Content
- 1 Indeterminate and determinant varieties
- 2 Care features
- 3 Planting different varieties of tomatoes in the greenhouse
- 4 How to grow determinate tomatoes in a greenhouse?
- 5 Best Tomato Seeds for Polycarbonate Greenhouse
- 5.1 Basic rules for selecting a variety
- 5.2 Fruit use
- 5.3 Red, yellow, green
- 5.4 High grades
- 5.5 Features of growing liana tomatoes
- 5.6 The best low-growing tomatoes
- 5.7 Care of undersized tomatoes
- 5.8 Tomatoes for sale
- 5.9 Cherry tomatoes in the greenhouse
- 5.10 Dutch tomatoes
- 5.11 New tomato seeds for greenhouses
- 5.12 Hybrids
- 5.13 A Few Tips
- 6 Low-growing tomatoes for the greenhouse: from selection to harvest
- 7 Determinant and indeterminate tomato varieties
- 8 Determinant and indeterminate tomato variety
- 8.1 Useful properties of tomatoes
- 8.2 Indeterminate tomato varieties
- 8.3 Determinant varieties
- 8.4 The choice of varieties of indeterminate tomatoes is huge:
- 8.5 Yielding determinant varieties:
- 8.6 Seed sowing dates
- 8.7 How to distinguish which variety by plants
- 8.8 Choosing a variety of tomatoes for planting
- 9 Indeterminate varieties of tomato for greenhouses (high)
- 10 Determinant (undersized) tomatoes for the greenhouse
- 11 For sale
- 12 Cherry varieties for greenhouses
- 13 Resistant Dutch varieties
- 14 Growing and shaping determinate tomatoes

Growing tomatoes of determinant varieties in a greenhouse allows you to get a fairly large harvest in a small area. The process does not require any special care rules, which makes it quite simple and affordable.

A garter of tomatoes to a peg, driven in immediately after planting the plants, if this is done during vegetative growth, you can damage the root system and bring in the disease.
Determinant tomato variety
It is believed that growing determinate tomatoes is very profitable, since they can give a large harvest, taking up a minimum of space in the greenhouse, and besides, caring for them is very simple. Only the formation of the bush is important, then the growth will stop on its own. These varieties of tomatoes are grown mainly in the northern regions, but they grow well in other regions as well. When growing tomatoes, tying is very important to prevent the stems from falling to the ground and to facilitate the process of caring for the plant.

Types of tomato formation - Standard. Indeterminate. Determinant.
Caring for grown tomatoes in a greenhouse is different from growing other crops. Many factors depend on the type of plant, although it is worth noting that basically all varieties of tomatoes are quite unpretentious.Determinant varieties of tomatoes grown in a greenhouse are capable of producing approximately 13-15 kg per 1 m². Formation must be carried out in compliance with certain rules.
The growth of determinant tomatoes occurs in one or two stems, which must be pinched during their development. Only 1-2 inflorescences can be left on one stem, which will further allow them to develop without hindrance. After the inflorescences, only 1-2 leaves do not break off. Tying the plant is imperative. The main advantage that distinguishes tomatoes of determinate varieties is the possibility of significant savings in greenhouse space.
When growing tomatoes in two stems, the stepson is awaited from the leaf axils. Care in this case will consist in tying two stems to the trellis. Biological features make it possible to self-regulate the growth of tomatoes, while ensuring a rich harvest. Compared to others, these varieties are the most profitable to grow.
Back to the table of contents
Formation of plants of determinant type with your own hands
For tomatoes of the determinant type, the low setting of the first inflorescences is characteristic. Inflorescences are located either one after another, or through 1-2 leaves. These features are precisely responsible for obtaining a high early harvest. After 3-6 inflorescences are formed, growth will stop, but due to biological characteristics, the lateral shoots will continue to grow. Formation transfers growth points to lateral shoots, which is responsible for lengthening the period of emergence and ripening of fruits. Therefore, it is possible to grow hybrids with this type of growth, even in the winter-spring period, in order to get an early harvest.

The scheme of the formation of determinant tomatoes.
The dynamics of the appearance of the crop provides for some cyclicality - the appearance of early fruits on the main shoots and after a while on the lateral, continuing growth of tomatoes. By limiting the growth of tomatoes on the main shoot, the fruiting period of the plants will be artificially reduced. This technique is used for determinate tomatoes outdoors. It turns out that the use of different varieties of determinant tomatoes is possible on different structures and in the open field.
The formation of determinant tomatoes largely depends on a number of factors - regional climatic conditions, the type of cultivation facilities and the goal of the gardener. The smallest yield is obtained from one plant when formed into one stem, the largest - without a clothespin, and all other options provide for intermediate options with different harvest ripening times.
When forming, the number of stems is also important - the fewer there are, the higher the planting density.
Back to the table of contents
Growing seedlings of determinant tomatoes and preparing the soil for planting
Determinant tomato varieties are planted in early April. Plants are grown in wooden boxes. When a second or third leaf appears, the plant is transferred to the greenhouse. Seedling care is quite simple - planting tomatoes takes place in the soil filled with azophos and superphosphate, the soil temperature should be up to 16 ° C. In about a month, inflorescences will appear on the seedlings, and this indicates the complete readiness of the seedlings for planting in the greenhouse. You can feed tomatoes with various varieties of slurry, but in small quantities.

