Content
This main component of the wine industry is more than 90 thousand years old, but it was the inhabitants of the regions between the Caspian and the Black Sea, as well as in Afghanistan and Iran that cultivated it. Grapes as a cultivated plant quickly spread to almost all regions, but the technology of its cultivation, naturally, differs in different climatic zones. The most effective are vegetative methods of plant propagation, including the Italian method, especially in Europe, where the soil is not infected with phylloxera. It is not without reason that Italy is considered the birthplace of winemaking.

The main types of bunches of grapes: 1 - cylindrical; 2 - conical with a "wing"; 3 - conical without "wing"; 4 - branched.
Scientists have calculated that climbing vines are the progenitors of today's cultivated grape varieties, and they have always strived for an abundance of sunlight and a sufficient amount of moisture in the soil, therefore, in order to grow a good grape bush, it is necessary to comply with these requirements as much as possible.
Biological features of grapes
The grape belongs to the Vitaceae Juss family, which has 14 genera and more than a thousand species. Almost all cultivated plant species belong to the genus Vitis, which unites 70 species. In the wild, these are perennials, in most cases producing large climbing bushes.
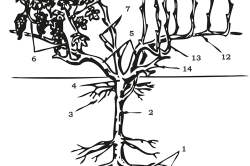
Diagram of the structure of the vine: 1. Calcaneal roots, 2. Underground bole, 3. Superficial roots, 4. Bush head, 5. Sleeves, 6. Fruitful shoots, 7. Fruit link, 8. Fruitless Escape, 9. Stepson, 10. Coppice shoot, 11. Annual shoots, 12. Arrow of fruiting, 13. Substitution knot, 14. Horn.
The cultivated grape bush consists of underground and aboveground parts. The underground part is made up of an underground bole and root system. The stem has a length of 40 to 50 cm and is used by gardeners as planting material, because it is reliably protected by a layer of soil from low temperatures in winter and drying out in summer. The root system nourishes the plant, absorbing nutrients from the soil, so no less attention should be paid to the roots: moisten, loosen the soil, apply fertilizers.
The above-ground part is the above-ground bole, the sleeve of the bush, its head, annual shoots and second-order shoots, called stepchildren, which, after flowering, turn into large clusters of juicy tasty berries.
The base of the underground stem is called the heel. The head is the part of the bush that is at or below ground level with the covering growing technique, which is most common in our country. Perennial vines that extend from the head are called sleeves if they are more than 35 cm long, and horns if they do not reach 35 cm in length.
The annual vine extending from the base of the bush is called the formation knot, and the one adjacent to the fruit vine is called the replacement knot. Fruit vines are called arrows if 5-8 eyes are left on it, an arc if there are 9-12, and a whip if there are more than 12. It is the fruit vine, together with the replacement knot, that form the fruiting links and require maximum care.
Back to the table of contents
Planting grapes: caring for bushes
Grapes are not very picky about the soil, but if the soil is infertile, it is better to dig planting holes to a depth of 1 m, adding organic fertilizers, black soil and sand to them. In black soil conditions, you can limit yourself to a depth of 60-70 cm.But the grape bush's worst enemy is the shade, where it grows intensively, but bears little fruit. If you plan to grow plants against the wall, choose the southern or southwestern part, because in this way the wall will heat up during the day and even at night the bush will be provided with heat.
If the grapes are grown in an open area, then a separate support can be made for each bush, but gardeners prefer, in order to save money, to plant plants in rows on a single support. Naturally, each variety must grow separately, because the grapes are intensively sawed. Bushes should be at a distance of at least 1.5 m, and the row spacing should be at least 2 m. Rows should be better formed in the east-west direction.

Grape planting scheme.
It is better to have planting pits prepared in the fall, laying soil mixed with manure along the bottom, and in its absence, water the pit with infused ash or bird droppings. For the winter, the planting hole is compacted with a thin layer of soil. And in the spring, seedlings are planted there, also harvested in the fall. If there is not enough material for planting, you can also use cuttings, but leave a deep hole above its surface.
Grapes can be planted vertically and obliquely, but one should not forget that in the first case, all roots are cut to 10 cm.In either case, the roots are soaked for two days in an infusion of rain water with the addition of 1 tablet of heteroauxin per 10 liters of water ... It is not recommended to disembark until the temperature reaches 10 ° C. The first watering should be done with warm rainwater.
Autumn planting is also possible, but this should be carried out until mid-October, when the plant goes into a dormant state. In this case, for the winter above the seedling, you need to build an earthen mound 25-30 cm high in order to avoid freezing.
It so happens that the stalk does not take root. The reason for this phenomenon may be its drying out, underdevelopment before the time of pruning, soil affected by rot, a stalk that has grown too much during planting, insufficient watering. For better survival of the cutting, the modern technique suggests planting it together with a part of a two-year-old vine about 1.5 meters long, laying it in a ring along the bottom of the planting pit.
It is very important to install supports for the bushes in time. In the fall of the first year, a single-row vertical trellis with a five-tiered wire is quite enough. When six to eight sleeves are formed in the bush (3-4 years of fruiting), a two-plane inclined trellis is required. Thus, the whole plant keeps well on the support and receives enough light from top to bottom.

Shelter scheme for the vine for the winter.
In the autumn period of the first year of the growing season, before the threat of frost, young shoots are covered without cutting. They can only be touched in spring, even if the vine is "crying" intensely. After four years, the formation of the bush is carried out exclusively in the fall, when the sap flow stops. A bush grown from a seedling is naturally older than a cuttings, but regardless of this, by autumn only one shoot with 2-3 eyes is preserved. In the case of the development of two shoots, it is better to cut each of them into two buds in order to form four sleeves in the future. But if there are three shoots, then the lowest one is cut off regardless of its thickness.
Summer work is reduced to loosening the soil near the bush, intensive watering, especially in hot summer conditions, and pest control. Also during this period, weak shoots develop from the central bud of the eye, which gardeners call a "panicle". They need to be cut, leaving only the two most developed lower shoots.
The worst enemy of the grape bush, and therefore of the future harvest, is mildew, which is resistant to frost and can remain in dry leaves. Even in spring, it is better to plant the planting with copper sulfate (100 g per 10 liters of water) without lime.In summer, the developing bush is sprayed with a polychrome solution (25 g per 10 l of water), and after each rain with the same solution, but in double concentration, without waiting for the leaves to dry. This will help protect the bushes from many fungal diseases and rot.
Against powdery mildew, sulfur is used as a preventive measure, which should be constantly on the bushes at the age of more than 4 years, in the form of pollination with crushed sulfur or spraying with a suspension of colloidal sulfur (80 g per 10 l of water). Acaricides are effective against ticks. If the plant is too badly affected, then it is better to remove it completely so as not to spread the infection.
The first feeding of grape bushes is carried out in early May. To do this, 60 g of nitrogen is dissolved in 10 l of water and poured into a hole around the base of the plant. Every 10 liters of solution is alternated with the same amount of clean warm water, watering is repeated two more times, and the soil is mulched. Such procedures are repeated once every two to three weeks, depending on the weather. It is recommended to combine them with fertilizer, which is applied to the aisles not earlier than in the second year of full fruiting.
For the winter, the bushes must be wrapped, especially in the climatic conditions of the greater territory of Russia. A week before warming, the upper roots are cut off without leaving hemp and with disinfection of the sections with a solution of copper sulfate. But this procedure can be repeated only once every two years. To carry out the manipulations, they dig a hole to a depth of 15 cm, and then cover it with clean sand without any admixture of clay. It is not recommended to tie up green shoots too tight, it is best to use the loop with a winding method, in which a loop is freely applied to the handle, and it is tied tightly to the mount.
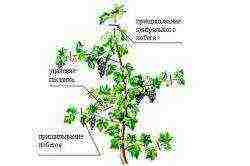
Scheme of pinching grapes.
