Content
- 1 Biological features
- 2 Aboveground part
- 3 Root system
- 4 Aboveground part of the plant: potato leaf and flower
- 5 Tuber formation mechanism
- 6 Tuber structure
- 7 Does the structure of the tuber depend on the variety of potatoes
- 8 Potato tuber: chemical composition
- 9 Reproduction
- 10 How did potatoes conquer Europe and Russia?
- 11 Plant structure
- 12 Root system
- 13 Tuber
- 14 Stem
- 15 Optimum planting depth for potatoes
- 16 How did potatoes conquer Europe and Russia?
- 17 Plant structure
- 18 Root system
- 19 Tuber
- 20 Stem
- 21 Leaves
- 22 Flower
- 23 Site preparation for landing
- 24 Prevention of diseases and pests
- 25 Planting potatoes
- 26 root of the word potato
- 27 What type of root system does corn, potatoes, cabbage, tomato, buttercup, strawberry and birch have? Neva system?
Potatoes occupy almost the main place in the human diet, yielding only bread in consumption. But few people think about how complicated this plant is from a scientific point of view. It has unique features that are unique to it.
Biological features
Potatoes are one of the leading food crops. It not only ranks 1st among agricultural crops for protein production, but also has one of the highest levels of fitness.
The homeland of the potato is the tropical zone of the continent of South America. The first centers of origin are located in Bolivia and Peru, in the highlands of the Andes (2000-4800 m above sea level), as well as in the temperate zones of Chile (0-250 m above sea level).
Man introduced potatoes to culture more than 8000 years ago. Initially, the territories in which it was cultivated were in South-East Peru and North-West Bolivia. In Russia, this agricultural crop appeared during the reign of Peter I. It was this ruler who legalized the widespread cultivation of potatoes.
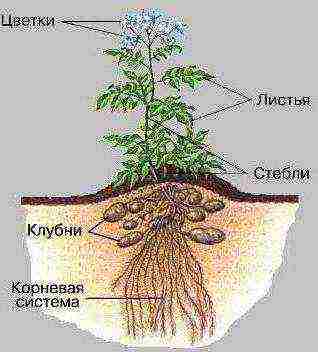
Aboveground part
A potato plant is a shrub that consists of 4-8 stems. Branching depends on the ripening period. In early maturing varieties, as a rule, there is a weak branching at the base of the stem, and in late maturing varieties, it is strong. Large seed potatoes, or rather a tuber, form a shoot with more stems than a small one.
Potato plants can also differ greatly in the number of leaves. The foliage may be weak, but there are also such shoots when the stems are almost invisible behind the numerous leaves. According to the shape of the bush, varieties are distinguished with compact bushes, spreading and semi-spreading bushes. Based on the position of the stems, there are erect, wobbly and half-walled bushes.
Root system
As for the potato root system, it is fibrous and in fact is a collection of root systems of individual stems. The penetration of roots into the soil largely depends on its type. But on average, the depth of penetration ranges from 20 to 40 cm.In addition, in the arable layer, the roots grow to the sides by 50-60 cm.
Aboveground part of the plant: potato leaf and flower
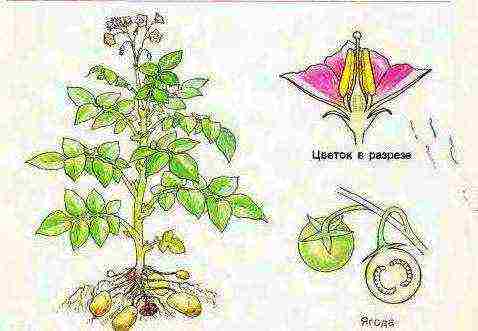
The leaf is of a simple unpaired-pinnately dissected type. If we consider its components, then you can see several pairs of lobes, lobules and lobules, which are located in various combinations on the main petiole. And the potato leaf ends with one unpaired share.The characteristic features of the leaf (the degree of dissection, the size and shape of the lobes, the size and position of the petiole) are important varietal traits. The leaf blade is always in a lowered position, the color varies from yellow-green to dark green.
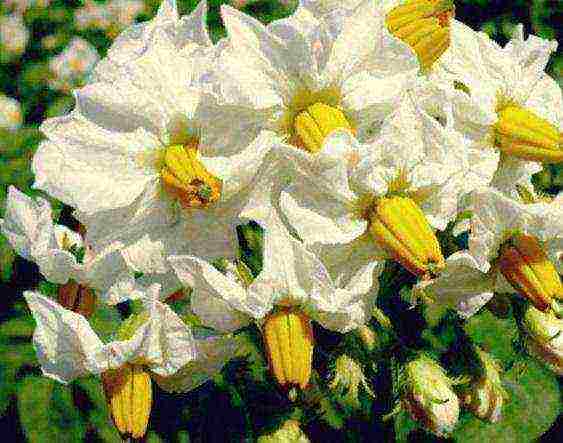 The potato inflorescence is a set of fork-shaped diverging curls, the number of which is from 2 to 4. They are located on the peduncle, which is laid in the leaf axil (6-8). The potato flower is 5-membered, has a spine-leaved calyx and incompletely accrete white, red-violet, blue-violet or blue corolla lobes. The number of stamens is 5. Their anthers are yellow or orange. The ovary is superior, as a rule, two-celled.
The potato inflorescence is a set of fork-shaped diverging curls, the number of which is from 2 to 4. They are located on the peduncle, which is laid in the leaf axil (6-8). The potato flower is 5-membered, has a spine-leaved calyx and incompletely accrete white, red-violet, blue-violet or blue corolla lobes. The number of stamens is 5. Their anthers are yellow or orange. The ovary is superior, as a rule, two-celled.
Tuber formation mechanism
Potato tuber is a shoot, but not aboveground, but underground. Its formation is as follows. Due to the increased concentration of nutrients in the upper part of the tuber, when planting, bud germination is observed not of all eyes, but only those that are located in the upper part of it. The color of the sprouts depends on the variety and can be green, red-violet or blue-violet. When the plant reaches a height of 10-20 cm, then the underground part of its stems gives off shoots - stolons, the thickness and length of which are 2-3 mm and 5-15 cm, respectively. Their ends gradually thicken, thus turning into tubers.
Tuber structure
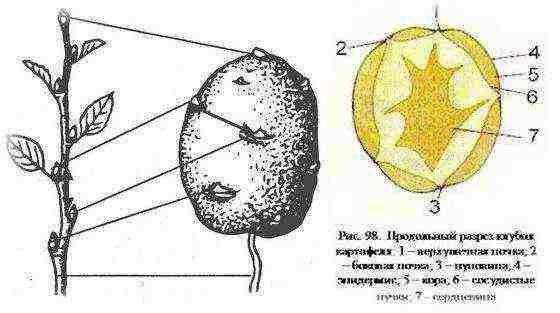
The potato tuber is a shortened, thickened stem, as evidenced by numerous similarities, especially noticeable at an early stage of development. This is, in particular, the presence of scaly leaves, in the sinuses of which resting buds are formed, the number of which varies from 2 to 4 in each ocellus. Also, the similarity lies in a similar alternation and arrangement of tissues and vascular bundles in tubers and stems. And the formation of chlorophyll in a tuber becomes apparent when it turns green under the influence of light. That is why in storage areas that are poorly protected from light, green potato tubers are often found, which should not be eaten.
The upper, youngest part of the tuber contains more eyes than the middle, and even more so the oldest, lower, or umbilical part. Therefore, the buds of the apical part develop stronger and more viable. It is known that most often in a single ocellus, the central bud, which is the most developed, grows first. In the case of removal of the sprout, reserve buds begin to develop and start growing, the plants from which will be weaker than those from the central bud. Therefore, seed potatoes during winter storage should not be regularly freed from sprouts. This can lead to the fact that the plants will not form from the central bud, but from the reserve ones, that is, they will be weaker.
 A young potato tuber covers the outside of the epidermis layer, which is subsequently replaced by a dense, air-tight integumentary tissue - the peridermis. In the process of growth and development of the tuber, the skin of the tuber is formed from the outer layer. This process is especially intense when the tops are removed a few days before harvesting.
A young potato tuber covers the outside of the epidermis layer, which is subsequently replaced by a dense, air-tight integumentary tissue - the peridermis. In the process of growth and development of the tuber, the skin of the tuber is formed from the outer layer. This process is especially intense when the tops are removed a few days before harvesting.
Respiration of tubers and evaporation of moisture is carried out with the help of lentils. Their laying under the stomata of the forming tuber occurs simultaneously with the formation of the periderm. It is through them that oxygen enters the tuber and carbon dioxide and water vapor are removed.
Does the structure of the tuber depend on the variety of potatoes
The structure of potato tubers in early and late varieties may differ. For example, late varieties are characterized by the presence of a denser cork tissue in tubers.
Tubers can have a wide variety of shapes, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Shape options - round, elongated, oval, round-oval, turnip, barrel-shaped, etc.
The most economically valuable varieties have round tubers and superficial eyes.This shape is ideal for mechanized planting and harvesting, and the superficial arrangement of the eyes facilitates mechanical peeling and washing.
The color of tubers can be very different - white, light yellow, pink, red, red and blue-violet. Thus, the external structure of the potato tuber is a varietal accessory. The flesh of the tubers also differs in color: it can be white, yellow or light yellow.
Potato tuber: chemical composition
The deepest state of natural dormancy of tubers is observed during the period of harvesting potatoes in the fall. As spring approaches, it gradually weakens, since growth inhibitors are no longer so active. At this time, the formation of substances that stimulate growth occurs. They also stimulate the growth of the kidney.
In winter, in a dry room with an air temperature of 1-3 ° C, potatoes are well stored without germinating for 6-7 months. After this time, when the air temperature rises to 10-12 ° C and a sufficient supply of oxygen, growth processes begin.
The potato tuber contains a significant supply of nutrients that are necessary for the growth and development of the plant in the initial period of life. Its dry matter contains more than 26 different chemical elements. The composition may vary depending on cultivar, soil, climatic conditions and fertilizers.
The average values of the content of various substances in the chemical composition of tubers are as follows: water 75%, starch 20.4%, sugar 0.3%, crude protein 2%, fat 0.1%, fiber 1.1%, ash 1.1%.
The starch in the potato tubers affects the palatability. The more starch, the tastier the potatoes. On the other hand, when the concentration of crude protein is increased, the palatability deteriorates. The starch content is used to judge the culinary properties of potatoes. Its increase causes an increase in the mealy of the pulp, an improvement in digestibility.
Reproduction
Reproduction of potatoes can be done in two ways - vegetatively and sexually.
The vegetative method of reproduction is the cultivation of potatoes from tubers. Also, this method includes reproduction using stem segments, on which there must be one apical or several lateral vegetative buds.
The most common way is to grow potatoes from tubers. And stem cuttings are planted in cases where the number of tubers is limited, and some new valuable variety requires a quick introduction into practice.
 The mechanism of sexual reproduction of potatoes is more complex and is associated with the use of true seeds that form in fruits (tomatoes), which are formed on the stems of adult plant organisms. The peculiarity is that in the case of sexual reproduction, all daughter plants have genetic diversity. The seeds contained in a single fruit can give rise to a wide variety of plant forms, but none of them will repeat the characteristics of the mother plant.
The mechanism of sexual reproduction of potatoes is more complex and is associated with the use of true seeds that form in fruits (tomatoes), which are formed on the stems of adult plant organisms. The peculiarity is that in the case of sexual reproduction, all daughter plants have genetic diversity. The seeds contained in a single fruit can give rise to a wide variety of plant forms, but none of them will repeat the characteristics of the mother plant.
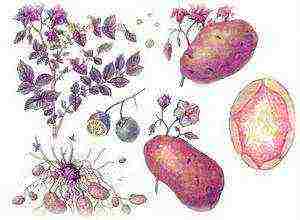 Today, potatoes occupy a significant niche in the diet in many parts of the world. Because of its nutritional value, relative cheapness and wide distribution, this vegetable is often called the "second bread". Despite the seeming simplicity, the structure of potatoes is much more complicated, and a detailed consideration of this issue will be useful for many agricultural producers and ordinary summer residents.
Today, potatoes occupy a significant niche in the diet in many parts of the world. Because of its nutritional value, relative cheapness and wide distribution, this vegetable is often called the "second bread". Despite the seeming simplicity, the structure of potatoes is much more complicated, and a detailed consideration of this issue will be useful for many agricultural producers and ordinary summer residents.
How did potatoes conquer Europe and Russia?
The homeland of potatoes is Central and Latin America. Spanish pioneers began to bring potatoes to Europe in the late 16th century. At first, European kings and nobles appreciated only the flowers of the plant, which they used as a decorative ornament. The peasants vehemently rejected this vegetable, as they were poorly informed about the nutritional properties of the tubers themselves.Frequent poisoning with potato fruits-berries often led to the fact that, in a fit of anger, the peasants simply uprooted the plants and burned them in the fire. The pleasant aroma of the baked tubers obviously made people taste them. So, gradually, the attitude of Europeans to the new vegetable has changed dramatically.
In Russia, potatoes appeared during the time of Peter I. The Tsar, as a lover of everything European, brought a small batch of potatoes from Holland and ordered them to be handed over to the peasants for cultivation. The lack of the necessary knowledge had bitter consequences, similar to what happened before with peasants in Europe. In addition, many clergymen convinced illiterate people about the inadmissibility of growing a foreign fruit and equated this with a sinful act.
Plant structure
Potatoes belong to the nightshade family. It is a perennial plant, however, for agricultural purposes, potatoes are grown as an annual crop. The generally accepted method of reproduction is planting tubers, however, experts also use seeds for selective work. The biological features of the potato as a crop consist in the specific formation of the root system, tubers and the aerial part of the plant.
Root system
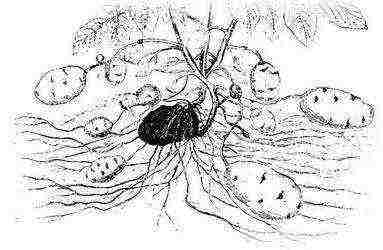 The root system of potatoes is of two types. A plant grown from seed has an embryonic taproot with many small roots. Secondary roots are also laid at the base of the stem. Potatoes grown from a tuber have a fibrous root system, consisting of sprout, stolonny and stolon roots.
The root system of potatoes is of two types. A plant grown from seed has an embryonic taproot with many small roots. Secondary roots are also laid at the base of the stem. Potatoes grown from a tuber have a fibrous root system, consisting of sprout, stolonny and stolon roots.
The usual depth of the potato root system is 25-40 cm, that is, the root mass is mainly located at the depth of the arable layer. In some cases, the roots can go to a depth of 80 cm or more. Late varieties have a more developed root system than earlier counterparts.
Interesting facts: you can increase the yield by deepening the arable layer, for example, up to 70 cm. Thus, the number of tubers will increase significantly.
In addition to the usual roots in the underground part of the plant, there are stolons - shoots growing from the mother tuber. In the process of development, stolons grow and young tubers begin to form on young shoots. Stolons are easy to distinguish from roots: they are lighter in color and thicker.
Tuber
 Many people believe that the tuber is the fruit of the potato. In fact, the tuber is part of an underground stem or stolon, or more precisely, a tuber is a modified shoot. The plant accumulates starch, sugar and other nutrients in it, which are necessary for further development.
Many people believe that the tuber is the fruit of the potato. In fact, the tuber is part of an underground stem or stolon, or more precisely, a tuber is a modified shoot. The plant accumulates starch, sugar and other nutrients in it, which are necessary for further development.
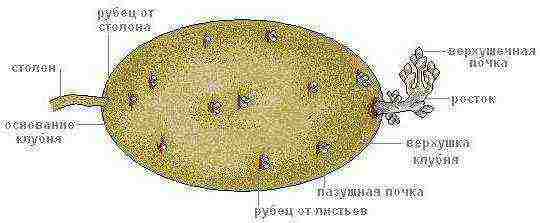
The potato tuber has a peculiar structure and appearance. On the smooth and dense surface of the tuber, the so-called "eyes", small black dots and scars are always present.
The eyes are the buds from which the stems of the plant sprout. The structure of the ocelli is quite interesting: near the main kidney, in each of the ocelli, there are always several additional buds, which are activated in case of damage to the main one. Each tuber can have from 4 to 15 eyes. They are located on the upper half of the tuber.
The structure of the potato tuber also includes lentils - small points through which gas exchange occurs in the tubers. The formation of lentils occurs in parallel with the formation of the peel. If there is too much moisture in the soil or the soil is clogged, then loose white neoplasms appear on the lenticels, which help to absorb air. An increase in the size of lentils is a bad signal, indicating that gas exchange in the tuber is impaired or it is affected by a disease.
Scars, vaguely resembling eyebrows, are atrophied scaly leaves that appear at an early stage of tuber development. It is in the sinuses of these leaves that the buds are later formed.
The rind of the tubers themselves can be smooth, netted or flaky, depending on the particular cultivar. The thickness of the periderm depends not only on the species, but also on the weather and climatic conditions, the quality of the soil and fertilizers. For example, the use of phosphorus-based fertilizers significantly thickens the skin, while potash fertilizers, on the contrary, make the peridermus thin.
Stem
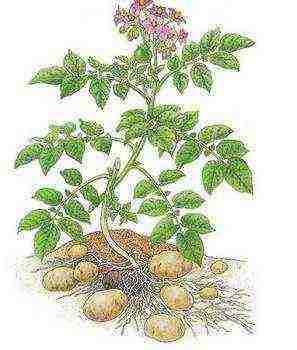 The stem of a potato is formed from a tuber bud. Since there are always several buds, the stems also grow from 2-3 pieces or more, depending on the variety and size of the tuber itself. Several stems form a bush. In cross section, they have a faceted shape (3-4 edges), much less often the stem looks rounded. Often the bushes reach a height of 80-90 cm, however, such luxurious plants often give a poor harvest, because all the strength goes into the development of the bush. Usually, this happens when there is an excess of fertilizer in the soil.
The stem of a potato is formed from a tuber bud. Since there are always several buds, the stems also grow from 2-3 pieces or more, depending on the variety and size of the tuber itself. Several stems form a bush. In cross section, they have a faceted shape (3-4 edges), much less often the stem looks rounded. Often the bushes reach a height of 80-90 cm, however, such luxurious plants often give a poor harvest, because all the strength goes into the development of the bush. Usually, this happens when there is an excess of fertilizer in the soil.
Each stem has wing-like appendages along its entire length.
Leaves
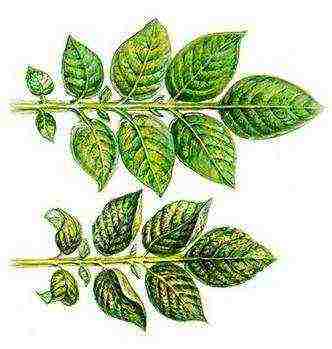 Each potato variety has its own characteristics, including the number, size and shape of the leaves. An experienced gardener can easily identify the variety by the appearance of the green mass. The leaf of the potato is intermittently pinnate. On the main shaft, between the paired lobes, usually smaller lobules are formed, and between them, in turn, there are lobules of an even smaller size.
Each potato variety has its own characteristics, including the number, size and shape of the leaves. An experienced gardener can easily identify the variety by the appearance of the green mass. The leaf of the potato is intermittently pinnate. On the main shaft, between the paired lobes, usually smaller lobules are formed, and between them, in turn, there are lobules of an even smaller size.
There are three degrees of dissection: weak, medium, and strong. On a weakly dissected leaf, there is one pair of lobules, but there are no lobules at all. On a strongly dissected leaf, there are more than 2 pairs of lobules and many lobules.
The structure of the leaves also differs in the way of placing the lobes, lobules and lobules. If they overlap each other, creating the appearance of a solid sheet, then this type is called densely. If the distance between the elements of the leaf is large enough, then we have a rare-sized leaf type.
Flower
 As you know, several centuries ago, a potato flower attached to clothing was considered a sign of belonging to the aristocracy.
As you know, several centuries ago, a potato flower attached to clothing was considered a sign of belonging to the aristocracy.
Potato flowers have a rather complex structure. The inflorescence has the shape of a complex curl and can be spreading or compact. Peduncle, peduncle and flower form an inflorescence. In addition to these components, there are upper leaves in the inflorescence of some potato varieties.
The flower itself, the structure of which we are considering, consists of 5 sepals collected in a calyx, 5 petals forming a corolla, 5 stamens and a pistil. The flower can have narrow, broadly styloid and long leaf-shaped sepals.
The flower can be white, blue, purple, or any other color. After flowering, the fruit ripens - a green poisonous berry, reaching a diameter of 2 cm. The structure of the berry is quite simple: it is divided into two nests, each of which contains many small flattened seeds.
Despite the relatively low content of nutrients in potatoes, this root vegetable occupies an important place in the diet of many peoples. The advantages of the vegetable lie in the relative ease of growing, decent yields, and, of course, in the excellent taste of potatoes.
The most important problem in the spring is seed preparation. She lays the foundation for the future harvest. Potatoes are usually propagated with tubers. For planting tubers, it is best to buy from nurseries and specialized stores. Certified high quality seed potatoes of the first reproduction, free from viruses and the most dangerous diseases and pests, can only be purchased there. By adhering to certain rules, you can successfully maintain the productivity of seed potatoes.
For planting, a well-sorted and sorted, practically healthy seed material is used.For a more complete identification of latent forms of infection of seed tubers with pathogens of fungal and bacterial diseases and to exclude their infection of healthy material, potatoes are sorted or sorted on a bulkhead, selecting tubers with obvious signs of disease, then warmed up at a temperature of 14-18 ° C and before planting, tubers with manifested symptoms are removed diseases. The size of the planting tubers is of great importance. The best option is medium-sized tubers (50-80 g). Tubers weighing 30-50, 80-100 g and more can be used. The main thing is that they are obtained from healthy plants.
About 30-35 days before planting, the seed tubers must be removed from the storage area. If the tubers were not sorted by size in the fall, then this can be done in the spring.

Depending on the size, the tubers are sorted into boxes. It should be remembered that small tubers have fewer eyes than medium and large ones, in addition, they have a more pronounced apical peephole, therefore they form fewer shoots and have less ability to germinate. When sorting by size, tubers of irregular and atypical shape for the variety, affected by rot and stem nematode, are removed. Sorted and sorted tubers are placed in boxes (you can take boxes for fruits and vegetables) or on wooden shelves, with a layer of 2-3 tubers, and placed in a heated, bright room with a temperature of 15-20 ° C for germination with access to light. The boxes are periodically rearranged to achieve uniform germination. After 20-25 days, strong shoots with root rudiments are formed on the tubers. Before planting, remove tubers that have not formed sprouts, with one sprout or with threadlike sprouts. Each batch is planted separately. Good results are obtained by sprouting seed tubers in the light, with a change in temperature. After the formation of 4-5 mm sprouts on the tubers, the temperature is reduced for 1-2 days to 6-8 ° C, then germination continues at 16-20 ° C. The temperature is changed several times. A sharp change in temperature contributes to the activation of the largest number of eyes. A kind of "hardening" during germination gives a guarantee of full-fledged germination after planting in the ground and a high-quality yield.
If it is not possible to germinate planting tubers with access to light, you can warm them well for 8-10 days. In this case, the planting material begins to be prepared 8-10 days before planting. The tubers are heated at a temperature of 18-20 ° C. It should be borne in mind that longer heating in the dark leads to the formation of long shoots, which break off during planting. A single breaking off of sprouts reduces the yield of potatoes of most varieties by 15-20%, twice - by 25-40% (varieties "Nevsky", "Zabava", "Slavyanka" may not germinate at all). There are varieties that do not reduce yields when the sprouts are cut off 2-3 times (for example, "Povin" and "Yavir"). It is more expedient to plant the tubers unsprouted than to germinate and cut off the sprouts twice. If, nevertheless, long sprouts have formed, such tubers are carefully removed from the box without breaking off the sprouts, planted in a hole and sprinkled with earth. It should be remembered that the first shoots are the most resilient.
There are varieties of potatoes with large tubers, in which the yield of standard tubers of seed fractions (30-80 g) does not exceed 20%, and it becomes necessary to use large tubers for planting. Tubers are cut into pieces weighing at least 40-50 g and with 2-3 sprouts, immediately before planting and must be sprinkled with plant or wood ash at the rate of 1 kg of ash per 40-50 kg of cut particles.
It must be remembered that cut tubers must not be planted in cold (below 5 ° C) waterlogged soil; planting must not be carried out in dry hot weather. In such conditions, sparse seedlings and a significant decrease in yield are inevitable.When growing early varieties of potatoes, it is better to use whole large tubers. To increase the number of sprouts and, later, stems, it is advisable to use stimulating incisions of large tubers of an elongated shape. An incision across the tuber with a depth of 1-1.5 cm is made with a sharp knife completely over the entire tuber or leaving a jumper. The knife used for cutting tubers must be disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate (50-60 g per 1 l of water), and cut tubers and tubers with stimulating incisions should be disinfected in a solution of the same potassium permanganate (8-10 g per 10 l of water), dipping tubers in nets into the solution before planting. For planting, you can also use parts of tubers, cutting large (up to 100 g) into 2 parts and very large (over 100 g) into 3-4 parts. Each part should have 2-3 eyes and a weight of at least 30 g. Cutting the tuber into 2 parts is necessary in the longitudinal direction, given that more eyes are concentrated at the apical end (compared to the umbilical cord). It is necessary to cut the tubers 20-25 days before planting in order for a cork layer to form on the cut surface. Planting small tubers weighing less than 30 g leads to a decrease in yield. For planting, the tops of potato tubers can be used, which can be harvested from unpeeled and unwashed large healthy tubers weighing 80-100 g or more. The weight of the tops should be in the range of 20-25 g. In order to preserve the tops before planting, they must be kept after cutting for 4-5 days at a temperature of 12-15 degrees, until the surface of the cut is covered with a crust. Then the tops are taken out into a cool room, where the temperature is maintained at 3-4 degrees Celsius, and folded in a layer of 15-20 cm. In case of damage, the tops must be sorted out and the rotten ones removed. The tops can begin to be harvested in winter, continuing until planting.
Treating tubers with protective and stimulating drugs
This is a very effective technique for increasing the yield and quality of tubers. For pre-planting treatment of tubers, growth stimulants, trace elements and insectofungicidal preparations are used. Among the growth stimulants, the most famous is Poteytin. One ampoule of the drug is dissolved in 1 liter of water and the resulting solution is treated with 50-60 kg of tubers. You can also use other growth promoters purchased from specialized stores. The technology of use is indicated on the package. The most effective when processing tubers before planting are trace elements copper, zinc, boron, molybdenum and manganese. All these microelements contain complex micronutrient fertilizer "Mikom". Use "Mikom" for pre-planting treatment of tubers in accordance with the recommendations on the package. Soil pests-wireworms, false wireworms, gnawing scoops, larvae of May beetles and a bear, as well as various fungal and bacterial rot that affect tubers in the soil, cause great harm to potatoes. To protect the tubers, they must be treated with insect-fungicidal preparations before planting. The most famous of them are: "Prestige", "Cruiser" and "Maxim". "Prestige" effectively protects potatoes from soil pests, rhizoctonia and Colorado potato beetle (100 ml of the drug is dissolved in 5-6 liters of water and 100 kg of planting material on a film is treated with a hand sprayer). It is necessary that at least 3/4 of the surface of the tuber was treated with the "Prestige" suspension. Combined application of Prestige and Maxim 025 FC (100 ml of Prestige and 70 ml of Maxim per 100 kg of tubers) is very effective. When preparing early varieties of potatoes, "Prestige" is not used. Good results are obtained by treating tubers with "Cruiser" (the rate of the preparation is 70 ml per 100 kg of tubers). This drug protects against soil pests, the Colorado potato beetle and various rot. For the treatment of tubers before planting, stimulants derived from organic substances can be used.The biostimulator "Vermistim" is effective (used according to the instructions on the package). There are a number of other biologically active substances obtained mainly from various organic substances. To combat pathogens of infectious diseases and saprophytic microflora, the seed material of potatoes is etched before planting, using drugs depending on the presence of certain diseases or pests. Of the preparations for etching, the most common: "Ditan M-45", "Vitavax-200", "Maxim", "Kolfugo-super", "Aktara". To increase the resistance of potatoes to diseases, copper sulfate (0.02-0.10%), superphosphate extract (2.0%), ammonium nitrate (2.0%) and trace elements (boron, zinc , manganese, magnesium, molybdenum).
Potatoes intended for early harvest, instead of warming up, should be germinated with access to light for 20–25 days at a temperature of 16–20 ° C. This will allow you to additionally reject tubers with filamentous sprouts.

Early harvest seed potatoes "Breeze"
Germination also contributes to the more rapid formation of tubers before the mass development of late blight. The growth of potato seedlings and the prevention of the development of diseases is facilitated by keeping the tubers in the light until the greenery appears. Cutting the tubers is not recommended, as this leads to infection with bacterial, fungal and viral diseases. To obtain early potatoes, combined germination is used: 20 days after the start of germination, tubers with sprouts are placed in a moistened substrate (humus, compost, peat, sawdust) or covered with moist burlap for 10-12 days at a temperature of 18-20 ° C. During this time, 3-5 cm long roots are formed. This speeds up the early harvest by 5-6 days.
Most read:
Ammonia: application in the garden and in the garden
Find a suitable ...
Diseases of red currants: harm done, effective treatment, general methods of prevention
Diseases of red ...
Growing onions on a head from a set: step-by-step recommendations
Head onions ...
Tomato varieties for the Urals
Good day…
Fertilizing pepper, feeding, growing: in the greenhouse and in the ground
Growing lane ...
Black currant Vologda: variety description, care, yield and reviews
The currant is black ...
Description and characteristics of the domestic apple variety Berkutovskoe
Description and hara ...
Gooseberry Grushenka is a profitable purchase and decoration for your personal plot
Highly winter-resistant ...
Three ways to propagate grapes with green cuttings video
Cutting vi ...
Dangerous Melon Pests and Effective Control Methods
Melon is exotic ...
Eggplant seedlings at home: proper cultivation and care
Growing races ...
Perfectly tolerates drought and severe frosts - Ashinskaya Stepnaya cherry
Ashinskaya cherry ...
Correct seed planting technology: how to grow eggplant seedlings?
Several secrets ...
The best varieties of strawberries (garden strawberries) for the Moscow region: photos and descriptions of promising varieties of garden ...
Garden earthlings ...
Pear Autumn Yakovleva: description and characteristics
How to plant and ...
Felt cherry varieties for the Moscow region: "Natalie", "Tsarevna", "Damanka", "Alice" and "Ogonyok"
Felt cherry ...
Gooseberry propagation - layering, cuttings, methods, video
You succeeded in ...
How to grow a good harvest of potatoes in the country and in the garden
Productivity ka ...
Eggplant Fabina: description and features of cultivation of the variety, yield indicators
Description of the variety ...
The best siderates for autumn and spring sowing
What are the 7 types with ...
Eight ways to grow potatoes 1
Is it possible to grow ...
Codryanka grapes: description of the variety, photo, video, reviews
Features ext ...
Growing strawberries using Dutch technology video
For a while ...
Growing cauliflower in the open field, cauliflower varieties photo video
Cauliflower…
Melon Aikido: characteristics and cultivation of the variety
Melon Aikido is ...
Dwarf pears: an overview and description of low-growing varieties
This dwarf ...
Why cauliflower is not tied: possible causes
Why not stuck ...
How to grow potato seeds at home
Reproduction of car ...
Optimum planting depth for potatoes
Similar articles
- Mulch can be used for several years. When planting the next year, the overwintered organic roller is pushed apart and seed tubers are laid on the soil. If there is not enough mulch, then small holes are made in the soil and the tubers are covered not with a continuous roller, but with separate mounds. In this case, the distance between the tubers is increased to 40 cm, because the tops then develop more powerful.
- If the stem-forming ability of tubers is increased by any methods, then they are planted sparsely. Planting density also depends on soil fertility. Large tubers are planted with a row spacing of 80-90 cm, smaller ones - 60-70 cm, in a row after 25-30 cm. On fertile soils, planting should be denser than on poorly cultivated without applying a sufficient amount of fertilizer.
- Each potato variety has its own characteristics, including the number, size and shape of the leaves. An experienced gardener can easily identify the variety by the appearance of the green mass. The leaf of the potato is intermittently pinnate. On the main shaft, between the paired lobes, usually smaller lobules are formed, and between them, in turn, there are lobules of an even smaller size.
- Many people believe that the tuber is the fruit of the potato. In fact, the tuber is part of an underground stem or stolon, or more precisely, a tuber is a modified shoot. The plant accumulates starch, sugar and other useful substances in it, which are necessary for further development.
Ridge landing
Today, potatoes occupy a significant niche in the diet in many parts of the world. Because of its nutritional value, relative cheapness and wide distribution, this vegetable is often called the "second bread". Despite the apparent simplicity, the structure of potatoes is much more complicated, and a detailed consideration of this issue will be useful for many agricultural producers and ordinary summer residents.
The lighter the soil, the warmer and drier the climate, the deeper the tubers are laid and the less they are huddled.
When the soil dries up, the planting depth of potatoes increases to 6-8 centimeters during planting.
You can sprinkle the tubers with earth with the same walk-behind tractor. To do this, change the wheels to rubber and spread the wings of the bipod to the maximum distance. The wheel of the walk-behind tractor will go over the potatoes, but the rubber will not damage it (if the sprouts are small), and the wings will fill the furrow.
The tubers are planted in two rows in a checkerboard pattern. This makes it possible to uniformly illuminate the plants, which increases their productivity. It is two or even three times more than with the traditional method of cultivation. And how much pride you will feel when showing your friends your wonderful garden!
Under the shovel
It is also used in areas with a close occurrence of groundwater. The height of the ridge there can reach 15 cm, while the planting depth of potatoes is 6-8 cm.
It is very important to plant potatoes on time. The size of the harvested crop largely depends on this. The distance between bushes, rows and planting depth matters. The latter is defined as the distance from the top of the tuber to the surface of the ground and depends on many reasons:
In ditches
This method requires the introduction of a large amount of organic matter (up to 800 kg per hundred square meters), however, a high and healthy potato yield pays for all the costs.
In containers
When planting small tubers, the background of organic and mineral nutrition should be 15-20% higher. Before planting potatoes, it is necessary to outline in advance the rows where the tubers should be planted. The markings are usually carried out with a special marker resembling a rake with wooden teeth. The first pass of the marker is made along the stretched cord from the edge of the site.The extreme tooth of the marker is led along the cord. In the reverse course, the extreme tooth is led along the track marked by the opposite tooth. Planting can be done under a cord, but it is less convenient and more time-consuming. To maintain the correct distance in the row, pre-measured sticks are used.
There are three degrees of dissection: weak, medium, and strong. On a weakly dissected leaf, there is one pair of lobules, but there are no lobules at all. On a strongly dissected leaf, there are more than 2 pairs of lobules and many lobules.
The potato tuber has a peculiar structure and appearance. On the smooth and dense surface of the tuber, the so-called "eyes", small black dots and scars are always present.
The homeland of potatoes is Central and Latin America. Spanish pioneers began to bring potatoes to Europe in the late 16th century. At first, European kings and nobles appreciated only the flowers of the plant, which they used as a decorative ornament. The peasants vehemently rejected this vegetable, as they were poorly informed about the nutritional properties of the tubers themselves. Frequent poisoning with potato fruits and berries often led to the fact that, in a fit of anger, the peasants simply uprooted the plants and burned them in the fire. The pleasant aroma of the baked tubers obviously made people taste them. So, gradually, the attitude of Europeans to the new vegetable has changed dramatically.
Under the black agrofibre
In the middle lane, they are first planted under a shovel or walk-behind tractor, and then they huddle up and get, in fact, a ridge landing.
If the ground has warmed up to a sufficient depth, it is well supplied with air, the tubers are deepened by 8-10 cm.
Landing under a walk-behind tractor
You can lay potatoes after two passes of the walk-behind tractor. Then the row spacing will turn out to be slightly smaller - from 55 to 60 cm.
It is easy and convenient to take care of potatoes in such a mini-vegetable garden. The soil does not need to be dug up. It is enough to loosen to a depth of 7 cm. This will be the planting depth of potatoes. You can plant very early. No need to spud. You don't have to bend low to get away. Tubers are not infected, clean, well kept.
After hilling, the height of the ridge approaches 30 cm. In this case, the soil is removed from the row spacings, and the water after the rain runs into the border.
Landing method;
Dutch technology for growing potatoes
Potatoes
To protect against fungal diseases, before planting, the holes can be poured with a solution of copper sulfate (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water), and to protect against the bear, add 1 teaspoon of crushed eggshell mixed with a small amount of vegetable oil.
The structure of the leaves also differs in the way of placing the lobes, lobules and lobules. If they overlap each other, creating the appearance of a solid sheet, then this type is called densely. If the distance between the elements of the leaf is large enough, then we have a rare-sized leaf type.
The eyes are the buds from which the stems of the plant sprout. The structure of the ocelli is quite interesting: near the main kidney, in each of the ocelli, there are always several additional buds, which are activated in case of damage to the main one. Each tuber can have from 4 to 15 eyes. They are located on the upper half of the tuber.
Dependence on soil composition
In Russia, potatoes appeared during the time of Peter I. The Tsar, as a lover of everything European, brought a small batch of potatoes from Holland and ordered them to be handed over to the peasants for cultivation. The lack of the necessary knowledge had bitter consequences, similar to what happened before with the peasants in Europe. In addition, many clergymen convinced illiterate people about the inadmissibility of growing a foreign fruit and equated it with a sinful act.
Large tubers are planted deeper than small tubers.
In light sandy loam soil, the culture is planted 10-12 cm from the surface of the earth.
Dutch varieties are by far the most productive. Therefore, they are trying to grow in various regions where potatoes can grow at all. Gardeners began to pay attention to what the Dutch use, what depth of planting potatoes are maintained at the same time. The whole process is strictly scheduled, and you cannot move away from it in any direction, as this will negatively affect the harvest.
It is used in areas with a high peat content.
The yield increases by a quarter. Harvesting with this growing method is easy and convenient. But planting is more difficult, because you have to shovel a lot of land even at the planting stage.
The size of the tubers;
To find the root in any word, you need to find the same root words. In this case - potatoes, potatoes, potatoes .... The common part of these words is potato / potato, where f and w alternate. This means that the root in your word is potatoes.
After that, 0.5 kg of compost or humus is added to each hole or a spoonful of ground bird droppings, also 1-2 tablespoons of wood ash. The fertilizers introduced into the holes are mixed with the soil and covered with a layer of earth of 2-3 cm, and then the tubers are planted to the required depth with the tops and sprouts upwards. After planting the potatoes, the area is leveled with a rake.
As you know, several centuries ago, a potato flower attached to clothing was considered a sign of belonging to the aristocracy.
The structure of the potato tuber also includes lentils - small points through which gas exchange occurs in the tubers. The formation of lentils occurs in parallel with the formation of the rind. If there is too much moisture in the soil or the soil is clogged, then loose white neoplasms appear on the lenticels, which help to absorb air. An increase in the size of lentils is a bad signal, indicating that gas exchange in the tuber is impaired or it is affected by a disease.
Potatoes belong to the nightshade family. It is a perennial plant, however, for agricultural purposes, potatoes are grown as an annual crop. The generally accepted method of reproduction is planting tubers, however, experts also use seeds for selective work. The biological features of potatoes as a crop are in the specific formation of the root system, tubers and the aerial part of the plant.
There are many more interesting ways to grow potatoes. You can cover it with straw. In this case, the potato planting depth is 7 cm.
Growing in a barrel
The depth of placement of potato tubers increases after hilling. It is carried out so that the soil becomes looser, improved aeration, increased the formation and growth of fruits.
It turns out that they focus on aerating plant roots, that is, improving air access to them.
In this way, usually early varieties of potatoes are grown. Prepare a garden bed. Cover it with agrofibre. Cut holes 10 cm long in it crosswise. The potato planting depth is about 8 cm. In order to place it in the ground, soil is selected from the holes with a narrow scoop. Tubers are placed, covered with earth on top. They do not huddle, because the moisture from under the bush does not evaporate due to the film. When it comes time to harvest, the stems are cut, then the film is removed and the tubers are taken out.
How did potatoes conquer Europe and Russia?
This is the easiest way. On the plowed field, they dig holes 8-10 cm deep. Then put the potatoes and cover them with earth taken from the hole in the next row. The distance between the bushes is 30 cm, between the rows - 70 cm. If you reduce it, then there will be nothing to spud the plants.
Soil quality;
Plant structure
The word is actually complicated. It is not worth checking it with a "potato", since the alternation of F / W does not exist in Russian. Better to take the row "potato" - "potato" - "potato". Then in "potato" the root is "potatoes", k is the suffix, and is the ending.
Root system
Planting depth.Potatoes should be planted as small as possible, embedding the tubers at the same depth. The maximum soil layer above them is 8 cm. With such a shallow planting depth, the tubers heat up better and germinate quickly. In Holland, the trendsetter in potato farming, potatoes are planted with the top of the tuber at ground level. A ridge is formed above it. A shallower planting can lead to re-greening of tubers of a new crop.
Potato flowers have a rather complex structure. The inflorescence has the shape of a complex curl and can be spreading or compact. Peduncle, peduncle and flower form an inflorescence. In addition to these components, there are upper leaves in the inflorescence of some potato varieties.
Scars, vaguely resembling eyebrows, are atrophied scaly leaves that appear at an early stage of tuber development. It is in the sinuses of these leaves that the buds are later formed.
The root system of potatoes is of two types. A plant grown from a seed has an embryonic taproot with many small roots. Secondary roots are also laid at the base of the stem. Potatoes grown from a tuber have a fibrous root system, consisting of sprout, stolonny and stolon roots.
Tuber
The straw is laid two times: the first - after planting, in a layer 10 cm high. Then, when the stems grow up, add more. In general, the protective layer reaches at least 25 cm. If it is less, then the straw will not overheat, and the weeds will be able to break through it.
Hilling is indicated on heavy clay soils, where planting was carried out early, which means shallow. As a result, the layer of earth increases to a height of 4 to 6 centimeters.
For this, special milling units are used. They very efficiently produce loosening of the soil. When planting, a high ridge is immediately poured, in which the potato tuber is located. As a result, the depth of planting potatoes according to Dutch technology turns out to be slightly deeper, about 15 cm.
This method speeds up the ripening of potatoes by a month.
The disadvantage of this method is the later planting and the short time interval between when the ground is still cold and when it is already dry. In rainy weather, such plants are more often damaged by various diseases due to the fact that the tuber is in wet soil.
Water regime.
Stem
However, it should be remembered that historically potatoes are one of the aforementioned versions of the name of potatoes, there are many such names: cartole, potato, potato, and so on. Isolation of a common root in such cases is not possible.
Potato grower V.R. Gorelov from the Kemerovo region proposes not to bury the seed tubers in the soil, but lay them on a slightly loosened surface and cover them with mounds or rollers of mulch 10-12 cm high.Mulch can be a mixture of humus with straw, peat, compost or a mixture of rotted sawdust (60%) and sand (40%), filled with a full dose of mineral fertilizers with trace elements. This mixture is especially effective on heavy, clayey soils. When the plants reach a height of 20-25 cm, you need to add additional mulch so that the tubers do not turn green.
Leaves
The flower itself, the structure of which we are considering, consists of 5 sepals collected in a calyx, 5 petals forming a corolla, 5 stamens and a pistil. The flower can have narrow, broadly styloid and long leaf-shaped sepals.
The skin of the tubers themselves can be smooth, netted or flaky, depending on the particular cultivar. The thickness of the periderm depends not only on the species, but also on the weather and climatic conditions, the quality of the soil and fertilizers. For example, the use of phosphorus-based fertilizers significantly thickens the skin, while potash fertilizers, on the contrary, make the peridermus thin.
The usual depth of the potato root system is 25-40 cm, that is, the root mass is mainly located at the depth of the arable layer. In some cases, the roots can go to a depth of 80 cm or more. Late varieties have a more developed root system than earlier counterparts.
Flower
This method is useful for those who practically do not have a personal plot, but want to eat potatoes grown with their own hands.
If the climate is dry, there is little rainfall, or droughts are frequent, hilling is advised not to be carried out. In such conditions, it can lead to a loss of moisture residues and a decrease in yield. But then the tubers can come to the surface and turn green. Therefore, you can loosen the soil and spud the plants a few centimeters.
On a field treated in this way, the potatoes are arranged in two rows, the distance between which is up to 30 cm. Further there is a row spacing of 1 m 20 cm. A technician walks along it, which takes care of the plants.
Motoblocks are increasingly being used by gardeners. They greatly facilitate the main labor-intensive work in the garden. With their help, they plow, loosen, cultivate the soil. The walk-behind tractor will also help in planting potatoes. For this, metal wheels with bushings and a bipod are installed. Set it up for a middle spread. It is advisable to pass the first furrow as evenly as possible.
An even more laborious process than on the ridges. In autumn, they dig trenches, place the remains of plants and weeds (without seeds), sawdust in them, and cover them with earth. In winter they get wet, and in spring, when the temperature rises, they begin to overheat. This generates heat, which heats up the earth. The top layer of the soil is removed, the tubers are laid and a ridge is formed. The potato is at ground level, and it is covered by 8-10 cm. The yield when grown in this way increases by 45% compared to planting "under a shovel". The potatoes are harvested clean, not contaminated. It has good keeping quality.
This is an old way of planting potatoes in heavy soils. In the treated area, furrows are dug along a stretched cord at a distance of 70 cm. The depth of planting potatoes in the ridges is from 5 to 10 centimeters. If fertilizer was not applied on the site, then humus and ash (respectively, half a shovel and a tablespoon) are added to the furrows, spreading them out after 30 centimeters. Potatoes are laid on top and covered with earth, forming a ridge 10 cm high.Its width is 20 cm.
Site preparation for landing
Potato
Prevention of diseases and pests
This mulch allows the roots to develop freely. It retains moisture and air, contains nutrients, regulates temperature in hot and cold weather, provides drainage around the roots, and suppresses weeds. Under the mulch near the soil surface, earthworms gather, which loosen and cultivate the soil, turn organic matter into precious humus. If you add green needles to the mulch, then the plants will suffer less from the Colorado potato beetle, wireworm and other pests, as well as from some diseases.
The flower can be white, blue, purple, or any other color. After flowering, the fruit ripens - a green poisonous berry, reaching a diameter of 2 cm. The structure of the berry is quite simple: it is divided into two nests, each of which contains many small flattened seeds.
Planting potatoes
The stem of a potato is formed from a tuber bud. Since there are always several buds, the stems also grow from 2-3 pieces or more, depending on the variety and size of the tuber itself. Several stems form a bush. In cross section, they have a faceted shape (3-4 edges), much less often the stem looks rounded. Often the bushes reach a height of 80-90 cm, however, such luxurious plants often give a poor harvest, because all the strength goes into the development of the bush. Usually, this happens when there is an excess of fertilizer in the soil.
Interesting facts: you can increase the yield by deepening the arable layer, for example, up to 70 cm. Thus, the number of tubers will increase significantly.
A 15 cm layer of soil is poured into a barrel of any material or a tall box on the bottom. Tubers with sprouts are placed on top. When they rise 5 cm, sprinkle them with another layer of earth and again wait for the shoots to appear. Having filled in this way a part of the barrel so that only a third of the height remains, they stop filling up the soil. Watering, feeding. The crop is harvested gradually, starting from the top layer. You can get up to four buckets of potatoes from one barrel.
The depth of planting potatoes in the Black Earth Region depends on the readiness of the soil. The seedlings are deepened into the warmed earth by 12-15 cm.
If the soil is clayey, and even wet, not warmed up, then it makes no sense to bury the tubers deeply. It will be difficult for the sprouts to get out of there. Therefore, the optimal planting depth of potatoes for such soils should be 4-5 cm. This is how early varieties are planted for sale, which are often covered with black agrofibre.
Putting the wheel of the walk-behind tractor near the edge of the resulting furrow, pass the second one. The distance will be about 70 cm. If you get less or more - adjust the width of the wings. Tubers are laid in the furrows at a distance of 30 cm.The depth of planting potatoes with a walk-behind tractor is 10-12 cm.
sad-dacha-
root of the word potato
Batman
A very interesting, but at the same time laborious way. Used in small areas. The walls of the future container are constructed from building materials. Width - up to a meter, height - from 30 to 50 cm. Their length should be from north to south. The passages between the beds are wide, about 80 cm. Composting from waste will take place right in these boxes. The remains of grass, leaves, straw, sawdust are placed on the bottom. There will be a layer of manure, compost or humus on top. All this is sprinkled with earth taken from the aisle or elsewhere. The garden bed is ready to use. Once you work hard, you can use it for many years. It is only necessary to renew the compost components.
Alexander Heinonen
As a result, the ground is at a height of 10 cm from the potatoes. This method is good because the tubers can be planted earlier, the beds warm up quickly, and the potatoes will soon sprout.
In maize (monocotyledonous) it is fibrous, in the rest (dicotyledonous) it is core. Please note that the type of root system can be traced well only in seedlings. In cabbage, buttercup and birch, it is preserved for life, in potatoes, tomatoes, strawberries, lateral and adventitious roots develop rapidly, the system becomes similar to a fibrous one. With special agricultural techniques, a person contributes to this.
In. R. Gorelov with this method of growing potatoes received twice the yield. Harvesting is easy as the soil does not hold the tubers. Almost all of them rise together with the tops almost clean.
Vetrova A.V.
Despite the relatively low content of nutrients in potatoes, this root vegetable occupies an important place in the diet of many peoples. The advantages of the vegetable lie in the relative ease of growing, decent yields, and, of course, in the excellent taste of potatoes.
What type of root system does corn, potatoes, cabbage, tomato, buttercup, strawberry and birch have? Neva system?
Alex
Each stem has wing-like appendages along its entire length.
In addition to the usual roots in the underground part of the plant, there are stolons - shoots growing from the mother tuber. In the process of development, stolons grow and young tubers begin to form on young shoots. Stolons are easy to distinguish from roots: they are lighter in color and thicker.