Cutting scheme for overgrown tomato seedlings.
Plant formation occurs only in specially created conditions, with optimal temperature and humidity indicators. Despite the unpretentiousness of determinant tomatoes, the soil for planting is still of great importance, especially in the preparatory stages.
Soil preparation is as follows. When processing the inside of the greenhouse, it is necessary to prepare the compost.Before planting, the soil must be treated with a mixture of water and bleach. It is believed that it is very good to use the soil in which the cucumbers were previously grown. In this case, it is necessary to remove the top soil layer (up to 10 cm) and lay the cucumber soil. The bed is laid with hay, and on top of it you need to pour compost in a layer of 15 cm. Burnt hay between the two layers will help create excellent conditions for growing tomatoes of determinant varieties.
To provide soil care, it is required to renew the soil annually by adding layers of hay, spraying to protect greenhouse tomatoes from various diseases.
In no case should manure be added to the soil in order to avoid the process of fattening the culture. If the plant has thick leaves, the ovaries will be small, which means the yield will be low. Adding soil to manure leads to improper formation of tomatoes, which threatens a complete lack of harvest.
In the autumn, the soil requires preliminary preparation with the introduction of superphosphates, lime, ash. Good tomatoes are obtained on soil with added plant residues (leaves, hay, stems).
Growing varieties of tomatoes in a greenhouse is possible after preliminary keeping the soil under plastic wrap.
Back to the table of contents
Planting tomatoes of various varieties in the greenhouse 
Compost formation scheme.
You can plant tomatoes in a greenhouse in various ways. This is due to the fact that this culture is flexible and very easy to take root. A very interesting fact - an unburied stepson can take root in a couple of days, even without the necessary care.
Determinant tomatoes, medium-sized crops, can independently regulate their growth if planted in a greenhouse. In the process of formation on the main shoot of 4-5 inflorescences, they are crowned. That is, growth simply stops. The laying of the branch part occurs only after the appearance of 6 leaves. Examples of such varieties are Raketa, Dana, Semko, Garant and others, ideally taking root in a greenhouse.
The process of planting a conventional determinant tomato variety in greenhouse soil takes place in a previously prepared hole with a depth of 1 sheet. Initially, seedlings are grown in pots, where there is sufficient space for the full development of the root system.
Planting of different varieties is allowed not only in holes, but also in furrows (horizontal position). The furrows should be about 15-17 cm deep, into which the seedlings are transferred very carefully. A top with 2-4 leaves should be left on the soil surface.
A gardener can plant a variety of determinant tomatoes in one of the ways suitable for him, and it can be not only grooves and holes. This crop differs from others in its high level of yield, unpretentiousness, the ability to grow both in a greenhouse and outdoors in bad weather conditions.
Back to the table of contents
Correct formation of determinate tomatoes 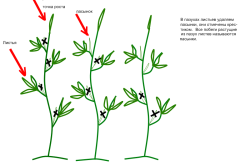
Scheme of options for the formation of tomato bushes in a greenhouse.
Correct formation contributes to better pollination of flowers, the process of fruit setting and an increase in the volume of the harvest.
The formation of lateral shoots is characteristic of tomatoes. This occurs after inflorescences appear in each leaf axil. Each of these shoots will become an additional stem and be able to bear fruit. But if the plant gives all its strength to growing stepsons, then the appearance of fruits (tomatoes) will be delayed, and the yield will drastically decrease. So it turns out that you can only grow a decent harvest by forming bushes. Formation is carried out taking into account the characteristics of each plant variety.
On average, our country is characterized by the cultivation and maturation of tomatoes in the open field, set before August 1, it turns out that these are the fruits from the first three inflorescences.This explains the method of acceleration by breaking off small stepsons and pinching the shoots at the end of July, so that the fruits that have already set are ripe.
For many, the question of growing and forming determinate tomatoes is very important. After all, it is necessary to carry out this procedure correctly.
The layout of the beds in the greenhouse and the size for tomatoes.
In cases where the determinant types of tomatoes are ultra-early ripening, shaping is not needed for them. A short, compact bush will yield a good harvest.
Formation of tomatoes into one stem is required for tall superdeterminate varieties. It is necessary to break out the side shoots about once a week. It is important to know that single-stem tomatoes will produce 2 times more fruits on the vine than bush tomatoes, and as a result, the yield from the entire area will be slightly less. That is why, when forming tomatoes into one stem, it is necessary to place them as often as possible.
The formation of two-stem tomatoes is acceptable for varieties that grow more intensively. In this case, the stepsons growing from the leaf axils, located under the first inflorescence and above it, are left. After the appearance of 8 inflorescences (and no more), the growth point is pinched.
Back to the table of contents
The process of forming tomatoes in a greenhouse
The cultivation of determinate tomatoes in greenhouses and tunnels is characterized by correct formation into one stem. But due to the limited formation of inflorescences, a small shoot should be left under the first of them, the pinching of which occurs after the formation of three leaves and a pair of inflorescences.
A month after planting seedlings on plants, it is necessary to remove the leaves located below. This procedure is performed on an early sunny morning. By the time the fruits ripen on the first inflorescence, there should be no leaves on the stem under them. Any remaining leaves should be removed over time. It is important that the leaves are not removed above the third inflorescence. Such formation is necessary to improve air exchange in the lower part of the plant and to accelerate fruit ripening.
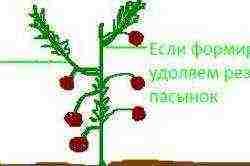
The scheme of the formation of tall determinant tomatoes.
About a month before the end of the growing season, the main stem should be pinned on the tomato, leaving two leaves behind the last inflorescence, while not forgetting to remove the new stepchildren. The process of correct formation of determinate tomatoes contributes to an increase in yield.
Features of growing determinant varieties of tomatoes and caring for them.
For the process of planting seedlings, the following materials will be required:
- seedling;
- scapula (hoe);
- the soil;
- fertilizer;
- sprayer;
- watering can.
Care includes compliance with the following requirements:
Timely weed control throughout the growing period.
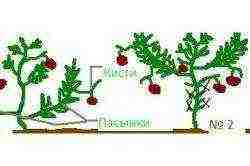
Scheme of the formation of superdeterminant tomatoes.
- The regularity of hilling.
- Correct pinning process.
- Plucking the stems to stimulate the branching process.
- Top dressing with various fertilizers, carried out before the hilling process.
- Watering as needed.
- Controlling pests and various diseases.
In film greenhouses, tomatoes of a determinant variety can be grown for quite a long time - up to 5 months. The advantage of determinate tomatoes is their early maturity and high yield.
The formation of determinant varieties, as well as hybrids in greenhouses, occurs more often in one stem, rarely it occurs in two stems. With one stem, a stepson is left in the leaf axil, located under the first inflorescence. It is pinched after one or two inflorescences are formed on it. After the inflorescence, you need to leave two leaves.
It is important to note that hybrids of determinant tomatoes absorb nutrients very poorly, which is why constant additional feeding is required. Seedlings must be planted in holes that correspond to the size of the rhizomes.Organic fertilizer is added to the hole before transplanting. Seedlings are planted at a distance of about 50 cm with intervals between rows of 60 cm.
The optimal time for transplanting is the time when the threat of frost has already disappeared, this happens around June. If the varieties are late ripening, it is better to plant them in May. It is important to know that early varieties take root much better and bear fruit at the end of July.
It is quite simple to grow tomatoes of determinant varieties in greenhouses, there are no special care rules, and biological features allow you to harvest a large crop with a minimum planting area.
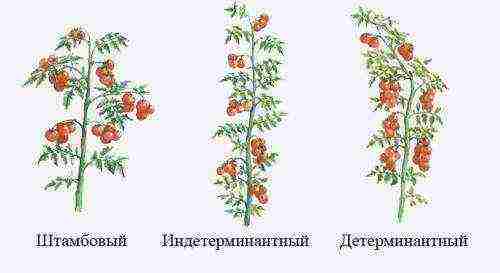
Types of tomato formation: (standard, indeterminate, determinant).
Indeterminate and determinant varieties
Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes have unlimited growth, they are more demanding in care than all others. Suitable for growing in the northern regions with a short summer, the harvest is quite late.
Growing determinant tomatoes is considered economically profitable, since with a large harvest they take up a minimum of space in the greenhouse, and their care is simple. Only the formation of a bush is required, growth stops on its own. It is recommended to grow tomatoes of this variety in the northern regions, although they grow well in the south, in the middle lane. Of the special requirements, there is only the need to tie lashes so that the plants do not fall to the ground, and in this case, caring for them is easier. The advantageous result is the main advantage of such varieties.
Back to the table of contents
Standard and semi-determinant tomatoes
Standard varieties are great for lazy gardeners. Such plants need minimal care: they do not need to be shaped, tied, or pinned. The planting of tomatoes of this variety begins in the spring, but in August it is already possible to harvest. Plants of this variety are distinguished by a strong stem and low growth.
All tomato varieties are divided into groups that have advantages when grown in certain climatic regions. In a mid-latitude greenhouse, it is best to give preference to semi-determinant varieties that cannot independently regulate their growth, but growing them in two stems gives the opportunity to get a bountiful harvest. They are unpretentious in care, the peculiarity is that their growth can stop at any time, so constant monitoring is necessary.
Back to the table of contents
Care features
Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse is very different from growing other vegetables. Much depends on the variety chosen, although all tomatoes are quite unpretentious. In a film greenhouse, determinant varieties are capable of producing about 12-15 kg per square meter. But the formation of tomatoes is strictly subject to certain rules.
The scheme of the formation of determinant tomatoes.
Determinant tomatoes usually grow in one or two stems and must be pinched during development. For one stem, it is permissible to leave one or two inflorescences with this procedure, which will give them the opportunity to develop well further. After the inflorescences, one or two leaves are left, the plant must be tied up. It is worth noting the main advantage that distinguishes determinant tomatoes is the ability to significantly save space in the used greenhouse.
If tomatoes are grown in two stems, then the second is the stepson of the leaf sinus. In this case, leaving differs only in that two stems should be tied to a trellis. Due to biological characteristics, such varieties of tomatoes independently regulate their growth, but at the same time they give powerful yields. The cultivation of such varieties is considered economically beneficial in comparison with others.
Growing indeterminate tomatoes is more difficult, the care is slightly different, the yield is much lower.
Back to the table of contents
Growing seedlings