The shrub formation process can be accelerated during the summer growing season. It is this method that allows Italian gardeners to achieve maximum fruiting. For this, a two-year or a developed one-year-old seedling is chosen, which has two shoots, cut into knots with three eyes each, of which six shoots will have formed by autumn. In early June, they are minted, leaving 5-6 leaves on each, and the uppermost shoots are removed from the bush.
The chased arrows are placed obliquely in two in different directions for the simultaneous growth of the stepsons. After 9-10 days, the stepson's shoots begin to grow from the leaves of the main ones. By the end of June, the main shoots have two uppermost shoots, while it is very important that the second one is external, like a future replacement knot. The rest of the stepsons gently pinch off, leaving leaves, thus forming a young sleeve with preserved leaves. The next year, in the spring, it is already possible to make the first trimming, for which on the sleeves the outer lower stepson is cut into a replacement knot with 2-3 eyes, and the upper one - into a fruit arrow with 7-8 eyes. So in the spring of the second year, you can get a formed four-arm bush with 30-35 eyes. In the first year, the inflorescences are removed from the bush, and in the second year it already fully bears fruit. Today, this is the most common technique for achieving maximum yield from each bush.
If the bush develops normally and bears fruit, then from about the beginning of October, when the last crop is harvested, make sure that the shoots turn light brown and crackle when bent. The time has come for sanitary clearing - removal of overgrowth shoots and leaves below the first wire, you can cut off the tops of young shoots. The lowest outer knot is cut into a new knot with 2-3 eyes, the next one - on a fruit arrow of 8-10 knots, and the upper shoot is removed. After 8-10 years, when fertility decreases, the bush should be replaced with a young one.
Back to the table of contents
How to properly grow planting material
Different methods of planting vineyards include the use of ripe annual vine cuttings, one- and two-year seedlings, rooted cuttings, layering and green seedlings grown in greenhouses as seedlings.
Cuttings can form a root system both from nodes and from any point between nodes. Cuttings shoot only from the buds of the eye. For growing seedlings, even one-eyed cuttings 50-60 cm in size are used. Autumn harvests obtained after the growing season have a greater viability than spring ones, because then it is impossible to accurately determine the number of kidneys damaged by frost and choose the surviving ones. From drying out and mold, autumn cuttings are soaked for two days and then placed in plastic bags. They are best preserved in wet sand or buried in the ground at a depth of 25-35 cm. A thin layer of sand is poured at the bottom of the groove, and a small mound is formed above it so that not too much moisture gets in. For cuttings, healthy shoots are chosen, and unripe shoots that do not crackle when bent, with traces of disease damage, are removed.
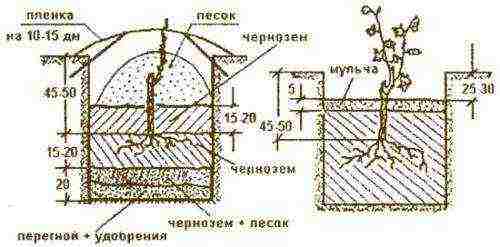
The scheme of preparing a pit for grape seedlings.
For growing seedlings, cuttings that have reached a length of 30-35 cm are harvested in advance. Sometimes they are left 70 cm long for better preservation, and cut in two before use. But this is not very effective, it is better to take good care of short cuttings. During the autumn rains, a trench is prepared so that it is moistened as well as possible in winter and warmed up by the spring sun. In the spring, it is abundantly watered with hot water, and at the end of March, cuttings are taken out, cut to the very knot, and soaked in warm sedimentary water for 24 hours with the addition of growth stimulants.
The prepared pits are carefully fertilized, followed by planting cuttings there at a slope in the south-north direction. The soil is compacted, and the entire surface of the seat is sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate without the use of lime (50 g per 10 l of water). There should be a furrow along the planting line for watering 3-4 times a week. When the first shoots appear, they are sprayed against diseases. For the winter, the school is well covered, and the next autumn they are planted in a permanent place.
Seedlings can also be grown in greenhouses using paper cups. To prevent the glasses from getting soaked, they are wrapped in foil. When the moment of planting comes, the film is removed, and the paper can be left in order to preserve the roots as much as possible. The main point is maintaining the temperature in the room at 25-30 ° C and additional lighting.
Saplings from green cuttings and cuttings are used less often, and sometimes grapes are propagated in a seedling-free way, using cuttings of green shoots. Whichever technology you choose, you need to take into account that this plant is quite picky, but the taste and usefulness of the berries justify all the efforts made, and the grape business is considered one of the most profitable today.
For a long time, everyone got used to the idea that there are cold-resistant plants, and there are thermophilic ones. Pineapples and bananas do not grow in our latitudes. No matter how hard you try, you can't grow a mango on the Kola Peninsula. There is no need to talk about mangosteen and other exotic things. Some varieties of southern plants grow in our latitudes, but they do not give especially high-quality fruits.

Growing grapes
Grape
The well-known grapes also belong to such plants. Wild and cultivated grapes are often found in the southern regions of the country. Some varieties grow in the temperate zone. However, we cannot grow it on an industrial scale in the open field. The fact is that although the plant itself can survive in our climate, its berries, in terms of their taste, are significantly inferior to their counterparts grown in the South.
Grapes are a thermophilic plant. It needs sunny, hot weather to ripen.In the south of France or in Spain the number of sunny days per year reaches 300. The berries are large, juicy, with a rich taste and aroma. Grapes in these countries are part of a thousand-year-old culture. No wonder the inhabitants of these countries say: "Why drink water or tea when there are so many wonderful wines in the world?"
Grapes in our area are not destined to enjoy such respect - after two weeks of heat, frosts can hit, which will certainly ruin most of the harvest. As for the remaining berries, one can only regret that they survived. The wine will turn out to be bad. The long winter also does not contribute to the growth of yields.

Exit
The need to regularly receive vitamins and simply indulge in fresh fruits and vegetables has long forced people to learn how to grow some plants not typical for the area in greenhouses. Thanks to the use of greenhouses, flowers are grown in the Arctic. Residents of Siberia and the Far North eat fresh cucumbers and tomatoes grown in greenhouses in these harsh regions every day.
Fruit plants are more capricious - many of them cannot be grown in greenhouse conditions. However, not so long ago, a technology for growing grapes in a greenhouse was developed. In this way, the whole country, or even its separate northern region, cannot be made to drink wine. Cultivation on an industrial scale is not yet available to our farmers. Given the tenderness of the plant and the constant need for careful care of it, growing grapes in a greenhouse is available mainly to small producers.

Greenhouse device
Given the fragility of this tropical plant, the usual flimsy structure, suitable for growing cucumbers at home in warm autumn, in the form of a metal frame covered with plastic wrap, is not suitable for growing it. Here you need a solid structure that can withstand unexpected cold snaps and protect plants from long winters. You can order the construction of such a greenhouse from a company specializing in this. However, it is much more pleasant and more economical to do it yourself.
The main structural elements of a greenhouse suitable for growing grapes are:
- Frame - made of a metal profile installed on a foundation. The frame, in turn, consists of vertical posts and arches for the roof;
- The roof - best of all - is of an arched type. This shape provides a larger volume of the room and prevents the accumulation of dust in summer and snow in winter.
It is recommended to lay a brick wall about a meter high along the sunny side of the greenhouse. During the day it will be heated in the sun, and in the evening it will warm the air, gradually giving it its warmth.
It is recommended to use transparent cellular polycarbonate as a material for the roof and walls. It transmits light well and, thanks to its cellular structure, ensures the preservation of the greenhouse effect. The optimum material thickness is 6 mm.
The disadvantage of this design is the possibility of excessive heating of the air in the greenhouse during the sunny summer period. To eliminate this drawback, it is necessary to make several vents in the walls on all sides of the greenhouse to allow regular ventilation of the room, which will not overheat the grapes in the greenhouse. The video shows the process of building a greenhouse.

Along the inner side of the surface of the walls, it is necessary to install T-shaped posts made of a metal profile.A wire should be pulled between the beams, as shown in the photo, along which the grapes will grow. Racks can be installed in multiple rows. Their number depends on the size of the greenhouse.
