Content
The artichoke is not often seen on personal plots, because it still belongs more to exotic cultures. Despite its popularity in southern latitudes and most European countries, only a few agricultural firms and single amateur gardeners grow it in our country. Meanwhile, this plant deserves to be paid attention to. The artichoke has a decorative appearance, its edible parts have a very pleasant taste and contain a lot of useful substances, and it is not at all difficult to grow it from seeds.
Artichoke
Main characteristics
The artichoke is a vegetable plant, but at the same time it is a close relative of the common thistle. This perennial is distinguished by a powerful taproot, a large rosette of wide thorny leaves of a bluish-green color and rounded scaly flowers. Under favorable conditions, the artichoke reaches a height of 1.5-2 m and occupies an area of at least a meter in diameter.
Artichoke is a rather exotic plant for our summer cottages.
Only unripe receptacles and juicy thick petioles can be used for food. The edible pulp has a nutty delicate flavor and contains inulin, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, carbohydrates, organic acids and vitamins. In the outer scales of the inflorescence there are also essential oils, which give the dishes a unique aroma.
Nutritional value of artichoke
Artichoke vegetation lasts 180-200 days, and in the central strip it is grown only through seedlings. With one-year cultivation, the plant bears little fruit, some varieties do not bloom at all in the first year, so it is impractical to grow an artichoke in cold regions. This culture is very thermophilic, for normal development it requires a temperature of 15 to 25 degrees.
Artichoke: growing
Artichoke seedlings can tolerate short-term frosts down to minus 3 ° С, while inflorescences die already at minus 1 ° С. The aboveground part of the plants dies off every autumn, and the root system can withstand only short frosts of about 10 ° C.
In the southern regions, the artichoke winters well, and can grow in one place for 12-14 years with appropriate care. Frequent thaws in winter and waterlogging of the soil can become a problem - in such conditions, the roots completely vanish. And severe frosts in spring are dangerous for young growth, which is just appearing at the roots. But the correct choice of place and the use of covering materials makes it possible to protect plants from the negative effects of weather conditions.
Artichoke in a greenhouse
There are a lot of types of artichoke, about 40 of them are considered edible, but only 10 are really valuable. The most popular among vegetable growers are prickly artichoke and Spanish artichoke. Each species has several varieties of different ripening periods.
|
Early purple |
Low-growing early variety. Bush height about 70 cm, forms 10-12 inflorescences weighing up to 100 g, purple color |
|
Sultan |
Tall, mid-season variety. The height of the bushes reaches 2 m, forms up to 15 inflorescences weighing 90 g |
|
Handsome man |
The most popular variety, bearing fruit in the year of planting. The height of the bush is about a meter, gives 10-12 peduncles weighing 70-110 g |
|
Gourmet |
Mid-season, bush height 1.3 m.Forms up to 15 inflorescences weighing 70-90 g |
Artichoke application
The artichoke has been consumed for hundreds of years, although in some countries it is considered a weed. For a long time it was grown as an ornamental plant. Now the artichoke is valued not only for its decorativeness and taste, but also for its medicinal properties, in addition, it is used as an oilseed and fodder crop.
Artichokes are widely used in cooking.
The artichoke is most widely used in cooking: it is served as a side dish, as an independent dish, in salads, appetizers and even desserts. It tastes great both cold and hot, goes well with other foods, and is often eaten raw. The method of preparation largely depends on the stage of maturation of the inflorescences. In some Asian countries, inedible parts of the plant are also used: healing artichoke tea is brewed from the roots, stems and leaves.
Artichoke tea
Medicinal extracts, tinctures and decoctions are made from artichoke, which have a healing effect in diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases, alkaloid poisoning, atherosclerosis and other ailments. Such drugs have almost no contraindications and are successfully used in traditional medicine. In addition, the artichoke is considered a dietary vegetable, therefore it is recommended for obesity and certain diseases of the digestive system.
Artichoke as medicine
Unblown artichoke inflorescences look like green round cones, and look very original in flower arrangements. This is actively used by florists, especially when decorating celebrations and drawing up wedding bouquets. Artichoke plants are also in demand in the garden landscape. With the help of large ornamental bushes with bright purple inflorescences, you can give a suburban area an original look, make an impassable hedge.
Artichoke inflorescences
The artichoke is also useful on the farm: its lush juicy greens are eaten with pleasure by livestock, and large seeds, containing a lot of oil, go to feed chickens and other birds. In addition, it is a melliferous plant and can be planted near an apiary.
Growing an artichoke
Growing from seeds
Sowing seedlings
One bag contains about 15 seeds, which is quite enough for the first time. You should not immediately purchase several varieties if you have not yet had to deal with such a plant. Sowing begins in early March, and the seeds are prepared 1-3 weeks before that, around mid-February.
Artichoke seeds
Step 1. The seeds are poured with settled water at room temperature and left for 10-12 hours. Swollen seeds are spread on a wet cloth, wrapped, covered with a film on top so that moisture does not evaporate quickly, and placed in a warm place for about 5 days until they hatch.
Seed preparation
After that, the bundle can be placed for another two weeks in the refrigerator on the lower shelf. This is not a prerequisite, but temporary cooling of the seeds increases the chances of flowering and fruiting of the bush in the year of planting.
Cold stratification
Step 2. Prepare containers for sowing. The best soil for an artichoke is a mixture of turf, sifted sand, and humus. All components are taken in equal proportions, mixed well and moisturized. When filling the boxes with earth, drainage must be poured onto the bottom.
We fill up the soil in the box
Step 3. In the boxes, grooves up to 1-1.5 cm deep are formed and seeds are laid out on them with an interval of about 3-4 cm.Since the seeds are large enough, it will not be difficult to do this, the main thing is not to damage the sprouts, which at the time of sowing reach a length of 0 , 7-1 cm.
Sowing artichoke seeds
Step 4. The seeds are sprinkled with a layer of soil no more than 1 cm thick, once again moistened with a spray bottle and placed on the windowsill. There is no need to cover the boxes with foil or glass, just make sure that the soil does not dry out.
How to plant artichoke seedlings
After a few days, the sprouts will appear from the ground, and after 12 days they will form the first true leaf. It is advisable during this period to lower the temperature to 15 degrees and provide the seedlings with illumination so that they do not stretch out. Watering should be done very sparingly; excess moisture will only harm delicate plants.
Artichoke seedlings
Pick and care for seedlings
If artichoke seeds were sown in a common box, it is imperative to dive the plants. Before planting in open ground, they will grow strongly, they will become cramped in the box, the seedlings will stretch out and weaken. For the same reason, the tanks for picking should be spacious enough. It is best to use 0.5 liter peat pots.
Step 1... The pots are filled with a mixture of earth, humus and sand, a depression is made in the center and poured over with water.
Fill individual pots with soil
Step 2. The seedlings are also watered, and then the plants are carefully removed one at a time and the tip of the central root is pinched. This promotes the growth of the rhizome in the adult artichoke.
Step 3. Seedlings are planted in separate pots, watered, placed in a bright, warm place.
Spiked seedlings
Two weeks after planting, the artichoke is fed with mullein infusion, diluted in a ratio of 1:10. After another two weeks, fertilizing with mineral fertilizers is carried out. In the same period, you can begin to harden the plants, taking them out for a couple of hours in the open air. This should be done on warm, windless days. Gradually, the time spent outdoors is increased to 10 hours, sheltering the plants from rain and direct sunlight. Watering should be done in moderation, not allowing the soil in the pots to dry out.
Landing in open ground
A lot depends on the choice of the place for the artichoke. In the shade, low ground, on dense soils, the plant stops growing and does not bloom. Areas open to northerly winds are also not suitable for him, and where there is a high level of groundwater, the bushes may die altogether. The roots of the artichoke penetrate very deeply, and with excess moisture they begin to rot. The optimal planting site is on the southern slope, with breathable, fertilized soil. Artichoke beds should be located away from tall fences, trees, or dense hedges.
Young plants can be planted in rows in the garden bed or in separate planting pits, depending on the purpose of growing. The optimal time is mid-May.
Option 1. If the artichoke is grown only for food and animal feed, choose a plot in the garden. They dig up the earth deeply, add humus (10 kg / m2), superphosphate (200 g) and potassium sulfate (40 g). Ridges up to 20 cm high are formed at a distance of 1 m from each other. At least 80 cm is left between the plants in a row. After planting, the artichoke is watered, the ridges are mulched with dry grass or straw.
We grow an artichoke on the site
Option 2. If the artichoke is planned to be grown for decorative purposes, a place for it is selected that is clearly visible and has a convenient approach, for example, along the driveway, on the lawn in front of the house, in an open area in the garden. They dig planting holes about half a meter deep and 70-80 cm in diameter, fill them with sod soil in half with compost. There should be a distance of 1.2-1.5 m between the pits. Plants are planted together with peat pots, watered, the soil surface is mulched with grass.
Plant care
When the artichoke adapts and begins to form new leaves, feed with slurry. After 2 weeks, complex mineral fertilizers are used, and so on until the end of the growing season. Watering is plentiful, but not frequent, so as not to overmoisten the earth. In the first 3 weeks, it is necessary to loosen the soil and remove the weeds, then the leaves will grow and nothing will grow under them. If aphids appear on the plants, you need to treat the leaves with a solution of wood ash with the addition of potassium chloride.
Artichoke care
Advice! If you want to get large receptacles, remove about a third of them in the lower part of the bush during the formation of peduncles. Leave the top 3-4 stalks with three baskets.
The artichoke begins to bloom in August-September, depending on the variety. After flowering, watering is gradually reduced, preparing the plants for wintering. If you plan to harvest seeds yourself, leave 2-3 inflorescences on the bush and let them fully ripen. Before the onset of cold weather, you need to cut off the central stem, remove the bulk of the leaves and cover the bed with a layer of peat or earth 20 cm thick. Cover the top with fallen leaves or straw.
How to harvest
Harvesting artichokes
In the absence of experience, it is rather difficult to immediately determine when the inflorescences are ready for cutting. Overripe baskets are unsuitable for food, and unripe ones can be eaten, but they do not yet have a rich taste. As a rule, inflorescences can be harvested two weeks after their formation at the ends of the stems. Since the formation of peduncles is uneven, the collection is carried out in stages, removing each artichoke separately.
Advice! The main sign of the ripeness of an artichoke is the mobility of the upper scales. They move slightly apart and bend outward, and the peduncle bump itself creaks when pressed.
Collecting heads can be continued until frost
Cones must be cut off together with part of the stem, about 3-4 cm long. You can store them fresh for a month by placing them on the lower shelf in the refrigerator. Also, the fruits of the artichoke are frozen, salted, pickled for long-term storage. But the most delicious and healthy are, of course, freshly picked.
Both young and more mature artichokes can be used in food.
Video - Artichoke: growing from seeds
Growing artichokes in Russia is not as popular as, for example, in France or other foreign countries. But if you ask yourself this question, you can grow this healthy and tasty delicacy right in your garden. How to do it correctly and what important nuances should be taken into account?

Artichoke cultivation methods
The Canary Islands are considered the birthplace of the artichoke, so it is not surprising that the plant is thermophilic and prefers sunny, wind-protected areas. In central Russia, artichoke cultivation is possible only by cuttings or seedlings. But in the south of the country, you can sow seeds directly into the ground. Let's take a closer look at each method.

Seedling method
You should start growing artichoke seedlings about 2 months before planting in open ground. That is, in the middle or end of March, you can start soaking the seeds. To do this, they are placed in water at room temperature for a day. Then they act according to the following scheme.
- Place the required amount of seeds on a wet napkin, burlap or sawdust.
- After germination, 10% of artichokes are hardened. For this, the swollen seeds are placed in a refrigerator for several days. The temperature must be kept at 0.
- Then they wait until the sprouts reach 1.5 cm in length, and plant them in containers with a volume of at least 0.5 liters. For soil, it is better to use a mixture of equal parts of humus, sand and turf.
- Further, the seedlings are grown at a temperature of 23-25 degrees.
- After about 2 weeks, the first real leaf appears, which means it's time to pinch and dive the artichoke seedlings. In order for the root system to grow powerful, the end of the root of the plant is carefully pinched off and then the seedlings are planted in different pots.
- After 2 weeks, the seedlings are fertilized with diluted manure (the ratio with water is 1 to 10), after another 2 - with complex mineral fertilizer.
- 2 weeks before planting in a permanent place, artichokes are hardened, gradually reducing the air temperature to 15 degrees Celsius.

Cuttings
When grown in this manner, the largest and healthiest artichokes are dug up in the fall. The rhizomes are separated from the aerial part and placed in a container.They are stored in the cellar, having previously sprinkled with dry peat. In the spring, all new shoots are cut off and the rhizomes are planted in pots with a nutrient mixture of sand, earth and humus. Saplings appear in about 3 weeks. Artichokes are transplanted into open ground in mid-May. They begin to bloom earlier than plants grown from seeds.

Sowing with seeds
You can sow artichoke seeds before winter or in spring and summer, when the earth warms up to 10 degrees. For planting, dig small holes 3-5 cm deep and place 2-3 seeds in each. The optimal distance is 50–70 cm, and for the southern regions - 90–140 cm. After germination of seedlings, no more than 2 plants are left in the hole. When grown in this way, the crop appears only in the second year.

Landing in open ground
The preparation of the site for the future planting of the artichoke begins in the fall. To do this, a hole is dug 1 square meter in size and 60 cm deep. Drainage from pebbles or expanded clay is laid down with a layer of 10 cm. After that, the hole is covered with earth, sand, humus and peat (ratio 3: 3: 3: 1). In the spring, 2 weeks before planting artichokes, the soil is loosened and mineral fertilizer is applied (100 g per square meter). Then, holes are made according to the scheme 70x50 cm (in the south - 140x90 cm) and humus is introduced into them, thoroughly mixing with the ground (500 g each).
As soon as the weather becomes steadily warm, and 3-4 true leaves appear on the plants, the seedlings are planted in a permanent place. The planting depth should be 5 cm more than the height of the pot. After planting, the plants are watered abundantly at the root.
Advice
Artichokes grow best after potatoes, legumes, root vegetables, cabbage.

Care
Growing an artichoke outdoors is not difficult. It is enough to water and feed the seedlings regularly. So how do you do it right?
- Watering.
Artichokes need regular watering, especially during dry periods. 1 square meter requires approximately 7 liters of water. During the flowering period, plants should be watered less frequently.
- Fertilizer.
For the entire period of growth, the artichoke needs 3-4 feeding. You can feed the seedlings with both organic and mineral fertilizers. It is optimal to alternate watering with slurry (0.5–1 l per plant) and spraying with a solution of superphosphate, wood ash and potassium chloride (ratio 10:25:10). The main thing is not to abuse nitrogen fertilizers, otherwise the artichoke will form a dense plant mass, and will not release flower stalks.
- Protection from pests.
To avoid the formation of rot, artichoke seedlings are sprayed with fungicides, and if aphids are affected, insecticides are used. If slugs eat the shoots in wet weather, special anti-slug granules are laid around the plants.
- Increased productivity.
In order for the heads to grow large, no more than 4 inflorescences are left on one artichoke, the rest are plucked and thrown away. In addition, 2 weeks before ripening, the stems under the heads are carefully pierced with a toothpick.
Advice
At first, artichokes grow slowly and do not use the entire area allocated for them. Therefore, it is advisable to plant some early ripening culture (for example, mustard, spinach or salad) on the plants.

Harvesting and storage
Artichoke is a rather large plant, its width and height can reach 2 meters. The peduncle stem appears around mid-August. The flowers resemble baskets in appearance, have a bluish tint. The diameter of one head can vary from 8 to 25 cm, and the weight - from 70 to 200 g. Their ripeness is determined by the upper scales. If they began to bend outward, it means that the artichoke is ripe and it's time to cut it off. It is desirable to do this together with a part of the stem (4–5 cm). When blue petals appear at the top, the artichoke will no longer be suitable for human consumption.
It is worth noting that the heads, as a rule, ripen unevenly, so it will not be possible to harvest overnight. Sometimes they continue to be cut until the very frost.Artichokes are stored at zero temperature, where they remain fresh for up to a month. Some people prefer to freeze the baskets immediately, but then the artichokes lose their color, as well as a significant part of the nutrients.
How to cook artichokes?
First - wash, then cut off the leg, get rid of the thorns and tops. Soak for an hour in water with lemon (1 citrus per 1 liter of water). The fruits are immersed in salted boiling water and boiled for 30 minutes.
In the south and in the middle lane, plants are left to winter in the ground. When frost approaches, the tops of the artichokes are cut off, leaving only the lower leaves. When they dry out a little, they are piled up and sprinkled with ash. Then, as the temperature drops, dry leaves or manure are placed on top. With large temperature fluctuations in winter, it is advisable to put brushwood under the bottom. The thickness of the shelter for cold regions can reach 30 cm. In spring, the rhizomes come to life and new stems develop from them.

Artichoke varieties
In total, there are about 140 species of this plant, but only a third of them are suitable for human consumption. Artichoke varieties are distinguished by the presence or absence of thorns on the leaves, the shape, color and size of the receptacle, the diameter of the bush. The most popular are the following:
- Early purple. This variety is originally from Italy, its inflorescences weigh about 100 g, the diameter ranges from 10 to 13 cm. When ripe, they acquire a dark purple hue. The receptacle is fleshy, flat-rounded.
- Gourmet. The inflorescence mass of this variety is slightly less - 70–90 g, the size is from 8 to 10 cm. The basket is spherical, purple in color with a bluish tinge, reaches ripeness in 120 days from the moment of emergence.
- Sultan. Inflorescences are blue, spherical. The weight of one basket is about 90 g, the size is 10-15 cm. Ripens 120-130 days after the first shoots appear.
- Handsome. Inflorescences are fleshy, large, their weight can reach 120 g. 10-12 baskets are formed on one plant. It has a delicate and pleasant taste.
- Maikop 41. The average mass of the receptacle is 160 g, the size ranges from 15 to 18 cm. Baskets are green with a blue tint, turn purple at high temperatures.
- Laonsky. The variety is originally from England, its inflorescence is flat-round, fleshy. The weight of one basket can reach 200 g. The most resistant to cold.
Growing artichokes in the garden allows you to get a valuable source of vitamins and minerals. The inflorescences of this plant contain calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins of group B, A, C, E, K. They can be eaten fresh or boiled, cook all kinds of dishes. Artichokes are especially useful for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver, headaches.
Planting a plant is carried out by cuttings, seedlings or sowing seeds directly into the ground. The delicacy is not difficult to care for, it lives up to 10 years. Therefore, having spent 1 year on its cultivation, you can reap the fruits of your labors for a long time.
A rather exotic vegetable culture called artichoke is not very popular at the moment. But those who have already met this vegetable and wants to plant it in their garden should know how to grow an artichoke from seeds in a garden. It is believed that before deciding to plant a particular vegetable in your area, you must first find out everything about it. There is a chance that this information will help you in the future.
Features of vegetable crops and the best varieties
The artichoke is a perennial plant that represents the Astrov family. His native land is the Mediterranean coast and the Canary Islands. But after a while, he became very popular not only in his homeland, but also in Australia and South America, in Europe, in North Africa, and also in California.
In Ukraine, artichoke cultivation is practiced in the south, since it will be quite difficult to grow this plant when it is -30 degrees outside the window. But many summer residents are also interested in the question of growing in central Russia and is it possible.Yes, there are chances, provided that you follow all the requirements and recommendations.
Many artichoke resembles a thistle by its appearance. The baskets of an unopened plant, as well as fleshy petioles and a receptacle, are used for food. Its leaves are petiolate, large, up to 50 centimeters long, from below they are pinnately dissected. Their color is green or grayish-green.
The flowering stems are not branching and they reach a height of 200 centimeters. The inflorescences of the plant are 15-20 centimeters in diameter, spherical, flat-round in shape. They taste like a delicate nut mousse.
Also, this perennial plant is prized for its nutritional properties. The dietary product contains inulin, vitamins of groups C, B, E and K, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, carotene and many other important microelements.
There are about 140 species of this plant in the world, but only 40 of them are considered edible and have great nutritional value. The varieties were divided according to the ripening period. In our latitudes, the following varieties are considered very popular:
- early: Violet early and May 41;
- middle: Gourmet, Sultan and Handsome;
- late: Laonsky, Large green, Maikop tall.
If you need to grow an annual artichoke, then summer residents often use a variety like Krasavets. But not everyone grows this plant just because it does not tolerate frost. That is, it can withstand short-term frosts with a temperature of -3 degrees. So you can forget about growing in the suburbs. He is also very picky about soil, watering and lighting. And without complying with their requirements, it will be difficult for you to grow an artichoke from seeds.
to the content ↑ Preparation and sowing of seeds
Before you start planting an artichoke outdoors, you first need to prepare the seeds and soil. Artichokes are planted in two ways:
- seeds;
- seedlings.
If you grow the second method through seedlings, then you will get a crop in the year of sowing. And when growing artichokes from seeds, you will get a harvest in the second year, since the seeds need to be prepared in advance.
Seed preparation begins in January. To begin with, they are poured with warm water, and then mixed with moistened clean sand and placed between layers of burlap. The temperature can range from + 20-25 degrees. It is necessary to ensure that the seeds are always in a humid environment. As soon as they bite, then they need to be sent to the refrigerator for vernalization for 6-10 days.
The seeds should stay there for 8-10 hours at a temperature of about zero degrees and 14-16 hours at a temperature of 16-18 degrees. After vernalization has ended, the seeds must be sown in rows in boxes. Before the first shoots appear, the temperature in the room where they are located should be from +18 to +20 degrees.
As soon as the first true leaves appear, the seedlings must be transplanted into pots. If you do not have them, then you can take ordinary disposable cups. After that, the seedlings must be covered with plastic wrap and a greenhouse must be created. Do not forget to place the seedlings indoors, for example, on a glassed-in balcony, where the plants will remain until they are planted in the ground.
The soil is also prepared in advance. Since autumn, it should be well processed, fertilized and fed with various organic and mineral fertilizers. Two weeks before planting, the soil must be well loosened. On even and fertilized beds, holes are made according to the scheme of 100x100 centimeters. And ash or humus is poured into each hole. And all this is done when the threat of frost has passed.
Sowing is carried out in late spring - early summer, when you will know for sure that the earth has warmed up. If you decide not to grow seedlings from seeds, but immediately plant them in the ground, then you need to put two or three seeds in each hole and cover them with a small layer of earth. But it is best to grow seedlings in advance, since this method will bring you a good harvest already in the first year of sowing.Growing artichokes in a garden from seeds is not an easy task, especially when the culture itself is also capricious.
back to content ↑ Seedling care
In order for an artichoke to grow healthy and productive, only three rules must be followed in care:
- watering;
- weeding;
- top dressing.
Watering should be regular and for every 1 square meter planted with artichokes, you need from 5-7 liters of water. And this should be done only during dry periods. Weeding and loosening should be carried out as needed. This is how you oxygenate the land and get rid of weeds.
If the soil is not particularly fertile, then it must be fed with mullein diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. You can also use ash or complex mineral fertilizer. Artichokes should be covered on cold nights.
If you want large stem heads, pierce the soil with a wooden hairpin. In dry weather, the artichoke can suffer from aphids, and in rainy weather it has every chance of developing black rot, which affects the baskets of plants.
The artichoke plant cannot hibernate in the northern regions and therefore it is better to dig them up together with a clod of earth. Store in a ventilated area. For this, shelves in the basements are suitable. The main thing is that the roots do not touch each other.
back to content ↑ Harvesting
The artichoke fades quickly and therefore should not be delayed with harvesting. Ripeness occurs when the inflorescences develop and the leaves in the upper part are just beginning to open. Usually this period comes at the end of August - beginning of September. If a blue flower appears at the top of the inflorescence, then this signals that the artichoke is already overripe and is no longer suitable for food.
Cleaning takes 1-2 months. The inflorescence must be cut with a knife. This way it is better preserved. Many people make additional cuts in the stems to increase the volume of the plant. If harvesting is late, then there is a possibility that the inflorescences and stems will die, so they should be covered with paper or leaves. The yield depends on the variety and growing conditions. If it is a perennial plant, then the yield is much higher.
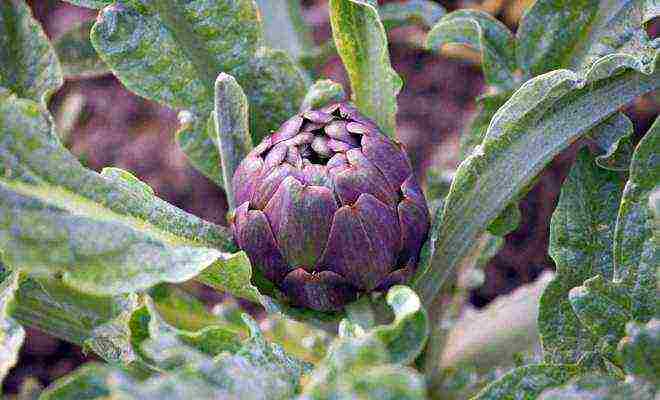

The artichoke is a rather exotic plant in our beds. Many gardeners are afraid to grow this vegetable, not knowing how to get large, edible baskets. Find out how to get a good harvest of this crop.
There are several ways to reproduce artichoke: by seeds, through seedlings, by growing root children and dividing the bush.
Growing artichoke seedlings
The artichoke is thermophilic; it can be planted in the ground only when stable warm weather arrives, not lower than 10 ° C. Seeds are sown about 1.5-2 months before planting in the beds. Before sowing, it is better to germinate the seeds and harden them in the refrigerator. It will take 1-3 weeks.
The prepared seeds are sown in a container with soil. The correct soil mixture should consist of equal parts of humus, sand and nutritious deciduous soil. As soon as the seedlings release their first true leaf, usually 1-2 weeks after sowing, they are transplanted into half-liter cups. At the same time, pinch the root by 1/3. After the seedlings are taken, they are fed with mullein and mineral fertilizer at intervals of two weeks. Before planting on the beds, the artichoke is tempered - they are taken out into the fresh air for an hour or two, then this time is lengthened.
Basic principles of planting and caring for an artichoke
- Choosing a suitable site. An artichoke takes up a lot of space.
- An abundance of sunlight. For this culture, planting in the shade will be disastrous.
- Nutrient soil. The artichoke loves oily, organic-rich and non-acidic soils.
- Good watering, but no stagnant water.
- Regular feeding with organics and fertilizers containing a mineral complex.
- The area under the artichoke is deeply dug in the fall, bringing in manure, humus at the rate of 1 bucket per square meter. Before planting, a large handful of humus and a little ash are poured into the holes.Seedlings are transferred into a hole directly with an earthen lump, deepening the root collar by a few centimeters. For an annual crop, the distance between the bushes is about 50 cm.If long-term cultivation is supposed, then 100-150 cm.
- Young artichokes are watered and loosened regularly. The hardened plants begin to feed. Mullein or bird droppings are great for root feeding. Mineral fertilizers are good for spraying the leaves. Together with feeding, spraying with aphid preparations is carried out.
How to get a good harvest of artichoke?
With long-term cultivation, there are no problems with the harvest. The artichoke blooms in the second year and bears fruit regularly. However, after a couple of years, it will grow, and the bushes can shade each other, making the baskets smaller.

Artichoke
To obtain large baskets in the first year of cultivation, the following tricks are used:
- Drying of seedlings. Young plants are watered less and less often two weeks before planting in the ground, and then they stop watering altogether. When the bushes drop their leaves, they are planted in a garden bed and watered abundantly. Further watering is carried out regularly.
- Removing unnecessary baskets. 4-5 inflorescences are left on the bush.
- Stalk piercing. Before flowering, when the baskets have not yet reached their maximum size, a puncture is made in the stem under the inflorescence. So the inflorescences will gain a large mass.
- The baskets are harvested at the very beginning of flowering. The artichoke ripens unevenly and very quickly. Therefore, there is no need to delay the harvest. Cut off the basket while it has not yet opened, and part of the stem.