Cutting scheme for overgrown tomato seedlings.
Determinant tomatoes are sown in early April. Plants begin to grow in small wooden boxes. After they have a second or third leaf, you need to start transferring them to the greenhouse. Care is simple: the temperature of the soil should be up to 16 degrees Celsius, the seedlings dive into the soil filled with nitrogen phosphate and superphosphates. Already a month later, the seedlings are covered with inflorescences, it is completely ready for planting. Top dressing includes the addition for any kind of slurry, but in moderation.
Growing tomatoes this way is very convenient and easy, especially if the weather is pretty cool until mid-spring.
Back to the table of contents
Soil preparation
Plants form excellently only if suitable temperature and humidity indicators are created for them. Although determinate tomatoes are quite unpretentious, the soil is of great importance for planting, especially with regard to its preparation. To begin with, we prepare the compost while the greenhouse is processing the interior.
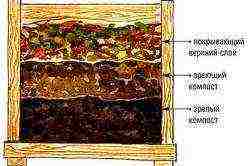
Compost formation scheme.
The soil for planting is sprayed with a mixture of water and bleach (400 g of lime per 10 liters of water). The ideal option is to use the land after growing cucumbers, in this case, after processing, the top layer of greenhouse soil is removed (by about 5-10 cm), and cucumber is placed in its place. The ridge is filled with hay, compost is poured on top in a layer of 15 cm. The hay between the two layers burns out, which creates excellent conditions for growing determinant tomatoes.
Soil care is as follows: the soil is renewed every year, new layers of hay are added; it is recommended to spray so that the tomatoes in the greenhouse are not susceptible to various diseases through the soil.
You cannot add manure to the potting mix, as fattening of crops may occur. In the presence of thick leaves, the ovaries will be small, the yield will be low. The formation of tomatoes when adding soil to manure becomes incorrect, usually the result is a complete lack of yield.
Autumn soil preparation includes the introduction of superphosphates, lime for deoxidation, ash and dolomite flour. Excellent cultivation of tomatoes is carried out on soil where plant residues are added, that is, cut flower stalks, reeds, dry hay (not rotten!), Foliage of shrubs and trees.
Tomato varieties can be grown in the greenhouse if the soil has been previously kept under plastic wrap.
Back to the table of contents
Planting different varieties of tomatoes in the greenhouse
Planting tomatoes in a greenhouse is possible in several ways, since this culture is quite plastic, it takes root easily. An untouched stepson is able to take root within just a couple of days, even in the absence of proper care!
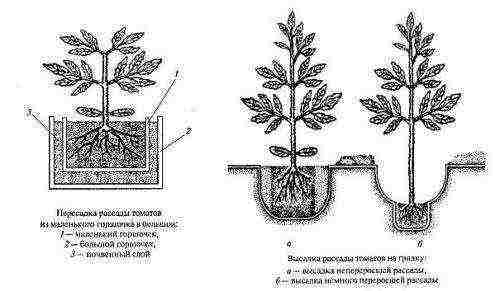
Scheme of planting tomato seedlings in the ground.
All determinant tomatoes (medium-sized crops) independently regulate their growth when planted in any type of greenhouse. After four or six inflorescences are formed on the main shoot, they end up on their own, that is, they stop growing. The branch brush is laid only after the appearance of the sixth leaf. These are such varieties as Ranny, Raketa, White filling, Garant, Novinka Pridnestrovya, Dana, Volzhsky, Semko and others, which perfectly take root in greenhouses.
Semi-determinant varieties, that is, tall ones, already form six to eight inflorescences on their main shoot, but at the same time they also grow on their own. After the sixth inflorescence, growth usually stops, but the flowering is very powerful. The yield is much higher than determinate tomatoes can give, the flower cluster is laid after 7-8 leaves appear.
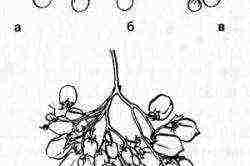
Types of tomato inflorescences.
Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes, that is, liana-like, do not have the ability to stop growth on their own, the first inflorescence is laid after 9-11 leaves. The yield is very high, the plants themselves are resistant to diseases, they can give ovaries under any conditions. These are such indeterminate varieties as Vitador, Samara, Typhoon, Flagman, Etude, Sreza, Favorite, Castalia. After each denomination, the indeterminate varieties are designated F1.
Planting ordinary determinant tomatoes in the ground in a greenhouse is carried out in a prepared hole, deepening is done in one sheet. The seedlings are initially grown in pots that are deep enough for proper root development.
You can plant various varieties in a horizontal position, that is, to use for this in the greenhouse, not holes, but furrows. First, furrows are prepared with a depth of 15-17 cm, after which the seedlings are carefully transferred to the prepared soil. The top on the surface should have 2-4 leaves.
The determinant tomato variety can be planted in a variety of ways, not only with the help of grooves and holes. Each gardener chooses the best option for himself. This crop is distinguished not only by abundant yields, but also by some unpretentiousness, which allows you to grow tomatoes not only in a greenhouse, but also outdoors, in the presence of the most unfavorable weather conditions.
How to grow determinate tomatoes in a greenhouse?
It is quite simple to grow tomatoes of determinant varieties in greenhouses, there are no special care rules, and biological features allow you to harvest a large crop with a minimum planting area.
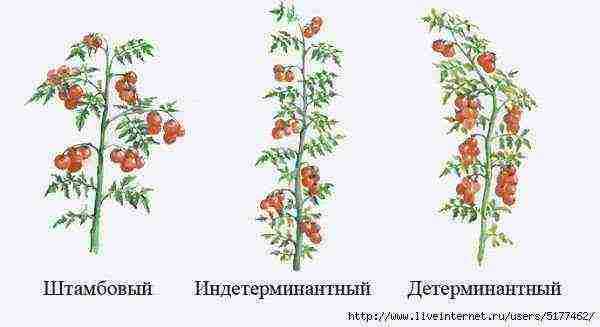
Types of tomato formation: (standard, indeterminate, determinant).
Indeterminate and determinant varieties
Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes have unlimited growth, they are more demanding in care than all others. Suitable for growing in the northern regions with a short summer, the harvest is quite late.
Growing determinant tomatoes is considered economically profitable, since with a large harvest they take up a minimum of space in the greenhouse, and their care is simple. Only the formation of a bush is required, growth stops on its own. It is recommended to grow tomatoes of this variety in the northern regions, although they grow well in the south, in the middle lane. Of the special requirements, there is only the need to tie lashes so that the plants do not fall to the ground, and in this case, caring for them is easier. The advantageous result is the main advantage of such varieties.
Standard and semi-determinant tomatoes
Standard varieties are great for lazy gardeners. Such plants need minimal care: they do not need to be shaped, tied, or pinned. The planting of tomatoes of this variety begins in the spring, but in August it is already possible to harvest. Plants of this variety are distinguished by a strong stem and low growth.
All tomato varieties are divided into groups that have advantages when grown in certain climatic regions. In a mid-latitude greenhouse, it is best to give preference to semi-determinant varieties that cannot self-regulate their growth, but growing them in two stems gives the opportunity to get a bountiful harvest. They are unpretentious in care, the peculiarity is that their growth can stop at any time, so constant monitoring is necessary.
Care features
Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse is very different from growing other vegetables. Much depends on the variety chosen, although all tomatoes are quite unpretentious. In a film greenhouse, determinant varieties are capable of producing about 12-15 kg per square meter. But the formation of tomatoes is strictly subject to certain rules.
The scheme of the formation of determinant tomatoes.
Determinant tomatoes usually grow in one or two stems, they must be pinched during development.For one stem, it is permissible to leave one or two inflorescences with this procedure, which will give them the opportunity to develop well further. After the inflorescences, one or two leaves are left, the plant must be tied up. It is worth noting the main advantage that distinguishes determinant tomatoes is the ability to significantly save space in the used greenhouse.
If tomatoes are grown in two stems, then the second is the stepson of the leaf sinus. In this case, leaving differs only in that two stems should be tied to a trellis. Due to biological characteristics, such varieties of tomatoes independently regulate their growth, but at the same time they give powerful yields. The cultivation of such varieties is considered economically beneficial in comparison with others.
Growing indeterminate tomatoes is more difficult, the care is slightly different, the yield is much lower.
Growing seedlings
Cutting scheme for overgrown tomato seedlings.
Determinant tomatoes are sown in early April. Plants begin to grow in small wooden boxes. After they have a second or third leaf, you need to start transferring them to the greenhouse. Care is simple: the temperature of the soil should be up to 16 degrees Celsius, the seedlings dive into the soil filled with nitrogen phosphate and superphosphates. Already a month later, the seedlings are covered with inflorescences, it is completely ready for planting. Top dressing includes the addition for any kind of slurry, but in moderation.
Growing tomatoes this way is very convenient and easy, especially if the weather is pretty cool until mid-spring.
Soil preparation
Plants form excellently only if suitable temperature and humidity indicators are created for them. Although determinate tomatoes are quite unpretentious, the soil is of great importance for planting, especially with regard to its preparation. To begin with, we prepare the compost while the greenhouse is processing the interior.
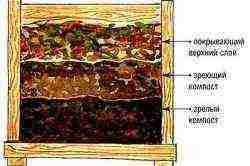
Compost formation scheme.
The soil for planting is sprayed with a mixture of water and bleach (400 g of lime per 10 liters of water). The ideal option is to use the land after growing cucumbers, in this case, after processing, the top layer of greenhouse soil is removed (by about 5-10 cm), and cucumber is placed in its place. The ridge is filled with hay, compost is poured on top in a layer of 15 cm. The hay between the two layers burns out, which creates excellent conditions for growing determinant tomatoes.
Soil care is as follows: the soil is renewed every year, new layers of hay are added; it is recommended to spray so that the tomatoes in the greenhouse are not susceptible to various diseases through the soil.
You cannot add manure to the potting mix, as fattening of crops may occur. In the presence of thick leaves, the ovaries will be small, the yield will be low. The formation of tomatoes when adding soil to manure becomes incorrect, usually the result is a complete lack of yield.
Autumn soil preparation includes the introduction of superphosphates, lime for deoxidation, ash and dolomite flour. Excellent cultivation of tomatoes is carried out on soil where plant residues are added, that is, cut flower stalks, reeds, dry hay (not rotten!), Foliage of shrubs and trees.
Tomato varieties can be grown in the greenhouse if the soil has been previously kept under plastic wrap.
Planting different varieties of tomatoes in the greenhouse
Planting tomatoes in a greenhouse is possible in several ways, since this culture is quite plastic, it takes root easily. An untouched stepson is able to take root within just a couple of days, even in the absence of proper care!
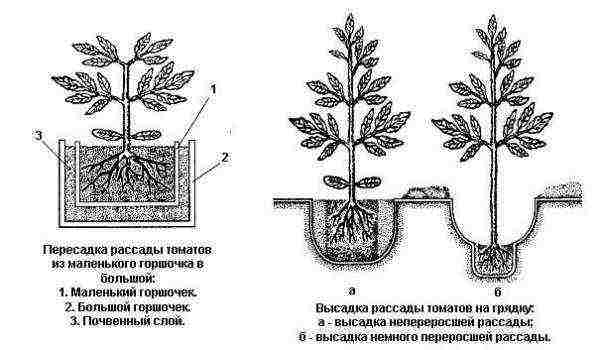
Scheme of planting tomato seedlings in the ground.
All determinant tomatoes (medium-sized crops) independently regulate their growth when planted in any type of greenhouse.After four or six inflorescences are formed on the main shoot, they end up on their own, that is, they stop growing. The branch brush is laid only after the appearance of the sixth leaf. These are such varieties as Early, Raketa, White filling, Garant, Novinka of Pridnestrovie, Dana, Volzhsky, Semko and others, which perfectly take root in greenhouses.
Semi-determinant varieties, that is, tall ones, already form six to eight inflorescences on their main shoot, but at the same time they also grow on their own. After the sixth inflorescence, growth usually stops, but the flowering is very powerful. The yield is much higher than determinate tomatoes can give, the flower cluster is laid after 7-8 leaves appear.
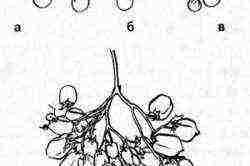
Types of tomato inflorescences.
Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes, that is, liana-like, do not have the ability to stop growth on their own, the first inflorescence is laid after 9-11 leaves. The yield is very high, the plants themselves are resistant to diseases, they can give ovaries under any conditions. These are such indeterminate varieties as Vitador, Samara, Typhoon, Flagman, Etude, Sreza, Favorite, Castalia. After each denomination, the indeterminate varieties are designated F1.
Planting ordinary determinant tomatoes in the ground in a greenhouse is carried out in a prepared hole, deepening is done in one sheet. The seedlings are initially grown in pots that are deep enough for proper root development.
You can plant various varieties in a horizontal position, that is, to use for this in the greenhouse, not holes, but furrows. First, furrows are prepared with a depth of 15-17 cm, after which the seedlings are carefully transferred to the prepared soil. The top on the surface should have 2-4 leaves.
The determinant tomato variety can be planted in a variety of ways, not only with the help of grooves and holes. Each gardener chooses the best option for himself. This crop is distinguished not only by abundant yields, but also by some unpretentiousness, which allows you to grow tomatoes not only in a greenhouse, but also outdoors, in the presence of the most unfavorable weather conditions.
Best Tomato Seeds for Polycarbonate Greenhouse
A good harvest of tomatoes in a greenhouse can only be obtained by choosing the right variety. First of all, it must be designed for indoor cultivation. When buying planting material, some other factors should be considered. In this article, we'll talk about how to choose the best tomato seeds for your greenhouse.
Basic rules for the selection of varieties
In a small area closed on all sides, favorable conditions arise for the development of various kinds of pathogenic microorganisms and harmful fungi. Therefore, when choosing tomato seeds for a polycarbonate greenhouse, you should pay attention to the resistance of a particular variety to diseases. This is especially true for late blight.

The selection of the variety also depends on the design of the greenhouse itself. For a small, not too high structure, the so-called determinant (undersized) tomatoes are well suited. Tomato bushes of this group take up very little space and are distinguished by their early maturity, combined with a good yield.
Liana tomatoes are usually grown in tall greenhouses. A distinctive feature of these tomatoes is the unlimited growth of the stem. Its length can reach 3 meters. Moreover, the whole plant is usually strewn with fruits. That is, growing high varieties, it is easy to compensate for the lack of soil area. The advantages of liana tomatoes, otherwise called identities, also include a long fruiting period and ease of care. From one such bush, you can collect up to 15 kg of fruit.
Sometimes both of these varieties of tomatoes are planted in greenhouses: high and low. In this case, liana-shaped tomatoes are placed in the center, and determinant ones - along the perimeter of the beds.
When choosing tomatoes for a greenhouse, you need to pay attention to one more factor. The variety should not be afraid of waterlogging of the soil. There is usually a lot of dampness in the closed space of the greenhouse.
Fruit use
When choosing the most suitable tomato seeds for a polycarbonate greenhouse, you should also consider what exactly this crop will be grown for. In specialized stores today you can buy planting material of three main types of tomatoes: salad, used for canning and for sale.
The fruits of the first group of tomatoes are usually sweet, juicy and large in size. The color of salad tomatoes is most often pink. A characteristic feature of the fruits of the varieties intended for canning are their small size and the ability to withstand heat treatment without changing their shape. Typically, these tomatoes have a classic bright red color. The fruits of the varieties grown for sale are distinguished by a neat shape, a fairly dense pulp structure and transportability.
Red, yellow, green
Many owners of suburban areas choose tomato seeds for a greenhouse made of polycarbonate, taking into account, among other things, what color the ripe fruits will have in the future. Most gardeners love the classic red, yellow or orange tomatoes. However, some gardeners like to experiment and acquire seeds of purple, green or black tomatoes.
Fruits of different colors can differ both in taste and in the composition of the nutrients they contain. So, yellow tomatoes, for example, are much less high in calories than red ones. In addition, their pulp contains much less allergy-causing substances. The yellow color of the fruit is given by provitamin A, which is able to prevent, among other things, oncological diseases.

Orange tomatoes contain a lot of lycopene, an antioxidant that can protect against various vascular and heart diseases.
The varieties with purple fruits are also very interesting. The pulp of such tomatoes contains large quantities of anthocyanin - a substance belonging to the group of glycosides, which has a beneficial effect on blood vessels and helps to strengthen the immune system.
Not so long ago, genetically modified purple and blue tomatoes were bred abroad. There is a lot of anthocyanin in them, but they can be purchased only in those countries where the use of GMO products is allowed. In our country, seeds of such tomatoes are not sold.

High grades
Based on some of the characteristics of mature plants, you can actually choose the best tomato seeds for your greenhouse. Tall tomatoes, due to their yield and endurance, enjoy well-deserved popularity among summer residents. Most often, domestic gardeners grow varieties such as:
- Honey saved. This medium-ripening lettuce tomato has yellow fruits, large and very tasty. An adult plant can reach a height of 1.5 m. The main advantages of this variety include resistance to disease and cracking. Productivity - 4-6 kg per bush.
- Mushroom basket. Indeterminate variety with large fruits (up to 500 g) of classic red color, the main distinguishing feature of which is a pronounced ribbed shape. The variety belongs to the mid-season and can reach a height of 2.5 m.
- Black Moor. An exotic variety up to 1.3 m high. Its rounded, slightly elongated smooth fruits, which have a chocolate-red color, are distinguished by their transportability, keeping quality, and suitable for canning.
Anyone who wants to get a good harvest should purchase just such tomato seeds. Tall tomatoes are actually very good for a greenhouse. Peculiar vertical beds formed by long plants allow using limited space as efficiently as possible.

