winter
After harvesting, caring for the grapes does not end - you need to prepare for the winter. Shoots must be protected from hypothermia. To do this, they are removed from the wires of the trellises and laid on the ground. It is desirable that this is the bottom of the trench, which lies below ground level. Then the shoots are covered from above with straw, spruce branches or other similar materials. It makes sense to put poison from mice there as well, otherwise rodents in the greenhouse can cause significant harm to plants.

Reed for shelter

Sheltered for the winter grapes
If it is possible to temporarily dismantle the roof of the greenhouse - do it, the snow that has fallen will help protect the grapes from hypothermia. Also, do not forget to make a snow shaft around the walls of the greenhouse in December so that the soil inside does not freeze too quickly.
As mentioned above, growing grapes in a greenhouse is a complex, laborious and long process. But the reward for the effort expended is also appropriate. And for experienced gardeners, grapes from greenhouses can be a good source of income.

For many years grapes remain a symbol of fertility, a source of useful vitamins and the best raw materials for the production of wines.
The owner of the vineyard will not be at a loss, especially if he takes care of the future harvest correctly. In our region grapes raise perspectively as a greenhouse culture, which causes a short summer period, an early onset of cold weather, and frequent spring frosts.
…
Pros of growing in a greenhouse
Growing grapes in a greenhouse is relevant both for the central zone of Russia and for the southern regions. In the first case varieties can be grown, which simply do not have time to ripen in open field conditions, and in the south you can get a harvest of berries much earlier than the established date. Besides:
- growing in greenhouse conditions allows you to protect the plant from the hardships of nature (rain, wind, fog, temperature changes);
- it is much more convenient to care, especially in spring and autumn;
- flavoring the quality of the berries is no worse those that ripen on plants in the open field;
- berries crack less, as they are protected from rain drops;
- the shelter allows you to protect from insects and birds, as well as from many diseases and pests. The number of chemical treatments against mildew, oidium is reduced;
- next to grapes you can plant other crops in the aisles: strawberries, radishes, turnips, herbs (parsley, onions, dill, basil);
- sometimes gardeners in the same room grow tulips and other bulbous flowers for further sale.
Selection of varieties
 Different grape varieties can be grown in greenhouse conditions. The experience of winegrowers shows that the most successful among them are table varieties with an early or very early ripening period:
Different grape varieties can be grown in greenhouse conditions. The experience of winegrowers shows that the most successful among them are table varieties with an early or very early ripening period:
Bulgaria resilient (Queen of Paris) is a Bulgarian amber yellow grape. Differs in high resistance to diseases, does not require chemical pollination, bears fruit well.
Song (White miracle) - it has a very early ripening period. The berries are large, sugar, yellow-green in color.
Laura - gives high yields, is distinguished by large bunches and juicy berries. With good care, the weight of individual bunches can reach 2-2.4 kg.
Transparent - a good variety for eating, preparing homemade meals and drinks. The berries ripen, sugar and aromatic.
In addition to the listed species, you can give a choice: Arcadia, Early Northern, Russian Korinka, Moscow Stable, Michurinsky and others.
Some growers acquire seedlings of different forcing dates, which allows you to harvest throughout the warm season from spring to late autumn. You can combine early varieties with later ones.
note that not every variety suits well for cultivation in a greenhouse, for example, Dekabrskiy and Vostorg bear fruit better in open field conditions.
Greenhouse requirements
How to grow grapes in a greenhouse? Before you start planting vines you need choose and equip the room correctly.
- arched structures are considered the most successful. These are often chosen for growing flowers;
- the height of the greenhouse should be between two and a half to three meters. The total area is selected based on the goals of cultivation. For eating berries and homemade preparations a small room is suitable, and for sale, its area can be more than 20-30 square meters.
You can find out on our website how to build and strengthen a polycarbonate greenhouse, how to make an arched, single-slope (wall), from window frames or choose a ready-made greenhouse, as well as how to correctly position a building on a site.
Types of greenhouses for grapes:
- Film - well suited as a seasonal shelter... They allow you to protect the plant from the vagaries of nature, support its development and growth, and get a better harvest.
- Shelter made of polycarbonate - suitable for off-season (year-round) use. They are equipped with a supporting structure and special air vents.
 In specialized stores, there is a wide selection of designs that can be purchased from the site. To each design detailed assembly instructions are attached and use. Some firms even offer assembly services for such a room.
In specialized stores, there is a wide selection of designs that can be purchased from the site. To each design detailed assembly instructions are attached and use. Some firms even offer assembly services for such a room.
This increases your cash costs, but minimizes the hassle and time wasted. Many gardeners prefer to make such designs. independently from improvised means, because it saves money costs by 4-5 times.
Preparatory work
Pay attention to the preparatory work that must be done before disembarking seedlings:
- The vine can be both inside the structure and outside. In this case, the main stem of the plant must necessarily enter the closed zone, therefore, a hole is made in the lower part of the wall.
- Prepare the soil. For growing suitable fertile, loose, light soil mixture, which can be prepared from earth, sand, loam, peat, crushed chalk (at the rate of 90 grams for every second ten-liter bucket of soil) and mineral fertilizers.
In order for the plant to develop strong deep roots, it is recommended to pour the mixture into a prepared deep trench.
- Please note that the soil temperature indoors should be warmer than outside. The optimum temperature can be achieved with artificial heating.
- To protect the plant from indoor sunburn stretching the support wire system (in a horizontal position) at intervals of 20-30 cm. The upper wire is placed 35-40 cm below the ridge and at least 35 cm from the glass.
- Be sure to provide good drainage. If not, lay additional pipes.
Landing features
The technology for growing grapes in a greenhouse includes a number of rules:
- young bushes begin to be planted at the end of winter;
- the scheme for planting grapes in the greenhouse is as follows: a deep and wide hole is dug for planting (at least 35-40 cm). At the bottom of the hole in the center you can make a small embankment (as when planting an apple tree), place the seedling vertically in the center, straighten the roots, cover with earth, lightly tamp and water;
- before planting, it is advisable to apply organic fertilizers (compost, overripe manure).
- pay attention to the distance between the seedlings, which should be at least 50-65 cm. This is the only way the vine will get enough free space for the development and formation of the main stem.
- do not forget to inspect the appearance of young bushes and roots before planting. The plant must be healthy and strong.
Pruning rules
 After planting seedlings, you need pinch... Weak shoots are cut so that the plant does not expend energy on them during growth, but directs them to healthy branches.
After planting seedlings, you need pinch... Weak shoots are cut so that the plant does not expend energy on them during growth, but directs them to healthy branches.
Inflorescences with unripe flowers as needed should also be deleted... Pruning of sterile stems is carried out to the level of 5 leaves. For second-order shoots - up to the first leaf.
Over time, it is necessary to thin out the bunches. Using sharp scissors, they carefully cut off the inner berries, together with which various small particles are removed on the vines. Remember to manually pollinate the grapes... To do this, it is enough to slightly shake the branches with blossoming inflorescences.
In autumn, long branches are cut to the level of the initial bud, and the stems are cut to two-thirds of the entire length.
Watering and feeding
To get a good harvest for grapes needs proper care, follow the rules of fertilizing and watering the plant.
Watering features:
- The first watering is carried out immediately after planting.
- Then, to maintain optimal soil moisture, young bushes are watered once every 6-7 days.
- During the flowering period, watering is suspended, as well as during the formation of berries. Excessive moisture will negatively affect the quality of the crop.
- Please note that greenhouse grapes are not watered in the evening. An excess of moisture in the air will lead to cracking of the berries.
Fertilization:
- use nitrogen fertilizing with extreme caution;
- it is advisable to apply organic fertilizers before planting;
- during bud break, ammonium nitrate can be removed for good leaf development and bud formation, and before flowering - superphosphate;
- during further growth, only foliar fertilizers are applied. Superphosphate and ash are used after the end of the flowering period.
Wintering grapes
 Before the onset of the first cold weather, the plant needs hide under cover (around mid-October).
Before the onset of the first cold weather, the plant needs hide under cover (around mid-October).
To do this, the vines are tilted to the ground, covered with a dense layer of spruce branches and roofing material.
As a covering material, you can also use blankets, synthetic winterizer, sawdust.
If the greenhouse roof is removed, the plant can winter outdoors under the snow.
Problems with fruiting
Why not produce grapes in a greenhouse?
- lack of nutrients (zinc, manganese, boron) - start feeding properly plant;
- the opposite situation can also occur - an excess of nitrogenous fertilizers.
In this case the plant gives all its strength on the formation of greenery, does not bear fruit well or does not bear berries at all;
- affects the yield and pruning technology. Untimely thinning of vines leads to peas, not ripening of berries. It should also carry out off-season pruning.
Growing grapes in a greenhouse is a troublesome task that takes a lot of time and effort. But, the result is worth it... Proper preparation of the premises, adherence to planting technology and good care will allow you to get a quick, plentiful, tasty harvest!
Useful videos about growing grapes in a greenhouse:
Table of contents:
- Features of greenhouse cultivation
- Basic conditions for greenhouse cultivation
- Soil preparation
- Grape variety selection
- Planting a vineyard
- Agrotechnical measures
- Vineyard pruning
Growing grapes in a greenhouse is essential in regions where weather conditions make it difficult to taste the fruit when planted outdoors. In areas with cold winters and short summers, the plant does not have time to give full mature brushes, and frost, despite all protective measures, creates a risk of freezing.
Scheme of the frame of a greenhouse for growing grapes.
In such conditions, only cultivation of grapes in a greenhouse makes it possible to ensure full ripening. The technology of this process is quite complicated and time-consuming, but with a great desire and enthusiasm, it can be done on a suburban area with your own hands.
Features of greenhouse cultivation 
Summer grape grafting scheme.
Greenhouse grapes are grown for two main reasons: the impossibility of bringing to full maturity in cold regions and getting an early harvest in the southern and temperate regions. The construction of a greenhouse requires certain financial costs, but the process of growing a plant itself has a lower cost compared to open ground. The most suitable and modern greenhouse for grapes is a polycarbonate greenhouse without artificial heating for temperate climatic zones and with individual heating for the northern regions.
Cultivation of a plant in greenhouses has a number of advantages: getting an early harvest (early July in unheated greenhouses and May-June when heated); increased productivity; protection from unexpected frosts and other vagaries of the weather (for example, hail); protection from pests; ease of care; optimal use of space. The technology of growing grapes allows you to plant other crops with early ripening between the rows of bushes.
Back to the table of contents
Basic conditions for greenhouse cultivation
For the correct cultivation of grapes in greenhouses, there are rules that include the following stages of work: soil preparation, selection of a vineyard variety, arrangement of trellises, planting and shaping of bushes, ensuring optimal temperature conditions, plant care.
Grape planting scheme.
The polycarbonate greenhouse for grapes is located in a north-south direction to ensure good illumination. The fertile layer of the earth is about 45-60 cm, which, with good drainage, makes it possible to plant a vineyard even with a close location of groundwater. An important element is the trellis strapping for placing the branches of the bush. Such strapping is usually performed in the form of racks and horizontally stretched wire with a step of 25-35 cm; at the same time, the distance to the polycarbonate should remain at least 35-50 cm.
The temperature regime in the greenhouse is maintained by heating or, in its absence, by adjusting the ventilation of the vents, as well as by opening the roof blocks. At different stages of culture development, different air and soil temperatures are needed. After harvesting, rest should be ensured for 2.5-3 months, at which the temperature in the greenhouse is maintained from minus 4-5 to plus 4-6 ° C. At the next stage (growth and budding), the temperature gradually increases to 9-15 ° C in the daytime and 7-9 ° C at night. At the stage of active growth of shoots and flowering, the recommended temperature range is 22-25 ° C during the day and 13-17 ° C at night, and during the maturation of the brushes - 27-32 and 17-22 ° C, respectively. The optimum soil temperature for active growth and maturation of the plant is 19-24 ° C.
Back to the table of contents
Soil preparation
The soil for the vineyard is prepared as follows: first, sand and fine granite chips are added to the soil - up to 35-38% (such soil breathes, warms up well and is better able to retain moisture), then a compost mixture is added with the addition of superphosphate and ash, everything is thoroughly mixed by volume. The use of a special extended-release fertilizer of the AVA type (about 20 mg / m2) is effective.
Back to the table of contents
Grape variety selection 
The scheme of growing grape cuttings.
The choice of a variety is largely determined by the region of cultivation, but one should not forget about the taste of the berry.
In general, it is advisable to choose a plant with early maturing bisexual flowers. Seedless types of berries are popular.
You can offer the following recommendations: for the regions located beyond the Urals, the varieties are offered: "Ideal Delight", "Bulgaria Resistant", "Early ripening Parlett", "Black Hamburg", "White Foster".
For the central regions of the Russian Federation - "Michurinsky", "Moscow stable", "Northern early", "Russian Korinka".
Seedless varieties "Irinka", "Hybrid-342", "Rusbol", "Ainset Sidlis", "Rylines Pink Sidlis", "Riddle of Sharova", "Aleshenkin" are especially popular.
Back to the table of contents
Planting a vineyard
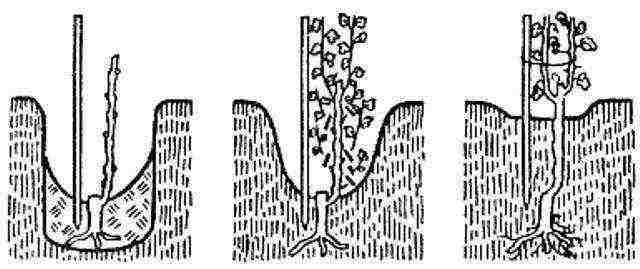
For planting, holes are dug 40-45 cm deep with a distance of 1.4-1.8 m between them. You can plant a vineyard in a greenhouse at any time, but the recommended period is November. A vine with a sprouted root system is placed in a hole and buried with a compaction, after which it is watered abundantly. Immediately after watering, the planted vine should be mulched, i.e. cover the soil around it with a black film to insulate and retain moisture.
An important nuance of planting is pruning and pinching the vine. Its length is shortened by 2/3 of the summer shoot, and the lateral shoots are cut to the first bud. All weak shoots are removed, only the strongest branches are left. All shoots are neatly fixed on the trellis strapping.
Back to the table of contents
Agrotechnical measures
Adequate vineyard maintenance is essential to ensure a good harvest. The main agricultural activities are watering, fertilizing and pruning.
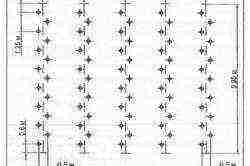
The scheme of planting grape bushes.
Watering. It is necessary to water the vineyard in the greenhouse correctly and in a timely manner. The first watering is carried out when planting a seedling in this mode: in the hole before lowering the vine - 15-20 liters, after instillation - 20-25 liters. It is best to use warm water when planting in the cold season. During the first year of development, a hole is formed around each bush at a distance of 25-35 cm from the trunk to the depth of a blade bayonet. Abundant watering and mulching with a film is carried out. Watering is not done during the ripening period of the vine.
Watering at the stage of bush growth is usually carried out with warm water 1 time in 6-7 days. It is recommended to warm up the water with the sun's rays and add mineral fertilizer at the rate of 20-25 mg per 10 liters of water. After a month of plant development, watering is limited to 1 time in 15-17 days. A mature plant is watered as the soil dries. For this, a circular hole 22-25 cm deep is formed at a distance of 45-55 cm from the center of the bush. Watering is done rarely, but abundantly: 50-65 l / sq.m.
Top dressing. The optimal scheme for feeding the vineyard is 4 times per season. The first top dressing is done in early spring: a complex composition is introduced into the irrigation hole - superphosphate (38-42 g), potash (28-32 g) and nitrogen (42-55 g) fertilizers for each bush. Additionally, together with the first spring watering, a liquid top dressing (100 g) is applied per 20 liters of water (for example, "Solution").
The second feeding is carried out 14-15 days before flowering, its composition is similar to the first feeding. You can add an aqueous solution of manure with the addition of potassium nitrate and superphosphate. The next feeding is carried out similarly to the previous one at the beginning of berry development. The fourth stage is carried out during the maturation of the brushes. Only phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are used, nitrogen fertilizers are not recommended. Foliar dressing of the vineyard is carried out 3-4 times with the help of ready-made products such as "Aquarin", "Novofert", "Kemira".
Back to the table of contents
Vineyard pruning
Vineyard maintenance involves pruning shoots. The first pruning is done when planting according to the described method.In summer, during flowering, pruning is carried out as follows: non-flowering shoots are cut to the fifth leaf, and branches with flowers - to the second leaf located after the inflorescence. After harvesting (before the dormant period), the main vine is shortened by half, and 2.5-4 cm (2 buds) are left on the branches.
In greenhouse cultivation of grapes, artificial pollination of flowers becomes an important agrotechnical measure due to the absence of bees. Cross-pollination is usually used, when pollen from one plant is transferred to the flowers of another bush (using a brush). The easiest way to pollinate is to sharply shake the branches of the plant every day in the evening.
Rate the article:


