 Today, the growing of aquatic (aquarium) plants, whether for sale or for decorating a home aquarium, is gaining in popularity. But no matter what the reasons for cultivating these beautiful exotic plants, most aquarists ultimately want to acquire a lovely and healthy specimen that will decorate even the most ordinary-looking aquarium.
Today, the growing of aquatic (aquarium) plants, whether for sale or for decorating a home aquarium, is gaining in popularity. But no matter what the reasons for cultivating these beautiful exotic plants, most aquarists ultimately want to acquire a lovely and healthy specimen that will decorate even the most ordinary-looking aquarium.
And yet, a novice hobbyist sometimes lacks the necessary knowledge that an experienced aquarist has acquired over the years of practice, so he cannot always correctly assess the situation and achieve the desired results. This is especially true for aquarium plants cultivated in nutrient substrates, the growth and development of which directly depends on the quality of the soil and on the state of their root system.
Having well-developed roots, many types of aquatic plants grow quite quickly due to the fact that they are adapted to assimilate the nutrients contained in the soil. This also applies to most aquatic plants belonging to the hydrophyte group, which, among other things, are adapted to obtain nutrients from water and air. Basically, representatives of this group tolerate the absence of a full-fledged substrate relatively easily. In addition, a systematic water change and the presence of organic matter supplied by aquarium fish provide most plants with perfectly acceptable conditions for growth, vegetative propagation and even flowering. And nevertheless, in order for the acquired specimen to develop well and be as attractive as possible, it must be planted in a special soil that contains a variety of additives.


These nutritional mixes, available from various companies, promote the good development of aquatic plants without harming fish or other aquarium inhabitants. When planting, the substrate is poured onto the bottom and covered with a layer of ordinary neutral soil on top. However, such actions will be useless if, along with them, you do not take care of creating the necessary conditions, including the competent organization of lighting and the availability of optimal water parameters that would meet the needs of this instance. When introducing the nutrient mixture into the soil, it is important to be very careful, since for some time after transplanting, aquarium plants are often in a painful state, and excess nutrition can lead to exactly the opposite result. But as soon as it becomes obvious that the plant has taken root in a new place, it should be provided with the most nutritious and varied feeding. As you can see, in order to achieve the desired effect, the creation of nutrient soil must be carried out on time and with great care.
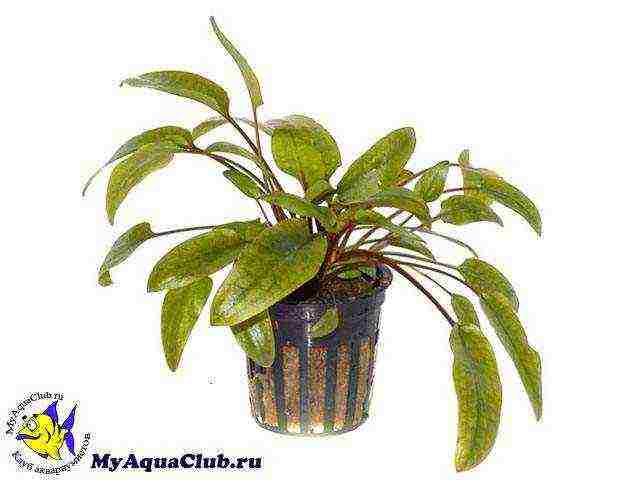
In the absence of mass plantings, aquarium plants are planted singly in separate containers with a nutrient substrate. Ordinary flower pots are fine for this purpose. In this case, the ratio of the area of the walls and the diameter of the holes at the bottom of the pot is important, since due to the exact location of the latter, proper respiration and nutrition of the root system is carried out due to the oxygen and nutrients supplied to it. Thus, by growing hydroponic and aquatic plants in a special container, excellent results can be achieved in a relatively short period. Using materials at hand, such as a plastic bottle, you can make your own pot.The height of such a pot should correspond to its diameter or, in extreme cases, be a quarter larger. Then the protruding parts located at the bottom of the bottle must be cut off so as to obtain holes with a diameter of 1 cm.This will allow the developing roots, which will become cramped in the plastic container, to grow through the holes into the common soil.
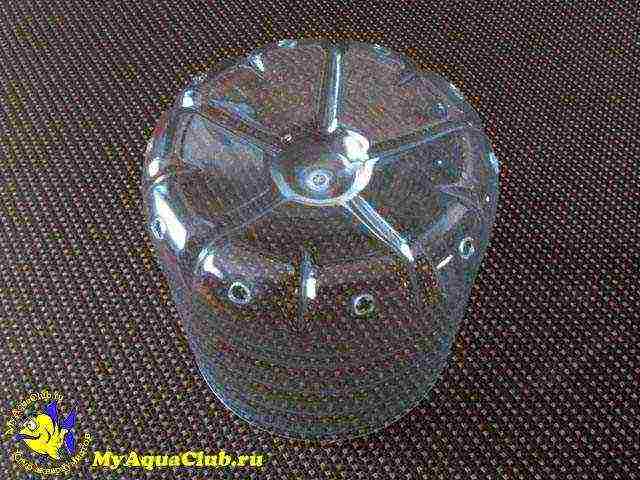


In a separate container, the soil is laid in several layers. First, a layer (about 2 cm) of large drainage is poured onto the bottom, and then a layer (1 cm) of shallow drainage. A nutrient mixture consisting of sand, two-year compost and garden soil with a peat content in a ratio of 1: 1: 2 is placed on top. Depending on the type of plant grown, sometimes coniferous soil, limestone or marble chips and clay, preferably blue Cambrian or red ferruginous, are added to this mixture. Having planted an aquarium plant in this layer, sprinkle the nutrient soil on top with a layer of pebbles about 2 cm thick.You can also use another mixture: white marsh sphagnum moss is placed on top of the substrate, covered in a pot, and then coconut substrate, which is mixed with "AVA" fertilizer. A small piece of porous limestone is placed in the center, the diameter of which is one and a half to two centimeters. In some cases, red clay can also be added there. Having planted the plant in this mixture, a thin layer of sphagnum moss is laid on top and covered with pebbles to the top. The container with the plant can now be placed in the paludarium or aquarium.
In order for the plant not to die as a result of transplantation into a nutrient substrate, it is necessary to prune the roots, and it is very important to do this correctly. When removing the plant from the soil, you will notice that some parts of the rhizome are slightly rotted. They should of course be removed. In elderly specimens, some of the roots, however, like the leaves, constantly die off and rot, forming a nutrient layer in the soil. However, at the same time, the main rhizome must still remain completely healthy without the slightest sign of rotting. When purchasing aquarium plants, preference should be given to young specimens, the roots of which are initially healthy, intact and clean. If, while transplanting an old specimen, you find rotten roots, then after removing the affected parts that are easily separated, it is advisable to use poor soil for planting the plant.
As for healthy roots, they are pruned in exceptional cases, for example, when they are too long and in the process of transplanting they would have to be twisted anyway. When planting, the rhizome should cover the prepared substrate in such a way that the length of the roots matches the radius of the pot. The neatly laid roots are sprinkled on top with soil, which is then slightly compacted. It is almost impossible to determine in advance what part of the roots will die after planting, but this will certainly happen, since in the process of even the most careful transplantation, partial damage to the root system occurs. Due to the fact that some of the roots are preserved, the plant adapts much faster to new conditions for it. Usually, new roots form and grow in the first few weeks.
Sometimes in the literature, recommendations are given that relate to the treatment of rhizomes of aquatic plants with a heteroauxin preparation that stimulates the growth and development of the root system. However, based on experience, it is safe to say that this does not bring any tangible changes. First of all, this concerns the planting of Echinodorus, in which, as a result of soaking the rhizomes in a solution, stronger roots are never formed. In comparison with them, semi-land-semi-aquatic specimens (hydrophytes) grown in a paludarium, after treatment with heteroauxin, root better.
Adhering to simple recommendations, you can count on the fact that, as a result, these excellent representatives of the aquatic flora, belonging to the hydrophyte group, will grow rapidly and develop well. The main thing is to transplant them on time and change the nutrient mixture in the pot every one to two years. As for Echinodorus, it can grow well without transplanting for two to three years, and this will only benefit the plant. It is important to remember that the pots in which aquarium plants are planted require careful handling, since an accidentally overturned container, whether by the aquarist himself or the nimble inhabitant of the aquarium, can cause a lot of trouble. At the very least, there will be a need for a thorough cleaning of the entire tank.
Thus, both experienced aquarists and novice hobbyists who do not have sufficient experience in handling special nutritional mixtures should weigh their options well before deciding on growing aquarium plants in pots, since this is a rather complex and time-consuming process that requires a lot strength and patience, and sometimes continuous control over the condition of the aquarium and its inhabitants.
Dear colleagues! Today we will talk about such an interesting topic as aquarium plants in pots. Growing aquarium plants for decoration of your aquarium or for sale is growing in popularity every day. And regardless of the goals pursued, aquarists try to cultivate the most beautiful and exotic plants. But on some decorative qualities you will not go far, it is also important the health of the plant itself, to which close attention is paid.
It just so happened, but the novice aquarist simply does not have the necessary information that accumulates over the years of keeping aquariums. For this reason, there are many erroneous assessments of situations to which the aquarist, due to his ignorance, reacts incorrectly. These actions lead to irreparable losses among aquarium fish and plants in particular. And plants that were cultivated in a nutritious aquarium soil are especially affected, since the normal development of a hydrophyte depends on the nature and quality of the substrate. After all, a healthy root system is the key to the health of the entire hydrophyte.
With a good root system, most aquarium plants (Ambulia, Cryptocoryne Blassa, Giant Vallisneria, Canadian Elodea, Kabomba) grow excellently, and most importantly, they grow quickly. And all because they have adapted to assimilate all the necessary nutrients from the soil. This statement also applies to other plants that absorb nutrients from water (Azolla, Pistia, Guadalupe Naiad, Riccia). As a rule, these representatives of hydrophytes tolerate the absence of aquarium soil without any problems. In addition, regular water changes for fresh and organic compounds, which are supplied by aquarium fish (swordtails, mollies, red neons, astronotuses, ancistrus), provide most hydrophytes with the necessary conditions for normal growth. But nevertheless, in order to buy a really good specimen that would grow excellently and be very attractive, it must be planted in a special nutrient substrate, which contains all kinds of additives.

Such substrates are produced in large quantities by different companies and they have a positive effect on the development of aquarium plants without harming other inhabitants of the aquariums. Before planting the hydrophyte, the soil is poured to the bottom, and then covered with neutral soil on top. But all these nutrient mixtures will be useless if the aquarium is not set to the correct light regime and there are no optimal aquarium water parameters that should meet all the needs of your chosen specimen.When adding nutrient supplements to the substrate, be careful, as after transplanting the plant can hurt, and excessive mineral fertilization can lead to the opposite result. After you see that the plant has taken root normally, then apply a variety of mineral fertilizing.
If the planting of plants is not massive, then they are mainly planted in special containers, in which a nutrient substrate is placed. For these purposes, ordinary flower pots are used. But here it is very important to take into account the ratio of the diameter of the holes in the bottom of the pot and the area of the walls, because thanks to the precise location of the holes, you help the hydrophyte to carry out proper root nutrition and respiration. It turns out that by growing aquatic hydroponic plants in a special container, you can achieve great results in a short period of time. You can make such a container yourself, just take a plastic bottle. The height of such pots should be equal to its diameter. Carefully cut off the protruding parts from the bottom of the bottle - you will get holes with a diameter of 1 centimeter. Thus, you will allow the plant's root system to develop further into common soil when it becomes cramped in a plastic container.

Nutrient soil is placed in a special container in layers. First, a two-centimeter layer of a large substrate is poured onto the bottom, then 1 centimeter of shallow drainage. And at the very top, you need to place a nutrient mixture consisting of garden soil, sand and two-year compost in a 2: 1: 1 ratio. Sometimes coniferous soil, marble or limestone chips and clay with a high iron content are added to such a container. After planting the plant in such a mixture, it must be sprinkled with a 2 cm layer of pebbles.
You can also prepare another mixture: sphagnum-marsh moss is poured onto the soil in a pot, then coconut substrate, pre-mixed with "AVA" fertilizers. In the middle, you need to put a small piece of porous limestone with a diameter of no more than 2 centimeters. Sometimes red clay is added to this mixture. After planting the plant in such a mixture, put sphagnum moss on top again and sprinkle it with pebbles to the top. After all these procedures, the plant is ready to be moved to the aquarium or paludarium.
If you do not want the hydrophyte not to die after transplanting into nutrient soil, it needs to be trimmed correctly by the roots. When removing the plant from the soil, note that some areas of the roots are slightly rotted. They must be removed. In old plants, some of the leaves and roots regularly die and rot. As a result, a nutrient layer appears in the substrate. But with all this, the roots should be healthy and without the slightest rot. If you buy plants in a store or at a bird, it is better to opt for young specimens, since their roots will in any case be healthy, clean and undamaged. If you are replanting an old specimen and you see a slightly rotted rhizome, remove the affected parts and plant the hydrophyte in poor soil.
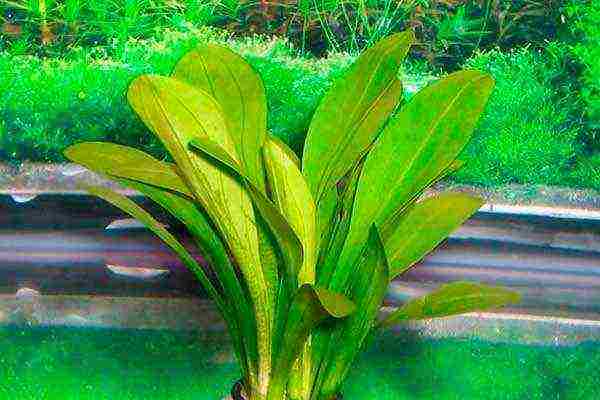

What about healthy roots? They are also trimmed, but rarely, mainly when they are long and after transplanting you will have to twist them. When replanting a plant, its roots should ideally lie in the prepared place so that the length of the roots is equal to the diameter of the prepared pot. Once the roots are neatly laid down, sprinkle them with substrate on top and compact. You will never be able to determine which roots will die as a result of the transplant, but this will happen anyway. The fact is that with the most careful manipulations during transplantation, in any case, you will cause minor damage to the rhizome. But since the main part of the roots will remain in good condition, the grass will quickly adapt to new conditions.As a rule, new roots are formed in such plants in a couple of weeks.
In the aquarium literature, you will be able to see tips that relate to the treatment of plant roots with heteroauxin, which stimulates root development and growth. But as the long experience of such manipulations has shown, such treatments do not have a special effect on the rhizome. In the first place, it doesn't really work with Echinodorus. When the roots are soaked in this preparation, most of the strong roots are never formed. But semi-land hydrophytes, which were grown under paludarium conditions, root much better as a result of soaking in heteroauxin.
If you adhere to the above recommendations, then you will get a lot of beautiful and healthy representatives of the aquatic flora, which will develop rapidly. It is very important that you transplant them on time and change the potted formula several times a year. Echinodorus without such replacement of mixtures can grow and not get sick for two to three years. You must remember that plant pots need to be handled with care. The fact is that some nimble hydrobiont (for example, a large girinoheilus) can overturn a container with a nutrient mixture and you will not end up in problems. At the very least, you will need to clean the aquarium well.
Therefore, before preparing the nutrient mixtures, the aquarist should properly assess their strengths and capabilities. After all, growing aquarium plants in pots is quite laborious and difficult. You will need a lot of patience and strength, and sometimes careful monitoring of the condition of the inhabitants and the aquarium as a whole.
Many hobbyists often see potted plants in aquariums.
These can be plastic, glass or ordinary ceramic pots. Unfired clay pots or wicker plastic "baskets", partially or completely dug into the ground, or just standing on the ground.

Why is this done?
First of all, it is necessary to clarify that we are talking specifically about growing plants in a biotope in pots, and not about hydroponics or about germinating hydrophytes in the air.
That is, instead of just sticking the root of the plant into the aquarium soil, the amateur "sticks" it into a pot of soil.
An obvious advantage of this type of hydrophyte cultivation is the ability to rearrange the pots over the entire area of the biotope bottom, as well as hang them in different places of the container: hydrophytes planted in this way are very transportable.
Indeed, if an amateur decided to create a beautiful composition of plants, then the ability to maneuver them will be very useful.
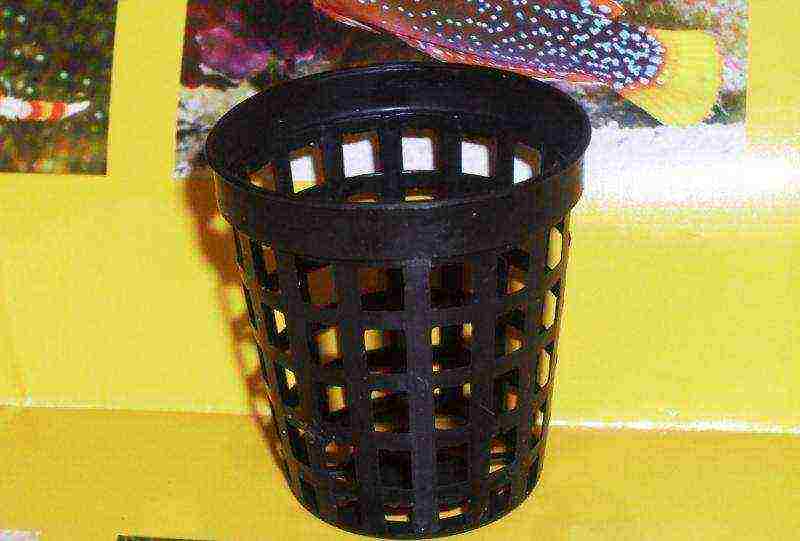

Pots are also used if the plant is planned to be rearranged in another biotope, or transported and sold, as well as if the plant has too large a root system capable of "clogging" a significant part of the soil area.
Most often, such pots are used to add nutrient soil to them.
If for some reason the aquarist does not want to add nutrient layers, either a large amount of fertilizers directly into the soil (for example, he is afraid of an algae outbreak, due to the fact that there are not so many plants in the soil, or he simply does not want to spend his time on maintaining, measuring and adjusting various parameters of the general environment in a biotope with a nutrient soil - it is known that this requires a lot of attention and time), then nutrients can only be added to the pots.
either a large amount of fertilizers directly into the soil (for example, he is afraid of an algae outbreak, due to the fact that there are not so many plants in the soil, or he simply does not want to spend his time on maintaining, measuring and adjusting various parameters of the general environment in a biotope with a nutrient soil - it is known that this requires a lot of attention and time), then nutrients can only be added to the pots.
In this case, their concentration will be insignificant and will definitely not harm the entire biotope.
This planting method is also used for plants that require individual feeding, for example, weak plants or very expensive ones. At the same time, the pots themselves are often hidden by snags and creeping plants.
Potted plants are a solution for a biotope in which fish digs heavily in the soil. And the roots of these plants are guaranteed not to "suffer" when cleaning the soil with a siphon.
However, seemingly ordinary pots, in fact, have a special design!
The peculiarity of this design is the presence of lateral openings that provide ventilation and metabolism with the environment, which makes it possible for the roots in the pot to breathe and receive from the biotope the substances necessary for the whole plant for development. In addition, some of the roots will be able to germinate into the surrounding soil (when rearranging the pot, they are cut off), since the roots will be "cramped" in the pot itself.
If you do not make holes in the walls of the pot, then the soil in it can begin to sour, and the roots can rot.
It is worth noting that planting in pots is also used when it is necessary to prevent the plant from growing too much. And if the process of growth has begun, then the roots that have grown outside the pot are cut off, and the pot itself is taken out, after which they are rearranged to another place, or put in the same place.

The holes in the pot are 1x1 cm in size, and the height should be approximately equal to the diameter or slightly larger. For most species, a diameter of 8-12 cm is suitable.
Drainage is done at the bottom of the pot: a large drainage is placed at the very bottom with a layer of about 2 cm, on top - a shallow drainage with a layer of about 1 cm.A nutritious soil layer is placed on the drainage (for example, based on peat or clay), and the next layer is covered with pebbles or coarse sand ... You can make such a pot yourself from a plastic bottle by cutting off the bottom from it and making holes in the walls.
A plant planted in this way must be transplanted at least once a year, otherwise the roots may begin to rot.
The volume of the pot must be large enough, otherwise the plant may die or give a "forest" of aerial roots.

Of the disadvantages of using pots in a biotope, it should be noted, again, the limited growth of hydrophyte. Indeed, in fact, the area of development of its roots is limited by the walls of the pot. If an amateur is waiting for the lush growth of hydrophyte, with the "capture" of shoots and root buds of a large area, then the pots are completely contraindicated.
In the case of plastic pots, over time, the plastic can start to poison the water.
In addition, as already mentioned, plants in pots must be transplanted at least once a year in order to avoid root rot. While "soil plants" are not recommended to be touched more often than once every three years!
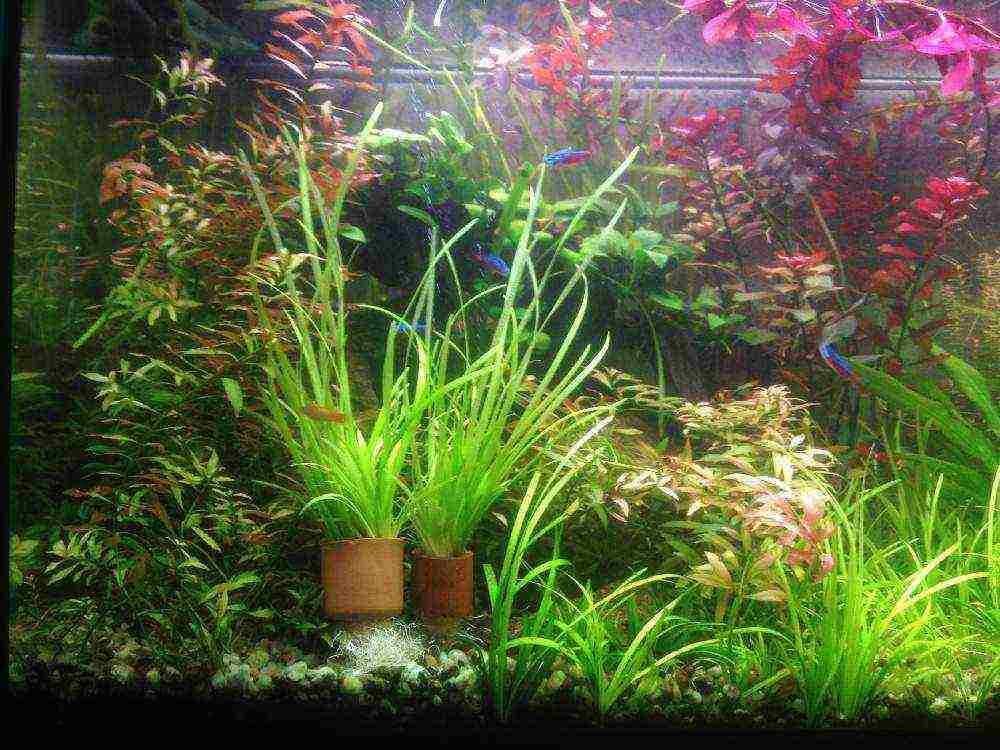

Planting aquarium plants

How to properly plant the plants in the aquarium? Very often, such a question arises for people who decide to get cichlids. And the fact is that these fish seem to be deliberately trying to nullify all your efforts to plant plants in the ground. They undermine them, dig them up - as a result, the plants float on the surface again. Naturally, this does not benefit them, and your patience is coming to an end. And the solution is very simple - to plant the plants in pots.

The pots can be purchased at the store or made yourself from the bottom of a plastic bottle. For a large plant, the pot should not be too small, because you need a place for the roots to grow. The height of the pot should ideally be equal to its diameter. For small plants, pots are usually used, which usually sell small cacti. Now you have a choice of how to plant your plants.

The first method is easier and more common. We take a pot, soil from the aquarium and plant a plant in it. It is advisable to pre-make several holes on the sides of the pot and at its bottom for ventilation of the roots. Do not forget that the lighting of the aquarium in the presence of living plants must be strong enough.

The second method is only for those who regularly (at least once a week up to 30% of the volume) change the water in the aquarium. In this case, the plant is planted in a nutritious soil. With this planting, the plant develops more intensively, acquiring a powerful root system. The nutritious soil consists of 30% garden soil or black soil, the remaining 70% # 8212; aquarium soil.A small layer of aquarium soil is placed on the bottom of the pot, then a layer of earth and everything is sprinkled on top with more aqua soil. Everything. And there is no need to be afraid that such a mixture will affect the composition of the water. With the correct water change, nothing threatens the fish.

Large fish can turn plant pots, so it is best to bury the pots in the ground.
Aquarium plants, aquarium design & # 8212; video
Aquarium plants in pots
I don't think potted aquarium plants look pretty, but managing a potted plant is much easier.
For example, everyone knows that there are fast-growing species of aquarium plants that, having grown, can drown out the growth of slow-growing species.
Also, fast-growing plants often have to thin out, while stirring up the soil and stirring up the silt. And plants in pots do not go beyond the limits of the pot and do not grow throughout the entire aquarium.
Aquariums with a variety of aquatic plants look very nice and it is much easier to achieve the normal development of all types of plants when the plants grow in pots. You can make plant pots from plastic bottles. If you have now imagined a terrible picture, where the bottom of your aquarium is filled with pots and even cut plastic bottles, you are greatly mistaken. The pots can be easily hidden in the ground.
This is done this way: the lower part of the plastic bottle is cut off and no more than the height of the soil laid in the aquarium. Further, the pots with the plants planted in them are placed in pre-made holes and carefully sprinkled with soil.
The pots disguised in the ground are completely invisible and no one will guess that aquarium plants grow in pots. By rearranging the potted aquarium plants in places, you can change the picture and control the design of the entire water garden. By growing aquarium plants in pots, we can fertilize each type of plant separately.
For example, when planting capricious plant species, you can add a small amount (one or two teaspoons) of red clay or even garden soil to them in pots without fearing that the earth or clay will stir up the water.

Adding garden land

Cutting the stem of the hygrophila

Filling the pot with small pebbles

Aquarium plants in pots
Aqualover
Plant pots in aquariums
Scale for total water hardness
Total, permanent and temporary water hardness
The circulatory system of fish. Organs of hematopoiesis and blood circulation
Many hobbyists often see potted plants in aquariums.
These can be plastic, glass or ordinary ceramic pots. Unfired clay pots or wicker plastic "baskets", partially or completely dug into the ground, or just standing on the ground.
First of all, it is necessary to clarify that we are talking specifically about growing plants in a biotope in pots, and not about hydroponics or about germinating hydrophytes in the air.
That is, instead of just sticking the root of the plant into the aquarium soil. an amateur "sticks" it into a pot of soil.
An obvious advantage of this type of hydrophyte cultivation is the ability to rearrange the pots over the entire area of the biotope bottom, as well as hang them in different places of the container: hydrophytes planted in this way are very transportable.
Indeed, if an amateur decided to create a beautiful composition of plants, then the ability to maneuver them will be very useful.

Pots are also used if the plant is planned to be rearranged in another biotope, or transported and sold, as well as if the plant has too large a root system capable of "clogging" a significant part of the soil area.
Most often, such pots are used to add nutritious soil to them.
If for some reason the aquarist does not want to add nutrient layers, either a large amount of fertilizers directly into the soil (for example, it is afraid of an outbreak of algae due to the fact that there are not so many plants in the soil or simply does not want to spend its time on maintaining, measuring and adjusting various parameters of the general environment in a biotope with a nutrient soil - it is known that this requires a lot of attention and time), then nutrients can only be added to the pots.
either a large amount of fertilizers directly into the soil (for example, it is afraid of an outbreak of algae due to the fact that there are not so many plants in the soil or simply does not want to spend its time on maintaining, measuring and adjusting various parameters of the general environment in a biotope with a nutrient soil - it is known that this requires a lot of attention and time), then nutrients can only be added to the pots.
In this case, their concentration will be insignificant and will definitely not harm the entire biotope.
This planting method is also used for plants that require individual feeding, for example, weak plants or very expensive ones. At the same time, the pots themselves are often hidden by snags and creeping plants.
Potted plants are a solution for a biotope in which fish digs heavily in the soil. And the roots of these plants are guaranteed not to "suffer" when cleaning the soil with a siphon.
However, seemingly ordinary pots, in fact, have a special design!
A feature of this design is the presence of side openings that provide ventilation and exchange of substances with the environment. which makes it possible for the roots in the pot to breathe and receive from the biotope the substances necessary for the whole plant for development. In addition, some of the roots will be able to germinate into the surrounding soil (when rearranging the pot, they are cut off), since the roots will be "cramped" in the pot itself.
If you do not make holes in the walls of the pot, then the soil in it can begin to sour, and the roots can rot.
It is worth noting that planting in pots is also used when it is necessary to prevent the plant from growing too much. And if the process of growth has begun, then the roots that have grown outside the pot are cut off, and the pot itself is taken out, after which they are rearranged to another place, or put in the same place.

The holes in the pot are 1x1 cm in size, and the height should be approximately equal to the diameter or slightly larger. For most species, a diameter of 8-12 cm is suitable.
Drainage is done at the bottom of the pot: a large drainage is placed at the very bottom with a layer of about 2 cm, on top - a shallow drainage with a layer of about 1 cm.A nutritious soil layer is placed on the drainage (for example, based on peat or clay), and the next layer is covered with pebbles or coarse sand ... You can make such a pot yourself from a plastic bottle by cutting off the bottom from it and making holes in the walls.
A plant planted in this way must be transplanted at least once a year, otherwise the roots may begin to rot.
The volume of the pot must be large enough, otherwise the plant may die or give a "forest" of aerial roots.
Of the disadvantages of using pots in a biotope, it should be noted, again, the limited growth of hydrophyte. Indeed, in fact, the area of development of its roots is limited by the walls of the pot. If an amateur is waiting for the lush growth of hydrophyte, with the "capture" of shoots and root buds of a large area, then the pots are completely contraindicated.
In the case of plastic pots, over time, the plastic can start to poison the water.
In addition, as already mentioned, plants in pots must be transplanted at least once a year in order to avoid root rot. While "soil plants" are not recommended to be touched more often than once every three years!

 Light in the life of aquarium plants
Light in the life of aquarium plants
 Selection of fish by water layers
Selection of fish by water layers
 Fakus, euglena
Fakus, euglena
Sources:
No comments yet!