Features of growing liana tomatoes
Of course, in order to get a good harvest, you need to choose high-quality tomato seeds in the store - from trusted manufacturers and not expired. Self-pollinated tomatoes are suitable for a greenhouse, as already mentioned, very well. But, of course, even the most unpretentious variety requires maintenance.
Tomatoes of this group are grown in greenhouses using almost the same technology as in the open field. The gardener, for example, will have to deal with shaping the bush without fail. The lateral processes of lianate tomatoes are removed. This stimulates the growth of the plant. According to the rules, only one stem should be left at the bush. However, there is usually not much space in greenhouses. Therefore, domestic gardeners often grow plants with two stems. The harvest in this case can also be very good.
Of course, for tall tomatoes you will need to arrange props. The most suitable option is considered to be an ordinary trellis, similar to grape. For its manufacture, two posts are installed along the edges of the beds and connected with a transverse crossbar. Along the entire height of the resulting structure, wire or cords are pulled in parallel rows.
It is not recommended to plant tall varieties too densely. There should be no more than 3-4 plants per 1 m2.
The best low-growing tomatoes
The advantage of determinant tomato varieties, among other things, is early maturity. Therefore, not only for the owners of small low greenhouses, but also for those who want to harvest as early as possible, it is worth purchasing the seeds of low-growing tomatoes. For greenhouses, varieties are perfect:
- Ballerina. Tomato with sweetish red elongated compact fruits of medium early ripening. Its bushes can reach a height of 0.5-1 m.
- Pink leader. An early ripe variety, the fruits of which are used both for canning and for salads.
- Fontanka. A very low standard grade (up to 50 cm), characterized by early maturity. The red fruits of the Fontanka are oval in shape. Among all the early ripening varieties, this one is considered the most productive. On one plant alone, up to 40-45 fruits can form.
- Summer resident. Also a very low grade (up to 50 cm). Differs in frost resistance. Its red fruits are round, small in size and great for canning.
Care of undersized tomatoes
The need for frequent feeding is what makes determinant varieties different. There are many varieties of tomato seed for this group of greenhouses. However, almost all undersized tomatoes have one characteristic feature. They do not absorb nutrients from the soil very well. It is best to feed small tomatoes with organic fertilizers. When planting seedlings, rotted manure must be added to the holes. During the growing season, tomatoes of this group are supposed to huddle. Pinching is also performed. Top dressing is carried out before each hilling.
Tomatoes for sale
Those who want to grow fruit for the market that are transportable, attractive and in demand by consumers should also choose the right tomato seeds first. For a polycarbonate greenhouse in this case, according to many gardeners, the following varieties are best suited:
- Monomakh's hat. This tomato is prized for its delicious and aromatic fruits. At the moment, it is considered one of the most fruitful in the domestic market. From a square meter of greenhouse area, you can collect up to 14 kg of tomato fruits of this variety.
- Cardinal. Another large-fruited variety (up to 800 gr). It can reach a height of 170 cm. The fruits are of a raspberry color and have a very pleasant pulp.
- Canadian giant. Tall plant with a stem length up to one and a half meters. The fruits are large, slightly flattened. The pulp is juicy, with sourness.
- Russian soul. Tall variety (up to 1.5 m) with large red fruits.It can be used for both salads and canning. The pulp has a pleasant slightly sour taste.
- Biysk rose tree. A salad variety with delicious red fruits of a slightly irregular shape.
Cherry tomatoes in the greenhouse
Indoors, these interesting little tomatoes are often grown as well. In this case, you can choose the best varieties for greenhouses, also focusing on the experience of domestic summer residents. Most often, our gardeners grow tomatoes under a polycarbonate shelter:
- Sweet Cherry. The stem height of this variety can be up to 2 m. Fruits have an even shape and smooth surface. Their color can be bright red or yellow, since the seeds are usually sold in a mixture. The pulp is very juicy and sweet. Up to 50-60 small fruits are collected in one brush. Tomatoes of this variety are allowed to be used for canning.
- Minibel. Low-growing early ripening variety with very small red fruits. The pulp of tomatoes is juicy, with sourness. You can use Minibel for both salads and canning.
- Bonsai. Almost the smallest variety in the world (height 20 cm). The fruits (30 grams) are very dense, as they ripen, they change color from green to yellow, then to orange. Ripe tomatoes are red. The variety is very resistant to all major tomato diseases.
In specialized stores today you can buy absolutely any cherry tomato seeds. For small greenhouses, tomatoes in this group may be just perfect.
Dutch tomatoes
Good harvests in greenhouses can give not only domestic, but also some foreign varieties. For example, Dutch tomatoes are very popular with our summer residents. The varieties bred in this country are usually characterized by unpretentiousness and high yields. It is very good for growing in a greenhouse, for example, a tomato Tulip. Its main distinguishing feature is the red fruits of an interesting shape, similar to a flower bud. Their flesh is very tender and juicy. The variety has a high yield. Dutch tomato seeds for greenhouses can also be easily purchased at a specialty store. Our gardeners usually grow such tomatoes using the same technology as domestic varieties.
New tomato seeds for greenhouses
Every year, breeders develop a large number of new varieties and hybrids. Also suitable for growing in greenhouses. Of the varieties that have recently appeared on the market, the most popular are:
- Pink flamingo-2. The fruits of this variety are distinguished by simply excellent taste. The advantages also include resistance to disease.
- Daddy. A large-fruited variety that quickly gained popularity among summer residents with pink fruits resembling a heart.
Hybrids
Of course, not only tomato varieties are grown in the greenhouse. Many summer residents prefer to plant hybrid tomatoes in greenhouses. The best varieties for greenhouses, the characteristics of which were discussed above, are distinguished by high yields and resistance to diseases. However, in this regard, they still cannot compare with hybrids. The latter are easier to grow. However, of course, you cannot get high-quality seeds from them. The most popular hybrids are:
- F1 Union 8. Early maturing determinant plant producing fruits well suited for salads. Their use is also allowed for canning. The hybrid is highly resistant to the main diseases of tomatoes. Its medium-sized red fruits are flat-rounded.
- Pablo F1. Mid-season hybrid with very good yields. The bright red dense fruits of this tomato are round in shape.
A Few Tips
Those who like to make pasta, "light" or tomato juice should buy seeds of large tomatoes. For a greenhouse, the same Monomakh Hat, Canadian giant or Cardinal are perfect.Large fruit varieties are also commonly used for salads. For pickling, it is worth buying seeds of varieties with compact tomatoes. Indeed, firstly, the fruit should easily pass into the neck, and secondly, when salting small fruits, the inner space of the jar is much more efficiently used.
Harvesting tomatoes for greenhouses of the varieties discussed above are distinguished by resistance to diseases and relative ease of care. However, of course, you can achieve good results when growing tomatoes indoors, as well as outdoors, only by paying maximum attention to the plants. Water your tomatoes on time, weed and loosen them, and don't forget about top dressing. And then you are guaranteed a good harvest of tomatoes of almost any variety.
Low-growing tomatoes for the greenhouse: from selection to harvest
Low-growing tomatoes are attractive for greenhouses, first of all, because they are much easier to care for than their tall relatives. That is why those gardeners who do not strive to spend all their time in the greenhouse for pinching and garter choose exactly low varieties of tomatoes.
Our article provides fairly detailed instructions for choosing a variety and growing selected tomatoes in a greenhouse. By following it, you will definitely get a high yield!

Planting determinant tomatoes indoors
Varieties of tomatoes in the shape of a bush
High and low grades
To understand what is the significant difference between tall and short varieties, you need to understand the terminology.
The thing is that what is meant here is not so much the height of the plant as the features of growth:
- Tall (indeterminate) variety or hybrid Is a tomato, the stem of which can grow indefinitely. Tall, but at the same time sufficiently productive varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses are excellent for warm regions and greenhouses with an established heating. In comfortable conditions, indeterminate varieties can grow all year round and give up to 40 brushes of the crop.

Tall varieties are more typical for greenhouses
However, caring for such plants is laborious, since it is necessary to control the branching process throughout the growing season. For this, periodic pinching is performed - the removal of side shoots.
- Low-growing (determinate) tomatoes stop growing after tying a certain number of flower brushes. The first inflorescence is laid over 6-7 leaves, each subsequent one - through one or two leaves.
Low-growing varieties are characterized by early and amicable fruiting. They are almost never tied to trellises: the only exceptions are those cases when the bush lies on the ground under the weight of the fruit.
Usually, determinate tomatoes are grown outdoors, but in cold regions they are often used for greenhouse cultivation as well. In addition, low varieties are grown as additional crops, because there is less fuss with them than with tall ones.
Note! In most determinate tomatoes, the absence of pinching does not affect the yield, which can reach 12-15 kg / m2 depending on the variety.
Typology of low-growing tomatoes
Determinant varieties, in turn, are divided into the following subgroups:
- Actually determinant.
- Semi-determinant.
- Superdeterminant.
Let's analyze their features:
- Semi-determinant varieties are intermediate between tall and short. These varieties of tomatoes do not have a clear tendency to complete growth, but stop developing unexpectedly. Sometimes growth does not stop even after the formation of ten to twelve inflorescences.

Semi-determinant plants
- Such medium-sized varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses are chosen for maintenance in two stems. To ensure high yields, the planting density is 3-4 plants per square meter.
Advice! If you want to get a harvest from mid-season semi-determinant bushes early, subject them to determinant pinching. With this treatment, the bush will begin to bear fruit quite early, and the fruits will ripen much more amicably.
- Superdeterminate tomatoes do not require pinching at all. 2-3 inflorescences are formed on the bush, the fruits of which ripen very early. The second growth wave is very weak and begins after the bush has borne fruit, and inflorescences are almost never formed. Such tomatoes are advised to be planted in heaps, 5-6 bushes per square meter.
- There is another subspecies of determinant tomatoes - standard tomatoes. This is, without exaggeration, a sort of "for the lazy". There is almost no hassle with them - there is no need to tie or pinch the bush. The reason for this lies in the shape of the plant: several branches with inflorescences are placed on a low stem, which practically do not grow.
The appearance of standard tomatoes
Basic rules for growing stunted tomatoes in greenhouses
Variety selection
Tomatoes, which belong to the stunted group, must be grown taking into account their biological characteristics. Of course, in general terms, the agricultural technology will be the same as for any tomatoes, but there are nuances.
It is worth starting work on the cultivation of determinant varieties by choosing a variety:
- Depending on the size of the fruit, plants are conventionally divided into small-fruited, medium- and large-fruited varieties. In the latter, fruits can reach 300 grams or more.
- Among small-fruited tomatoes (they also include cherry tomatoes), there are such varieties as Early Sun, Lollipop, Raisins, etc.

Photo of cherry tomatoes
- Medium-sized tomatoes with a compact bush are, first of all, Tayana, Dusya red, Volovye ear.
- If you are a lover of large vegetables, then you should think about growing Yamal tomatoes, Snow Tale, Nastenka, etc.

Variety Snow Fairy Tale
- To get the earliest harvest in the greenhouse, you can plant the Hermitage, Sanka or Igranda varieties.
- If you plan to receive products in late summer - early autumn, then the choice of late-ripening varieties Venta or Hercules will be preferable.

Fruit of the Hercules variety
Also, one of the deciding factors when choosing a variety of tomatoes to be grown is the price. And here it is better not to save money, but to acquire really high-quality, albeit expensive, material - then the results will be worthy.
Seedling
When the variety is selected, you can start preparing the planting material. For low-growing tomatoes, it is very important that the seedlings are healthy and strong - then the plant will quickly gain green mass and begin to bear fruit together.
There are no special tricks when growing young plants from seeds, so the farmer only needs to strictly adhere to the algorithm:
- We examine and sort the purchased seeds. You need to sow only whole and healthy seeds - this way we will increase the likelihood of getting strong seedlings.
Advice! The easiest sorting method is to soak the seeds in brine. At the same time, we reject pop-up seeds, since they have insufficient mass, which means that they do not have the necessary supply of nutrients.
- Sowing for seedlings is carried out in late March - early April. If the greenhouse has autonomous heating, then the material can be prepared earlier.
- For sowing, we use a special soil mixture based on sod land, manure and peat. We take a shallow box for seedlings - so the root system will grow in width.
- We spread the seeds on abundantly moistened soil with an interval of 1.5-2 cm. Sprinkle the nursery with a layer of dry soil mixture on top.
- Germination is carried out at temperatures up to 220C. On the 10th day, we perform a pick - transplanting young plants with pinching the main root.
Note! Some varieties of undersized tomatoes do not tolerate picking well. This information is usually found on the seed package.
Planting and forming a bush
We plant low-growing varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses in closed ground after the first buds are formed on the bushes of seedlings. As a rule, this occurs at the age of 45-50 days.
Scheme of work with planting material
The landing technology is as follows:
- Two to three days before planting, we loosen the soil, add organic fertilizing and form holes. The optimal distance for most varieties of tomatoes is about 35 cm.
- Immediately before planting, we deepen the holes to 20 cm and pour a glass of potassium permanganate solution into them.
Advice! If possible, then it is worth adding a root growth stimulant, superphosphate or saltpeter.
- Next, we take out the bush from the pot, knead the lump of earth on the roots with our own hands and put the plant in the hole. After leveling the tomato, sprinkle it with soil.
- After 5-7 days after planting, we carry out the first watering and feeding with a mullein solution.
As soon as the plants rise, you need to install props and tie the stems to them. The exception is the standard varieties - they can be grown without a garter.
Further, we provide our plantation with water and fertilizers, not forgetting about regular pinching:
- When growing undersized varieties in a greenhouse, it is very important to form a bush correctly. To do this, during the development of the plant, we pinch the shoot, which is responsible for vertical growth.
- After that, the tomato begins to branch. Having selected the largest side shoots (two or three), we remove the rest.
- In the process of formation and ripening of fruits, we periodically carry out pinching. During this procedure, you need to cut or break out young shoots that are laid in the axils of the leaves.
- Also, do not forget about removing the leaves at the bottom of the shoot. This should be done gradually, removing no more than three sheets per week.
Scheme of a well-formed bush
Conclusion
The correct selection of a variety of low-growing tomatoes for greenhouses, as well as adherence to growing recommendations are prerequisites for success. At the same time, labor costs will be much lower than when breeding tall varieties, and the taste of the fruits will be just as wonderful. If you are seriously interested in this topic, we recommend watching the video in this article - it contains a lot of useful information (also learn about the features of growing bell peppers in a greenhouse).
Determinant and indeterminate tomato varieties
Experienced gardeners can easily understand all special terms, but for people new to this business it may seem difficult even to read such long names of varieties the first time. However, in fact, everything is very simple, and we will try to help you figure out what's what.
Types of tomatoes
Determinant and indeterminate varieties of tomatoes are, in a broad sense, a designation of the strength of their growth. For better understanding, some seed producers and sellers have started to write instead of these definitions simply "short" and "tall".
What does a determinant tomato variety mean in a broader sense? These are early and super-early varieties of tomatoes that ripen as early as 95 days after planting. Their growth is limited and it stops after the formation of 4-5 clusters of fruits.
Plants of super-determinant varieties do not require pinching, while determinate bushes still need a little maintenance so that the plant is not overloaded with fruits. In general, the advantage of such varieties is an early and harmonious yield of the harvest.
Among the best determinant varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses are the following: Alpha, Dwarf, Dubok, Golden Heart, Yamal, Sultan, Harem, Siberian early ripening, Cameo, Aurora, Grotto, Amurskaya Zarya, Alaska, Balkonnoe miracle, Betalyux, Grand, Delicatessen, and etc.
As for indeterminate varieties, these are varieties and hybrids of tomatoes that have unlimited stem growth.If grown in heated greenhouses, these plants can grow continuously for more than a year. At the same time, up to 50 clusters of tomatoes can be formed on each stem. Isn't it fantastic?
Truth and care for this type of plant needs a special one. So, they need the constant removal of all stepsons, so that only one main stem is actively formed. Such varieties are harvested somewhat later than other species. Ideal for residents of the southern regions and the middle zone, however, it is not very convenient to grow them in the northern latitudes, since they need a lot of heat and light, respectively, you need to have specially equipped greenhouses.
The best indeterminate tomato varieties for greenhouses: Wild rose, Pink giant, Bull heart, Admiral, Bravo, Orange, Bull heart red and pink, Vlad, Jubilee Tarasenko, Yellow giant, La Bayadere, Intuition, Aristocrat, Caliber, Kinglet, Pepper red, Chinese pink, Pepper pink, De Barao, Black Prince.
People, in our time, with a deteriorating ecology, prefer vegetables without chemical treatment. Therefore, most begin to grow vegetables on their own. Some even grow vegetables on loggias. Tomatoes are very popular with gardeners.
The choice of the right variety of novice gardeners sometimes leads to bewilderment. In specialized stores, the selection of seeds is simply huge. On all packages it is written in the same way that this particular variety is the best and most productive. But sometimes the phrases that are on the seed packages become incomprehensible. What is it - determinant and indeterminate tomato varieties? Let's take a closer look at what it means
Determinant and indeterminate tomato variety
Useful properties of tomatoes
Tomatoes are very healthy vegetables. They contain various biological substances. Tomato normalizes acidity in the intestinal microflora. Prevents cell aging. Continuous consumption of tomatoes reduces the risk of cancer cell formation. Tomatoes cleanse the walls of blood vessels, thereby stopping strokes and heart attacks. If tomatoes are present in your diet, then you will never suffer from stomach ulcers. Tomatoes ground to the appearance of porridge are used for the external treatment of ulcers, abscesses, and skin inflammation. Tomatoes also help to reduce human weight, improve carbohydrate metabolism in the body.
Indeterminate tomato varieties
These are tall tomatoes that reach a height of two to three meters. The first tomato cluster is usually formed above the ninth leaf. Growth can be long depending on weather conditions and usually the top of the bush is pinched to allow ripening to ripen the fruits.
This variety is suitable for residents of the southern regions.
In medium-sized regions, this variety is also quite popular. It is grown both outdoors and in greenhouses. Of course, they are suitable for greenhouses and northern regions, but compared to determinant varieties, the fruits will be later. You can easily guess such a variety in your garden or greenhouse. This tomato will be the highest, almost resting on the roof of the greenhouse.
Indeterminate variety
Benefits of indeterminate varieties:
- Tomatoes of this variety are very tall. The trunks are tied up vertically. This allows the plant to increase the number of brushes. That is, from a small area of these tomatoes, you can collect a large number of fruits. A crop of this variety can yield up to sixteen kilograms per square meter.
- Tomatoes are less susceptible to disease. Tall tomatoes must be tied to a trellis, remove the lower leaves and stepsons. This gives access to uniform lighting and air circulation.
- Fruiting of these tomatoes lasts longer than the determinant varieties. This allows you to enjoy the harvest from July until the first frost.
- The variety is quite easy to care for. It will be enough for you to shape it. You just need to leave one stem and remove the stepsons.
- It is more convenient to work with the plant and harvest while standing, and not in the position of a summer resident.
Disadvantages of indeterminate varieties:
- It is necessary to have support for the plant. Otherwise, it will lie on damp ground, which will lead to rotting of the fruit.
- Fruit ripening takes a long time. This variety requires a long summer period or additional lighting and heating.
- The need to make pinching. It is necessary to constantly remove stepchildren on the plant so that they do not overload it.
Determinant varieties
These tomato varieties are usually short in stature. The word determinant itself, translated from Latin, means limited growth. This variety finishes growing when two to six clusters are formed on the stem, the last cluster being the top of the bush. Growth continues from the stepson growing from the leaf below. Sometimes the number of brushes can be more.
Stepsons on this tomato variety are very strong and continue to grow and form the crop. Most gardeners prefer this variety, since the fruiting of these tomatoes occurs before the indeterminate varieties.
determinant tomato variety
In addition, determinant varieties have a variety - standard varieties.
Stamp
It is an industrial tomato. This variety does not require being tied up and pinned. This variety has a strong stem. The earliest variety among tomatoes. The fruits ripen from about the seventy-fifth day. This is the earliest variety that can bear fruit as early as June. The first brush is usually laid above 4-5 leaves, while others grow after 1-2 leaves.
That's not all - there are varieties in the middle that cannot be fully attributed to determinant or indeterminate varieties.
Semi-determinant varieties
They do not complete their growth as quickly as the undersized variety, but they can stop growing at any time. Better to grow them in greenhouses, you need to lead in two stems.
Benefits of determinant varieties:
- These tomato varieties are among the earliest.
- Not very fussy about the garter. One tying is enough, and some tomatoes of this variety do not require a garter at all.
- The variety, in contrast to the indeterminate, is more compact. They do not create a "jungle" in the greenhouse.
- The variety is widespread and very popular.
- Fruit ripening occurs more amicably. This variety is suitable for mass preservation.
- The best variety for the northern regions. Growing this type of tomato in greenhouse conditions, you can get a quick and large harvest. Manages to give the harvest in the open field in a short summer.
Disadvantages of determinant varieties:
- Lower yield. Several brushes form on the plant, and it stops growing. After the fruit ripens, if the plant is still completely green, it will have to be removed. Can continue to form crops on stepchildren.
- More mineral fertilizers are needed, as new brushes are constantly being formed.
- Fruits of different sizes. The first are larger, the next are smaller, but for personal consumption this is an insignificant drawback.
The choice of varieties of indeterminate tomatoes is huge:
A large selection of different varieties in the article "The best varieties of tomatoes with photos and descriptions". There are many tall varieties in the article - "Tomato varieties for a polycarbonate greenhouse"
«Miracle of the earth"Is an early maturing variety. Grows up to two meters. Productivity up to four kilograms. Fruits are heart-shaped, weighing about half a kilogram. Differs in drought resistance. The fruits do not crack, they are transportable. The variety lives up to its name.
«Christina Plume»- tomato type tiger cream. The plant grows up to two meters. With good care, you can collect up to eight kilograms of tomatoes from one bush. Has a sweet taste and high yield.
«Cherokee»This variety is very popular. But one brush ripens up to eight fruits. This variety has an excellent presentation. The fruits keep their shape, do not crack.
«Star Gold"- these are miniature fruits up to thirty grams. The variety is distinguished by its unpretentiousness, golden hue of the fruit and sweet taste.
Yielding determinant varieties:
«Rocket»Oblong-oval tomatoes. Fruit weight ranges from sixty to one hundred grams. The bushes of this variety are compact. Six to seven bushes can be planted on one square meter.
«Nevsky»Tomato. One of the earliest shrubs. The shape is flat-round. The color is light red. The mass of a tomato is up to fifty grams.
Tomato "White filling". The variety is very juicy, weighing up to one hundred and thirty grams.
Considering all of the above, you can determine which variety is best for you. Think about what you need tomatoes for. Just pamper yourself or for canning?
Seed sowing dates
If you decide to grow both determinant and indeterminate seed varieties in your garden, then you need to pay attention to sowing seeds. Indeterminate varieties take longer to mature. It is recommended to plant tall seedlings in the ground on the sixtieth day. Therefore, when sowing seeds for seedlings, first sow indeterminate varieties, and after two weeks you can start sowing determinant varieties.
Again, note that the standard varieties can be planted in the ground at 50 days of age. All this will allow you to plant seedlings in the ground at the same time. It will enable tomatoes of different varieties to start bearing fruit almost at the same time.
How to distinguish which variety by plants
If you suddenly mix two varieties when soaking seeds for sowing, do not worry. When shoots appear after three to four days, the seedling's cotyledonous knee straightens out. You can easily distinguish varieties by its length.
In indeterminate varieties, the knee is longer, about three to five centimeters. The determinant variety will be about a centimeter. When diving tomatoes, you can correct the situation by planting different varieties in different boxes.
Choosing a variety of tomatoes for planting
Even when choosing a variety, it is necessary to take into account your climatic zone and growing conditions. It will be open ground or a greenhouse.
If you live in the northern regions, determinate varieties grown in greenhouses are suitable for you. They ripen quickly and will have time to bring you crops in a short summer.
In the middle lane, you can grow determinate varieties in the open field and indeterminate ones in a protected one.
In the southern regions, both of these varieties will feel great.
Therefore, make a choice in favor of the variety you need. Now you are well aware of the differences between determinant and indeterminate tomato varieties. Happy harvest.
Best regards, Sophia Guseva.
The high yield of greenhouse tomatoes depends largely on the variety. Which of them to choose for planting is decided by the grower based on his own preferences. The main rule when choosing seeds is the purpose of growing them directly in greenhouses. But this is not the only point to which you should pay attention when purchasing high-yielding varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses.
In the closed space of a polycarbonate greenhouse, conditions are created for the development of fungi and pathogenic microorganisms that provoke plant diseases (late blight, tobacco mosaic, gray rot, phomosis, etc.) When choosing tomato seeds, you should pay attention to their resistance to various diseases, especially to phytophthora.
The design of the greenhouse also influences the selection of the variety. For a small and low building, undersized (determinant) tomatoes are better suited. Along with the fact that the bushes of low-growing tomatoes take up little space, they are distinguished by early maturity and high productivity. For large, tall greenhouses, it is better to choose tall (identical) tomatoes. The length of their stem can reach 3 m, while the whole plant is abundantly strewn with fruits. Thus, the lack of area of the soil itself is compensated.Long-term fruiting and easy care are the undoubted advantages of such tomatoes. One bush can give up to 15 kg of harvest.
Sometimes both varieties of tomatoes are planted in polycarbonate greenhouses. Tall ones are placed in the center of the greenhouse, and undersized ones along the perimeter.
It is important to consider for what purpose tomatoes will be used. Today, the seed industry offers salad varieties as well as those suitable for canning and for sale.
Lettuce tomatoes are distinguished by the sweetest taste, large size and juicy pulp. Most often they are pink.
Tomatoes for canning are medium-sized, capable of retaining their shape after heat treatment. They usually have a deep red color.
Tomatoes for sale have a neat shape and a firm flesh; their main advantage is transportability.
Many vegetable growers choose polycarbonate tomatoes for greenhouses taking into account the aesthetic qualities, in this case, the color. Specialty stores offer the very best seeds not only for red and pink tomatoes. Today, tomatoes can be grown in yellow, orange, green, purple and even black.
Indeterminate varieties of tomato for greenhouses (high)
Consider several popular varieties of indeterminate tomatoes for polycarbonate greenhouses and film shelters.
- Honey saved- refers to tall tomatoes. Mid-season salad variety with large yellow fruits with delicate sweet pulp. An adult plant reaches 1.5 m. The yield is 4-6 kg per bush. Resistant to phytophthora and cracking.
- Mushroom basket - an indeterminate mid-season tomato with large red fruits and a pronounced ribbed shape, reaching 500 g. The plant reaches 2.5 m.
- Black moor - a variety of exotic tomatoes. Plant height reaches 1.3 m. Fruits of chocolate-red color, rounded elongated shape with a smooth texture. These tomatoes are highly transportable, suitable for canning, and are well stored.
Determinant (undersized) tomatoes for the greenhouse
Low-growing (determinant) tomatoes are early ripening. Therefore, they deserve the attention of not only the owners of small greenhouses, but also those who want to get the harvest as early as possible in the open field. Let's consider several popular options.
- Ballerina- medium-sized fruits of red color, elongated shape, mid-ripening period. The bushes reach a height of 0.5-1 m.
- Pink leader - early tomato used for salads and canning.
- Fontanka- standard early undersized variety. The height of the bush is up to 50 cm. Fruits are red oval in shape. 40-45 fruits can be removed from one plant.
- Summer resident. Plant height up to 50 cm. Resistant to frost. Rounded medium-sized red tomatoes are great for canning.
For sale
Tomatoes grown for sale deserve special attention. They must have a high-quality presentation and be transportable.
- Monomakh's hat. High yield, good taste. From each square, you can collect up to 14 kg of products.
- Cardinal. Large-fruited tomato, fruit weight reaches 800 g. They have a raspberry color and tasty tender pulp.
- Canadian giant. A tall shrub with a stem length of up to 1.5 m. Fruits are red with a flattened shape. The pulp is juicy with a slight sourness.
- Russian soul. Tall variety with large red fruits. It is used both for use in salads and for preparations. The pulp has a characteristic sour taste.
Cherry varieties for greenhouses
Popular cherry tomatoes are also grown in a polycarbonate greenhouse. Some varieties of these tomatoes have proven themselves well among summer residents.
- Sweet Cherry. Indeterminate tomato with a stem height of up to 2 m. Fruits are even with a smooth surface and tasty sweet pulp.Tomatoes can be bright red and yellow. The seeds are usually sold as a mixture. Up to 50-60 tomatoes can be harvested from one brush. It is possible to use this cherry variety for canning.
- Minibel. Low-growing early variety with very small red fruits. The pulp is juicy with a slight sourness.
- Bonsai. The shortest tomato. The bush barely reaches 20 cm in height. The fruits are very dense, as they ripen, they change color from green to yellow, and then to orange. Ripe tomatoes take on a classic red color. The variety is resistant to diseases, including late blight.
Resistant Dutch varieties
The best tomato yields in polycarbonate greenhouses can be obtained by planting Dutch tomatoes. The varieties bred in Holland are distinguished by their endurance and unpretentiousness.
- Tulip. Red fruits have an unusual shape that resembles a flower bud. The pulp is tender and juicy, the yield is high.
Hybrid Dutch varieties that are resistant to many diseases and pests are very popular. They give the best yields.
- F1 Union 8. An early determinant salad variety. Red rounded flattened fruits are also suitable for harvesting for the winter. Differs in high resistance to late blight, gray rot and other diseases.
- Pablo F1. Mid-season high-yielding hybrid. Fruits are red, dense, rounded.
- Crystal F1. Early maturing indeterminate hybrid. Fleshy fruits, which weigh up to 140 g. Tomatoes of this variety have high transportability. They are immune to diseases such as verticillium, tobacco mosaic and late blight.
If you plant tomatoes of different ripening periods in a greenhouse, then you can have a harvest throughout the season and use tomatoes for different purposes: from preparing salads to preparations from red, and in autumn and green fruits. You can use this combination: "Verlioka plus" early grade, "Pink capia"- mid-season, "Russian size"- late.
Do not forget that the quality of the crop depends on how the plants are taken care of.
Growing and shaping determinate tomatoes
It is profitable to grow tomatoes of a determinant type of growth, they are able to set fruits in any conditions, therefore they are suitable for open ground not only in the south, but also in the middle lane. When planting in greenhouses, they take up very little space and can be content with tunnel-type shelters. They are very productive, it is enough just to form and tie up the bush correctly.
