Content
- 1 Seed preparation
- 2 Seedling
- 3 Landing in the ground
- 4 Subtleties of care
- 5 Description and characteristics of the kolkhoz melon
- 6 Breeding history and growing region
- 7 Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- 8 Open ground planting rules
- 9 Growing conditions
- 10 Features of this variety
- 11 Diseases and pests
- 12 Melon Kolkhoz woman, its advantages and disadvantages
- 13 Planting seeds for seedlings and further care
- 14 Correct melon bed and planting seeds directly into the soil
- 15 Tips for growing melon Collective farmer in the open field and in the greenhouse
- 16 Melons in Siberia
- 17 Gardeners reviews
- 18 The history of the Kolkhoznitsa melon variety
- 19 Description of the variety
- 20 Advantages and disadvantages of a melon Kolkhoz woman - table
- 21 Landing features
- 22 Melon care, bush formation
- 23 Harvesting and storage
- 24 Melon reviews Kolkhoznitsa

Melon variety Kolkhoznitsa 749/753 is the most popular variety in the regions of risky farming. The Volga region, the Urals and further north, the summer is short, often rainy, and it is impossible to grow a delicious melon, especially without a greenhouse.
The Kolkhoz Woman Melon was bred in 1943 and since then has been in constant demand among gardeners, because it yields tasty fruits in any summer in the open field.
Melon Kolkhoz Woman 749/753 - small 0.5-1.5 kg, but very sweet and aromatic. The fruit is roundish yellow or yellow-green, mostly covered with a net. The pulp is white, the skin is thin. The Kolkhoznitsa variety is mid-ripening, 80-100 days from germination to harvest, so you need to grow melon through seedlings.
Seed preparation
Seeds of this variety are not in short supply, they can be bought at any point of sale that sells seeds. Better to buy in a white bag. In order not to overpay for a color picture. The cost of a white package of Melon Kolkhoz Woman will cost no more than 5 rubles, and a color package from 10 rubles. The variety is not hybrid, so you can collect and prepare your seeds for the future, from the best fruits.
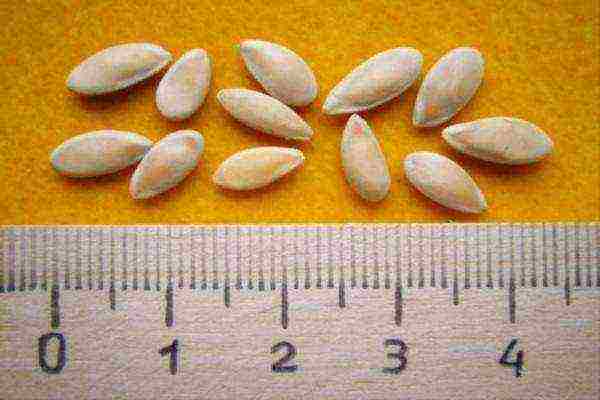

Try to choose large seeds for planting.
It is important: melons should not be planted next to cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins and squash. These crops are pollinated among themselves and can give ugly fruits, tough and tasteless. Seeds from such fruits cannot be harvested either.
Seedling
Before planting seeds for seedlings, they must be germinated. To do this, the seeds are wrapped in a bandage or toilet paper, immersed in a ceramic mug, poured with warm water, and placed in a warm place for several days. It must be ensured that they are always moist and warm. Seedlings will appear in a couple of days.
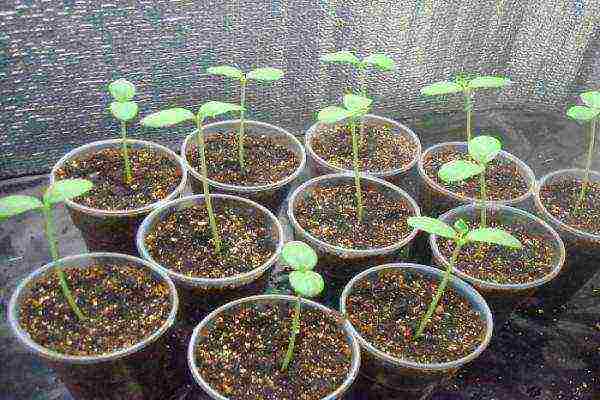

It is better to plant melon for seedlings on April 30, and plant it in the ground in early June (after the 10th)
Each seed must be planted in a separate container. The container for planting can be a disposable glass, a peat glass or a square pack of kefir cut in half.The main thing is to then remove the seedlings from the container without damage, in order to plant them in the ground.
Melon rises and grows quickly. It is necessary to keep the seedlings in a sunny place and make sure that the soil is moist. Seedlings are planted in a permanent place when all frosts have passed, at the age of 1-1.5 months.
Landing in the ground

Planting melons outdoors
In a sunny place, sheltered from the north wind, they make a bed for planting melons. The ground is already dry, warm, crumbly, the threat of frost has passed. So it's time to plant melon seedlings.
There are two ways to plant melons in the ground:
- High bed. Rotted manure is laid in a layer 20 cm high along the entire length of the bed. Then they make boards from the manure, it turns out such a manure box. You can strengthen such a bed on all sides with boards. Then this bed is filled with garden soil. The soil layer should also be at least 20 cm. Such a bed for planting melons can be used for many years, only the earth can be added to it and the sides can be raised. Melon seedlings are planted in the ground, to the depth of the developed root system. They make a hole, spill it well with water, then plant a melon. The roots are pressed tightly with earth, there is no need to water from above. It is advisable to shade the seedlings after disembarkation for several days while acclimatization is in progress. The grandfather's way is to cover each melon with a burdock leaf, changing it every morning. Can be temporarily covered with a nonwoven cover. After 3-5 days, the melons will stop withering during the day. You need to water abundantly, at night.
- An ordinary bed in which large holes are made. The distance between the pits in a row is 30 cm, between the rows is 60 cm. A spoon of azofoska or "Field of Miracles" is placed in the pits, rotted manure can be used. Then a fertile soil layer is poured, everything is spilled well with water and a melon is planted. The root system is tightly covered with moist soil, sprinkled with dry soil on top so that the moisture does not evaporate. The rest of the care is the same as in the first method of planting.
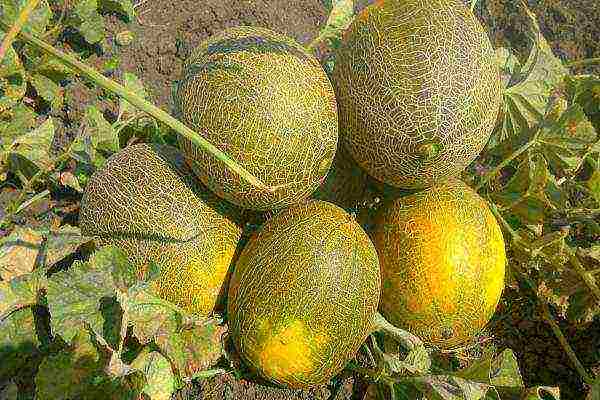

The first three fruits of the melon are left on the vine before ripening. The lash is then pinched so that it does not grow further, and all the nutrients enter the left fruits. Then the melons will grow large and sweet
If this is not done, then there will be a lot of melons, but they will be the size of an apple and have a mediocre taste.
Subtleties of care
Melons are not difficult to care for. When the seedlings acclimate and grow, they will need to be hilled once, and before that they will need to be fed with liquid mineral fertilizer. To do this, you can use Zdraven for cucumbers and zucchini.

Melon is not capricious in leaving
In addition, you need to take care of watering: the melon needs a lot of moisture. Water the melon overnight, abundantly, with warm water.
Already in August it will be possible to enjoy sweet melons of the Kolkhoznitsa variety grown in the open field.
Look video about growing melon in the open field:
Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
This culture is considered capricious, requires special conditions for growing. Many varieties are cultivated exclusively in the southern regions. But the kolkhoz melon is perfect for breeding in the middle lane, even in the open field.
Description and characteristics of the kolkhoz melon
This variety is popular in areas with risky farming. Indeed, in the Volga region or in the Urals there is no way to grow a normal berry without planting it in a greenhouse.
The variety has been known since 1943, since then it has been very popular among gardeners, as it pleases with good harvests in any summer, even not very sunny. The fruits are small, not exceeding one and a half kilograms, but very sweet and aromatic. The skin of the berry is thin, the flesh is white.
The variety belongs to the mid-season, from the emergence of sprouts to harvesting, it takes no more than a hundred days, so this melon variety should be grown only by the seedling method.
 Melon kolkhoz woman cutaway
Melon kolkhoz woman cutaway
Breeding history and growing region
In greenhouse conditions, melon is excellently grown in Holland, Italy, France, Japan and Bulgaria. Since the nineteenth century, the collective farmer began to be grown on the territory of Russia in greenhouses, since then she has not reached a greater distribution.In the middle lane, subject to all requirements for cultivation, the first harvest can be obtained in May.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Here is a description of the main advantages of the variety, thanks to which it is popular among gardeners:
- excellent taste;
- resistance to temperature extremes during cultivation;
- good transportability.
Minus one - not a very long storage period. Only unripe specimens are able to lie a little longer.
Open ground planting rules
To grow melons, you should choose a bed well-lit by the sun, securely sheltered from the winds and having a fertile, well-fertilized soil. It will be better if you start preparing the garden in advance, in the fall. For this, the territory allotted for planting is dug up, organic matter is added to the soil.
If there is a lot of clay in the soil, then it is recommended to add sand to give the soil the necessary looseness.
In spring, the bed is dug up, fertilizers of the phosphorus and potassium group are introduced into it. After the work done, it is allowed to land. For seedlings, seeds should be chosen larger. They are pretreated with growth stimulants or boric acid containing zinc sulfate. After completing this treatment, the seeds should be soaked in water for twelve hours.
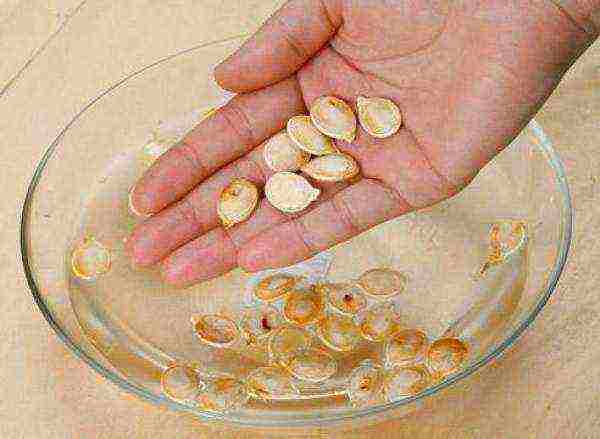 Seed hardening by soaking in water
Seed hardening by soaking in water
Gardeners with experience of the seed are hardened. To do this, they:
- pour the seeds with water, the temperature of which is thirty-five degrees;
- take out the inoculum and keep it at room temperature for a day;
- for twenty hours, the seeds are transferred to a place where the temperature regime is zero degrees;
- then they return the seeds to their previous conditions.
Such actions with seeds are performed at least three times a week before planting.
Seeds are planted in peat containers that protect the roots at the time of transplantation. Young plants do not even have to be taken out of the cups - they are planted directly in them. Such a measure even additionally fertilizes the beds.
Before sowing, the cups are filled with soil, which is purchased in stores or prepared by hand. In this case, the mixture should consist of nine parts of peat, and one part each of sand and wood ash. Pre-soaking the seed will sort out empty seeds that will float on the surface.
Seeds are planted to a depth of five centimeters, two each. Until shoots appear, the containers should be kept in a room with an air temperature of about twenty degrees during the day and at least fifteen at night. The melon begins to sprout in about a week. When the seedlings have formed the third leaf, the plants are pinched to allow them to start forming lateral branches.
Sowing seeds is done in April. The seedlings are transferred to the ground after twenty-five days.
Growing conditions
Seedlings are transplanted into small holes according to the scheme "seventy to seventy" centimeters. You just need to wait until the threat of night frosts has passed. Water is poured into the arranged holes, a little humus is introduced, then the seedlings are planted in such a way that an earthen lump is slightly visible above the surface of the garden. The plant is watered, a little sprinkled with earth. For a few days after planting, the seedlings should be lightly shaded.
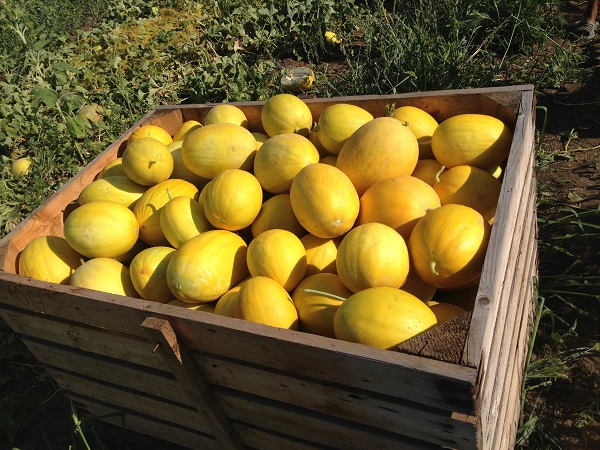 Melon field and harvest kolkhoz woman
Melon field and harvest kolkhoz woman
Features of this variety
- the culture is famous for the fact that under any climate conditions it can give a good harvest;
- melon seeds can be dried and then eaten separately;
- it is contraindicated to eat it with milk or alcoholic beverages - there is a high probability of poisoning;
- melon pulp is white, crunches.
Diseases and pests
Like many vegetable crops, melon is capable of transferring various diseases that affect the weight and taste of the fruit.Sources for infection can be considered the soil composition, weeds, seed stock, and the remains of last year's plants.
Most often, the melon is sick with powdery mildew. It appears with a special whitish bloom on the stem parts and foliage of plants, causing drying. The discarded foliage stops the development of the fetus, its quality deteriorates. But the collective farmer is distinguished by good resistance to such a disease.
The second melon problem is fusarium. It is spread through the soil by seeds and debris. The disease spreads quickly, and plants can die within a few days. Such viruses are prevented by chemical treatment.
Another disease is cucumber and watermelon mosaic viruses. Infection occurs with the help of aphids, which carry the infection from infected plants to healthy ones. As a rule, this happens at the second stage of the growing season and almost halves the yield.
By following all the recommendations, you can always grow a good harvest of this berry on your site. True, fresh fruits do not last long. But experts have found a way out - in dried form, the melon is very tasty, retains almost all useful components.
There is hardly a gardener who has never seen or tasted a kolkhoz woman melon. The honey taste is reminiscent of childhood. Now many are trying to grow melons on their personal plots, but not always undertakings are accompanied by success. The culture, although it belongs to the same family as cucumbers and zucchini, which have long been well known to gardeners, is much more demanding in care. The Kolkhoznitsa variety is a pleasant exception, combining relative non-capriciousness with good cold resistance and abundant yield. Many gardeners will not trade this melon variety for any modern hybrids.
Melon Kolkhoz woman, its advantages and disadvantages
Melon Kolkhoz woman, as you might guess from its name, is an achievement of Soviet breeders. It was introduced in the Rostov region at the end of the 30s of the last century, and entered the State Register in 1943. The variety is recommended for cultivation in the Black Sea region, in the North Caucasus, in the Volga region, in the Urals, in Siberia and in the Far East, that is, in almost all regions of Russia. This is due to cold resistance, atypical for melons, which is one of the main advantages of the Kolkhoz woman. And in taste it almost does not differ from the southern "honey" fruits.
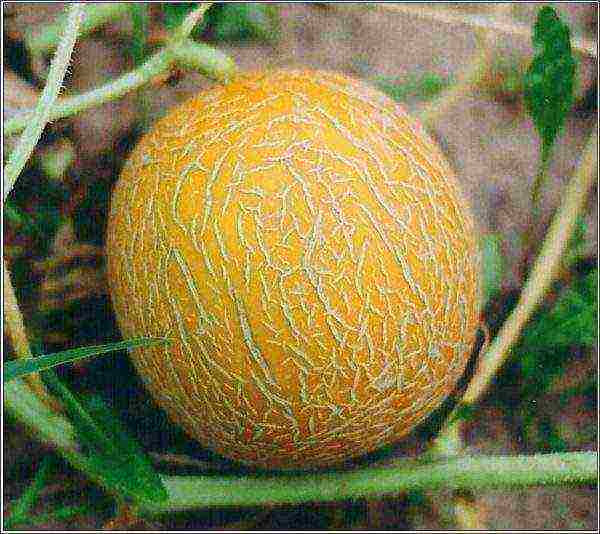 Melon Kolkhoznitsa is a variety that has not lost its popularity over more than 70 years of cultivation, it has been tested by more than one generation of gardeners
Melon Kolkhoznitsa is a variety that has not lost its popularity over more than 70 years of cultivation, it has been tested by more than one generation of gardeners
This type of melon belongs to the mid-season category. From the moment the seeds germinate to the cutting of the first fruits, 77–95 days pass. The specific ripening period is strongly influenced by the weather.
The bushes are not too sprawling, but they cannot be called compact either. The shoots of the collective farmer spread far enough. Stems are thin, slightly rough to the touch. The leaves are medium-sized, heart-shaped, the edges are carved with small notches.
 The plant of the Kolkhoz Woman cannot be called compact, its whips are quite long
The plant of the Kolkhoz Woman cannot be called compact, its whips are quite long
The fruit (pumpkin) is in the form of an almost regular ball or broadly oval. Melon weight is small - 0.7-1.3 kg. We come across "champions" weighing about 2 kg, but rarely. Some even consider this size to be an advantage of the variety. Melon can be eaten at a time, it will not wind up in the refrigerator. If the planting scheme is followed, the total yield is approximately 2.1–2.6 kg / m².
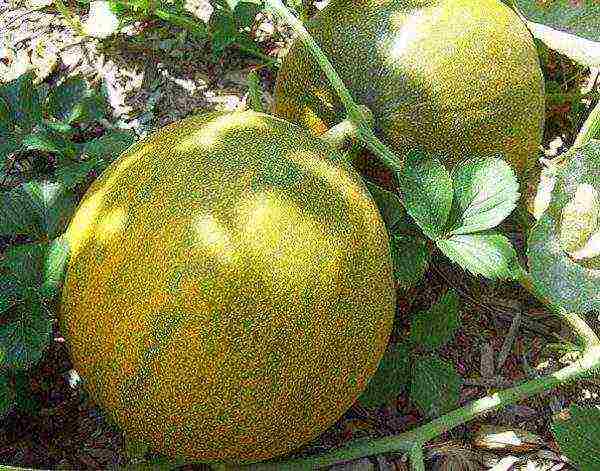 Melons Kolkhoz woman are small, some do not like it, others, on the contrary, consider the size of the fruits to be one of the advantages of the variety
Melons Kolkhoz woman are small, some do not like it, others, on the contrary, consider the size of the fruits to be one of the advantages of the variety
The skin is shiny in the sun, smooth to the touch, of a bright yellow-orange or golden color, in most cases without a pattern. Only sometimes a coarse mesh appears on the side that was facing the sun. The skin is not thick. It is flexible but strong enough. This leads to good portability.But to keep the collective farmer for a long time will not work. You can only slightly extend this period by removing slightly unripe melons.
The pulp is creamy white or butter-colored, dense, with weak fibers, slightly crunchy. There is no need to talk about taste - everyone is familiar with it and almost everyone likes it. Also, the pulp has a characteristic aroma with honey and vanilla notes. Melon The collective farmer is praised for its sweetness and juiciness. The sugar content of the pulp is high - 11–12%.
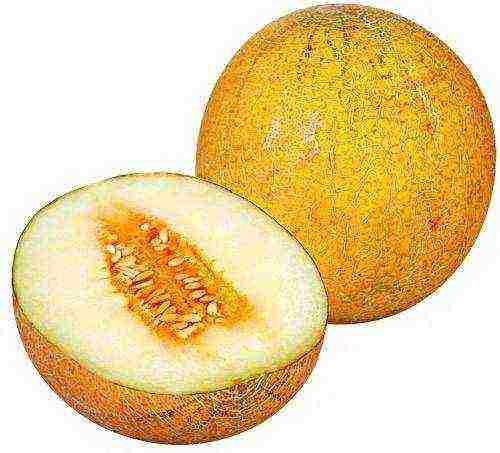 Melon pulp Kolkhoz woman is remarkably tasty and aromatic
Melon pulp Kolkhoz woman is remarkably tasty and aromatic
The variety has an "innate" immunity to all types of bacteriosis, but is susceptible to other diseases. Especially often the collective farmer suffers from downy and true powdery mildew, anthracnose and fusarium.
Most often, this melon is eaten fresh. But the collective farmer is also suitable for household preparations. It is canned in sugar syrup, jams, preserves, marshmallows are made, and even candies, candied fruits and marmalade are made. At the same time, the taste is preserved, only the aroma disappears.
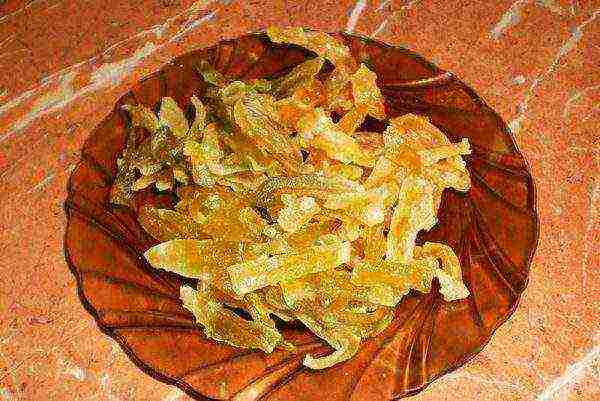 The collective farmer is suitable both for fresh consumption and for all kinds of homemade preparations, desserts and canning
The collective farmer is suitable both for fresh consumption and for all kinds of homemade preparations, desserts and canning
A collective farmer is a variety, not a hybrid; therefore, the seeds can be harvested on their own. But all the same, after a few years, the plants obtained in this way tend to degenerate, varietal characteristics are largely lost. Therefore, the planting material needs to be updated.
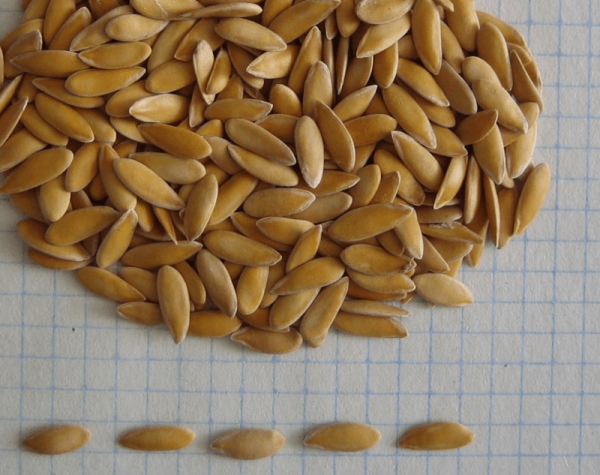 Kolkhoz woman melon seeds, collected on their own, are quite viable
Kolkhoz woman melon seeds, collected on their own, are quite viable
Melon Kolkhoz Woman is not only tasty, but also extremely healthy. The pulp contains a lot of vitamins A, C, E, group B. Of the trace elements, the presence of potassium, magnesium, zinc, copper, manganese, iodine can be noted. Fresh fruits due to their low calorie content (33–35 kcal per 100 g) are a very pleasant addition to any diet. But for those who want to lose weight, it is better to refrain from eating dried melon. The calorie content of such a dessert is almost 10 times higher.
Melon promotes the production of hormones, in particular serotonin. It is also known as the "happiness hormone". Regular consumption of pulp in food helps to get rid of chronic depression, attacks of causeless anxiety, and cope with insomnia.
Fiber promotes the digestion of heavy food, so melon is often served with ham, boiled pork, it is part of many meat salads. This is mainly typical of Mediterranean cuisine. It also helps to cope with the consequences of poisoning, removing toxins, toxins, salts of heavy metals and radionuclides from the body.
 Melon with ham - at first glance, an unexpected combination, but it is very tasty
Melon with ham - at first glance, an unexpected combination, but it is very tasty
The berry is also in demand in cosmetology. Beta-carotene contained in the pulp improves skin color, nourishes and softens it, helps smooth out fine wrinkles. Melon masks help get rid of age spots and freckles. When juice is added to the water to rinse the hair, they acquire a natural shine, the bulbs are strengthened, and dandruff disappears.
Video: health benefits of melon
Planting seeds for seedlings and further care
The kolkhoz woman's melon can be grown from either purchased or self-collected seeds. But in the latter case, they need to be allowed to lie down for 2-3 years. The germination rate of fresh seeds is noticeably lower, and the plants obtained from them form "male" flowers much more than "female" ones. The largest and "heaviest" melon seeds are selected for planting. Pre-planting preparation is required. This helps to increase germination and helps protect future plants from fungal diseases.
The first thing to do is to soak the seeds for at least 10-12 hours in the biostimulant solution. A wide variety of these products are available in specialized stores. The most common of them are Epin, Kornevin, potassium humate, Heteroauxin. Some substances of natural origin have a similar effect - aloe juice, honey, succinic acid, boric acid mixed with zinc sulfate.
 You can soak melon seeds both in plain water and in a biostimulant solution.
You can soak melon seeds both in plain water and in a biostimulant solution.
Then hardening is carried out. During the day, melon seeds are kept in a thermos filled with hot (about 40 ° C) water. Then the same amount - at normal room temperature. The final step is to place the seeds in the refrigerator (not in the freezer) for 18–20 hours.
Fungal diseases are the weak point of the Kolkhoznitsa variety. Therefore, shortly before planting in pots or in a garden bed, seeds are immersed for a quarter of an hour or a little more in biofungicide diluted with water in the proportion specified in the manufacturer's instructions. The most commonly used drugs are Alirin-B, Tiovit-Jet, Strobi, Raek, Topaz. Treated seeds should be rinsed under running cold water and dried until they become free flowing again. You can also use a raspberry-purple solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. But the procedure time increases to one and a half to two hours.
 Potassium permanganate solution is one of the most common disinfectants
Potassium permanganate solution is one of the most common disinfectants
Video: soaking melon seeds before planting
Any transplant, as well as a pick, is perceived by the melon very negatively. This is a serious test, especially for young seedlings, who walk away from it as from a serious illness. Therefore, the seeds are immediately sown in individual peat pots, the volume of which is slightly larger than a glass. They cannot boast of a high percentage of germination, so it is better to insure yourself by placing not one, but 2-3 pieces in each. Then the seedlings are transferred to the garden bed together with the container, which gradually "dissolves" in the soil.
 Planting melon seeds in peat pots avoids replanting and associated stress in the future
Planting melon seeds in peat pots avoids replanting and associated stress in the future
In principle, a collective farmer will arrange a melon with a universal substrate purchased in a store. But the best option for her is a mixture of humus and peat with the addition of a small amount of sand and chalk or activated carbon crushed to a powdery state. The last two components effectively prevent the attacks of pathogenic fungi. Any substrate must be sterilized before use.
 Several melon seeds are planted in each pot.
Several melon seeds are planted in each pot.
Seedlings develop quite quickly, reaching the required height of 15–17 cm in 25–30 days. At this point, 4–5 true leaves have already been formed. Therefore, the seeds are sown no earlier than the 20th of April. Sufficiently developed specimens are planted in a permanent place at the end of May, and possibly at the beginning of June. The specific date is determined based on the climatic conditions of the region. It should be noted that overripe plants adapt to a different habitat much worse and longer. If it is planned to cultivate a collective farmer in greenhouses, all terms are shifted back 15–20 days.
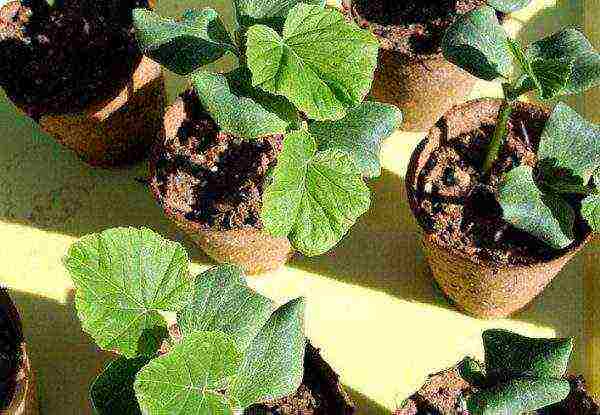 Melon seedlings develop quickly enough, in about a month
Melon seedlings develop quickly enough, in about a month
Even a novice gardener can grow healthy seedlings:
- In containers filled with the prepared substrate, two seeds are sown, dipping them into the soil by 4–5 cm. The substrate is moderately moistened before and after that. The containers are turned into a greenhouse, covered with glass or transparent film. Non-germinated seeds do not need lighting. The temperature in the room where the pots are located is maintained at 25–30 ° С during the day, lowering it to 20–22 ° С at night.
- The seed germination process takes about a week. After that, the seedlings need to be provided with a day of light with a duration of at least 12 hours. Most likely, it will not be possible to do this in a natural way, therefore supplementary lighting is practiced using either conventional LED or fluorescent lamps, or special phytolamps. The most suitable temperature for the formation of healthy seedlings is 25-28 ° C.
- To prevent the development of the "black leg", a little fine sand is added to the bases of the seedlings. The substrate is moistened abundantly, but only when it dries up after the previous watering.The first time the seedlings are watered only after they see the first real unfolded leaf. There is no urgent need to feed developing seedlings. The soil is nutritious enough to provide it with everything it needs until it is transferred to the garden or greenhouse. The exception is plants that do not look very healthy. Their after a couple of weeks after the emergence of shoots with store-bought fertilizer, specially designed for seedlings. It is diluted with water, keeping exactly the proportion recommended by the manufacturer. It should not contain chlorine. The culture reacts unequivocally negatively to this microelement.
- In the phase of the appearance of the second true leaf, a less developed specimen is removed from the pots in which both seeds have germinated. In order not to damage the roots of the remaining seedling, it is not pulled out of the soil, but cut or pinched as close to its surface as possible.
- Melons, on which three leaves have formed, are pinched to stimulate the formation of new lateral shoots by the plant.
- The specimens remaining in the pots definitely need hardening. This activity begins about 7-9 days before the expected transplant. On the first day, they only have one hour in the open air, then this time is gradually increased so that on the last day the seedlings are left to “spend the night” in the open air.
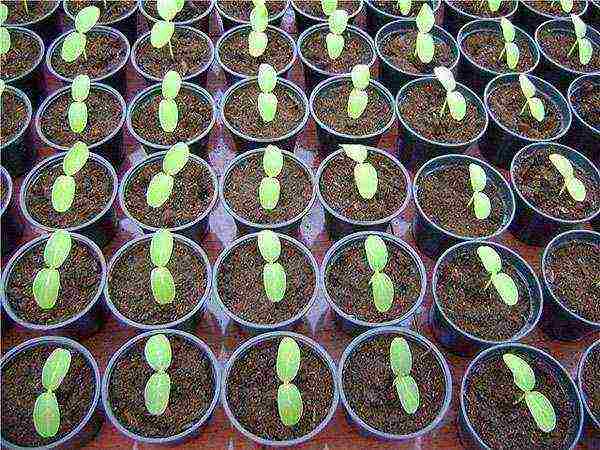 Melon seedlings emerge quickly and in large quantities.
Melon seedlings emerge quickly and in large quantities.
Video: how to grow and care for healthy melon seedlings
Even a seasoned melon is transferred to a prepared garden bed only after the threat of spring frosts is likely to pass. Even a cold-resistant Kolkhoz woman will not survive freezing temperatures. By this time, the substrate should warm up to 12-15 ° C at a depth of 10 cm.
 Melon seedlings are planted so that the base of the stem rises slightly above the soil surface
Melon seedlings are planted so that the base of the stem rises slightly above the soil surface
An interval of 80–90 cm is maintained between neighboring plants in the garden bed, the row spacing is 120–140 cm. The holes are plentifully spilled with heated soft water. A handful of humus and a teaspoon of simple superphosphate are poured onto the bottom. The seedlings are placed in the holes in such a way that the earthen lump rises slightly (no more than 5 cm) above the ground level. It is not necessary to compact the soil strongly. Then, for a couple of weeks, it is advisable to protect the seedlings from the effects of the bright sun by placing arcs over the bed and pulling any white covering material over them. You can also close them with thick paper caps or coniferous branches.
 Soon after planting, the melon is pinched again, stimulating it to further branching.
Soon after planting, the melon is pinched again, stimulating it to further branching.
Correct melon bed and planting seeds directly into the soil
Melon, in comparison with cucumbers and zucchini, is much more demanding on the quality of the soil. This also applies to the not particularly fastidious Kolkhoz Woman. Therefore, the preparation of the garden in the fall should be given the main attention.
The substrate needs to be light. Moisture does not stagnate in such soil. Gray soil or loam works well. To give the necessary "fluffiness" it is dug up twice - in autumn and spring, about a couple of weeks before planting. In a heavy substrate, you will have to add sand - about 5 l / m².
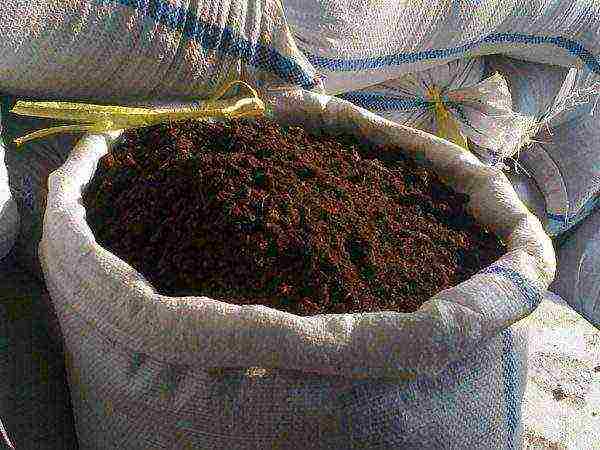 The introduction of humus allows you to provide the soil fertility necessary for the melon
The introduction of humus allows you to provide the soil fertility necessary for the melon
Another requirement of the collective farmer to the soil is nutritional value. Therefore, in the process of digging, humus or rotted compost (but not fresh cow dung) is necessarily introduced. The latter has a negative effect on the immunity of the culture, taste and appearance of the fruit. One running meter will require about 10 liters. If the acid-base balance differs from neutral, it is brought back to normal. Dolomite flour, wood ash or chicken egg shells crushed to a powdery state are added to the acidic substrate. In alkaline - peat chips or fresh sawdust (best of all from coniferous trees).
 Dolomite flour is a natural soil deoxidizer, when the dosage is observed, it has no side effects
Dolomite flour is a natural soil deoxidizer, when the dosage is observed, it has no side effects
Mineral fertilizers are applied twice. During the digging of the selected area in the fall - phosphorus (35–45 g / m²) and potash (20–30 g / m²), in the spring - nitrogen (10–15 g / m²).
The culture tolerates a slightly salty substrate, as well as an excessively dry one. But groundwater approaching the surface closer than 1.5 m is a serious reason to look for another area for a garden bed. Hills are better for melons than lowlands. The culture is not too afraid of winds, but damp air and moisture stagnating in the soil for a long time are destructive for it.
 Melons only ripen if they get enough heat and sunshine.
Melons only ripen if they get enough heat and sunshine.
For each next season, a new place is selected for the cultivation of melons. It should be open, well warmed up by the sun. Be sure to take into account what grew in the garden before that. Winter cereals, any legumes, all varieties of cabbage, onions, garlic, siderates do not harm the plantings. The collective farmer grows poorly after beets (ordinary and leafy), carrots and Solanaceae (especially tomatoes). The culture can be returned to the old garden bed only after 2-3 years, and if the plants have suffered from any disease, the "quarantine" is extended to 5 years. It is planted as far as possible from cucumbers, zucchini, and other "relatives" from the Pumpkin family. Pollination is possible with completely unpredictable results. Also, the "migration" of pests is very likely.
 Tomatoes, like other Solanaceae, are undesirable precursors for melons, crops suffer from the same diseases
Tomatoes, like other Solanaceae, are undesirable precursors for melons, crops suffer from the same diseases
Planting melon seeds A collective farmer immediately on the garden bed, without shelter, is a method available only to residents of the Black Sea region and the North Caucasus on the territory of Russia. In all other cases, the beds will have to be tightened with covering material on arcs, removing it in the heat and closing the planting again when it becomes cool. 10 ° С for a kolkhoz woman melon is already a critical minimum, the vegetation slows down sharply, and in the Urals and Siberia such temperatures in summer are by no means uncommon. Accordingly, the gardener will have to permanently live on the site, which is not practiced by everyone.
The procedure is planned for the second decade of May or early June. The above seed treatment procedure is mandatory. The recommended landing pattern is also observed. Seeds in prepared and moistened holes are sown in pairs, sprinkled on top with crushed peat or humus mixed with ash. The optimum layer thickness is 4–5 cm. Until the seeds of the collective farmer sprout, the garden bed is kept under a black plastic wrap. Then it is turned into a "greenhouse" by pulling the covering material over the arcs. Only when the seedlings reach the size of seedlings suitable for planting in the ground, it can be removed for a day. After another 20-25 days, the "greenhouse" is removed completely. Such a shelter is also useful for protecting the substrate from waterlogging. Therefore, those who have a long "experience" of growing melons are advised to restore it, in the case when the summer is rainy and cool.
 Covering material protects melons from cold, heat and waterlogging
Covering material protects melons from cold, heat and waterlogging
Caring for seedlings in a garden bed is almost in every way similar to what is required for a collective farmer's seedlings on a windowsill. Abundant watering of the drying substrate is required. For the first time, melons are fed no earlier than 1.5 months after seed germination. It is imperative to devote time and effort to preventing pest attacks. They can do much more harm to young seedlings than to adult plants.
 When planting melon seeds in the ground, the required interval between them must also be maintained.
When planting melon seeds in the ground, the required interval between them must also be maintained.
Tips for growing melon Collective farmer in the open field and in the greenhouse
The Kolkhoz woman compares favorably with her “relatives” by being less capricious in her care, but this does not mean that one can hope to get a good harvest without having an idea of the nuances of agricultural technology.
How long between waterings is affected by the age of the plant and the weather.For one and a half to two weeks after transferring the seedlings to a permanent place, the soil is kept in a moderately moist state all the time, watering the collective farmer every 2-3 days. Then the intervals between procedures are increased to 6-7 days (in the absence of precipitation). But in the heat, daily moisture of the substrate may also be required. 14-16 days before the planned cutting of fruits, watering is stopped altogether so that the melon gains maximum sweetness and does not crack.
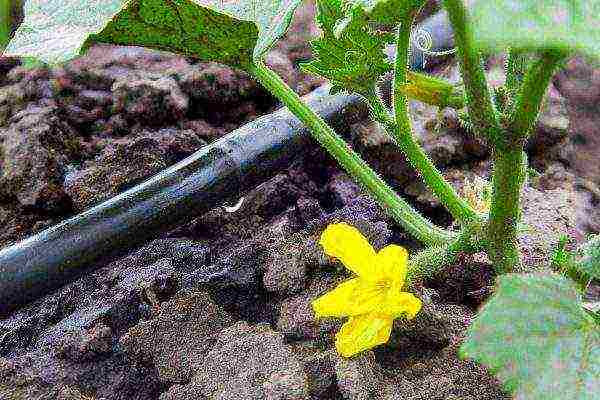 Drip irrigation is the most suitable method not only for melons, but also for its "relatives" - cucumbers and zucchini
Drip irrigation is the most suitable method not only for melons, but also for its "relatives" - cucumbers and zucchini
The rate of water consumption for specimens recently transferred to the garden is 1.5–2 liters, for adult melons - 3.5–4 liters. It is best for the plant if the procedure is carried out early in the morning. Each time after it, the soil is carefully loosened. Water is poured into row-spacing grooves or annular grooves around the base of the stems. Drip irrigation is ideal for crops, but organizing everything you need is not always purely technical. But sprinkling and watering from a watering can, a hose for a collective farmer is not recommended very strongly. Drops falling on leaves and shoots provoke the development of rot, the fall of flowers and fruit ovaries, especially if cold water is used. Pouring it under the roots is also not worth it - the substrate is quickly washed off from them, they become bare and dry out.
 Drops falling on leaves, shoots, flowers and fruit ovaries can provoke the development of rot
Drops falling on leaves, shoots, flowers and fruit ovaries can provoke the development of rot
For harmonious development, the melon regularly requires new portions of macronutrients, therefore, it is fed every two weeks. For the first time, the procedure is carried out after a couple of weeks (or a little more) from the moment the seedlings are transplanted into the ground. Until fruit ovaries are formed, the culture needs nitrogen. The most common fertilizers containing this macronutrient are carbamide, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate. They are brought in dry, scattered over the bed after loosening, or diluted with water. A high concentration of the drug in the solution will not benefit the plants, 10–15 g per 10 liters is enough.
 Urea, like other nitrogen-containing fertilizers, stimulates melons to actively build up green mass
Urea, like other nitrogen-containing fertilizers, stimulates melons to actively build up green mass
You can prepare top dressing yourself. Fresh cow dung, chicken droppings, nettle greens, dandelion leaves are used as raw materials. The container is filled with about a third of it and warm water is added. Then the container is tightly closed and left in the sun for 3-4 days. The fact that the fertilizer is ready can be judged by the appearance of a characteristic "aroma". Before using it, it must be filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. The concentration of droppings in the solution is reduced by another 1.5 times.
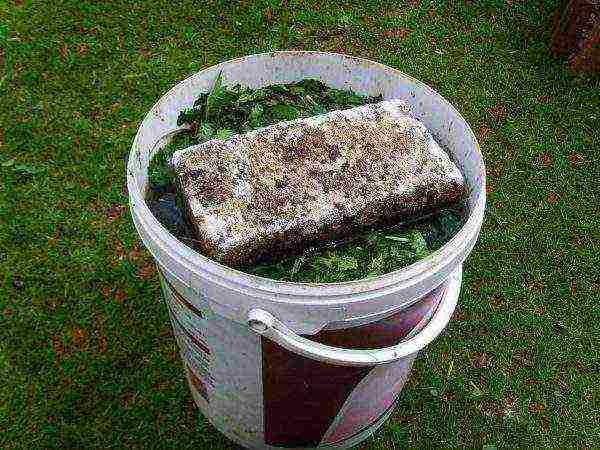 Nettle infusion is an absolutely natural and completely free fertilizer
Nettle infusion is an absolutely natural and completely free fertilizer
Ripening fruits mainly need phosphorus and potassium. To feed the melons during this period, they switch to store-bought fertilizers for melons (Gumi-Omi, Clean sheet, Master, Bona Forte). Gardeners who dislike chemicals replace them with wood ash. You can simply sprinkle it on the bases of the stems or prepare an infusion by pouring 0.5 liters of raw materials with three liters of boiling water.
 Wood ash - a natural source of potassium and phosphorus
Wood ash - a natural source of potassium and phosphorus
Video: Melon Care Tips
Formation for a collective farmer is a mandatory procedure. The experience of gardeners shows that exclusively "male" flowers are formed on the main shoot. "Female", and, accordingly, the fruits are formed only on the side lashes. To stimulate the plant to branch, pinch the melon at the stage of growing seedlings. But you shouldn't overload it either. In a southern climate suitable for culture, you can leave 3-4 shoots, in the Urals, Siberia, and other regions with similar weather conditions - no more than two.
 As a rule, there are much more “male” flowers on melon strings than “female” ones, especially if the seeds are fresh
As a rule, there are much more “male” flowers on melon strings than “female” ones, especially if the seeds are fresh
On powerful bushes, collective farmers leave 5-6 fruits, on underdeveloped - a maximum of 2-3 pieces.They should be distributed more or less evenly. The minimum interval between them is about 30 cm. They are also guided by how warm and sunny it is outside. If the weather is clearly unsuitable for the melon, the load on the plants is reduced.
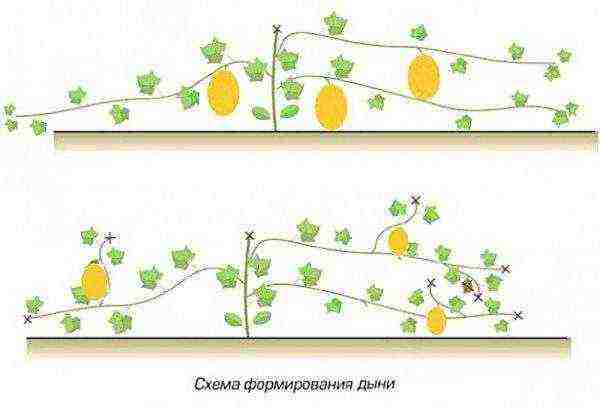 The amount of fruit left on the melon strings depends on several factors.
The amount of fruit left on the melon strings depends on several factors.
Then you need to wait until the fruit ovaries reach the size of a chicken egg. Selected shoots are pinched after five leaves from the last fruit. Also on them you need to remove all the side "stepsons". Foil, glass, plywood, roofing material are placed under the ripening fruits to protect them from contact with the ground. This can provoke the development of rot. For the same purpose, the remains of flower petals are removed from the fruit ovaries.
 It is impossible for the ripening melons to lie directly on the ground, this often causes the development of rot
It is impossible for the ripening melons to lie directly on the ground, this often causes the development of rot
Video: Melon Formation
Determining if a melon is ripe is not difficult. It begins to spread a characteristic aroma, the skin acquires a typical shade for the variety, the greenish undertone disappears, the stalk dries up. If you knock on a melon, a dull sound is heard. The collective farmer is cut in the morning or in the evening, in dry weather, together with a part of the stalk 4–5 cm long. At the same time, you cannot pull the whip or twist it.
 Ripe melon of the Kolkhoznitsa variety in any case is not stored for a long time, but for unripe fruits this period is slightly longer
Ripe melon of the Kolkhoznitsa variety in any case is not stored for a long time, but for unripe fruits this period is slightly longer
The fruits are handled very carefully. The peel of the Kolkhoz Woman is quite dense, but even minor damage to it leads to decay of the melons. The process goes very quickly, literally in 3-4 days. Store the harvested crop in the refrigerator away from apples and bananas, which actively emit ethylene. It is not recommended to delay harvesting. An overripe Kolkhoz woman acquires an unpleasant bitter aftertaste.
Melon has the property of ripening after being cut from the plant. This allows you to slightly extend the shelf life. Such fruits are kept in a dark place with good ventilation at a temperature of 8-10 ° C and an air humidity of 60-65%.
Growing a collective farmer in a greenhouse allows you to get a crop 2–2.5 weeks earlier than in the open field. In autumn, the substrate must be cleaned of plant debris and sterilized by spilling it with boiling water or a dark raspberry solution of potassium permanganate. Be sure to add a layer of fresh humus with a thickness of at least 15–20 cm. Glasses and other surfaces are wiped with a solution of slaked lime. For disinfection, you can also burn a small piece of a sulfur checker inside.
A significant difference from cultivation in the open field is that the gardener will have to take care of pollination on his own. To do this, you need to pick the "male" flower, cut off the petals and manually, with a soft brush or cotton pad, transfer the pollen to the "female" specimens (they can be easily distinguished by the presence of a fruit ovary at the base).
The space in the greenhouse is limited, so the melons are grown only on the trellis. This allows you to slightly reduce the spacing between plants (up to 70 cm). The emerging shoots are directed upward and, as they grow, are tied to horizontally stretched wires. The collective farmer is not able to independently "crawl" on the support, clinging to it.
 The greenhouse for growing melons must be high, at least 2 m
The greenhouse for growing melons must be high, at least 2 m
When the fruit ovaries have reached the size of a tennis ball, each is placed in a net. She, in turn, is hooked onto a hook attached to the same support. Melons grown in a greenhouse are much more presentable than those grown in the open field. They are symmetrical, evenly colored, with a smooth skin without "bumps".
 The shoots of the Kolkhoz woman are rather thin, they can break off by the weight of the fruit
The shoots of the Kolkhoz woman are rather thin, they can break off by the weight of the fruit
The greenhouse must be regularly ventilated. High humidity and stale air are ideal conditions for the life of many pests. They are also suitable for pathogenic fungi.
Melon homeland is Central Asia. Therefore, she is tolerant of the heat.But if the temperature rises above 35 ° C, the process of plant development slows down, it "hibernates". To avoid this, in hot sunny weather, the paths in the greenhouse are poured with cold water, and the glass from the inside is sprayed with slaked lime diluted with water.
Video: caring for greenhouse melons
A significant drawback of the variety is its tendency to be affected by pathogenic fungi. Proper care, crop rotation and sufficient spacing between plants are good prevention, but there are other effective measures. The most dangerous for the Kolkhoz woman:
- Powdery mildew. Leaves and shoots are covered with a thin layer of bloom, reminiscent of spilled flour. Gradually, it thickens and darkens, changing color to gray-brown. Affected tissues dry up and die off.
- Peronosporiosis (downy mildew). On the front side of the sheet, pale yellow spots of irregular shape are blurred, the wrong side is covered with a continuous layer of ash-purple bloom. Affected tissues rot, turn black, die off.
- Fusarium (root rot). The bases of the stems are softened, covered with "weeping" brownish spots. An unpleasant putrid smell comes from the soil.
- Anthracnose. The leaves are covered with yellowish-brown spots, small sunken "ulcers" of beige or pinkish color are formed on the shoots and fruits. Affected tissues rot and die off.
Photo Gallery: Symptoms of Diseases Typical for Melon Kolkhoz Woman
It is much easier to prevent the development of the disease than to deal with the negative consequences later. For prophylaxis in the process of loosening, the substrate in the garden bed is sprinkled with colloidal sulfur, the plants themselves are powdered with crushed chalk or wood ash. Several crystals of potassium permanganate are periodically added to the water for irrigation, giving it a pinkish tint. Onions and garlic are planted along the perimeter and in the aisles. These plants produce phytoncides that destroy disease-causing fungi.
 It is useful to surround a garden with melons around the perimeter with onions or garlic, this is an effective prevention of fungal diseases
It is useful to surround a garden with melons around the perimeter with onions or garlic, this is an effective prevention of fungal diseases
The plantings should be inspected regularly for suspicious symptoms. In the early stages of development, folk remedies are quite enough for treatment. The most common of them are laundry soap or green potash soap, soda ash or baking soda diluted with water, and mustard powder infusion. Also diluted 1:10 kefir or milk whey with the addition of iodine (drop per liter).
If time is lost or the expected effect is not there, they resort to “heavy artillery” - fungicides. The causative agents of diseases do not tolerate copper compounds. But it should be remembered that they cannot be used for processing flowering plants and if less than a month is left before harvest.
Preference is given to drugs of biological origin, they least of all harm the environment. But there are also reliable, proven by many generations of gardeners means - Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate. As a rule, 3-4 treatments with an interval of 4-6 days are sufficient. But in the later stages of the development of the disease, success is not guaranteed. Fusarium is especially dangerous in this sense. For a long time, the fungus develops exclusively on the roots, without manifesting itself in the aerial part of the plant.
 Bordeaux liquid is a very common fungicide that is easy to prepare yourself
Bordeaux liquid is a very common fungicide that is easy to prepare yourself
Strongly damaged specimens that can no longer be saved should not be regretted. This is the source of the spread of the infection. Therefore, they are immediately removed from the garden and burned. The substrate in this place is disinfected by spilling with a saturated purple solution of potassium permanganate or 5% copper sulfate.
Melons in Siberia
It is quite possible to grow a collective farmer's melon in Siberia, even in the open field. The variety is quite suitable for this due to its frost resistance and short growing season.
A good option for this region is the so-called warm bed. In the chosen place, a layer of soil 10–12 cm thick is removed and a layer of rotted cow dung 4–5 cm thick is placed on the bottom. Then the resulting hole is covered with fallen leaves, small twigs, sawdust, and other plant debris. From above, all this is spilled with a solution of nitrogen fertilizer (20–25 g per 10 l) and a layer of fertile soil 20–25 cm thick is poured.
 A warm bed in spring warms up faster than usual
A warm bed in spring warms up faster than usual
Return frosts in Siberia are not uncommon not only in spring, but also in summer. If a sharp cold snap is expected, the seedlings are protected from negative consequences by making fires around the perimeter of the garden. Another way is to sprinkle the melons with Epin diluted with cold water (5 liter ampoule). The effect of this treatment lasts 7-8 days.
 Epin Treatment Helps Protect Melons from Cold Temperatures
Epin Treatment Helps Protect Melons from Cold Temperatures
Video: growing melons and gourds in Siberia
Video: growing melons and gourds in Siberia
Gardeners reviews
Growing melons in your garden is difficult enough. But there are also varieties that are quite suitable for not too experienced gardeners, for example, the Kolkhoz Woman, who has many indisputable advantages, thanks to which she has withstood constant competition from new breeding products for more than 70 years. Caring for a plant is not too difficult, although, of course, you need to familiarize yourself with the nuances of agricultural technology in advance. The collective farmer will thank the gardener for the efforts spent with a harvest of delicious fruits.
27 years old, higher education in law, broad outlook and interest in a variety of topics. Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Melon Kolkhoznitsa is the most popular variety; it is known to gardeners in the Astrakhan Region, the North Caucasus, Western and Eastern Siberia, and the Far East. In each region, the collective farmer receives only positive feedback. The fruits grow small, but very sweet and fragrant. The cultivation technique is understandable even for beginners.
The history of the Kolkhoznitsa melon variety
The variety has been listed in the State Register of Breeding Achievements since the pre-war 1943. But he appeared even earlier at the Biryuchekutskaya selection experimental station, located in Novocherkassk, Rostov region. It was this organization that in 1939 applied for the inclusion of the Collective Farm Woman in the register. The variety is approved for cultivation in all regions of Russia, except for the North and North-West.

The collective farmer is a commercial variety, among others it is clearly distinguished by its spherical shape, smooth bark and compact size
For eight decades, this melon has been at the peak of its popularity. It is grown in private gardens and commercially. Supermarkets and hypermarkets in many regions sell only two varieties of melons during the height of the seasons. One of them is a collective farmer. The large-fruited torpedo competes with it, and more often complements it. The Kolkhoz woman and summer residents fell in love with her for her ability to present crops even in a cool or short summer. Her fruit is not large, so the growing season, from germination to harvest, is short. At the same time, the taste is real, melon, with a characteristic aroma and a high sugar content - 11–12%.
Description of the variety
This is a mid-season variety. From the moment the first sprouts hatch, 77–95 days pass until the first sweet melons are harvested. The weight of ripe fruits is 0.7–1.3 kg. They are spherical, the average diameter is 20 cm. The variety can be called portioned, that is, one berry can be eaten at a time, it is not necessary to store it cut in the refrigerator.
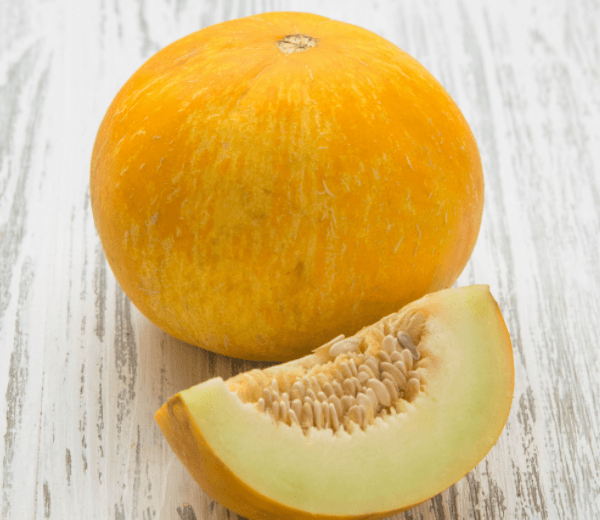

The pulp of a ripe melon The collective farmer is white, the bark is of medium thickness without a pattern, there are a lot of seeds
The bark is bright yellow, orange, sometimes with a green tint. The surface is usually smooth, in places it can be covered with a coarse mesh. The skin is flexible, but firm, of medium thickness, which contributes to good transportability of the fruit. This is the second factor after the excellent taste, thanks to which the variety became commercial.
The pulp is thin, which is logical for a medium-sized fruit, white, moderately crispy, juicy, fibrous and very sweet. But in cool summer or when grown in the shade, it accumulates less sugar. There are many seeds inside. This is not a hybrid. You don't need to buy seeds every year. If you raised a Kolkhoz woman and you liked her, then for sowing next year you can collect your seeds from the largest and most delicious melons.
Video: how the collective farmer, Altai and Pineapple melons grow in the greenhouse
The collective farmer's bush looks like a cucumber bush. Only the leaves are lighter, have a rounded shape, without chipping. It is affected by the same diseases. Most of all, this variety is afraid of powdery mildew and anthracnose. But since the Kolkhoz woman remains a favorite for so many years, it means that melon growers have learned to cope with this problem successfully.
Advantages and disadvantages of a melon Kolkhoz woman - table
Landing features
The very first thing to do when growing a Kolkhoz woman is to decide on the timing of sowing. They differ in different regions, in addition, they are planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse 2-3 weeks earlier than in the ground. Wherever you planted: in open or closed ground, it should not be colder there at night + 10 ... +15 ⁰C. This is the critical temperature at which the melons stop developing, and die with a prolonged cold snap.

Melon seeds Kolkhoz woman can be sown directly into the ground or for seedlings
To harvest the collective farmer's harvest in August, sowing should be done in the first half of May at the latest. Based on the weather conditions in your region, orient yourself where at this time you can sow the melon: in a greenhouse, greenhouse, open ground or at home for seedlings. The seedling period lasts 30–35 days. When sowing a house in April, you will bring the harvest closer by a month.
In an effort to start working with the land as soon as possible, to get an early harvest, you do not need to sow the melon before April. In February - March, there is still not enough light and heat on the windows. Need a backlight. In addition, overgrown seedlings of melons with a long stem and many leaves will not take root well and hurt for a long time, will lag behind those plants that are sown on time and planted at the optimum age for seedlings.
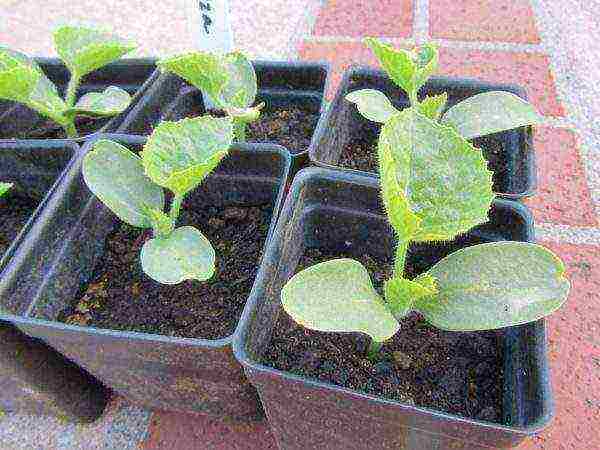

If your area does not have 90 sunny days, grow the Kolkhoz Woman through seedlings
Since the variety is prone to fungal diseases, be sure to disinfect the seeds in one of the following ways:
- Soak for 15–20 minutes in a dark purple opaque solution of potassium permanganate. Then rinse with clean water.
- Dip in hot water (+50 ⁰C) and hold for 5-10 minutes.
Sowing and growing seedlings
The classic way of growing seedlings begins with buying cups or cassettes, as well as suitable soil (for melons or pumpkin seeds). You can take soil from your garden and mix it in equal proportions with humus and peat. If the mixture is not loose enough (it clumps wet), add perlite, vermiculite or coarse sand. Be sure to warm up the soil in any way to +100 ⁰C (the ground should soar) and give it a week to recover. Pour a glass of wood ash into a bucket of this mixture and stir. This completes the preparation of your own soil.
Video: recipes for soil mixtures for workaholics
Melon does not tolerate transplanting and picking, each such procedure pushes the harvest date by a week. Therefore, sow seeds in individual cups: dry - 2-3 seeds in each, germinated - one at a time. The volume of the cups depends on the period during which you plan to keep the melons on the windowsill: if it is 2-3 weeks, then a volume of 150-200 ml is enough (one-time cup). If you sow a collective farmer a month before planting, then take pots with a volume of 300-500 ml.

It is better to break peat and paper cups during planting and remove, with insufficient watering they can turn into an impenetrable crust for the roots
Optimum temperature for emergence and further growth: + 25… +30 ⁰C. Expose melon seedlings to the lightest window. If 2-3 shoots have appeared in the glass, leave only one of the strongest ones, do not pull the rest by the root, but pinch them above the ground. Water generously as the topsoil dries up to allow water to flow from the drain holes. There is no need to feed, since the soil is fertile, the seedling period is short, there is enough nutrition for the melons.
Video: advice from Kherson, professional sowing of melon seeds
Today, the traditional method of growing seedlings is being replaced by a more progressive one, which does not require pots or even land:
- Spread a standard sized cellophane bag on the table, fold it in half to halve the width. Or take a strip of film 10-15 cm wide, and the length is equal to twice the number of seeds.
- Place 2–3 layers of toilet paper on the film and moisten it from a room sprayer.
- Step 2–3 cm from the top edge, spread the seeds 1–2 cm apart.
- Roll into a tight roll, secure with an elastic band for money or tape and place in a glass of water. The water should only cover the bottom edge of the toilet paper.
Video: seedlings of melons, watermelons and cucumbers without soil (in rolls)
In such a roll-up, you can sow 10–20 seeds of a collective farmer. And all this in one glass. Seedlings appear in 3-4 days, can grow without soil for about two weeks, before the first true leaf appears. Then you need to land it in a permanent place or unfold the roll, sprinkle the earth with a layer of 1–2 cm and roll it up again. With this method, the roots are not injured, but are always available. During transplantation to a permanent place, each plant is easily separated along with a piece of toilet paper, it will quickly rot in the ground.

Roll-grown melon seedlings are easily detached with a piece of damp paper, while the roots are not injured.
With any method of growing, accustom the seedlings to open air a week before planting. Take it outside, gradually increasing sun exposure from 1 hour to a full day.
Sowing immediately to a permanent place, soil preparation, planting scheme
Residents of the south, as well as owners of greenhouses and those who have the opportunity to approach their plantings at least twice a day in order to shelter them in the evening and remove a temporary shelter in the morning, can grow a Kolkhoz Woman in a reckless way. It is recommended to prepare the soil for melon in the fall, since phosphorus fertilizers need to be applied, and they dissolve for a very long time. If you add superphosphate in the spring, then it will go into an easily digestible form at the time of melons ripening, although it is needed throughout the growing season.

Superphosphate granules can be used to fertilize perennial crops throughout the warm season, but under melons that grow for only one season, it is brought in in advance, in the fall
Fertilizers for planting melons on 1 m² of the garden:
- In the fall - a tablespoon of superphosphate and potassium fertilizer, a bucket of humus.
- In the spring - 0.5 liters of wood ash, a bucket of humus or compost. Organic matter can be replaced with 1 tbsp. l. ammonium nitrate or urea.
For looseness, it is not necessary to pour sand; you can use small pieces of bark, thin twigs, leaves, hay dust and other plant residues, which will also enrich the soil by rotting.

The soil on the melon should be loose, allow air and moisture to pass to the roots
In regions of risky agriculture with cool and rainy summers, as well as in areas with a close occurrence of groundwater, it is customary to make high beds. Under a layer of earth of 20 cm, "pillows" of about the same thickness are laid from natural materials: grass, branches, household waste, sawdust, etc. In this case, the melons will be raised above the level of the garden, they will be better warmed up by the sun, and dry faster after rains. Many grow melons in barrels and boxes freed up after growing cabbage seedlings.
Video: device of a warm bed
Sowing technology, as in the classic cultivation of seedlings: seed preparation, seeding depth, temperature conditions are the same. Choose the lightest place on the site. The scheme of planting seeds and seedlings of a collective farmer in the open field: 140x100 cm, in a greenhouse with a garter to the trellises - 70x70 cm.
Melon care, bush formation
If grown by seedlings, then shade the first days after planting young melons. In cool summer conditions, do not rush to remove temporary shelters. Leave them on until the temperature stops dropping below +15 ⁰C at night. At the end of summer - in autumn, cover the garden again to protect it from cold and dew and allow the fruits to ripen.

A warm bed imitates a south-facing slope; stagnation of water is excluded, the top is covered with agrofibre, dark water bottles serve as heat accumulators
Do not remove the arcs even at the height of summer, you can stretch the film on them if prolonged rains come. However, in this case, do not close the bed tightly, leave the ends open for ventilation. All these measures are aimed at providing the Kolkhoz woman with more heat, fresh air and protection from dampness, in which pathogenic fungi develop well.
Video: growing melons in the open field
The irrigation regime depends on the age of the collective farmer and the weather. Water small plants in dry weather often to keep the ground always moist, adults - once a week, if there was no rain. Stop watering 2 weeks before harvest. Melons need to be fed every 10-14 days. Give the first top dressing two weeks after germination or transplanting.
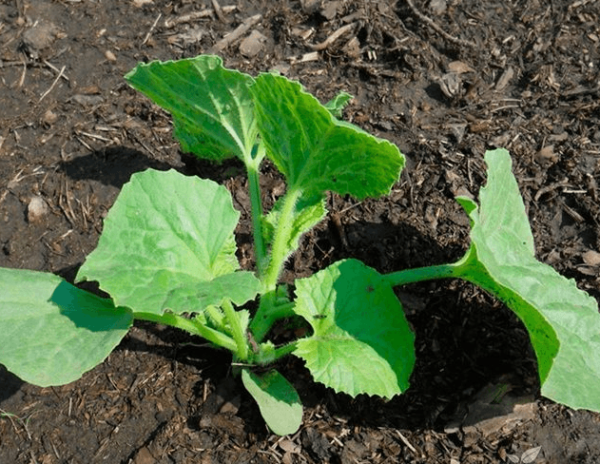

Start feeding when the bushes grow up, at least 3-4 leaves will appear on them
Until the ovaries begin to grow, feed with bird droppings (1:20), mullein (1:10), infusion of weeds (1: 5) or other nitrogen-containing fertilizers, including mineral fertilizers. In the growth phase of fruits, you can do with ash feeding (powder the earth with a thin layer, loosen and water), ready-made complex mixtures for melons are also suitable: Pure leaf, Gumi-Omi, etc.
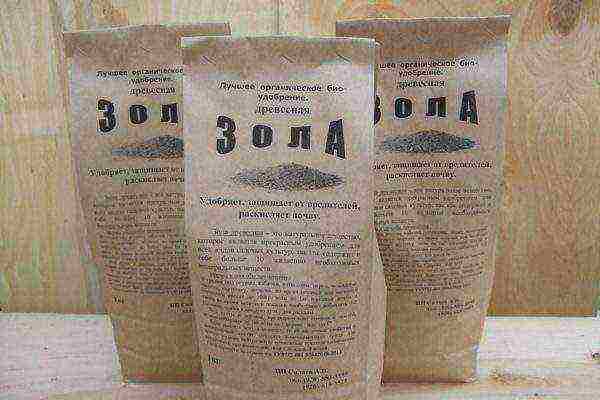

Melon is very fond of wood ash, this fertilizer contains all the necessary micro and macro elements, except for nitrogen
Melons need to be formed, otherwise you will not wait for the harvest. On the main stem, only a barren flower is formed - male flowers, and the ovaries grow on lateral shoots. Their active growth must be called. To do this, pinch the main lash over 4-5 sheets. Shoots will grow from the sinuses of the remaining ones. In the middle lane and Siberia, it is better to leave only two of the strongest, in the south a bush can consist of 3-4 lashes.
Video: forming a melon bush
Next, watch the formation and growth of the ovaries, do not rush to do any additional pinching until the phase until they grow into a goose egg. It happens that having reached this size, the fruits turn yellow and fall off. How many melons to leave on the bush, decide, focusing on the strength of the bush and the weather. If the bush is powerful, the summer is hot, then you can leave 5-6, on a weak bush in rainy weather - 2-3. Once you decide on the quantity and make sure that the ovaries grow well, pinch all the shoots above the fruits, counting 5 sheets from them. Remove stepchildren without ovaries entirely.

Do not rush to pinch and remove the side stepsons, first make sure that the melons you have chosen increase in size every day and are not going to turn yellow and fall off
In a greenhouse, all lashes should be tied to a trellis. Open doors and windows wide during flowering to let bees in, or manually pollinate female flowers. Put nets on already growing melons and tie them too. In the open field, to protect the fruit from rotting, place a plank, a piece of plastic, old ceramic tiles, etc. under each.

The collective farmer has thin lashes, they may not hold their fruits in weight, so also tie the melons to the trellises
To prevent powdery mildew and other fungal diseases, before flowering and at the beginning of the growth of the ovaries, spray with fungicides: HOM (40 g per 10 L), Skor (2 ml per 10 L), etc. Chemistry can be processed no later than 3-4 weeks before ripening of fruits.
Harvesting and storage
Unlike watermelons, melons clearly signal that it is time to remove them from the bush. The skin turns yellow, the berries begin to exude a characteristic sweet aroma. A collective farmer can ripen at home on a window, under a bed or in another place, as long as it is dry there. Cut the fruits with a "tail", that is, leave the stalk 3-5 cm long.
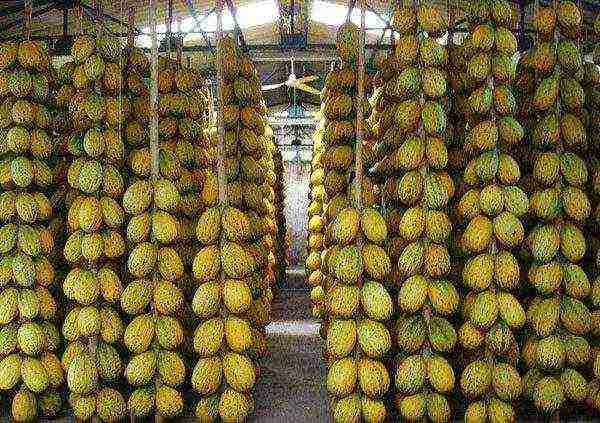

Melons are stored hanging in a cool room, a large number are collected in braids or garlands
Handle melons carefully, you cannot throw them, drop them, put them on top of each other in several layers. Any damage to the crust: dent, bruise, crack, will lead to rotting of the fruit. Absolutely whole melons can be stored in the basement until the New Year, hanging each separately by the tail or in a net. Storage temperature: + 1… +3 ⁰C, humidity - 70–80%.
Video: tasting eight varieties of melons, including the Kolkhoz Woman
The main purpose of the collective farmer, like all melons, is for table, that is, fresh consumption. However, if you have a rich harvest, there is no storage room, or there are many damaged fruits, then treat melons as you would regular berries. You can make jams, compotes, jams, jam, candied fruits from their slices. Melon is pickled, dried, frozen.
In addition to a large amount of vitamins and minerals, this berry contains folic acid, which improves blood formation and reduces the proportion of bad cholesterol. Lovers of melons are less sick with colds, they have stronger immunity. In addition, this berry is a good anti-stress agent, reduces anxiety, and improves mood. Of course, melon has a diuretic effect and helps with kidney disease.

Melon marmalade is a beautiful and tasty delicacy
Melon reviews Kolkhoznitsa
When growing a collective farmer, four agricultural practices are important. The first is to sow in time, so that the harvest can ripen before the onset of cold weather. The second is to protect against diseases by carrying out preventive spraying. The third is to correctly form a bush, to ration the harvest. Fourth - in the conditions of a short and cool summer, provide warmth using a covering material and high beds.
My hobbies: plant growing, healthy lifestyle, Tibetan medicine, home winemaking. Merchandise expert by education. Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)