When installing stands and planting, it is necessary to ensure that the plant does not reach the walls of the greenhouse - otherwise, this climbing plant can penetrate outside the greenhouse or get burned from direct sunlight.
Advantages
Growing grapes in a greenhouse (video shows the construction process) has the following advantages:
- care - the plant is under constant supervision of the owner;
- protection - the plant is sheltered from wind, cold and excessive heat;
- health - isolated from other plants, a greenhouse crop is less likely to get sick (plants also get sick)

- inaccessibility - with sufficient isolation from the surrounding nature, the plant will not interfere with the growth and development of various rodents, insects and their larvae;
- hygiene - dust and dirt do not accumulate on leaves, branches and fruits;
- environmental friendliness - the absence of the need to constantly conduct a merciless pest control almost excludes the use of various agrochemicals;
- compactness - a greenhouse vineyard can be planned in such a way as to plant as many plants as possible without being particularly tied to the terrain - to mountain slopes, streams and other natural factors;

- longevity - thanks to all of the above factors, the plant will outlive its owner;
- the economic factor is the relatively low cost of cultivation and a quite tangible harvest.
Flaws
In the process of growing grapes in a greenhouse, as elsewhere, there are disadvantages:
- Labor intensity - despite all the seeming simplicity - this is a rather troublesome occupation, requiring attention and concentration;
- Science intensity - the cultivation of grapes is an art developed for centuries by entire nations. This is a whole science, which is impossible to study without preliminary preparation;
- Quality - the taste of greenhouse grapes will be inferior to the taste of berries grown on the southern slopes of the Italian mountains;
- Time - growing grapes is generally a long process.
Despite the presence of disadvantages, they are still much less than advantages. Over time, the self-taught winegrower will learn how to properly care for the plants and will be more than rewarded for his work. In short, this is the whole technology of growing grapes in a greenhouse. The video shows the highlights of this process.
Vineyards have been cultivated in our country for decades. Of course, the main harvest went to the production of wine, but the grapes themselves are also a very valuable, tasty product. What is valuable about the idea of growing grapes is that it grows on sandy, rocky soils, unsuitable for other crops. Let's try to find out if a vineyard is a successful business idea.
Agricultural business for growing grapes
Suitable soil for vineyards
Most of the vineyards in our country grow in the southern region (Krasnodar Territory), where the history of winemaking dates back to several centuries. Viticulture requires a lot of natural sunlight, and well-drained soil. The best places for vineyards in Russia are soils with a slight slope to the south and sheltered from the wind by hills on the west side. Loamy soils are suitable and it is strongly discouraged to grow the vineyard in wetlands.
Harvesting a rich harvest
Planting and growing
Before planting a vineyard, the soil must be fertilized with manure and lime. Vines also require nitrogen-rich soils for good growth.
If you do not have sufficient experience in growing grapes, you should not make costly mistakes, it is better to seek help from an experienced oenologist (specialist in growing vineyards).
The quantity and quality of the crop is highly dependent on weather conditions.
The fact is that the composition of the soil and mineral fertilizers have a great influence on taste and productivity, so the issue of education in this matter should be approached very responsibly. With the advice of professionals, you can avoid many setbacks and increase the likelihood that your vineyard will produce a rich, quality crop.
In central Russia, the following grape varieties are grown:
- Arcadia
- Augustine
- Donskoy arat
- White beauty
- Bulgaria
- Buffalo
- Delight
- Decorative
- Diana
- Isabel
- Kazachka
- Cardinal
- Michurinsky
- Kishmish
- Muromets
- Muscat
- Special
- Premier
- Platonovsky
- Early Magaracha
- Russian amber
- Ukraine
- Early purple
It is best to plant vineyards at a slight slope so that the groundwater does not stagnate
Necessary equipment
In addition to the vineyard, you should set up your own comfortable wine cellar, where you will process your grape harvest, store wine and possibly arrange wine tastings for potential buyers.
To process grapes, you will need: a crusher, vats, wine barrels, a press, alambiks. Get beautiful bottles and designer labels. You need to prepare a wine cellar for storage and arrange a tasting area. Wine should have its own atmosphere and a cozy place to relax with a glass of wine in hand.
In addition to selling grapes, you can also do wine production
Analysis of the benefits and risks of winemaking
Growing grapes is as risky as it is risky. Therefore, it is worth immediately calculating what are the opportunities, threats, strengths and weaknesses of this project?
| Strengths of the project | Possibilities |
| Creation of a unique Russian product of local production
Production of high quality environmentally friendly product A popular tourist attraction can be created Comparatively low level of chemical use in grape growing |
Steadily growing demand for quality wines
Russia has a limited supply of local quality wines and little competition from other producers Increased interest in local and regional products Interest in wine has increased among the more educated and wealthy part of society, and among young people there is a demand for the so-called culinary tourism, including wine tourism There is an opportunity to improve the reputation of Russian agricultural products and food products |
| Flaws | Threats |
| High risk due to variable climatic conditions
Lack of local experience in vineyard cultivation Insufficient experience in the competent management of investment funds and relatively high initial costs You will have to wait a long time for the first income (at least three years after planting the vineyard) Niche character of Russian wine As a result of climatic conditions and the complexities of cultivation, as well as the complexity of the rules and administrative procedures associated with the production and sale of wine |
Despite steady growth, low percentage of wine consumption per capita
Deeper interest in wine belongs to a rather narrow circle of consumers The characteristics of the characteristics of Russian wine (high acidity, dryness) are not able to impress the tastes of the average consumer Manufacturing organic products is usually costly and requires a smart marketing approach to make the business profitable |
Wine Vault
Estimated costs of growing vineyards
The costs of planting and growing a vineyard are high and therefore not a popular investment. To start and develop an agricultural business, you will need:
- Buying land
- Preparing the soil for the vineyard
- Purchase and planting of seedlings
- Wine Consulting
- Employee salary costs
- Purchase of machinery and equipment
- Creation of a wine cellar
- Vineyard maintenance costs
- Taxes and fees
- and promotion
The costs of creating vineyards on an area of 1 hectare will amount to approximately 4 million rubles.
Home wine cellar
How much can you earn from industrial grape growing?
Of course, if you are cultivating good varietal grapes, you can count on a profit of tens of thousands of dollars per year from 1 hectare. It should be remembered that this is a long-term investment, and you can expect the first money only a few years after the planting of the grapes and the founding of the winery. This is a business that, as in the case of growing walnuts, will be owned by more than one generation, and the vineyard planted by you can bring profit to your children and grandchildren.
Making sustainable products is costly, and to get to market, try to create a product with a story. You can tell about the region where the grapes were grown, a local legend or the story of the creation of a unique wine recipe from several grape varieties.
Wine tasting
Also, you can produce an analogue of the Spanish "Sangria", infusing the wine with local fruits and berries. Think up what will distinguish your product and create a profitable marketing ploy and advertising campaign on this difference.
Do not neglect the possibilities of the Internet - create a website where you can tell about your product, post a photo, description and price.
Wine tasting and sale can be turned into an exciting attraction
When investing in your own vineyard, you should be aware of the high costs of growing the vineyard and climatic conditions that are not always favorable for the ripening of a high harvest. But if you bring this successful business idea to life, you can trade delicious, healthy berries, sell grapes as raw materials to a private distillery, or open your own small winery. In any case, you will always have your own wine and be able to enjoy drinking it.
HACKED BY SudoX - HACK A NICE DAY.
Many gardeners want to grow grapes in the country to please themselves, their loved ones and enjoy ripe berries or aromatic wine. The grape is a thermophilic plant and thrives in the southern regions, characterized by an abundance of sunny days and stable positive temperatures. However, not only the happy inhabitants of the southern regions, but also the inhabitants of Moscow dream about viticulture.
WITHToday, planting grapes in the suburbs is quite common. It became possible to cultivate a crop in an unstable and cold climate thanks to the scientific discoveries of breeders who bred hybrid varieties with a short ripening period of berries. Previously, grapes in the Moscow region were used mainly for decorative purposes, for decorating gazebos, arches, and landscape design. But with the emergence of new early varieties with a growing season and the formation of mature bunches of about 110 days, it became possible to get a full harvest before the onset of the winter period.
You can find out how to plant grapes from our website. We will also consider the features of grapes for the Moscow region, non-covering varieties.
If you decide to grow grapes in the suburbs, pay attention to a number of factors that determine the success of your business:
- selection of the optimal landing site;
- competent planting of bushes;
- correct and careful plant care;
- selection of a variety corresponding to the climatic conditions of the area.
A heat-loving plant needs an abundance of sunlight, so it is recommended to plant it in the southern part of your site, protected from open drafts and strong winds. You can choose the southern wall of a house or outbuilding, or a blank fence. Grapes are not whimsical to soils, but they do not like wetlands, so choose a place with low groundwater levels or a hill. If the soil of the site is not very fertile, it can be fertilized in advance with natural compost.

If you are planting grapes near the wall, you need to retreat from the building from 0.5 to 1.5 meters so as not to harm the structure.The bushes are planted at a distance of about two meters from each other, and three meters are left between the rows. This will create comfortable conditions for the development of the plant and will facilitate further care and harvesting of a ripe crop. In case of non-observance of the recommended norms, it is possible that the lighting and airing of the plant are disrupted, which will lead to the development of diseases and the formation of a low-quality crop. The bushes are placed in the direction from south to north, which will provide the best lighting on both sides. Trellis for grapes are installed from the west, at a distance of 25 to 30 cm.
It is recommended to grow grapes in the open ground in the Moscow region in spring, when a stable positive temperature has been established and the likelihood of late frosts has disappeared. The optimal time for planting seedlings with an open root system is June, and with a closed one - early spring or autumn.
At the beginning, holes are dug with an approximate size of 40 x 40 x 40 cm.A drainage layer of gravel is installed at the bottom, covered with earth, organic fertilizers and a stake is driven into the center, which will serve to support the vine. The soil is allowed to settle for two weeks and then the seedlings are lowered into it at a slight slope to the north. In order to increase the survival rate of seedlings, they are soaked in water or humate solution to form roots. Then everything is covered with soil, watered with water and mulching is carried out.
For more information on how to plant grapes, you can find out from the video on our website.
Despite its unpretentiousness, caring for grapes in the Moscow region should be correct and careful.
Different grape varieties are characterized by high fertility, this leads to an abundance of buds that are forming, which must be removed periodically to avoid overloading the bush and the formation of small berries. To standardize the yield, the vine is pruned 3 cm above the bud for every 7 to 9 eyes in spring and autumn.
Autumn pruning of grapes is carried out when all the leaves have fallen, while removing old and diseased shoots. In August, the tops of the stepchildren are minted and pruned to provide the main shoots with nutrients and to strengthen the plant.

It is recommended to water the vineyard along the grooves between the bushes in order to avoid direct moisture ingress on the plant trunk, as it does not like sudden changes in moisture levels. It is usually watered during the growing season, while the plant is gaining green mass, and when the berries ripen.
The ripening of the vine requires a large amount of additional nutrients that must be supplied to the plant periodically. Every autumn, mineral fertilizing is carried out with nitrogen, potash and phosphorus fertilizers, and organic fertilizers are used every three years.

Depending on the selected grape variety and on its resistance to fungal diseases, it is recommended to periodically spray the bushes to protect against diseases and rot. The most dangerous is mildew, characterized by the formation of light yellow spots on the leaves, passing on to the berries and causing them to rot. Oidium is a dark gray formation that affects inflorescences and berries. It is advisable to spray in compliance with all instructions before, after and during the ripening of berries.
One of the mandatory activities is preparing the plant for wintering. Even if you have chosen frost-resistant grape varieties for your site, you need to know how to cover the grapes in order to protect the fruiting buds from freezing temperatures and not harm the plant during the winter. It is recommended to cover the bushes before the onset of the first frost so that the vine does not come into contact with the ground and does not rot. It is covered with sawdust, leaves, or covering material or wooden shields are installed. After the snow falls, the bushes can be covered with it.
In addition to growing grapes in an open area, it can be grown in greenhouses. To do this, they prefer to use varieties with an early ripening period and bisexual flowers, which facilitate the process of pollination and do not require additional pollinators.
> In the spring, at the end of March, at the beginning of April, after the snow thaws, the bushes are gradually opened after wintering during the day to dry them, and at night they are closed again to protect them from frost. With the onset of constant positive temperatures, the vine is tied to trellises.
The final ripening of the berries occurs in late August, early September. Some grape varieties can remain on the bushes for about a month after reaching full maturity, but it is still advisable to harvest on time so as not to harm the quality of the final product. Many hybrid grape varieties are distinguished by good transportability, satisfactory keeping quality and high commercial qualities. This will allow you to cultivate crops not only for personal purposes, but also on an industrial scale.
It is not difficult to grow grapes in the Moscow region, since planting and caring for the plant is simple and quite accessible to both experienced winegrowers and beginners. However, you need to choose a suitable variety with high frost resistance, capable of withstanding negative temperatures from minus 25 degrees. Grapes in the Moscow region, the cultivation of which is possible thanks to the bred hybrid varieties, will become not only a decoration of your table, but also of the site.
It is worth paying attention to the varieties of raisins, which do not contain seeds and are distinguished by excellent taste and appearance. The Lydia variety is suitable not only for fresh consumption, but also for making table wine. Muscat grapes are also very popular and frost-resistant. Alpha variety of American selection of uncovered grapes for the Moscow region is able to withstand negative temperatures up to 40 degrees Celsius. Find out more about grape varieties for the Moscow region.
Grapes planted in early spring will yield a rich harvest by autumn. Hybrid forms are easy to care for due to their stability and high survival rate. After reading the recommendations, you can easily get a high-quality harvest of a healthy product.
3>Most read:
How to care for grapes in the first year of planting, in spring and summer video
Grapes are ...
Growing cilantro and coriander
Cultivation of co ...
How to plant a beetroot: features of preparation and sowing of culture
There are 3 ra ...
How to process potato tubers from the Colorado potato beetle before planting?
Carto ...
Garden quince - reproduction, diseases, planting and care
In the last ...
Indoor plant hygiene: how to clean it properly
Observing hygiene ...
Prepare dill for the winter? It's simple!
To each person ...
Apple tree Simirenko: history and characteristics of the variety
History of discovery ...
Growing celery in the open field Celery root leaf and petiole from seeds for seedlings ...
Celery is grown ...
Foliar dressing of tomatoes in the greenhouse and in the open field
Foliar under ...
How long does an apple tree live
With the right ...
Wireworm in potatoes - how to get rid of a dangerous pest video
The main enemy ...
How to prune a peach: instructions for beginners, pruning scheme, timing
Peach pruning ...
Planting a melon in the open field: how to grow, care, seedlings, how a melon grows
Melon is popular ...
Growing cucumbers on the balcony step by step: the secrets of agricultural technology
Features ext ...
Gardener's lunar calendar for March 2018: auspicious days
Lunar calendar ...
Peach grafting: methods, choice of scion and rootstock
When and how with ...
7 best varieties of decorative indoor peppers: home care
Decorating care ...
When is the best time to plant tomatoes in 2018 for the perfect harvest
When everything is better ...
How to grow large garlic in the garden, PRIVATE HOUSE
Good afternoon, uv ...
How to sprinkle tomatoes from diseases
2. Fruits in the set ...
Dill on the windowsill: growing from seeds, caring for the harvest
Home green ...
Bell peppers - outdoor cultivation and care
Bulgarian translation ...
Bordeaux tomato mix - spray liquid
Bordeaux mix ...
How to prepare carrots for storage for the winter after harvesting: how and how to properly process
How to correctly p ...
Bell peppers: tips for growing and care
Eat weak ...
Scab on potatoes: causes and methods of treatment
Scab on potatoes ...
How to feed beets for a good harvest
How to feed ...