They stop growing on their own. Varieties and hybrids of the determinant type of growth are very popular among amateur vegetable growers. Their plants are weak (1.0-1.3 m) and medium-sized (1.2-1.3 m), have a compact bush. The limitation of the growth of the main shoot occurs after the formation of 4-6 shoots, and then the stepson continues to grow. The first inflorescence on the plant forms above the 6-7th leaf, the subsequent ones are located after 1-2, sometimes follow each other.
Tomatoes of determinant growth are easy to form. The second wave of vegetative growth in them begins earlier than in superdeterminant ones, and is observed almost immediately after the formation of fruits on the first inflorescences. As a rule, these are mid-early varieties and hybrids, in which 105-115 days pass from germination to the first harvest.
Three important nuances in growing determinant tomatoes
Tomato bush formation
The photo on the left - the formation of a tomato bush in one stem, the photo on the right - the formation of tomatoes in two stalks1. It is advisable to combine the first pinching of tomatoes with a garter of plants to supports or a trellis.
I begin to do this in such a way as to have time to remove the stepsons before the first brush opens. 2. The stepchildren break out with their hands until their length does not exceed 4-5 cm. At this time, they easily come off, small wounds in the leaf axils quickly overgrow.
Stepsons determinant tomatoes
Determinant tomatoes must be grazed.All methods are quite simple, mainly using one or more stepsons in the upper part of the plant. For a long time I have been growing a hybrid of Verlioko, which has a determinant type of growth.
This, as they say, is my workhorse: in any weather it will provide both an early harvest to eat and a plentiful one - for processing into juices, ketchup and seaming. For a long time I let it go into two stems, forming the second of the stepson growing out from under the first inflorescence. Now I form a tomato into one stem, until the plant throws out 3-4 brushes on the main stem, then I start at two, choosing any strong stepson for this. After 1-2 inflorescences, I can leave one more, already the third.
It all depends on the weather. I reckon so that the harvest has time to form by the end of September. I have a glass greenhouse. I came to the conclusion that the formation of two stems at once noticeably slows down the development of a tomato.
Therefore, at first I give him to gain strength, and only then I load the crop. I plant 2.8-3.0 plants per square meter, by the time the first brush ripens, gradually removing one leaf once a week. This technique improves the ventilation of the bushes, inhibits the development of diseases, and, most importantly, ensures the outflow of nutrients to the fruits.
Grassing and shaping a tomato bush
Grassing and forming a tomato bush
1. At the same time, in one stem, while stepson in the upper part, do not rush to cut off all the stepsons. Constantly leave at least two reserve ones so that the plant continues its growth in the future due to one of them (the weaker one is removed) as soon as the main stem stops growing .This is the easiest way. It is good for both open ground and small greenhouses. 2.
In one stem, leaving 2-3 stepsons with 2-3 inflorescences on each. At the same time, lateral shoots are left on the main stem, located in the stepchildren of the leaves under the inflorescences. 3. Growth is constantly transferred to the lateral shoot.
It is formed from the stepson, located in the bosom of the 3rd sheet. In this case, the main stem is pinched over the 3-4th inflorescence, leaving 1-2 leaves. Then, on the formed shoot from the stepson, which has grown in the axil of the first leaf under the first inflorescence, the next continuation shoot is formed, and the previous one is pinched, leaving 1-3 leaves over the second inflorescence. And so they continue as long as space in the greenhouse allows. ZASTENKINA, agronomist Photos and drawings by the author
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
Many novice gardeners are wondering what is pinching a tomato in greenhouses and greenhouses, why is all this needed? If you do not remove stepchildren, the price of such inaction is a huge number of leaves, with a small harvest. That is why you should not give up pinching, you just need to clearly understand how to pinch tomatoes correctly in the greenhouse so that the plants receive all the necessary nutrients and can please you with a good harvest. Let's take a closer look at how and when to carry out pinching, as well as how to distinguish the stepson from the sheet.
What is pinning?
Tomato grazing is the removal of all unnecessary lateral shoots - stepchildren that grow from the leaf axils. It is necessary to carry out this procedure, since the stepsons take most of the nutrients coming from the roots to the aerial part of the tomato.
- Getting an earlier harvest of fruits. (See How to equip the beds for a good harvest) Extension of the fruiting period of tomato bushes. Getting more fruits of high quality from a unit of greenhouse area.
How to distinguish a stepson from a leaf?
How to distinguish a stepson from an ordinary leaf In order to distinguish a stepson from a leaf, you need to carefully consider the tomato bush. A leaf grows on the stem itself, but in its bosom, between it and the trunk, an shoot appears - a stepson.
Such a lateral shoot actively grows and grows leaves, as well as the so-called stepchildren of the second level. You need to remove the stepchildren until they are very large - 3-5 cm in length. This is necessary so that the plant does not waste nutrients for their growth, and also so as not to unnecessarily injure the bush by removing large shoots.
When should you stepchild?
Given the simplicity of this procedure, the answer to this question will be very simple: as soon as you saw stepsons on a tomato bush. They form most actively after the first flower clusters appear on the bushes. The most difficult to carry out pinching tomatoes in the greenhouse in the event that you have not cut off the stepsons for a long time.
The most difficult thing is to understand which of the large grown stems is the stepson, and which is the real one. Advice: you can determine the stepson by its location: they usually grow from under the first flower brush. The most favorable time to spend picking tomatoes in the greenhouse, according to the video, is morning. It is at this time that they break off most easily. In addition, in a day, the wound formed after breaking the stepson will heal.It is important: in order to prevent the spread of various viral diseases from one plant to another, the stepson must be broken out, trying to prevent the juice from getting on your hands.
How to carry out the correct pinching
Before proceeding with the removal of all unnecessary shoots, you need to decide on the following:
- How often will you do this, since you need to pinch tomatoes in the greenhouse at least once every 10 days, and best of all - weekly. How many stems will your greenhouse tomatoes have? Depending on the type of tomato and the area of the greenhouse, you can form a bush into one, two or three stems.
Possible options for the formation of tomato bushes in a greenhouse
Formation of a bush into one stem
According to experts in the field of agriculture, the single-stem type of tomato bush formation is the most suitable for greenhouses. Experienced gardeners disagree with them: in their opinion, the more stems the tomatoes have, the higher the yield of fruits can be obtained from each greenhouse bush. stem, however, all flower clusters are retained, including the lowest one.
Forming in two stems
Formation of a tomato bush in two stems When forming a tomato bush in two stems, not only the main stem is left, but also the first stepson, as a rule, is the strongest and most actively developing. It is located directly under the very first flower cluster of the bush.
All other stepsons are removed. This is clearly seen in the photo.
Forming into three stems
To get three stems on one bush tomatoes you need:
- We leave the stepson under the first flower brush, and find and leave another strong and well-developed stepson. Usually it is located directly under the first stepson. Remove all the remaining stepsons.
It is important to remember that there are different types of tomatoes:
Peculiarities of pinching of various types of tomatoes Each of these types has its own peculiarities of formation and pinching. You can watch video materials on how to pinch tomatoes in a greenhouse.
Indeterminate varieties
These are tomato varieties that have no growth restrictions. These varieties tend to form into one stem.
This is due to the fact that indeterminate plants tend to form many lateral shoots.To form a tomato bush into one stem, it is necessary to remove all stepchildren. It is advisable to leave a "stump" at the site of the remote shoot, about 1 cm high.
This contributes to the slower formation of new shoots.On such a tall plant, as a rule, about 10 flower shoots are left, removing all the rest. If the size of your greenhouse allows, then you can form such bushes in two stems. (Cm.
The size of the greenhouse is made of polycarbonate) To do this, leave the first or second stepson, after which the bush is spud and mulched. On the second stem, you can leave 4-5 flower brushes, be sure to remove all lateral and basal shoots.
Semi-determinant varieties
Semi-determinant tomatoes can grow up to 180cm. If the plants are not very densely planted, then they can be formed in both two and three stems.
In tomatoes belonging to semi-determinant varieties, it often happens that after pinching, the main stem stops its growth - it is edged. Therefore, if semi-determinant varieties prevail in your greenhouse, you should not immediately pinch all the plants. Make sure first that the main stem has not stopped growing. If the stem is terminated, then the bush can be formed into several stems.
Determinant varieties
This group includes the smallest varieties of tomatoes, and, as a rule, they do not require pinching. When growing such varieties, it is necessary to carefully read the recommendations of the growers for the formation of a tomato bush, which are given on the package of seeds. Most often, it is on low-growing plants formed into one stem that tomatoes are harvested early. For this you need:
- Remove all stepchildren. Leave 2-3 inflorescences, removing all the rest. After the last inflorescence, a few leaves are left and pinch the top - the growth point.
Important: when forming semi-determinant and determinant varieties of tomatoes in one stem, with 3-4 flower clusters preserved, tomatoes on such bushes will appear a couple of weeks earlier. In conclusion, a small instruction on the general rules for pinching tomatoes grown in a greenhouse:
- Carry out pinching of tomatoes only in the morning, in sunny and dry weather. When the stepsons are removed at this time, the wounds heal well and the plant does not get sick. If you have to remove stepchildren in damp weather with high humidity, then the instrument that will be removed must be disinfected with 1% potassium permanganate solution, after working with each plant. It is necessary to grow greenhouse tomatoes weekly, it can be combined with the removal of leaves. All stepchildren must be removed, regardless of their size. However, the most painless for a plant is the removal of stepchildren 5-7 cm in size.First of all, bushes of the most valuable varieties of tomatoes, as well as the healthiest plants, are pinched. All tomato bushes on which there are any specks, yellowing and other troubles, stepchildren are better to break out, trying not to let the juice of the plant get on your hands.
You can learn more about how to properly pinch a tomato in a greenhouse from the video materials located here.
Materials: