Content
- 1 These mysterious mushrooms ...
- 2 And again the conspiracy theorists fantasized ...
- 3 What are mushrooms?
- 4 When is it better to just admire the gift of the forest?
- 5 The mushroom season is truly a wonderful time!
- 6 Spring outing for mushrooms
- 7 Summer-autumn location of mushrooms
- 8 Specific habitats of forest gifts
- 9 Gourmet treat
- 10 Interesting Facts
- 11 New trends in the mushroom market
- 12 Consumption of mushrooms in Russia
- 13 Import of products
- 14 Mushroom production volumes
- 15 Production of cultivated mushrooms (champignons)
- 16 Feasibility study of the project
- 17 Price analysis
It is difficult to find an occupation more contemplative and bringing happiness than the summer picking of mushrooms. If you once walk through the woods with a basket, you will be drawn to this exciting activity over and over again. Can't believe it? And you try, on an early summer morning, when the sun's rays break through the mighty branches of the trees, and the air is still full of night coolness ...
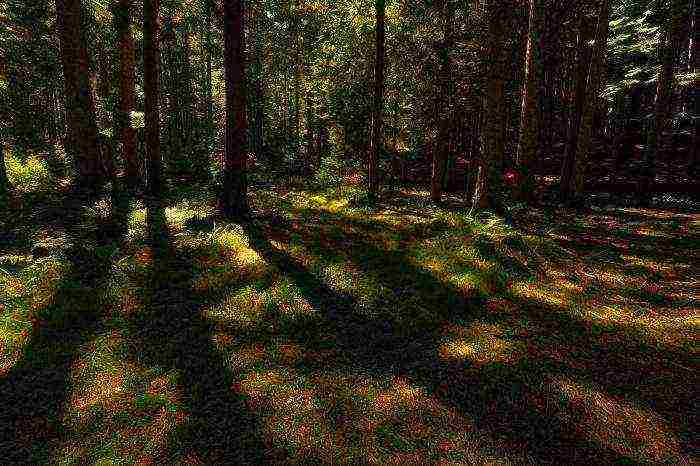

These mysterious mushrooms ...
Mushrooms are one of the most interesting kingdoms in nature. They combine both the characteristics of plants and animals. Incredibly diverse in shape and color, they inhabit the most unexpected corners of our planet. There are known specimens that have settled on the seabed.
And again the conspiracy theorists fantasized ...
Since ancient times, people have been studying the properties of mushrooms. To this day, these amazing organisms are not fully understood. There are two unexplained, but proven facts about mushrooms:
- Incredible energy. Science knows mushrooms capable of breaking open asphalt, absorbing radiation and changing their shape in a very short period of time.
- Influence on the consciousness of people. There are no other plants in living nature that can change the biochemistry of the brain so dramatically. That is, to have a pronounced psychedelic effect.
This leads to an interesting hypothesis about the extraterrestrial origin of the organisms under consideration.
What are mushrooms?
Living in the forest, growing on trees and even entering into close symbiosis with humans. We are interested in those specimens that grow in the forest.
Scientists divide forest mushrooms into edible, conditionally edible and poisonous. Boletus, Polish mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, chanterelles, honey agarics and oyster mushrooms are recognized as edible (and very tasty) gifts of the forest. During the mushroom season, a real hunt goes after them!
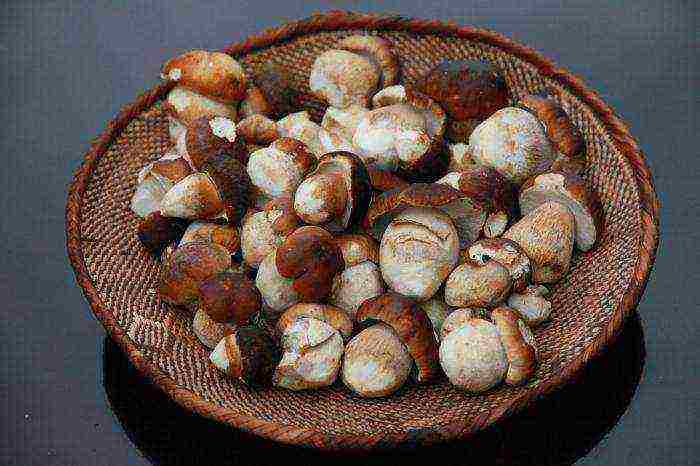

You can also eat conditionally edible mushrooms. Just to begin with, they need to be brought to the correct condition. That is, in a certain way, soak, evaporate, carry out cunning manipulations, and only then eat it. This class of mushrooms includes black milk mushrooms.
But it's better not to joke with poisonous mushrooms ... Why - read on.
When is it better to just admire the gift of the forest?
When there is even the slightest suspicion of the edibility of the mushroom.
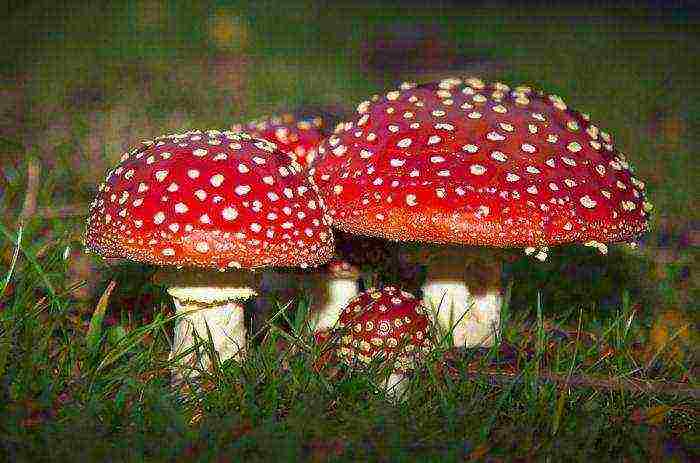
The most poisonous mushrooms in the Leningrad region are pale grebe, satanic mushroom and red fly agaric. And also - all the unfamiliar and dubious gifts of the forest. This is the rule of the wise mushroom picker. Even the most experienced specialist will not take an incomprehensible mushroom in his basket.
Finally, I would like to reassure the reader: only poisoning by all the well-known pale toadstool leads to death. In all other cases, people survive (the consequences depend on how strong the liver and kidneys are). Another thing is that such experiments are obviously pointless. Next, we will tell you about edible and healthy mushrooms of the Leningrad Region, a photo is attached.

The mushroom season is truly a wonderful time!
Spring nature is mesmerizing: insects frolic in the air, streams flow, and the sky becomes starry and inviting in the evenings.
The first mushrooms of the Leningrad Region (a photo assortment will follow the cute fly agarics) appear at the end of April. And these are undoubtedly morels.They do not differ in their beautiful appearance, but only young boletus can compete with them in taste. The map of mushroom places in the Leningrad region will tell you more about their favorite places.
Next comes the summer harvesting season. Fresh boletus and boletus mushrooms appear in June. They love to grow in birch groves. Butterlings almost always live in families: if you find one cute oily mushroom, then you should very carefully study the area around. The second decade of June gives mushroom pickers white podgruzdiki.
July is another mushroom month. Boletus, chanterelles and mushrooms appear in the forests. And from the middle of the month, the earth is decorated with multi-colored russula hats. These mouth-watering mushrooms amaze with their rich color palette ...
August is traditionally recognized as the most mushroom month. The number of porcini mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, russules and chanterelles is increasing. Specifically, honey agarics and belugas are considered August mushrooms. The first ones appear at the beginning of the month, the second ones - closer to its end. Poisonous mushrooms of the Leningrad region (fly agarics and pale toadstools) also grow actively in the last month of summer. They catch the eye with their bright red hats with white pimples. Amanita muscaria grow in forest lowlands and along roadsides.

The autumn mushroom season in the Leningrad Region is September and the first two weeks of October. Traditionally, summer mushrooms are gradually declining. In the forests, more and more often there are a variety of rows - belugas, jaundice and greenfinches. Also, on old stumps and next to majestic trees, you can find friendly honey agaric families. The season ends with the onset of the first frost and the temperature drop to 5 degrees with a plus sign.
Spring outing for mushrooms
Let's start the story about mushroom places in the Leningrad Region with the habitat of the first spring mushroom - morel. To be more precise, the morel is conical. This mushroom grows in the coniferous and deciduous forests of the Leningrad Region; it can be found in the place of clearings, fireplaces and burnt forests. Having found one conical morel, in 99% of cases the whole family can be found.

Most often, the mushroom grows in the southern part of the region, namely, in the area of the village of Tosno. The map of mushroom places of the Leningrad region, located further, confirms this. At the end of April, in addition to a basket of morels, you can also collect birch sap. This wonderful spring drink restores strength and invigorates.
Summer-autumn location of mushrooms
The most pressing question for lovers of the forest and its gifts is where to pick mushrooms in the Leningrad region in the summer. The easiest way to answer this question is with a map of mushroom spots. There are successful routes on it, drawn up by experienced hunters for the gifts of the forest (mushroom places in the Leningrad region are marked with symbolic icons). However, it should be remembered that year after year is not necessary. And if the mushroom places of 2014 were the same, then there is a high probability that in 2015 the gifts of the forest will choose other locations.
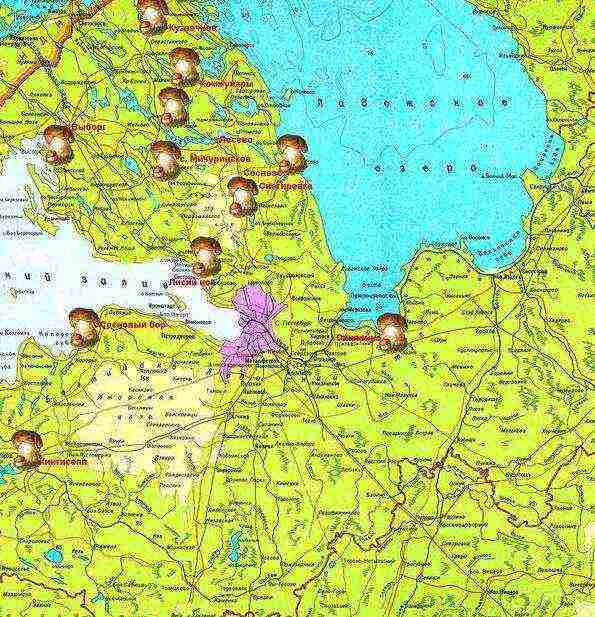
However, there are statistics. And she, as you know, is an incredibly stubborn and precise thing. Let's turn to her with our mushroom question.
Specific habitats of forest gifts
So, mushroom spots in the Leningrad Region - where are they?
- Near the village of Sinyavino (59.54 N, 31.04 E). The settlement is located 45 km southeast of St. Petersburg. You can get to it both by car and by train. The latter runs 3 times a day from the Ladozhsky railway station. Boletus, chanterelles and mushrooms grow in the forests around the village, sometimes you can find porcini mushrooms and podgruzdi.
- In the forests around Vyritsa (59.24 N, 30.20 E). This is again the southern direction: the town is located 60 km south of St. Petersburg. At the end of July, chanterelles, milk mushrooms and russules grow in local forests. In order not to get lost, you should walk along the Oredezh River. In addition to picking mushrooms, the traveler has every chance to get vivid impressions of summer nature.
- In Sosnovo (60.33 N, 30.14 E). Mushroom places in the Leningrad Region are unthinkable without this wonderful place.The forests around the village are famous for a variety of mushrooms. What gifts of the forest can you not find in the coniferous and spruce forests that surround this settlement! These are boletus, boletus, and boletus, and boletus in the area of sun-drenched glades! Closer to autumn, here it is quite possible to pick up a basket of milk mushrooms or chanterelles for pickling. You can devote a whole day to picking mushrooms in Sosnovo. It will be remembered, like everything beautiful that is associated with summer and wonderful nature.
- Near the village of Stekolnoye, which is located in the Tosno district (59.33 north latitude, 30.54 east longitude). Local forests invariably delight mushroom pickers with a rich harvest of young boletus. But no one promises that the search for these noblest representatives of flora (or fauna?) Will be easy. We'll have to stray, look, strain logic ... Only a patient and resourceful mushroom picker will be generously rewarded according to his deserts.
In this section, we have listed the coordinates of mushroom sites in the Leningrad Region. We hope they will help everyone find their favorite gifts of the forest.
Gourmet treat
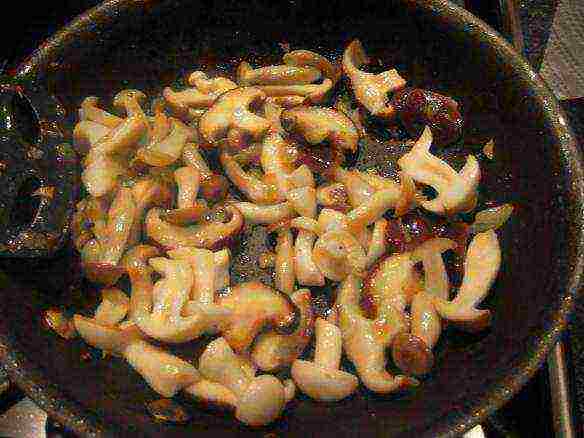
We simply have no right to ignore any mushroom dish. Let's tell you a recipe for a simple but incredibly mouth-watering delicacy.
Here you have returned from nature with a basket of boletus mushrooms, there is not much to eat at home, and hunger has been tormenting for more than one hour ... Right now, you can turn a small part of the catch into a hearty dish that will satisfy your hunger until the end of the day ... So, the recipe! Required Ingredients:
- White mushrooms;
- salt;
- onion;
- butter.
Thoroughly wash 5-6 pieces of young boletus. Dry them with a napkin, cut into medium-sized slices.
Melt butter in a skillet. Finely chop the onion, pour it over the frying. The whole point is that the onions do not burn, but form a viscous substance together with butter. When this metamorphosis has taken place, add chopped mushrooms to the onion. Simmer for 10 minutes over medium heat, then salt the dish. Then simmer over low heat until tender. Put it on a plate.
If any summer greens are found in the refrigerator, then finely chop it and sprinkle on the dish. Bon Appetit!

Interesting Facts
There are many fascinating stories associated with mushrooms, but we will pay attention to the most useful ones for those who like picking. Go:
- To twist or cut the mushroom? How is it correct? Both methods are acceptable. Scientists have come to the conclusion that careful twisting of the mushroom does not harm the mycelium.
- Some fly agarics are not only edible, but also delicious! The edible is a gray-pink representative of this family. You can find it in the summer, in the tall, spiky grass. You should take young and fresh-looking fly agarics. Before frying, these mushrooms will have to be boiled and drained.
- Russula and porcini mushrooms can be eaten raw. The name of the first mushroom already suggests that you can eat it just like that. The second one generally has an excellent taste (slightly sweetish). There is always something to eat in the forest!
- Chanterelles are enemies of parasites. Inside this red mushroom contains a substance that destroys helminths on the spot. Eating chanterelles is the best prevention against parasites.
- Glowing mushrooms. It is not joke! Some forest gifts glow fancifully in the darkness of the night. Science knows rare species that flicker with an inviting green-yellow light. It feels like there are electric bulbs inside them.
 Mushrooms are unique organisms. And the process of collecting them is an addictive affair. It is worth remembering: interesting mushrooms love logical searches and extraordinary solutions. He who seeks will always find. Good luck!
Mushrooms are unique organisms. And the process of collecting them is an addictive affair. It is worth remembering: interesting mushrooms love logical searches and extraordinary solutions. He who seeks will always find. Good luck!
Calendar of the mushroom picker of the Leningrad region and other northern places of Russia
Published: 30 August 2011
There are many mushrooms around St. Petersburg, and there are many mushroom places in the Leningrad Region. And although there is no dispute about tastes, the mushrooms are delicious. Think of a frying pan of chanterelles in homemade sour cream or porcini mushrooms in cream.And how do you like stewed potatoes with boletus mushrooms, and if it is also cooked in a Russian oven? And roast mushroom from freshly picked platter ... And delicious mushroom soup from dried whites, yes in February evening, and on top fried, hot onion ... And so that a spoon in it stood from cold sour cream with sourness with butter eyes spreading over the hot soup ... such a soup will go well - you can think of it yourself! Want some delicious mushrooms? Then we go to nature - to walk, relax from the city noise, breathe fresh air, admire the scenery, improve health and enrich our diet!
Edible mushrooms in the Leningrad Region provide a huge selection and variety of mushroom species. Everyone knows bright boletus and mouth-watering boletus boletus, rich in appearance and taste, royal white and boletus, the most delicate chanterelles, boletus and mushrooms melting in the mouth, an unsurpassed snack for any table of waves, milk mushrooms and honey mushrooms. You can also type exotic for many, but delicious morels, lines and even milk raincoats familiar to many strangers. Mushrooms provide a huge variety of mushroom recipes and even help to heal on occasion.
So - we look at the mushroom calendar and select mushrooms, look at the weather outside, decide on the route, prepare a set of mushroom pickers, set the alarm for 5 o'clock in the morning and see dreams about prey. However, the prey will dream after a successful mushroom hunt.
Let's decide on the season. The mushroom season in the forests near St. Petersburg is considered to be from August to November, but edible mushrooms can be found in the Leningrad region almost all year round. Be guided by the mushroom picker calendar below - it covers the most popular of the more than 200 species of edible mushrooms growing in the forests of the Leningrad Region.
| Mushroom picker calendar for the Leningrad region | ||
| Collection month | Types of mushrooms | Collection features |
| January | Oyster mushroom | For mushroom pickers, the empty month, there is practically nothing to look for in the forest. But if the winter is warm, you can find fresh oyster mushrooms. They usually grow on trees, the cap of such a mushroom is one-sided or round, the plates run down on the leg, as if growing to it. It is not difficult to distinguish oyster mushroom from inedible mushrooms - it has a cap that is completely skinless to the touch. |
| February | Oyster mushroom, wood mushrooms | If the thaw has not come, there is practically nothing to look for in the forest |
| March | Oyster mushroom, wood mushrooms, talker | There are practically no mushrooms, but at the end of the month the first snowdrops may appear. |
| April | Oyster mushroom, wood mushrooms, talker, morel, stitching | Snowdrop mushrooms are quite common - morels and stitches |
| May | Morel, stitching, oiler, oyster mushroom, raincoat | Most of the mushrooms can be found not under the trees, but in the clearings, in the dense grass. |
| June | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey mushroom, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, raincoat | In June, mushrooms of the highest (first) category begin to appear. |
| July | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, raincoat, honey mushroom, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, flywheel | There are already a lot of mushrooms - both in the glades and under the trees. In addition to mushrooms, strawberries and blueberries are already found. |
| August | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey mushroom, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, flywheel | At this time, mushrooms can be found almost everywhere: in the grass, under trees, near stumps, in ditches and trees, and even in city squares and on the sides of roads. In addition to mushrooms, lingonberries have already ripened, and cranberries appear in the swamps. |
| September | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey mushroom, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, flywheel. | September is the most fruitful month for mushrooms. But you need to be careful: autumn comes to the forests, and in the bright foliage it is difficult to see the multi-colored caps of mushrooms. |
| October | Valuy, oyster mushroom, mushroom, honey mushroom, champignon, boletus, porcini mushroom, milk mushroom, flyworm, russula | The number of mushrooms in the glades begins to decrease. In October, it is better to look for mushrooms near stumps and under trees. |
| November | Butter dish, green tea, oyster mushrooms, woody mushrooms. | Freezing begins, and there is a high probability of finding frozen mushrooms. |
| December | Oyster mushroom, wood mushrooms | There are almost no mushrooms anymore - but if you're lucky, you can find remnants of the autumn abundance |
Return to the homepage
You can
leave a comment
, or
Trackback
from your site.

2014 and 2015 are critical years for the Russian economy. Foreign manufacturers and suppliers are leaving the market, and instead, domestic entrepreneurs are trying to diversify production and enter new niches while they are not busy.
What is happening with mushroom products now? Have the trends in the mushroom market changed, and is it worth entering it? Let's take a look at the current situation.
For reference:
- Estimated market capacity - 9,120,000,000 rubles. *
- Share of imports, in% 85 - 90%
* Estimated indicator, sales in tonnes multiplied by average wholesale prices.
The Russian mushroom market is conventionally divided into 2 main segments:
- wild;
- cultivated.
In this article, only the second segment will be considered, since it is this segment that can be evaluated as a full production cycle.
Cultivated mushrooms, in turn, are divided into:
- champignons;
- oyster mushrooms;
- flammulin;
- shiitake, etc.
New trends in the mushroom market
When studying the market, one should first of all remember the ban on the import of imported products. At the beginning of the introduction of the sanctions, mushrooms were almost the only product that they did not affect, but from August 6, 2014, mushrooms also came under the embargo. The list includes the whole group TN VED 0709 Other vegetables, fresh or chilled, which also includes these products.
This factor will undoubtedly lead to an increase in the number of domestic manufacturers. Today it is planned:
-
Start of production of oyster mushrooms in the Azov district of the Omsk region by the company "Gribnaya Polyana". The management plans to grow up to 18 tons / month (0.216 thousand tons / year), and before reaching the design capacity - at 60-70 kg / day. The volume of investments will be about 12 million rubles.
The choice of mushrooms by the initiators of the project was based on the fact that the production of oyster mushrooms is cheaper than mushrooms. In the future, the company also plans to process mushrooms.
- Opening of oyster mushroom production in Shemysheisky district of the Penza region by an investor from China. According to the Penzenskaya Pravda Information Center, about 90 million rubles will be invested in the project, which means that production volumes will be several times higher than that of the previous company. It is estimated that up to 1.6 thousand tons per year can be predicted
-
Opening of a mushroom growing complex in the Kaliningrad region. A potential investor will be Agroprom-MDT, which is also considering Lipetsk, Voronezh and Orel regions.
The investment in this project is about 200 million rubles, and the production volume is planned at the level of 2.5 thousand tons / year of fresh champignons.
- Truffle production in Novorossiysk - "Truffle Valley". This is the most interesting project of the year, since such a company is the first in Russia, where not only mushrooms will be grown (on an area of 200 hectares), but also frozen and preserved (workshop area - 20 thousand m2 (2 hectares)). The investment cost of the project is 203.9 million rubles.
Such projects are very interesting due to the fact that about 85-90% of the Russian market was previously occupied by imports, mainly from Poland.
Diagram 1. Distribution of importing countries by shares,%, 2013
Now that the embargo has been imposed, entrepreneurs are undoubtedly finding other ways to develop the industry.
Consumption of mushrooms in Russia
The demand for mushrooms in general (including truffles) in Russia has been growing since 2009. At the same time, it cannot be said that it is very active. From 2009 to 2013, the volume changed only by 4.1%, eventually reaching 155 thousand tons in physical terms. In 2014, it is forecasted that the growth rate of demand will keep the trend (2% per year), and will amount to 158 thousand tons
Diagram 2. Volume of demand and volume of sales of cultivated mushrooms in kind, thous.tons, 2009-2014 Source: Federal State Statistics Service
A specific feature of the market is that the demand for mushrooms greatly exceeds the sales volume (2 times): in 2013, the sales level amounted to 75 thousand tons.
The growth rate of sales in 2014 can be predicted at the level of 1% due to market growth in the first three quarters of the year, as well as an increase in the supply of domestic players. Estimated in kind, it is 76 thousand tons.
In monetary terms, the market looks like this:
Diagram 3. Sales volume of cultivated mushrooms in monetary terms, thousand rubles, 2013-2014
A significant increase in the market volume in monetary terms is explained by an increase in product prices. By the end of 2014, the purchase price of cultivated mushrooms has doubled (178.8 rubles / kg in 2014 against 90.6 rubles / kg in 2013).
Import of products
As already mentioned, the market is import-dependent - in 2013, the volume of imported cultivated mushrooms amounted to 67 thousand tons. But due to the current situation in the country, one should not expect that in 2014 the volume of supplies will exceed this indicator, rather, on the contrary, it will decrease.
A significant part of the deficit will still be able to be covered at the expense of entrepreneurs who quickly responded. For example, in the Leningrad region, a peasant farm for the industrial cultivation of oyster mushrooms has already been launched.
Mushroom production volumes
Until 2014, mushroom cultivation inside the country was not at all developed, as imports crowded out domestic entrepreneurs, making it impossible to compete freely. Thus, in 2013, the production volume instead of the expected growth decreased by 2.6%, and amounted to 7, 87 thousand tons. This low level was last recorded in 2005.
But at the moment, in the face of the forced closure of borders, new complexes for the cultivation of cultivated mushrooms are being launched. With the launch of the industrial capacities presented above, the production volume will increase by at least another 6.1 thousand tons.
Diagram 4. The volume of production of cultivated mushrooms in Russia, thousand tons, 2012-15.
In 2014, there will not yet be a tangible growth in the domestic market (only 8.02 thousand tons), but a sharp jump is expected in 2015. Indicators will double compared to 2013, and will be at the level of 14.2 thousand tons.
But, for the complete import substitution of cultivated mushrooms, the capacities on the territory of the Russian Federation are still not enough. It will be possible to cover only 10% of imported products, and in order to satisfy the entire deficit on the market, it is necessary to produce at least 158 thousand tons of mushrooms per year.
Therefore, opening new enterprises for the production of mushrooms is today a very interesting business.
Production of cultivated mushrooms (champignons)
There are three approaches to the production of cultivated mushrooms in the world today:
The first is characterized by low investment and extensive use of labor. Thus, about 12 kg of crops can be harvested from a square meter of land. The approach has been used successfully in China and Hungary.
The next approach requires moderate investment and a high degree of manual labor (works effectively in the US). With this approach, the yield can be increased to 30 kg per square meter.
The third includes a high level of investment (due to complete automation of production) and minimal use of manual labor. Used in Holland. Allows harvesting up to 33 kg / m2.

Figure 1. An example of mushroom cultivation
Feasibility study of the project
If you have a minimum start-up capital, and you have chosen the first approach, then first of all you need to find a place where the products will actually be produced. The room should include:
|
1. Premises for making compost |
400 m2 |
1 mini tractor, 2 grain crushers (one for straw, the other for droppings), central water supply and sewerage. |
|
|
2. Rooms for compost pasteurization |
50 m2 |
Steam boiler, steam expander, steam supply system (metal pipes) with automatic supply system |
|
|
3. Room for growing mycelium |
50 m2 |
Heating system, ventilation system, irrigation system. Racks |
1 000 |
|
4. Premises for growing mushrooms |
50 m2 |
1 000 |
|
|
5. Warehouse for finished products |
50m2 |
Shelving. Heating system. |
|
|
6. Annual rent of premises |
600 m2 |
The cost of renting production space is about 150 rubles / m2 |
1 080 |
|
Total |
4 416 |
||
Taking into account all registration fees, etc., it is necessary to invest approximately 4.5 million rubles. But this amount does not include the costs of working capital for the purchase of compost, mycelium, as well as the costs of employees' salaries.
In order to carry out 1 production cycle (lasting 2 months), you will need:
-
Compost. You will need to purchase:
straw (2000 rubles / 1000 kg);
litter (600 rubles / 300 kg);
other (another 500 rubles).
Total for 30 tons of fertilizer will require about 63 thousand rubles.
- Staff. It would be optimal to attract 6 employees who would work in shifts. Assuming that the salary of each will be 25 thousand rubles, the payroll for 2 months will be 300 thousand rubles.
- Workshop maintenance costs. Let's take about 100 thousand rubles.
In total, we will need 463 thousand rubles for 1 full cycle.
When calculating expenses for a year, it is worth taking 5 full cycles. Still, this is the production of mushrooms and sometimes their maturation can last up to 3 months.
Price analysis
Wholesale prices for domestic champignons have recently increased: before the embargo - 85-100 rubles / kg, after - 170-200 rubles / kg.
|
Price 1 |
190-200 |
|
|
Price 2 |
||
|
Price 3 |
||
|
Price 4 |
||
|
Price 5 |
||
|
Price 6 |
||
|
average price |
For the Russian manufacturer, the rise in prices is positive, since earlier they lost to competitors from Poland due to the higher cost of production - about 80 rubles / kg.
Now let's see what we will earn. From 30 tons of compost, about 6 tons of mushrooms will be obtained (the return is about 20%). With a purchase price of 180 rubles. per kilogram we will get 1,080 thousand rubles. income.
If we deduct expenses and return on investment (10%), then our profit will be 555.3 thousand rubles. for the production cycle. Not bad enough, because not every business can boast of the fact that already from 2-3 months the enterprise will reach self-sufficiency.
These indicators were calculated taking into account the fact that cultivation will take place naturally without the involvement of any growth stimulating funds. But if an entrepreneur has a desire to speed up the process, then there are such options on the market. With their help, the production cycle can be shortened to 3-4 weeks, and the revenue can double.
The forecast is undoubtedly optimistic and simplified, since inflation, taxes and other economic and political factors are not taken into account, but based on the current situation in the country and market trends, the mushroom business should be recognized as very profitable.
Note: Typical business plan for a mushroom farm, price 24,000 rubles.
Material prepared by Success Brand Management Consulting Group
Download free marketing research of the mushroom market in Russia


