Content
- 1 Greenhouse requirements
- 2 Selection of vegetables
- 3 Seedling preparation
- 4 Soil and fertilizers
- 5 Care features
- 6 Preparation for growing greenery in a greenhouse
- 7 Features of growing vegetable greens in winter
- 8 Growing onions on a feather
- 9 Growing dill in a greenhouse
- 10 Growing parsley in a greenhouse
- 11 What's next?
- 12 Growing greens in a greenhouse in winter
- 13 Growing seedlings of vegetables in a winter greenhouse
A capital greenhouse made of polycarbonate allows you not to interrupt the cultivation process even in the coldest time. It is necessary to choose what can be planted in the greenhouse for the winter, based on considerations of economic feasibility, personal preferences and the ability to fully care. It is important to study the needs of the plants, recommendations for ensuring reliable operation and possible difficulties. With a competent approach and investment of certain funds, it is easy to organize even your own business.
Advantages and disadvantages of winter landing
For the winter, seeds of frost-resistant crops are planted in the open ground that can withstand the harsh climate of the cold period without damage. A positive aspect of sub-winter planting is the shift in the beginning of the growing season to an earlier time, which speeds up the possibility of harvesting by two to three weeks.
The seeds undergo stratification at a low temperature and are hardened, the seedlings are disease-resistant and strong, with powerful roots, and are less damaged by pests. The yield of such plants in a greenhouse in winter is usually much higher.

Greenhouse economy in winter
But there is always a threat of complete or partial death of seedlings if the weather is unstable with prolonged warming, contributing to their premature development. Insufficient snow cover may not cope with protective functions. It is necessary to consume more seeds during podzimny planting, since their germination rate is lower.
This can be avoided by sowing the necessary crops for seedlings or greens in the greenhouse in the fall. Even without heating the premises, plants have a chance to get some protection from strong temperature changes, flooding with melt water followed by its freezing, strong winds. With a sharp cold snap in winter, it is advisable to additionally cover the plants.

Greens in a greenhouse
Greenhouse crops at different times of the year
In the spring-summer period, polycarbonate greenhouses are used for the most capricious southern crops that are unable to ripen in the local climate, as well as for growing planting material for open ground. In winter, plants that are more adapted to the lack of light and heat can be planted, which will allow you to grow vitamin fruits or greens without damage.
Examples of plant selection
What can you plant for your family in the winter in a greenhouse? The main vegetables for all-season greenhouses are cucumbers, zucchini, and tomatoes. Eggplants and peppers are more demanding to external conditions and difficult to care for. Not every greenhouse is suitable for growing them. A variety of greens (onions, dill, parsley) are massively grown in winter, even in unheated rooms.

Unheated underground greenhouse
Before winter, you can plant popular root crops in the greenhouse - beets, radishes or carrots, but you should choose the most cold-resistant and early ripening varieties.It is advisable to fill the greenhouse with several types of plants with similar conditions.
Flower lovers can grow suitable varieties of roses, chrysanthemums, asters, lilies, crocuses and other flowering species. Also, in free areas, it is worth sowing vegetable and ornamental crops for seedlings for open ground, so as not to clutter up the window sills in the house.
What should be a winter greenhouse
The greenhouse should be with a strong and stable frame, located on an elevated site or on the south side of the house (outbuilding). It is advisable to deepen the foundation by about 0.8 m and additionally insulate it from the outside. A greenhouse for winter should be well lit by the sun and have a system of protection against flooding by ground and melt water.

An example of a winter building with a foundation
In winter, trouble-free heating systems (water, electric or air), ventilation and irrigation are important (better than drip - saves water consumption). Also, you can not do without installing additional lighting devices (better than LED). It is advisable to use vertical adjustment of the position of the lamps.
In the most severe frosts, the value of the air temperature in the room should not fall below +15 ° С, and during most of the time it should be within + 20-25 ° С.
What to sow in a greenhouse for the winter
Before planting vegetables or other crops in an unheated greenhouse, you need to find out the necessary microclimate parameters in order to contain a particular plant, because the temperature in such a room is low. Conditions in a heated greenhouse vary depending on its design and equipment, and the climate of the region. After all, heating devices have a limited resource, which is also affected by the cost of energy carriers.
What can be planted in an unheated greenhouse
The positive qualities of the greenhouse are the exclusion of the negative impact of atmospheric phenomena (strong winds, precipitation). Additional insulation measures (sealing all cracks, deepening the soil, using reflective screens and dark film) improve conditions in the greenhouse in winter. Biofuels are increasingly used, building warm beds on warming mixtures based on manure or straw.
If there are no devices for artificial heating, then the negative temperature in winter, especially in the northern area, does not allow growing any plants. In an unheated greenhouse, various cold-resistant horticultural crops successfully winter, which in open ground can freeze, get wet or weaken.

Using the greenhouse for forcing and storing flower crops
During the cold season, the greenhouse can be used as follows:
- sow parsley, lettuce, celery, early carrots and beets, radishes, which are harvested in spring;
- plant onion sets for seedlings or onions on greens;
- store during the dormant period the bulbs of flower crops (hyacinths, crocuses), as well as rhizomes of dahlias, chrysanthemums, followed by their cutting;
- add saffron, iris, daffodil bulbs for forcing flowers in February;
- place two-year-old insufficiently cold-resistant plants for wintering;
- sow flower and ornamental crops - lily, begonia, gloxinia, coleus;
- sow legumes, corn, thyme closer to spring for transplanting to open areas.
Growing greens
The weather conditions must be monitored and in the event of a sharp cold snap in winter, protect the plants in the greenhouse with the available covering materials.
Planting plants in a greenhouse with heating
After harvesting the summer-autumn harvest, thorough cleaning of the soil from plant residues, applying top dressing and sanitary-preventive work, it is necessary to finally decide what is better to plant in a greenhouse in the winter. You need to know the upper limit of the temperature that is stably maintained in the greenhouse. When its value is less than +15 ° С, many plants stop developing and may die or shed fruit ovaries.
A polycarbonate greenhouse with heating can be used for breeding early-ripening varieties of vegetables (cucumbers, tomatoes), getting seedlings, growing greenery or flowers (peonies, roses, dahlias) year-round. Rational use of the area will help the installation of shelving, the use of the trellis method or vertical beds.
A more costly and time-consuming, but interesting activity is to plant strawberries for the winter. It is worth trying the convenient way of placing the bushes in bags of soil mixture, in pipes or Dutch longline technology. It is important to stock up on high-quality seedlings that can give a good harvest, better than remontant varieties.

Winter strawberry
In a heated room, the soil does not freeze, which contributes to its disinfection from pathogens and various pests. Planting green manure plants (mustard, rye, vetch) will help improve the general condition of the soil, saturating it with useful substances and microelements, loosening and eliminating insects and weeds.
Growing cucumbers in winter
Growing cucumbers in the autumn-winter turnover, compared to other vegetable crops, is not so troublesome and costly. They are moderately demanding on temperature and its changes, and the yield of high-intensity hybrids, subject to the recommended microclimate parameters, is at least 30-35 kg / m2.
First of all, suitable hybrids are selected. These should be shade-tolerant, fairly compact early ripening varieties. The timing of sowing seeds for seedlings to obtain a winter harvest in the greenhouse should be from mid-October to mid-November. In the first 5 days, seedlings need round-the-clock supplemental lighting, then 16-18 hours.
After 2.5-3 weeks, in the presence of a developed root system and four true leaves, they are planted. The arrangement of the bushes is planned in such a way that the leaves absorb the maximum amount of available light, and do not allow shading. The average planting density is approximately 5 plants per 2 m2.

Growing greenhouse cucumber
They adhere to these basic recommendations for caring for cucumbers in winter:
- maintain the temperature during the day at least + 20-22 ° С, at night - 16-18 ° С, and the relative humidity at the level of 70-75%;
- watered regularly with water at a temperature of + 20-22 ° C;
- bushes are tied up and twisted, all side shoots are removed completely;
- to increase the fruiting period, six leaves are removed weekly, but not more than three at a time.
- the harvest is harvested daily, while making sure that the load on the lashes is not excessive.
Planting greenery in a greenhouse
Even a gardener with little experience can cope with the cultivation of unpretentious greens in a greenhouse in winter - dill or parsley. The yield of these crops is high, and labor and seed and fertilizing costs are low. They have enough ordinary soil, simple care (watering, weeding) and a temperature of about + 15 ° C with a humidity of about 80%.
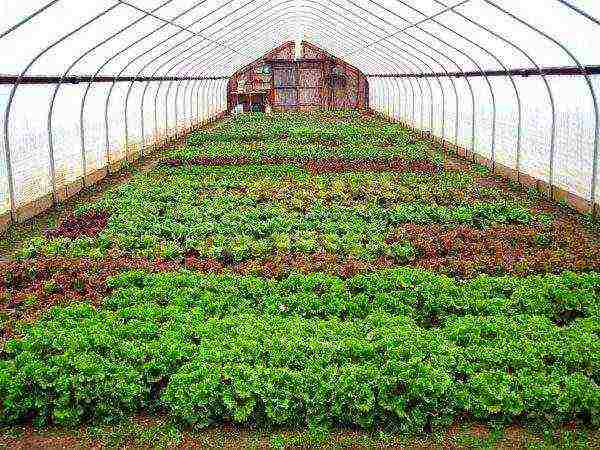

Growing different types of greens
Dill with parsley grows successfully together with other plants in free areas. Adequate light is required for dill. The prepared seeds are sown directly into the ground, and the crop maturity is reached in one and a half to two months. For continuous harvesting, sowing is done every two weeks.
In winter, green onions can also be planted, which for good development needs a daytime temperature of +20 ° C (at night - 12-15 ° C). Onions need fertile soil, saturated with organic matter and minerals (potassium and phosphorus). Pour cold water on the onion daily. The crop is harvested in about a month.
Head, leafy and varietal varieties of lettuce thrive in winter indoors. The culture requires a loose soil enriched with organic matter, a temperature of about + 18-20 ° C, ensuring daylight hours within 12 hours, watering two to three times a week. Early maturing species give a harvest in three weeks.

Growing flowers for sale
Growing crops for sale
Even in a small home-made greenhouse, skillful hands can harvest a good harvest with surplus. And a modern and economical polycarbonate greenhouse makes it even more possible to grow greens, vegetables or flowers, not only for personal consumption, but also for sale.
When choosing what to plant in a greenhouse for sale in the winter, one should take into account the economic feasibility of energy costs and the possibilities of a particular greenhouse structure. In the northern regions, the costs are higher, but accordingly the price of fresh products is higher.
To organize a greenhouse business, it is required to draw up planting plans and calculate the necessary costs for planting material, soil preparation and fertilization, provision of agrotechnical conditions (heating, lighting, water), and fight against diseases and pests. It is worth studying the needs of the sales market.
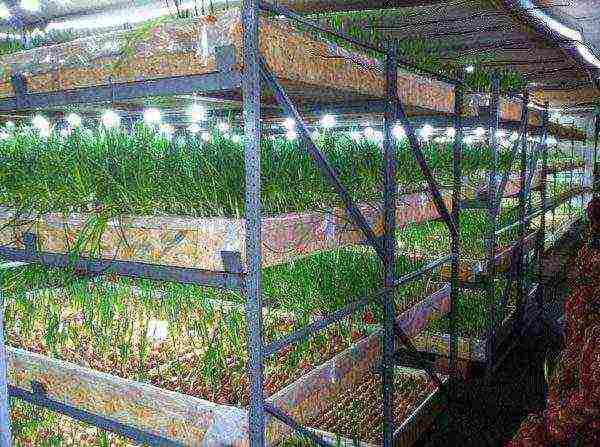

Growing greens
The most suitable market crops are fast maturing and expensive. The most common cultivation in winter is to sell greens (green onions, parsley, dill, lettuce, mint and basil) or seedlings (peppers, tomatoes, flowers). Some people recommend mushrooming, pointing to a profitable and easy marketing.
The flower business is considered the fastest payback. Often flower products (tulips, daffodils, roses, hyacinths, crocuses) are grown for sale on February 14 and March 8.
Video: features of year-round cultivation
With a year-round operation of the greenhouse, additional efforts have to be spent not only on maintaining the optimal temperature regime, but also on supplementary lighting of plants in a winter time poor in sunlight. In order to save and facilitate the operations performed in winter, useful inventions of experienced specialists can be used.
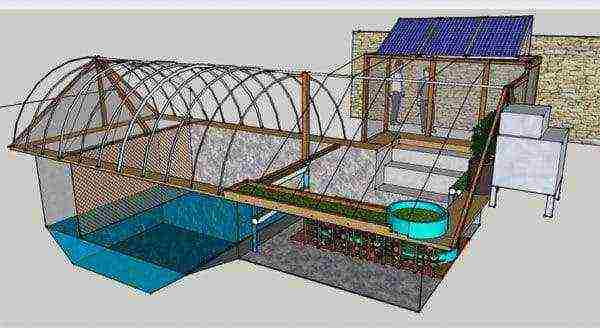
Underground greenhouse
Projects have been developed for structures with high thermal insulation properties that do not require heating devices or with unconventional heating. For example, a thermos greenhouse or a deepening in a foundation pit up to two meters.
Particular attention is paid to the condition of the soil, since during continuous intensive agrotechnical work, its rapid depletion occurs. A modern and convenient way of growing in a greenhouse is soilless, based on a hydroponic system. At the same time, the plants feed on a special solution that contains everything necessary for full development.
Growing vegetables and greens in winter does not negate the fight against harmful insects, since the spider mite and whitefly can be active all year round. Preventive measures should be taken and lesions detected in a timely manner.
Video: What is planted in the greenhouse in the winter
Video: Errors when forcing tulips
Permanent greenhouse owners can get the most out of them in cold weather. It is important to correctly assess the costs, familiarize yourself with advanced technological methods, advice from specialists and experienced owners of household farms. A valuable winter harvest or a bright bouquet of flowers will be a reward for the work done.

Growing vegetables in a greenhouse - simple and effective way provide your family with valuable and healthy products. Most of the farm owners uses greenhouses and greenhouses in the spring-autumn period, extending the harvest until frost.
However, an insulated shelter equipped in accordance with all the rules helps to pick fresh vegetables even in winterwhen vitamins are especially needed. The greenhouse will allow you to earn money on growing vegetables in the cold season, when the demand for them is especially high. How to grow vegetables in a greenhouse in winter, we will consider below.
…
Greenhouse requirements
How to equip a greenhouse for growing vegetables in winter? When constructing a year-round greenhouse, it is important to meet all the conditions for successful plant growth: ensuring the required temperature and humidity, the amount of sunlight, the possibility of airing. At the same time, it is necessary to calculate the costs of heating and lighting the greenhouse so that they do not block the benefits of winter vegetables.
Year-round greenhouse must have a solid foundation... To provide the required height for the plants, the structure can be slightly deepened. This little trick will help you save on heating costs and not lose the natural light you need.
It is best to grow vegetables in a medium-sized greenhouse, up to 20 m long and 2.5-3 m wide... The optimal roof design is pitched. The north wall can be laid out with cinder blocks or wooden beams, protecting the plants from the winter wind. The greenhouse should have a vestibule and double doors. Comfortable air vents.
Most often, capital greenhouses are made on a welded frame with an anti-corrosion coating. Such a foundation will stand for many years, the greenhouse will be strong and reliable. As a coating, you can use dense polyethylene or tempered industrial glass. But the most expensive and high quality material - cellular polycarbonate. It transmits light well and retains heat even in the most severe frosts.
 For heating, pipes laid on both sides of the greenhouse are suitable. The heat source will be an electric boiler. It is possible to heat the structure with modern wood-burning stoves that save fuel.
For heating, pipes laid on both sides of the greenhouse are suitable. The heat source will be an electric boiler. It is possible to heat the structure with modern wood-burning stoves that save fuel.
Increasing the temperature inside the greenhouse will help and biofuel - rotted manuremixed with straw. The mixture is laid out under the top layer of soil. Biofuel is suitable for growing cucumbers, radishes and other crops that are particularly heat-demanding.
Selection of vegetables
In a winter greenhouse can grow all kinds of crops, from popular tomatoes to cabbage lettuce and herbs. Among the most popular and fruitful vegetables:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- radish;
- head salad;
- eggplant;
- Bell pepper;
- various varieties of cabbage;
- zucchini.
It should be borne in mind that crops have different requirements for humidity and temperature, so they need to be placed in separate greenhouses. For example, tomatoes and bell peppers require moderate moisture (no more than 60%) and frequent ventilation. Such a regime is destructive for cucumbers, which need a humid and hot atmosphere.
In the cold season, the greenhouse effect with high humidity is easier to maintain.
Therefore, many novice gardeners focus on popular and productive crops that need just this mode: cucumbers and radishes.
Choosing varieties, it is worth giving preference to hybridscultivated specifically for indoor use. These plants have a shortened growing season and do not require insect pollination. Most greenhouse varieties have good yields and pest resistance.
Seedling preparation
Some gardeners buy grown seedlings at markets and other farms. But grow your own seedlings from seed much more profitable... In addition, the process can be started at any time to ensure a year-round harvest.
 It is better to grow seedlings in a separate greenhouse or in a house. Seed germination conditions are different from those to which adult plants exist. In some cases, a lower temperature or higher humidity is required. In the same greenhouse, you can place seedlings of different crops with similar requirements for agricultural technology.
It is better to grow seedlings in a separate greenhouse or in a house. Seed germination conditions are different from those to which adult plants exist. In some cases, a lower temperature or higher humidity is required. In the same greenhouse, you can place seedlings of different crops with similar requirements for agricultural technology.
If there is no opportunity to organize a greenhouse for seedlings, the seeds can be germinated on a separate rack in a common room located as close to the lamps as possible. The seeds can be germinated in peat cups, but this method is not suitable for eggplants and other crops with a weak root system. For year-round cultivation, the conveyor method is recommended.
Seeds are sown every 2 weeks, which makes it possible to get seedlings of different ages. If different crops are planted, after a year it is recommended to alternate them... Eggplant seedlings are planted in the places that were occupied by tomatoes, and cucumbers are replaced with radishes or zucchini.
This technique does not allow the soil to deplete. The first sowing can be started in January.Depending on the growing season of a particular plant, the seedlings will ready for transplant in 3-5 weeks after sowing seeds.
Soil and fertilizers
How to grow vegetables in a greenhouse all year round? Vegetables need light, not too acidic soils. For most crops, a mixture of garden soil, sand and peat is suitable.
Before laying in the greenhouse the soil needs to be calcined or disinfected using an aqueous solution of copper sulfate. Such treatment kills harmful microorganisms and insect larvae.
After processing, ash or a complex of mineral fertilizers can be added to the soil. The mixture is thoroughly loosened and distributed over the ridges. In the greenhouse, you can organize both ground and rack cultivation. The racks are suitable for radishes, head lettuce and other small crops. Some vegetable growers successfully grow tomatoes and zucchini on shelves.
Indoor ground is quickly depleted, so the plants in the greenhouse need to be constantly fertilized. Rotted compost or complex mineral fertilizers are added to the soil. This treatment is repeated every 2 weeks, before feeding the soil must be loosened and weeds removed. During the period of active growth of seedlings, special attention should be paid to nitrogen fertilization, from time to time the plants can nourish with medicinal preparations.
Care features
In winter, you need to maintain an average daily temperature of 18 to 22 degrees. Overheating has a bad effect on tomatoes, eggplants and bell peppers, and a cold snap can have a detrimental effect on radishes and cucumbers. On frosty days, greenhouses are not ventilated, when the outside temperature rises, the vents need to be opened 1-2 times a day.
Vegetables in the greenhouse watered 2-3 times a weekwhen the soil dries up a little. It is advisable to use water at the same temperature as the air in the greenhouse. Cold water can cause shock and slow plant development.
 As the plant grows, it is necessary to tie up the stems. Cucumbers need special supports to be mounted on the roof of the greenhouse. With their help, the stems of plants can be directed in the right direction, which is especially convenient for rack cultivation.
As the plant grows, it is necessary to tie up the stems. Cucumbers need special supports to be mounted on the roof of the greenhouse. With their help, the stems of plants can be directed in the right direction, which is especially convenient for rack cultivation.
With the onset of fruit formation it is recommended to remove the lower leaves on the stems. Excessive green mass interferes with fruit development. In addition, this technique will improve air exchange and access to sunlight, plants will not be affected by pests and fungi.
In the greenhouse it is important to maintain the atmospherefavorable for plants. The humidity level will help increase watering of heating pipes and floor with water, as well as placing open tanks in the room. For the successful ripening of tomatoes in the greenhouse, you can put tanks with an aqueous solution of mullein. Good increase moisture and hot water barrels, moreover, they additionally heat the room.
With conveyor cultivation, harvesting takes place all year round. In early summer and late autumn, preventive treatment of premises with partial replacement of soil and thorough washing of all surfaces is recommended. After airing and fertilizing, a new stage of planting begins.
Success growing vegetables in a greenhouse in winter, depends on the region... The most profitable option is to use greenhouses in temperate and climates. Regions with short summers and long frosty in winter will require high heating costs.
In such an area, it is more advisable to extend the summer period until the end of October and practice early planting in heated soil. Using correctly selected varieties of vegetable crops, you can achieve a good harvest.
Simple innovations in the design of greenhouses for growing vegetables all year round, in the video below:
In a small dacha or a large local area there is always a place for a greenhouse, which can be used almost all year round, including the greenhouse off-season, to grow fresh herbs for the dining table.
In winter, in heated greenhouses in cold regions and unheated ones in the south, you can grow dill, parsley, salads, celery, and onions. Greens and onions, as a rule, belong to early ripening vegetables with a short growing season, which allows you to harvest several crops during the autumn-winter season and constantly have greens on the table.
Greenhouse grown in winter
Preparing to grow greens in a greenhouse
You can grow greens in the autumn-winter period in 2 ways:
- using the main area. But this is not always desirable. Especially if the soil has already been prepared for the main greenhouse crops;
- on the additional area created by the racks for placing boxes and other containers for greenery. This is the easiest and cheapest option and is a win-win for beginners.
Preparation for growing greenery in greenhouses:
- Knock down the racks (or 1 rack),
- Purchase boxes and other containers,
- Prepare the soil mixture and fill the container, sign for which crop,
- Enter in the garden diary a list and agrotechnical requirements for the culture,
- Purchase the required seeds.
That is, perhaps, all the preparatory work. With the acquisition of practical experience, it is possible to introduce other crops, except for dill, parsley, onions on a feather. You will get a rack culture rotation, and even compacted. Try it and you will definitely succeed.
Features of growing vegetable greens in winter
For winter cultivation, crops are usually selected that are unpretentious to care, do not require special temperature and light conditions. A short growing season makes it possible to harvest several harvests during the winter season.
An important role in winter cultivation is given to the location of the crop. So, dill tolerates shading and therefore it can be placed in a greenhouse in low-light places, the salad is so unpretentious that it grows in any conditions, and parsley requires lighting and a certain thermal regime.
Growing onions on a feather
Onions on a feather are the most popular crop in winter. The specific taste perfectly complements any dish, but also helps to strengthen the immune system, contains a huge list of vitamins necessary for the body.
For growing in a greenhouse, the following varieties can be recommended: Bessonovsky, Karatalsky, Arzamas, Strigunovsky, Rostov onions (early maturing). For forcing, bows are used that do not have a dormant period and after harvesting, are ready for the formation of new crops (multi-tiered, slug), as well as species with a very short rest period - chives and batun onions.
Preparatory work
So, from boxes and other containers on the shelves, a prefabricated plot has been prepared, convenient in that it is always possible to transfer crops and place them next to the desired neighbor. Under the onion, prepare a simple soil mixture of garden soil and peat or other loosening material. We spread the film to the bottom, pierce several holes (in case of waterlogging) and fill it 2/3 with the prepared substrate.
Sprinkle and mix nitrogen fertilizer with the top layer of the soil substrate. Since onions for feathers and harvesting are scheduled in a short time (modified forcing method), the dose of mineral fertilizers should not exceed 10 g / sq. m of the total area of boxes. If the soil is depleted in nutrients, we fertilize the prepared soil with 15-20 g of nitroammofoska per sq. m. We water the soil with a warm solution of trichodermine or planriz from fungal diseases and leave the soil to ripen.
Preparing and planting bulbs
- The bulbs left for winter forcing are calibrated by size. It is advisable to occupy a separate box with one-size planting material. The most acceptable turnip is 3-5 cm in diameter.
- We cut off the neck of the onion with a pruner, even if it is germinated. Reception helps to interrupt the dormant period in this culture.
- Pour the prepared onion into separate bags or knots made of gauze or other thinned material and lower it for 10-15 minutes in water heated to +40 .. + 45 ° С. You can immediately use a 0.5% solution of potassium permanganate.
- We immediately plant the processed bulbs in a prepared container and place them on the shelves or racks of the greenhouse.
- We plant the turnip at a distance of 1-1.5 cm from each other. The distance between the rows of bulbs is at least 2-3 cm. The heads are buried 1/3 into the ground.
Covering material as additional protection against frost in the greenhouse
Greenhouse onion care
Onion care includes watering, feeding, regulation of temperature and light conditions.
Watering
During forcing, the onion is watered 2 times. After planting, a plentiful rate until wet. The second - after 1.5-2.0 weeks, with a fine-mesh watering can with warm water at room temperature. The watering rate correlates with the soil condition (the more drying, the higher the watering rate). The week before the mass cutting, the onion is watered for the last time. If the onion is used gradually (if necessary), then the soil is kept moist (not wet).
Top dressing
If the soil is fertile enough, then it is undesirable to feed the culture. On depleted soils, top dressing is carried out 1 time with a solution of nitrophoska (10-15 g / 10 l of water) or ammonium nitrate (15-20 g / 10 l of water) 2 weeks after planting. For feeding, you can use a solution of a mixture of 20 g of water-soluble superphosphate and potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water. Mix the solutions thoroughly and pour from a fine-mesh watering can. The fertilizer solution must always be washed off the leaf surface with clean water. You can sprinkle the soil with wood ash - a source of micro- and macroelements in an accessible form.
Temperature regime
For closed ground, it is very important to maintain the temperature regime of the air within the range of +10 .. + 15 ° C.
If you fence off a separate compartment in the greenhouse and raise the daytime air temperature to +18 .. + 20 ° С, and reduce the night temperature to +12 .. + 15 ° С, you can get a green feather in 25-30 days.
With a strong unwanted growth of greenery, the air temperature is reduced to +10 .. + 12 ° C. At the same time, the growth and yield of bulbous greens is reduced.
Lighting for onions in the greenhouse
Onions grow and develop normally in natural light from the greenhouse, but the leaves are pale green. Additional lighting increases the elasticity of the leaves and the intensity of their color. In case of rack cultivation, to save light energy, only the lower racks with excessive shading can be illuminated. Phytolamps are usually used for lighting in greenhouses.
Greenhouse-grown lettuce under cover material
Harvest
Onion feathers can be cut as needed when they reach 15-20 cm.
Growing dill in a greenhouse
To prolong the production of dill greens, sowing it in the allotted area is carried out in several stages with a gap of 10-12 days or used as a compactor for onions (changing the planting pattern of bulbs) lettuce, Chinese cabbage and other crops.
Dill seed preparation
For accelerated production of greens, dill is sown with sprouted seeds. To do this, 3-4 days before sowing, we wrap the seeds in double gauze. Soak in water at 40-50 ° C. This technique is necessary to remove essential oils from the seed surface, which will accelerate the emergence of seedlings and a more friendly growth of seedlings. During soaking, we change the water once a day, and rinse the seeds thoroughly under running water. At the end of the 3rd day, spread the glued seeds on a dry cloth to dry.
Greenhouse dill varieties
It is most rational to grow early maturing varieties in a greenhouse for distillation for a family.
- Aurora (cutting greenery on the 25th day from germination),
- Gribovsky (cutting greens on the 30th day from germination),
- Distant (cut on day 38 from germination).
They form fragrant juicy greens within a month, which must be removed immediately, since then without interruption the plants move to flowering.
Rack in a greenhouse for winter growing greenery
Preparing the soil for dill
Dill is undemanding to the soil, therefore, as a compactor, it grows normally and develops in the substrate of the main crop. When grown separately, forcing dill is sown in a separate container - a container or box. We mix the soil with peat, humus, biohumus, sand, any other baking powder to increase water and air permeability. In heavy, dense soils, the roots of dill begin to rot, the plant becomes ill with powdery mildew, treatment with drugs is not recommended.
Further soil preparation, as well as for onions. Add to the substrate by 1 sq. m of the area of boxes of 20 g of urea and 15 g of potassium sulfate, can be replaced with wood ash. Mix thoroughly with the soil and water. The soil under the dill should be constantly loose for more oxygen access.
Sowing dill
In the prepared moist soil, after 12-15 cm, we make grooves 2 cm deep. We sow the seeds line by line and sprinkle them with a small layer of soil. Most often, a one-line sowing pattern is used, but you can sow in a belt method in 3-5 lines. In this case, the distance between the grooves in the tape is 8-12 cm, and between the tapes is 15-20 cm.
Moisturizing
For dill, constant soil moisture is optimal (without excessive moisture, since the greens will be watery, they can get sick). Before germination, the soil is moistened daily from a sprayer. With the emergence of seedlings, the seedlings are watered every 5-7 days with a moderate rate of water when the top layer of the soil dries up.
Top dressing
Top dressing is carried out twice before the first cut: nitrofoskoy 15-20 g / sq. m. area of boxes or a solution of fertilizers used when sowing seeds. After a large cut on the greens, the remaining 5-10 cm of "hemp" is fed with an ammonia solution of 10-15 g / 10 l of water. If the cutting is done selectively (for the family), then no additional fertilizing is carried out on the greens until the final harvest.
Temperature and light conditions
Dill is a fairly cold-resistant culture, therefore, the air temperature in the greenhouse is maintained at 15..18 ° C without drafts. It can be placed closer to the doors. Dill is so unpretentious that it can endure cultivation in shaded areas. When growing in boxes on racks, we additionally illuminate with phytolamps only the lower racks, where the highest shading of plants is observed.
Harvest
For the bushes to be leafy, dill needs a sufficient area for nutrition. Therefore, at a height of 10 cm, we thin out the culture, carefully pulling out the plants by the roots or pinching off at the soil level. Plugged plants can be transplanted or used for food.
Greens in the greenhouse
Growing parsley in a greenhouse
Preparing parsley seeds
Parsley has a very long pre-emergence period, which, depending on the variety and growing conditions, is about 45 days. To shorten the pre-emergence period, it is better to sow parsley with germinated seeds. To do this, before sowing, the seeds are kept for 5 days in a moist two-layer gauze.
Sprouted seeds are transferred to a room with a temperature of + 1 ° C for 10 days. When sowing, such seeds germinate on days 15-17 and form an aboveground mass 3 times faster than with conventional sowing.
Sowing parsley
Divide the prepared substrate into furrows every 10 cm, 2 cm deep. Evenly after 4-5 cm, place the seeds in the furrows and cover them with soil, smoothing them with your hand.
After sowing, we moisten the soil through a sprayer so as not to wash the seeds out of the substrate. The air temperature is maintained within +12 .. + 18 ° С not higher. At + 20 ° C, parsley leaves wither from overheating.
Greenhouse parsley care
If the seedlings are dense, we carry out thinning, leaving the distance between the seedlings at least 5 cm.
We water the parsley when the top layer dries out, since the plants do not tolerate high humidity well.
Until the rows close, we loosen the soil and destroy the weeds. Top dressing cannot be carried out.
For home use, the aboveground mass with a height of 10-12 cm can be cut into greenery.
After the first cut, the remaining "hemp" of parsley is fed with a solution of nitrogen-potassium fertilizers at the rate of 7-10 g / 10 l of warm water. During the cold period in the greenhouse, you can harvest a 5-fold harvest of parsley, supplying the family with fortified greens throughout the winter.
What's next?
For novice gardeners, it will be a good practice and help to grow 2-3 green crops in a greenhouse that do not require complex care. Experienced greenhouses can grow a wider list of early ripening crops with a short growing season in a greenhouse over the winter, using them as the main and sealant: salads (leafy, cabbage, crass salad), radishes of different varieties, rhubarb and other crops.
Growing vegetables, berries, herbs and even mushrooms in a greenhouse in winter is a great idea! If you follow the simple rules for installing and equipping the premises, as well as planting and growing certain crops, you can get several harvests a year.
We have already talked about how to equip a full-fledged winter greenhouse on the site. They also talked about how to choose the right heating system to maintain a stable temperature in the greenhouse during the cold months. Today we will help you decide what exactly can be grown in winter from our familiar garden crops.
Growing greens in a greenhouse in winter
In the coldest and darkest time of the year, the body needs energy more than ever. Of course, you can go to the supermarket for green vitamins, but why not try to grow much tastier and healthier fresh greens yourself? It's not difficult at all!
The growing season is short (a guarantee of several harvests at once in the autumn-winter season), and the greens are quite resistant to temperature extremes (you don't even need round-the-clock heating in the greenhouse).
Basically, greens in greenhouses are grown not on the main area, but on shelves, saving space. With a competent approach to the process, you will not only provide your household with vitamins, but you will also be able to make money on the sale of early greens.
Most often, in a greenhouse in winter they cultivate:
Bow on feather
For forcing onions on a feather, species are used with a very short dormant period or none at all (they are ready to form a new harvest immediately after harvesting) - multi-tiered, batun, chives, slugs.
Onions are suitable for an ordinary soil mixture of peat and garden soil, fed with nitrogen fertilizer. The bulbs are cut by the shoulders and soaked for 15 minutes in heated water, after which they are immediately planted in prepared boxes with soil close to each other and watered abundantly.
For the first week, it is desirable to maintain the temperature in the range of 10-15 ° C, then the daily rate is raised to 18-20 ° C. Watering is carried out as the soil dries up. Onions will drive out feathers in natural light, but they will turn out brighter and denser when illuminated with phytolamps.
Feathers are cut as needed - under good conditions, you will take off the first crop in 25-30 days.
Salad
Another unpretentious plant for a winter greenhouse is lettuce. Without much effort on your part (moderate watering, minimal lighting, temperature about 15 ° C), you can harvest its crop every three weeks. Watercress is the most suitable for this kind of cultivation.
Rhubarb, chicory, Swiss chard and asparagus will also delight you with fresh greens in winter. At the same time, they do not even need a lot of light - containers with rhizomes sprinkled with moist earth can be kept in the lowest, dimly lit areas of the greenhouse. The crop is harvested by cutting off the peripheral large leaves and leaving the young to grow.
Dill
Dill is also a fairly cold and shade-resistant crop, undemanding to the soil and suitable for winter cultivation in a greenhouse. It is more rational to use early-ripening varieties for forcing (Aurora, Redoubt, Gribovsky, Grenadier, Dalny, etc.), and sowing already germinated seeds into prepared grooves about 2 cm deep.
Dill can be planted on its own or as a sealant for onions or lettuce. For him, a loose, well-moistened soil is desirable, a temperature of at least 15 ° C and a complete absence of drafts are important. Before germination, moisten the soil daily from a sprayer, and then water the seedlings every 5-7 days when the top layer of the soil dries out. If you see an excessive thickening of the area, carefully thin out the plantings.
You can get the first harvest of dill in a month or two after sowing the seeds. After a particularly plentiful cut, you can feed the remaining bushes with a solution of ammonium nitrate (10 g per 10 liters of water).
Parsley
This is the most capricious of all winter greenhouse inhabitants, requiring good lighting and a certain thermal regime. Of the two possible ways to grow parsley (from root crops or from seeds), we advise you to choose seed - so there will be less worries.
Like dill, parsley in a greenhouse should be grown from prepared, hardened and germinated seeds - this way you will shorten the pre-emergence period, which may otherwise drag on for a month and a half.
Parsley seeds are sown in grooves about 2 cm deep and lightly sprinkled with soil. After that, the sown area is well moistened with a spray bottle.
In the process of growth, parsley needs a temperature in the range of 12-18 ° C (at higher values, the leaves will turn yellow and wither en masse). Also, do not allow waterlogging - watering is carried out only after the topsoil dries up.
Dense seedlings should be thinned out, before the rows close - regularly loosen and remove weeds.
As soon as the plants have reached a height of 10-15 cm, the first harvest can be taken. As in the previous case, if you removed too much greens, it is worth feeding the remaining hemp with a urea solution (a tablespoon per 10 liters of water).
Growing seedlings of vegetables in a winter greenhouse
But for growing seedlings of vegetables, your greenhouse must already be equipped with full-fledged heating.
Of course, if your needs for vegetables are small, then a couple of boxes of seedlings can be placed at home on the windowsill. However, if the volume of vegetables grown is close to industrial (for example, you are selling them), there will definitely not be enough space in the apartment - a greenhouse will come to the rescue.
Only self-pollinating plants are suitable for winter cultivation in a greenhouse!
Growing garden crops in a winter greenhouse differs from their cultivation in the open field, so it is important to observe some nuances.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes can be planted on seedlings from the beginning of December.
Seeds are sown in boxes with prepared soil, watered with sprinkler irrigation and kept under polyethylene until germination (about 5-8 days).
Tomato seedlings need regular watering with warm water and mandatory additional lighting - the first three days continuously, after 12-14 hours.
The optimum air temperature for growing tomatoes: 24-26 ° С during the day and about 15 ° С at night. After the emergence of seedlings for 4-5 days, they are "hardened" - the daytime temperature is temporarily reduced to 15-20 ° C, after which they return to the original mode.
The picking of tomato seedlings is carried out in the phase of cotyledons. After two weeks, it is worth feeding the plants with complex mineral fertilizer (1 tsp for 5 liters of water). After another 2-3 weeks, fertilize again (0.5 tsp superphosphate + 0.5 tsp potassium sulfate per 5 l of water).
Growing plants in pots are moved from time to time so that the leaves of neighbors do not shade each other.
In February, tomato seedlings can be planted in the beds, remembering to tie the stems vertically. Watering is carried out at the root, stepchildren are removed.When the plant reaches a height of one and a half meters, the top is pinched to it and the leaves growing below the formed fruits are cut off.
Cucumbers
Starting from the first days of January, in the winter greenhouse, you can already plant cucumbers for seedlings.
Sprouted cucumber seeds are sown in pots (ideally peat ones) with prepared uniformly moistened soil and covered with a film until shoots appear (about 5-6 days). Additional lighting is performed 10-12 hours a day.
Suitable temperatures for growing cucumber seedlings are around 23 ° C during the day and 17-18 ° C at night. After the emergence of seedlings, they are "hardened" in the above-described way, for several days lowering the daytime temperature to 15-20 ° C, and then increasing to its former level.
Top dressing of cucumbers is also done twice - with a complex mineral fertilizer with the formation of two true leaves (1 tsp for 5 l of water) and 10 days after that with a mixture of 20 g of potassium nitrate, 30 g of ammonium nitrate and 40 g of superphosphate (all this is on 10 liters of water).
Seedlings are planted in beds in February with a distance between plants of about 40 cm (planting depth - up to cotyledons or the first pair of true leaves) and tied to a trellis. Watering is necessary regular, moderate, the soil should be loose.
If you grow several crops in a winter greenhouse, make sure that tomatoes and cucumbers are not neighbors, they really do not like this.
Eggplant
Eggplants are planted for seedlings in a winter greenhouse at the very beginning of February.
Eggplant seeds are sown in boxes with prepared soil, watered with sprinkler irrigation and kept under the covering material until shoots appear (about 10-14 days). Eggplants are illuminated for about 12 hours a day.
Before the emergence of seedlings, the temperature in the greenhouse is maintained at 20-25 ° C during the day and about 12-15 ° C at night. After emergence, they are hardened as described above. The humidity in the room is maintained within the range of 75-85%.
Instead of picking, eggplants in the phase of 1-2 true leaves are transferred into larger containers, trying not to damage the roots. Then the plants should be fed - 10-15 days after transshipment and then every two weeks (mineral fertilizers alternate with organic matter, the type of fertilizer is the same as for cucumbers).
The term for planting mature eggplant plants in the beds is April. They need regular watering and loosening of the soil. The main stem of the plant must be tied to a trellis, and the top must be pinched.
Bell pepper
Peppers, like eggplants, are planted for seedlings in a winter greenhouse in early February.
Pepper seeds are sown in a container with prepared soil, watered with sprinkling and kept under a film until shoots appear (about 3-6 days). Additional lighting is provided 10-12 hours a day.
Before the plants hatch, the air temperature is maintained at 22-26 ° C during the day and about 15-18 ° C at night. After emergence, they are hardened and watered as described above.
Just like eggplants, bell peppers do not dive, but are transferred together with a lump of earth so that the leaf remains above the surface at a height of at least 1 cm. After that, fertilizing (with fertilizers similar to those used for cucumbers) is carried out twice - through 2-3 weeks after transshipment and when 4-5 leaves appear.
Pepper plants are planted in the ground in April. Further care consists in timely watering (make sure that water does not fall on the leaves) and loosening the soil, as well as the introduction of mineral fertilizers 1-2 times a month.
Of course, these are not all crops that can be grown in a winter greenhouse. Zucchini, potatoes, carrots, radishes, strawberries, raspberries and even grapes with melons are also suitable for this. However, for a start, we advise you not to set out on grandiose plans, but to master more unpretentious and less labor-intensive crops.


